
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Genet., 28 January 2021
Sec. RNA
Volume 11 - 2020 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2020.625977
This article is part of the Research TopicDecoding Non-Coding RNA Implicated in Cancer Cell Survival & Growth ModulationView all 18 articles
Early and precise prediction is an important way to reduce the poor prognosis of lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) patients. Nevertheless, the widely used tumor, node, and metastasis (TNM) staging system based on anatomical information only often could not achieve adequate performance on foreseeing the prognosis of LUAD patients. This study thus aimed to examine whether the long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), known highly involved in the tumorigenesis of LUAD through the competing endogenous RNAs (ceRNAs) mechanism, could provide additional information to improve prognosis prediction of LUAD patients. To prove the hypothesis, a dataset consisting of both RNA sequencing data and clinical pathological data, obtained from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database, was analyzed. Then, differentially expressed RNAs (DElncRNAs, DEmiRNAs, and DEmRNAs) were identified and a lncRNA–miRNA–mRNA ceRNA network was constructed based on those differentially expressed RNAs. Functional enrichment analysis revealed that this ceRNA network was highly enriched in some cancer-associated signaling pathways. Next, lasso-Cox model was run 1,000 times to recognize the potential survival-related combinations of the candidate lncRNAs in the ceRNA network, followed by the “best subset selection” to further optimize these lncRNA-based combinations, and a seven-lncRNA prognostic signature with the best performance was determined. Based on the median risk score, LUAD patients could be well distinguished into high-/low-risk subgroups. The Kaplan–Meier survival curve showed that LUAD patients in the high-risk group had significantly shorter overall survival than those in the low-risk group (log-rank test P = 4.52 × 10–9). The ROC curve indicated that the clinical genomic model including both the TNM staging system and the signature had a superior performance in predicting the patients’ overall survival compared to the clinical model with the TNM staging system only. Further stratification analysis suggested that the signature could work well in the different strata of the stage, gender, or age, rendering it to be a wide application. Finally, a ceRNA subnetwork related to the signature was extracted, demonstrating its high involvement in the tumorigenesis mechanism of LUAD. In conclusion, the present study established a lncRNA-based molecular signature, which can significantly improve prognosis prediction for LUAD patients.
Lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD), a major type of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), has a low survival rate and an increasing incidence (Matsuda and Machii, 2015; Denisenko et al., 2018). The etiology of LUAD is multifactorial, involving a large number of environmental factors and internal factors (Rajer et al., 2014). So far, because of the lack of specific symptoms and signs, LUAD coupling with complex and diverse clinical manifestations is easily missed and misdiagnosed (Del et al., 2017). Hence, when most LUAD patients are diagnosed, they are already in an advanced stage. Although many kinds of treatments, including surgical resection, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and chemo-radiotherapy, were applied to improve patient’s survival rate, the overall 5-year survival rate is still extremely bleak (Wakeam et al., 2017). Therefore, early detection and diagnosis is vital to improve LUAD patient’s poor prognosis.
The TNM staging system is currently the most common tumor prognosis predictor and a powerful tool for guiding adjuvant therapy at present (Mittendorf et al., 2015; Pontius et al., 2017). According to the invasion extent of the primary tumor stage (T stage), regional lymph node metastasis stage (N stage), and distant metastasis stage (M stage), the total pathologic stage of the malignant tumor (the TNM stage) could be determined (Hutter, 1991). In general, the higher the TNM stage, the higher the degree of the malignant tumor is. However, the TNM staging system, which is limited to the anatomical extent rather than the biological behavior of the disease, has obvious limitations compared with the multifactorial prognostic index (Fouad et al., 2017; Ball, 2019). Given the shortcomings of the TNM staging system in LUAD patient’s prognosis prediction, it is highly demanding to develop a molecular diagnostic and predictive biomarker.
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are defined as any ncRNA that is 200 nucleotides to 100 kb in length (Yin et al., 2018). Many studies reported that lncRNA plays an important role in the pathogenesis of cancer and has significant clinical value in prognosis and diagnosis (Knoll et al., 2015; Evans et al., 2016; Huang et al., 2017; Tripathi et al., 2018). It was also demonstrated that lncRNA can act as a “sponge” to regulate the targeted gene expression by competitively binding with miRNA (Zhang et al., 2016). This novel model of gene regulation is a part of the competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) hypothesis, which was first proposed in 2011 (Salmena et al., 2011). ceRNAs (including lncRNA, circRNA, and mRNA) competitively bind with microRNA via sharing microRNA response elements (MREs) to weaken the inhibition effect for the target gene. The regulatory relations among lncRNAs, miRNA, and mRNA form a complex ceRNA network, and the abnormal expression of lncRNA would destroy the balance of the ceRNA network to lead to the initiation and progression of cancer (Karreth and Pandolfi, 2013).
Owing to the heterogeneity and polygenic mutation in lung cancer, a single genomic mutation is difficult to explain the various phenotypes and the variable risks of complex disease (Andreassen et al., 2014). Compared with a single gene and single factor, a biomolecular network(s) including multiple disease-related factors, which perform their dysfunctions through physical and biochemical interactions in a network (Zhao and Liu, 2019), represents various molecular relationships underlying complex diseases and depicts a clear global picture of interactions among disease-related factors (Jinawath et al., 2016). As a biomolecular network, the ceRNA network, describing post-transcriptional interactions between ceRNAs and miRNAs, had great value in prognosis, diagnosis, and therapy of cancers (Lin et al., 2018; Zhang Y. et al., 2018; Eissa et al., 2019). In recent years, there are several successful attempts that use the ceRNA networks to identify prognostic signatures for different cancers (Hu et al., 2019; Wang et al., 2019b).
The aim of the present study was to establish a multi-lncRNA prognosis predictor. To this end, a LUAD-related lncRNA–miRNA–mRNA ceRNA network was constructed based on integrated transcriptome data from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database. Then, by using lasso-Cox regression model, a seven-lncRNA prognostic signature was identified from the LUAD-related ceRNA network. Survival analysis and the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve suggested the seven-lncRNA prognostic signature is a robust and independent prognostic factor. Most importantly, our study demonstrated that the seven-lncRNA prognostic signature effectively enhanced the prognosis prediction performance over the conventional TNM staging system.
RNA and miRNA sequencing raw count data and corresponding clinical data of LUAD patients were obtained from TCGA database by using the GDC Data Transfer Tool. Then, individual sample expression files were merged into an expression matrix using the Perl language for further processing. To eliminate the adverse effect of low abundance, RNAs with an average value of less than 1 were excluded in further analysis. Finally, the trimmed mean of the M-values (TMM) method was used to normalize RNA sequencing data (Smid et al., 2018).
Differentially expressed RNAs (DE-lncRNAs, DE-miRNAs, and DE-mRNAs) were identified by comparing the expression values between LUAD samples and adjacent normal tissue samples based on the edgeR package of R platform (Robinson et al., 2010). The cutoff criterion was set at | logFC| > 1 and FDR < 0.05 for the screening of DE-lncRNAs, DE-miRNAs, and DE-mRNAs. Volcano plot was used to display the differentially expressed RNAs.
Regulatory relationships among DE-RNAs were identified by mining knowledge of several public databases. miRcode database (Jeggari et al., 2012) was used to predict the regulatory relationships between lncRNAs and miRNAs, while miRDB, miRTarBase, and TargetScan databases (Zheng et al., 2019) were used to define the regulatory relationship between miRNAs and mRNAs. According to the ceRNA theory, there should be a negative regulatory relationship between ceRNAs and miRNAs (Taulli et al., 2013). Therefore, the Pearson correlation coefficient between lncRNAs/mRNAs and miRNAs was calculated to identify negatively correlated RNA–RNA regulatory pairs (P < 0.05). In short, the regulatory relationships between lncRNAs/mRNAs and miRNAs were determined by three facts: (1) having a biological basis, supported by knowledge bases; (2) being a negative relationship, which agrees with the competing endogenous RNA theory; and (3) achieving the significance level in the Pearson correlation analysis based on their expression data. Finally, based on the shared miRNAs among these regulatory pairs, the lncRNA–miRNA–mRNA ceRNA network was built by connecting negative lncRNA–miRNA and miRNA–mRNA regulatory pairs. Cytoscape v3.7.1 was used for network visualization (Shannon et al., 2003).
To reveal the biological function(s) that ceRNA regulatory network involved, the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG)-based enrichment analysis was conducted to assess the ceRNA regulatory network using clusterProfiler package in R (Yu et al., 2012). The enriched KEGG pathway(s) with a FDR less than 0.05 was considered as statistically significant.
In order to identify the lncRNAs and optimal subset(s) related to the overall survival of LUAD patients, lasso-Cox model (R package glmnet) was run 1,000 times to recognize the potential survival-related combinations of the candidate lncRNAs in the ceRNA network, followed by the “best subset selection” (the area under the ROC curve, AUC > 0.70 with the minimal set size) to further optimize these lncRNA-based combinations (i.e., the survival-related signatures). Finally, in order to evaluate the joint effect of the best signature, a risk score was calculated based on a linear combination of the expression levels of the included lncRNAs weighted by their regression coefficients derived from the multivariate Cox regression analysis.
The risk score formula was defined as following:
Here, n represents the number of lncRNAs in the model, expi represents the expression level of lncRNA i, and βi is the regression coefficient of lncRNA i in multivariate Cox regression model.
First, in order to evaluate its potential to classify the LUAD patients, according to the median risk score of the signature, LUAD patients were divided into low- and high-risk groups. The Kaplan–Meier method was used to display the difference in survival time between low-risk and high-risk LUAD groups. The statistical significance of the difference between the survival profiles of the two groups was determined by using the log-rank test. ROC curve was used to estimate its sensitivity and specificity. Second, to assess whether combining the lncRNA-based signature with the TNM stages could improve the prognosis prediction for LUAD, a clinical genomic model with the TNM stages and the lncRNA-based signature combined was constructed, and AUC was compared to the model with the TNM stages only. Third, in order to explore its applicability, a stratification analysis by the TNM stages, gender, or age was performed. Finally, to explore its biological role(s), a core ceRNA network was constructed and its functional involvements were identified by a KEGG-based enrichment analysis.
The detailed workflows of the proposed strategies for identifying and assessing the survival-related lncRNA-based signature are illustrated in Figure 1.
In total, RNA-seq data for 535 LUAD samples and 59 adjacent normal samples, miRNA-seq data for 519 LUAD samples and 48 adjacent normal samples, and the corresponding clinical data for 504 LUAD patients were obtained. According to the cutoff criteria (| logFC| > 1 and FDR < 0.05), 5,537 mRNAs (3,721 upregulated and 1,816 downregulated), 352 miRNAs (273 upregulated and 79 downregulated), and 3,939 lncRNAs (3,202 upregulated and 737 downregulated) were found differentially expressed (named DE-lncRNAs, DE-miRNAs, and DE-mRNAs, respectively). Their volcano plots are shown in Figure 2.
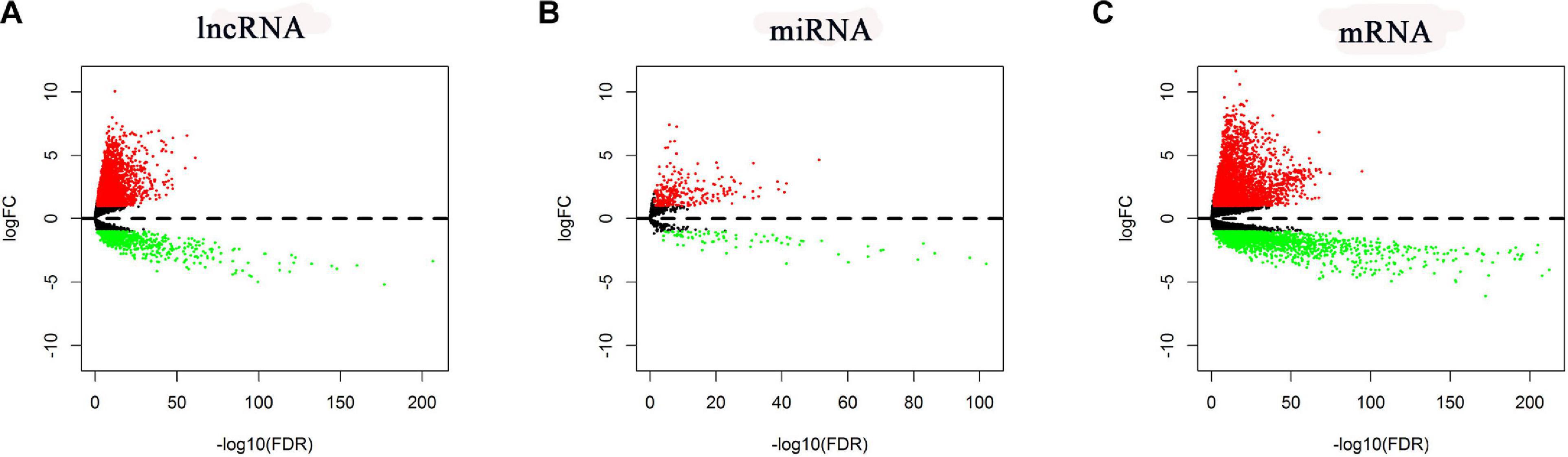
Figure 2. Volcano plots of the DE-lncRNAs, DE-miRNAs, and DE-mRNAs. (A) DE-lncRNAs. (B) DE-miRNAs. (C) DE-mRNAs.
Among these DE-RNAs, 475 lncRNA–miRNA pairs between 197 lncRNAs and 39 miRNAs and 198 miRNA–mRNA pairs between 39 miRNAs and 140 mRNAs were found showing a significant negative correlation (P < 0.05), after excluding positively correlated pairs. Based on 39 shared miRNAs among these regulatory pairs, the lncRNA–miRNA–mRNA (ceRNA) network was established (Figure 3A). The top 15 KEGG pathways (P-value < 0.05) that the network was involved are shown in Figure 3B, indicating that the ceRNA network for LUAD was closely related to some cancer-associated pathways, such as microRNAs in cancer, transcriptional misregulation in cancer, cellular senescence, cell cycle, p53 signaling pathway, small cell lung cancer, and so on.
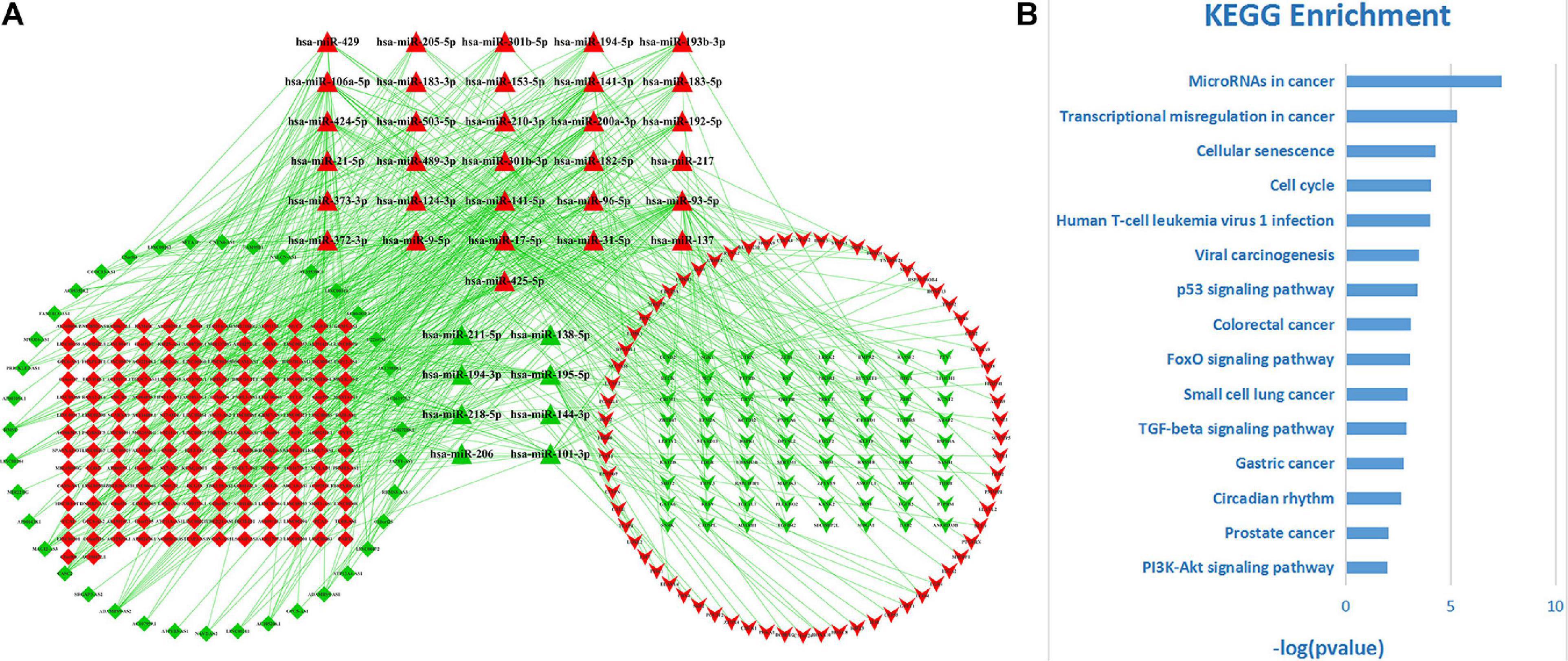
Figure 3. The ceRNA network for LUAD and its functional involvements. (A) The topological structure of the ceRNA network for LUAD. Red nodes represent upregulation DE-RNAs and green ones downregulation DE-RNAs. Diamond, triangle, and inverse-triangle represent lncRNA, miRNA, and mRNA, respectively. (B) The top 15 KEGG pathways (P-value < 0.05) that the network was involved.
Among 1,000 lncRNA sets, constructed by using lasso-Cox regression analysis of 197 lncRNAs included in the ceRNA network for LUAD, five had AUC > 0.7. The optimal set with minimal size was selected as the lncRNA-based prognostic signature for LUAD, which was consisted of seven lncRNAs (SNHG12, DLEU7_AS1, FAM41C, FAM181A_AS1, AC022148.1, CCDC13_AS1, and LINC00319). Figures 4A,B shows the convergence of the lasso-based variable selection (or called feature shrinkage) with the log of the penalty parameter lambda (λ) as well as the changes of model fitting statistics (partial likelihood deviance).

Figure 4. The lncRNA-based prognostic signature for LUAD. (A) The convergence of the lasso-based variable selection with the log of the penalty parameter lambda (λ). (B) The changes of model fitting statistic, partial likelihood deviance, and its range, obtained from 10-fold cross-validation. (C) The expression patterns (heat maps) of the seven lncRNAs for patients of two groups (low-risk group, type low and high-risk group, type high). (D) The dot plot of survival time for patients sorted by the lncRNA-based risk score. Red dots indicate death events while green ones survivals. (E) Kaplan–Meier curves for patients of two categories (low-risk groups versus high-risk groups) defined by the lncRNA-based prognostic signature. (F) ROC analysis of the lncRNA-based prognostic signature to estimate AUC values of survival over two different periods.
Then, a predictive model for the lncRNA set was constructed according to their lncRNA expression values and their corresponding coefficients derived from the multivariate Cox regression analysis. The risk score based on the lncRNA set was defined as following:
Based on the median value of the risk score, 504 patients were subdivided into high-risk and low-risk groups. The expression patterns (heat maps) for patients of two groups (low-risk group and high-risk group) are shown in Figure 4C, while their risk score distribution, as well as their survival, data are shown in Figure 4D, which clearly indicated that with the increase of the risk score, LUAD patients tended to have a shorter survival time. Kaplan–Meier survival analysis showed that the patients in the low-risk group had a better prognosis than those with high-risk scores (P = 4.52e–9) (Figure 4E). ROC analysis estimated that the AUC values of the lncRNA-based prognostic signature for survival were 0.721 for the third year and 0.72 for the fifth year, respectively (Figure 4F).
In order to verify whether combining the lncRNA-based signature with the TNM stages could improve the prognosis prediction for LUAD, a clinical genomic model with the TNM stages and the lncRNA-based signature combined was constructed, and its area under the ROC curve (AUC) was compared to the model with the TNM stages only. As shown in Figure 5A, the AUC values for the model with the TNM stages only were 0.688 and 0.684 for 3- and 5-year survival, respectively, which were markedly lower than the estimates for the clinical genomic model with both the TNM stages and the lncRNA-based signature (0.751 and 0.782 for the two periods, respectively) (Figure 5B). A comparison of the two models for prognosis prediction over the two periods separately all demonstrated that the clinical genomic model performed significantly better than the conventional model with the TNM stage (all P < 0.01) (Figures 5C,D). These results suggest that lncRNAs could provide additional information on the prognosis prediction for LUAD, and more importantly, this fact may render an earlier prognosis prediction for LUAD to be practical.
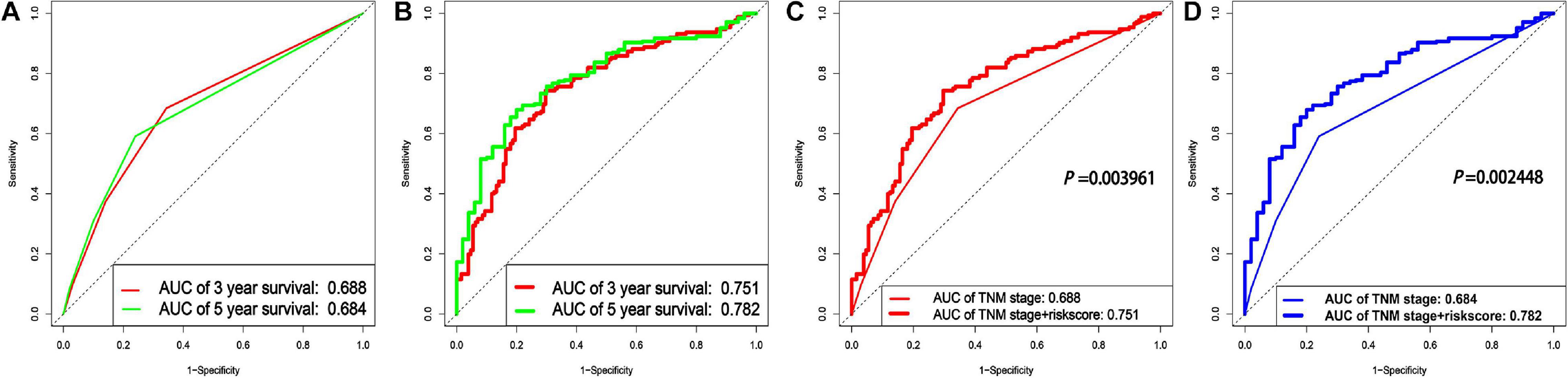
Figure 5. A comparison between the clinical genomic model with both the TNM stages and the lncRNA signature and with the clinical model with the TNM stages only. (A) The ROCs of two periods of survival for the conventional model with the TNM stages only. (B) The ROCs of two periods of survival for the clinical genomic model with both the TNM stages and the lncRNA-based signature included. (C,D) Comparison of the two models for prognosis prediction over the two periods (3 and 5 years), respectively.
In order to explore its applicability, a stratification analysis by the TNM stages (overall rating, divided into four ranks), gender, or age was performed. The results indicated that the lncRNA-based prognostic signature could work well in most strata of the TNM stages, gender, or age (Figures 6A–C,E–H), i.e., having a good capacity in separating the LUAD patients into high-risk and low-risk groups. For the TNM stages, stage IV was the only exception where no statistical significance was found between the low- and high-risk groups defined by the lncRNA-based signature (Figure 6D), which might be due to the small sample size (n = 26). These results suggested that the lncRNA-based prognostic signature was largely independent of tumor stage, gender, and age, which was agreed well with the multivariate Cox regression analysis where the lncRNA-based prognostic signature remained to be the most significant factor (P < 0.001) even after adjusting for several demographic and clinical factors (Figure 6I).
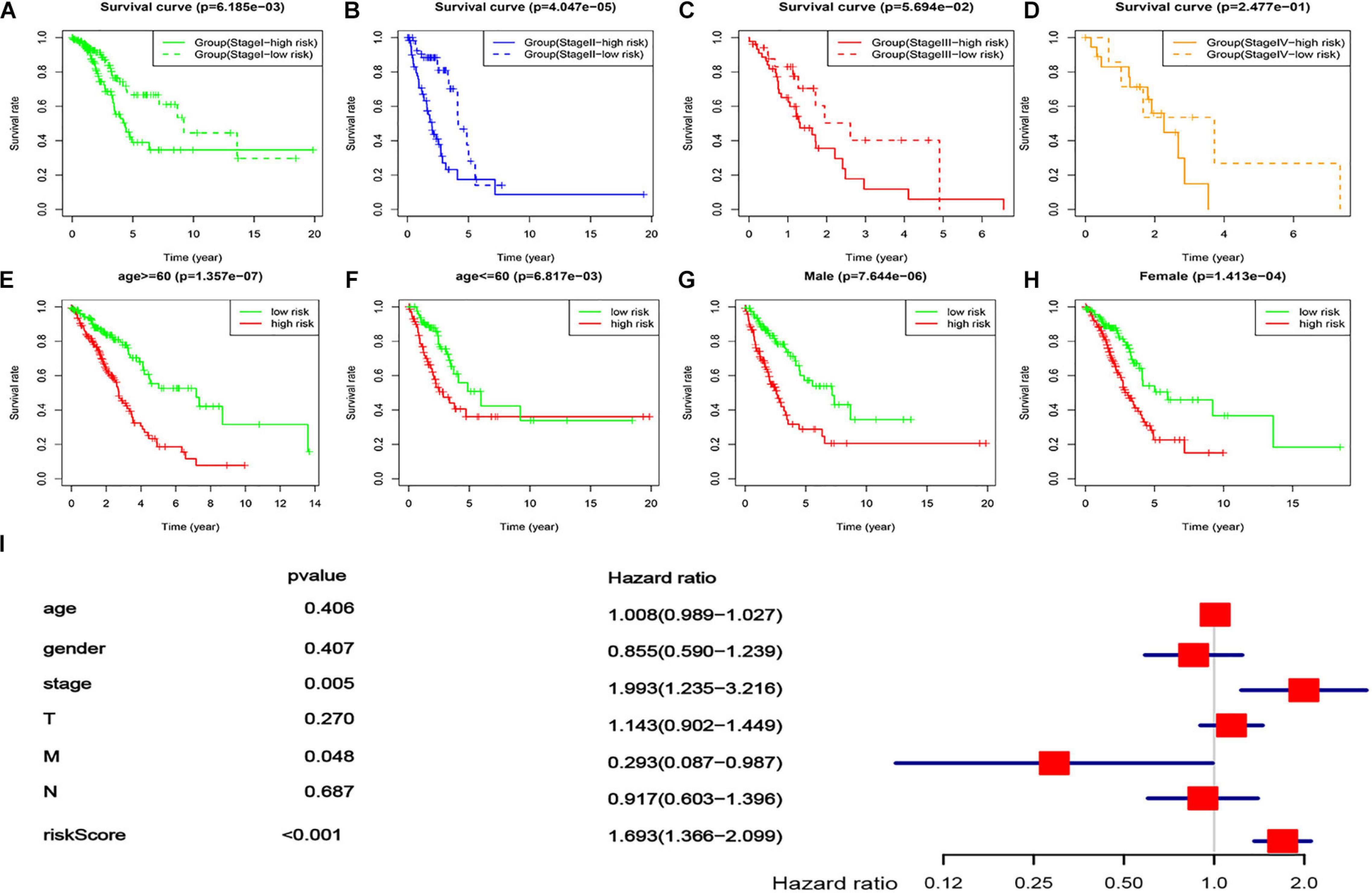
Figure 6. Applicability of the lncRNA-based prognostic signature. (A–D) survival curves of the LUAD patients in different risk groups, stratified by four tumor stages [stage I (A), stage II (B), stage III (C), and stage IV (D)]. (E,F) Survival curves of the LUAD patients in different risk groups, stratified by two ages [age ≤60 (E) and age <60 (F)]. (G,H) Survival curves of the LUAD patients in different risk groups, stratified by gender [male (G) and female (H)]. (I) Multivariate Cox regression with the lncRNA-based signature (risk score) and all available demographic and clinical factors included.
On basis of the seven lncRNAs contained in the prognostic signature for LUAD, a core network (Figure 7A) was extracted from the primary ceRNA network. KEGG-based functional enrichment analysis demonstrated that this lncRNA-mediated ceRNA subnetwork was highly involved in several cancer-associated signaling pathways (Figure 7B), which implicated that the seven lncRNAs play vital roles in the tumorigenesis mechanism of LUAD via regulating related gene expressions by competitively sponging several miRNAs.
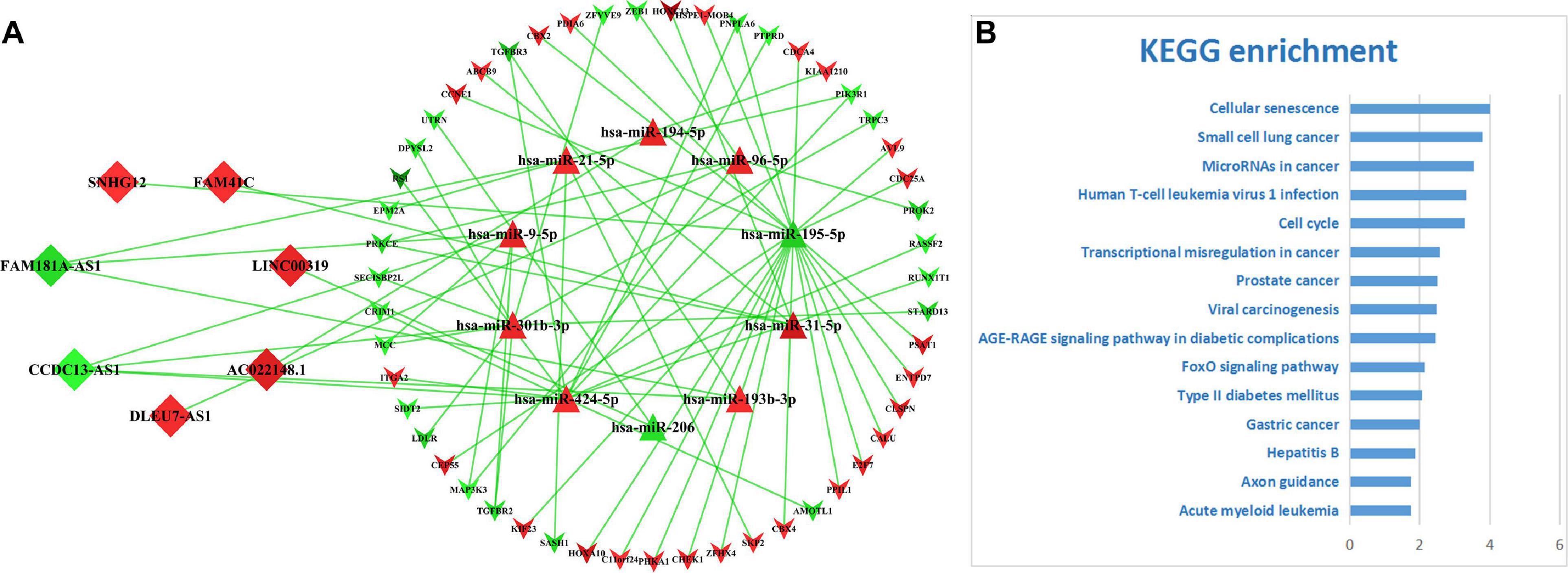
Figure 7. The ceRNA subnetwork mediated by the lncRNA-based signature. (A) The ceRNA subnetwork depicting the relationships between seven lncRNAs and their counterparts. Diamonds represent lncRNAs, triangles miRNAs, and inverse-triangles mRNAs. The red color depicts upregulation and green downregulation. (B) The top 15 significantly enriched KEGG pathways.
As the most common malignancy, LUAD had an unfavorable 5-year survival rate at an advanced stage. Early detection and diagnosis was an important way to improve the LUAD patient’s prognosis. Although it had been confirmed as an effective prognosis predictor for LUAD patients (Carter et al., 2018), the TNM staging system, which was founded on the anatomical information only, could not perfectly perform prognosis prediction. An increasing amount of evidence demonstrated that genetic disorders and alterations were of significance in tumorigenesis and the progression of LUAD, suggesting that molecular markers had great value in the prediction of overall survival of LUAD patients (Trimarchi et al., 2014; Timmer et al., 2016).
With the development of high-throughput sequencing technology, the roles of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) in human cancers had received more and more attention. Previous studies demonstrated that lncRNAs play an important role in tumor proliferation, migration, and invasion (Zhang G. et al., 2018) and have potential value in applications to early prognosis and diagnosis for cancers (Takahashi et al., 2014). Zhai et al. (2017) demonstrated that the lower expression of lncRNA-SARCC influenced downstream genes such as K-RAS, MMP-13, AKT, and P-ERK expression by suppressing miR-143-3p expression, which could enhance RCC cell invasion, migration, and proliferation. Wu et al. (2017) first reported that lncRNA CASC9, as an oncogene, promoted ESCC cell growth by negatively regulating PDCD4 expression via recruiting EZH2, which could be a potential diagnosis and prognosis biomarker for ESCC. All these facts highlight the importance of the large number of lncRNAs to be the molecular biomarkers for early prognosis prediction or early diagnosis of cancers.
Compared with the coding RNAs, it was more complex to study the functional meanings of lncRNAs. The ceRNA hypothesis provided a new solution for achieving better functional studies of lncRNAs. In the ceRNA theory, lncRNAs regulate the expression of the targeted genes by competitively absorbing miRNAs at the post-transcriptional level, forming a huge ceRNA regulatory network (Calloni and Bonatto, 2019). In most scenarios, “communications” between ceRNAs and miRNAs were in dynamic balance (Cai and Wan, 2018). However, an abnormal expression of lncRNA destroyed the balance of the ceRNA network, which was closely related to tumorigenesis (Shao et al., 2015). In this study, a total of 3,939 DE-lncRNAs, 352 DE-miRNA, and 5,537 DE-mRNAs were identified. According to the ceRNA theory, the negatively correlated RNA–RNA regulatory pairs were built among DE-lncRNAs, DE-miRNA, and DE-mRNA. Subsequently, a lncRNA–miRNA–mRNA ceRNA network including 197 DE-lncRNAs, 39 DE-miRNAs, and 140 DE-mRNAs was constructed by connecting the negatively correlated RNA–RNA regulatory pairs. Further functional enrichment analysis showed that the ceRNA network was mainly involved in some cancer-related pathways including “microRNAs in cancer,” “transcriptional misregulation in cancer,” “cell cycle,” “p53 signaling pathway,” “colorectal cancer,” “small cell lung cancer,” etc., which was not surprising at all to us because more and more evidence indicated that at the molecular levels various cancers were interconnected. In brief, the ceRNA regulatory network including complex molecular regulatory relationships not only had potential value to mine prognosis-related biomarkers (Bai et al., 2019) but also provided a new avenue to broaden our knowledge on massive lncRNAs and their functional involvements in the pathogenic mechanisms for cancers like LUAD.
Most of the preceding studies focused on single lncRNAs related to lung cancer. Nie et al. (2016) found that LncRNA-UCA1 upregulated ERBB4 by sponging miR-193a-3p to exert oncogenic functions. Guan et al. (2019) demonstrated that LINC00673-v4 enhanced cancer cell invasion, migration, and metastasis by overactivating WNT/β-catenin signaling and could be a candidate for the therapeutic target of LUAD patients. Nevertheless, as a complex disease, LUAD was thought to be a series of biological cascades resulting from the perturbations of intracellular and intercellular elements (Fiscon et al., 2018), and it was impossible to have a global picture about the sophisticated pathogenic mechanism of LUAD by studying only a single biomarker. Therefore, compared with a single biomarker, a prognostic signature integrating multiple biomarkers could achieve more power in prognosis prediction for LUAD (Kratz et al., 2019). This study demonstrated that the newly identified lncRNA-based signature with seven lncRNAs could provide >9% improvement in prognosis prediction over various periods for LUAD and was deemed to a robust complement for the conventional TNM staging system.
Among the seven lncRNAs containing the prognostic signature, four (AC022148.1, DLEU7_AS1, LINC00319, and SNHG12) were found to be involved in tumorigenesis, migration, and metastasis in cancers. Qi et al. (2019) demonstrated that a seven-lncRNA prognostic model including AC022148.1 was a robust indicator to assess the prognosis risk of lung squamous cell carcinoma patients. Liu et al. (2018) found that DLEU7_AS1, as an adverse prognosis factor, was closely associated with colorectal cancer (CRC) staging, lymph node metastasis, and distant metastasis and may regulate the Wnt/β-catenin pathway to promote the occurrence and development of CRC. Zhou et al. (2017) demonstrated that LINC00319 strengthened proliferation and invasion of lung cancer cells by downregulating the expression of miR-32 and upregulating the expression levels of miR-32 target genes. Wang et al. (2019a) revealed that knockdown of SNHG12 inhibited migration and invasion of NSCLC cells via the Slug/zinc finger E-box-binding homeobox 2 EMT signaling pathway by upregulating the expression of miR-218 and could be a potential prognostic marker and therapeutic target for NSCLC. Up to date, there is dearth of information about the roles of the remaining three lncRNAs in tumors, waiting for further studies to clarify.
Compared with several previous studies, our approach has the following improvements. First, for constructing the ceRNA network, we used only negatively correlated lncRNAs/mRNAs–miRNAs regulatory pairs, which fits well the definition of the ceRNA network compared to the previous method without this distinction (Li et al., 2018; Fan et al., 2020; Wu et al., 2020). Second, we applied 1,000 rounds of lasso-Cox regression model fittings to identify the optimal lncRNA-based set, which is deemed to be more robust than the conventional Cox model utilized in a previous study (Zheng et al., 2017). Third, consequently, our study achieved better performance on predicting the survival of the LUAD patients by using a seven-lncRNA-based signature (AUC = 0.72 and 0.721 for 3- and 5-year survival, respectively) than a previous study (Yao et al., 2020), who identified an eight-lncRNA signature for LUAD (AUC = 0.702 and 0.671 for 3- and 5-year survival). Up to date, only the clinical genomic model built by the present study has achieved adequate improvement over the conventional TNM staging system (P = 0.003961 and 9.16% for the third year; P = 0.002448 and 14.33% for the fifth year), compared to a previous similar study (Zheng et al., 2017), who reported a non-significant improvement (P > 0.05 and 4.24% for the fifth year).
In conclusion, we applied an integrated ceRNA network analysis to identify a lncRNA-based signature for predicting the prognosis of LUAD patients. The established molecular signature with seven lncRNAs, derived from the ceRNA network, was demonstrated to be a robust and independent factor for the survival prediction of LUAD patients and, hence, could be an important complement for the conventional TNM staging system.
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/supplementary material.
SR, RL, and KH conceived and designed the study. RL, KH, SR, YL, SS, and SL performed data analysis. RL, XC, and DX contributed in the software and programming. RL, SR, KH, XC, and DX wrote, reviewed, and edited the manuscript. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 31071166 and 81373085 to SR) and the High-level Hospital Construction Research Project of Maoming People’s Hospital (ZX2020013 to KH).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Andreassen, O. A., Zuber, V., Thompson, W. K., Schork, A. J., Bettella, F., Djurovic, S., et al. (2014). Shared common variants in prostate cancer and blood lipids. Int. J. Epidemiol. 43, 1205–1214. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyu090
Bai, Y., Long, J., Liu, Z., Lin, J., Huang, H., Wang, D., et al. (2019). Comprehensive analysis of a ceRNA network reveals potential prognostic cytoplasmic lncRNAs involved in HCC progression. J. Cell. Physiol. 234, 18837–18848. doi: 10.1002/jcp.28522
Ball, D. (2019). TNM in non-small cell lung cancer: A staging system for all oncologists or just for surgeons? Ann. Transl. Med. 7:S103. doi: 10.21037/atm.2019.04.84
Cai, Y., and Wan, J. (2018). Competing endogenous RNA regulations in neurodegenerative disorders: current challenges and emerging insights. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 11:370. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2018.00370
Calloni, R., and Bonatto, D. (2019). Characteristics of the competition among RNAs for the binding of shared miRNAs. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 98, 94–102. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2019.04.001
Carter, B. W., Lichtenberger, J. R., Benveniste, M. K., de Groot, P. M., Wu, C. C., Erasmus, J. J., et al. (2018). Revisions to the TNM staging of lung cancer: rationale, significance, and clinical application. Radiographics 38, 374–391. doi: 10.1148/rg.2018170081
Del, C. A., Franchi, P., Contegiacomo, A., Cicchetti, G., Bonomo, L., and Larici, A. R. (2017). Missed lung cancer: When, where, and why? Diagn. Interv. Radiol. 23, 118–126. doi: 10.5152/dir.2016.16187
Denisenko, T. V., Budkevich, I. N., and Zhivotovsky, B. (2018). Cell death-based treatment of lung adenocarcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 9:117. doi: 10.1038/s41419-017-0063-y
Eissa, S., Safwat, M., Matboli, M., Zaghloul, A., El-Sawalhi, M., and Shaheen, A. (2019). Measurement of Urinary Level of a Specific Competing endogenous RNA network (FOS and RCAN mRNA/miR-324-5p, miR-4738-3p, /lncRNA miR-497-HG) enables diagnosis of bladder cancer. Urol. Oncol. 37, 292.e19–292.e27. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2018.12.024
Evans, J. R., Feng, F. Y., and Chinnaiyan, A. M. (2016). The bright side of dark matter: lncRNAs in cancer. J. Clin. Invest. 126, 2775–2782. doi: 10.1172/JCI84421
Fan, F., Ping, Y., Yang, L., Duan, X., Resegofetse, M. N., Li, B., et al. (2020). Characterization of a non-coding RNA-associated ceRNA network in metastatic lung adenocarcinoma. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 24, 11680–11690. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15778
Fiscon, G., Conte, F., Farina, L., and Paci, P. (2018). Network-based approaches to explore complex biological systems towards network medicine. Genes 9:437. doi: 10.3390/genes9090437
Fouad, T. M., Barrera, A., Reuben, J. M., Lucci, A., Woodward, W. A., Stauder, M. C., et al. (2017). Inflammatory breast cancer: a proposed conceptual shift in the UICC-AJCC TNM staging system. Lancet Oncol. 18, e228–e232. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30192-4
Guan, H., Zhu, T., Wu, S., Liu, S., Liu, B., Wu, J., et al. (2019). Long noncoding RNA LINC00673-v4 promotes aggressiveness of lung adenocarcinoma via activating WNT/beta-catenin signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 116, 14019–14028. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1900997116
Hu, J., Xu, L., Shou, T., and Chen, Q. (2019). Systematic analysis identifies three-lncRNA signature as a potentially prognostic biomarker for lung squamous cell carcinoma using bioinformatics strategy. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 8, 614–635. doi: 10.21037/tlcr.2019.09.13
Huang, M., Hou, J., Wang, Y., Xie, M., Wei, C., Nie, F., et al. (2017). Long noncoding RNA LINC00673 is activated by SP1 and exerts oncogenic properties by interacting with LSD1 and EZH2 in Gastric Cancer. Mol. Ther. 25, 1014–1026. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2017.01.017
Hutter, R. V. (1991). The role of the pathologist in the management of breast cancer. CA Cancer J. Clin. 41, 283–299. doi: 10.3322/canjclin.41.5.283
Jeggari, A., Marks, D. S., and Larsson, E. (2012). miRcode: a map of putative microRNA target sites in the long non-coding transcriptome. Bioinformatics 28, 2062–2063. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts344
Jinawath, N., Bunbanjerdsuk, S., Chayanupatkul, M., Ngamphaiboon, N., Asavapanumas, N., Svasti, J., et al. (2016). Bridging the gap between clinicians and systems biologists: from network biology to translational biomedical research. J. Transl. Med. 14:324. doi: 10.1186/s12967-016-1078-3
Karreth, F. A., and Pandolfi, P. P. (2013). ceRNA cross-talk in cancer: when ce-bling rivalries go awry. Cancer Discov. 3, 1113–1121. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-13-0202
Knoll, M., Lodish, H. F., and Sun, L. (2015). Long non-coding RNAs as regulators of the endocrine system. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 11, 151–160. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2014.229
Kratz, J. R., Haro, G. J., Cook, N. R., He, J., Van Den Eeden, S. K., Woodard, G. A., et al. (2019). Incorporation of a molecular prognostic classifier improves conventional non-small cell lung cancer staging. J. Thorac. Oncol. 14, 1223–1232. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2019.03.015
Li, L., Peng, M., Xue, W., Fan, Z., Wang, T., Lian, J., et al. (2018). Integrated analysis of dysregulated long non-coding RNAs/microRNAs/mRNAs in metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma. J. Transl. Med. 16:372. doi: 10.1186/s12967-018-1732-z
Lin, P., Wen, D. Y., Li, Q., He, Y., Yang, H., and Chen, G. (2018). Genome-wide analysis of prognostic lncRNAs, miRNAs, and mRNAs forming a competing endogenous rna network in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 48, 1953–1967. doi: 10.1159/000492519
Liu, X. B., Han, C., and Sun, C. Z. (2018). Long non-coding RNA DLEU7-AS1 promotes the occurrence and development of colorectal cancer via Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 22, 110–117. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201801_14107
Matsuda, T., and Machii, R. (2015). Morphological distribution of lung cancer from Cancer Incidence in Five Continents Vol. X. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 45:404. doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyv041
Mittendorf, E. A., Ballman, K. V., McCall, L. M., Yi, M., Sahin, A. A., Bedrosian, I., et al. (2015). Evaluation of the stage IB designation of the American Joint Committee on Cancer staging system in breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 33, 1119–1127. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2014.57.2958
Nie, W., Ge, H. J., Yang, X. Q., Sun, X., Huang, H., Tao, X., et al. (2016). LncRNA-UCA1 exerts oncogenic functions in non-small cell lung cancer by targeting miR-193a-3p. Cancer Lett. 371, 99–106. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2015.11.024
Pontius, L. N., Oyekunle, T. O., Thomas, S. M., Stang, M. T., Scheri, R. P., Roman, S. A., et al. (2017). Projecting survival in papillary thyroid cancer: a comparison of the seventh and eighth editions of the American joint commission on cancer/union for international cancer control staging systems in two contemporary national patient cohorts. Thyroid 27, 1408–1416. doi: 10.1089/thy.2017.0306
Qi, L., Zhang, T., Yao, Y., Zhuang, J., Liu, C., Liu, R., et al. (2019). Identification of lncRNAs associated with lung squamous cell carcinoma prognosis in the competitive endogenous RNA network. PeerJ 7:e7727. doi: 10.7717/peerj.7727
Rajer, M., Zwitter, M., and Rajer, B. (2014). Pollution in the working place and social status: co-factors in lung cancer carcinogenesis. Lung Cancer 85, 346–350. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2014.06.012
Robinson, M. D., McCarthy, D. J., and Smyth, G. K. (2010). edgeR: a Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 26, 139–140. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp616
Salmena, L., Poliseno, L., Tay, Y., Kats, L., and Pandolfi, P. P. (2011). A ceRNA hypothesis: The Rosetta Stone of a hidden RNA language? Cell 146, 353–358. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.07.014
Shannon, P., Markiel, A., Ozier, O., Baliga, N. S., Wang, J. T., Ramage, D., et al. (2003). Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 13, 2498–2504. doi: 10.1101/gr.1239303
Shao, T., Wu, A., Chen, J., Chen, H., Lu, J., Bai, J., et al. (2015). Identification of module biomarkers from the dysregulated ceRNA-ceRNA interaction network in lung adenocarcinoma. Mol. Biosyst. 11, 3048–3058. doi: 10.1039/c5mb00364d
Smid, M., Coebergh, V. D. B. R., van de Werken, H., van Riet, J., van Galen, A., de Weerd, V., et al. (2018). Gene length corrected trimmed mean of M-values (GeTMM) processing of RNA-seq data performs similarly in intersample analyses while improving intrasample comparisons. BMC Bioinformatics 19:236. doi: 10.1186/s12859-018-2246-7
Takahashi, K., Yan, I., Haga, H., and Patel, T. (2014). Long noncoding RNA in liver diseases. Hepatology 60, 744–753. doi: 10.1002/hep.27043
Taulli, R., Loretelli, C., and Pandolfi, P. P. (2013). From pseudo-ceRNAs to circ-ceRNAs: a tale of cross-talk and competition. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 20, 541–543. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2580
Timmer, M. R., Martinez, P., Lau, C. T., Westra, W. M., Calpe, S., Rygiel, A. M., et al. (2016). Derivation of genetic biomarkers for cancer risk stratification in Barrett’s oesophagus: a prospective cohort study. Gut 65, 1602–1610. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2015-309642
Trimarchi, T., Bilal, E., Ntziachristos, P., Fabbri, G., Dalla-Favera, R., Tsirigos, A., et al. (2014). Genome-wide mapping and characterization of Notch-regulated long noncoding RNAs in acute leukemia. Cell 158, 593–606. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.05.049
Tripathi, M. K., Doxtater, K., Keramatnia, F., Zacheaus, C., Yallapu, M. M., Jaggi, M., et al. (2018). Role of lncRNAs in ovarian cancer: defining new biomarkers for therapeutic purposes. Drug Discov. Today 23, 1635–1643. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2018.04.010
Wakeam, E., Acuna, S. A., Leighl, N. B., Giuliani, M. E., Finlayson, S., Varghese, T. K., et al. (2017). Surgery versus chemotherapy and radiotherapy for early and locally advanced small cell lung cancer: a propensity-matched analysis of survival. Lung Cancer 109, 78–88. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2017.04.021
Wang, Y., Liang, S., Yu, Y., Shi, Y., and Zheng, H. (2019a). Knockdown of SNHG12 suppresses tumor metastasis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the Slug/ZEB2 signaling pathway by targeting miR-218 in NSCLC. Oncol. Lett. 17, 2356–2364. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.9880
Wang, Y., Liu, X., Guan, G., Xiao, Z., Zhao, W., and Zhuang, M. (2019b). Identification of a five-pseudogene signature for predicting survival and its ceRNA network in Glioma. Front. Oncol. 9:1059. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.01059
Wu, X., Sui, Z., Zhang, H., Wang, Y., and Yu, Z. (2020). Integrated analysis of lncRNA-mediated ceRNA network in lung Adenocarcinoma. Front. Oncol. 10:554759. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.554759
Wu, Y., Hu, L., Liang, Y., Li, J., Wang, K., Chen, X., et al. (2017). Up-regulation of lncRNA CASC9 promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma growth by negatively regulating PDCD4 expression through EZH2. Mol. Cancer 16:150.
Yao, Y., Zhang, T., Qi, L., Liu, R., Liu, G., Wang, J., et al. (2020). Comprehensive analysis of prognostic biomarkers in lung adenocarcinoma based on aberrant lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA networks and Cox regression models. Biosci. Rep. 40:BSR20191554. doi: 10.1042/BSR20191554
Yin, H., Wang, X., Zhang, X., Wang, Y., Zeng, Y., Xiong, Y., et al. (2018). Integrated analysis of long noncoding RNA associated-competing endogenous RNA as prognostic biomarkers in clear cell renal carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 109, 3336–3349. doi: 10.1111/cas.13778
Yu, G., Wang, L. G., Han, Y., and He, Q. Y. (2012). clusterProfiler: an R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. OMICS 16, 284–287. doi: 10.1089/omi.2011.0118
Zhai, W., Sun, Y., Guo, C., Hu, G., Wang, M., Zheng, J., et al. (2017). LncRNA-SARCC suppresses renal cell carcinoma (RCC) progression via altering the androgen receptor(AR)/miRNA-143-3p signals. Cell Death Differ. 24, 1502–1517. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2017.74
Zhang, G., Li, S., Lu, J., Ge, Y., Wang, Q., Ma, G., et al. (2018). LncRNA MT1JP functions as a ceRNA in regulating FBXW7 through competitively binding to miR-92a-3p in gastric cancer. Mol. Cancer 17:87. doi: 10.1186/s12943-018-0829-6
Zhang, P., Cao, L., Fan, P., Mei, Y., and Wu, M. (2016). LncRNA-MIF, a c-Myc-activated long non-coding RNA, suppresses glycolysis by promoting Fbxw7-mediated c-Myc degradation. EMBO Rep. 17, 1204–1220. doi: 10.15252/embr.201642067
Zhang, Y., Li, X., Zhou, D., Zhi, H., Wang, P., Gao, Y., et al. (2018). Inferences of individual drug responses across diverse cancer types using a novel competing endogenous RNA network. Mol. Oncol. 12, 1429–1446. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12181
Zhao, X., and Liu, Z. P. (2019). Analysis of topological parameters of complex disease genes reveals the importance of location in a biomolecular network. Genes 10:143. doi: 10.3390/genes10020143
Zheng, H., Liu, J., Tycksen, E., Nunley, R., and McAlinden, A. (2019). MicroRNA-181a/b-1 over-expression enhances osteogenesis by modulating PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling and mitochondrial metabolism. Bone 123, 92–102. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2019.03.020
Zheng, S., Zheng, D., Dong, C., Jiang, J., Xie, J., Sun, Y., et al. (2017). Development of a novel prognostic signature of long non-coding RNAs in lung adenocarcinoma. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 143, 1649–1657. doi: 10.1007/s00432-017-2411-9
Keywords: lung adenocarcinoma, prognosis, lncRNA, molecular signature for survival, ceRNA network
Citation: Li R, Han K, Xu D, Chen X, Lan S, Liao Y, Sun S and Rao S (2021) A Seven-Long Non-coding RNA Signature Improves Prognosis Prediction of Lung Adenocarcinoma: An Integrated Competing Endogenous RNA Network Analysis. Front. Genet. 11:625977. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.625977
Received: 13 November 2020; Accepted: 21 December 2020;
Published: 28 January 2021.
Edited by:
Wei Jiang, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, ChinaReviewed by:
Antonio Mora, Guangzhou Medical University, ChinaCopyright © 2021 Li, Han, Xu, Chen, Lan, Liao, Sun and Rao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Shaoqi Rao, cmFvc2hhb3FAZ2RtdS5lZHUuY24=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.