- 1Department of Geriatrics, The Second Medical Center and National Clinical Research Center for Geriatric Diseases, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing, China
- 2Medical School of Chinese PLA, Beijing, China
- 3Department of Geriatric Cardiology, The Second Medical Center, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing, China
- 4Department of Outpatient, The First Medical Center, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing, China
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is the most common and conserved internal eukaryotic mRNA modification. m6A modification is a dynamic and reversible post-transcriptional regulatory modification, initiated by methylase and removed by RNA demethylase. m6A-binding proteins recognise the m6A modification to regulate gene expression. Recent studies have shown that altered m6A levels and abnormal regulator expression are crucial in the ageing process and the occurrence of age-related diseases. In this review, we summarise some key findings in the field of m6A modification in the ageing process and age-related diseases, including cell senescence, autophagy, inflammation, oxidative stress, DNA damage, tumours, neurodegenerative diseases, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). We focused on the biological function and potential molecular mechanisms of m6A RNA methylation in ageing and age-related disease progression. We believe that m6A modification may provide a new target for anti-ageing therapies.
1 Introduction
Ageing is a process of molecular and cellular damage accumulating over time, leading to a progressive decline in physical and mental capacity and an increased risk of disease and death (Borghesan et al., 2020). At present, changes in molecular and cellular ageing processes are believed to be the basis of age-related diseases, including cell senescence, autophagy, inflammation, oxidative stress, DNA damage, telomere depletion, protease inactivation, and epigenetic disorders (Ungvari et al., 2020). Ageing is the greatest risk factor for most chronic diseases, leading to morbidity and mortality (Kennedy et al., 2014). Presently, the field of ageing has focused on understanding the molecular mechanisms that regulate the ageing process and identifying biomarkers that could help to predict age-related processes. New therapeutic targets mainly focus on improving the health of the elderly population.
Epigenetics regulate gene and non-coding RNA expression without altering primary DNA sequences through many mechanisms, such as DNA methylation, histone modification, and nucleosome localisation (Portela and Esteller, 2010). Epigenetic imprinting persists during development and can be passed on to the offspring (Fraga et al., 2005; Kaminsky et al., 2009). Known epigenetic mechanisms include DNA methylation, histone modification, chromatin remodelling, and RNA methylation (Wang and Chang, 2018). At present, it is believed that during the ageing process, a decrease in histone synthesis and a change in chromatin structure leads to a general loss of structural heterochromatin (Lee et al., 2020). Histone variants have also been observed in ageing organisms, which have different primary sequences and properties compared to typical histones, thus changing the gene transcription program (Henikoff and Smith, 2015). In addition, the ageing process involves DNA methylation changes (Day et al., 2013; Horvath, 2015; Unnikrishnan et al., 2019), ATP-dependent chromatin remodelling (Clapier et al., 2017), histone modifications (including methylation, acetylation, ubiquitination) (Lawrence et al., 2016), and miRNA changes (Huan et al., 2018).
As one of the most common post-transcriptional modifications in eukaryotic mRNA, N6-methyladenosine (m6A) adds a methyl group to the nitrogen-containing base at the sixth position of the adenine residue of RNA. It was first found in the eukaryotic mRNA of Novikov hepatoma cells and mouse L cells (Desrosiers et al., 1974; Schäfer, 1982). m6A modification has a conservative identification motif, RRACH (R = G/A, H = A/C/U) (Csepany et al., 1990). The evolutionary conservatism and dynamic reversibility of its modification make it unique for gene expression regulation. m6A RNA methylation has become a key regulator of various post-transcriptional gene regulation processes and acts as a translation initiation mechanism in protein synthesis (Karthiya and Khandelia, 2020). In addition, numerous reports have indicated that m6A modification may cause important changes in the ageing process and affect the occurrence and development of many age-related diseases. In this review, we focused on m6A RNA methylation mechanisms related to the ageing process and emphasised their significance in age-related diseases. We believe that m6A RNA methylation is a potential target for treating age-related diseases.
2 Overview of N6-Methyladenosine Modification
RNA modification is a post-transcriptional process that regulates gene expression by binding to proteins without involving the RNA sequence. More than 160 types of RNA modifications, ubiquitous in both coding and non-coding RNA, have been identified. First discovered in 1974, m6A modification refers to the methylation of the sixth nitrogen atom of adenylate. It is considered the most abundant internal modification in eukaryotic mRNA (Desrosiers et al., 1974). With recent improvements in detection techniques, such as high-throughput sequencing, the study of m6A RNA methylation is booming. Presently, it has been reported that there are three m6A residues per average mRNA transcript in mammalian cells (Dominissini et al., 2012). In addition to mRNA, m6A RNA methylation covers almost all types of RNA, including transfer RNAs (tRNAs), ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs), cyclic RNAs (circRNAs), microRNAs, and small nucleolar RNA (snoRNA) (Sergiev et al., 2016).
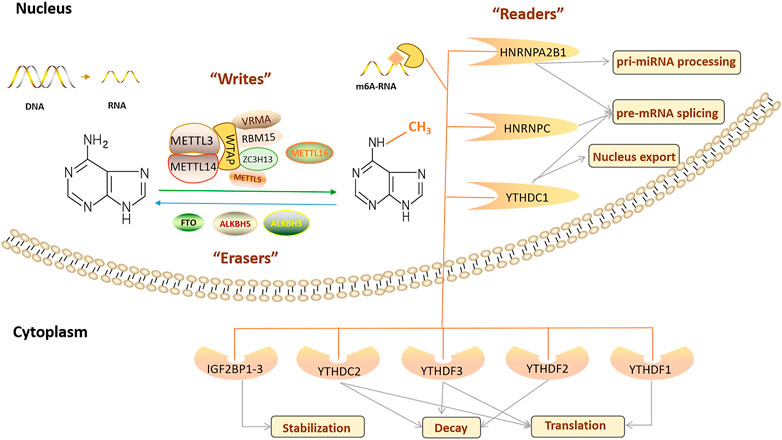
m6A RNA methylation is a dynamic and reversible RNA modification, and its function is determined by three types of enzymes: RNA methyltransferase, RNA demethylase, and m6A-binding proteins (Figure 1) (Fu et al., 2014). m6A modification is crucial in regulating gene expression, splicing, RNA editing, RNA stability, controlling mRNA lifespan and degradation, and mediating ring RNA translation (Zhao et al., 2017). In addition, m6A modification is related to many physiological processes, pathological processes, and human diseases, including the circadian rhythm (Zhong et al., 2018), reproductive system development (Hongay and Orr-Weaver, 2011; Hsu et al., 2017; Ivanova et al., 2017; Kasowitz et al., 2018), haematopoietic system development (Wang et al., 2014a; Zhang et al., 2017), nervous system development and degeneration (Hess et al., 2013; Lence et al., 2016; Li et al., 2017a; Yen and Chen, 2021), cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) (Chen et al., 2021a), nutritional and metabolic diseases (Wu et al., 2020a), and tumorigenesis (Wang et al., 2020a; Zhou et al., 2020).
2.1 RNA Methyltransferases
RNA methyltransferases, including RNA methyltransferase-like protein 3 (METTL3) (Bokar et al., 1997), RNA methyltransferase-like protein 14 (METTL14) (Liu et al., 2014), Wilms’ tumour 1-associating protein (WTAP) (Agarwala et al., 2012), RNA-binding motif protein 15 (RBM15) and its analogue RBM15B (Patil et al., 2016), Vir-like m6A RNA methyltransferase associated protein (VIRMA)/KIAA1429 (Schwartz et al., 2014), Zinc finger CCCH domain-containing protein 13 (ZC3H13) (Wen et al., 2018), RNA methyltransferase-like protein 16 (METTL16) (Pendleton et al., 2017), and RNA methyltransferase-like protein 5 (METTL5) (van Tran et al., 2019; Richard et al., 2019), mediate m6A modification, are mainly located in nuclear speckles, and are called “m6A writers.” Among these, METTL3 was the first key RNA methyltransferase and core RNA methyltransferase subunit of m6A methylation. It is critical in the occurrence of m6A modifications and participates in various physiological processes (Bokar et al., 1997). Abnormal METTL3 expression changes m6A RNA methylation levels. As the structural support for METTL3, METTL14 is co-located in the nucleus in a 1:1 ratio and forms a stable RNA methyltransferase complex responsible for m6A modification (Liu et al., 2014). WTAP in the RNA methyltransferase complex is primarily used as a connecting protein between METTL3 and METTL14. WTAP lacks a conserved catalytic methylation domain and cannot catalyse m6A modification, but its deletion significantly affects m6A modification levels and physiological processes, such as embryonic differentiation (Ping et al., 2014). METTL3/METTL14/WTAP is considered to be the core RNA methyltransferase component, and in recent years, some studies have reported new RNA methyltransferase complex components, such as RBM15/15B, which assists in the binding of METTL3 and WTAP, and its deletion leads to damage to X-inactive specific transcript (XIST)-mediated gene silencing on the X chromosome (Knuckles et al., 2018). ZC3H13 (Wen et al., 2018), VIRMA (Yue et al., 2018), and other proteins also participate in m6A RNA methylation as cofactors of the m6A RNA methyltransferase complex. In addition, Warda et al. (2017) reported on an independent m6A writer, METTL16, finding that its binding site does not overlap with the METTL3/METTL14 methylation complex, and it regulates the stability and splicing of mRNA by catalysing m6A modification in snoRNAs, U6 small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs), and other long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs). There are continuous reports of new RNA methyltransferases, such as METTL5, the enzyme responsible for 18S rRNA m6A modification, and ZCCHC4, a confirmed 28S rRNA m6A modification enzyme (van Tran et al., 2019; Richard et al., 2019). Some studies reported that WTAP interacts with many proteins and lncRNAs, of which more than 100 may bind to METTL3 or METTL14 (Schöller et al., 2018). Therefore, “writer” may include the reported proteins and other components that need further exploration.
2.2 RNA Demethylases
RNA demethylases, including fat mass and obesity-related proteins (FTO) (Jia et al., 2011), AlkB homologue 5 (ALKBH5) (Huang et al., 2020a), and AlkB homologue 3 (ALKBH3) (Ueda et al., 2017; Sun et al., 2019), can remove the m6A modification. They are called “m6A erasers” and are located in nuclear spots with RNA methyltransferase. In 2011, FTO was identified as the first m6A RNA demethylase, verifying that m6A RNA methylation is a dynamic and reversible RNA modification. FTO-mediated m6A demethylation acts in various biological processes, inhibiting peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPARβ/δ) and AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) pathways, disrupting skeletal muscle lipid utilisation, inhibiting macrophage lipid influx by downregulating PPARγ protein expression, and accelerating cholesterol outflow via AMPK phosphorylation. Thus, foam cell formation and atherosclerosis development were inhibited (Yang et al., 2022). FTO regulates the alternative splicing of RUNT-related transcription factor 1 (RUNX1) through m6A modifications (Zhao et al., 2014), whereas FTO regulates fat formation and deposition by altering the expression of PPARγ (Lee et al., 2011) and angiopoietin-like 4 (ANGPTL4) (Wang et al., 2015a). In addition, FTO is widely involved in regulating the cell cycle (Li et al., 2019a), tumour growth (Li et al., 2019b), proliferation and migration (Tang et al., 2019), stem cell maintenance (Su et al., 2020) and other biological processes.
ALKBH5 is the second m6A RNA demethylase and is expressed in most tissues, especially the testes (Aik et al., 2014). ALKBH5 inactivation increases m6A RNA methylation levels, leading to male-mouse infertility (Tang et al., 2018a). In addition, ALKBH3 has recently been considered a new m6A RNA demethylase that preferentially catalyses m6A demethylation in tRNA (Ueda et al., 2017; Woo and Chambers, 2019).
2.3 N6-Methyladenosine Binding Proteins
The “m6A writers” and “m6A erasers” determine whether RNA is methylated, but m6A-binding proteins (“m6A readers”) determine the final biological function of m6A modification. “m6A readers” recognise and bind to an m6A modified transcript, then regulate mRNA stability (Zhao et al., 2014), mRNA splicing (Xiao et al., 2016), mRNA structure (Spitale et al., 2015), mRNA output (Roundtree et al., 2017), translation efficiency (Wang et al., 2015b) and microRNA (miRNA) biogenesis (Alarcón et al., 2015). “Readers” include proteins containing YTH domains (YTHDF1/2/3 and YTHDC1/2), heterogeneous ribonucleoproteins including heterogenous nuclear ribonucleoprotein (HNRNP) C (HNRNPC), HNRNP G (HNRNPG), and HNRNP A2B1 (HNRNPA2B1), and insulin-like growth factor 2 binding proteins (IGF2BPs), which are members of a protein family involved in regulating some aspects of ageing. Different “readers” have different cellular localisations and thus perform various biological functions. YTH domain containing 1 (YTHDC1) regulates mRNA splicing by recruiting the splicing factor serine- and arginine-rich splicing factor 3 (SRSF3) or blocking serine- and arginine-rich splicing factor 10 (SRSF10) in the nucleus (Xiao et al., 2016). In addition, it increases the output of circRNA NOP2/SUN domain family, member 2 (circNSUN2) in the cytoplasm by interacting with nuclear output factor 1 (Chen et al., 2019a). HNRNPA2B1 and HNRNPC are also located in the nucleus. HNRNPA2B1 regulates RNA splicing and promotes miRNA maturation by recognising pri-miRNA markers and interacting with DiGeorge syndrome critical region 8 (DGCR8) (Zhao et al., 2017). HNRNPC selectively recognizes m6A modified transcripts to promote pre-RNA processing (Liu et al., 2015). YTHDF1/2/3, YTH domain containing 2 (YTHDC2), and IGF2BP1/2/3 are localised in the cytoplasm. YTH domain family protein 1 (YTHDF1) initiates RNA translation by interacting with translation initiation factors and ribosomes, whereas YTH domain family protein 2 (YTHDF2) selectively binds m6A modified transcripts and accelerates their degradation (Wang et al., 2015b). On the other hand, YTH domain family protein 3 (YTHDF3) and YTHDF1/2 play a synergistic role, not only promoting YTHDF1-mediated translation but also affecting the decline in YTHDF2-mediated m6A modification (Wang et al., 2014b; Shi et al., 2017). Like YTHDF3, YTHDC2 is an RNA helicase, and its helix-unwinding region contributes to RNA binding and promotes mRNA translation or degradation (Hsu et al., 2017). Other proteins located in the cytoplasm are IGF2BP1–3, which recognise and bind to m6A modified transcripts, thus enhancing mRNA stability (Huang et al., 2018).
3 N6-Methyladenosine Changes in Molecular Processes Associated With Ageing
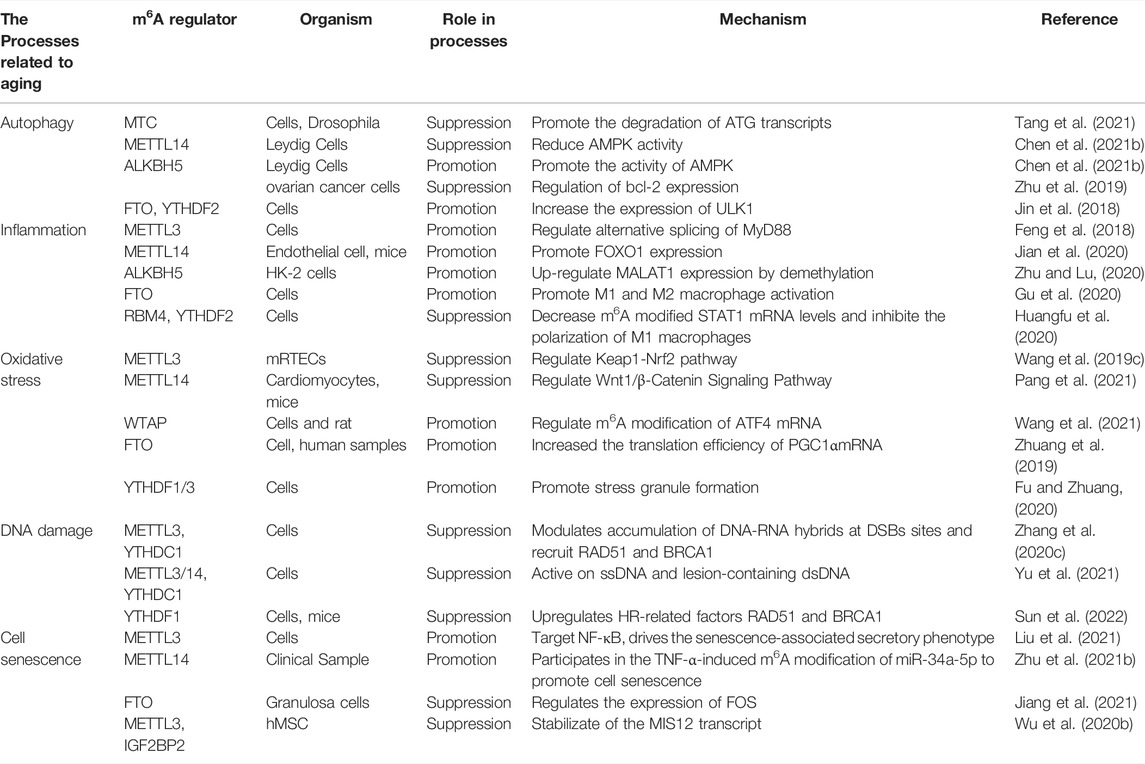
Many studies have confirmed that m6A methylation regulates several physiological processes that are crucial in the ageing process. Here, we focused on the mechanisms of m6A RNA methylation in autophagy, inflammation, oxidative stress, DNA damage, and cell senescence (Table 1).
3.1 N6-Methyladenosine and Autophagy
Autophagy is a highly conserved intracellular clearance mechanism regulated by various proteins and is important for maintaining homeostasis in the internal environment. The mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) is a key factor in autophagy regulation. Protein kinase B (AKT) and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signalling pathways activate mTOR to inhibit autophagy, whereas AMPK and p53 pathways negatively regulate mTOR to promote autophagy (Alers et al., 2012). After mTOR inactivation, UNC-51-like kinase 1/2 (ULK1/2) is activated and binds to the focal adhesion kinase family interacting protein of 200 kDa (FIP200) to form a ULK1 complex with autophagy-related 13 (ATG13) proteins, promoting autophagosome formation (Codogno et al., 2011). m6A methylation and related regulators regulate autophagy by regulating ATG expression or by affecting autophagy-related signalling pathways. In 2018, Jin et al. first reported a positive regulatory effect of FTO on autophagy, accomplished by affecting the abundance of Unc-51 like autophagy activating kinase 1 (ULK1) (Jin et al., 2018). Another RNA demethylase, ALKBH5, has been shown to enhance autophagy by reducing m6A methylation in FIP200 transcripts (Li et al., 2020), suggesting a negative correlation between m6A modification and autophagy. A study of RNA methyltransferases further confirmed this. METTL3 upregulates methylation and triggers YTHDF1 and Forkhead box O3 (FOXO3) binding to promote the translation of FOXO mRNA. FOXO further blocks ATG gene expression to inhibit autophagy (Lin et al., 2020). A decrease in METTL14 levels increases the stability of calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase 2 (CAMKK2) mRNA and activates the AMPK and ULK1 complex to initiate autophagy (Chen et al., 2021b).
Abnormal autophagy can lead to diseases, some of which may be associated with ageing. Studies have shown that autophagy decreases with age. Increasing autophagy levels can inhibit the accumulation of damaged proteins, delay the occurrence of degenerative changes, and prolong life (Rubinsztein et al., 2011; Papp et al., 2016). There is evidence that autophagy regulates some age-related diseases in lower organisms (such as Drosophila and Caenorhabditis elegans), but this hypothesis has not been confirmed in mammals. Accelerating ageing by decreasing autophagy is controversial. Nevertheless, several studies have reported that deleting autophagy proteins leads to the accumulation of misfolded proteins and abnormal mitochondria in cells, resulting in premature senescence, organ dysfunction, and eventually the development of various ageing-related diseases, such as neurodegenerative diseases, cancer, CVDs, and metabolic syndrome (Linton et al., 2015; Guo et al., 2018; Luo et al., 2020). In summary, autophagy regulation is closely related to ageing, in which m6A modification plays an important role. Therefore, further studies on the relationship between m6A modification and autophagy in ageing may provide a new method for anti-ageing research.
3.2 N6-Methyladenosine and Inflammation
RNA methylation is involved in inflammation. m6A methylation affects pathways related to metabolic reprogramming, stress response, and ageing by regulating type I interferon (IFN) mRNA stability (Rubio et al., 2018). Lipopolysaccharides (LPSs) induce inflammation. It has been found that LPS stimulation promotes METTL3 expression and biological activity in macrophages, and METTL3 overexpression alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation through the nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) signalling pathway, further confirming the relationship between m6A methylation and inflammation (Wang et al., 2019a). In addition, the interaction between m6A modification and inflammation is crucial for various diseases to occur. YTHDF2 deletion aggravates the inflammatory state and metastasis of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells (Hou et al., 2019). After an ischaemic stroke, FTO expression is downregulated, and m6A methylation is increased in the main inflammatory pathways, including interleukin (IL)-6 cytokines, tumour necrosis factor (TNF), toll-like receptor (TLR), and NF-κB signalling pathways (Chokkalla et al., 2019). It has been suggested that m6A may regulate secondary brain injury after cerebral ischaemia by affecting inflammation.
In summary, m6A methylation affects inflammation under physiological and pathological conditions. Presently, the chronic inflammatory state is considered one of the characteristics of ageing, namely “inflammatory ageing” (inflamm-ageing), which is mainly characterised by inflammatory cell infiltration and an increase in pro-inflammatory factors [TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, C-reactive protein (CRP), etc.] Although most current studies on the relationship between m6A modification and inflammation are based on specific diseases and signalling pathways, the study of epigenetic changes in inflammation potentiates the development of effective drugs with specific anti-ageing targets.
3.3 N6-Methyladenosine and Mitochondria: Oxidative Stress
Oxidative damage accumulates with ageing in many species and tissues. RNA modification is mobilised to activate or inhibit stress-resistant signalling pathways (Peters et al., 2021). Li et al. (2017b) found that the activities of METTL3/METLL14, p21, and senescence-related β-galactosidase (SA-βGAL) increased significantly after oxidative damage stimulated HCT116 p53−/−cells, indicating that METTL3/METLL14 may trigger the p53 independent effect of ageing in the oxidative damage response, which needs to be further tested. Arsenite et al. stimulated human keratinocytes to induce reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, increasing WTAP, METTL14, and total m6A expression levels (Zhao et al., 2019). FTO induces oxidative stress and increases ROS levels by reducing m6A methylation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator-1 alpha (PGC1α) (an important regulator of mitochondrial metabolism that is also affected by the ageing process) and increasing PGC1α mRNA translation efficiency.
3.4 N6-Methyladenosine and DNA Damage
DNA damage refers to changes in DNA structure caused by physical or chemical stimuli in the environment. The persistence of DNA damage can lead to a prolonged DNA damage response (DDR) and induce senescence (Di Micco et al., 2021). m6A is critical in DNA damage and repair. It has been reported that METTL3/METTL14 and METTL16 are recruited to DNA damage sites to facilitate DNA repair and the DDR by adjusting m6A modifications under ultraviolet (UV) radiation stimulation (Svobodová Kovaříková et al., 2020). This repair is carried out through the nucleotide excision repair (NER) pathway because knockout of the non-homologous end junction (NHEJ) enzyme SUV391H/H2 does not affect m6A recruitment under UV stimulation (Svobodová Kovaříková et al., 2020).
3.5 N6-Methyladenosine and Cell Senescence
Cell senescence results from many processes, including telomere wear, macromolecular damage, and oncogene-activated signal transduction (Childs et al., 2015). Senescent cells widely exist in ageing and diseased tissues, secreting numerous pro-inflammatory cytokines, called the ageing-associated secretory phenotype [senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP)]. These cytokines regulate the tissue microenvironment and affect how nearby normal cells function. Studies have shown that senescent cells are involved in atherosclerosis (Ito et al., 2014), Alzheimer’s disease (AD) (Boccardi et al., 2015), Parkinson’s disease (PD) (Chinta et al., 2013), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (Barnes et al., 2019), insulin resistance (Aravinthan et al., 2015), age-related chronic inflammation (Campisi and Robert, 2014), cancer (Calcinotto et al., 2019), osteoporosis (Farr and Khosla, 2019), and loss of haematopoietic stem cell function (de Haan and Lazare, 2018) in the elderly.
In 2017, Li et al. (2017b) reported a link between m6A methylation and cellular senescence. They found that p21 protein methylation increased with m6A methylation, whereas the p21 mRNA level was not affected by m6A, suggesting that m6A methylation regulates p21 translation. In another study, breast cancer cells were exposed to sublethal concentrations of ammonium trifluoride (SFN). m6A methylation levels decreased, the activity of SA-βGAL increased, and p53, p21, and p27 protein levels increased, but the corresponding mRNA levels remained unchanged. SFN may lead to senescence by reducing m6A methylation levels (Lewinska et al., 2017). Min et al. reported an m6A RNA modification map of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from young and old groups. They found that the total level of m6A modification in PBMCs of the elderly was significantly lower than that in the young PBMCs, while the expression of m6A modified transcripts was higher than that of unmodified transcripts (Min et al., 2018). Shafik et al. have reported dynamic changes in m6A RNA methylation during brain ageing. In their study, they compared the m6A spectra of Brodmann area 9 (BA9) in the cerebral cortex of 6-week-old and 52-week-old mice and post-mortem pubertal and elderly human brains, and the results showed that the m6A modification sites were significantly increased with increasing age, both in mice and humans. Functional enrichment analysis showed that differential m6A loci mainly occurred in the untranslated regions of genes that affect ageing-related pathways, which are related to the strong negative effect of mRNA expression (Shafik et al., 2021).
A recent study reported that METTL3 downregulation decreased m6A modification of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (hMSC) with premature senescence, and hMSCs showed accelerated ageing after METTL3 gene knockout. The m6A modifications in Hutchinson-Gilford progeria (HGPS) and Werner syndrome (WS) increased with METTL3 overexpression and delayed disease progression. They identified MIS12 as the specific target of m6A modification deletion in the premature ageing process using RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) and m6A methylation RNA immunoprecipitation sequencing (MERIP-seq) analysis. m6A deletion accelerates hMSC ageing, while IGF2BP2 recognises and stabilizes m6A modified MIS12 mRNA to prevent accelerating senescence in hMSCs. Based on the above results, Wu et al. (2020b) proposed a regulatory model in which METTL3-mediated m6A modification improves the stability of IGF2BP2-mediated MIS12 mRNA, thus reversing the ageing phenotype of hMSCs.
Cellular senescence is an important component of the ageing process. Selective clearance of senescent cells is currently the focus of anti-senescence research. Senolytics (a mixture of dasatinib and quercetin), agents that target cellular senescence, have completed small clinical trials in patients with idiopathic fibrosis with promising efficacy and safety results (Justice et al., 2019). The results need to be validated in larger samples and populations with other age-related diseases. The link between m6A methylation and cellular senescence may provide novel therapeutic targets for localising senescent cells, with important clinical implications.
4 N6-Methyladenosine Changes in Ageing Associated Diseases/Disorders
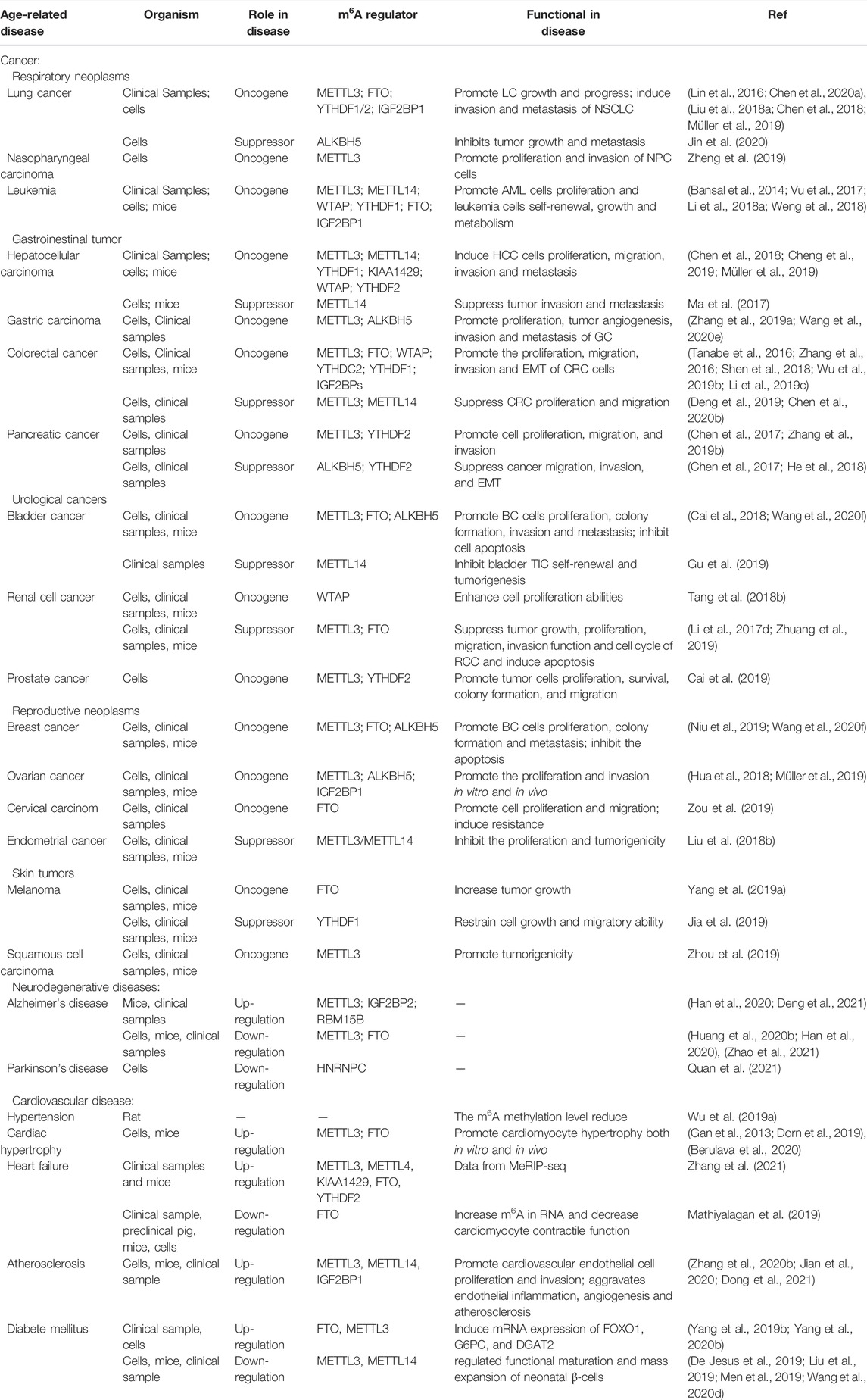
The study of m6A RNA methylation and the ageing process has laid the foundation for more comprehensive and in-depth exploration into the epigenetic mechanisms of various ageing-related diseases. At present, several studies focus on the role of m6A RNA methylation in ageing-related pathological processes, such as cancer. Here, we summarise the latest reports on m6A modification and ageing-related diseases, focusing on cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, diabetes mellitus, and CVDs (Table 2).
4.1 Cancer
In recent years, many studies on m6A RNA methylation have reported that changes in m6A modification levels and the imbalance of regulatory factors are related to the activation and inhibition of cancer-related signalling pathways. Therefore, m6A modification is widely involved in the occurrence (Uddin et al., 2021), progression (Wang et al., 2020a), and drug resistance of cancer (Huang et al., 2020a) and may be a promising biomarker and potential therapeutic target for the diagnosis and prognosis of many kinds of tumours. High METTL3 (Vu et al., 2017), WTAP (Bansal et al., 2014; Naren et al., 2021), FTO (Li et al., 2017c), ALKBH5 (Shen et al., 2020a; Wang et al., 2020b), and YTHDF2 (Paris et al., 2019) expression has been observed in all subtypes of acute myelogenous leukaemia (AML), and high WTAP (Naren et al., 2021), ALKBH5 (Shen et al., 2020a; Wang et al., 2020b) and IGF2BP1 expression (Elcheva et al., 2020) are related to the poor prognosis of AML patients. The same phenomenon has been observed in solid tumours. METTL3, RBM15, KIAA1429, YTHDF1, YTHDF2, HNRNPA2B1, HNRNPC, and IGF2BP1/2/3 expression levels in lung cancer tissues are significantly higher than those in normal tissues (Shi et al., 2019; Zhang et al., 2020a; Li and Zhan, 2020; Sheng et al., 2020).
METTL3 may regulate the growth, differentiation, and apoptosis of AML cells by affecting the phosphoinositide 3-kinases (PI3K)/AKT pathway (Vu et al., 2017). Mechanistically, METTL3 promotes c-MYC, B-cell CLL/lymphoma 2 (BCL2), and phosphatase and tensin homologue (PTEN) mRNA translation by regulating m6A modification levels. Deleting METTL3 increases phosphorylated AKT (p-AKT) levels. METTL3 also regulates drug resistance and invasiveness of lung cancer cells by inducing m6A modification of enhancer of zeste homologue 2 (EZH2) mRNA in A549 cells (Chen et al., 2020a). In addition, it has been reported that the tumour suppressor miR-33a targets the 3′-UTR of METTL3 mRNA to reduce METTL3 expression, thus inhibiting A549 and NCI-H460 cell proliferation (Du et al., 2017). This suggests that METTL3 may be a new target for lung cancer therapy. Recently, Yankova et al. found that STM2457, a small molecule METTL3 inhibitor, reduced AML growth and increased apoptosis by reducing the expression of an mRNA known to cause leukaemia. Further animal experiments showed that STM2457 prolongs the survival time of various AML mouse models (Yankova et al., 2021). METTL14 acts in various solid tumours and leukaemia through different mechanisms. METTL14 expression is downregulated in AML cells. However, it still plays a carcinogenic role in AML. METTL14 increases MYB/MYC expression through the SPI1-METTL14-MYB/MYC signal axis to promote AML occurrence (Weng et al., 2018). METTL14 inhibits the migration and invasion of renal cancer cells by downregulating purinergic receptor P2X 6 (P2RX6) protein translation and ATP-P2RX6-Ca2+-p-ERK1/2-MMP9 signalling in renal cell carcinomas (Wang et al., 2019b).
The RNA demethylases FTO and ALKBH5 are also crucial in tumours. FTO may act as a tumour promoter. FTO increases the expression of myeloid zinc finger 1 (MZF1) by reducing m6A mRNA modification, and promotes lung cancer progression (Liu et al., 2018a). Knockdown of FTO increases the expression of tumour suppressor genes ASB2 and retinoic acid receptor alpha (RARA) and inhibits AML proliferation and differentiation (Li et al., 2017c). It also reduces the mRNA stability of ubiquitin-specific protease (USP7) and inhibits cancer cell growth (Li et al., 2019b).
In addition, some studies have focused on the function of m6A-binding proteins in tumours. YTHDF1 and YTHDF2 can be used as oncogenes and tumour suppressors. YTHDF1 deficiency regulates the transformation efficiency of cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2), cyclin-dependent kinase 4 (CDK4), and cyclin D1 (CCND1) through the Keap1-Nrf2-AKR1C1 pathway to inhibit tumour cell proliferation and xenograft tumorigenesis. YTHDF1 deletion also inhibits new lung adenocarcinoma (ADC) progression (Shi et al., 2019). However, the study also found that YTHDF1 knockdown leads to cell resistance to cisplatin, whereas high YTHDF1 expression leads to better clinical outcomes (Shi et al., 2019). The results of studies on the role of YTHDF2 in lung cancer are complex. One study reported that YTHDF2 promotes METTL3-induced tumorigenesis by increasing suppressor of cytokine signalling 2 (SOCS2) degradation (Chen et al., 2018). However, another study found that YTHDF2 overexpression inhibits non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cell growth and invasion by promoting a decrease in yes-associated protein (YAP) mRNA in NSCLC cells (Jin et al., 2020). However, these studies have repeatedly confirmed the dual role of YTHDF1/2 in tumorigenesis and progression. IGF2BP1 exerts its carcinogenic function by regulating the expression of key transcriptional and metabolic factors, such as TNF receptor 2 (TNFR2), MYB, and MYC (Li et al., 2018a; Paris et al., 2019; Elcheva et al., 2020).
At present, m6A modification and its regulatory factors have proven to be crucial in the occurrence, metastasis, immune escape, and drug resistance of various tumours, including haematological tumours (Vu et al., 2017), respiratory tumours [lung cancer (Du et al., 2018) and nasopharyngeal carcinoma (Zheng et al., 2019)], digestive tract tumours (gastric cancer (Yang et al., 2020a), colorectal cancer (Ni et al., 2019; Shen et al., 2020b; Chen et al., 2021c), pancreatic cancer (Geng et al., 2020), and hepatocellular carcinoma (Chen and Wong, 2020)), urinary tumours [bladder cancer (Han et al., 2019), renal cell carcinoma (Zhuang et al., 2019), and prostate cancer (Zhu et al., 2021a)], reproductive system tumours [breast cancer (Cai et al., 2018), cervical squamous cell carcinoma (Wang et al., 2020c), epithelial ovarian cancer (Hua et al., 2018), and endometrial cancer (Liu et al., 2018b)], skin tumours [melanoma (Yang et al., 2019a; Jia et al., 2019), skin squamous cell carcinoma (Zhou et al., 2019)], and glioblastoma (Cui et al., 2017). Current research results show that m6A regulators may play a dual role in the pathogenesis of tumours, not only as oncogenes but as tumour suppressors. The biological effects of the same m6A regulator are different in different tumours. Some studies have reported the opposite role for an m6A regulator in the same cancer. In short, m6A modification can be used as a marker for a variety of tumours to diagnose and evaluate prognosis and potential therapeutic targets. However, our understanding of the role of m6A modification in tumours is still in its infancy. Numerous studies are still needed to explore the exact molecular mechanism of m6A and tumours to develop new targeted drugs for clinical treatment.
4.2 Diabetes Mellitus
m6A plays an important role in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2D). It has been reported that the mRNA expression of RNA demethylase FTO in T2D patients is upregulated compared with that in a normal control group, inducing the increased expression of key genes involved in glucose and fat metabolisms, such as FOXO1, FASN, G6PC, and DGAT2. This suggests that FTO participates in glucose metabolism by regulating target gene expression (Yang et al., 2019b). In addition, some studies have found that METTL3/14 expression in the β cells of T2D patients and diabetic mice is decreased, leading to decreased β cell proliferation and impaired insulin secretion by reducing the m6A modification levels of several transcripts related to cell cycle progression, insulin secretion, and insulin/IGF1-AKT-PDX1 pathway (De Jesus et al., 2019; Wang et al., 2020d). In addition, loss of METTL3/14 is associated with abnormal glucose tolerance, hyperglycaemia, and hypoinsulinemia in neonatal mice (Liu et al., 2019; Men et al., 2019; Wang et al., 2020d). A recent study found that METTL3 mRNA and miR-25-3p expression were downregulated in PBMCs and retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cells stimulated by high glucose. RPE cells overexpressing METTL3 could upregulate p-AKT levels through the miR-25-3p/PTEN axis, thus rescuing the viability of RPE cells stimulated by high glucose (Zha et al., 2020). However, inconsistently, Yang et al. found that METTL3 expression was upregulated in human diabetic cataract tissue samples and high glucose-induced human lens epithelial cells (HLECs), and the total level of m6A modification increased (Yang et al., 2020b). In summary, m6A modification is involved in the occurrence of T2D and its related complications. It is expected to provide a new diagnostic and treatment strategy for T2D and its complications.
4.3 Neurodegenerative Diseases
Currently, m6A modification is considered very important for nervous system development (Hess et al., 2013; Lence et al., 2016; Li et al., 2017a). In addition, some studies have found that abnormal m6A modifications are related to degenerative changes in the nervous system. Neurodegenerative diseases, including AD and PD, are caused by the gradual loss of neuronal structure or function. It has been reported that m6A modification levels are downregulated in 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA)-treated PC12 cells and rat striatum, whereas 6-OHDA increases the level of oxidative stress and Ca2+ influx by inducing N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptor one expression, leading to the death of dopaminergic neurons that eventually develops into PD (Chen et al., 2019b). In addition, some studies have focused on the correlation between m6A modification and AD. Compared with the control group, METTL3 expression in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus of AD model mice was upregulated, FTO expression was downregulated, and modification levels were significantly increased, suggesting that m6A methylation promotes AD development (Han et al., 2020). Mechanistic studies have reported that FTO activates the TSC1-mTOR-Tau signalling pathway by reducing m6A modification levels and then participates in the occurrence of AD (Li et al., 2018b; Annapoorna et al., 2019; Chen et al., 2019b). However, FTO expression was increased in the brains of ternary transgenic AD mice, and conditional knockout of FTO in the neurons of AD mice improved their cognitive ability (Li et al., 2018b). Previous studies have reported that FTO is associated with structural brain atrophy in healthy elderly subjects (Ho et al., 2010), and a prospective cohort study also found that FTO interacts with apolipoprotein E (APOE) to increase the risk of dementia, especially AD (Keller et al., 2011). In summary, the above studies showed that m6A modification is related to neurodegenerative changes, and its regulatory factors may be used as candidate therapeutic targets for neurodegenerative diseases. However, its role and mechanism need further exploration.
4.4 CVDs
Age is an independent risk factor for CVDs. Studies have shown that m6A modification may affect the occurrence and development of various CVDs. The level of m6A RNA methylation in pericytes of spontaneously hypertensive rats was decreased, suggesting that m6A is involved in blood pressure regulation (Wu et al., 2019a). In addition, under pressure overload stimulation, METTL3 induces compensatory cardiac hypertrophy by regulating the m6A modification of kinase and intracellular signal pathway transcripts. However, mice with conditional knockout of the METTL3 gene show the morphology and function of heart failure after stress or ageing stimulation (Dorn et al., 2019). Another study found that FTO expression increased after adipose factor-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy, whereas FTO knockout inhibited the hypertrophy of neonatal rat cardiomyocytes (Gan et al., 2013). Berulava et al. (2020) further confirmed these results. They found that the ejection fraction was significantly decreased in cardiomyocyte-specific knockout FTO mice, and heart failure progressed faster (Gan et al., 2013). However, another study found that increasing FTO expression in the hearts of mice with heart failure prevented the myocardial contractile transcript from degrading by reducing its m6A modification then reducing the decrease in myocardial contractility caused by ischaemia (Mathiyalagan et al., 2019). These studies suggest that m6A modification and its regulatory factors are crucial in maintaining normal myocardial homeostasis, compensatory myocardial hypertrophy, and heart failure progression.
In addition, m6A also acts in atherosclerosis progression. METTL14 increases the expression of mature miR-19a by upregulating the m6A modification of miR-19a and accelerates the proliferation of cardiovascular endothelial cells (Zhang et al., 2020b). Additionally, a study reported that METTL14 mediates endothelial cell inflammation, interacts with FOXO1, and promotes vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1) and intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) transcription, while METTL14 knockout inhibits the progression of atherosclerotic plaques in mice (Jian et al., 2020). It is believed that m6A modification affects the process of atherosclerosis by regulating cardiovascular endothelial proliferation and endothelial cell inflammation.
In summary, numerous studies have confirmed the correlation between m6A modification and CVDs, but further research needs to verify its established molecular changes and pathological process. In addition, most of the current reports focus on METTL3 and FTO, and the role of other m6A regulators, such as m6A binding proteins in CVDs, is still unclear. m6A modification still needs further exploration to provide a new treatment strategy for CVDs.
5 Conclusion and Perspectives
Alterations in the epigenetic transcriptome are key regulators of gene expression and cellular physiology. m6A, the most abundant internal modification of mRNAs and lncRNAs, is widely involved in regulating various cellular processes. Therefore, exploring the changes and molecular mechanisms of m6A modification in a pathological state and developing new targeted drugs will provide a new strategy for the early diagnosis and accurate treatment of diseases in the future.
Although several studies have reported on the functional role of m6A RNA methylation in ageing and related diseases, many major knowledge gaps remain to be filled. First, numerous studies have confirmed the correlation between m6A and age-related diseases. However, current research results are controversial. In tumours, for example, the same m6A regulatory factor may play different roles in different tumour types. For instance, METTL14 promotes the migration and invasion of breast cancer (Yi et al., 2020), whereas METTL14 downregulates the cancer-causing long-chain non-coding RNA X-inactive specific transcript (lncRNA XIST) and inhibits tumour proliferation and metastasis in colon cancer (Yang et al., 2020c). This may be due to the difference in disease types, but research on m6A is still in its infancy. The level of m6A modification, the biological role of regulatory factors in the occurrence and development of various diseases, and their molecular mechanisms require further study. There is still a way to go before m6A related drugs can be applied. Second, the epigenetic clock based on the DNA methylation site is recognised as the most promising marker of ageing and has been used to evaluate anti-ageing efficacy. m6A, a methylated form of epigenetics and DNA methylation, has been shown to function in ageing and ageing-related diseases. Whether it cooperates with DNA methylation to regulate gene expression during ageing or whether it has a potential relationship with other types of RNA modification or epigenetic methods remains to be further studied.
In addition, several reports have shown that m6A modification has great potential as a diagnostic marker and therapeutic target in the treatment of anti-ageing and age-related diseases, but few have identified inhibitors specifically targeting m6A regulatory proteins. Previous studies have found that the natural product rhein competitively binds the FTO active site in vitro (Chen et al., 2012), inhibits inflammation (Hu et al., 2019) and improves virus-induced lung injury (Shen et al., 2019). However, it is unclear whether m6A methylation regulation mediates these effects. Therefore, more drugs modified by m6A are required to fill this gap. In addition, the exact function of each m6A regulatory factor is not consistent in different cells, diseases, and even different stages of disease development. Our understanding of this is not comprehensive, which is also a challenge for applying m6A in anti-ageing therapy.
Author Contributions
JS proposed the idea and drafted the manuscript, BC, YS, ML, SM, and YZ revised and corrected the initial manuscript, AZ, SC, and QB were involved in the accumulation of the relevant references, SW and PZ contributed to the conception of the study and helped perform the revision with constructive discussions. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the “National Key R&D Program of China” (Funding No. 2020YFC2008900), co-funded by Logistics Scientific Research Project of the Chinese PLA (Funding No.19BJZ30), National defense science and technology innovation projects (Funding No. 19-163-15-ZD-009-001-10) and Health care project of Second Medical Center of PLA General Hospital (Funding No. NLBJ-2019012).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Reference
Agarwala, S. D., Blitzblau, H. G., Hochwagen, A., and Fink, G. R. (2012). RNA Methylation by the MIS Complex Regulates a Cell Fate Decision in Yeast. Plos Genet. 8 (6), e1002732. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1002732
Aik, W., Scotti, J. S., Choi, H., Gong, L., Demetriades, M., Schofield, C. J., et al. (2014). Structure of Human RNA N6-Methyladenine Demethylase ALKBH5 Provides Insights into its Mechanisms of Nucleic Acid Recognition and Demethylation. Nucleic Acids Res. 42 (7), 4741–4754. doi:10.1093/nar/gku085
Alarcón, C. R., Lee, H., Goodarzi, H., Halberg, N., and Tavazoie, S. F. (2015). N6-methyladenosine marks Primary microRNAs for Processing. Nature 519 (7544), 482–485. doi:10.1038/nature14281
Alers, S., Löffler, A. S., Wesselborg, S., and Stork, B. (2012). Role of AMPK-mTOR-Ulk1/2 in the Regulation of Autophagy: Cross Talk, Shortcuts, and Feedbacks. Mol. Cel Biol 32 (1), 2–11. doi:10.1128/mcb.06159-11
Annapoorna, P. K., Iyer, H., Parnaik, T., Narasimhan, H., Bhattacharya, A., and Kumar, A. (2019). FTO: An Emerging Molecular Player in Neuropsychiatric Diseases. Neuroscience 418, 15–24. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2019.08.021
Aravinthan, A., Challis, B., Shannon, N., Hoare, M., Heaney, J., and Alexander, G. J. M. (2015). Selective Insulin Resistance in Hepatocyte Senescence. Exp. Cel. Res. 331 (1), 38–45. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2014.09.025
Bansal, H., Yihua, Q., Iyer, S. P., Ganapathy, S., Proia, D., Penalva, L. O., et al. (2014). WTAP Is a Novel Oncogenic Protein in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Leukemia 28 (5), 1171–1174. doi:10.1038/leu.2014.16
Barnes, P. J., Baker, J., and Donnelly, L. E. (2019). Cellular Senescence as a Mechanism and Target in Chronic Lung Diseases. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 200 (5), 556–564. doi:10.1164/rccm.201810-1975TR
Berulava, T., Buchholz, E., Elerdashvili, V., Pena, T., Islam, M. R., Lbik, D., et al. (2020). Changes in m6A RNA Methylation Contribute to Heart Failure Progression by Modulating Translation. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 22 (1), 54–66. doi:10.1002/ejhf.1672
Boccardi, V., Pelini, L., Ercolani, S., Ruggiero, C., and Mecocci, P. (2015). From Cellular Senescence to Alzheimer's Disease: The Role of Telomere Shortening. Ageing Res. Rev. 22, 1–8. doi:10.1016/j.arr.2015.04.003
Bokar, J. A., Shambaugh, M. E., Polayes, D., Matera, A. G., and Rottman, F. M. (1997). Purification and cDNA Cloning of the AdoMet-Binding Subunit of the Human mRNA (N6-Adenosine)-Methyltransferase. Rna 3 (11), 1233–1247.
Borghesan, M., Hoogaars, W. M. H., Varela-Eirin, M., Talma, N., and Demaria, M. (2020). A Senescence-Centric View of Aging: Implications for Longevity and Disease. Trends Cell Biology 30 (10), 777–791. doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2020.07.002
Cai, J., Yang, F., Zhan, H., Situ, J., Li, W., Mao, Y., et al. (2019). RNA m6A Methyltransferase METTL3 Promotes the Growth of Prostate Cancer by Regulating Hedgehog Pathway. Ott 12, 9143–9152. doi:10.2147/ott.S226796
Cai, X., Wang, X., Cao, C., Gao, Y., Zhang, S., Yang, Z., et al. (2018). HBXIP-elevated Methyltransferase METTL3 Promotes the Progression of Breast Cancer via Inhibiting Tumor Suppressor Let-7g. Cancer Lett. 415, 11–19. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2017.11.018
Calcinotto, A., Kohli, J., Zagato, E., Pellegrini, L., Demaria, M., and Alimonti, A. (2019). Cellular Senescence: Aging, Cancer, and Injury. Physiol. Rev. 99 (2), 1047–1078. doi:10.1152/physrev.00020.2018
Campisi, J., and Robert, L. (2014). Cell Senescence: Role in Aging and Age-Related Diseases. Interdiscip. Top. Gerontol. 39, 45–61. doi:10.1159/000358899
Chen, B., Ye, F., Yu, L., Jia, G., Huang, X., Zhang, X., et al. (2012). Development of Cell-Active N6-Methyladenosine RNA Demethylase FTO Inhibitor. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134 (43), 17963–17971. doi:10.1021/ja3064149
Chen, H., Gao, S., Liu, W., Wong, C.-C., Wu, J., Wu, J., et al. (2021). RNA N6-Methyladenosine Methyltransferase METTL3 Facilitates Colorectal Cancer by Activating the m6A-GLUT1-mTORC1 Axis and Is a Therapeutic Target. Gastroenterology 160 (4), 1284–1300. e1216. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.11.013
Chen, J., Sun, Y., Xu, X., Wang, D., He, J., Zhou, H., et al. (2017). YTH Domain Family 2 Orchestrates Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition/proliferation Dichotomy in Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Cell Cycle 16 (23), 2259–2271. doi:10.1080/15384101.2017.1380125
Chen, M., Wei, L., Law, C.-T., Tsang, F. H.-C., Shen, J., Cheng, C. L.-H., et al. (2018). RNA N6-Methyladenosine Methyltransferase-like 3 Promotes Liver Cancer Progression through YTHDF2-dependent Posttranscriptional Silencing of SOCS2. Hepatology 67 (6), 2254–2270. doi:10.1002/hep.29683
Chen, M., and Wong, C.-M. (2020). The Emerging Roles of N6-Methyladenosine (m6A) Deregulation in Liver Carcinogenesis. Mol. Cancer 19 (1), 44. doi:10.1186/s12943-020-01172-y
Chen, R.-X., Chen, X., Xia, L.-P., Zhang, J.-X., Pan, Z.-Z., Ma, X.-D., et al. (2019). N6-methyladenosine Modification of circNSUN2 Facilitates Cytoplasmic export and Stabilizes HMGA2 to Promote Colorectal Liver Metastasis. Nat. Commun. 10 (1), 4695. doi:10.1038/s41467-019-12651-2
Chen, W. W., Qi, J. W., Hang, Y., Wu, J. X., Zhou, X. X., Chen, J. Z., et al. (2020). Simvastatin Is Beneficial to Lung Cancer Progression by Inducing METTL3-Induced m6A Modification on EZH2 mRNA. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 24 (8), 4263–4270. doi:10.26355/eurrev_202004_21006
Chen, X., Xu, M., Xu, X., Zeng, K., Liu, X., Sun, L., et al. (2020). METTL14 Suppresses CRC Progression via Regulating N6-methyladenosine-dependent Primary miR-375 Processing. Mol. Ther. 28 (2), 599–612. doi:10.1016/j.ymthe.2019.11.016
Chen, X., Yu, C., Guo, M., Zheng, X., Ali, S., Huang, H., et al. (2019). Down-Regulation of m6A mRNA Methylation Is Involved in Dopaminergic Neuronal Death. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 10 (5), 2355–2363. doi:10.1021/acschemneuro.8b00657
Chen, Y.-s., Ouyang, X.-p., Yu, X.-h., Novák, P., Zhou, L., He, P.-p., et al. (2021). N6-Adenosine Methylation (m6A) RNA Modification: an Emerging Role in Cardiovascular Diseases. J. Cardiovasc. Trans. Res. 14, 857–872. doi:10.1007/s12265-021-10108-w
Chen, Y., Wang, J., Xu, D., Xiang, Z., Ding, J., Yang, X., et al. (2021). m6A mRNA Methylation Regulates Testosterone Synthesis through Modulating Autophagy in Leydig Cells. Autophagy 17 (2), 457–475. doi:10.1080/15548627.2020.1720431
Cheng, X., Li, M., Rao, X., Zhang, W., Li, X., Wang, L., et al. (2019). KIAA1429 Regulates the Migration and Invasion of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Altering m6A Modification of ID2 mRNA. Ott 12, 3421–3428. doi:10.2147/ott.S180954
Childs, B. G., Durik, M., Baker, D. J., and van Deursen, J. M. (2015). Cellular Senescence in Aging and Age-Related Disease: from Mechanisms to Therapy. Nat. Med. 21 (12), 1424–1435. doi:10.1038/nm.4000
Chinta, S. J., Lieu, C. A., Demaria, M., Laberge, R.-M., Campisi, J., and Andersen, J. K. (2013). Environmental Stress, Ageing and Glial Cell Senescence: a Novel Mechanistic Link to Parkinson's Disease? J. Intern. Med. 273 (5), 429–436. doi:10.1111/joim.12029
Chokkalla, A. K., Mehta, S. L., Kim, T., Chelluboina, B., Kim, J., and Vemuganti, R. (2019). Transient Focal Ischemia Significantly Alters the M 6 A Epitranscriptomic Tagging of RNAs in the Brain. Stroke 50 (10), 2912–2921. doi:10.1161/strokeaha.119.026433
Clapier, C. R., Iwasa, J., Cairns, B. R., and Peterson, C. L. (2017). Mechanisms of Action and Regulation of ATP-dependent Chromatin-Remodelling Complexes. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cel Biol 18 (7), 407–422. doi:10.1038/nrm.2017.26
Codogno, P., Mehrpour, M., and Proikas-Cezanne, T. (2011). Canonical and Non-canonical Autophagy: Variations on a Common Theme of Self-Eating? Nat. Rev. Mol. Cel Biol 13 (1), 7–12. doi:10.1038/nrm3249
Csepany, T., Lin, A., Baldick, C. J., and Beemon, K. (1990). Sequence Specificity of mRNA N6-Adenosine Methyltransferase. J. Biol. Chem. 265 (33), 20117–20122. doi:10.1016/s0021-9258(17)30477-5
Cui, Q., Shi, H., Ye, P., Li, L., Qu, Q., Sun, G., et al. (2017). m 6 A RNA Methylation Regulates the Self-Renewal and Tumorigenesis of Glioblastoma Stem CellsA RNA Methylation Regulates the Self-Renewal and Tumorigenesis of Glioblastoma Stem Cells. Cel Rep. 18 (11), 2622–2634. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2017.02.059
Day, K., Waite, L. L., Thalacker-Mercer, A., West, A., Bamman, M. M., Brooks, J. D., et al. (2013). Differential DNA Methylation with Age Displays Both Common and Dynamic Features across Human Tissues that Are Influenced by CpG Landscape. Genome Biol. 14 (9), R102. doi:10.1186/gb-2013-14-9-r102
de Haan, G., and Lazare, S. S. (2018). Aging of Hematopoietic Stem Cells. Blood 131 (5), 479–487. doi:10.1182/blood-2017-06-746412
De Jesus, D. F., Zhang, Z., Kahraman, S., Brown, N. K., Chen, M., Hu, J., et al. (2019). m6A mRNA Methylation Regulates Human β-cell Biology in Physiological States and in Type 2 diabetesA mRNA Methylation Regulates Human β-Cell Biology in Physiological States and in Type 2 Diabetes. Nat. Metab. 1 (8), 765–774. doi:10.1038/s42255-019-0089-9
Deng, R., Cheng, Y., Ye, S., Zhang, J., Huang, R., Li, P., et al. (2019). m6A Methyltransferase METTL3 Suppresses Colorectal Cancer Proliferation and Migration through P38/ERK pathwaysA Methyltransferase METTL3 Suppresses Colorectal Cancer Proliferation and Migration through P38/ERK Pathways. Ott 12, 4391–4402. doi:10.2147/ott.S201052
Deng, Y., Zhu, H., Xiao, L., Liu, C., Liu, Y.-L., and Gao, W. (2021). Identification of the Function and Mechanism of m6A Reader IGF2BP2 in Alzheimer's Disease. Aging 13 (21), 24086–24100. doi:10.18632/aging.203652
Desrosiers, R., Friderici, K., and Rottman, F. (1974). Identification of Methylated Nucleosides in Messenger RNA from Novikoff Hepatoma Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 71 (10), 3971–3975. doi:10.1073/pnas.71.10.3971
Di Micco, R., Krizhanovsky, V., Baker, D., and d’Adda di Fagagna, F. (2021). Cellular Senescence in Ageing: from Mechanisms to Therapeutic Opportunities. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cel Biol 22 (2), 75–95. doi:10.1038/s41580-020-00314-w
Dominissini, D., Moshitch-Moshkovitz, S., Schwartz, S., Salmon-Divon, M., Ungar, L., Osenberg, S., et al. (2012). Topology of the Human and Mouse m6A RNA Methylomes Revealed by m6A-Seq. Nature 485 (7397), 201–206. doi:10.1038/nature11112
Dong, G., Yu, J., Shan, G., Su, L., Yu, N., and Yang, S. (2021). N6-Methyladenosine Methyltransferase METTL3 Promotes Angiogenesis and Atherosclerosis by Upregulating the JAK2/STAT3 Pathway via m6A Reader IGF2BP1. Front. Cel Dev. Biol. 9, 731810. doi:10.3389/fcell.2021.731810
Dorn, L. E., Lasman, L., Chen, J., Xu, X., Hund, T. J., Medvedovic, M., et al. (2019). The N 6 -Methyladenosine mRNA Methylase METTL3 Controls Cardiac Homeostasis and Hypertrophy. Circulation 139 (4), 533–545. doi:10.1161/circulationaha.118.036146
Du, M., Zhang, Y., Mao, Y., Mou, J., Zhao, J., Xue, Q., et al. (2017). MiR-33a Suppresses Proliferation of NSCLC Cells via Targeting METTL3 mRNA. Biochem. biophysical Res. Commun. 482 (4), 582–589. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.11.077
Du, Y., Hou, G., Zhang, H., Dou, J., He, J., Guo, Y., et al. (2018). SUMOylation of the m6A-RNA Methyltransferase METTL3 Modulates its Function. Nucleic Acids Res. 46 (10), 5195–5208. doi:10.1093/nar/gky156
Elcheva, I. A., Wood, T., Chiarolanzio, K., Chim, B., Wong, M., Singh, V., et al. (2020). RNA-binding Protein IGF2BP1 Maintains Leukemia Stem Cell Properties by Regulating HOXB4, MYB, and ALDH1A1. Leukemia 34 (5), 1354–1363. doi:10.1038/s41375-019-0656-9
Farr, J. N., and Khosla, S. (2019). Cellular Senescence in Bone. Bone 121, 121–133. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2019.01.015
Feng, Z., Li, Q., Meng, R., Yi, B., and Xu, Q. (2018). METTL 3 Regulates Alternative Splicing of MyD88 upon the Lipopolysaccharide‐induced Inflammatory Response in Human Dental Pulp Cells. J. Cel Mol Med 22 (5), 2558–2568. doi:10.1111/jcmm.13491
Fraga, M. F., Ballestar, E., Paz, M. F., Ropero, S., Setien, F., Ballestar, M. L., et al. (2005). Epigenetic Differences Arise during the Lifetime of Monozygotic Twins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 102 (30), 10604–10609. doi:10.1073/pnas.0500398102
Fu, Y., Dominissini, D., Rechavi, G., and He, C. (2014). Gene Expression Regulation Mediated through Reversible m6A RNA Methylation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 15 (5), 293–306. doi:10.1038/nrg3724
Fu, Y., and Zhuang, X. (2020). m6A-binding YTHDF Proteins Promote Stress Granule Formation. Nat. Chem. Biol. 16 (9), 955–963. doi:10.1038/s41589-020-0524-y
Gan, X. T., Zhao, G., Huang, C. X., Rowe, A. C., Purdham, D. M., and Karmazyn, M. (2013). Identification of Fat Mass and Obesity Associated (FTO) Protein Expression in Cardiomyocytes: Regulation by Leptin and its Contribution to Leptin-Induced Hypertrophy. PloS one 8 (9), e74235. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0074235
Geng, Y., Guan, R., Hong, W., Huang, B., Liu, P., Guo, X., et al. (2020). Identification of m6A-Related Genes and m6A RNA Methylation Regulators in Pancreatic Cancer and Their Association with Survival. Ann. Transl Med. 8 (6), 387. doi:10.21037/atm.2020.03.98
Gu, C., Wang, Z., Zhou, N., Li, G., Kou, Y., Luo, Y., et al. (2019). Mettl14 Inhibits Bladder TIC Self-Renewal and Bladder Tumorigenesis through N6-Methyladenosine of Notch1. Mol. Cancer 18 (1), 168. doi:10.1186/s12943-019-1084-1
Gu, X., Zhang, Y., Li, D., Cai, H., Cai, L., and Xu, Q. (2020). N6-methyladenosine Demethylase FTO Promotes M1 and M2 Macrophage Activation. Cell Signal. 69, 109553. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2020.109553
Guo, F., Liu, X., Cai, H., and Le, W. (2018). Autophagy in Neurodegenerative Diseases: Pathogenesis and Therapy. Brain Pathol. 28 (1), 3–13. doi:10.1111/bpa.12545
Han, J., Wang, J.-z., Yang, X., Yu, H., Zhou, R., Lu, H.-C., et al. (2019). METTL3 Promote Tumor Proliferation of Bladder Cancer by Accelerating Pri-miR221/222 Maturation in m6A-dependent Manner. Mol. Cancer 18 (1), 110. doi:10.1186/s12943-019-1036-9
Han, M., Liu, Z., Xu, Y., Liu, X., Wang, D., Li, F., et al. (2020). Abnormality of m6A mRNA Methylation Is Involved in Alzheimer's Disease. Front. Neurosci. 14, 98. doi:10.3389/fnins.2020.00098
He, Y., Hu, H., Wang, Y., Yuan, H., Lu, Z., Wu, P., et al. (2018). ALKBH5 Inhibits Pancreatic Cancer Motility by Decreasing Long Non-coding RNA KCNK15-AS1 Methylation. Cell Physiol Biochem 48 (2), 838–846. doi:10.1159/000491915
Henikoff, S., and Smith, M. M. (2015). Histone Variants and Epigenetics. Cold Spring Harb Perspect. Biol. 7 (1), a019364. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a019364
Hess, M. E., Hess, S., Meyer, K. D., Verhagen, L. A. W., Koch, L., Brönneke, H. S., et al. (2013). The Fat Mass and Obesity Associated Gene (Fto) Regulates Activity of the Dopaminergic Midbrain Circuitry. Nat. Neurosci. 16 (8), 1042–1048. doi:10.1038/nn.3449
Ho, A. J., Stein, J. L., Hua, X., Lee, S., Hibar, D. P., Leow, A. D., et al. (2010). A Commonly Carried Allele of the Obesity-Related FTO Gene Is Associated with Reduced Brain Volume in the Healthy Elderly. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A. 107 (18), 8404–8409. doi:10.1073/pnas.0910878107
Hongay, C. F., and Orr-Weaver, T. L. (2011). Drosophila Inducer of MEiosis 4 (IME4) Is Required for Notch Signaling during Oogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 108 (36), 14855–14860. doi:10.1073/pnas.1111577108
Horvath, S. (2015). Erratum to: DNA Methylation Age of Human Tissues and Cell Types. Genome Biol. 16 (1), 96. doi:10.1186/s13059-015-0649-6
Hou, J., Zhang, H., Liu, J., Zhao, Z., Wang, J., Lu, Z., et al. (2019). YTHDF2 Reduction Fuels Inflammation and Vascular Abnormalization in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Mol. Cancer 18 (1), 163. doi:10.1186/s12943-019-1082-3
Hsu, P. J., Zhu, Y., Ma, H., Guo, Y., Shi, X., Liu, Y., et al. (2017). Ythdc2 Is an N6-Methyladenosine Binding Protein that Regulates Mammalian Spermatogenesis. Cell Res 27 (9), 1115–1127. doi:10.1038/cr.2017.99
Hu, F., Zhu, D., Pei, W., Lee, I., Zhang, X., Pan, L., et al. (2019). Rhein Inhibits ATP-Triggered Inflammatory Responses in Rheumatoid Rat Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes. Int. immunopharmacology 75, 105780. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2019.105780
Hua, W., Zhao, Y., Jin, X., Yu, D., He, J., Xie, D., et al. (2018). METTL3 Promotes Ovarian Carcinoma Growth and Invasion through the Regulation of AXL Translation and Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition. Gynecol. Oncol. 151 (2), 356–365. doi:10.1016/j.ygyno.2018.09.015
Huan, T., Chen, G., Liu, C., Bhattacharya, A., Rong, J., Chen, B. H., et al. (2018). Age-associated microRNA Expression in Human Peripheral Blood Is Associated with All-Cause Mortality and Age-Related Traits. Aging Cell 17 (1), e12687. doi:10.1111/acel.12687
Huang, H., Camats-Perna, J., Medeiros, R., Anggono, V., and Widagdo, J. (2020b). Altered Expression of the m6A Methyltransferase METTL3 in Alzheimer's Disease. eNeuro 7 (5), 0125–220. doi:10.1523/eneuro.0125-20.2020
Huang, H., Weng, H., and Chen, J. (2020a). m6A Modification in Coding and Non-coding RNAs: Roles and Therapeutic Implications in CancerA Modification in Coding and Non-coding RNAs: Roles and Therapeutic Implications in Cancer. Cancer cell 37 (3), 270–288. doi:10.1016/j.ccell.2020.02.004
Huang, H., Weng, H., Sun, W., Qin, X., Shi, H., Wu, H., et al. (2018). Recognition of RNA N6-Methyladenosine by IGF2BP Proteins Enhances mRNA Stability and Translation. Nat. Cel Biol 20 (3), 285–295. doi:10.1038/s41556-018-0045-z
Huangfu, N., Zheng, W., Xu, Z., Wang, S., Wang, Y., Cheng, J., et al. (2020). RBM4 Regulates M1 Macrophages Polarization through Targeting STAT1-Mediated Glycolysis. Int. immunopharmacology 83, 106432. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106432
Ito, T. K., Yokoyama, M., Yoshida, Y., Nojima, A., Kassai, H., Oishi, K., et al. (2014). A Crucial Role for CDC42 in Senescence-Associated Inflammation and Atherosclerosis. PloS one 9 (7), e102186. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0102186
Ivanova, I., Much, C., Di Giacomo, M., Azzi, C., Morgan, M., Moreira, P. N., et al. (2017). The RNA M 6 A Reader YTHDF2 Is Essential for the Post-transcriptional Regulation of the Maternal Transcriptome and Oocyte Competence. Mol. Cel. 67 (6), 1059–1067. e1054. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2017.08.003
Jia, G., Fu, Y., Zhao, X., Dai, Q., Zheng, G., Yang, Y., et al. (2011). N6-methyladenosine in Nuclear RNA Is a Major Substrate of the Obesity-Associated FTO. Nat. Chem. Biol. 7 (12), 885–887. doi:10.1038/nchembio.687
Jia, R., Chai, P., Wang, S., Sun, B., Xu, Y., Yang, Y., et al. (2019). m6A Modification Suppresses Ocular Melanoma through Modulating HINT2 mRNA Translation. Mol. Cancer 18 (1), 161. doi:10.1186/s12943-019-1088-x
Jian, D., Wang, Y., Jian, L., Tang, H., Rao, L., Chen, K., et al. (2020). METTL14 Aggravates Endothelial Inflammation and Atherosclerosis by Increasing FOXO1 N6-Methyladeosine Modifications. Theranostics 10 (20), 8939–8956. doi:10.7150/thno.45178
Jiang, Z.-x., Wang, Y.-n., Li, Z.-y., Dai, Z.-h., He, Y., Chu, K., et al. (2021). The m6A mRNA Demethylase FTO in Granulosa Cells Retards FOS-dependent Ovarian Aging. Cell Death Dis 12 (8), 744. doi:10.1038/s41419-021-04016-9
Jin, D., Guo, J., Wu, Y., Yang, L., Wang, X., Du, J., et al. (2020). m6A Demethylase ALKBH5 Inhibits Tumor Growth and Metastasis by Reducing YTHDFs-Mediated YAP Expression and Inhibiting miR-107/lats2-Mediated YAP Activity in NSCLCA Demethylase ALKBH5 Inhibits Tumor Growth and Metastasis by Reducing YTHDFs-Mediated YAP Expression and Inhibiting miR-107/lats2-Mediated YAP Activity in NSCLC. Mol. Cancer 19 (1), 40. doi:10.1186/s12943-020-01161-1
Jin, S., Zhang, X., Miao, Y., Liang, P., Zhu, K., She, Y., et al. (2018). m6A RNA Modification Controls Autophagy through Upregulating ULK1 Protein abundanceA RNA Modification Controls Autophagy through Upregulating ULK1 Protein Abundance. Cel Res 28 (9), 955–957. doi:10.1038/s41422-018-0069-8
Justice, J. N., Nambiar, A. M., Tchkonia, T., LeBrasseur, N. K., Pascual, R., Hashmi, S. K., et al. (2019). Senolytics in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Results from a First-In-Human, Open-Label, Pilot Study. EBioMedicine 40, 554–563. doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.12.052
Kaminsky, Z. A., Tang, T., Wang, S.-C., Ptak, C., Oh, G. H. T., Wong, A. H. C., et al. (2009). DNA Methylation Profiles in Monozygotic and Dizygotic Twins. Nat. Genet. 41 (2), 240–245. doi:10.1038/ng.286
Karthiya, R., and Khandelia, P. (2020). m6A RNA Methylation: Ramifications for Gene Expression and Human Health. Mol. Biotechnol. 62 (10), 467–484. doi:10.1007/s12033-020-00269-5
Kasowitz, S. D., Ma, J., Anderson, S. J., Leu, N. A., Xu, Y., Gregory, B. D., et al. (2018). Nuclear m6A Reader YTHDC1 Regulates Alternative Polyadenylation and Splicing during Mouse Oocyte Development. Plos Genet. 14 (5), e1007412. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1007412
Keller, L., Xu, W., Wang, H.-X., Winblad, B., Fratiglioni, L., and Graff, C. (2011). The Obesity Related Gene, FTO, Interacts with APOE, and Is Associated with Alzheimer's Disease Risk: a Prospective Cohort Study. Jad 23 (3), 461–469. doi:10.3233/jad-2010-101068
Kennedy, B. K., Berger, S. L., Brunet, A., Campisi, J., Cuervo, A. M., Epel, E. S., et al. (2014). Geroscience: Linking Aging to Chronic Disease. Cell 159 (4), 709–713. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2014.10.039
Knuckles, P., Lence, T., Haussmann, I. U., Jacob, D., Kreim, N., Carl, S. H., et al. (2018). Zc3h13/Flacc Is Required for Adenosine Methylation by Bridging the mRNA-Binding Factor Rbm15/Spenito to the m6A Machinery Component Wtap/Fl(2)d. Genes Dev. 32 (5-6), 415–429. doi:10.1101/gad.309146.117
Lawrence, M., Daujat, S., and Schneider, R. (2016). Lateral Thinking: How Histone Modifications Regulate Gene Expression. Trends Genet. 32 (1), 42–56. doi:10.1016/j.tig.2015.10.007
Lee, E. K., Lee, M. J., Abdelmohsen, K., Kim, W., Kim, M. M., Srikantan, S., et al. (2011). miR-130 Suppresses Adipogenesis by Inhibiting Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor γ Expression. Mol. Cel Biol 31 (4), 626–638. doi:10.1128/mcb.00894-10
Lee, J.-H., Kim, E. W., Croteau, D. L., and Bohr, V. A. (2020). Heterochromatin: an Epigenetic point of View in Aging. Exp. Mol. Med. 52 (9), 1466–1474. doi:10.1038/s12276-020-00497-4
Lence, T., Akhtar, J., Bayer, M., Schmid, K., Spindler, L., Ho, C. H., et al. (2016). m6A Modulates Neuronal Functions and Sex Determination in DrosophilaA Modulates Neuronal Functions and Sex Determination in Drosophila. Nature 540 (7632), 242–247. doi:10.1038/nature20568
Lewinska, A., Adamczyk-Grochala, J., Kwasniewicz, E., and Wnuk, M. (2017). Downregulation of Methyltransferase Dnmt2 Results in Condition-dependent Telomere Shortening and Senescence or Apoptosis in Mouse Fibroblasts. J. Cel Physiol 232 (12), 3714–3726. doi:10.1002/jcp.25848
Li, G., Song, Y., Liao, Z., Wang, K., Luo, R., Lu, S., et al. (2020). Bone-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Alleviate Compression-Induced Apoptosis of Nucleus Pulposus Cells by N6 Methyladenosine of Autophagy. Cel Death Dis 11 (2), 103. doi:10.1038/s41419-020-2284-8
Li, H., Ren, Y., Mao, K., Hua, F., Yang, Y., Wei, N., et al. (2018). FTO Is Involved in Alzheimer's Disease by Targeting TSC1-mTOR-Tau Signaling. Biochem. biophysical Res. Commun. 498 (1), 234–239. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.02.201
Li, J., Zhu, L., Shi, Y., Liu, J., Lin, L., and Chen, X. (2019). m6A Demethylase FTO Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Tumorigenesis via Mediating PKM2 Demethylation. Am. J. Transl Res. 11 (9), 6084–6092.
Li, J., Han, Y., Zhang, H., Qian, Z., Jia, W., Gao, Y., et al. (2019). The m6A Demethylase FTO Promotes the Growth of Lung Cancer Cells by Regulating the m6A Level of USP7 mRNA. Biochem. biophysical Res. Commun. 512 (3), 479–485. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.03.093
Li, L., Zang, L., Zhang, F., Chen, J., Shen, H., Shu, L., et al. (2017). Fat Mass and Obesity-Associated (FTO) Protein Regulates Adult Neurogenesis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 26 (13), 2398–2411. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddx128
Li, N., and Zhan, X. (2020). Identification of Pathology-specific Regulators of m6A RNA Modification to Optimize Lung Cancer Management in the Context of Predictive, Preventive, and Personalized Medicine. EPMA J. 11 (3), 485–504. doi:10.1007/s13167-020-00220-3
Li, Q., Li, X., Tang, H., Jiang, B., Dou, Y., Gorospe, M., et al. (2017). NSUN2-Mediated m5C Methylation and METTL3/METTL14-Mediated m6A Methylation Cooperatively Enhance P21 Translation. J. Cel. Biochem. 118 (9), 2587–2598. doi:10.1002/jcb.25957
Li, T., Hu, P.-S., Zuo, Z., Lin, J.-F., Li, X., Wu, Q.-N., et al. (2019). METTL3 Facilitates Tumor Progression via an m6A-igf2bp2-dependent Mechanism in Colorectal Carcinoma. Mol. Cancer 18 (1), 112. doi:10.1186/s12943-019-1038-7
Li, X., Tang, J., Huang, W., Wang, F., Li, P., Qin, C., et al. (2017). The M6A Methyltransferase METTL3: Acting as a Tumor Suppressor in Renal Cell Carcinoma. Oncotarget 8 (56), 96103–96116. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.21726
Li, Z., Qian, P., Shao, W., Shi, H., He, X. C., Gogol, M., et al. (2018). Suppression of m6A Reader Ythdf2 Promotes Hematopoietic Stem Cell Expansion. Cel Res 28 (9), 904–917. doi:10.1038/s41422-018-0072-0
Li, Z., Weng, H., Su, R., Weng, X., Zuo, Z., Li, C., et al. (2017). FTO Plays an Oncogenic Role in Acute Myeloid Leukemia as a N 6 -Methyladenosine RNA Demethylase. Cancer cell 31 (1), 127–141. doi:10.1016/j.ccell.2016.11.017
Lin, S., Choe, J., Du, P., Triboulet, R., and Gregory, R. I. (2016). The M 6 A Methyltransferase METTL3 Promotes Translation in Human Cancer Cells. Mol. Cel. 62 (3), 335–345. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2016.03.021
Lin, Z., Niu, Y., Wan, A., Chen, D., Liang, H., Chen, X., et al. (2020). RNA M 6 A Methylation Regulates Sorafenib Resistance in Liver Cancer through FOXO 3‐mediated Autophagy. Embo J. 39 (12), e103181. doi:10.15252/embj.2019103181
Linton, P.-J., Gurney, M., Sengstock, D., Mentzer, R. M., and Gottlieb, R. A. (2015). This Old Heart: Cardiac Aging and Autophagy. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 83, 44–54. doi:10.1016/j.yjmcc.2014.12.017
Liu, J., Eckert, M. A., Harada, B. T., Liu, S.-M., Lu, Z., Yu, K., et al. (2018). m6A mRNA Methylation Regulates AKT Activity to Promote the Proliferation and Tumorigenicity of Endometrial cancerA mRNA Methylation Regulates AKT Activity to Promote the Proliferation and Tumorigenicity of Endometrial Cancer. Nat. Cel Biol 20 (9), 1074–1083. doi:10.1038/s41556-018-0174-4
Liu, J., Luo, G., Sun, J., Men, L., Ye, H., He, C., et al. (2019). METTL14 Is Essential for β-cell Survival and Insulin Secretion. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (Bba) - Mol. Basis Dis. 1865 (9), 2138–2148. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2019.04.011
Liu, J., Ren, D., Du, Z., Wang, H., Zhang, H., and Jin, Y. (2018). m 6 A Demethylase FTO Facilitates Tumor Progression in Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma by Regulating MZF1 expressionA Demethylase FTO Facilitates Tumor Progression in Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma by Regulating MZF1 Expression. Biochem. biophysical Res. Commun. 502 (4), 456–464. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.05.175
Liu, J., Yue, Y., Han, D., Wang, X., Fu, Y., Zhang, L., et al. (2014). A METTL3-METTL14 Complex Mediates Mammalian Nuclear RNA N6-Adenosine Methylation. Nat. Chem. Biol. 10 (2), 93–95. doi:10.1038/nchembio.1432
Liu, N., Dai, Q., Zheng, G., He, C., Parisien, M., and Pan, T. (2015). N6-methyladenosine-dependent RNA Structural Switches Regulate RNA-Protein Interactions. Nature 518 (7540), 560–564. doi:10.1038/nature14234
Liu, P., Li, F., Lin, J., Fukumoto, T., Nacarelli, T., Hao, X., et al. (2021). m6A-independent Genome-wide METTL3 and METTL14 Redistribution Drives the Senescence-Associated Secretory phenotypeA-independent Genome-wide METTL3 and METTL14 Redistribution Drives the Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype. Nat. Cel Biol 23 (4), 355–365. doi:10.1038/s41556-021-00656-3
Luo, R., Su, L.-Y., Li, G., Yang, J., Liu, Q., Yang, L.-X., et al. (2020). Activation of PPARA-Mediated Autophagy Reduces Alzheimer Disease-like Pathology and Cognitive Decline in a Murine Model. Autophagy 16 (1), 52–69. doi:10.1080/15548627.2019.1596488
Ma, J. z., Yang, F., Zhou, C. c., Liu, F., Yuan, J. h., Wang, F., et al. (2017). METTL14 Suppresses the Metastatic Potential of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Modulating N 6 ‐methyladenosine‐dependent Primary MicroRNA Processing. Hepatology 65 (2), 529–543. doi:10.1002/hep.28885
Mathiyalagan, P., Adamiak, M., Mayourian, J., Sassi, Y., Liang, Y., Agarwal, N., et al. (2019). FTO-dependent N 6 -Methyladenosine Regulates Cardiac Function during Remodeling and Repair. Circulation 139 (4), 518–532. doi:10.1161/circulationaha.118.033794
Men, L., Sun, J., Luo, G., and Ren, D. (2019). Acute Deletion of METTL14 in β-Cells of Adult Mice Results in Glucose Intolerance. Endocrinology 160 (10), 2388–2394. doi:10.1210/en.2019-00350
Min, K.-W., Zealy, R. W., Davila, S., Fomin, M., Cummings, J. C., Makowsky, D., et al. (2018). Profiling of m6A RNA Modifications Identified an Age-Associated Regulation of AGO2 mRNA Stability. Aging Cell 17 (3), e12753. doi:10.1111/acel.12753
Müller, S., Glaß, M., Singh, A. K., Haase, J., Bley, N., Fuchs, T., et al. (2019). IGF2BP1 Promotes SRF-dependent Transcription in Cancer in a m6A- and miRNA-dependent Manner. Nucleic Acids Res. 47 (1), 375–390. doi:10.1093/nar/gky1012
Naren, D., Yan, T., Gong, Y., Huang, J., Zhang, D., Sang, L., et al. (2021). High Wilms' Tumor 1 Associating Protein Expression Predicts Poor Prognosis in Acute Myeloid Leukemia and Regulates m6A Methylation of MYC mRNA. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 147 (1), 33–47. doi:10.1007/s00432-020-03373-w
Ni, W., Yao, S., Zhou, Y., Liu, Y., Huang, P., Zhou, A., et al. (2019). Long Noncoding RNA GAS5 Inhibits Progression of Colorectal Cancer by Interacting with and Triggering YAP Phosphorylation and Degradation and Is Negatively Regulated by the m6A Reader YTHDF3. Mol. Cancer 18 (1), 143. doi:10.1186/s12943-019-1079-y
Niu, Y., Lin, Z., Wan, A., Chen, H., Liang, H., Sun, L., et al. (2019). RNA N6-Methyladenosine Demethylase FTO Promotes Breast Tumor Progression through Inhibiting BNIP3. Mol. Cancer 18 (1), 46. doi:10.1186/s12943-019-1004-4
Pang, P., Qu, Z., Yu, S., Pang, X., Li, X., Gao, Y., et al. (2021). Mettl14 Attenuates Cardiac Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Regulating Wnt1/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway. Front. Cel Dev. Biol. 9, 762853. doi:10.3389/fcell.2021.762853
Papp, D., Kovács, T., Billes, V., Varga, M., Tarnóci, A., Hackler, L., et al. (2016). AUTEN-67, an Autophagy-Enhancing Drug Candidate with Potent Antiaging and Neuroprotective Effects. Autophagy 12 (2), 273–286. doi:10.1080/15548627.2015.1082023
Paris, J., Morgan, M., Campos, J., Spencer, G. J., Shmakova, A., Ivanova, I., et al. (2019). Targeting the RNA m6A Reader YTHDF2 Selectively Compromises Cancer Stem Cells in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cell stem cell 25 (1), 137–148. e136. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2019.03.021
Patil, D. P., Chen, C.-K., Pickering, B. F., Chow, A., Jackson, C., Guttman, M., et al. (2016). m6A RNA Methylation Promotes XIST-Mediated Transcriptional repressionA RNA Methylation Promotes XIST-Mediated Transcriptional Repression. Nature 537 (7620), 369–373. doi:10.1038/nature19342
Pendleton, K. E., Chen, B., Liu, K., Hunter, O. V., Xie, Y., Tu, B. P., et al. (2017). The U6 snRNA M 6 A Methyltransferase METTL16 Regulates SAM Synthetase Intron Retention. Cell 169 (5), 824–835. e814. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2017.05.003
Peters, A., Nawrot, T. S., and Baccarelli, A. A. (2021). Hallmarks of Environmental Insults. Cell 184 (6), 1455–1468. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2021.01.043
Ping, X.-L., Sun, B.-F., Wang, L., Xiao, W., Yang, X., Wang, W.-J., et al. (2014). Mammalian WTAP Is a Regulatory Subunit of the RNA N6-Methyladenosine Methyltransferase. Cel Res 24 (2), 177–189. doi:10.1038/cr.2014.3
Portela, A., and Esteller, M. (2010). Epigenetic Modifications and Human Disease. Nat. Biotechnol. 28 (10), 1057–1068. doi:10.1038/nbt.1685
Quan, W., Li, J., Liu, L., Zhang, Q., Qin, Y., Pei, X., et al. (2021). Influence of N6-Methyladenosine Modification Gene HNRNPC on Cell Phenotype in Parkinson's Disease. Parkinson's Dis. 2021, 1–10. doi:10.1155/2021/9919129
Richard, E. M., Polla, D. L., Assir, M. Z., Contreras, M., Shahzad, M., Khan, A. A., et al. (2019). Bi-allelic Variants in METTL5 Cause Autosomal-Recessive Intellectual Disability and Microcephaly. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 105 (4), 869–878. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2019.09.007
Roundtree, I. A., Luo, G.-Z., Zhang, Z., Wang, X., Zhou, T., Cui, Y., et al. (2017). YTHDC1 Mediates Nuclear export of N6-Methyladenosine Methylated mRNAs. Elife 6. doi:10.7554/eLife.31311
Rubinsztein, D. C., Mariño, G., and Kroemer, G. (2011). Autophagy and Aging. Cell 146 (5), 682–695. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2011.07.030
Rubio, R. M., Depledge, D. P., Bianco, C., Thompson, L., and Mohr, I. (2018). RNA M6 A Modification Enzymes Shape Innate Responses to DNA by Regulating Interferon β. Genes Dev. 32 (23-24), 1472–1484. doi:10.1101/gad.319475.118
Schäfer, K. P. (1982). RNA Synthesis and Processing Reactions in a Subcellular System from Mouse L Cells. Hoppe-Seyler´s Z. für physiologische Chem. 363 (1), 33–44. doi:10.1515/bchm2.1982.363.1.33
Schöller, E., Weichmann, F., Treiber, T., Ringle, S., Treiber, N., Flatley, A., et al. (2018). Interactions, Localization, and Phosphorylation of the m6A Generating METTL3-METTL14-WTAP Complex. Rna 24 (4), 499–512. doi:10.1261/rna.064063.117
Schwartz, S., Mumbach, M. R., Jovanovic, M., Wang, T., Maciag, K., Bushkin, G. G., et al. (2014). Perturbation of m6A Writers Reveals Two Distinct Classes of mRNA Methylation at Internal and 5′ Sites. Cel Rep. 8 (1), 284–296. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2014.05.048
Sergiev, P. V., Golovina, A. Y., Osterman, I. A., Nesterchuk, M. V., Sergeeva, O. V., Chugunova, A. A., et al. (2016). N6-Methylated Adenosine in RNA: From Bacteria to Humans. J. Mol. Biol. 428 (10 Pt B), 2134–2145. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2015.12.013
Shafik, A. M., Zhang, F., Guo, Z., Dai, Q., Pajdzik, K., Li, Y., et al. (2021). N6-methyladenosine Dynamics in Neurodevelopment and Aging, and its Potential Role in Alzheimer's Disease. Genome Biol. 22 (1), 17. doi:10.1186/s13059-020-02249-z
Shen, C., Sheng, Y., Zhu, A. C., Robinson, S., Jiang, X., Dong, L., et al. (2020). RNA Demethylase ALKBH5 Selectively Promotes Tumorigenesis and Cancer Stem Cell Self-Renewal in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cell stem cell 27 (1), 64–80. e69. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2020.04.009
Shen, C., Xuan, B., Yan, T., Ma, Y., Xu, P., Tian, X., et al. (2020). m6A-dependent Glycolysis Enhances Colorectal Cancer progressionA-dependent Glycolysis Enhances Colorectal Cancer Progression. Mol. Cancer 19 (1), 72. doi:10.1186/s12943-020-01190-w
Shen, C., Zhang, Z., Xie, T., Ji, J., Xu, J., Lin, L., et al. (2019). Rhein Suppresses Lung Inflammatory Injury Induced by Human Respiratory Syncytial Virus through Inhibiting NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation via NF-Κb Pathway in Mice. Front. Pharmacol. 10, 1600. doi:10.3389/fphar.2019.01600
Shen, X. P., Ling, X., Lu, H., Zhou, C. X., Zhang, J. K., and Yu, Q. (2018). Low Expression of microRNA-1266 Promotes Colorectal Cancer Progression via Targeting FTO. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 22 (23), 8220–8226. doi:10.26355/eurrev_201812_16516
Sheng, H., Li, Z., Su, S., Sun, W., Zhang, X., Li, L., et al. (2020). YTH Domain Family 2 Promotes Lung Cancer Cell Growth by Facilitating 6-phosphogluconate Dehydrogenase mRNA Translation. Carcinogenesis 41 (5), 541–550. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgz152
Shi, H., Wang, X., Lu, Z., Zhao, B. S., Ma, H., Hsu, P. J., et al. (2017). YTHDF3 Facilitates Translation and Decay of N6-Methyladenosine-Modified RNA. Cel Res 27 (3), 315–328. doi:10.1038/cr.2017.15
Shi, Y., Fan, S., Wu, M., Zuo, Z., Li, X., Jiang, L., et al. (2019). YTHDF1 Links Hypoxia Adaptation and Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Progression. Nat. Commun. 10 (1), 4892. doi:10.1038/s41467-019-12801-6
Spitale, R. C., Flynn, R. A., Zhang, Q. C., Crisalli, P., Lee, B., Jung, J.-W., et al. (2015). Structural Imprints In Vivo Decode RNA Regulatory Mechanisms. Nature 519 (7544), 486–490. doi:10.1038/nature14263
Su, R., Dong, L., Li, Y., Gao, M., Han, L., Wunderlich, M., et al. (2020). Targeting FTO Suppresses Cancer Stem Cell Maintenance and Immune Evasion. Cancer cell 38 (1), 79–96. e11. doi:10.1016/j.ccell.2020.04.017
Sun, T., Wu, R., and Ming, L. (2019). The Role of m6A RNA Methylation in Cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 112, 108613. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108613
Sun, Y., Dong, D., Xia, Y., Hao, L., Wang, W., and Zhao, C. (2022). YTHDF1 Promotes Breast Cancer Cell Growth, DNA Damage Repair and Chemoresistance. Cel Death Dis 13 (3), 230. doi:10.1038/s41419-022-04672-5
Svobodová Kovaříková, A., Stixová, L., Kovařík, A., Komůrková, D., Legartová, S., Fagherazzi, P., et al. (2020). N6-Adenosine Methylation in RNA and a Reduced m3G/TMG Level in Non-coding RNAs Appear at Microirradiation-Induced DNA Lesions. Cells 9 (2), 360. doi:10.3390/cells9020360
Tanabe, A., Tanikawa, K., Tsunetomi, M., Takai, K., Ikeda, H., Konno, J., et al. (2016). RNA Helicase YTHDC2 Promotes Cancer Metastasis via the Enhancement of the Efficiency by Which HIF-1α mRNA Is Translated. Cancer Lett. 376 (1), 34–42. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2016.02.022
Tang, C., Klukovich, R., Peng, H., Wang, Z., Yu, T., Zhang, Y., et al. (2018). ALKBH5-dependent m6A Demethylation Controls Splicing and Stability of Long 3′-UTR mRNAs in Male Germ Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 115 (2), E325–e333. doi:10.1073/pnas.1717794115
Tang, H.-W., Weng, J.-H., Lee, W. X., Hu, Y., Gu, L., Cho, S., et al. (2021). mTORC1-chaperonin CCT Signaling Regulates M 6 A RNA Methylation to Suppress Autophagy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 118 (10), e2021945118. doi:10.1073/pnas.2021945118
Tang, J., Wang, F., Cheng, G., Si, S., Sun, X., Han, J., et al. (2018). Wilms' Tumor 1-associating Protein Promotes Renal Cell Carcinoma Proliferation by Regulating CDK2 mRNA Stability. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 37 (1), 40. doi:10.1186/s13046-018-0706-6
Tang, X., Liu, S., Chen, D., Zhao, Z., and Zhou, J. (2019). The Role of the Fat Mass and Obesity-associated P-rotein in the P-roliferation of P-ancreatic C-ancer C-ells. Oncol. Lett. 17 (2), 2473–2478. doi:10.3892/ol.2018.9873
Uddin, M. B., Wang, Z., and Yang, C. (2021). The m6A RNA Methylation Regulates Oncogenic Signaling Pathways Driving Cell Malignant Transformation and Carcinogenesis. Mol. Cancer 20 (1), 61. doi:10.1186/s12943-021-01356-0
Ueda, Y., Ooshio, I., Fusamae, Y., Kitae, K., Kawaguchi, M., Jingushi, K., et al. (2017). AlkB Homolog 3-mediated tRNA Demethylation Promotes Protein Synthesis in Cancer Cells. Sci. Rep. 7, 42271. doi:10.1038/srep42271
Ungvari, Z., Tarantini, S., Sorond, F., Merkely, B., and Csiszar, A. (2020). Mechanisms of Vascular Aging, A Geroscience Perspective. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 75 (8), 931–941. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2019.11.061
Unnikrishnan, A., Freeman, W. M., Jackson, J., Wren, J. D., Porter, H., and Richardson, A. (2019). The Role of DNA Methylation in Epigenetics of Aging. Pharmacol. Ther. 195, 172–185. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2018.11.001
van Tran, N., Ernst, F. G. M., Hawley, B. R., Zorbas, C., Ulryck, N., Hackert, P., et al. (2019). The Human 18S rRNA m6A Methyltransferase METTL5 Is Stabilized by TRMT112. Nucleic Acids Res. 47 (15), 7719–7733. doi:10.1093/nar/gkz619
Vu, L. P., Pickering, B. F., Cheng, Y., Zaccara, S., Nguyen, D., Minuesa, G., et al. (2017). The N6-Methyladenosine (m6A)-Forming Enzyme METTL3 Controls Myeloid Differentiation of normal Hematopoietic and Leukemia Cells. Nat. Med. 23 (11), 1369–1376. doi:10.1038/nm.4416
Wang, C.-Y., Shie, S.-S., Wen, M.-S., Hung, K.-C., Hsieh, I.-C., Yeh, T.-S., et al. (2015). Loss of FTO in Adipose Tissue Decreases Angptl4 Translation and Alters Triglyceride Metabolism. Sci. Signal. 8 (407), ra127. doi:10.1126/scisignal.aab3357
Wang, H., Xu, B., and Shi, J. (2020). N6-methyladenosine METTL3 Promotes the Breast Cancer Progression via Targeting Bcl-2. Gene 722, 144076. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2019.144076
Wang, J., Ishfaq, M., Xu, L., Xia, C., Chen, C., and Li, J. (2019). METTL3/m6A/miRNA-873-5p Attenuated Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis in Colistin-Induced Kidney Injury by Modulating Keap1/Nrf2 Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 10, 517. doi:10.3389/fphar.2019.00517
Wang, J., Li, Y., Wang, P., Han, G., Zhang, T., Chang, J., et al. (2020). Leukemogenic Chromatin Alterations Promote AML Leukemia Stem Cells via a KDM4C-ALKBH5-AXL Signaling Axis. Cell stem cell 27 (1), 81–97. e88. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2020.04.001
Wang, J., Yan, S., Lu, H., Wang, S., and Xu, D. (2019). METTL3 Attenuates LPS-Induced Inflammatory Response in Macrophages via NF-Κb Signaling Pathway. Mediators Inflamm. 2019, 1–8. doi:10.1155/2019/3120391
Wang, J., Zhang, J., Ma, Y., Zeng, Y., Lu, C., Yang, F., et al. (2021). WTAP Promotes Myocardial Ischemia/reperfusion Injury by Increasing Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress via Regulating m6A Modification of ATF4 mRNA. Aging 13 (8), 11135–11149. doi:10.18632/aging.202770
Wang, K. C., and Chang, H. Y. (2018). Epigenomics. Circ. Res. 122 (9), 1191–1199. doi:10.1161/circresaha.118.310998
Wang, Q., Chen, C., Ding, Q., Zhao, Y., Wang, Z., Chen, J., et al. (2020). METTL3-mediated m6A Modification of HDGF mRNA Promotes Gastric Cancer Progression and Has Prognostic Significance. Gut 69 (7), 1193–1205. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2019-319639
Wang, Q., Guo, X., Li, L., Gao, Z., Su, X., Ji, M., et al. (2020). N6-methyladenosine METTL3 Promotes Cervical Cancer Tumorigenesis and Warburg Effect through YTHDF1/HK2 Modification. Cel Death Dis 11 (10), 911. doi:10.1038/s41419-020-03071-y
Wang, Q., Zhang, H., Chen, Q., Wan, Z., Gao, X., and Qian, W. (2019). Identification of METTL14 in Kidney Renal Clear Cell Carcinoma Using Bioinformatics Analysis. Dis. markers 2019, 1–11. doi:10.1155/2019/5648783
Wang, T., Kong, S., Tao, M., and Ju, S. (2020). The Potential Role of RNA N6-Methyladenosine in Cancer Progression. Mol. Cancer 19 (1), 88. doi:10.1186/s12943-020-01204-7
Wang, X., Lu, Z., Gomez, A., Hon, G. C., Yue, Y., Han, D., et al. (2014). N6-methyladenosine-dependent Regulation of Messenger RNA Stability. Nature 505 (7481), 117–120. doi:10.1038/nature12730
Wang, X., Zhao, B. S., Roundtree, I. A., Lu, Z., Han, D., Ma, H., et al. (2015). N6-methyladenosine Modulates Messenger RNA Translation Efficiency. Cell 161 (6), 1388–1399. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2015.05.014
Wang, Y., Li, Y., Toth, J. I., Petroski, M. D., Zhang, Z., and Zhao, J. C. (2014). N6-methyladenosine Modification Destabilizes Developmental Regulators in Embryonic Stem Cells. Nat. Cel Biol 16 (2), 191–198. doi:10.1038/ncb2902
Wang, Y., Sun, J., Lin, Z., Zhang, W., Wang, S., Wang, W., et al. (2020). m6A mRNA Methylation Controls Functional Maturation in Neonatal Murine β-CellsA mRNA Methylation Controls Functional Maturation in Neonatal Murine β-Cells. Diabetes 69 (8), 1708–1722. doi:10.2337/db19-0906
Warda, A. S., Kretschmer, J., Hackert, P., Lenz, C., Urlaub, H., Höbartner, C., et al. (2017). Human METTL16 Is a N 6 ‐methyladenosine (M 6 A) Methyltransferase that Targets pre‐mRNAs and Various Non‐coding RNAs. EMBO Rep. 18 (11), 2004–2014. doi:10.15252/embr.201744940
Wen, J., Lv, R., Ma, H., Shen, H., He, C., Wang, J., et al. (2018). Zc3h13 Regulates Nuclear RNA m6A Methylation and Mouse Embryonic Stem Cell Self-Renewal. Mol. Cel 69 (6), 1028–1038. e1026. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2018.02.015
Weng, H., Huang, H., Wu, H., Qin, X., Zhao, B. S., Dong, L., et al. (2018). METTL14 Inhibits Hematopoietic Stem/Progenitor Differentiation and Promotes Leukemogenesis via mRNA m6A Modification. Cell stem cell 22 (2), 191–205. e199. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2017.11.016
Woo, H.-H., and Chambers, S. K. (2019). Human ALKBH3-Induced m1A Demethylation Increases the CSF-1 mRNA Stability in Breast and Ovarian Cancer Cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (Bba) - Gene Regul. Mech. 1862 (1), 35–46. doi:10.1016/j.bbagrm.2018.10.008
Wu, J., Frazier, K., Zhang, J., Gan, Z., Wang, T., and Zhong, X. (2020). Emerging Role of M 6 A RNA Methylation in Nutritional Physiology and Metabolism. Obes. Rev. 21 (1), e12942. doi:10.1111/obr.12942
Wu, Q., Yuan, X., Han, R., Zhang, H., and Xiu, R. (2019). Epitranscriptomic Mechanisms of N6-Methyladenosine Methylation Regulating Mammalian Hypertension Development by Determined Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats Pericytes. Epigenomics 11 (12), 1359–1370. doi:10.2217/epi-2019-0148
Wu, Y., Yang, X., Chen, Z., Tian, L., Jiang, G., Chen, F., et al. (2019). m6A-induced lncRNA RP11 Triggers the Dissemination of Colorectal Cancer Cells via Upregulation of Zeb1A-Induced lncRNA RP11 Triggers the Dissemination of Colorectal Cancer Cells via Upregulation of Zeb1. Mol. Cancer 18 (1), 87. doi:10.1186/s12943-019-1014-2
Wu, Z., Shi, Y., Lu, M., Song, M., Yu, Z., Wang, J., et al. (2020). METTL3 Counteracts Premature Aging via m6A-dependent Stabilization of MIS12 mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 48 (19), 11083–11096. doi:10.1093/nar/gkaa816
Xiao, W., Adhikari, S., Dahal, U., Chen, Y.-S., Hao, Y.-J., Sun, B.-F., et al. (2016). Nuclear M 6 A Reader YTHDC1 Regulates mRNA Splicing. Mol. Cel 61 (4), 507–519. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2016.01.012
Yang, J., Liu, J., Zhao, S., and Tian, F. (2020). N6-Methyladenosine METTL3 Modulates the Proliferation and Apoptosis of Lens Epithelial Cells in Diabetic Cataract. Mol. Ther. - Nucleic Acids 20, 111–116. doi:10.1016/j.omtn.2020.02.002
Yang, S., Wei, J., Cui, Y.-H., Park, G., Shah, P., Deng, Y., et al. (2019). m6A mRNA Demethylase FTO Regulates Melanoma Tumorigenicity and Response to Anti-PD-1 blockadeA mRNA Demethylase FTO Regulates Melanoma Tumorigenicity and Response to Anti-PD-1 Blockade. Nat. Commun. 10 (1), 2782. doi:10.1038/s41467-019-10669-0
Yang, X., Zhang, S., He, C., Xue, P., Zhang, L., He, Z., et al. (2020). METTL14 Suppresses Proliferation and Metastasis of Colorectal Cancer by Down-Regulating Oncogenic Long Non-coding RNA XIST. Mol. Cancer 19 (1), 46. doi:10.1186/s12943-020-1146-4
Yang, Y., Shen, F., Huang, W., Qin, S., Huang, J.-T., Sergi, C., et al. (2019). Glucose Is Involved in the Dynamic Regulation of m6A in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 104 (3), 665–673. doi:10.1210/jc.2018-00619
Yang, Z., Jiang, X., Li, D., and Jiang, X. (2020). HBXIP Promotes Gastric Cancer via METTL3-Mediated MYC mRNA m6A Modification. Aging 12 (24), 24967–24982. doi:10.18632/aging.103767
Yang, Z., Yu, G.-l., Zhu, X., Peng, T.-h., and Lv, Y.-c. (2022). Critical Roles of FTO-Mediated mRNA m6A Demethylation in Regulating Adipogenesis and Lipid Metabolism: Implications in Lipid Metabolic Disorders. Genes Dis. 9 (1), 51–61. doi:10.1016/j.gendis.2021.01.005
Yankova, E., Blackaby, W., Albertella, M., Rak, J., De Braekeleer, E., Tsagkogeorga, G., et al. (2021). Small-molecule Inhibition of METTL3 as a Strategy against Myeloid Leukaemia. Nature 593 (7860), 597–601. doi:10.1038/s41586-021-03536-w
Yen, Y.-P., and Chen, J.-A. (2021). The m6A Epitranscriptome on Neural Development and Degeneration. J. Biomed. Sci. 28 (1), 40. doi:10.1186/s12929-021-00734-6
Yi, D., Wang, R., Shi, X., Xu, L., Yilihamu, Y. e., and Sang, J. (2020). METTL14 Promotes the Migration and Invasion of Breast Cancer Cells by Modulating N6-methyladenosine and hsa-miR-146a-5p E-xpression. Oncol. Rep. 43 (5), 1375–1386. doi:10.3892/or.2020.7515
Yu, D., Horton, J. R., Yang, J., Hajian, T., Vedadi, M., Sagum, C. A., et al. (2021). Human MettL3-MettL14 RNA Adenine Methyltransferase Complex Is Active on Double-Stranded DNA Containing Lesions. Nucleic Acids Res. 49 (20), 11629–11642. doi:10.1093/nar/gkab460
Yue, Y., Liu, J., Cui, X., Cao, J., Luo, G., Zhang, Z., et al. (2018). VIRMA Mediates Preferential m6A mRNA Methylation in 3′UTR and Near Stop Codon and Associates with Alternative Polyadenylation. Cell Discov 4, 10. doi:10.1038/s41421-018-0019-0
Zha, X., Xi, X., Fan, X., Ma, M., Zhang, Y., and Yang, Y. (2020). Overexpression of METTL3 Attenuates High-Glucose Induced RPE Cell Pyroptosis by Regulating miR-25-3p/PTEN/Akt Signaling cascade through DGCR8. Aging 12 (9), 8137–8150. doi:10.18632/aging.103130
Zhang, B., Xu, Y., Cui, X., Jiang, H., Luo, W., Weng, X., et al. (2021). Alteration of m6A RNA Methylation in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 8, 647806. doi:10.3389/fcvm.2021.647806
Zhang, B. Y., Han, L., Tang, Y. F., Zhang, G. X., Fan, X. L., Zhang, J. J., et al. (2020). METTL14 Regulates M6A Methylation-Modified Primary miR-19a to Promote Cardiovascular Endothelial Cell Proliferation and Invasion. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 24 (12), 7015–7023. doi:10.26355/eurrev_202006_21694
Zhang, C., Chen, L., Peng, D., Jiang, A., He, Y., Zeng, Y., et al. (2020). METTL3 and N6-Methyladenosine Promote Homologous Recombination-Mediated Repair of DSBs by Modulating DNA-RNA Hybrid Accumulation. Mol. Cel. 79 (3), 425–442. e427. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2020.06.017
Zhang, C., Chen, Y., Sun, B., Wang, L., Yang, Y., Ma, D., et al. (2017). m6A Modulates Haematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cell specificationA Modulates Haematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cell Specification. Nature 549 (7671), 273–276. doi:10.1038/nature23883
Zhang, J., Bai, R., Li, M., Ye, H., Wu, C., Wang, C., et al. (2019). Excessive miR-25-3p Maturation via N6-Methyladenosine Stimulated by Cigarette Smoke Promotes Pancreatic Cancer Progression. Nat. Commun. 10 (1), 1858. doi:10.1038/s41467-019-09712-x
Zhang, J., Guo, S., Piao, H.-y., Wang, Y., Wu, Y., Meng, X.-y., et al. (2019). ALKBH5 Promotes Invasion and Metastasis of Gastric Cancer by Decreasing Methylation of the lncRNA NEAT1. J. Physiol. Biochem. 75 (3), 379–389. doi:10.1007/s13105-019-00690-8
Zhang, J., Tsoi, H., Li, X., Wang, H., Gao, J., Wang, K., et al. (2016). Carbonic Anhydrase IVinhibits colon Cancer Development by Inhibiting the Wnt Signalling Pathway through Targeting the WTAP-WT1-TBL1 axis. Gut 65 (9), 1482–1493. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2014-308614
Zhang, Y., Liu, X., Liu, L., Li, J., Hu, Q., and Sun, R. (2020). Expression and Prognostic Significance of m6A-Related Genes in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Med. Sci. Monit. 26, e919644. doi:10.12659/msm.919644
Zhao, B. S., Roundtree, I. A., and He, C. (2017). Post-transcriptional Gene Regulation by mRNA Modifications. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cel Biol 18 (1), 31–42. doi:10.1038/nrm.2016.132
Zhao, F., Xu, Y., Gao, S., Qin, L., Austria, Q., Siedlak, S. L., et al. (2021). METTL3-dependent RNA m6A Dysregulation Contributes to Neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's Disease through Aberrant Cell Cycle Events. Mol. Neurodegeneration 16 (1), 70. doi:10.1186/s13024-021-00484-x
Zhao, T., Li, X., Sun, D., and Zhang, Z. (2019). Oxidative Stress: One Potential Factor for Arsenite-Induced Increase of N6-Methyladenosine in Human Keratinocytes. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 69, 95–103. doi:10.1016/j.etap.2019.04.005
Zhao, X., Yang, Y., Sun, B.-F., Shi, Y., Yang, X., Xiao, W., et al. (2014). FTO-dependent Demethylation of N6-Methyladenosine Regulates mRNA Splicing and Is Required for Adipogenesis. Cel Res 24 (12), 1403–1419. doi:10.1038/cr.2014.151
Zheng, Z.-Q., Li, Z.-X., Zhou, G.-Q., Lin, L., Zhang, L.-L., Lv, J.-W., et al. (2019). Long Noncoding RNA FAM225A Promotes Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Tumorigenesis and Metastasis by Acting as ceRNA to Sponge miR-590-3p/miR-1275 and Upregulate ITGB3. Cancer Res. 79 (18), 4612–4626. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.Can-19-0799
Zhong, X., Yu, J., Frazier, K., Weng, X., Li, Y., Cham, C. M., et al. (2018). Circadian Clock Regulation of Hepatic Lipid Metabolism by Modulation of m6A mRNA Methylation. Cel Rep. 25 (7), 1816–1828. e1814. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2018.10.068
Zhou, R., Gao, Y., Lv, D., Wang, C., Wang, D., and Li, Q. (2019). METTL3 Mediated m6A Modification Plays an Oncogenic Role in Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma by Regulating ΔNp63. Biochem. biophysical Res. Commun. 515 (2), 310–317. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.05.155
Zhou, Z., Lv, J., Yu, H., Han, J., Yang, X., Feng, D., et al. (2020). Mechanism of RNA Modification N6-Methyladenosine in Human Cancer. Mol. Cancer 19 (1), 104. doi:10.1186/s12943-020-01216-3
Zhu, H., Gan, X., Jiang, X., Diao, S., Wu, H., and Hu, J. (2019). ALKBH5 Inhibited Autophagy of Epithelial Ovarian Cancer through miR-7 and BCL-2. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 38 (1), 163. doi:10.1186/s13046-019-1159-2
Zhu, H., Sun, B., Zhu, L., Zou, G., and Shen, Q. (2021). N6-Methyladenosine Induced miR-34a-5p Promotes TNF-α-Induced Nucleus Pulposus Cell Senescence by Targeting SIRT1. Front. Cel Dev. Biol. 9, 642437. doi:10.3389/fcell.2021.642437
Zhu, K., Li, Y., and Xu, Y. (2021). The FTO m6A Demethylase Inhibits the Invasion and Migration of Prostate Cancer Cells by Regulating Total m6A Levels. Life Sci. 271, 119180. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119180
Zhu, S., and Lu, Y. (2020). Dexmedetomidine Suppressed the Biological Behavior of HK-2 Cells Treated with LPS by Down-Regulating ALKBH5. Inflammation 43 (6), 2256–2263. doi:10.1007/s10753-020-01293-y
Zhuang, C., Zhuang, C., Luo, X., Huang, X., Yao, L., Li, J., et al. (2019). N6-methyladenosine Demethylase FTO Suppresses clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma through a Novel FTO-PGC-1α Signalling axis. J. Cel Mol Med 23 (3), 2163–2173. doi:10.1111/jcmm.14128
Zou, D., Dong, L., Li, C., Yin, Z., Rao, S., and Zhou, Q. (2019). The m6A Eraser FTO Facilitates Proliferation and Migration of Human Cervical Cancer Cells. Cancer Cel Int 19, 321. doi:10.1186/s12935-019-1045-1
Glossary
6-OHDA 6-hydroxydopamine
AD Alzheimer's disease
ADC adenocarcinoma
AKT Protein kinase B
ALKBH3 AlkB homologue 3
ALKBH5 AlkB homologue 5
AML acute myeloid leukaemia
AMPK AMP-activated protein kinase
ANGPTL4 angiopoietin-like 4
APOE apolipoprotein E
ASB2 ankyrin repeat and SOCS box containing 2
ATG13 autophagy-related 13
BA9 Brodmann area 9
BCL2 B-cell CLL/lymphoma 2
CAMKK2 calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase 2
CCND1 cyclin D1
CDK2 cyclin-dependent kinase 2
CDK4 cyclin-dependent kinase 4
circNSUN2 circRNA NOP2/SUN domain family, member 2
circRNA cyclic RNA
CRP C-reactive protein
CVD cardiovascular disease
DDR DNA damage response
DGCR8 DiGeorge syndrome critical region 8
DNMT3A DNA methyltransferase 3α
EGFR epidermal growth factor
EZH2 enhancer of zeste homologue 2
FIP200 family interacting protein of 200kDa
FOXO3 Forkhead box O3
FTO fat mass and obesity-related proteins
HDF human diploid fibroblasts
HGPS Hutchinson-Gilford progeria
HLEC human lens epithelial cell
hMSC human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell
HNRNPC heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein C
HNRNPG heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein G
HNRNPA2B1 heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A2B1
ICAM-1 intercellular adhesion molecule 1
IFN: interferon
IGF2BP insulin-like growth factor 2 binding protein
IL Interleukin
LPS Lipopolysaccharides
lncRNA long non-coding RNA;
lncRNA XIST long-chain non-coding RNA X-inactive specific transcript
m6A N6-methyladenosine; MAPK: mitogen-activated protein kinase
MERIP-seq m6A methylation RNA immunoprecipitation sequencing
METTL3 RNA methyltransferase-like protein 3
METTL5 RNA methyltransferase-like protein 5
METTL14 RNA methyltransferase-like protein 14
METTL16 RNA methyltransferase-like protein 16
miRNA microRNA
MK2 MAPKAPK2
mTOR mammalian target of rapamycin
MZF1 myeloid zinc finger 1
NER nucleotide excision repair
NF-κB nuclear factor-κB
NHEJ non-homologous end junction
NMDA N-methyl-D-aspartate
NSCLC non-small cell lung cancer
P13K phosphoinositide 3-kinases
P2RX6 purinergic receptor P2X 6
p-AKT phosphorylated AKT
PBMC peripheral blood mononuclear cell
PD Parkinson's disease
PGC1α peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator-1 alpha
PPARβ/δ peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor
PTEN phosphatase and tensin homologue
RARA retinoic acid receptor alpha
RBM15 RNA -binding motif protein 15
RNA-seq RNA sequencing
ROS reactive oxygen species
RPE retinal pigment epithelial
rRNA ribosomal RNA
RUNX1 RUNT-related transcription factor 1
SA-βGAL senescence-related β-galactosidase
SAM S-Adenosyl Methionine
SASP senescence-associated secretory phenotype
SFN ammonium trifluoride
snoRNA small nucleolar molecule RNA
snRNA small nuclear RNA
SOCS2 suppressor of cytokine signalling 2
SRSF10 serine- and arginine-rich splicing factor 10
SRSF3 serine- and arginine-rich splicing factor 3
T2D type 2 diabetes mellitus
TAZ PDZ binding motif-based transcriptional coactivator
TLR toll-like receptors
TNF tumour necrosis factor
TNFR2 tumour necrosis factor receptor 2
tRNA transfer RNA
ULK1 Unc-51 like autophagy activating kinase 1
ULK1/2 UNC-51-like kinase
USP7 ubiquitin specific protease 7
UV ultraviolet
VCAM-1 vascular cell adhesion molecule 1
VIRMA Vir-like m6A RNA methyltransferase associated protein
WS Werner syndrome
WTAP Wilms’ tumour 1-associating protein
XIST X-inactive specific transcript
YAP yes associated protein
YTHDC1 YTH domain containing 1
YTHDC2 YTH domain containing 2
YTHDF1 YTH domain family protein 1
YTHDF2 YTH domain family protein 2
YTHDF3 YTH domain family protein 3
ZCCH4 zinc finger CCHC-type containing 4
ZC3H13 zinc finger CCCH domain-containing protein 13
Keywords: N6-methyladenosine, aging, aging-related disease, epigenetics, RNA methylation
Citation: Sun J, Cheng B, Su Y, Li M, Ma S, Zhang Y, Zhang A, Cai S, Bao Q, Wang S and Zhu P (2022) The Potential Role of m6A RNA Methylation in the Aging Process and Aging-Associated Diseases. Front. Genet. 13:869950. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.869950
Received: 05 February 2022; Accepted: 31 March 2022;
Published: 20 April 2022.
Edited by:
Giovanni Nigita, The Ohio State University, United StatesReviewed by:
Xiangting Wang, University of Science and Technology of China, ChinaPiyush Khandelia, Birla Institute of Technology and Science, India
Copyright © 2022 Sun, Cheng, Su, Li, Ma, Zhang, Zhang, Cai, Bao, Wang and Zhu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ping Zhu, emh1cGluZzMwMWhvc3BpdGFsQDE2My5jb20=; Shuxia Wang, d2FuZ3N4MzAxQDE2My5jb20=
 Jin Sun1,2
Jin Sun1,2 Ping Zhu
Ping Zhu