- 1China Overseas Construction Limited, Shenzhen, Guangdong, China
- 2Key Laboratory of Karst Georesources and Environment, Ministry of Education, College of Resources and Environment Engineering, Guizhou University, Guiyang, China
In order to investigate the adsorption properties of modified rosa roxburghii residue biochar to antimony (Sb) in water, the modified rosa roxburghii residue biochar (BC-FeOOH) was prepared from rosa roxburghii residue factory in Guizhou Processing plant. The adsorption characteristics of BC-FeOOH on Sb(V) in water were investigated by batch test experiments with different pH, biochar dosage and adsorption time. The results showed that the best adsorption effect of BC-FeOOH on antimony was achieved at the dosage of 0.05 g and pH 2.0, and the adsorption amount reached 5.7 mg/g. The results of adsorption kinetic modeling showed that the equilibrium time of the adsorption of BC-FeOOH on Sb(V) in water was in the range of 8–10 h, and the mechanism of adsorption was mainly chemical adsorption. Langmuir model can better describe the adsorption process of BC-FeOOH on Sb(V), and the surface adsorption process is monomolecular layer chemisorption. The experimental results showed that BC-FeOOH is a good adsorbent for Sb pollution remediation in water. This study provides n ew insights for the development of Sb contamination removal strategies in water and offers a new way for the resource utilization of prickly pear pomace.
1 Introduction
Antimony (Sb) is an emerging pollutant that has been shown to be highly toxic and carcinogenic (Deng et al., 2017). Excessive intake of antimony compounds is potentially toxic to the human immune, nervous system, genes and development (Cavallo et al., 2002). Sb exists in the natural environment mainly in two valence states, trivalent antimony (Sb(III)) and pentavalent antimony (Sb(V)), of which Sb(III) is about 10 times more toxic than Sb(V) (Shan et al., 2014). Increasing anthropogenic activities such as smelting, mining, fuel combustion and the widespread use of products containing Sb compounds (e.g., rubber, alloys) have resulted in the release of large amounts of Sb into the aquatic environment, posing a potential threat to human health (Jia et al., 2020). Sb pollution of water bodies has become a global environmental problem, in which the water environment of New Zealand, Australia, France, Japan, China and other countries are subject to varying degrees of Sb pollution (Druzbicka and Craw, 2015; Jia et al., 2020). Many countries have listed it as a priority pollutant for control. China is rich in Sb ore resources, and its reserves and production rank first in the world. China’s Sb mining, extraction, smelting and waste water discharge from abandoned Sb mines are important sources of Sb pollution in water bodies. In recent years, several river basins in China have suffered from Sb pollution incidents (Tang et al., 2023), such as the Duliu River pollution in 2009 and Sb contamination in the Sunshui River, where concentrations exceeded the standard for 38 months. These incidents have significantly impacted water quality, aquatic ecosystems, and drinking water supplies. Frequent Sb pollution problems in water bodies lead to serious impacts on regional water quality, and even adversely affect the drinking water of residents and the growth of aquatic plants and animals. Therefore, how to effectively remove Sb from water to provide a safe and reliable drinking water environment for human life has become the focus of research in countries around the world and the urgent need to solve the important environmental issues closely related to people’s livelihood.
Currently, the main methods for the removal of Sb from wastewater include adsorption, coagulation, locculation, membrane separation, ion exchange, electrochemical and extraction (Li et al., 2018). Among them, adsorption method is widely used due to the advantages of low process requirements, high efficiency, low cost and simple operation, which is considered to be the most effective method to mitigate Sb pollution in water (Rahaman et al., 2008). Many scholars have used iron oxides (Liu et al., 2023), graphene and biochar as adsorbents for the removal of Sb from water. Among them, biochar, which has the characteristics of low cost, wide source, rich pore structure, abundant functional groups, and adjustable specific surface area, has been widely used for the removal of heavy metals, metalloids, and organic pollutants, etc., from water (Li et al., 2017), and is considered to be the most promising adsorbent. In addition, biochar can be modified by various advanced means to obtain modified biochar with more surface functions and high adsorption capacity, which has stronger adsorption and removal capacity of toxic elements in polluted water (Zhou et al., 2020). Studies have shown that the adsorption capacity of modified biomass charcoal for Sb was significantly improved, such as the adsorption capacity of magnetically modified biochar for Sb(V) was greatly improved, and its adsorption capacity increased from 2.22 mg/g to 18.92 mg/g at pH 7.0 (Wang C. et al., 2018); the maximum adsorption capacity of iron-containing cow dung biochar for Sb(V) was 58.3 mg/g, with a removal rate of 98.5% (Park et al., 2021); the saturated adsorption capacity of iron-modified rice husk hydrothermal carbon for Sb(V) was as high as 60.76 mg/g. This indicates that the adsorption removal of Sb from water by modified biochar has excellent application potential.
Rosa roxburghii residue, is an abundant and underutilized agricultural byproduct (Peidong et al., 2023). It has a high lignocellulosic content. Moreover. Rosa roxburghii residue contains significant amounts of phenolic compounds and other organic molecules (Xu et al., 2024), the biomass’s composition is rich in oxygen-containing functional groups (such as carboxyl and hydroxyl groups) (Wang et al., 2021), which are known to facilitate the adsorption of heavy metals and other pollutants. However, Rosa roxburghii residues are often discarded as waste, making them a sustainable and cost-effective source for biochar production, promoting the principles of circular economy and waste valorization (Zhou et al., 2019). In recent years, Guizhou has experienced a significant increase in the production of prickly pear, which has led to the generation of a considerable amount of prickly pear pomace. According to statistical data, Guizhou can produce approximately 15,000 tons of prickly pear pomace annually (Li et al., 2022). Prickly pear pomace is typically discarded as waste, and the accumulation of prickly pear pomace is prone to decomposition, which not only represents a waste of resources but also produces hazardous substances that can pollute the environment (Jain et al., 2024). Therefore, exploring the resource utilization of prickly pear pomace not only can effectively alleviate the waste of prickly pear pomace but also has great significance in promoting the sustainable development of the prickly pear industry. While the use of biochar in environmental remediation is well-documented (Yi et al., 2020), our work uniquely focuses on the use of Rosa roxburghii, a lesser-explored biomass source, and the modification of its biochar to enhance its adsorption capacity for Sb(V). To our knowledge, no other study has explored this specific biomass source for the removal of antimony from aqueous environments, making this an innovative approach. Additionally, our study provides a detailed characterization of the biochar’s surface properties, demonstrating how modifications influence its adsorption mechanisms and effectiveness. This combination of using a novel biomass source, modifying biochar, and targeting the specific removal of Sb(V) from water constitutes the distinctive contribution of this research. Based on this point or Based on this viewpoint, the present study selected prickly pear pomace as the raw material for the preparation of biochar, which was modified with hydroxyl iron oxide (Fe-OOH) by the hydrothermal method. The modified prickly pear pomace biochar (BC-FeOOH) was then subjected to kinetic adsorption and isothermal adsorption tests to investigate its removal of Sb(V) in water under varying conditions, including biochar dosage, pH, and adsorption time. The findings of this study will provide theoretical support for the removal of Sb in water and serve as a reference for the green utilization pathway of prickly pear pomace. The study investigated the availability of BC-FeOOH under different conditions, including varying biochar dosages, pH levels, and adsorption times. This research aimed to provide theoretical support for the removal of Sb in water and to establish a green resource utilization pathway for prickly pear.
2 Material and method
2.1 Main reagents and instruments
The principal reagents employed in this study were ferrous sulfate heptahydrate (FeSO4.7H2O, 99%, Sigma-Aldrich), ethylene glycol [(CH2OH)2, 99%, Sinopharm)], ethanol (C2H5OH, 99%, Sinopharm) sodium hydroxide (NaOH, 99%, Sinopharm), citric acid (C6H8O7, 99%, Sinopharm), and antimony standard storage solution (Sb(V), 99%, Sinopharm). The reagents utilized in the test were analytically pure reagents, and the test water was ultrapure water.
The principal instruments employed in this study were a tubular muffle furnace (L 9/11, Nabertherm, China), a hydride generation atomic fluorescence spectrometer (HG-AFS9700, HAIGUANG INSTRUMENT, China), a pH meter (PHS-3C, Lei-ci, China), and a constant temperature oscillator.
2.2 Preparation and characterization of modified biochar
2.2.1 Preparation of biochar
Firstly, the prickly pear pomace, derived from the prickly pear processing plant, was subjected to a crushing process and subsequently placed in an oven at a temperature of 60°C for a period of 24 h. Following this, the material was removed and placed in a tube muffle furnace at a temperature of 450°C for a duration of 4 h, this temperature range effectively enhances the surface area and functional groups of biochar while maintaining the structural integrity of the biomass (Caidi et al., 2021; Fatouma et al., 2023; Hamzah et al., 2018), during which time it underwent a transformation into prickly pear pomace biochar (BC). After cooling, the material was ground and crushed through a 100-mesh sieve. It was then soaked in 1 mol/L HCl for 2 h to remove the ash on the surface of BC. The material was subsequently washed with deionized water on several occasions until the pH was neutral. Finally, the material was dried in an oven at 60°C for 24 h and then placed in a sealed bag for use.
2.2.2 Preparation of BC-FeOOH modification
5 g of BC were weighed and dispersed uniformly into an aqueous ethylene glycol solution (the volume ratio of ethylene glycol to water was 1:7). Subsequently, 0.111 g of FeSO4.7H2O was added and stirred for 10 min before being transferred to a high-pressure reactor. The hydrothermal reaction was then carried out at 120°C for 12 h before being cooled down to room temperature. The biochar was washed with ethanol several times to achieve a neutral pH, and then dried under vacuum at 60°C for 12 h. The solid was ground into powder and sieved through a 100-mesh sieve, resulting in the modified biochar (An et al., 2020), which was recorded as BC-FeOOH. Two control experiments were conducted simultaneously. The first group lacked a Fe source and only contained ethylene glycol, designated as BC-(CH2OH)2. The second group lacked both a Fe source and ethylene glycol, serving as a blank control. This group was designated as BC-(CH2OH)2. The third group lacked both a Fe source and ethylene glycol and was used as a blank control. This group was designated as BC-blank control group and indicated by (BC-control) in the figure.
2.2.3 BC-FeOOH modification characterization
The specific surface area, average pore size, and pore volume of distinct biochar samples were quantified employing the Brunauer-Emmett-Teller system (BET, ASAP2020).
2.3 Batch experiment
2.3.1 Determination of optimal dosage
The biochar modified by the three methods of 0.05 g, 0.10 g, 0.20 g and 0.3 g was placed in a 50 mL centrifuge tube, and 40 mL of Sb(V) solution with an initial concentration of 10 mg/L was added, respectively. Oscillate at a constant speed of 200 r/min and 25°C for 24 h on a constant temperature oscillator. After the reaction, 2 mL was sampled with a needle syringe and filtered with a 0.45 μm aqueous filter membrane. The concentration of Sb(V) in the solution was determined by atomic fluorescence spectrometer, and the adsorption capacity and removal rate of Sb by the three adsorbents were calculated to determine the optimal dosage of biochar. Three parallel groups were set in each group to obtain the highest adsorption amount of biochar for subsequent tests.
2.3.2 Determination of optimal pH value
The optimal amount of biomass charcoal was weighed into a 50 mL centrifuge tube, and 40 mL of Sb(V) solution with an initial concentration of 10 mg/L was added. The pH of the reaction system was then adjusted to 2, 4, 6, and 7 with The reaction system was then treated with 0.1 mol/L HCl and NaOH, and shaken on a thermostatic oscillator at a constant temperature of 200 r/min and 25°C for 24 h. The optimal pH value was used as the control condition for the subsequent adsorption experiments.
2.3.3 Adsorption kinetics experiment
In the experiments, the reaction temperature was 25°C, and under the optimal biomass charcoal dosage and pH conditions, the biomass charcoal was dosed into 40 mL of 10 mg/L Sb(V) solution, which was shaken on a constant temperature oscillator at a constant speed of 200 rpm for 5, 10, 15, 30, 60, 300, 720, 960, 1,440, 1920 and 2,770 min, respectively, after the start of the experiments. To study the adsorption kinetic characteristics of Sb(V), samples of 2 mL were taken with a needle syringe, filtered, and then determined by atomic fluorescence spectrometer, and three parallel groups were set up during the experiment.
The adsorption of Sb in water by biochar, Q (mg/g), was calculated Equation 1:
where C0 and Ct represent the concentration of Sb solution before and after adsorption by biochar in mg/L, respectively; Q represents the adsorption amount in mg/g; V is the volume of solution added (mL); m is the mass of adsorbent poured in g.
The removal rate of Sb from water by biochar was calculated Equation 2:
The experimental results obtained were used to fit the adsorption kinetics using the fitted first-order equations as well as the fitted second-order equations calculated to fit the equations:
The fitted equations were modeled by the fitted first-order Equation 3:
Fitting a second-order fitted Equation 4:
where Qe represents the maximum adsorption amount of Sb by biochar when the adsorption reaches adsorption equilibrium, in mg/g; while Qt denotes the adsorption amount of biomass char corresponding to the moment t; and k1, k2 represent the adsorption rate constants for the proposed primary kinetics and the adsorption rate constants for the proposed secondary kinetics, respectively.
2.3.4 Isothermal adsorption experiments
Under the conditions of optimal pH and optimal biochar dosage, the three modified BCs were sequentially added to 40 mL of Sb solution with mass concentrations of: 5, 10, 30, 50, and 80 mg/L. After adsorption for 15 min, the adsorption amount was calculated by constant temperature oscillation on a thermostatic oscillator at 200 rpm and 25 °C for 24 h, and the adsorption isotherm model was used to fit the experimental data.
According to the results obtained from the experiments, the adsorption thermodynamics was fitted to the experimental results, and the fitting models were: Langmuir equation and Freundlich equation, whose expressions are Equations 5, 6:
Langmuir isotherm:
Freundlich isotherm:
where KL and KF are Langmuir and Freundlich constants in L/mg, respectively; Ce is the concentration at which the adsorption reaches equilibrium in mg/L; Qe is the equilibrium adsorption capacity in mg/g; Qmax is the maximum adsorption capacity of the adsorbent; and 1/n is a dimensionless number representing the adsorption strength.
3 Results and analysis
3.1 Characteristics of specific surface area and pore size changes before and after biomass charcoal modification
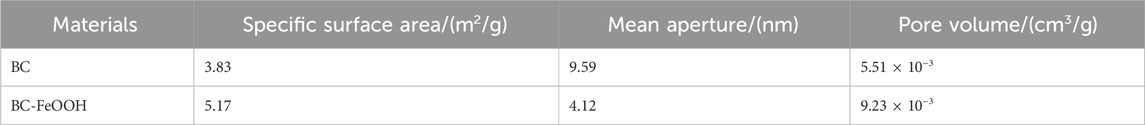
As shown in Table 1, the BC-FeOOH pore size decreased from 9.59 nm to 4.12 nm, the BET specific surface area increased from 3.83 m2/g to 5.17 m2/g before modification, and the pore volume increased from 5.51 × 10−3 cm3/g to 9.23 × 10−3 cm3/g. The decrease in pore size of BC-FeOOH was mainly due to the fact that the biomass charcoal in the glycol and Fe(II) added during the modification process favored the increase in the number of micropores and adsorption sites, thus increasing its specific surface area and pore volume (Zeng et al., 2023). The BET results show a significant increase in surface area, providing more sites for Sb(V) molecules to be “physically adsorbed” or trapped within the pores. The micropores and mesopores (2–50 nm) are particularly important, as Sb(V) ions can be adsorbed through van der Waals forces and electrostatic interactions in these small spaces (Waldemar et al., 2020). Additionally, the high porosity of the biochar enhances the contact surface area between the adsorbent and the solution, further promoting the adsorption process.
3.2 Influence of biochar dosage on the adsorption effect of Sb
The adsorption performance of different dosages of the Sb(V) solution with an initial concentration of 10 mg/L was determined. As shown in Figure 1, with the increase of biochar dosage, the adsorption amount per unit mass of Sb by the three materials showed a decreasing trend. This indicates that their biochar dosage was inversely proportional to the adsorption amount. The reduction in adsorption capacity per unit mass of biochar with increasing biochar dosing was primarily attributable to the fact that the total quantity of Sb(V) in the water body was insufficient to saturate the adsorption process with excess biochar. Additionally, the decrease in adsorption capacity may be attributed to the aggregation of adsorption sites due to the increase in biochar, which results in the covering of some of the adsorption sites on the surface of the biochar, thereby reducing the adsorption capacity per unit mass (Mahdi et al., 2020). Throughout the adsorption process, the adsorption of Sb(V) onto biochar occurs through surface complexation and ion exchange. Oxygen-containing functional groups on the biochar surface, such as hydroxyl (-OH) and carboxyl (-COOH), interact with Sb(V) ions via electrostatic attraction or coordination, forming surface complexes that enhance adsorption. Additionally, ion exchange plays a key role, where exchangeable cations (e.g., Ca2⁺, K⁺) on the biochar are displaced by Sb(V) ions. This mechanism is pH-dependent (Trakal et al., 2014), with higher adsorption occurring in acidic conditions where the biochar surface carries a positive charge, promoting ion exchange and Sb(V) uptake. As illustrated in the figure, all three materials exhibited the highest adsorption capacity at a dosage of 0.05 g. The adsorption capacity of modified BC-FeOOH was up to 4.4 mg/g, which was significantly higher than that of ethylene glycol-modified biochar and unmodified biochar. Therefore, based on considerations of cost and removal effect, the optimal dosage of biochar was determined to be 0.05 g. Additionally, the maximum removal capacities of activated carbon and activated alumina for antimony generally range between 10–100 mg/g (Lee et al., 2024; Xu et al., 2001). While these adsorbents exhibit higher adsorption capacities compared to the 4.4 mg/g removal capacity of biochar modified with Rosa roxburghii residue, the relatively high costs associated with activated carbon and activated alumina may hinder their economic viability for large-scale applications. The adsorption capacities of silicate minerals, when used as adsorbents for antimony, exhibit significant variability. For instance, some silicate minerals, such as bentonite and kaolinite, have adsorption capacities of less than 1.0 mg/g (Xi et al., 2010). In contrast, the modified biochar derived from Rosa roxburghii residue demonstrates superior adsorption properties, outperforming these low-efficiency silicate minerals.
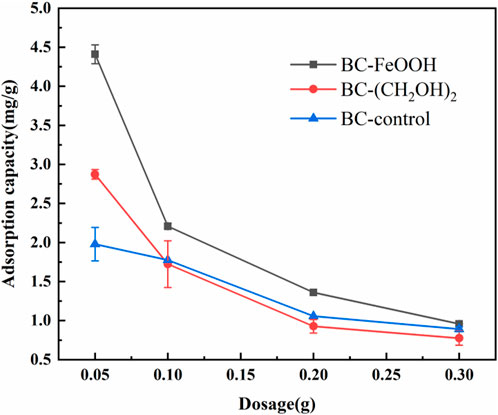
Figure 1. Effect of dosage on adsorption of antimony in water by biochar, the errors are based on the results of three parallel experiments.
3.3 Effect of pH on adsorption properties of biochar
Solution pH represents a pivotal variable influencing the adsorption efficacy of solution Sb. pH exerts a dual influence on the biochar surface functional groups, affecting both their effectiveness and the morphology, existence, and chemical characteristics of Sb(V) in aqueous solution (Sun et al., 2011). The adsorption of Sb by the three types of biochar exhibited a slight decrease with an increase in pH (Figure 2). The maximum adsorption amount of the three types of biochar was observed at pH = 2, with the maximum adsorption amounts of BC-FeOOH, BC-(CH The adsorption amounts of the three biochars at pH 6 were 5.7 mg/g, 4.8 mg/g, and 4.5 mg/g, respectively. At pH 6, the adsorption amounts of the respective biochars reached the lowest values. The results of the present experimental study are in general agreement with those of previous studies. This may be due to the fact that the type of Sb(V) in the solution and the surface charge of the adsorbent are affected by pH (Deng et al., 2020). When the solution is acidic, the presence of a large amount of H+ in the solution induces the protonation of functional groups on the surface of the biochar, which in turn leads to an increase in the positive charge on the surface of the biochar. This contributes to the electrostatic attraction and complexation reactions between the Sb in the solution and the functional groups on the surface of the biochar (Di et al., 2021). Furthermore, it has been demonstrated that the surface of biochar is susceptible to positive charging under strong acidic conditions, and with increasing pH, the surface of biochar is negatively charged (Wan et al., 2020). Consequently, an increase in solution pH may result in an electrostatic repulsion effect between the surface of biochar and Sb(OH)- ions, which impairs the biochar’s ability to adsorb and remove Sb (Li et al., 2022). Consequently, the adsorption of Sb by the three biochar species demonstrated a declining trend with increasing solution pH.
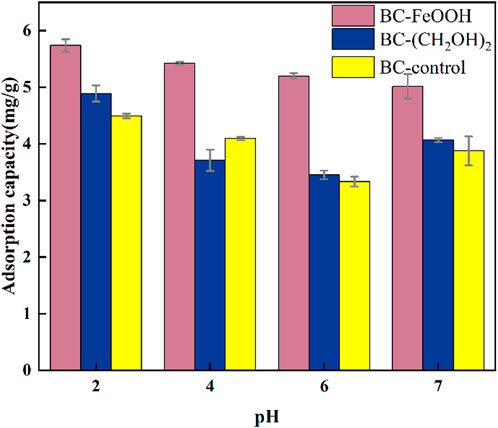
Figure 2. Effect of solution pH on adsorption of Sb(V) in water by biochar, the errors are based on the results of three parallel experiments.
3.4 Adsorption kinetics
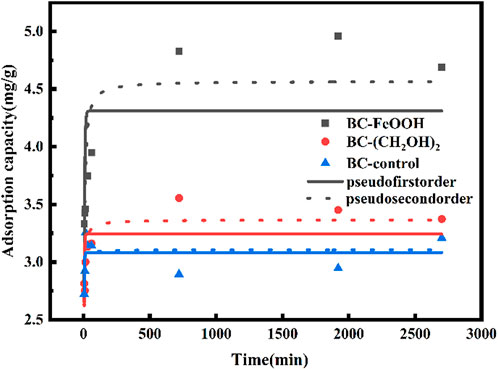
Adsorption kinetics can be employed as the primary criterion for evaluating the potential practical application of biochar adsorbents. In cases where the adsorption process is rapid and efficient, the associated costs can be reduced. Figure 3 illustrates the trends in adsorption amount and removal rate of Sb(V) in water over time for the three biochars. The adsorption amount increased rapidly during the initial two hours of the adsorption process, after which the growth slowed down to reach equilibrium after 10 ours. The equilibrium adsorption amounts of Sb(V) by biochar prepared from different modified materials were 4.8 mg/g, 3.6 mg/g, The equilibrium adsorption amounts were 2.9 mg/g, and the equilibrium removal rates were 35%, 26.5%, and 22%, respectively. These results indicated that BC-FeOOH exhibited the best adsorption effect. The presence of FeOOH may provide additional adsorption sites, beyond those provided by surface functional groups, which could enhance the adsorption efficiency of BC-FeOOH. Furthermore, it was demonstrated that biochar with larger pores exhibited a higher rate of adsorption of Sb removal (Chen et al., 2022), indicating that the pore structure of the surface of prickly pear pomace modified biochar by Fe was enhanced, which accelerated the diffusion rate of Sb within the pores and resulted in a faster rate of BC-FeOOH adsorption.
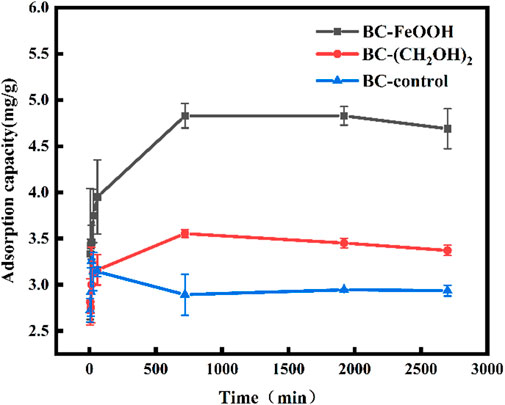
Figure 3. Effect of adsorption time on antimony adsorption by biochar, the errors are based on the results of three parallel experiments.
During the adsorption of Sb from solution by biochar, there were more adsorption sites and functional groups on the surface of the adsorbent at the beginning stage of adsorption, and the competition between ions was minimal. Additionally, functional groups with high adsorption affinity on the adsorbent surface were occupied first, which led to a rapid increase in adsorption efficiency. However, as adsorption proceeds, the limited adsorption sites are gradually saturated, and heavy metal ions begin to diffuse into the interior of the adsorbent. This leads to a gradual increase in diffusion resistance and a decrease in diffusion rate. At the same time, the remaining adsorption sites with lower adsorption affinity begin to function, and gap diffusion may occur. The adsorption rate gradually slows down and eventually tends to adsorption equilibrium (Zhou et al., 2017).
The adsorption mechanism of Sb by prickly pear pomace biochar was further investigated based on the study of the adsorption amount and removal rate of Sb(V) in solution, as well as the effect of different adsorption times on the adsorption performance of biochar. The adsorption of Sb(V) by prickly pear pomace biochar was used in this study. Table 2 presents the fitting parameters of the proposed primary equation and the proposed secondary kinetic equation model for the adsorption of Sb(V) by prickly pear pomace biochar. Figure 4 depicts the results of the adsorption kinetic equation. The adsorption rate of the three biochar samples exhibited a trend of initial acceleration followed by a deceleration with increasing time, reaching equilibrium after approximately 8 h. The adsorption amount of BC-FeOOH was the highest at equilibrium, reaching 4.6 mg/g, while the adsorption amount of BC-control was the lowest, at 3.1 mg/g. The adsorption of Sb(V) in water by FeOOH-modified prickly pear pomace biochar was found to be the most effective.
The pseudo-primary kinetic fitted R2 values of the three biochars were 0.34, 0.33, and 0.49, respectively, while the proposed secondary kinetic fitted R2 values were 0.71, 0.75, and 0.31. These results indicated that the proposed secondary kinetic equations better responded to the adsorption mechanism of modified prickly pear pomace biochar on Sb(V), and also indicated that the surface adsorption energy of the modified prickly pear pomace biochar in the adsorption process was uniformly distributed. The proposed primary kinetic adsorption is physical adsorption, whose adsorption process is mainly controlled by diffusion, and the proposed secondary equation is mainly chemical adsorption, whose adsorption process is mainly controlled by binding force (Fang et al., 2021). Therefore, the adsorption mechanism of Sb by the two biochars, BC-FeOOH and BC-(CH2OH)2, is mainly chemisorption, and BC-control’s mainly exhibits physisorption.
3.5 Adsorption isothermal process
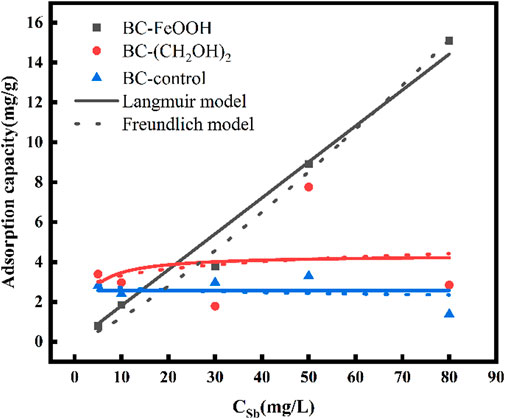
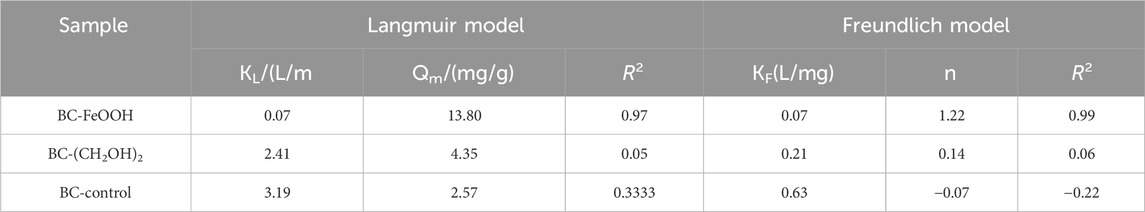
The adsorption isotherms of Sb in water by the three biochars are presented in Figure 5. It can be observed that the adsorption of Sb in water by BC-FeOOH increased with the increase of the initial concentration, and that the adsorption and removal capacity of Sb in solution was stronger. The adsorption amount of BC-control and BC-(CH2OH)2 was greater than that of BC-FeOOH when the concentration was lower, and the adsorption amount of BC-FeOOH exceeded that of BC-(CH2OH)2when the concentration reached up to 20 mg/L, with a greater adsorption capacity. This indicates that BC-(CH2OH)2 can be used for the treatment of low concentrations of Sb in water, while BC-FeOOH can be efficiently adsorbed to remove Sb from water. The parameters calculated by Langmuir and Freundlich models are shown in Table 3. The adsorption effects of BC-(CH2OH)2 and BC-control were not obvious. Therefore, these parameters are not discussed further. The Langmuir and Freundlich equations for BC-FeOOH both have R2 values greater than 0.9, indicating that these isothermal adsorption equations can fit the experimental data better. This also indicates that the adsorption process of modified prickly pear pomace on Sb from water may be affected by a variety of adsorption mechanisms. The R2 value of the Freundlich equation is greater than that of the Langmuir equation, indicating that the Langmuir equation more accurately describes the adsorption process of BC-FeOOH on Sb as homogeneous monolayer chemisorption (Zhou et al., 2016). Its 1/n is 0.81, which is less than 1, suggesting that this adsorption process is more facile (Wang L. et al., 2018).
4 Conclusion
In this study, modified prickly pear pomace biochar (BC-FeOOH) was prepared from prickly pear pomace as the raw material. The adsorption characteristics of modified prickly pear pomace biochar on Sb in water were investigated with different biochar dosages, pH values, and reaction times. The results confirmed the feasibility of the modified prickly pear pomace biochar for the removal of Sb in water. The experimental results demonstrated that the maximum adsorption of antimony in water was achieved at a biochar dosage of 0.05 g and a pH of 2.0. The kinetic and isothermal modeling indicated that the reaction kinetics of the adsorption process of Sb by BC-FeOOH conformed to the proposed second-order kinetic equation, and the isothermal adsorption curves conformed to the Langmuir model. The adsorption The adsorption of Sb in water by BC-FeOOH was a mono-molecular-layer chemical adsorption process. The adsorption of Sb in water by BC-FeOOH exhibited excellent adsorption performance, and it is an adsorbent with considerable potential for application. The application of BC-FeOOH to the adsorptive removal of Sb in water not only provides an efficient, inexpensive, and fast way to remove Sb from wastewater, but also realizes the efficient green resourcefulness and harmless utilization of prickly pear residue.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
YD: Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Writing–original draft. SZ: Supervision, Validation, Writing–review and editing. RZ: Investigation, Methodology, Writing–review and editing, Supervision.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
Author YD was employed by China Overseas Construction Limited.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
An, Q., Miao, Y., Zhao, B., Li, Z., and Zhu, S. (2020). An alkali modified biochar for enhancing Mn2+ adsorption: performance and chemical mechanism. Mater. Chem. Phys. 248, 122895. doi:10.1016/j.matchemphys.2020.122895
Caidi, Y., Jingjing, L., and Shenggao, L. (2021). Pyrolysis temperature affects pore characteristics of rice straw and canola stalk biochars and biochar-amended soils. Geoderma, 397. doi:10.1016/J.GEODERMA.2021.115097
Cavallo, D., Iavicoli, I., Setini, A., Marinaccio, A., Perniconi, B., Carelli, G., et al. (2002). Genotoxic risk and oxidative DNA damage in workers exposed to antimony trioxide. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 40, 184–189. doi:10.1002/em.10102
Chen, H. B., Gao, Y. R., El-Naggar, A., Niazi, N. K., Sun, C. H., Shaheen, S. M., et al. (2022). Enhanced sorption of trivalent antimony by chitosan-loaded biochar in aqueous solutions: characterization, performance and mechanisms. J. Hazard. Mater., 425. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127971
Deng, J. Q., Li, X. D., Wei, X., Liu, Y. G., Liang, J., Shao, Y. N., et al. (2020). Different adsorption behaviors and mechanisms of a novel amino-functionalized hydrothermal biochar for hexavalent chromium and pentavalent antimony. Bioresour. Technol. 310, 123438. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123438
Deng, R. J., Jin, C. S., Ren, B. Z., Hou, B. L., and Hursthouse, A. S. (2017). The potential for the treatment of antimony-containing wastewater by iron-based adsorbents. Water 9, 794. doi:10.3390/w9100794
Di, F. J., Zhang, C., Song, G. F., Jiang, S. X., Shan, B. Q., and Song, Z. X. (2021). The adsorption mechanism of kapok biochar on Cr(VI) in aqueous solution. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 41 (05), 1891–1900.
Druzbicka, J., and Craw, D. (2015). Metalloid attenuation from runoff waters at an historic orogenic gold mine, New Zealand. Mine Water Environ. 34, 417–429. doi:10.1007/s10230-014-0316-2
Fang, Z., Suhua, H., Xu, L., Jian, F., Qi, L., Zhiwei, W., et al. (2021). Adsorption kinetics and thermodynamics of rare earth on Montmorillonite modified by sulfuric acid. Colloids Surfaces a-Physicochemical Eng. Aspects 627, 127063. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.127063
Fatouma, A. M., Ayoub, A., Touria, H., Abbi, R., Achira, M., Abourriche, A., et al. (2023). Materials derived from olive pomace as effective bioadsorbents for the process of removing total phenols from oil mill effluents. Molecules 28 (11), 4310. doi:10.3390/molecules28114310
Hamzah, S., Razali, A. N., Yatim, I. N., Alias, M., Ali, A., Zaini, S. N., et al. (2018). Characterisation and performance of thermally treated rice husk as efficient adsorbent for phosphate removal. J. Water Supply Res. Technology—AQUA 67 (8), 766–778. doi:10.2166/aqua.2018.087
Jain, A., Sarsaiya, S., Gong, Q. H., Wu, Q., and Shi, J. S. (2024). Chemical diversity, traditional uses, and bioactivities of Rosa roxburghii Tratt: a comprehensive review. Pharmacol. and Ther., 259. doi:10.1016/J.PHARMTHERA.2024.108657
Jia, X., Zhou, J., Liu, J., Liu, P., Yu, L., Wen, B., et al. (2020). The antimony sorption and transport mechanisms in removal experiment by Mn-coated biochar. Sci. Total Environ. 724, 138158. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138158
Lee, S. H., Chung, J., and Lee, Y. W. (2024). Adsorption removal characteristics of hazardous metalloids (antimony and arsenic) according to their ionic properties. Water 16 (5), 767. doi:10.3390/w16050767
Li, H., Dong, X., da Silva, E. B., de Oliveira, L. M., Chen, Y., and Ma, L. Q. (2017). Mechanisms of metal sorption by biochars: biochar characteristics and modifications. Chemosphere 178, 466–478. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.03.072
Li, J., Zheng, B., He, Y., Zhou, Y., Chen, X., Ruan, S., et al. (2018). Antimony contamination, consequences and removal techniques: a review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 156, 125–134. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.03.024
Li, Q., Ma, X., Qi, C., Li, R., Zhang, W., Li, J., et al. (2022). Facile preparation of novel magnetic mesoporous Fe Mn binary oxides from Mn encapsulated carboxymethyl cellulose-Fe(III) hydrogel for antimony removal from water. Sci. Total Environ., 821. doi:10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2022.153529
Liu, Y., Zhong, D. J., Xu, Y. L., Chang, H. X., Dong, L., Han, Z. F., et al. (2023). Facile synthesis of lanthanum-doped Fe-based MOF for phosphate removal from water: high adsorption capacity, tuneability, and reproducibility. Water Air Soil Pollut. 234, 321. doi:10.1007/s11270-023-06340-6
Mahdi, Z., El Hanandeh, A., and Yu, Q. J. (2020). Electro-assisted adsorption of heavy metals from aqueous solutions by biochar. Water Sci. Technol. 81, 801–812. doi:10.2166/wst.2020.163
Park, S.-J., Lee, Y.-J., Kang, J.-K., Lee, J.-C., and Lee, C.-G. (2021). Application of Fe-impregnated biochar from cattle manure for removing pentavalent antimony from aqueous solution. Appl. Sci. 11, 9257. doi:10.3390/app11199257
Peidong, L., Chao, L., Xiong, F., Huang, Q., and Qing, C. (2023). Physicochemical, functional and biological properties of soluble dietary fibers obtained from Rosa roxburghii Tratt pomace using different extraction methods. Process Biochem., 12840–12848. doi:10.1016/J.PROCBIO.2023.02.021
Rahaman, M. S., Basu, A., and Islam, M. R. (2008). The removal of As(III) and As(V) from aqueous solutions by waste materials. Bioresour. Technol. 99, 2815–2823. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2007.06.038
Shan, C., Ma, Z., and Tong, M. (2014). Efficient removal of trace antimony(III) through adsorption by hematite modified magnetic nanoparticles. J. Hazard. Mater. 268, 229–236. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.01.020
Sun, F. H., Wu, F. C., Liao, H. Q., and Xing, B. S. (2011). Biosorption of antimony(V) by freshwater cyanobacteria Microcystis biomass: chemical modification and biosorption mechanisms. Chem. Eng. J. 171, 1082–1090. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2011.05.004
Tang, H. Y., Hassan, M. U., Nawaz, M., Yang, W. T., Liu, Y., and Yang, B. J. (2023). A review on sources of soil antimony pollution and recent progress on remediation of antimony polluted soils. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 266, 115583. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2023.115583
Trakal, L., Bingöl, D., Pohořelý, M., Hruška, M., and Komárek, M. (2014). Geochemical and spectroscopic investigations of Cd and Pb sorption mechanisms on contrasting biochars: engineering implications. Bioresour. Technol. 171, 171442–171451. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2014.08.108
Waldemar, K., Malte, B., and Sergej, F. (2020). Measurement of sub-nanonewton forces inside a scanning electron microscope. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 91 (4), 043701. doi:10.1063/1.5144653
Wan, S., Qiu, L., Li, Y., Sun, J., Gao, B., He, F., et al. (2020). Accelerated antimony and copper removal by manganese oxide embedded in biochar with enlarged pore structure. Chem. Eng. J. 402, 126021. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2020.126021
Wang, C., Wang, H., and Cao, Y. (2018a). Pb(II) sorption by biochar derived from Cinnamomum camphora and its improvement with ultrasound-assisted alkali activation. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 556, 177–184. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2018.08.036
Wang, L., Wang, J., Wang, Z., He, C., Lyu, W., Yan, W., et al. (2018b). Enhanced antimonate (Sb(V)) removal from aqueous solution by La-doped magnetic biochars. Chem. Eng. J. 354, 623–632. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2018.08.074
Wang, L., Zhang, P., Chen, Y., Tian, Y., and Chen, J. (2021). Physicochemical characterization and in vitro biological activities of water-extracted polysaccharides fractionated by stepwise ethanol precipitation from Rosa roxburghii Tratt fruit. J. Food Meas. Charact. 16, 38–48. doi:10.1007/s11694-021-01125-z
Xi, J., He, M., and Lin, C. (2010). Adsorption of antimony(III) and antimony(V) on bentonite: kinetics, thermodynamics and anion competition. Microchem. J. 97 (1), 85–91. doi:10.1016/j.microc.2010.05.017
Xu, S., Deng, J., Wu, S., Fei, Q., Lin, D., Chen, H., et al. (2024). Dynamic changes of active components and volatile organic compounds in rosa roxburghii fruit during the process of maturity. Foods Basel, Switz. 13 (18), 2893. doi:10.3390/foods13182893
Xu, Y. H., Ohki, A., and Maeda, S. (2001). Adsorption and removal of antimony from aqueous solution by an activated alumina. Toxicol. and Environ. Chem. 80 (3-4), 133–144. doi:10.1080/02772240109359004
Yi, Y., Huang, Z., Lu, B., Xian, J., Tsang, E. P., Cheng, W., et al. (2020). Magnetic biochar for environmental remediation: a review. Bioresour. Technol. 298, 298122468. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122468
Zeng, W., Zhu, J., Guo, X. Q., and Yin, H. (2023). Adsorption effect of FeOOH loaded rosa roxburghii residue biomass carbon on fluorine (F-) in water. J. Sichuan Normal Univ. 41 (04), 690–697. doi:10.16036/j.issn.1000-2650.202203175
Zhou, L., Liu, Y., Liu, S., Yin, Y., Zeng, G., Tan, X., et al. (2016). Investigation of the adsorption-reduction mechanisms of hexavalent chromium by ramie biochars of different pyrolytic temperatures. Bioresour. Technol. 218, 351–359. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2016.06.102
Zhou, X., Zeng, Z., Zeng, G., Lai, C., Xiao, R., Liu, S., et al. (2020). Persulfate activation by swine bone char-derived hierarchical porous carbon: multiple mechanism system for organic pollutant degradation in aqueous media. Chem. Eng. J. 383, 123091. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2019.123091
Zhou, X., Zhu, G., Lu, Y., Du, B., Lin, D., and Ran, Z. (2019). Optimization of insoluble dietary fiber preparation technology from Rosa roxburghii Tratt pomace by enzyme method. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 330 (4), 042052. doi:10.1088/1755-1315/330/4/042052
Zhou, Y. Y., Liu, X. C., Xiang, Y. J., Wang, P., Zhang, J. C., Zhang, F. F., et al. (2017). Modification of biochar derived from sawdust and its application in removal of tetracycline and copper from aqueous solution: adsorption mechanism and modelling. Bioresour. Technol. 245, 266–273. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2017.08.178
Keywords: BC-FeOOH, Sb(V), adsorption, biochar, rosa roxburghii residue
Citation: Dai Y, Zhao S and Zheng R (2025) Adsorption and removal of pentavalent antimony from water by biochar prepared from modified rosa roxburghii residue. Front. Environ. Sci. 12:1540638. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2024.1540638
Received: 06 December 2024; Accepted: 26 December 2024;
Published: 09 January 2025.
Edited by:
Yaoguang Guo, Shanghai Polytechnic University, ChinaReviewed by:
Fang Li, Donghua University, ChinaHuiqing Han, Guizhou Institute of Technology, China
Fuxing Kang, Nanjing Agricultural University, China
Copyright © 2025 Dai, Zhao and Zheng. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yong Dai, ZGFpeW9uZ0Bjb2hsLmNvbQ==
 Yong Dai1*
Yong Dai1* Ruyi Zheng
Ruyi Zheng