- 1College of Mathematics and Computer Science, Zhejiang A&F University, Hangzhou, China
- 2College of Chemistry and Materials Engineering, Zhejiang A&F University, Hangzhou, China
- 3Zhejiang Provincial Key Laboratory of Forestry Intelligent Monitoring and Information Technology Research, Zhejiang A&F University, Hangzhou, China
- 4Key Laboratory of Carbon Cycling in Forest Ecosystems and Carbon Sequestration of Zhejiang Province, Zhejiang A&F University, Lin’an, China
Soil respiration (Rs) is the largest source of atmospheric CO2, and an accurate understanding of the relationship between near-surface winds, CO2 release from the soil surface, and measurement methods is critical for predicting future atmospheric CO2 concentrations. In this study, the relationship between wind speed and soil CO2 fluxes is elucidated on a global scale through meta-analysis, and the flux measurement methodology is further explored in conjunction with the results of a controlled trial to clarify the uncertainty of the measurement results. The results indicate that near-surface wind speed is positively correlated with soil CO2 release and that near-surface winds result in increased soil CO2 gas release. Wind disturbance affects both the concentration gradient and gas chamber measurements, and the lower calculated soil CO2 release conflicts with the notion that the wind pump effect and Bernoulli effect of negative pressure cause a greater surface gas exchange. The results of the log-response ratios indicate that near-surface winds lead to an underestimation of 12.19–19.75% in widely-used gas chamber method measurements. The results of this study imply that some of the current Rs measurements are biased and that the influence of near-surface winds on Rs measurements needs to be urgently addressed to assess the terrestrial carbon cycle more accurately and develop climate change response strategies.
1 Introduction
Soil respiration (Rs) is the largest source of atmospheric CO2. The annual flux of carbon dioxide released into the atmosphere from Rs (98 ± 12 Pg C) is approximately ten times greater than the flux of carbon dioxide from fossil fuel combustion (Yang et al., 2022; Zhou et al., 2013). This implies that small changes in Rs lead to large changes in atmospheric CO2 concentrations, which in turn affect the global climate in close proximity (Liu et al., 2022; Takeda et al., 2023; Tian et al., 2019). Therefore, accurate monitoring of CO2 fluxes released by Rs is essential for assessing the terrestrial carbon cycle and predicting future atmospheric CO2 concentrations.
Soil-released CO2 fluxes are dependent on complex interactions between biological, chemical, and physical processes and are significantly influenced by environmental factors (Nissan et al., 2023). In recent years, researchers have found that CO2 flux measurements released by Rs have become highly uncertain owing to the influence of near-surface winds (Jian et al., 2022; Konings et al., 2019; Li et al., 2016; Maier et al., 2019; Tharammal et al., 2019). This phenomenon also makes it extremely challenging to accurately observe, measure, and model soil CO2 fluxes. The vast majority of current flux calculation models still use molecular diffusion as the only transport mechanism for CO2 gas in the soil (Hutchinson and Livingston, 2001; Lebel et al., 2020; Livingston et al., 2006; Maier et al., 2012; Tammadid et al., 2024). However, recent studies have shown that non-diffusive transport is an efficient form of transport in the presence of soil gases (Campeau et al., 2024; Levintal et al., 2019). Moya et al. (2022) found that the non-diffusive transport of gases induced by subsurface ventilation led to a significant enhancement in soil CO2 release from stored CO2 gases in the soil to the atmosphere through soil pores and cracks. In addition, changes in the ‘quasi-static pressure field’ caused by wind blowing over irregular terrain can also lead to non-diffusive transport of soil gases (Bowling and Massman, 2011; Jiang et al., 2023a; Poulsen and Møldrup, 2006; Takle et al., 2004), facilitating gas exchange. Some scholars have applied adjustable wind speeds above the soil surface in the laboratory and similarly found a strong correlation between wind speed and gas transport, verifying that wind turbulence enhances gas transport rates in porous media such as soil (Maier et al., 2012; Poulsen et al., 2018; Pourbakhtiar et al., 2017). These studies have shown that wind turbulence significantly affects transport and enhances the release of soil CO2 gas (Bowling and Massman, 2011; Jiang et al., 2023b; Laemmel et al., 2018; Poulsen and Møldrup, 2006; Redeker et al., 2015) and is an important influencing factor in the actual measurement process.
Interestingly, only a few studies using the air chamber method to measure soil CO2 fluxes have found a positive correlation between wind speed and flux values, but they attributed this to the Venturi effect occurring at artificially designed air chamber ventilation ports (Bain et al., 2005; Conen and Smith, 2003; Xu et al., 2006). However, most studies have found a negative correlation between wind speed and flux. Maier et al. (2019) used the air chamber method to explore the effect of changes in wind speed on soil CO2 fluxes and found that flux measurements were negatively correlated with wind speed. It has been found that near-surface winds will reduce soil CO2 release from boreal coniferous forests by extending the time of gas chamber deployment (Lai et al., 2012; Lebel et al., 2020). Fleming et al. (2021) used the gas chamber method to monitor the gas release around abandoned oil wells and found that wind turbulence could severely affect gas chamber measurements. Seok et al. (2009) found that near-surface winds significantly affected CO2 gas concentrations and gradients in snowpacks using the gradient method, with calculated fluxes dropping to 5% of non-wind conditions under high wind speed conditions. These measurements appear to contradict wind-induced non-diffusive transport of soil gases, which causes greater surface gas exchange. Therefore, as far as the present study is concerned, the effect of near-surface wind disturbances on CO2 release from the soil surface and on the measurement methodology is still highly questionable.
In order to determine the effect of near-surface winds on CO2 release from the soil surface and measurement methods, 101 global records of the relationship between near-surface winds and CO2 release from the soil surface were collected in this study (Figure 1). The meta-analysis method was then used to systematically integrate the results of several studies, to provide more comprehensive insights and so enhance the credibility and application value of the conclusions with respect to determining the relationship between wind speed and soil CO2 fluxes, explore methods of measuring in combination with experimental results, and clarify the influence of near-surface wind speed on flux measurement methods, particularly those used for air chambers (Jian et al., 2020). This provided opportunity to reliably quantify the effect of near-surface winds on Rs, which is critical for predicting future atmospheric CO2 concentrations and the global carbon budget.
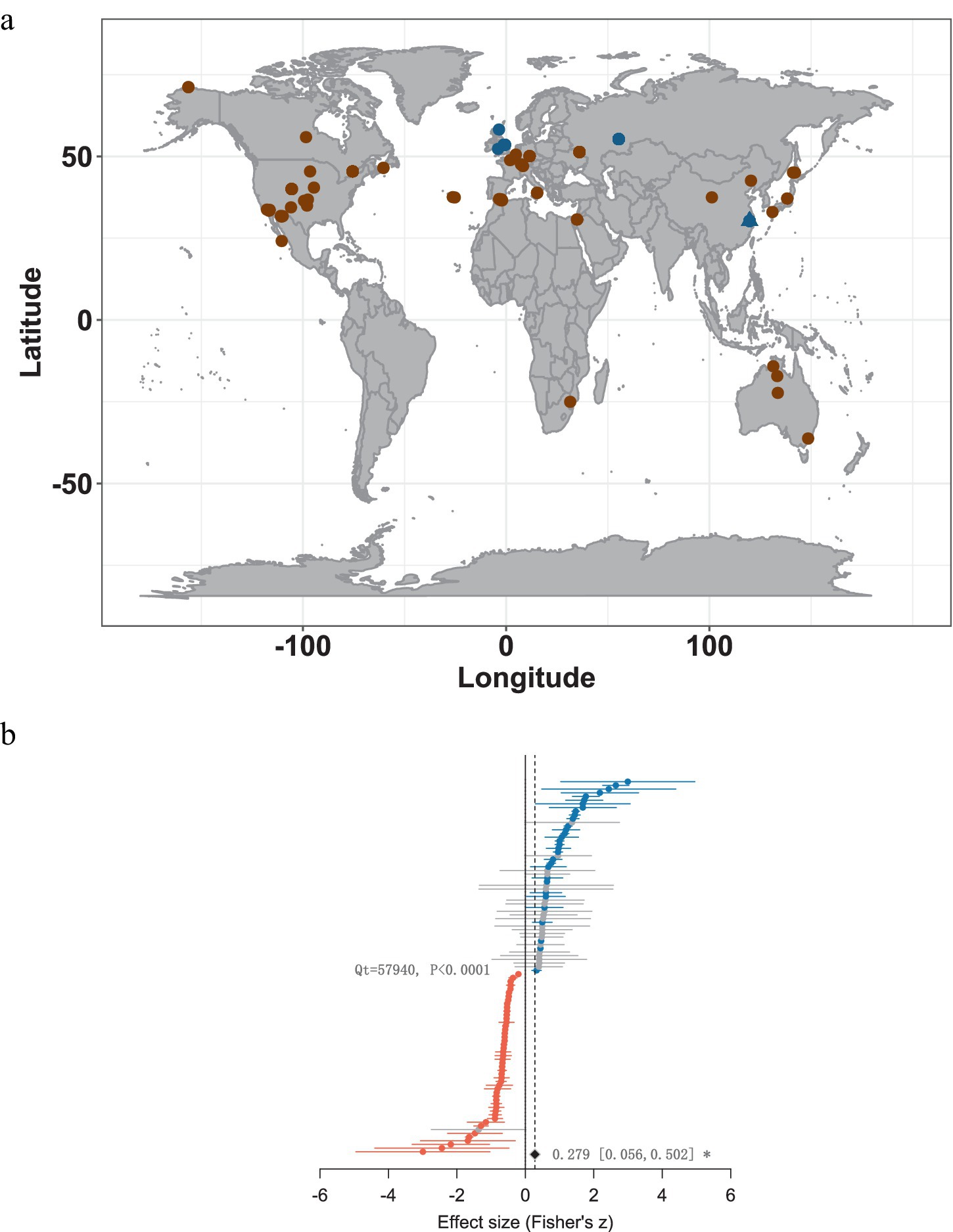
Figure 1. Global-scale study of soil CO2 gas release in response to near-surface wind disturbances. (a) World map of all cases included in the study, with each point representing a single study, where brown represents data from the correlation studies (N = 55 studies and 101 cases of correlation studies), and dark blue represents data from the control experiments (N = 5 studies and 141 cases of studies). (b) World map of the 101 correlation studies of the forest plot, where dots represent mean effect sizes, grey lines represent 95% confidence intervals, diamond dots represent total effect sizes, and light blue (positive) and orange (negative) represent significant results.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Systematic evaluation
In March 2023, the Web of science (ISI) and China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI) databases were searched using the keywords “TS = (wind or ventilate)” and “TS = (“soil respiration” or soil CO2 or flux or efflux)” and “TS = (effect or affect or increase*)” to retrieve the literature related to wind and CO2 gas release. The publication time interval of the literature was chosen to be 1992 to 2022, and the predefined version of the literature that did not pass the peer-review was excluded. Articles that matched the study topic could not be retrieved from the China National Knowledge Infrastructure Database.1 The search was then limited to ecology, soil science, and earth science research neighborhoods by reading the titles, abstracts, and conclusions of the retrieved literature. The relevant literature were then proximally screened by reading the full text using the following criteria: (1) observational or experimental studies in the field were selected, and literature reviews and studies in controlled laboratory environments excluded, in order to make the results more general and generalizable; (2) this study focused only on the release of CO2 gas from the soil surface and did not include the release of other gases and the release of CO2 gas from the water surface of lakes, oceans, etc.; and (3) this study focused only on the report of near-surface winds and soil CO2 release, and other physical parameters such as air pressure fluctuations, temperature, and volumetric water content of the soil; (4) No further distinction was made between growing and non-growing seasons in this study because of the consideration that near-surface winds interfere with soil CO2 release on a transient basis, and because we included factors related to surface vegetation in our study. Studies derived from the reference lists of relevant articles were crosschecked to investigate the availability of additional publications. A total of 14,737 studies were searched in the Web of Science online database, of which 221 were considered potentially relevant (Supplementary Figure S1). By carefully reading and eliminating controlled environment studies, 31 field site studies (including two flux control trials) were identified, along with the results of our team’s research, whose data are shown in Figure 1a. The trial data focused on the Northern Hemisphere. For the final literature review, relevant descriptive information was extracted from each study and its characteristics categorized (Table 1). Regarding the extraction of the measurement methods, those for gas chamber methods included all chamber types, such as steady state, unsteady state, and open and closed, in addition to convective diffusion models and special experimental equipment.
2.2 Data collection
Experimental data were pooled after extraction from the texts, tables, graphs, and appendices of related studies. If the study explicitly reported a correlation between near-surface wind speed and soil CO2 gas release, Pearson’s correlation coefficient (r) was extracted directly from the study (if available) or r was calculated from the regression coefficients, R2. If the study reported Spearman’s correlation coefficients (rs), we converted rs to Pearson’s correlation coefficients using the formula (Rupinski and Dunlap, 1996) as follows:
The relationship between wind speed and soil CO2 release (positive/negative correlation) is usually clearly expressed in studies; however, the results of one study were not uniform (being positive and then negative). Therefore, positive and negative relationships were defined separately in the analysis of the overall effect. However, during the analysis of the individual variables, we excluded the one piece of data that was inconsistent, which guarantees the numerical superiority of the studies but does not compromise the reliability of the results of the explanatory variable analyses for any study. Most studies provided explicit values for latitude and longitude to describe spatial extent, and the few that did not had their location determined from the description of the study area (Peng et al., 2019). Attention was given to the results of the control experiments, and CO2 flux measurements before and after wind disturbance were obtained. Where standard deviations were not reported, they were derived, where possible, from sample sizes and standard errors or confidence intervals. If required, data points were extracted from the graphs using GetData Graph Digitizer software.2 If this was not possible (e.g., due to sample sizes that were not reported), authors were contacted to provide the missing values. Studies which had missing values unable to be obtained were only included in the unweighted analyses.
A control field experiment was conducted in January 2022 at the Maple Garden of Zhejiang Agriculture and Forestry University. The data from the experiment were collected using a diffusion device (Supplementary Figure S2), similar to those developed by Maier et al. (2012) and Jiang et al. (2022), and which were buried in the soil. The soil CO2 release was calibrated by controlling the flow rate of gas into and out of the diffusion device, as well as the CO2 concentration. Soil CO2 gas fluxes were measured in wind and windless environments to assess the reliability of the measurement method under different wind disturbances.
2.3 Statistical analyses
To analyze the correlation data, the Pearson’s correlation coefficient (r) was normalized for each case using the Fisher z-transform as the effect size. When the magnitude of Pearson’s correlation coefficient approaches ±1, the distribution becomes skewed. Therefore, rather than using the correlation directly, it was transformed into a metric with desirable statistical properties. This was performed using the Fisher’s z-transformation (Koricheva et al. 2013). Initial data exploration was performed using OpenMEE software (Wallace et al., 2016) (software available online), and full analyses were performed in R version 3.4.0, using the “metafor” package (Viechtbauer, 2010). The control trial data were analyzed using the “metafor” package in R. The natural log-transformed response ratio (RR) was used to measure the effect size (Hedges et al., 1999 Koricheva et al., 2013) as follows:
where Xt is the mean treatment value and Xc is the mean value of the control. The variance (v) for each effect size was calculated as follows:
where Nt and Nc are the sample sizes of the treatment and control groups, respectively; and St and Sc are the standard deviations of the treatment and control groups, respectively.
For each response variable, a multilevel meta-analysis model with random effects was used to account for differences across studies because statistically obtaining multiple observations from the same publication may have compromised statistical independence. Specifically, random effects at the study location level were included to reduce potential data dependence (Peng et al., 2019). Total heterogeneity can be divided into the variance explained by the moderator (Qm, the Q statistic that provides information on whether the moderator explains any significant heterogeneity in the data) and the residual error variance (Qe). The Qm statistic is a Wald-type test of the model coefficients, which, if significant, suggests that the moderator contributes to the heterogeneity of the effect sizes (Viechtbauer, 2010). The effect sizes were considered significant if the 95% confidence interval (CI) did not overlap with zero. All parameters in the meta-analysis model were estimated using maximum likelihood, which is preferred when fitting stratified mixed-effect models (Zuur et al., 2009). Any likelihood of publication bias and temporal changes in effect sizes were examined by using radar and loss-of-safety coefficient analyses.
The following covariates were selected for inclusion in the stratified mixed-effects meta-regression models to account for heterogeneity in effect sizes: (1) ecosystem type, (2) measurement method, (3) surface vegetation height, (4) latitude and longitude, and (5) soil parameters. Ecosystem types were categorized as forest, grassland (including savannas and prairie), scrub, wetland, farmland, volcanic land, tundra, or other (more than one ecotype). Measurement methods include air chambers, gradients, eddy covariance (EC), and others (e.g., advection–diffusion modelling or special experimental equipment). Vegetation height and soil parameters were not included in the final analysis due to incomplete data.
3 Results
From the study data (Figure 1b), it can be found that the relationship between near-surface wind speed and soil CO2 fluxes did not follow a uniform trend, with almost the same sample data for positive and negative correlations (positive: 51%, negative: 49%). However, from the cumulative effect values of the analysed results, we can see that near-surface wind speed is positively correlated with soil CO2 release [Zr: 0.279, (95% CI: 0.056, 0.502); Figure 1b], and the wind speed will promote the release of CO2 from the soil to the atmosphere. In addition, we found from the meta-analysis results that there is a significant inter-case between near-surface wind speed and soil CO2 release heterogeneity (Qt = 57,940, p < 0.001, I2 = 99%), which we will try different explanatory variables to analyse.
3.1 Analysis of measurement methods
To further investigate the effect of near-surface wind speed on soil CO2 release, explanatory variables (measurement methods) were added for a detailed analysis. It was found that the relationship between near-surface wind speed and soil CO2 release was affected by the measurement method (Qm = 82.481, df = 3, p < 0.001) and that the relationship between CO2 release and wind speed measured using the different methods was quite different, forming two opposite results, as shown in Figure 2. Among them, soil CO2 release was found to be significantly positively correlated with wind speed using the eddy covariance method [Zr: 0.614, (95% CI: 0.370, 0.858), p < 0.001]; soil CO2 release was found to be significantly negatively correlated with wind speed using the concentration gradient method [Zr: −0.956, (95% CI: −1.362, −0.550), p < 0.001]; soil CO2 release was found to be significantly positively correlated with wind speed using other experimental setups or methods [Zr: 1.723, (95% CI: 1.229, 2.216), p < 0.001]; however, our measurements using the gas chamber method did not show significant correlation [Zr: 0.014, (95% CI: −0.252, −0.280), p > 0.001]; and significant correlations with wind speed using the air chamber method were not found [Zr: 0.014, (95% CI: −0.252, −0.280), p > 0.050].
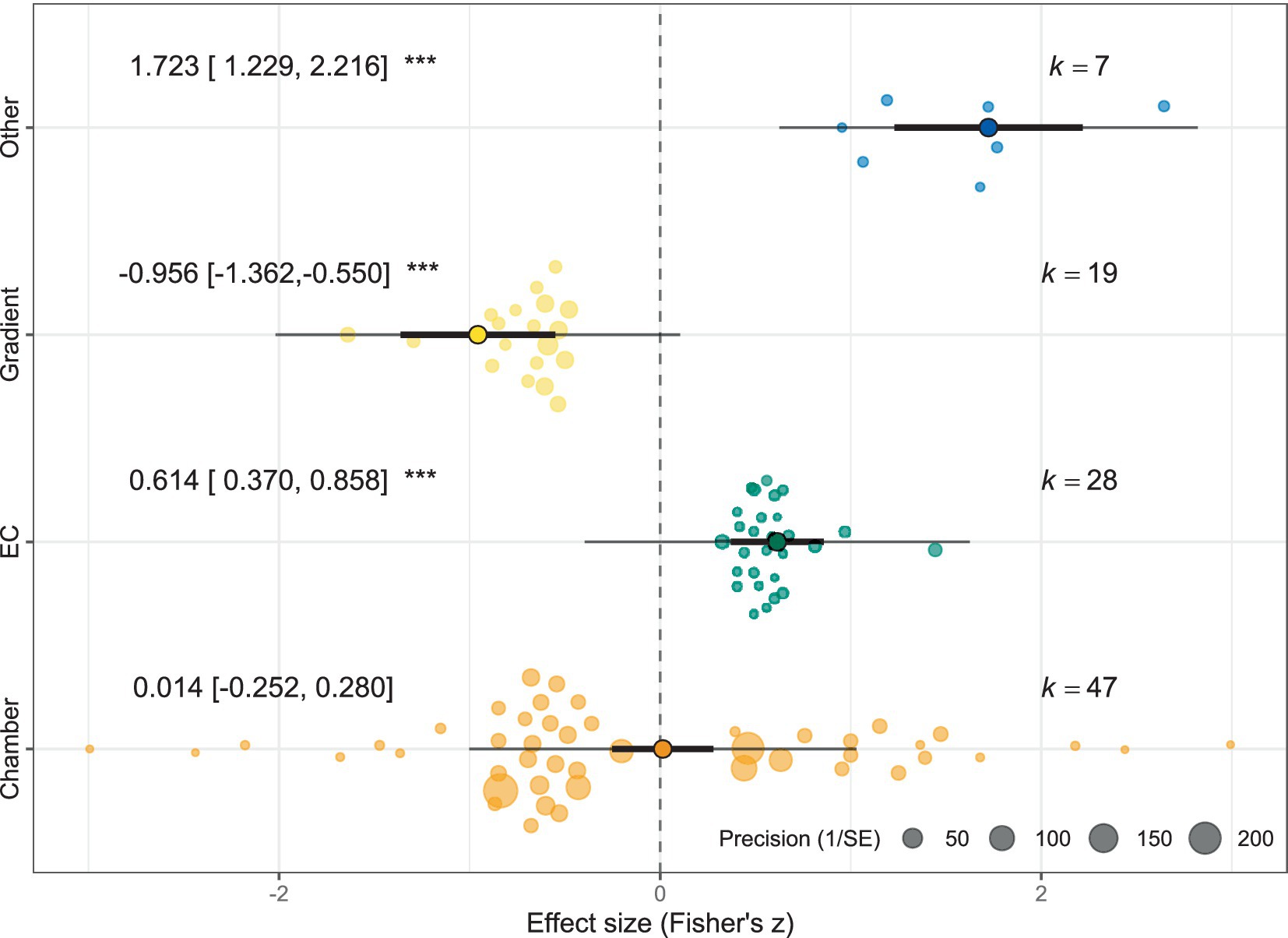
Figure 2. Relationship between near-surface wind speed and soil CO2 release (Fisher’ z) grouped by measurement method. Where the thick black line segment represents the 95% confidence interval for the mean effect value of each measurement method, and the midpoint of the line segment represents the mean effect value; the other dots of different sizes represent the effect value of each case, and the radius of the circle is the inverse variance of each case, i.e., the study with the larger circle has a smaller z-variance; k represents the number of cases; the thin line segment represents the prediction intervals; “***” represents p < 0.001.
3.2 Analysis of surface vegetation
The relationship between wind speed and soil CO2 release in different surface vegetation environments were analyzed. However, a significant effect of surface vegetation on the relationship between near-surface wind speed and soil CO2 release was not found (Qm = 17.880, df = 7, p = 0.013), and a significant effect was observed only in grasslands [Zr: 0.646, (95% CI: 0.171, 1.121), p = 0.008] and shrublands [Zr: 0.685, (95% CI. 0.239, 1.130), p = 0.003] in which a positive correlation between near-surface wind speed and soil CO2 release was observed (Supplementary Figure S3). Similarly, the relationship between soil CO2 release and near-surface wind speed measured using the air chamber and eddy covariance methods for different vegetation types were analyzed. Soil CO2 release, measured using the eddy covariance method for different vegetation types, was positively correlated with wind speed (Supplementary Figure S4a). The air chamber method did not reveal a significant correlation between soil CO2 release measured for different vegetation types and wind speeds, as shown in Supplementary Figure S4b.
3.3 Analysis of measurement technology updates
To verify whether there was publication bias in the studies, the regression results showed a significant correlation between effect size and year of publication (Qm = 11.254, df = 1, p < 0.001), as shown in Figure 3a. The effect values changed from negative to positive between 2002 and 2022, and most studies prior to 2012 showed a negative correlation between near-surface wind speed and soil CO2 release and a positive correlation after 2012, at which point the studies are usually considered to have a publication bias. However, the increase in the value of this effect with the publication year is more likely attributed to the development of flux measurement techniques and the maturation of the field. In recent years, the application of vorticity covariance techniques and the study of soil-gas transport devices and models in the field have shown that near-surface wind speeds lead to increased soil CO2 gas emissions (Moya et al., 2022). However, different results were obtained using the gas chamber method, as shown in Figure 3b. The relationship between the CO2 release measured by the gas chamber method and near-surface wind speed was strongly influenced by the publication year (Qm = 7.063, df = 1, p = 0.008, slope = −0.089), and the effect value was negatively correlated with the publication year. It can also be seen in Figure 3b that the CO2 release measured using the gas chamber method was positively correlated with the near-surface wind speed in the pre-2012 studies. In contrast, most of the post-2012 studies found a negative correlation between the CO2 release measured using the gas chamber method and the near-surface wind speed, and warrants further investigation.
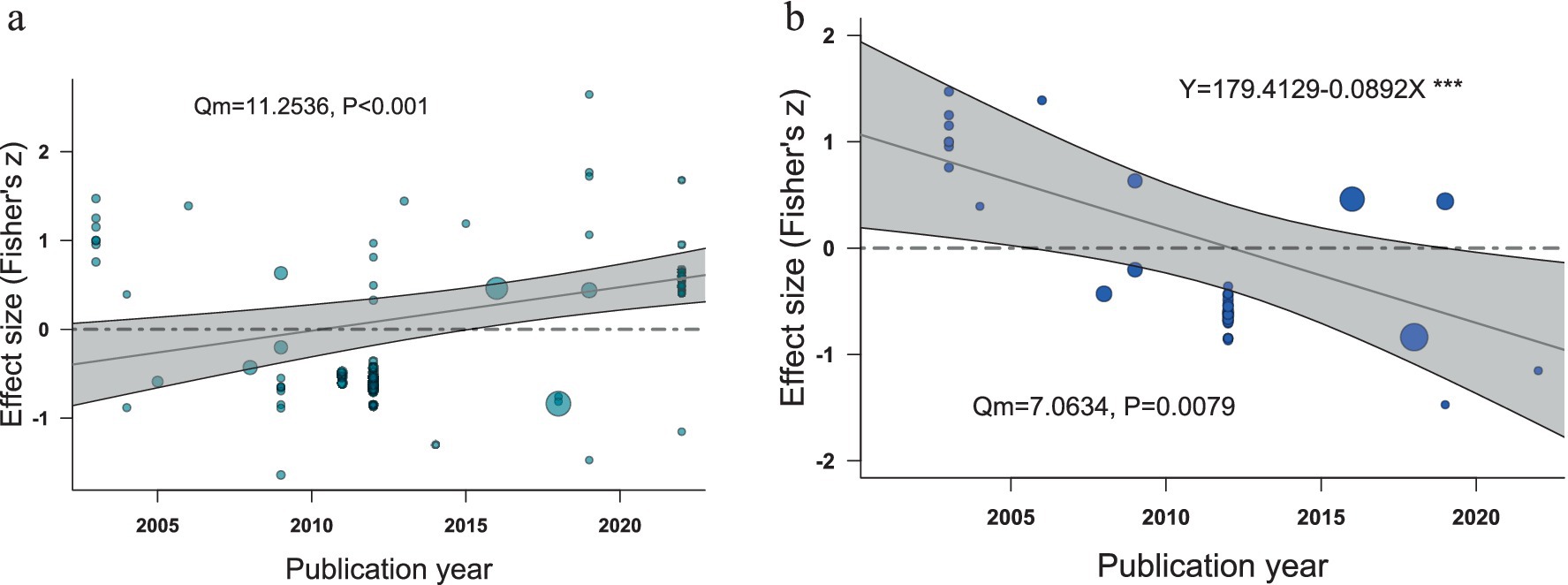
Figure 3. Relationship between near-surface wind speed and soil CO2 release as affected by publication year. (a) is the meta-regression of all Fisher‘z (near-surface wind speed vs. soil CO2 release) vs. publication year. (b) is the meta-regression of Fisher’ z [(near-surface wind speed vs. soil CO2 release measured by the air chamber method) vs. publication year release] versus year of publication meta-regression. Shaded areas represent 95% confidence intervals; dots represent effect values for each case, and the radius of the circle is the inverse variance for each case; and “***” represents a significant correlation (p < 0.0001).
3.4 The underestimation effect of measurements
From the results shown in Figures 2, 3b, it cannot be concluded that there is a clear relationship between the CO2 flux data measured using the gas chamber method and wind speed. However, as the most widely used method for measuring soil-gas fluxes, accounting for more than 95% of the total (Jian et al., 2020), the uncertainty in the measurement results of this method affects the assessment and research of the global carbon cycle. Therefore, it is important to clarify the effect of near-surface wind speed on the measurement of soil CO2 flux using the gas-chamber method. In this study, the results of two independent controlled experiments from other teams were collected and incorporated into our team’s experimental results for analysis, with a total of 140 valid data points, as shown in Figures 1a, 4a. As shown in Figure 4a, except for Study 1, in which there was no significant difference in the mean values of wind speed in the air chamber measurements (p = 0.093), significant differences were observed in both studies, with p = 0.003 and p < 0.001, respectively. As observed from the medians in Figure 4a, the values measured in the no-wind environment were greater than those in the snowy environment for all three studies, and the wind speed resulted in an overall decrease in the flux measured by the air chamber method. This suggests that the air chamber method is prone to underestimating soil CO2 fluxes measured in cloudy environments.
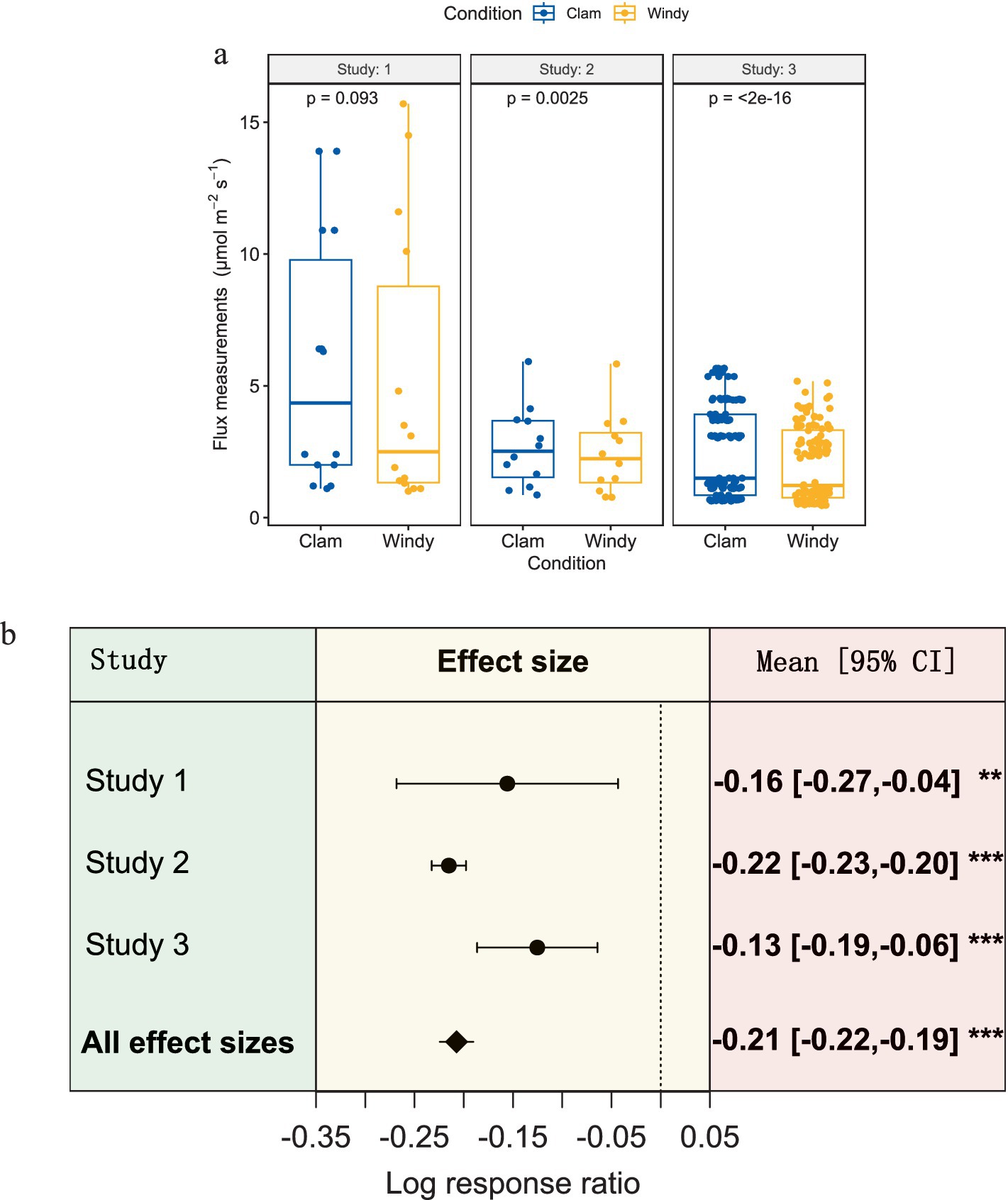
Figure 4. Effect of wind disturbances on air chamber method measurements. (a) shows statistical data for air chamber method measurements under windy and windless conditions. Studies 1 and 3 are data from studies Redeker et al. (2015) and Brændholt et al. (2017), and study 2 is data from its own study. (b) shows a forest plot of the data from the three studies, where the dots represent the mean effect values (RR) of the three studies, the diamonds represent the total effect values of the three studies, and the line segments are the 95% confidence intervals, with “***” representing p < 0.0001, “**” represents p < 0.001.
To quantify the underestimated effect of near-surface wind speed on soil CO2 fluxes measured using the air chamber method, 140 data points were analyzed using log-response ratios, the results of which are shown in Figure 4b. The interference of near-surface winds was negative for the measurement of soil CO2 fluxes using the air chamber method [total effect value InRR = −0.210, (95% CI: −0.220, −0.190), p < 0.001], and the effect values of three of the studies also exhibited negative results [InRR = −0.160, InRR = −0.220, InRR = −0.210]. This result indicates that near-surface wind speeds led to an underestimation of the fluxes measured by the air chamber method in all three studies, with an underestimation of 14.79% (3.92–23.66%) in Study 1, 19.75% (18.13–20.55%) in Study 2, and 12.19% (5.82–17.30%) in Study 3, with an overall underestimation of 18.94% (17.30–19.75%) for all three studies.
3.5 Publishing offsets
Radar plots, Egger’s tests, and fail-safe numbers were used to test for potential publication bias. The data showed no significant signs of publication bias (Extended Data Supplementary Figure S5; Egger’s test: z = 2.366, p = 0.018; Fail-safe N: 44723). However, linear regression showed a significant relationship between effect size and the year of publication (Figure 3a), which was negative in the early years and gradually became positive in recent years for reasons elaborated in the Discussion.
4 Discussion
4.1 Soil CO2 gas response to near-surface wind speeds
The results of the cumulative effect values indicate that near-surface wind speed is positively correlated with soil CO2 release (Figure 1) and that near-surface winds lead to increased soil CO2 gas release. In addition, the effect values of the eddy covariance technique with field soil gas transport devices and modelling studies indicate that wind speed increases soil CO2 gas release (Figure 2), which is consistent with the results of several recent laboratory studies (Maier et al., 2012; Poulsen and Liberzon, 2018; Poulsen et al., 2018; Pourbakhtiar et al., 2017). This is because near-surface wind action can affect soil CO2 gas transport through two different non-diffusive mechanisms: (i) high-frequency subsurface gas velocity fluctuations generated by surface air pressure fluctuations associated with wind turbulence conditions near the surface (Laemmel et al., 2017; Poulsen and Møldrup, 2006; Poulsen et al., 2017), often described as the “wind pumping effect,” and (ii) subsurface gas flow due to the downward transfer of momentum from above the soil-atmosphere interface into the soil gas phase (Manes et al., 2009; Poulsen et al., 2018; Suga and Kuwata, 2014), which is also referred to as the “wind washout phenomenon.” This non-diffusive gas transport induced by near-surface wind action leads to sustained large air flows in the soil, which induces gas transport rates that are much higher than molecular diffusion rates, thereby enhancing soil CO2 gas transport. Simultaneously, the CO2 gas concentration in the soil is likely to decrease by several orders of magnitude, particularly in dry, highly porous media (Sánchez-Cañete et al., 2016), or in the surface layer of plowed soils (Reicosky et al., 2008), and which is attributed to the wind-pumping effect or wind-scouring phenomenon induced by near-surface winds. This also explains the negative correlation between soil CO2 release measured by the concentration gradient method and wind speed (Figure 2). Therefore, there are significant problems with soil gas fluxes calculated solely based on Fick’s concentration-diffusion law, which does not fully describe the actual transport of soil CO2 gas (Livingston and Hutchinson, 1995). Recently, however, a number of researchers have also started to focus on this issue by correcting the original gas molecular diffusion coefficients by defining more enhanced diffusion coefficients (“apparent diffusion coefficients”) to compensate for the underestimation of the gradient method calculations. Despite this drawback, the gradient method has great potential to become the most used technique for monitoring atmospheric–soil CO2 exchange in the future. This technique has the potential to help us understand the sources and transport of CO2 within the infiltration zone and between the soil and atmosphere in real time.
In addition, the interaction between near-surface wind speed and ground cover had a significant effect on soil CO2 gas. Under windy conditions, gas concentration gradients and transient diffusive fluxes decrease more in sedge-dominated sites than in shrub-dominated sites (Lai et al., 2012). Laemmel et al. (2018) and Maier et al. (2010) found that wind velocities at the subcanopy level decreased due to wind turbulence above the canopy or enhanced soil gas transport in stands with low wind speeds at the soil surface. However, the interaction of surface vegetation with near-surface winds, which results in different responses to soil CO2 gas, was not observed in the collected data (Supplementary Figure S3). This does not suggest that the interaction of cover, such as surface vegetation, with wind speed does not have an effect on soil CO2 gas, something attributed to the limitations of the number of studies conducted so far with a more significant effect of the measurement methods.
4.2 Influence of near-surface wind speed on measured fluxes by the air chamber method
Currently, the air chamber method is the most widely used measurement technique for calculating soil CO2 fluxes, accounting for more than 95% of the quantities used. The results measured using this method are directly relevant to the assessment of the global carbon cycle; therefore, it is important to clarify the effect of near-surface wind speed on the fluxes measured using the air chamber method. Because the 4% error in air chamber measurements due to wind disturbances cannot be ignored when estimating the global annual CO2 release from soils (98 ± 12 Pg C), as predicted by Bond-Lamberty and Thomson (2010) using the SRDB database, this error could ultimately affect the Paris Agreement goal of limiting the global average temperature increase to less than 2°C.
In contrast, the uncertainty of the near-surface winds in the gas chamber method measurements is shown in both Figures 2, 3b, with some studies showing a positive correlation between CO2 release and wind speed and others showing a negative correlation, with a clear discrepancy between the two. However, by time sorting the data from the gas chamber measurements, it was found that the positively correlated results were mainly concentrated before 2012, whereas the negatively correlated data were concentrated after 2012 (Figure 3b). Rayment and Jarvis (2000) used an open, dynamic air chamber that allowed changes in atmospheric pressure to be transmitted to the soil surface and found that atmospheric turbulence enhanced the soil CO2 efflux from boreal black spruce forests, with a stronger effect at sites with thicker porous peat layers. Subke et al. (2003) observed a positive correlation between the horizontal wind speed and CO2 efflux rates in spruce forest soils using the same air chamber system. They concluded that the increase in soil CO2 flux could be attributed to the wind-pumping effect caused by wind action. This is consistent with the conclusion that high-frequency pressure fluctuations at the soil surface result in enhanced soil-gas emissions when wind passes over uneven surfaces or changes in speed and direction (Laemmel et al., 2018).
However, measurements by other researchers using closed dynamic gas chambers fitted with vents have shown that the CO2 efflux from deciduous forests and temperate cropland soils is higher when wind speeds increase (Bain et al., 2005; Conen and Smith, 2003; Suleau et al., 2009; Xu et al., 2006). This is more likely to be a soil gas efflux due to gas chamber aeration or the gas chamber Venturi effect (Bain et al., 2005). It has been shown that under windy conditions, when wind blows through the external open end of an exhaust pipe, a pressure shift (negative ΔP) occurs within the chamber, compensating for the large amount of carbon dioxide-rich air that is vented from the soil into the top of the chamber. This phenomenon is known as “gas chamber ventilation” or the “gas chamber Venturi effect” (Conen and Smith, 2003). To avoid the Venturi effect, Xu et al. (2006) designed special vents for gas chambers to limit wind-induced pressure fluctuations and measured gas transport using a molecular diffusion mechanism, which is now widely used in gas chamber monitoring techniques. However, new vents are likely to be the main reason why later studies found a negative correlation between soil CO2 release and near-surface winds. This is because near-surface winds flush soil gas, particularly around aboveground structures, and higher wind speeds induce pressure gradients within the soil (Riley et al., 1994; Takle et al., 2004), increasing CO2 outgassing around the measurements, decreasing CO2 entry into the gas chamber structure, and even removing diffused soil CO2 gas from the collar, leading to a negative correlation between the flux and wind speed. This explains the variability in the results of studies that used the gas chamber method before and after 2007.
The lower soil CO2 efflux measured by the air chamber method under snowy conditions conflicts with the notion that the wind pumping effect and Bernoulli effect of negative pressure cause greater surface gas exchange (Poulsen and Møldrup, 2006; Poulsen et al., 2017; Redeker et al., 2015). However, we clarified that near-surface wind speeds led to increased soil CO2 release, which also necessitates further exploration of the effects of wind perturbations on the measurement of soil CO2 fluxes using the air chamber method. Because the air chamber method usually only measures diffusive and transpiration fluxes and not mass fluxes, the actual rate of soil-atmosphere gas exchange is not accurately estimated in humid environments. Such phenomena have been elaborated on in the results of several studies (Fleming et al., 2021; Maier et al., 2019; Redeker et al., 2015), but most did not quantify measurement bias. The final results of this study, analyzed by combining data from recently published experiments with data from our own experiments, show that interference from near-surface winds resulted in an underestimation of soil CO2 fluxes measured by the air chamber method by 3.92 to 23.66%. Although these underestimations may be closely related to unconsidered factors that explain the true variability in soil exhumation, the observed lower CO2 exhumation is most likely due to the measurement bias of the equipment used (Maier et al., 2019). This is because in environments with near-surface winds, higher wind speeds result in changes in the pore pressure gradient within the soil and more rapid gas exchange. However, the presence of closed gas chambers has an insulating effect on these changes and attenuates the gas exchange rate. In contrast, higher wind speeds increase soil CO2 release and potentially migrate soil CO2 gas within the collar, or attenuate soil CO2 gas transport within the collar because of atmospheric gas washing through the soil, particularly around the monitoring gas chamber (Fleming et al., 2021; Lai et al., 2012). To improve the accuracy of the calculation results of the gas chamber method, which isolates the wind pumping effect during the measurement process, the design of the gas chambers should consider monitoring equipment that is more consistent with the actual gas transport mechanism or underestimated compensation models through pressure correction of the external and internal environments within the chamber With regard to the phenomenon of near-surface wind scouring of soil gases during measurements, it is recommended that the bias in gas chamber measurements due to wind scouring be corrected by the gas storage flux in the pore space in order to solve this problem.
5 Conclusion
A meta-analysis of 101 study cases from around the world revealed that wind speed induces non-diffusive transport of soil CO2 and enhances soil CO2 release. In addition, significant between-case heterogeneity was found between near-surface wind speed and soil CO2 release from the meta-analysis results (Qt = 57,940, p < 0.001, I2 = 99%), which were analyzed using different explanatory variables. Based on vegetation classification, no significant effect of surface vegetation on the relationship between near-surface wind speed and soil CO2 release was found. Instead, based on the different measurement methods and updating of the measurement techniques, it was found that the most widely used air chamber method significantly underestimated soil CO2 fluxes when measured under windy conditions. This underestimation ranged from 12.19 to 19.75% and was mainly due to the fact that wind speed disturbances affect the gas concentration gradient as well as the measurements of the gas chamber method, resulting in a calculated soil CO2 release lower than the actual value. This underestimation may have far-reaching implications for the assessment of the global carbon cycle and the development of climate change response strategies. Therefore, future studies should improve the measurement method under windy conditions and further explore how to correct this underestimation effect to improve the accuracy of soil CO2 flux measurements and provide more reliable data support for global carbon cycle studies and climate change predictions.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
LF: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. JJ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. JH: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant numbers 32371668 and 31971493).
Acknowledgments
We thank the editor and reviewers for their contributions to the peer review of our work.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/ffgc.2024.1459948/full#supplementary-material
Footnotes
References
Bain, W., Hutyra, L., Patterson, D., Bright, A., Daube, B., Munger, J., et al. (2005). Wind-induced error in the measurement of soil respiration using closed dynamic chambers. Agric. For. Meteorol. 131, 225–232. doi: 10.1016/j.agrformet.2005.06.004
Bond-Lamberty, B., and Thomson, A. M. (2010). A global database of soil respiration data. Biogeosciences 7, 1915–1926. doi: 10.5194/bg-7-1915-2010
Bowling, D. R., and Massman, W. J. (2011). Persistent wind-induced enhancement of diffusive CO2 transport in a mountain forest snowpack. J. Geophys. Res. 116:G04006. doi: 10.1029/2011JG001722
Brændholt, A., Steenberg Larsen, K., Ibrom, A., and Pilegaard, K. (2017). Overestimation of closed-chamber soil CO2 effluxes at low atmospheric turbulence. Biogeosciences. 14, 1603–1616. doi: 10.5194/bg-14-1603-2017
Campeau, A., He, H., Riml, J., Humphreys, E., Dalva, M., and Roulet, N. (2024). Wind as a driver of peat CO2 dynamics in a northern bog. Ecosystems 27, 621–635. doi: 10.1007/s10021-024-00904-1
Conen, F., and Smith, K. (2003). A re-examination of closed flux chamber methods for the measurement of trace gas emissions from soils to the atmosphere. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 49, 701–707. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2389.1998.4940701.x
Fleming, N., Morais, T., Mayer, K., and Ryan, M. (2021). Spatiotemporal variability of fugitive gas migration emissions around a petroleum well. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 12:101094. doi: 10.1016/j.apr.2021.101094
Hedges, L., Gurevitch, J., and Curtis, P. (1999). The Meta-analysis of response ratios in experimental ecology. Ecology 80, 1150–1156. doi: 10.1890/0012-9658(1999)080[1150:TMAORR]2.0.CO;2
Hutchinson, G., and Livingston, G. (2001). Vents and seals in non-steady state chambers used for measuring gas exchange between soil and atmosphere. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 52, 675–682. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2389.2001.00415.x
Jian, J., Bailey, V., Dorheim, K., Konings, A. G., Hao, D., Shiklomanov, A. N., et al. (2022). Historically inconsistent productivity and respiration fluxes in the global terrestrial carbon cycle. Nat. Commun. 13:1733. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-29391-5
Jian, J., Gough, C., Sihi, D., Hopple, A. M., and Bond-Lamberty, B. (2020). Collar properties and measurement time confer minimal bias overall on annual soil respiration estimates in a global database. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 125:e2020JG006066. doi: 10.1029/2020JG006066
Jiang, J., Gu, K., Xu, J., Li, Y., Le, Y., and Hu, J. (2023a). Effect of barometric pressure fluctuations on gas transport over soil surfaces. Land 12:161. doi: 10.3390/land12010161
Jiang, J., Hu, J., Xu, X., Li, Y., and Sheng, J. (2023b). Effect of near-surface winds on the measurement of forest soil CO2 fluxes using closed air chambers. Front. Ecol. Evol. 11:1163704. doi: 10.3389/fevo.2023.1163704
Jiang, J., Yin, W., Hu, J., and Hu, Y. (2022). Study of a calibration system for soil respiration measurement chambers. Environ. Res. Commun. 4:095006. doi: 10.1088/2515-7620/ac8f16
Konings, A. G., Bloom, A. A., Liu, J., Parazoo, N. C., Schimel, D. S., and Bowman, K. W. (2019). Global satellite-driven estimates of heterotrophic respiration. Biogeosciences 16, 2269–2284. doi: 10.5194/bg-16-2269-2019
Koricheva, J., Gurevitch, J., and Mengersen, K. (2013). Handbook of Meta-analysis in ecology and evolution. Princeton: Princeton University Press.
Laemmel, T., Mohr, M., Bernard, L., Schack-Kirchner, H., Lang, F., Schindler, D., et al. (2018). From above the forest into the soil – how wind affects soil gas transport through air pressure fluctuations. Agric. For. Meteorol. 265, 424–434. doi: 10.1016/j.agrformet.2018.11.007
Laemmel, T., Mohr, M., Schack-Kirchner, H., Schindler, D., and Maier, M. (2017). Direct observation of wind-induced pressure-pumping on gas transport in soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 81, 770–774. doi: 10.2136/sssaj2017.01.0034n
Lai, D. Y. F., Roulet, N., Humphreys, E., Moore, T., and Dalva, M. (2012). The effect of atmospheric turbulence and chamber deployment period on autochamber CO2 and CH4 flux measurements in an ombrotrophic peatland. Biogeosciences 9, 3305–3322. doi: 10.5194/bg-9-3305-2012
Lebel, E., Lu, H., Vielstädte, L., Kang, M., Banner, P., Fischer, M., et al. (2020). Methane emissions from abandoned oil and gas wells in California. Environ. Sci. Technol. 54, 14617–14626. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.0c05279
Levintal, E., Dragila, M., and Weisbrod, N. (2019). Impact of wind speed and soil permeability on aeration time in the upper vadose zone. Agric. For. Meteorol. 269-270, 294–304. doi: 10.1016/j.agrformet.2019.02.009
Li, W., Ciais, P., Wang, Y., Peng, S., Broquet, G., Ballantyne, A., et al. (2016). Reducing uncertainties in decadal variability of the global carbon budget with multiple datasets. PNAS 113, 13104–13108. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1603956113
Liu, Z., Deng, Z., He, G., Wang, H., Zhang, X., Lin, J., et al. (2022). Challenges and opportunities for carbon neutrality in China. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 3, 141–155. doi: 10.1038/s43017-021-00244-x
Livingston, G. P., and Hutchinson, G. L. (1995). Enclosure-based measurement of trace gas exchange: application and sources of error. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 105, 8865–8875.
Livingston, G. P., Hutchinson, G. L., and Spartalian, K. (2006). Trace gas emission in chambers. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 70, 1459–1469. doi: 10.2136/sssaj2005.0322
Maier, M., Mayer, S., and Laemmel, T. (2019). Rain and wind affect chamber measurements. Agric. For. Meteorol. 279:107754. doi: 10.1016/j.agrformet.2019.107754
Maier, M., Schack-Kirchner, H., Aubinet, M., Goffin, S., Longdoz, B., and Parent, F. (2012). Turbulence effect on gas transport in three contrasting forest soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 76, 1518–1528. doi: 10.2136/sssaj2011.0376
Maier, M., Schack-Kirchner, H., Hildebrand, E. E., and Holst, J. (2010). Pore-space CO2 dynamics in a deep, well-aerated soil. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 61, 877–887. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2389.2010.01287.x
Manes, C., Pokrajac, D., McEwan, I., and Nikora, V. (2009). Turbulence structure of open channel flows over permeable and impermeable beds: a comparative study. Phys. Fluids 21:125109. doi: 10.1063/1.3276292
Moya, M., López-Ballesteros, A., Sánchez-Cañete, E., Serrano-Ortiz, P., Oyonarte, C., Domingo, F., et al. (2022). Ecosystem CO2 release driven by wind occurs in drylands at global scale. Glob. Chang. Biol. 28, 5320–5333. doi: 10.1111/gcb.16277
Nissan, A., Alcolombri, U., Peleg, N., Galili, N., Jimenez-Martinez, J., Molnar, P., et al. (2023). Global warming accelerates soil heterotrophic respiration. Nat. Commun. 14:3452. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-38981-w
Peng, S., Kinlock, N., Gurevitch, J., and Peng, S. (2019). Correlation of native and exotic species richness: a global meta-analysis finds no invasion paradox across scales. Ecology 100:e02552. doi: 10.1002/ecy.2552
Poulsen, T. G., Furman, A., and Liberzon, D. (2017). Effects of wind speed and wind gustiness on subsurface gas transport. Vados Zone J. 16, 1–10. doi: 10.2136/vzj2017.04.0079
Poulsen, T. G., Furman, A., and Liberzon, D. (2018). Effect of near-surface wind speed and gustiness on horizontal and vertical porous medium gas transport and gas exchange with the atmosphere. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 69, 279–289. doi: 10.1111/ejss.12531
Poulsen, T., and Liberzon, D. (2018). Measuring horizontal pore gas velocity profiles in porous media in response to near-surface wind speed and gustiness. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 69, 997–1007. doi: 10.1111/ejss.12722
Poulsen, T., and Møldrup, P. (2006). Evaluating effects of wind-induced pressure fluctuations on soil-atmosphere gas exchange at a landfill using stochastic modelling. ISWA 24, 473–481. doi: 10.1177/0734242X06066363
Pourbakhtiar, A., Poulsen, T. G., Wilkinson, S., and Bridge, J. W. (2017). Effect of wind turbulence on gas transport in porous media: experimental method and preliminary results. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 68, 48–56. doi: 10.1111/ejss.12403
Rayment, M., and Jarvis, P. (2000). Temporal and spatial variation of soil CO2 efflux in a Canadian boreal forest. Soil Biol. Biochem. 32, 35–45. doi: 10.1016/S0038-0717(99)00110-8
Redeker, K., Baird, A. J., and Teh, Y. A. (2015). Quantifying wind and pressure effects on trace gas fluxes across the soil–atmosphere interface. Biogeosciences 12, 7423–7434. doi: 10.5194/bg-12-7423-2015
Reicosky, D., Gesch, R. W., Wagner, S., Gilbert, R. A., Wente, C. D., and Morris, D. R. (2008). Tillage and wind effects on soil CO2 concentrations in muck soils. Soil Tillage Res. 99, 221–231. doi: 10.1016/j.still.2008.02.006
Riley, W., Gadgil, A., Bonnefous, Y., and Nazaroff, W. (1994). The effect of steady winds on radon222 entry from soil into houses. Atmos. Environ. 30, 1167–1176. doi: 10.1016/1352-2310(95)00248-0
Rupinski, M. T., and Dunlap, W. P. (1996). Approximating Pearson Product-Moment Correlations from Kendall’s Tau and Spearman’s Rho. Educational and Psychological Measurement. 56, 419–429. doi: 10.1177/0013164496056003004
Sánchez-Cañete, E., Oyonarte, C., Serrano-Ortiz, P., Curiel Yuste, J., Pérez-Priego, O., Domingo, F., et al. (2016). Winds induce CO2 exchange with the atmosphere and vadose zone transport in a karstic ecosystem: dynamics of CO2 within the vadose zone. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 121, 2049–2063. doi: 10.1002/2016JG003500
Seok, B., Helmig, D., Williams, M., Liptzin, D., Chowanski, K., and Hueber, J. (2009). An automated system for continuous measurements of trace gas fluxes through snow: An evaluation of the gas diffusion method at a subalpine forest site, Niwot ridge, Colorado. Biogeochemistry 95, 95–113. doi: 10.1007/s10533-009-9302-3
Subke, J. A., Reichstein, M., and Tenhunen, J. D. J. S. B. (2003). Explaining temporal variation in soil CO2 efflux in a mature spruce forest in southern Germany. Biochemistry 35, 1467–1483. doi: 10.1016/S0038-0717(03)00241-4
Suga, K., and Kuwata, Y. (2014). Turbulence over/inside porous surfaces and challenges to its modelling. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 530:012004. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/530/1/012004
Suleau, M., Debacq, A., Dehaes, V., and Aubinet, M. (2009). Wind velocity perturbation of soil respiration measurements using closed dynamic chambers. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 60, 515–524. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2389.2009.01141.x
Takeda, S., Majima, R., Makita, N., and Takahashi, K. (2023). Five-year measurement data along a 1200 m elevational gradient reveals that global warming increases soil respiration. Front. For. Glob. Change 6:1145474. doi: 10.3389/ffgc.2023.1145474
Takle, E., Massman, W., Brandle, J., Schmidt, R. A., Zhou, X., Litvina, I., et al. (2004). Influence of high-frequency ambient pressure pumping on carbon dioxide efflux from soil. Agric. For. Meteorol. 124, 193–206. doi: 10.1016/j.agrformet.2004.01.014
Tammadid, W., Sangkachai, B., Chanonmuang, P., Chidthaisong, A., and Hanpattanakit, P. (2024). Comparison and environmental controls of soil respiration in primary and secondary dry dipterocarp forests in Thailand. Front. For. Glob. Change 7:1294942. doi: 10.3389/ffgc.2024.1294942
Tharammal, T., Govindasamy, B., Narayanappa, D., and Nemani, R. (2019). A review of the major drivers of the terrestrial carbon uptake: model-based assessments, consensus, and uncertainties. Environ. Res. Lett. 14:093005. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/ab3012
Tian, J., Dungait, J., Lu, X., Yang, Y., Hartley, I., Zhang, W., et al. (2019). Long-term nitrogen addition modifies microbial composition and functions for slow carbon cycling and increased sequestration in tropical forest soil. Glob. Chang. Biol. 25, 3267–3281. doi: 10.1111/gcb.14750
Viechtbauer, W. (2010). Conducting Meta-analyses in R with the metafor package. J. Stat. Softw. 36, 1–48. doi: 10.18637/jss.v036.i03
Wallace, B., Lajeunesse, M., Dietz, G., Dahabreh, I., Trikalinos, T., Schmid, C., et al. (2016). OpenMEE: intuitive, open-source software for meta-analysis in ecology and evolutionary biology. Methods Ecol. Evol. 8, 941–947. doi: 10.1111/2041-210X.12708
Xu, L., Furtaw, M. D., Madsen, R. A., Garcia, R. L., Anderson, D. J., and McDermitt, D. K. (2006). On maintaining pressure equilibrium between a soil CO2 flux chamber and the ambient air. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 111:D08S10. doi: 10.1029/2005JD006435
Yang, Y., Li, T., Pokharel, P., Liu, L., Qiao, J., Wang, Y., et al. (2022). Global effects on soil respiration and its temperature sensitivity depend on nitrogen addition rate. Soil Biol. Biochem. 174:108814. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2022.108814
Zhou, L., Zhou, X., Zhang, B., Lu, M., Luo, Y., Liu, L., et al. (2013). Different responses of soil respiration and its components to nitrogen addition among biomes: a meta-analysis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 20, 2332–2343. doi: 10.1111/gcb.12490
Keywords: near-surface wind, soil respiration, gas chamber method, meta-analysis, measurement bias
Citation: Feng L, Jiang J and Hu J (2024) Underestimation of global soil CO2 flux measurements caused by near-surface winds. Front. For. Glob. Change. 7:1459948. doi: 10.3389/ffgc.2024.1459948
Edited by:
Ziliang Zhang, Northwestern Polytechnical University, ChinaReviewed by:
Pengpeng Duan, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), ChinaYuanshuang Yuan, Guizhou Minzu University, China
Mengguang Han, Peking University, China
Min Li, Zhejiang Normal University, China, in collaboration with reviewer MH
Copyright © 2024 Feng, Jiang and Hu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Junguo Hu, aHVqdW5ndW9AemFmdS5lZHUuY24=
†These authors share first authorship
 Lingxia Feng1†
Lingxia Feng1† Junjie Jiang
Junjie Jiang