- 1Centre for Research in Animal Behavior, Psychology, University of Exeter, Exeter, Devon, United Kingdom
- 2University Centre Sparsholt, Sparsholt College Hampshire, Winchester, Hampshire, United Kingdom
- 3WWT, Slimbridge Wetland Centre, Slimbridge, Gloucestershire, United Kingdom
Natural behavior performance in captive animals is traditionally utilized as a metric to establish welfare states, with an increase in natural behavior associated with positive welfare. Captive environments, including zoos strive to replicate ecologically relevant environments that promote species-specific, adaptive behavior performance. However, spatial restrictions and complex habitats required by some species create various challenges for zoo staff to implement management and husbandry practices to achieve this. Some species struggle to adapt and cope in captive environments, with increased abnormal behavior performance which may reduce welfare. Other species may adapt to captivity in novel ways, demonstrating flexibility in their behavior patterns without compromising welfare. However, research indicating positive behavioral flexibility in captive animals is sparse. The main aim of this review was to categorize animals as being fully behaviorally flexible, partially behaviorally flexible, or behaviorally inflexible. Effect sizes (Hedges’ g) were calculated to compare behavioral categories of animals in the wild and zoo, grouped by taxonomic Order (Testudines, Primates, Artiodactyla, Psittaciformes and Carnivora) and ecological traits to determine their level of behavioral flexibility. Effect sizes were also analyzed to determine behaviors suggestive of good welfare that were absent in zoo species. Despite variation across all groups, abnormal behavior was consistently highest in zoo animals, with reproductive and foraging behaviors most often compromised. Overall, complete positive behavioral flexibility was suggested in Testudines (potentially a result from temperature variation to maintain homeostasis), completely migratory species who are exposed to heterogenous landscapes when traveling long distances, and for a specific primate, the ring-tailed lemur (Lemur catta) potentially to improve resource access due to their terrestrial nature. All other groups evaluated demonstrated partial behavioral flexibility or behavioral inflexibility. Abnormal behavior prevalence and reduced foraging and reproductive behaviors in these groups suggests an inability to adapt to captivity. This necessitates more focused investigations that identify environmental features or aspects of managed environments that can meet a species’ needs in the zoo.
Introduction
Performance of “natural behavior” has widely been utilized as a measure of welfare states (Clubb and Mason, 2007; Hill and Broom, 2009) and may be defined as “behavior that animals tend to exhibit under natural conditions” (Bracke and Hopster, 2006). Natural behavioral repertoires may be used to inform decisions regarding the environment provided for captive animals to make judgment on physical health and maintain positive welfare states (Fraser and Weary, 2021). Further, application of behavioral frameworks, such as Tinbergen’s Four Questions are necessary to encourage objective measurement of animal welfare by understanding the function and adaptive benefits of behavior performance (Kelly and Rose, 2024). Repertoires predominated by species-appropriate behavior including play and affiliative behavior, such as allogrooming in primates may suggest positive emotional states and good welfare (Boissy et al., 2007; Miller et al., 2020; Yates et al., 2022). When captive animals are accommodated within environments that enable the performance of species-specific behaviors and enable behavioral choice, it positively influences their welfare (Veasey, 2006; Boissy et al., 2007; Brando and Buchanan-Smith, 2018). Environments that involve complex tasks like moving through tough terrain to access forage provide positive challenge, or eustress and promote behavioral diversity and thus, welfare (Villalba and Manteca, 2019). However, there is currently little research to indicate which behaviors are deemed important, or indeed not important in terms of promoting welfare in captivity. This review will compare behavioral repertoires of animals in the wild and the zoo to understand whether key ecologically relevant behaviors, such as foraging and exploration are replaced by those indicative of reduced welfare states (e.g., abnormal behavior) in captivity.
Modification of captive environments in line with an animal’s natural history and ecology, including social configurations and diet breadth may promote welfare, based on the inference that natural behaviors performed increase and abnormal behaviors decrease (Spain et al., 2020). Sociality can be integral to behavioral development and learning which influences reproductive success in wild animals (Brakes, 2019). In zoo mammals, suboptimal group configurations may lead to reduced reproductive success and increased abnormal behavior performance (Price and Stoinski, 2007). Thus, welfare outcomes in captive animals may be influenced by how closely social structures are mimicked when compared with wild counterparts (Carlstead et al., 2013). Simulating morphological and mechanical responses in captive animals through diet presentation may benefit welfare. For example, feeding calf carcasses to zoo felids decreases the presentation of stereotypical behaviors (Hartstone-Rose et al., 2014). Providing food to captive animals using methods that mimic wild feeding strategies may encourage natural behaviors and promote well-being (Skibiel et al., 2007).
Components of an animal’s ecology, including migratory and activity patterns may be challenging to provide and not easily replicated in the captive environment. For example, migratory species may be exposed to high level of habitat complexity due to traversal through different environments (De Azevedo et al., 2023). The rapid onset and uniqueness of the associated complexity make it difficult to replicate in captivity (Harbicht et al., 2020; Bandeli et al., 2023). Species that are highly migratory may therefore be predisposed to negative welfare when housed in captivity compared to those that do not migrate (Rose et al., 2017).
Diel activity (i.e. activity patterns performed over a 24-hour period) exhibited by animals can be disrupted due to exogenous variables, including zoo opening hours, conspecific interactions, inadequate exhibit design and the presence of humans (Forthman and Bakeman, 1992; Margulis et al., 2003; Gupta et al., 2022; Chiapero et al., 2021). Replicating the day and night activity patterns of wild animals is reliant on being able to control such factors in the captive environment. Further, animal care staff working patterns can restrict timings of food provision and may not reflect natural feeding patterns across species (Brando et al., 2023). Therefore, implemented systems should promote natural foraging patterns that align with wild conspecifics. Diurnal mammals in zoos, including chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes) may exhibit increased inactivity due to heightened visitor presence (Queiroz and Young, 2018), which could indicate poor welfare Fureix and Meagher, 2015). However, inactivity can be due to contentment (Tallo-Parra et al., 2023) and so normal activity patterns should be considered when making behavioral assessments of welfare. Further, other potential stressors in captivity such as anthropogenic noise pollution may far exceed what animals are exposed to in the wild and thus, compromise welfare. For example, intense noise associated with construction activities caused behaviors indicative of agitation in giraffes (Giraffa camelopardalis) and elephants (Elephas maximus), including vigilance and abnormal behaviors (Jakob-Hoff et al., 2019). However, behavioral responses to altered soundscapes varies across species (Harley et al., 2022) and research on the associated welfare impacts is scarce in many taxa.
Animals accommodated in unstimulating captive environments may develop inflexible behavioral repertoires through reduced neural pathway development (Burn, 2017) and perform abnormal repetitive behaviors (ARBs) which are either motor based (stereotypic) such as pacing in felids or redirected goal orientated (Garner, 2006), including feather-destructive behavior in Psittaciformes or oral stereotypies in the giraffe (Giraffa camelopardalis), a specialist herbivore. When captive environments lack the provision of ecologically relevant features, animals may channel their motivation toward abnormal behaviors, including stereotypies (McPhee and Carlstead, 2010). Complexities associated with adequately housing primates in zoos, and socioecological differences across species may cause reduced behavioral flexibility. Behavioral inflexibility reduces an animal’s ability to cope (Gaillard et al., 2014), thus limiting resilience and environmental adaptation which compromises welfare (Colditz and Hine, 2016). Some species may be able to respond to challenges in novel ways, demonstrating positive flexibility in behavioral repertoires. For example, zoo chimpanzees thermoregulate and maintain homeostasis by performing novel shade-seeking behaviors compared to wild conspecifics which utilize natural canopy gradients (Duncan and Pillay, 2013). Homeostatic mechanisms are essential processes that allow animals to adapt to changing external conditions (Beaulieu, 2024), and disruption to these states causes physiological imbalances, thus reducing welfare (Ritskes-Hoitinga and Strubbe, 2007). This suggests that when exposed to novel challenges, some species can cope through exhibiting flexibility in behavioral repertoires and elicit behavioral responses that infer adaptability to their external environment. Some species may display partial behavioral flexibility, in which there are differences in the performance of some behaviors, but key behaviors are still performed, and welfare is not compromised. For example, despite the importance of hunting behaviors in wild Amur tigers (Panthera tigris altaica), providing novel methods that enable acquisition of food through foraging opportunities promotes positive experiences without compromising welfare (Veasey, 2020). Even though behaviors my not reflect those in the wild, the motivation is still rewarded, and partial behavioral flexibility is inferred. Despite growing interest in proximate mechanisms underlying behavioral development, there is limited evidence identifying which animals, apart from primates, exhibit behavioral flexibility (Plotnik and Jacobson, 2022).
To better understand how species may respond to captive environments and features of enclosure design that promote animal health and welfare (Bartlett et al., 2024), multi-zoo behavioral research is beneficial. Further, multi-zoo research may also help in ascertaining interspecific behavioral flexibility across captive populations. For example, Carlstead et al. (1999) found that male black rhinoceros (Diceros bicornis) across zoos were more reproductively successful when displaying adaptable behavioral traits. To quantify the proportion of time that animals dedicate to different behaviors, time-activity budgets may be utilized. Historically, activity budgets have been used in wild and zoo contexts to evaluate species responses to different environmental factors including food access and provision (Bekoff and Wells, 1981) and habitat and enclosure use (Mahler, 1984; Quick and Pappas, 1986; Paulus, 1988). Further, analyzing wild species activity budgets function as useful reference points to evaluate behaviors performed in zoo conspecifics and help understand what behaviors are acceptable (Rose and Riley, 2021). However, in many species there is a paucity in wild behavioral data available and may not be truly representative of a wild population. For example, despite primates being popular candidates for behavioral studies in the zoo, wild data are scarce (Howell and Cheyne, 2019) and in species including felids, activity budgets are often focused on post-release monitoring of ex situ populations (Hayward and Hayward, 2007; Ruble et al., 2022).
Ring-tailed lemurs (Lemur catta) are known for exhibiting high levels of terrestrial behavior (Gould and Sauther, 2007) with strict female dominant hierarchies (Peragine et al., 2016). The likely cause of their prevalence in the literature is due to their popularity as a zoo exhibit species (Baker et al., 2018), and the scale of conservation-focused research performed on their wild populations (Caselli et al., 2022). Due to the availability of multiple zoo and wild behavioral studies in ring-tailed lemurs, they were considered a suitable species to focus on in this review.
The main objective of this review is to identify potential flexibility in the behavioral repertoires of species grouped by taxonomic Order and ecological trait kept in captivity, and to determine which of these behaviors are inflexible (i.e. welfare is poor if behaviors performed in captivity are different to the wild), partially behaviorally flexible (i.e. some key behaviors must be provided for, but deviation from wild behavioral repertoires does not reduce welfare) and completely positively behaviorally flexible (i.e. large differences in captive behavioral repertoires compared to the wild does not negatively impact welfare) in the zoo. This will aid in identifying animals that may be more susceptible to the challenges associated with captive environments, thus informing on management practices to meet animal needs. It is predicted that behaviors suggestive of poor welfare states will replace ecologically relevant behaviors in species grouped by taxonomic Order or ecological trait, indicating behavioral inflexibility and an inability to adapt to novel captive environments.
Materials and methods
Literature search, inclusion criteria and data extraction
To analyze data on time-activity budgets performed by species in the zoo and in the wild, a quantitative review was conducted. All studies were screened manually to ensure that they included an activity budget of the species, either as a percentage, or units of time that were converted to a percentage. Literature searches were conducted using Web of Science Core Collection and repeated using Google Scholar to find any articles from institutions not identified in Web of Science Core Collection. In the databases, the following were searched with combinations of the following search terms: behav*, repertoire, compare, zoo, natural, captivity, welfare, stereotypical, stereotypies, activity, budget, ethogram and inventory. The reference list of relevant papers were scanned to identify studies that were initially missed, and four that included activity budgets were identified and contributed to the pooled data, as per Bell et al. (2009). Searches for relevant papers were conducted periodically from December 2021 until July 2023. PRISMA guidelines (Moher et al., 2009) were used to identify all original and unpublished papers related to activity budgets of species in captivity and in the wild (Figure 1). In the final dataset, activity budgets were extracted from papers which focus either on wild or zoo animals, due to a scarcity of published studies where wild and zoo comparisons are combined in the same paper. Due to this, and because it is not likely that differences in activity budgets from the selected species would have an influence on whether the studies would be published, publication bias calculations were not conducted for this review. The complete PRISMA checklist is shown in Supplementary Appendix S1.
Figure 1. Identification of literature following the Page et al. (2021) method for using a PRISMA flowchart.
In total, 1,042 papers were returned using combinations of the search terms with 72 papers in total and 104 activity budgets included in the final dataset after excluding studies using “semi-captive” or “semi-wild” environments as these may cause behavioral alterations due to external influences such as human interaction (Al Hakim et al., 2022). Due to higher levels of activity typically observed in juvenile animals (Ali et al., 2024), activity budgets where juveniles predominate were excluded. Abnormal behavior performance associated with previous captive environments, meant that captive-origin wild animals were also excluded from the dataset (Dunston et al., 2016). To gain a better understanding of behavioral differences between conspecifics in the wild and zoo, multi-institutional zoo studies and multiple wild studies analyzed for lemurs.
The database that shows all papers included in the quantitative review can be found at: 10.6084/m9.figshare.25883830.
Species activity budgets were grouped by taxonomic Orders; Testudines (n=12), Primates (n= 23), Artiodactyla (n=18), Psittaciformes (n=11) and Carnivora (n= 30). Species were grouped by taxonomic Order because species-specific activity budgets in both the zoo and wild are small in number. Activity budgets from other taxonomic Orders were extracted, but due to only including a maximum of two per Order, they were only included in analyses of ecological variables. Each activity budget was categorized based on whether it was from animals in the wild or the zoo and ecological variables for each species were included in the dataset: migratory patterns, activity patterns, sociality and diet breadth and categorized as shown in Table 1.
The complete ethogram for all included species and associated categories for each, adapted from all published papers are shown in Supplementary Table S1.
Ring-tailed lemurs (Lemur catta), hereafter referred to as ‘lemurs’, were included as a case study due to the availability of both zoo and wild activity budgets for this species. This allowed for a comprehensive evaluation of wild and captive time budgets, which was not feasible for other species. Once all data were reviewed only for one specific species could further evaluation of wild and captive time-budgets be performed fully. For lemur data, a larger number of activity budgets were available across multiple wild environments (n= 5, 310 data points) and zoos (n= 4, 248 data points) and were extracted. The complete lemur ethogram, adapted from the papers that wild and zoo data were extracted, is shown in Supplementary Table S2. Subsequently, literature searches were conducted using Web of Science Core Collection and Google Scholar to review lemur ecology and behavior in the wild to determine the level of flexibility in their behavioral repertoires.
Across taxonomic Orders, ecological variables and those with multiple activity budgets, animals were categorized as follows: behaviorally inflexible- welfare will be poor if the behavioral repertoire is different in the zoo from that of the same species in the wild; partially behaviorally flexible- some key activities must be provided for, however if some behaviors are different in the zoo than the wild, welfare is not negatively impacted; fully behaviorally flexible- despite not performing all natural behaviors and with a change in behavioral repertoire, the species still experiences good welfare.
Statistical analyses
In total, 6,324 data points were collected from the 104 activity budgets analyzed from 72 studies. All statistical analyses were performed with R v.4.3.2 (R Core Team, 2023) using RStudio v. 2023.06.1 + 524 (RStudio Team, 2023). To test the effect of behavioral differences in animals grouped by taxonomic Order (Testudines, Primates, Artiodactyla, Psittaciformes and Carnivora) and ecological trait (migratory patterns, activity patterns, sociality and diet breadth) in the zoo and the wild, effect sizes were calculated using the “effsize” package (Torchiano, 2016) in R (R version 4.3.2; R Core Team, 2023). As Cohen’s d can inflate effect size estimates when sample sizes are low (i.e., N < 20; Hedges, 1981), Hedges’ g was used which applies a correction factor to Cohen’s d:
where g is the calculated effect size, mwild is the mean calculated in the wild, mzoo is the mean calculated in the zoo, and δ is the standard error (Cohen, 1988), whereas df are the degrees of freedom for two independent groups (i.e., n1 + n2 – 2). For interpretation of Hedges’ g, effect size values of 0.2, 0.5 and 0.8 equate to small, medium, and large effect respectively (Nakagawa and Cuthill, 2007). The 95% confidence intervals (CI), lower 95% confidence intervals (LCI) and upper 95% confidence intervals (UCI) represent the range of values that with 95% certainty the mean will fall within were also reported. Abnormal behaviors are not typically present in wild animals (Bacon, 2018) and include stereotypies and bar pecking in the dataset. The inclusion of abnormal behaviors in the analysis enabled the effect size to be calculated to give an indication of how commonly they are performed in the zoo. This could also be used to determine whether abnormal behaviors replaced other behavioral categories suggestive of positive welfare.
To test for significance between mean behaviors performed in lemurs, all behaviors were analyzed using two sample t-tests with an alpha value of 0.05. Bar charts with standard deviation depicting full activity budgets of lemurs in the wild and the zoo were also constructed.
Results
Comparison of behaviors grouped by taxonomic order
As illustrated in Figure 2, in Testudines, the effect of exploratory (Hedges’ g, 95% CIs [LCI, UCI]: −1.19 [−2.65, 0.27] and out of sight, hereafter termed “OOS” behavior (Hedges’ g, 95% C.I.s [LCI, UCI]: −1.19 [−2.65, 0.27] were the largest in zoo animals, relative to those in the wild. In Primates, the effect size in foraging behaviors (Hedges’ g, 95% CIs [LCI, UCI]: −1.19 [−2.65, 0.27] was the largest in wild animals, relative to the wild. In Artiodactyla, the effect size in positive social behavior (Hedges’ g, 95% CIs [LCI, UCI]: -0.71 [−1.71, 0.31] was the largest, followed by agonistic behavior (Hedges’ g, 95% CIs [LCI, UCI]: −0.7 [−1.7, 0.3] both in zoo animals, relative to the wild. In Psittaciformes, after OOS (Hedges’ g, 95% CIs [LCI, UCI]: −1.35 [−2.78, 0.075], the largest difference was in agonistic behavior (Hedges’ g, 95% CIs [LCI, UCI]: −1.03 [−2.41, 0.34]. In Carnivora, the largest difference was in reproductive behavior (Hedges’ g, 95% CIs [LCI, UCI]: 0.81 [−0.07, 1.69].
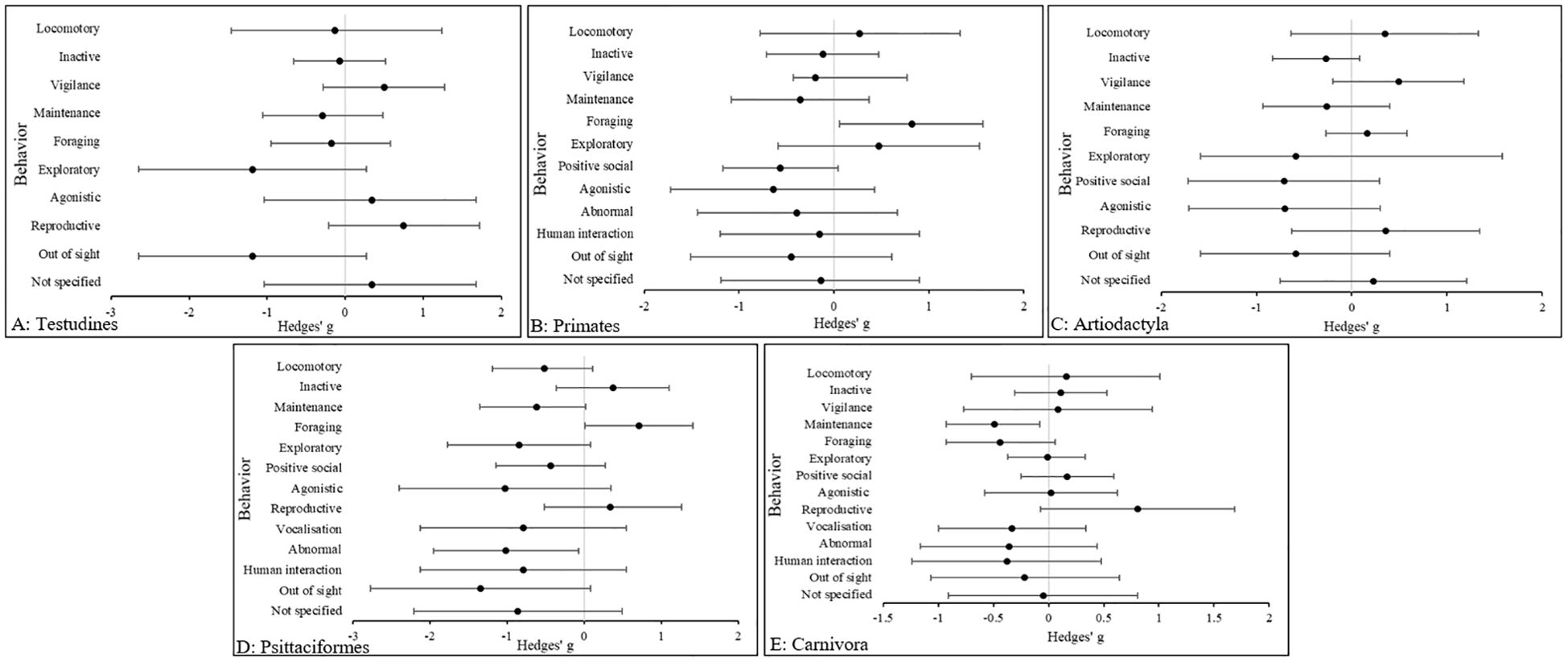
Figure 2. The overall effect of the wild versus zoos on the mean effect size (95% CIs) for all dependent variables (behavior categories) in (A) Testudines, (B) Primates, (C) Artiodactyla, (D) Psittaciformes and (E) Carnivora. Negative numbers indicate a decrease in the variable in wild animals relative to zoo animals, and vice versa for positive numbers.
Reproductive behavior was more common in the wild, but so was agonistic behavior and their absence in the zoo was replaced in part with exploratory behavior. However, OOS was commonplace in the zoo and therefore some key behaviors may not be represented in the data. Similar results are seen in Artiodactyla, however agonistic behaviors occur more in zoo species. In Psittaciformes, large effect sizes for agonistic and abnormal behavior are replaced by foraging and reproductive behaviors in the wild. Again, it should be noted that a large effect size for OOS behaviors in the zoo are also reported, so some behaviors in the zoo are not accounted for. The results for behavioral categories in Primates show a large positive effect in foraging behavior and strong negative effect in both agonistic and positive social behaviors.
Comparison of behaviors in animals grouped by migratory patterns
Figure 3 indicates a large effect size in agonistic behavior in non-migratory (Hedges’ g, 95% C.I.s [LCI, UCI]: −0.48 [-0.98, 0.017] and complete migratory species (Hedges’ g, 95% CIs [LCI, UCI]: −0.94 [−1.91, 0.035], being more common in zoo animals compared to those in the wild. In partially migratory species, the difference in agonistic behavior was also large (Hedges’ g, 95% CIs [LCI, UCI]: −0.84 [−2.14, 0.47] and more prevalent in zoo animals, but was predominated by vigilance behavior (Hedges’ g, 95% CIs [LCI, UCI]: −1.8 [−3.28, -0.34]. Interestingly, this was followed by exploratory behavior in partially migratory species (Hedges’ g, 95% CIs [LCI, UCI]: −1.61 [−3.04, -0.18], but in non-migratory species exploratory behaviors were more common in wild animals (Hedges’ g, 95% CIs [LCI, UCI]: 0.09 [−0.12, 0.31], however the effect size was small. Abnormal behavior was also prevalent in zoo animals that were partially migratory (Hedges’ g, 95% C.I.s [LCI, UCI]: -0.84 [−-2.15, 0.47]. In each category, reproductive behaviors are compromised in the zoo, and in partially and non-migratory animals abnormal and agonistic behaviors are more prevalent in zoos. However, abnormal behavior was not present in complete migratory species in the zoo.
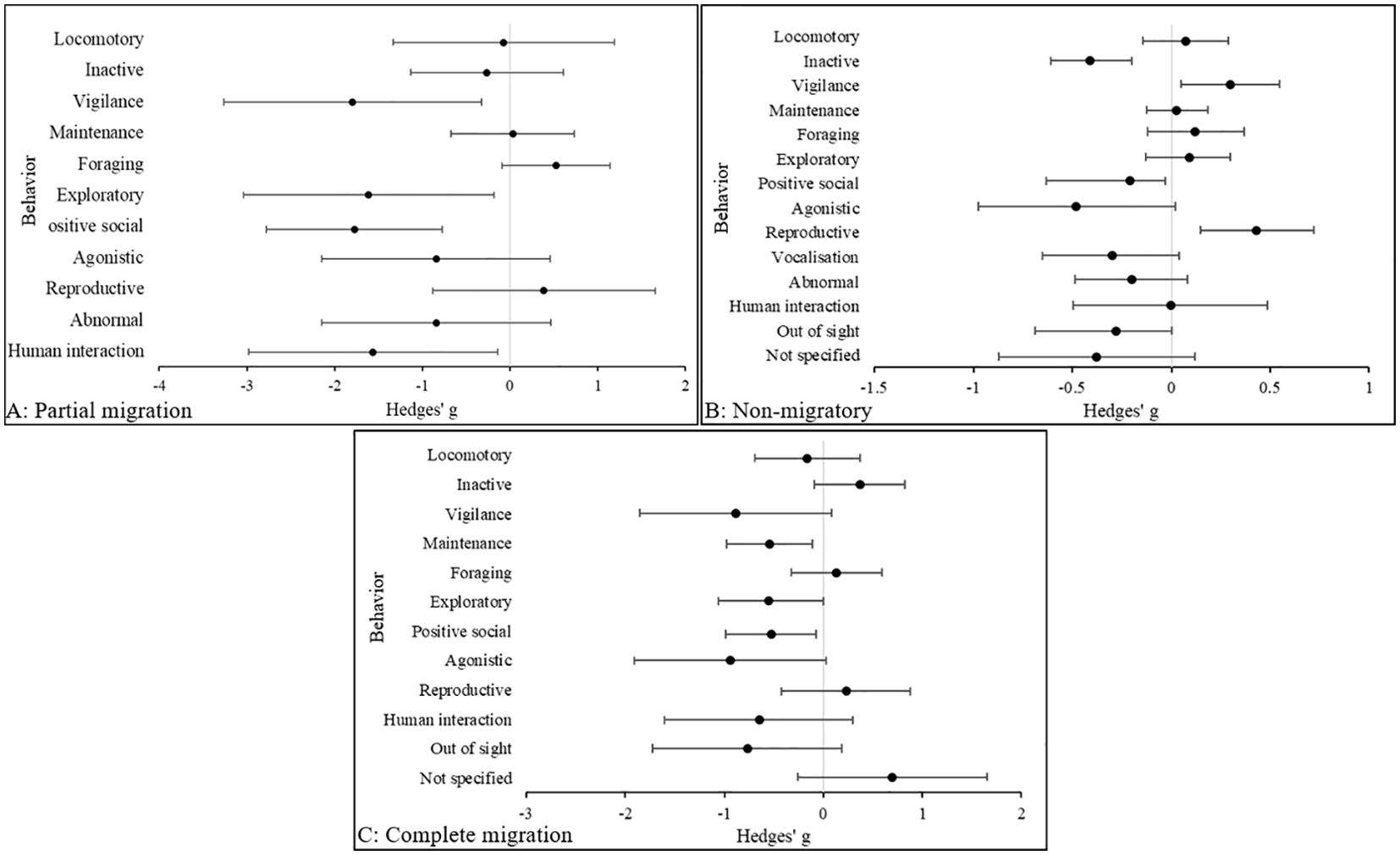
Figure 3. The overall effect of the wild versus zoos on the mean effect size (95% CIs) for all dependent variables (behavior categories) in (A) partially migratory, (B) non-migratory and (C) complete migratory species. Negative numbers indicate a decrease in the variable in wild animals relative to zoo animals, and vice versa for positive numbers.
Comparison of behaviors in animals grouped by activity patterns
The results in Figure 4 indicate that in diurnal species, there was a medium effect size is in agonistic behaviors (Hedges’ g, 95% CIs [LCI, UCI]: −0.6 [−1.1, -0.13] being more prevalent in zoo animals compared to the wild. Perhaps unsurprisingly, human interaction behaviors (Hedges’ g, 95% CIs [LCI, UCI]: −0.46 [−0.92, 0.0065] were more common in zoo animals, as were abnormal behaviors (Hedges’ g, 95% CIs [LCI, UCI]: −0.22 [−0.51, 0.072] although the effect size was small. In nocturnal species, the largest effect size was in vigilance behavior (Hedges’ g, 95% CIs [LCI, UCI]: 1.29 [0.49, 2.1], which was more common in wild animals compared to the zoo. In zoo nocturnal animals, vocalization behavior (Hedges’ g, 95% CIs [LCI, UCI]: −0.5 [−1.87, 0.86] is the most common compared to wild species. In crepuscular species, the largest effect size was in vigilance behavior (Hedges’ g, 95% CIs [LCI, UCI]: 0.94 [−0.11, 2] and was more common in wild animals. However, it is noted that the large positive effect size for “not specified” behaviors (Hedges’ g, 95% CIs [LCI, UCI]: 0.9 [−0.15, 2] in crepuscular animals means it is difficult to draw more accurate conclusions regarding behavioral repertoires in wild species. In diurnal species there was a negative, small effect and in nocturnal and crepuscular species there was a negative, medium effect for abnormal behaviors. In diurnal and nocturnal species, medium negative effects were reported for OOS occurrences. Conversely, in crepuscular species a large positive effect was reported for OOS occurrences and unspecified behaviors.
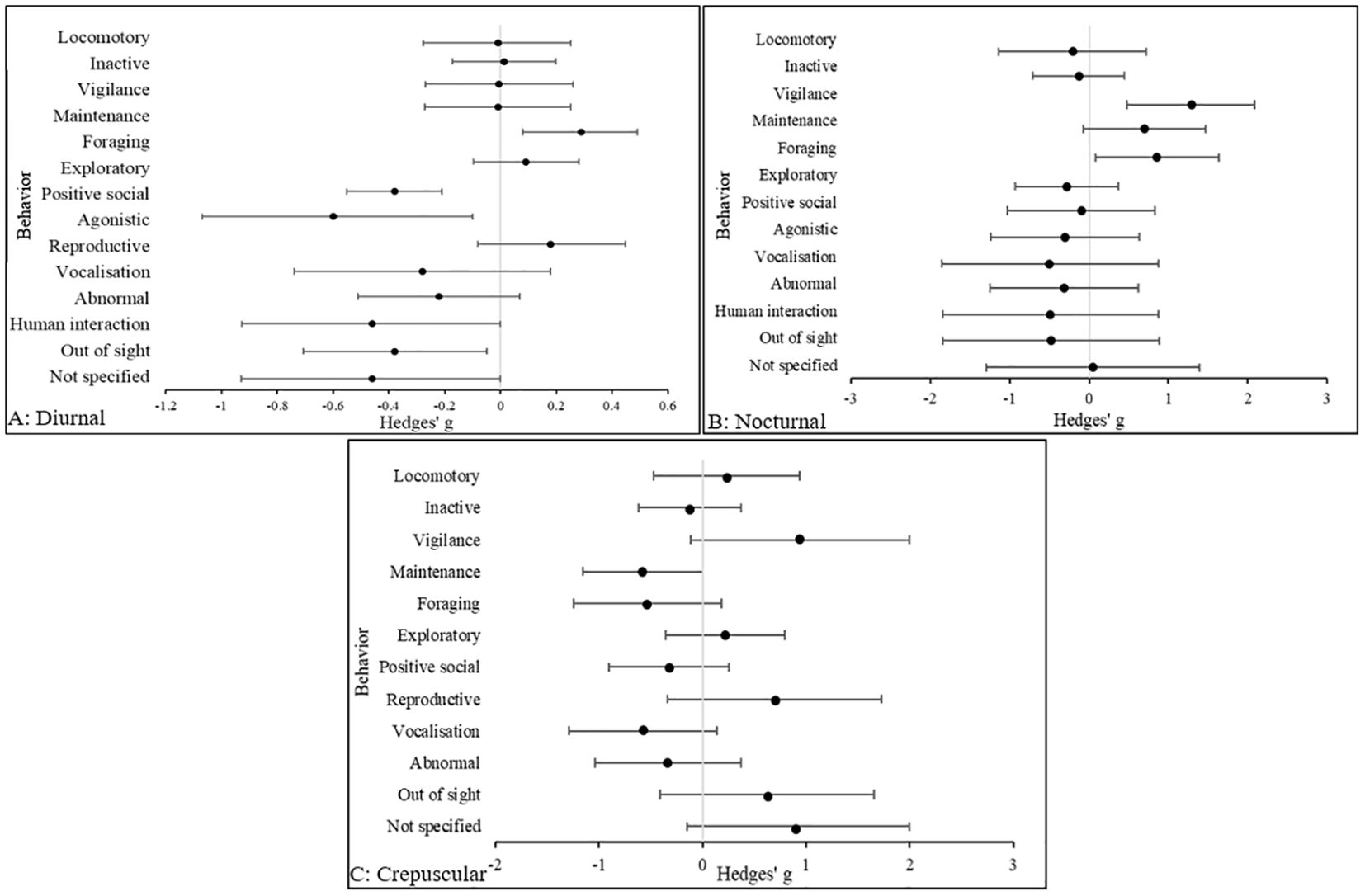
Figure 4. The overall effect of the wild versus zoos on the mean effect size (95% CIs) for all dependent variables (behavior categories) in (A) diurnal, (B) nocturnal and (C) crepuscular species. Negative numbers indicate a decrease in the variable in wild animals relative to zoo animals, and vice versa for positive numbers.
Comparison of behaviors in animals grouped by sociality
Figure 5 illustrates that the largest effect size in solitary species was inactive behaviors (Hedges’ g, 95% CIs [LCI, UCI]: −0.82 [-1.66, 0.021], indicating higher levels of inactivity in zoo animals compared with wild counterparts. This is followed by human interaction (Hedges’ g, 95% CIs [LCI, UCI]: −0.57 [-1.31, 0.16], which was more prevalent in zoo animals. In presocial species, effect sizes are small for each behavioral category. However, the largest effect size was in foraging behaviors (Hedges’ g, 95% CIs [LCI, UCI]: 0.41 [0.1, 0.72], which are more common in wild animals compared with zoo counterparts. In eusocial species, the largest effect size is in agonistic behaviors (Hedges’ g, 95% CIs [LCI, UCI]: −0.71 [-1.45, 0.033], and these were more common in zoo animals compared to wild counterparts. In all remaining behaviors, with the exception of “not specified” and OOS categories, all effect sizes were small.
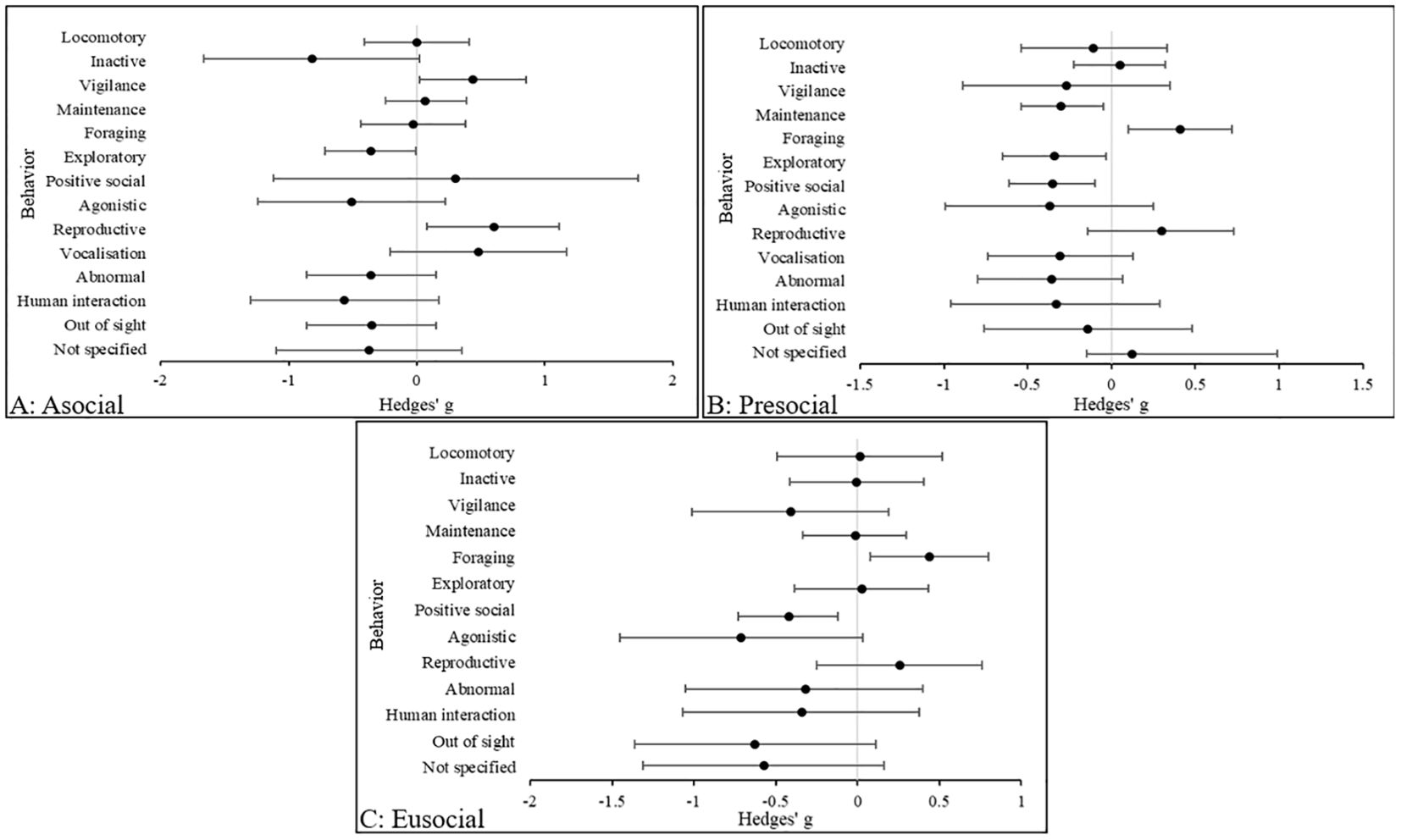
Figure 5. The overall effect of the wild versus zoos on the mean effect size (95% CIs) for all dependent variables (behavior categories) in (A) solitary, (B) presocial and (C) eusocial species. Negative numbers indicate a decrease in the variable in wild animals relative to zoo animals, and vice versa for positive numbers.
High levels of inactivity, and agonistic and abnormal behaviors in zoo solitary species suggests behavioral inflexibility. Presocial species may demonstrate some behavioral flexibility in the zoo due to overall low effect sizes across all behaviors, however foraging and reproductive behaviors are compromised compared to wild counterparts. Perhaps unsurprisingly, agonistic behaviors are more commonplace in zoo eusocial species and similar to presocial animals, foraging and reproductive behaviors are observed more in wild animals. However, abnormal behaviors are observed in presocial and eusocial species which suggests that some species may struggle to adapt to zoo environments.
Comparison of behaviors in animals grouped by diet breadth
Figure 6 indicates that in generalist carnivores, the largest effect sizes were in vocalization (Hedges’ g, 95% CIs [LCI, UCI]: −0.46 [−1, 0.072] and agonistic behaviors (Hedges’ g, 95% CIs [LCI, UCI]: −0.4 [−1.16, 0.38], both being prevalent in zoo animals compared to wild counterparts. Similarly, in generalist omnivores the largest effect size was in agonistic behaviors (Hedges’ g, 95% CIs [LCI, UCI]: −0.72 [−1.47, 0.031], also being more common in zoo animals. In generalist herbivores, the largest effect size is in positive social behaviors (Hedges’ g, 95% CIs [LCI, UCI]: −0.7 [−1.15, -0.26], which were more common in zoo animals, relative to those in the wild. Finally, identical large effect sizes (Hedges’ g, 95% CIs [LCI, UCI]: −2.18 [3.98, -0.38] were observed in exploratory, vocalization and abnormal behaviors in specialist herbivores, being observed more commonly in zoo animals. However, only 14 activity budgets represented this category, and therefore the effect sizes may be slightly inflated.
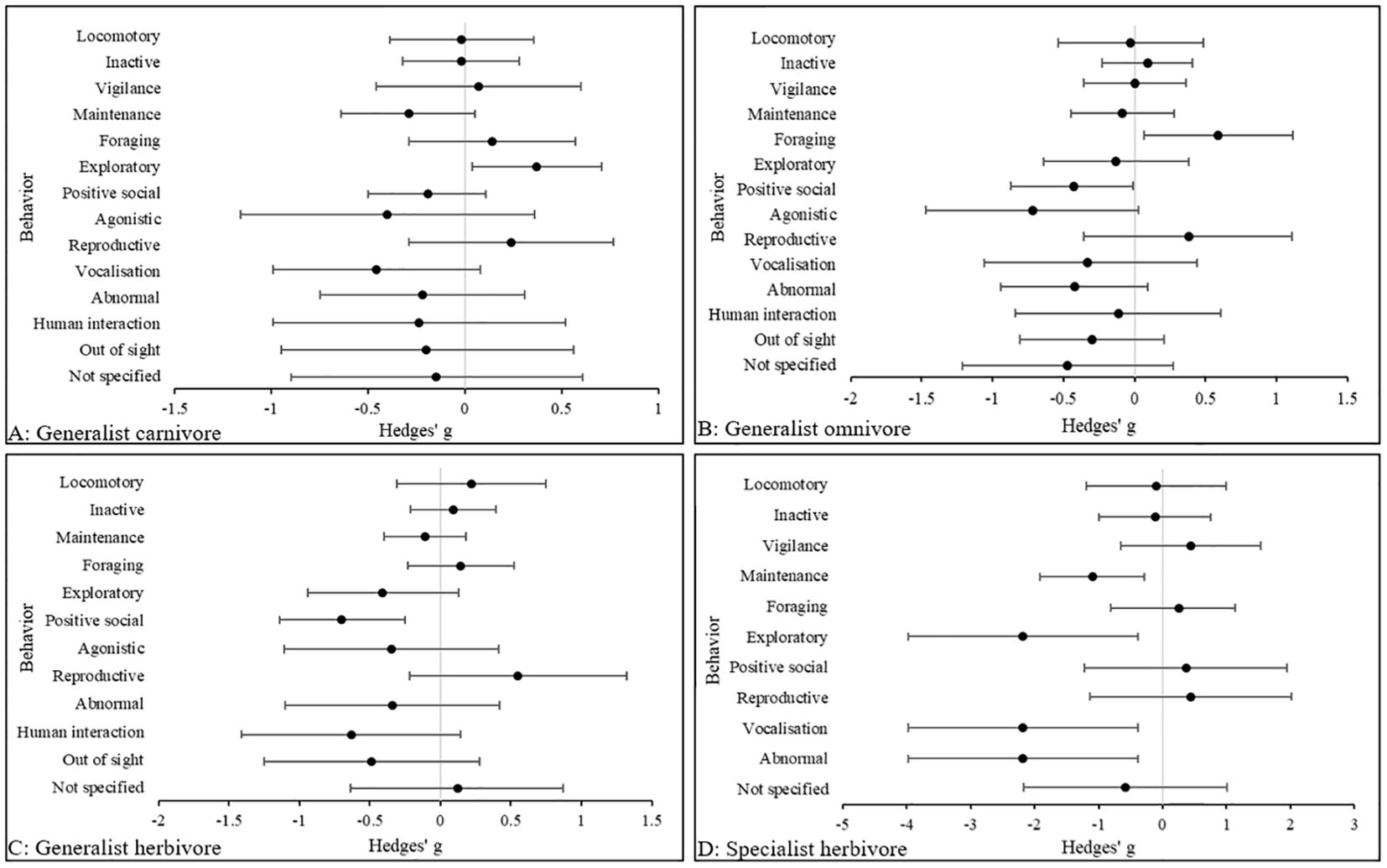
Figure 6. The overall effect of the wild versus zoos on the mean effect size (95% CIs) for all dependent variables (behavior categories) in (A) generalist carnivores, (B) generalist omnivores, (C) generalist herbivores and (D) specialist herbivores. Negative numbers indicate a decrease in the variable in wild animals relative to zoo animals, and vice versa for positive numbers.
Despite exploratory behaviors being more commonly performed in wild generalist carnivores, a small effect size across all behavioral categories including abnormal behaviors suggests full behavioral flexibility in the zoo. The effect sizes in generalist omnivores and generalist herbivores draw similarities, with foraging and reproductive behaviors prevalent in wild animals and higher levels of agonistic behavior in the zoo. Despite exploratory behavior being more common in zoo animals, abnormal behaviors were also observed which suggest partial behavioral flexibility. A very large effect size in abnormal behaviors for specialist herbivores in the zoo indicates that they may be behaviorally inflexible, although the sample size was small (n= 14).
Overall, these results indicate that although animals grouped by taxonomic Order and ecological trait demonstrate varying levels of behavioral flexibility, reproductive and foraging behaviors are mostly absent in the zoo compared to other behavior categories. In some groups of animals such as the partially migratory, presocial and specialist herbivore groups, these behaviors are replaced by those suggestive of poor welfare, including agonistic and abnormal behaviors.
Activity budgets in ring-tailed lemurs
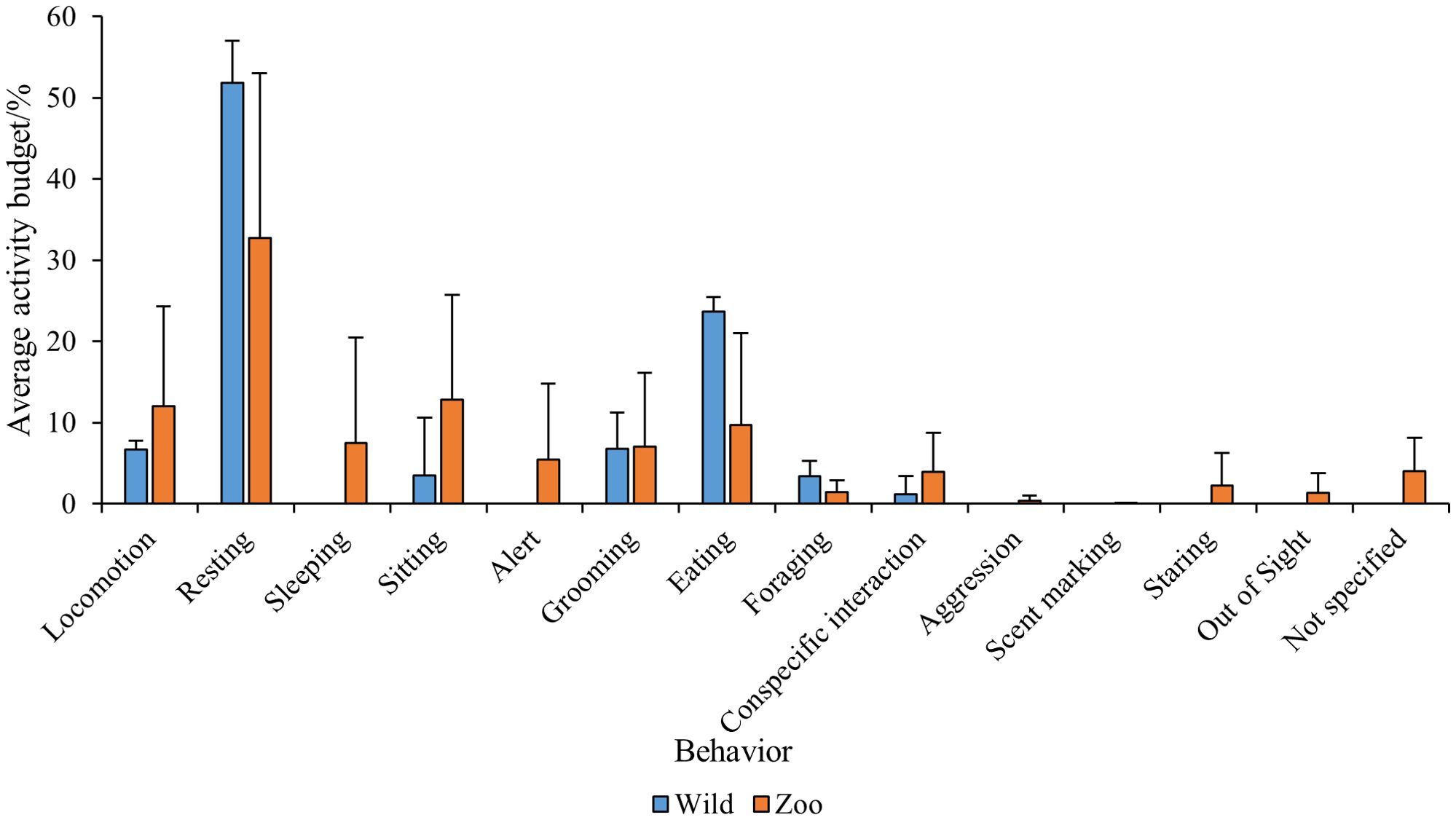
Due to the prevalence of (ring-tailed) lemur data within the available literature, this species was further analyzed to understand trends and patterns in behavioral performance between the wild and the zoo. For both wild and zoo lemurs, resting was the most commonly performed behavior as illustrated in Figure 7. Resting occurred more in wild lemurs (52%) compared to zoo lemurs (33%). In wild lemurs, the next most common behavior was eating (24%), compared with sitting in zoo lemurs (13%). Sleeping, alert, exploration, aggression and staring behavior was not recorded in any of the wild lemurs and scent marking was the least common behavior in zoo lemurs (0.08%).
The results in Table 2 indicate that there was no significance in the behaviors performed by wild and zoo lemurs when comparing average activity budgets in the two conditions. However, foraging behavior approaches significance, making up a larger proportion of activity in the wild compared to zoo lemurs.
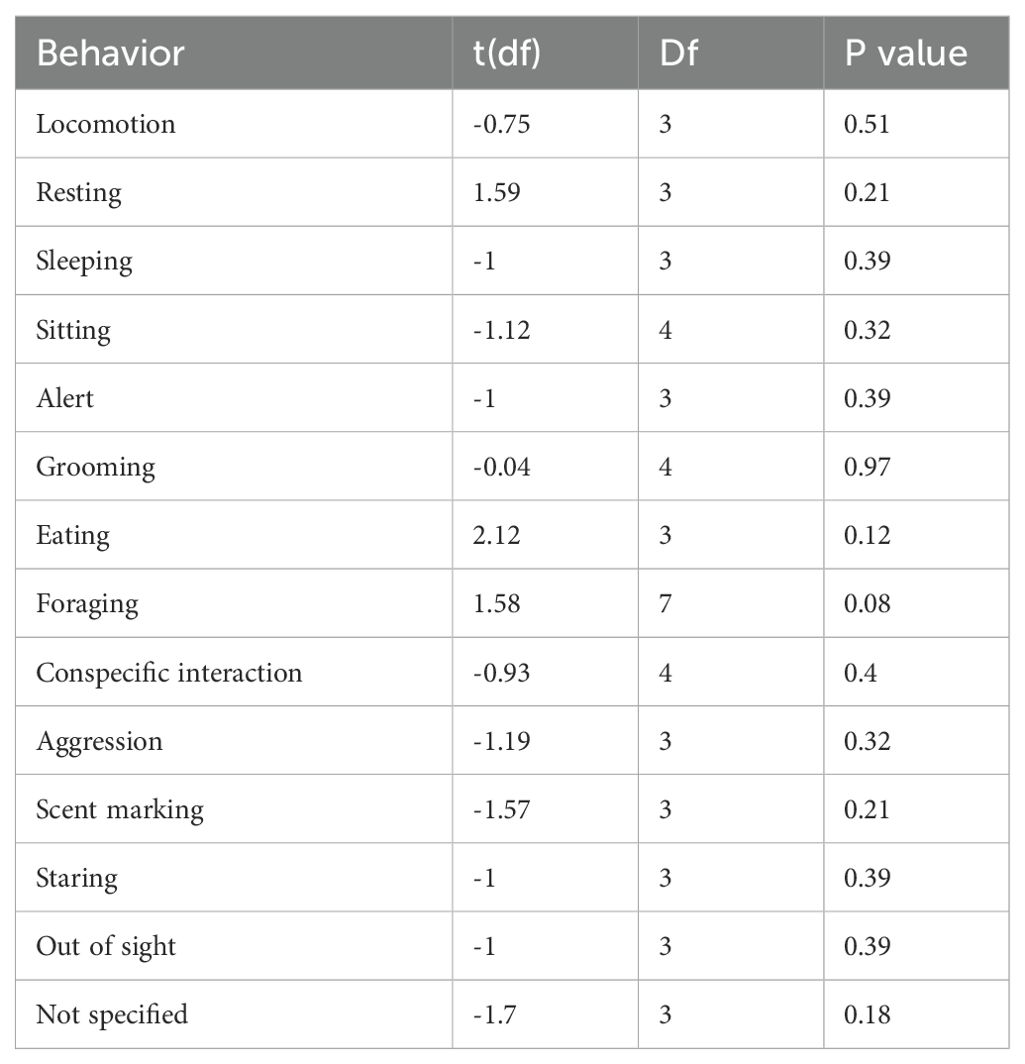
Table 2. The effect of wild and zoo environments on both behavioral performance and occurrences of “out of sight” in lemurs.
Discussion
The aim of this quantitative review was to identify, by analyzing time-activity budgets, which behaviors suggestive of positive welfare may be absent in zoo species and thus should be encouraged in captivity. Further, the research aimed to determine the flexibility of time-activity budgets in captive species compared with their wild counterparts and thus, categorize them as either behaviorally inflexible, partially behaviorally flexible, or fully behaviorally flexible according to the effect sizes of behavioral categories.
Behavioral flexibility by taxonomic order
The results indicate that for all analyzed groups, abnormal behaviors are prevalent in zoo species and appear to replace reproductive and foraging behaviors, inferring reduced behavioral flexibility. Further, agonistic behaviors were performed more in zoo Primates, Artiodactyla and Psittciformes compared to their wild counterparts. These behavioral categories may be associated with increased stress and compromised welfare (Wiepkema and Koolhaas, 1993; Manteca et al., 2016) and suggest reduced behavioral flexibility in the zoo. In all analyzed taxonomic Orders, the largest difference in both abnormal and agonistic behaviors between the wild and zoo was in Psittaciformes. Cognitive ability may be a risk factor for the development of abnormal behavior in captivity. Zoo-housed parrot species with larger brains relative to body size demonstrate oral and whole-body stereotypy susceptibility (Mellor et al., 2021). Further, reduced foraging behaviors in zoo Psittaciformes suggests that opportunities to promote such behaviors are not successfully provided in captivity. Implementing enrichment programs may promote foraging activity in parrots, however the duration spent on such behavior is not representative of wild conspecifics (Van Zeeland et al., 2013) and species atypical behaviors subsequently increase (Rodríguez-López, 2016). This study therefore indicates that Psittaciformes may be behaviorally inflexible, suggesting that they struggle to cope in captive environments when deviating from natural behavioral repertoires. Future studies should explore the application of species-focused enrichment programs and environmental factors that can satiate the behavioral needs of zoo Psittaciformes and maintain captive well-being (Mellor et al., 2021).
Primates, like Psittaciformes are known for high levels of cognitive ability across species (Marino, 2002). This necessitates increased environmental complexity, space and social configurations for captive species to provide for their socioecological and behavioral needs (Poole, 1991; Ross and Shender, 2016). However, this study demonstrates a prevalence of abnormal behaviors in zoo primates, which may manifest due to impoverished housing conditions (Honess and Marin, 2006). Additionally, agonistic behaviors are more commonplace in zoo primates compared to the wild. Features of the zoo environment including human presence, restricted space, disturbances to social dynamics and changes to social and reproductive status may influence these behaviors (Davis et al., 2009). Environmental enrichment programs are implemented to ameliorate detrimental behaviors. Despite research on the effects of environmental enrichment being skewed toward primates (Brereton and Rose, 2022), there is still a lack of consensus on programs that can best promote their well-being (Bennett et al., 2014; Brando et al., 2023). The complexities around adequately housing primates in zoos align with the findings of this review, indicating that they are behaviorally inflexible, with deviation from natural behavior repertoires leading to an increase in behaviors linked to negative welfare. However, differences such as socioecological characteristics across species (Clutton-Brock and Janson, 2012) warrants further investigation to confirm which species are more susceptible to the negative effects of captivity.
Human interaction behaviors were present in zoo Primates, Psittaciformes and Carnivora. In combination with increased noise levels, human presence can induce stress in primates (Hashmi and Sullivan, 2020). However, research by Cairo-Evans et al. (2022) suggests that visitor presence does not impact behavioral indicators of welfare in primates, and that they do not actively withdraw from crowds. In fact, an inverse correlation was observed in decreasing abnormal behaviors and increase in visitor correlation in rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta) (Sharma et al., 2023). Additionally, the effect size of human interaction behaviors on Primates was measurably small for species included within this study and therefore it cannot be concluded if the impact of visitors was positive, neutral or negative. Research into the ‘visitor effect’ often focusses on primate species, however, there has been a recent steady increase in studies encompassing a range of taxa (Williams et al., 2023). The quantitative review findings demonstrate a notably large effect size of human interaction behaviors in Psittaciformes. Although this does not necessarily mean that such behaviors are linked with poor welfare, it should be noted that agonistic and abnormal behaviors are also more prevalent in zoo housed Psittaciformes and seem to correspond with an absence of foraging and reproductive behavior. Research indicates that birds can respond neutrally to interactions with humans (Williams et al., 2023), and so further research should carefully analyze the relationship between behaviors exhibited in zoo birds when human interaction behaviors are also present.
This review indicates that Testudines and Artiodactyla demonstrate full positive behavioral flexibility. Historically, Testudines, along with other reptiles have not always warranted behavioral research in captivity due to perceived unintelligence (Warwick, 1990). However, a suite of cognitive abilities has been unraveled, including complex social and adaptive spatial cognition (Wilkinson and Glass, 2022). As shown for Psittaciformes and Primates, high cognitive ability can predispose animals to poorer welfare if environments are not complex, but Testudines do not appear to suffer a similar fate, and research in wild species indicates temporal and spatial adaptability (Du et al., 2023). Additionally, behavioral flexibility in response to seasonal changes in temperature to conserve water and thermoregulate to maintain homeostasis in Aldabra giant tortoises (Aldabrachelys gigantea) has been observed (Falcón et al., 2018). This supports the findings of this review that Testudines demonstrate fully positive behavioral flexibility due to adaptation to heterogenous environmental conditions.
This review found that despite increased agonistic and reduced reproductive and foraging behaviors zoo Artiodactyla, abnormal behaviors were absent. This contradicts the findings of others that suggest the prevalence of oral stereotypies among ungulate species (Bergeron et al., 2006; Duggan et al., 2016; Fernandez et al., 2008), resulting from an absence of ad libitum feeding and providing concentrate-only diets. This renders the motivation to forage unfulfilled and an increase in stereotypy performance as the animal attempts to cope (Lewis et al., 2022). Exploratory behavior, which suggests positive emotional states (Zupan et al., 2016), increased at the expense of foraging behavior and can be promoted through enrichment provision. For example, tree trunks introduced to blackbucks (Antilope cervicapra) were unfamiliar and novel, thus encouraging engagement with them (Bono et al., 2016). Therefore, carefully designed enrichment programs may negate captive restrictions on foraging behavior by encouraging exploratory behaviors. However, given their taxonomic diversity, future research should identify which even-toed ungulates are more susceptible to the implications of reduced foraging opportunities and which are more able to adapt to its absence through positive behavioral flexibility.
Behavioral flexibility by ecological traits
In completely migratory animals, positive behavioral flexibility is greater in zoos compared with partially and non-migratory categories. This is surprising, given that migration and large home range size has previously been associated with increased stereotypies in captive animals (Gandia et al., 2023). However, recent findings from Bandeli et al. (2023) suggest that it is not necessarily migration distance that infers poor welfare in captivity, but a lack of potential to explore new environments and decision-making opportunities which they would normally have access to in the wild. Further, wild migratory species are exposed to habitat heterogeneity, driven by changes in availability of resources (e.g., nesting or food) (Stanley et al., 2021). Such dynamic adaptation to geographical and ecological variation infers behavioral flexibility (Eggeman et al., 2016). Thus, migratory species, if provided with choice and control, including varied foraging opportunities may demonstrate positive behavioral flexibility. This hypothesis warrants further exploration across populations and species due to considerable intra- and interspecific variation (Morelli et al., 2022; Teitelbaum et al., 2015).
This review demonstrates that despite subtle behavioral differences, when animals are grouped by activity pattern, behaviors indicating negative welfare remain relatively low in the zoo, suggesting partial behavioral flexibility. In wild animals, diel activity may be influenced by prey abundance as in the northern brown bandicoot (Isoodon macrourus), who display increased nocturnal activity to maintain energy intake when food availability is low (Diete et al., 2017). Temperature also influences activity, as in the six-banded armadillo (Euphractus sexcinctus) which maximizes diurnal activity when air temperature decreases (Maccarini et al., 2015). Changing activity patterns in Duvaucel’s geckos (Hoplodactylus duvaucelii) enable them to persist in sympatry in response to predator presence (Hoare et al., 2007). This indicates other ecological factors take precedence and influence temporal niche to benefit life-history strategies of wild animals. Conversely, some animals may struggle to adapt to environmental change, reducing reproductive success, especially in the case of human-induced rapid environmental change (HIREC) (Mason et al., 2013; Sih, 2013). For example, unfavorable conditions in urban environments such as reduced food availability cause increased nest abandonment in great tits (Parus major) (Bailly et al., 2016). However, research into the evolution of cognitive abilities in response to changing environments is lacking in many non-mammalian species (Sarkar and Bhadra, 2022). Due to the global rise of HIREC, species are becoming increasingly exposed to novel challenges not previously encountered (Geffroy et al., 2020). Therefore, it is essential that traits that confer evolutionary potential and behavioral adaptations that aid survivability in underrepresented species are understood in both urbanized wild and captive environments.
There is a paucity of research into the behavioral flexibility of animals based on their sociality. Invertebrate research suggests that social conformity may occur in solitary animals, and is influenced by individual personality, causing increased activity (Fürtbauer and Fry, 2018). High levels of agonistic behavior were evident in solitary zoo-species. Conspecific aggression can occur when individuals are in close proximity (Labão Catapani et al., 2020; Wiggins, 1991). This may suggest that zoos accommodate solitary animals in inadequate captive social configurations. Similarly, eusocial and presocial animals displayed more agonistic behavior in zoos, which may be due to spatial restrictions (Cassinello and Pieters, 2000; Li et al., 2007), or resource limitations; access to nest sites (Hinton et al., 2013) or predictable feeding schedules (Howell et al., 1993). However, primates may regulate behavioral responses when subjected to spatial restrictions, thus mediating aggressive conspecific interactions (Duncan et al., 2013). Therefore, further research should focus on under-represented taxa to investigate mediatory responses in the context of behavioral flexibility in captive social species.
Generalists are considered more behaviorally flexible when compared with specialist species in the wild, through increased opportunism in foraging strategies (Ducatez et al., 2015). However, some generalist species such as the European starling (Sturnus vulgaris) display reduced reproductive success in urbanized locations (Mennechez and Clergeau, 2006). Recent research indicates that individual personality heavily contributes to behavioral flexibility in generalist herbivores (Herath et al., 2021), and thus there may be variation across species. This review suggests that generalist herbivores are more behaviorally flexible than specialist herbivores. This may be attributed to occupancy of a narrower niche by specialists and reduced adaptability to habitat variance (Pagani-Núñez et al., 2016). However, the chisel-toothed kangaroo rat (Dipodomys microps) is a specialist herbivore that can respond positively to changing environments by broadening its habitat and diet niche to persist (Terry et al., 2017). This indicates that ecological traits may infer flexibility in behavioral repertoires when exposed to novel environments, however other factors including individual personality, temporal scales and cognitive capacity must also be accounted for.
Behavioral flexibility in ring-tailed lemurs
This review suggests low levels of variance between behaviors performed by lemurs in the zoo and the wild and behaviors suggestive of poor welfare were uncommon. Wild lemurs demonstrate flexibility in behavioral repertoires when inhabiting anthropogenically modified areas (Cameron and Gould, 2013). Additionally, employing both terrestrial and arboreal tendencies enables better access to forage depending on where resources are most abundant (Eppley et al., 2016). Zoos presents lemurs with more novel stimuli including visitor presence, which may increase abnormal or negative behavior prevalence, causing stress in some animals (Quadros et al., 2014; Queiroz and Young, 2018). However, lemurs demonstrate adaptability to increased visitor interactions, with limited effects on behaviors including foraging and locomotion, and overall behavioral diversity (Collins et al., 2017; Goodenough et al., 2019). Flexibility in hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) activity, used as a physiological measure of stress also indicates adaptability of lemurs in zoos in response to changing social configurations (Smith et al., 2016). The evidence in this review supports existing research that lemurs can thrive through employing positive flexibility in their behavioral responses, Further research should analyze activity budgets from across prosimian species and compare to other primates to determine whether taxonomic differences are present in degree of behavioral flexibility. Such differences may relate to larger brains relative to body size in simians (Armstrong, 1985).
Opportunities and challenges
In this review, effect sizes were calculated allowing for clear interpretation of the proportion of variance between behavior categories between wild and zoo housed animals (R2) (Jennions, 2003). Relative to Cohen’s d, another measure of effect size, Hedges’ g produces a less biased estimator of effect size for smaller sample sizes by using pooled weighted standard deviations instead of pooled standard deviations in Cohen’s d. Several non-mammalian groups were not well represented in the data set, and so Hedges’ g was selected as the most appropriate effect size measure. The approach of comparing R2 across behavior categories allowed for a novel method to determine potential behavioral flexibility in animals grouped by taxonomic Order or ecological trait.
Behavioral flexibility was previously considered a vague concept (Coppens et al., 2010) and it is still poorly understood in many species (Gruber et al., 2019). Nonetheless, interpreting the extent of behavioral flexibility in captive species, and exploring this further in conjunction with other metrics such as behavioral diversity (Miller et al., 2020) may validate behavioral flexibility as a welfare indicator. However, this relationship has not yet been explored in many taxa and research is needed to validate these possible behavioral welfare predictors. This review provides an opportunity to spotlight those species requiring further investigation into the application of behavioral flexibility as an indicator of welfare.
Due to a lack of published data, it was not possible to draw direct comparisons of wild and zoo activity budgets in many species. Thus, species were grouped by taxonomic Order. Although this was useful as it allowed for larger samples to be pooled together, interspecific differences could not be determined. Further research should aim to identify behavioral repertoires of selected species in both contexts for future meta-analyses to be performed and apply Phylogenetic Comparative Methods (PCM). For example, a meta-analysis in captive ungulates using PCM determined that browser and mixed feeder species performed more stereotypical behavior compared with grazers (Lewis et al., 2022). A similar methodology used in Psittaciformes identified that species with larger brain sizes were most susceptible to stereotypy performance in captivity (Mellor et al., 2021). These approaches are still underutilized (Mellor and Mason, 2023), despite clear benefits to animal welfare. Applying PCM in research across species could help in understanding whether species-specific or evolutionary constraints on behavioral repertoires exist (Garamszegi et al., 2012), provide clearer insights into interspecific behavioral variability (Strier et al., 2014) and shed light on species that may better adapt to captive environments (Mellor et al., 2021) through positive behavioral flexibility. Therefore, it is proposed that advances in these analyses are applied to underrepresented taxonomic groups to shed light on the relationship between species biology, and behavioral mechanisms that serve to promote their ability to thrive in the captive managed environment.
Studying wild animals and collecting behavioral information can be fraught with challenges, which may have limited the availability of data across taxonomic Orders. Observing animals in the wild means that they might flee at the presence of an observer (Löttker et al., 2009) or subtle behavioral changes may bias the data collected (Canine, 1990). Also, logistical issues such as unnavigable terrain may obscure individuals from view (Veasey et al., 1996), leading to interpretation difficulties. However, technological advancements may alleviate some of these challenges. For example, the use of remote sensing and bio-loggers, including GPS can map population movements in response to environmental influences (Hughey et al., 2018). Utilizing video surveillance has been used successfully to eliminate the impact of human presence on individuals and acquire more objective behavioral data in wild Eurasian lynx (Lynx lynx) (Krofel et al., 2019), also saving time through its remote application. Therefore, adopting technological-based methods for collecting wild behavioral data has clear benefits over direct observations. Future research should therefore incorporate the aforementioned methods to collect behavioral data on species where the research is scarce, including birds, reptiles and amphibians to help better understand behavioral and ecological differences in captive contexts which support the development of captive management practice (Yamanashi and Hayashi, 2011).
Research extensions
During data extraction, it was evident that mammals dominate behavioral research, with 71 mammal activity budgets collected for this review, compared to 18 for birds and 12 for reptiles. A bias in research output toward larger charismatic mammals, including carnivores and primates is widely reported (Rose et al., 2019; Dos Santos et al., 2020; Ellison et al., 2021). However, for many zoo species, applied welfare research that provides insight into reliable welfare indicators is still inadequate (Tallo-Parra et al., 2023). Future research must pivot toward under-represented taxa, for example birds, reptiles and fish which account for a small number of welfare-focused studies despite their prevalence in zoos (Hamilton et al., 2022; Woods et al., 2022; Oldfield and Bonano, 2023). Expediting this information will help to shed light on the effectiveness of current husbandry practices and subsequent impacts on animal welfare.
For all species in this review apart from lemurs, it was not possible to collect multiple activity budgets in the wild and zoo and therefore, activity budgets may not accurately represent the behavioral repertoire for other included species. For example, in zoos, factors including visitor presence may influence animal behavior either positively by promoting play behavior or negatively through increased aggression (Stoinski et al., 2012; Sherwen and Hemsworth, 2019; Boyle et al., 2020). Further, environmental factors such as predator susceptibility and variation in resource accessibility influence phenotypic changes that cause individually distinctive behavioral attributes in wild animals (Nussey et al., 2007; Merrick and Koprowski, 2017; Hertel et al., 2020). Also, comparing behaviors of wild species to zoo conspecifics across institutions can support in drawing conclusions on the appropriateness of captive behavioral repertoires (Kelley et al., 2006) by understanding whether environmentally relevant species-specific behaviors are performed or if environmental challenges are responded to appropriately (Howell and Cheyne, 2019). Conducting cross-institutional behavioral studies can assess current husbandry and management practices and determine the ecological relevance of enclosures (Rose and Rowden, 2020) which may support in providing optimal welfare conditions (Troxell-Smith et al., 2017). Thus, to improve the validity of behavioral data and better understand intraspecific differences, future research should clarify activity budgets for species across institutions and wild populations to enable more accurate comparisons.
Conclusions
This research aimed to determine whether different captive species of non-domestic animal can be considered positively behaviorally flexible or not. Our results indicate that complete positive behavioral flexibility is most prevalent among Testudines, Artiodactyla, completely migratory species and ring-tailed lemurs, inferring better adaptability to the zoo environment, with behavioral inflexibility suggested in groups where abnormal behaviors replace foraging and reproductive behaviors. However, it remains challenging to assign a species to a category of behavioral flexibility due to intraspecific differences in behavior patterns. Due to a paucity of research in determining wild and zoo baseline behavioral repertoires in non-mammals including birds, reptiles, and fish, we encourage future research to ascertain their potential to employ novel behavioral mechanisms and subsequent positive behavioral flexibility. Overall, the findings of this review indicate species which may thrive within the captive environment, and which exhibit behavioral repertoires that are less flexible and thus require more carefully strategized management practices to ensure good welfare is achieved.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
RK: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MF: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. PR: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fetho.2025.1517294/full#supplementary-material
Supplementary Appendix S1 | PRISMA checklist.
Supplementary Table 1 | Ethogram for all taxa included in the dataset, including non-specified behaviors and out of sight occurrences.
Supplementary Table 2 | Ethogram for ring-tailed lemurs (Lemur catta) adapted from the papers that behavior data was extracted from, including non-specified behaviors and out of sight occurrences.
References
Al Hakim R. R., Imtiyaaz C. D., Setyawaty D., Rahayu F., Rianti P. (2022). Daily behavior of long-tailed macaque in the captive, semi-wild, and wild habitats: preliminary reports. Indonesian J. Primatol. 1, 25–32. doi: 10.29244/primatology.1.01.25-32
Ali Z., Ahmad R., Naeem N. (2024). Effect of seasonal variations on the behavior of captive lions (Panthera leo) and tigers (Panthera tigris). Pak. J. Zool. 56 (4), 1961. doi: 10.17582/journal.pjz/20221127151159
Armstrong E. (1985). Relative brain size in monkeys and prosimians. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 66, 263–273. doi: 10.1002/ajpa.1330660303
Bacon H. (2018). Behavior-based husbandry—A holistic approach to the management of abnormal repetitive behaviors. Animals 8, 103. doi: 10.3390/ani8070103
Bailly J., Scheifler R., Berthe S., Clément-Demange V.-A., Leblond M., Pasteur B., et al. (2016). From eggs to fledging: negative impact of urban habitat on reproduction in two tit species. J. Ornithol. 157, 377–392. doi: 10.1007/s10336-015-1293-3
Baker B., Taylor S., Montrose V. T. (2018). The effects of olfactory stimulation on the behavior of captive ring-tailed lemurs (Lemur catta). Zoo Biol. 37, 16–22. doi: 10.1002/zoo.21392
Bandeli M., Mellor E. L., Kroshko J., Maherali H., Mason G. J. (2023). The welfare problems of wide-ranging Carnivora reflect naturally itinerant lifestyles. R. Soc. Open Sci. 10, 230437. doi: 10.1098/rsos.230437
Bartlett A., Brereton J. E., Freeman M. S. (2024). A comparative multi-zoo survey investigating the housing and husbandry of callimico goeldii. J. Zool. Botanic. Gardens 5, 66–79. doi: 10.3390/jzbg5010005
Beaulieu M. (2024). Capturing wild animal welfare: a physiological perspective. Biol. Rev. 99, 1–22. doi: 10.1111/brv.13009
Bekoff M., Wells M. C. (1981). Behavioural budgeting by wild coyotes: the influence of food resources and social organization. Anim. Behav. 29, 794–801. doi: 10.1016/S0003-3472(81)80013-9
Bell A. M., Hankison S. J., Laskowski K. L. (2009). The repeatability of behavior: a meta-analysis. Anim. Behav. 77, 771–783. doi: 10.1016/j.anbehav.2008.12.022
Bennett A. J., Perkins C. M., Harty N. M., Niu M., Buelo A. K., Luck M. L., et al. (2014). Assessment of foraging devices as a model for decision-making in nonhuman primate environmental enrichment. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 53 (5), 452 463.
Bergeron R., Badnell-Waters A. J., Lambton S., Mason G. (2006). “Stereotypic oral behavior in captive ungulates: foraging, diet and gastrointestinal function,” in Stereotypic animal behavior: fundamentals and applications to welfare, 2 ed. Eds. Mason G., Rushen J. (Wallingford UK: CABI), 19–57.
Boissy A., Manteuffel G., Jensen M. B., Moe R. O., Spruijt B., Keeling L. J., et al. (2007). Assessment of positive emotions in animals to improve their welfare. Physiol. Behav. 92, 375–397. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2007.02.003
Bono L., Mongillo P., De Boni-Russo G., Gabai G., Normando S. (2016). Effects of 2 forms of environmental enrichment on a group of captive blackbucks (Antilope cervicapra): A pilot study. J. Vet. Behav. 12, 66–72. doi: 10.1016/j.jveb.2016.02.003
Boyle S. A., Berry N., Cayton J., Ferguson S., Gilgan A., Khan A., et al. (2020). Widespread behavioral responses by mammals and fish to zoo visitors highlight differences between individual animals. Animals 10, 2108. doi: 10.3390/ani10112108
Bracke M. B. M., Hopster H. (2006). Assessing the importance of natural behavior for animal welfare. J. Agric. Environ. Ethics 19, 77–89. doi: 10.1007/s10806-005-4493-7
Brakes P. (2019). Sociality and wild animal welfare: future directions. Front. Vet. Sci. 6. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2019.00062
Brando S., Buchanan-Smith H. M. (2018). The 24/7 approach to promoting optimal welfare for captive wild animals. Behav. Process. 156, 83–95. doi: 10.1016/j.beproc.2017.09.010
Brando S., Vitale A., Bacon M. (2023). Promoting good nonhuman primate welfare outside regular working hours. Animals 13, 1423. doi: 10.3390/ani13081423
Brereton J., Rose P. (2022). An evaluation of the role of ‘biological evidence’ in zoo and aquarium enrichment practices. Anim. Welf. 31, 13–26. doi: 10.7120/09627286.31.1.002
Burn C. C. (2017). Bestial boredom: a biological perspective on animal boredom and suggestions for its scientific investigation. Anim. Behav. 130, 141–151. doi: 10.1016/j.anbehav.2017.06.006
Cairo-Evans A., Wierzal N. K., Wark J. D., Cronin K. A. (2022). Do zoo-housed primates retreat from crowds? A simple study of five primate species. Am. J. Primatol. 84, e23386. doi: 10.1002/ajp.23386
Cameron A., Gould L. (2013). “Fragment-adaptive Behavioral Strategies and Intersite Variation in the Ring-Tailed Lemur (Lemur catta) in South-Central Madagascar,” in Primates in Fragments. Eds. Marsh L. K., Chapman C. A. (New York: Springer), 227–243.
Canine N. G. (1990). Unrecognized anti-predator behavior can bias observational data. Anim. Behav. 39, 195–197. doi: 10.1016/S0003-3472(05)80741-9
Carlstead K., Mellen J., Kleiman D. G. (1999). Black rhinoceros (Diceros bicornis) in U.S. zoos: I. individual behavior profiles and their relationship to breeding success. Zoo Biol. 18, 17–34. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-2361(1999)18:1<17::AID-ZOO4>3.0.CO;2-K
Carlstead K., Mench J. A., Meehan C., Brown J. L. (2013). An epidemiological approach to welfare research in zoos: the elephant welfare project. J. Appl. Anim. welf. Sci. 16, 319–337. doi: 10.1080/10888705.2013.827915
Caselli M., Messeri P., Dessì-Fulgheri F., Bandoli F. (2022). Enriching zoo-housed ring-tailed lemurs (Lemur catta): assessing the influence of three types of environmental enrichment on behavior. Animals 12, 2836. doi: 10.3390/ani12202836
Cassinello J., Pieters I. (2000). Multi-male captive groups of endangered dama gazelle: Social rank, aggression, and enclosure effects. Zoo Biol. 19, 121–129. doi: 10.1002/1098-2361(2000)19:2<121::AID-ZOO3>3.0.CO;2-1
Chiapero F., Ferrari H. R., Prieto M. V., García Capocasa M. C., Busso J. M. (2021). Multivariate analyses of the activity pattern and behavior of the lesser anteater on open and closed days at Córdoba zoo, Argentina. J. Appl. Anim. welf. Sci. 24, 83–97. doi: 10.1080/10888705.2020.1799214
Clubb R., Mason G. J. (2007). Natural behavioral biology as a risk factor in carnivore welfare: How analysing species differences could help zoos improve enclosures. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 102, 303–328. doi: 10.1016/j.applanim.2006.05.033
Clutton-Brock T., Janson C. (2012). Primate socioecology at the crossroads: Past, present, and future. Evolution. Anthropol.: Issues News Rev. 21, 136–150. doi: 10.1002/evan.21316
Cohen J. (1988). Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. 2nd ed (Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum).
Colditz I. G., Hine B. C. (2016). Resilience in farm animals: biology, management, breeding and implications for animal welfare. Anim. Product. Sci. 56, 1961. doi: 10.1071/AN15297
Collins C., Corkery I., Haigh A., McKeown S., Quirke T., O’Riordan R. (2017). The effects of environmental and visitor variables on the behavior of free-ranging ring-tailed lemurs (Lemur catta) in captivity. Zoo Biol. 36, 250–260. doi: 10.1002/zoo.21370
Coppens C. M., De Boer S. F., Koolhaas J. M. (2010). Coping styles and behavioral flexibility: towards underlying mechanisms. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B: Biol. Sci. 365, 4021–4028. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2010.0217
Davis N., Schaffner C. M., Wehnelt S. (2009). Patterns of injury in zoo-housed spider monkeys: A problem with males? Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 116, 250–259. doi: 10.1016/j.applanim.2008.08.008
De Azevedo C. S., Cipreste C. F., Pizzutto C. S., Young R. J. (2023). Review of the effects of enclosure complexity and design on the behavior and physiology of zoo animals. Animals 13, 1277. doi: 10.3390/ani13081277
Diete R. L., Meek P. D., Dickman C. R., Lisle A., Leung L. K.-P. (2017). Diel activity patterns of northern Australian small mammals: variation, fixity, and plasticity. J. Mammal. 98, 848–857. doi: 10.1093/jmammal/gyx003
Dos Santos J. W., Correia R. A., Malhado A. C. M., Campos-Silva J. V., Teles D., Jepson P., et al. (2020). Drivers of taxonomic bias in conservation research: a global analysis of terrestrial mammals. Anim. Conserv. 23, 679–688. doi: 10.1111/acv.12586
Du W.-G., Li S.-R., Sun B.-J., Shine R. (2023). Can nesting behaviour allow reptiles to adapt to climate change? Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 378 (1884), 20220153. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2022.0153
Ducatez S., Clavel J., Lefebvre L. (2015). Ecological generalism and behavioral innovation in birds: technical intelligence or the simple incorporation of new foods? J. Anim. Ecol. 84, 79–89. doi: 10.1111/1365-2656.12255
Duggan G., Burn C. C., Clauss M. (2016). Nocturnal behavior in captive giraffe (Giraffa camelopardalis)-A pilot study: Nocturnal Behavior in Captive Giraffe. Zoo Biol. 35, 14–18. doi: 10.1002/zoo.21248
Duncan L. M., Jones M. A., Van Lierop M., Pillay N. (2013). Chimpanzees use multiple strategies to limit aggression and stress during spatial density changes. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 147, 159–171. doi: 10.1016/j.applanim.2013.06.001
Duncan L. M., Pillay N. (2013). Shade as a thermoregulatory resource for captive chimpanzees. J. Therm. Biol. 38, 169–177. doi: 10.1016/j.jtherbio.2013.02.009
Dunston E. J., Abell J., Doyle R. E., Evershed M., Freire R. (2016). Exploring African lion (Panthera leo) behavioral phenotypes: individual differences and correlations between sociality, boldness and behavior. J. Ethol. 34, 277–290. doi: 10.1007/s10164-016-0473-9
Eggeman S. L., Hebblewhite M., Bohm H., Whittington J., Merrill E. H. (2016). Behavioral flexibility in migratory behavior in a long-lived large herbivore. J. Anim. Ecol. 85, 785–797. doi: 10.1111/1365-2656.12495
Ellison G., Jones M., Cain B., Bettridge C. M. (2021). Taxonomic and geographic bias in 50 years of research on the behavior and ecology of galagids. PloS One 16, e0261379. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0261379
Eppley T. M., Donati G., Ganzhorn J. U. (2016). Determinants of terrestrial feeding in an arboreal primate: The case of the southern bamboo lemur (Hapalemur meridionalis). Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 161, 328–342. doi: 10.1002/ajpa.23034
Falcón W., Baxter R. P., Furrer S., Bauert M., Hatt J. M., Schaepman-Strub G., et al. (2018). Patterns of activity and body temperature of Aldabra giant tortoises in relation to environmental temperature. Ecol. Evol. 8, 2108–2121. doi: 10.1002/ece3.3766
Fernandez L. T., Bashaw M. J., Sartor R. L., Bouwens N. R., Maki T. S. (2008). Tongue twisters: feeding enrichment to reduce oral stereotypy in giraffe. Zoo Biol. (American Zoo and Aquarium Association) 27 (3), 200 212. doi: 10.1002/zoo.20180
Forthman D. L., Bakeman R. (1992). Environmental and social influences on enclosure use and activity patterns of captive sloth bears (Ursus ursinus). Zoo Biol. 11, 405–415. doi: 10.1002/zoo.1430110607
Fraser D., Weary D. M. (2021). “Applied Animal Behavior and Animal Welfare,” in The Behavior of Animals, 2nd Edition. Eds. Bolhuis J. J., Giraldeau L. A., Hogan J. A. (Hoboken NJ, USA: WIley-Blackwell), 251–280.
Fureix C., Meagher R. K. (2015). What can inactivity (in its various forms) reveal about affective states in non-human animals? A review. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 171, 8–24. doi: 10.1016/j.applanim.2015.08.036
Fürtbauer I., Fry A. (2018). Social conformity in solitary crabs, Carcinus maenas, is driven by individual differences in behavioral plasticity. Anim. Behav. 135, 131–137. doi: 10.1016/j.anbehav.2017.11.010
Gaillard C., Meagher R. K., Von Keyserlingk M. A. G., Weary D. M. (2014). Social housing improves dairy calves’ Performance in two cognitive tests. PloS One 9, e90205. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0090205
Gandia K. M., Herrelko E. S., Kessler S. E., Buchanan-Smith H. M. (2023). Understanding circadian and circannual behavioral cycles of captive giant pandas (Ailuropoda melanoleuca) can help to promote good welfare. Animals 13, 2401. doi: 10.3390/ani13152401
Garamszegi L. Z., Markó G., Herczeg G. (2012). A meta-analysis of correlated behaviors with implications for behavioral syndromes: mean effect size, publication bias, phylogenetic effects and the role of mediator variables. Evolution. Ecol. 26, 1213–1235. doi: 10.1007/s10682-012-9589-8
Garner J. P. (2006). “Perseveration and stereotypy - systems-level insights from clinical psychology,” in Stereotypic animal behavior: fundamentals and applications to welfare, 2 ed. Eds. Mason G., Rushen J. (Wallingford UK: CABI), 121–152.
Geffroy B., Alfonso S., Sadoul B., Blumstein D. T. (2020). A world for reactive phenotypes. Front. Conserv. Sci. 1. doi: 10.3389/fcosc.2020.611919
Goodenough A. E., McDonald K., Moody K., Wheeler C. (2019). Are “visitor effects” overestimated? Behavior in captive lemurs is mainly driven by co-variation with time and weather. J. Zoo Aqua. Res. 7, 59–66. doi: /10.19227/jzar.v7i2.343
Gould L., Sauther M. L. (2007). “Anti-Predator Strategies in a Diurnal Prosimian, the Ring-Tailed Lemur (Lemur catta), at the Beza Mahafaly Special Reserve, Madagascar,” in Primate Anti-Predator Strategies. Developments in Primatology: Progress and Prospects. Eds. Gursky S. L., Nekaris K. A. I. (Springer, Boston, MA), 277–288.
Gruber T., Luncz L., Mörchen J., Schuppli C., Kendal R. L., Hockings K. (2019). Cultural change in animals: a flexible behavioral adaptation to human disturbance. Palgrave Commun. 5, 64. doi: 10.1057/s41599-019-0271-4
Gupta A, Vashisth S, Sharma M, Hore U, Lee H, Pandey P., et al. (2022). Does visitation dictate animal welfare in captivity? – A case study of tigers and leopards from National Zoological Park, New Delhi. Proc. Natl. Inst. Ecol. Republic Korea. 3 (2), 103-14. doi: 10.1101/2020.07.17.208322
Hamilton J., Gartland K. N., Jones M., Fuller G. (2022). Behavioral assessment of six reptile species during a temporary zoo closure and reopening. Animals 12, 1034. doi: 10.3390/ani12081034
Harbicht A. B., Fraser D. J., Ardren W. R. (2020). Minor shifts towards more natural conditions in captivity improve long-term survival among reintroduced Atlantic salmon. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 77, 931–942. doi: 10.1139/cjfas-2019-0201
Harley J. J., Rowden L. J., Clifforde L. M., Power A., Stanley C. R. (2022). Preliminary investigation of the effects of a concert on the behavior of zoo animals. Zoo Biol. 41, 308–327. doi: 10.1002/zoo.21676
Hartstone-Rose A., Selvey H., Villari J. R., Atwell M., Schmidt T. (2014). The three-dimensional morphological effects of captivity. PloS One 9, e113437. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0113437
Hashmi A., Sullivan M. (2020). The visitor effect in zoo-housed apes: the variable effect on behaviour of visitor number and noise. J. Zoo Aqua. Res. 8, 268–282. doi: 10.19227/jzar.v8i4.523
Hayward M. W., Hayward G. J. (2007). Activity patterns of reintroduced lion Panthera leo and spotted hyaena Crocuta crocuta in the Addo Elephant National Park, South Africa. Afr. J. Ecol. 45, 135–141. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2028.2006.00686.x
Hedges L. V. (1981). Distribution theory for glass’s estimator of effect size and related estimators. J. Educ. Stat 6, 107–128. doi: 10.3102/10769986006002107
Herath A. P. H. M., Wat K. K. Y., Banks P. B., McArthur C. (2021). Animal personality drives individual dietary specialisation across multiple dimensions in a mammalian herbivore. Funct. Ecol. 35, 2253–2265. doi: 10.1111/1365-2435.13893
Hertel A. G., Niemelä P. T., Dingemanse N. J., Mueller T. (2020). A guide for studying among-individual behavioral variation from movement data in the wild. Move. Ecol. 8, 30. doi: 10.1186/s40462-020-00216-8
Hill S. P., Broom D. M. (2009). Measuring zoo animal welfare: theory and practice. Zoo Biol. 28, 531–544. doi: 10.1002/zoo.20276
Hinton M. G., Bendelow A., Lantz S., Wey T. W., Schoen L., Brockett R., et al. (2013). Patterns of aggression among captive American flamingos (Phoenicopterus ruber): Aggression in Captive American Flamingos. Zoo Biol. 32, 445–453. doi: 10.1002/zoo.21078
Hoare J. M., Pledger S., Nelson N. J., Daugherty C. H. (2007). Avoiding aliens: Behavioral plasticity in habitat use enables large, nocturnal geckos to survive Pacific rat invasions. Biol. Conserv. 136, 510–519. doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2006.12.022
Honess P. E., Marin C. M. (2006). Enrichment and aggression in primates. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 30, 413–436. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2005.05.002
Howell C. P., Cheyne S. M. (2019). Complexities of using wild versus captive activity budget comparisons for assessing captive primate welfare. J. Appl. Anim. welf. Sci. 22, 78–96. doi: 10.1080/10888705.2018.1500286
Howell S. M., Matevia M., Fritz J., Nash L., Maki S. (1993). Pre-feeding agonism and seasonality in captive groups of chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes). Anim. Welf. 2, 153–163. doi: 10.1017/S0962728600015670
Hughey L. F., Hein A. M., Strandburg-Peshkin A., Jensen F. H. (2018). Challenges and solutions for studying collective animal behavior in the wild. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B: Biol. Sci. 373, 20170005. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2017.0005
Jakob-Hoff R., Kingan M., Fenemore C., Schmid G., Cockrem J. F., Crackle A., et al. (2019). Potential impact of construction noise on selected zoo animals. Animals 9, 504. doi: 10.3390/ani9080504
Jennions M. D. (2003). A survey of the statistical power of research in behavioral ecology and animal behavior. Behav. Ecol. 14, 438–445. doi: 10.1093/beheco/14.3.438
Kelley J. L., Magurran A. E., Macías García C. (2006). Captive breeding promotes aggression in an endangered Mexican fish. Biol. Conserv. 133, 169–177. doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2006.06.002
Kelly R., Rose P. (2024). Sixty years of Tinbergen’s four questions and their continued relevance to applied behaviour and welfare research in zoo animals: A commentary. J. Zool. Botanic. Gardens 5, 338–357. doi: 10.3390/jzbg5020024
Krofel M., Skrbinšek T., Mohorović M. (2019). Using video surveillance to monitor feeding behavior and kleptoparasitism at Eurasian lynx kill sites. Folia Zool. 68, 274. doi: 10.25225/fozo.037.2019
Labão Catapani M., Theodoro Molina K., Martins Costa Lopes A., Miranda F. (2020). Report of three non-agonistic encounters of free-living giant anteaters (Myrmecophaga tridactyla) Vol. 20 (Edentata: The Newsletter of the IUCN/SSC Anteater, Sloth and Armadillo Specialist Group), 31–34. doi: 10.2305/IUCN.CH.2019.Edentata-20-1.6.en
Lewis K., Parker M. O., Proops L., McBride S. D. (2022). Risk factors for stereotypic behavior in captive ungulates. Proc. R. Soc. B: Biol. Sci. 289, 20221311. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2022.1311
Li C., Jiang Z., Tang S., Zeng Y. (2007). Influence of enclosure size and animal density on fecal cortisol concentration and aggression in Père David’s deer stags. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 151, 202–209. doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2007.01.014
Löttker P., Rummel A., Traube M., Stache A., Šustr P., Müller J., et al. (2009). New possibilities of observing animal behavior from a distance using activity sensors in gps-collars: an attempt to calibrate remotely collected activity data with direct behavioral observations in red deer cervus elaphus. Wildl. Biol. 15, 425–434. doi: 10.2981/08-014
Maccarini T. B., Attias N., Medri Í.M., Marinho-Filho J., Mourão G. (2015). Temperature influences the activity patterns of armadillo species in a large neotropical wetland. Mamm. Res. 60, 403–409. doi: 10.1007/s13364-015-0232-2
Mahler A. E. (1984). Activity budgets and use of exhibit space by South American tapir (Tapirus terrestris) in a zoological park setting. Zoo Biol. 3, 35–46. doi: 10.1002/zoo.1430030105
Manteca X., Amat M., Salas M., Temple D. (2016). Animal-based indicators to assess welfare in zoo animals. CABI Rev., 1–10. doi: 10.1079/PAVSNNR201611010
Margulis S. W., Hoyos C., Anderson M. (2003). Effect of felid activity on zoo visitor interest. Zoo Biol. 22, 587–599. doi: 10.1002/zoo.10115
Marino L. (2002). Convergence of complex cognitive abilities in cetaceans and primates. Brain Behav. Evol. 59, 21–32. doi: 10.1159/000063731
Mason G., Burn C. C., Dallaire J. A., Kroshko J., McDonald Kinkaid H., Jeschke J. M. (2013). Plastic animals in cages: behavioral flexibility and responses to captivity. Anim. Behav. 85, 1113–1126. doi: 10.1016/j.anbehav.2013.02.002
McPhee M. E., Carlstead K. (2010). “The Importance of Maintaining Natural Behaviors in Captive Animals,” in Wild Mammals in Captivity: Principles and Techniques for Zoo Management, 2nd ed. Eds. Kleiman D. G., Thompson K. V., Baer C. K. (Chicago IL, USA: The University of Chicago Press).
Mellor E. L., Mason G. J. (2023). Feeding, mating and animal wellbeing: new insights from phylogenetic comparative methods. Proc. R. Soc. B: Biol. Sci. 290, 20222571. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2022.2571
Mellor E. L., McDonald Kinkaid H. K., Mendl M. T., Cuthill I. C., Van Zeeland Y. R. A., Mason G. J. (2021). Nature calls: intelligence and natural foraging style predict poor welfare in captive parrots. Proc. R. Soc. B: Biol. Sci. 288, 20211952. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2021.1952
Mennechez G., Clergeau P. (2006). Effect of urbanisation on habitat generalists: starlings not so flexible? Acta Oecol. 30, 182–191. doi: 10.1016/j.actao.2006.03.002
Merrick M. J., Koprowski J. L. (2017). Should we consider individual behavior differences in applied wildlife conservation studies? Biol. Conserv. 209, 34–44. doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2017.01.021
Miller L., Vicino G., Sheftel J., Lauderdale L. (2020). Behavioral diversity as a potential indicator of positive animal welfare. Animals 10, 1211. doi: 10.3390/ani10071211
Moher D., Liberati A., Tetzlaff J., Altman D. G., Group T. P. (2009). Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PloS Med. 6, e1000097. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097
Morelli F., Benedetti Y., Blumstein D. T. (2022). Resident birds are more behaviorally plastic than migrants. Sci. Rep. 12, 5743. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-09834-1
Nakagawa S., Cuthill I. C. (2007). Effect size, confidence interval and statistical significance: a practical guide for biologists. Biol. Rev. 82, 591–605. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-185X.2007.00027.x
Nussey D. H., Wilson A. J., Brommer J. E. (2007). The evolutionary ecology of individual phenotypic plasticity in wild populations. J. Evolution. Biol. 20, 831–844. doi: 10.1111/j.1420-9101.2007.01300.x
Oldfield R. G., Bonano P. E. (2023). Psychological and social well-being of bony fishes in zoos and aquariums. Zoo Biol. 42, 185–193. doi: 10.1002/zoo.21729
Pagani-Núñez E., Barnett C. A., Gu H., Goodale E. (2016). The need for new categorizations of dietary specialism incorporating spatio-temporal variability of individual diet specialization. J. Zool. 300, 1–7. doi: 10.1111/jzo.12364
Page M. J., McKenzie J. E., Bossuyt P. M., Boutron I., Hoffmann T. C., Mulrow C. D., et al. (2021). The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Int. J. Surg. 88, 105906. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2021.105906
Paulus S. L. (1988). Time-activity budgets of nonbreeding Anatidae: a review. Waterfowl winter, 135–152.
Peragine D. E., Yousuf Y., Fu Y., Swift-Gallant A., Ginzberg K., Holmes M. M. (2016). Contrasting effects of opposite- versus same-sex housing on hormones, behavior and neurogenesis in a eusocial mammal. Hormones Behav. 81, 28–37. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2016.03.005
Plotnik J. M., Jacobson S. L. (2022). A “thinking animal” in conflict: studying wild elephant cognition in the shadow of anthropogenic change. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 46, 101148. doi: 10.1016/j.cobeha.2022.101148
Poole T. B. (1991). “Criteria for the provision of captive environments,” in Primate Responses to Environmental Change. Ed. Box H. O. (Dordrecht: Springer Science Business Media), 357–374.
Price E. E., Stoinski T. S. (2007). Group size: Determinants in the wild and implications for the captive housing of wild mammals in zoos. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 103, 255–264. doi: 10.1016/j.applanim.2006.05.021
Quadros S., Goulart V. D. L., Passos L., Vecci M. A. M., Young R. J. (2014). Zoo visitor effect on mammal behavior: Does noise matter? Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 156, 78–84. doi: 10.1016/j.applanim.2014.04.002
Queiroz M., Young R. (2018). The different physical and behavioral characteristics of zoo mammals that influence their response to visitors. Animals 8, 139. doi: 10.3390/ani8080139
Quick D. L. F., Pappas T. C. (1986). Enclosure utilization, activity budgets, and social behavior of captive chamois (Rupicapra rupicapra) during the rut. Zoo Biol. 5, 281–292. doi: 10.1002/zoo.1430050306
R Core Team (2023). R: A language and environment for statistical computing (Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for Statistical Computing). Available at: https://www.R-project.org/ (Accessed December 21, 2023).
Ritskes-Hoitinga M., Strubbe J. H. (2007). “Nutrition and animal welfare,” in The Welfare of Laboratory Animals, vol. 2 . Ed. Kaliste E. (Dordrecht: Springer), 51–80.
Rodríguez-López R. (2016). Environmental enrichment for parrot species: Are we squawking up the wrong tree? Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 180, 1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.applanim.2016.04.016
Rose P. E., Brereton J. E., Rowden L. J., De Figueiredo R. L., Riley L. M. (2019). What’s new from the zoo? An analysis of ten years of zoo-themed research output. Palgrave Commun. 5, 128. doi: 10.1057/s41599-019-0345-3
Rose P. E., Nash S. M., Riley L. M. (2017). To pace or not to pace? A review of what abnormal repetitive behavior tells us about zoo animal management. J. Vet. Behav. 20, 11–21. doi: 10.1016/j.jveb.2017.02.007
Rose P. E., Riley L. M. (2021). Conducting behavioral research in the zoo: A guide to ten important methods, concepts and theories. J. Zool. Botanic. Gardens 2, 421–444. doi: 10.3390/jzbg2030031
Rose P. E., Rowden L. J. (2020). Specialised for the swamp, catered for in captivity? A cross-institutional evaluation of captive husbandry for two species of lechwe. Animals 10, 1874. doi: 10.3390/ani10101874
Ross S. R., Shender M. A. (2016). Daily travel distances of zoo-housed chimpanzees and gorillas: implications for welfare assessments and space requirements. Primates 57, 395–401. doi: 10.1007/s10329-016-0530-6
RStudio Team (2023). RStudio: Integrated Development for R (Boston, MA: RStudio, PBC). Available at: http://www.rstudio.com/ (Accessed December 21, 2023).
Ruble D. B., Verschueren S., Cristescu B., Marker L. L. (2022). Rewilding apex predators has effects on lower trophic levels: cheetahs and ungulates in a woodland savanna. Animals 12, 3532. doi: 10.3390/ani12243532
Sarkar R., Bhadra A. (2022). How do animals navigate the urban jungle? A review of cognition in urban-adapted animals. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 46, 101177. doi: 10.1016/j.cobeha.2022.101177
Sharma S., Khanal L., Shrestha S., Pandey N., Bellanca R. U., Kyes R. C. (2023). Zoo visitors as a source of enrichment to reduce abnormal behavior in captive rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta) in the Central Zoo, Kathmandu, Nepal. J. Anim. Behav. Biometeorol. 11, 1–10. doi: 10.31893/jabb.23005
Sherwen S. L., Hemsworth P. H. (2019). The visitor effect on zoo animals: implications and opportunities for zoo animal welfare. Animals 9, 366. doi: 10.3390/ani9060366
Sih A. (2013). Understanding variation in behavioral responses to human-induced rapid environmental change: a conceptual overview. Anim. Behav. 85, 1077–1088. doi: 10.1016/j.anbehav.2013.02.017
Skibiel A. L., Trevino H. S., Naugher K. (2007). Comparison of several types of enrichment for captive felids. Zoo Biol. 26, 371–381. doi: 10.1002/zoo.20147
Smith T. E., McCusker C. M., Stevens J. M. G., Elwood R. W. (2016). Patterns of behavior, group structure and reproductive status predict levels of glucocorticoid metabolites in zoo-housed ring-tailed lemurs, lemur catta. Folia Primatol. 86, 506–524. doi: 10.1159/000442587
Spain M., Fuller G., Allard S. (2020). Effects of habitat modifications on behavioral indicators of welfare for Madagascar giant hognose snakes (Leioheterodon Madagascariensis). Anim. Behav. Cogn. 7, 70–81. doi: 10.26451/abc.07.01.06.2020
Stanley C. Q., Dudash M. R., Ryder T. B., Shriver W. G., Serno K., Adalsteinsson S., et al. (2021). Seasonal variation in habitat selection for a Neotropical migratory songbird using high-resolution GPS tracking. Ecosphere 12, e03421. doi: 10.1002/ecs2.3421
Stoinski T. S., Jaicks H. F., Drayton L. A. (2012). Visitor effects on the behavior of captive western lowland gorillas: the importance of individual differences in examining welfare. Zoo Biol. 31, 586–599. doi: 10.1002/zoo.20425
Strier K. B., Lee P. C., Ives A. R. (2014). Behavioral flexibility and the evolution of primate social states. PloS One 9, e114099. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0114099
Tallo-Parra O., Salas M., Manteca X. (2023). Zoo animal welfare assessment: where do we stand? Animals 13, 1966. doi: 10.3390/ani13121966
Teitelbaum C. S., Fagan W. F., Fleming C. H., Dressler G., Calabrese J. M., Leimgruber P., et al. (2015). How far to go? Determinants of migration distance in land mammals. Ecol. Lett. 18, 545–552. doi: 10.1111/ele.12435
Terry R. C., Guerre M. E., Taylor D. S. (2017). How specialized is a diet specialist? Niche flexibility and local persistence through time of the Chisel-toothed kangaroo rat. Funct. Ecol. 31, 1921–1932. doi: 10.1111/1365-2435.12892
Troxell-Smith S., Whelan C., Magle S., Brown J. (2017). Zoo foraging ecology: development and assessment of a welfare tool for captive animals. Anim. Welf. 26, 265–275. doi: 10.7120/09627286.26.3.265
Van Zeeland Y. R. A., Schoemaker N. J., Ravesteijn M. M., Mol M., Lumeij J. T. (2013). Efficacy of foraging enrichments to increase foraging time in Grey parrots (Psittacus erithacus erithacus). Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 149, 87–102. doi: 10.1016/j.applanim.2013.09.005
Veasey J. S., Waran N. K., Young R. J. (1996). On comparing the behaviour of zoo housed animals with wild conspecifics as a welfare indicator, using the giraffe (Giraffa camelopardalis) as a model. Anim. Welfare 5 (2), 139 153. doi: 10.1017/S0962728600018571
Veasey J. (2006). “Concepts in the care and welfare of captive elephants,” in International Zoo Yearbook, vol. 40. , 63–79. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1090.2006.00063.x
Veasey J. S. (2020). Can Zoos Ever Be Big Enough for Large Wild Animals? A Review Using an Expert Panel Assessment of the Psychological Priorities of the Amur Tiger (Panthera tigris altaica) as a Model Species. Animals 10, 1536. doi: 10.3390/ani10091536
Villalba J. J., Manteca X. (2019). A case for eustress in grazing animals. Front. Vet. Sci. 6. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2019.00303
Warwick C. (1990). Reptilian ethology in captivity: Observations of some problems and an evaluation of their aetiology. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 26, 1–13. doi: 10.1016/0168-1591(90)90082-O
Wiepkema P. R., Koolhaas J. M. (1993). Stress and animal welfare. Anim. Welf. 2, 195–218. doi: 10.1017/S0962728600015876
Wiggins D. A. (1991). Foraging success and aggression in solitary and group-feeding great egrets (Casmerodius albus). Colon. Waterbirds 14, 176. doi: 10.2307/1521508
Wilkinson A., Glass E. (2022). “Testudines Cognition,” in Encyclopedia of Animal Cognition and Behavior. Eds. Vonk J., Shackelford T. K. (Switzerland: Springer International Publishing), 6927–6931.
Williams E., Hunton V., Hosey G., Ward S. J. (2023). The impact of visitors on non-primate species in zoos: A quantitative review. Animals 13, 1178. doi: 10.3390/ani13071178
Woods J. M., Eyer A., Miller L. J. (2022). Bird welfare in zoos and aquariums: general insights across industries. J. Zool. Botanic. Gardens 3, 198–222. doi: 10.3390/jzbg3020017
Yamanashi Y., Hayashi M. (2011). Assessing the effects of cognitive experiments on the welfare of captive chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes) by direct comparison of activity budget between wild and captive chimpanzees. Am. J. Primatol. 73, 1231–1238. doi: 10.1002/ajp.20995
Yates K., Stanley C. R., Bettridge C. M. (2022). The effects of allogrooming and social network position on behavioral indicators of stress in female lion-tailed macaques (Macaca silenus). Behav. Process. 202, 104740. doi: 10.1016/j.beproc.2022.104740
Keywords: zoo animal welfare, behavioral flexibility, time activity budgets, zoo animal behavior, wild and captive animal behavior
Citation: Kelly R, Freeman M and Rose P (2025) What behavior is important behavior? A systematic review of how wild and zoo-housed animals differ in their time-activity budgets. Front. Ethol. 4:1517294. doi: 10.3389/fetho.2025.1517294
Received: 25 October 2024; Accepted: 07 January 2025;
Published: 29 January 2025.
Edited by:
Paolo Baragli, University of Pisa, ItalyReviewed by:
Gazzola Andrea, University of Pavia, ItalyYann Henaut, ECOSUR Conservation and Biodiversity, Mexico
Copyright © 2025 Kelly, Freeman and Rose. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Robert Kelly, cms1MjhAZXhldGVyLmFjLnVr
 Robert Kelly
Robert Kelly Marianne Freeman
Marianne Freeman Paul Rose
Paul Rose