- 1College of Civil Engineering and Architecture, China Three Gorges Univerisity, Yichang, China
- 2College of hydraulic and environmental engineering, China Three Gorges Univerisity, Yichang, China
- 3College of Biological and Pharmaceutical Sciences, China Three Gorges Univerisity, Yichang, China
- 4Hubei Provincial Engineering Research Center of Cement-based Ecological Restoration Technology, China Three Gorges University, Yichang, Hubei, China
Background: To improve the scientificity of the evaluation results of the planting performance of the Yellow River sediment based on planting substrate.
Methods: This study replaced the natural soil with Yellow River sediment, used cement as the cementing material, added different proportions of organic matter and amendment of habitat material to prepare planting substrate based on the Yellow River sediment, and carried out experiments by using oats and proposed a combined SQI-CRITIC combined weighting calculation method based on the least square method for its evaluation.
Results: The results showed that (1) different proportions of cement and amendment of habitat material led to significant variations in the planting performance of the planting substrate based on Yellow River sediment: among the 5# mix ratio, the plant height (12.5 cm) and biomass (3.06 g) of oats reached extreme values. Photosynthetic rate (1.97
Conclusion: The experimental results can be extended to more areas that need to use sandy soil for ecological restoration, with a view to providing a theoretical basis for soil quality evaluation, soil and water conservation control, and ecological construction in the Yellow River Basin.
1 Introduction
As the second largest river in China and the largest sand-producing river in the world, the Yellow River produced an average of 661 million metric tons of sand per year from 1952 to 2015 (Zhang et al., 2020a; Xu et al., 2023). The massive deposition of sediments in the Yellow River causes the riverbed to rise, obstructing the flow of water and reducing the effective storage capacity of reservoirs, affecting their normal operation and consequently triggering the problem of water shortage in downstream areas. The Yellow River Basin occupies an important position in the national ecological security strategy, but the region is mainly located in arid and semi-arid zones with limited water resources, sandy chalky soils, and poor plant growth conditions, which are highly lead to ecological degradation (Weber et al., 2007).Therefore, it is important to utilise the Yellow River sediment to improve soil properties and plant growth performance.
Currently, the most dominant sand control technologies are mainly engineering sand fixation, chemical sand fixation, and biological sand fixation. Fixing sandy soils can significantly improve the physical and chemical properties of the sediment, facilitate the soil formation process, and improve the regional microclimate (Wan et al., 2022). Silicate cements, especially common silicate cement (PC), are widely used as soil binders,due to their easy availability and high setting strength (Wang et al., 2024a). However, the widespread use of cement is associated with large amounts of CO2 emissions, which have a negative impact on the environment (Zhang et al., 2021). It is clear that there is an urgent need to reduce the use of cement and to explore more environmentally friendly methods of soil improvement, such as using plant fibers to replace part of the cement. Therefore, adopting green ecological methods to improve the Yellow River sediment can improve soil properties, promote plant growth, and reduce environmental impacts, thus contributing to sustainable development. Research has demonstrated that the amalgamation of planting soil with cement, organic matter, and amendment of habitat material to form a planting substrate for artificial ecological slope protection possesses the characteristics of rich soil fertility, rapid vegetation succession, low economic cost, and high benefit (Gao et al., 2020; Xu et al., 2024). However, it is important to note that the addition of diverse substances can significantly influence the evaluation indexes, thereby impacting the evaluation outcomes. Currently, there is no uniform soil quality evaluation standard or fixed evaluation method in the international arena. The evaluation will be considered in terms of the type of ecosystem, the function of the soil, and the land use mode, as well as the purpose of the evaluation and the scale of the evaluation (Chen et al., 2013; Damiba et al., 2024). A comprehensive overview of the available methods reveals two predominant approaches: qualitative evaluation, which includes techniques such as the soil quality card, and quantitative evaluation, encompassing methods like the soil quality index method, soil quality model, fuzzy mathematical method, multiple linear regression, and relative soil quality method, among others. It is noteworthy that soil quality method has garnered significant popularity for soil evaluation purposes (Bünemann et al., 2018).This paper summarized various methods of soil quality evaluation and found that the selection of evaluation indicators and their weights in soil quality evaluation model was very important. However, the selection of weights is predominantly determined by a single method, which introduces a certain degree of bias. Consequently, a comprehensive approach is recommended, integrating the weights to perform soil quality evaluation. This approach not only circumvents the influence of subjective human factors and objective data factors, such as extreme values, on the weights but also enhances the evaluation accuracy of the model (Raiesi, 2017; Xu et al., 2023; Nasir et al., 2024). Research has demonstrated that the amalgamation of planting soil with cement, organic matter, and amendment of habitat material to form a planting substrate for artificial ecological slope. However, the combination assignment is challenging to apply due to its complexity and computational intricacy. Mao et al. (2024) utilized the combination assignment method to predict greenhouse environmental changes, and Wang et al. (2024b) employed the MULTIMOORA-Borda method to determine the weights of each index for the evaluation of ecological management in the Yellow River. It is evident that the combination assignment method has been adaptively employed in diverse fields of research (Liang et al., 2023; Tang et al., 2023), though its utilization in the evaluation of enhanced soil remains limited. Nonetheless, it is imperative for endeavors aimed at ecological restoration and environmental protection. Protection possesses the characteristics of rich soil fertility, rapid vegetation.
To address the above problems, this study uses the Yellow River sediment to replace the natural soil, uses cement as the cementing material, adds different ratios of organic matter and amendment of habitat materials to prepare the planting substrate based on Yellow River sediment; the oat was used in the planting experiment, and combined with the evaluation theory of Soil Quality Index (SQI) method and CRITIC method, a combined weight calculation method of SQI-CRITIC based on the least square method was proposed to evaluate the oat. The purpose of this system is to provide reference for quantitative evaluation of the planting performance of the planting substrate based on Yellow River sediment, to improve the quality of planting substrate after ecological restoration in cold and arid areas, and to provide theoretical basis for the evaluation of the soil quality in Yellow River Basin.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Experimental material
The main materials of Yellow River sediment based planting substrate include sediment, amendment of habitat material, organic matter and cement (Luo et al., 2023; Guo et al., 2024). The sediment was sourced from the Yellow River sediment of Lake Wuhai in the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, which is classified as chalky sandy soil with an approximate clay content of 5.3%, a base pH of 8.54, and a weakly alkaline nature, with a total of 1.42 g/kg of soil organic matter (SOM), 0.21 g/kg of total nitrogen (TN), 0.33 g/kg of total phosphorus (TP), and 1.95 g/kg of total potassium (TN) (Liu et al., 2024). The amendment of habitat material and organic matter was sourced from Hubei Yichang, where the amendment of habitat material was supplied by Three Gorges University (Patent No. 01138343.7). This amendment of habitat material contains a variety of functional microorganisms that can activate the substrate, provide nutrients, and regulate the alkaline environment of cement hydration and promote the growth of plants and microorganisms without affecting the strength of the substrate (Xia et al., 2022). For the organic matter fraction, wood chips were selected as the source for this experiment, with the aim of increasing the nutrient content and improving the internal pore structure of the concrete, thus optimizing the overall performance (Li et al., 2019; Guo et al., 2023). The wood chips used were factory-processed fir wood chips, the majority of which showed small granularity. The density was low, between 0.2 and 0.5 g/cm3. The aeration pores are large, while the water-holding pores are small, resulting in poor water retention (Smith et al., 2023). The pH is usually between neutral and weakly alkaline, and the main components are cellulose (about 40%–50%), hemicellulose (about 20%–30%), and lignin (about 20%–30%), with a small amount of ash, extractives, etc. The wood chips employed in this study are factory-processed for wood chips, with the majority exhibiting a small particle size.
2.2 Experiment design
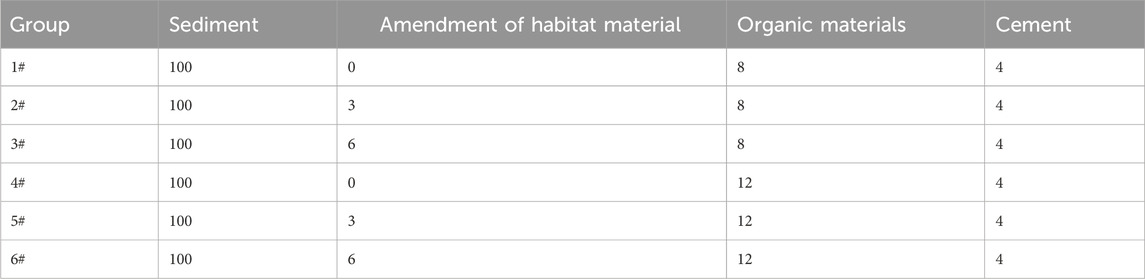
To maximize the resource use of the Yellow River sediment and reduce the cost of planting substrate, this study used sediment as a complete replacement for planting soil. In each set of ratios, a mass percentage of 100% of the sediment was used as the reference base, and the mass percentages of all the other component materials were calculated relative to this benchmark. According to the results of historical literature (Liu et al., 2012), the gradient of amendment of habitat material was set to 0%, 3%, and 6%, and the gradient of the organic matter was set to 8%, 12%. The detailed mixes are shown in Table 1. The components were prepared according to Table 1 below and then mixed. According to the results of the preliminary experiment, oat has adaptability in the planting substrate based on Yellow River, so oat was chosen as the test grass species. The planting experiment was carried out in Wuhai test base, and we sprayed the planting substrate use technology of vegetative concrete (Song et al., 2024), the process is as follows: (1) clean up the slope surface and cover with 30 cm of Yellow River sediment, (2) level the slope, (3) Lay the reinforced layer and hang the net, (4) mix the material, (5) spay the 8 cm base layer of planting substrate, (6) spread the seeds, (7) spray the 2 cm surface layer of planting substrate, (8) covered with grass curtains for natural curing.
2.3 Index of experiment
Six standard sample squares (0.5 m × 0.5 m) were randomly selected from each side slope for the experiment. Oats have a growth cycle of 3∼5 months and grow rapidly. The pre-test showed that all oats could be achieved after 7 days and the indicators could be measured by portable photosynthetic meter after 2 weeks. Consequently, the germination rate of oats was recorded at 10 a.m. each day. When the growth reached 15 days, the photosynthetic rate (Pn), transpiration rate (Tr), stomatal conductance (Gs), intercellular carbon dioxide (Ci), and water utilization (WUE) were measured using a portable photosynthesizer (Li-6800, LI-COR Biosciences, Lincoln, NE, United States) (Lu et al., 2016; Wang et al., 2021; Smith et al., 2023). The study of oat stomatal morphology was conducted using a method of blotting, followed by observation and photography using an electron microscope (Leica DM2500). The measurement of stomatal length (SL), stomatal width (SW), stomatal area (SA), stomatal perimeter (SP), and stomatal density (SD) index was then performed in oats (Behdad et al., 2021). Subsequent to the measurement of plant height (PLH) using a scale, the plants were cut flush and placed in an oven at 105°C for 2 h, after which they were dried at a transverse temperature of 80°C until constant weight. The biomass (Bi) of the plants was then weighed.
2.4 Data analysis
2.4.1 SQI assessment method
This study employs the SQI method to evaluate planting performances of the planting substrate based on Yellow River. The comprehensive evaluation of the vegetation performance is divided into four steps: 1) select indicators; 2) calculate affiliation; 3) determine the weight of the indicators 4) scores the indicator of vegetation performance of the planting substrate based on Yellow River. Due to the different units of growth, gas exchange and stomatal morphology indicators, each plant growth indicator was transformed and normalized to a value between 0 and 1, before the assessment of the planting performance (Damiba et al., 2024).The formula for calculating the affiliation function is shown below:
Where
We used Equation 1, when the indicator is positively correlated with planting performance, however we used Equation 2, when the indicator is negatively correlated with planting performance. In order to determine the extent of each indicator contributes to planting performance, we used a principal component analysis (PCA) to get the weighting values of indicators. Subsequently, we calculated the planting performance scores of the planting substrate based on Yellow River under different mixing ratios considering the weight and affiliation of each index. The calculation formula is as follows:
Where n is the number of planting performance indicators;
2.4.2 CRITIC assessment method
This study employs the CRITIC method to evaluated planting performances of the planting substrate based on Yellow River. The calculation formula is as follow Equations 3–7:
1) The original data are processed according to Equations 1, 2.
2) Form each indicator into a vector
3) Use MATLAB to calculate the linear correlation coefficients
4) Calculate the amount of information
where
5) Normalisation of the indicator’s information vector
2.4.3 The SQI-CRITIC combination model based on the least squares method
We combined the weights
where
The evaluation value of combination and the weight evaluation value of SQI and CRITIC method:
to ensure the final combined weight is most effective, it is essential to minimize the Euclidean distance
where u is the degree of preference for SQI method (0 ≤ u ≤ 1). A Lagrangian function is established and the Partial derivatives are taken:
According to the existence condition of extreme values, it can be obtained from the Partial derivative formula:
Take the Partial derivative of the independent variables
2.5 Data processing
One-way analyses of variance (ANOVA) and Duncan’s multiple comparison test were used to assess statistically significant difference (P < 0.05) among Plant growth, gas exchange, and stomatal characteristics. All data statistical analyses were performed using Matlab and SPSS, and using Origin 2023 for correlation plotting.
3 Results
3.1 Determination of the index system
3.1.1 Growth indicator
Figure 1 illustrates the statistics of germination rate, plant height, and biomass of oats in the planting substrate based on the Yellow River sediment, using different organic materials and amendment of habitat materials. The germination rate of oats exceeded 90% under all six groups, indicating suitability for growth in this planting substrate (Figure 1A). Organic matter and amendment of habitat materials showed a non-linear relationship with oat growth indices (Figure 1B). When the proportion of organic matter was fixed, oat plant height and biomass initially increased with increasing habitat amendments, reaching a peak at the 5# mix ratio (plant height: 12.5 cm, biomass: 3.06 g). Conversely, with a fixed proportion of amendment of habitat materials, increasing organic matter led to an increase in plant height and biomass. These findings highlight the optimal mix ratio of the planting substrate based on the Yellow River for maximizing oat growth parameters.
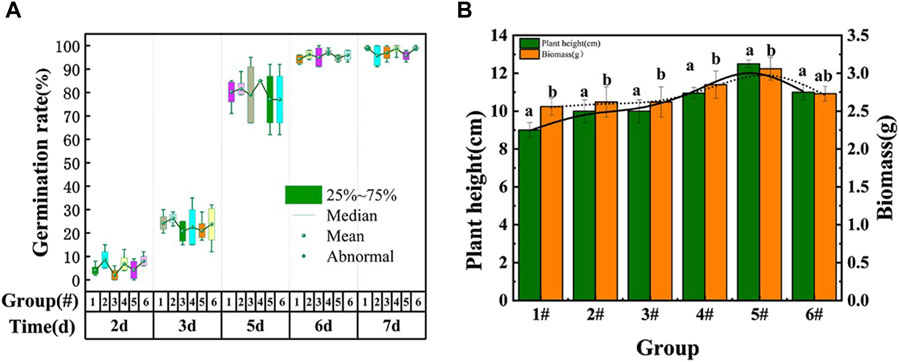
Figure 1. (A) Germination rate. (B) Plant height and biomass. Statistical chart of growth index of Avena sativa.
3.1.2 Gas exchange parameter
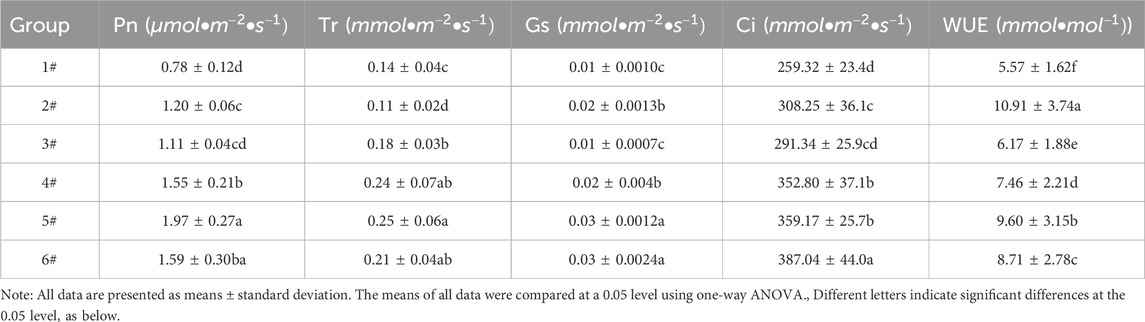
In our investigation of the stomatal exchange parameters of oats, a fixed proportion of organic matter, we increased the amount of amendment of habitat materials, which led to improved photosynthetic and transpiration rates. These rates peaked and then diminished as the proportion of amendment of habitat materials continued to increase, with mixture 5# displaying notably higher net photosynthetic and transpiration rates (P < 0.05). This suggests an optimal threshold for mix proportions that maximizes photosynthetic efficiency. Statistical analysis conducted using one-way ANOVA revealed significant differences across the groups, indicated by the letters in Table 2, underscoring the influence of mixture composition on oat physiology. These findings have considerable implications for the development of vegetation concrete mixtures optimized for ecological restoration, particularly for enhancing the photosynthetic capacity of plants.
3.1.3 Stomatal morphological characteristics
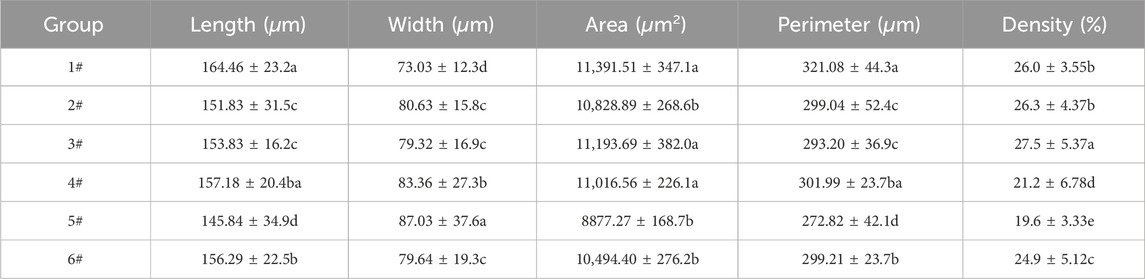
As shown in Figure 2, we obtained the morphological indices of oat stomata by using the imprinting method under different mix proportions, in which we observed the distribution of stomata in the leaves of the oat plant. At a fixed proportion of organic matter, the number of stomata per unit area of oat on the vegetation concrete was less, with a more significant proportion of organic matter added. Figure 2; Table 3 show that stomatal density increased with an increase in the amendment of habitat materials in the 8% organic matter group. However, when the organic matter content was 12%, stomatal density first increased and then decreased with an increase in habitat material amendment. This suggests that excess nutrients can inhibit stomatal density.
As shown in Table 3, different mixing ratios affected the stomatal density and width of the oats (P < 0.05). The stomatal width was the largest at 5#, and the stomatal length, area, and density were the smallest (P < 0.05). When the organic matter addition ratio was certain, the amendment of habitat material increased within the range of 4∼6#, the stomatal width increased and then decreased, and the stomatal density was significantly reduced (P < 0.05). This indicates that oats adapt to the damage caused by excess nutrients by regulating their stomatal density. With the addition of a certain proportion of habitat materials, organic matter decreased, and stomatal area increased. Additionally, there was a nonlinear negative correlation between organic matter and stomata. The results show that oats resist soil nutrient deficiency by adjusting stomatal width.
3.2 Comprehensive evaluation of soil quality based on SQI analysis
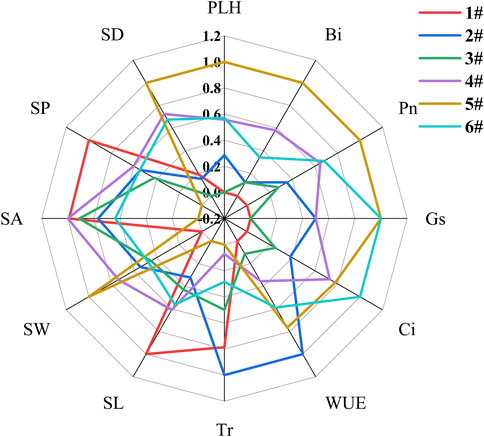
Based on Formulas 1, 2, we calculate the membership degree of each indicator, and Figure 3 presents the radar chart illustrating the membership degrees for each oat indicator. The membership function, also known as a scoring function, characterizes the advantages and disadvantages of these indicators. The closer the affiliation degree is to 1, it is considered that the indicators are “excellent”, and the affiliation degree is close to 0, it is considered that the indicators are “poor”. According to the principle of maximum affiliation, we can judge the optimal indexes of the different planting substrate based on the Yellow River sediment. It can be seen that the axial intersection curves significantly under different mixing ratios. Within the 5# group, six optimal indicators emerged, including plant height, biomass, photosynthetic rate, stomatal conductance, stomatal width, and stomatal density. Groups 1#, 2#, and 6# each exhibited two sets of optimal indicators, while only one set appeared in group 4#, which was stomatal area.
Using the SQI method, we determined the weights of the 12 indicators. According to the results of the SQI analysis (Table 4), the first principal component accounts for 67.294% of the variance, the second principal component explains 16.264%, and the third principal component explains 9.948%, resulting in a cumulative contribution rate of 93.506% for the first three components. It can reflect the information of the original variables well. With cumulative contribution rates exceeding 90% and eigenvalues greater than 1, the first three principal components are selected for calculating the weights of vegetation performance evaluation indices of the planting substrate based on Yellow River sediment in this study.
3.3 Comprehensive evaluation of soil quality based on CRITIC analysis
Figure 4 shows the correlation for planting performance indicators of oat. Oat biomass and plant height were found to be positively correlated (P < 0.05). Generally, oat plant height and biomass exhibited strong correlations with net photosynthetic rate, transpiration rate, stomatal conductance, and intercellular carbon dioxide levels (P < 0.05). Additionally, both oat plant height and biomass were positively correlated with stomatal width and density (P < 0.05). Photosynthetic rate and transpiration rate were positively correlated (P < 0.05). Furthermore, photosynthetic rate showed a significant correlation (P < 0.05) with stomatal width and stomatal density. Stomatal width exhibited a negative correlation with stomatal perimeter, whereas stomatal perimeter was positively correlated with stomatal area (P < 0.05). The experiment demonstrated that the planting substrate based on Yellow River sediment, with varying mixing ratios, influenced oat photosynthesis by affecting stomatal width, thus impacting oat growth.
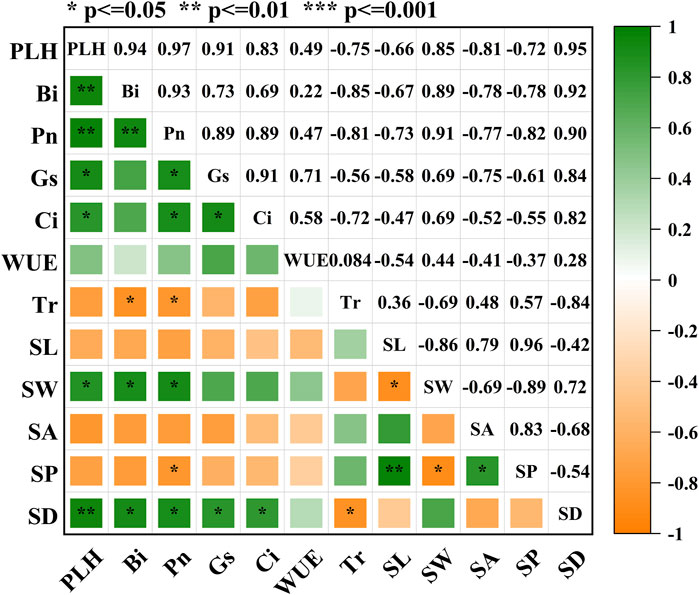
Figure 4. Correlation among indicators. Note: PLH, Plant height; Bi, Biomass; Pn, Photosynthetic rate; Tr, Transpiration rate; Gs, Stomatal conductance; Ci, Intercellular carbon dioxide; WUE, Efficiency of water application; SL, Stomata Length; SW, Stomata Width; SA, Stomata Area; SP, Stomata Perimeter; SD, Stomata Density.
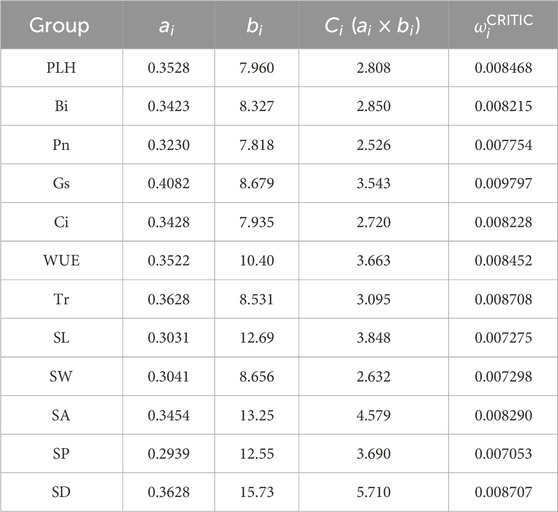
Table 5 shows the weight of planting performance indice of the planting substrate based on Yellow River sediment with different organic materials and amendment of habitat material content, evaluated using the CRITIC method. First, we calculated affiliation of the data. Second, the weights were calculated, then the conflict and variability were calculated, and finally the weights were calculated. The weight values for the 15 groups of planting performance indicators ranged from 0.00705 to 0.0098, with stomatal conductance being the only indicator exceeding the overall average weight of 0.0098.
3.4 Comparison of the assessment scores for the planting performance under different weightings
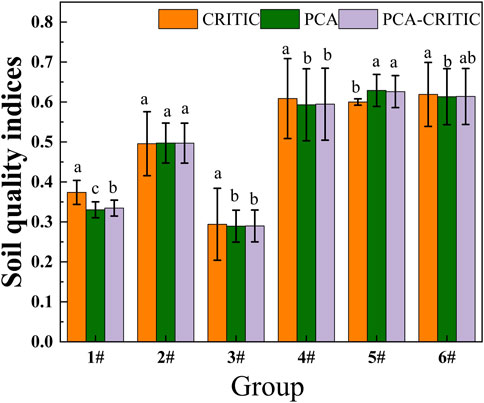
Figure 5 illustrates the comparative evaluation results using three methods. The evaluation results of group 1∼3# have a large variation, and the average value of the evaluation results of the three groups increases from 34.62% to 49.67% and then decreases to 29.11%. Conversely, the evaluation results of group 4∼6# have a smaller difference, and the variation of the average value is in the range of 59.88%–61.83%, and all the three evaluation results have reached the maximum value in the group 5#. Specifically, the CRITIC method resulted in an evaluation of 60.00%, the SQI analysis yielded 62.89%, and the SQI-CRITIC combination using the least squares method achieved 62.60%. This suggests that group 5# offers suitable soil fertility and structure conducive to oat cultivation.
4 Discussion
4.1 Effect of different mixing ratios on the performance of planting
Successful plant growth is the key to the success of the planting substrate based on Yellow River sediment. Relatively few studies have been conducted to explore the relationship between changes in plant stomatal morphology and plant growth under varying organic matter and amendments of habitat material contents in the planting substrate based on Yellow River sediment. Figure 4 demonstrates that biomass and plant height of oats were positively correlated (P < 0.05). Overall, both oat plant height and biomass showed strong positive correlations (P < 0.05) with net photosynthetic rate, transpiration rate, stomatal conductance, and intercellular carbon dioxide levels, as well as positive correlations (P < 0.05) with stomatal width and density. When stomata are closed, the intake of carbon dioxide into the leaf decreases, thereby restricting carbon fixation in the Calvin cycle and reducing photosynthetic efficiency (Yuan et al., 2019; Zhang et al., 2020a; Zhang et al., 2020b). As depicted in Figure 1B, oat height and biomass increased with higher levels of organic matter when certain amendments of habitat material contents were present. Oat height and biomass reached peak values within the 5# ratio. This conclusion was further validated (Wang et al., 2024c). Table 3 Statistical table of morphological indicators of oat stomata, indicates that with a fixed ratio of organic matter, stomatal width initially increased and then decreased with the addition of amendments of habitat material ranging from 4# to 6#. This is due to the fact that the amendments of habitat material contains a large number of decomposing bacteria carrying out the secretion of exogenous enzymes, which are able to decompose the macromolecules such as cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin in the wood chips. Bacteria, fungi and other microbial communities act synergistically to gradually break down wood fibres into soluble sugars, fatty acids and other simple organic matter. Through cellular uptake, it undergoes oxidative metabolism, releasing carbon dioxide, water and mineral elements, completing the mineralisation process and providing directly useable nutrients to the plant. When nutrients exceed a certain threshold, oat growth is inhibited and stomata are closed, further reducing the plant’s ability to accumulate nutrients through photosynthesis and limiting plant growth. The whole experiment shows that appropriate nutrients promote plant growth, but too much or too little nutrients will inhibit plant growth. Therefore, it is necessary to find the optimal combination of organic matter and amendments of habitat material contents content to improve the vegetative performance of the planting substrate based on Yellow River sediment and promote plant growth.
4.2 Comprehensive evaluation result of SQI-CRITIC combination model based on least square method
The comprehensive evaluation theory of the SQI method and CRITIC method is integrated, and we have innovatively established the least squares SQI-CRITIC combination model for comprehensively evaluating the planting performance of substrates based on Yellow River sediment. Since the specific functions and continuous values vary depending on the soil properties of the planting substrate, as provided in ecological restoration, the selection of evaluation indices the planting performance of the planting substrate based on Yellow River sediment should be scientifically and professionally justified. In this study, growth indices, gas exchange parameters, and stomatal morphology of oats were selected to establish the index system for substrate planting performance based on Yellow River sediment. Key indicators were analyzed as follows: biomass serves as a growth indicator for oats, showing a positive correlation with gas exchange rates and stomatal aperture (P < 0.05). The study observed that oat biomass exhibited an initial increase followed by a decrease with increasing amendments of habitat materials when the organic matter proportion was fixed. Conversely, biomass increased with higher organic matter proportions when amendments of habitat materials were fixed, suggesting an optimal mixing ratio that maximizes oat growth parameters. The photosynthetic rate of oats was significantly higher with 12% organic matter compared to 8%. Additionally, the photosynthetic rate of the 5# group (1.97
In this study, the SQI-CRITIC combined model, based on the least squares method, was utilized to conduct a comprehensive evaluation of soil quality. The results indicated significant variation in the evaluation scores of groups 1∼3#, whereas the scores for groups 4∼6# exhibited less fluctuation. Notably, the evaluation results peaked at a maximum value of 62.60% within group 5. The study further uncovered that organic matter can notably enhance soil planting performance. Specifically, when the organic matter addition rate was set at 12% and the amendments of habitat materials addition rate at 3%, oat growth status was optimal. Taking these factors into account, the study suggests adopting a 5# mass ratio, with a composition of sediment: amendment of habitat material: organic matter: cement = 100:3:12:4, for ecological restoration projects aiming to achieve optimal oat growth and effective ecological renewal.
4.3 Comparative analysis of different evaluation results
The weight values differed among the three methods used for calculation, but the evaluated results showed a consistent trend of change: the lowest value was observed in group 3#, while the highest was in group 5#. Specifically, the analysis yielded results of 60.00% using the CRITIC method, 62.89% for the SQI method, and 62.60% for the SQI-CRITIC combined model based on the least squares method. Studies indicate that organic matter promotes plant growth, and amendment of habitat materials aid in organic matter decomposition (Jiang et al., 2021; Guo et al., 2023). However, excessive amounts of organic matter and amendment of habitat materials can inhibit plant growth. In this study, the least squares method was utilized to combine the weights derived from the SQI and CRITIC methods, enabling quantification of assessment results and model establishment. The calculated results showed differences within 15% compared to the other two methods, validating the scientific rigor of our research. Results obtained from the combined model were slightly lower than those from the SQI method, suggesting greater accuracy and alignment with actual conditions using the SQI-CRITIC combined model based on the least squares method. The evaluation system covers growth indices, gas exchange parameters, and stomatal characteristics, providing a comprehensive and professional assessment framework that is scientifically sound and practical. These findings can serve as a valuable reference for quantitatively evaluating vegetative performance in planting substrates based on Yellow River sediment.
5 Conclusion
In order to improve the scientificity of the evaluation results of the planting performance of Yellow River sediment-based planting substrate, this study used Yellow River sediment to prepare the planting substrate, used oats to conduct the planting experiments, and proposed a combined SQI-CRITIC assignment calculation method based on the least square method. After comparing the calculation results of both SQI and CRITIC methods, the conclusions are as follows:
(1) Different cement and ecological agent contents produced significant changes in the planting performance of the planting substrate based on Yellow River sediment. Within the 5# mix ratio, the plant height (12.5 cm) and biomass (3.06 g) of oats reached extreme values. Photosynthetic rate (1.97
(2) The findings obtained by the SQI-CRITIC combined model employing the least squares (LS) method are scientifically valid, more accurate, and realistic.
(3) The study demonstrates that organic matter can significantly enhance the planting performance of soil, particularly when the proportion of organic matter added is 12%, which results in the optimum plant growth performance. Consequently, it is recommended to utilize the mass ratio of sediment, amendment of habitat material, organic matter, and cement mixture = 100:3:12:4 in ecological restoration.
Due to the limitations of time and test site conditions, the test results were not verified by a large number of tests, which will be the focus of future research. The results of the study can provide a reference for the quantitative evaluation of the planting performance of planting substrate based on Yellow River sediments and a theoretical basis for the evaluation of soil quality, soil and water conservation control, and ecological construction in the Yellow River Basin.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
NW: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Validation, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. DX: Writing–review and editing. XD: Investigation, Methodology, Writing–original draft. BZ: Investigation, Supervision, Validation, Writing–review and editing. WX: Funding acquisition, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by Research on Modification of Lake Sediment and Ecological Restoration Technology of Landfills in Cold and Dry Areas in Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region (2021ZD0007-03).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fenvs.2025.1462404/full#supplementary-material
References
Behdad, A., Mohsenzadeh, S., and Azizi, M. (2021). Growth, leaf gas exchange and physiological parameters of two Glycyrrhiza glabra L. Populations subjected to salt stress condition. Rhizosphere 17, 100319. doi:10.1016/j.rhisph.2021.100319
Bünemann, E. K., Bongiorno, G., Bai, Z., Creamer, R. E., Deyn, G. D., Goede, R. D., et al. (2018). Soil quality – a critical review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 120, 105–125. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2018.01.030
Chen, Y. D., Wang, H. Y., Zhou, J. M., Xing, L., Zhu, B. S., Zhao, Y. C., et al. (2013). Minimum data set for assessing soil quality in farmland of northeast China. Pedosphere 23, 564–576. doi:10.1016/s1002-0160(13)60050-8
Damiba, W. A. F., Gathenya, J. M., Raude, J. M., and Home, P. G. (2024). Soil quality index (sqi) for evaluating the sustainability status of kakia-esamburmbur catchment under three different land use types in narok county, Kenya. Heliyon 10, e25611. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e25611
Fan, X., Cao, X., Zhou, H., Hao, L., Dong, W., He, C., et al. (2020). Carbon dioxide fertilization effect on plant growth under soil water stress associates with changes in stomatal traits, leaf photosynthesis, and foliar nitrogen of bell pepper (capsicum annuum L.). Environ. Exp. Bot. 179, 104203. doi:10.1016/j.envexpbot.2020.104203
Gao, J., Liu, D., Xu, Y., Chen, J., Yang, Y., Xia, D., et al. (2020). Effects of two types of activated carbon on the properties of vegetation concrete and cynodon dactylon growth. Sci. Rep. 10, 14483. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-71440-w
Guo, H., Zhang, Q., Chen, Y., and Lu, H. (2023). Effects of biochar on plant growth and hydro-chemical properties of recycled concrete aggregate. Sci. Total Environ. 882, 163557. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.163557
Guo, S., Xia, L., Xia, D., Li, M., Xu, W., and Liu, L. (2024). Enhancing plant resilience: arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi’srole in alleviating droughtstress in vegetation concrete. Front. Plant Sci. 15 (2024), 1401050. doi:10.3389/fpls.2024.1401050
Jiang, D., Jiang, D., Lv, S., Cui, S., Sun, S., Song, X., et al. (2021). Effect of flame-retardant rice straw fibers on properties of fiber cement-based composites at high temperatures. J. Build. Eng. 44, 102923. doi:10.1016/j.jobe.2021.102923
Li, Z., Qiul, K., Schneider, L., Rebecca, J., morreale, S., and Xie, Y. (2019). Comparison of microbial communitystructures in soils with woody organicamendments and soils with traditionallocal organic amendments in Ningxia of Northern China. PeerJ 7, 6854. doi:10.7717/peerj.6854
Liang, H., Jiang, X., Yang, Y., Zhou, S., Wang, Y., and Yang, L. (2023). A risk assessment method of the energy supply chain based on combination weights and technique for order preference by similarity to an ideal solution. Energy Rep. 9, 1647–1656. doi:10.1016/j.egyr.2023.04.227
Liu, B., Liao, M., Wan, Y., He, X., and Wang, D. (2024). Hydraulic Characteristics and Vegetation Performance of the Yellow River Sediment Modified By Biochar[J]. Biogeotechnics 2, 100070. doi:10.1016/j.bgtech.2024.10007
Liu, D., Li, S., Xu, W., and Cheng, Z. (2012). Rational selection of organic matter types and proportions for vegetated concrete. Water Conservancy Hydropower Technol. Prog. 32 (04), 37–40. doi:10.3880/j.issn.1006-7647.2012.04.009
Lu, Z., Ren, T., Pan, Y., Li, X., Cong, R., and Lu, J. (2016). Differences on photosynthetic limitations between leaf margins and leaf centers under potassium deficiency for Brassica napus L. Sci. Rep. 6, 21725. doi:10.1038/srep21725
Luo, T., Xia, L., Xia, D., Liu, W., Xu, Y., He, Z., et al. (2023). Impact of typical land use type on the stability and content of carbon and nitrogen of soil aggregates in western Hubei. Ecosphere 14. doi:10.1002/ecs2.4736
Ma, Y., Wei, Z., Liu, J., Liu, X., Hou, J., and Liu, F. (2021). Effects of K+ and Ca2+ supplement during fertigation on leaf gas exchange and salt tolerance of cotton at full and deficit irrigation regimes. Environ. Exp. Bot. 186, 104435. doi:10.1016/j.envexpbot.2021.104435
Mao, X., Ren, N., Dai, P., Jin, J., Wang, B., Kang, R., et al. (2024). A variable weight combination prediction model for climate in a greenhouse based on bigru-attention and lightgbm. Comput. Electron. Agric. 219, 108818. doi:10.1016/j.compag.2024.108818
Nasir, M. J., Haider, M. F., Ali, Z., Akhtar, W., and Alam, S. (2024). Evaluation of soil quality through simple additive soil quality index (sqi) of tehsil charsadda, khyber pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 23, 42–54. doi:10.1016/j.jssas.2023.09.001
Raiesi, F. (2017). A minimum data set and soil quality index to quantify the effect of land use conversion on soil quality and degradation in native rangelands of upland arid and semiarid regions. Ecol. Indic. 75, 307–320. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2016.12.049
Sharifi, P., and Bidabadi, S. S. (2020). Strigolactone could enhances gas-exchange through augmented antioxidant defense system in salvia nemorosa L. Plants subjected to saline conditions stress. Industrial Crops Prod. 151, 112460. doi:10.1016/j.indcrop.2020.112460
Smith, E. N., Aalst, M. V., Tosens, T., Niinemets, Ü., Stich, B., Morosinotto, T., et al. (2023). Improving photosynthetic efficiency toward food security: strategies, advances, and perspectives. Mol. Plant 16, 1547–1563. doi:10.1016/j.molp.2023.08.017
Song, L., Zhao, B., Xia, D., Wu, X., Hu, X., Xu, W., et al. (2024). Study on the effect of planting substrate based on Yellow River sediment for ecological restoration in mining area. Coal Sci. Technol., 1–16. doi:10.12438/cst.2023-1702
Tang, X., Wang, J., and Zhang, X. (2023). Optimal combination weight interval-valued carbon price forecasting model based on adaptive decomposition method. J. Clean. Prod. 427, 139232. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.139232
Wan, Y., Hui, X., He, X., Xue, J., Feng, D., Chen, Z., et al. (2022). Utilization of flue gas desulfurization gypsum to produce green binder for dredged soil solidification: strength, durability, and planting performance. J. Clean. Prod. 367, 133076. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.133076
Wang, N., Xia, D., Duan, X., Song, L., Zhao, B., and Xu, W. (2024a). Effects of cement and straw fiber on water retention of plant substrate based on Yellow River sediment. Coal Sci. Technol. 6, 1–12. doi:10.12438/cst.2024-0513
Wang, P., Fu, Y., Liu, P., Zhu, B., Wang, F., and Pamucar, D. (2024b). Evaluation of ecological governance in the Yellow River Basin based on uninorm combination weight and multimoora-borda method. Expert Syst. Appl. 235, 121227. doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2023.121227
Wang, S., Zhang, G., Liang, C., Huang, T., and Zhang, P. (2024c). Insight into the early hydration characteristics of portland cement with hydroxyethyl methyl cellulose highlighted by 1h low-field nmr. Constr. Build. Mater. 424, 135904. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2024.135904
Wang, Z., Wang, Z., Ma, L., Lv, X., Meng, Y., and Zhou, Z. (2021). Straw returning coupled with nitrogen fertilization increases canopy photosynthetic capacity, yield and nitrogen use efficiency in cotton. Eur. J. Agron. 126, 126267. doi:10.1016/j.eja.2021.126267
Weber, J., Karczewska, A., Drozd, J., Licznar, M., Licznar, S., Jamroz, E., et al. (2007). Agricultural and ecological aspects of a sandy soil as affected by the application of municipal solid waste composts. Soil Biol. Biochem. 39, 1294–1302. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2006.12.005
Xia, L., Zhao, B. Q., Luo, T., Xu, W., Guo, T., and Xia, D. (2022). Microbial functional diversity in rhizosphere and non-rhizosphere soil of different dominant species in a vegetation concrete slope. Biotechnol. and Biotechnol. Equip. 36, 379–388. doi:10.1080/13102818.2022.2082319
Xu, W., Yao, W., Bai, Z., Yang, J., and Li, L. (2023). Ecological risk evaluation and ecological restoration model of mining in the source area of the Yellow River Basin. Land 12, 933. doi:10.3390/land12040933
Xu, Y., Luo, T., Wu, B., Xia, Z., Xu, W., and Gao, J. (2024). Soil carbon emissions and influential factors across various stages of vegetation succession in vegetated concrete. Sci. Rep. 14, 5963. doi:10.1038/s41598-024-56473-9
Yuan, W., Suo, J., Shi, B., Zhou, C., Bai, B., Bian, H., et al. (2019). The barley Mir393 has multiple roles in regulation of seedling growth, stomatal density, and drought stress tolerance. Plant Physiology Biochem. 142, 303–311. doi:10.1016/j.plaphy.2019.07.021
Zhang, J., Shang, Y., Liu, J., Fu, J., and Cui, M. (2020a). Improved ecological development model for lower Yellow River floodplain, China. Water Sci. Eng. 13, 275–285. doi:10.1016/j.wse.2020.12.006
Zhang, R., Arrigoni, A., and Panesar, D. K. (2021). Could reactive mgo cement Be a green solution? The effect of Co2 mineralization and manufacturing route on the potential global warming impact. Cem. Concr. Compos. 124, 104263. doi:10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2021.104263
Keywords: planting substrate, Yellow River sediment, planting performance, comprehensive evaluation, ecological restoration
Citation: Wang N, Xia D, Duan X, Zhao B and Xu W (2025) Evaluation of the planting performance for planting substrate using the SQI-CRITIC combination model based on the least squares method. Front. Environ. Sci. 13:1462404. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2025.1462404
Received: 24 September 2024; Accepted: 15 January 2025;
Published: 06 February 2025.
Edited by:
Jifu Ma, Yan’an University, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Wang, Xia, Duan, Zhao and Xu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Dong Xia, eGlhZG9uZ3NhbnhpYUAxNjMuY29t
 Ning Wang
Ning Wang Dong Xia2,3,4*
Dong Xia2,3,4* Bingqin Zhao
Bingqin Zhao