- 1Department of Biostatistics and Bioinformatics, Center for Predictive Medicine, Duke Clinical Research Institute, Duke University, Durham, NC, USA
- 2Division of Cardiovascular Medicine, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, USA
- 3Department of Medicine, Stanford Prevention Research Center, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, USA
by Goldstein, B. A., Knowles, J. W., Salfati, E., Ioannidis, J. P. A. and Assimes TL (2014). Front. Genet. 5:254. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2014.00254
The original Figure 2 did not display the full sample risk report as described in the paper. Here we illustrate how one can convey personalized genetic risk to a patient and how the inclusion of the Genetic Risk Score changes the clinical interpretation of the individual's risk.
Funding
BG is supported by an NIH career development award K25DK097279. JK is supported by an American Heart Association, National Fellow to Faculty Award, 10FTF3360005. TA is supported by an NIH career development award K23DK088942.
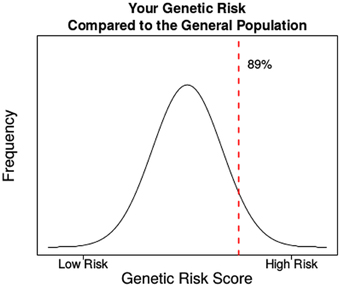
YOUR RISK SCORE
Based on the traditional Framingham risk score, your risk of coronary heart disease over the next 10 years is approximately 5.5%.
We tested for a total of 90 possible risks variants or alleles. Out of these 90, you carry 49 variants that are associated with higher risk. Your genetic profile puts you in the 89 percentile for risk. This means 89% of the general population have a genetic risk score more favorable than you and 11% have a genetic risk score less favorable than you.
Based on the traditional Framingham risk score plus the genetic risk score, your risk of coronary heart disease over the next 10 years is approximately 7.6%.
Your 10 year risk of coronary heart disease risk is ≥7.5% when considering your genetic risk. This information may be discussed with your physician in terms of what would be recommended as most appropriate management given your estimated risk.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Keywords: risk prediction, genetic risk score (GRS), electronic health records, cardiovascular diseases, coronary disease, biomarkers
Citation: Goldstein BA, Knowles JW, Salfati E, Ioannidis JPA and Assimes TL (2015) Corrigendum: Simple, standardized incorporation of genetic risk into non-genetic risk prediction tools for complex traits: coronary heart disease as an example. Front. Genet. 6:231. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2015.00231
Received: 27 May 2015; Accepted: 16 June 2015;
Published: 07 July 2015.
Edited and reviewed by: Helena Kuivaniemi, Geisinger Health System, USA
Copyright © 2015 Goldstein, Knowles, Salfati, Ioannidis and Assimes. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) or licensor are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Benjamin A. Goldstein,YmVuLmdvbGRzdGVpbkBkdWtlLmVkdQ==
 Benjamin A. Goldstein
Benjamin A. Goldstein Joshua W. Knowles
Joshua W. Knowles Elias Salfati
Elias Salfati John P. A. Ioannidis3
John P. A. Ioannidis3 Themistocles L. Assimes
Themistocles L. Assimes