- School of Finance and Economics, Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang, Jiangsu, China
Digital infrastructure, as a core component of new infrastructure, plays a powerful engine role in driving urban development. It not only profoundly shapes the future landscape of cities but also plays an irreplaceable role in accelerating the dual transition of industries toward digitization and greening. This process not only promotes the deep integration and synergistic development of urban digitization and greening but also cleverly builds a bridge for the dual benefits of pollution reduction and carbon reduction, laying a solid foundation for achieving an environmentally friendly and resource-saving society. This study adopt a multifaceted approach to explore the impact of digital infrastructure on the synergistic management of urban pollution abatement and carbon reductions. The coefficient for this effect was statistically significant at a 1% significance level (0.1056), demonstrating its capacity to support reductions in both pollution and carbon emissions, with regional variations observed. Furthermore, examining factor flows reveals that digital infrastructure promotes enhanced labor, capital, and innovation flows. Notably, the impact of digital infrastructure on these sectors exhibited coefficients of 57.5616, 0.0097, and 0.0189 respectively. These findings point to a significant nexus between digital infrastructure and sustainable urban development. A nonlinear U-shaped relationship was observed between digital infrastructure and the joint effect of both pollution mitigation and carbon reduction. This study concludes with policy recommendations aiming to optimize the utilization of digital infrastructure for achieving sustainable urban development goals.
1 Introduction
Air pollution and carbon emissions, recognized as pivotal contributors to global warming (Allen et al., 2009; Amann et al., 2013), present substantial challenges to the attainment of sustainable development goals (SDGs). Therefore, reducing air pollution and mitigating carbon emissions holds a universal imperative for global progress.
China’s extensive economic development model has fueled a continuous increase in carbon emissions (Zheng H. et al., 2023), while simultaneously grappling with elevated levels of air pollution compared to other nations. Notably, over 40% of Chinese cities are projected to exceed the international average PM2.5 concentration by 2021 (Hu et al., 2022), impacting both public health and economic wellbeing. Based on this, the Chinese government has implemented a series of measures to reduce pollution and carbon emissions, such as promoting clean energy and strengthening environmental regulation. However, with the acceleration of urbanization and rapid economic development, pollution and carbon emission issues remain severe. Against this backdrop, how to further innovate management methods and enhance the effectiveness of pollution reduction and carbon emission reduction has become an important topic in the management practices of urban pollution and carbon reduction.
Digital infrastructure, as an emerging technological force, is gradually demonstrating its potential in promoting green economic transformation and reducing pollution and carbon emissions. Driven by data innovation, built on communication networks, and centered around data computing facilities, digital infrastructure possesses the powerful ability to break down barriers, optimize resource allocation, and facilitate industrial advancement (Guo et al., 2023; Tranos, 2012).The burgeoning field of digital infrastructure research is exploring the impact on environmental quality (J. Hu et al., 2023; Zhuo et al., 2023). Digital infrastructure plays a critical role in facilitating industrial digitalization by enabling seamless integration with traditional sectors, thereby fostering transformative changes within industrial structures (Ren et al., 2021; Xue et al., 2022). This integration has the potential to mitigate air pollutants and carbon emissions through industrial transformation. However, certain studies raise concerns regarding the possibility of increased energy consumption arising from extensive digital infrastructure deployment (Ren et al., 2021; Xue et al., 2022). However, there is still controversy regarding how digital infrastructure affects air pollutants and carbon emissions, necessitating deeper analysis and discussion. It is essential to clarify the mechanisms by which digital infrastructure influences the synergistic effects of pollution reduction and carbon reduction.
This study examines the impact of digital infrastructure on the synergistic effects of pollution reduction and carbon reduction using relevant data from 282 cities in China from 2011 to 2021. The research objectives are as follows: first, to clarify the specific role of digital infrastructure in current urban pollution and carbon reduction management practices; second, to reveal how digital infrastructure indirectly promotes pollution reduction and carbon reduction by influencing the flow of factors; and finally, to explore potential nonlinear effects of digital infrastructure on the synergistic effects of pollution reduction and carbon reduction, as well as to identify key influencing factors. It is hoped that this research will provide scientific evidence and practical guidance for policymakers, facilitating greater effectiveness in urban pollution and carbon reduction efforts in China and globally.
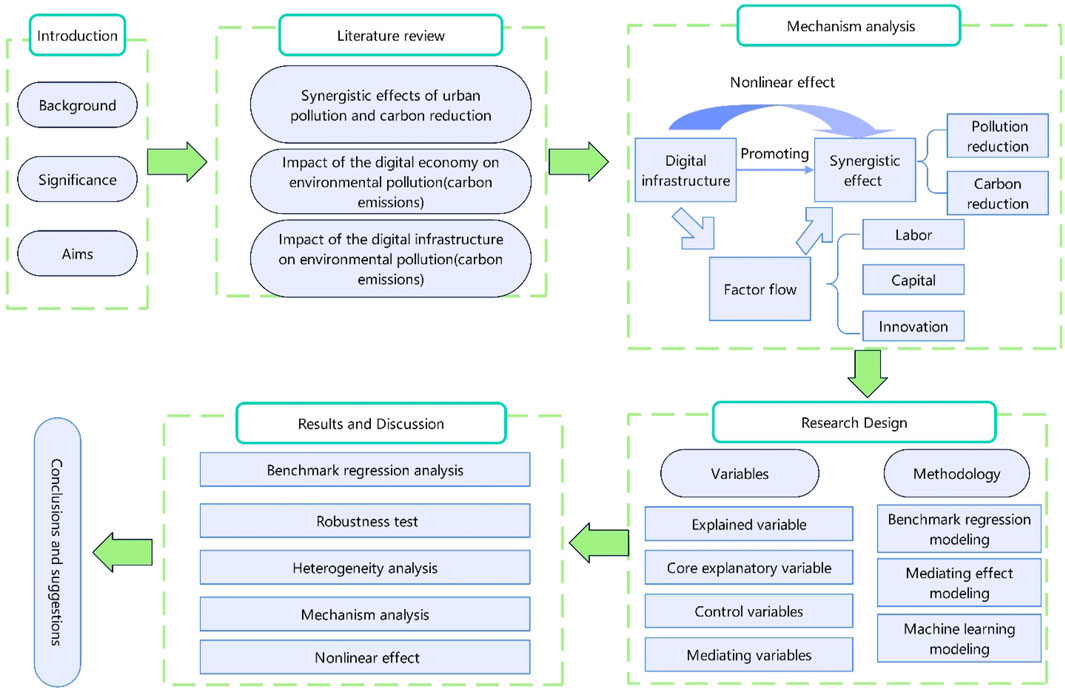
The paper is structured as follows: the second section presents a comprehensive review of relevant literature; the third section employs mechanism analysis to elucidate causal relationships between variables; the fourth section details the methodology employed in this study, emphasizing methodological rigor and transparency; the fifth section synthesizes findings and offers an in-depth discussion; and the concluding section provides actionable recommendations for policy development and implementation. The structure of this paper is shown in Figure 1.
2 Literature review
Economic and societal development has driven a substantial increase in carbon emissions and air pollutants (He et al., 2011), posing a severe threat to both the ecological environment and public health (Chen D. et al., 2021). Existing research focuses on measuring the level of coordinated management of carbon emissions and air pollutants, as well as assessing the influencing factors and impacts. For example, Henneman et al. (2016) utilized the GAINS model to investigate the complex interactions between air pollution and carbon emissions under various environmental scenarios. Liu et al. (2024) used an improved Tapio Decoupling Principle and Probit model to explore the factors affecting the synergistic effects of urban pollution reduction and carbon emission mitigation, and ultimately found that environmental regulation is the main influencing factor. Fujimori et al. (2015) emphasized the effectiveness of carbon trading in mitigating both air pollutants and carbon emissions, leading to positive ecological outcomes. In addition, some scholars have conducted research specifically on the construction industry, aiming to explore the actual effects of construction waste sorting on promoting pollution reduction and carbon emission reduction (Liu et al., 2023), as well as the potential impact of this measure on economic growth (Wang Z. et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2024).
The burgeoning digital economy exerts a profound influence on urban development, necessitating comprehensive analysis of its multifaceted relationship with environmental sustainability. Existing research has focused primarily on elucidating the nexus between the digital economy and urban pollution reduction, as well as the regulatory mechanisms governing carbon emissions. Nonetheless, the scholarly discourse regarding the impact of digital economic expansion on pollution reduction remains fragmented. While some scholars espouse a positive outlook, anticipating transformative potential for reducing air quality issues, others advocate a cautious stance, citing concerns about an “energy rebound effect”. Heddeghem et al. (2014) posit that the digital economy’s growth may trigger increased energy consumption, thereby exacerbating regional atmospheric pollution levels. Che and Wang (2022), on the other hand, leveraged PM2.5 data to assess haze pollution levels and employed multiperiod DID modeling to demonstrate a positive correlation between the digital economy and reduced haze pollution levels. Further research into this complex dynamic is critical for a nuanced understanding of the digital economy’s contribution to environmental conservation.
The digital economy presents a nuanced landscape for carbon reduction, with Bai et al. (2023) emphasizing its capacity to curtail emissions through industrial transformation and upgrading. However, their work highlights the potential for such progress to trigger a relocation of heavy industries to underdeveloped regions, thereby exacerbating localized carbon emissions in those areas. Li and Wang (2022), in contrast, investigated the spatial spillover effects of the digital economy on carbon emissions, revealing an inverted U-shaped pattern in their findings. This complexity underscores the need for deeper investigation into this phenomenon. Further research delves into the intricate interplay between the digital economy and pollution reduction strategies. Hu (2023), employing a DID method within a quasi-natural experimental setup in the Big Data Comprehensive Experimental Zone, examined this dynamic. Their findings revealed that advancements in the digital economy effectively mitigate environmental pollution and carbon emissions while highlighting technological innovation and energy efficiency as pivotal drivers of these positive impacts.
Research into the impact of digital infrastructure on urban air pollution and carbon emissions has yielded a complex picture (Tang and Yang, 2023). While Qiao et al. (2021) found that improving energy efficiency through traditional infrastructure upgrades can lead to decreased air pollution, Zou and Pan (2023) emphasize the role of digital infrastructure in mitigating this issue, attributing its positive impact to green innovations. Studies by Zhang P. et al. (2022) further highlight the potential for digital infrastructure to enhance air quality through industrial structure upgrades and technological advancements, particularly within Chinese provinces. However, some scholars caution that digital infrastructure can exacerbate air pollutant emissions. Notably, increased ICT development in specific South American countries has been linked to exacerbated air pollution levels, highlighting the need for careful consideration (Avom et al., 2020; Cheng et al., 2019). Based on an analysis of comprehensive data from 83 countries worldwide, Che et al. (2024) concluded that the development of digital infrastructure has significantly driven the increase in national carbon emissions by promoting capital aggregation and increasing the consumption of fossil energy.
The deployment of digital infrastructure in the context of carbon reduction is multifaceted and subject to ongoing investigation. Dong et al. (2022) employed a double difference model to analyze this relationship, revealing that technological innovation, industrial structure upgrades, optimized factor allocation, and fostering industrial concentration are key drivers of carbon reductions facilitated by digital infrastructure. However, the spatial spillover effects of digital infrastructure on carbon emissions have also been scrutinized, with scholars observing distinct regional variations (Liu and Wan, 2023; Sun and Kim, 2021). Notably, a subset of researchers posit that the relationship between digital infrastructure and carbon emission reduction is not straightforward. Hu et al. (2023) employed threshold and quantile models to delve into this dynamic, uncovering an increasing marginal effect of digital infrastructure on carbon emissions reduction, suggesting potential benefits for cities with advanced low-carbon practices, but perhaps hindering efforts in those lagging behind. Conversely, Sadorsky (2012) conducted a dynamic panel data study focusing on the influence of ICT growth on electricity demand, revealing that its impact surpasses income levels, potentially indicating a negative impact on carbon reduction efforts by expansion of digital infrastructure. Wang and Zhong (2023), further explored this point, identifying an energy-intensive distribution scenario resulting from digital infrastructure expansion, which ultimately leads to diminished energy efficiency and subsequently heightened carbon emissions.
Despite a wealth of research endeavoring to elucidate the implications of the digital economy for environmental pollution and carbon emissions, the existing body of literature is notably sparse with respect to the specific influence of digital infrastructure on these critical issues. The majority of extant studies have concentrated on the direct effects of the digital economy on environmental indicators, often overlooking the complex, synergistic interplay between digital infrastructure and the mitigation of pollution. This gap in understanding stems from a lack of comprehensive analysis of the intricate nonlinear dynamics that govern the relationship between digital infrastructure and environmental conservation, which are influenced by a myriad of factors, including evolving energy demands and advancements in energy efficiency technologies. Therefore, there is an urgent need for further research to delve into the complex interplay between digital infrastructure and carbon mitigation strategies. Such an investigation is essential for a nuanced evaluation of the role digital infrastructure plays in environmental conservation, particularly through a thorough examination of its nonlinear dynamics. An integrated analysis of the governance of pollution and carbon reduction will be instrumental in achieving a more accurate assessment of the contribution of digital infrastructure to sustainable urban development.
3 Mechanism analysis
Digital infrastructure, a cornerstone of the contemporary infrastructure paradigm, plays a crucial role in modernizing daily life through the integration of information technology. Unlike traditional infrastructure reliant on physical components like iron and concrete, digital infrastructure offers inherent eco-friendly advantages, consuming significantly less energy than its counterpart (Lan and Zhu, 2023). This results in reduced ecological footprints within urban environments. Moreover, digital infrastructure fosters cleaner industrial practices by enabling residents to embrace more sustainable lifestyles. Smart home technologies empower individuals to exert precise control over their energy consumption, while intelligent air conditioning systems adapt output based on temperature fluctuations to minimize wastage (Favoretto et al., 2022; Ghosh et al., 2022). Similarly, smart lighting systems intelligently adjust based on ambient light conditions. The integration of digital infrastructure into daily routines supports the decarbonization of household routines and contributes to reduced energy usage, air pollution, as well as environmental sustainability in various sectors. Specifically, digital infrastructure promotes a notable enhancement in manufacturing sector’s energy efficiency (Rathore et al., 2018; Yong et al., 2020), achieved by leveraging big data and cloud computing to optimize production processes, streamline operations, and reduce unnecessary energy and carbon emissions. Furthermore, digital infrastructure supports collaborative efforts between industries, encourages resource recycling, waste reduction, thereby decreasing pollutants and greenhouse gas emissions. In transportation, where significant emissions are prevalent, digital infrastructure provides crucial solutions for reducing carbon footprints through smart transportation systems, data-driven traffic forecasting, congestion prediction, and route optimization (Chen et al., 2016; Guerrero-ibanez et al., 2015). The adoption of new energy vehicles fueled by digital infrastructure further mitigate pollution and carbon emissions in transit operations (Li J. et al., 2024). These advancements underpin the research hypothesis that:
H1. Digital infrastructure can accelerate the process of urban pollution reduction and carbon reduction and realize the synergy of pollution reduction and carbon reduction.
Digital infrastructure has revolutionized the dynamics of production factors, transcending geographical barriers to facilitate a self-sustaining and efficient circulation of resources within a more robust market ecosystem. This transformation is driven by digital infrastructure’s ability to break down physical limitations and foster interconnectedness (Ndubuisi et al., 2021).This expansion dramatically broadens information dissemination, mitigating informational disparities within the workforce (Hu et al., 2023), thereby streamlining workforce integration into suitable roles and enhancing labor mobility. Furthermore, digital infrastructure enhances knowledge access through online platforms, empowering individuals to acquire essential skills for diverse occupational contexts (Raab et al., 2001), ultimately elevating overall workforce education levels and fostering greater versatility (Tang and Zhao, 2023). This enhanced skill acquisition further promotes labor market fluidity. Digital infrastructure’s impact is not limited to labor; it also drives capital mobility at unprecedented speeds. Digital trading platforms facilitate swift mutual understanding between trading entities (He et al., 2020), accelerating the financing process and optimizing capital utilization. These innovations stimulate financial markets through novel financial products, derived from digital integration (Stein, 2002). Consequently, the flow of capital is facilitated significantly. Furthermore, enhancing digital infrastructure fosters financial innovation, which involves integrating digital technologies to create new financial products (Li et al., 2022). This expansion in investment options for investors leads to increased market activity and further accelerates the movement of capital. Third, digital infrastructure facilitates the movement of factors that drive creativity. By leveraging internet platform connectivity and interaction capabilities, digital infrastructure enables unrestricted innovation factor exchange across geographical boundaries (Hu et al., 2023). This dismantles traditional limitations imposed by geographic locations, fostering greater knowledge spillover effects (Wood et al., 2018), thereby accelerating the exchange of innovative ideas between cities.
The enhanced mobility of production factors stands as a key driver in accelerating the reduction of urban pollution and the effective management of carbon emissions. This transformation is mediated by several interconnected mechanisms, all contributing to the broader goal of achieving environmental sustainability within urban environments: First, labor mobility holds the potential to significantly expedite efforts aimed at decreasing urban pollutants and carbon emissions. By addressing labor supply and demand imbalances, labor mobility promotes a more efficient allocation of human capital (Yashiv, 2007), ultimately leading to enhanced talent availability in energy-intensive sectors. This increased capacity for specialized workforce development paves the way for a smoother transition toward sustainable practices, thereby resulting in reduced emissions of both carbon and other pollutants (Ouyang and Sun, 2015). Furthermore, labor mobility fosters environmental conservation ethos by facilitating the transfer of skilled individuals to smaller cities, stimulating regional industries and driving innovation (Chen et al., 2021b; Wu et al., 2022). Second, capital factor flows can act as a catalyst for mitigating urban pollution and reducing carbon emissions. Capital flows can direct capital toward green industries (Wang and Wang, 2021; Wei et al., 2015), offering financial assistance for the eco-friendly transformation of energy-consuming sectors. This process facilitates the upgrading of urban industries and contributes to a more coordinated approach to managing urban pollution and carbon reduction (Hao et al., 2020; Wu and Chen, 2001).Cross-border capital movement also introduces advanced production management knowledge, ultimately boosting industrial labor productivity while curtailing emissions, thereby meeting environmental objectives (Wu and Chen, 2001).Third, the flow of innovative elements accelerates clean energy technology adoption within urban settings, a phenomenon known as the “Porter effect.” This transformative force revitalizes urban energy frameworks and increases the share of clean energy, ultimately enhancing the cityscape’s overall environmental footprint (Malhotra et al., 2019; Steffen et al., 2018). Moreover, this increased adoption of clean energy technologies can trigger stronger governmental regulations surrounding environmental protection, prompting enterprises to implement stricter environmental policies. This, in turn, helps curb urban carbon and pollutant emissions (Liao, 2018), demonstrating the interconnected nature of innovation, policy, and environmental sustainability. In light of these insights, a compelling hypothesis emerges:
H2. Digital infrastructure promotes the synergistic effect of urban pollution reduction and carbon reduction by accelerating the flow of factors (labor, capital and innovation).
Digital infrastructure plays a pivotal role in addressing urban pollution and carbon reduction efforts, exhibiting complex nonlinear dynamics that render simplistic linear models inadequate. The expansion of digital infrastructure historically results in heightened energy consumption as the demand for essential components such as data centers and communication stations surges (Dayarathna et al., 2015; Sharma et al., 2020). This increased demand can lead to significant environmental resource depletion and ecological damage, potentially exacerbating both urban pollution and carbon emissions (Dian et al., 2023). However, advancements in digital infrastructure innovation are driving a shift towards greener and more sustainable practices. These innovations have significantly enhanced the energy efficiency of IT equipment and communication networks through the implementation of cutting-edge energy-saving techniques, optimization strategies, and the integration of renewable sources (Uddin et al., 2012). This transition has positioned digital infrastructure as a key player in achieving urban pollution and carbon reduction targets. Digital infrastructure is evolving from a significant energy consumer to a green and sustainable energy carrier (Wu et al., 2021), fueling the sustainable development of cities. Through intelligent management, digital infrastructure facilitates the rational allocation and economic utilization of resources, reducing unnecessary energy consumption and emissions. Furthermore, its extensive deployment underpins urban environmental surveillance, pollution control, and eco-friendly transportation, further advancing the objectives of urban pollution reduction (Bibri, 2018). Based on these insights, the following research hypothesis is proposed:
H3. The impact of digital infrastructure on the synergistic effect of pollution reduction and carbon reduction in cities is nonlinear.
4 Research design
4.1 Variable definitions
The explained variable is the synergistic effect of pollution reduction and carbon reduction (se).To elucidate the intricate relationship between pollution reduction and carbon reduction subsystems, a comprehensive index system for evaluating their synergistic effects is developed in line with the methodology of Yi et al. (2022). This system, detailed in Table 1, provides a framework to quantify mutual influence between these two subsystems. Given the lack of carbon emission data at the urban level, this study references the research by Chen et al. (2020) and uses nighttime light data along with provincial carbon emission data to estimate the annual carbon dioxide emissions for cities (measured in tons).Utilizing coupling coordination models (as exemplified by Equations 1,2), the analysis delves into the intrinsic connections and dynamic patterns of change between pollution reduction and carbon reduction, shedding light on their interconnected nature.
where X is the pollution reduction index and Y is the carbon reduction index, both of which are measured via the projection tracing method. The value range of C is [0,1].
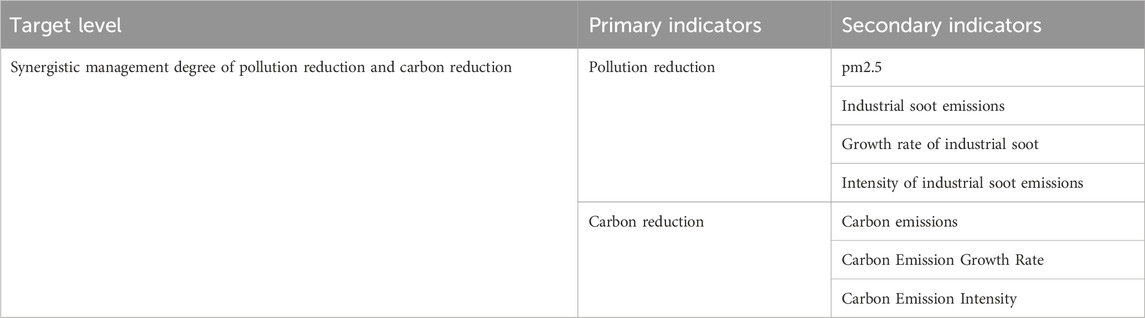
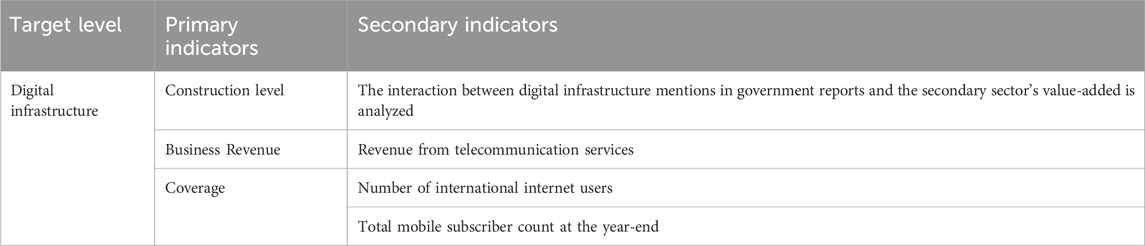
Table 1. Evaluation index system of the synergistic effect of urban pollution reduction and carbon reduction.
Core Explanatory Variable: Digital infrastructure (inform). Digital infrastructure refers to the foundational facilities that support the digital operation and smart development of cities, including but not limited to communication networks, data centers, cloud computing platforms, and Internet of Things (IoT) devices. Given the data accessibility at the city level, we utilize the indicator system developed by Tang and Yang (2023), as presented in Table 2. Additionally, we employ the projection pursuit model, optimized using a genetic algorithm, to assess the extent of urban digital infrastructure development. Regarding the construction level of digital infrastructure, we rely on the research conducted by Wen et al. (2022) to select the frequency of words related to digital infrastructure in government work reports each year as a metric for measuring the extent of digital infrastructure development.
Control variables: Based on a synthesis of multiple studies (Lee and Zhao, 2023; Tang and Yang, 2023), this paper controls for relevant variables to explore the synergistic effects of urban pollution reduction and carbon emission reduction in depth.: Economic development level(pgdp) is measured by per capita development, which typically shows a positive correlation with urban pollution reduction and carbon emission reduction outcomes. (Zhang H. et al., 2022); urbanization rate(urb) is reflected by the proportion of the resident urban population; the advancement of urbanization helps improve resource use efficiency and achieve emission reduction targets. Human capital(hum) is measured by the number of higher education students per ten thousand people; enhancing human capital can increase public environmental awareness and promote sustainable development actions. (Fan et al., 2024).The level of transportation infrastructure(trans) is assessed by the ratio of urban road mileage to administrative area; well-developed transportation infrastructure is a key factor in enhancing urban energy efficiency (Zhang X. et al., 2023). Industrial structure upgrading(is) is indicated by the proportion of the tertiary industry in GDP, reflecting the development status of urban services and the level of industrial advancement. Finally, energy consumption intensity (energy) is benchmarked by energy consumption per ten thousand GDP; its reduction directly reflects the improvements in urban energy efficiency and the effectiveness of pollution reduction and carbon emission reduction efforts.
The mediating factors include labor factor flows (lff), capital factor flows (cff), and innovation factor flows (iff). The labor factor flow (lff), capital factor flow (cff), and innovation factor flow (iff) play vital and decisive roles in economic progress, serving as the primary driving forces behind the promotion of sustainable urban transformation. Hence, we utilize the Jones et al. (1986) model on factor flow to develop separate calculation models for labor factor flow, capital factor flow, and innovation factor flow. As exemplified by Equations 3-5.
In this context,
4.2 Econometric modeling
4.2.1 Benchmark regression modeling
This research aims to investigate the correlation between digital infrastructure and the synergistic effect of urban pollution and carbon emissions. To achieve this, an econometric model is constructed as outlined below:
In this context,
4.2.2 Mediating effect modeling
This paper examines the precise mechanism through which digital infrastructure influences the synergistic effect of reducing urban pollution and carbon emissions. It does so by analyzing the flow of labor factors, capital factors, and innovation factors from three different perspectives. According to Yi et al. (2022), the following mediated effect model is established:
The variable
4.2.3 Machine learning modeling
To further investigate the nonlinear effects between digital infrastructure and the collaborative effects of urban pollution reduction and carbon emission reduction, this study first employs a random forest model to explore the nonlinear relationship between the two, and then uses the SHAP method to rank and interpret the results.
4.2.3.1 Random forest model
The random forest model, as an efficient ensemble learning method, consists of multiple decision trees. When constructing the model, it first randomly selects samples and subsets of features from the original dataset to build several decision trees, ensuring that each tree is trained independently. Finally, during the prediction phase, it uses a voting method for classification tasks and an averaging method for regression tasks to combine the predictions of all the decision trees, resulting in a final prediction that is accurate and stable. As exemplified by Equation 8. In this study, we have constructed such a random forest model to deeply explore the complex nonlinear relationship between digital infrastructure and the collaborative effects of urban pollution reduction and carbon emission reduction:
4.2.3.2 SHAP interpretation method
SHAP is a powerful method for interpreting machine learning model predictions. It is based on the Shapley value from game theory, which assigns an importance score to each feature, quantifying its contribution to the model’s predictions. A key concept within the SHAP framework is the SHAP decomposition method, which allows us to break down the model’s predictions into the contributions of individual features.
The core idea of the SHAP decomposition method is to express the model output (i.e., the prediction) as a weighted sum of the contributions from all features, plus a baseline value. The baseline value represents the model’s predicted outcome when no features are provided. The contribution of each feature (the SHAP value) reflects its marginal impact on the model’s prediction. This decomposition method enables us to intuitively understand how each feature influences the model’s predictions.
Furthermore, to reveal the marginal effects of digital infrastructure on the collaborative effects of pollution reduction and carbon emission reduction, we can construct partial dependence functions
4.3 Data source
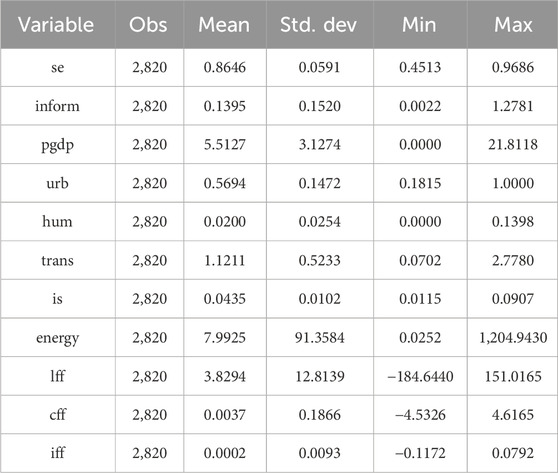
This study investigates the impact of inform on se in China, utilizing a dataset comprising 282 prefecture-level cities between 2012 and 2021. Primary data sources include the China Statistical Yearbook and China Urban Statistical Yearbook. Carbon emissions at the city level are estimated through assimilating DMSP and VIIRS nighttime lighting data (Wu et al., 2022). PM2.5 data were sourced from the Atmospheric Composition Analysis Group at Dalhousie University, Canada. Missing data points are interpolated using linear interpolation methods. Descriptive statistics of variables are shown in Table 3.
5 Results and discussion
5.1 Benchmark regression analysis
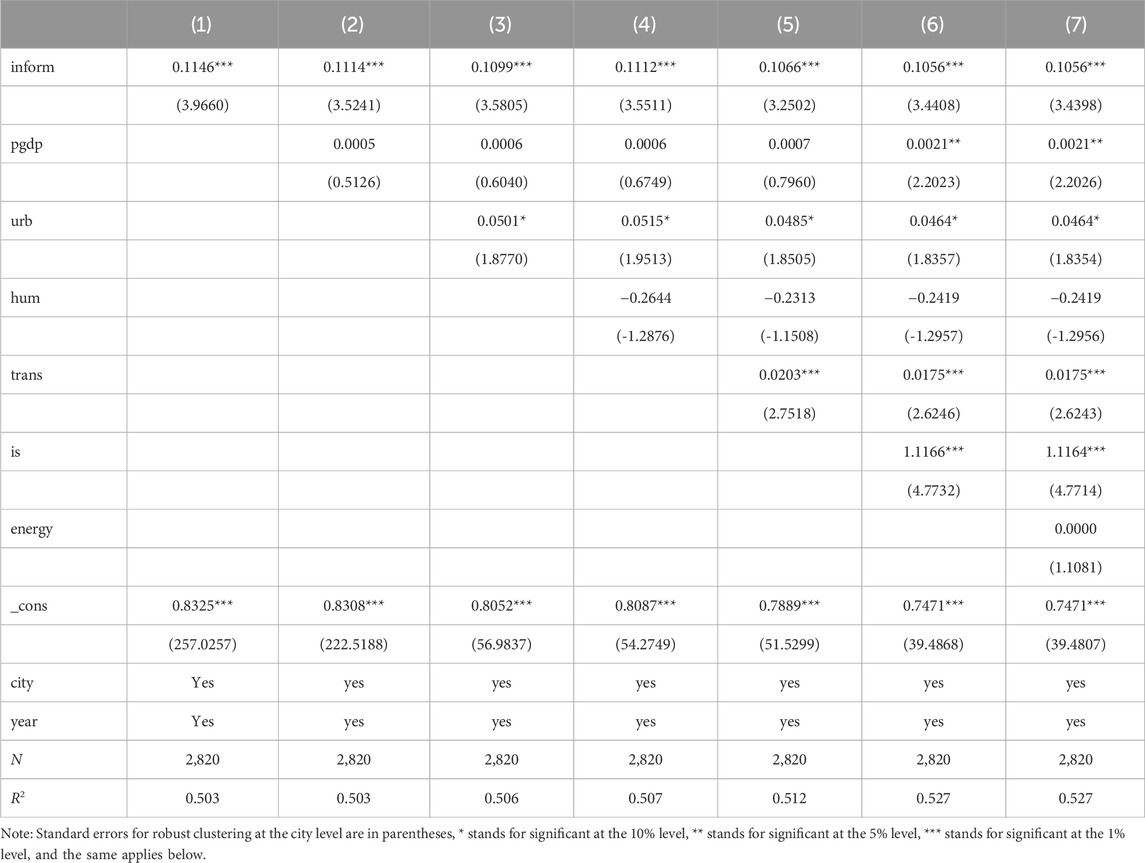
To disentangle the specific impact of inform on se, we employed stepwise regression analysis, incorporating control variables to account for their influence. The results presented in Table 4 demonstrate that core explanatory variables exhibit statistically significant positive relationships at a 1% significance level. Importantly, the inclusion of additional control variables yielded no alterations in outcomes, suggesting the critical role of digital infrastructure in fostering synergy between urban pollution reduction and carbon abatement (Du et al., 2023). This finding further supports the validity of hypothesis H1.
Control variable analysis reveals a strong synergistic relationship between digital infrastructure and the reduction of pollution and carbon emissions. Higher levels of economic development, urbanization rates, transportation infrastructure, and industrial structure upgrading all positively impact combined reductions in pollutants and greenhouse gases. This synergy can be attributed to the positive correlation between higher economic development, technological progress, and strengthened environmental standards, which drive enterprises towards adopting more sustainable production practices, leading to decreased pollution. Furthermore, urban sprawl is linked to resource efficiency, the promotion of eco-friendly infrastructure, and the emergence of environmentally focused facilities. In transportation, advancements contribute to increased network efficiency, reduced traffic congestion, and limited vehicular emissions. Meanwhile, the transformation of industrial structures involves restructuring heavily polluting industries towards cleaner production methods and green innovations, resulting in reduced carbon emissions (Mentel et al., 2022). In contrast, previous studies have shown that human capital can positively influence environmental outcomes when accompanied by sufficient technological expertise and investment in education(Wang Q. et al., 2022). This suggests that the negative impact observed in this analysis may stem from a current mismatch between educational outcomes and industry needs in China, leading to inefficiencies in carbon reduction initiatives. Additionally, other research highlights that energy intensity’s impact on emissions varies significantly across regions, with some regions achieving better results through targeted energy-saving technologies(Hosan et al., 2022). The negligible influence of energy intensity in this study may indicate a broader systemic issue, where cities fail to implement effective energy-saving strategies, as suggested by the persistent high energy consumption rates in many Chinese urban centers.
5.2 Robustness test
To confirm the trustworthiness of the benchmark regression results, this research performs robustness tests in the following manner:
5.2.1 Endogeneity test
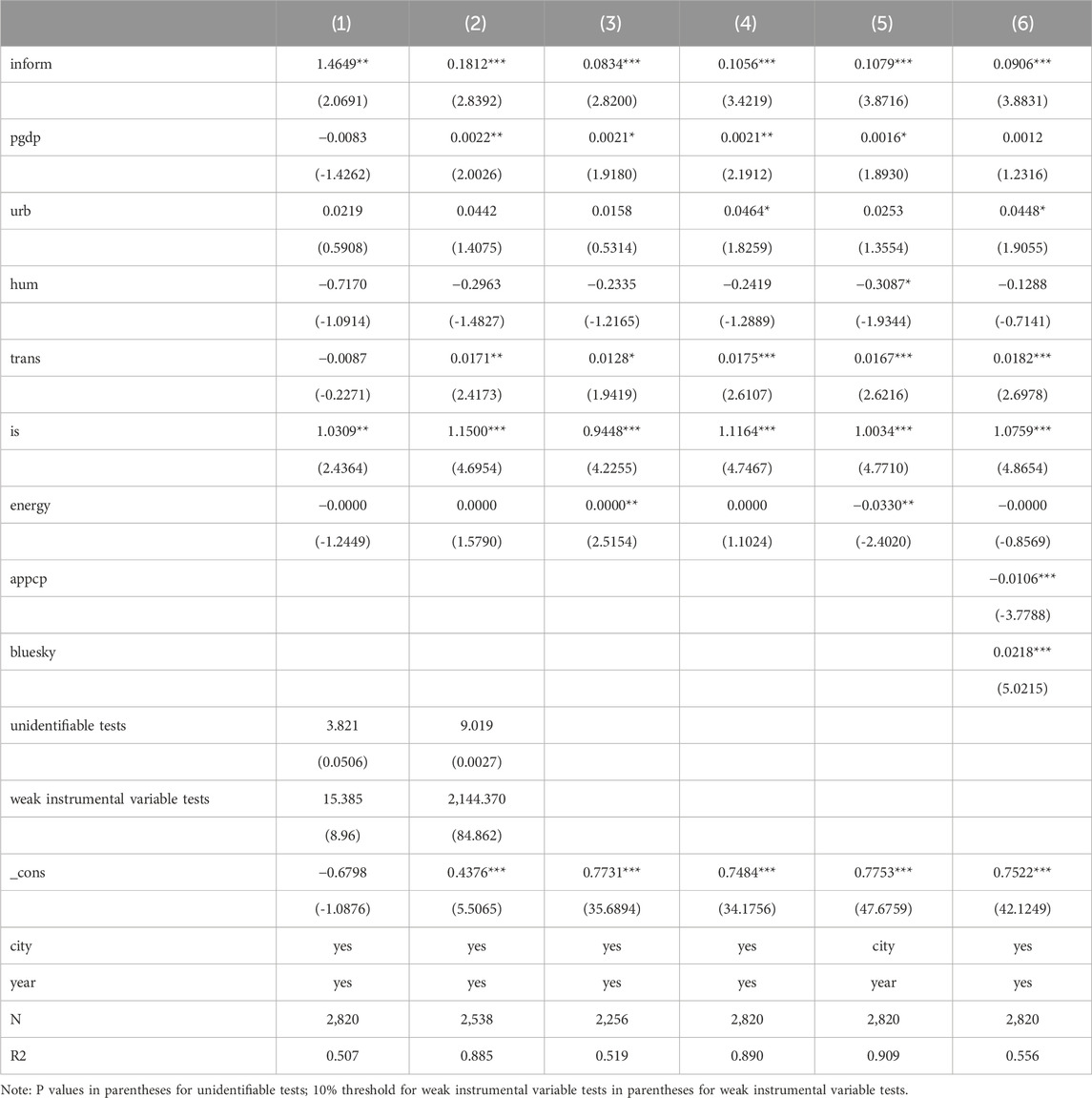
To investigate potential reciprocal relationships between the advancement of digital infrastructure and integrated pollution and carbon reduction management in urban areas, an endogeneity test is conducted. Drawing upon Gao et al. (2022), post offices from 1984 are selected as instrumental variables for 2SLS estimation alongside digital infrastructure level data from the preceding year. This approach acknowledges the historical role of postal services as crucial information exchange channels, reflecting a precursor to modern digital infrastructure. Notably, the shift towards contemporary communication technologies renders the post office less relevant today. Moreover, 1984 falls outside the study’s timeframe, ensuring its exogeneity and applicability for this analysis. Considering cross-sectional data, an interaction term is constructed by incorporating both the number of post offices in 1984 and national internet investment levels from the preceding year. This approach aligns with the methodology of Nunn and Qian (2014), further emphasizing the instrumental variable strategy. We also utilize the digital infrastructure level from the previous year as an additional instrumental variable to account for its dynamic nature and impact on current-year development.
The regression results are presented in columns (1) and (2) of Table 5. These findings demonstrate that coefficients of primary explanatory factors maintain statistically significant positive correlations, highlighting the continued relevance of digital infrastructure in facilitating coordinated pollution and carbon reduction management. In addition to this, both instrumental variables successfully passed the nonidentification test and weak instrumental variable test, strengthening their validity and emphasizing the significance of digital infrastructure for mitigating urban pollution and carbon emissions.
5.2.2 Controlling for high-dimensional fixed effects
To account for potential unobservable province-level characteristics, province fixed effects are incorporated into the baseline regression model. This adjustment mitigates their influence on the regression coefficients, as shown in column (3) of Table 5. These results reveal notably positive regression coefficients for key explanatory variables, suggesting that digital infrastructure demonstrably fosters a synergistic effect in reducing urban pollution and carbon emissions. This implies a substantial impact of digital infrastructure on achieving these goals.
5.2.3 Bilateral tailoring process
This paper addresses the issue of distorted or biased regression coefficients stemming from unrealistic extreme values. To achieve this, we analyze bilateral shrinkage of the tail in the upper and lower 1% quartiles as shown in Table 5 column (4). The results reveal consistently positive regression coefficients for digital infrastructure that are consistent with those obtained from a benchmark regression model.
5.2.4 Adjusting the sample interval
The implementation of the Broadband China pilot policy in 2013 directly correlates with digital infrastructure development, thus rendering this study’s focus on the period between 2014 and 2021 particularly relevant. Column (5) of Table 5 reveals significant positive impacts at the 1% level for key explanatory variables, indicating reliable and strong conclusions derived from the benchmark regression analysis.
5.2.5 Control of other policies
The influence of environmental policies such as the Action Plan for Prevention and Control of Air Pollution (2013–2017) and the Three-Year Action Plan for Winning the Battle for the Blue Sky, as documented by Li L. et al. (2024) and Liu et al. (2021), exerts a significant influence on collaborative pollution reduction and carbon abatement efforts. To account for potential perturbations caused by these policies on air pollutants and carbon emissions, this study integrates both policies as dummy variables into the benchmark regression (column 6 of Table 5). Remarkably, even after incorporating policy shocks, primary explanatory variables consistently demonstrate significant positive effects, affirming the role of digital infrastructure in accelerating synergy between pollution reduction and carbon abatement. This underscores its crucial contribution to advancing collaborative urban environmental enhancement efforts.
5.3 Heterogeneity analysis
The impact of digital infrastructure development varies across cities, influencing their collaborative capabilities for pollution reduction and carbon mitigation strategies. Geographic location, city size, and available resources all contribute to these distinct impacts.
5.3.1 Geographic location heterogeneity
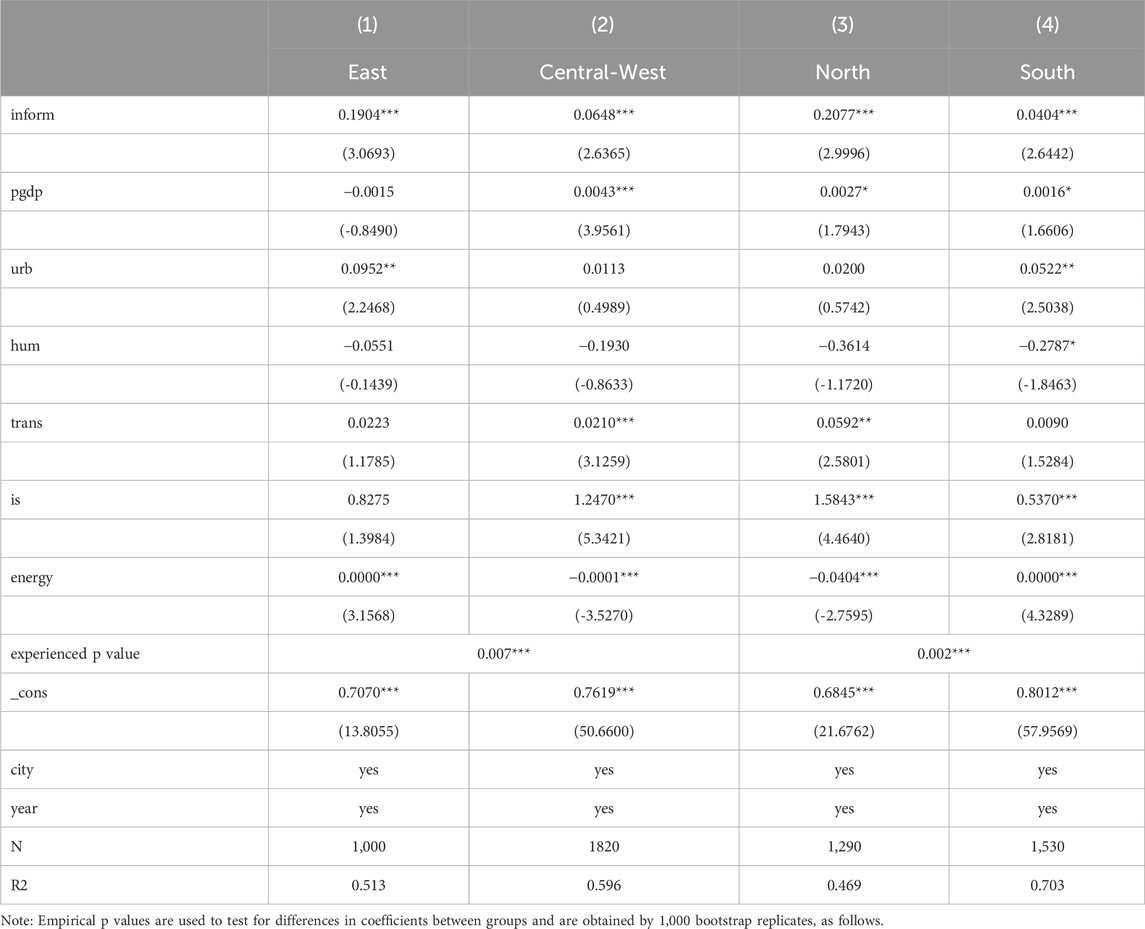
To investigate the influence of inform on se, it is crucial to account for regional variations. Studies conducted by Liang et al. (2021) and Pu et al. (2020) have categorized the country into three regions: East, Central-West, and North-South. Utilizing a permutation test, this study assessed the variation in regression coefficients across these groups. The findings are presented in Table 6.
Statistical analysis reveals significant intergroup differences between regions classified as Eastern, Central-Western, and North-South. Regression coefficients for core explanatory variables within the Eastern and Central-Western regions demonstrate significantly positive values with the Eastern region exhibiting a coefficient exceeding that of the Central-West region. This indicates that in the eastern region, the role of digital infrastructure in promoting pollution reduction and carbon emission mitigation is more pronounced, which may not be consistent with the conclusions of existing studies (Zhong et al., 2024). This could be due to the more rapid development of digital infrastructure in the eastern region (Ma and Lin, 2023), which makes it easier to leverage the connectivity advantages of digital infrastructure. This facilitates cross-regional cooperation and resource sharing, and more effectively integrates resources, thereby improving the efficiency of coordinated pollution reduction and carbon emission mitigation efforts. Analysis comparing the Northern and Southern regions reveals a significant regression coefficient of 0.2077 for the Northern region (passing the 1% significance test), aligning with research by Zhang et al. (2023) who highlight the Northern region’s position as a major heavy industrial base in China and its distinct air pollution challenges due to severe winter climate conditions. This emphasizes the need to bolster environmental governance and infrastructure development, leveraging digital technology effectively for monitoring and addressing environmental challenges within the region.
5.3.2 Heterogeneity of city size
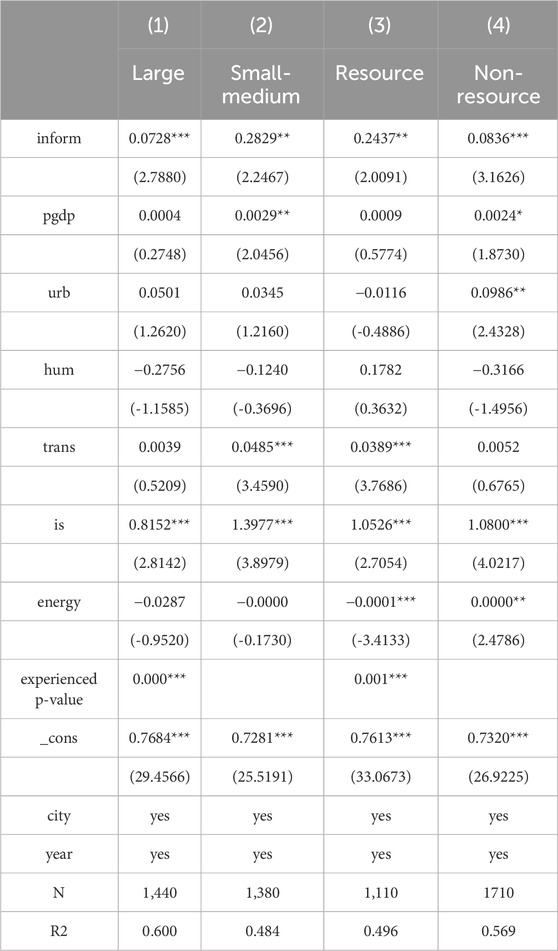
Considering that urban size may have an impact on the pollution reduction and carbon emission effects of digital infrastructure, this study explores the heterogeneity of urban size from the perspective of population scale1. As shown in columns (1) and (2) of Table 7, the differences in coefficients between the aforementioned groups are highly significant. Notably, the coefficient for large cities is notably smaller at 0.0728. This is in line with the research of other scholar(Liao and Liu, 2024), which may be due to the fact that larger cities require more resource elements during the digital transformation process, resulting in poor coverage of digital infrastructure(Lin and Ma, 2022). This discrepancy could be attributed to the resource-intensive nature of digital transformation within larger cities, leading to inadequate digital infrastructure coverage and hindering its role in synergistic pollution and carbon reduction processes. Furthermore, large cities’ broader regional scope necessitates increased coordination and investment in resources for policy implementation, potentially posing greater challenges compared to smaller cities(Yang, Yeh and Wang, 2018).
5.3.3 Resource endowment heterogeneity
Given the significant differences in industrial structure, energy consumption patterns, and environmental challenges between resource-based and non-resource-based cities, we will categorize the samples into these two types of cities to explore in more detail the differing roles of digital infrastructure in helping them achieve pollution reduction and carbon emission targets. The results are shown in columns (3) and (4) of Table 7. A significant positive correlation is observed in the regression coefficients of primary explanatory variables, evident across both resource-based and non-resource-based cities. The disparity between these groups is highly statistically significant. Digital infrastructure plays a crucial role in enabling cities to achieve their pollution and carbon reduction objectives, particularly for resource-based cities, where industries heavily reliant on extractive and heavy energy sources dominate(Cai and Lin, 2022). Consequently, environmental pollution and carbon emissions become increasingly pronounced, highlighting the urgent need for enhanced environmental governance measures. In resource-based cities, digital infrastructure deployment can accelerate industrial digital transformation, improve energy utilization efficiency, and simultaneously mitigate carbon and pollutant emissions (Pan et al., 2023), fostering a mutually beneficial outcome in achieving both pollution and carbon reduction goals.
5.4 Mechanism analysis
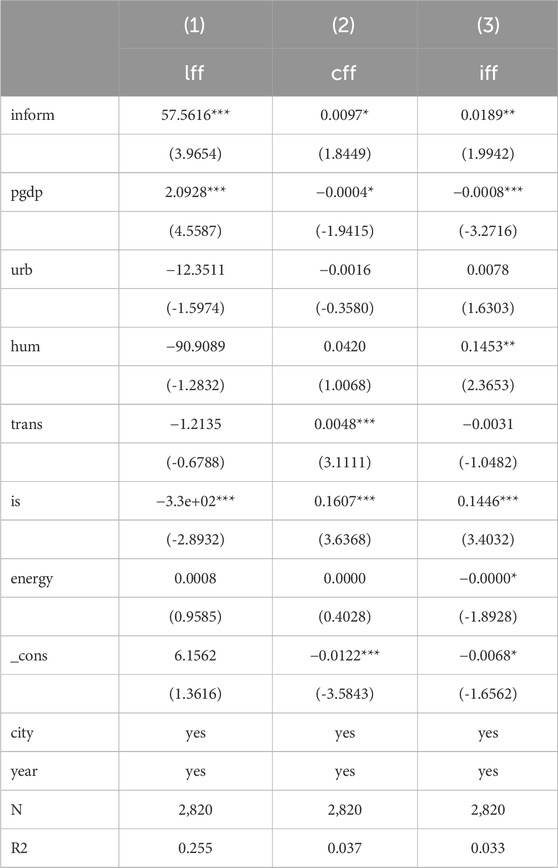
To validate the hypothesis H2, regression analysis was conducted using Equation 7, as presented in Table 8. The results clearly demonstrate a significantly positive correlation between digital infrastructure and the flow of labor, capital, and innovation factors. This suggests that digital infrastructure fosters a synergistic effect by accelerating these factor flows, ultimately contributing to cleaner air and reduced carbon emissions.
Digital infrastructure facilitates efficient movement of all three factors. For instance, the adoption of digital technologies enhances transparency in labor markets, reduces labor mobility costs (Hua and Zhang, 2024), and optimizes labor allocation. In relation to capital flow, digital infrastructure offers enhanced trading platforms and risk management tools within the capital market, leading to improved liquidity and allocation efficiency (Dong et al., 2022). Regarding innovation factors, digital infrastructure serves as a strong catalyst for scientific and technological advancements (Bygstad and Øvrelid, 2020), fostering efficient sharing and integration of innovation resources and promoting urban industrial structure upgrades. The acceleration of these factor flows ultimately alters the city’s industrial structure by optimizing resource allocation, enhancing production efficiency, improving energy utilization efficiency, reducing energy waste, and lowering pollutant emissions. Simultaneously, industrial restructuring promotes environmentally friendly and sustainable practices, further bolstering pollution reduction and carbon mitigation efforts.
5.5 Nonlinear effect
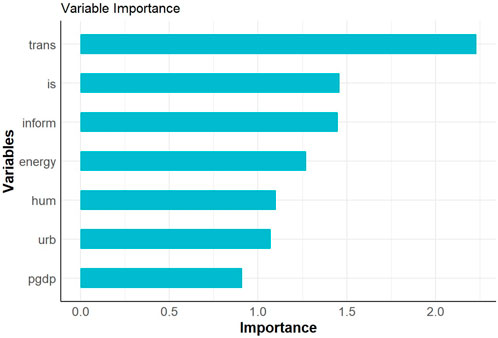
This study employs a random forest model with regression trees as the base learner to investigate the relationship between inform and se, utilizing the minimum mean square error criterion (Li et al., 2018). A biased dependence model is employed to elucidate the marginal influence of digital infrastructure on this synergistic effect. Figure 2 presents the ranking of importance for various feature variables, revealing that the driving factors for the synergistic effect of urban pollution reduction and carbon mitigation are, in order: transportation infrastructure level, industrial structure level, digital infrastructure level, energy consumption intensity, human capital, urbanization rate, and per capita economic development level. To analyze the manner in which digital infrastructure influences the synergistic effect of urban pollution reduction and carbon mitigation, this paper further employs a partial dependence plot to illustrate the dependency relationship between digital infrastructure and the synergistic effect of urban pollution reduction and carbon mitigation.
Figure 3 displays a diagram illustrating these relationships. Specifically, the synergistic impact of digital infrastructure on urban pollution reduction and carbon mitigation exhibits a distinct U-shaped relationship. This discrepancy can be attributed to the stage of development in urban digital infrastructure: early stages may not effectively contribute to enhanced synergistic effects in both pollution and carbon reduction. However, once digital infrastructure reaches a certain degree of maturity, it facilitates the adoption of sustainable practices across various sectors, accelerating progress towards cleaner air and reduced emissions.
In contrast, other studies have indicated a more linear relationship between digital infrastructure and environmental outcomes (Tao et al., 2023; Zheng et al., 2023c).These studies suggest that even at early stages of digital infrastructure development, there can be immediate benefits in terms of efficiency improvements and better data management for pollution control. The differences in findings may arise from varying contextual factors, such as the specific technological tools implemented or the regulatory environments of different regions. For instance, regions that prioritize smart technologies and have supportive policies may experience immediate improvements, while others may lag due to insufficient investment or planning.
6 Conclusions and suggestions
6.1 Conclusions
This study employs a multi-faceted approach to analyze panel data from 282 Chinese cities, employing a two-way fixed-effect model, a mediated-effects model, and a machine learning model for comprehensive assessment. The objective is to investigate the influence of digital infrastructure on coordinated urban pollution and carbon emissions reduction, quantifying its impact through an evaluation of urban digital infrastructure levels.
The study reveals:
(1) The study provides a deeper understanding of how digital infrastructure plays a pivotal role in amplifying the efficacy of urban pollution and carbon emissions reduction initiatives, leading to their synergistic governance. By examining geographical disparities, urban dimensions, and resource endowments, it is evident that regions in the east, northern cities, and smaller or resource-dependent municipalities witness a more pronounced beneficial effect. This suggests that the spatial distribution and characteristics of cities significantly influence the capacity of digital infrastructure to drive environmental improvements.
(2) The research underscores the transformative impact of digital infrastructure in harmonizing urban pollution and emission reduction efforts. It does so by enabling the smooth circulation of labor, capital, and innovative elements, which are crucial for optimizing resource distribution. This optimization is instrumental in steering the economy towards a greener trajectory. As a result, there is a notable enhancement in energy efficiency, a reduction in emissions, and a subsequent decline in environmental pollution levels, highlighting the critical role of digital infrastructure in advancing sustainable urban development.
(3) Employing a random forest model, the study reveals the complex, non-linear dynamics between digital infrastructure and the concurrent management of pollution and carbon emissions. It is observed that during the initial stages of digital infrastructure expansion, high energy consumption may counteract environmental efforts. However, as the infrastructure evolves, it becomes a catalyst for industry-wide digital transformation, which is essential for environmental conservation and emission reduction. This transition underscores the importance of maturation in digital infrastructure as a key factor in aligning pollution and carbon mitigation strategies effectively.
This study deepens the integration of digital economy and sustainable development theories, clarifying how digital infrastructure accelerates urban pollution reduction and carbon reduction processes in a nonlinear manner by facilitating the flow of labor, capital, and innovation factors. More importantly, this research provides policymakers with a theoretical foundation for precise policy implementation, aiding them in making more informed decisions while promoting regional differentiated development, optimizing resource allocation, and seeking a balance between digital infrastructure construction and environmental protection goals. This not only aligns closely with the national strategy of actively promoting “new infrastructure” and achieving “dual carbon” goals but also offers practical strategies and pathways for achieving a green transformation of the economy and society.
6.2 Recommendations for countermeasures
Based on these findings, the paper recommends several strategic approaches to maximize the impact of digital infrastructure on urban pollution and carbon emissions mitigation:
(1) Policymakers will use differentiated strategies based on New Infrastructure Plan and carbon peaking/neutrality targets to promote digital infrastructure development for emission reduction. Areas with strong economies and tech capabilities (east and north) should focus on optimizing existing infrastructure to maximize emission reductions potential. Smaller cities and resource-rich areas can leverage regional development policies to increase digital infrastructure investment, enabling green transitions in traditional industries through technology. Finally, promoting interregional digital infrastructure connectivity aligned with initiatives like the Belt and Road Initiative will facilitate resource sharing and collaborative governance for stronger emissions reduction effect.
(2) To enhance the green economy, governments will promote green industries and low-carbon fields through the strategy on developing a quality workforce. This includes providing job training and information to help workers develop green skills. Additionally, policies like green finance encourage capital investment in green projects. Digital innovation platforms will also be created to attract new talent and innovation resources for emissions reduction and accelerate the city’s green transformation.
(3) During digital infrastructure development, prioritize environmental management and oversight throughout construction to control energy consumption and emissions. Post-completion, encourage industries to leverage digital technologies for green transformation (energy efficiency, reducing carbon and pollution) and maximize the impact of this infrastructure on emission reduction and coordinated governance. Leveraging big data and AI technology can establish a dynamic evaluation mechanism for timely policy adjustments, enabling more precise and effective management.
6.3 Research outlook
This study examines how digital infrastructure impacts pollution and carbon reduction efforts, contributing to a dual-carbon strategy. However, further optimizations are necessary:
(1) While this research focuses on Chinese cities, future studies should broaden to include diverse nations and regions worldwide. Comparative analyses across these distinct contexts will reveal the varying influences of digital infrastructure on climate change mitigation strategies. Such insights can yield actionable guidelines for global climate efforts.
(2) The impact of digital infrastructure is particularly potent when integrated into crucial sectors like manufacturing and transportation. Deeper research should focus on assessing the specific effects of this integration on the collaborative management of pollution and emissions reduction. A thorough analysis can highlight the vital role of digital infrastructure in pollution and carbon mitigation, providing a more robust foundation for policy development and implementation.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
FL: Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Writing – review and editing. ZD: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
This study is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under the “Analysis of Corporate Environmental Behavior and Reconstruction of Guiding Mechanisms for Reimbursable Use and Trading of Emission Rights” (71974081) and the Postgraduate Research and Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province (KYCX24_3882).
Acknowledgments
The authors are very grateful to all the reviewers and editors for their comments on this paper.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Footnotes
1According to the “Notice from the State Council on Adjusting the Standards for Urban Size Classification,” based on the resident population of municipal districts in 2015, cities with a population of over one million are classified as large cities, those with a population between 500,000 and one million are classified as medium-sized cities, and those with a population of less than 500,000 are classified as small cities
References
Allen, M., Frame, D., Huntingford, C., Jones, C., Lowe, J., Meinshausen, M., et al. (2009). Warming caused by cumulative carbon emissions towards the trillionth tonne. Nature 458 (7242), 1163–1166. doi:10.1038/nature08019
Amann, M., Klimont, Z., and Wagner, F. (2013). Regional and global emissions of air pollutants: recent trends and future scenarios. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 38 (1), 31–55. doi:10.1146/annurev-environ-052912-173303
Avom, D., Nkengfack, H., Fotio, H. K., and Totouom, A. (2020). ICT and environmental quality in Sub-Saharan Africa: effects and transmission channels. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 155, 120028. doi:10.1016/j.techfore.2020.120028
Bai, T., Qi, Y., Li, Z., and Xu, D. (2023). Digital economy, industrial transformation and upgrading, and spatial transfer of carbon emissions: the paths for low-carbon transformation of Chinese cities. J. Environ. Manag. 344, 118528. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.118528
Bibri, S. E. (2018). The IoT for smart sustainable cities of the future: an analytical framework for sensor-based big data applications for environmental sustainability. Sustain. Cities Soc. 38, 230–253. doi:10.1016/j.scs.2017.12.034
Bygstad, B., and Øvrelid, E. (2020). Architectural alignment of process innovation and digital infrastructure in a high-tech hospital. Eur. J. Inf. Syst. 29 (3), 220–237. doi:10.1080/0960085x.2020.1728201
Cai, Y., and Lin, G. (2022). Pathways for sustainable municipal energy systems transition: a case study of Tangshan, a resource-based city in China. J. Clean. Prod. 330, 129835. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.129835
Che, S., and Wang, J. (2022). Digital economy development and haze pollution: evidence from China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 29 (48), 73210–73226. doi:10.1007/s11356-022-20957-w
Che, S., Wen, L., and Wang, J. (2024). Global insights on the impact of digital infrastructure on carbon emissions: a multidimensional analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 368, 122144. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2024.122144
Chen, D., Lu, X., Hu, W., Zhang, C., and Lin, Y. (2021a). How urban sprawl influences eco-environmental quality: empirical research in China by using the Spatial Durbin model. Ecol. Indic. 131, 108113. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.108113
Chen, J., Gao, M., Cheng, S., Hou, W., Song, M., Liu, X., et al. (2020). County-level CO2 emissions and sequestration in China during 1997–2017. Sci. Data 7 (1), 391. doi:10.1038/s41597-020-00736-3
Chen, Y., Ardila-Gomez, A., and Frame, G. (2016). Achieving energy savings by intelligent transportation systems investments in the context of smart cities. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 54, 381–396. doi:10.1016/j.trd.2017.06.008
Chen, Y., Tian, W., Zhou, Q., and Shi, T. J. J. o. C. P. (2021b). Spatiotemporal and driving forces of Ecological Carrying Capacity for high-quality development of 286 cities in China. J. Clean. Prod. 293, 126186. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126186
Cheng, Z., Li, L., and Liu, J. (2019). The effect of information technology on environmental pollution in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 26 (32), 33109–33124. doi:10.1007/s11356-019-06454-7
Dayarathna, M., Wen, Y., and Fan, R. J. (2015). Data center energy consumption modeling: a survey. A Surv. 18 (1), 732–794. doi:10.1109/comst.2015.2481183
Dian, J., Song, T., and Li, S. (2023). Facilitating or inhibiting? Spatial effects of the digital economy affecting urban green technology innovation. Energy Econ. 129, 107223. doi:10.1016/j.eneco.2023.107223
Dong, F., Li, Y., Qin, C., Zhang, X., Chen, Y.-H., Zhao, X., et al. (2022). Information infrastructure and greenhouse gas emission performance in urban China: a difference-in-differences analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 316, 115252. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.115252
Du, Y., Zhou, J., Bai, J., and Cao, Y. (2023). Breaking the resource curse: the perspective of improving carbon emission efficiency based on digital infrastructure construction. Resour. Policy 85, 103842. doi:10.1016/j.resourpol.2023.103842
Fan, X., Zhou, Y., and Xie, Q. (2024). Assessment on the synergistic effect of pollution and carbon reductions in low-carbon city pilot policy: based on effectiveness and efficiency perspectives. Environ. Dev. Sustain. doi:10.1007/s10668-023-04421-4
Favoretto, C., Mendes, G. H. d. S., Filho, M. G., Gouvea de Oliveira, M., Ganga, G. M., and Marketing, I. (2022). Digital transformation of business model in manufacturing companies. challenges Res. agenda. 37(4), 748–767. doi:10.1108/jbim-10-2020-0477
Fujimori, S., Masui, T., and Matsuoka, Y. (2015). Gains from emission trading under multiple stabilization targets and technological constraints. Energy Econ. 48, 306–315. doi:10.1016/j.eneco.2014.12.011
Gao, D., Li, G., and Yu, J. (2022). Does digitization improve green total factor energy efficiency? Evidence from Chinese 213 cities. Energy 247, 123395. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2022.123395
Ghosh, S., Hughes, M., Hodgkinson, I., and Hughes, P. J. T. (2022). Digital transformation of industrial businesses. A Dyn. Capab. approach, 113.102414. doi:10.1016/j.technovation.2021.102414
Guerrero-ibanez, J. A., Zeadally, S., and Contreras-Castillo, J. (2015). Integration challenges of intelligent transportation systems with connected vehicle, cloud computing, and internet of things technologies. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 22 (6), 122–128. doi:10.1109/mwc.2015.7368833
Guo, Q., Geng, C.-x., Yao, N., and Zhao, L. (2023). Can digital infrastructure enhance economic efficiency? Evidence from China. Qual. and Quantity 58 (2), 1729–1752. doi:10.1007/s11135-023-01710-y
Hao, Y., Wu, Y., Wu, H., and Ren, S. (2020). How do FDI and technical innovation affect environmental quality? Evidence from China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 27 (8), 7835–7850. doi:10.1007/s11356-019-07411-0
He, C., Pan, F., and Yan, Y. (2011). Is economic transition harmful to China’s urban environment? Evidence from industrial air pollution in Chinese cities. Urban Stud. 49 (8), 1767–1790. doi:10.1177/0042098011415719
He, X., Meng, X., Wu, Y., Chan, C. S., and Pang, T. (2020). Semantic matching efficiency of supply and demand texts on online technology trading platforms: taking the electronic information of three platforms as an example. Inf. Process. and Manag. 57 (5), 102258. doi:10.1016/j.ipm.2020.102258
Heddeghem, W. V., Lambert, S., Lannoo, B., Colle, D., Pickavet, M., and Demeester, P. (2014). Trends in worldwide ICT electricity consumption from 2007 to 2012. Comput. Commun. 50, 64–76. doi:10.1016/j.comcom.2014.02.008
Henneman, L. R. F., Rafaj, P., Annegarn, H., and Klausbruckner, C. (2016). Assessing emissions levels and costs associated with climate and air pollution policies in South Africa. Energy Policy 89, 160–170. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2015.11.026
Hosan, S., Karmaker, S. C., Rahman, M. M., Chapman, A. J., and Saha, B. (2022). Dynamic links among the demographic dividend, digitalization, energy intensity and sustainable economic growth: empirical evidence from emerging economies. J. Clean. Prod. 330, 129858. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.129858
Hu, J. (2023). Synergistic effect of pollution reduction and carbon emission mitigation in the digital economy. J. Environ. Manag. 337, 117755. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.117755
Hu, J., Zhang, H., and Irfan, M. (2023). How does digital infrastructure construction affect low-carbon development? A multidimensional interpretation of evidence from China. J. Clean. Prod. 396, 136467. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.136467
Hu, Y., Ji, J. S., and Zhao, B. (2022). Deaths attributable to indoor PM2.5 in urban China when outdoor air meets 2021 WHO air quality guidelines. Environ. Sci. and Technol. 56 (22), 15882–15891. doi:10.1021/acs.est.2c03715
Hua, Y., and Zhang, H. (2024). Labour misallocation and digital infrastructure: evidence from a quasi-natural experiment of ‘broadband China strategy. Appl. Econ. Lett., 1–7. doi:10.1080/13504851.2024.2332574
Jones, R. W., Coelho, I., and Easton, S. T. (1986). The theory of international factor flows: the basic model. J. Int. Econ. 20 (3-4), 313–327. doi:10.1016/0022-1996(86)90024-3
Lan, M., and Zhu, Y. (2023). Digital infrastructure construction, carbon total factor productivity, and carbon rebound effect. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 30 (38), 88968–88985. doi:10.1007/s11356-023-28738-9
Lee, C.-C., and Zhao, Y.-N. (2023). Heterogeneity analysis of factors influencing CO2 emissions: the role of human capital, urbanization, and FDI. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 185, 113644. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2023.113644
Li, C., Tao, Y., Ao, W., Yang, S., and Bai, Y. (2018). Improving forecasting accuracy of daily enterprise electricity consumption using a random forest based on ensemble empirical mode decomposition. Energy 165, 1220–1227. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2018.10.113
Li, F., Wu, Y., Liu, J., and Zhong, S. (2022). Does digital inclusive finance promote industrial transformation? New evidence from 115 resource-based cities in China. PLOS ONE 17 (8), e0273680. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0273680
Li, J., Jiang, M., and Li, G. (2024a). Does the New Energy Vehicles subsidy policy decrease the carbon emissions of the urban transport industry? Evidence from Chinese cities in Yangtze River Delta. Energy 298, 131322. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2024.131322
Li, L., He, M., Liang, X., Deng, H., and Yang, R. (2024b). How does the impact of a two-stage air pollution control policy on air quality different? Evidence from 258 cities in China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 15 (7), 102148. doi:10.1016/j.apr.2024.102148
Li, Z., and Wang, J. (2022). The dynamic impact of digital economy on carbon emission reduction: evidence city-level empirical data in China. J. Clean. Prod. 351, 131570. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.131570
Liang, L., Chen, M., Luo, X., and Xian, Y. (2021). Changes pattern in the population and economic gravity centers since the Reform and Opening up in China: the widening gaps between the South and North. J. Clean. Prod. 310, 127379. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.127379
Liao, K., and Liu, J. (2024). Digital infrastructure empowerment and urban carbon emissions: evidence from China. Telecommun. Policy 48 (6), 102764. doi:10.1016/j.telpol.2024.102764
Liao, Z. (2018). Environmental policy instruments, environmental innovation and the reputation of enterprises. J. Clean. Prod. 171, 1111–1117. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.10.126
Lin, B., and Ma, R. (2022). How does digital finance influence green technology innovation in China? Evidence from the financing constraints perspective. J. Environ. Manag. 320, 115833. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.115833
Liu, G., and Wan, S. (2023). The impact of information and communication technology on carbon emissions in China: spatial effect and mechanism discussion. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 30 (6), 16178–16194. doi:10.1007/s11356-022-23201-7
Liu, J., Li, Y., and Wang, Z. (2023). The potential for carbon reduction in construction waste sorting: a dynamic simulation. Energy 275, 127477. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2023.127477
Liu, K., Ren, G., Dong, S., and Xue, Y. (2024). The synergy between pollution reduction and carbon reduction in Chinese cities and its influencing factors. Sustain. Cities Soc. 106, 105348. doi:10.1016/j.scs.2024.105348
Liu, Z., Xue, W., Ni, X., Qi, Z., Zhang, Q., and Wang, J. (2021). Fund gap to high air quality in China: a cost evaluation for PM2.5 abatement based on the Air Pollution Prevention and control Action Plan. J. Clean. Prod. 319, 128715. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.128715
Ma, R., and Lin, B. (2023). Digital infrastructure construction drives green economic transformation: evidence from Chinese cities. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 10 (1), 1–10. doi:10.1057/s41599-023-01839-z
Malhotra, A., Schmidt, T. S., and Huenteler, J. (2019). The role of inter-sectoral learning in knowledge development and diffusion: case studies on three clean energy technologies. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 146, 464–487. doi:10.1016/j.techfore.2019.04.018
Mentel, G., Tarczyński, W., Azadi, H., Abdurakmanov, K., Zakirova, E., and Salahodjaev, R. (2022). R&D human capital, renewable energy and CO2 emissions: evidence from 26 countries. Energies 15 (23), 9205. doi:10.3390/en15239205
Ndubuisi, G., Otioma, C., and Tetteh, G. K. (2021). Digital infrastructure and employment in services: evidence from Sub-Saharan African countries. Telecommun. Policy 45 (8), 102153. doi:10.1016/j.telpol.2021.102153
Nunn, N., and Qian, N. (2014). US food aid and civil conflict. Am. Econ. Rev. 104 (6), 1630–1666. doi:10.1257/aer.104.6.1630
Ouyang, X., and Sun, C. (2015). Energy savings potential in China's industrial sector: from the perspectives of factor price distortion and allocative inefficiency. Energy Econ. 48, 117–126. doi:10.1016/j.eneco.2014.11.020
Pan, M., Zhao, X., Lv, K., Rosak-Szyrocka, J., Mentel, G., and Truskolaski, T. (2023). Internet development and carbon emission-reduction in the era of digitalization: where will resource-based cities go? Resour. Policy 81, 103345. doi:10.1016/j.resourpol.2023.103345
Pu, L., Wang, X., Tan, Z., Wang, H., Yang, J., and Wu, J. (2020). Is China's electricity price cross-subsidy policy reasonable? Comparative analysis of eastern, central, and western regions. Energy Policy 138, 111250. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2020.111250
Qiao, L., Li, L., and Fei, J. (2021). Information infrastructure and air pollution: empirical analysis based on data from Chinese cities. Econ. Analysis Policy 73, 563–573. doi:10.1016/j.eap.2021.12.014
Raab, R. T., Ellis, W. W., and Abdon, B. R. (2001). Multisectoral partnerships in e-learning: a potential force for improved human capital development in the Asia Pacific. Internet High. Educ. 4 (3-4), 217–229. doi:10.1016/s1096-7516(01)00067-7
Rathore, M. M., Paul, A., Hong, W.-H., Seo, H., Awan, I., and Saeed, S. (2018). Exploiting IoT and big data analytics: defining smart digital city using real-time urban data. Sustain. Cities Soc. 40, 600–610. doi:10.1016/j.scs.2017.12.022
Ren, S., Hao, Y., Xu, L., Wu, H., and Ba, N. (2021). Digitalization and energy: how does internet development affect China's energy consumption? Energy Econ. 98, 105220. doi:10.1016/j.eneco.2021.105220
Sadorsky, P. (2012). Information communication technology and electricity consumption in emerging economies. Energy Policy 48, 130–136. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2012.04.064
Sharma, P. K., Kumar, N., and Park, J. H. J. I. N. (2020). Blockchain technology toward green IoT: opportunities and challenges. IEEE Netw. 34 (4), 263–269. doi:10.1109/mnet.001.1900526
Steffen, B., Matsuo, T., Steinemann, D., and Schmidt, T. S. (2018). Opening new markets for clean energy: the role of project developers in the global diffusion of renewable energy technologies. Bus. Polit. 20 (4), 553–587. doi:10.1017/bap.2018.17
Stein, J. C. (2002). Information production and capital allocation: decentralized versus hierarchical firms. J. Finance 57 (5), 1891–1921. doi:10.1111/0022-1082.00483
Sun, H., and Kim, G. (2021). The composite impact of ICT industry on lowering carbon intensity: from the perspective of regional heterogeneity. Technol. Soc. 66, 101661. doi:10.1016/j.techsoc.2021.101661
Tang, J., and Zhao, X. (2023). Does the new digital infrastructure improve total factor productivity? Bull. Econ. Res. 75 (4), 895–916. doi:10.1111/boer.12388
Tang, K., and Yang, G. (2023). Does digital infrastructure cut carbon emissions in Chinese cities? Sustain. Prod. Consum. 35, 431–443. doi:10.1016/j.spc.2022.11.022
Tao, M., Poletti, S., Wen, L., Sheng, M. S., Wang, J., Wang, G., et al. (2023). Appraising the role of the digital economy in global decarbonization: a spatial non-linear perspective on globalization. J. Environ. Manag. 347, 119170. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.119170
Tranos, E. (2012). The causal effect of the internet infrastructure on the economic development of European city regions. Spat. Econ. Anal. 7 (3), 319–337. doi:10.1080/17421772.2012.694140
Uddin, M., Rahman, A. A., and Reviews, S. E. (2012). Energy efficiency and low carbon enabler green IT framework for data centers considering green metrics. 16(6), 4078–4094.
Wang, Q., Zhang, F., and Li, R. (2022a). Revisiting the environmental kuznets curve hypothesis in 208 counties: the roles of trade openness, human capital, renewable energy and natural resource rent. Environ. Res. 216, 114637. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2022.114637
Wang, X., and Wang, Q. (2021). Research on the impact of green finance on the upgrading of China's regional industrial structure from the perspective of sustainable development. Resour. Policy 74, 102436. doi:10.1016/j.resourpol.2021.102436
Wang, X., and Zhong, M. (2023). Can digital economy reduce carbon emission intensity? Empirical evidence from China’s smart city pilot policies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 30 (18), 51749–51769. doi:10.1007/s11356-023-26038-w
Wang, Z., Han, F., Xia, B., Liu, J., and Zhang, C. (2022b). Regional differences and heterogeneity of construction and demolition waste with economic growth: evidence from China. Constr. Manag. Econ. 41 (1), 44–59. doi:10.1080/01446193.2022.2137882
Wang, Z., Hu, T., and Liu, J. (2024). Decoupling economic growth from construction waste generation: comparative analysis between the EU and China. J. Environ. Manag. 353, 120144. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2024.120144
Wei, Z., Yuguo, J., and Jiaping, W. (2015). Greenization of venture capital and green innovation of Chinese entity industry. Ecol. Indic. 51, 31–41. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2014.10.025
Wen, H., Zhong, Q., and Lee, C.-C. (2022). Digitalization, competition strategy and corporate innovation: evidence from Chinese manufacturing listed companies. Int. Rev. Financial Analysis 82, 102166. doi:10.1016/j.irfa.2022.102166
Wood, A. J., Lehdonvirta, V., and Graham, M. (2018). Workers of the Internet unite? Online freelancer organisation among remote gig economy workers in six Asian and African countries. New Technol. Work Employ. 33 (2), 95–112. doi:10.1111/ntwe.12112
Wu, H.-L., and Chen, C.-H. (2001). An assessment of outward foreign direct investment from China's transitional economy. Europe-Asia Stud. 53 (8), 1235–1254. doi:10.1080/09668130120093219
Wu, Y., Shi, K., Chen, Z., Liu, S., and Chang, Z. (2022). Developing improved time-series DMSP-OLS-like data (1992–2019) in China by integrating DMSP-OLS and SNPP-VIIRS. IEEE Trans. Geoscience Remote Sens. 60, 1–14. doi:10.1109/tgrs.2021.3135333
Wu, Y., Wu, Y., Guerrero, J., and Vasquez, J. (2021). A comprehensive overview of framework for developing sustainable energy internet: from things-based energy network to services-based management system. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 150, 111409. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2021.111409
Xue, Y., Tang, C., Wu, H., Liu, J., and Hao, Y. (2022). The emerging driving force of energy consumption in China: does digital economy development matter? Energy Policy 165, 112997. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2022.112997
Yang, F. F., Yeh, A. G., and Wang, J. J. A. G. (2018). Regional effects of producer services on manufacturing productivity in China, 97, 263–274.
Yashiv, E. (2007). Labor search and matching in macroeconomics. Eur. Econ. Rev. 51 (8), 1859–1895. doi:10.1016/j.euroecorev.2007.06.024
Yi, H., Zhao, L., Qian, Y., Zhou, L., and Yang, P. (2022). How to achieve synergy between carbon dioxide mitigation and air pollution control? Evidence from China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 78, 103609. doi:10.1016/j.scs.2021.103609
Yong, X., Xinxin, T., Su, Z., Yao, W., and Rui, C. (2020). Construction and application of digital creative platform for digital creative industry based on smart city concept. Comput. and Electr. Eng. 87, 106748. doi:10.1016/j.compeleceng.2020.106748
Zhang, H., Sun, X., Bi, C., Ahmad, M., and Wang, J. (2022a). Can sustainable development policy reduce carbon emissions? Empirical evidence from resource-based cities in China. Sci. Total Environ. 838, 156341. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.156341
Zhang, P., Chen, P., Xiao, F., Sun, Y., Ma, S., and Zhao, Z. (2022b). The impact of information infrastructure on air pollution: empirical evidence from China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 19 (21), 14351. doi:10.3390/ijerph192114351
Zhang, W., Fan, H., and Zhao, Q. (2023). Seeing green: how does digital infrastructure affect carbon emission intensity? Energy Econ. 127, 107085. doi:10.1016/j.eneco.2023.107085
Zhang, X., He, P., Liu, X., and Lu, T. (2023a). The effect of low-carbon transportation pilot policy on carbon performance: evidence from China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 30 (19), 54694–54722. doi:10.1007/s11356-023-25940-7
Zheng, H., Zhang, Z., Dietzenbacher, E., Zhou, Y., Többen, J., Feng, K., et al. (2023b). Leveraging opportunity of low carbon transition by super-emitter cities in China. Sci. Bull. 68 (20), 2456–2466. doi:10.1016/j.scib.2023.08.016
Zheng, R., Wu, G., Cheng, Y., Liu, H., Wang, Y., and Wang, X. (2023c). How does digitalization drive carbon emissions? The inverted U-shaped effect in China. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 102, 107203. doi:10.1016/j.eiar.2023.107203
Zhong, W., Liu, Y., Dong, K., and Ni, G. (2024). Assessing the synergistic effects of artificial intelligence on pollutant and carbon emission mitigation in China. Energy Econ. 138, 107829. doi:10.1016/j.eneco.2024.107829
Zhuo, C., Wen, Y., and Wu, H. (2023). The environmental externality of China’s digital infrastructure: does institution supply matter? Appl. Econ. 56, 4875–4888. doi:10.1080/00036846.2023.2219887
Keywords: digital infrastructure, pollution and carbon reduction synergies, labor factor flow, capital factor flow, innovation factor flow
Citation: Li F and Diao Z (2025) The impact of digital infrastructure on the synergistic effects of urban pollution and carbon reduction: empirical evidence from China. Front. Environ. Sci. 13:1453151. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2025.1453151
Received: 22 June 2024; Accepted: 01 April 2025;
Published: 10 April 2025.
Edited by:
Mariarosaria Lombardi, University of Foggia, ItalyReviewed by:
Jingkuang Liu, Guangzhou University, ChinaZhenshuang Wang, Dongbei University of Finance and Economics, China
Copyright © 2025 Li and Diao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ziyu Diao, MjIxMjIxOTAyN0BzdG1haWwudWpzLmVkdS5jbg==
 Fanglin Li
Fanglin Li Ziyu Diao
Ziyu Diao