
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
COMMUNITY CASE STUDY article
Front. Environ. Sci. , 19 March 2025
Sec. Environmental Policy and Governance
Volume 13 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2025.1521494
 Allison K. Drake1*
Allison K. Drake1* 2Paulatuk Hunters and Trappers Committee
2Paulatuk Hunters and Trappers Committee Tony Green2
Tony Green2 Jody Illasiak2
Jody Illasiak2 Bill S. Ruben2
Bill S. Ruben2 Candace Ruben2
Candace Ruben2 Lawrence Ruben2
Lawrence Ruben2 Karen M. Dunmall1
Karen M. Dunmall1In the Canadian Arctic, we posit that locally-relevant Indigenous data governance frameworks are necessary in light of a paucity of guiding practices and policies for environmental researchers working in partnership with communities. To centre data governance decision-making in a community and to support Indigenous self-determination as affirmed in federal commitments, Fisheries and Oceans Canada researchers and the Paulatuk Hunters and Trappers Committee (Paulatuk, Inuvialuit Settlement Region) co-developed a data governance Statement of Shared Understanding for Traditional Knowledge Documentation specific to an interview project. We detail the steps and dialogue that characterized the creation of this statement over several months, so that others may build from these efforts when appropriate. Second, we highlight five emergent considerations that may strengthen future data governance efforts and inform policy, including: community and project context, the changing digital landscape, individual and collective knowledge protections, planned project outputs, and confidentiality and anonymity nuances. We offer these insights to advance evolving Indigenous data governance conversations, initiatives, and policies in institutional and community spaces.
Indigenous data1 governance conversations are beginning to take shape as efforts to elevate Indigenous knowledge systems2 in environmental research, monitoring, and co-management expand (e.g., Williamson et al., 2022; Jennings et al., 2023; Cannon et al., 2024; Kawerak Inc., 2024). Considered both a process (see Bruhn, 2014), and a right (see Williamson et al., 2022), Indigenous data governance concerns community ownership and management over the compilation, access, and use of data related to Indigenous Peoples, land, and cultural heritage (Rainie et al., 2017; Reyes-García et al., 2022). In Inuit Nunangat in the Canadian Arctic3, data governance is highly relevant to community-researcher collaborations that apply Indigenous knowledges alongside or independent of Western science methods to monitor and assess rapidly-changing ecosystems. Within the Inuvialuit Settlement Region, the focus of this manuscript, there are opportunities for local data governance in community-oriented research and monitoring projects, such as those centered on marine mammals (e.g., Ostertag et al., 2018; Ovitz et al., 2024), fishes (e.g., Brewster et al., 2016; McNicholl et al., 2021; 2024; Chila et al., 2022), or larger-scale ecological change (e.g., Andrews et al., 2016; Ziegler et al., 2024), among other topics. Yet, there is a paucity of frameworks to guide data practices in such endeavours4, which challenges communities and researchers alike, and at the same time, creates space for community-led data governance.
In Inuvialuit and Inuit homelands, communities and environmental researchers can draw guidance surrounding respectful engagement with Indigenous knowledge holders and knowledges from Inuit Tapiriit Kanatami5, the Nunavut Research Institute, and the Inuit Circumpolar Council (see ITK and NRI, 2007; ITK, 2018; ICC, 2021). Inuit Tapiriit Kanatami’s National Inuit Strategy on Research references First Nations Information Governance Centre OCAP® principles (ownership, control, access, and possession; FNIGC, 2014; FNIGC, 2019), where ownership refers to the relationship of Indigenous Peoples with their knowledge, data, and information; control affirms that it is the right of Indigenous Peoples and communities to be actively involved at all stages of a research project; access indicates that Indigenous Peoples and communities must have access to information and data about themselves regardless of where it is stored; and possession references the physical control of data (FNIGC, 2014; FNIGC, 2019)6. This report also briefly discusses Chapter 9 of the Tri-Council Policy Statement on Ethical Conduct for Research Involving Humans 2 (TCPS 2) (CIHR et al., 2022). While helpful in outlining foundational concepts, researchers should be mindful of the limitations of both of these forms of guidance, as the former “operates as a set of specifically First Nations–not Indigenous–principles” (FNIGC, 2024), and the latter is anchored in a system designed to protect academic institutions (Dingwall, 2012; Champagne, 2015; Hayward et al., 2021).
Arctic researchers affiliated with academia rely heavily on these principles through university-specific and mandatory human research ethics protocols; however, most federal scientists, such as those working with Fisheries and Oceans Canada (DFO; authors AD and KD) do not have Indigenous data governance frameworks available. Currently and to our knowledge, few federal departments have organizational policies and/or human Research Ethics Boards (REBs) (but see Natural Resources Canada, Health Canada and the Public Health Agency of Canada) (Natural Resources Canada, 2024; Health Canada, 2024). Existing DFO guidelines provide scaffolding for future data governance policies; for example, all research activities must be consistent with “relevant and applicable standards of scientific excellence, research ethics, and responsible research conduct” (Government of Canada, 2019). Additionally, comprehensive processes are in place to ensure that scientific standards are met concerning species and habitats (e.g., License to Fish for Scientific, Experimental, or Educational Purposes, Animal Care Committees); yet, these do not extend to human research ethics. We posit that an absence of DFO directives creates an important opportunity to support Indigenous self-determination in data governance (Bruhn, 2014; Kukutai and Taylor, 2016; Rainie et al., 2017; ITK, 2018; Carroll et al., 2020; ICC, 2021; Hayward et al., 2021; Rowe et al., 2021; Williamson et al., 2022; Garba et al., 2023; Ignace et al., 2023; Cannon et al., 2024), as affirmed in and mandated by the United Nations Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples Act (Government of Canada, 2021b)7.
Unfortunately, the centralization of human research ethics bodies outside of Inuvialuit and Inuit homelands can lead to research projects where “non-Inuit tend to retain exclusive decision-making authority about whether or not ethical guidelines are being met” (ITK, 2018, p. 24; CIHR et al., 2022). As a result, Indigenous knowledge holders often must “make difficult decisions regarding the sharing of their knowledge as they decide whether or not they are willing to risk having their knowledge misused and appropriated” (Chapman and Schott, 2020, p. 932) through decontextualization, translation, or manipulation (McDowell et al., 2016). In this manuscript, we make a case for locally-relevant data governance practices that account for community needs and priorities, which we stipulate must translate into DFO policies. Such policies would enable researchers to best navigate and meet DFO’s dual mandates of reconciliation and climate change research and monitoring, while elevating Indigenous knowledges with communities in a purposefully “good way” (see Ball and Janyst, 2008; AHA Centre, 2018; Reid et al., 2024).
Toward this end, AD and KD worked directly with the Paulatuk Hunters and Trappers Committee (PHTC) to co-develop a data governance Statement of Shared Understanding for Traditional Knowledge8 Documentation (also referred to as a Statement of Shared Understanding throughout) specific to an interview project in Paulatuk, Inuvialuit Settlement Region. PHTC Board members are community-elected leaders in wildlife management and conservation, while AD and KD are DFO researchers of settler descent with experience applying community-grounded approaches to assess coastal biodiversity change across Inuit Nunangat. Both researchers are actively unlearning and learning as part of an ongoing effort to decolonize the spaces they occupy. This manuscript arose from a collaboration among all authors, was drafted by DFO authors, and reviewed and revised by the PHTC. The authorship reflects both the contributions of the entire PHTC Board, and individual PHTC Board members who are named in the paper (see Table 1; Section 4), and chose to be co-authors with their informed consent (TG, JI, BSR, CR, LR). Authorship was confirmed during a meeting held between the lead author and the PHTC on 24 October 2024.

Table 1. Data governance topics discussed during a phone meeting between AD and the PHTC on 1 March 2023. These topics became sections of a project- and community-specific Statement of Shared Understanding for Traditional Knowledge Documentation. AD received consent to include the names of PHTC Board members in this table in meetings on 19 June 2024, and 24 October 2024.
Here, our first objective is to describe the Statement of Shared Understanding for Traditional Knowledge Documentation co-development process and content for reference for other researchers and community leaders. Second, as an extension of this statement, we offer five non-prescriptive considerations to strengthen future data governance efforts and policies (e.g., local, regional, territorial, federal): community and project context, the changing digital landscape, individual and collective knowledge protections, planned project outputs, and confidentiality and anonymity nuances. It is our hope to influence actions in support of responsible data practices in endeavours that engage with Indigenous Peoples and knowledges.
“[D]ata management needs to become central to the design of CBM [community-based monitoring] programs, rather than an afterthought…” (Johnson et al., 2021, p. 463; Castleden et al., 2012; Tengö et al., 2021; Ellam et al., 2022). With this in mind, a Statement of Shared Understanding for Traditional Knowledge Documentation was co-developed to support a project that used interview methods to highlight and characterize leadership by the community of Paulatuk9 in coastal research and monitoring within the Anguniaqvia Niqiqyuam Marine Protected Area10. In this Statement of Shared Understanding, we clarified the intent of all parties (DFO researchers and Paulatuk Hunters and Trappers Committee) before project onset so that the community could make informed decisions about knowledge shared during the interviews. In this section, we detail the statement co-development process, which occurred from late February to May 2023 (Figure 1).
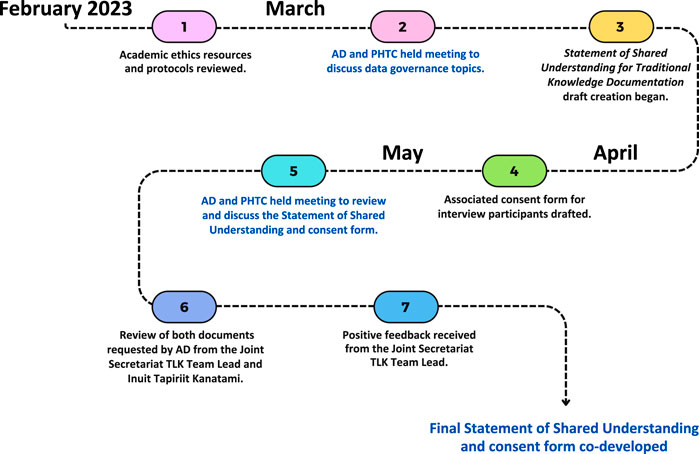
Figure 1. Timeline of the co-development of a Statement of Shared Understanding for Traditional Knowledge Documentation and a corresponding consent form, from February to May 2023. Note that AD completed Steps 1, 3, 4, 6, and 7 (in black) with the support of the PHTC to reduce burdens on community partners (see Cannon et al., 2024), while Steps 2 and 5 (in blue) involved meetings between AD and the PHTC to discuss progress. “TLK Team Lead” refers to “Traditional and Local Knowledge Team Lead” (Steps 6, 7).
In late February 2023, AD briefly reviewed academic ethics resources and documents to derive central data governance topics that could be relevant to this project. These included: written consent, confidentiality, audio and video recording, interview transcript verification, physical storage of transcripts, access to transcripts, result formats, and withdrawals from the project. On 1 March 2023, AD and the PHTC met over the phone to discuss Board member thoughts on these topics (see Table 1 for PHTC input received). It was decided that AD would compile PHTC input, and draft a document that we called a Statement of Shared Understanding for Traditional Knowledge Documentation for PHTC review at a later meeting. The document would also be used to develop a corresponding consent form for interview participants.
Throughout the remainder of March and April 2023, AD drafted a Statement of Shared Understanding for Traditional Knowledge Documentation for PHTC review, adding three sections that provided context relevant to this project: existing research relationship, progress to-date, and next steps. AD also developed a consent form based on content from the draft Statement of Shared Understanding11. On 3 May 2023, AD and the PHTC met over the phone to review the drafts of both the Statement of Shared Understanding and the consent form, where both were approved with no modifications. At this meeting, AD proposed that we request a review of the Statement of Shared Understanding for Traditional Knowledge Documentation and consent form by the Joint Secretariat12 Traditional and Local Knowledge Team Lead and Inuit Tapiriit Kanatami towards greater due diligence, and received PHTC support to do so13. In late May, positive feedback was received from the Joint Secretariat, and none from Inuit Tapiriit Kanatami; this resulted in no changes to the documents (see Supplementary Material S1, S2 for the Statement of Shared Understanding for Traditional Knowledge Documentation and consent form, respectively). A summary of content in both documents can be found in Table 2. We note that both are living documents, and can be updated as needed and when applicable to other projects within Paulatuk.
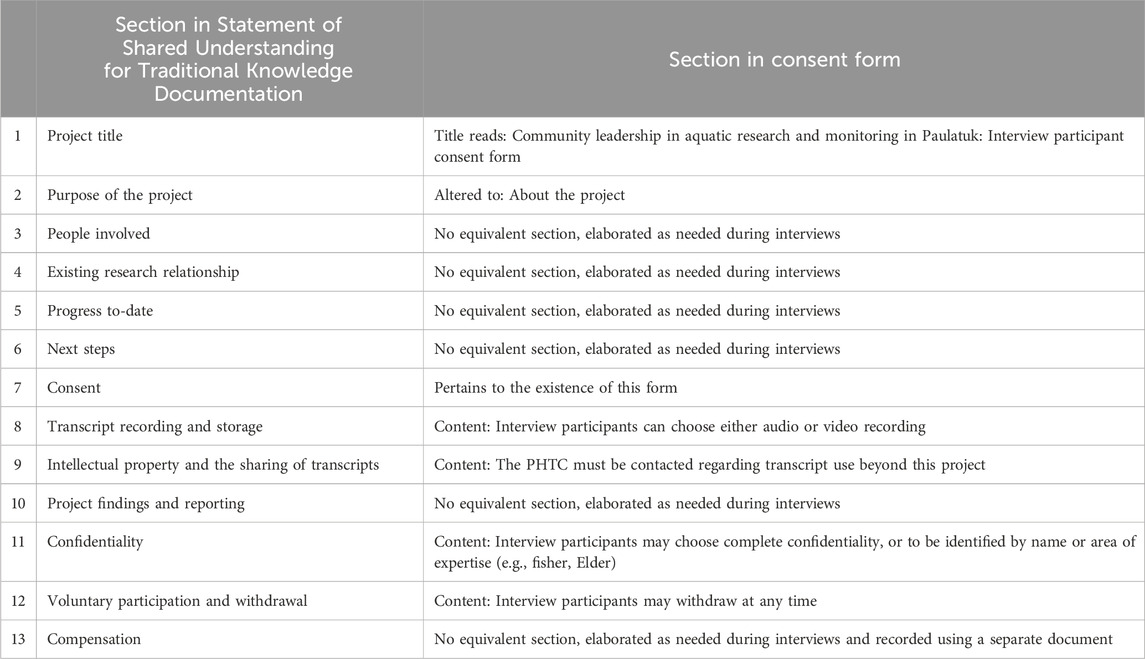
Table 2. Summary of Statement of Shared Understanding for Traditional Knowledge Documentation and consent form content.
Indigenous data governance statements and policies that “embody respect for and legal recognition of community protocols, Indigenous institutions, and customary law” (Fernández-Llamazares et al., 2021, p. 158–159; Bruhn, 2014; Champagne, 2015; Rainie et al., 2017) are needed in all DFO-community research partnerships that involve Indigenous knowledges. Indeed, in a 2019 Reconciliation Strategy, DFO committed to ensuring that “policies, programs, and processes are in place that enable Indigenous management and decision-making” (Fisheries and Oceans Canada, 2019). As an extension of the co-developed Statement of Shared Understanding for Traditional Knowledge Documentation; an initial effort to create a community-level data governance structure, we identify non-exhaustive and non-prescriptive practical considerations towards future data governance efforts and policy drafting. These include: community and project context, the changing digital landscape, individual and collective knowledge protections, planned project outputs, and confidentiality and anonymity nuances (Figure 2), where each consideration is aligned with relevant sections14 of the Statement of Shared Understanding for Traditional Knowledge Documentation. Elucidating these considerations responds to the most recent federal department-wide progress report on the implementation of the United Nations Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples Act articulating that “discussions around the complexities of Indigenous data sovereignty…are of utmost importance” (Department of Justice Canada, 2024, p. 25).
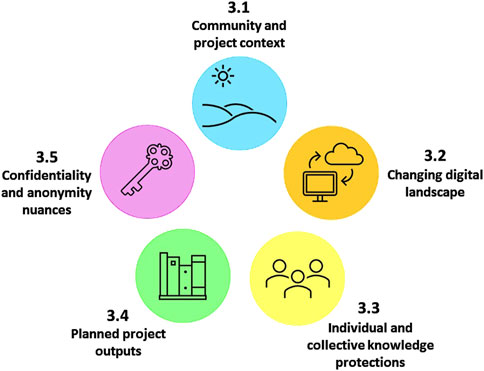
Figure 2. Considerations to inform Indigenous data governance efforts (e.g., statement development) and policy. Note that these considerations are non-exhaustive and non-prescriptive.
Value can be drawn from providing comprehensive community and project context in Indigenous data governance statements and policies; this is relevant to Section 1 through 6 in the Statement of Shared Understanding for Traditional Knowledge Documentation. These sections include project purpose, people involved, existing research relationships, progress to-date, and planned next steps. Grounding data governance frameworks in community-researcher relationships, which may include previous or current research and/or monitoring efforts, helps solidify ethical obligations of researchers towards community members (Jennings et al., 2023), and allows research participants to “assess the researcher’s credibility, and thus the validity of the research” (McGregor et al., 2018, p. 11; Kovach, 2009). Often, the four Rs (respect, relevancy, reciprocity, responsibility) are used to characterize mutually-beneficial partnerships (Kirkness and Barnhardt, 1991; Wilson, 2008), with the strength of such partnerships influencing the degree and nature of knowledge sharing and co-production (Wilson, 2008; Bohensky and Maru, 2011; Hayward et al., 2021; Ellam et al., 2022). Information regarding community backgrounds (i.e., cultural or social history) and study areas (i.e., ecological importance) will also support a locally-specific interpretation of protections (FNIGC, 2019; Garba et al., 2023).
Awareness of a changing digital landscape is relevant to Section 8 in the Statement of Shared Understanding for Traditional Knowledge Documentation concerning interview recording and transcript storage. We articulated that recordings of interviews would be transcribed, after which paper and/or electronic copies would be stored in appropriate spaces with encryptions15; these protections were deemed to be adequate. However, the growing use of digital platforms across research stages (e.g., compiling, archiving, sharing, and applying Indigenous knowledges) requires careful consideration of associated privacy laws and unique vulnerabilities (Cannon et al., 2024), as risks span from lessened community control and access to data to removal from context or misinterpretation (Johnson et al., 2021; Williamson et al., 2022; Nicholas, 2022). Of note, many Indigenous communities are beginning to use technical tools and services to protect and manage their own data (e.g., Community Knowledge Keeper, TrailMark Service, Mukurtu, Local Contexts16) (see Anderson and Christen, 2013; The Watershed Futures Initiative, 2022; Jennings et al., 2023; Cannon et al., 2024). Ever-evolving digital options and associated risks and/or benefits must be accounted for in Indigenous data governance conversations.
Recognizing challenges related to protecting individual and collective knowledges is relevant to Sections 9 and 12 in the Statement of Shared Understanding for Traditional Knowledge Documentation concerning the sharing of transcripts and project withdrawal. We have underscored that the data shared belong to both the interview participant and the Paulatuk Hunters and Trappers Committee. Participants have the right to withdraw from the project at any time; yet, disentangling and removing individual contributions from a collective narrative may be challenging once data are aggregated. In the future, it will be necessary to hold discussions at project onset regarding managing project withdrawals at all stages of the research process, and to discuss potential collective permissions to use community knowledges (Kovach, 2009; Hudson et al., 2023). Ultimately, balancing individual and collective rights “depends on the nature of the knowledge” and must always be “appropriate to, or accountable to, the knowledge that was shared” (Wilson, 2008, p. 116; Hayward et al., 2021; Williamson et al., 2022).
The need to identify planned project outputs at project onset is relevant to Section 10 in the Statement of Shared Understanding for Traditional Knowledge Documentation, focused on project findings and reporting. Section 10 details possible outputs from this project, including publications, reports, and presentations; however, we have not specified how these outputs will be developed (e.g., through verification of interview transcripts, interpretation of research findings by the community, co-interpretation by knowledge holders and researchers), or for whom they are intended (e.g., Indigenous communities, academic scholars, government biologists). Additional details should enable a clear understanding of how data will be represented in published written or visual materials (Hudson et al., 2023; Jennings et al., 2023), and associated approval processes that will be undertaken prior to publication (Castleden et al., 2012; Cannon et al., 2024; Kawerak Inc., 2024). Of course, community-oriented outputs are more likely to safeguard the context and integrity of Indigenous knowledges, and enhance the accessibility (e.g., through translation, plain-language summaries, and/or presentations), applicability, and utility of outcomes to communities.
Accounting for confidentiality and anonymity is relevant to Section 11, by a similar name, in the Statement of Shared Understanding for Traditional Knowledge Documentation. We specified that interview participant contributions would be known by the interviewer and assistant; however, holding interviews at a community camp identifies interview participants to others. For confidentiality, options given included identification by name, area of expertise, experience level and/or gender (e.g., non-Elder male harvester), or complete confidentiality. Despite this, deductive disclosure, where characteristics are combined in a way that associates them with specific individuals (Snipp, 2016), remains a concern in small communities (Love et al., 2022). In some research projects, acknowledging contributions by name may be necessary if the significance of the knowledge is linked to the individual, to “honour the relationships that they share with the knowledge we are writing down for our research. We do not claim ownership over it then” (Wilson, 2008, emphasis in original, p. 115; Castleden et al., 2012). One should also consider confidentiality at various research stages, for example, whether it will be maintained in raw data (e.g., transcripts) or only in published outcomes. This is linked to the need for clarity in data governance statements concerning de-identified data; where personal identifiers have been removed but could later be re-associated with the data, or anonymized data; where the removal of personal identifiers is permanent, which were not included in this statement.
Indigenous data governance is integral to mutually-beneficial research partnerships that are necessary in an era of rapid environmental change (e.g., Williamson et al., 2022; Jennings et al., 2023; Department of Justice Canada, 2024; Cannon et al., 2024; Kawerak Inc., 2024). Advancing data governance requires that researchers recognize that communities have “the authority to…uphold standards of research according to their cultural knowledge and understanding” (Champagne, 2015, p. 60–61; Fernández-Llamazares et al., 2021; Jennings et al., 2023)17. This tenet forms the basis of two linked avenues for researchers to strengthen Indigenous data governance with northern partners that have become apparent: 1) by supporting community-led actions to realize data governance, and 2) by advocating for institutional governance reform (Carroll et al., 2019; 2021; Ignace et al., 2023; Cannon et al., 2024). We touched upon both here, through the co-development of a community-grounded, locally-relevant data governance statement, and by providing emergent considerations to inform federal policies.
Through a partnership between DFO researchers and the Paulatuk Hunters and Trappers Committee, we co-developed a Statement of Shared Understanding for Traditional Knowledge Documentation for an interview project in Paulatuk to clarify the intent of all parties and enable informed decision-making. While data governance decision-making must always be community- and project-specific (Leone, 2021; Cannon et al., 2024; Kawerak Inc., 2024), we expect that both the co-development process (i.e., use of drafts, continuous communication through regular meetings, request for reviews by external organizations) and Statement of Shared Understanding content (e.g., transcript storage, confidentiality, voluntary withdrawal) may be helpful for other researchers and communities. In a June 2024 phone meeting, PHTC Board member and co-author Lawrence Ruben iterated that this data governance statement could “become an example for other agreements” (personal communication, L. Ruben, 19 June 2024). We offer a reminder that researchers should be prepared to take on additional responsibilities while co-generating data resources whenever necessary, and that over the long-term, increasing community capacity for governing Indigenous data (e.g., through repositories or other data infrastructure) can further enhance local data stewardship (Kukutai and Taylor, 2016; Leone, 2021; Cannon et al., 2024).
Second, we suggest that policy drafting be informed by several considerations, including: community and project context, the changing digital landscape, individual and collective knowledge protections, planned project outputs, and confidentiality and anonymity nuances. However, these policies should be continuously shaped and re-shaped by the needs of individual communities, which requires that “Indigenous Peoples [be] equal collaborators with the government throughout the policy production process” (Rowe et al., 2021, p. 94). We emphasize, that logistical and technical details are less important than relationality (i.e., to each other, to Inuvialuit or Inuit knowledges; e.g., Wilson, 2008; McGregor et al., 2018; Rowe et al., 2021) and should never “overwhelm the way data [are] discussed” (Rainie et al., 2017, p. 6). Similar to this, it is essential to recognize that the development of all community-centered practices, and subsequent transition from practice to policy, requires systemic changes and hinges upon “transformative changes in relationships with Indigenous [P]eoples” (Nicholas, 2022, p. 411; Gazing Wolf et al., 2024). This includes a repositioning of power within Indigenous communities (Castleden et al., 2012; Anderson and Christen, 2013; Carroll et al., 2019; 2020; Leone, 2021; Love et al., 2022; Ignace et al., 2023; Cannon et al., 2024)18.
Many scholars have iterated that we are in the midst of a ‘data revolution’ that has outpaced our ability to develop effective data governance policies (e.g., Kukutai and Taylor, 2016; Rainie et al., 2017; Garba et al., 2023), with existing Indigenous governance challenges slated to become greater in an era of ‘open data’ and ‘big data’19 movements. Both could “undermine Indigenous sovereignty more broadly” (Cannon et al., 2024, p. 2; Smith, 2016; Carroll et al., 2019; Leone, 2021; Hudson et al., 2023; Jennings et al., 2023), exacerbating an existing need for community-led data practices and policies that sustain, protect, and elevate Indigenous knowledge systems. We recognize that data governance will “drastically change and develop in the coming years and decades as agreements are made, technical capacities are established, and as…communities and organizations continue to assert and implement self-governance and self-determination practices” (Leone, 2021, p. 173).
We offer the reminder that ultimately, Indigenous data governance “is a journey, not a destination” (Carroll et al., 2019, p. 15; Smith, 2016). For now, we leave readers with the words of Paulatuk Hunters and Trappers Committee Board member and co-author Jody Illasiak, who commented that the Statement of Shared Understanding for Traditional Knowledge Documentation is a starting place that “gives us access to ensuring our process up here is right” (personal communication, J. Illasiak, 19 June 2024), and Board member and co-author Lawrence Ruben, who remarked that “we are amongst a group of people who are putting pen to paper and ensuring that this is going to protect us” (personal communication, L. Ruben, 19 June 2024).
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
AD: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Validation, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. PHTC: Conceptualization, Methodology, Project administration, Validation, Visualization, Writing–review and editing. TG: Conceptualization, Methodology, Project administration, Validation, Visualization, Writing–review and editing. JI: Conceptualization, Methodology, Project administration, Validation, Visualization, Writing–review and editing. BSR: Conceptualization, Methodology, Project administration, Validation, Visualization, Writing–review and editing. CR: Conceptualization, Methodology, Project administration, Validation, Visualization, Writing–review and editing. LR: Conceptualization, Methodology, Project administration, Validation, Visualization, Writing–review and editing. KD: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing–review and editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. Funding was provided by Fisheries and Oceans Canada.
We are grateful to the assistants who worked with the lead author to apply the Statement of Shared Understanding through consent forms in interviews in Paulatuk: Denise Tiffany Wolki (July 2023), Heather Thrasher (January and February 2024), Wendy Ruben (January 2024), and Donna Ruben (January 2024). Thank you also to Bessie Lennie and Melanie Wolki (PHTC Resource Persons). We thank the two reviewers for their helpful comments.
This project was completed in Inuvialuit homelands in Paulatuk, Inuvialuit Settlement Region, and Treaty No. 1 Territory in the traditional lands of the Anishinaabe, Ininew, Oji-Cree, Dene, and Dakota, and the homeland of the Métis Nation in Winnipeg, Manitoba.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fenvs.2025.1521494/full#supplementary-material
1“Knowledges” better reflects the holism and interconnectedness of Indigenous ways of understanding (sensu Grenz, 2024); however, we use “data” within this manuscript for alignment with the most commonly used and understood term.
2We define Indigenous knowledge systems as a “cumulative body of knowledge, practice, and belief, evolving by adaptive processes and handed down through generations by cultural transmission, about the relationship of living beings (including humans) with one another and with their environment” (Berkes, 2018, p. 8). Indigenous knowledge systems are a “way of life” and “something that you do” (McGregor, 2004, p. 79).
3Inuit Nunangat (Inuit homelands in Canada; includes lands, waters, and ice) includes four regions: Inuvialuit Settlement Region (Northwest Territories), Nunavut, Nunavik (Northern Québec), and Nunatsiavut (Northern Labrador).
4Hayward et al. (2021) conducted a scoping review of Indigenous ethics board, frameworks, and protocols across Canada, where only one Inuit and Inuvialuit-specific framework was found (Inuit Tapiriit Kanatami’s National Inuit Strategy on Research). This report is discussed in later paragraphs.
5Inuit Tapiriit Kanatami (ITK), based in Ottawa, Ontario, is the national representational organization protecting and advancing the rights and interests of Inuit in Canada. ITK has identified five priority areas for research in their National Inuit Strategy on Research, several of which centre on data governance. The priority areas include: advancing local governance in research, enhancing the ethical conduct of research, aligning funding with community research priorities, ensuring Inuit and Inuvialuit access, ownership, and control over data and information, and building capacity for research (ITK, 2018).
6The introduction of OCAP® principles in 1998 influenced the development of global Indigenous data governance principles in Aotearoa New Zealand, Australia, and the United States. In 2019, the Global Indigenous Data Alliance released the CARE Principles for Indigenous Data Governance: Collective benefit, Authority to control, Responsibility, and Ethics (Carroll et al., 2020; 2021; Jennings et al., 2023).
7DFO is mandated to implement the United Nations Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples Act (Government of Canada, 2021a; Government of Canada, 2022; Government of Canada, 2024), affirming that Indigenous Peoples have the right to “revitalize, use, develop and transmit to future generations their histories, languages, oral traditions, philosophies, writing systems and literature…” (Article 13) and “to maintain, control, protect and develop their cultural heritage, traditional knowledge and traditional cultural expressions…[and] their intellectual property…” (Article 31) (Government of Canada, 2021b).
8Note that we use the term “Traditional Knowledge” in alignment with community term use, in addition to “Indigenous knowledges” elsewhere in the manuscript where appropriate.
9The hamlet of Paulatuk (population: 298, Statistics Canada, 2023), is located adjacent to Darnley Bay in the Amundsen Gulf. Paulatuk is one of six communities within the Inuvialuit Settlement Region. In Siglitun, the dialect of Inuvialuktun that was (and in some cases, still is) spoken primarily in Paulatuk, Sachs Harbour, and Tuktoyaktuk, the spelling is Paulatuuq. This means “place of soot”, in reference to the soot that settled on the ground from coal used as a heat source.
10The Anguniaqvia Niqiqyuam Marine Protected Area (ANMPA, 2,358 km2) was established by DFO and Inuvialuit in 2016, and is located on the western side of Darnley Bay within the Amundsen Gulf in the Beaufort Sea. Anguniaqvia Niqiqyuam means “Nelson Green’s hunting area” for an Elder whose harvesting area was called by the same name and who passed away on the land in 1999.
11Cannon et al. (2024) have similarly put forth that conducting preliminary research and providing a draft data sharing agreement in advance can be a helpful action to reduce burdens on community partners.
12The Joint Secretariat is based in Inuvik, and provides support to co-management committees in the Inuvialuit Settlement Region established under the Inuvialuit Final Agreement (IFA, 1984).
13In a phone meeting held between the PHTC and AD on 24 October 2024 to review this manuscript, the PHTC noted that the Inuvialuit Game Council was likely also positioned to provide a review of this document; however, this avenue was not explored given that the project had already concluded. The Inuvialuit Game Council represents Inuvialuit interests in all matters that pertain to the management of wildlife and wildlife habitat (IFA, 1984).
14We do not refer to Sections 7 and 13 of the Statement of Shared Understanding for Traditional Knowledge Documentation, as they pertain to the existence of the consent form and interview participant compensation, respectively.
15Limiting access to data through mechanisms such as tiered systems of access or end-to-end encryption (i.e., data is encrypted when stored and when accessed) can provide further protections and should be considered on a project-by-project basis.
16The Local Contexts web portal allows Indigenous communities and collaborators (e.g., researchers) to customize Traditional Knowledge (TK) and Biocultural Labels for materials related to Indigenous knowledges and cultural practices; these have gained significant traction in recent years (Anderson and Hudson, 2020; Carroll et al., 2021; Williamson et al., 2022; Nicholas, 2022; Jennings et al., 2023).
17In the 2024 Third annual progress report on the implementation of the United Nations Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples Act, Indigenous partners had acknowledged the “challenge presented by insufficient and limited recognition of Indigenous data sovereignty, [and] community-owned data protocols…” (Department of Justice, 2024, p. 37).
18Such a repositioning requires that institutions (e.g., academic) with entrenched and inadequate data practices relinquish decision-making authority regarding Indigenous data (Castleden et al., 2012; Champagne, 2015; Hayward et al., 2021; Williamson et al., 2022).
19Open data renders data available to be freely used by all, while big data amalgamates open data to create large-scale datasets (Cowan et al., 2014; Leone, 2021; Cannon et al., 2024).
Aboriginal HIV/AIDS Community-Based Research Collaborative Centre (AHA Centre) (2018). AHA Centre: “Doing research in a good way”. Available at: https://www.ahacentre.ca/uploads/9/6/4/2/96422574/research_in_a_good_way_finaljune_2018.pdf.
Anderson, J., and Christen, K. (2013). Chuck a copyright on it’: dilemmas of digital return and the possibilities for Traditional Knowledge licenses and labels. Mus. Anthropol. Rev. 7 (1–2), 105–126.
Anderson, J., and Hudson, M. (2020). The Biocultural Labels Initiative: supporting Indigenous rights in data derived from genetic resources. Biodivers. Inf. Sci. Stand. 4, e59230. doi:10.3897/biss.4.59230
Andrews, T. D., Kokelj, S. V., MacKay, G., Buysse, J., Kritsch, I., Andre, A., et al. (2016). Permafrost thaw and Aboriginal cultural landscapes in the Gwich’in region, Canada. APT Bull. J. Preserv. Technol. 47 (1), 15–22.
Ball, J., and Janyst, P. (2008). Enacting research ethics in partnerships with Indigenous communities in Canada: “Do it in a good way.”. J. Empir. Res. Hum. Res. Ethics 3 (2), 33–51. doi:10.1525/jer.2008.3.2.33
Bohensky, E. L., and Maru, Y. (2011). Indigenous knowledge, science, and resilience: what have we learned from a decade of international literature on “integration”. Ecol. Soc. 16 (4), 6. doi:10.5751/ES-04342-160406
Brewster, J. D., Neumann, D., Ostertag, S. K., and Loseto, L. L. (2016) Traditional Ecological Knowledge (TEK) at Shingle Point, YT: observations on changes in the environment and fish populations, 3174. Canadian Technical Report of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 23.
Bruhn, J. (2014). Identifying useful approaches to the governance of Indigenous data. Int. Indig. Policy J. 5 (2). doi:10.18584/iipj.2014.5.2.5
Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR), Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC), Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council of Canada (SSHRC) (2022). Tri-Council Policy Statement: Ethical Conduct for Research Involving Humans, 288. Available at: https://ethics.gc.ca/eng/documents/tcps2-2022-en.pdf.
Cannon, S. E., Moore, J. W., Adams, M. S., Degai, T., Griggs, E., Griggs, J., et al. (2024). Taking care of knowledge, taking care of salmon: towards Indigenous data sovereignty in an era of climate change and cumulative effects. FACETS 9, 1–21. doi:10.1139/facets-2023-0135
Carroll, S. R., Garba, I., Figueroa-Rodríguez, O. L., Holbrook, J., Lovett, R., Materechera, S., et al. (2020). The CARE principles for Indigenous data governance. Data Sci. J. 19 (1), 1–12. doi:10.5334/dsj-2020-043
Carroll, S. R., Herczog, E., Hudson, M., Russell, K., and Stall, S. (2021). Operationalizing the CARE and FAIR principles for Indigenous data futures. Sci. Data 8 (1), 108. doi:10.1038/s41597-021-00892-0
Carroll, S. R., Rodriguez-Lonebear, D., and Martinez, A. (2019). Indigenous data governance: strategies from United States Native nations. Data Sci. J. 18, 31. doi:10.5334/dsj-2019-031
Castleden, H. E., Morgan, V. S., and Lamb, C. (2012). “I spent the first year drinking tea”: exploring Canadian university researchers’ perspectives on community-based participatory research involving Indigenous peoples. Can. Geogr. 56 (2), 160–179. doi:10.1111/j.1541-0064.2012.00432.x
Champagne, D. (2015). Centering Indigenous Nations within Indigenous methodologies. Wicazo Sa Rev. 30 (1), 57–81. doi:10.5749/wicazosareview.30.1.0057
Chapman, J. M., and Schott, S. (2020). Knowledge coevolution: generating new understanding through bridging and strengthening distinct knowledge systems and empowering local knowledge holders. Sustain. Sci. 15 (3), 931–943. doi:10.1007/s11625-020-00781-2
Chila, Z., Dunmall, K. M., Proverbs, T. A., and Lantz, T. C. (2022). Inuvialuit knowledge of Pacific salmon range expansion in the western Canadian Arctic. Can. J. Fish. Aquatic Sci. 79 (7), 1042–1055. doi:10.1139/cjfas-2021-0172
Cowan, D., Alencar, P., and McGarry, F. (2014). “Perspectives on open data: issues and opportunities,” in 2014 IEEE International Conference on Software Science, Ramat Gal, Israel (Waterloo, Canada: Technology and Engineering).
Department of Justice Canada (2024). Third annual progress report on the implementation of the United Nations Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples Act. Available at: https://www.justice.gc.ca/eng/declaration/report-rapport/2024/pdf/UNDA_Third_annual_report.pdf.
Dingwall, R. (2012). “How did we ever get into this mess? The rise of ethical regulation in the social sciences,” in Ethics in social research. Editor K. Love (Emerald Group Publishing Limited), 3–26. doi:10.1108/S1042-3192(2012)0000012004
Ellam, Y., Raymond-Yakoubian, J., Daniel, R. A., and Behe, C. (2022). A framework for co-production of knowledge in the context of Arctic research. Ecol. Soc. 27 (1), 34. doi:10.5751/ES-12960-270134
Fernández-Llamazares, Á., Lepofsky, D., Lertzman, K., Armstrong, C. G., Brondízio, E. S., Gavin, M. C., et al. (2021). Scientists’ warning to humanity on threats to Indigenous and Local Knowledge systems. J. Ethnobiol. 41 (2), 144–169. doi:10.2993/0278-0771-41.2.144
First Nations Information Governance Centre (FNIGC) (2014). Ownership, control, access and possession (OCAP®): the path to First Nations information governance. Available at: https://achh.ca/wp-content/uploads/2018/07/OCAP_FNIGC.pdf.
First Nations Information Governance Centre (FNIGC) (2019). First Nations data sovereignty in Canada. Stat. J. IAOS 35 (1), 47–69. doi:10.3233/SJI-180478
First Nations Information Governance Centre (FNIGC) (2024). The First Nations principles of OCAP®. Available at: https://fnigc.ca/ocap-training/.
Fisheries and Oceans Canada (2019). DFO-Coast Guard Reconciliation Strategy. Available at: https://waves-vagues.dfo-mpo.gc.ca/Library/40947208.pdf.
Garba, I., Sterling, R., Plevel, R., Carson, W., Cordova-Marks, F. M., Cummins, J., et al. (2023). Indigenous Peoples and research: self-determination in research governance. Front. Res. Metrics Anal. 8, 1272318. doi:10.3389/frma.2023.1272318
Gazing Wolf, J., Ignace, D. D., David-Chavez, D. M., Jennings, L. L., Smiles, D., Blanchard, P., et al. (2024). Centering Indigenous Knowledges in ecology and beyond. Front. Ecol. Environ. 22 (7). doi:10.1002/fee.2776
Government of Canada (2019). Policy on Science Integrity. Available at: https://www.dfo-mpo.gc.ca/about-notre-sujet/publications/policy-politiques/science-integrity-integrite-scientifique/index-eng.html.
Government of Canada (2021a). Minister of Fisheries, Oceans and the Canadian Coast Guard Mandate Letter. Available at: https://pm.gc.ca/en/mandate-letters/2021/12/16/minister-fisheries-oceans-and-canadian-coast-guard-mandate-letter.
Government of Canada (2022). Mandate letter and other issues related to DFO-CCG. Available at: https://www.dfo-mpo.gc.ca/transparency-transparence/briefing-breffage/2022/mandate-other-mandat-autre-eng.htm#_Toc95983253.
Government of Canada (2024). Implementing the United Nations Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples Act. Available at: https://www.justice.gc.ca/eng/declaration/index.html.
Grenz, J. (2024). Medicine Wheel for the Planet: A Journey Toward Personal and Ecological Healing. Toronto, Canada: Knopf Canada.
Hayward, A., Sjoblom, E., Sinclair, S., and Cidro, J. (2021). A new era of Indigenous research: community-based Indigenous research ethics protocols in Canada. J. Empir. Res. Hum. Res. Ethics 16 (4), 403–417. doi:10.1177/15562646211023705
Health Canada (2024). Research Ethics Board: overview of the Health Canada and Public Health Agency of Canada REB. Available at: https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/science-research/science-advice-decision-making/research-ethics-board.html.
Hudson, M., Carroll, S. R., Anderson, J., Blackwater, D., Cordova-Marks, F. M., Cummins, J., et al. (2023). Indigenous Peoples’ rights in data: a contribution toward Indigenous research sovereignty. Front. Res. Metrics Anal. 8, 1173805. doi:10.3389/frma.2023.1173805
Ignace, L., Burton, L., Mynott, S., Meehan, M., Olson, E., Steel, J., et al. (2023). Researchers’ responsibility to uphold Indigenous rights. Science 381 (6654), 129–131. doi:10.1126/science.adh4470
Inuit Circumpolar Council (ICC) (2021). “Ethical and equitable engagement synthesis report: a collection of Inuit rules, guidelines, protocols, and values for the engagement of Inuit communities and Indigenous knowledge from across Inuit Nunaat,” in Synthesis report. International, 40.
Inuit Tapiriit Kanatami (ITK) (2018). National Inuit Strategy on Research. Available at: https://www.itk.ca/wpcontent/uploads/2018/03/National-Inuit-Strategy-on-Research.pdf.
Inuit Tapiriit Kanatami (ITK), and Nunavut Research Institute (NRI) (2007). in Negotiating research relationships with Inuit communities: a guide for researchers. Editors S. Nickels, J. Shirley, and G. Laidler, 38. Available at: https://www.itk.ca/negotiating-research-relationships-guide/.
Inuvialuit Final Agreement (IFA) (1984). The Western Arctic Claim: The Inuvialuit Final Agreement (Ottawa, Canada: Indian and Northern Affairs Canada).
Jennings, L., Anderson, T., Martinez, A., Sterling, R., Chavez, D. D., Garba, I., et al. (2023). Applying the “CARE principles for Indigenous data governance” to ecology and biodiversity research. Nat. Ecol. & Evol. 7 (10), 1547–1551. doi:10.1038/s41559-023-02161-2
Johnson, N., Druckenmiller, M. L., Danielsen, F., and Pulsifer, P. L. (2021). The use of digital platforms for community-based monitoring. Bioscience 71 (5), 452–466. doi:10.1093/biosci/biaa162
Kawerak Inc., Chinik Eskimo Community, King Island Native Community, Native Village of Brevig Mission, Native Village of Council, Native Village of Diomedeet al. (2024). Kawerak-Region tribal protocols, guidelines, expectations & best practices related to research. Prep. by Kawerak Soc. Sci. Program Sandhill.Culture.Craft. Nome, Alaska. Available at: https://kawerak.org/download/kawerak-region-tribal-research-protocols-guidelines-expectations-best-practices/?tmstv=1712337991.
Kirkness, V., and Barnhardt, R. (1991). First Nations and higher education: the four Rs—respect, relevance, reciprocity, responsibility. J. Am. Indian Educ. 30, 1–15. doi:10.2307/24397980
Kovach, M. (2009). Indigenous methodologies: characteristics, conversation, and contexts. Toronto, Canada: University of Toronto Press.
Kukutai, T., and Taylor, J. (2016). Indigenous Data Sovereignty: Toward An Agenda. Canberra, Australia: Australian National University Press.
Leone, D. Z. (2021). Data colonialism in Canada: decolonizing data through Indigenous data governance. Ottawa, Ontario: Carleton University. PhD dissertation.
Love, R. P., Hardy, B.-J., Heffernan, C., Heyd, A., Cardinal-Grant, M., Sparling, L., et al. (2022). Developing data governance agreements with Indigenous communities in Canada: toward equitable tuberculosis programming, research, and reconciliation. Health Hum. Rights 24 (1), 21–33. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9212824/.
McDowell, G., Ford, J., and Jones, J. (2016). Community-level climate change vulnerability research: trends, progress, and future directions. Environ. Res. Lett. 11, 033001. doi:10.1088/1748-9326/11/3/033001
McGregor, D. (2004). “Traditional ecological knowledge and sustainable development: towards coexistence,” In The Way of Development: Indigenous Peoples, Life Projects and Globalization, Editors M. Blaser, H. A. Feit, and G. McRae (London, United Kingdom: Zed Books).
D. McGregor, J.-P. Restoule, and R. Johnston (2018). Indigenous research: Theories, Practices, And Relationships. Toronto, Canada: Canadian Scholars.
McNicholl, D. G., Christie, L. R., Dunmall, K. M., Illasiak, S., Ruben, N., Illasiak, D., et al. (2024) Anguniaqvia Niqiqyuam Marine Protected Area coastal monitoring: synthesis of 2017-2021 summer and winter field programs, 3595. Canadian Technical Report of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences. xiv + 103.
McNicholl, D. G., Harris, L. N., Loewen, T., May, P., Tran, L., Akeeagok, R., et al. (2021). Noteworthy occurrences among six marine species documented with community engagement in the Canadian Arctic. Anim. Migr. 8 (1), 74–83. doi:10.1515/ami-2020-0113
Natural Resources Canada (2024). RCan’s Draft Policy on Ethics for Research involving Indigenous Peoples and Territories. Available at: https://natural-resources.canada.ca/our-natural-resources/indigenous-peoples-and-natural-resources/nrcans-draft-policy-on-ethics-for-research-involving-indigenous-peoples-and-territori/25747.
Nicholas, G. (2022). Protecting Indigenous heritage objects, places, and values: challenges, responses, and responsibilities. Int. J. Herit. Stud. 28 (3), 400–422. doi:10.1080/13527258.2021.2009539
Ostertag, S. K., Loseto, L. L., Snow, K., Lam, J., Hynes, K., and Gillman, D. V. (2018). “That’s how we know they’re healthy”: the inclusion of traditional ecological knowledge in beluga health monitoring in the Inuvialuit Settlement Region. Arct. Sci. 4 (3), 1–29. doi:10.1139/as-2017-0050
Ovitz, K. L., Matari, K. G. A., O’Hara, S., Esagok, D., and Loseto, L. L. (2024). Observations of social and environmental change on Kendall Island (Ukiivik), a traditional whaling camp in the Inuvialuit Settlement Region. Arct. Sci. 10 (1), 140–168. doi:10.1139/as-2022-0016
Rainie, S. C., Schultz, J. L., Briggs, E., Riggs, P., and Palmanteer-Holder, N. L. (2017). Data as a strategic resource: self-determination, governance, and the data challenge for Indigenous Nations in the United States. Int. Indig. Policy J. 8 (2), 1–29. doi:10.18584/iipj.2017.8.2.1
Reid, A. J., McGregor, D. A., Menzies, A. K., Eckert, L. E., Febria, C. M., and Popp, J. N. (2024). Ecological research “in a good way” means ethical and equitable relationships with Indigenous Peoples and Lands. Nat. Ecol. & Evol. 8 (4), 595–598. doi:10.1038/s41559-023-02309-0
Reyes-García, V., Tofighi-Niaki, A., Austin, B. J., Benyei, P., Danielsen, F., Fernández-Llamazares, Á., et al. (2022). Data sovereignty in community-based environmental monitoring: toward equitable environmental data governance. BioScience 72 (8), 714–717. doi:10.1093/biosci/biac048
Rowe, R. K., Bull, J. R., and Walker, J. D. (2021). “Indigenous self-determination and data governance in the Canadian policy context,” in Indigenous Data Sovereignty and Policy. Editors M. Walter, T. Kukutai, S. R. Carroll, and D. Rodriguez-Lonebear (New York, United Kingdom: Routledge), 244. doi:10.4324/9780429273957-6
Smith, D. E. (2016). “Governing data and data for governance: the everyday practice of Indigenous sovereignty,” in Indigenous Data Sovereignty: Toward An Agenda. Editors T. Kukutai, and J. Taylor (Canberra, Australia: Australian National University Press), 344. Available at: https://press-files.anu.edu.au/downloads/press/n2140/pdf/book.pdf.
Snipp, C. M. (2016). “What does data sovereignty imply: what does it look like?,” in Indigenous Data Sovereignty: Toward An Agenda. Editors T. Kukutai, and J. Taylor (Canberra, Australia: Australian National University Press), 344. Available at: https://press-files.anu.edu.au/downloads/press/n2140/pdf/book.pdf.
Statistics Canada (2023). Paulatuk, Hamlet Northwest Territories [census subdivision]. Census profile. 2021 Census. Stat. Can. Cat. no. 98-316-X2021001. Available at: https://www12.statcan.gc.ca/census-recensement/2021/dp-pd/prof/index.cfm?Lang=E.
Tengö, M., Austin, B. J., Danielsen, F., and Fernández-Llamazares, Á. (2021). Creating synergies between citizen science and Indigenous and Local Knowledge. Bioscience 71 (5), 503–518. doi:10.1093/biosci/biab023
The Watershed Futures Initiative (2022). Indigenous Data Sovereignty in Salmon Watersheds Toolkit. Available at: https://www.watershedfuturesinitiative.com.
Williamson, B., Provost, S., and Price, C. (2022). Operationalising Indigenous data sovereignty in environmental research and governance. Environ. Plan. 2 (1-2), 281–304. doi:10.1177/26349825221125496
Wilson, S. (2008). Research is Ceremony: Indigenous Research Methods. Winnipeg, Canada: Fernwood Publishing.
Keywords: Indigenous data governance, Inuvialuit, co-development, shared understanding, policy, Paulatuk, Canada
Citation: Drake AK, Paulatuk Hunters and Trappers Committee, Green T, Illasiak J, Ruben BS, Ruben C, Ruben L and Dunmall KM (2025) Advancing Indigenous data governance through a shared understanding in Paulatuk, Inuvialuit Settlement Region. Front. Environ. Sci. 13:1521494. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2025.1521494
Received: 11 November 2024; Accepted: 13 January 2025;
Published: 19 March 2025.
Edited by:
James Kevin Summers, Office of Research and Development, United StatesReviewed by:
Melanie McDermott, The College of New Jersey, United StatesCopyright © 2025 Paulatuk Hunters and Trappers Committee, Tony Green, Jody Illasiak, Bill S. Ruben, Candace Ruben, Lawrence Ruben and His Majesty the King in Right of Canada, as represented by the Ministry of Fisheries, Oceans, and the Canadian Coast Guard. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Allison K. Drake, YWxsaXNvbi5kcmFrZUBkZm8tbXBvLmdjLmNh
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.