- 1China Overseas Construction Limited, Guangdong Shenzhen, Shenzhen, China
- 2Resource and Environmental Engineering College, Guizhou University, Guiyang, Guizhou, China
In this study, vegetative eco-concrete was prepared based on electrolytic manganese slag/phosphogypsum composite cementitious material as binder and clayey ceramic grains as aggregate. Based on the conditions of porosity and water-cement ratio, the optimal proportion of phosphogypsum-based eco-concrete was investigated, and concrete specimens with good performance were prepared (14 days compressive strength: 3.49 MPa, permeability coefficient: 1.37, total porosity: 24.5%, Improved compressive strength by 15% and water retention by 20%). The nutrient matrix of vegetative eco-concrete with different phosphogypsum/electrolytic manganese slag ratios was designed and modified, and the vegetative performance of the eco-concrete was investigated using four-season grass, ryegrass, clippings and clover as the grass species. The results showed that the eco-concrete based on phosphogypsum as raw material was rich in nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium, which could meet the requirements of plant growth, Supporting plant growth with a 30% increase in root length and 25% improvement in biomass compared to control concrete. The addition of improvers had a good passivation effect on heavy metals such as As, Cu, Cr, Zn, Sb and Pb in the phytogenic substrate. The adaptability of different grass species to the planting substrate was Four Seasons > ryegrass > shepherd’s purse > clover, alfalfa, dogbane; the application of electrolytic manganese slag substrate had the best performance of planting, and the planting substrate with the application of improver inhibited the growth of plants. The study addresses the challenge of using phosphogypsum as a binder in concrete, which has traditionally faced issues with strength and stability. By optimizing the mix ratio and curing process, we were able to achieve a concrete material that not only performs well mechanically but also supports plant growth.
1 Introduction
Phosphogypsum (PG), a byproduct of the phosphorus chemical industry, is characterized by high production and stockpiling volumes, along with a low rate of resource utilization (Liu et al., 2022). Globally, PG accumulations have reached approximately 6 billion tons, increasing by 150 million tons annually, while the overall utilization rate remains below 20% (Liu et al., 2022; Du et al., 2022). In China, annual PG production is around 75 million tons, with an estimated 40% utilization rate. Notably, five provinces—Hubei, Yunnan, Guizhou, Sichuan, and Anhui—account for approximately 85% of the country’s total PG production, largely due to their substantial phosphate fertilizer output (Cui et al., 2022). The primary component of PG is CaSO4·2H2O, yet it also contains hazardous impurities such as calcium fluoride, acid-insoluble materials, soluble phosphorus, heavy metals, and radioactive elements, which pose health risks to humans and harm plant growth (Liu et al., 2022). PG disposal mainly relies on long-term stockpiling, which not only occupies significant land resources but also presents considerable environmental and safety risks. This situation exerts substantial pressure on China’s ecological protection efforts and poses a significant obstacle to the sustainable development of phosphorus chemical enterprises. Consequently, enhancing the resource utilization of PG has become a critical issue urgently requiring industry solutions.
Currently, the resource utilization of PG is primarily applied in areas such as road construction, building materials, agriculture, and mine reclamation (Cui et al., 2022; Huang et al., 2023; Jin et al., 2024). Among these, the use of PG in the building materials industry—such as for producing bricks, lightweight aggregates, and binders—represents an effective large-scale approach to PG resource utilization (Huang et al., 2019; Junakova and Junak, 2017; Liang and Li, 2015). However, impurities like phosphorus and fluorine in PG may impact the performance of construction materials. To mitigate these effects, PG is typically calcined at high temperatures to produce hemihydrate or anhydrite gypsum, which is then used to manufacture cement and slag-based composite binders, addressing the impurity issues to a certain extent (Garg, 1995; Yang and Qian, 2011). For instance, Zhang Yi and colleagues successfully prepared gypsum-based binders with desirable mechanical properties using PG (Cao, 2018; Huang et al., 2016; Zhang et al., 2011). Therefore, developing innovative methods for preparing PG-based binders can significantly enhance the efficiency of PG utilization. Additionally, numerous studies have demonstrated effective modification of PG using quicklime, industrial alkaline wastes, and fly ash to produce cement retarders, with the resulting cement products meeting national standards (Yang et al., 2003; Li et al., 2002; Zhou et al., 2007). At present, the production of cement retarders from PG remains the primary method for large-scale PG consumption.
Ecological concrete, also known as “vegetative concrete,” is an innovative concrete material distinct from conventional concrete, designed to support plant growth, regulate ecological balance, enhance environmental aesthetics, and provide protective functions (Chen, 2021). It is widely applied in ecological protection of slopes along highways, riverbanks, and reservoirs, as well as in municipal engineering, ecological landscaping, mountain restoration, and vertical greening (Ismaeel et al., 2023; M S et al., 2020; Yatesh et al., 2023; Said Awad et al., 2024a), playing a critical role in preventing soil erosion and enhancing environmental quality. This material offers promising application potential. Ecological concrete consists of coarse aggregate, binding materials, and water mixed in specific proportions, providing a high porosity that creates space and water cycling conditions conducive to plant growth (Song, 2009). Though traditionally cement is used as the primary binding material in most ecological concrete, its high energy consumption and elevated alkalinity are unfavorable for plant growth. To mitigate the environmental impacts associated with traditional cement, researchers have explored alternative materials that can enhance both the sustainability and performance of ecological concrete. One such material is phosphogypsum (PG), which, when incorporated as a binder, not only reduces the reliance on cement but also offers additional environmental benefits, such as waste recycling and reduced carbon footprint. Alongside PG, the ongoing challenge of managing waste materials, such as plastic waste, has spurred innovative solutions in the construction industry. Incorporating waste plastics into concrete not only addresses the growing issue of plastic pollution but also improves the material’s thermal properties. Similar to the use of phosphogypsum in concrete, recycling plastic waste provides a sustainable alternative to traditional concrete, offering significant environmental benefits (Said et al., 2024b; Hameed et al., 2023; Jassam et al., 2023).
Research has demonstrated that electrolytic manganese residue (EMR) can be processed into a low-strength binder suitable for ecological concrete production, presenting a viable expansion path (Zhang, 2022). EMR has demonstrated versatility in construction materials, including cement, road bases, and ceramics, with the potential for direct incorporation into Portland cement without high-temperature pretreatment. This approach reduces costs and environmental impacts while functioning effectively as a low-strength binder in ecological concrete (Fu et al., 2023; Shichao et al., 2023). Research has also shown that EMR enhances concrete durability and performance, with its gypsum and sulfate content activating slag pozzolanic activity to improve the microstructure and overall properties (Wang et al., 2013). These findings highlight EMR’s significant potential for sustainable construction practices. However, there has been limited research on using PG as a binder for ecological concrete. While the benefits of incorporating industrial by-products like phosphogypsum into concrete are known, most studies have focused solely on the material’s mechanical properties. In contrast, this study examines its dual role—enhancing both the mechanical performance and ecological functions of concrete, specifically its superior water retention and its ability to promote plant growth. By building on our previous work, this study expands the scope to include the ecological impact of phosphogypsum-based concrete, addressing the research gap where few studies have investigated its combined effects on sustainability and plant growth.
This study aims to develop a plant-compatible ecological concrete using PG as a primary material, mixed with electrolytic manganese residue and slag powder to create composite binders at various PG-to-manganese residue ratios. This composite binder is then used to produce vegetative ecological concrete. The study examines the effects of different mix designs on the water absorption, porosity, and compressive strength of the ecological concrete. Additionally, PG and electrolytic manganese residue are blended with diatomaceous earth and straw biochar to create an improved planting substrate. The vegetative performance of common grass species is tested to explore novel pathways for PG resource utilization.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Materials
2.1.1 Test raw materials
PG was sourced from a phosphogypsum stockpile at a Wengfu facility. After thorough mixing, it was air-dried to a moisture content of ≤1%, ground to pass through a 0.25 mm sieve, and stored in a sealed container for later use. Electrolytic manganese residue was obtained from a stockpile in Songtao County, Guizhou Province. S95-grade ground granulated blast furnace slag (GGBFS) was purchased from Taiyuan Iron & Steel Group Co., Ltd. Ordinary Portland cement (P·O42.5), with a residue of 3.5% on a 180-mesh sieve, was commercially available. Lightweight clay ceramsite (particle size 1–1.5 mm, compressive strength 1.3 MPa) was acquired from the local market. Luminescent bacteria (from Photobacterium phosphoreum) were provided by Beijing Hamamatsu Photon Techniques Co., Ltd. All chemicals used in the experiments were of analytical grade, and distilled water was used as the experimental water source.
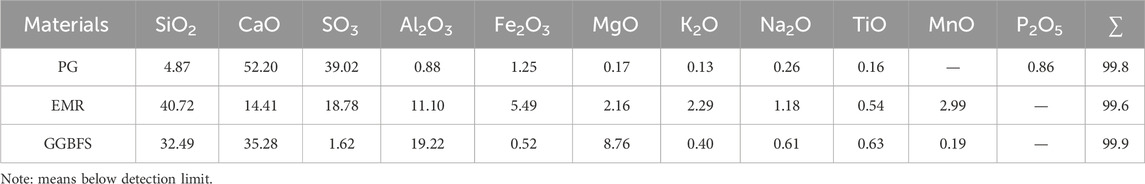
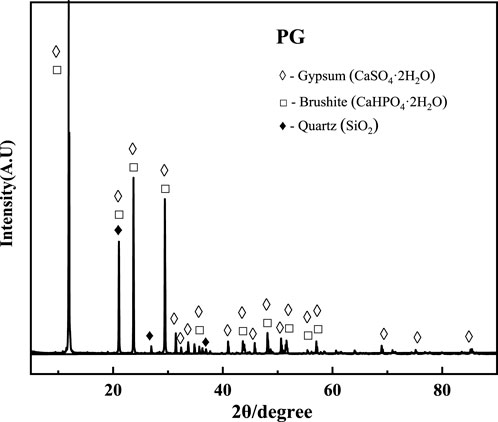
The chemical compositions of PG, EMR, and GGBFS are presented in Table 1. PG mainly consists of CaO, SO3, and SiO2, while EMR’s primary components include SiO2, SO2, CaO, Fe2O3, and MgO. The main constituents of GGBFS are SiO2, CaO, Al2O3, and MgO. The X-ray diffraction (XRD, BrukerAXSD8 Advance, Germany) pattern of PG is shown in Figure 1, indicating gypsum (CaSO4·2H2O), monetite (CaHPO4·2H2O), and quartz (SiO2) as the primary mineral phases.
2.1.2 Composite cementitious material preparation
A composite cementitious material was prepared using PG, EMR and ground granulated blast furnace slag (GGBFS). In this experiment, a mass ratio of 50:10:20:10 was used for EMR, PG, slag powder, and cement to produce the EMR-PG composite binder, with an addition of 4% CaO (AR, 99%, Sinopharm). After combining the binder materials with EMR, 30% distilled water was added, and the mixture was stirred at a constant speed until thoroughly mixed. It was then left to stand in a ventilated area for 12 h before conducting a toxicity leaching test. The prepared EMR was dried at 40°C to a constant weight and passed through a 60-mesh sieve for later use. The materials were thoroughly mixed at a ratio of EMR:PG: slag = 50:20:20:10 and further blended with water at the standard consistency requirement. The resulting slurry was poured into molds measuring 40 mm × 40 mm × 40 mm. The molds were sealed with plastic film and cured at a constant temperature of 60°C and 95% ± 5% humidity for 12 h, followed by an additional 4 h at 60°C to remove excess surface moisture for easy demolding. Finally, the samples were cured at (25 ± 3)°C and 95% ± 5% humidity until the specified curing age was reached.
2.1.3 Eco-concrete mixing ratio
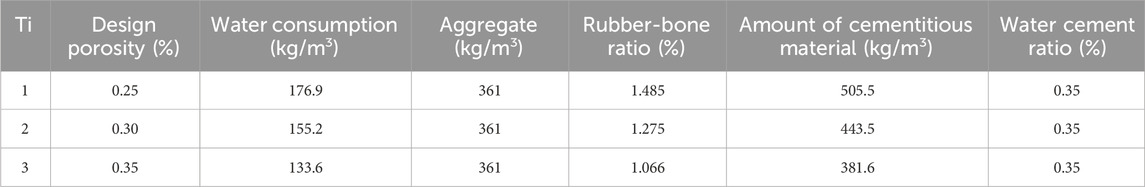
Ecological concrete was prepared according to the mix proportions shown in Table 2. The aggregate ceramsite was first combined with 50% of the mixing water and stirred for 30 s. Then, 50% of the composite binder, prepared as described in Section 2.1.2, was added and mixed thoroughly. The remaining 50% of the mixing water and binder were then added, and the mixture was stirred until homogenous. The mixture was then placed in molds measuring 70 mm × 70 mm × 70 mm in three layers, with each layer compacted to ensure even distribution. The surfaces of the specimens were smoothed, and the molds were wrapped in plastic film to retain moisture and prevent water evaporation. After curing for 14 days, the specimens were removed and set aside for further testing.
2.1.4 Method for determining the vegetative properties of eco-concrete
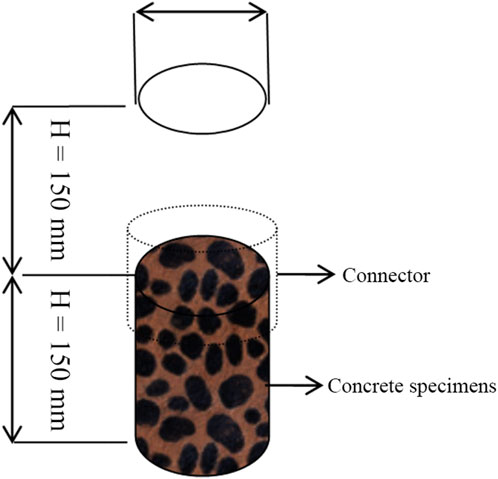
The molds used in this study had an outer diameter of 50 mm (with a wall thickness of 2 mm), a length of 150 mm, and were made of PVC. Three specimens were formed for each mix proportion. Additionally, an identical PVC pipe was prepared, with one end glued to a PVC joint to form the upper structure of a permeability testing device. The concrete was first thoroughly mixed according to the designated proportions, compacted, and leveled. To prevent moisture loss, the specimens were sealed with plastic film and cured at 60°C and 95% ± 5% humidity for 12 h. To facilitate demolding, excess surface moisture was removed by further curing the specimens at (25 ± 3)°C and 95% ± 5% humidity for 7 days. For the permeability test setup, a layer of petroleum jelly was applied to the top end of the mold containing the specimen and to the bottom end of an empty PVC pipe, which were then secured together with connectors. The structure of the permeability testing device is shown in Figure 2. To perform the test, 5 L of tap water was prepared, and water was introduced into the device, allowing the water level to gradually rise. When it reached 295 mm, additional water was added as needed to maintain a water level of 295 ± 5 mm throughout the experiment.
(1) The water permeability coefficient of concrete is calculated using Equation 1 below:
In the formula: KT represents the permeability coefficient of ecological concrete at a water temperature of T °C, measured in cm/s. Q is the volume of water passing through the ecological concrete between time t1 and t2 measured in cm³.L denotes the thickness of the permeable specimen.A is the cross-sectional area of the specimen, in cm2. H represents the hydraulic head, in cm.t1 is the initial time of measurement, in seconds. t2 is the final time of measurement, in seconds.
(2) Water absorption and porosity were calculated as shown in Equations 2–4, respectively:
The water absorption is determined as follows (Yu, 2016):
In the formula: Q represents the water absorption rate after soaking for xxx time, expressed as a percentage (%); Wx denotes the mass of a single specimen after soaking for xxx time, in grams (g); W0 is the mass of the specimen dried to a constant weight at 40°C, in grams (g).
The porosity test is conducted as follow (Peng et al., 2013):
In the formula: P1 represents the total porosity of the specimen, expressed as a percentage (%); P2 denotes the connected porosity of the specimen, expressed as a percentage (%); W1 is the weight of the specimen after 24 h of soaking in water, in grams (g); W2 represents the weight of the specimen in air after being removed from water and left to stand naturally for 24 h, in grams (g); W3 is the weight of the specimen in water after standing naturally for 24 h, in grams (g).
2.2 Experimental design of planting substrate
2.2.1 Experiment on the proportion of planting substrate and its improvement
EMR and PG were passed through a 60-mesh sieve, then mixed at mass ratios of 9:1, 8:2, 7:3, 6:4, and 5:5. The EMR and PG mixtures, along with water and slag at a mass ratio of 10:1, were oscillated at a speed of 110 ± 10 rpm for 8 h and allowed to stand for 16 h before measuring the contents of alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen, available phosphorus, and available potassium in the supernatant. To improve the planting substrate, 2.5% diatomaceous earth and 2.5% straw biochar were added to each substrate (Lou et al., 2020). This modification aims to stabilize and adsorb metal ions released from EMR and PG, reducing their toxicity to plant growth and development.
2.2.2 Toxicity leaching test
In this study, the toxicity leaching test was conducted according to the method described in Leaching Toxicity Testing for Solid Waste—Horizontal Oscillation Method (HJ557-2010). A mixture of EMR and distilled water at a mass ratio of 1:10 was placed in a container, leached at 110 ± 10 rpm for 8 h, and then allowed to stand for 16 h. Additionally, To assess substrate toxicity, the sample pH (PHS-3C, Lei-ci, China), was initially adjusted to approximately 7.0 for testing with luminescent bacteria. Afterward, it was filtered, and the heavy metal content in the filtrate was measured.
Following Ma Mei’s medium formula, a culture medium for luminescent bacteria was prepared (Ma, 2002). The luminescent bacteria were placed in an incubator for 15 min, to which 1 mL of bacterial recovery solution was added to activate the bacteria, followed by incubation for 12 h. This activation step was repeated three times before an appropriate amount of bacterial colonies was inoculated. The bacteria were then incubated in a constant-temperature shaker for 12–16 h for subsequent toxicity testing. Under the same conditions, second- and third-generation bacteria were obtained and preserved for future use. A standard white opaque 96-well enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) plate was used as the carrier. Into each well, 150 µL of the test sample and 50 µL of the cultured bacterial solution were added. The ELISA plate was placed in a microplate reader (Varioskan LUX, Thermofisher, US), shaken, and after 15 min of reaction, the luminescence intensity was measured. A 3% NaCl (AR, 99%, Sinopharm) solution served as the blank control, and each sample was tested in triplicate. The relative luminescence intensity was calculated using the Equations 5, 6:
In the formula: L represents the relative luminescence of the sample. L0 is the luminescence of the blank sample. Li denotes the luminescence of the test sample. 1 L represents the inhibition rate of the sample’s luminescence.
2.2.3 Selection of grass species and determination of their vegetative performance
Grass species adapted to the local substrate (clover, alfalfa, wild ryegrass, blackgrass, Bermuda grass, and holly) were selected for a seed germination experiment. Ten seeds were placed in a petri dish, and 2 mL of vegetation substrate leachate was added. The dishes were incubated at 25°C ± 1°C with light exposure, with daily water replenishment to compensate for evaporation. The germination rate and germination index of the seeds were measured.
According to the designed ecological concrete formulation, concrete was poured into transparent plastic pots and shaped, followed by demolding after 7 days of curing. Sixty seeds were mixed with 10 g of the improved vegetation substrate, and 5 g of mushroom compost was added to enhance the physical and chemical properties of the substrate. The mixture was irrigated to allow the plant solution to permeate the concrete pores. Commercially available organic potting soil and untreated phosphogypsum were used as blank controls. After 45 days, plant height, germination rate, and biomass were measured.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Structural performance of vegetative eco-concrete
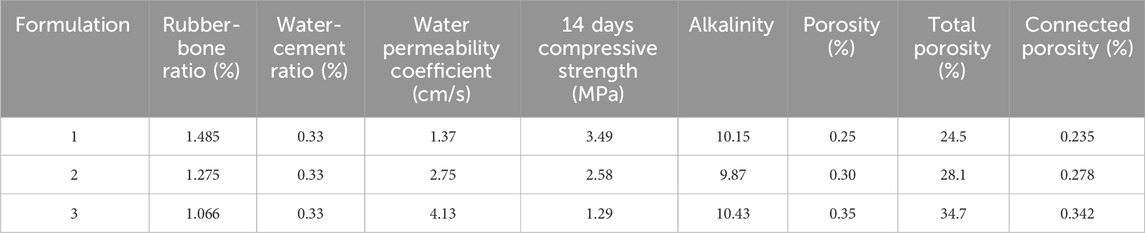
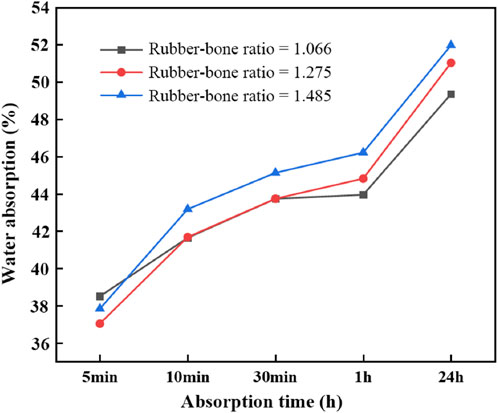
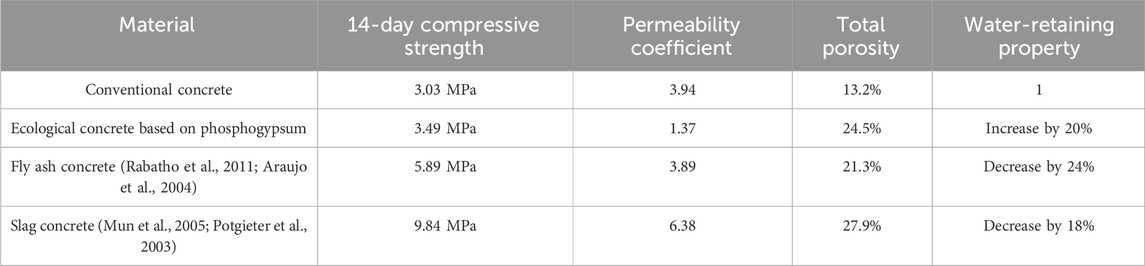
The strength of environmentally-friendly concrete is determined by the binder material, the aggregate, and the bonding strength between the binder and aggregate. Among these factors, the one with the lowest strength has the most significant impact on the overall strength of the eco-concrete. Experimental results for eco-concrete prepared according to the mix ratios in Table 2 are presented in Table 3. In Mix Design 3, the primary failure occurred at the bonding points between binder materials, resulting in the lowest compressive strength at 14 days. The failure in eco-concretes from Mix Designs 1 and 2 was primarily due to infiltration of the aggregate. Mix Design 1 showed a 14-day compressive strength of 3.49 MPa, significantly higher than that of Mix Designs 2 and 3.When force is applied to eco-concrete with shale aggregate, it is transmitted through the connection points between aggregates. If the aggregate has high strength and the bond area and thickness between the aggregate and binder are minimal, failure usually does not occur within the aggregate itself but at the interface between the aggregate and binder or within the hardened binder (Liang, 2010). On the other hand, if the aggregate strength is lower, the bonding between binder materials thickens, causing initial failure within the aggregate, which gradually extends into the hardened binder layer.The porosity of vegetative eco-concrete should be between 20% and 35% to meet plant growth requirements (Hu et al., 2006), and all three mixes satisfied this porosity criterion. As shown in Figure 3, the water absorption rate of eco-concrete made with various rubber-bone ratios was initially the lowest at approximately 38% within 5 min, gradually increasing to 50% after 24 h, which aids rapid water retention. This characteristic mainly results from using lightweight ceramsite aggregate, which reduces the overall mass of the eco-concrete. The absorption rate of Mix Design 1 surpassed that of Mix Designs 2 and 3 after the initial 5 min. Based on these comprehensive tests, Mix Design 1 was identified as the optimal ratio for eco-concrete. Compared to fly ash and slag-based concretes, phosphogypsum-based ecological concrete demonstrates slightly lower 14-day compressive strength (Table 4) (Rabatho et al., 2011; Araujo et al., 2004; Mun et al., 2005; Potgieter et al., 2003). However, its significantly enhanced total porosity and water retention offer distinct advantages for ecological restoration and plant growth applications. The increased porosity provides an optimal environment for plant root aeration and water absorption, while the improved water retention ensures consistent moisture availability, particularly under arid or low-rainfall conditions. Additionally, the lower permeability coefficient of phosphogypsum concrete reduces water loss, making it an essential feature for vegetation-supporting ecological concretes. Experimental results further highlight that the percentage improvements in both compressive strength and water retention validate its feasibility and underscore its potential to balance mechanical performance with ecological functionality.
3.2 Analysis of nutrient composition in the planting substrate
The pH and nutrient content of the planting substrate are crucial for plant growth. As shown in Table 5, PG has a pH of 2.39, and as the amount of PG increases, the pH gradually rises, neutralizing its acidity. PG provides a rich phosphorus source, with an available phosphorus content as high as 4,295.9 mg/kg, while EMR supplies abundant nitrogen, with an alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen content of 7,509.6 mg/kg. The alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen content in the PG-based planting substrate is relatively low, and in combination with EMR, this nitrogen content is balanced in the substrate and decreases as PG content increases. The phosphorus content in the planting substrate increases with the addition of PG, while both substrates have relatively high potassium content. After mixing, the pH, alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen, available phosphorus, and potassium levels in the substrate are balanced, with the nutrient elements in PG and EMR complementing each other to support plant growth.When PG is mixed with the humus components of the soil (EMR), the phosphorus (P) can be readily adsorbed and immobilized by metal ions in EMR, transforming plant-available phosphorus into an insoluble form. EMR contains high levels of Fe and Al, making it likely that phosphorus will exist in forms such as iron phosphate (Fe-P), aluminum phosphate (Al-P), or occluded phosphorus (O-P) (Lu et al., 2013). These insoluble phosphates provide a slow-release fertilizing effect that is not easily absorbed by plants but offers a sustained, long-term nutrient supply. When phosphorus in the substrate is insufficient for plant needs, plant roots release organic acids, which gradually dissolve insoluble phosphates, improving the phosphorus microenvironment around the root system and maintaining essential plant life processes (Liu et al., 2018). Therefore, the PG-modified planting substrate, rich in nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, can adequately meet the nutrient requirements for plant growth.
3.3 Leaching toxicity of the planting substrate
3.3.1 Toxicity leaching of planting substrate under different ratios
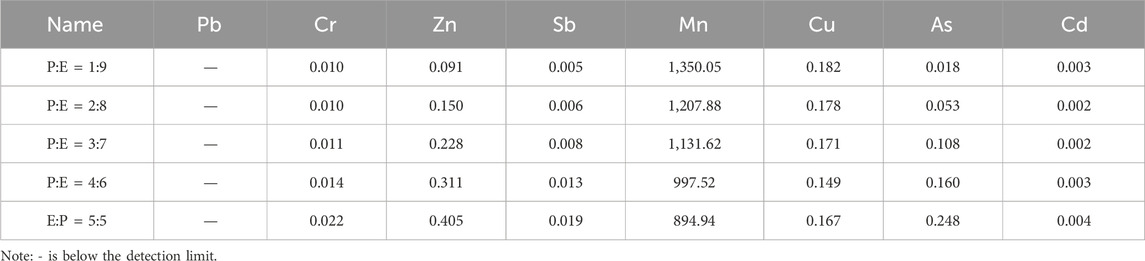
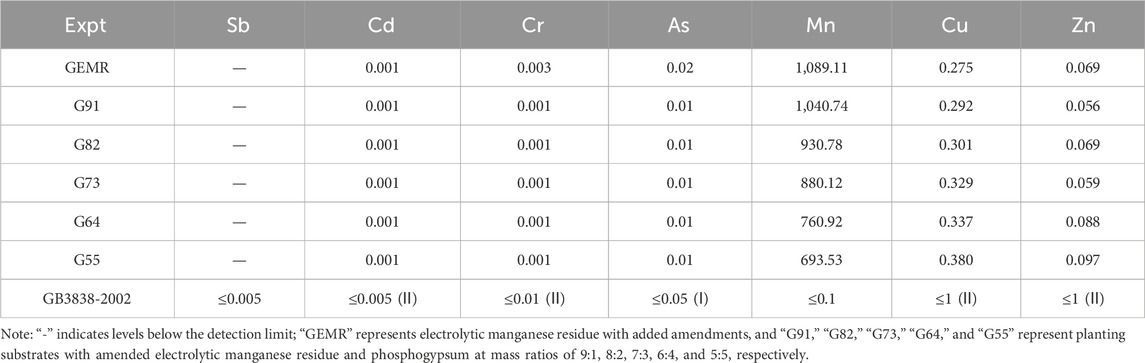
Although the PG-EMR composite substrate is nutrient-rich and meets the requirements for plant growth, both PG and EMR contain various heavy metals and metalloids such as As, Cd, Cr, Cu, and Sb, which have high toxicity (Liu et al., 2022; Ismaeel et al., 2023), These metals can be absorbed and accumulated by plants from the substrate, potentially adversely affecting plant growth. Therefore, conducting a toxicity leaching test on the planting substrate is essential. As shown in Table 6, the manganese (Mn) concentration in the leachate of the PG-EMR composite substrate ranged from 894.94 to 1,350.05 mg/L, exceeding the Class I emission standard of the Integrated Wastewater Discharge Standard (GB 8978-1996) by over 447 times. In contrast, the levels of other heavy metals were relatively low. Excessive Mn in the substrate could hinder plant growth by obstructing the uptake of essential elements such as Fe, Mg, Ca, and Mo, potentially damaging chloroplast structure in leaves and reducing photosynthetic rates, leading to oxidative damage in plants (Zhang et al., 2010). Therefore, further improvements to the planting substrate are necessary to stabilize and immobilize the excessive Mn content.
3.3.2 Acute toxicity of luminescent bacteria
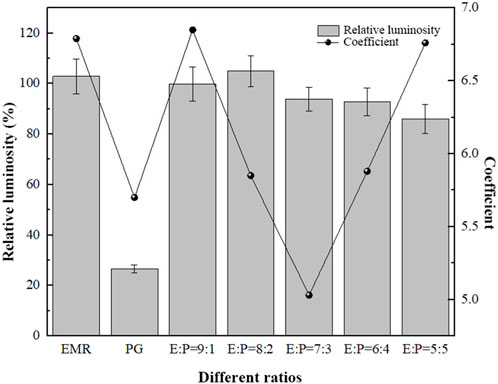
Studies indicate that luminescent bacteria maintain stable luminescence within a pH range of 5.0–9.0, so no further pH adjustment is required for water samples within this range (Wang et al., 2004). In this experiment, pH was left unadjusted, and the leachate from the planting substrate was directly used for toxicity testing. Toxicity levels were classified according to the relative luminescence intensity using the Microtox acute toxicity classification method (Sang, 2004). As shown in Figure 4, the relative luminescence intensity in the EMR-mixed substrate exceeded 100%, indicating a non-toxic level; the high manganese concentration in EMR did not inhibit luminescent bacterial activity, but rather appeared to promote it. Conversely, PG had a significant inhibitory effect on luminescent bacteria, exhibiting high toxicity. As PG concentration increased, the toxicity of the sample also increased. When the PG to EMR ratio reached 1:1, the relative luminescence of the bacteria remained above 75%, indicating a low toxicity level. This suggests that the combined PG and EMR planting substrate is classified as non-toxic or minimally toxic.
A filtrate with pH >4 can be toxic to luminescent bacteria, while the pH of the PG filtrate is typically below 3, resulting in strong inhibition of luminescent bacteria. In comparison, when PG was mixed with EMR, the pH of the leachate from the experimental plant substrate stabilized between 5.0 and 9.0, reducing toxicity to the luminescent bacteria. This reduction in toxicity can be attributed, in part, to the buffering effect of EMR on PG’s low pH. Additionally, certain nutrients in the mixture may have antagonistic effects on toxic substances, further lowering the filtrate’s toxicity (Zhao et al., 2010). Moreover, the plant substrate, rich in nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and other nutrients, may stimulate bacterial activity and enhance luminescence under low-toxicity conditions, which can ultimately support plant growth.
3.4 Effect of amendments on the leaching toxicity of the planting substrate
The results of the leaching toxicity test indicated that the PG-EMR composite planting substrate contains elevated levels of certain heavy metals, particularly Mn. To stabilize and immobilize the excess heavy metals within the substrate, 2.5% straw biochar and 2.5% diatomaceous earth were added as amendments. Comparison of Tables 6, 7 shows that, except for an increase in Cu content, the concentrations of other metals decreased in the amended substrate, suggesting that the addition of amendments effectively immobilizes heavy metals in the substrate. Specifically, Mn concentration was reduced to only 79.86% of its original level, demonstrating effective stabilization.Furthermore, the heavy metal content in the amended planting substrate meets the limits set by the Soil Environmental Quality Agricultural Land Soil Pollution Risk Control Standard (Trial) (GB15618-2018). Overall, the amendments significantly improved the substrate quality, making it suitable for use as a planting substrate.
3.5 Germination rate and germination potential of the planting substrate at different ratios
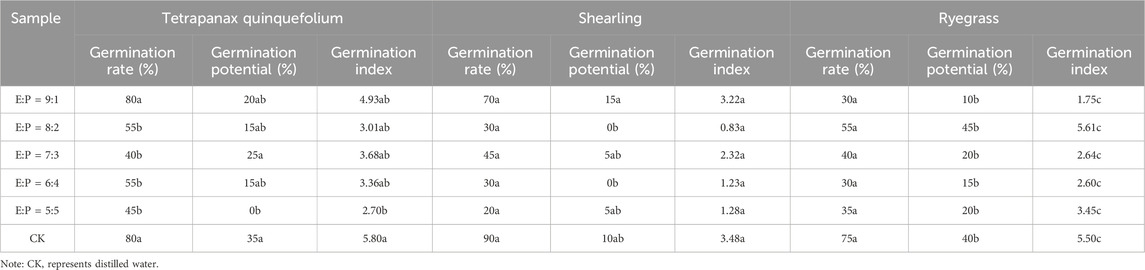
In the germination rate and germination potential tests for substrates with various ratios, clover, Bermuda grass, and alfalfa were excluded due to a 7-day germination rate of zero, with some alfalfa seeds showing signs of decay. As shown in Table 8, the germination rates of perennial ryegrass, ryegrass, and bentgrass decrease with increasing PG content, indicating a clear inhibitory effect on seed germination. The G91 planting substrate exhibited relatively high germination rates and germination potential, suggesting that it may be suitable for further planting experiments.
3.6 Testing the vegetative performance of ecological concrete
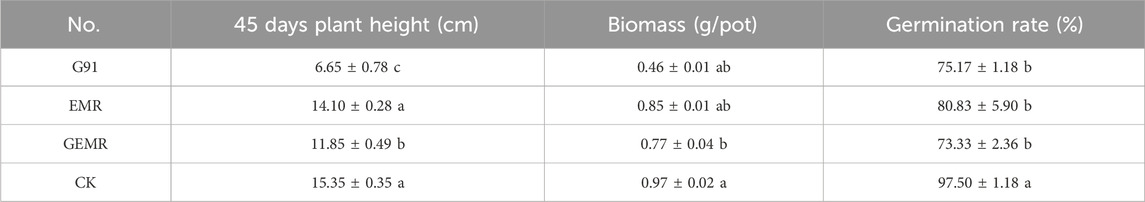
As shown in Table 9, plants grown in the CK group with organic nutrient soil as the substrate performed well, exhibiting the highest germination rate, plant height, and biomass after 45 days. EMR significantly inhibited germination rate and plant height, with notable differences in germination rate and biomass compared to the CK group. The amendment-treated groups, GEMR and G91, did not show significant improvement and adversely affected plant growth, although the germination rate of G91 increased slightly compared to the substrate without amendments. This is primarily because Ca(OH)₂ in the ecological concrete effectively inhibited heavy metals in EMR during early plant growth, maintaining growth within acceptable limits. Furthermore, it was observed that an excess of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in biochar significantly inhibited seed germination and seedling growth (Li et al., 2015). In the later stages of the experiment, all plant groups except the control exhibited signs of drying and wilting, likely due to nutrient depletion in the substrate, ongoing carbonation of the concrete, and a gradual decrease in alkalinity. Additionally, heavy metals in the substrate may have been absorbed by the plants, accumulating to a toxic level and resulting in plant toxicity.
4 Conclusion
(1) In this study, ecological concrete specimens were prepared using a composite binder of PG and EMR as the adhesive and ordinary clay ceramsite as the aggregate. With a rubber-bone ratio of 1.485, the 14-day compressive strength reached 3.49 MPa, the permeability coefficient was 1.37, and the total porosity was 24.5%, meeting the requirements for vegetative concrete. The high content of available phosphorus, alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen, and available potassium in PG and EMR can satisfy the nutrient needs of vegetative concrete, making it possible to create a nutrient-rich planting substrate.
(2) Adding a mixed amendment of biochar and diatomaceous earth effectively stabilized heavy metals within the substrate, demonstrating a strong immobilization effect. After amendment, the manganese concentration in the leachate from the planting substrate decreased by 79.86%, indicating a successful stabilization outcome.
(3) The germination rate tests for the planting substrate indicated that bentgrass, perennial ryegrass, and Kentucky bluegrass adapted well, while alfalfa, clover, and Beruda grass showed poor adaptability, with no germination observed within 7 days.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
RL: Conceptualization, Writing–original draft. CL: Investigation, Writing–review and editing, Methodology. JD: Project administration, Writing–review and editing. CW: Methodology, Writing–review and editing. YY: Formal Analysis, Visualization, Writing–review and editing. XZ: Software, Validation, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
Authors RL, CL, JD, CW, and YY were employed by China Overseas Construction Limited.
The remaining author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Araujo, A., Viana, P., and Peres, A. (2004). Reagents in iron ores flotation. Miner. Eng. 18 (2), 219–224. doi:10.1016/j.mineng.2004.08.023
Cao, B. D. (2018). Study on the influence factors of strength of phosphogypsum-based composite cementitious materia. New Build. Mater. 45 (03), 23–26. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1001-702X.2018.03.007
Chen, Y. F. (2021). Low alkalinity porous ecological permeable concrete based on solid waste and its preparation method. Sichuan Cem. (10), 7–8. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1001-702X.2018.03.007
Cui, R. Z., Bai, H. D., Gao, Y. F., and Xue, X. F. (2022). Current situation of comprehensive utilization of phosphogypsum and its development trend of 14th Five-Year Plan. Inorg. Chem. Ind. 54 (04), 1–4. doi:10.19964/j.issn.1006-4990.2022-0086
Du, M., Wang, J., Dong, F., Wang, Z., Yang, F., Tan, H., et al. (2022). The study on the effect of flotation purification on the performance of α-hemihydrate gypsum prepared from phosphogypsum. Sci. Rep. 12 (1), 95. doi:10.1038/s41598-021-04122-w
Fu, F., Qiao, H. X., Feng, Q., Li, Y. Q., and Xue, C. Z. (2023). Review of new methods for resource utilisation of electrolytic manganese residue and its application in building materials. Constr. Build. Mater., 401.
Garg, M. S. a. M. (1995). Activation of gypsum anhydrite-slag mixtures. Cem. Concr. Researc 25, 332–338. doi:10.1016/0008-8846(95)00018-6
Hameed, M. O., Usman, F., Hayder, G., and Al-Ani, Y. (2023). Investigation of mechanical and thermal performance of nanoclay modified concrete for energy efficiency. Ann. de Chimie - Sci. des Matériaux 47 (4), 225–235. doi:10.18280/acsm.470405
Hu, Y. Y., Hu, C. M., Xie, L., Guo, Q. W., Wang, X., Zhang, T. P., et al. (2006). Effect of void status in eco-concrete for planting on plant G rowth. J. South China Univ. Technol. Sci. Ed. (12), 5–9. doi:10.3321/j.issn:1000-565X.2006.12.002
Huang, D., Zong, S. R., Ma, H., Wan, B. L., Nian, Z. W., Li, D. G., et al. (2023). Research and application progress of resource utilization technology of phosphogypsum. Eco-industry Sci. and Phosphorus Fluor. Eng. 38 (05), 17–22. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1007-6220.2023.05.006
Huang, X. Q., Zhao, X. R., Tang, C. L., Du, Y. J., and Chen, B. Y. (2016). Properties and leaching characteristics of cemented phosphate tailings backfill with phosphogypsum-based cementation material. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 10 (10), 5957–5963. doi:10.12030/j.cjee.201601080
Huang, Y., Qian, J., Kang, X., Yu, J., Fan, Y., Dang, Y., et al. (2019). Belite-calcium sulfoaluminate cement prepared with phosphogypsum: influence of P2O5 and F on the clinker formation and cement performances. Constr. Build. Mater. 203, 432–442. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.01.112
Ismaeel, M. A., Usman, F., Hayder, G., and Al-Ani, Y. (2023). Analysis of mechanical and environmental effects of utilizing waste glass for the creation of sustainable ultra-high performance concrete. Ann. de Chimie - Sci. des Matériaux 47 (2), 111–123. doi:10.18280/acsm.470208
Jassam, A. Z., Usman, F., Hayder, G., and Al-Ani, Y. (2023). Investigating the mechanical and thermal properties of concrete with recycled nanoplastics for enhanced sustainability. Ann. de Chimie - Sci. des Matériaux 47 (5), 341–350. doi:10.18280/acsm.470508
Jin, Y. T., Yang, D., Wu, Y. H., Zhou, F., Yu, J. X., Chi, R., et al. (2024). Preparation of biofertilizer with phosphogypsum and straw: microbial community changes and plant growth effects. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 31, 17511–17523.
Junakova, N., and Junak, J. (2017). Sustainable use of reservoir sediment through partial application in building material. Sustainability 9 (5), 852. doi:10.3390/su9050852
Li, B. X., Li, L. C., Ma, Y., and Zhou, M. K. (2002). Modification of phosphogypsum using circulating fluidized bed fly ash and carbide slag for use as cement retarder. Construc. Building. Materi. (10), 11–13.
Li, Y., Shen, F., Guo, H., Wang, Z., Yang, G., Wang, L., et al. (2015). Phytotoxicity assessment on corn stover biochar, derived from fast pyrolysis, based on seed germination, early growth, and potential plant cell damage. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 22 (12), 9534–9543. doi:10.1007/s11356-015-4115-5
Liang, H.-H., and Li, J.-L. (2015). The influence of hydration and swelling properties of gypsum on the preparation of lightweight brick using water supply reservoir sediment. Constr. Build. Mater. 94, 691–700. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2015.07.111
Liang, L. M. (2010). Preparation, porous structure and Camouflage performance of porousecological conerete. Nanjing, China: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics.
Liu, S., Wu, F. H., Qu, G. F., Zhao, C. Y., Chen, B. J., Yang, Y. Y., et al. (2022). Migration and transformation of heavy metals in phosphogypsum stor-age process and their ecological effect. Asian J. Ecotoxicol. 17 (04), 302–314. doi:10.7524/AJE.1673-5897.20210803002
Liu, X. L., Zhang, B. X., Wang, G. J., Miao, L. L., and Wu, J. J. (2018). Research progress of root exudates for Efficient Dissociation of insoluble phosphorus. Heilongjiang Agric. Sci. (12), 157–160. doi:10.11942/j.issn1002-2767.2018.12.0157
Lou, Y., Liu, F., Ren, J., and Zhu, J. (2020). Effects of rooting media amendments on seed germination and seedling growth of four bioenergy grass species grown on electrolytic manganese residue. Acta Prataculturae Sin. 29 (11), 118–128. doi:10.11686/cyxb2020005
Lu, X. C., Han, X. Z., and Zou, W. X. (2013). Advance in the efficient utilization of soil phosphorus by crops. Soils Crops 2 (04), 164–172. doi:10.11689/j.issn.2095-2961.2013.04.004
Ma, M. (2002). Development and application of new bioassay methods in aquatic ecotoxicology. Beijing, China: Graduate school of the chinese academy of sciences Ecological Environment Research Center.
M S, D., Andrzej, B., Arkadiusz, G., Raczko, J., Mordak, K., Grądziel, I., et al. (2020). Phosphogypsum and clay mineral/phosphogypsum ceramic composites as useful adsorbents for uranium uptake. Appl. Geochem. 123 (prepublish), 104793. doi:10.1016/j.apgeochem.2020.104793
Mun, K., Hyoung, W., Lee, C., So, S., and Soh, Y. (2005). Basic properties of non-sintering cement using phosphogypsum and waste lime as activator. Constr. Build. Mater. 21 (6), 1342–1350. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2005.12.022
Peng, B., Jiang, C. b., and Xiang, T. S. (2013). Experimental study on porosity of vegetation type porous concrete. China Water Transp. 13 (05), 281–282.
Potgieter, J., Potgieter, S., McCrindle, R., and Strydom, C. (2003). An investigation into the effect of various chemical and physical treatments of a South African phosphogypsum to render it suitable as a set retarder for cement. Cem. Concr. Res. 33 (8), 1223–1227. doi:10.1016/s0008-8846(03)00036-x
Rabatho, J., Tongamp, W., Kato, J., Haga, K., Takasaki, Y., and Shibayama, A. (2011). Effect of flotation reagents for upgrading and recovery of Cu and Mo from mine tailing by flotation. Resour. Process. 58 (1), 14–21. doi:10.4144/rpsj.58.14
Sang, L. Y. (2004). Law of silica powder influence on cement stone strength development. Drill. Fluid and Complet. Fluid 21, 41–43.
Said, A., Mohamad, E., Aicha, B., Kamar, M., and Midani, M. (2024b). Properties, purification, and applications of phosphogypsum: a comprehensive review towards circular economy. Mater. Circ. Econ. 6 (1), 9. doi:10.1007/s42824-024-00100-5
Said, A., Mohamad, E., Aicha, B., Mohamed, K., and Midani, M. (2024a). Properties, purification, and applications of phosphogypsum: a comprehensive review towards circular economy. Mater. Circ. Econ. 6 (1), 9. doi:10.1007/s42824-024-00100-5
Shichao, C., Fang, W., Lihua, M., and Che, J. (2023). Study on physical properties of desulfurized electrolytic manganese residue cement and properties of mortar. Mater. Basel, Switz. 16 (11), 4035. doi:10.3390/ma16114035
Song, F. L. (2009). Studies on the Technology of ecological slope protection based on the material-vegetation system[D]. Anhui, China: Anhui Agricultural University.
Wang, J., Peng, B., Chai, L., Zhang, Q., and Liu, Q. (2013). Preparation of electrolytic manganese residue–ground granulated blastfurnace slag cement. Powder Technol. 241, 24112–24118. doi:10.1016/j.powtec.2013.03.003
Wang, L. S., Wei, D. B., and Hu, H. Y. (2004). Optimization of luminescent bacteria toxicity test and application of toxicity reference substance. Res. Environ. Sci. 04, 61–62. doi:10.13198/j.res.2004.04.63.wanglsh.016
Yang, M., and Qian, J. (2011). Activation of anhydrate phosphogypsum by K2SO4 and hemihydrate gypsum. J. Wuhan Univ. Technology-Mater. Sci. Ed. 26 (6), 1103–1107. doi:10.1007/s11595-011-0371-5
Yang, S. Z., Song, H. T., Yang, X. Y., and Zhu, Y. Q. (2003). Modification of phosphogypsum and its application for cement retarder. Wuhan, China: Journal of Wuhan University of Technology, 23–25. doi:10.3321/j.issn:1671-4431.2003.01.007
Yatesh, T., Akanksha, T., and Sudipta, S. (2023). Utilization of industrial waste phosphogypsum as geomaterial: a review. J. Hazard. Toxic, Radioact. Waste 27 (2). doi:10.1061/jhtrbp.hzeng-1181
Yu, Y. Y. (2016). Study on the composite cementitions material based on gypsu[D]. Xi'an, China: Chang’an University.
Zhang, X. (2022). Study on the preparation and Planting performance of Eco-concrete based on electrolytic manganese slag[D]. Guiyang, China: Guizhou University.
Zhang, Y., Wang, X. P., and Li, D. X. (2011). Performance research on the gypsum based cementing material incorporating with large dosage of waste gypsum. Bull. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 32 (02). doi:10.16552/j.cnki.issn1001-1625.2011.02.029
Zhang, Y. X., Li, L. F., Chai, T. Y., Lin, D., and Zhang, H. M. (2010). Mechanisms of manganese toxicity and manganese tolerance in plants. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 45 (04), 506–520. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-3466.2010.04.014
Zhao, Y. Y., Hu, J. L., and Shao, L. J. (2010). Study on the influencing factors of luminescent bacteria toxicity testing. Mod. Sci. Instrum. No.131 (03), 75–78.
Keywords: ecological concrete, electrolytic manganese slag, phytogenic performance, phosphogypsum, planting substrate
Citation: Liu R, Liu C, Du J, Wang C, Yuan Y and Zhang X (2025) Preparation of phosphogypsum ecological concrete and study on its phytogenic properties. Front. Environ. Sci. 12:1539964. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2024.1539964
Received: 05 December 2024; Accepted: 23 December 2024;
Published: 09 January 2025.
Edited by:
Yaoguang Guo, Shanghai Polytechnic University, ChinaReviewed by:
Chunqiao Xiao, Wuhan Institute of Technology, ChinaPeng Zhang, China University of Geosciences Wuhan, China
Yasir Al-Ani, University of Anbar, Iraq
Copyright © 2025 Liu, Liu, Du, Wang, Yuan and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Rongxin Liu, MTM1OTUzNjMwNjdAMTYzLmNvbQ==
 Rongxin Liu
Rongxin Liu Chunduo Liu1
Chunduo Liu1