- 1Department of Medical Laboratory Sciences, College of Medicine and Health Science, Adigrat University, Adigrat, Ethiopia
- 2School of Medical Laboratory Sciences, College of Health and Medical Sciences, Haramaya University, Harar, Ethiopia
Background: Chronic kidney disease (CKD) has a significant impact on public health with a high morbidity and death rate. Most diabetic patients, in the course of their lives, develop diabetic kidney disease. In the least developed nations, its size is outstripping itself. This study aimed to determine the prevalence of chronic kidney disease and associated factors among adult diabetic patients.
Methods: A hospital-based cross-sectional study was conducted on 328 adult diabetic patients from 1 December 2023 to 4 April 2024 at the Ayder Comprehensive Specialized Hospital, northern Ethiopia. A systematic random sampling method was utilized to select the study participants. Pretested structured questionnaires were used to collect sociodemographic, economic, and behavioral/lifestyle factors. Medical records were also reviewed to collect clinical data. Creatinine analysis was performed by kinetic alkaline picrate method and Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration 2021 equation was used to calculate the glomerular filtration rate from the serum creatinine, age, and sex. Proteinuria was determined by using the dipstick semiquantitative method. Data were entered and analyzed using SPSS version 29. A variable with a p-value of <0.25 in bivariate logistic regression analyses was analyzed in multivariate logistic regression to identify the associated factors. In multivariable logistic regression, a variable was deemed statistically significant if it had a p-value <0.05. Associations were presented as odds ratio (OR) along with 95% confidence intervals (CIs).
Results: The prevalence of chronic kidney diseases in adult diabetic patients was 26.5% (95% CI, 21.8%–31.7%). About 5.2%, 12.5%, 7.3%, 0.9%, and 0.6% had stage 1–5 chronic kidney diseases, respectively. Hypertension [adjusted OR (AOR) = 2.390; 95% CI, 1.394–4.099, p = 0.002], >10-year duration of diabetes (AOR = 2.585; 95% CI, 2.321–5.807; p = 0.001), and family history of kidney diseases (AOR = 2.884; 95% CI, 1.338–6.218; p = 0.007) were associated factors of chronic kidney diseases.
Conclusions: The study revealed that one in four diabetic patients had chronic kidney disease. Special attention should be given to patients with family history of CKD, long duration on diabetes, and concomitant hypertension.
Introduction
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a condition where there are abnormal alterations in the functioning or structure of the kidneys. This is indicated by a glomerular filtration rate (GFR) that is below 60 ml/min/1.73 m2 or the presence of proteinuria, or both, for a duration of more than 3 months (1). According to the guidelines of the Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes, CKD is classified into five stages. Individuals with an estimated GFR (eGFR) of ≥90 ml/min/1.73 m2 are grouped into stage 1 with a normal kidney function. The second stage is when eGFR is 60–89 ml/min/1.73 m2 with a mild decrease in kidney function. The third stage is separated into two categories: stage 3a (eGFR 45–59 ml/min/1.73 m2) and stage 3b (eGFR 30–44 ml/min/1.73 m2). The fourth stage of CKD occurs when the eGFR drops to 15–29 ml/min/1.73 m2, and the final stage occurs when the GFR falls below 15 ml/min/1.73 m2 (2).
Most diabetic patients will eventually develop diabetic kidney disease (DKD) (3). The pathophysiology of DKD is multifactorial and involves several key mechanisms. Hyperglycemia is the primary cause of DKD. High blood sugar levels directly damage the kidneys’ filtering system over time. Altered tubuloglomerular feedback, renal hypoxia, and activation of the renin–angiotensin system contribute to the hemodynamic changes. Hyperglycemia also triggers inflammation, with increased levels of cytokines, chemokines, oxidative stress, and advanced glycation end-products also playing a role in DKD pathogenesis (4–7).
Diabetes and elevated blood pressure are the most frequent causes of CKD in most adults. Heart disease, a family history of CKD, having inherited renal problems, past kidney injury, being older, and being obese are additional risk factors for CKD (8).
Chronic kidney disease affects more than 10% of the world's population. The disease was ranked 16th among the major causes of death in 2016, and it is anticipated to rise to 5th by 2040 (9). It is estimated that 850 million people worldwide suffer from kidney disease, with the majority residing in lower middle income and low income countries. Globally, CKD resulted in approximately 3.16 million deaths and 76.5 million disability-adjusted life years (10).
In Ethiopia, CKD is also a major public health problem (11) with prevalence ranges from 9.3% to 25.9% in diabetes mellitus (DM) patients (12). Most of the studies on CKD were modification of diet in renal disease (MDRD) and Cockcroft–Gault equations to estimate GFR (13–15). However, the Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI) equation is known to have the highest accuracy in estimating GFR and is currently recommended for use to estimate GFR by Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) clinical practice guidelines (2). Thus, this study was conducted to determine the prevalence of CKD using the CKD-EPI equation and to identify associated factors among diabetic patients.
Methods and materials
Study design, area, and period
A hospital-based cross-sectional study was conducted at Ayder Comprehensive Specialized Hospital from 1 December 2023 to 4 April 2024. The hospital is located in Mekelle, in the Tigray Region, 783 km north of Addis Ababa, Ethiopia's capital. The hospital has more than 500 inpatient beds with 36 Intensive care units and more than 3,600 employees in 2022. It offers a wide range of medical treatments, such as dialysis, cancer treatment, and neonatal care, to both inpatients and outpatients of all ages. In addition, it acts as a research and teaching hospital for medicine and other health sciences. During the time of data collection, there were about 2,300 diabetic patients receiving care at the hospital's diabetic clinic.
Study population
The study included adult patients (≥18 years) who had been previously diagnosed with diabetes mellitus and attended the hospital's follow-up diabetes clinic during the study period. Patients with diabetes who were pregnant, critically ill, had incomplete clinical and laboratory data, or had a short follow-up period (<6 months) were not included in the study.
Sample size determination
A minimum sample size of 328 was determined using a single population proportion formula, n = 1/d2 × [(Zα/2)2 × P (1 − P)], where n is the sample size, Z = 1.96 [95% confidence interval (CI)], P = 0.263, the proportion of chronic kidney disease among DM patients from a previous study (15), and d is the assumed margin of error (5%), and a 10% non-response rate was considering. Sample size was also calculated for selected variables and found to be below 328.
Sampling procedure
According to the hospital report, 2,300 diabetic patients were in regular follow-up at the diabetic clinic. By taking their medical registration book as a sampling frame, interval size (k) was calculated by dividing the total number of diabetic patients on a follow-up by the desired sample size (i.e., k = 2,300/328 = 7). By using a systematic random sampling method, the participants were selected every 7 intervals from the list of medical registration book. If the kth or selected patients were not willing to participate in the study or did not fulfill the inclusion criteria, the next diabetic patient was recruited to the study.
Data collection and laboratory measurements
Data on sociodemographic, economic, and behavioral/lifestyle factors were collected using pretested, structured questionnaires. Medical records of the patients were also reviewed for clinical history including types of DM, blood glucose levels, and a history of hypertension. The average blood pressure and blood glucose over the previous 3 months were utilized to calculate the participants’ blood pressure and glycemic status.
Blood pressure measurements were carried out using a manual sphygmomanometer after patients had been comfortably resting for at least 5 min. About 5 ml of venous blood specimens were drawn and processed, and the serum was separated for biochemical analysis. Serum creatinine analysis was carried out using kinetic alkaline picrate method on the Cobas C311 clinical chemistry analyzer. Participants with abnormal creatinine measurements were checked again for persistence after 3 months.
Fresh 10 ml urine specimen was collected from each participant to detect proteinuria using dipsticks. Participants with positive proteinuria were reexamined for persistence after 3 months.
The eGFR was calculated by using the CKD-EPI 2021 equation (16):
where GFR is the glomerular filtration rate (ml/min/1.73 m2), min is the minimum of Scr/k or 1, max is the maximum of Scr/k or 1, Scr is the serum creatinine level (in mg/dl), k = 0.7 (females) or 0.9 (males), and α = −0.241 (females) and −0.302 (males).
Operational definitions
• Chronic kidney disease: having eGFR of less than 60 ml/min/1.73 m2 and/or proteinuria, for at least 3 months (1).
• Stages of CKD (1):
○ Stage 1: persistent proteinuria with eGFR ≥90 ml/min/1.73 m2
○ Stage 2: persistent proteinuria with eGFR of 60–89.9 ml/min/1.73 m2
○ Stage 3a: eGFR 45–59.9 ml/min/1.73 m2 with or without proteinuria
○ Stage 3b: eGFR 30–44.9 ml/min/1.73 m2 with or without proteinuria
○ Stage 4: eGFR 15–29.9 ml/min/1.73 m2 with or without proteinuria
○ Stage 5: eGFR <15 ml/min/1.73 m2 with or without proteinuria
• Proteinuria: Presence of protein in urine indicated by manual urine dipstick result of 1+ or above (approximately greater than 30 mg/dl).
• Regular physical activity: Any kind of movement performed in a regular way to make the body refresh and active. This includes walking, running, swimming, cycling, wheeling, and others. It was assessed by asking the participants, “how often do you engage in physical activity regularly per week?”
• Smoking habit: If the respondents had an act of inhaling and exhaling the fumes of burning plants or other chemicals. It was assessed by asking the participants, “did you smoke a cigarette or other chemicals currently?” and “did you smoke before?”
• Alcohol consumption: Act of drinking alcoholic fluids. Assessed by asking the participants, “did you consume alcohol currently?” and “did you consume alcohol before?”
• Alcohol ex-consumer: A participant who did not consume alcohol in the last 1 year but previously did that.
Data quality assurance
Data collectors and a supervisor received 1-day training on data collection instruments and study objectives to guarantee that the data quality was not compromised. Questionnaire was pretested using 5% of the total participants (17 patients) at the Mekelle General Hospital before data collection, and appropriate modifications were made. Close follow-up and supervision were carried out during the data collection period jointly by the first author and the supervisor. The collected data were reviewed and checked for its completeness before data entry. For creatinine analysis, the reaction was monitored every working shift by using both normal and pathological control samples. Quality control of the urine dipstick testing was also done in accordance with the standard operating procedure.
Statistical analysis
The data were entered into SPSS version 29 for analysis. A descriptive statistic was used to describe the study participants and relevant variables. The associations between chronic kidney disease and all above mentioned variables were evaluated in bivariable logistic regressions. Those variables that showed a p-value of 0.25 or smaller in these bivariable regressions were further included in a multivariable logistic regression model. The final multivariable model only included variables that were significantly associated based on p-values ≤0.05. Adjusted odds ratios (AORs) and 95% CIs are reported to measure the strength of the associations. Hosmer and Lemeshow goodness of fit was typically utilized to assess model fitness.
Results
Sociodemographic characteristics
A total of 328 adult diabetic patients participated in the study. Of them, 169 (51.5%) were in the age group of ≤45 years old, more than half [191 (58.2%)] were female, 243 (74.1%) were urban dwellers, 289 (88.1%) were ethnic Tigrayans, 241 (73.5%) were married, 125 (38.1%) had primary education, and 205 (62.5%) had less than 3,000 Ethiopian birr in monthly income (Table 1).
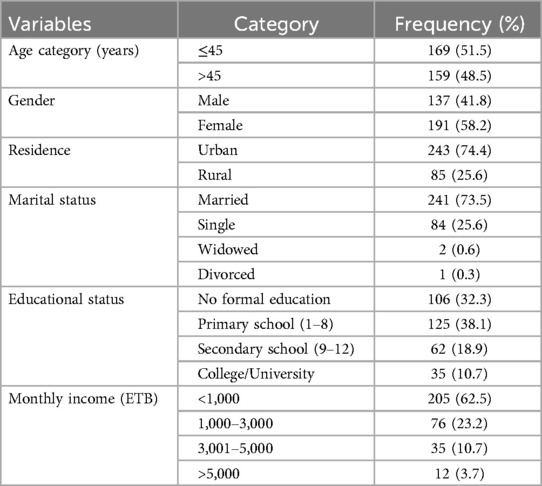
Table 1. Sociodemographic characteristics of diabetic patients at the Ayder Comprehensive Specialized Hospital, northern Ethiopia, 2024 (n = 328).
Clinical and behavioral characteristics
The proportion of patients with type 2 and type 1 diabetes mellitus was 181 (55.2%) and 147 (44.8%), respectively. Among the study participants, 97 (29.6%) had hypertension. The majority of the participants [200 (61%)] were classified as having normal BMI and 35 (10.7%) had family history of kidney disease.
Furthermore, 89 (27.1%) had a long duration of diabetes (>10 years), almost all [325 (99.1%)] never smoked, and 308 (93.9%) had no alcohol consumption habit. The majority [314 (95.7%)] had never engaged in regular physical exercise. About half of the participants 165 (50.3%) had normal systolic blood pressure (<120 mmHg), and the majority [239 (72.9%)] had normal diastolic blood pressure (60–79 mmHg) (Table 2).
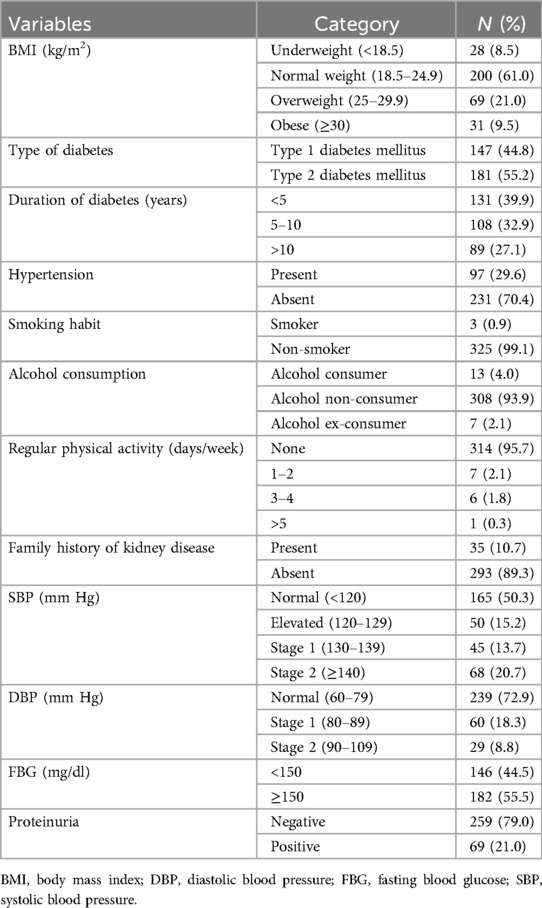
Table 2. Clinical and behavioral characteristics of diabetic patients attending at the Ayder Comprehensive Specialized Hospital, northern Ethiopia, 2024 (N = 328).
Prevalence and stages of chronic kidney diseases
The overall prevalence of CKD was 26.5% (95% CI: 21.8%–31.7%), of which, 29 (8.8%) had eGFR <60 ml/min/1.73 m2 and 69 (21%) had proteinuria. From the total patients with CKD (87), 17 (5.2%), 41 (12.5%), 24 (7.3%), 3 (0.9%), and 2 (0.6%) were categorized as stage 1–5, respectively.
From the total patients with CKD (87), 11 (13%) had both impaired GFR (<60 ml/min/1.73 m2) and proteinuria, 13 (14%) had only impaired GFR (eGFR < 60 ml/min/1.73 m2), and 63 (74%) had only proteinuria.
Factors associated with chronic kidney diseases among study participants
When it was analyzed with multivariate logistic regression, hypertension, >10 years duration of diabetes, and family history of kidney disease were independently associated factors for chronic kidney disease (p < 0.05).
Patients with concomitant hypertension were 2.390 (AOR = 2.390; 95% CI, 1.394–4.099; p = 0.002) times more likely to develop CKD compared with non-hypertensive patients. The odds of CKD was 2.585 (AOR = 2.585; 95% CI, 2.321–5.807; p = 0.001) times higher among patients who have had a longer (>10 years) duration of diabetes compared with patients having a short duration. Patients with a family history of kidney diseases were 2.884 (AOR = 2.884; 95% CI, 1.338–6.218; p = 0.007) times more likely to have CKD than having no family history of kidney diseases (Table 3).
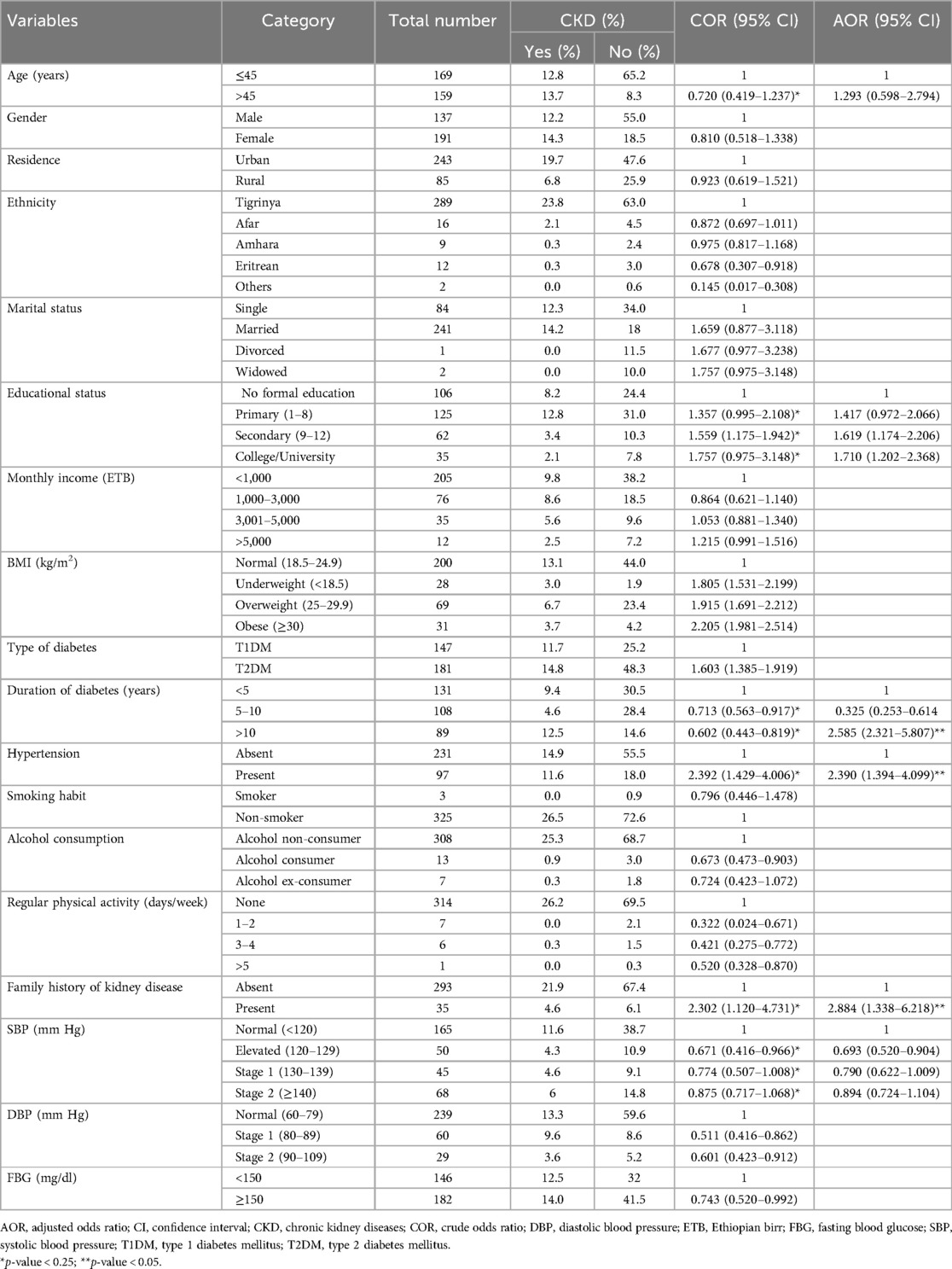
Table 3. Bivariate and multivariate logistic regression analysis of factors associated with chronic kidney disease among adult diabetic mellitus patients at the Ayder Comprehensive Specialized Hospital, northern Ethiopia, 2024 (n = 328).
Discussion
This study showed that 26.5% of patients with diabetes mellitus had CKD. Factors found to be associated with CKD in a multivariable logistic regression model were hypertension, longer duration on diabetes, and having a family history of chronic kidney diseases.
The finding of this investigation is consistent with the prevalence of CKD among diabetic patients in Northeast Ethiopia, which was reported to be 26.3% (15). In addition, the prevalence is in line with studies conducted in Northern Thailand (24.4%) (17), but pooled prevalence was observed in Africa (24.7%) (18) and the Middle East region (28.96%) (19). In comparison to earlier studies carried out in Ethiopia, the current study's result was higher: 16.7% in Bahir Dar (20), 14.3% in Gondar (21), 2.7% in Jinka (22), and 18.2% in Butajira (13). The observed discrepancies could be caused by differences in the eGFR calculation equation and the criteria used to define CKD. In contrary, the result of our study was lower than the prevalence in Southwest Nigeria (39.8%) (23). Differences in study setting, sample size, and ethnicity may have contributed to the observed discrepancies. The study also used a more sensitive method to detect albuminuria, which aided in identifying more cases.
In our study, concomitant hypertension was independently associated with the presence of CKD (p = 0.002). Among 97 diabetes patients with hypertension, 39.18% had CKD, and it was 2.390 times more likely to have CKD as compared with diabetic patients without hypertension. This is consistent with other related studies that showed hypertension was an associated factor for CKD in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (24, 25). Hypertension can cause the arteries surrounding the kidneys to narrow, weaken, and harden. These damaged arteries are unable to send sufficient blood to the renal tissue. As a result, blood pressure regulation is a vital and critical component in avoiding and slowing the advancement of chronic kidney disease.
Duration of diabetes >10 years was independently associated with the development of CKD (p = 0.001). Among 89 patients who have had long duration of diabetes (>10 years), 46% developed CKD. Our study findings were consistent with others in this regard (13–15). Evidence indicated that having diabetes for a long time leads to a buildup of advanced glycation end-products, which play a role in causing diabetic kidney problems and other microvascular disorders (26). In another way, as the disease progress over time, β-cell function and insulin secretion decrease. This in turn facilitates for the advancement of CKD among the patients (12).
In addition, the family history of CKD was independently associated with CKD (p = 0.007) in which the odds of developing CKD among the study participants were 2.884 times increased as compared to no family history of kidney diseases. Thus, this finding reveals that the family history of kidney disease may be useful for early identification of individuals at high risk of CKD. Our study is in line with the study conducted among diabetic patients in a tertiary hospital of Nepal (25) and Southern Ethiopia (13). As described in a study conducted among Koreans, higher risk of kidney disease with an affected family member indicates that shared environment and shared genes likely contribute to kidney disease (27).
Limitations of the study
Our study had a number of limitations. First, since it was a facility-based study, it might not reflect the true prevalence of CKD in patients with diabetes in the community. Second, we used a cross-sectional study design. Therefore, we could not establish any causal relationship between CKD and its risk factors. This study, therefore, proposes that a longitudinal study with representative samples from health facilities and communities should be conducted to provide up-to-date data for policymakers and program planners. Furthermore, we considered a descriptive multivariable modeling approach without considering the causal dependencies between the variables in the model. Third, even though albumin creatinine ratio is a stronger indicator of CKD, we assessed proteinuria using semiquantitative methods (dipstick), which may affect the reliability of the results due to its low specificity and sensitivity. Another limitation of our study is that we used average blood glucose over 3 months, and this might not represent the true glycemic status. HbA1c would have been a better option to assess glycemic control. Hence, the results should be interpreted with caution.
Conclusion
The study revealed that one in four diabetic patients had chronic kidney disease. Routine CKD screening should be implemented in patients with diabetes for early detection and delayed progression of CKD. Special attention should be given to patients with a family history of CKD, long duration on diabetes, and concomitant hypertension.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Haramaya University College of Health and Medical Sciences, Institutional Health Research Ethics Review Committee (IHRERC). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
KA: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing, Project administration. GKM: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. RB: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Data curation, Project administration, Resources, Software, Validation, Visualization. WK: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was funded by the Haramaya University.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank all the study participants for their willingness to take part in this study and to the data collectors for their dedicated efforts to gather and organize the relevant data, ensuring its correctness and reliability during the time of data collection.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fepid.2024.1467911/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Levey AS, Eckardt KU, Tsukamoto Y, Levin A, Coresh J, Rossert J, et al. Definition and classification of chronic kidney disease: a position statement from kidney disease: improving global outcomes (KDIGO). Kidney Int. (2005) 67(6):2089–100. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-1755.2005.00365.x
2. Levin A, Stevens PE. Summary of KDIGO 2012 CKD guideline: behind the scenes, need for guidance, and a framework for moving forward. Kidney Int. (2014) 85(1):49–61. doi: 10.1038/ki.2013.444
3. Otieno FCF, Ogola EN, Kimando MW, Mutai K. The burden of unrecognized chronic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes at a county hospital clinic in Kenya: implications to care and need for screening. BMC Nephrol. (2020) 21(1):1–11. doi: 10.1186/s12882-020-1705-3
4. DeFronzo RA, Reeves WB, Awad AS. Pathophysiology of diabetic kidney disease: impact of SGLT2 inhibitors. Nat Rev Nephrol. (2021) 17(5):319–34. doi: 10.1038/s41581-021-00393-8
5. Kumar M, Dev S, Khalid MU, Siddenthi SM, Noman M, John C, et al. The bidirectional link between diabetes and kidney disease: mechanisms and management. Cureus. (2023) 15(9):1–13. doi: 10.7759/cureus.45615
6. Vallon V, Komers R. Pathophysiology of the diabetic kidney. Compr Physiol. (2011) 1(3):1175–232. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c100049
7. Khanijou V, Zafari N, Coughlan MT, MacIsaac RJ, Ekinci EI. Review of potential biomarkers of inflammation and kidney injury in diabetic kidney disease. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. (2022) 38(6):1–40. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.3556
8. Luyckx VA, Tuttle KR, Garcia-Garcia G, Gharbi MB, Heerspink HJL, Johnson DW, et al. Reducing major risk factors for chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int Suppl. (2017) 7(2):71–87. doi: 10.1016/j.kisu.2017.07.003
9. Elshahat S, Cockwell P, Maxwell AP, Griffin M, O'Brien T, O'Neill C. The impact of chronic kidney disease on developed countries from a health economics perspective: a systematic scoping review. PLoS One. (2020) 15(3):1–19. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0230512
10. Francis A, Harhay MN, Ong ACM, Tummalapalli SL, Ortiz A, Fogo AB, et al. Chronic kidney disease and the global public health agenda: an international consensus. Nat Rev Nephrol. (2024) 20(July):473–85. doi: 10.1038/s41581-024-00820-6
11. Kebede KM, Abateneh DD, Teferi MB, Asres A. Chronic kidney disease and associated factors among adult population in southwest Ethiopia. PLoS One. (2022) 17(3):1–19. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0264611
12. Tolossa T, Fetensa G, Regassa B, Yilma MT, Besho M, Fekadu G, et al. Burden and determinants of chronic kidney disease among diabetic patients in Ethiopia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Public Health Rev. (2021) 42(April):1–14. doi: 10.3389/phrs.2021.1603969
13. Fiseha T, Kassim M, Yemane T. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease and associated risk factors among diabetic patients in southern Ethiopia. Am J Health Res. (2014) 2(4):216–21. doi: 10.11648/j.ajhr.20140204.28
14. Damtie S, Biadgo B, Baynes HW, Melak T, Asmelash D, Abebe M. Chronic kidney disease and associated risk factors assessment among diabetes mellitus patients at a tertiary hospital, Northwest Ethiopia. Ethiop J Health Sci. (2018) 28(56):691–9. doi: 10.4314/ejhs.v28i6.3
15. Fiseha T, Tamir Z. Prevalence and awareness of chronic kidney disease among adult diabetic outpatients in Northeast Ethiopia. BMC Nephrol. (2020) 21(1):1–7. doi: 10.1186/s12882-020-01768-y
16. Inker LA, Eneanya ND, Coresh J, Tighiouart H, Wang D, Sang Y, et al. New creatinine- and cystatin C–based equations to estimate GFR without race. N Engl J Med. (2021) 385(19):1737–49. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2102953
17. Jitraknatee J, Ruengorn C, Nochaiwong S. Prevalence and risk factors of chronic kidney disease among type 2 diabetes patients: a cross-sectional study in primary care practice. Sci Rep. (2020) 10(1):1–10. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-63443-4
18. Elhafeez S A, Bolignano D, D'Arrigo G, Dounousi E, Tripepi G, Zoccali C. Prevalence and burden of chronic kidney disease among the general population and high-risk groups in Africa: a systematic review. BMJ Open. (2018) 8(1):1–32. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2016-015069
19. Naser AY, Alwafi H, Alotaibi B, Salawati E, Samannodi M, Alsairafi Z, et al. Prevalence of chronic kidney diseases in patients with diabetes mellitus in the Middle East: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Endocrinol. (2021) 2021:1–9. doi: 10.1155/2021/4572743
20. Tesfe D, Adugna M, Nigussie ZM, Woldeyohanins AE, Kifle ZD. The proportion of chronic kidney disease and its associated factors among adult diabetic patients at Tibebe Ghion Specialized Hospital, Bahir Dar, Ethiopia. Metab Open. (2022) 15(May):100198. doi: 10.1016/j.metop.2022.100198
21. Alemu H, Hailu W, Adane A. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease and associated factors among patients with diabetes in northwest Ethiopia: a hospital based cross-sectional study. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. (2020) 92:100578. doi: 10.1016/j.curtheres.2020.100578
22. Israel E, Borko UD, Mota K, Tesfaw M, Feleke T, Abraham A, et al. Out of sight: chronic kidney diseases among diabetic patients attending care and follow up. Findings from pastoralist health facilities of Southern Ethiopia. Front Public Health. (2024) 12:01–7. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1326011
23. Akpor OA, Adeoye AO, Ibitoba FA, Akpor OB. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease among diabetes and hypertensive patients in a teaching hospital in Ekiti State, southwest Nigeria. Open Public Health J. (2022) 15(1):1–13. doi: 10.2174/18749445-v15-e221220-2022-99
24. Islam SMS, Salehin M, Bin ZS, Tansi T, Das GR, Barua L, et al. Factors associated with chronic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes in Bangladesh. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2021) 18:12277. doi: 10.3390/ijerph182312277
25. Joshi R, Subedi P, Yadav GK, Khadka S, Rijal T, Amgain K, et al. Prevalence and risk factors of chronic kidney disease among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus at a tertiary care hospital in Nepal: a cross-sectional study. BMJ Open. (2023) 13:e067238. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-067238
26. Busch M, Franke S, Rüster C, Wolf G. Advanced glycation end-products and the kidney. Eur J Clin Invest. (2010) 40(8):742–55. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.2010.02317.x
Keywords: prevalence, chronic kidney disease, glomerular filtration rate, diabetes mellitus, Ethiopia
Citation: Aregawi K, Kabew Mekonnen G, Belete R and Kucha W (2024) Prevalence of chronic kidney disease and associated factors among adult diabetic patients: a hospital-based cross-sectional study. Front. Epidemiol. 4:1467911. doi: 10.3389/fepid.2024.1467911
Received: 21 July 2024; Accepted: 31 October 2024;
Published: 19 November 2024.
Edited by:
Susanne Strohmaier, Medical University of Vienna, AustriaReviewed by:
Queran Lin, Imperial College London, United KingdomJeremiah Laktabai, Moi University, Kenya
Copyright: © 2024 Aregawi, Kabew Mekonnen, Belete and Kucha. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Rebuma Belete, cmVidW1hLmJlbGV0ZTIwMTZAZ21haWwuY29t
 Kibrom Aregawi
Kibrom Aregawi Getachew Kabew Mekonnen
Getachew Kabew Mekonnen Rebuma Belete
Rebuma Belete Winner Kucha
Winner Kucha