
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Future Transp., 25 February 2025
Sec. Connected Mobility and Automation
Volume 6 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/ffutr.2025.1519759
The technical requirements for securing safety-related applications in connected autonomous vehicles (CAVs) include security (e.g., authentication, integrity, non-repudiation depending on the specific applications), privacy (e.g., anonymity and unlinkability) and computing efficiency of the solutions designed to address security and privacy aspects. Several cryptographic techniques have been considered in the literature to meet these technical requirements. A notable category of these techniques is often referred to as pseudonym schemes in the context of CAVs, which aim to address security and privacy simultaneously. This paper provides an overview of the state-of-the-art research on pseudonym techniques for CAVs, including a comparative evaluation of their performance in the context of two representative safety-related CAV applications: Cooperative positioning and intersection collision avoidance. This study aims to guide the effective adoption of such schemes for various applications in CAVs. In this paper, three main categories of pseudonym schemes are considered: public key schemes, identity-based signatures, and group signatures. We compare these schemes with respect to security and privacy requirements as identified for several CAV applications. We also implement several representative pseudonym schemes in each category to evaluate their processing efficiency for signing and verifying messages used in CAV applications to provide insight into their applicability for CAV applications.
Cooperative positioning and intersection collision avoidance are two representative safety applications for CAVs. Such applications leverage the exchange of safety-related messages through wireless communications between cars and infrastructures to extend the information horizons of the autonomous vehicle sensors onboard for safer operation. An example is periodic cooperative awareness messages (CAM), which help increase contextual awareness through cooperation between connected vehicles. To achieve this, each vehicle periodically transmits its kinematic information, such as position, heading, velocity, and acceleration, to its neighbor vehicles and nearby infrastructures. To enable such cooperation, it is crucial to deploy security mechanisms appropriately to facilitate trust in the information disseminated by such messages; otherwise, the system is inherently vulnerable to various malicious attacks that can cause accidents, injuries, or fatalities. Ensuring trust in the messages exchanged between vehicles and infrastructures typically depends on the authenticity of the nodes and messages. However, authentication of nodes in vehicular networks can create a situation where the system can be easily abused for vehicle tracking, raising privacy concerns since an eavesdropper can deduce the mobility patterns of an individual user and reveal the real identity of the user. For example, remote and long-term tracking is possible due to the message broadcasting mechanism. In addition to security and privacy concerns, safety-critical applications have latency requirements; therefore, the communication and processing overhead of security mechanisms must be kept as low as possible to facilitate efficient and scalable use of the wireless medium (Petit and Mammeri, 2013).
A large body of work has recently emerged that proposes crypto-optimized solutions for vehicular communications. These techniques are often called pseudonym schemes in the context of CAVs. The main purpose of such pseudonym schemes is to authenticate the sender as a valid vehicle while protecting the sender’s real identity. Pseudonyms are used to sign outgoing messages and verify received messages. The typical lifecycle of a pseudonym consists of issuance, use, change, resolution, and revocation. Pseudonyms are usually created by a trusted issuing authority. This authority may retain the link between the real identity of a vehicle and pseudonyms to allow identity resolution in the case of liability investigation. Each pseudonym should have an expiration date or a validity period so that it is valid only for a short period, such as 100 s (Eichler, 2007). The actions performed under the same pseudonym can be linked together; thus, the frequency of pseudonym changes decides the level of security and privacy. Frequent change of pseudonym typically introduces a large overhead for pseudonym management and creates ’ghost vehicles’, jeopardizing safety applications (Bißmeyer et al., 2012). Recent studies, such as those of Qi et al. (2022) and Saini et al. (2022), continue to explore pseudonym-based and certificate-less authentication schemes, indicating that this area remains active and crucial for developing secure vehicular communication systems. The ongoing standardisation efforts within ETSI and IEEE also indicate that the problem remains active, requiring further evaluation of practical trade-offs in computation, scalability, and security. However, the longer a pseudonym is used, the more vehicle behaviors are linked together, and the lower the level of privacy maintained.
To this end, analyzing the state-of-the-art of pseudonym schemes is crucial to helping system developers make informed decisions for CAV applications. There are three main categories of pseudonym schemes for vehicular networks. Schemes based on public key cryptography use public key infrastructure (PKI) where pseudonyms are represented by public keys and their certificates. A sender signs outgoing messages with private keys to produce signatures. Receivers can verify the authenticity of the messages and the source by verifying the signatures and pseudonym certificates. Schemes based on identity-based cryptography use a similar idea, but remove the need for public-key certificates. Identity-based cryptography enables each user to use an identifier as its public key. The corresponding private key is derived from the identifier by a trusted authority and only a legitimate user can obtain the private key; therefore certificates are no longer needed. A sender signs its messages using the private key and a receiver can verify the messages using the sender’s identifier. Schemes based on group signatures enable a group member to produce a signature on behalf of the group. The group member stays anonymous within the group. Group signatures eliminate the large overhead for generating, delivering, storing, and verifying numerous public key certificates or identifiers. Note that authenticity can also be based on symmetric cryptography, but this category of schemes is not compelling since it requires the receiver and the sender to have a pre-established shared secret key.
Pseudonym schemes have been extensively explored to address security and privacy concerns in vehicular ad hoc networks (VANETs). Several works have explored cryptographic techniques, anonymisation strategies, and their trade-offs between privacy, computational efficiency and memory, and scalability. This section reviews key contributions from the literature and highlights how this study provides a more comprehensive evaluation.
Gao and Zhao (2021) presents a comprehensive overview of location privacy protection schemes, including pseudonym-changing strategies, mix zones, and group-based techniques. The authors highlight challenges in integrating these schemes into large-scale VANETs but do not provide experimental validations. In contrast, the current work focuses on practical feasibility by experimentally evaluating pseudonym schemes on PC and ARM platforms. Boualouache et al. (2017) classifies pseudonym-changing strategies and evaluates their effectiveness in protecting privacy. However, it lacks a performance-based comparison of cryptographic pseudonym schemes that measure the computational overhead due to frequent ECDSA/ECC signing and verification. This can degrade performance in large-scale VANET deployments. The current study fills this gap by quantitatively comparing public-key schemes, identity-based signatures, and group signatures.
Khodaei and Papadimitratos (2017) evaluates on-demand pseudonym acquisition policies, focusing on privacy and system performance. Although the study is informative, it focuses mainly on PKI-based schemes and does not consider cross-border interoperability challenges. The IEEE (United States) and ETSI (Europe) standards diverge in cryptographic mechanisms, leading to compatibility issues for international V2X communication (IEEE, 2016a; IEEE, 2016b; IEEE, 2016c; IEEE, 2020); ETSI (2021a), ETSI (2021b). The current work broadens the scope by incorporating identity-based and group signature schemes and evaluating their computational efficiency. Emara et al. (2016) This work introduces a context-based pseudonym-changing scheme that adapts to traffic density and user preferences. Although innovative, it focuses on specific applications such as collision warnings and does not explore broader deployment scenarios. The current paper generalizes pseudonym schemes for various VANET applications, enhancing their practical utility. Amro (2018) proposes mix zones for pseudonym changes, leveraging the infrastructure for enhanced privacy. However, its reliance on infrastructure limits scalability. The present work provides solutions suitable for resource-constrained environments.
Ali et al. (2018) introduces SPATA, a lightweight pseudonym-based authentication framework, with distributed pseudonym mapping. Although efficient, it requires extensive infrastructure support. The current study evaluates cryptographic schemes that can be implemented with minimal infrastructure. Deng et al. (2022) proposes a pseudonym-changing protocol with adaptive strategies, focusing on resisting the tracking by adversaries. However, computational efficiency and scalability are underexplored. This study provides a balanced evaluation of privacy, efficiency, and scalability.
Qi et al. (2022) proposes a certificateless privacy-preserving authentication scheme with reduced storage overhead. However, if a vehicle loses connectivity, it may not be able to retrieve a new pseudonym in time, which poses an identity exposure risk. The present manuscript incorporates multiple cryptographic paradigms, including group signatures and identity-based schemes. While Studer et al. (2009) focuses on revocation challenges in PKI, large-scale vehicular networks face significant constraints due to the overhead of Certificate Revocation Lists (CRLs). The scalability issues of CRLs impact network efficiency, especially in highway environments where real-time revocation (via OCSP) remains a challenge. The current work complements this by examining pseudonym generation times and sizes across schemes. Petit and Mammeri (2013) evaluates the overhead of the authentication algorithms and their impact on the performance of VANET. It primarily addresses authentication without detailed evaluations of privacy-preserving pseudonym schemes, which can lead to vulnerabilities such as man-in-the-middle and replay attacks where attackers can intercept pseudonym updates before transition. This study integrates privacy considerations into pseudonym evaluations.
Unlike prior studies, this work combines theoretical and practical insights to bridge existing gaps in the literature, presenting a comprehensive framework for the adoption of pseudonym schemes in CAVs:
• Comprehensively Evaluates Schemes: Includes public key schemes, identity-based signatures, and group signatures, offering a comprehensive view of pseudonym technologies.
• Experimental Validation: Conducts practical evaluations on PC and ARM platforms, providing insights into real-world feasibility.
• Quantitative Metrics: Analyses pseudonym sizes, generation times, and processing overheads, addressing scalability and resource constraints.
• Balanced Analysis: Examines trade-offs between privacy, efficiency, and scalability in diverse deployment scenarios.
As such, recent studies have investigated alternatives to public-key-based pseudonym schemes to reduce computational and storage overhead through simulation-based approaches, providing insights into large-scale vehicular network behavior. However, these studies often rely on assumed computational models rather than actual cryptographic implementations. In addition, there exisits clear gaps in efficiency and deployment feasibility. This work complements these efforts by experimentally evaluating pseudonym generation and verification processes under practical constraints. Moreover, this paper indicates that alternative approaches are vigorously investigated; however, there is still an absence of a unified scheme to replace PKI-based solutions in standardization. This paper supports these efforts.
This section will first describe three categories of pseudonym schemes, i.e., public key cryptography, identity-based cryptography, and group signatures, and discuss their advantages and limitations. Then, we will compare these pseudonym schemes considering security and privacy requirements. Finally, we implement several representative schemes from each category and evaluate their processing time for signing and verification on PC and ARM platforms. Since cooperative positioning and intersection management use cases are based on CAM messages, the applications of these pseudonym schemes to these use cases are straightforward and are excluded in this paper (Benslimane, 2005; Colombo and Wymeersch, 2015; Drawil and Basir, 2010).
Public-key cryptography provides pseudonym solutions based on traditional PKI. Each vehicle is equipped with a set of public/private key pairs and the corresponding public key certificates. The public keys of a vehicle and the corresponding certificates serve as digital identities of the vehicle and are used as pseudonyms. The private keys are used to sign outgoing messages from the vehicle to produce signatures. Signatures can guarantee the authenticity of the messages, that is, the messages come from a trusted source and have not been tampered with during transmission. Receivers can verify the authenticity of messages by verifying signatures and certificates.
The signature
where
Here,
The private keys of a vehicle are kept secret and only known to the vehicle itself, while the corresponding public keys are certified using public key certificates, which are distributed in networks. Public-key certificates are created by a trusted authority (CA). The key pairs and certificates do not contain any identification information about the vehicle and are unlinkable from each other. However, the CA keeps the pseudonyms-to-identity mapping between a vehicle’s real identity and the issued pseudonyms in case of liability investigation.
It was first proposed in Gollan and Meinel (2002) and El Zarki et al. (2002) to use public key cryptography in vehicular networks. The WAVE standard specification in IEEE 1609 (2016d) is based on the Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm (ECDSA) to support authentication in a vehicular environment. For pseudonym issuance, it was proposed in Papadimitratos et al. (2008) that long-term certificates are issued and maintained by CAs while pseudonyms are created by some pseudonym providers. The role of pseudonym providers is usually assigned to infrastructure-based entities such as RSUs. The actions of a vehicle performed under the same pseudonym are linked; therefore, each pseudonym should only be valid for a short period of time to protect privacy (Papadimitratos et al., 2008). When a vehicle pseudonym expires, the vehicle loads a new pseudonym from its storage or requests new pseudonyms from some provider. Due to scalability reasons, pseudonym revocation is usually limited to revocation of a vehicle’s long-term identity, which prevents the vehicle from obtaining new pseudonyms. In Fischer et al. (2006) a pseudonym issuance protocol was proposed to guarantee that multiple authorities are required to cooperate in pseudonym resolution by using blind signatures and secret sharing. Misbehaving or malicious vehicles need to be held accountable and revoked from the networks. Revocation of pseudonym certificates is usually based on the technique of Certificate Revocation Lists (CRL). While Fischer et al. (2006) introduced a multi-authority pseudonym issuance model using blind signatures, a compromised or coerced Certificate Authority (CA) could still link pseudonyms to real identities, posing a privacy risk. However, letting each vehicle verify every message against CRLs is impractical due to the large number of exchanged messages and revoked pseudonyms. A typical method is to revoke the long-term identity of a vehicle and let the pseudonym providers limit the issuance of new pseudonyms to the revoked vehicle. A revoked vehicle may continue to use its existing pseudonyms until all have expired. A solution to mitigate this issue is to reduce the lifetime of pseudonyms, increasing the frequency of pseudonym refills.
Generally speaking, public key schemes are efficient and straightforward to use. Signatures based on public key cryptography can be used to ensure the authenticity of messages and their sources. Using a changing set of public/private keys can prevent linking a vehicle’s actions and achieve a certain level of privacy. However, it also raises some challenges in pseudonym management. The downside of using a changing set of pseudonyms is the large overhead for generating, delivering, storing and verifying numerous certificates for all pseudonym public keys.
In public key infrastructure, a public key is computed from a randomly selected private key and needs to be certified using public key certificates. In comparison, identity-based cryptography (IBC) in Shamir (1985) enables a vehicle to use an identifier, such as a plate number or an email address, as its “public key”. The corresponding private key is derived from the identifier by a trusted authority. The private key
where
The recipient verifies the signature using
A vehicle signs its messages using the private key and sends the signature together with the corresponding identifier. The receiver can verify the messages using the sender’s identifier and some public parameters generated by the authority. Only the legitimate vehicle will be able to receive a private key corresponding to an identifier from the authority. Therefore, vehicle authenticity is implicitly guaranteed and no certificate is required. To improve anonymity, a vehicle can have multiple pseudonym identifiers, which can be arbitrary strings. The trusted authority derives private keys from these pseudonym identifiers and gives these private keys to the vehicle. Since IBC avoids the explicit use and dissemination of public keys and certificates, less storage space is required in IBC because only pseudonym identifiers and private keys need to be stored.
Several efficient identity-based signature schemes were proposed, e.g., in Choon and Hee Cheon (2002) and Hess (2003), using cryptographic pairings. The role of the trusted authority for computing pseudonyms can be distributed among multiple authorities to prevent a single authority from learning all the issued private keys (Kamat et al., 2006). An anonymous IBC scheme called AnonySign was proposed in Kim et al. (2007) and corrected in Zhang and Xu (2012),1 which enables the message receiver to verify signatures without knowing the pseudonym identifier of the sender. More specifically, the sender signs messages with its private key, while the receiver verifies the signature using its own private key. Note that only authorised users can sign and verify messages in this system. The resolution of pseudonyms requires the trusted authority to perform cryptographic pairing operations with the secret keys of all registered vehicles, which is a computationally expensive process (Kim et al., 2007; Zhang and Xu, 2012). Revoking a vehicle’s private key is impossible without either revoking a vehicle’s ID or changing the master public key and re-issuing private keys to all the vehicles.
Revoking all a vehicle’s pseudonym identifiers with the revocation list method raises scalability issues, as for PKI certificates, while re-issuing all the private keys is infeasible. A better revocation method is to combine a vehicle’s identifier with a time component, which creates a short-lived pseudonym identifier.
Compared to public-key schemes, IBC removes the overhead of storing and disseminating public-key certificates, although it still requires managing a large set of identifiers. Another drawback of IBC is that a trusted authority generates private keys from vehicle identifiers rather than having vehicles generate their own key pairs. In addition, IBC schemes are cryptographic pairing-based cryptography schemes which are less efficient than public-key schemes.
Group signatures allow a member of the group to produce a signature on behalf of the group (Chaum and Van Heyst, 1991). A group signature
where
where
A group signature scheme typically involves two authorities: an issuer and an opener. Each group has a shared group public key, and each group member has its own group signing key issued by the group issuer, who has a unique issuing key. A group member signs messages with its group signing key to produce signatures. The receiver verifies the signatures with the group public key. Two signatures generated by the same signer are unlinkable, since one can only verify that these are valid signatures created by some group members but not by which member. Thus, the signer remains anonymous within the group and there is no need to use explicit pseudonyms in group signatures. The anonymity of a malicious group member can be revoked by the group opener, who possesses a unique opening key. The group issuer can revoke the group signing keys of malicious or compromised members by generating a new group public key and deriving new group signing keys for other legitimate group members.
Short group signatures were originally proposed in Boneh and Shacham (2004) to provide anonymous authentications for each message broadcast on vehicular networks. Threshold authentication protocols were proposed in Wu et al. (2010), Chen et al. (2011) and Shao et al. (2016) for vehicular communications where a message is considered trustworthy only after a certain number of vehicles have endorsed it. A time-dependent linking system in Emura and Hayashi (2014) enables vehicle-to-infrastructure communications where a token generation unit periodically transmits a time token. Most of the group signature schemes are based on cryptographic pairing operations, which are known to be time-consuming. This makes group signatures unsuitable for direct message authentication in vehicular communications. In Calandriello et al. (2007), Rabadi and Mahmud (2007), Lu et al. (2008), and Studer et al. (2009) it was suggested to use group signatures to issue and certify traditional public keys without any interaction with the authorities.
A revocation mechanism in Boneh and Shacham (2004) can revoke malicious signers without affecting the signing ability of other users. To do so, the group signing keys of all revoked users are published, and other users can compute their new group signing keys without using the group issuer’s secret key. The drawback of this revocation mechanism is that it requires all users to update their signing keys. Verifier-local revocation in Boneh and Shacham (2004) and Emura and Hayashi (2014) enables verifiers to only process the revocation messages. The verification algorithm for the group signatures checks each signature against a revocation list, which contains a token for each revoked user. Signatures issued by revoked users are no longer accepted. The downside of this revocation mechanism is that it introduces considerable overhead to transmit the revocation list and verify each signature.
Group signatures simultaneously achieve authenticity, data integrity, anonymity, and accountability while eliminating the heavy overhead of generating, delivering, storing, and verifying numerous pseudonym public keys in public-key schemes (or private keys in IBC). However, it is generally not effective to directly apply a group signature scheme to sign massive outgoing messages from a vehicle. This is because most group signature schemes are based on cryptographic pairings, which are time consuming.
In this section, we compare pseudonym schemes considering the security and privacy requirements of unforgeability, traceability, short-term linkability, anonymity, and distributed resolution authority. The reason is that 1) for digital signatures, authentication and integrity are usually modeled together in unforgeability, anonymity and unlinkability are merged in anonymity, and non-repudiation is formalized as traceability; 2) pseudonym schemes cannot achieve availability, content awareness, and policy and consent compliance. Availability can be achieved using network tools, such as firewalls and spam detection, while content awareness2 and compliance3 are usually improved by technology that improves transparency. Table 1 compares and rates public key schemes, identity-based, and group signatures, considering the above requirements.
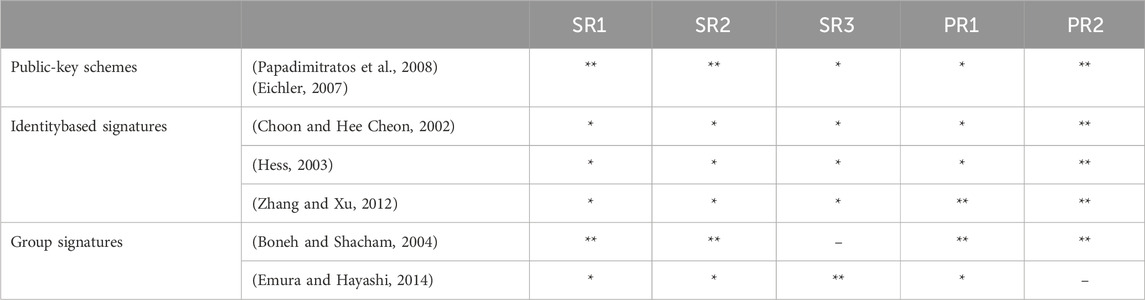
Table 1. Comparison of security and privacy. SR1 = Unforgeability, SR2 = Traceability, SR3 = Short-term linkability, PR1 = Anonymity, PR2 = Distributed resolution authority. “–“ means a scheme cannot meet a certain requirement. “*” means a scheme can somehow satisfy a requirement, but the solution has some weaknesses. “**” means a scheme provides strong solutions.
Unforgeability means that no one can forge a signature on behalf of an honest member or falsely accuse the member of producing a signature. Unforgeability can be satisfied in all schemes, but the security implications can be very different. In public key schemes and group signature schemes, users can choose their own secret keys and keep them secure. Therefore, unforgeability can be expected even when trusted authorities are compromised. In the group signatures in Boneh and Shacham (2004), the issuing key and the opening key are two different keys and can be kept with two different authorities. For each user, some part of its group signing key is chosen by the user and is only known to the user, making it impossible to forge a user’s signature even if the issuer and the opener are both corrupted. But for the group signature scheme proposed in Emura and Hayashi (2014), a single group issuer generates all secret signing keys of users, and thus unforgeability will be broken in case the issuer is broken. In identity-based signatures, users’ secret keys are created by a trusted authority. If the authority is corrupted or compromised, then the entire system collapses and there will be no security or privacy left for any user. In identity-based signatures, the issuing key to create user credentials and the opening key to identify malicious users must be the same (Choon and Hee Cheon, 2002; Hess, 2003; Kim et al., 2007; Zhang and Xu, 2012).
Traceability ensures that a valid signature can be traced back to its original signer. Typically, trace execution is performed by a trusted authority possessed of a special opening key. Identity tracing using identity-based signatures in Choon and Hee Cheon (2002), Hess (2003), Zhang and Xu (2012) and group signatures in Emura and Hayashi (2014) require the authority to perform time-consuming cryptographic operations on each group member. This computationally expensive process does not scale well with the number of members. The group signatures in Boneh and Shacham (2004) support efficient identity opening by integrating encryption of the signer’s identity into each signature, which can be decrypted by the authority. Identity resolution in public-key schemes is more straightforward: The authority checks the mapping between user pseudonyms and real identities.
Short-term linkability is a balance between security and privacy originally proposed in (Golle et al., 2004). In the context of vehicular communications, it means linking the movement of a vehicle in a short period of time. Short-term linkability aims to prevent Sybil attacks while preserving long-term privacy of a vehicle. Some work, such as in Studer et al. (2009) and Hajny et al. (2013), fixes the temporary pubic key or the randoms used in group signatures to obtain linkability on pseudonyms. However, this is not a secure mechanism because it relies on trusting the users to honestly follow the protocol and not change their pseudonyms. In public key schemes, short-term linkability can be achieved by integrating a validity period in each public key certificate. For multiple public keys of one user, the validity period of each public key cannot overlap with each other. Otherwise, the user can switch between pseudonyms freely, breaking the short-term linkability. However, this approach lacks flexibility on pseudonym changes and may require a large number of pseudonyms when the validity period is short. For group signatures, linkability can be implemented based on messages as shown in Wu et al. (2010), Chen et al. (2011), Shao et al. (2016), or as time-dependent linkability in Emura and Hayashi (2014). In the approach of message linkability, a message is viewed as trustworthy only after a certain number of vehicles have endorsed it. Since all vehicles must sign the same message to increase the trustworthiness of the message, this method has several limitations. First, a safety message must be associated with a timestamp to ensure its effectiveness, but the timestamp may vary from vehicle to vehicle and messages from different vehicles cannot be exactly the same. Secondly, the threshold method does not apply to relevant use cases where a vehicle measures and signs its own kinematic info, which cannot be endorsed by any other vehicle. The time-dependent linking system (Emura and Hayashi, 2014) links messages from the same vehicle for a certain period. It uses a token generation unit to periodically broadcast a token. However, the signing and verification algorithms in (Emura and Hayashi, 2014) are time consuming and are not appropriate for direct message authentication. Moreover, the revocation mechanism of (Emura and Hayashi, 2014) requires frequent updates of a large revocation list, which means that the scheme can only be used for vehicle-to-infrastructure communication.
Anonymity in public key schemes is achieved by using a changing set of public keys and certificates, that is, pseudonyms. Since actions performed under one pseudonym can be linked together, a vehicle must change pseudonyms over time to avoid the linkability of actions. Each pseudonym is valid for a short period. When a pseudonym expires, a vehicle has to load a new pseudonym from its storage or obtain new pseudonyms from the pseudonym providers. The pseudonym change rate impacts the level of privacy and the overhead of computation, communication, and storage. There are different pseudonym-changing strategies, such as the fixed-time change in Eckhoff et al. (2010), the random change in Pan et al. (2011), and the silent period between changes in Sampigethaya et al. (2007). However, pseudonym changes introduce a large overhead for generating, delivering, storing, and verifying numerous public keys and certificates for all pseudonym public keys. Anonymity in identity-based signatures can be achieved in a similar way by using a changing set of identities and private keys. Since identity-based signatures avoid using public keys and public-key certificates, the overhead is lighter compared to that of public-key schemes. The anonymous version of identity-based signatures in Kim et al. (2007) and Zhang and Xu (2012) avoids the use of the message signer’s identity in signature verification, therefore obviates the need for the change in the set of identities and private keys. Group signatures also provide anonymous signatures verified using a shared public key. Two messages signed by the same user cannot be linked and the signer remains anonymous within the group.
Distributed resolution authority requires that the capability of identifying malicious group members be distributed among different authorities. This is done to prevent a single authority with a very powerful key from abusing its power. Splitting roles between Certificate Authorities (CA), Pseudonym Providers (PP), and Registration Authorities (RA) can protect vehicle privacy against trusted authorities. For public key schemes, the role of CA can be split between one RA, one CA, and two Linkable Authorities (LAs), to prevent a single authority from tracking a vehicle by linking its multiple certificates. Linking certificates require all authorities to collaborate, improving vehicle privacy and increasing communication overhead between authorities. A distributed pseudonym issuance protocol in Fischer et al. (2006), called SRAAC, uses blind signatures and secret sharing to allow multiple authorities to cooperate in pseudonym resolution. For identity-based signatures in Choon and Hee Cheon (2002), Hess (2003), and (Zhang and Xu, 2012) and group signatures in Boneh and Shacham (2004), the resolution authority can be distributed using secret-sharing schemes in Dawson and Donovan (1994), but the role of the issuing authority and the resolution authority cannot be divided. For group signatures, the issuing authority can be different from the resolution authority, and the latter can be distributed using secret-sharing schemes (Boneh and Shacham, 2004). But for group signatures in, the role of the issuing authority and the resolution authority cannot be split or distributed (Emura and Hayashi, 2014).
Therefore, past proposals have sought to optimize pseudonym schemes through strategies such as certificateless cryptography and dynamic pseudonym changes. However, these approaches require further empirical evaluation to determine their feasibility in large-scale deployments. This study provides a comparative analysis of established and emerging schemes, demonstrating that public-key solutions still present a practical balance between security, privacy, and computational efficiency.
Safety-critical applications have latency requirements, and the communication and processing overhead of security mechanisms must be kept as low as possible to facilitate efficient and scalable use of the wireless medium (Petit and Mammeri, 2013). The processing time for the construction of a message should not exceed 50 ms, and large packet sizes would drastically affect the number of packets being delivered (ETSI TS102637-2, 2011). We have implemented several of the best known public key schemes, identity-based signatures, and group signatures to compare the signature size and computation time for signing and verification and demonstrate their applicability to CAV applications. We use the Pairing-Based Cryptography (PBC) Library (Lynn, 2007). Although currently there is no agreement about a vehicle’s on-board hardware capabilities, we present illustrative measures taken from an experiment on a PC platform with Intel core i7-4790 CPU clocked at 3.60 GHz and 8 GB memory and an experiment on an ARM platform with NXP IMX6 UltraLite board which is believed to be a reasonable example of a platform that could be used on a vehicle for cryptographic processing. Although some studies employ large-scale simulations for performance evaluation, this work focuses on empirical measurements by implementing cryptographic pseudonym schemes on actual hardware (PC and ARM platforms). This approach provides practical insights into computational feasibility and real-world performance constraints, complementing theoretical and simulation-based evaluations in the literature. Future work can integrate real-time traffic data and large-scale vehicular simulations to further refine these findings.
The PBC library currently implements 5 types of pairings, i.e., type A, D, E, F and G pairings. Type A is symmetric and fastest. Type D is asymmetric and has short group elements. The identity-based signatures are based on symmetric pairings and tested with type-A curves. The other schemes are tested with asymmetric pairings, using type-D curves for 80-bit and 112-bit security, and type-F curves for 256-bit security. Pairings involve three groups of prime order:
To estimate the overall storage overhead of group signatures, the total signature size can be expressed as:
Here,
Processing Time: Table 2 shows the running time of signature generation and verification tested on the PC platform, while Table 3 shows the running time tested on the ARM platform. For each scheme, each test result is the average of 1,000 tests. The test results show that public-key schemes are more suitable for resource constraint scenarios. The deployment of identity-based and group signatures in vehicular communications poses a real challenge here.
We also evaluate the running time for group operations, including multiplication, exponentiation, and pairing. The results of the experiment on the PC and the ARM platforms are given in Supplementary Appendix SC. We can see that the operations on
To analyze the computational overhead of pseudonym schemes, the following equations quantify the signing and verification times based on the underlying cryptographic operations.
Signing Time:
Verification Time:
Here,
Signature Length: Table 4 summarizes the comparison of the size of a signature of each pseudonym scheme in terms of the number of group elements and the security overhead. The security overhead is the size of a signature and is expressed as a percentage of 200 Bytes, which is the typical size of messages exchanged in vehicular communications (ETSI TS103324, 2011). Note that the security overhead is computed with some compression mechanism4 provided in the PBC library to represent elements in
The size of pseudonyms is an important factor in the evaluation of their feasibility for CAVs. Each pseudonym includes cryptographic components such as private keys, public keys, certificates, and identifiers, depending on the scheme. Based on Annex B, the pseudonym sizes for different schemes at varying security levels are as follows:
• Public Key Schemes: A pseudonym consists of a private key and a public key certificate. For 112-bit security, the size of the private key (Zr) is approximately 28 bytes, while the certificate size (G1) is 192 bytes. The total pseudonym size is approximately 220 bytes.
• Identity-Based Signatures: IBC eliminates the need for public key certificates, reducing overall storage requirements. A pseudonym comprises an identifier and a private key. At 112-bit security, the size of the private key is similar to PKI (28 bytes), but the absence of certificates lowers the storage overhead.
• Group Signatures: Group signatures avoid explicit pseudonyms, embedding the authentication data within the group structure. However, the size of the group signature increases due to its cryptographic complexity. For 112-bit security, a group signature requires 2 G1 and 4 Zr elements, resulting in an overhead of 85% relative to a 200-byte CAM message, as shown in Table 4.
• These sizes highlight the trade-offs between the schemes in terms of storage efficiency, with IBC offering reduced storage at the cost of computational complexity and group signatures providing anonymity at the expense of larger pseudonym sizes.
The time required to generate pseudonyms is another important aspect, especially during revocation or pseudonym refresh scenarios. Pseudonym generation involves cryptographic operations such as key pair creation, certificate signing, and group key derivation. Based on the processing times reported in Supplementary Appendix SC:
• Public Key Schemes: The generation of pseudonyms involves creating a key pair and signing the public key. For 112-bit security on an ARM platform, the average signing time is approximately 20.79 ms. The key pair generation time is typically shorter than the signing time and is estimated to be less than 10 ms.
• Identity-Based Signatures: Pseudonym generation involves the generation of a private key from an identifier, which requires pairing operations. For 112-bit security, the average pairing time on an ARM platform is approximately 32.64 ms. This makes IBC slower than PKI for pseudonym generation in resource-constrained environments.
• Group Signatures: Group signature pseudonym generation is more complex due to the cryptographic pairing operations required. At 112-bit security, signing requires 286.72 ms on an ARM platform, as shown in Table 3. The need for additional pairing operations during revocation further increases computational overhead, making this approach less efficient for large-scale deployments.
While public-key-based pseudonym schemes remain the dominant approach, recent advances in certificateless and dynamic pseudonym strategies indicate that research in this domain is ongoing. The absence of a standardized alternative highlights the need for continued comparative evaluations such as this study to guide future adoption and regulatory decisions. Moreover, this study focuses on empirical evaluation rather than large-scale simulations, and future work will explore real-time vehicular data to assess scheme effectiveness in dynamic traffic scenarios. Furthermore, integrating comparative analyses with novel state-of-the-art techniques will further strengthen the conclusions presented here.
Although recent work has introduced novel mechanisms for pseudonym management and location privacy, this article provides a comprehensive experimental evaluation in multiple cryptographic paradigms, addressing practical concerns of scalability, efficiency, and deployability. This ensures its continued relevance in addressing the dynamic needs of CAV systems. We classify pseudonym schemes into three categories based on the underlying cryptography techniques. We describe the general concept for each category and analyze its advantages and limitations. The pseudonym schemes are compared considering security and privacy requirements, including unforgeability, traceability, short-term linkability, anonymity, and distributed resolution authority. Since safety-critical applications are highly delay sensitive, we implemented several best known public key schemes, identity-based signatures, and group signatures to compare the signature size and computation time for signing and verification and demonstrate their applicability to CAV applications.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
AS: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. JL: Writing–original draft. MD: Writing–review and editing. CM: Writing–review and editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. The work leading to this deliverable was carried out in collaboration with the \href{https://petras-iot.org}{EPSRC PETRAS} hub user partners involved in this project, TRL, Pinsent Masons, and Thales. In particular, Thales contributes to the simulation platform used for some of the results in this report by performing the tests on an NXP IMX6 board.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/ffutr.2025.1519759/full#supplementary-material
1As pointed out in (Zhang and Xu, 2012), the scheme proposed in (Kim et al., 2007) is not traceable.
2A user is unaware of the information disclosed to the system.
3The system complies with the advertised policies.
4Points on an elliptic curve are defined by
Ali, Q. E., Ahmad, N., Malik, A. H., Ali, G., Asif, M., Khalid, M., et al. (2018). Spata: strong pseudonym-based authentication in intelligent transport system. IEEE Access 6, 79114–79123. doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2883134
Amro, B. (2018). Protecting privacy in vanets using mix zones with virtual pseudonym change. Int. J. Netw. Secur. and Its Appl. 10, 11–21. doi:10.5121/ijnsa.2018.10102
Benslimane, A. (2005). “Localization in vehicular ad hoc networks,” in 2005 systems communications (Montreal, QC: ICW’05, ICHSN’05, ICMCS’05, SENET’05), 19–25. doi:10.1109/ICW.2005.54
Bißmeyer, N., Njeukam, J., Petit, J., and Bayarou, K. M. (2012). “Central misbehavior evaluation for vanets based on mobility data plausibility,” in Proceedings of the ninth ACM international workshop on Vehicular inter-networking, systems, and applications, 73–82.
Boneh, D., and Shacham, H. (2004). “Group signatures with verifier-local revocation,” in Proceedings of the 11th ACM conference on Computer and communications security, 168–177.
Boualouache, A., Senouci, S.-M., and Moussaoui, S. (2017). A survey on pseudonym changing strategies for vehicular ad-hoc networks. arXiv preprint
Calandriello, G., Papadimitratos, P., Hubaux, J.-P., and Lioy, A. (2007). “Efficient and robust pseudonymous authentication in vanet,” in Proceedings of the fourth ACM international workshop on Vehicular ad hoc networks, 19–28.
Chaum, D., and Van Heyst, E. (1991). “Group signatures,” in Advances in cryptology—eurocrypt’91: workshop on the theory and application of cryptographic techniques brighton, UK, april 8–11, 1991 proceedings 10 (Springer), 257–265.
Chen, L., Ng, S. L., and Wang, G. (2011). Threshold anonymous announcement in vanets. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 29, 605–615. doi:10.1109/jsac.2011.110310
Choon, J. C., and Hee Cheon, J. (2002). An identity-based signature from gap diffie-hellman groups. Public Key Cryptogr. 2003 6th Int. Workshop Pract. Theory Public Key Cryptogr. Miami, FL, U. S. A. January 6–8, 2003 Proc. 6, 18–30. doi:10.1007/3-540-36288-6_2
Colombo, A., and Wymeersch, H. (2015). “Cooperative intersection collision avoidance in a constrained communication environment,” in 2015 IEEE 18th international Conference on intelligent transportation systems (IEEE), 375–380.
Dawson, E., and Donovan, D. (1994). The breadth of shamir’s secret-sharing scheme. Comput. and Secur. 13, 69–78. doi:10.1016/0167-4048(94)90097-3
Deng, X., Gao, T., Guo, N., Zhao, C., and Qi, J. (2022). Pcp: a pseudonym change scheme for location privacy preserving in vanets. Entropy 24, 648. doi:10.3390/e24050648
Drawil, N. M., and Basir, O. (2010). Intervehicle-communication-assisted localization. IEEE Trans. Intelligent Transp. Syst. 11, 678–691. doi:10.1109/TITS.2010.2048562
Eckhoff, D., Sommer, C., Gansen, T., German, R., and Dressler, F. (2010). “Strong and affordable location privacy in vanets: identity diffusion using time-slots and swapping,” in 2010 IEEE vehicular networking conference, 174–181. doi:10.1109/VNC.2010.5698239
Eichler, S. (2007). “Strategies for pseudonym changes in vehicular ad hoc networks depending on node mobility,” in 2007 IEEE intelligent vehicles symposium (IEEE), 541–546.
El Zarki, M., Mehrotra, S., Tsudik, G., and Venkatasubramanian, N. (2002). “Security issues in a future vehicular network,” in Proceedings of the European wireless conference (euro wireless 2002), 35.
Emara, K., Woerndl, W., and Schlichter, J. (2016). Context-based pseudonym changing scheme for vehicular adhoc networks. arXiv preprint
Emura, K., and Hayashi, T. (2014). Road-to-vehicle communications with time-dependent anonymity: a lightweight construction and its experimental results. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 67, 1582–1597. doi:10.1109/tvt.2017.2763145
ETSI (2021a). ETSI TS 102 941: intelligent transport systems (ITS); security; trust and privacy management
ETSI (2021b). ETSI TS 103 097: intelligent transport systems (ITS); security; security header and certificate formats
Etsi, T. S. 102 637-2 (2011a). Intelligent transport systems (ITS); vehicular communications; basic set of applications; Part 2: specification of cooperative awareness. Basic Serv.
Etsi, T. S. 103 324 (2011b). Intelligent transport system (ITS). Veh. Commun. Basic Set Appl. Collect. Percept. Serv.
Fischer, L., Aijaz, A., Eckert, C., and Vogt, D. (2006). “Secure revocable anonymous authenticated inter-vehicle communication (sraac),” in 4th conference on embedded security in cars (ESCAR 2006). Berlin, Germany 148.
Gao, T., and Zhao, L. (2021). “Pseudonym schemes based on location privacy protection in vanets: a survey,” in International conference on innovative mobile and internet services in ubiquitous computing (IMIS) (Springer), 597–605. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-50399-4_59
Gollan, L., and Meinel, C. (2002). Digital signatures for automobiles?!. Trier, Germany: Inst. für Telematik.
Golle, P., Greene, D., and Staddon, J. (2004). “Detecting and correcting malicious data in vanets,” in Proceedings of the 1st ACM international workshop on vehicular ad hoc networks (New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery), 29–37. doi:10.1145/1023875.1023881
Hajny, J., Malina, L., Martinasek, Z., and Zeman, V. (2013). “Privacy-preserving svanets: privacy-preserving simple vehicular ad-hoc networks,” in 2013 international conference on security and cryptography (SECRYPT), 1–8.
Hess, F. (2003). “Efficient identity based signature schemes based on pairings,” in Selected areas in cryptography: 9th annual international workshop, SAC 2002 St. John’s, newfoundland, Canada, august 15–16, 2002 revised papers 9 (Springer), 310–324.
IEEE (2016a). IEEE standard for wireless access in vehicular environments - security services for applications and management messages. doi:10.1109/IEEESTD.2016.7442703
IEEE (2016b). IEEE standard for wireless access in vehicular environments (WAVE) - multi-channel operation. doi:10.1109/IEEESTD.2016.7786251
IEEE (2016c). IEEE standard for wireless access in vehicular environments (WAVE) - networking services. doi:10.1109/IEEESTD.2016.7786250
IEEE (2020). IEEE standard for certificate management interfaces for V2X communications. doi:10.1109/IEEESTD.2020.9090898
IEEE 1609 (2016d). Ieee standard for wireless access in vehicular environments-security services for applications and management messages, 1609. IEEE.
Kamat, P., Baliga, A., and Trappe, W. (2006). “An identity-based security framework for vanets,” in Proceedings of the 3rd international workshop on Vehicular ad hoc networks, 94–95.
Khodaei, M., and Papadimitratos, P. (2017). Evaluating on-demand pseudonym acquisition policies in vehicular communication systems. arXiv preprint.
Kim, B. H., Choi, K. Y., Lee, J. H., and Lee, D. H. (2007). “Anonymous and traceable communication using tamper-proof device for vehicular ad hoc networks,” in 2007 international conference on convergence information technology (ICCIT 2007) (IEEE), 681–686.
Lu, R., Lin, X., Zhu, H., Ho, P.-H., and Shen, X. (2008). “Ecpp: efficient conditional privacy preservation protocol for secure vehicular communications,” in IEEE INFOCOM 2008-the 27th Conference on computer communications (IEEE), 1229–1237.
Lynn, B. (2007). On the implementation of pairing-based cryptosystems. Stanford University Stanford.
Pan, Y., Li, J., Feng, L., and Xu, B. (2011). An analytical model for random changing pseudonyms scheme in vanets. 2011 Int. Conf. Netw. Comput. Inf. Secur. 2, 141–145. doi:10.1109/NCIS.2011.127
Papadimitratos, P., Buttyan, L., Holczer, T., Schoch, E., Freudiger, J., Raya, M., et al. (2008). Secure vehicular communication systems: design and architecture. IEEE Commun. Mag. 46, 100–109. doi:10.1109/mcom.2008.4689252
Petit, J., and Mammeri, Z. (2013). Authentication and consensus overhead in vehicular ad hoc networks. Telecommun. Syst. 52, 2699–2712. doi:10.1007/s11235-011-9589-y
Qi, J., Gao, T., Deng, X., and Zhao, C. (2022). A pseudonym-based certificateless privacy-preserving authentication scheme for vanets. Veh. Commun. 38, 100535. doi:10.1016/j.vehcom.2022.100535
Rabadi, N. M., and Mahmud, S. M. (2007). “Privacy protection among drivers in vehicle-to-vehicle communication networks,” in 2007 4th IEEE consumer communications and networking conference (IEEE), 281–286.
Saini, I., Saad, S., and Jaekel, A. (2022). A comprehensive pseudonym changing scheme for improving location privacy in vehicular networks. Internet Things 19, 100559. doi:10.1016/j.iot.2022.100559
Sampigethaya, K., Li, M., Huang, L., and Poovendran, R. (2007). Amoeba: robust location privacy scheme for vanet. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 25, 1569–1589. doi:10.1109/JSAC.2007.071007
Schnorr, C.-P. (1991). Efficient signature generation by smart cards. J. Cryptol. 4, 161–174. doi:10.1007/bf00196725
Shamir, A. (1985). Identity-based cryptosystems and signature schemes. Adv. Cryptol. Proc. CRYPTO 84 4, 47–53. doi:10.1007/3-540-39568-7_5
Shao, J., Lin, X., Lu, R., and Zuo, C. (2016). A threshold anonymous authentication protocol for vanets. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 65, 1711–1720. doi:10.1109/tvt.2015.2405853
Studer, A., Shi, E., Bai, F., and Perrig, A. (2009). “Tacking together efficient authentication, revocation, and privacy in vanets,” in 2009 6th annual IEEE communications society Conference on sensor, Mesh and ad hoc Communications and networks (IEEE), 1–9.
Wu, Q., Domingo-Ferrer, J., and Gonzalez-Nicolas, U. (2010). Balanced trustworthiness, safety, and privacy in vehicle-to-vehicle communications. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 59, 559–573. doi:10.1109/tvt.2009.2034669
Keywords: security, privacy, pseudonym, signatures, authentication, connected autonomous vehicles (CAVs)
Citation: Sheik AT, Liu J, Dianati M and Maple C (2025) Comparative evaluation of pseudonym-based anonymisation techniques for connected autonomous vehicles (CAVs). Front. Future Transp. 6:1519759. doi: 10.3389/ffutr.2025.1519759
Received: 30 October 2024; Accepted: 29 January 2025;
Published: 25 February 2025.
Edited by:
Ignacio Soto, Universidad Politécnica de Madrid., SpainReviewed by:
Manuel Urueña, International University of La Rioja, SpainCopyright © 2025 Sheik, Liu, Dianati and Maple. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Al Tariq Sheik, dC5zaGVpa0B3YXJ3aWNrLmFjLnVr; Mehrdad Dianati, bS5kaWFuYXRpQHF1Yi5hYy51aw==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.