- 1School of Public Administration, China University of Geosciences (Wuhan), Wuhan, China
- 2School of Mathematics and Physics, China University of Geosciences (Wuhan), Wuhan, China
- 3School of Economics and Trade, Hubei University of Economics, Wuhan, China
- 4Wuhan Municipal Planning Research Institute, Wuhan, China
Ecosystems worldwide are facing significant challenges resulting from the dual pressures of global climate change and human activities, particularly in terms of significant biodiversity loss associated with land-use change. Focusing on the Yangtze River Economic Belt (YREB), this study uses the System Dynamics (SD) - Patch-generating Land Use Simulation (PLUS) model to simulate land-use development under different scenarios of shared socio-economic pathways (SSPs) and representative concentration pathways (RCPs) from 2030 to 2050. Furthermore, the InVEST model is applied to evaluate changes in habitat quality (HQ) over the period 2000 to 2050. A hotspot analysis further highlights the spatial heterogeneity of HQ within the YREB. The study showed that the land-use pattern in the YREB from 2020 to 2050 will be dominated by cropland in the eastern region, grassland in the north-west, and forest land in the central and southern regions, with a steady increase in built-up land in the east. The HQ index exhibits a gradual increase from east to west, ultimately declining to 0.726 under the SSP585 scenario for 2050. This trend reflects moderate habitat degradation (HD), with the degree of degradation shifting towards lower and higher proportions of HQ. Spatial analysis of HQ further reveals that the eastern region is identified as a cold spot, the central region is categorized as non-significant, while the western region emerges as a hot spot, where HQ exceeds 40%. These findings offer a scientific foundation for promoting high-quality development and enhancing biodiversity conservation in the YREB.
1 Introduction
The rapid evolution of the socio-economic landscape, coupled with the persistent processes of the urbanization and industrialization, has led to increasing disturbance of natural habitats by human activities, exacerbating the problem of habitat fragmentation (Tu et al., 2023; Zhao et al., 2024). In this context, the Sustainable Development Goal (SDG15), as articulated in the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, underscores the critical importance of protecting, restoring, and sustainably utilizing terrestrial ecosystems to safeguard natural habitats and promote biodiversity (Palmer, 2015). Over the past 4 decades, China has undergone significant land-use changes (LUC) (Kong et al., 2023; Luan and Li, 2021; Luo et al., 2022). These alterations in land-use have directly modified the distribution of natural biological habitats, thereby exacerbating habitat fragmentation and contributing to biodiversity loss (Haddad et al., 2015; Oliver et al., 2015). In the future, urban expansion is expected to lead to ecological fragmentation, which will pose an ongoing threat to biological habitats (Li et al., 2022). Habitat fragmentation disrupts the migration of organisms between habitat patches and impairs the exchange of materials and energy (O'Connor et al., 2020; Zhang G. et al., 2023), ultimately leading to a deterioration in HQ. This phenomenon has emerged as a critical focus in global ecological research. Considering the intensifying global habitat fragmentation, investigating the impact of LUC on HQ is of paramount importance for advancing the objectives of SDG15.
HQ is the ability of an ecosystem to provide suitable natural ecological conditions (Hillard et al., 2017; Weber et al., 2018). It is critical for maintaining stability in biodiversity within natural ecosystems and plays a significant role in enhancing human wellbeing (Riedler and Lang, 2018). The advancement of 3S technologies has facilitated the development of various ecosystem assessment models (Hall et al., 1997). Among these, the Maxent model (West et al., 2016), ARIES model (Dai et al., 2024), SoLVES model (Sherrouse et al., 2022), and the InVEST model (Zhang K. et al., 2024) have emerged as prominent tools widely utilized in the field. Notably, the InVEST model provides intuitive visual representations, thus addressing the limitations of previous ecosystem service assessments that often relied on abstract and less comprehensible textual descriptions (Lin et al., 2017; Sallustio et al., 2017). Moreover, this model is well-established and has been extensively applied in research conducted at various scales (Qin et al., 2024; Ren et al., 2022; Zheng et al., 2022), across diverse administrative units (Bai et al., 2019; Wang et al., 2023), and in biodiversity assessments (Gong et al., 2019; Li G. et al., 2024).
Climate change and LUC serve as the principal driving factors behind modifications in HQ, with LUC themselves being influenced by both climate dynamics and socio-economic development (Bian et al., 2024; Li X. et al., 2024). Among the latest generation of climate models, the sixth Coupled Model Intercomparison Project (CMIP6) represents the most recent advancements in predicting future climate scenarios (Brunner et al., 2020). This model primarily incorporates Shared SSPs and RCPs. In recent years, researchers have increasingly utilized SSPs-RCPs scenarios to investigate land-use prediction studies within the framework of projected climate change (Dong et al., 2018; Tian et al., 2022). Zhang X. et al (2024) developed a novel integrated framework by combining the SD-FLUS-InVEST models to simulate the dynamic evolution of ecosystem services under LUC in the Yellow River Basin across three scenarios: SSP1-1.9, SSP2-4.5, and SSP5-8.5. Lu et al. (2024) utilized the SD model to investigate the supply and demand relationships of six ecosystem services in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration under the SSP-RCP scenarios from 2018 to 2050, proposing corresponding management measures.
Land-use simulation encompasses two fundamental aspects: quantitative structure and spatial distribution. In predicting quantitative demand, SD is an enhanced top-down model (Wang et al., 2022), adeptly accounting for the comprehensive influences of both social and natural factors on LUC. Conversely, the PLUS model has become widely adopted for spatial distribution simulation, primarily due to its high accuracy and user-friendly interface (Liang et al., 2021). Given the inherent complexity of predicting land-use evolution, reliance on a single model is inadequate for a thorough assessment. Numerous studies have explored the impact of LUC under future development scenarios on HQ. However, several gaps remain in the research on HQ. First, the influence of climate factors on both LUC and HQ has often been neglected in the formulation of future development scenarios. Second, previous predictive simulations typically suffer from arbitrary and subjective decisions in the configuration of land-use demand shifts across multiple scenarios, thereby increasing the uncertainty of the projections. In contrast, the SD model offers a more robust approach by effectively capturing the nonlinear dynamic changes within complex systems and the interrelationships among their various components. Consequently, integrating the SD-PLUS model facilitates a more robust simulation of LUC, effectively capturing the interplay between social and natural factors across various prospective development scenarios.
The rapid economic development and accelerated urbanization of the YREB present significant challenges to the regional ecological environment. Despite robust economic growth, there remains a critical gap in research regarding land use quantity, structure, and spatial dynamics. This study addresses this gap by constructing a comprehensive assessment framework based on the latest SSP future development scenarios. The framework integrates SD–PLUS - HQ models to evaluate the spatiotemporal evolution of LUC quantity and their implications for HQ under varying development scenarios. The primary objectives of this research are as follows: 1) to utilize the SD-PLUS model to simulate the quantity, structure, and spatial distribution of land-use within the context of future development scenarios; 2) to couple the SSP-PLUS-HQ model to analyze the spatiotemporal evolution of HQ structure across different scenarios, thereby elucidating the characteristics of HQ evolution and the overall degradation processes; and 3) to examine the response of various LUT to changes in HQ and to identify the spatiotemporal clustering characteristics of HQ through hotspot analysis. The findings of this study will provide a scientific foundation for optimizing land-use structure and advancing ecological sustainability within the YREB.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Overview of the study area
The YREB is located at geographical coordinates 108°30′E to 122°15′E and 24°30′N to 35°45′N, and spans eastern, central and western China. This economic belt comprises 11 provinces and municipalities (Figure 1). The region has an annual precipitation of 1,067 mm and an annual temperature of 16°C. It covers an area of approximately 2,0523 million km2, accounting for 21.4% of China. In 2023, the population of the YREB is about 608 million, accounting for 42% of China. The region’s GDP is about 58.43 trillion-yuan, accounting for 46.7% of China’s. In addition, the YREB has more than 40% of China’s forest cover and about 20% of China’s water cover, positioning the region as an innovative demonstration zone for ecological conservation and restoration efforts.
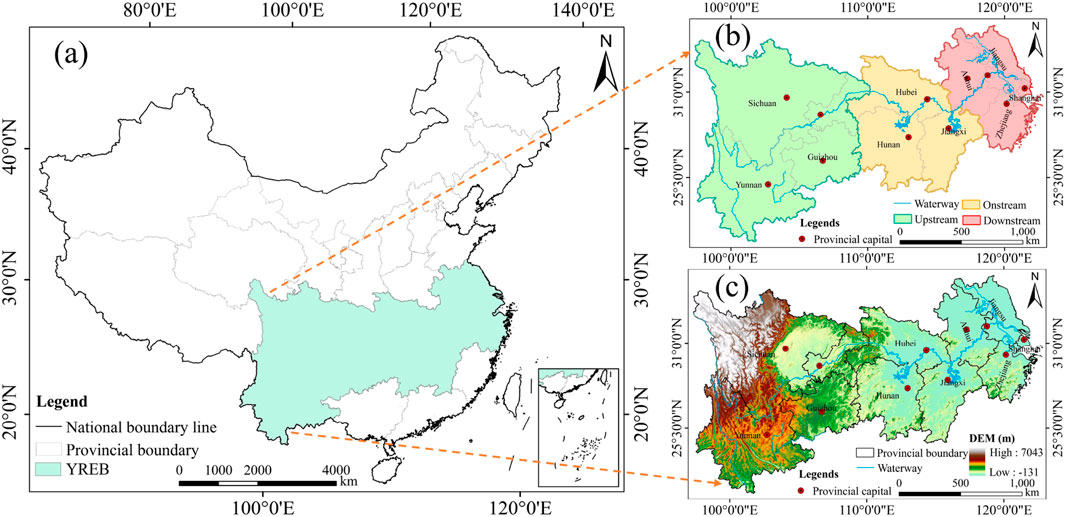
Figure 1. Location map of the YREB. (A) The location of the YREB in China. (B) Provincial capital cities of the YREB, (C) DEM of the YREB.
The YREB constitutes a vital element of China’s three principal development strategies and serves as a critical link in the framework of the “21st Century Maritime Silk Road” (Shi and Zhou, 2023). Nevertheless, the region is confronted with a myriad of severe environmental challenges resulting from sustained high-intensity development and urban expansion (Zhang L. et al., 2023). These challenges manifest as heightened environmental pollution, ecological degradation, water and air quality deterioration, soil erosion, and a significant decline in ecosystem functionality (Chen et al., 2024; Liu et al., 2022). As the longest and most expansive economic belt in China, the YREB, characterized by its unique geographical location, abundant natural resources, and favorable ecological conditions, plays an indispensable role in the country’s ecological security framework. Consequently, the preservation of a robust ecological environment within the YREB is imperative for fostering global ecological security.
2.2 Research methodology
2.2.1 Data sources and preprocessing
The land-use data we used comes from the Wuhan University team (Yang Jie and Huang, 2021), which constructed spatiotemporal features based on Landsat data obtained from the Google Earth Engine (GEE) platform and generated land use classification results by combining with the Random Forest Classifier. To improve the spatiotemporal consistency of the classified data (CLCD), the team also proposed a post-processing method that combines spatiotemporal filtering with logical inference. The dataset has an overall classification accuracy of 80% and is specific to the Chinese region, so it was chosen as the base data for analysis in this study. The digital elevation model (DEM), slope, precipitation, temperature, population density and nighttime lighting data used in this study were obtained from the Resource and Environment Data Centre of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (http://www.resdc.cn/); and the data on roads, railways, rivers, lakes and urban land were obtained from the National Geographic Information Resource Catalogue Service System (https://www. webmap.cn). Details of the specific data are shown in Table 1.
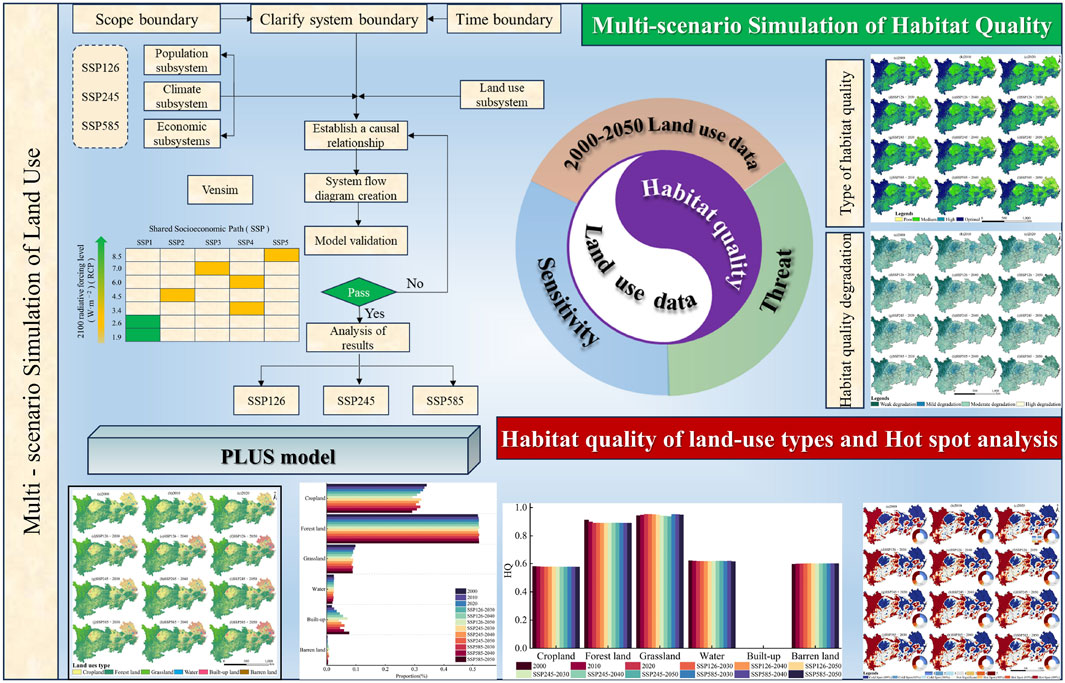
2.2.2 Research framework
The research framework consists of four key components (Figure 2). Firstly, multiple scenario simulation parameters are established based on socioeconomic and climate change projection data across various SSP-RCP scenarios. The SD model is employed to simulate land-use and cover demands for each scenario. Secondly, the PLUS model is applied to analyze the spatiotemporal distribution of land-use across three distinct scenarios. Thirdly, the InVEST model evaluates the spatiotemporal variations in regional HQ, elucidating the dynamics of HQ and its degradation process, while also examining the influence of different LUT on HQ. Finally, hotspot analysis techniques are utilized to explore the spatial clustering patterns of HQ.
2.2.3 Invest model
HQ is an index of an ecosystem’s potential to provide species with the ability to survive and reproduce. The HQ module quantitatively assesses the effects of different LUT on habitat suitability for both flora and fauna, while also evaluating the intensity of threats posed by various habitat stressors. This comprehensive approach enables the simulation of the spatial distribution of HQ. The specific formula employed in this analysis is as follows (Equation 1):
where Qiy denotes the HQ index for grid cell i within LUT y; Hiy represents the habitat suitability for grid cell i within the same LUT; and Diy indicates the level of HD for grid cell i in LUT y. The parameter k signifies the semi-saturation parameter, while z refers to the model’s default constant. This study establishes the year 2020 as the baseline for evaluating HQ. Given the specific conditions of the YREB, cropland, built-up land, and barren land are identified as the primary factors threatening HQ, as these LUT are significantly influenced by human activities. The values for the parameters are determined based on the recommended reference values provided in the InVEST model user manual and are further corroborated by findings from relevant literature (Ji et al., 2023; Qin et al., 2024; Zheng et al., 2023). See annex for details.
2.2.4 PLUS model
The PLUS model is an advanced simulation tool designed for LUC, grounded in the principles of cellular automata (CA) (Liang et al., 2021). This model innovatively integrates a novel Land Expansion Analysis Strategy (LEAS) with a variety of random patch seeds (CARS) within the CA framework, with the objective of predicting and simulating the generation and evolution of diverse land type patches. Specifically, based on the land-use in the two historical periods, a map of the distribution of land-use development potential is produced through historical land-use expansion trends and influencing factors, and finally land-use projections for future years are obtained. See annex for details. The study used land-use data from 2000 to 2020, coupled with 12 driving factors, to accurately simulate the LUT for the year 2020. Comparison of the simulated data with actual land-use data for 2020 showed a Kappa coefficient of 0.841 and a FoM of 0.184, indicating a high degree of prediction accuracy and validating the effectiveness of the predictive simulation methodology.
2.2.5 SD coupled SSP-RCP multi-scenario
To examine the nonlinear relationship between socio-economic factors and LUC, we employed a SD model for land-use scenario simulation. This model comprises four primary components: the land-use, the population, the climate, and the economy. It has been extensively utilized in research related to LUC simulations across various future scenarios (Qiu and Shi, 2015), See annex for details.
An important distinction between scenario analysis and predictive models is that scenario analysis considers the inherent uncertainties of social and ecological systems from the outset, incorporating potential future states into a transparent problem-solving framework. In simulating possible changes in ecological systems, scenario analysis showcases unique advantages that can help decision-makers develop strategies more effectively. Currently, scenarios formed by combining SSPs and RCPs are applicable to ecological system analysis at different scales and across multiple fields, and can also be used for future land-use predictions and land cover modeling studies.
The scenarios in CMIP6 are combinations of various SSPs and RCPs, emphasizing the driving role of different socioeconomic development models in climate change and revealing the potential impacts of future socioeconomic development. To address future changes in climate and socioeconomic conditions, relying on a single future development scenario is no longer sufficient for current research needs. We selected three development scenarios from the SSP-RCP framework: SSP126, SSP245, and SSP585.
The SSP126 scenario is a combination of SSP1 and RCP1.9, representing sustainable socioeconomic development under low levels of greenhouse gas emissions. In this scenario, land is strictly regulated, and grassland and forest land remain intact, constituting the current lowest radiative forcing sustainable development scenario. The SSP245 scenario combines SSP2 with RCP4.5, representing a medium radiative forcing scenario, where land regulation is relatively strict and socioeconomic development continues in the current trajectory. Lastly, SSP585 is a combination of SSP5 and RCP8.5, representing a high radiative forcing scenario with moderate land regulation, reliance on substantial fossil fuel resources, and resulting in high levels of greenhouse gas emissions, thereby driving rapid socioeconomic development.
2.2.6 Hotspot analysis
HQ hotspots are defined as regions within a designated area that exhibit a relatively high capacity for HQ, whereas cold spots are characterized by a diminished level of HQ. This study employs the Getis-Ord Gi* module within ArcGIS software to conduct a comprehensive hotspot analysis of HQ (Equation 2). This module effectively delineates the spatial distribution and aggregation characteristics of areas with elevated HQ (hotspots) and those with reduced HQ (cold spots) (Wu et al., 2022; Zhang X. et al., 2023).
where Gi* represents the aggregation index for raster cell i; ai denotes the attribute value associated with raster cell i; Qij refers to the weight matrix; n signifies the total number of units; and aˉ represents the mean value of HQ across all pixels.
3 Results
3.1 Spatiotemporal evolution characteristics of land-use
3.1.1 Spatial change of LUT
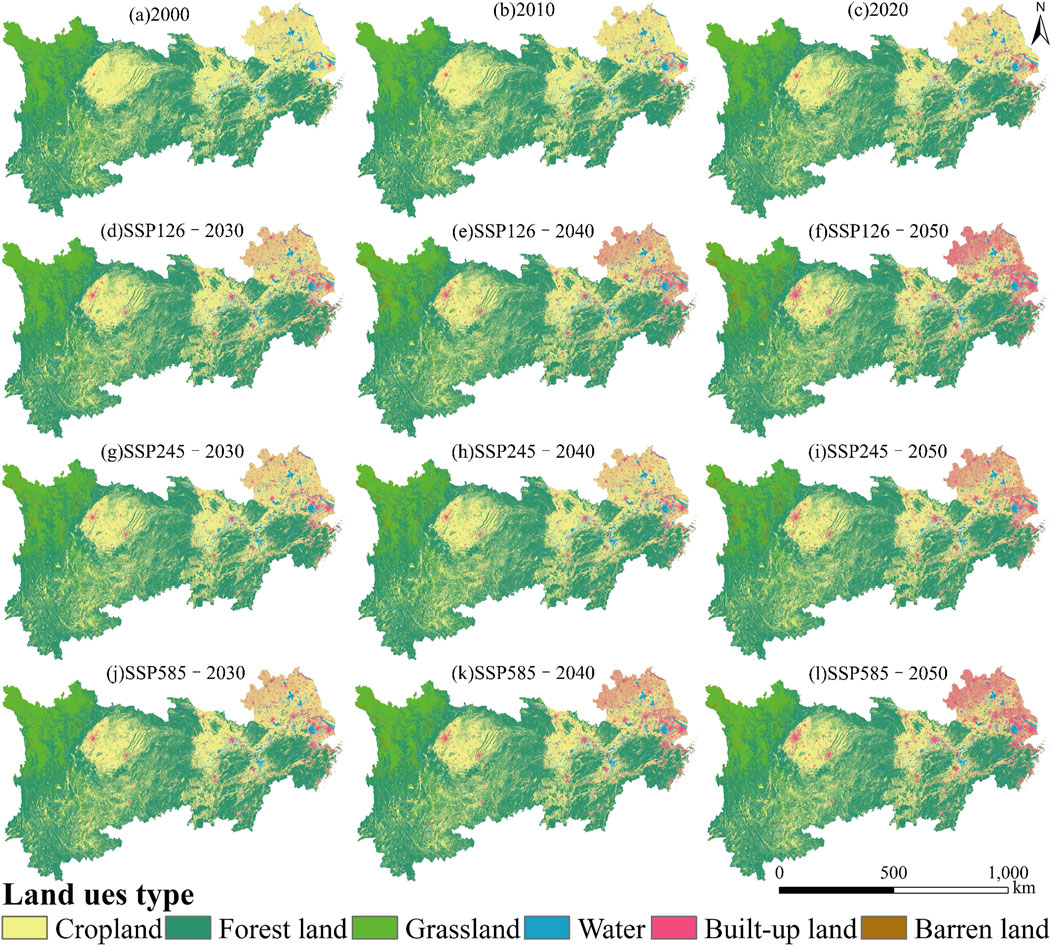
Between 2000 and 2020, the spatial distribution of land-use demonstrated a predominant presence of cropland, forest land, and grassland. In particular, the eastern region was characterized primarily by cropland, whereas the northwest was largely covered by grassland. The central and southern regions were predominantly composed of forest land. The eastern area, notably situated in the lower YREB plain, exhibited significant expanses of cropland. Conversely, the northwest remained dominated by grassland, while the central and southern areas were primarily characterized by forest land coverage. Water was predominantly located in the eastern region, and built-up land exhibited a radial distribution around the urban centers within the YREB, with a marked concentration in the east (Figure 3).
Under the three scenarios, the spatial characteristics of land-use projected from 2030 to 2050 remain largely consistent (Figure 3). Notably, the land-use distribution in 2030 is expected to be similar to that in 2020. By 2040, the area designated as built-up land in the east is anticipated to expand across all development pathways, while the west and centre will primarily comprise forest land and grassland systems. In 2050, built-up land in the east is projected to achieve a dominant position, continuing its outward expansion, with a discernible radial diffusion trend of built-up land also emerging in the centre. It is noteworthy that the rate of expansion of built-up land is significantly higher in the SSP126 and SSP585 compared to the SSP245.
3.1.2 Regional land-use structure change
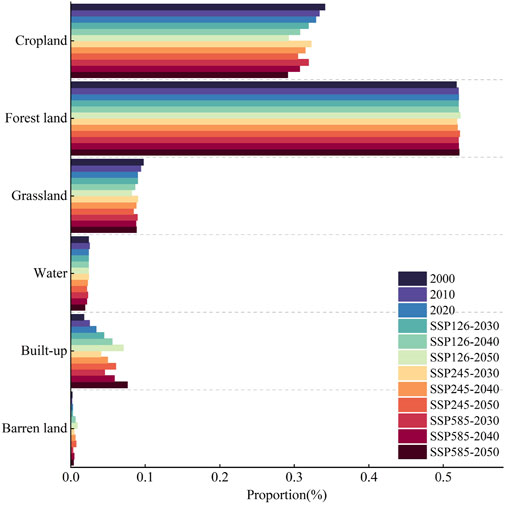
From 2000 to 2020, the predominant LUT in the YREB were forest land, which comprised an average of 51.96%, and cropland, accounting for an average of 33.46% (Figure 4). Grassland constituted an average of 9.38%. In contrast, water (average proportion of 2.43%) and built-up land (average proportion of 2.56%) occupied relatively minor areas, while barren land represented the smallest fraction, averaging 0.21%. Notably, the areas designated as cropland and grassland experienced continuous declines, with proportion changes of −1.21% and −0.78%, respectively. Conversely, forest land and built-up land exhibited consistent growth, with proportion changes of 0.31% and 1.63%, respectively. Furthermore, both water (proportion change of 0.01%) and barren land (proportion change of 0.04%) showed a dynamic increase.
This study examines the land-use structure under three scenarios, revealing a continuity with patterns observed between 2000 and 2020 (Figure 4). In the SSP126 scenario, both 2030 and 2050 demonstrate significant reductions in cropland (with a proportion change of −2.66%) and grassland (with a proportion change of −0.81%). Conversely, built-up land experiences a notable increase (with a proportion change of 2.59%). Furthermore, there are slight increases in forest land (with a proportion change of 0.25%), water (with a proportion change of 0.01%), and barren land (with a proportion change of 0.62%). In the SSP245 scenario for the same years, cropland (proportion change of −1.80%), grassland (proportion change of −0.60%), and water (proportion change of −0.27%) continue their downward trend. In contrast, forest land (proportion change of 0.38%), built-up land (proportion change of 2.01%), and barren land (proportion change of 0.27%) exhibit ongoing growth, with built-up land reflecting the most pronounced increase. Under the SSP585 scenario, the years 2030 and 2050 reveal the most significant changes in cropland (proportion change of −2.77%) and built-up land (proportion change of 3.10%). Additionally, grassland (proportion change of −0.14%) and water (proportion change of −0.38%) show declines, while forest land (proportion change of 0.10%) and barren land (proportion change of 0.09%) demonstrate slight increases.
3.1.3 Transfer of LUT
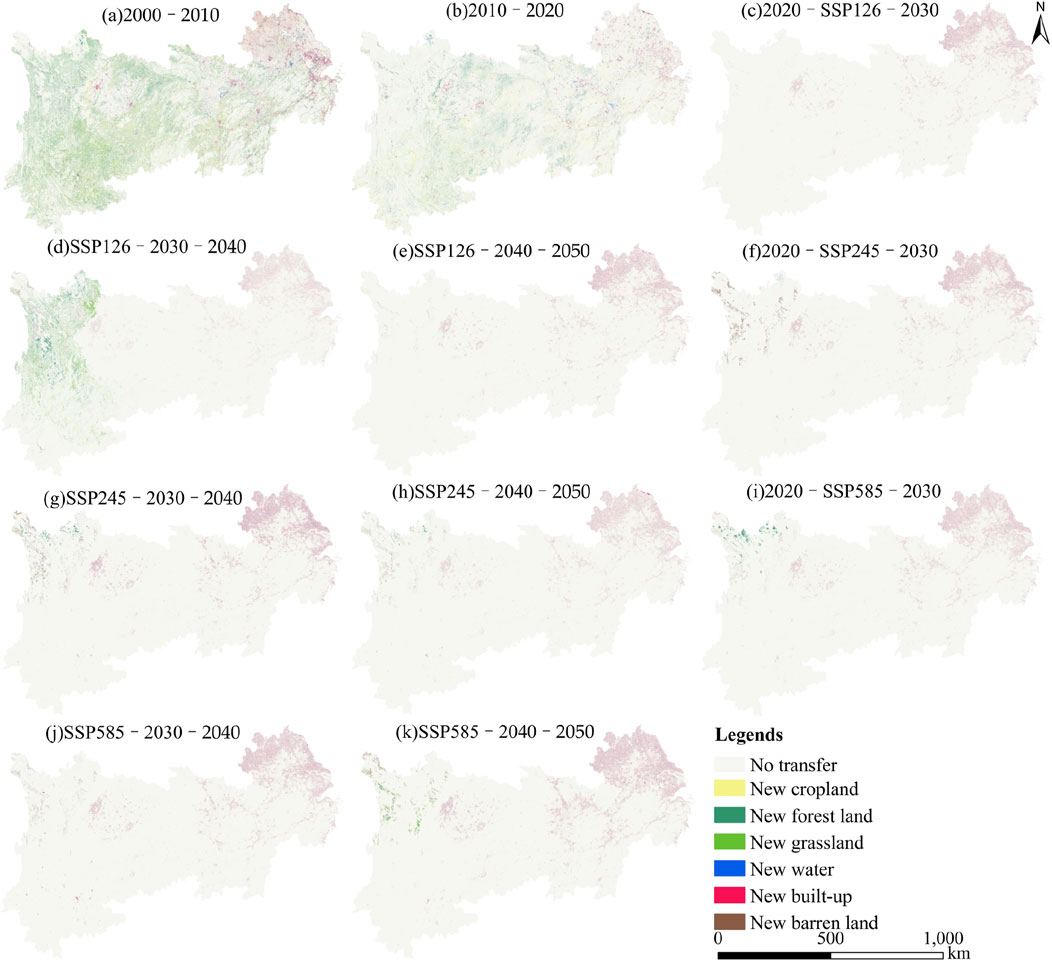
To improve the understanding of the relationships between different LUC, a quantitative assessment was conducted to analysis the spatial distribution patterns of land-use transitions under three scenarios from 2000 to 2050 (Figure 5). The specific transition periods are categorized as follows: 2000–2010, 2010–2020, 2020–2030, 2030–2040, and 2040–2050. This analysis elucidates the transition characteristics of different LUT, thereby revealing the patterns of land-use evolution within the YREB. In terms of spatial distribution, the characteristics of land-use transitions from 2000 to 2010 were marked by a predominant increase in built-up land in the east, accompanied by an expansion of forest land and grassland in the south. This transition was primarily driven by the conversion of cropland, forest land, and grassland. In the subsequent period from 2010 to 2020, built-up land in the east continued to dominate, while the distribution of forest land and grassland systems became increasingly dispersed. From 2020 to 2050, as indicated by the scenarios SSP126, SSP245, and SSP585, land-use transitions were characterized by a further increase in built-up land in the east, with only minor changes observed in other land types. Notably, during the period from 2030 (SSP126) to 2040 (SSP126), there was not only a significant increase in built-up land in the east but also substantial expansions of grassland and forest land in the west.
From 2000 to 2010, the cropland transferred to forest land was approximately equal to the forest land transferred back to cropland. In contrast, the cropland transferred to built-up land significantly exceeded the built-up land transferred back to cropland. Furthermore, the grassland transferred to forest land was greater than the forest land transferred to grassland, and the water transferred to cropland also surpassed the cropland transferred to water. The primary change in built-up land during this period was attributed to conversions from other land-uses, whereas barren land exhibited only minor fluctuations. The characteristics of land-use transitions from 2000 to 2010 were consistent with the overarching transition patterns of the period; however, the transition areas among cropland, forest land, grassland, and water remained relatively small, while the built-up land conversion showed a notable increase. Looking ahead to the period from 2020 to 2030 (for scenarios SSP126, SSP245, and SSP585), cropland, forest land, grassland, and barren land were primarily transferred to built-up land, with other land types remaining largely stable (Figure 5). Similarly, during the subsequent periods from 2030 to 2040 and from 2040 to 2050 under the same scenarios, the patterns of land-use transition continued to be fundamentally consistent with those observed from 2020 to 2030, reflecting a predominant trend of converting other land types into built-up land.
3.2 Spatiotemporal evolution characteristics of HQ
3.2.1 Distribution pattern evolution of HQ
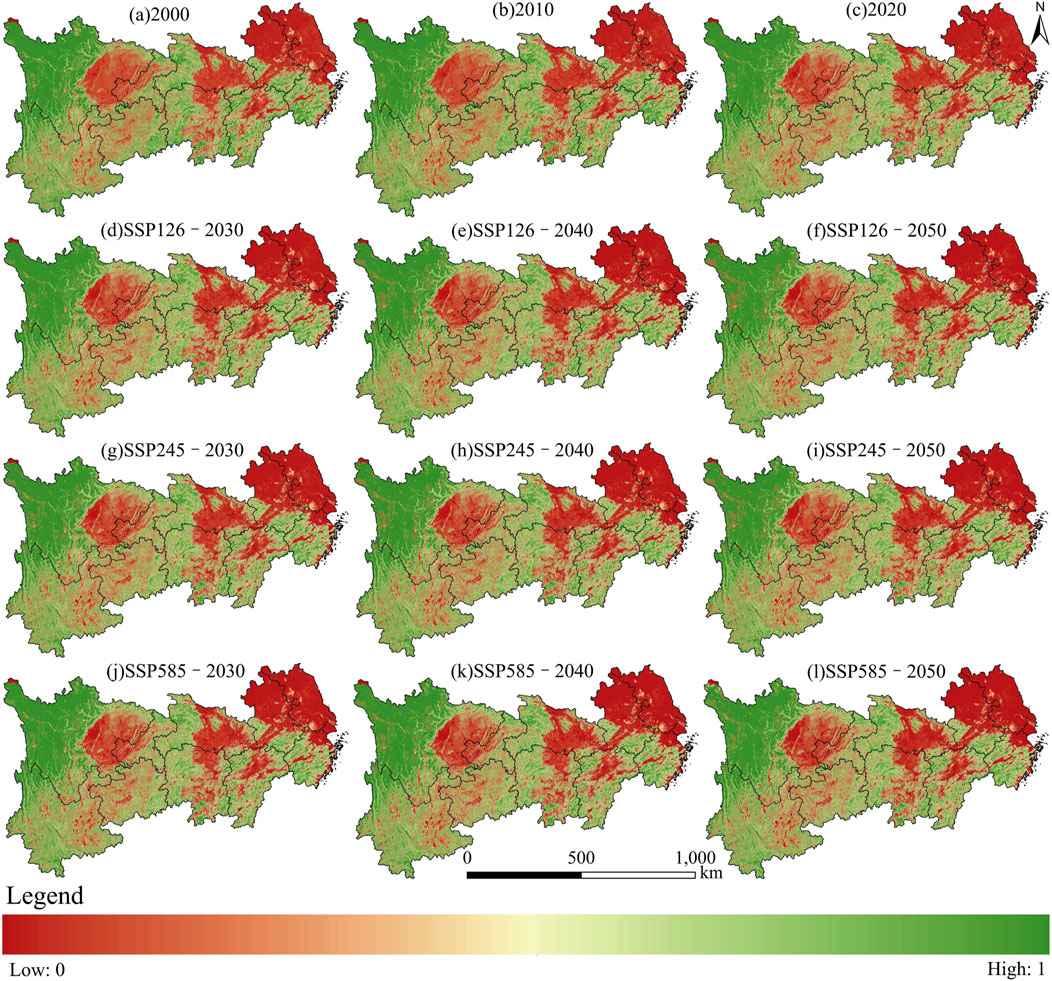
The multi-scenario analysis (SSP126, SSP245, SSP585) conducted from 2000 to 2050 reveals a spatial distribution of HQ within the YREB that increases from the northeast to the northwest (Figure 6). Specifically, the provinces of Jiangsu and Anhui exhibit lower HQ, while Hubei, Hunan, and Jiangxi display moderately low levels. In contrast, the surrounding regions generally present relatively high HQ. Similarly, the eastern region of Sichuan and the Chongqing area are characterized by lower HQ, whereas western Sichuan demonstrates higher quality, with Yunnan and Guizhou reflecting intermediate levels.
Overall, the analysis indicates a persistent downward trend in HQ from 2000 to 2050 across all scenarios. Notably, HQ was highest in 2000, with a mean value of 0.770, which subsequently declined to 0.752 by 2020, reflecting a decrease of 2.34% over this period. From 2030 to 2050, the mean HQ continues to decline across all scenarios, with the lowest mean value recorded in 2025 (SSP585) at 0.726. Specifically, during the period from 2030 to 2050, HQ is projected to decrease by 2.28% under SSP126, by 1.74% under SSP245, and by 2.55% under SSP585.
3.2.2 Structural changes of HQ
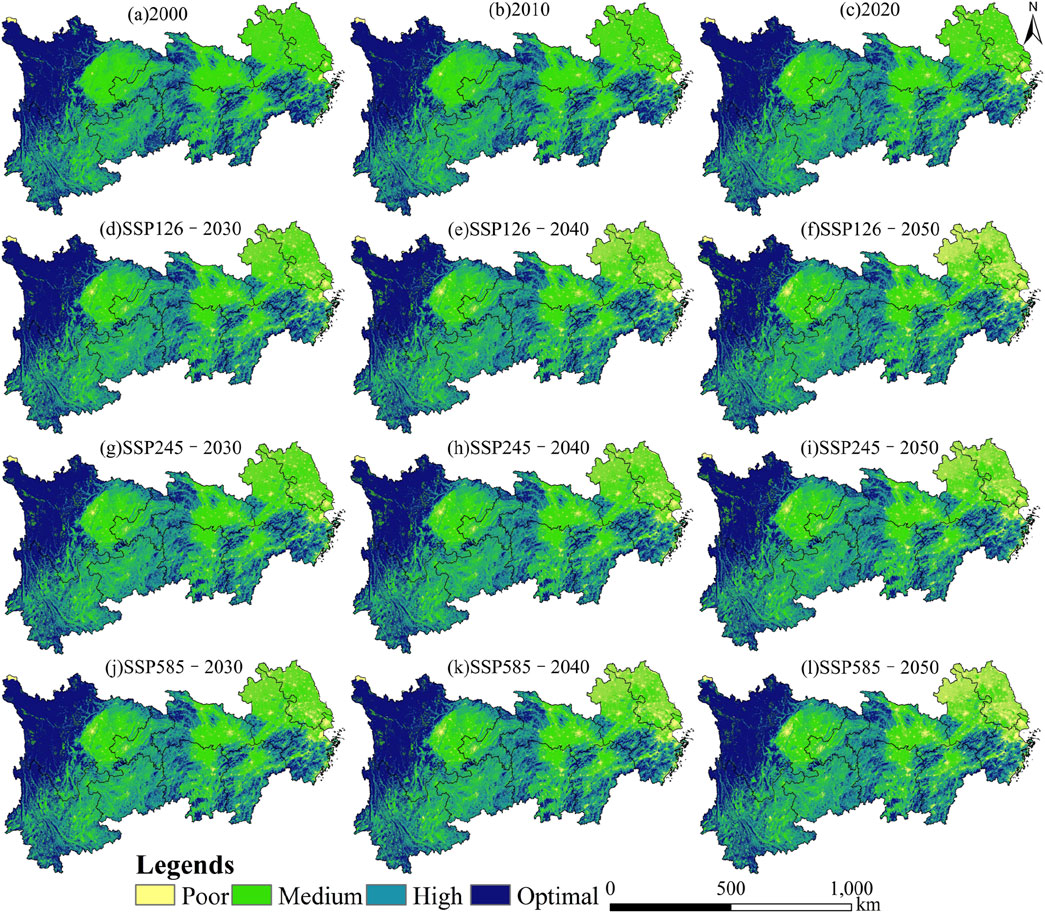
From 2000 to 2050, the HQ classification structure of the YREB shows a spatial distribution trend that gradually improves from east-west (Figure 7). Specifically, from 2000 to 2020, the HQ in the eastern region was poor (average proportion 2.896%), the central region had medium HQ (average proportion 36.389%), the southern region had relatively high HQ (average proportion 33.778%), and the western region exhibited the optimal HQ (average proportion 26.937%).
During this period, the changes in HQ classifications manifested as a continuous increase in areas of poor HQ (proportion 1.624%) and high HQ (proportion 1.349%), while the medium HQ (proportion −1.21%) and optimal HQ (proportion −1.762%) continued to decrease. For the forecast period from 2030 to 2050, the HQ structure under the three development pathways (SSP126, SSP245, SSP585) remains largely consistent with that from 2000 to 2020.
In detail, during the years 2030 and 2050 under SSP126, the proportion of poor HQ (proportion 2.584%) continues to increase, the proportion of high HQ (proportion 0.077%) slightly rises, while the moderate HQ (proportion −2.041%) and optimal HQ (proportion −0.62%) continue to decline. During the periods 2030–2050 under both SSP245 and SSP585, the trends in HQ structural changes are consistent with those observed under SSP126. Among them, the reduction in medium HQ during the SSP245 period (proportion −1.804%) is the smallest, while the changes in poor HQ (proportion 3.087%) and medium HQ (proportion −3.068%) during the SSP585 period are the most pronounced.
3.2.3 Evolutionary characteristics of HD
In the multi-scenario analysis conducted from 2000 to 2050, the overarching trend of HD reveals a pronounced gradient, intensifying from west to east (Figure 8). Specifically, areas characterized by weak HD are predominantly situated in the northwestern section of the YREB, while the eastern and central regions of Sichuan demonstrate relatively weak HD. The eastern region exhibits moderate HD, whereas the southern and northern regions manifest higher degrees of HD, with these areas displaying an interwoven distribution pattern relative to those experiencing moderate HD.
Regarding the average characteristics of HD over the period from 2000 to 2050, a consistent increase in HD levels is observed between 2000 and 2020, culminating in a total rise of 5.54%. Across the various scenarios assessed, the most significant HD is projected under SSP126 (2030), accounting for 25.75% of the total area affected, closely followed by SSP585 (2030) at 25.57%. Conversely, the weak HD is anticipated under SSP126 (2050), representing 24.99%.
In terms of HD categories from 2000 to 2020, moderate HD emerges as the predominant classification, comprising 34.91% of the YREB. This is succeeded by weak HD at 23.25%, while the proportions of high (21.59%) and mild HD (20.25%) are notably smaller. During this interval, the area classified as experiencing high HD has steadily increased, now representing 6.02%, whereas the areas categorized as weak, mild, and moderate HD have seen respective reductions of −2.12%, −1.97%, and −1.94%.
The structural characteristics of HD projected for the period from 2030 to 2050 across multiple scenarios demonstrate a substantial degree of spatial consistency with those identified during the years 2000–2020, primarily indicating a prevalence of moderate HD. In both the SSP126 and SSP585 scenarios for 2030–2050, there is an observed increase in the proportions of weak and high HD, while the proportions of mild and moderate HD exhibit a corresponding decrease. Conversely, in the SSP245 scenario for the same period, the proportion of weak HD is found to increase, whereas the proportions of mild, moderate, and high HD decline. Notably, during the SSP126 phase, the most significant increase in weak HD is recorded, with a change of 1.90%, while moderate HD experiences the most pronounced decrease, amounting to −2.53%. Similarly, in the SSP585 phase, the most considerable reduction in mild HD is documented, reflecting a change of −1.16%.
3.3 Evolution of HQ with LUC
3.3.1 Impact of different LUT on HQ
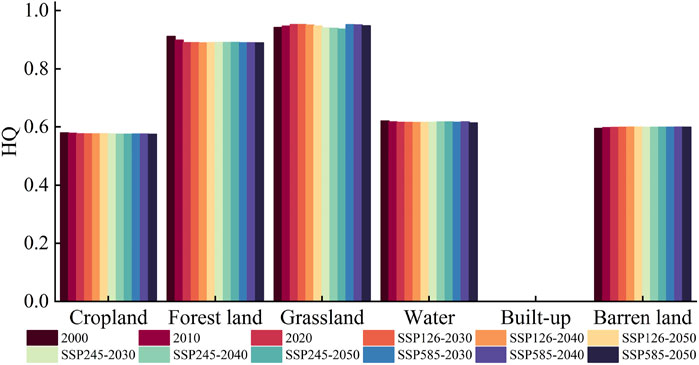
To elucidate the impact of various LUT on HQ changes, we conducted a quantitative assessment of HQ associated with each land-use category (Figure 9). From 2000 to 2050, the characteristics of HQ changes across different LUT exhibited a high degree of consistency. The overall ranking of HQ was established as follows: grassland > forest land > water > barren land > cropland > built-up land. The average HQ values for each LUT were: cropland (0.576), forest land (0.893), grassland (0.947), water (0.617), built-up land (0), and barren land (0.599).
During this timeframe, HQ for cropland, forest land, and water was observed to be highest in 2000, whereas HQ for grasslands peaked in 2020. By 2050 (SSP126), a notable increase in HQ for barren land was documented. Throughout the period from 2030 to 2050, the HQ of cropland and forest land remained stable, with a balanced transition observed between the two categories. Additionally, in the 2030–2050 period (SSP585), both grassland and forest land demonstrated the highest levels of HQ.
3.3.2 Transfer analysis of HQ
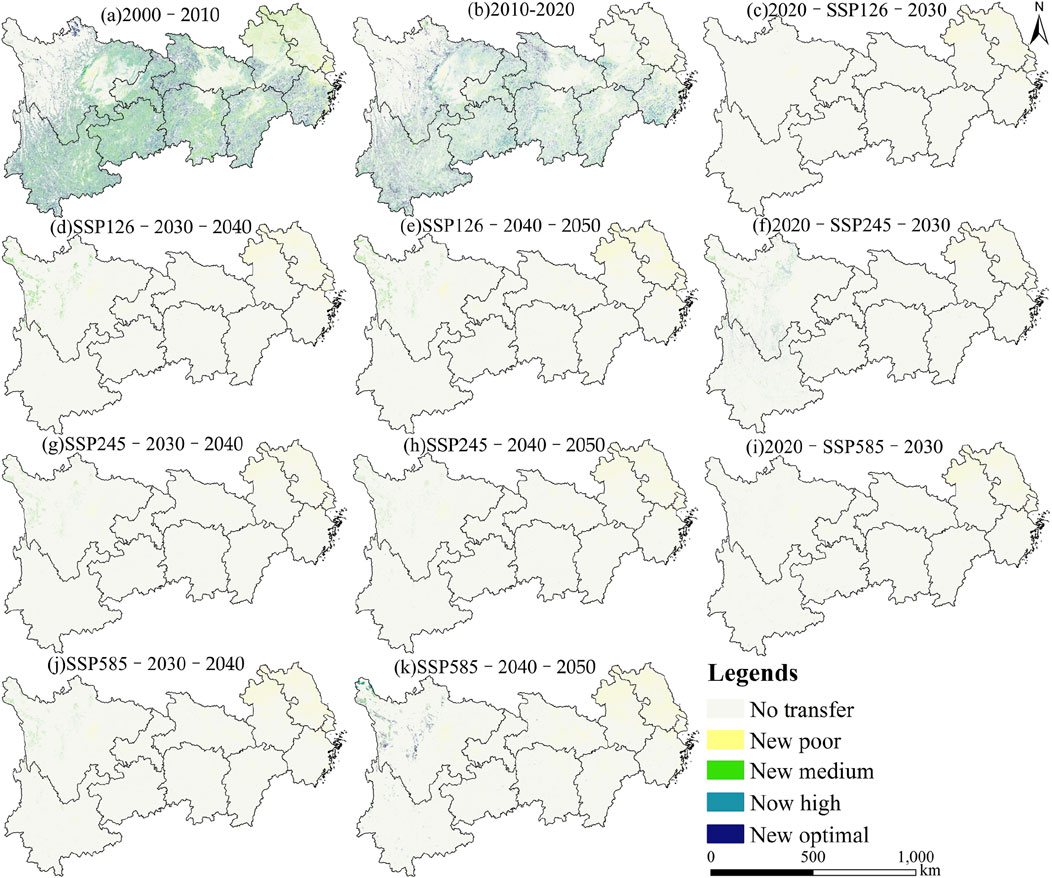
To elucidate the relationships between changes in various HQ types, we undertook a quantitative assessment of the spatial distribution characteristics associated with HQ type transitions from 2000 to 2050 across multiple scenarios (Figure 10). The temporal divisions for these transitions were specifically aligned with alterations in land-use structures. By analyzing the transition characteristics of different HQ types, we identified the evolving patterns of HQ within the YREB.
Regarding spatial distribution, the period from 2000 to 2010 revealed a notable increase in areas characterized by weak HQ in the eastern region. Simultaneously, there was an expansion in the areas classified as having medium and high HQ in the southern region, primarily driven by transitions toward medium HQ. The transition characteristics observed from 2010 to 2020 were largely consistent with those of the preceding decade, both reflecting a trend of higher HQ levels transitioning to lower ones. In the subsequent period from 2020 to 2050, the poor HQ in the eastern region continued to expand, while the medium and high HQ in the western region showed slight increases; other regions remained relatively stable.
From 2000 to 2010, the area exhibiting a transition from poor to medium HQ was significantly smaller than that reflecting the transition from medium to poor HQ. Furthermore, the areas involved in the transition from high to medium HQ were approximately equivalent to those associated with the transition from medium to high HQ. In contrast, the area corresponding to the transition from optimal to high HQ was substantially larger than that for the reverse transition from high to optimal. In the subsequent period from 2010 to 2020, the area transitioning from high to medium HQ remained consistent with that transitioning from medium to high HQ, while the area for the transition from optimal to high HQ continued to increase. During the period from 2020 to 2030, the predominant transition observed was from medium to poor HQ, followed closely by the transition from optimal to medium HQ. In the periods from 2030 to 2040 and from 2040 to 2050, the transition characteristics of HQ types closely mirrored those observed from 2020 to 2030, with the most significant transition occurring from medium to poor HQ between 2030 and 2040.
3.4 Hotspot analysis of HQ
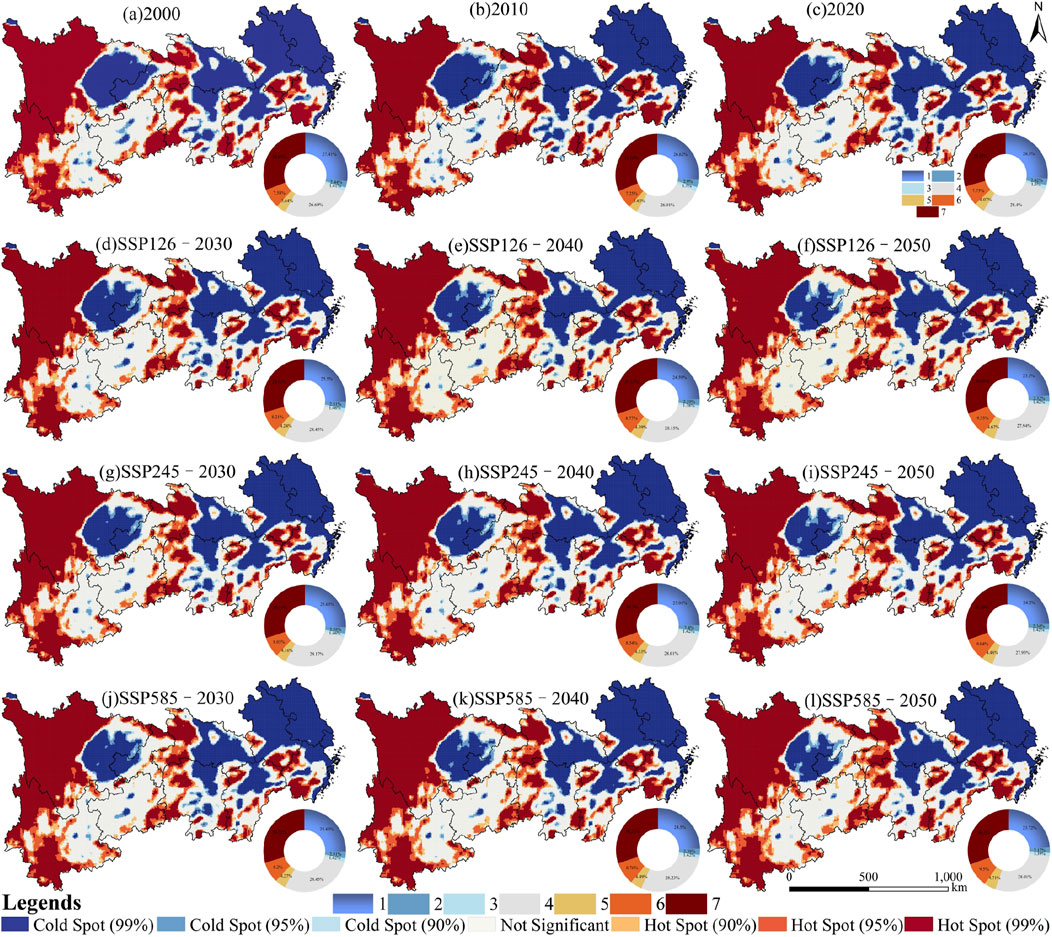
To elucidate the spatiotemporal distribution characteristics of HQ heterogeneity, we employed hotspot analysis to examine the spatiotemporal variations in HQ across multiple scenarios from 2000 to 2050 (Figure 11). The analysis reveals a distinct distribution pattern, characterized by the presence of cold spots in the east, areas of negligible significance in the centre, and hot spots in the west. Furthermore, the south exhibits an alternating distribution of cold and hot spots, which is characterized by small, patchy dispersal patterns.
Specifically, in the eastern regions of Sichuan and Chongqing, the extent of cold spots shows a gradual decline over time. Projections indicate that by 2050 (SSP126, SSP245, SSP585), the area occupied by cold spots in this region will reach its minimum, reflecting a trend towards increasing fragmentation. Between 2000 and 2050, the distribution of hotspots (>40%) constitutes a primary characteristic of the YREB, followed by cold spots (>30%), while the proportion of insignificant areas (<30%) remains the lowest. As time progresses, the area classified as hotspots (99%) exhibits a gradual decline, paralleled by a decreasing trend in cold spots (99%). Conversely, the insignificant zones show a consistent increase. Notably, under the SSP585 scenario for the period from 2030 to 2050, the hotspots (99%) begin to increase, while the cold spots (99%) continue to decline, and the insignificant zones further expands. This dynamic indicates that both cold and hotspot regions primarily undergo outward expansion or contraction based on their existing spatial distributions.
4 Discussion
4.1 Impact of LUC on HQ
The spatial distribution of HQ indices exhibits a high degree of correspondence with the spatial distribution of LUT (Wu et al., 2022). In the context of three distinct climatic scenarios projected for the future YREB, substantial alterations in HQ are anticipated, with the patterns of these changes closely associated with land-use transformations. Therefore, the accuracy of future HQ assessments will be contingent upon the precision of land-use simulations. This study demonstrates a high degree of simulation accuracy, with the predictive model developed being extensively applied in various contexts, including urban agglomerations (Chen and Ning, 2024) and watersheds (Ji et al., 2023). The model has consistently exhibited superior simulation precision across these diverse regions. Furthermore, there has been an increase in regions experiencing HD, which coincides with the expansion of urban development, particularly in the economically advanced eastern areas (Pan et al., 2023). This expansion of built-up land has led to a significant reduction in cropland, which is identified as the primary driver of declining HQ. The HD is predominantly concentrated in regions characterized by high levels of urbanization and dense population clusters. This phenomenon is similarly evident within the Yellow River Basin (Ji et al., 2023).
As a cornerstone of high-quality economic development in China, the YREB imposes significant pressures on the regional ecological environment throughout the processes of comprehensive urbanization-industrialization (Chen et al., 2021; Ding et al., 2021). Within this context, land types exhibiting high habitat suitability—such as forest land, grassland, and water are increasingly being transformed into poor habitat suitability types, particularly built-up land, which results in a marked decline in HQ. Furthermore, the total population within the YREB constitutes over 40% of China’s, while its geographical area represents only 21.4% of the country’s total landmass. Accelerated urbanization has driven a substantial influx of people into urban centers, intensifying the demand for built-up land in both major urban districts and their surrounding counties (Chen et al., 2023). This phenomenon has not only facilitated the unplanned expansion of built-up land, encroaching upon cropland ecological spaces—such as forest land, grassland, and water—but has also led to severe disturbances and threats to the surrounding ecological environment, thereby contributing to the HD. This result aligns with the decline in ecosystem service functions associated with anticipated urban land expansion in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration. Notably, it indicates that the rate of HD is occurring at an accelerated pace (Yang et al., 2024). Notably, regions of high HQ are predominantly located in the upstream areas of the YREB, particularly in Sichuan and Yunnan provinces. These areas, characterized by relatively high altitudes and abundant forest land and grassland resources, are less vulnerable to development pressures, resulting in comparatively minimal disturbances to their HQ (Sun et al., 2023). Our research findings are strongly corroborated by the analysis demonstrating that HQ in the upstream regions of the Yangtze River Basin is minimally affected by human activities. In contrast, the Sichuan Basin and western areas are identified as critical zones for HQ restoration (Bian et al., 2024).
In the future development scenarios, SSP126 and SSP245 are generally regarded as more desirable pathways. The SSP126 promotes a sustainable development model that prioritizes stringent land-use controls to safeguard the ecological environment. In 2020–2050, this scenario anticipates a substantial reduction in cropland and grassland, coupled with a significant expansion of built-up land. Forest land and water, on the other hand, show moderate growth, particularly in the eastern regions, though HQ in these areas deteriorates. Conversely, the western regions experience substantial restoration of grassland and forest land from 2030 to 2040, facilitated by the effective implementation of sustainable development policies. In contrast, the SSP245 represents a more gradual transition towards sustainability, with slower economic growth and moderate levels of population growth and urbanization. Despite these trends, habitat quality continues to decline. The scenario is characterized by pronounced LUC, particularly the expansion of built-up land, which results in the reduction of cropland and forest-grassland. Furthermore, the increase in ecological land in the western regions is limited, exacerbating the HD in these areas. The most extreme of the SSP585, envisions rapid economic growth and energy-intensive development, which drive accelerated urban expansion and a dramatic loss of ecological land. This results in significant encroachment on cropland and a considerable reduction in grassland and water, leading to a severe decline in HQ. Overall, the SSP126 appears to offer the most favorable pathway for sustainable development. By employing effective land-use management strategies and region-specific policies, it can mitigate the HD. In contrast, both the SSP245 and SSP585 pose greater risks. The SSP245 scenario may exacerbate ecological degradation due to the unchecked expansion of built-up land, while the SSP585 highlights the environmental costs of an over-reliance on economic growth. Consequently, ensuring ecological sustainability while promoting economic development is crucial for achieving a balanced and harmonious future, where both ecological integrity and economic prosperity are prioritized.
4.2 Policy implications
The transformation of land-use patterns is driving significant global habitat loss (Li X. et al., 2024). In the downstream region of the YREB, these patterns are undergoing profound changes, particularly due to the acceleration of urbanization and the expansion of infrastructure. This shift has led to increasing habitat loss and a decline in biodiversity, which have become critical challenges to the ecological environment (Guan et al., 2018; Yu, 2021). The effects of different land-use patterns on the environment are variable; however, the expansion of built-up land is particularly damaging, often resulting in the encroachment upon natural ecosystems such as forest land, grassland, and water, thereby exacerbating ecosystem degradation. Under projected future development scenarios, HD is expected to intensify. Consequently, addressing the adverse effects of LUC on HQ is essential for improving the ecological environment. This necessitates a careful balance between economic development and ecological preservation, particularly through the enhanced delineation and enforcement of ecological redlines to safeguard areas of high HQ and prevent overdevelopment.
To mitigate the ecological challenges arising from LUC, policies should prioritize ecological restoration and the transformation of agricultural practices. In regions where LUC are especially pronounced, a combination of natural restoration and controlled intervention can be employed to enhance ecosystem functions, restore vegetation cover, and improve biodiversity. Simultaneously, agricultural development models should shift toward more sustainable, eco-friendly practices such as crop rotation, fallowing, and other techniques that promote the long-term health of the ecological environment. The formulation of differentiated protection and development strategies based on the HQ of specific areas is critical to ensuring the rational use of resources and maintaining ecological stability over time.
Within the context of ecological protection policies in the YREB, it is imperative to establish an integrated ecological management framework that emphasizes enhanced cross-regional policy coordination. By scientifically delineating ecological redlines, improving the management of ecological function zones, and promoting targeted ecological engineering initiatives, the stability of ecosystems and biodiversity can be better safeguarded. Additionally, the land-use structure should be optimized to ensure that the functional roles of different land types are appropriately positioned, facilitating a mutually beneficial outcome for both green development and economic growth. Governments must foster cooperation and coordination to navigate the tension between socio-economic development and ecological protection, advance the construction of an ecological civilization, and ultimately achieve the harmonious and sustainable development of the economy, society, and ecology in the region.
4.3 Limitations and uncertainties
This study integrates a top-down SD model with a bottom-up PLUS model, incorporating SSPs and RCPs scenarios to evaluate future trends in LUC from both socioeconomic and natural climate perspectives. Furthermore, the InVEST model is utilized to assess HQ across multiple scenarios from 2000 to 2050. Nevertheless, these models exhibit certain limitations. The SSP-RCP scenario data primarily focus on global and national levels, with relatively few studies addressing regional scales. To mitigate this issue, we have taken local development needs into account when establishing the SSP-RCP scenario parameters. Additionally, the InVEST model is frequently adjusted based on prior research, which introduces an element of subjectivity. Consequently, future studies should adopt a more rigorous approach to develop more accurate and reliable model parameters.
5 Conclusion
This study employs a coupled SD-PLUS model to simulate and predict land-use patterns in the YREB for the period from 2030 to 2050, based on scenarios that integrate SSP-RCP. In conjunction with the InVEST model, we conducted a comprehensive assessment of HQ across various scenarios from 2000 to 2050, elucidating the spatiotemporal dynamics of HQ and the associated degradation patterns. The results indicate a declining trend in HQ between 2000 and 2020, with a spatial distribution that demonstrates a gradient of increasing quality from east to west. HD is predominantly concentrated in agroforestry transition zones and urban, revealing a clustering pattern characterized by cold spots in the eastern region, negligible degradation in the centre, and hot spots in the west.
In the context of three future development scenarios projected for the period 2030–2050, HQ is expected to primarily shift from medium to poor, followed by a transition from high to medium. Specifically, in the SSP126, HQ is projected to decrease by 2.28%. In the SSP245, it is expected to decline by 1.74%; and in the SSP585, the decline is projected to be 2.55%. The pattern of HD remains largely consistent with the trends observed during the 2000–2020 period, with moderate HD being the dominant trend. Notably, the HQ of both cropland and forest land remains stable, and a balanced transition is evident between these land types. The YREB is characterized by the presence of hotspots (>40%), followed by cold spots (>30%), with areas exhibiting insignificant quality (<30%) representing the smallest proportion. The distribution of these cold and hot spots is primarily driven by the expansion or contraction of existing regions.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
BD: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. TH: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing–review and editing. TT: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Writing–review and editing. DH: Data curation, Project administration, Supervision, Writing–review and editing. CT: Formal Analysis, Visualization, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was funded by Major Project of Philosophy and Social Science Research in Hubei Higher Education Institutions (Grant No. 21ZD007).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge all colleagues and friends who have voluntarily reviewed the translation of the survey and the manuscript of this study. The reviewers and editor are appreciated for their contributions to improve the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fenvs.2024.1516703/full#supplementary-material
References
Bai, L., Xiu, C., Feng, X., and Liu, D. (2019). Influence of urbanization on regional habitat quality: a case study of Changchun city. Habitat Int. 93, 102042. doi:10.1016/j.habitatint.2019.102042
Bian, C., Yang, L., Zhao, X., Yao, X., and Xiao, L. (2024). The impact of human activity expansion on habitat quality in the yangtze river basin. Land 13, 908. doi:10.3390/land13070908
Brunner, L., Pendergrass, A. G., Lehner, F., Merrifield, A. L., Lorenz, R., and Knutti, R. (2020). Reduced global warming from cmip6 projections when weighting models by performance and independence. Earth Syst. Dyn. 11, 995–1012. doi:10.5194/esd-11-995-2020
Chen, D., Jiang, P., and Li, M. (2021). Assessing potential ecosystem service dynamics driven by urbanization in the yangtze river economic belt, China. J. Environ. Manage 292, 112734. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112734
Chen, M., Tan, Y., Xu, X., and Lin, Y. (2024). Identifying ecological degradation and restoration zone based on ecosystem quality: a case study of yangtze river delta. Appl. Geogr. 162, 103149. doi:10.1016/j.apgeog.2023.103149
Chen, Q., and Ning, Y. (2024). Projecting LUCC dynamics and ecosystem services in an emerging urban agglomeration under SSP-RCP scenarios and their management implications. Sci. Total Environ. 949, 175100. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.175100
Chen, W., Wang, G., Gu, T., Fang, C., Pan, S., Zeng, J., et al. (2023). Simulating the impact of urban expansion on ecosystem services in Chinese urban agglomerations: a multi-scenario perspective. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 103, 107275. doi:10.1016/j.eiar.2023.107275
Dai, D., Bo, M., Ren, X., and Dai, K. (2024). Application and exploration of artificial intelligence technology in urban ecosystem-based disaster risk reduction: a scoping review. Ecol. Indic. 158, 111565. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2024.111565
Ding, T., Chen, J., Fang, Z., and Chen, J. (2021). Assessment of coordinative relationship between comprehensive ecosystem service and urbanization: a case study of yangtze river delta urban agglomerations, China. Ecol. Indic. 133, 108454. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.108454
Dong, N., You, L., Cai, W., Li, G., and Lin, H. (2018). Land use projections in China under global socioeconomic and emission scenarios: utilizing a scenario-based land-use change assessment framework. Glob. Environ. Change 50, 164–177. doi:10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2018.04.001
Gong, J., Xie, Y., Cao, E., Huang, Q., and Li, H. (2019). Integration of invest-habitat quality model with landscape pattern indexes to assess mountain plant biodiversity change: a case study of bailongjiang watershed in gansu province. J. Geogr. Sci. 29, 1193–1210. doi:10.1007/s11442-019-1653-7
Guan, X., Wei, H., Lu, S., Dai, Q., and Su, H. (2018). Assessment on the urbanization strategy in China: achievements, challenges and reflections. Habitat Int. 71, 97–109. doi:10.1016/j.habitatint.2017.11.009
Haddad, N. M., Brudvig, L. A., Clobert, J., Davies, K. F., Gonzalez, A., Holt, R. D., et al. (2015). Habitat fragmentation and its lasting impact on earth’s ecosystems. Sci. Adv. 1, e1500052. doi:10.1126/sciadv.1500052
Hall, L. S., Krausman, P. R., and Morrison, M. L. (1997). The habitat concept and a plea for standard terminology. Wildl. Soc. Bull., 173–182. Available at: https://www.jstor.org/stable/3783301.
Hillard, E. M., Nielsen, C. K., and Groninger, J. W. (2017). Swamp rabbits as indicators of wildlife habitat quality in bottomland hardwood forest ecosystems. Ecol. Indic. 79, 47–53. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2017.03.024
Ji, X., Sun, Y., Guo, W., Zhao, C., and Li, K. (2023). Land use and habitat quality change in the yellow river basin: a perspective with different CMIP6-based scenarios and multiple scales. J. Environ. Manage 345, 118729. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.118729
Kong, L., Wu, T., Xiao, Y., Xu, W., Zhang, X., Daily, G. C., et al. (2023). Natural capital investments in China undermined by reclamation for cropland. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 7, 1771–1777. doi:10.1038/s41559-023-02198-3
Li, G., Fang, C., Li, Y., Wang, Z., Sun, S., He, S., et al. (2022). Global impacts of future urban expansion on terrestrial vertebrate diversity. Nat. Commun. 13, 1628. doi:10.1038/s41467-022-29324-2
Li, G., Fang, C., Watson, J. E., Sun, S., Qi, W., Wang, Z., et al. (2024a). Mixed effectiveness of global protected areas in resisting habitat loss. Nat. Commun. 15, 8389. doi:10.1038/s41467-024-52693-9
Li, X., Zhang, X., Feng, H., Li, Y., Yu, J., Liu, Y., et al. (2024b). Dynamic evolution and simulation of habitat quality in arid regions: a case study of the hexi region, China. Ecol. Modell. 493, 110726. doi:10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2024.110726
Liang, X., Guan, Q., Clarke, K. C., Liu, S., Wang, B., and Yao, Y. (2021). Understanding the drivers of sustainable land expansion using a patch-generating land use simulation (plus) model: a case study in Wuhan, China. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 85, 101569. doi:10.1016/j.compenvurbsys.2020.101569
Lin, Y., Lin, W., Wang, Y., Lien, W., Huang, T., Hsu, C., et al. (2017). Systematically designating conservation areas for protecting habitat quality and multiple ecosystem services. Environ. Model. Softw. 90, 126–146. doi:10.1016/j.envsoft.2017.01.003
Liu, Y., Yang, P., Zhang, S., and Wang, W. (2022). Dynamic identification and health assessment of wetlands in the middle reaches of the yangtze river basin under changing environment. J. Clean. Prod. 345, 131105. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.131105
Lu, Z., Li, W., and Yue, R. (2024). Investigation of the long-term supply–demand relationships of ecosystem services at multiple scales under SSP–RCP scenarios to promote ecological sustainability in China's largest city cluster. Sustain Cities Soc. 104, 105295. doi:10.1016/j.scs.2024.105295
Luan, W., and Li, X. (2021). Rapid urbanization and its driving mechanism in the pan-third pole region. Sci. Total Environ. 750, 141270. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141270
Luo, Q., Zhou, J., Zhang, Y., Yu, B., and Zhu, Z. (2022). What is the spatiotemporal relationship between urbanization and ecosystem services? A case from 110 cities in the yangtze river economic belt, China. J. Environ. Manage 321, 115709. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.115709
O'Connor, B., Bojinski, S., Röösli, C., and Schaepman, M. E. (2020). Monitoring global changes in biodiversity and climate essential as ecological crisis intensifies. Ecol. Inf. 55, 101033. doi:10.1016/j.ecoinf.2019.101033
Oliver, T. H., Isaac, N. J., August, T. A., Woodcock, B. A., Roy, D. B., and Bullock, J. M. (2015). Declining resilience of ecosystem functions under biodiversity loss. Nat. Commun. 6, 10122. doi:10.1038/ncomms10122
Palmer, E. (2015). Introduction: the 2030 agenda. J. Glob. Ethics 11, 262–269. doi:10.1080/17449626.2015.1119928
Pan, Z., Gao, G., Fu, B., Liu, S., Wang, J., He, J., et al. (2023). Exploring the historical and future spatial interaction relationship between urbanization and ecosystem services in the yangtze river basin, China. J. Clean. Prod. 428, 139401. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.139401
Qin, X., Yang, Q., and Wang, L. (2024). The evolution of habitat quality and its response to land use change in the coastal China, 1985–2020. Sci. Total Environ. 952, 175930. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.175930
Qiu, Y., and Shi, X. (2015). A system dynamics modeling framework for urban logistics demand system with a view to society, economy and environment. Econ. Environ., 299–303. doi:10.1007/978-3-662-43871-8_45
Ren, Q., He, C., Huang, Q., Shi, P., Zhang, D., and Güneralp, B. (2022). Impacts of urban expansion on natural habitats in global dryland. Nat. Sustain 5, 869–878. doi:10.1038/s41893-022-00930-8
Riedler, B., and Lang, S. (2018). A spatially explicit patch model of habitat quality, integrating spatio-structural indicators. Ecol. Indic. 94, 128–141. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2017.04.027
Sallustio, L., De Toni, A., Strollo, A., Di Febbraro, M., Gissi, E., Casella, L., et al. (2017). Assessing habitat quality in relation to the spatial distribution of protected areas in Italy. J. Environ. Manage 201, 129–137. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.06.031
Sherrouse, B. C., Semmens, D. J., and Ancona, Z. H. (2022). Social values for ecosystem services (Solves): open-source spatial modeling of cultural services. Environ. Model. Softw. 148, 105259. doi:10.1016/j.envsoft.2021.105259
Shi, Z., and Zhou, S. (2023). A study on the dynamic evaluation of ecosystem health in the yangtze river basin of China. Ecol. Indic. 153, 110445. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2023.110445
Sun, L., Yu, H., Sun, M., and Wang, Y. (2023). Coupled impacts of climate and land use changes on regional ecosystem services. J. Environ. Manage 326, 116753. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.116753
Tian, L., Tao, Y., Fu, W., Li, T., Ren, F., and Li, M. (2022). Dynamic simulation of land use/cover change and assessment of forest ecosystem carbon storage under climate change scenarios in guangdong province, China. Remote Sens. 14, 2330. doi:10.3390/rs14102330
Tu, D., Cai, Y., and Liu, M. (2023). Coupling coordination analysis and spatiotemporal heterogeneity between ecosystem services and new-type urbanization: a case study of the yangtze river economic belt in China. Ecol. Indic. 154, 110535. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2023.110535
Wang, J., Wu, Y., and Gou, A. (2023). Habitat quality evolution characteristics and multi-scenario prediction in shenzhen based on plus and invest models. Front. Environ. Sci. 11, 1146347. doi:10.3389/fenvs.2023.1146347
Wang, Z., Li, X., Mao, Y., Li, L., Wang, X., and Lin, Q. (2022). Dynamic simulation of land use change and assessment of carbon storage based on climate change scenarios at the city level: a case study of bortala, China. Ecol. Indic. 134, 108499. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.108499
Weber, D., Schaepman-Strub, G., and Ecker, K. (2018). Predicting habitat quality of protected dry grasslands using landsat ndvi phenology. Ecol. Indic. 91, 447–460. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2018.03.081
West, A. M., Kumar, S., Brown, C. S., Stohlgren, T. J., and Bromberg, J. (2016). Field validation of an invasive species maxent model. Ecol. Inf. 36, 126–134. doi:10.1016/j.ecoinf.2016.11.001
Wu, J., Luo, J., Zhang, H., Qin, S., and Yu, M. (2022). Projections of land use change and habitat quality assessment by coupling climate change and development patterns. Sci. Total Environ. 847, 157491. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.157491
Yang, H., Wang, Y., Tu, P., Zhong, Y., Huang, C., Pan, X., et al. (2024). Evaluating the effects of future urban expansion on ecosystem services in the Yangtze river Delta urban agglomeration under the shared socioeconomic pathways. Ecol. Indic. 160, 111831. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2024.111831
Yang Jie, H. X., and Huang, X. (2021). The 30 m annual landcover dataset and its dynamics in China from 1990 to 2019. Earthsystem Sci. 13, 3907–3925. doi:10.5194/essd-13-3907-2021
Yu, B. (2021). Ecological effects of new-type urbanization in China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 135, 110239. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2020.110239
Zhang, G., Roslan, S. N. A., Quan, L., and Yuan, P. (2023a). Simulation of spatiotemporal patterns of habitat quality and driving mechanism in anhui province, China. Front. Environ. Sci. 11, 1145626. doi:10.3389/fenvs.2023.1145626
Zhang, K., Fang, B., Zhang, Z., Liu, T., and Liu, K. (2024a). Exploring future ecosystem service changes and key contributing factors from a “past-future-action” perspective: a case study of the Yellow river basin. Sci. Total Environ. 926, 171630. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.171630
Zhang, L., Fang, C., Zhao, R., Zhu, C., and Guan, J. (2023b). Spatial–temporal evolution and driving force analysis of eco-quality in urban agglomerations in China. Sci. Total Environ. 866, 161465. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.161465
Zhang, X., Jin, X., Liang, X., Shi, X., Sun, R., Zhu, W., et al. (2024b). Assessment and management for future habitat risks under the implementation of China's territorial spatial planning: a case study from hainan island. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 106, 107474. doi:10.1016/j.eiar.2024.107474
Zhang, X., Tian, Y., Dong, N., Wu, H., and Li, S. (2023c). The projected futures of water resources vulnerability under climate and socioeconomic change in the yangtze river basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 147, 109933. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2023.109933
Zhao, J., Yu, L., Newbold, T., and Chen, X. (2024). Trends in habitat quality and habitat degradation in terrestrial protected areas. Conserv. Biol., e14348. doi:10.1111/cobi.14348
Zheng, L., Wang, Y., and Li, J. (2023). Quantifying the spatial impact of landscape fragmentation on habitat quality: a multi-temporal dimensional comparison between the yangtze river economic belt and yellow river basin of China. Land Use Policy 125, 106463. doi:10.1016/j.landusepol.2022.106463
Keywords: habitat quality, SD model, PLUS model, InVEST model, SSP-RCP scenarios, Yangtze River economic belt
Citation: Dong B, Huang T, Tang T, Huang D and Tang C (2025) Impact of multi-scenario land-use changes on habitat quality evolution in the Yangtze River economic belt. Front. Environ. Sci. 12:1516703. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2024.1516703
Received: 24 October 2024; Accepted: 23 December 2024;
Published: 09 January 2025.
Edited by:
Sérgio António Neves Lousada, University of Madeira, PortugalReviewed by:
Liang Yuan, China Three Gorges University, ChinaZhonglin Tang, Chongqing Technology and Business University, China
Copyright © 2025 Dong, Huang, Tang, Huang and Tang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Tiantian Huang, aHR0MTEwMkAxMjYuY29t
 Bowen Dong
Bowen Dong Tiantian Huang2*
Tiantian Huang2*