- Shanghai Collaborative Innovation Centre for WEEE Recycling, School of Resources and Environmental Engineering, Shanghai Polytechnic University, Shanghai, China
The treatment or resource utilization of high-salinity wastewater from printing and dyeing has received great attention in recent decades due to their negative impacts on the surrounding environment. To improve the direction of research, we analyzed the published papers in the online version of the Science Citation Index Expanded database for 1991–2022—a total of 1090 articles or reviews—using VOSviewer, Python, origin 2023, and the statistical software R. The results showed that the published papers in this field have increased exponentially in the past 17 years. The Journal of Membrane Science, Desalination, the Chemical Engineering Journal, and the Journal of Hazardous Materials are the most important for publishing relevant research. Van Der Bruggen B was the most productive author. Katholieke University Leuven and Donghua University were the main research institutions. There were additional needs to enhance collaboration relationships between different authors, institutions, and countries. At present, research focused on methods that are closer to “real” field or ground conditions, “photocatalysis,” “loose nanofiltration membranes”, and “dye/salt separation” are the research frontier. The present study determines the trends of this field of research by visualizing the current landscape to facilitate future collaborative research.
1 Introduction
Dyeing is the process of adding chemicals such as metals, salts, surfactants, and sulfide to improve the adsorption of dye into the fibers. In the dyeing process, large volumes of water are normally required for the dye bath and rinsing (Song et al., 2023). Whether or not these dyes are degradable, the highly colored effluents are highly objectionable. Suspended solids, urea, solvents, and metals liberated by printing are also of concern (Ewuzie et al., 2022). Consequently, the wastewater from high salinity printing and dyeing has received great attention in the recent decades in the treatment of salt/dyes and in achieving resource utilization, as well as to minimize negative impacts on the surrounding environment (Fadzli et al., 2022). Despite the large number of articles and reviews on the progress of treatment or resource utilization for high salinity printing and dyeing wastewater, no bibliometric analysis of this topic has been published to our knowledge.
Researchers can benefit from bibliometrics to analyze the evolution and dynamics of scientific information and the characteristics of the existing literature in high salinity printing and dyeing wastewater research. Such analysis can help them identify cost-effective processes, future research priorities, and initiate new research (Usman and Ho, 2020).
The present study consists of a bibliometric study of 1,090 publications related to the progress of treatment or resource utilization for high salinity printing and dyeing wastewater from the online version of the Science Citation Index Expanded (SCIE), which is the most efficient database, thus ensuring selected papers with high quality and representativeness. The results were evaluated according to the most prominent authors on this topic, and the countries, institutions, and scientific journals that have made the greatest contribution to this theme. The Reference Publication Year Spectroscopy is of great significance in determining the origin and intellectual roots of this field of research. Keyword co-occurrence analysis and research frontier identification would allow the identification of the potential research hotspots and latest trends in this field. The present study is significant for providing new insights into further research on the treatment or resource utilization for high salinity printing and dyeing wastewater.
2 Methods
Data used in the present study were retrieved on 10 January 2023 from the Clarivate Analytics Web of Science Core Collation, the online version of SCIE. The search strategy for the data was set as: TS = (high sal* OR excess salt) AND TS = (dye* OR textile OR dying) AND TS = (wastewater OR waste water OR effluent) AND TS = (resource* OR *utilization OR treat* OR process* OR handling). The search was limited to 1991–2022 and the language to English. The study was restricted to articles and reviews; conference proceedings and papers published online were thus excluded. To improve the validity of bibliometrics, documents irrelevant to the theme were removed after manual screening. These data were downloaded and exported in text-based format, including full records and cited references. Finally, 1090 valid documents were obtained. The bibliometric analysis was performed and visualized using VOS viewer, Python, origin 2023, and the statistical software R.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Descriptive statistical analysis
The distribution of publications over the year can be used to evaluate the current research status of a field and further predict development trends. Figure 1 shows that the earliest document date of the treatment or resource utilization of high salinity printing and dyeing wastewater was 1991. The annual number of publications in the field increased slowly from 1991 to 2004. Thereafter, the annual number of publications stabilized at more than double digits each year. There has been a notable increase in the past 4 years, with articles published accounting for more than half the total number. The cumulative number of publications of this field can be roughly divided into two periods through a logic curve model. Period Ⅰ (1991–2004) shows the beginning of the scientific production of this field, with new theories and methods being established, so it was a time when the numbers of scientific publications lacked regularity. Additionally, there was no notable growth in scientific production, with a total of 57 documents that accounted for 5.23% of the total. Period Ⅱ (2005–2022) has shown an exponentially upward trend (R2 = 0.9982) over the past 17 years, signifying that the field is in a state of rapid development (Wang D. M. et al., 2022). Therefore, systematic and comprehensive analyses of the progress of a scientific research field are necessary. All in all, researchers the world over have devoted a great number of resources to high salinity printing and dyeing wastewater research due to the severity of the situation of high salinity printing and dyeing wastewater.
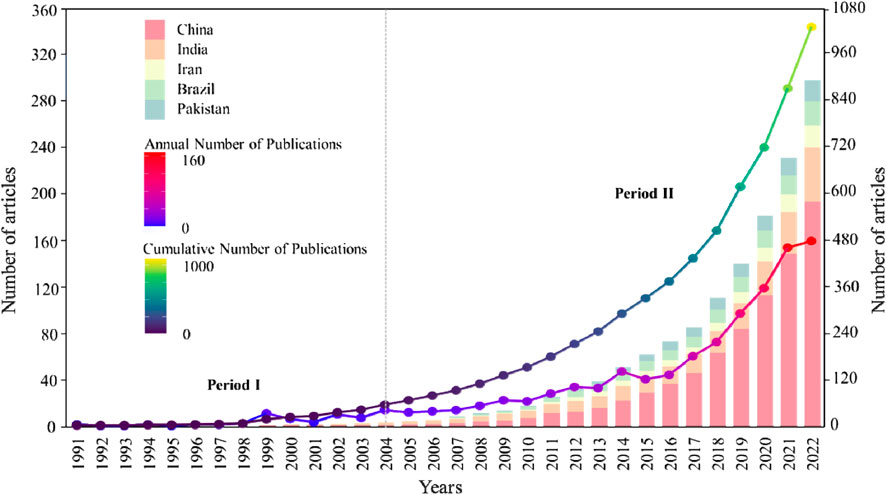
Figure 1. Temporal development of publications about high salinity printing and dyeing wastewater, 1991–2022.
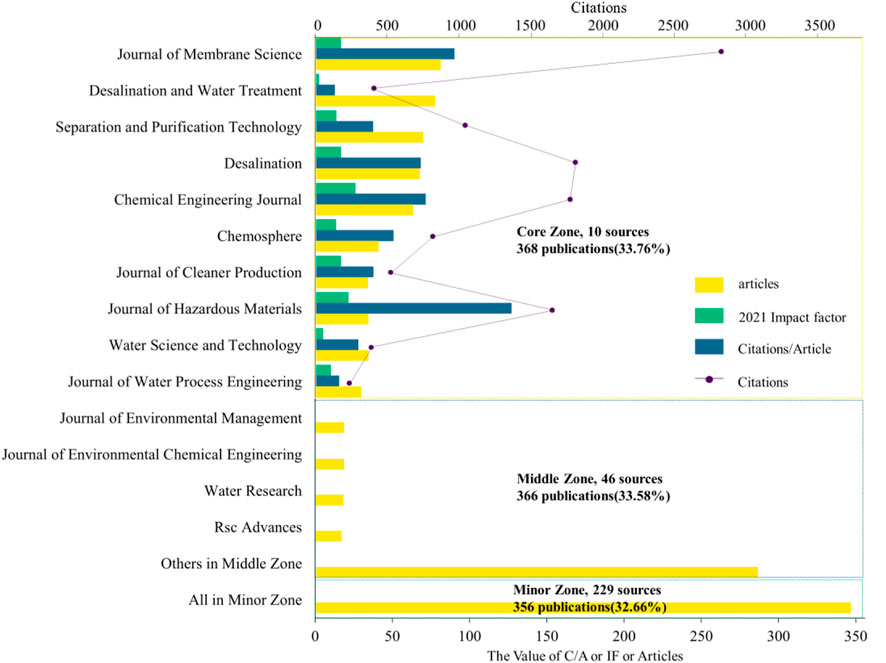
3.2 Most relevant sources
Most relevant sources can help identify the influence and preferences of core journals and then further guide follow-up research. According to Bradford’s law that most professional papers are concentrated in a few professional journals, we used the statistical software R and the bibliometrix codes to conduct the core area journal analysis. As is shown in Figure 2, the articles were published in 285 different journals, revealing that the distribution of journals in this field is relatively scattered, with a large proportion publishing 17 or more papers, accounting for 40.37% of the total sources. The core area journals with more than 40 published articles were the Journal of Membrane Science (n = 56), Desalination and Water Treatment (n = 54), Separation and Purification Technology (n = 49), Desalination (n = 47), and the Chemical Engineering Journal (n = 44). In relation to the most local cited sources, the journal ranking first is the Journal of Membrane Science (n = 3,532), followed by Desalination (n = 2,235), the Chemical Engineering Journal (n = 2,185), and the Journal of Hazardous Materials (n = 2037). Notably, the ratio of citations per article is highest in the Journal of Hazardous Materials (C/A = 88.57), followed by the Journal of Membrane Science (C/A = 63.07), the Chemical Engineering Journal (C/A = 49.66), and Desalination (C/A = 47.55). The Chemical Engineering Journal has the highest impact factor (IF = 16.744), followed by the Journal of Hazardous Materials (IF = 14.224), Desalination (IF = 14.224), and the Journal of Cleaner Production (IF = 11.072). The 102 journals mentioned can provide a better understanding of the importance and scientific depth of the field under investigation (Wang D. M. et al., 2022).
3.3 Contribution and collaboration
3.3.1 Authors
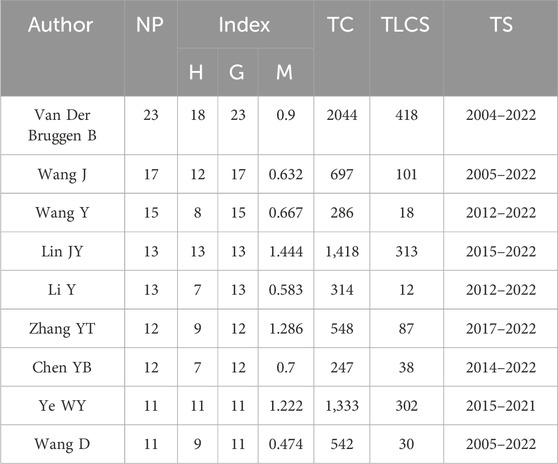
Author productivity was analyzed based on Lotka’s law and several measurements, including the number of publications, H-, G-, and M-indexes, total citations, total local citation score, and the time span. The H-index, which is based on the number of the publications and total citations written by a particular researcher, is a widely accepted measure of scientific performance (Hirsch, 2005). As an improvement of the H-index, the G-index applies a higher weight to find the author with high citations in only a single publication (Egghe, 2006). Unlike the H-index, the M-index considers the time span of an author’s research (Hirsch, 2005). Table 1 compares the number of publications of the top nine authors with some measurements. The premier author is Van Der Bruggen B, who records high progress with 23 articles and holds the highest bibliometric measurements (H-index = 18, G-index = 23, total citations = 2044, total local citation score = 418). Lin JY, Wang J, and Ye WY are the other authors who performed better in the field with a high H-index. The G-index of Wang Y, Li Y, and Chen YB is approximately twice that of the H-index, indicating that only few of their publications with high citations need to be focused on. The research of Lin JY, Zhang YT, and Ye WY began late but score a high citation of publications with a relatively higher M-index. The publications of Van Der Bruggen B, Lin JY, and Ye WY in the field have attracted 2044, 1418, and 1333 total citations, respectively. The total citations of the other authors are less than 700 in this field. The local citations score presented in Table 1 is substantially lower than the total citations of the corresponding papers. The main reason for this discrepancy is that a large proportion of the references are cited by papers outside high salinity printing and dyeing wastewater research (Marx et al., 2017).
These 1090 documents involve 4148 authors. A total of 19 independent authors published 21 scientific studies. The documents have 5.13 co-authors per document on average and 25.05% international co-authorships, indicating that the treatment or resource utilization of high salinity printing and dyeing wastewater is typically a multi-author cooperative field. Figure 3 displays the collaboration network of authors in the treatment or resource utilization of high salinity printing and dyeing wastewater. These results reveal that frequent author cooperation occurs in the field and that many authors tend to have a stable cooperative relationship with others. We found that the top nine authors in Table 1, except for Chen YB, have a direct or indirect cooperative relationship. As for the total link strength, the author ranking first is Van Der Bruggen B (n = 57), followed by Lin JY (n = 45) and Ye WY (n = 38), who provide highly individualized scientific references to other relevant researchers in the field (Ouyang et al., 2018). According to the analysis of the corresponding collaboration time through VOS viewer, we found that most author collaborations occurred after 2017. Figure 3 also reveals a lack of collaboration between many authors. Thus, there is a need to enhance the collaboration relationships between authors.
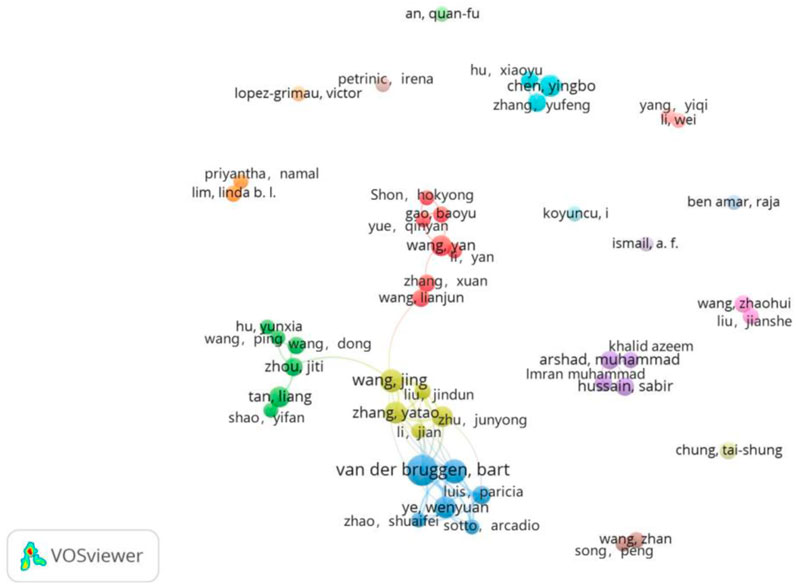
Figure 3. Collaboration network of the authors. Nodes represent authors. Node size represents the number of authors cooperating. Distance between nodes represents the association strength of authors. The straight line represents the collaboration between authors. Colors correspond to different author cooperation clusters.
3.3.2 Affiliations
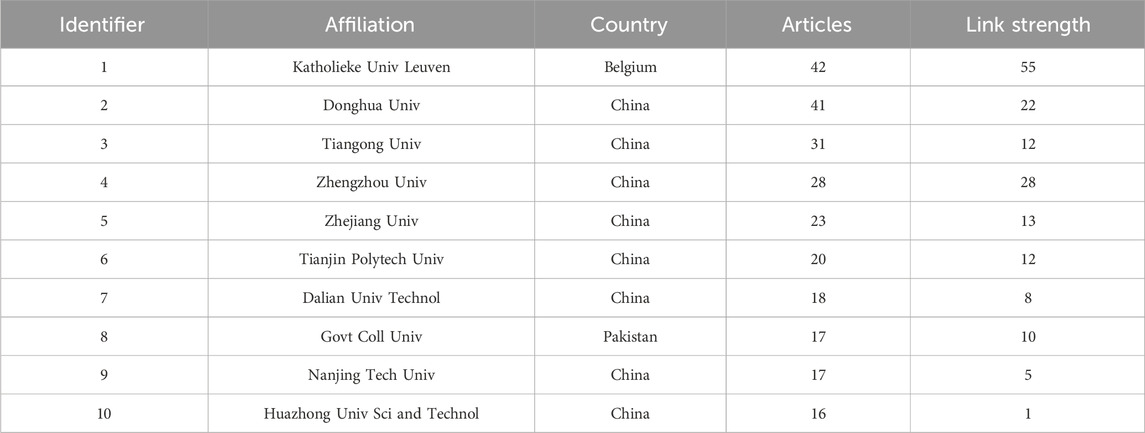
The analysis of collaborative affiliations can help identify the research capacity and potential of institutions globally and track the leading institutions in the treatment or resource utilization in high salinity printing and dyeing wastewater research (Liu et al., 2019). The results show 1161 institutions globally have engaged in the field. As shown in Table 2, the most productive institution was Katholieke University Leuven (n = 42) and Donghua University (n = 41). Occupying second position is Tiangong University, followed by Zhengzhou University, Zhejiang University, Tianjin Polytech University, Dalian University of Technology, Govt College University, Nanjing Tech University, and Huazhong University of Science and Technology. China was the most productive country in the field, but the publications were not centralized in any one institution, suggesting that many research groups in different organizations are concerned with the high salinity printing and dyeing wastewater problem. There exists direct or indirect collaboration among the affiliations mentioned above; their collaboration relationships are presented in Figure 4. In addition, in terms of the total link strength, Katholieke University Leuven is significantly higher than for other institutions. Thus, although China ranks first globally in the number of publications in this field, Belgium was certainly a dominant pioneer on research into high salinity printing and dyeing wastewater.
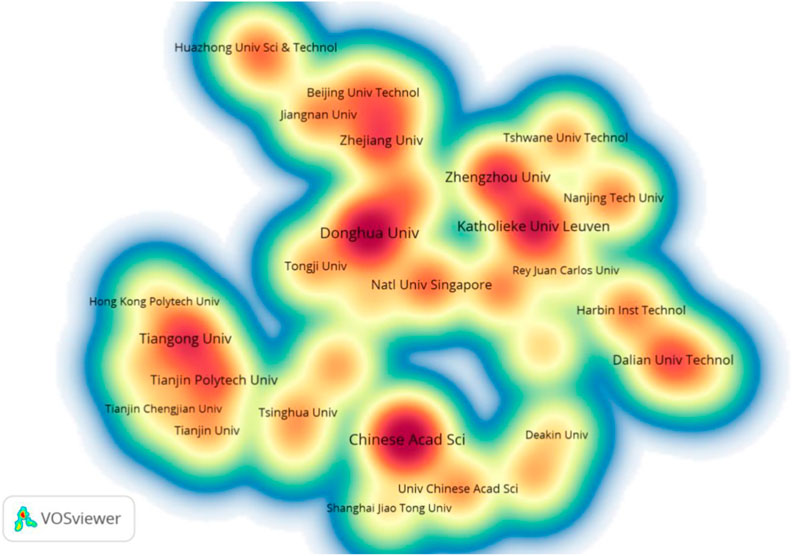
Figure 4. Density visualization of collaboration between institutions. The closer the color is to red, the more the co-authored papers.
3.3.3 Countries
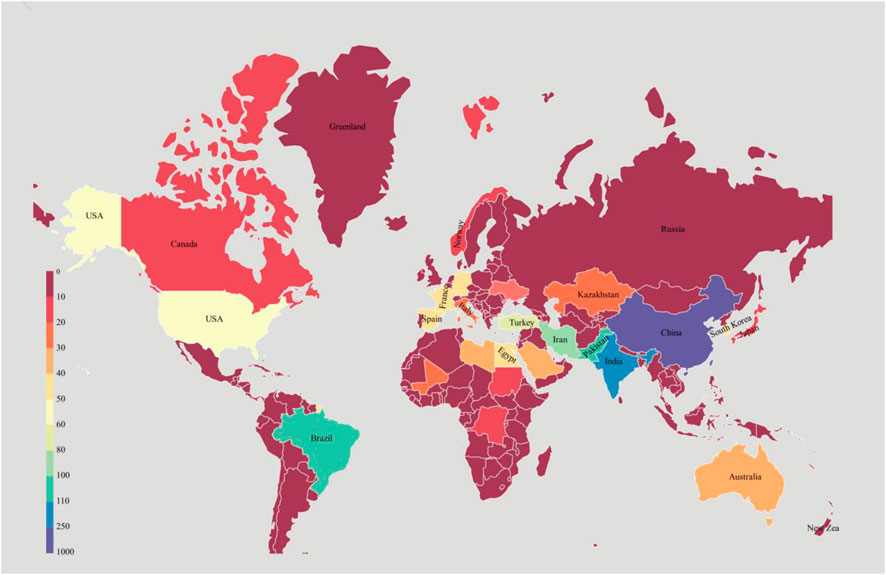
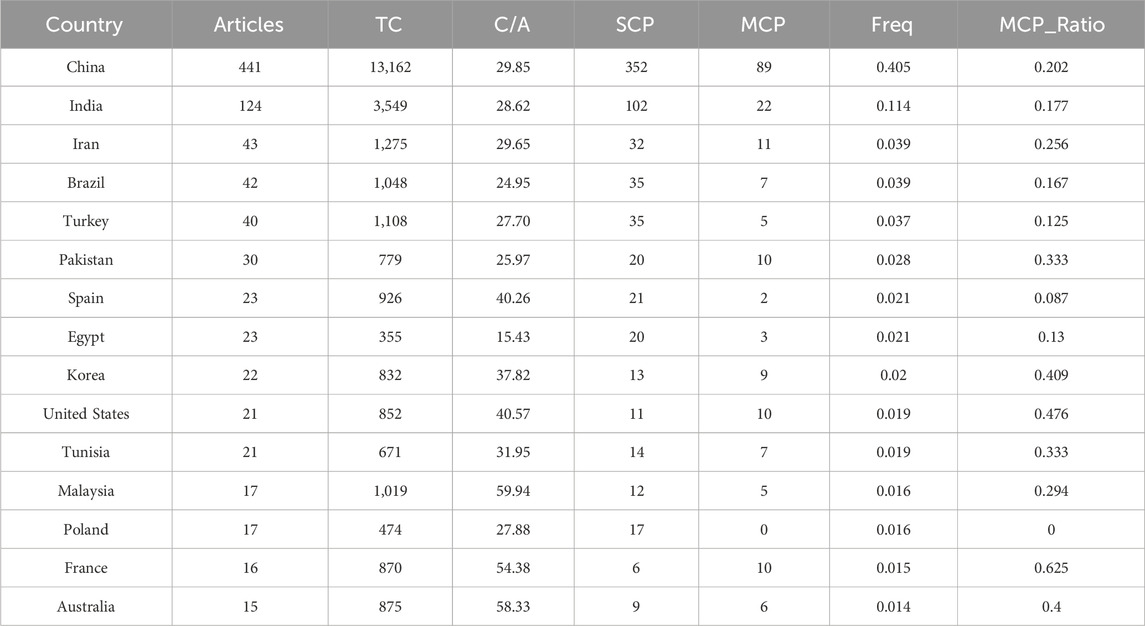
A total of 72 countries have contributed to research into the treatment or resource utilization of high salinity printing and dyeing wastewater. The contribution of countries is visualized through a world map. Figure 5 shows that the geographical distribution of scientific production in this research area is very uneven, being centralized in several dominant countries—China is far ahead with 981 records, followed by India (234 publications), Brazil (104), Pakistan (102), and Iran (98), whereas other countries made only limited contributions. In addition, the results of the top five countries’ dynamic analysis (Figure 1) show that China has had a rapid growth rate and contributes much to this field. Thus, China may become one of the most powerful drivers in high salinity printing and dyeing wastewater research in the future.
Table 3 shows the cooperation achievements of the 15 leading countries in this study area. For citations, China is far ahead with 13,162, and India is second with 3,549 citations, followed by three countries with approximately 1,000 citations—Iran, Brazil, and Turkey. However, in terms of the ratio of citations per article, these countries above are significantly lower than Iraq (C/A = 150, A = 1), Czech Republic (C/A = 125 A = 4), Denmark (C/A = 120, A = 1), and Belgium (C/A = 102.14, A = 14). According to the SCP and MCP values, which indicate the number of publications co-authored with researchers of the same and different nationality, respectively, it is apparent that all countries in Table 3 except France have a closer cooperation relationship with domestic researchers. France with a higher MCP ratio, indicating closer foreign cooperation, while the number of publications revealed the weaker focus in France. China has actively participated in domestic cooperation, but foreign cooperation for China is relatively lower. China has established certain cooperative relationships with many countries in recent years, especially the United States, Belgium, and Australia. Moreover, Figure 6 reveals that China played a significant and core role in the cooperation network, so it will enhance its international academic influence with more publications in the near future.
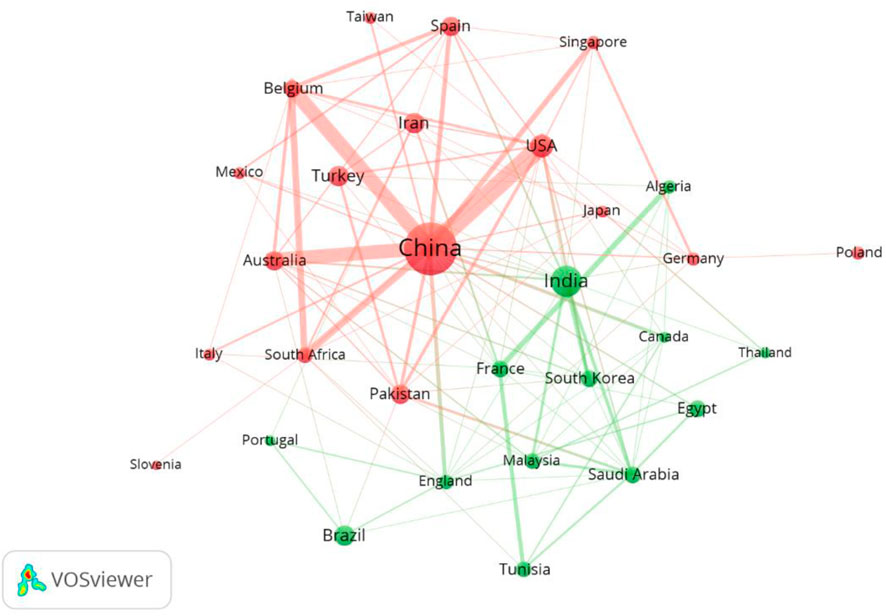
Figure 6. Mapping knowledge domains of co-authoring countries/regions. Inter-country cooperation networks are classified into two categories, represented by red and green. Items within each cluster are assigned the same or similar color, typically automatically determined based on similarity algorithms.
3.4 Co-citation analysis of documents
The Reference Publication Year Spectroscopy (RPYS) indicates the single early publications which were most frequently cited. These frequently cited papers are of great significant for us in finding the origin and intellectual roots of the treatment or resource utilization of high salinity printing and dyeing wastewater (Ballandonne and Cersosimo, 2021). The red line in Figure 7 shows the results from the RPYS based on the field for the period 1958–2022, between which there are no references with reference counts above the minimum of ten citations in total. The blue line in Figure 7 makes the distinct peaks more clearly visible. According to Figure 7, there are pronounced peaks in the following five reference publication years: 2001, 2007, 2009, 2012, and 2015. It is possible that there are two or more important referenced papers within one and the same peak (e.g., see the two cited references with RPY = 2001 or the four cited references with RPY = 2015 in Table 4). The years 2017, 2018, and 2019 have stable reference publication and occur particularly frequently among all the references, but these years do not appear in the distribution of the reference publication years as pronounced peaks. Therefore, RPYS indicates that the most frequently cited references are from the reference publication years 2001, 2007, 2009, 2012, 2015, 2017, 2018, and 2019. According to Figure 7 and Table 4, it is obvious that RPYS can help determine the majority of important cited references and has a relatively high accuracy.
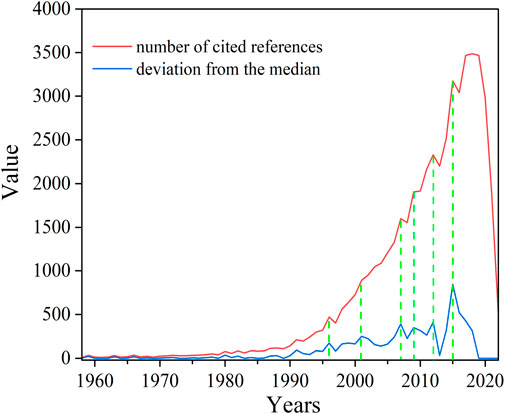
Figure 7. Annual distribution of reference spectroscopy 1958–2022 cited in the treatment or resource utilization of high salinity printing and dyeing wastewater (published 1991–2022).

Table 4. Most frequently cited references from specific reference publication years in Figure 6 cited more than 30 times.
3.5 Keyword co-occurrence analysis
Keywords are highly condensed on the document subjects. Research hotspots and important issues in the field can be investigated based on higher frequency keywords and different clusters (Wang D. M. et al., 2022). Keywords with a frequency of 30 or more occurrences were selected for visual analysis, with a total of 45 keywords meeting the threshold. As shown in Figure 8, it can be seen from the large number of keywords that research on the field is relatively extensive, but the research field’s hotspots are mainly concentrated in the following three ways.
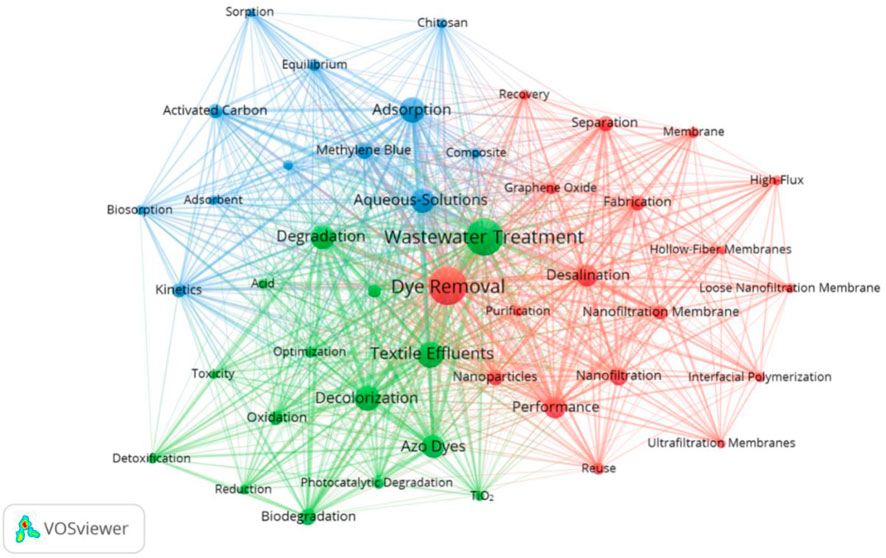
Figure 8. Keyword co-occurrence analysis in the field. The node represents a keyword, node size represents the frequency of the keyword’s occurrence, and the density of the connecting line between the nodes represents the strength of the co-occurrence between the keywords.
Cluster1 (blue color) concentrates on the biodegradation of dye wastewater at the laboratory stage. Textile dyes that can absorb light with wavelengths in the visible region (350–700 nm) create problems for algae and photosynthetic aquatic plants (Sarayu and Sandhya, 2012). Sorption and biosorption are emerging as a potential tool for controlling textile dyes pollution (Nilssonm et al., 2006). A number of microorganisms, especially pure cultures, can decolorize dyes and even completely mineralize many azo dyes under certain environmental conditions, but high salts, high temperature, heavy metals, and pH may potentially cause inhibition on the biosorption and biodegradation processes (Guo et al., 2021; Liu et al., 2017). To address these issues, some research on the biodegradation of textile dyes has focused on applying Laccase to high salinity printing and dyeing wastewater to gain noticeable effects. Laccase has thus been proposed as an industrial enzyme (Ambika et al., 2022; De Paula et al., 2022; Guo, et al., 2021; Si et al., 2021; Yang et al., 2018).
Cluster2 (blue color) concentrates on conventional treatments of decolorization that are closer to “real” field or ground conditions. Adsorption and the advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) using nanomaterials, especially TiO2 particles, have been demonstrated to be efficient techniques for degrading recalcitrant organic contaminants in environmentally friendly ways (Azzaz et al., 2021; Domingues et al., 2019; El-Fawal et al., 2020). Moreover, Liu et al. (2023) have successfully achieved H2 production and simultaneous advanced degradation of various organic pollutants via the MoS2/Fe0/PMS ternary piezo catalytic system. Immobilized TiO2 on inert surfaces, including cotton and activated carbon, reduce costs in the settling times or filtration, as well as obtaining superior adsorption properties and surface HO• (Changotra et al., 2024). Textile wastewater can be used to create clean water, for hydrogen production, and for other resources. Gao et al. (2020) used TiO2/Ag nanofibers (NFs) and strong water absorber chitosan polymer to design a photothermal catalytic (PTC)gel; they obtained approximate hydrogen production of 4,600 μmol m−2 and freshwater production of 5,000 g m−2 under natural sunlight irradiation in 1 day. Peng et al. (2021) utilized a one-way asymmetric nanofluidic photothermal evaporator system to produce electricity and freshwater; it can induce a voltage output of 363 mV and effectively prevent salt accumulation.
Cluster3 (red color) concentrated on dye/salt removal through a nanofiltration (NF) membrane. The textile wastewater with inorganic salts makes it difficult to achieve purification through conventional treatments, such as biodegradation, coagulation, adsorption, and oxidative processes (Irfan et al., 2019; Jasper et al., 2017). Moreover, cost-effective technologies are the preferred focus. NF membranes, whose operational pressure is lower than reverse osmosis (RO) membranes, while rejection of organic molecules are higher than ultrafiltration (UF) membranes, are considered one of the most useful filtration processes to remove dye/salt (Arola et al., 2019; Muntha et al., 2017). The primary focus of current membrane research is to exhibit membranes with good hydrophilicity, antifouling property, and excellent stability by changing the properties and structural characteristics of the membranes. Thus, a number of studies using an interfacial polymerization (IP) technique to prepare loose nanofiltration (LNF) membranes have been reported (Cheng et al., 2022; Zhao et al., 2022). At present, the incorporation of carbon-based nanomaterials, especially graphene oxide (GO), with the hollow fiber structure is attracting much research attention (Bandehali et al., 2020; Bandehali et al., 2021; Jhaveri and Murthy, 2016; Wang C. F. et al., 2022; Zhang et al., 2019). After achieving dye/salt removal from wastewater, we can treat the concentrated saline liquor and dyes as reusable resources for energy saving (Cheng et al., 2022).
3.6 Research frontier identification
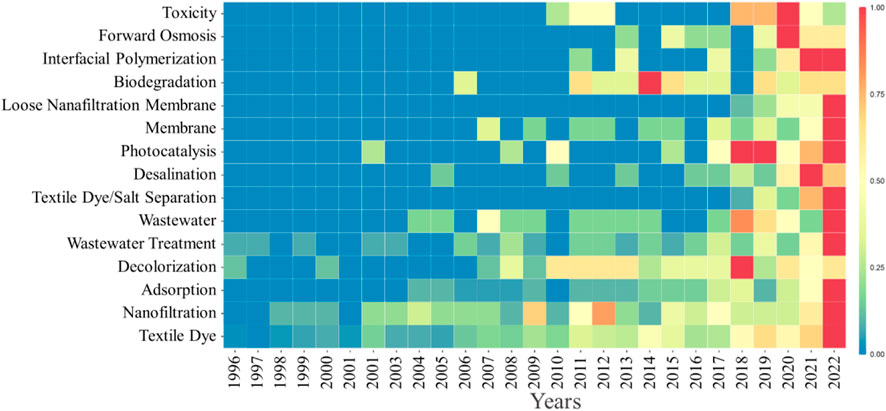
We used of the statistical software R to combine synonyms to avoid statistical errors (Xu et al., 2022). Figure 8 shows the timeline view where the X-axis shows the year and the Y-axis shows the author keywords. Obviously, the number of publications for the keywords “loose nanofiltration membranes” and “dye/salt separation” increased rapidly from 2018 to 2022—a recent hotspot of high salinity printing and dyeing wastewater research. Simple and scalable IP has evolved as a platform technology for loose nanofiltration membranes and other membranes fabrication in the past 2 years. The forward osmosis member can selectively foster desalination and recover organic sources from textile wastewater (Jingxi et al., 2019; Peng et al., 2020; Wu et al., 2020; Zhou et al., 2020). There were thus a number of studies of forward osmosis published from 2013 and a burst in 2020, followed by a burst of the keyword “desalination” in 2021. Conventional treatments, especially biodegradation, focus on the decolorization of high salinity printing and dyeing wastewater but not resource reuse. Thus, the quantity of the keywords “biodegradation,” “decolorization” gradually decrease. The keyword “nanofiltration” can remove dye/salt that can foster the reuse of the concentrated saline liquor, and the dyes will achieve instant development. Photocatalysis is an advanced oxidation process that can harvest efficient H2 from wastewater by coupling piezo catalysis (Liu, et al., 2023). Adsorption is an important way to reduce the processing difficulty of high salinity printing and dyeing wastewater. Therefore, many articles on “photocatalysis” and “adsorption” will be reported in the future.
4 Conclusion
This bibliometric study on the treatment or resource utilization for high salinity printing and dyeing wastewater in the WOS core database was conducted to obtain a knowledge map. This knowledge map is intended to facilitate researchers in analysis of the published literature that could improve the research direction for better scientific contribution. The results show the following characteristics.
(1) Regarding the global research trend of publications per year on the treatment or resource utilization of high salinity printing and dyeing wastewater, the cumulative number of publications has shown an exponential upward trend in the past 17 years to cover a wider range of research in the field. The Journal of Membrane Science, Desalination, the Chemical Engineering Journal, and the Journal of Hazardous Materials were the most influential journals. Van Der Bruggen B was the most productive author. Katholieke University Leuven and Donghua University were the main research institutions. China was far ahead other countries in scientific production and citations. References published in 2001, 2007, 2009, 2012, 2015, 2017, 2018, and 2019 have been the most frequently cited papers. For readers interested in exploring more articles on high-salt wastewater treatment, we recommend focusing on the journals, authors, institutions, and years mentioned above during their search.
(2) The research trends determined in this study indicate that research methods in the field are becoming increasingly diverse. Early processes for high salinity printing and dyeing wastewater were predominantly based on color and dye removal. Photocatalytic processes combined with TiO2 particles were proposed as an environmental-friendly treatment of this wastewater for completing the mineralization of most organics without producing sludge or harmful by-products. Later, as people increasingly focused on resource utilization, AOPs were applied as not only a method to simultaneously degrade various organic pollutants but as a means of H2 production. Dye/salt separation can be realized through thermal concentration technology and membrane concentration, but nanofiltration membrane is of great concern. Therefore, this information can help researchers quickly identify current developments in the hotspot and the most dominant of its various research areas.
4.1 Statement of novelty
An analysis of the current state of the treatment and resource utilization for high salinity printing and dyeing wastewater is essential, and bibliometrics can provide a new approach to identify the evolution of research hotspots and frontiers in this topic.
4.2 Statement of industrial relevance
This work provides the theoretical framework and research methods for this study, and its analysis has important implications for further research.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
QW: formal analysis, software, visualization, writing–original draft. XZ: funding acquisition, methodology, supervision, validation, writing–review and editing.
Funding
The authors declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work is supported by the Science and Technology Development Fund of Pudong New Area (PKJ2022-C10) and the Shanghai Polytechnic University Postgraduate Program Fund.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Ambika, , Kumar, V., Jamwal, A., Kumar, V., and Singh, D. (2022). Green bioprocess for degradation of synthetic dyes mixture using consortium of laccase-producing bacteria from Himalayan niches. J. Environ. Manage 310, 114764. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.114764
Arola, K., Van der Bruggen, B., Manttari, M., and Kallioinen, M. (2019). Treatment options for nanofiltration and reverse osmosis concentrates from municipal wastewater treatment: a review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 49 (22), 2049–2116. doi:10.1080/10643389.2019.1594519
Azzaz, A. A., Jellali, S., Hamed, N. B., El Jery, A., Khezami, L., Assadi, A. A., et al. (2021). Photocatalytic treatment of wastewater containing simultaneous organic and inorganic pollution: competition and operating parameters effects. Catalysts 11 (7), 855. doi:10.3390/catal11070855
Ballandonne, M., and Cersosimo, I. (2021). A note on reference publication year spectroscopy with incomplete information. Scientometrics 126 (6), 4927–4939. doi:10.1007/s11192-021-03976-1
Bandehali, S., Moghadassi, A., Parvizian, F., Zhang, Y. T., Hosseini, S. M., and Shen, J. N. (2020). New mixed matrix PEI nanofiltration membrane decorated by glycidyl-POSS functionalized graphene oxide nanoplates with enhanced separation and antifouling behaviour: heavy metal ions removal. Sep. Purif. 242, 116745. doi:10.1016/j.seppur.2020.116745
Bandehali, S., Parvizian, F., Ruan, H. M., Moghadassi, A., Shen, J. N., Figoli, A., et al. (2021). A planned review on designing of high-performance nanocomposite nanofiltration membranes for pollutants removal from water. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 101, 78–125. doi:10.1016/j.jiec.2021.06.022
Changotra, R., Yang, J., Rajput, H., Hu, Y. L., and He, Q. S. (2024). Mechanism and performance evaluation of spent-coffee grounds-derived nanocomposite materials for highly efficient photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutant. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 133, 428–438. doi:10.1016/j.jiec.2023.12.019
Cheng, J., Li, Z., Bao, X., Zhang, R., Yin, S., Huang, W., et al. (2022). A novel polyester-amide loose composite nanofiltration membrane for effective dye/salt separation: the effect of long molecule on the interfacial polymerization. J. Membr. Sci. 657, 120675. doi:10.1016/j.memsci.2022.120675
De Paula, N. M., da Silva, K., Brugnari, T., Haminiuk, C. W. I., and Maciel, G. M. (2022). Biotechnological potential of fungi from a mangrove ecosystem: enzymes, salt tolerance and decolorization of a real textile effluent. Microbiol. Res. 254, 126899. doi:10.1016/j.micres.2021.126899
Domingues, F. S., Freitas, T., de Almeida, C. A., de Souza, R. P., Ambrosio, E., Palacio, S. M., et al. (2019). Hydrogen peroxide-assisted photocatalytic degradation of textile wastewater using titanium dioxide and zinc oxide. Environ. Technol. 40 (10), 1223–1232. doi:10.1080/09593330.2017.1418913
Egghe, L. (2006). Theory and practise of the g-index. Scientometrics 69 (1), 131–152. doi:10.1007/s11192-006-0144-7
El-Fawal, E. M., Younis, S. A., Moustafa, Y. M., and Serp, P. (2020). Preparation of solar-enhanced AlZnO@carbon nano-substrates for remediation of textile wastewaters. J. Environ. Sci. 92, 52–68. doi:10.1016/j.jes.2020.02.003
Ewuzie, U., Saliu, O. D., Dulta, K., Ogunniyi, S., Bajeh, A. O., Iwuozor, K. O., et al. (2022). A review on treatment technologies for printing and dyeing wastewater (PDW). J. Water. Process. Eng. 50, 103273. doi:10.1016/j.jwpe.2022.103273
Fadzli, J., Hamid, K. H. K., Him, N. R. N., and Puasa, S. W. (2022). A critical review on the treatment of reactive dye wastewater. Desalination. Water. Treat. 257, 185–203. doi:10.5004/dwt.2022.28028
Gao, M. M., Peh, C. K., Zhu, L. L., Yilmaz, G., and Ho, G. W. (2020). Photothermal catalytic gel featuring spectral and thermal management for parallel freshwater and hydrogen production. Adv. Energy. Mater 10 (23). doi:10.1002/aenm.202000925
Guo, G., Liu, C., Hao, J. X., Tian, F., Ding, K. Q., Zhang, C., et al. (2021). Development and characterization of a halo-thermophilic bacterial consortium for decolorization of azo dye. Chemosphere 272, 129916. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.129916
Hirsch, J. E. (2005). An index to quantify an individual's scientific research output. PNAS 102 (46), 16569–16572. doi:10.1073/pnas.0507655102
Irfan, M., Ge, L., Wang, Y. M., Yang, Z. J., and Xu, T. W. (2019). Hydrophobic side chains impart anion exchange membranes with high monovalent-divalent anion selectivity in electrodialysis. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 7 (4), 4429–4442. doi:10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b06426
Jasper, J. T., Yang, Y., and Hoffmann, M. R. (2017). Toxic byproduct formation during electrochemical treatment of latrine wastewater. Environ. Technol. 51 (12), 7111–7119. doi:10.1021/acs.est.7b01002
Jhaveri, J. H., and Murthy, Z. V. P. (2016). A comprehensive review on anti-fouling nanocomposite membranes for pressure driven membrane separation processes. Desalination 379, 137–154. doi:10.1016/j.desal.2015.11.009
Jingxi, E. Z., De Jager, D., Augustine, R., Petrinic, I., Helix-Nielsen, C., and Sheldon, M. S. (2019). Forward osmosis: dyeing draw solutions for water reclamation from feed water resources. Water Sci. Technol. 80 (6), 1053–1062. doi:10.2166/wst.2019.359
Liu, W., Fu, P., Zhang, Y., Xu, H., Wang, H., and Xing, M. (2023). Efficient hydrogen production from wastewater remediation bypiezoelectricity coupling advanced oxidation processes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 120 (7), e2218813120. doi:10.1073/pnas.2218813120
Liu, W. J., Liu, C., Liu, L., You, Y. T., Jiang, J. H., Zhou, Z. K., et al. (2017). Simultaneous decolorization of sulfonated azo dyes and reduction of hexavalent chromium under high salt condition by a newly isolated salt tolerant strain Bacillus circulans BWL1061. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 141, 9–16. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.03.005
Liu, Z. Q., Yang, J. Y., Zhang, J. E., Xiang, H. M., and Wei, H. (2019). A bibliometric analysis of research on acid rain. Sustainability 11 (11), 3077. doi:10.3390/su11113077
Marx, W., Haunschild, R., Thor, A., and Bornmann, L. (2017). Which early works are cited most frequently in climate change research literature? A bibliometric approach based on Reference Publication Year Spectroscopy. Scientometrics 110 (1), 335–353. doi:10.1007/s11192-016-2177-x
Muntha, S. T., Kausar, A., and Siddiq, M. (2017). Advances in polymeric nanofiltration membrane: a review. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 56 (8), 841–856. doi:10.1080/03602559.2016.1233562
Nilsson, I., Moller, A., Mattiasson, B., Rubindamayugi, M. S. T., and Welander, U. (2006). Decolorization of synthetic and real textile wastewater by the use of white-rot fungi. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 38 (1-2), 94–100. doi:10.1016/j.enzmictec.2005.04.020
Ouyang, W., Wang, Y. D., Lin, C. Y., He, M. C., Hao, F. H., Liu, H. B., et al. (2018). Heavy metal loss from agricultural watershed to aquatic system: a scientometrics review. Sci. Total Environ. 637, 208–220. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.04.434
Peng, H. Y., Wang, D., and Fu, S. H. (2021). Unidirectionally driving nanofluidic transportation via an asymmetric textile pump for simultaneous salt-resistant solar desalination and drenching-induced power generation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 13 (32), 38405–38415. doi:10.1021/acsami.1c10877
Peng, L. E., Yao, Z. K., Chen, J. X., Guo, H., and Tang, C. Y. Y. (2020). Highly selective separation and resource recovery using forward osmosis membrane assembled by polyphenol network. J. Membr. Sci. 611, 118305. doi:10.1016/j.memsci.2020.118305
Sarayu, K., and Sandhya, S. (2012). Current technologies for biological treatment of textile wastewater-A review. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 167 (3), 645–661. doi:10.1007/s12010-012-9716-6
Si, J., Wu, Y., Ma, H. F., Cao, Y. J., Sun, Y. F., and Cui, B. K. (2021). Selection of a pH- and temperature-stable laccase from Ganoderma australe and its application for bioremediation of textile dyes. J. Environ. Manage 299, 113619. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113619
Song, Y. L., Wang, L. J., Qiang, X., Gu, W. H., Ma, Z. L., and Wang, G. C. (2023). An overview of biological mechanisms and strategies for treating wastewater from printing and dyeing processes. J. Water Process. Eng. 55, 104242. doi:10.1016/j.jwpe.2023.104242
Usman, M., and Ho, Y. S. (2020). A bibliometric study of the Fenton oxidation for soil and water remediation. J. Environ. Manage 270, 110886. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110886
Wang, C. F., Chen, Y. B., Yang, K., Hu, X. Y., and Zhang, Y. F. (2022a). Fabrication of tight GO/PVDF hollow fiber membranes with improved permeability for efficient fractionation of dyes and salts in textile wastewater. Polym. Bull. 79 (1), 443–462. doi:10.1007/s00289-020-03513-9
Wang, D. M., Huangfu, Y. B., Dong, Z. J., and Dong, Y. Q. (2022b). Research hotspots and evolution trends of carbon neutrality-visual analysis of bibliometrics based on CiteSpace. Sustainability 14 (3), 1078. doi:10.3390/su14031078
Wu, X., Ding, M. M., Xu, H., Yang, W., Zhang, K. S., Tian, H. L., et al. (2020). Scalable Ti3C2TxMXene interlayered forward osmosis membranes for enhanced water purification and organic solvent recovery. Acs. Nano 14 (7), 9125–9135. doi:10.1021/acsnano.0c04471
Xu, Y., Yang, Y. P., Chen, X. N., and Liu, Y. X. Y. (2022). Bibliometric analysis of global NDVI research trends from 1985 to 2021. R.S. Remote Sens. (Basel). 14 (16), 3967. doi:10.3390/rs14163967
Yang, Q. H., Zhang, M. L., Zhang, M. M., Wang, C. Q., Liu, Y. Y., Fan, X. J., et al. (2018). Characterization of a novel, cold-adapted, and thermostable laccase-like enzyme with high tolerance for organic solvents and salt and potent dye decolorization ability, derived from a marine metagenomic library. Front. Microbiol. 9, 2998. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2018.02998
Zhang, P., Gong, J. L., Zeng, G. M., Song, B., Cao, W. C., Liu, H. Y., et al. (2019). Novel “loose” GO/MoS2 composites membranes with enhanced permeability for effective salts and dyes rejection at low pressure. J. Membr. Sci. 574, 112–123. doi:10.1016/j.memsci.2018.12.046
Zhao, R., Li, Y., Mao, Y., Li, G., Croes, T., Zhu, J., et al. (2022). Recycling the high-salinity textile wastewater by quercetin-based nanofiltration membranes with minimal water and energy consumption. Environ. Sci. Technol. 56 (24), 17998–18007. doi:10.1021/acs.est.2c06397
Keywords: desalination, biodegradation, decolorization, photocatalysis, dye/salt separation, loose nanofiltration membranes
Citation: Wang Q and Zhang X (2025) Progress of treatment and resource utilization for high salinity printing and dyeing wastewater based on bibliometric study. Front. Environ. Sci. 12:1526220. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2024.1526220
Received: 11 November 2024; Accepted: 16 December 2024;
Published: 14 January 2025.
Edited by:
Ji Qi, Chung-Ang University, Republic of KoreaReviewed by:
Min Lv, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), ChinaXiang Li, Donghua University, China
Qiaoning Wang, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China
Ying Huang, Ningbo University, China
Copyright © 2025 Wang and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiaojiao Zhang, eGp6aGFuZ0Bzc3B1LmVkdS5jbg==
 Qiannan Wang
Qiannan Wang Xiaojiao Zhang
Xiaojiao Zhang