
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
BRIEF RESEARCH REPORT article
Front. Environ. Sci., 31 March 2025
Sec. Environmental Economics and Management
Volume 13 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2025.1557902
This article is part of the Research TopicEnvironmental degradation, health, and socioeconomic impactsView all 7 articles
 Chao Li1,2*
Chao Li1,2* Liping Chen3*
Liping Chen3*Reducing carbon emissions is critical for addressing the challenges of climate change and represents an important step toward achieving the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). How to minimize disruptions to price levels within the economic system during the process of carbon reduction is an urgent issue that requires systematic investigation. In this paper, the nonlinear impact of carbon emissions on PPI (Producer Price Index) and CPI (Consumer Price Index) is deeply explored by using the Quantile-on-Quantile approach. In addition, the dynamic characteristics of this impact in the short-, middle- and long-term are systematically investigated through wavelet decomposition. It is found that, in general, there is significant heterogeneity in the impact of carbon emissions on PPI with the movement of the quantiles of the two factors. From a dynamic perspective, the impact of carbon emissions on PPI is not obvious in the short-term, shows a negative effect in the middle-term, and exhibits volatile effects in the-long term across different quantiles of PPI. In contrast, the effect of carbon emissions on CPI is relatively insignificant. However, in the middle-term and long-term, carbon emissions have negative effects on CPI within certain quantile intervals. Further analysis reveals that PPI exerts a positive impact on CPI, with this positive effect becoming more pronounced over time. These findings offer valuable insights for mitigating the disruptions caused by carbon reduction measures on production and consumer prices.
Climate change is widely recognized as one of the most significant challenges facing the world today (Chai et al., 2022). Greenhouse gas emissions, especially carbon emissions, have been identified as a major driver of global warming, receiving extensive attention worldwide in recent years (Hu et al., 2024). Excessive carbon emissions disrupt the natural balance in various ways, including reducing crop yields (Warsame and Abdi, 2022), diminishing vegetation diversity, and threatening ecological communities and the entire ecosystem (Kumar et al., 2022). These disruptions result in global climate change, manifesting in rising temperatures, decreasing salinity, and fluctuations in sea level (Martin, 2023). Carbon emissions also have profound implications for the economy. Wang C. et al. (2023) suggested that rising costs associated with higher carbon emissions directly stimulate technological innovation and increase related labor demand in high-carbon-emitting firms, thereby promoting low-carbon transformation of these firms and boosting employment. Zhang Y. et al. (2023), in their study on the income distribution effects of carbon pricing mechanisms, found that carbon pricing results in larger wage declines for rural labor compared to urban labor. Conversely, Zhou et al. (2022) demonstrated that carbon emissions negatively impact productivity development.
The international community has widely recognized the need to reduce carbon emissions, not only as a key to curbing global warming but also as a means to promote sustainable economic development (Wang X. et al., 2022). Many countries have committed to achieving carbon neutrality by 2050 (Wu et al., 2023) and implemented various policies to reduce emissions such as carbon tax and carbon emissions trading scheme (Zhu et al., 2023; Cui et al., 2024). However, the existing research has several limitations. First, the majority of studies have predominantly focused on the direct environmental benefits of carbon reduction, while there is a significant gap in understanding the disturbances to the economic system, especially the price transmission mechanism (Gan et al., 2024). As core indicators of the economic system, the stability of PPI and CPI is critical for the smooth functioning of the macroeconomy. However, the mechanisms through which policies such as carbon pricing and energy transition affect the price system through cost-push channels have not been systematically investigated. Second, traditional research methods are mostly based on linear framework and mean reversion, which are inadequate for capturing the complex, non-linear dynamic relationships between carbon emissions and price levels (Chevallier, 2010; Li et al., 2021). These theoretical gaps have led to serious policy dilemmas: policymakers are faced with the dual constraints of “rigidity in emission reduction” and “price stability”. Most existing studies rely on static analyses based on specific scenarios, which fail to capture the dynamic and evolving nature of the factors influencing the price system during the emission reduction process. For instance, changes in the energy structure and adjustments in the industrial structure exhibit significantly different impacts on the price system across various time scales. Existing studies mainly focus on carbon reduction measures, while the impacts and perturbations on the economic system during the carbon reduction process have not been systematically discussed. Therefore, it is necessary to explore the impact of carbon emissions on the economic system, especially on price indices. As essential tools for measuring the fluctuations in the price levels of goods and services over time, price indices are widely utilized to reflect inflation, deflation, and broader trends in economic activity. Among the most commonly referenced price indices are the PPI, CPI, Wholesale Price Index (WPI), and Import and Export Price Index. Specifically, the PPI measures changes in the prices of raw materials, semi-finished goods, and finished products acquired by producers during the production process. In contrast, the CPI tracks changes in the retail prices of goods and services closely tied to residents’ daily lives. The WPI measures the changes in the prices of goods in the wholesale market, including bulk commodities and raw materials. Meanwhile, the Import and Export Price Index measures fluctuations in the prices of imported and exported goods. Although numerous price indices exist, the PPI and CPI are the most widely utilized in macroeconomic analysis. They can respectively reflect the inflationary pressure from the consumption side and the production side (Aphane et al., 2024; Jatuporn, 2024). Due to their widespread application, the relevant data for the PPI and CPI are more readily accessible. Additionally, research findings based on these indices are more easily understood and accepted by other researchers and policymakers. Therefore, this article selects the PPI and CPI as the research objects.
Based on existing research gaps, understanding how to minimize the perturbation to the price level in the economic system during carbon reduction is of utmost importance. In this context, this paper aims to fill this research gap. We employ the Quantile-on-Quantile (Q-Q) approach based on wavelet decomposition to systematically study the nonlinear and dynamic effects of carbon emissions on PPI and CPI. Specifically, wavelet analysis is utilized to decompose the time series of carbon emissions and price indexes into ten scales. The scales ranging from 1 to 3 denote the short-term, the scales from 4 to 6 signify the middle-term, and the scales from 7 to 10 represent the long-term. Furthermore, the Q-Q approach is used to examine the heterogeneous effects of different quantiles and the dynamic impacts over the short-, middle- and long-term. By comparing the results of the Q-Q approach with those from the traditional quantile regression approach, the robustness of the findings is tested and confirmed. The research outline is presented in Supplementary Figure S1A. of the supplementary material.
This study makes three significant contributions to the existing literature. First, the Q-Q approach is utilized to systematically examine the heterogeneous effects of carbon emissions on different quantiles of PPI and CPI. The analysis demonstrates that carbon pricing and the backward shifting of carbon reduction burden raises the price of production inputs, leading to an increase in PPI (Mardones, 2024; Fang et al., 2024; Wen et al., 2024). Similarly, carbon emissions stimulate a higher CPI by promoting economic growth and carbon taxes (Khurshid et al., 2024; Ullah et al., 2024; Goulder et al., 2019). However, this paper finds that the effects of carbon emissions on PPI and CPI vary significantly at different quantiles. For example, while carbon emissions generally lead to an increase in the PPI, carbon emissions may cause a decline in PPI when it is at lower quantiles. This suggests that carbon reduction at this stage could push up the price level, potentially exerting adverse effects on economic development. Second, based on the wavelet decomposition method, this paper investigates the dynamic characteristics of the effects of carbon emissions on PPI and CPI at different time scales, a dimension largely overlooked in previous studies (Marques and Junqueira, 2022; Goulder et al., 2019; Wen and Jia, 2022). In contrast, the findings of this study reveal that carbon emissions have a weak positive effect on CPI in the short-term, while exhibit negative effects in certain intervals in the middle- and long-term. Further analysis reveals that PPI exerts a positive impact on CPI, with this positive effect becoming more pronounced over time. Third, this paper employs wavelet decomposition to dissect the transmission mechanism of carbon emissions on price indices into short-term, middle-term, and long-term components. By delineating these temporal dimensions, the study provides robust empirical evidence supporting the hypothesis of time-varying policy effectiveness in climate change economics. This challenges the traditional static analysis framework and provides a novel framework for quantifying the economic risks in the decarbonization process from a dynamic perspective.
The rest of the paper is structured as follows: Section 2 reviews the literature on the relationship between carbon emissions and PPI and CPI, Section 3 introduces the methodology used in this study, Section 4 demonstrates the data sources of this paper, Section 5 presents the results of the empirical analyses and the discussion, and Section 6 summarizes the findings and makes policy recommendations.
On the one hand, the PPI is an indicator of price changes based on producers’ prices for means of production. From a production perspective, Goulder et al. (2019) analyzed the impact of carbon emissions on the PPI. Their findings suggest that as the tax burden on carbon-intensive industries is transferred upstream to energy-consuming firms, the resulting reduction in energy demand by producers leads to a decline in producer prices. Besides, Yu et al. (2023) demonstrated that certain emission reduction measures, such as time-of-use electricity pricing, can effectively incentivize enterprises to reduce carbon emissions while simultaneously lowering production costs, thus curbing the increase in the PPI. On the other hand, Mardones (2024) argued that the carbon tax policy exerts a significant upward pressure on the PPI by raising the cost of coal energy, subsequently leading to higher prices for downstream firms. Similarly, Jia (2023) demonstrated that the carbon tax policy is able to directly drive up the price levels of the energy-producing industries, which in turn indirectly contributes to higher price levels across the entire industry. Fang et al. (2024) analyzed the short-term effects of the carbon tax on China’s economic system and found that the carbon tax policy results in an increase in the average price level of the industry. However, in the long-term, firms improve their energy efficiency to cope with the carbon tax, leading to reduced production costs and, consequently, lower product prices (Wu et al., 2024; Wang Z. et al., 2022). In the agricultural sector, Shabani et al. (2024) found that carbon taxes can indirectly increase production costs by raising the price of diesel, which may drive up the PPI of agricultural products. Similarly, Fikru and Kilinc-Ata (2024) observed that accounting for firms’ abatement benefits significantly lowers the technological costs associated with emission reduction. Considering the impact of carbon pricing policies, Wen et al. (2024) showed that carbon pricing leads to a significant increase in the price of means of production. In addition, energy prices play a pivotal role in influencing the PPI. For instance, Wang et al. (2024) emphasize that coal, as the primary energy source for China’s industrial sector, serves as a critical determinant of production costs. Fluctuations in coal prices can be directly transmitted to producer prices through the supply chain. It is worth noting that the rapid expansion of renewable energy can also contribute to an increase in PPI. As highlighted by Feng et al. (2022), the substantial costs associated with constructing power generation facilities and energy storage systems are often passed through the industrial chain, ultimately influencing the prices of industrial products. Conversely, Gao et al. (2024) found that the increase in total factor productivity significantly reduces the PPI. As economic growth is closely related to the increase in total factor productivity (Ahmad et al., 2019; Zhang M. et al., 2023), it suggests that economic growth may exert a downward pressure on the PPI. Building on the existing literature on the relationship between carbon emissions and economic growth, it can be hypothesized that a complex dynamic relationship exists between carbon emissions and the PPI.
Environmental quality indicators are crucial in analyzing the factors influencing consumer price level. Azam et al. (2023) identified a significant negative correlation between carbon emissions and the CPI. Contrary to the traditional cost pass-through theory, Wu and Zhu (2023) also found that the CPI in pilot provinces with Carbon Emissions Trading System (ETS) did not increase but instead decreased. This may be attributed to the fact that in the initial stage of the policy, enterprises absorbed the costs through efficiency improvement rather than price pass-through. However, Marques and Junqueira (2022) suggested that the long-term utilization of different energy sources can result in inverse trends between carbon emissions and the CPI. In addition, CPI is an indicator of price changes based on the prices paid by consumers for goods and services, indicating a positive correlation between price level and the CPI. Therefore, the price level can serve as a direct mediating variable affecting the relationship between carbon emissions and the CPI. Djedaiet (2023), through an analysis of the dynamic relationship between carbon emissions and inflation rate, concluded that a high inflation rate in the long-term is associated with low carbon emissions. However, Akhtar and Masud (2022), in their study on the impact of climate change on agriculture, found that the adverse effects of carbon dioxide on crop yields lead to higher prices for agricultural commodities. Secondly, economic growth can drive an increase in commodity prices (Wang and Liao, 2022; Wang Z. et al., 2023), which in turn has a positive impact on the CPI. In this regard, research has established a significant positive correlation between carbon emissions and economic growth (Hasan et al., 2021). Khurshid et al. (2024), examining the relationship between economic development and carbon emissions in the case of Pakistan, concluded that in the long-term carbon emissions have a favorable impact on economic development. Similarly, Ullah et al. (2024) found a long-term causal relationship between carbon emissions and economic growth across 47 Asian countries. In contrast, some scholars hold an opposing view. Mohsin et al. (2022) analyzed the relationship between environment and economic growth in European and Central Asian countries, finding a significant negative long-term correlation and a significant positive short-term correlation between carbon emissions and GDP. Besides, Rehman et al. (2021) found that increased low carbon emissions from the transportation sector in Pakistan hinders the country’s economic growth in the long-term. Huang et al. (2022) believed that when weighing its long-term benefits, the low-carbon target exerted downward pressure on CPI in the short-term. Conversely, a reduction in carbon emissions contributes to economic growth in both short- and long-term. Finally, in order to cope with the impacts of climate change, governments are implementing various abatement policies to control carbon emissions. From the perspective of consumption, the impact of these abatement policies on the CPI warrants attention. Feng et al. (2022) found that the development of low-carbon energy can lead to an increase in CPI, underscoring the financial burden placed on consumers during the green energy transition. Goulder et al. (2019), in their study of the effects of a carbon tax on households with different income levels in the U.S., argued that the implementation of a carbon tax would lead to an increase in the CPI. Moreover, the abatement process has both direct and indirect effects on consumption. On the one hand, residents’ cooperation with emission reduction policies fosters “guilt-free” consumption, leading to higher consumption levels (Günther et al., 2020). Consumers are also more willing to pay a price premium for low-carbon products, which directly drives up the CPI for environmentally friendly products. This phenomenon of “green inflation” is gradually emerging in developing countries, reflecting the stimulating effect of environmental protection preferences on consumer prices (Valenciano-Salazar et al., 2021). On the other hand, the development of new products and services associated with emission reduction efforts can boost consumer demand (Niamir et al., 2024). The increased demand for consumption subsequently drives up the overall market price level. Nevertheless, Wen and Jia (2022) demonstrated that the implementation of emission reduction policies had a negligible impact on consumption, with the CPI increasing by no more than 1. In addition to the unidirectional positive or negative impacts, some studies have revealed the potential for a bidirectional causal relationship between carbon emissions and CPI (Tariq et al., 2023). Based on the literature discussed above, it is evident that the relationship between carbon emissions and CPI is relatively complex and still requires further investigate.
In this study, the complex dynamic relationship between carbon emissions (CO2) and CPI and PPI was assessed using the Q-Q approach (Sim and Zhou, 2015), which is based on a standardized quantile regression model with a local linear regression (LLR) model, systematically examining the effects of each quantile of the explanatory variable on the quantiles of the explained variable. Specifically, traditional quantile regression demonstrates the relationship between dependent variable and independent variable across various quantiles. For a given quantile
To analyze the relationship between the explanatory variables and the explained variables at the
In this model,
Substituting Equation 5 into Equations 1, 2 yields the following functional form of the Q-Q regression:
where
where
Similarly, a first-order Taylor expansion of
where
Substituting Equation 11 into Equation 3 yields the following functional form of the Q-Q regression:
Equation 12 quantifies the impact of the
To systematically examine the dynamic effects of explanatory variables on the explained variables across the short-, middle- and long-term, this study integrates the Q-Q approach with wavelet analysis methods (Khan et al., 2022). The wavelet analysis method allows for the examination of information within a time series corresponding to specific time horizons and time points (Ganda, 2019), enabling it to effectively address the non-stationary characteristics inherent in time series data. Therefore, in this study, the wavelet dynamics are constructed as a specific pair of functions as follows:
where father wavelet
where
As the world’s largest carbon emitter, China has taken significant responsibility for reducing its emissions. In 2016, China became a signatory to the Paris Climate Change Agreement, and in September 2020, China set explicit targets to achieve “carbon peaking” by 2030 and “carbon neutrality” by 2060. These commitments make China’s data particularly relevant for studying the impact of carbon emissions on prices. Therefore, China’s data are well-suited for examining the price perturbations caused by carbon emissions. In this paper, we utilize monthly data spanning January 1993 to December 2023, encompassing carbon emissions, PPI and CPI in China. Carbon emissions data are sourced from the EU Global Atmospheric Emissions Database (EDGAR) (https://edgar.jrc.ec.europa.eu/), while PPI and CPI data are obtained from the National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBS) (https://www.stats.gov.cn/sj/ndsj/). The sample size is determined solely on the basis of the most recent data available on these variables.
As shown in Figure 1a, the results of the original series indicate that the effect of carbon emissions on PPI varies across quantiles. The effect of CO2 on PPI is negative when PPI is at the low to middle quantiles (0.2–0.5) and the high quantiles (0.6–0.8; 0.9–1.0), and this negative effect becomes more pronounced as the quantile of CO2 increases. However, a positive effect of CO2 on PPI is observed when PPI is at certain quantiles (0.5–0.6; 0.8–0.9). Due to varying cost pass-through capabilities across sectors, industries such as low-cost, labor-intensive manufacturing and high-cost services can either partially or fully transfer the cost of CO2 or reduce production costs by utilizing emitted CO2 as a raw material (Ullah et al., 2022), which results in a lower PPI. Sectors such as electricity and natural gas production, which are associated with higher costs, are subject to government price controls. As a result, the cost of emitted CO2 cannot be passed on to consumers and must instead be internalized into production costs, leading to a positive relationship between emitted CO2 and PPI in the higher PPI range (Ma et al., 2021). To further explore the comprehensive interaction between emitted CO2 and PPI, this study utilizes wavelet analysis to decompose the time series of emitted CO2 into three different frequencies: short-term, middle-term, and long-term. Figures 1b–d demonstrates the relationship between emitted CO2 and PPI across short-, middle- and long-term, respectively.
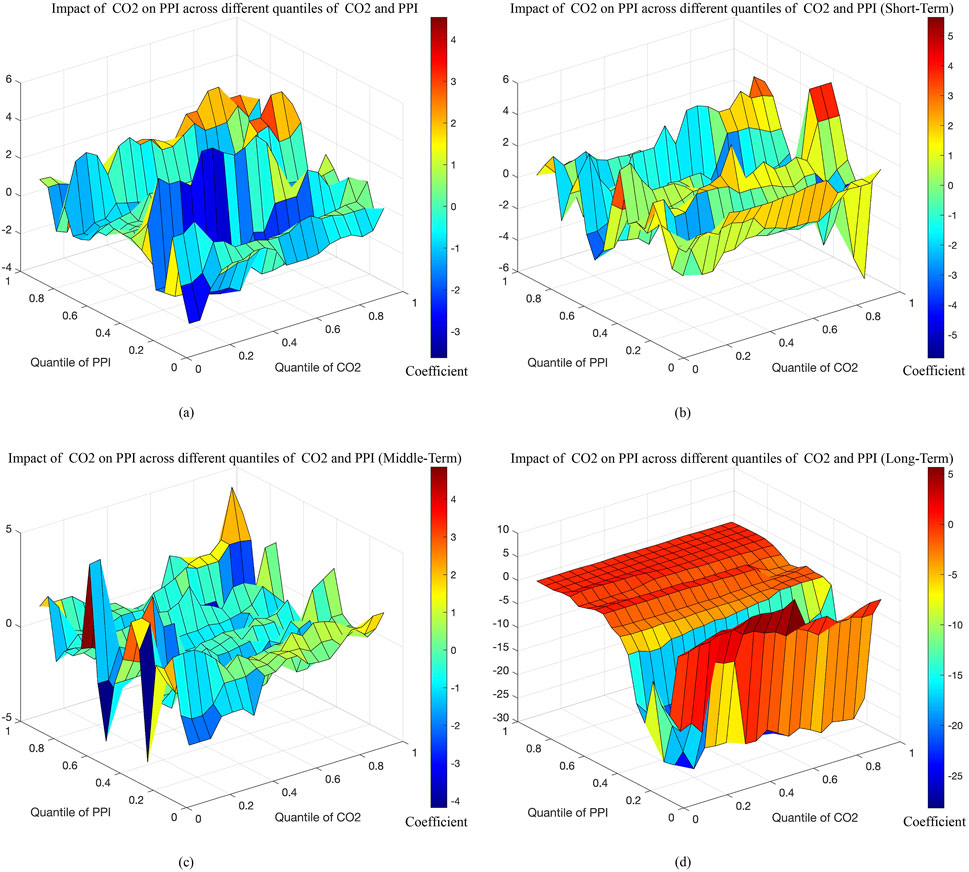
Figure 1. The coefficients between CO2 and PPI. Note: This Figure displays the estimation results of Quantile-on-Quantile analysis on the raw data as well as the data from the wavelet decomposition of CO2 and PPI. Different colors represent statistical significance of the impact of CO2 on PPI. (a) Impact of CO2 on PPI. (b) Impact of CO2 on PPI (Short-Term). (c) Impact of CO2 on PPI (Middle-Term). (d) Impact of CO2 on PPI (Long-Term).
According to Figure 1b, the correlation between emitted CO2 and PPI is not significant in the short-term, indicating that emitted CO2 have minimal impact on PPI over this period. This finding is inconsistent with Ma et al. (2020), who argue that the short-term effect of reducing CO2 on China’s economic system leads to an increase in the average industrial price, suggesting a negative correlation between CO2 and PPI in the short-term. In the middle-term, as depicted in Figure 1c, the weak negative effect of CO2 on PPI is predominant. This reflects the negative economic effect of the implementation of emission reduction policies. Specifically, producers who reduce carbon emissions face dual pressures: the need to lower emission reduction costs and the rising cost of raw materials associated with carbon emissions, resulting in a negative impact of CO2 on PPI (Tost et al., 2020). Figure 1d shows the long-term effect of CO2 on PPI, presenting a more significant positive impact of CO2 on PPI across the middle to high quantiles of PPI (0.4–1.0). This reflects the positive economic effect of emission reduction policies, particularly at the higher quantiles of PPI. Specifically, producers reduce carbon emissions while simultaneously improving production technologies and energy efficiency to meet emission reduction targets, leading to lower costs for producers (Șerbănoiu et al., 2022; Dorsey-Palmateer and Niu, 2020; Zhang and Zhang, 2020). It is worth noting that CO2 has a more significant negative effect on PPI at a lower level of PPI (0.1–0.4). At this level, an increase in CO2, which are closely related to production, implies an increase in output, thereby driving long-term economic growth (Khan et al., 2020). However, the increase in total factor productivity associated with economic growth leads to a significant reduction in PPI (Wen and Jia, 2022), thus establishing a negative relationship between CO2 and PPI.
Although the estimates are statistically significant in the Q-Q analysis as depicted in Supplementary Figures S1Ba-d shown in the supplementary material, this paper further assess the validity of the results by comparing the traditional quantile regression method with the Q-Q approach. In Figures 2a-d, the red dashed lines represent the mean values of the effect of an independent variable on the dependent variable across various quantiles, obtained through Q-Q analysis. Besides, the black solid lines depict how the independent variable influences the other variable across different quantiles in the traditional quantile regression. The results indicate that the effect of CO2 on PPI exhibits a less significant effect in the short- and middle-term, but in the long-term, it exhibits significant positive and negative effects across different quantiles of PPI. Furthermore, reducing carbon emissions has a non-significant effect on PPI in the short-term. In the middle-term, it increases manufacturers’ production costs and generate a slight upward pressure on the PPI. In the long-term, at the higher levels of PPI, emission reductions lead to improvements in production technology and efficiency, significantly lowering the PPI, which has a positive economic impact. Conversely, in the lower quantiles of PPI, emissions reductions result in a substantial increase in the PPI, causing a more pronounced negative impact on economic development.
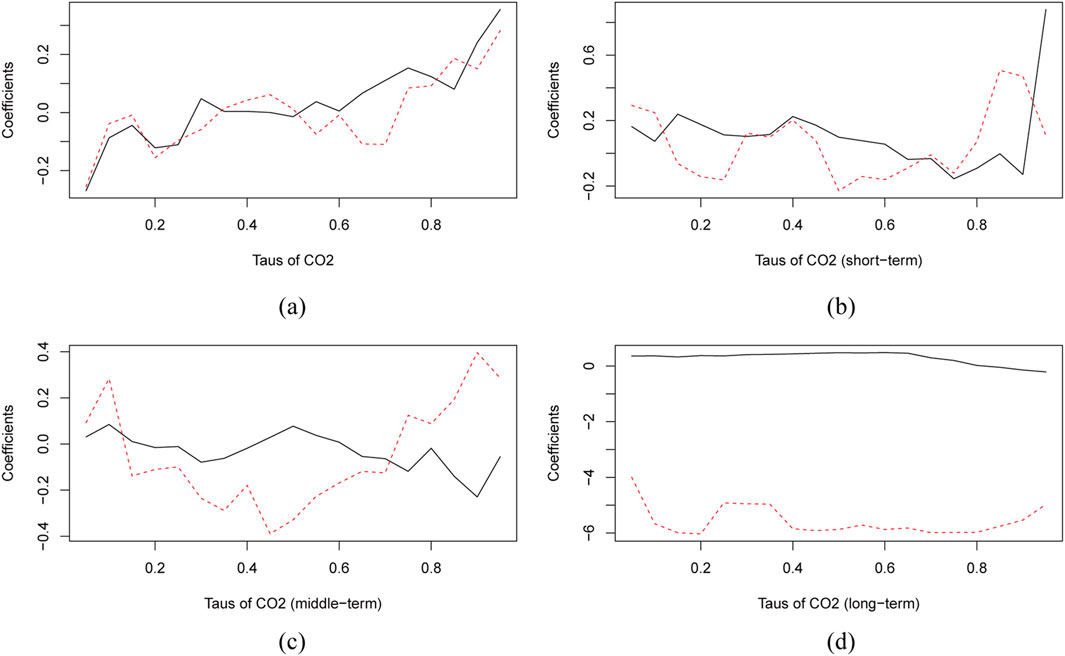
Figure 2. Quantile Regression (the black line) and Q-Q estimates (the red line) of CO2’s impact on PPI. (a) Quantile on quantile impact of CO2 on PPI. (b) Quantile on quantile impact of CO2 on PPI (Short-term). (c) Quantile on quantile impact of CO2 on PPI (Middle-term). (d) Quantile on quantile Impact of CO2 on PPI (Long-term).
CPI is another important indicator reflecting socio-economic performance, making it essential to explore the effect of CO2 on CPI. Based on Figure 3a, the effect of CO2 on CPI across different quantiles in the original series is evident, with a predominantly positive relationship. This finding is inconsistent with the conclusion of Alam et al. (2014), which reported a significant negative correlation between CO2 and CPI. However, when CO2 is at the higher quantiles (0.7–1.0) and CPI is at the lower (0.0–0.1) or middle quantiles (0.3–0.6), the overall impact of CO2 on CPI is significantly positive, but this specific effect is not significant in Supplementary Figure S2Ba.
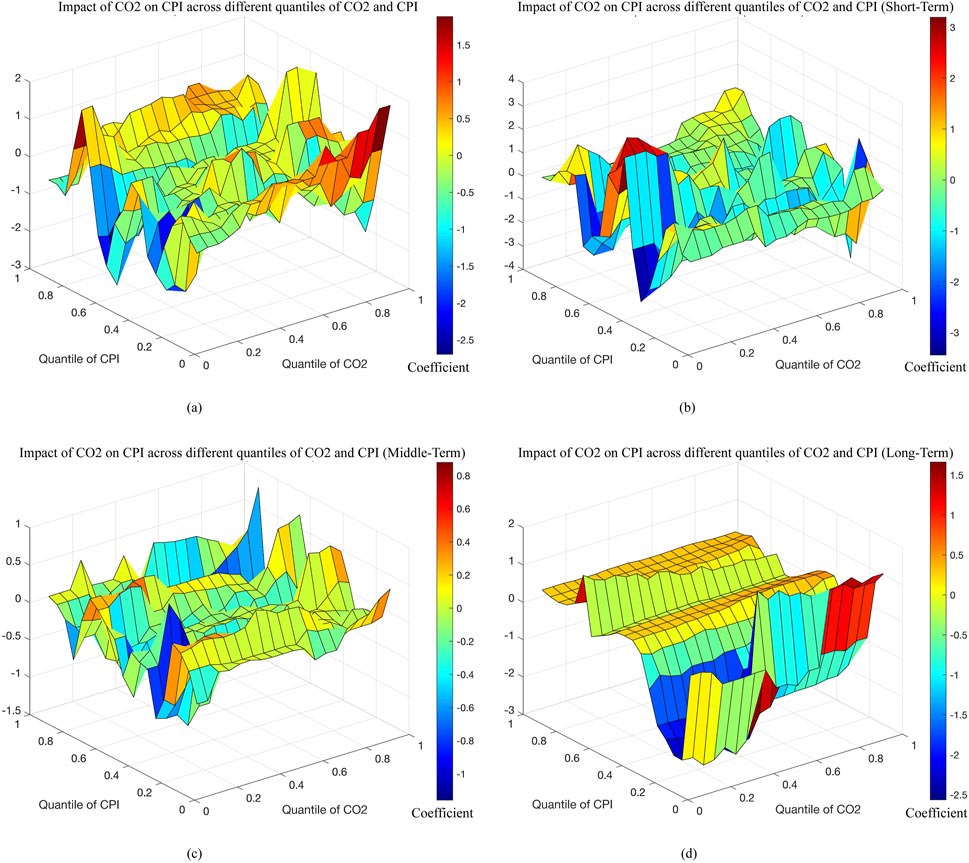
Figure 3. The coefficients between CO2 and CPI. Note: This figure displays the estimation results of Quantile-on-Quantile analysis on the raw data as well as the data from the wavelet decomposition of CO2 and CPI. Different colors represent statistical significance of the impact of CO2 on CPI. (a) Impact of CO2 on CPI. (b) Impact of CO2 on CPI (Short-Term). (c) Impact of CO2 on CPI (Middile-Term). (d) Impact of CO2 on CPI (Long-Term).
Figure 3b depicts the short-term effect of CO2 on CPI, indicating a weak positive relationship between CO2 and CPI. This reflects the short-term positive economic impact of CO2, specifically, an increase in CO2 promotes economic growth (Khan et al., 2020; Abbasi et al., 2021; Mohsin et al., 2022). As economic growth tends to drive an increase in CPI (Garnaut, 2012), the rise in CO2 fosters economic growth while exerting a positive effect on CPI. Figure 3c shows that, in the middle-term, CO2 has a negative effect on the CPI in the higher range of CPI (0.7–1.0), and this negative effect becomes particularly pronounced when CO2 is at the higher quantiles. Figure 3d illustrates a weak positive effect of CO2 on CPI across the low to high quantiles of CPI (0.3–1.0) in the long-term. The study also finds that the positive impact of carbon emissions on the economy becomes more pronounced over time. In response to the pressure of increased carbon emissions, the population develops low-carbon awareness and exhibits increased demand for low-carbon consumption in the long-term. This stimulates the growth of consumer demand (Zou et al., 2020; Wilson et al., 2020; Günther et al., 2020), which raises the prices of products and services, thereby increasing the CPI. However, according to Figure 3d, CO2 has a more pronounced negative impact on the CPI in the lower quantiles of CPI (0.1–0.3) and this negative effect is more significant when CO2 is at the lower quantiles (0.0–0.6). This reflects the long-term negative economic impact of high emissions when CPI is at a lower level, where an increase in carbon emissions suppresses economic growth (Khan et al., 2020), ultimately leading to a decrease in CPI. Furthermore, the low level of CO2 contributes to higher CPI values in the long-term (Alola et al., 2019), making the negative effect of CO2 on CPI more pronounced at lower levels of CO2. Marques and Junqueira (2022) reached similar conclusions, observing that in the long-term, there is an inverse relationship between CO2 and CPI. The statistical significance of the impact of CO2 on CPI across the short-, middle- and long-term is depicted in Supplementary Figures S2Bb-d.
Figures 4a–d demonstrates a comparison of the Q-Q approach and traditional quantile regression, highlighting the robustness of the Q-Q analysis results. The findings reveal that CO2 exhibits a weaker positive effect on CPI in both the short-term and middle-term. However, in the long-term, CO2 exhibits a weak positive effect and a significant negative effect across different quantiles of CPI. Furthermore, reducing carbon emissions has some adverse effects on the economy in the short- and middle-term, and these effects are relatively more significant across the low to high quantiles of CPI in the long-term. However, at the lower quantiles of CPI in the long-term, emission reductions significantly increase CPI and stimulate economic growth.
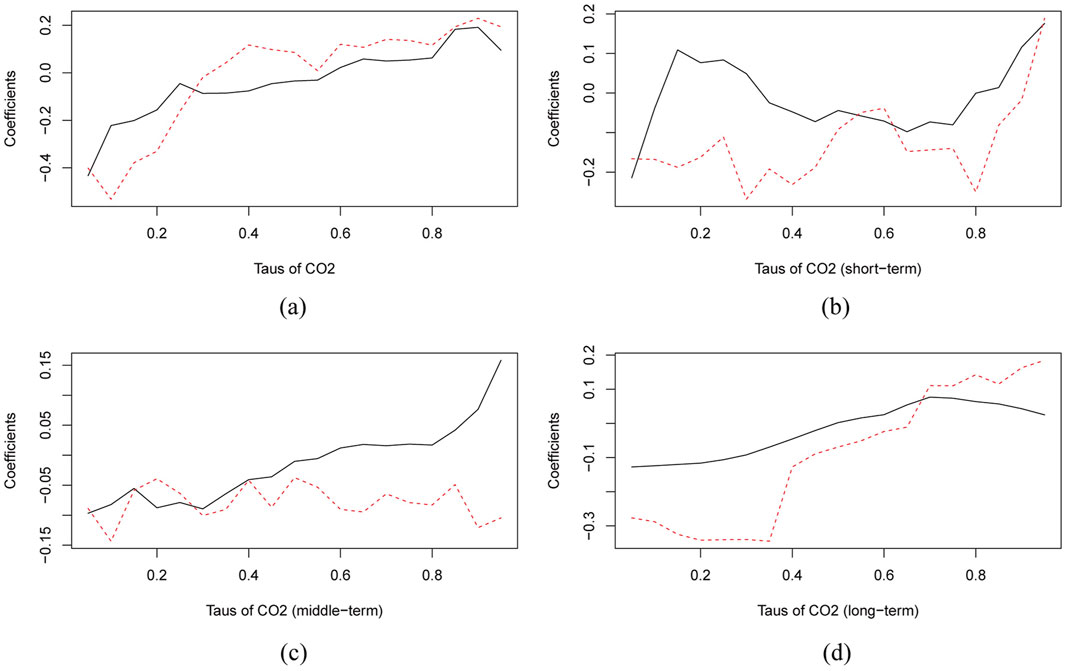
Figure 4. Quantile regression (the black line) and Q-Q estimates (the red line) of CO2’s impact on CPI. (a) Quantile on quantile impact of CO2 on CPI. (b) Quantile on quantile impact of CO2 on CPI (Short-term). (c) Quantile on quantile impact of CO2 on CPI (Middle-term). (d) Quantile on quantile impact of CO2 on CPI (Long-term).
Considering that the impact of carbon emissions on CPI is transmitted through its effect on PPI, this paper further examines the dynamic relationship between PPI and CPI. The results shown in the supplementary material align with economic theory: in the short-term, the relationship between PPI and CPI is not immediately apparent, because the impact of the producer price level on the consumer price level requires time to materialize. In the middle-term, a positive correlation between the two gradually becomes evident. In the long-term, the positive effect of PPI on CPI becomes particularly pronounced. To further test the endogeneity of the effect of CO2 on PPI and CPI as well as the impact of PPI on CPI across various quantiles, the Granger-causality in quantiles analysis is performed. The results are presented in the section D of the supplementary material, showing that CO2 is the Granger cause of PPI and CPI considering quantile heterogeneities. Similarly, the Granger causality from PPI to CPI are overall highly significant. This further confirms the robustness of the Q-Q analysis results presented above, suggesting significant impacts of CO2 on PPI and CPI as well as PPI on CPI at different quantiles.
Compared with previous studies, the methodological system of this paper has achieved innovative breakthroughs in two dimensions. First, this paper employs the Q-Q method, a significant methodological innovation that overcomes the limitations of traditional linear models, revealing the nonlinear impacts of carbon emissions on PPI and CPI. For example, Chevallier (2010) once used the ARMA (1,1)-GARCH(1,1) model to evaluate the impact of Australian emission trading system on the wholesale spot electricity prices. Li et al. (2021) estimated the economic benefits of reducing greenhouse gas emissions based on Benefit-Cost Analysis. While these methods largely remained confined to linear framework, the Q-Q method adopted in this paper represents a significant advancement in terms of non-linear analysis. Second, most previous studies have focused on the static impacts of carbon emissions on the economic system. This paper employs the wavelet decomposition method to analyze the dynamic effects of carbon emissions over different time horizons, filling the gap in dynamic research. Compared with the static analysis of the impact of low-carbon fuels on the production side using annual data (Canabarro et al., 2023), this paper focuses on the dynamic evaluation of the impact of carbon emissions on price indices, emphasizing that emission reduction policies need to take into account the time-lag effect.
In order to minimize disruptions to price levels within the economic system during the process of carbon reduction, we systematically study the nonlinear and dynamic effects of carbon emissions on PPI and CPI. Overall, there is significant heterogeneity in the impact of carbon emissions on the PPI across different quantiles. When the level of PPI is high, the impact of carbon emissions on the PPI is negative, implying that carbon reduction measures increase the PPI. In contrast, when PPI is at the lower quantiles, the effect of carbon emissions on the PPI is characterized by significant uncertainty. Dynamically, in the short-term, the impact of carbon emissions on PPI is negligible, indicating that carbon reduction measures do not exert a significant perturbation effect on the economic system in the short-term. In the middle-term, the effect of carbon emissions on the PPI is generally negative, implying that carbon reduction measures during this period will lead to an increase in the PPI. In the long-term, the impact of carbon emissions on the PPI is positive across most quantiles, implying that carbon reduction measures ultimately help stabilize the PPI. However, when the level of the PPI is low, the long-term effect of carbon reduction may also be negative, leading to an increase in the price level. This is primarily due to the fact that, when the PPI is low, the perturbation of the economic system caused by carbon emissions is more likely to result in price increases.
Compared with the effect of carbon emissions on the PPI, the effect of carbon emissions on CPI is relatively negligible. When carbon emissions are at the low quantiles, the effect of carbon emissions on CPI is negative, while at high levels of carbon emissions, the impact on CPI is positive. Dynamically, in the short-term, there is a weak positive impact of carbon emissions on the CPI, implying carbon reduction measures lead to a decrease in consumer price levels. In the middle-term, carbon emissions have a negative effect on CPI in certain intervals, particularly when the level of carbon emissions is high. It implies that carbon reduction measures will gradually increase the CPI over the middle-term. In the long-term, the relationship between carbon emissions and CPI is negative across the lower quantiles of CPI, while it becomes insignificant in other intervals. In summary, the theoretical contributions of this paper are mainly reflected in three aspects: First, this paper challenges the traditional linear model by using the Q-Q approach, providing a more nuanced theoretical framework for analysing the complex interactions between the environment and the economy. Second, this paper enriches macroeconomic theories by integrating environmental policy lags into the price formation model through distinguishing short-term, middle-term and long-term impacts. Third, through a systematic comparison of the impacts of carbon emissions on PPI and CPI, this paper reveals that carbon emissions have a more intense and long-lasting impact on the PPI. This highlights the crucial role of cost transmission at the production end in environmental economics and provides theoretical foundation for future policy design.
Based on the findings of this paper, the following policy implications can be drawn.
First, in the middle-term, carbon reduction policies may lead to an increase in the PPI, while in the long-term, carbon reduction measures will ultimately help stabilize the PPI. Therefore, the government should adopt asymmetric implementation timelines. For example, heavy industries with rigid production chains could be granted longer adaptation periods, while sectors with flexible technologies face earlier deadlines. Considering the long-term stabilization effect, government should provide clear guidance to enterprises by setting long-term carbon reduction targets and timetables, ensuring the consistency and continuity of these policies. At the same time, an incentive mechanism should be established to encourage enterprises to actively engage in carbon reduction efforts by providing tax incentives, granting subsidies, and implementing carbon pricing and carbon emissions trading scheme. Specially, the government can set a carbon price range for specific industries. Within this range, the price of emission permits can be automatically adjusted in real-time according to the fluctuations of PPI. For industries with a relatively high PPI, a more lenient price floor can be set to mitigate the risk of cost-push inflation. Besides, government should also support front-loaded investments in green infrastructure to accelerate the transition to the equilibrium phase. Public support for carbon reduction policies is also crucial, particularly in light of the short-term price increases that may result. To this end, the government should undertake extensive public outreach campaigns to promote the concept of carbon reduction. These campaigns should aim to raise public awareness and understanding of carbon reduction, foster social acceptance, and garner support for the carbon reduction policies. By reducing resistance, these efforts will help ensure the consistent implementation of the policy.
Second, since the impact of carbon emissions on the CPI exhibits a negative effect in certain intervals across the middle-to long-term, the implementation of the carbon reduction policies may lead to price increases. To mitigate this impact, the government can adopt a phased implementation approach for the carbon reduction policies. For example, the government can begin by implementing the emission reduction policies in large-scale enterprises and high-emission industries, while promoting technological innovation and changes in production methods. The policy can then be gradually extended to small and medium-sized enterprises and low-emission industries. Simultaneously, it is essential to monitor and assess the impact of policy implementation at each stage, making flexible adjustments as needed to prevent excessive disruption to prices. This approach will help ensure a smooth transition in market and maintain a balance between supply and demand. In addition, the government can also set price ceilings and price floors in the carbon emissions trading market to ensure that the cost of carbon emissions fluctuates within a certain range, thereby preventing sharp price increases. Furthermore, government can implement green inflation compensation mechanisms, such as temporary Value-Added Tax reductions on essential goods during intensive decarbonization process in critical supply chains.
Third, it is important to improve market regulations and establish a flexible price transmission mechanism. This paper finds that the positive price transmission effect of PPI on CPI becomes more significant over time. As companies pass the cost of carbon emissions onto consumers, the long-term increase in CPI may distort consumer choices and economic outcomes, ultimately leading to efficiency losses. To ensure market efficiency, the government should implement stricter measures to bolster anti-monopoly regulations and address issues such as enterprises abusing their monopoly power to manipulate prices, thereby enabling the carbon market to fully support the low-carbon transition of businesses. At the same time, the government must protect the rights and interests of consumers and maintain economic stability.
While this study provides novel insights into the heterogeneous and time-varying effects of carbon emissions on price indices, several limitations warrant consideration. First, the analysis relies on aggregated national data, which may obscure regional or sector-specific dynamics in carbon-price transmission. Second, there may be a bidirectional relationship between economic activities and emissions. While the quantile regression framework employed in this paper has effectively captured the nonlinear relationship, the exploration of the bidirectional relationship remains an area ripe for further in-depth research. Future research could extend this work along three dimensions: (1) investigating cross-country heterogeneity using multi-regional input-output models to disentangle global value chain effects. (2) innovative models or methods should be employed to analyze the bidirectional relationship between carbon emissions and price indices, providing theoretical support for better addressing economic challenges under the “Dual Carbon” goal. (3) incorporating firm-level data to analyze how carbon cost pass-through mechanisms differ across market structures and production technologies. These extensions would enhance both the predictive power and policy relevance of environmental macroeconomics research.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
CL: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Supervision, Writing–original draft. LC: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Validation, Visualization, Writing–review and editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was funded by the Project of National Social Science Fund of China [grant number 23CJL007].
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fenvs.2025.1557902/full#supplementary-material
Abbasi, K. R., Shahbaz, M., Jiao, Z., and Tufail, M. (2021). How energy consumption, industrial growth, urbanization, and CO2 emissions affect economic growth in Pakistan? A novel dynamic ARDL simulations approach. Energy 221, 119793. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2021.119793
Ahmad, M., Zhao, Z., and Li, H. (2019). Revealing stylized empirical interactions among construction sector, urbanization, energy consumption, economic growth and CO2 emissions in China. Sci. Total Environ. 657, 1085–1098. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.112
Akhtar, R., and Masud, M. M. (2022). Dynamic linkages between climatic variables and agriculture production in Malaysia: a generalized method of moments approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 29 (27), 41557–41566. doi:10.1007/s11356-021-18210-x
Alam, A., Azam, M., Abdullah, A. B., Malik, I. A., Khan, A., Hamzah, T. a. a. T., et al. (2014). Environmental quality indicators and financial development in Malaysia: unity in diversity. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 22 (11), 8392–8404. doi:10.1007/s11356-014-3982-5
Alola, A. A., Yalçiner, K., and Alola, U. V. (2019). Renewables, food (in)security, and inflation regimes in the coastline Mediterranean countries (CMCs): the environmental pros and cons. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 26 (33), 34448–34458. doi:10.1007/s11356-019-06576-y
Aphane, T. R., Muchopa, C. L., and Senyolo, M. P. (2024). Causality relationship between producer and consumer price indexes of selected meat commodities in South Africa from 1991 to 2023. Economies 12 (12), 336. doi:10.3390/economies12120336
Azam, M., Islam, F., and Rashid, S. (2023). Health, environment, and sustainable development: evidence from panel data from ASEAN countries. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 17 (4), 827–842. doi:10.1007/s11869-023-01483-1
Canabarro, N. I., Silva-Ortiz, P., Nogueira, L. A., Cantarella, H., Maciel-Filho, R., and Souza, G. M. (2023). Sustainability assessment of ethanol and biodiesel production in Argentina, Brazil, Colombia, and Guatemala. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 171, 113019. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2022.113019
Chai, K. C., Ma, X. R., Yang, Y., Lu, Y. J., and Chang, K. C. (2022). The impact of climate change on population urbanization: evidence from China. Front. Environ. Sci. 10, 945968. doi:10.3389/fenvs.2022.945968
Chevallier, J. (2010). The impact of Australian ETS news on wholesale spot electricity prices: an exploratory analysis. Energy Policy 38, 3910–3921. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2010.03.014
Cui, Y., Feng, W., and Gu, X. (2024). Research on the spatial spillover effect of carbon trading market development on regional emission reduction. Front. Environ. Sci. 12, 1356689. doi:10.3389/fenvs.2024.1356689
Djedaiet, A. (2023). Does environmental quality react asymmetrically to unemployment and inflation rates? African OPEC countries’ perspective. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 30 (46), 102418–102427. doi:10.1007/s11356-023-29621-3
Dorsey-Palmateer, R., and Niu, B. (2020). The effect of carbon taxation on cross-border competition and energy efficiency investments. Energy Econ. 85, 104602. doi:10.1016/j.eneco.2019.104602
Fang, X., He, W., Wen, F., An, M., Song, M., Wang, B., et al. (2024). Simulation study on the effect of differentiated carbon tax adjustment on CO2 emissions reduction in China from the perspective of carbon footprint. J. Clean. Prod. 434, 140071. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.140071
Feng, Y., Song, F., and Chen, P. (2022). Evaluating the cost impacts to meet China’s renewable electricity portfolio standard target in 2030. Int. J. Green Energy 20 (13), 1434–1450. doi:10.1080/15435075.2022.2155969
Fikru, M. G., and Kilinc-Ata, N. (2024). Do mineral imports increase in response to decarbonization indicators other than renewable energy? J. Clean. Prod. 435, 140468. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.140468
Gan, T., Zhou, Z., Li, S., and Tu, Z. (2024). Carbon emission trading, technological progress, synergetic control of environmental pollution and carbon emissions in China. J. Clean. Prod. 442, 141059. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2024.141059
Ganda, F. (2019). The impact of innovation and technology investments on carbon emissions in selected organisation for economic Co-operation and development countries. J. Clean. Prod. 217, 469–483. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.01.235
Gao, Z., Zhang, Y., Li, L., and Hao, Y. (2024). Will resource tax reform raise green total factor productivity levels in cities? Evidence from 114 resource-based cities in China. Resour. Policy 88, 104483. doi:10.1016/j.resourpol.2023.104483
Garnaut, R. (2012). The contemporary China resources boom. Aust. J. Agric. Resour. Econ. 56 (2), 222–243. doi:10.1111/j.1467-8489.2012.00581.x
Goulder, L. H., Hafstead, M. A., Kim, G., and Long, X. (2019). Impacts of a carbon tax across US household income groups: what are the equity-efficiency trade-offs? J. Public Econ. 175, 44–64. doi:10.1016/j.jpubeco.2019.04.002
Günther, S. A., Staake, T., Schöb, S., and Tiefenbeck, V. (2020). The behavioral response to a corporate carbon offset program: a field experiment on adverse effects and mitigation strategies. Glob. Environ. Change 64, 102123. doi:10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2020.102123
Hasan, M. A., Nahiduzzaman, K. M., Aldosary, A. S., Hewage, K., and Sadiq, R. (2021). Nexus of economic growth, energy consumption, FDI and emissions: a tale of Bangladesh. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 24 (5), 6327–6348. doi:10.1007/s10668-021-01704-6
Hu, J., Sun, Q., and Wang, W. (2024). The role of green and digital technology convergence on carbon emission reduction: evidence from China. Front. Environ. Sci. 12, 1490657. doi:10.3389/fenvs.2024.1490657
Huang, K. X. D., Tian, G., and Zhao, L. (2022). Propelling steady growth and high-quality development through deeper reform and more comprehensive opening up: outlook, policy simulations, and reform implementation—a summary of the annual sufe macroeconomic Report (2021–2022). Int. Stud. Econ. 17, 2–20. doi:10.1002/ise3.2
Jatuporn, C. (2024). Assessing the impact of global oil prices on domestic price levels in Thailand: a nonlinear ARDL investigation. Energy Nexus 14, 100307. doi:10.1016/j.nexus.2024.100307
Jia, Z. (2023). What kind of enterprises and residents bear more responsibilities in carbon trading? A step-by-step analysis based on the CGE model. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 98, 106950. doi:10.1016/j.eiar.2022.106950
Khan, K., Su, C., and Zhu, M. N. (2022). Examining the behaviour of energy prices to COVID-19 uncertainty: a quantile on quantile approach. Energy 239, 122430. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2021.122430
Khan, S., Khan, M. K., and Muhammad, B. (2020). Impact of financial development and energy consumption on environmental degradation in 184 countries using a dynamic panel model. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 28 (8), 9542–9557. doi:10.1007/s11356-020-11239-4
Khurshid, N., Akram, N., and Hameed, G. (2024). Asymmetric variations in economic globalization, CO2 emissions, oil prices, and economic growth: a nonlinear analysis for policy empirics. Environ. Dev. Sustain., 1–29. doi:10.1007/s10668-023-04364-w
Kumar, A., Kumar, A., Kumar, M., and Bhat, J. A. (2022). Editorial: greenhouse gas emissions and terrestrial ecosystems. Front. Environ. Sci. 10, 834444. doi:10.3389/fenvs.2022.834444
Li, Z., Qi, Z., Jiang, Q., and Sima, N. (2021). An economic analysis software for evaluating best management practices to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions from cropland. Agric. Syst. 186, 102950. doi:10.1016/j.agsy.2020.102950
Ma, N., Li, H., Wang, Y., Zhang, J., Li, Z., and Arif, A. (2020). The short-term roles of sectors during a carbon tax on Chinese economy based on complex network: an in-process analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 251, 119560. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119560
Ma, N., Li, H., Zhang, J., Han, X., Feng, S., and Arif, A. (2021). The short-term price effects and transmission mechanism of CO2 cost pass-through in China: a partial transmission model. Resour. Policy 70, 101972. doi:10.1016/j.resourpol.2020.101972
Mardones, C. (2024). Contribution of the carbon tax, phase-out of thermoelectric power plants, and renewable energy subsidies for the decarbonization of Chile − A CGE model and microsimulations approach. J. Environ. Manage 352, 120017. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2024.120017
Marques, A. C., and Junqueira, T. M. (2022). European energy transition: decomposing the performance of nuclear power. Energy 245, 123244. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2022.123244
Martin, C. (2023). “Using biometrics, behavioral observations, and multiple molecular techniques to assess the impacts of changes in temperature and salinity on the common bay mussel (Mytilus trossulus),”. Master's thesis (United States: Portland State University). doi:10.15760/etd.3676
Mohsin, M., Naseem, S., Sarfraz, M., and Azam, T. (2022). Assessing the effects of fuel energy consumption, foreign direct investment and GDP on CO2 emission: new data science evidence from Europe and Central Asia. Fuel 314, 123098. doi:10.1016/j.fuel.2021.123098
Niamir, L., Verdolini, E., and Nemet, G. F. (2024). Social innovation enablers to unlock a low energy demand future. Environ. Res. Lett. 19 (2), 024033. doi:10.1088/1748-9326/ad2021
Rehman, A., Ma, H., Ozturk, I., Murshed, M., and Dagar, V. (2021). The dynamic impacts of CO2 emissions from different sources on Pakistan’s economic progress: a roadmap to sustainable development. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 23 (12), 17857–17880. doi:10.1007/s10668-021-01418-9
Șerbănoiu, A. A., Grădinaru, C. M., Muntean, R., Cimpoeșu, N., and Șerbănoiu, B. V. (2022). Corn cob ash versus sunflower stalk ash, two sustainable raw materials in an analysis of their effects on the concrete properties. Materials 15 (3), 868. doi:10.3390/ma15030868
Shabani, E., Hayati, B., Pishbahar, E., Ghorbani, M. A., and Ghahremanzadeh, M. (2024). The potential role of a carbon tax on CO2 emission reduction in the agriculture sector of Iran. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 21, 6965–6980. doi:10.1007/s13762-024-05485-z
Sim, N., and Zhou, H. (2015). Oil prices, US stock return, and the dependence between their quantiles. J. Bank. Financ. 55, 1–8. doi:10.1016/j.jbankfin.2015.01.013
Tariq, G., Sun, H., Ali, I., Ali, S., and Shah, Q. (2023). Influence of access to clean fuels and technology, food production index, consumer price index, and income on greenhouse gas emissions from food system: evidence from developed countries. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 30, 59528–59539. doi:10.1007/s11356-023-26628-8
Tost, M., Hitch, M., Lutter, S., Feiel, S., and Moser, P. (2020). Carbon prices for meeting the Paris agreement and their impact on key metals. Extr. Ind. Soc. 7 (2), 593–599. doi:10.1016/j.exis.2020.01.012
Ullah, H. I., Dickson, R., Mancini, E., Malanca, A. A., Pinelo, M., and Mansouri, S. S. (2022). An integrated sustainable biorefinery concept towards achieving zero-waste production. J. Clean. Prod. 336, 130317. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.130317
Ullah, S., Arif, M., Hussain, S., and Al-Faryan, M. a. S. (2024). Climate change, governance, and economic growth in Asia: a panel cointegration analysis. Cogent Econ. Finance 12 (1), 2299125. doi:10.1080/23322039.2023.2299125
Valenciano-Salazar, J. A., André, F. J., and Soliño, M. (2021). Paying for sustainable coffee in a developing country: consumers’ profile in Costa Rica. Sustainability 13 (16), 9360. doi:10.3390/su13169360
Wang, C., Liu, X., Li, H., and Yang, C. (2023a). Analyzing the impact of low-carbon city pilot policy on enterprises’ labor demand: evidence from China. Energy Econ. 124, 106676. doi:10.1016/j.eneco.2023.106676
Wang, C., Xu, G., Sun, C., Xu, J., Xu, K., Jiang, L., et al. (2024). Modeling and forecasting of coal price based on influencing factors and time series. J. Clean. Prod. 467, 143030. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2024.143030
Wang, F., and Liao, H. (2022). Unexpected economic growth and oil price shocks. Energy Econ. 116, 106430. doi:10.1016/j.eneco.2022.106430
Wang, X., Iqbal, K., and Wang, Y. (2022a). Energy use greisenization, carbon dioxide emissions, and economic growth: an empirical analysis based in China. Front. Environ. Sci. 10, 871001. doi:10.3389/fenvs.2022.871001
Wang, Z., Xie, W., and Zhang, C. (2023b). Towards COP26 targets: characteristics and influencing factors of spatial correlation network structure on U.S. carbon emission. Resour. Policy 81, 103285. doi:10.1016/j.resourpol.2022.103285
Wang, Z., Zhou, Y., Zhao, N., Wang, T., and Zhang, Z. (2022b). Spatial correlation network and driving effect of carbon emission intensity in China’s construction industry. Buildings 12, 201. doi:10.3390/buildings12020201
Warsame, A. A., and Abdi, A. H. (2022). Towards sustainable crop production in Somalia: examining the role of environmental pollution and degradation. Cogent Food Agric. 9 (1). doi:10.1080/23311932.2022.2161776
Wen, F., Wang, K., and Zeng, A. (2024). Return spillover across the carbon market and financial markets: a quantile-based approach. Res. Int. Bus. Financ. 69, 102298. doi:10.1016/j.ribaf.2024.102298
Wen, S., and Jia, Z. (2022). The energy, environment and economy impact of coal resource tax, renewable investment, and total factor productivity growth. Resour. Policy 77, 102742. doi:10.1016/j.resourpol.2022.102742
Wilson, C., Kerr, L., Sprei, F., Vrain, E., and Wilson, M. (2020). Potential climate benefits of digital consumer innovations. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 45 (1), 113–144. doi:10.1146/annurev-environ-012320-082424
Wu, G., Sun, M., and Feng, Y. (2024). How does the new environmental protection law affect the environmental social responsibility of enterprises in Chinese heavily polluting industries? Humanit. soc. Sci. commun. 11 (1), 168–214. doi:10.1057/s41599-024-02674-6
Wu, L., and Zhu, Q. (2023). Has the Emissions Trading Scheme (ETS) promoted the end-of-pipe emissions reduction? Evidence from China's residents. Energy 277, 127665. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2023.127665
Wu, Y., Peng, B., and Lao, Y. (2023). The emission reduction effect of financial agglomeration under China’s carbon peak and neutrality goals. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 20 (2), 950. doi:10.3390/ijerph20020950
Yu, X., Dong, Z., and Zheng, D. (2023). Research on critical peak price decision optimization considering industrial consumer’s risk appetite under the carbon neutrality goal. Sustainability 15, 9347. doi:10.3390/su15129347
Zhang, J., and Zhang, Y. (2020). Examining the economic and environmental effects of emissions policies in China: a Bayesian DSGE model. J. Clean. Prod. 266, 122026. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122026
Zhang, M., Li, W., Wang, Z., and Liu, H. (2023b). Urbanization and production: heterogeneous effects on construction and demolition waste. Habitat Int. 134, 102778. doi:10.1016/j.habitatint.2023.102778
Zhang, Y., Jiang, S., Lin, X., Qi, L., and Sharp, B. (2023a). Income distribution effect of carbon pricing mechanism under China’s carbon peak target: CGE-based assessments. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 101, 107149. doi:10.1016/j.eiar.2023.107149
Zhou, Z., Ma, Z., and Lin, X. (2022). Carbon emissions trading policy and green transformation of China’s manufacturing industry: mechanism assessment and policy implications. Front. Environ. Sci. 10, 984612. doi:10.3389/fenvs.2022.984612
Zhu, W., Dong, W., Qin, G., and Yang, Y. (2023). Coordinated carbon reduction mechanism and policy design to achieve carbon peak and neutrality goals in the Yangtze River Delta. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 56, 103113. doi:10.1016/j.seta.2023.103113
Keywords: carbon emissions, CPI, PPI, wavelet decomposition, quantile-on-quantile approach
Citation: Li C and Chen L (2025) Heterogeneous and dynamic impacts of carbon emissions on PPI and CPI: important insights into the consequences on the price system in tackling climate change. Front. Environ. Sci. 13:1557902. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2025.1557902
Received: 09 January 2025; Accepted: 20 March 2025;
Published: 31 March 2025.
Edited by:
Gabriela Mustata Wilson, University of Louisiana at Lafayette, United StatesReviewed by:
Mohammad Subhan, Aligarh Muslim University, IndiaCopyright © 2025 Li and Chen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Liping Chen, bGlwaW5nX2NoZW5AbXVjLmVkdS5jbg==; Chao Li, Y2hhb19saUBzZHUuZWR1LmNu
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.