- 1Engineering and Technology Research Center for Agricultural Land Pollution Integrated Prevention and Control of Guangdong Higher Education Institute, College of Resources and Environment, Zhongkai University of Agriculture and Engineering, Guangzhou, China
- 2College of College of Natural Resources and Environment, South China Agricultural University, Guangzhou, China
The flow field distribution and clogging process in HFCWs are complex, the hydraulic characteristics, distribution and size of dead zone of HFCW were studied by using the Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD). The results showed that (1) The ceramsite system’s filtration efficacy in treating wastewater is primarily driven by deep filtration processes. The distribution of water flow within the ceramsite wetland system is more homogenous than that observed in the blast furnace slag wetland system. Furthermore, the ceramsite system exhibits enhanced utilization of the primary bed area, the underlying drainage layer, and the catchment zone. (2) The blast furnace slag system possesses a smaller porosity and particle size distribution, which results in non-uniform flow rates and pressure distributions. Consequently, this system is prone to clogging, leading to a decline in both hydraulic performance and the overall functionality of the wetland. (3) The ceramsite system exhibits a lower occurrence of dead zones within the main bed compared to the blast furnace slag system, with a reduction of 12.58% and 27.93% in the dead zone percentages, respectively. This suggests that the ceramsite system outperforms the blast furnace slag system in terms of hydraulic efficiency, resistance to clogging, and contaminant removal efficacy.
1 Introduction
Horizontal flow constructed wetland (HFCW) are widely used in the field of water pollution treatment because of their advantages, such as good treatment effects and low infrastructure and operation costs (House et al., 1999). However, clogging is common in HFCWs after a period of operation. Relevant statistics show that 50% of wetlands experience some extent of clogging within 5 years of operation (USEAP, 1993). Clogging causes uneven hydraulic distribution in the wetland system, reduces the porosity of the substrate, shortens the hydraulic retention time (HRT) of the system, affects the pollutant treatment efficiency, and, in severe cases, reduces the service life of the wetland (Nivala et al., 2012). The clogging problem of HFCWs has received attention in recent years, several studies have been reported to initially explore the clogging distribution patterns in HFCWs (Knowles et al., 2010; Petitjean et al., 2016), clogging extent monitoring (Morris et al., 2011; Hughes-Riley et al., 2016; Corbella et al., 2016), and two-dimensional models of clogging (Hua et al., 2010). The spatial and temporal distribution, as well as the flow field characteristics of clogged areas within artificial wetlands, have been investigated using Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) (Dai et al., 2024). Nonetheless, the flow field characteristics, the extent and location of dead zones, and the size of clogging volumes in wetland systems remain relatively underexplored, particularly in ceramic and blast furnace slag wetland systems.
Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) is a product of the combination of recent fluid mechanics, numerical mathematics, and computer science that analyzes complex physical problems containing fluid flow and heat transfer through computer numerical calculation and image display, and finally can obtain the basic physical quantities such as velocity, pressure, temperature, and concentration in the flow field and a quantitative description to solve various practical problems (Persson et al., 1999; Fan et al., 2008). In recent years, CFD numerical simulation methods have also been applied to the study of artificial wetland flow fields, laying the foundation for the establishment of hydrodynamic models of constructed wetland as well as the simulation and analysis of flow patterns inside wetlands (Fan et al., 2008; Rengers et al., 2016). Rengers used CFD methods to study the hydrodynamic performance of constructed wetland systems, and the results showed that flow velocity, length, and interaction between flow rate and length had significant effects on the content of pollutants in the effluent; Jang used numerical simulation to determine the factors affecting the nitrate reduction process in aquifer heterogeneity (Rengers et al., 2016; Jang et al., 2017). Garcia mainly studied the effects of different constructed wetland sizes and substrates of different particle sizes on the hydraulics of horizontal flow constructed wetland and found that larger wetland aspect ratios and smaller particle sizes, as well as the filling form of the substrate and the location of the inlet and outlet, directly affected the dead zone and particle removal efficiency within the constructed wetland (Garcia et al., 2004; Kjellin et al., 2006; Choi and Park, 2013). Rajabzadeh et al. (2015) simulated the flow field and biokinetics in a vertical flow wetland using CFD. The results showed that biofilm growth created dead zones in the substrate, which was the first prediction of the bio-clogging process. Wei et al. (2024) optimized the hydraulic performance of a bulkhead-style horizontal subsurface flow artificial wetland by utilizing CFD modeling. Similarly, Du et al. (2024) demonstrated that CFD models are a potent tool for the hydraulic characterization of surface flow constructed wetlands (SSF-CW) through their CFD modeling efforts. However, none of these studies were able to determine the location of the system’s short flows, dead zones, or specific clogging volumes.
Based on the above findings, this study conducted flow field simulation by constructing HFCW clogging simulation experiments with CFD simulations using blast furnace slag and ceramsite, which are commonly used in engineering practice for nitrogen and phosphorus removal with good effect and low price, as wetland substrates. The objectives of this study are (1) to clarify the distribution of the flow state field within the blast furnace slag and ceramsite wetland systems, (2) to analyze the differences in velocity and pressure in different matrix systems and their causes, and (3) a comparative analysis of the location and volume size of dead zone distribution across wetland systems employing various substrates, and an examination of their impact on hydraulic performance and overall wetland efficacy. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first time that the ANSYS SCDM software module is used to build an HFCW 3D model at a scale of 1:1 with the actual device. Numerical simulations are performed using the ANSYS Fluent solver, and data are processed by the post-processing software module ANSYS CFD-post to examine the distribution characteristics and blockage of the HFCW steady-state flow field. The results of the study can provide new ideas and technical support for the targeted prevention and control of clogging in blast furnace slag and ceramsite constructed wetlands (Rajabzadeh et al., 2015).
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Clogging experiments with HFCWs
2.1.1 Construction of the wetland system
A plastic box was used as a clogging test device, whose length, width, and height were 560 mm, 360 mm and 250 mm, respectively. The HFCWs device was divided into zones such as a water distribution zone, a surface fine sand zone, a main bed zone, a bottom water guide zone, a water collection zone, etc. The main bed zone was filled with ceramsite and blast furnace slag matrix, respectively, and the function, size, and filler type of each zone and the relevant parameters of these filler parameters are shown in Figure 1 and Supplementary Table S1.
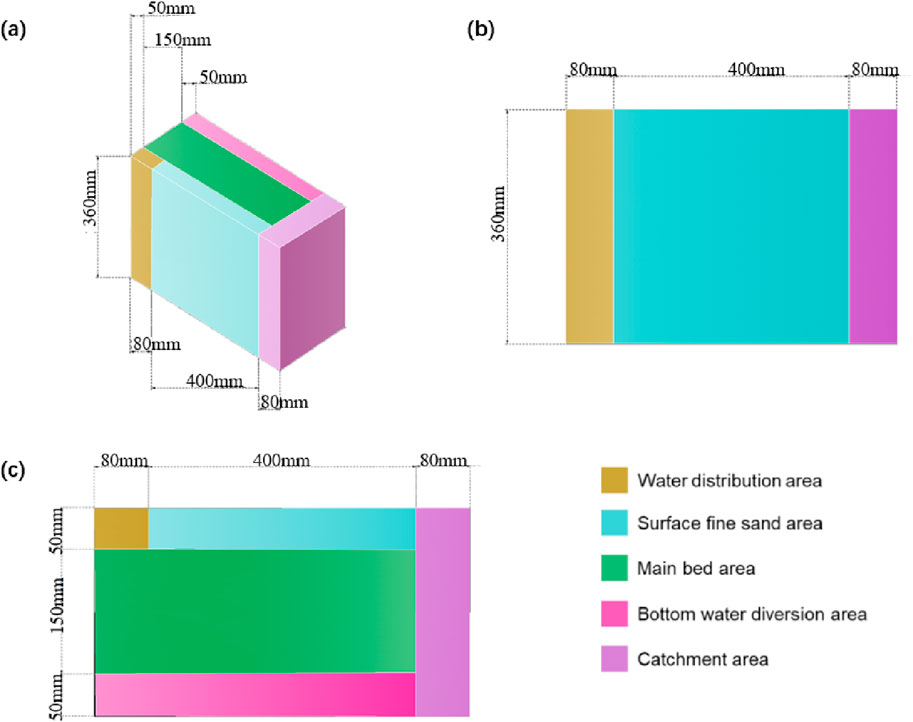
Figure 1. Three-D view of the structure of the test apparatus: (A) is the main view; (B) is the top view; (C) is the side view.
Each wetland device is laid with two inlets, which are 90 mm away from the side walls of both sides of the box, and 10 mm away from the surface of the bed position; the four outlets were set up from the bottom of the device at a height of 0, 5, 20, 25 cm, respectively. The outlet at 0, 5, 20 cm can be used to determine the porosity of each bed, and the outlet at 25 cm can prevent the device from overflowing. The outlet at 25 cm can prevent the device from overflowing. The diameter of the inlet and outlet straight pipes is 5.8 mm, and the water inlet is controlled by a glass rotor flow meter.
2.1.2 Experimental design
The experiment was conducted using two different types of fillers: blast furnace slag and ceramsite as the main bed of the wetland system was designed with three replications for each treatment, as shown in Figure 2. And the parameters for tracer simulation were established as indicated in Supplementary Table S2 and subsequently validated through tracer experiments. A 0.3 m/d hydraulic loading rate (HLR) operating system was used.
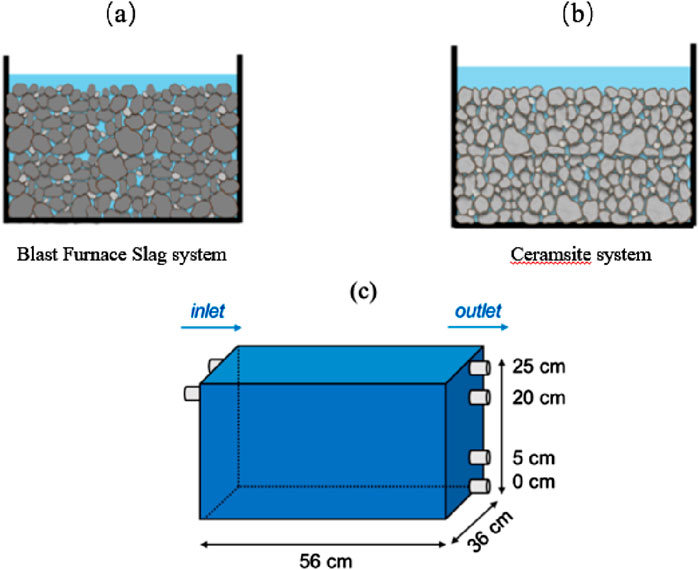
Figure 2. Schematic diagram (A) and photo (B) of HFCW systems and their influent and effluent sampling sites (C).
2.2 Creation of the 3D model of the device
Based on the experimental setup parameters, 3D modeling of the wetland bed was performed using ANSYS SCDM software, with the bottom right vertex of the inlet side of the setup as the coordinate origin (X = 0, Y = 0, Z = 0, X, Y, Z represent the length, width, and height of the system, respectively); the specific partitioning of the bed function and substrate parameters are shown in Figure 1 and Supplementary Table S3, respectively.
2.3 Division of network model
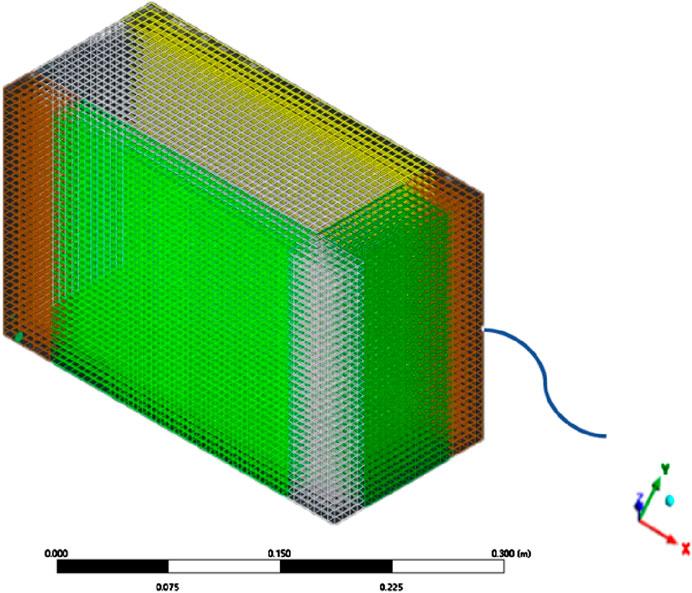
The principle of CFD calculations is to discretize the computational region in space into many small volume cells using methods such as the finite volume method and to solve within this volume cell using the governing equations of hydrodynamics, etc. (Yamasaki et al., 2022; Sakib et al., 2022). The model was meshed using ANSYS mesh software according to the finite volume method (Stolarski et al., 2018). The 3D model in 2.2 was divided into a total of 566720 meshes, and the specific meshing method and related parameters are shown in Figure 3 and Supplementary Table S4, respectively.
2.4 ANSYS fluent calculation principle
Within HFCWs, the saturated water flow state is classified as laminar or turbulent. Re is used to measure the flow state of the fluid in the system and is calculated as shown in Equation 1.
where Re is the mathematical symbol for Reynolds number, a dimensionless number that can be used to characterize fluid flow; ρ is the density of the fluid, kg/m3;
The flow of wastewater in the bed is subject to various resistances, so the momentum conservation equation for porous media (Equation 2) can be constructed by adding the resistance source term belonging to the porous media model to the momentum control equation for fluid flow.
where Si is the drag source term; D and C are the viscous drag and inertial loss coefficient matrices, respectively, with 1/α and C2 brought diagonally into the matrices D and C, respectively. α and C2 are related to the particle size of the wetland bed matrix and the bed porosity, and the equations for calculating α and C2 are shown in (Equation 3) and (Equation 4), respectively.
where D is the particle size of a single matrix; ε is the porosity of the bed (Vafai, 2015; Bear, 2003).
The theoretical Hydraulic Retention Time (HRT) and the actual average HRT were computed using the formulas provided in Equations 5, 6, respectively.
where tn represents the theoretical Hydraulic Retention Time (HRT) of the experimental system, expressed in minutes; tm denotes the actual average HRT of the experimental system, also in minutes; Qt is the inlet flow rate of the system, measured in milliliters per minute; Ct is the concentration of the tracer fluorescein sodium at the outlet, given in grams per milliliter; and vt is the volume of fluid that the experimental system can hold in its saturated state, specified in milliliters.
The effective volume ratio, denoted as e, is computed according to the formula presented in Equation 7.
The tracer recovery, denoted as R, is determined using the formula provided in Equation 8.
where Mi represents the total input mass of the tracer fluorescein sodium recovered during the tracer experiment, measured in grams; R denotes the recovery rate of the tracer fluorescein sodium obtained from the tracer experiment.
The number of continuously stirred reactors, denoted as N, can be used to reflect the flow conditions within the wetland and is calculated according to the formula presented in Equation 9.
where tp represents the time, in hours, at which the tracer concentration at the outlet of the wetland system attains its peak value.
The overall hydraulic efficiency, denoted as λ, is computed using the formula provided in Equation 10, with tp being the duration, in hours, during which the tracer concentration at the outlet of the wetland system reaches its maximum.
2.5 Parameter settings for ANSYS fluent calculations
The simulation calculation setup for Fluent is as follows:
(1) Start-up setting: Set the calculation accuracy to double precision in the Fluent startup item.
(2) Solver settings: select pressure as the solver type in the Fluent general solver column, and the time calculation mode is selected as steady state, constant flow.
(3) Physical Model Settings: Set the solution model to K-epsilon Realizable in the Physical Model Settings field, set the direction of gravitational acceleration to the negative direction of the Z-axis, and its magnitude to 9.81 m/s2.
(4) Computational domain settings: the computational fluid is set to water, and its density and viscosity coefficient (20°C) are 998.2 kg/m3 and 0.001003 kg/(m·s), respectively; the laminar flow control and the relevant parameters of the porous medium model are set in Supplementary Table S5.
(5) Boundary condition settings: the inlet boundary condition is set to velocity inlet, the system hydraulic load (HLR) is set to 0.3 m/d, then its inlet velocity is 0.0133 m/s, and the hydraulic diameter, the inlet valve diameter, is 0.0058 m. The outlet boundary condition is set to pressure outlet; the boundary condition of the intersection between the functional zones within the wetland system is set to the interior (internal surface), sharing the geometric topology between the zones to achieve a seamless link between the zones; for the rest of the wall conditions, the standard wall model with static and no-slip is used.
(6) Solution method settings: the solution method uses the pressure-velocity coupling method SIMPLE; the spatial discretization format is kept as default; and warped-face gradient correction is turned on.
(7) Experimental Setup for Tracer Simulation: Building on the steady-state simulation, the two most representative middle sections within the system were identified for further analysis. The transient solver was activated, and the component transport model was enabled. Physical parameters such as the relative molecular mass of the tracer fluorescein sodium (376.27), the diffusion coefficient (10−9 m2/s), and others were incorporated and input into Fluent’s mixture components to facilitate the configuration of chemical component transport. The PISO (Pressure-Implicit with Splitting of Operators) method was employed for transient computations. A tracer stock solution of 60 mL was simultaneously injected into each of the two inlets of the simulation apparatus. Given an inlet flow rate of 0.0133 m/s, the injection of the stock solution was completed in approximately 86 s. Consequently, the time step for the transient calculation was set to 0.5 s, with a total of 172 iterative steps. Following the addition of the tracer, the system’s inlet water was switched to pure water, and an outlet monitoring surface was established. Transient data collection was scheduled at the following time points: 1.5, 60, 600, and 2,160 min, respectively. This setup allowed for a detailed analysis of the tracer’s movement and dispersion throughout the system over time.
(8) Calculation accuracy setting: to ensure the calculation accuracy, the residual convergence condition is set to 10−6.
2.6 Validation of tracer simulation experiments
The tracer was introduced into the interior of the apparatus via a “hanging bottle” method, utilizing gravity flow to ensure that the tracer feed rate for each apparatus was consistent with the simulation trials. During the initial and mid-phases of the experiment, sampling intervals were set at every 5–30 min; however, in the later phase of the experiment, the sampling interval was adjusted to approximately every 60 min. For each system, a total of 48 samples were collected, with the entire experimental duration lasting for 36 h. The sample pretreatment and analysis methods adhered to the procedures outlined by Seeger et al. (2013).
2.7 Data acquisition and analysis
After the calculation is completed, CFD-post is used for processing and exporting the data, such as streamlines and cloud maps. The exported image format is uniformly in PNG format; the color scale of the cloud map is the traditional rainbow color scale.
Velocity and pressure data were collected using the cross-section method: three longitudinal cross-sections, Y = 0.09 m, Y = 0.18 m, and Y = 0.27 m, were selected in the simulation model to correspond to inlet 1 (Y = 0.09 m), inlet 2 (Y = 0.27 m), and the middle section of the system (Y = 0.18 m). The system outlet was located on this section, and the X coordinate within the section represents the horizontal direction of the inlet-outlet end of the system (unit: m); the Z coordinate represents the height of the system (unit: m); and the velocity cloud shows a maximum value of 1 × 10−4 m/s, and the pressure cloud shows a global range. Also to quantify the variation of velocity and pressure within different beds of different installations, data collection was carried out at the mid-section of the wetland system (Y = 0.18 m) divided into fixed lines: data were collected at the midline of each bed in fixed lines with Z = 0.025 m (upper layer: sand layer), Z = 0.125 m (middle layer: blast furnace slag layer/ceramsite layer of the main bed), and Z = 0.225 m (lower layer: jute layer).
Since the configurations of the blast furnace slag and ceramsite test groups are identical in terms of bed size and other configurations except for the difference in the main substrate, the difference analysis of cloud diagrams can be performed directly by using the Case Comparison function for the absolute value difference operation of multi-case cloud diagram data based on CFD post software, to obtain the difference cloud diagrams of multiple cases and other related data.
In addition, for the analysis and comparison of the water flow field in the system from a 3D perspective, volumetric data acquisition at the 3D level is carried out using the Isovolume function within the CFD post.
Microsoft Excel 365 was used for the statistics of the data, and Origin 9.8 was used for the graphing.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Water flow status of blast furnace slag and ceramsite wetland system
From Figures 4A, B, it can be seen that the main flow paths within the blast furnace slag wetland system are “inlet → front of the main bed → bottom conductive layer → outlet”. These areas have more dense flow lines and carry most of the hydraulic conductivity load of the entire bed, which are theoretically the dominant flow areas within the system (Altman et al., 2015; Emelko, 2003). In HFCW systems, the filtering action of the bed is largely responsible for wastewater treatment (Nakamura et al., 2017). The filtration action of the filter bed is divided into surface filtration as well as deep filtration, and the blast furnace slag has a small particle size (0.25–1.45 mm) and its bed is mainly based on surface filtration (Xu et al., 2019). The hydraulic conductivity load in the densely flowed area in Figure 4B is higher than that in other areas, and its effluent flux is somewhat higher than that in other areas, so the front area of the blast furnace slag bed is more prone to clogging than the middle and rear ends; while the areas with sparse flow lines (fine sand area, middle and rear ends of the main area, etc.) have lower hydraulic conductivity and are prone to forming dead zones. Thus, the HFCW with a fine-grained blast furnace slag matrix as the main bed has a lower hydraulic distribution efficiency and a higher risk of blockage.
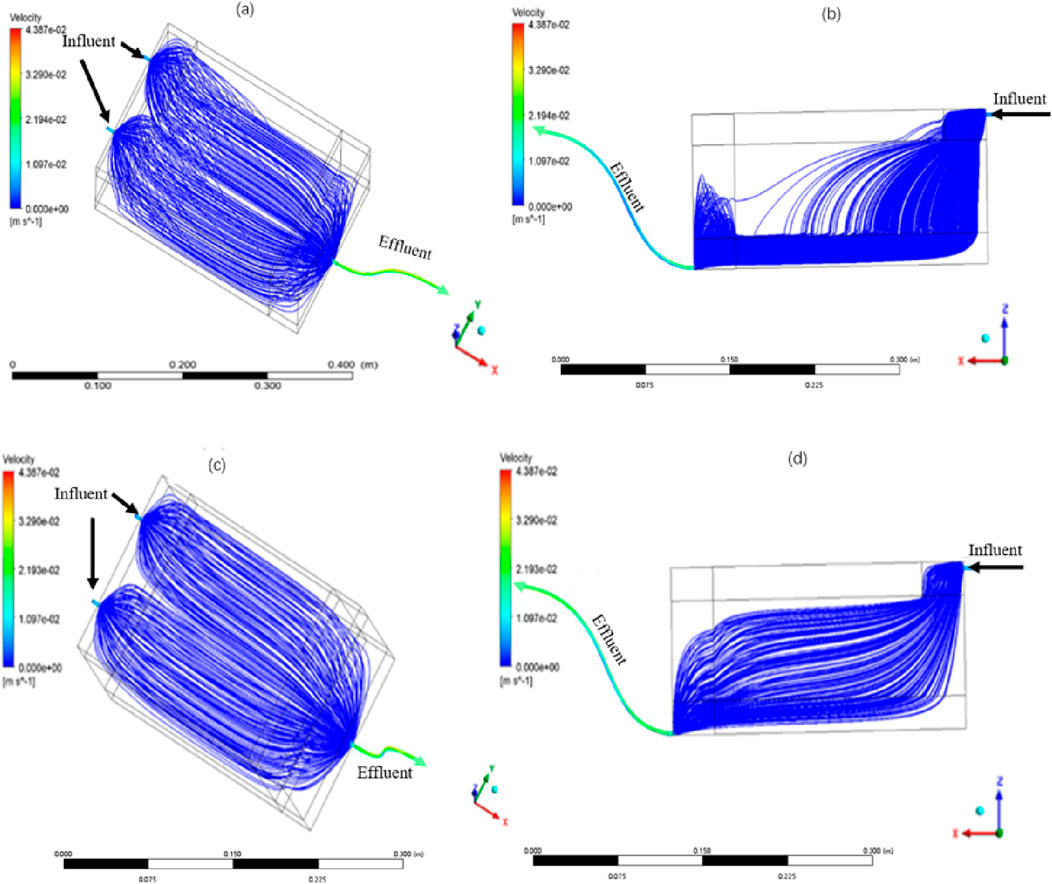
Figure 4. Global flow diagram of blast furnace slag, ceramsite wetland system unit ((A,B) are main and side views of blast furnace slag wetland, respectively, (C,D) are main and side views of ceramsite wetland, respectively).
From Figures 4C, D, it can be seen that the hydraulic distribution of the ceramsite wetland system is more uniform, and the utilization rate of the main bed area, the bottom spar area, and the catchment area are all higher, and the possibility of forming dead zones or short flow areas in the system is less. In addition, the ceramsite particles themselves belong to the large particle size matrix (5–20 mm), and the filtration effect for wastewater is mainly deep filtration (Liu et al., 2020; Wu et al., 2016), and the ceramsite areas The uniform distribution of flow lines indicates that the filtration burden at its front end is low and the possibility of clogging is low.
3.2 Velocity and pressure differences between blast furnace slag and ceramsite wetland systems
As shown in Figure 5A, the velocity difference between the blast furnace slag and ceramsite systems mainly occurs near the intersection of the system’s water distribution zone, water collection zone, and the main bed. As shown in Figure 6A, the velocity difference gradually increases with increasing x along the collection line z = 0.125 m, which corresponds to the main bed zone (x = 0–0.4 m). The hydraulic distribution of the blast furnace slag bed is mainly concentrated at the front end of the bed, and the hydraulic distribution at the middle and rear ends is sparse; while the water flow in the ceramsite bed is uniformly distributed throughout the ceramsite bed. The water flow velocity in the middle and rear parts of the ceramsite bed is larger than that in the middle and rear parts of the blast furnace slag bed. As shown in Figures 5B, 6B, the pressure drop at the front end of the blast furnace slag bed exhibited a more pronounced variation compared to that of the ceramic bed, with the pressure distribution being notably non-uniform. This sharp change in pressure drop leads to increased resistance to water flow within the system, resulting in suboptimal hydraulic performance. This observation aligns with the findings reported by Zhong et al. (2022). As indicated by Wang et al. (2021), in artificial wetlands with smaller porosity and particle size, the pathways available for water flow are reduced, thereby increasing the propensity for clogging. When clogging occurs in the wetland system, the permeability coefficient and treatment efficacy of the substrate experience a significant decline (Boog et al., 2019; Al-Isawi et al., 2015). In contrast, the ceramsite system displayed more uniform flow rates and pressure, signifying superior hydraulic performance and overall wetland functionality compared to the blast furnace slag bed. This is in agreement with the research conducted by Zhu (2020), Bai et al. (2014).
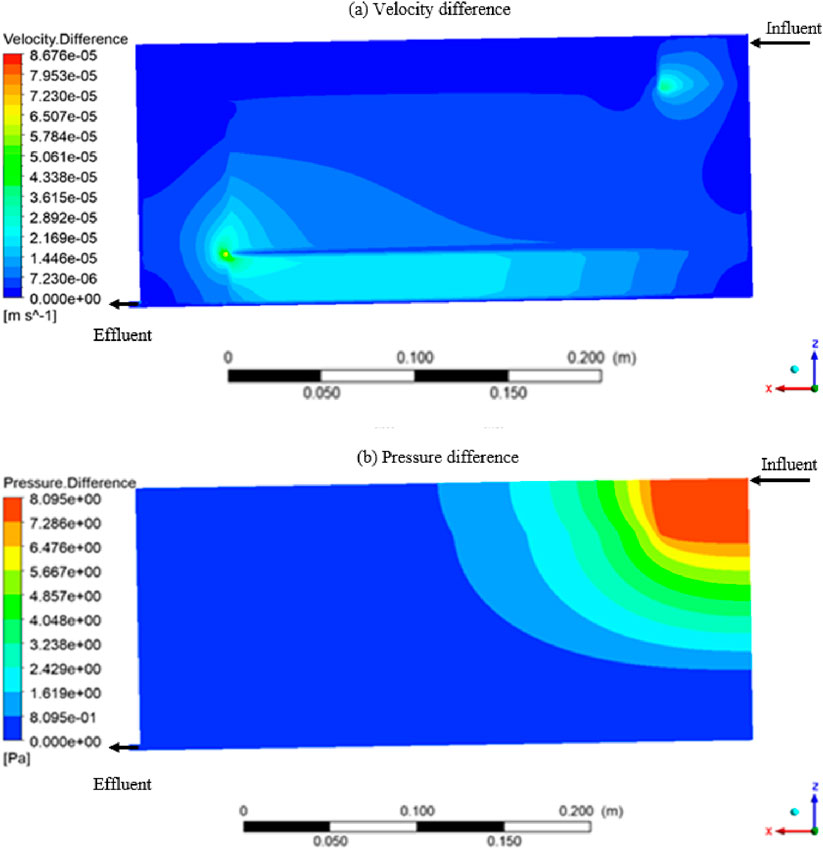
Figure 5. Intra-system variation diagram of blast furnace slag and ceramsite wetland (Y = 0.18 m): (A) velocity variation diagram; (B) pressure variation diagram.
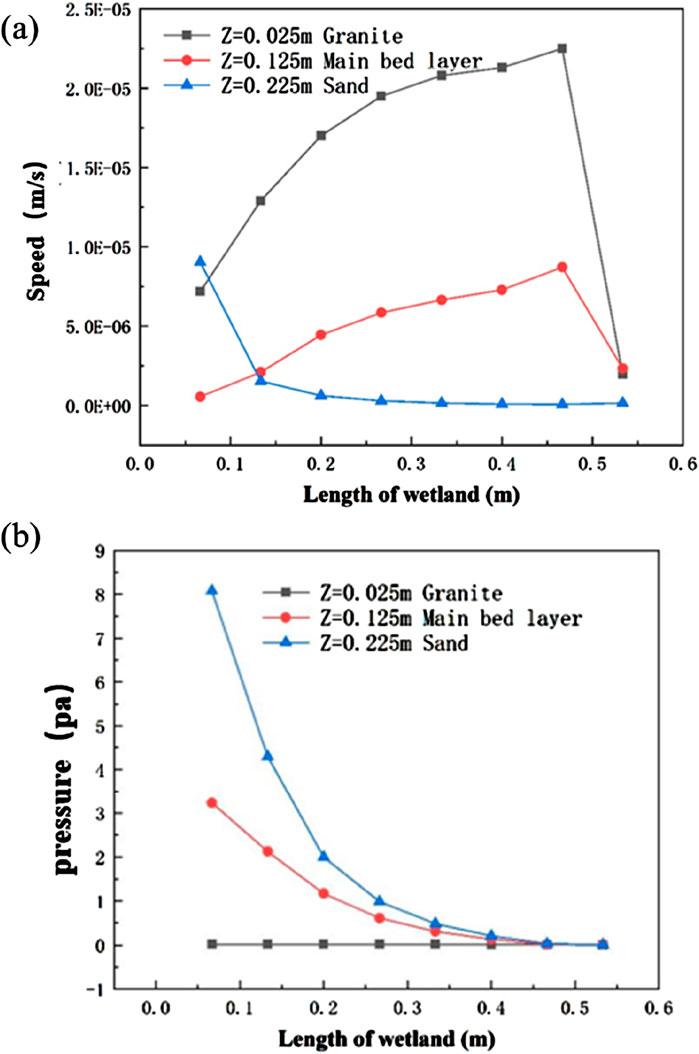
Figure 6. Values of velocity differences (A) and pressure differences (B) for the fixed line collection at Y = 0.18 m cross-section within the two wetland systems.
3.3 Flow field dead zones for blast furnace slag and ceramsite wetland systems comparison
A dead zone within a horizontal submerged wetland system is a region where the saturated water essentially does not participate in the flow of the main flow field and only moves slowly and locally in place or is nearly stationary. The dead zone can essentially be identified as an ineffective or extremely inefficient zone of action within the system, which also tends to have an infinitely long HRT (Cui et al., 2009). In this simulation experiment, the setting is made as follows: when the flow velocity of the region within the system is below 1 × 10−6 m/s (1 mm/s), the region is defined as the non-dominant flow field region, i.e., the dead region. As shown in Figure 7, the dead zones within the two groups of systems exist mainly within the non-dominant flow field regions with sparse streamline coverage, such as the fine sand areas in the surface layer, the corners of the system, and the dead ends.
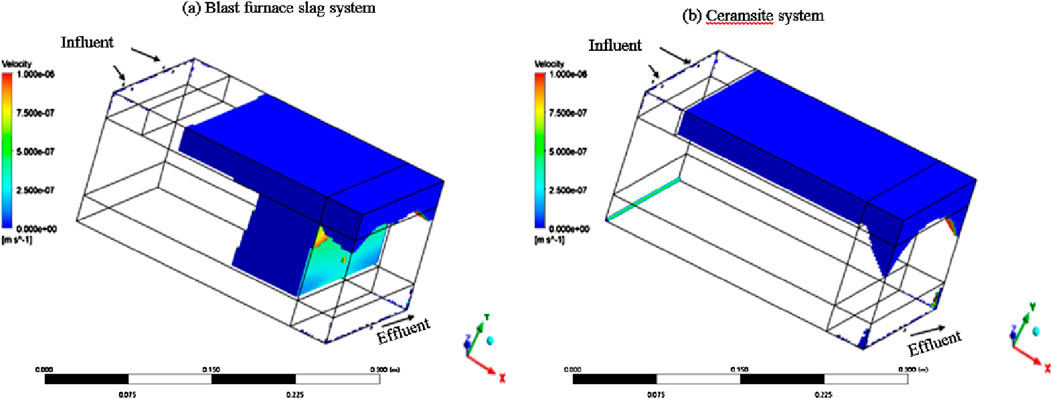
Figure 7. Distribution of regions with velocity values less than 1.0E-6 m/s within the blast furnace slag (A) and ceramsite system (B).
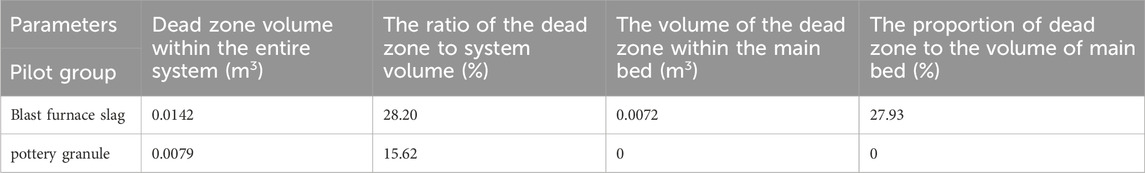
It can also be seen from Figure 7 that the dead zone distribution of the blast furnace slag system is larger than that of the ceramsite system, for which volume data were collected for the relevant region and volume integration was performed to obtain the results in Table 1. As shown in Table 1, the dead zone volumes for the blast furnace slag and ceramsite system are 0.0142 m3 and 0.0079 m3, respectively; the dead zone to the whole system bed is 28.20% and 15.62%, respectively. The dead zones within the blast furnace slag bed were mainly distributed in the upper fine sand zone, and the middle blast furnace slag zone, while the dead zones in the ceramsite bed were mainly concentrated in the upper fine sand zone of the bed. For the main bed zone, the dead zone volume percentage in the main bed zone of the ceramsite system is 0 under the existing velocity threshold, and there is no dead zone in its main bed; while the dead zone volume percentage in the main bed of the blast furnace slag system is 27.93%, which indicates that the ceramsite is not easy to form a dead zone, and also confirms the thesis that the ceramsite has better hydrodynamic performance in Sections 3.1, 3.2.
Therefore, the ceramsite substrate is significantly better than the blast furnace slag substrate in terms of hydrodynamic properties, bed resistance to clogging, and avoidance of dead zone formation. The efficiency of pollutant treatment in artificial wetlands is intrinsically linked to their hydraulic performance (Shih and Wang, 2020). As noted by Zeng et al. (2023), the occurrence of dead zones within the system can result in excessively high flow rates in certain areas while other regions experience no water flow at all. This uneven distribution of flow can exacerbate substrate clogging, as the areas of rapid flow are more likely to capture fine particulate matter, which may then be deposited in the dead zone areas, thereby intensifying clogging. Such conditions can negatively impact the overall hydraulic performance and pollutant removal efficiency of the system. Shih and Wang (2021) discovered that the formation of dead zones diminishes the wetland’s ability to remove pollutants. In contrast, Bai et al. (2016) found that a multi-layer substrate configuration can reduce dead zones and short-circuiting when compared to a single-layer setup, leading to a marked improvement in pollutant removal. The ceramsite system exhibited a lower percentage of dead zones and a reduced percentage of dead zones in the main bed compared to the blast furnace slag system by 12.58% and 27.93%, respectively. This indicates that the ceramsite system surpasses the blast furnace slag system in terms of hydraulic performance, resistance to clogging, and removal efficiency.
3.4 Comparative analysis between simulation results and measured results
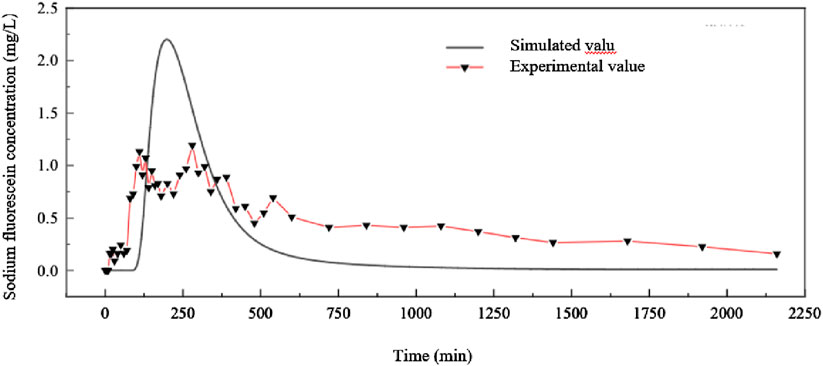
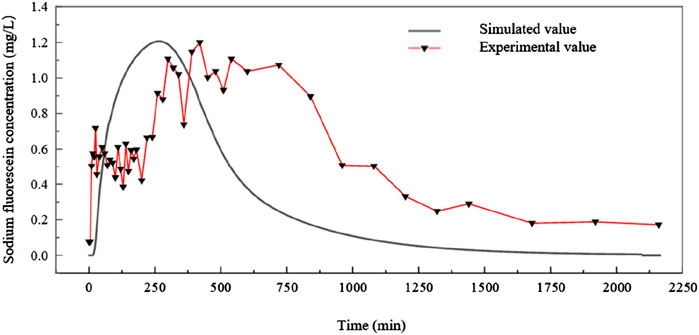
The figures you’re referring to, Figures 8, 9, seem to present a visual comparison between the simulated and measured tracer concentration results for two different artificial wetland systems: one using blast furnace slag and the other using ceramsite. Here’s an interpretation of the data presented in these figures:
In Figure 8, which represents the blast furnace slag system, the simulation results are compared with the measured results. The similarity between the simulation curve and the measured curve, including the trend and the overlapping peaks, suggests that the simulation model is reliable and accurately represents the actual system behavior to a certain extent. However, the measured peak concentration is lower than the simulated peak, and there are multiple peaks observed in the measured data. This discrepancy is attributed to the smaller particle size and porosity of the blast furnace slag, which can lead to short-circuiting and back-mixing within the system. These phenomena can cause the tracer to pass through the system more quickly and mix with the water in a way that reduces the height of the peaks observed in the measured data.
In Figure 9, which represents the ceramic granule system, the tracer RTD curves show a more complex waveform with more pronounced fluctuations and a certain degree of delay. This complexity is likely due to the larger particle size and greater internal porosity of the ceramic granules. The internal pores can adsorb the tracer, affecting the flow dynamics within the bed. Despite the bed being water-saturated, the internal porosity of the ceramic particles still influences the flow field, leading to more intense short-circuiting and back-mixing. This results in a more intricate and delayed tracer response compared to the blast furnace slag system.
In summary, the differences between the simulation and measured results for the two systems can be explained by the physical characteristics of the substrates used, with the ceramsite system exhibiting more complex behavior due to its larger particle size and internal porosity. These findings highlight the importance of substrate selection in the design and operation of artificial wetland systems for pollutant treatment.
3.5 Economic benefits and sustainability analyses
Artificial wetlands are a low-cost treatment process with high pollutant removal rates, low operation and maintenance costs and high sustainability, i.e., 1%–2% of the plant cost (Parde et al., 2021). Ceramsite as a filler in artificial wetlands have good adsorption effect on pollutants and have good economic benefits (He and Wang, 2019). Ceramsite can be used as raw materials of industrial waste, and the production of ceramic granules with uniform texture, high strength, stable physical and chemical properties, good durability, light weight and excellent thermal insulation properties. In conclusion, ceramsite wetland systems are low cost, sustainable and suitable for use in treating water pollution.
3.6 Future study
This investigation examined the hydraulic performance, clogging resistance, and overall wetland functionality of a plantless wetland system, excluding the influences of plant roots, biofilms, and aeration. Subsequent research is encouraged to expand upon these findings by assessing the impact of plant roots, biofilms, and air on water flow dynamics within wetland ecosystems.
4 Conclusion
(1) The ceramsite system’s filtration efficacy in treating wastewater is primarily driven by deep filtration processes. The distribution of water flow within the ceramsite wetland system is more homogenous than that observed in the blast furnace slag wetland system. Furthermore, the ceramsite system exhibits enhanced utilization of the primary bed area, the underlying drainage layer, and the catchment zone.
(2) The blast furnace slag system possesses a finer porosity and particle size distribution, which results in non-uniform flow rates and pressure distributions. Consequently, this system is prone to clogging, leading to a decline in both hydraulic performance and the overall functionality of the wetland.
(3) The ceramsite slag system exhibits a lower occurrence of dead zones within the main bed compared to the blast furnace slag system, with a reduction of 12.58% and 27.93% in the dead zone percentages, respectively. This suggests that the ceramsite slag system outperforms the blast furnace slag system in terms of hydraulic efficiency, resistance to clogging, and contaminant removal efficacy.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
WL: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. SL: Writing–review and editing. KY: Writing–review and editing. XZ: Writing–original draft. YL: Writing–review and editing. MZ: Writing–review and editing. YD: Writing–review and editing. WQ: Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was supported by Key Research and Development Plans in Guangzhou City (2023B03J1362), Special projects in Key Fields of Ordinary Colleges and Universities in Guangdong Province (2022ZDZX4018 and 2022ZDZX4020) and Technology Project of Guangzhou City, China (2024E04J1228).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fenvs.2024.1525757/full#supplementary-material
References
Al-Isawi, R., Scholz, M., Wang, Y., and Sani, A. (2015). Clogging of vertical-flow constructed wetlands treating urban wastewater contaminated with a diesel spill. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 22, 12779–12803. doi:10.1007/s11356-014-3732-8
Altman, J., Ruhl, A. S., Sauter, D., Pohl, J., and Jekel, M. (2015). How to dose powdered activated carbon in deep bed filtration for efficient micropollutant removal. Water Res. 78, 9–17. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2015.03.031
Bai, S., Lv, T., Ding, Y., Li, X., You, S., Xie, Q., et al. (2016). Multilayer substrate configuration enhances removal efficiency of pollutants in constructed wetlands. Water 8 (12), 556. doi:10.3390/w8120556
Bai, S., Song, Z., Ding, Y., You, S., and He, S. (2014). Correlation of substrate structure and hydraulic characteristics in subsurface flow constructed wetlands. Environ. Sci. 35 (2), 592–596.
Boog, J., Kalbacher, T., Nivala, J., Forquet, N., van Afferden, M., and Müller, R. A. (2019). Modeling the relationship of aeration, oxygen transfer and treatment performance in aerated horizontal flow treatment wetlands. Water Res. 157, 321–334. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2019.03.062
Choi, Y. G., and Park, M. C. (2013). Evaluation of hydraulic dead-zone and particle removal efficiency in the base frame of a constructed wetland using computational fluid dynamics. J. Korean Soc. Water Wastewater 27 (4), 495–502. doi:10.11001/jksww.2013.27.4.495
Corbella, C., García, J., and Puigagut, J. (2016). Microbial fuel cells for clogging assessment in constructed wetlands. Sci. Total Environ. 569, 1060–1063. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.06.163
Cui, L. H., and Lu, S. Y. (2009). Construction technology of constructed wetland for wastewater treatment. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press.
Dai, S., Wang, R., Lin, J., Zhang, G., Chen, Z., Li, L., et al. Study on physical clogging process and practical application of horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetland. 2024. (28 August 2024, PREPRINT (Version 1) available at Research Square). doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-4782338/v1
Du, X., Ma, W., Cao, Y., Gan, Y., Li, K., Zhong, D., et al. (2024). Quantification of hydraulic characteristics and validation of CFD simulation of subsurface flow constructed wetlands using tracer. J. Water Process Eng. 64, 105626. doi:10.1016/J.JWPE.2024.105626
Emelko, M. B. (2003). Removal of viable and inactivated Cryptosporidium by dual- and tri-media filtration. Water Res. 37 (12), 2998–3008. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(03)00113-1
Fan, L., Hai, R., Wang, W., Lu, Z., and Yang, Z. (2008). Application of computational fluid dynamic to model the hydraulic performance of subsurface flow wetlands. J. Environ. Sci. 20, 1415–1422. doi:10.1016/S1001-0742(08)62542-5
Garcia, J., Chiva, J., Aguirre, P., Álvarez, E., Sierra, J. P., and Mujeriego, R. (2004). Hydraulic behaviour of horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetlands with different aspect ratio and granular medium size. Ecol. Eng. 23 (3), 177–187. doi:10.1016/j.ecoleng.2004.09.002
He, B., and Wang, G. (2019). Is ceramsite the last straw for sewage sludge disposal: a review of sewage sludge disposal by producing ceramsite in China. Water Sci. Technol. 80 (1), 1–10. doi:10.2166/wst.2019.223
House, C. H., Bergmann, B., Stomp, A., and Frederick, D. (1999). Combining constructed wetlands and aquatic and soil filters for reclamation and reuse of water. Ecol. Eng. 12, 27–38. doi:10.1016/S0925-8574(98)00052-4
Hua, G. F., Zhu, W., and Zhang, Y. H. (2010). A conceptual approach based on suspended solids to estimate clogging time in constructed wetlands. J. Environ. Sci. Health A 45 (12), 1519–1525. doi:10.1080/10934529.2010.506105
Hughes-Riley, T., Dye, E. R., Anderez, D. O., Hill-Casey, F., Newton, M. I., and Morris, R. H. (2016). Temperature dependence of magnetic resonance probes for use as embedded sensors in constructed wetlands. Sens. actuators. A Phys. 241, 19–26. doi:10.1016/j.sna.2016.01.050
Jang, E., He, W., Savoy, H., Dietrich, P., Kolditz, O., Rubin, Y., et al. (2017). Identifying the influential aquifer heterogeneity factor on nitrate reduction processes by numerical simulation. Adv. Water Resour. 99, 38–52. doi:10.1016/j.advwatres.2016.11.007
Kjellin, J., Wörman, A., Johansson, H., and Lindahl, A. (2006). Controlling factors for water residence time and flow patterns in Ekeby treatment wetland, Sweden. Adv. Water Resour. 30 (4), 838–850. doi:10.1016/j.advwatres.2006.07.002
Knowles, P. R., Griffin, P., and Davies, P. A. (2010). Complementary methods to investigate the development of clogging within a horizontal sub-surface flow tertiary treatment wetland. Water Res. 44 (1), 320–330. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2009.09.028
Liu, C., Li, X., Yang, Y., Fan, X., Tan, X., Yin, W., et al. (2020). Double-layer substrate of shale ceramsite and active alumina tidal flow constructed wetland enhanced nitrogen removal from decentralized domestic sewage. Sci. Total Environ. 703, 135629. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135629
Morris, R. H., Newton, M. I., Knowles, P. R., Bencsik, M., Davies, P. A., Griffin, P., et al. (2011). An analysis of clogging in constructed wetlands using magnetic resonance. Analyst 136 (11), 2283–2286. doi:10.1039/C0AN00986E
Nakamura, K., Hatakeyama, R., Tanaka, N., Takisawa, K., Tada, C., and Nakano, K. (2017). A novel design for a compact constructed wetland introducing multi-filtration layers coupled with subsurface superficial space. Ecol. Eng. 100, 99–106. doi:10.1016/j.ecoleng.2016.11.052
Nivala, J., Knowles, P., Dotro, G., García, J., and Wallace, S. (2012). Clogging in subsurface-flow treatment wetlands: measurement, modeling and management. Water Res. 46 (6), 1625–1640. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2011.12.051
Parde, D., Patwa, A., Shukla, A., Vijay, R., Killedar, D. J., and Kumar, R. (2021). A review of constructed wetland on type, treatment and technology of wastewater. Environ. Technol. Innov. 21, 101261. doi:10.1016/J.ETI.2020.101261
Persson, J., Somes, N., and Wong, T. (1999). Hydraulics efficiency of constructed wetlands and ponds. Water Sci. Technol. 40 (3), 291–300. doi:10.2166/wst.1999.0174
Petitjean, A., Forquet, N., and Boutin, C. (2016). Oxygen profile and clogging in vertical flow sand filters for on-site wastewater treatment. J. Environ. Manag. 170, 15–20. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2015.12.033
Rajabzadeh, A. R., Legge, R. L., and Weber, K. P. (2015). Multiphysics modelling of flow dynamics, biofilm development and wastewater treatment in a subsurface vertical flow constructed wetland mesocosm. Ecol. Eng. 74, 107–116. doi:10.1016/j.ecoleng.2014.09.122
Rengers, E. E., Da Silva, J. B., Paulo, P. L., and Janzen, J. G. (2016). Hydraulic performance of a modified constructed wetland system through a CFD-based approach. J. Hydroenviron. Res. 12, 91–104. doi:10.1016/j.jher.2016.04.002
Sakib, S., Besse, G., Yin, P., Gang, D., and Hayes, D. (2022). Sediment transport simulation and design optimization of a novel marsh shoreline protection technology using computational fluid dynamics (CFD) modeling. Int. J. Sediment Res. 37, 14–25. doi:10.1016/j.ijsrc.2021.06.004
Seeger, E. M., Maier, U., Grathwohl, P., Kuschk, P., and Kaestner, M. (2013). Performance evaluation of different horizontal subsurface flow wetland types by characterization of flow behavior, mass removal and depth-dependent contaminant load. Water Res. 47 (2), 769–780. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2012.10.051
Shih, S. S., and Wang, H. C. (2020). Flow uniformity metrics for quantifying the hydraulic and treatment performance of constructed wetlands. Ecol. Eng. 155, 105942. doi:10.1016/j.ecoleng.2020.105942
Shih, S. S., and Wang, H. C. (2021). Spatiotemporal characteristics of hydraulic performance and contaminant transport in treatment wetlands. J. Contam. Hydrology 243, 103891. doi:10.1016/j.jconhyd.2021.103891
Stolarski, T. A., Nakasone, Y., and Yoshimoto, S. (2018). Engineering analysis with ANSYS software. Oxford: RM.
Wang, H., Sheng, L., and Xu, J. (2021). Clogging mechanisms of constructed wetlands: a critical review. J. Clean. Prod. 295, 126455. doi:10.1016/J.JCLEPRO.2021.126455
Wei, J., Cotterill, S., and Keenahan, J. (2024). Optimizing the hydraulic performance of a baffled horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetland through computational fluid dynamics modelling. J. Environ. Manag. 351, 119776. doi:10.1016/J.JENVMAN.2023.119776
Wu, H., Fan, J., Zhang, J., Ngo, H. H., Guo, W., Liang, S., et al. (2016). Intensified organics and nitrogen removal in the intermittent-aerated constructed wetland using a novel sludge-ceramsite as substrate. Bioresour. Technol. 210, 101–107. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2016.01.051
Xu, R., Zhang, Y., Liu, R., Cao, Y., Wang, G., Ji, L., et al. (2019). Effects of different substrates on nitrogen and phosphorus removal in horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetlands. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 26 (16), 16229–16238. doi:10.1007/s11356-019-04945-1
Yamasaki, T. N., Walker, C., Janzen, J. G., and Nepf, H. (2022). Flow distribution and mass removal in floating treatment wetlands arranged in series and spanning the channel width. J. Hydroenviron. Res. 44 (9), 1–11. doi:10.1016/j.jher.2022.07.001
Zeng, L., Yuan, Y., Wang, P., and Tan, X. J. (2023). Research progress on clogging mechanism and prevention measures for constructed wetland. Water Purif. Technol. 42 (11), 18–26. doi:10.15890/j.cnki.jsjs.2023.11.003
Zhong, H., Hu, N., Wang, Q., Chen, Y., and Huang, L. (2022). How to select substrate for alleviating clogging in the subsurface flow constructed wetland. Sci. Total Environ. 828, 154529. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.154529
Keywords: CFD, tracer experiments, constructed wetlands, dead zone distribution, hydraulic characteristics
Citation: Liu W, Li S, Yang K, Zeng X, Li Y, Zou M, Deng Y and Qian W (2025) CFD-based study of flow field characteristics and clogging in horizontal flow constructed wetlands. Front. Environ. Sci. 12:1525757. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2024.1525757
Received: 11 November 2024; Accepted: 17 December 2024;
Published: 07 January 2025.
Edited by:
Fabio Masi, IRIDRA Srl, ItalyReviewed by:
Krzysztof Jóźwiakowski, University of Life Sciences of Lublin, PolandGiuseppe Mancuso, University of Bologna, Italy
Copyright © 2025 Liu, Li, Yang, Zeng, Li, Zou, Deng and Qian. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Wei Qian, cWlhbndlaTcxMEB6aGt1LmVkdS5jbg==
 Wen Liu1
Wen Liu1 Shitao Li
Shitao Li Wei Qian
Wei Qian