- 1Division of Health Analytics, Beckman Research Institute, City of Hope, Duarte, CA, United States
- 2Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, University of California San Francisco, San Francisco, CA, United States
- 3Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, David Geffen School of Medicine, University of California Los Angeles, Los Angeles, CA, United States
- 4Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center, University of California Los Angeles, Los Angeles, CA, United States
- 5UCLA AIDS Institute, University of California, Los Angeles, Los Angeles, CA, United States
- 6Department of Environmental Medicine and Climate Science, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, United States
Objective: To evaluate the associations between brominated flame retardants (BFRs), including polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs), exposure and circulating immune markers in a subset of women from the California Teachers Study cohort.
Methods: In this cross-sectional study, serum from 813 female participants in the California Teachers Study collected in 2013–2016 were evaluated for 11 BFR congeners and 16 immune markers. Three BFR congeners [BDE153 [2,2′,4,4′,5,5′-Hexabromodiphenyl ether], BDE47 [2,2′,4,4′-Tetrabromodiphenyl ether], PBB153 [2,2′,4,4′,5,5′-Hexabromobiphenyl]] had median levels that were above the level of detection and were further evaluated for associations with circulating immune markers. Odds ratios (OR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) were calculated by a logistic regression model where BFR congeners (in quartiles) were associated with immune markers (dichotomized as above and below the respective median), adjusted for age and total lipids. Sensitivity analyses were also conducted evaluating BFR congeners as a continuous exposure (per pg/ml).
Results: All participants had at least one of the 11 measured BFR congeners detected in their serum. Increasing levels of BDE47 were associated with elevated levels of BAFF (B-cell activating factor; ORQuartile 4 = 1.67, 95% CI = 1.11–2.51), soluble CD27 (sCD27, cluster of differentiation 27; ORQuartile 4 = 1.69, 95% CI = 1.12–2.55) and IL6 (interleukin 6; ORQuartile 4 = 1.74, 95% CI = 1.13–2.66). Increasing levels of PBB153 were associated with elevated levels of CXCL13 (chemokine ligand 13; ORQuartile 4 = 1.55, 95% CI = 1.02–2.35) but inversely associated with sCD27 (ORQuartile 4 = 0.57, 95% CI = 0.38–0.87). Results from continuous models of BFR were largely consistent. No associations were observed between BDE153 and any of the immune markers assessed.
Conclusions: Two BFR congeners were statistically associated with altered levels of circulating immune markers involved in B cell activation pathways; replication and further evaluation of these novel associations are warranted. If confirmed, our results add to the current literature regarding possible immune mechanisms by which BFR exposures contribute to immune-related health endpoints and conditions where B cell activation is prominent, including autoimmune conditions.
1 Introduction
Brominated flame retardants (BFRs), including polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs), are chemicals that were first manufactured in the 1970s and used as flame retardants in various materials and products, such as plastic, automobiles and wiring material (1). The use of these chemicals is often associated with commercial mixtures known as pentabromodiphenyl ether (c-pentaBDE), hexabromodiphenyl ether (c-hexaBDE), octabromodiphenyl ether (c-octaBDE), and decabromodiphenyl ether (c-decaBDE). Per the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), BFR congener levels are often correlated due to their production and use within commercial mixtures (2); the detected levels indicate cumulative effects of long-term exposures (2). In the early 2000s, the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) released a biomonitoring summary to describe the overall human exposure and potential health risks caused by BFR exposure, resulting in the replacement of these chemicals (e.g., c-pentaBDE, c-octaPBDE, and c-decaBDE) in production (2).
Despite restriction of their use, BFRs remain pervasive in the environment and persistently detected in humans and are of particular concern for aging populations which have the highest accumulated levels during a period of time in which they are likely to face health effects. There are multiple routes of exposure to BFR during one's lifetime, including through inhalation, dermal contact, dietary intake and through contaminated water (3). A cross-sectional study conducted in 2008 within the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) that assessed BFR levels in 2,062 adult serum samples found that at least one BFR congener was detected in 99% of the samples (4). Similar prevalences demonstrating the pervasiveness of BFR in human populations have been reported in various studies (5, 6).
BFR exposure has been linked to hormone dysregulation, thyroid dysfunction, and altered metabolic activity; it has also been linked to increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes, increased cancer risk, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (7–10). Additionally, PBDE congeners have been reported at high values in young children from gestational exposure (3, 11–13). Previous studies have reported that PBDEs are metabolized by cytochrome P450 and form OH-PBDEs, which can bind hormone receptors and thus act as endocrine disrupting chemicals (8). Importantly, endocrine disrupting chemical exposure has been linked to altered immune responses (14). Exposure to BFR congeners has been shown to cause adverse immune responses through multiple posited biological mechanisms: (i) directly through immune cell function, (ii) by disrupting hormonal balance that can result in altered thyroid activity, and (iii) inducing oxidative stress and producing reactive oxygen species (3, 14).
At present, there are sparse population-based studies that have assessed the associations between BFR exposure and circulating immune markers (5). However, there is growing in vivo and in vitro evidence to support an association (15–19). An in vivo study of BDE47 (2,2′,4,4′-Tetrabromodiphenyl ether)-exposed mice over a period of 30 days across varying dosages and found that exposure to BDE47 reduced the production of both interleukin 6 (IL6) and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) (16). Similarly, Longo et al. (2019) found reduced levels of interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β), IL6 and TNF-α in an in vitro study that exposed human macrophages to various levels of BDE47 (18). There remains inconsistency in study results, however, as Wei et al. (2020) reported a positive association between BDE47 with TNF-α, IL-1β and IL6 in an in vivo mouse study (17). Another in vitro study reported that penta-BDE and octa-BDE were positively associated with elevated IL6 and interleukin 8 (IL8) expression in human bronchial epithelial cells (19). Of note, because humans are exposed to BFR congeners through a variety of mediums, including direct contact with fire retardant products and through diet, in vitro/in vivo studies may not exemplify human exposure and whether results from mechanistic studies will be observed in human populations has yet to be determined.
In the present study, we measured 11 BFR congeners in blood collected between 2013 and 2016 from a cross-sectional sample of 813 female participants in the California Teachers Study and evaluated the association between BFR congeners with 16 circulating immune markers from the same blood collection. Due to the persistent nature and bioaccumulation of BFR congeners, identifying the potential underlying biological mechanism by which BFR may contribute to adverse health effects is of public health significance. Our study population is targeted among women as immune function decreases with age and women notably have higher risk for autoimmune disease development than men; our study thus provides the opportunity to investigate the associations between BFR exposure and immune markers in a particularly susceptible population subset that may be more at risk for adverse immune-specific health outcomes (20). We hypothesized that individuals with higher circulating levels of BFR congeners would also have higher levels of circulating immune markers.
2 Methods
2.1 Study population
The California Teachers Study (CTS) is a prospective cohort study that began in 1995 and is comprised of women who were active or recently retired public school professionals. The study population has been previously described, and the study has been approved by the Institutional Review Boards of participating institutions, including City of Hope National Medical Center (21). For this cross-sectional study, participants were selected based on the completion of the coinciding follow-up questionnaire (Questionnaire 5; administered 2012–2015; N = 61,984) with the CTS biobanking study (2013–2016; N = 13,888); of the eligible population, 814 participants who were cancer-free at the time of blood collection were selected for measurement of BFR congeners, of which data from 813 participants were analyzable. These individuals were initially selected for an immune profiling project where immune markers were assessed as part of a larger study on sleep characteristics.
2.2 Cytokine and immune marker measurements
Methods and results for measuring cytokine levels in serum for the participants in this study are previously described (22, 23). Briefly, all immune marker measurements were conducted at the University of California, Los Angeles (M.E.) by multiplexed immunometric assays (Luminex platform) and a Bioplex 200 system (Bio-Rad) using two Luminex panels (R&D Systems): Soluble Receptor Human Panel (soluble receptors and chemokines) and Human Biomarker A Panel (human inflammatory cytokines) (22). The Soluble Receptor Human Panel included the detection of BAFF (B-cell activating factor), CXCL13 (chemokine ligand 13), CD14 (cluster of differentiation 14), sCD27 (soluble cluster of differentiation 27), GP130 (glycoprotein 130), IL-2Rα (interleukin 2 receptor subunit alpha), IL6Rα (interleukin 6 receptor subunit alpha), and TNFR2 (tumor necrosis factor receptor 2). The Human Biomarker A Panel included the detection of IL1β (interleukin-1 beta), IL2 (interleukin-2), IL4 (interleukin-4), IL6 (interleukin-6), IL8 (interleukin-8), IL10 (interleukin-10), IFN-γ (interferon gamma), and TNF-α (Tumor necrosis factor alpha) (22). The serum samples used in the assays were not previously thawed and stored at −80 for 6–9 years. As previously described, all specimens were handled in a single batch and 10% of quality control samples were interspersed (n = 83) (22). Another 10% (n = 83) of participants were tested in duplicate permitting calculation of coefficient of variations which ranged from 5.17% to 27.74%, with the majority <10% (22).
2.3 BFR measurements
A total of 11 BFR congeners were assessed at the Mount Sinai Targeted Analysis Laboratory Hub: 2,2′,4-Tribromodiphenyl ether (BDE17), 2,4,4′-Tribromodiphenyl ether (BDE28), 2,2′,4,4′-Tetrabromodiphenyl ether (BDE47), 2,3′,4,4′-Tetrabromodiphenyl ether (BDE66), 2,2′,3,4,4′-Pentabromodiphenyl ether (BDE85), 2,2′,4,4′,5-Pentabromodiphenyl ether (BDE99), 2,2′,4,4′,6-Pentabromodiphenyl ether (BDE100), 2,2′,4,4′,5,5′-Hexabromodiphenyl ether (BDE153), 2,2′,4,4′,5,6′-Hexabromodiphenyl ether (BDE154), 2,2′,3,4,4′,5′,6-Heptabromodiphenyl ether (BDE183) and 2,2′,4,4′,5,5′-Hexabromobiphenyl (PBB153). BFR congeners were measured at the Senator Frank R. Lautenberg Environmental Health Sciences Laboratory at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai using 500ul serum samples. The analytical method was based on published methods by Hovander et al. (2000) (24), EPA (25) and CDC (26) with modifications. Briefly, samples were spiked with 13C isotopically labeled internal standard prior to extraction. Liquid-liquid extraction was automated using a liquid handler (epMotion 5073; Eppendorf, Hauppauge, NY). Hexane and dichloromethane mixture (4:1 v/v) was use for the extraction. Co-extracted impurities were removed from the extract using multi sorbent multi layered cleanup columns. Purified extracts were evaporated under a gentle stream of nitrogen and reconstituted in hexane for instrumental analysis. The GC-MS/MS analysis was performed using an Agilent 7010B triple quadrupole mass spectrometer coupled with Agilent 8890 gas chromatograph (Agilent Technologies, Wilmington, DE). Chromatographic separation was achieved by using a 30 m BD-XLB (0.25 mm ID×0.1 µm film thickness) capillary column with a helium carrier gas flow rate set at 1.4 ml/min. The MS was operated in the EI mode at −70 ev. Multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) was utilized during data acquisition. Isotope dilution internal standard calibration method was used for the quantitative analysis. NIST standard reference material SRM 1958 (Organic Contaminants in Fortified Human Serum), spiked and un-spiked matrix, procedural and instrumental blanks were analyzed alongside samples as quality assurance measures. Within the duration of sample analysis, the analytical lab successfully completed two rounds of AMAP proficiency testing for persistent organics analyses in human serum. All BFR measurements were processed within a 28-hour time period and exhibited low pre-analytical variability due to the adherence to previously established standardized procedures (over 99.5% protocol compliance resulted in minimal pre-processing sample errors). Serum triglycerides and total cholesterol were analyzed at the Clinical Chemistry Laboratory of Mount Sinai Hospital (1425 Madison Ave. New York NY 10029). One batch of lipid analysis consisted of 40 study samples and 2 blinded QC samples (HHEAR Pool C and D) for a total of 22 batches. Additionally, all analyses occurred on the same day. According to previous studies of the California Teachers Study that assessed PBDE concentration, total lipid measurements were calculated by aggregating log-transformed triglycerides and cholesterol measurements per participant (27). The BFR congener dataset presented in this study can be found in the online Human Health Exposure Analysis Resource data repository (https://hhearprogram.org/data-services).
2.4 Covariates
Participant characteristics and potential confounders were assessed at baseline, including age (40–49, 50–59, 60–69, or 70+ years), race/ethnicity (non-Hispanic White or other), socioeconomic status (SES; in quartiles determined by occupation, education, and income), rural/urban residence (rural, town, city, metropolitan suburban, or metropolitan urban; according to the 1990 census block groups), as well as updated information ascertained during Questionnaire 5, including weight [for which updated body mass index (BMI) was calculated; BMI: 15–24, 25–29, or 30+ kg/m2], physical activity (moderate/strenuous: 0–2.37, 2.38–5.88, 5.88+ hrs/week), nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) use (none/1/week or >1/week), and statin use (none or >1/week) (22).
2.5 Statistical analysis
Immune marker and BFR congener measurements were characterized for percent detection, medians, and ranges and both log-transformed for univariate and multivariable analyses to normalize the data distribution. Statistical models were constructed for the three BFR congeners that had detectable median values (BDE153, BDE47, and PBB153), which is consistent with other population studies (4, 5, 28, 29). The associations between BFR congeners (defined as the exposures) and immune markers/pathways (defined as the outcomes) were assessed by both linear and logistic regression, allowing evaluation of exposure (BFR congeners) as continuous and categorical exposure variables. For logistic regression models, BFR congeners were evaluated as quartiles so that no threshold effect would be missed, and immune markers were dichotomized as above and below the respective median value based on methods reported in the literature (22, 27). Immune markers that had <50% detection frequency (IFN-γ, IL2, and IL4) were dichotomized as detectable vs. non-detectable. Multivariable models included adjustments for age (categorical), BMI (categorical), and total serum lipids (log-transformed triglycerides and cholesterol). Final multivariable models for BDE47 also included adjustment for PBB153, and vice versa. Multivariable models were also conducted stratified by key participant characteristics (age, BMI, statin use and diabetes status) to ensure that associations of the BFR exposures and immune marker outcomes did not differ by key covariates.
Immune marker pathways were defined as previously described (22) and assessed for association with BFR congeners, with individual cytokines first dichotomized as above or below the respective median and subsequently categorized as: (1) Pro-inflammatory/macrophage activation: elevated levels of TNF-α, TNFR2, IL6, IL1β, IL8, IL6Rα, IL10, and CD14, (2) Th1: elevated IFN-γ and decreased IL10 and IL-4, (3) B-cell activation: elevated levels of BAFF, IL10, IL4, IL6, sCD27, CXCL13, and (4) T-cell activation: elevated levels of IL2, IL2Rα, IFN-γ, IL4, IL6. Individuals who had specified immune marker that was above its respective median were considered to be “positive” for that immune marker, which further contributed to their potential categorization in the corresponding immune pathway. An individual was considered “positive” for a specified immune pathway if the number of immune markers identified as “positive” was above the median overall. We conducted pathway-based analyses in order to identify if there were associations (beyond those individually assessed with the immune markers) between BFR congener exposure and broad immune pathways that could provide more insight into specific biological pathways. All data analyses were performed utilizing the California Teachers Study Researcher Platform (30). Statistical analyses were performed using SAS 9.4 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC), and figures were created using GraphPad Prism 9.5.0.
3 Results
3.1 Study participant characteristics
Select study participant characteristics are shown in Table 1. In general, our study participants were younger (44.8% are 60–69 years old) than the overall California Teachers Study population that completed the follow-up questionnaire (40.4% are 70+ years old) but reflected the sampling of participants that participated in the cohort's biobanking study. Our study participants were also more racially diverse than the overall cohort (79.2% non-Hispanic White vs. 87.6%).
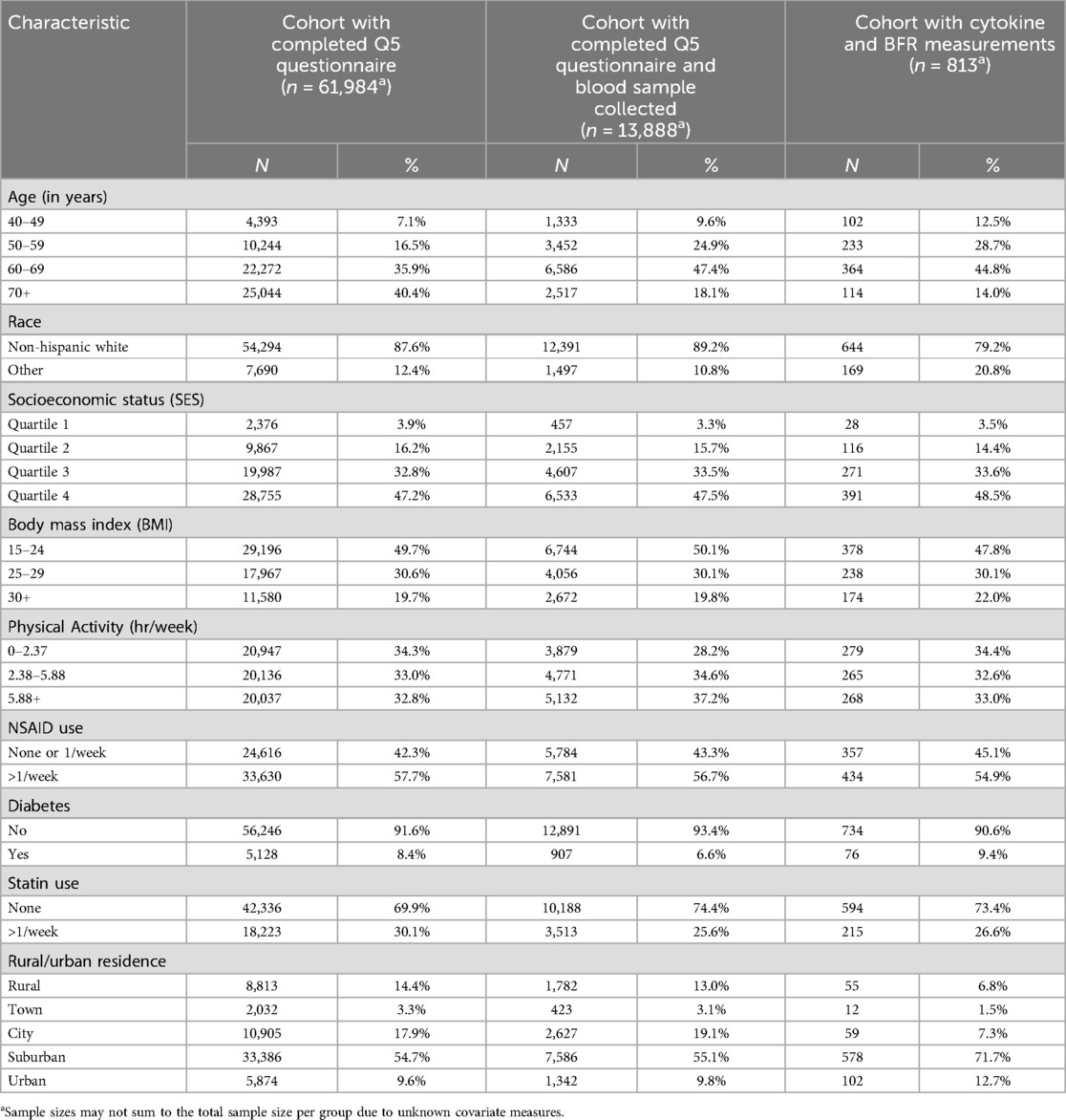
Table 1. Distribution of demographic and host characteristics among a subset of 813 participants in the California Teachers Study cohort with simultaneous measurements of serum immune markers and brominated flame retardants (BFR) in 2013–2016.
3.2 BFR congener and immune marker measurements
Descriptive statistics (median and range) for the 11 BFR congeners are shown in Supplementary Table S1. Three congeners with median levels that were above the limit of detection (BDE153 = 33.4 pg/ml, BDE47 = 70.3 pg/ml, and PBB153 = 18.6 pg/ml) were evaluated further for associations with immune markers and immune pathways. The remaining BFR congeners (i.e., BDE100, BDE154, BDE17, BDE183, BDE28, BDE74, BDE66, BDE85, and BDE99) had medians that were below the limit of detection value and were not further evaluated for associations with immune markers. Descriptive statistics for the 16 immune markers are shown in Supplementary Table S2. BFR congener correlation coefficients (via Spearman's correlation coefficients) are presented in Supplementary Table S3. Of the congeners included in further analyses (BDE153, BDE47, and PBB153), there were no notable correlations. The correlations did not change by population subsets (age, BMI, statin use, diabetes use) (data not shown).
3.3 Univariate models
Participant characteristics shown previously to be associated with circulating immune markers were evaluated with BDE153, BDE47 and PBB153 (4, 29, 31, 32), and the results are displayed in Table 2. While higher BMI was associated with increasing levels of BDE47 (30+ kg/m2: OR = 1.83, 95% CI = 1.33–2.54), higher BMI was associated with lower levels of both BDE153 (BMI 30+ kg/m2 OR = 0.61, 95% CI = 0.44–0.84) and PBB153 (BMI 30+ kg/m2 OR = 0.54, 95% CI = 0.39–0.75). Individuals who reported having diabetes also had higher levels of BDE47 (OR = 1.65, 95% CI = 1.07–2.52). Regular NSAID use was associated with lower levels of BDE47 (OR = 0.71, 95% CI = 0.55–0.92) and PBB153 (OR = 0.77, 95% CI = 0.60–0.99). Statin use >1/week was also associated with higher levels of BDE47 (OR = 1.38, 95% CI = 1.04–1.83) but not associated with BDE153 or PBB153. Finally, non-White race was also associated with higher levels of BDE47 (OR = 1.37, 95% CI = 1.01–1.86).
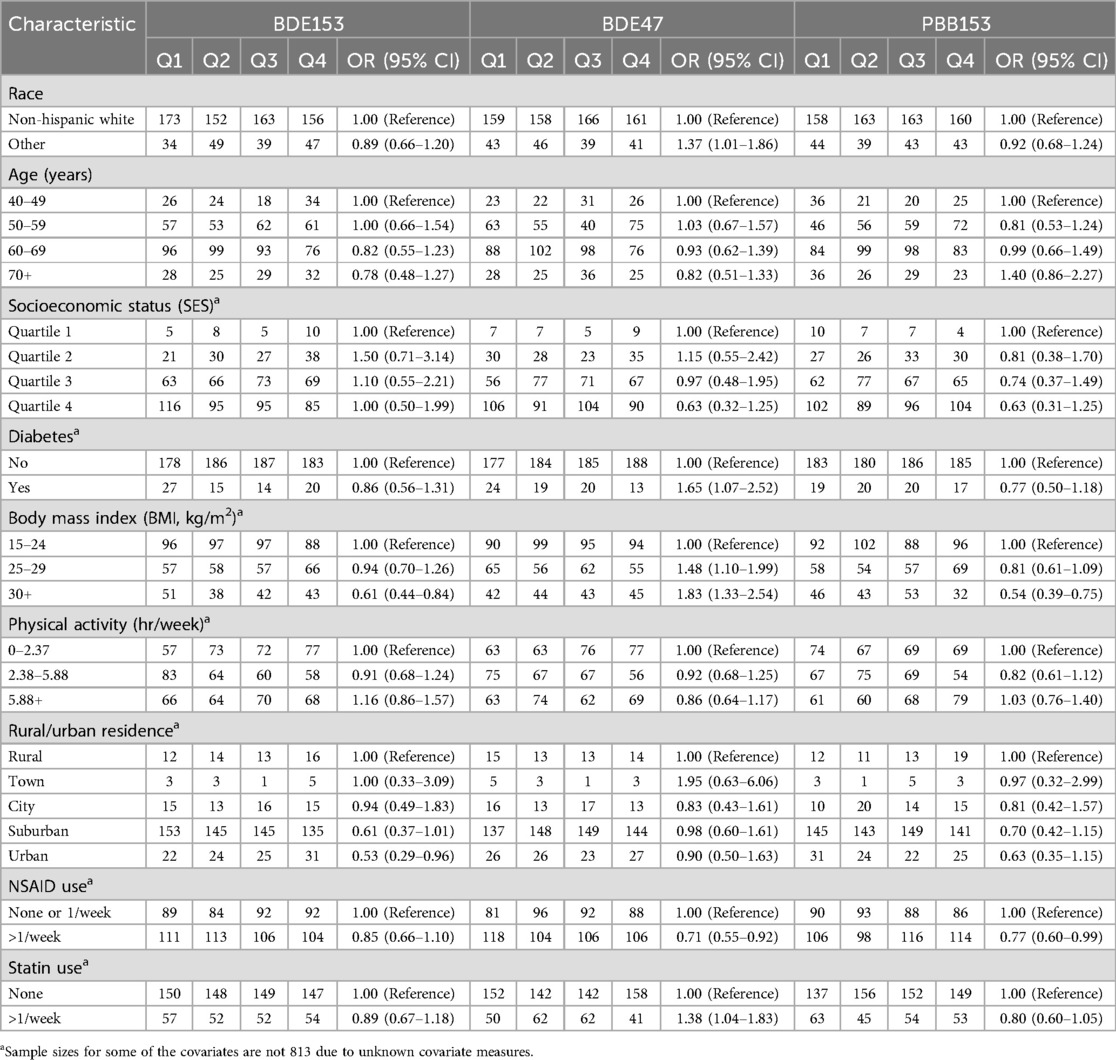
Table 2. Associations between participant characteristics and each quartile of log-transformed BFR congener (BDE153, BDE47 and PBB153) and among the subset of 813a participants in the California Teachers Study cohort who had concurrent immune marker and BFR congener measurements from blood collected from 2013–2016. Associations were adjusted for total lipids.
3.4 Multivariable models
Results of multivariable analyses evaluating the association between BDE153, BDE47 and PBB153 with each immune marker are shown in Supplementary Table S4; results for BDE47 and PBB153 are displayed graphically in Figure 1. Increasing levels of BDE47 were significantly associated with increasing levels of circulating sCD27 (ORquartile4 = 1.69, 95% CI = 1.12–2.55), IL6 (ORquartile4 = 1.74 95% CI = 1.13–2.66), and BAFF (ORquartile4 = 1.67, 95% CI = 1.11–2.51). PBB153 was associated with higher levels of CXCL13 (ORquartile4 = 1.18, 95% CI = 1.02–2.35) and lower levels of sCD27 (ORquartile4 = 0.57, 95% CI = 0.38–0.87). No significant results were observed for BDE153 and any immune marker (Supplementary Table S4). Continuous models [continuous BFR congeners (pg/ml) and dichotomized immune markers] resulted in relatively similar trends as the logistic models; specifically, in continuous models, for each unit (pg/ml) of increase in BDE47, we observed an odds ratio of 1.26 (95% CI = 1.11–144) and 1.18 (95% CI = 1.04–1.34) for IL6 and sCD27, respectively (Figure 1 and Supplementary Table S4). Multivariable models stratified by key participant characteristics (age, BMI, statin use) are presented in Supplementary Table S6. Overall, the magnitudes of effect were consistent across strata for the indicated immune markers (e.g., BDE47 and sCD27, IL6 and BAFF). We further present the associations between the participant characteristics and the dichotomized immune markers in Supplementary Table S7.
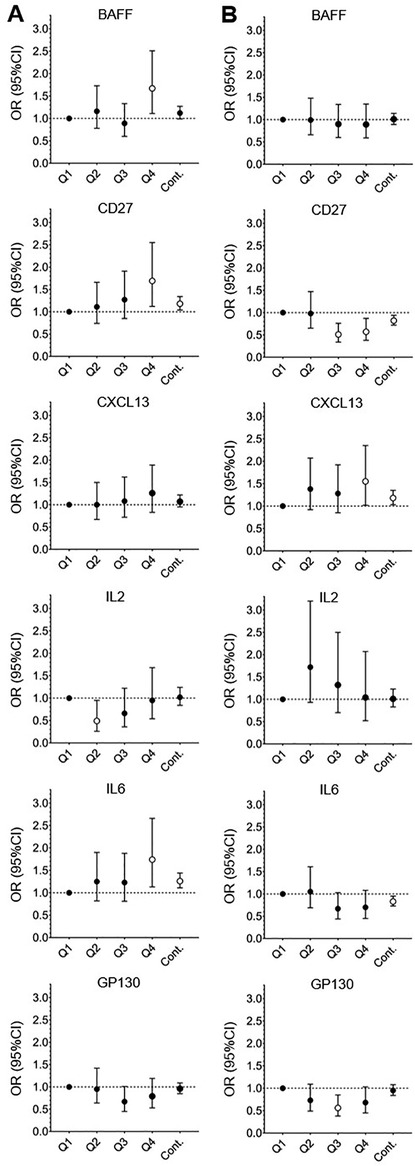
Figure 1. Significant associations from the multivariable association of dichotomized cytokines and log-transformed BFR congeners for the participants in the California Teachers Study who had a serum sample collected from 2013 to 2016. (A) Significant quartile 1, 2, 3, 4 (Q1–4, respectively) and continuous model (Cont.) results for BDE47. (B) Significant quartile 1, 2, 3, 4 and continuous model results for PBB153. Quartile model: adjusted for age, BMI, and total lipids. Continuous model: BFR congeners = per 1 unit increase (pg/ml), cytokines are dichotomized as above or below the median; adjusted for age and total lipids. BDE47 models were additionally adjusted for PBB153, and PBB153 quartile models were additionally adjusted for BDE47. Open circle symbols indicate a significant association, while closed symbols indicate a non-significant association. Errors bars indicate 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) for the respective odds ratio (OR). Dashed horizontal line indicates OR = 1.00 (null results).
3.5 BFR and immune pathways
Elevated levels of BDE47 (quartiles) were associated with the B cell activation pathway (ORquartile 4 = 1.59, 95% CI = 1.06–2.39) (Table 3). Consistent with associations with individual cytokines, there were no associations present between BDE153 and any of the immune pathways. We also observed no consistent trends or major associations between PBB153 with any immune pathway.
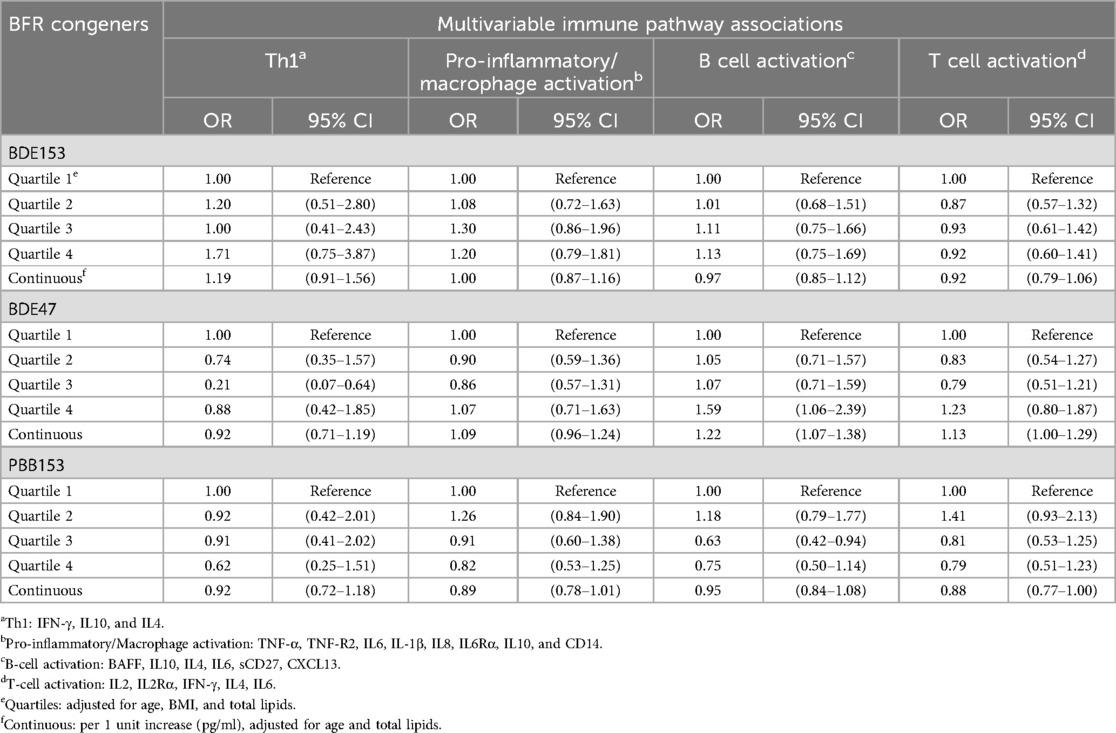
Table 3. Multivariable logistic and continuous models of the association of immune pathways and log-transformed BFR congeners for the participants (N = 813) in the California teachers study who had a serum sample, cytokines measured and BFR congeners measured from 2013 to 2016.
4 Discussion
In our evaluation of 813 participants from the California Teacher Study whose sera was collected between 2013 and 2016 and measured for 11 BFR congeners and 16 circulating immune/inflammation markers, we found: (1) positive associations between BDE47 exposure and elevated levels of sCD27, IL6, and BAFF, (2) inverse associations between PBB153 exposure and sCD27 and IL6 but positive associations with CXCL13, and (3) no associations between BDE153 exposure and any immune marker evaluated. To clarify the complexities of the associations between participant characteristics, immune markers and BFR congeners, a directed acyclic graph (DAG) is presented in Figure 2.
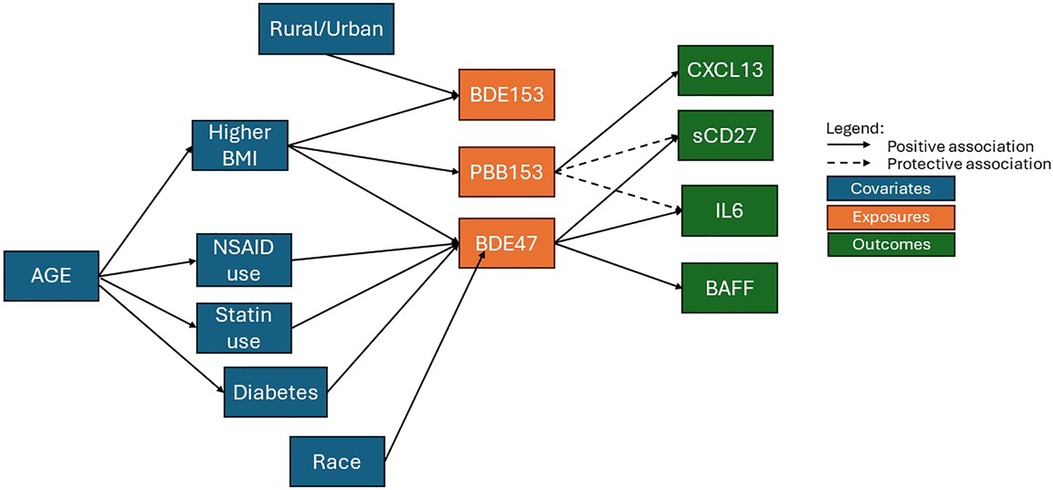
Figure 2. A directed acyclic graph (DAG) representing the complex associations between participant characteristics, immune markers, and BFR congeners.
The lipid-adjusted means and medians for BDE153, BDE47 and PBB153 appear relatively similar to prior reports in human population samples; however, we note that corresponding values from our older population of women were higher than national sampling data from the NHANES study in White non-Hispanic women (ages 16–49 years old) (4, 6). Compared to comparable age- and sex-matched data, our population exposure levels were relatively higher than those presented in NHANES data from 2013 to 2015 (Supplementary Table S5). This is expected as California populations have previously been shown to possess higher levels of BFR congeners and PBDE levels when compared to the national averages (4, 12, 33).
Our evaluation of participant characteristics and BFR congener exposure adds substantively to the current literature. Specifically, our results support the positive association observed between non-White races with elevated levels of BDE47 (4, 31, 32). Sjodin et al. (2008) previously reported non-Hispanic Black and Mexican Americans having higher levels of BFR congeners than non-Hispanic Whites, although this may be attributable to oversampling of the NHANES data for these demographic groups (4). The positive association between higher levels of BMI and BDE47 exposure also supports findings previously reported in several studies (31, 32). The association reported in our study of higher levels of BMI and decreased levels of PBB153 have also been previously suggested in a study measuring PBB exposure in 861 chemical workers, farmers and community members (ages 7–88) in Michigan, United States between 2012 and 2015, though these results were not statistically significant (29). Additionally, none of the population characteristics included in our study were associated with the total lipid variable included in the multivariable models. BFR congeners are commonly produced and used within commercial mixtures, thus congeners are typically correlated. Within our data, we report no notable correlations between BDE153, BDE47, and/or PBB153.
Our data illustrate positive associations between increasing BDE47 exposure and elevated circulating levels of IL6, sCD27, and BAFF. As markers of B-cell activation, their elevation with BDE47 exposure support a potential link between BDE47 and health conditions associated with B-cell activation, such as autoimmune conditions (34). Efforts to delineate if exposure to BDE47 that generates an inflammatory environment that provides an environment triggering the onset of autoimmune conditions are warranted.
Our reported association between BDE47 and IL6 supports prior reports from a number of in vivo and in vitro studies (15–17, 19, 35). In an in vivo study where 24 mice were orally exposed to varied levels (0, 1, 10, 100 mg/kg body weight) of BDE47 via gastric infusion, BDE47 exposure increased the gene expression of IL6 measured by quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) (17). An in vitro study that utilized human bronchial epithelial cells exposed to 0.01–10 μg/ml of PBDE congeners for 24 h also assessed levels of IL6 via enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and found that c-pentaBDE and c-octaBDE both increased IL6 levels (19). Notably, one component of c-pentaBDE is BDE47, and c-octaBDE is composed in part by c-pentaBDE. The association between BDE47 and elevated IL6 has also been suggested in one population study of 103 pregnant women in California, United States between 2011 and 2013, though the association was not statistically significant (5). We note inconsistency in the prior literature among the in vivo and in vitro studies (15, 16, 35) and suggest that differences in methodologies of administering exposure and their measurements may contribute to these inconsistencies. Notably, our population-based study measures circulating immune markers vs. specific target tissues as measured in prior in vitro and in vivo studies. To our knowledge, associations between BDE47 exposure and increased levels of sCD27 and BAFF, which are both B-cell activation markers, have not been previously reported in epidemiology-based or in vitro/in vivo studies and thus require further confirmation in all study types. In analyses of immune pathways, we observed associations between elevated BDE47 levels and the B-cell activation pathway, consistent with the robust associations between BDE47 and individual cytokines in the pathway (i.e., BAFF and sCD27).
Our data also yielded associations between elevated levels of PBB153 with elevated CXCL13, decreased levels of IL6 and decreased levels of sCD27, the latter of which are notably the opposite association observed for BDE47. Additionally, the inverse association is robust in both multivariable models that adjust for BDE47 and in stratified models whereby associations are evaluated by BDE47 strata. To date, the association between higher levels of PBB153 with higher levels of CXCL13 and lower levels of sCD27 have not been previously reported in epidemiology-based studies or in vivo/in vitro studies. An association between PBB153 exposure and IL6 levels has only been reported in one in vitro study, though Arita et al. reported the opposite (i.e., increased) levels of IL6 when human placenta cells were exposed to 20 uM of PBB153 (15). While we cannot rule out differences in methodologies in the sparse but inconsistent results across study designs, the potential novel associations warrant replication and further investigation.
Participant characteristics were also interrogated as they, too, were associated with immune markers and in some cases, congeners. We note, however, that characteristics such as statin use, BMI, and diabetes were also associated with increasing age. Indeed, the addition of most characteristics beyond age did not affect the resulting risk estimates. Nevertheless, we further conducted stratified analyses and demonstrated that associations between BDE47 and the main immune markers of interest (sCD27, IL6, and BAFF) were consistent by strata where possible. Finally, we note that there is precedence for varying associations observed for each congener. In addition to the congeners not being correlated in our study, and despite their similarities in chemical structure, there is growing data demonstrating adverse health outcomes resulting from different toxicological pathways and mechanisms (e.g., BDE153 has been shown to impact lipid metabolism, and BDE47 has been associated with increased risk for type 2 diabetes and fatty acid alterations in the liver) (7).
Our study is among the only large epidemiologic studies that have investigated the associations between a wide number of BFR congeners and circulating immune marker levels. Notably, our study population reflects a population with a high exposure prevalence, making it an ideal population for investigating associations with BFR congeners. Our study strengths include our large sample size, the use of a large cohort population subset, the high quality of our biospecimens which were all processed within 28 h and exhibited low pre-analytical variability (over 99.5% protocol compliance), and the use of several multiplex immune marker assays. Limitations to our study include the use of an all-women cohort, thus minimizing the generalizability of the study, and the cross-sectional nature of our study which may not fully capture variance in circulating immune markers. Although an all-female cohort may restrict generalizability, there is value in studying these associations between BFR exposure and immune markers in women due to declining immune response with age and due to the overall susceptibility women have for developing autoimmune conditions compared to men (20). The observed risk emphasizes the need to further investigate the immune-related biological pathways that BFR can negatively impact, especially in women. Although BFR congener exposure can also occur via dietary intake (3), and such data would have complemented our analyses, the measurement of BFR in circulating blood does reflect a snapshot of a person's exposure from multiple sources, including diet. Finally, we cannot exclude the possibility that these results may be due to chance; our study integrates multiple comparisons and the hypotheses generated from our data requires replication. In addition to replicating our data, future research should incorporate mechanistic studies to expand the findings reported here. Importantly, future efforts to understand the functional relevance of common combinations of BFRs on immune responses are needed.
5 Conclusions
In summary, our data show that measurable BFR congeners, specifically BDE47 and PBB153, are associated with specific circulating immune markers, and that these associations differ by BFR congener. Given their pervasiveness, understanding how BFR exposures and specific congeners may contribute to health endpoints is critical, and our results suggest a role in immune alterations as part of this process. Our results add to prior in vivo and in vitro studies that have reported potential associations with immune markers with BFR congener exposure; however, expanded human and epidemiologic studies are needed to confirm our novel results, and to compare the biological effects between congeners with relatively similar chemical structures (BDE153 vs. PBB153).
Data availability statement
All data associated with this publication are available for research use. The California Teachers Study welcomes all inquiries (https://www.calteachersstudy.org/for-researchers). Additionally, the PFAS analyte dataset presented in this study can be found in the online Human Health Exposure Analysis Resource data repository (https://hhearprogram.org/data-services). Data associated with this publication are also publicly available through the Human Health Exposure Analysis Resource (HHEAR) Data Center (https://hheardatacenter.mssm.edu/).
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Institutional Review Board of City of Hope. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
EC: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. PeR: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. ME: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. PD: Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Methodology. LM: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. DB: Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Methodology. PrR: Investigation, Writing – review & editing, Methodology. JV: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. OM: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. DG: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. ES: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. JL: Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing. SW: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Software, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The California Teachers Study and the research reported in this publication were supported by the National Cancer Institute of the National Institutes of Health under award number R01-CA207020; NIEHS HHEAR project #2020-00496; U01-CA199277; P30-CA033572; P30-CA023100; UM1-CA164917; and R01-CA077398. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Cancer Institute or the National Institutes of Health. The collection of cancer incidence data used in the California Teachers Study was supported by the California Department of Public Health pursuant to California Health and Safety Code Section 103885; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention's National Program of Cancer Registries, under cooperative agreement 5NU58DP006344; the 3 National Cancer Institute's Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results Program under contract HHSN261201800032I awarded to the University of California, San Francisco, contract HHSN261201800015I awarded to the University of Southern California, and contract HHSN261201800009I awarded to the Public Health Institute. The opinions, findings, and conclusions expressed herein are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the official views of the State of California, Department of Public Health, the National Cancer Institute, the National Institutes of Health, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention or their Contractors and Subcontractors, or the Regents of the University of California, or any of its programs. Lastly, laboratory analysis for this work was supported in part by funding from the National Institutes of Health (NIH)/National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS) under award no. U2CES026561.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the women who have contributed their invaluable time and information towards participating in the California Teachers Study to further our understanding of cancer and women's health. The authors also acknowledge the sustained contributions of the California Teachers Study Steering Committee that is responsible for the formation and maintenance of the Study within which this research was conducted. A full list of California Teachers Study team members is available at https://www.calteachersstudy.org/team. We gratefully also acknowledge Dr. Robert O. Wright and Dr. Mary S. Wolff (Department of Environmental Medicine and Climate Science at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai) for the supervision and consultation for the laboratory analysis.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fepid.2025.1452934/full#supplementary-material
References
1. (EPA) USEPA. Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers (PBDEs). Available at: https://www.epa.gov/assessing-and-managing-chemicals-under-tsca/polybrominated-diphenyl-ethers-pbdes (Accessed March 02, 2025).
2. Prevention CfDCa. Biomonitoring Summary Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers and 2,2′,4,4′,5,5′-Hexabromobiphenyl (BB-153) (2017). Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/biomonitoring/PBDEs_BiomonitoringSummary.html (Accessed March 02, 2025).
3. Kodavanti PRS, Stoker TE, Fenton SE, Curras-Collazo M. Chapter 36—Brominated flame retardants. In: Gupta RC, editor. Reproductive and Developmental Toxicology, 3rd ed. Orlando, FL: Academic Press (2022). p. 691–726.
4. Sjodin A, Wong LY, Jones RS, Park A, Zhang Y, Hodge C, et al. Serum concentrations of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) and polybrominated biphenyl (PBB) in the United States population: 2003–2004. Environ Sci Technol. (2008) 42(4):1377–84. doi: 10.1021/es702451p
5. Zota AR, Geller RJ, Romano LE, Coleman-Phox K, Adler NE, Parry E, et al. Association between persistent endocrine-disrupting chemicals (PBDEs, OH-PBDEs, PCBs, and PFASs) and biomarkers of inflammation and cellular aging during pregnancy and postpartum. Environ Int. (2018) 115:9–20. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2018.02.044
6. (EPA) USEPA. America's Children and the Environment. 3rd ed. Washington, DC: Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) (2013).
7. Renzelli V, Gallo M, Morviducci L, Marino G, Ragni A, Tuveri E, et al. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) and human health: effects on metabolism, diabetes and cancer. Cancers. (2023) 15(17):4237. doi: 10.3390/cancers15174237
8. Zota AR, Park JS, Wang Y, Petreas M, Zoeller RT, Woodruff TJ. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers, hydroxylated polybrominated diphenyl ethers, and measures of thyroid function in second trimester pregnant women in California. Environ Sci Technol. (2011) 45(18):7896–905. doi: 10.1021/es200422b
9. Vuong AM, Braun JM, Webster GM, Thomas Zoeller R, Hoofnagle AN, Sjodin A, et al. Polybrominated diphenyl ether (PBDE) exposures and thyroid hormones in children at age 3 years. Environ Int. (2018) 117:339–47. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2018.05.019
10. Han L, Wang Q. Associations of brominated flame retardants exposure with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a US population-based cross-sectional analysis. Front Public Health. (2023) 11:1138811. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1138811
11. Hartley K, MacDougall MC, Terrizzi B, Xu Y, Cecil KM, Chen A, et al. Gestational exposure to polybrominated diphenyl ethers and social skills and problem behaviors in adolescents: the HOME study. Environ Int. (2022) 159:107036. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2021.107036
12. Wu X, Bennett DH, Moran RE, Sjödin A, Jones RS, Tancredi DJ, et al. Polybrominated diphenyl ether serum concentrations in a Californian population of children, their parents, and older adults: an exposure assessment study. Environ Health. (2015) 14(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s12940-015-0002-2
13. Lam J, Lanphear BP, Bellinger D, Axelrad DA, McPartland J, Sutton P, et al. Developmental pbde exposure and IQ/ADHD in childhood: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ Health Perspect. (2017) 125(8):086001. doi: 10.1289/EHP1632
14. Liu Z, Lu Y, Zhong K, Wang C, Xu X. The associations between endocrine disrupting chemicals and markers of inflammation and immune responses: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. (2022) 234:113382. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.113382
15. Arita Y, Yeh C, Thoma T, Getahun D, Menon R, Peltier MR. Effect of polybrominated diphenyl ether congeners on placental cytokine production. J Reprod Immunol. (2018) 125:72–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jri.2017.12.002
16. Xue D, Wei J, Lu W, Xia B, Li S, Liu D, et al. BDE-47 disturbs the immune response of lymphocytes to LPS by downregulating NF-kappaB pathway. Chemosphere. (2022) 308(Pt 3):136562. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.136562
17. Wei J, Li X, Xiang L, Song Y, Liu Y, Jiang Y, et al. Metabolomics and lipidomics study unveils the impact of polybrominated diphenyl ether-47 on breast cancer mice. J Hazard Mater. (2020) 390:121451. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121451
18. Longo V, Longo A, Di Sano C, Cigna D, Cibella F, Di Felice G, et al. In vitro exposure to 2,2′,4,4′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether (PBDE-47) impairs innate inflammatory response. Chemosphere. (2019) 219:845–54. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.12.082
19. Koike E, Yanagisawa R, Takigami H, Takano H. Penta- and octa-bromodiphenyl ethers promote proinflammatory protein expression in human bronchial epithelial cells in vitro. Toxicol in Vitro. (2014) 28(2):327–33. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2013.10.014
20. Kronzer VL, Bridges S Jr, Davis J 3rd. Why women have more autoimmune diseases than men: an evolutionary perspective. Evol Appl. (2021) 14(3):629–33. doi: 10.1111/eva.13167
21. Bernstein L, Allen M, Anton-Culver H, Deapen D, Horn-Ross PL, Peel D, et al. High breast cancer incidence rates among California teachers: results from the California teachers study (United States). Cancer Causes Control. (2002) 13(7):625–35. doi: 10.1023/A:1019552126105
22. Wang SS, Zhong C, Epeldegui M, Nunes S, Magpantay L, DeHart JC, et al. Host characteristics associated with serologic inflammatory biomarkers in women. Cytokine. (2022) 149:155726. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2021.155726
23. Cauble EL, Reynolds P, Epeldegui M, Andra SS, Magpantay L, Narasimhan S, et al. Associations between per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substance (PFAS) exposure and immune responses among women in the California Teachers study: a cross-sectional evaluation. Cytokine. (2024) 184:156753. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2024.156753
24. Hovander L, Athanasiadou M, Asplund L, Jensen S, Wehler EK. Extraction and cleanup methods for analysis of phenolic and neutral organohalogens in plasma. J Anal Toxicol. (2000) 24(8):696–703. doi: 10.1093/jat/24.8.696
25. (EPA) USEPA. Method 1614A Brominated Diphenyl Ethers in Water, Soil, Sediment, and Tissue by HRGC/HRMS. (2010).
26. Sjodin A, Jones RS, Lapeza CR, Focant JF, McGahee EE 3rd, Patterson DG Jr. Semiautomated high-throughput extraction and cleanup method for the measurement of polybrominated diphenyl ethers, polybrominated biphenyls, and polychlorinated biphenyls in human serum. Anal Chem. (2004) 76(7):1921–7. doi: 10.1021/ac030381/
27. Hurley S, Goldberg D, Park JS, Petreas M, Bernstein L, Anton-Culver H, et al. A breast cancer case-control study of polybrominated diphenyl ether (PBDE) serum levels among California women. Environ Int. (2019) 127:412–9. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2019.03.043
28. Mancini FR, Cano-Sancho G, Mohamed O, Cervenka I, Omichessan H, Marchand P, et al. Plasma concentration of brominated flame retardants and postmenopausal breast cancer risk: a nested case-control study in the French E3N cohort. Environ Health. (2020) 19(1):54. doi: 10.1186/s12940-020-00607-9
29. Chang CJ, Terrell ML, Marcus M, Marder ME, Panuwet P, Ryan PB, et al. Serum concentrations of polybrominated biphenyls (PBBs), polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in the Michigan PBB registry 40 years after the PBB contamination incident. Environ Int. (2020) 137:105526. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2020.105526
30. Lacey JV Jr, Chung NT, Hughes P, Benbow JL, Duffy C, Savage KE, et al. Insights from adopting a data commons approach for large-scale observational cohort studies: the California teachers study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. (2020) 29(4):777–86. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-19-0842
31. Horton MK, Bousleiman S, Jones R, Sjodin A, Liu X, Whyatt R, et al. Predictors of serum concentrations of polybrominated flame retardants among healthy pregnant women in an urban environment: a cross-sectional study. Environ Health. (2013) 12:23. doi: 10.1186/1476-069X-12-23
32. Mehta SS, Applebaum KM, James-Todd T, Coleman-Phox K, Adler N, Laraia B, et al. Associations between sociodemographic characteristics and exposures to PBDEs, OH-PBDEs, PCBs, and PFASs in a diverse, overweight population of pregnant women. J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol. (2020) 30(1):42–55. doi: 10.1038/s41370-019-0173-y
33. Zota AR, Rudel RA, Morello-Frosch RA, Brody JG. Elevated house dust and Serum concentrations of PBDEs in California: unintended consequences of furniture flammability standards? Environ Sci Technol. (2008) 42(21):8158–64. doi: 10.1021/es801792z
34. Ishihara K, Hirano T. IL-6 in autoimmune disease and chronic inflammatory proliferative disease. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. (2002) 13(4–5):357–68. doi: 10.1016/S1359-6101(02)00027-8
Keywords: brominated flame retardants (BFRs), polybrominated diphenyl ether (PBDE) congeners, cytokines, immune responses, inflammatory markers, women, human population
Citation: Cauble EL, Reynolds P, Epeldegui M, Dassanayake PS, Magpantay L, Blyakher D, Regmi P, Von Behren J, Martinez-Maza O, Goldberg D, Spielfogel ES, Lacey JV Jr and Wang SS (2025) Associations between brominated flame retardants, including polybrominated diphenyl ethers, and immune responses among women in the California Teachers Study. Front. Epidemiol. 5:1452934. doi: 10.3389/fepid.2025.1452934
Received: 21 June 2024; Accepted: 28 February 2025;
Published: 19 March 2025.
Edited by:
Glinda Cooper, Retired, Washington DC, United StatesReviewed by:
Emily C. Somers, University of Michigan, United StatesRuthann Rudel, Silent Spring Institute, United States
Copyright: © 2025 Cauble, Reynolds, Epeldegui, Dassanayake, Magpantay, Blyakher, Regmi, Von Behren, Martinez-Maza, Goldberg, Spielfogel, Lacey and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Sophia S. Wang, c293YW5nQGNvaC5vcmc=
 Emily L. Cauble
Emily L. Cauble Peggy Reynolds2
Peggy Reynolds2 Marta Epeldegui
Marta Epeldegui Daniel Blyakher
Daniel Blyakher Julie Von Behren
Julie Von Behren Otoniel Martinez-Maza
Otoniel Martinez-Maza Sophia S. Wang
Sophia S. Wang