- 1School of Smart City, Chongqing Jiaotong University, Chongqing, China
- 2No.107 Geological Team, Chongqing Bureau of Geology and Mineral Exploration, Chongqing, China
- 3Chongqing Academy of Ecology and Environmental Sciences (Southwest Branch of Chinese Academy of Environmental Sciences), Chongqing, China
- 4Chongqing Vocational College of Culture and Arts, Chongqing, China
- 5Chongqing Geomatics And Remote Sensing Center, Chongqing, China
Green development is key to promoting regional sustainable development. We construct an evaluation index system for green development levels based on the “sansheng” dimensions—production, living, and ecology. We rely on the “sansheng” (production, living, and ecology) dimensions, combined with the analytic hierarchy process (AHP) and the entropy weight method to analyze indicator weights, to construct an evaluation index system for green development levels. This system enables the identification of the evolution patterns of green development and the analysis of driving factors in the Chengdu-Chongqing economic zone from the “sansheng” perspective. The results indicate that: (1) The green development level in the Chengdu-Chongqing Economic Zone has been continuously rising, with the average index increasing from 0.197 to 0.254. Yuzhong District and Chengdu City have shown particularly high green development levels; in 2020, the green development level index for Yuzhong District reached 0.568, while Chengdu City’s index reached 0.522. (2) The spatial clustering of green development levels in the Chengdu-Chongqing economic zone exhibited a trend of first strengthening and then weakening, with the highest clustering degree observed in 2015. (3) National strategies have significantly promoted the improvement of regional green development levels. The average green development index during the pre-establishment, initial development, and rapid development stages of the Chengdu-Chongqing Economic Zone increased from 0.205 to 0.229, and then to 0.254. (4) The Theil index results show an increase in the disparity of green development levels among different regions within the Chengdu-Chongqing Economic Zone.The results of the optimal scaling regression model show that the driving factors with a significant impact on the level of green development include the Number of physicians per million people, Public library book collections Per 100 people, Per capita regional GDP, and Number of secondary schools Per million people, each contributing over 15% to the impact. These findings provide valuable data support for formulating regional economic development strategies and are conducive to advancing sustainable development.
1 Introduction
In recent years, both the global economy and China’s economy have developed rapidly. However, many countries, including China, have adopted an extensive development model characterized by “development first, management later,” which has caused significant damage to the ecological environment (Wang et al., 2022). The overexploitation of natural resources, worsening environmental pollution, excessive use of Fertilizers, and the spread of industrial waste and emissions have led to a continuous decline in environmental quality, posing challenges to public health.
Green development and low-carbon transition have become significant trends in global development (Topi et al., 2016). As the largest developing country in the world, China faces considerable challenges in environmental governance compared to other emerging economies (Wang et al., 2024). To address this, the Chinese government has implemented various measures. In 2016, it introduced a new development concept emphasizing the integration of green development into the entire process of economic construction. In 2021, the government proposed accelerating green and low-carbon development to promote a comprehensive green transformation of economic and social development. In 2024, opinions on accelerating the comprehensive green transformation of economic and social development were put forward, systematically planning and deploying strategies to advance this transformation. These measures demonstrate China’s commitment to green development. As a key region in western China and the upper reaches of the Yangtze River (Zhu et al., 2024), the Chengdu-Chongqing economic zone not only holds significant economic development potential but also has an important ecological status. With a complex natural environment, the region’s green and sustainable development is crucial for reinforcing the ecological barrier in the upper Yangtze and contributing to the “Beautiful China” initiative and other major strategies. In its past development, the Chengdu-Chongqing economic zone also experienced periods of neglecting environmental protection and engaging in extensive development. The problems brought by such rapid growth require not only strengthened governance by policymakers but also a shift in development methods through the adoption of green development concepts (Phoochinda, 2019). Therefore, identifying the region’s green development status and analyzing its spatiotemporal evolution patterns and driving factors is a critical issue that must be addressed to promote regional sustainable development.
Green development and low-carbon transition have become important global development trends (Topi et al., 2016). In recent years, many scholars have conducted in-depth studies on evaluating green development levels across various dimensions. In terms of constructing the indicator system, Grzebyk and Stec, (2015) considered economic, social, and environmental indicators of EU countries to establish a comprehensive standard for measuring sustainable development levels. Cui, (2022) developed an evaluation index system for assessing the high-quality economic development levels of Latin American countries by combining a weighted method across six dimensions: economic strength, innovation, coordination, green development, openness, sharing and entropy. In terms of the application of measurement methods, Aziz and Anwar, (2024) used a social analysis method through multiple linear regression to evaluate the urban sustainability of Pakistan’s capital. Han et al. (2022) applied the entropy weight method combined with spatiotemporal analysis to study green development levels in ASEAN regions, evaluating the current status, trends, and spatial characteristics of green development among ASEAN member countries. In terms of the analysis and evaluation of the current situation, Yu et al. (2020) analyzed green development outcomes in his study of the coastal regions of southern Fujian, China, finding that the three cities in the region focused primarily on economic indicators. Cui et al. (2021) constructed a performance evaluation index system for urban green development in the Yangtze River Economic Belt from the perspectives of green growth, green carrying capacity, and green security capability, concluding that the green development levels in most cities have improved. In terms of the analysis of driving factors, Li et al. (2024) conducted a driving factor analysis of the sustainable development level of tourism ecology in the Chengdu-Chongqing urban agglomeration using a multi-dimensional analysis method and found that openness and green development have a promoting effect. Tang et al. (2023), using a comprehensive index calculation to evaluate GDI, concluded that different driving factors exist at different GDI levels. It is evident that existing research commonly employs mathematical and statistical methods to establish evaluation systems from various dimensions. However, most studies focus on exploring and discussing the development path of specific areas in the economy and society, lacking comprehensive quantitative evaluation and analysis of influencing factors for green development levels over a certain period.
“Production-living-ecology”, referred to as “sansheng”, includes three core areas: production, living, and ecology. It reflects a region’s overall performance in achieving sustainable progress by measuring economic development, improvement in residents’ quality of life, and harmonious ecological protection. These three dimensions are both independent and interrelated, collectively forming the spatial activity scope of human social life. They serve as the fundamental carriers of human economic and social development and play a critical role in evaluating green development levels (Huang et al., 2020). Xie et al. (2019), from the perspective of green development, assessed the coordinated development degree of the “sansheng”—production, living, and ecology—in rural China and proposed policy recommendations to advance green rural revitalization. Wang, (2020) conducted a measurement and analysis of Inner Mongolia’s green development capacity, spatiotemporal patterns, and influencing factors from the “sansheng” spatial perspective, revealing a trend of annual improvement in overall green development capacity. Wu et al. (2023) used panel data based on the “sansheng” (production-living-ecology) dimensions and employed the entropy weight method and TOPSIS method to measure the level of green ecological transformation in Chengdu. This indicates that green development from the “sansheng” perspective is currently a popular research topic with broad applications across different regions. However, no studies have yet assessed the green development level of the “sansheng” dimensions specifically in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River, particularly in the Chengdu-Chongqing economic zone.
Given the lack of quantitative evaluation of green development levels over a period and the absence of “sansheng” dimension assessments in the Chengdu-Chongqing economic zone, this study focuses on this region to develop a green development level evaluation method based on the “sansheng” perspective. It conducts an analysis of the evolution of green development levels in the region for the years 2005, 2010, 2015, and 2020. By innovatively applying the entropy weight method and analytic hierarchy process, the study constructs an evaluation model for the green development level in the Chengdu-Chongqing economic zone, summarizes development patterns over a period, and analyzes its driving factors. This fills the gap in applying the “sansheng” dimension evaluation of green development levels within the Chengdu-Chongqing economic zone and has significant practical implications for formulating regional economic development and ecological protection strategies.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Study area and data sources
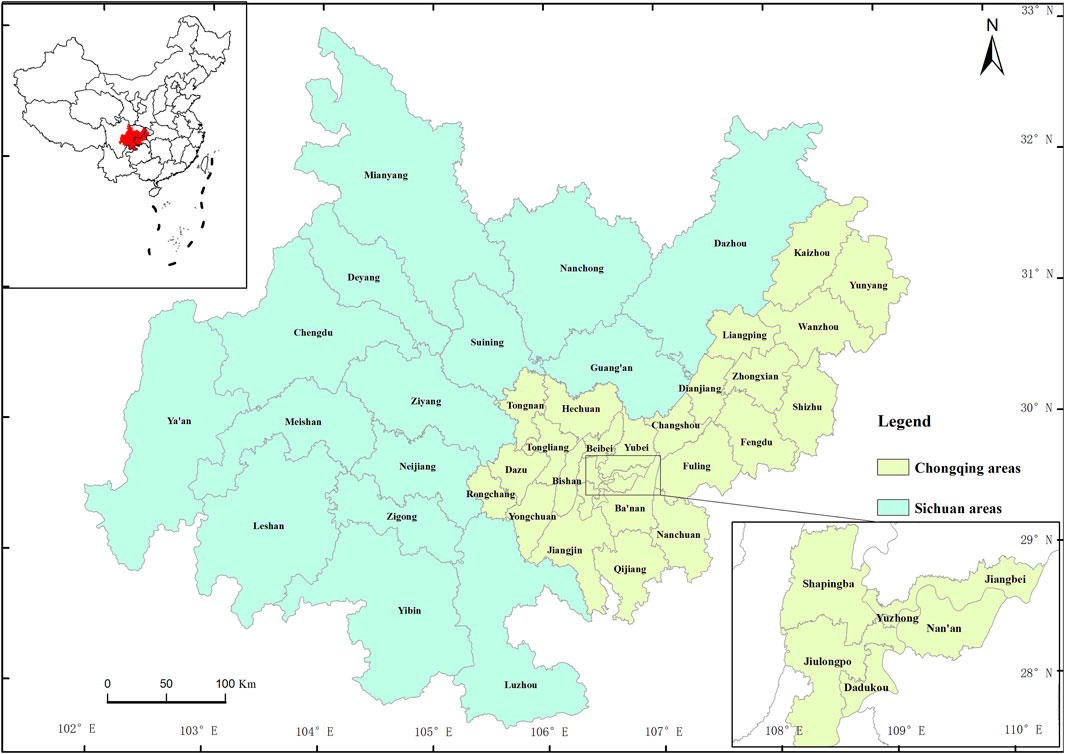
The Chengdu-Chongqing Economic Zone is located in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River, spanning the Sichuan Basin. It borders Gansu and Shaanxi to the north, Yunnan and Guizhou to the south, Tibet to the west, and Hunan and Hubei to the east. The Chengdu-Chongqing Economic Zone is endowed with abundant natural resources, providing a foundational support for economic development. It complements other regions of the Yangtze River Economic Belt in terms of resources, market interactions, and industrial synergies, holding significant strategic importance in the overall national development plan (Figure 1).
As an important ecological barrier in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River, the Chengdu-Chongqing Economic Zone has received significant attention from the Chinese government. The region has made remarkable progress in both economic development and ecological civilization. Over the past 20 years, the standard of living has greatly improved, with people enjoying a richer cultural life. Per capita GDP has grown rapidly, and the number of healthcare, education, and cultural facilities has increased significantly. While focusing on economic development, the region has also continuously improved and enhanced ecological environment quality. The Chengdu-Chongqing Economic Zone features diverse terrain, including basins, hills, and mountains, leading to variations in economic levels and green development across different areas. Major urban centers exhibit higher economic levels, while suburban areas maintain better ecological quality. Therefore, establishing a system to measure green development levels is particularly necessary (Chen et al., 2023).
The sample data primarily include economic development, ecological environment, and cultural resource data for 15 cities in Sichuan Province and 29 districts and counties in Chongqing. The data sources are mainly the Statistical Yearbooks of Sichuan Province and Chongqing Municipality (2005, 2010, 2015, and 2020), the National Economic and Social Development Bulletins of Sichuan Province and Chongqing Municipality, regional ecological environment reports, and annual work reports from local (district and county) governments. The vector data include urban boundary data and district/county boundary data, which are sourced from the planning departments of Sichuan Province and Chongqing Municipality.
2.2 Methods
2.2.1 Construction of the green development level evaluation model
2.2.1.1 Selection of evaluation indicators
Before determining the weights of the indicators, preliminary selection, analysis, re-evaluation, and final determination are required.The selection of indicators should adhere to the principles of comprehensiveness, quantifiability, comparability, and practicality. Xue et al. (2021) proposed the “Belt and Road” Green Development Index based on three dimensions: green nature, green economy, and green society. Yang et al. (2020) evaluated green cooperative development in the Yangtze River Delta region using four dimensions: ecology, economy, society, and policy. We selected three dimensions: the ecological dimension “Ecological Harmony”, the living dimension “Livability and Habitability”, and the production dimension “Efficient and Intensive Production”. These dimensions were used to construct a green development model for the Chengdu-Chongqing Economic Zone.
At the initial stage of selecting indicators, by reviewing relevant literature and employing frequency analysis, commonly used indicators were identified and organized. Liu and Zhou, (2023) selected 22 indicators, including Urbanization Rate, Scale amount of chemical fertilizer application, Amount of public toilets, Soil erosion control area, and Cultivated land area. Sun et al. (2020) chose 20 indicators, such as Per capita GDP, Water consumption per unit of GDP, and Total social labor productivity (Yuan/person). Three dimensions with a total of 21 indicators were preliminarily selected: Ecological Harmony (Forest coverage rate, Precipitation, Soil stability, Ecological environment stability, Natural shoreline retention rate, Wetland area, and Area under soil erosion control),Livability and Habitability (Population density, Per capita regional GDP, Number of secondary schools, Number of physicians, Public library book collections, Quantity of pollution-free agricultural products, Rural tap water penetration rate, Rural domestic sewage collection rate),Efficient and Intensive Production (Added value of the secondary industry, Added value of the tertiary industry, Fertilizer application volume, Total industrial profits, Total ammonia nitrogen emissions, Hazardous waste disposal and utilization rate, Effective utilization coefficient of farmland irrigation water, and Total chemical oxygen demand emissions).
In the re-selection phase, the practical significance of each indicator was analyzed. Precipitation is an important factor that can provide water for urban green spaces and reduce airborne dust. However, in practical application, if the precipitation is too high, it can damage the environment, making it difficult to determine the relationship between precipitation levels and ecological quality. Therefore, this indicator was excluded. Similarly, high population density can reduce livability, but a reasonable population density can achieve a moderate level of livability. On the other hand, an excessively low population density does not necessarily indicate better livability, so this indicator was also excluded. Among the indicators reflecting the production structure, both the added value of the secondary industry and the added value of the tertiary industry can indicate the degree of industrial transformation. Based on the principle of independence, the advanced industrial structure index (tertiary industry/secondary industry) was introduced to represent the development of industrial transformation. For other indicators, such as the number of secondary schools, the number of physicians, public library book collections, Fertilizer application volume, and total industrial profits, they each reflect the level of urban development from different perspectives. However, expressing these indicators in terms of per capita or per unit area can more accurately reflect the actual situation, so these indicators were revised accordingly. Furthermore, indicators such as rural tap water penetration rate, rural domestic sewage collection rate, and the effective utilization coefficient of farmland irrigation water face issues of missing data or discontinued statistical reporting in highly urbanized areas, leading to their exclusion. After removing certain indicators, the revised set includes 10 indicators across three dimensions: Ecological Harmony (Forest coverage rate, Soil stability, Ecological sensitivity),Livability and Habitability (Per capita regional GDP, Number of secondary schools per million people, Number of physicians per million people, Public library book collections per 100 people),Efficient and Intensive Production (Advanced industrial structure index, Fertilizer application volume per 1,000 ha, Per capita industrial profits).Indicators such as forest coverage rate, soil stability, and ecological sensitivity reflect the improvement of the local ecological environment from various perspectives. Indicators like per capita regional GDP, number of secondary schools per million people, number of physicians per million people, and public library book collections per 100 people represent the wellbeing and happiness of local residents. Meanwhile, indicators such as the advanced industrial structure index, fertilizer application volume per 1,000 ha, and per capita industrial profits illustrate the degree of green development in local industries.
2.2.1.2 Determination of the index weight
Awad and Jung, (2022) conducted an expert survey on the sustainable urban planning elements of Dubai and used the analytic hierarchy process (AHP) to determine the importance of these elements. Lee and Park, (2020) conducted a comprehensive literature review and expert survey to build an AHP model, followed by an AHP survey of landscape designers to identify the importance of evaluation factors, thereby assessing landscape sustainability in Korea. The Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) is a method with a high degree of subjectivity that can address complex decision-making problems by relying on expert scoring. It converts subjective judgments and qualitative factors into quantitative weights, leading to more rational decision-making (Myeong et al., 2018). The main steps include: constructing a judgment matrix, where each element represents the relative importance or priority between a pair of factors; calculating the weights using the eigenvector method; determining the weights using the eigenvalue method; and conducting a consistency test on the judgment matrix to ensure its reasonableness and stability.
Tang et al. (2023) applied the entropy weight method to obtain the weights of evaluation indicators, which were used to analyze the spatiotemporal evolution trends of green development in the Harbin-Changchun urban agglomeration. Shen et al. (2021) used the entropy weight method to determine the entropy values and weights of indicators to establish an evaluation system for analyzing the development of green transportation in Zhoushan City. Compared to the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP), the entropy weight method does not require pre-determining the relative importance of weights. Instead, it quantifies the uncertainty of criteria (Zhu et al., 2020), thereby avoiding the influence of subjective factors. The main steps include: dividing each element in the decision matrix by the sum of the corresponding column elements to ensure that the sum of each column equals 1; calculating the normalized column vector for each criterion; and normalizing the calculated weights to ensure that the sum of all weights equals 1.
To ensure a more scientifically determined weighting, we adopted a combination of subjective and objective methods (Analytic Hierarchy Process and entropy weight method) (Fan, 2017). The weights of each indicator were calculated using both methods and then integrated to produce the final weights for all indicators (Table 1).
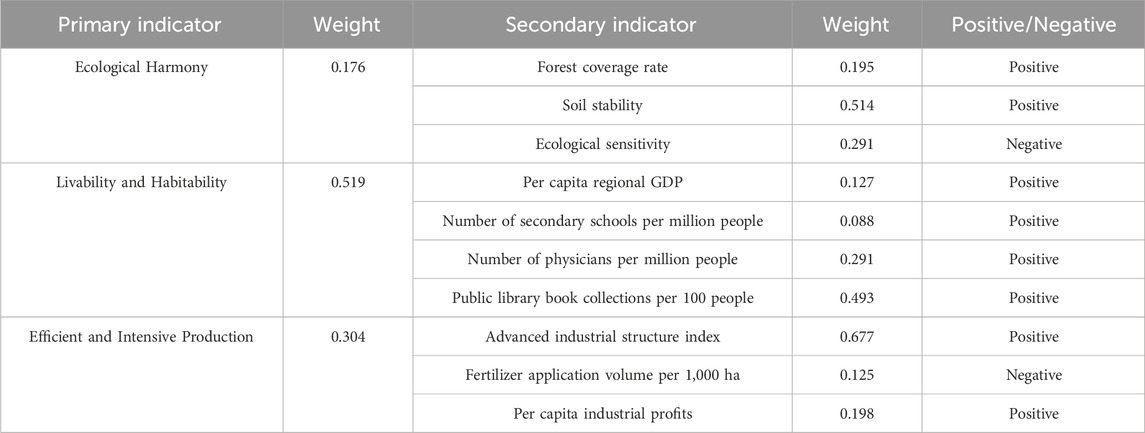
Table 1. Evaluation index system and weight of green development level in Chengdu-Chongqing Economic Zone.
2.2.1.3 Evaluation of the model construction
After ensuring that the selected indicators meet the principles of combining scientific rigor with guidance, criticality with complementarity, and completeness with independence, while also adhering to the principle of computability, an evaluation model was established to qualitatively or quantitatively assess the selected indicators. For positive indicators, such as forest coverage rate and per capita GDP, where higher values indicate a higher level of development, the calculation of the standardized value follows the process outlined in Equation 1.
In this context, X represents the standardized value, xi represents the actual value, and xmax represents the maximum actual value across all regions over the four periods.
For negative indicators, such as ecological sensitivity and Fertilizer application per 1,000 ha, where higher values indicate a relatively lower level of development, the calculation of the standardized value follows the process outlined in Equation 2.
In this context, X represents the standardized value, xi represents the actual value, and xmax represents the maximum actual value across all regions over the four periods.
The comprehensive evaluation index of the green development level evaluation model is shown in Equation 3.
In this context, S represents the green development level index, Xj denotes the standardized value of the indicator, Bj represents the weight of the primary indicator, and Cij represents the weight of the secondary indicator.
2.2.1.4 Determination of the grading method
We used the natural break method to divide the assessment results of the four periods into five grades. To enhance comparability between different periods, we used the classification values from the overall natural break method of the four periods as a unified standard. The grades are assigned as follows: (0, 0.20) corresponds to level 1, [0.20, 0.23) to level 2, [0.23, 0.29) to level 3, [0.29, 0.43) to level 4, and [0.43, 1] to level 5. A higher level indicates a higher green development level.
2.2.2 Thiel Index
The Theil index is an indicator used to measure inequality and disparity (Zhong et al., 2020), ranging from 0 to 1. From the perspective of information theory and entropy, a larger Theil index indicates greater disparity in development levels between regions. Conversely, a smaller Theil index suggests smaller differences in development levels across regions.
Drawing on the discussion of the Theil index by Theil (1967) and others, we adjusted the formula for the Theil index to assess the development levels in the Chengdu-Chongqing Economic Zone as follows: The Chengdu-Chongqing Economic Zone is divided into the Sichuan Province region and the Chongqing Municipality region, with the overall disparity (denoted as Tz), inter-regional disparity (denoted as Tj), and intra-regional disparity (denoted as Tn) calculated separately. The calculation process is shown in Equations 4–6.
In this context, Yi represents the comprehensive green development index of region i (i = 1,2,3, … ,n), Y represents the total sum of the indices for all regions, Xi represents the number of cities within region i, and X represents the total number of cities.
In this context, Yz represents the sum of the comprehensive green development indices within region z (z = 1,2.m), and Xz represents the number of cities within region z.
2.2.3 Moran’s I index
Moran’s I Index is a commonly used indicator for spatial autocorrelation analysis (Chen, 2023), which can measure the correlation of spatial data to determine whether a variable exhibits clustering, dispersion, or random distribution in space. The value of I ranges from −1 to 1. When I > 0, it indicates positive spatial autocorrelation, meaning similar variables tend to cluster in space. When I < 0, it indicates negative spatial autocorrelation, meaning dissimilar variables tend to be adjacent in space. When I = 0, it indicates a random spatial distribution, suggesting no significant clustering or dispersion pattern. The z-value is used to evaluate the statistical significance, with values greater than 1.96 or less than −1.96 considered significant.
We used the global Moran’s I Index to make an overall assessment of the green development level in the Chengdu-Chongqing economic zone. The calculation process is shown in Equation 7.
In this context,
2.2.4 Getis-Ord Gi* statistic
The Getis-Ord Gi* statistic is an important tool in spatial autocorrelation analysis, capable of identifying clusters of high and low values in spatial data (Rousta et al., 2017). A larger Gi* value indicates a stronger aggregation of high values within a location and its neighborhood, while a smaller Gi* value signifies a stronger aggregation of low values in the same context. The z-score is used to evaluate statistical significance; when the z-score is greater than 1.96 or less than −1.96, the result is considered significant.
We employ hotspot analysis (Getis-Ord Gi* statistic) to explore the spatiotemporal evolution of green development levels in the Chengdu-Chongqing economic zone. The calculation process is shown in Equations 8, 9:
In this context, the Gi* statistic represents the z-score,
2.2.5 Optimal scaling regression model
The optimal scaling regression model is widely recognized in the field of statistics for its core advantage of establishing relationships between variables of different scales (Barlin et al., 2021). The model is constructed based on a key concept: considering the relationships between variables of different scales and applying appropriate scaling and weighting to more accurately describe the connections between variables within the model. The optimal scaling regression model has been extensively applied in various disciplines, including economics, biostatistics, environmental science, and geography (Liu et al., 2018). This model allows for a deeper understanding of the patterns and trends underlying the data, thereby providing a robust data foundation for decision-making. In our specific application, we use the comprehensive green development index of each county (district, city) in the Chengdu-Chongqing Economic Zone as the dependent variable, and 10 indicators—including Forest coverage rate, Soil stability, Ecological sensitivity, and Per capita regional GDP—as independent variables. The calculations were performed using the optimal scaling regression analysis tool in SPSS.
2.2.6 Geographically and temporally weighted regression model
Geographically and Temporally Weighted Regression (GTWR) is an extension of the Geographically Weighted Regression (GWR) model into the spatiotemporal dimension (Fan et al., 2024). Huang incorporated a time variable into the GWR model, accounting for both spatial and temporal variations. The calculation process is shown in Equation 10.
In this context, (
3 Results and analysis
3.1 Measurement results of green development levels
To understand the regional disparities in development levels across the Chengdu-Chongqing economic zone, the collected statistical data were standardized, calculated, and categorized. This process yielded the green development levels for 44 counties (districts, cities) within the Chengdu-Chongqing economic zone.The green development levels of each region were calculated, and the green development levels and rankings of each county (district, city) were compared, as shown in Table 2. The green development level index shows a clear upward trend, with the average green development level increasing from 0.197 to 0.254. Specifically, the average level in the Chengdu region rose from 0.187 to 0.244, while in the Chongqing region, it increased from 0.202 to 0.259. Yuzhong District and Chengdu City consistently ranked among the top five across the four periods, while regions such as Jiangbei District, Shapingba District, and Yubei District also ranked high in green development levels. In contrast, regions like Kaizhou District, Neijiang City, Deyang City, and Dianjiang County ranked lower in green development levels.
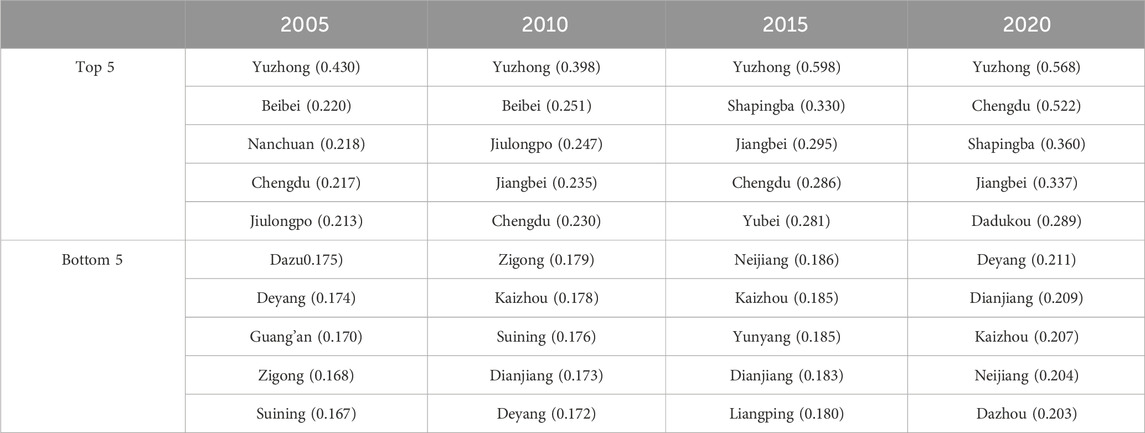
Table 2. Comprehensive score of the green development level of counties (districts and cities) in the Chengdu-Chongqing Economic Zone.
3.2 Temporal and spatial evolution of green development levels
3.2.1 Change in green development level
To understand the spatiotemporal evolution of green development levels across the Chengdu-Chongqing Economic Zone, further calculations were performed on the comprehensive green development indices of each county (district, city) within the zone. The results, as illustrated in Figure 2, show the comprehensive green development indices and their changes across the Chengdu-Chongqing Economic Zone. From a spatial distribution perspective, the comprehensive green development index across all regions increased to varying degrees from 2005 to 2020, with an overall trend of higher levels in the south and lower levels in the north. Chengdu and Chongqing’s Yuzhong District serve as two growth poles for the enhancement of green development levels within the Chengdu-Chongqing Economic Zone. Yuzhong District in Chongqing and its surrounding counties and districts entered higher levels of green development earlier, indicating that the central urban area represented by Yuzhong District has had a radiating effect on the green development levels of adjacent regions, driving the development of surrounding counties and districts. These areas have shared in the favorable development atmosphere created by the central urban area. In contrast, the regional development center in Sichuan Province is located in Chengdu, but its radiating effect on surrounding cities is significantly less pronounced. Although Deyang, Ziyang, Meishan, and Ya’an all border Chengdu, except for Ya’an in certain years, which had higher development levels than other cities in Sichuan, the green development levels in these cities did not show significant advantages.
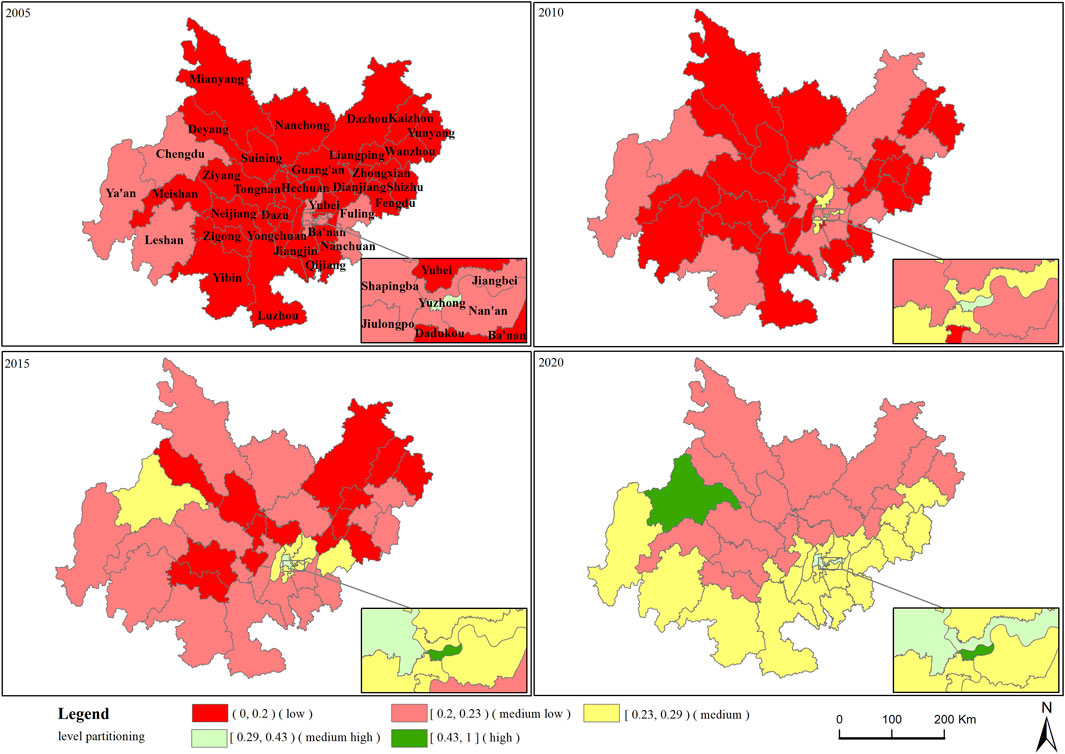
Figure 2. Distribution and change of green development level among counties (districts and cities) in Chengdu-Chongqing Economic Zone. This map is based on the standard map with the approval number GS (2022) 1873, downloaded from the Map Technical Review Center of the Ministry of Natural Resources of China. The base map has not been modified. The same applies to Figures 2, 4, 6.
As shown in Figure 3, the overall green development index in the Chengdu-Chongqing Economic Zone has significantly increased over time. In 2005, 2010, 2015, and 2020, the regions with a green development level of 1 (low) accounted for 75%, 52%, 32%, and 0%, respectively, while those at level 2 (medium low) accounted for 23%, 36%, 41%, and 36%, respectively, indicating notable progress in green development. Between 2010 and 2015, 10 cities moved from level 1 (low) to level 2 (medium low), with one city directly advancing from level 1 (low) to level 3 (medium), and one city moving from level 3 (medium) to level 4 (medium high), showing a significant improvement in development speed compared to the period from 2005 to 2010. Between 2015 and 2020, 12 cities progressed from level 1 (low) to level 2 (medium low), two cities advanced from level 1 (low) to level 3 (medium), and 14 cities moved from level 2 (medium low) to level 3 (medium), with one city advancing from level 3 (medium) to the highest green development level of 5 (high). By 2020, all cities had reached at least level 2 (medium low). From 2005 to 2020, the Chengdu-Chongqing Economic Zone witnessed significant improvements in green development, with all cities achieving a level of 2 (medium low) or higher, demonstrating substantial progress in the region’s green development efforts.
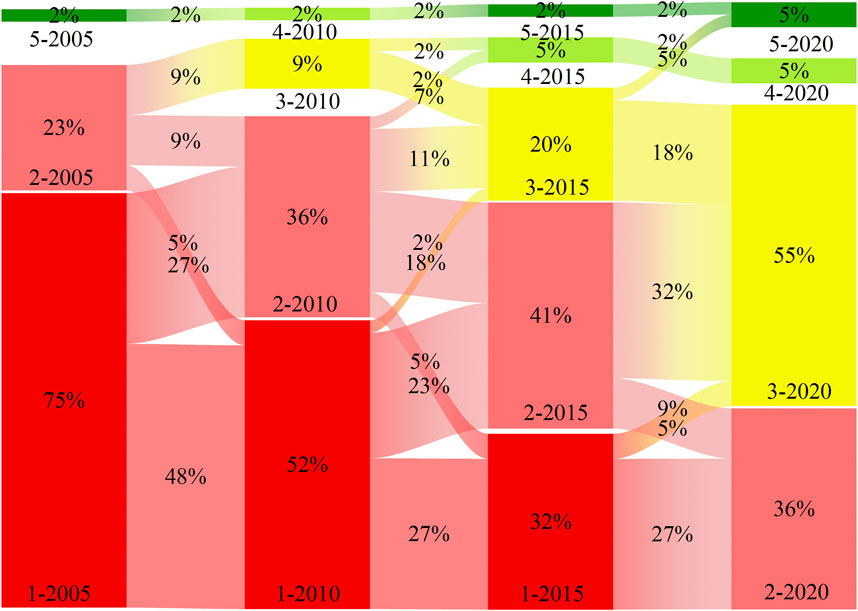
Figure 3. The green development level of counties (districts, cities) in Chengyu Economic Zone changes by grade by grade.
3.2.2 Change in the green development level ranking
From a spatial distribution perspective (Figure 4), the regions in Sichuan Province that experienced the fastest improvements in green development levels are primarily located in the northern and southern parts of the province. Overall, the development speed shows a pattern of being higher in the north and south, with slower progress in the central areas. The northeastern part of Sichuan saw rapid development between 2005 and 2010, but this trend did not continue in subsequent years. In Chongqing, most areas in the eastern part saw a decline in their rankings, while regions with improved rankings were concentrated in the central and southern parts. Between 2005 and 2020, the areas that experienced the most significant increases in green development rankings were Dadukou District (rising 17 places), followed by Changshou District (12 places), Bishan District (12 places), Guang’an City (11 places), Dazu District (11 places), Nanchong City (8 places), Yibin City (7 places), Luzhou City (7 places), Zhongxian (7 places), and Banan District (6 places).
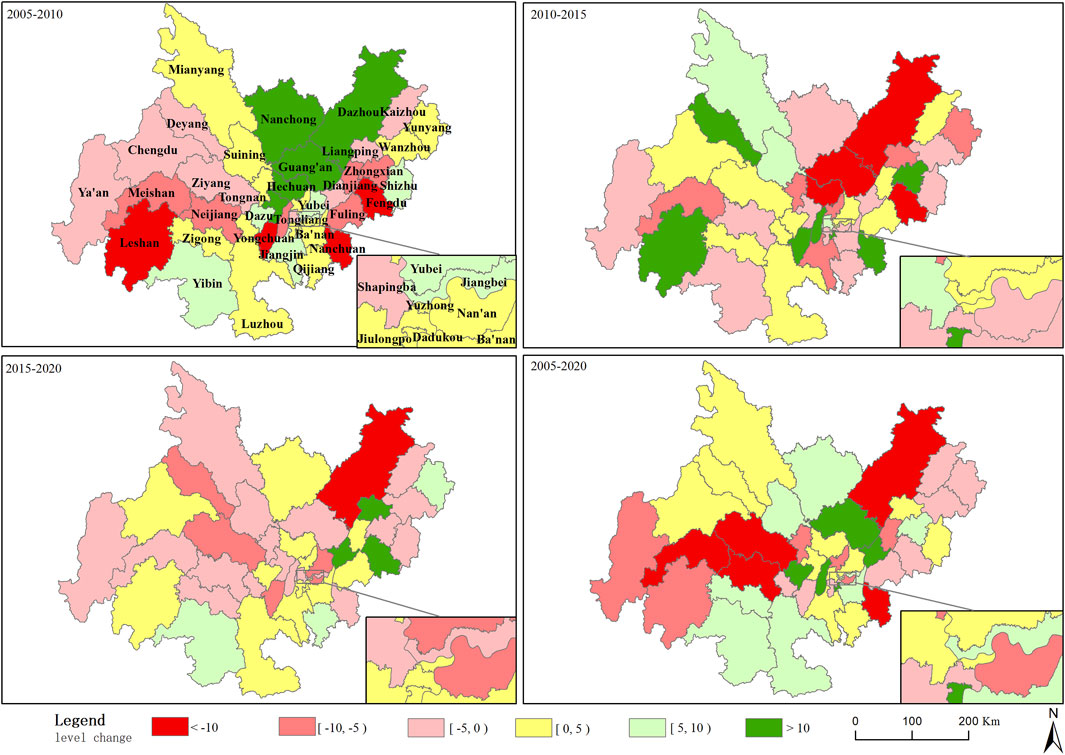
Figure 4. The ranking of green development level of counties (districts, cities) in Chengdu-Chongqing Economic Zone has changed.
3.3 Analysis of regional development differences
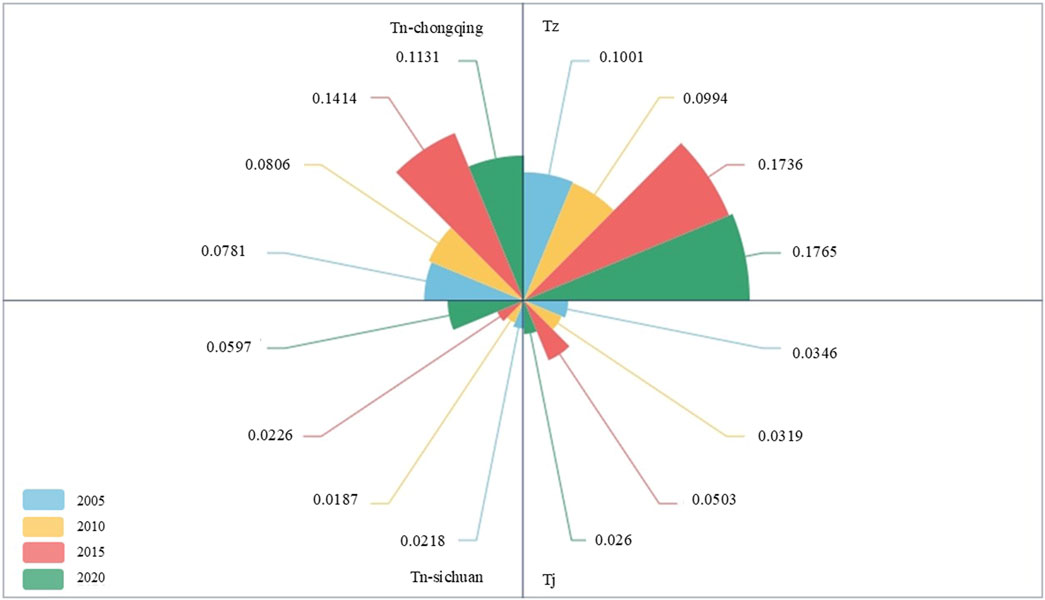
Theil index calculations, as shown in Figure 5, indicate that the overall regional Theil index values (Tz) in 2005, 2010, 2015, and 2020 were 0.1001, 0.0994, 0.1736, and 0.1765, respectively. A significant increase in 2015 reflects that the overall regional disparities had grown compared to 2005. Similarly, both interregional disparities (Tj) and intra-regional disparities within Chongqing (Tn-chongqing) saw substantial increases in 2015,thus, the overall disparity in 2015 was due to the increase in internal disparities within Chongqing. The interregional Theil index values for 2005, 2010, 2015, and 2020 were 0.0346, 0.0319, 0.0503, and 0.0260, respectively. After a sharp increase in 2015, the index dropped rapidly in 2020, showing an overall downward trend, which indicates that the differences between the Chengdu region and Chongqing are gradually narrowing. The intra-regional Theil index for Sichuan (Tn-sichuan) was 0.0218, 0.0187, 0.0226, and 0.0597 in 2005, 2010, 2015, and 2020, respectively, remaining relatively stable during the first 3 years, but showing a sudden increase in 2020. One of the reasons for the sudden increase in internal disparities in Sichuan Province was the green development level index of Chengdu city, which increased from 0.286 in 2015 to 0.522. For Chongqing, the intra-regional Theil index values were 0.0781, 0.0806, 0.1414, and 0.1131 for the same periods, with a rapid increase in 2015, followed by a gradual decline by 2020. The merging of Qijiang County and Wansheng District into Qijiang District, Dazu County and Shuangqiao District into Dazu District in 2011 promoted the rapid development of these new regions, contributing to the increased internal disparities within Chongqing in 2015.
3.4 Spatial autocorrelation analysis of green development levels
The results of spatial autocorrelation analysis indicate that the global Moran’s I indices for the green development levels in the Chengdu-Chongqing economic zone in 2005, 2010, 2015, and 2020 are significant at the 5% level, with z-scores all exceeding 1.96. This demonstrates strong spatial autocorrelation of green development levels across the region, with a high degree of integration and clustering. As shown in Table 3, Moran’s I index exhibits a trend of first increasing and then decreasing, indicating that the spatial clustering of green development levels strengthened initially and then weakened, peaking in 2015.
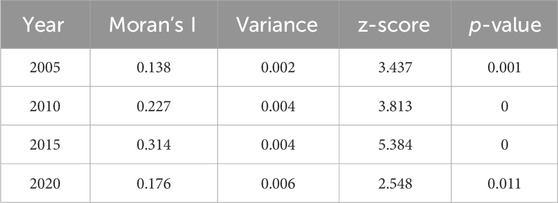
Table 3. Global Moran’s I calculation results for green development levels in the chengdu-chongqing economic zone.
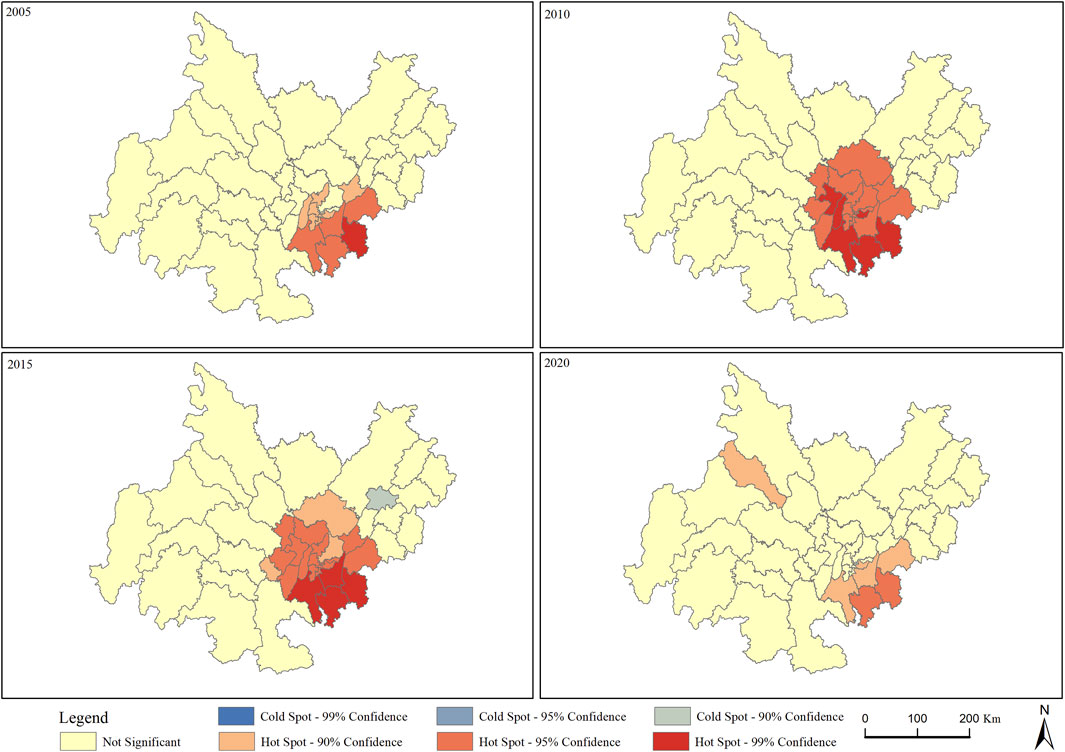
To further investigate the spatial clustering of green development levels in the Chengdu-Chongqing economic zone, a Getis-Ord Gi* statistical analysis was performed on the green development indices for each region, and a heatmap was generated (Figure 6). Spatially, the hotspots of green development are concentrated in the southeastern part of the zone, primarily around the central urban areas of Chongqing, suggesting a strong radiation and driving effect of Chongqing’s core urban areas. Temporally, from 2005 to 2015, the spatial clustering of green development levels gradually increased, while from 2015 to 2020, the clustering weakened, indicating a relative increase in spatial distribution uniformity. These findings align closely with the global Moran’s I results.
3.5 Analysis of the factors affecting green development
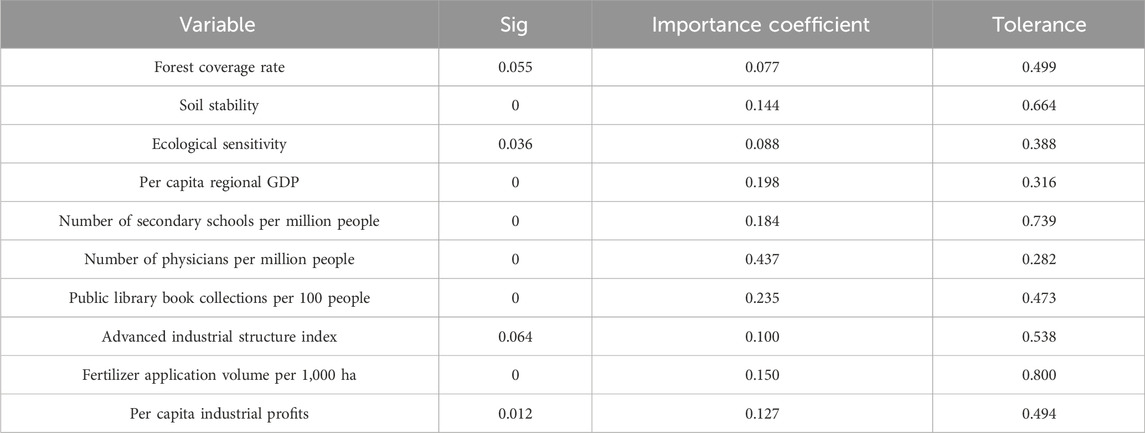
Using the optimal scaling regression analysis tool in SPSS, we analyzed the factors influencing the green development index. The results indicated that the adjusted R-squared value for the model summary was 0.874, with a Sig value of less than 0.001, confirming that the overall model passed the variance test. This suggests that the model is statistically significant and that at least one independent variable significantly affects the green development index. As shown in Table 4, variables such as Forest coverage rate, Ecological sensitivity, Advanced industrial structure index, and Per capita industrial profits failed to pass the significance test at the 1% level, while other indices did pass the test at this level. Tolerance, which ranges from 0 to 1, was used to assess the linear correlation of a variable with other variables in the model. Lower tolerance values indicate stronger multicollinearity with other variables; therefore, higher tolerance values are preferred. The results showed that Per capita regional GDP and Number of physicians per million people was relatively low, but overall, none of the factors had excessively low tolerance values, indicating that multicollinearity was not a major concern, and the optimal scaling regression model performed well.
The importance coefficient results indicate the order of impact on the green development level as follows: Number of physicians per million people > Public library book collections Per 100 people > Per capita regional GDP > Number of secondary schools Per million people > Fertilizer application volume per 1,000 ha > Soil stability. This suggests that Number of physicians per million people, Public library book collections Per 100 people, Per capita regional GDP, and Number of secondary schools Per million people have a significant influence on the green development level, with each contributing over 15% to the overall impact.
Using the Geographically and Temporally Weighted Regression (GTWR) model, the regression coefficients of the number of physicians per million people, public library book collections per 100 people, per capita regional GDP, and the number of secondary schools per million people on green development levels were calculated. Box plots for each factor were created by year to explore their temporal heterogeneity, as shown in Figure 7. During the study period, all four factors exerted a positive influence on green development levels. The impact of the number of physicians per million people exhibited an inverted “U-shaped” Kuznets curve, indicating that as economic development progressed, its influence first increased and then declined. In contrast, the effects of public library book collections per 100 people, per capita regional GDP, and the number of secondary schools per million people reached their peak in 2005, followed by a decreasing trend and then an upward rebound.

Figure 7. The box plot of the regression coefficients of the GTWR model for the green development level of the Chengdu-Chongqing Economic Zone.
4 Discussion
4.1 Selection of evaluation indicators conforms to the characteristics of the actual region
To establish a practical evaluation system, it is crucial to select scientifically sound evaluation indicators (Wang and Zhang, 2023). The evaluation indicators for urban green development should adhere to the following principles: comprehensiveness, meaning that the indicators should cover environmental, economic, and social aspects to fully reflect the level of green development; quantifiability and measurability, ensuring that the selected indicators can be specifically measured and quantified (Xue et al., 2021); comparability, meaning that the indicators should be defined and measured consistently across different cities to allow for meaningful comparisons; and practicality, ensuring that the indicators provide results that can guide policymakers in improving green development strategies and promoting sustainable urban green development (Sharma et al., 2023). In existing studies, Meng used indicators related to green production, green living, and green ecology in his research on measuring green economic development, its influencing factors, and spatial spillover effects in China (Meng and Shao, 2022); Li, in studying the impact of clean energy development on the green economy, employed indicators encompassing social life, economic development, and ecological environment (Li et al., 2023); Yuan utilized indicators of economic growth, social stability, and environmental friendliness in his study on the development of green industries in China (Yuan et al., 2020); and Yang applied indicators covering regional ecological environment, economic environment, social environment, and policy environment in his research on regional ecological green development in the Yangtze River Delta (Yang et al., 2020). In summary, existing research largely focuses on establishing indicators around social, economic, and environmental dimensions. The green development evaluation indicators for each county (district, city) in the Chengdu-Chongqing Economic Zone were selected based on the principles outlined above, encompassing three dimensions: ecology, livability, and production. The evaluation system is constructed using 10 indicators such as forest coverage rate, per capita educational resources, and the advanced industrial structure index. Therefore, the selection of our evaluation indicators is scientifically sound and aligns well with the characteristics of the actual region.
In studies on green development levels in small-scale regions, the selection of evaluation indicators should be optimized based on well-founded reasoning and the specific characteristics of the region. In practice, natural factors such as topography, landforms, and climate conditions have profound impacts on green development paths in different areas. For instance, mountainous regions should emphasize indicators related to forest resource conservation and eco-tourism development, while coastal regions should focus on the sustainable use of marine resources and marine ecological protection.From a policy perspective, local governments should be encouraged to develop personalized evaluation systems tailored to their unique natural and geographical characteristics. At the national level, a categorized guidance framework could be provided to ensure that the evaluation indicators reflect both the common requirements of green development and regional realities, offering a reliable basis for precise decision-making.
4.2 National strategy has played a significant role in promoting the improvement of the regional green development level
National strategies have achieved remarkable success in advancing regional green development practices. During the implementation of the Yangtze River Economic Belt development strategy, significant progress has been made in ecological restoration and the green transformation of industries in riverine areas. By systematically closing, consolidating, and transforming heavily polluting enterprises, the transition of traditional manufacturing industries toward intelligent and green manufacturing has been effectively promoted.At the same time, substantial investments in the ecological protection of the Yangtze River have not only led to notable improvements in water quality but also elevated the overall green development level across the region.The Chengdu-Chongqing Economic Zone was officially approved by the State Council in May 2011, covering 15 regions in Sichuan Province and 29 regions in Chongqing. From 2005 to 2010, before the establishment of the economic zone, 36% of the regions advanced to a higher level of green development, with the average green development index in the region being 0.197 in 2005 and 0.205 in 2010. From 2010 to 2015, during the initial development phase of the Chengdu-Chongqing Economic Zone, 40% of the regions advanced to a higher level of green development, with the average green development index reaching 0.229 in 2015. From 2015 to 2020, during the rapid development phase, 66% of the regions advanced to a higher level of green development, with the average green development index reaching 0.254 in 2020. Since the establishment of the Chengdu-Chongqing Economic Zone, both the development speed and the green development index in the region have significantly improved, indicating that the establishment of the economic zone has contributed to the joint development of the two regions.
The implementation of national strategies also faces challenges, such as inadequate policy enforcement and funding shortages in certain regions. Therefore, it is crucial to strengthen the supervision and evaluation mechanism of national strategies to ensure their effective implementation. Additionally, the central government should increase fiscal transfers to local projects, encourage the participation of social capital, and create a diversified financial support system. Establishing regional cooperation mechanisms will also promote close collaboration among regions in the pursuit of green development.
4.3 Synergy of the “sansheng” dimensions is key to enhancing green development levels
The level of green development reflects a region’s capacity for healthy and sustainable growth and is influenced by factors such as economic development, social capital, and governance efficiency. In his research, Li found that the use of clean energy significantly promotes green economic development (Li et al., 2023). Liu emphasized the necessity of controlling energy consumption, reducing pollution emissions, and protecting water and mineral resources for the green development of the Yangtze River Economic Belt (Liu L. et al., 2023). Huang’s research revealed that promoting energy transitions, strengthening environmental protection efforts, and avoiding hasty industrial restructuring can enhance urban green development efficiency (GDE) (Huang et al., 2023). Cui found that improving living services and ecological protection is crucial for enhancing green development levels (Cui et al., 2021), while Qin’s research highlighted that green development encompasses multiple dimensions, including economic, environmental, and social aspects (Qin and Huang, 2023). For example, in 2020, the Nanan District ranked 17th in comprehensive green development, indicating a lagging position among core urban districts. Analysis of its performance across the three dimensions revealed that while it ranked seventh in the “livability” dimension, outperforming most cities, it fell significantly behind in the “ecology” and “production” dimensions. Poor scores in indicators like “Fertilizer usage” and “forest coverage” contributed to its lower overall ranking, despite strong economic development and living standards. Productive activities enhance quality of life in both material and spiritual aspects but simultaneously lead to resource consumption and environmental pollution, impacting the ecological environment. Changes in the ecological environment, in turn, constrain production through resource scarcity, regulatory measures, and public pressure, while also influencing the living sphere in terms of health and living costs. Therefore, in the process of advancing green development levels, it is essential to adjust production methods, strengthen public infrastructure services, and improve the ecological environment in a coordinated manner. To enhance urban green development levels, the “sansheng” dimensions must progress collaboratively.
In the practice of “sansheng” coordinated development, numerous challenges persist.At the production level, promoting environmentally friendly technologies faces obstacles such as high costs and limited market acceptance. At the living level, although public awareness of eco-friendly consumption has improved, the high prices of green products and restricted purchasing channels hinder the widespread adoption of sustainable lifestyles. At the ecology level, the long-term and complex nature of ecosystem restoration and conservation often conflicts with short-term local economic development goals.To address these issues, it is essential to implement green production incentives, such as tax breaks and financial subsidies, to reduce the cost burden on businesses for adopting sustainable practices. Strengthening regulation in the green consumer market, coupled with scaling up production and optimizing supply chains, can help lower the prices of eco-friendly products. Additionally, establishing long-term ecological compensation mechanisms can ensure that local residents receive stable economic benefits from ecological protection efforts, thereby fostering the coordinated development of production, livability, and ecology.
4.4 Rural and cities need to develop in harmony
In promoting green development, both urban and rural areas must participate jointly, as harmonious urban-rural development promotes urbanization and fosters rapid and healthy socio-economic growth. Since the 20th century, there has been a shift from initial urban-rural opposition to emphasizing coordinated and integrated development. The 18th National Congress once again highlighted the importance of urban-rural development and related policy measures (Li, 2023). In his study on spatial disparities and influencing factors in the integrated development of urban and rural areas in the Yangtze River Delta, Liu found that integration is uneven, with central cities driving the development of neighboring cities (Liu N. et al., 2023). Chen argued that urban-biased urbanization has widened the urban-rural development gap, and integrating new urbanization with rural revitalization can facilitate coordinated and high-quality development (Chen et al., 2021). Li emphasized that the development of urban and rural areas requires balanced infrastructure and public services (Li, 2023), while Fang suggested that future government efforts should aim at synchronizing and deepening the integration between urbanization and rural revitalization (Fang, 2022).The Yuzhong District, as a central urban area, plays a radiating role in driving the coordinated development of surrounding counties and rural areas, creating a positive trend in urban-rural integration. In contrast, Chengdu needs to advance the coordinated development process with its surrounding cities and counties. Therefore, it is essential to enhance the green development level in urban areas while simultaneously increasing support for underdeveloped rural areas by improving local infrastructure and optimizing industrial structures, thereby promoting coordinated urban-rural development.
Challenges in coordinating rural and urban development include significant rural-urban disparities, underdeveloped infrastructure, and a shortage of skilled personnel. Policies should prioritize enhancing rural infrastructure in areas such as transportation, communication, and wastewater treatment; providing livelihood support through entrepreneurship subsidies, housing allowances, and talent attraction initiatives; and promoting the integration of urban and rural industries by establishing development zones that encourage the flow of urban capital, technology, and talent into rural areas.
4.5 Recommendations
Under the concept of sustainable development, the Chengdu-Chongqing Economic Zone shows a promising trend in green development, but attention should be given to the following issues:
(1) Develop custom evaluation systems to reflect local characteristics. Design layered and multidimensional green development assessment systems tailored to regional natural, economic, and social conditions to guide transitions. Resource-based cities should prioritize indicators like resource efficiency, while tourism-based cities should emphasize tourism environmental carrying capacity. A dynamic evaluation indicator adjustment mechanism should be established to maintain scientific accuracy and adapt to regional characteristics.
(2) Integrate national strategies with local specifics. While implementing national strategies, regions should develop detailed execution plans tailored to local contexts, ensuring alignment between national strategies and regional plans. For instance, based on regional advantages in transportation, resources, and markets, differentiated green development strategies can be crafted to form locally distinctive green industry clusters and enhance collaboration and exchange in green development.
(3) Promote policy integration and innovation for “sansheng” coordination. Governments should integrate existing green development policy resources to achieve coherence and synergy. In production, offer tax, financial, and land incentives to encourage enterprises to transition to green production and innovation. In daily living, foster public awareness of green consumption through campaigns and education, while assisting businesses in promoting green products. For ecological preservation, establish compensation mechanisms and implement systemic governance of ecosystems, including mountains, rivers, forests, farmlands, lakes, grasslands, and deserts, to enhance economic and social benefits.
(4) Strengthen comprehensive policy support for urban-rural coordination. Coordinate funding and projects to create integrated urban-rural infrastructure plans and construction. Establish talent attraction mechanisms to bring skilled individuals to rural areas, fostering partnerships between academic institutions and rural communities. Support urban enterprises in cooperating with rural entities, driving urban-rural economic integration.
5 Conclusion
We developed a green development evaluation method that integrates the dimensions of ecology, production, and livability, and applied it to the Chengdu-Chongqing Economic Zone to identify evolution patterns and analyze driving factors. This study primarily reveals the influencing factors of green development in the Chengdu-Chongqing Economic Zone and discusses in depth the role of national policies, regional coordination, and other factors in promoting green development. The key conclusions are as follows:
(1) The measurement results show a clear upward trend in the green development level of the Chengdu-Chongqing Economic Zone, with the average green development index rising from 0.197 to 0.254. In the Chengdu region, the average index increased from 0.187 to 0.244, while in the Chongqing region, it rose from 0.202 to 0.259. Notably, Yuzhong District and Chengdu have the highest levels of green development, with green development indices of 0.568 and 0.522, respectively, in 2020.
(2) The spatial clustering of green development levels in the Chengdu-Chongqing economic zone exhibited a trend of first strengthening and then weakening, with the highest clustering degree observed in 2015. In terms of spatial distribution, the regions with the fastest improvements in green development in Sichuan Province are primarily located in the northern and southern parts, showing a pattern of faster development in the north and south, with slower progress in the middle. In Chongqing, areas with rising rankings are concentrated in the central and southern regions, while most eastern regions experienced a decline in rankings.
(3) The establishment of the Chengdu-Chongqing Economic Zone has positively influenced the green development levels of various cities. In 2010, before the zone was established, the average green development index was 0.205. By 2015, during the initial development phase, the index rose to 0.229, and by 2020, during the rapid development phase, it further increased to 0.254. Since the zone’s establishment, both the development speed and green development index within the region have seen significant improvements.
(4) The Theil index results indicate that in 2005, 2010, 2015, and 2020, the Theil indices were 0.1001, 0.0994, 0.1736, and 0.1765, respectively, reflecting an increase in the disparities in green development levels across the regions within the Chengdu-Chongqing Economic Zone.The results of the optimal scaling regression model show that the driving factors with a significant impact on the level of green development include the Number of physicians per million people, Public library book collections Per 100 people, Per capita regional GDP, and Number of secondary schools Per million people, each contributing over 15% to the impact.
Due to limitations in data sources and research methods, we believe the following constraints still exist: (1) Due to the limited data available from statistical yearbooks and bulletins, we only conducted statistical analysis using panel data for the years 2005, 2010, 2015, and 2020. In the future, we plan to collaborate further with relevant departments to include additional environmental monitoring data and conduct a series of studies. (2) The classification of statistical indicators requires further research, such as categorizing each indicator into high, correlated high, correlated low, and low levels based on their characteristics. In the future, scientific classification standards for different indicators will be developed.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
KZ: Methodology, Software, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. TW: Software, Investigation, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. JH: Data curation, Validation, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. DS: Formal analysis, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. LW: Formal analysis, Writing–original draft. DW: Validation, Writing–review and editing. SH: Supervision, Writing–review and editing. LZ: Validation, Writing–review and editing. JL: Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was supported and funded by the Key Project for Technology Innovation and Application Development of Chongqing (CSTB2024TIAD-KPX0079), the National Natural Science Foundation of China Youth Science Fund Project (No. 42301353), Key projects of the Chongqing Municipal Education Commission’s research projects (No. KJZD-K202400702), Research and Innovation Program for Graduate Students in Chongqing (Chongqing Jiaotong University graduate Research Innovation Project) (No. CYS240526), Team Building Project for Graduate Tutors in Chongqing (No. JDDSTD2022002), and this work was also supported by the Innovation Center for Green Intelligent Environmental Protection Technology and Equipment Technology in Chongqing and the Chongqing Key Laboratory of Spatial and Temporal Information in Mountainous Cities.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fenvs.2024.1506618/full#supplementary-material
References
Awad, J., and Jung, C. (2022). Extracting the planning elements for sustainable urban regeneration in Dubai with AHP (analytic hierarchy process). Sustain. Cities Soc. 76, 103496. doi:10.1016/j.scs.2021.103496
Aziz, A., and Anwar, M. M. (2024). Assessing the level of urban sustainability in the capital of Pakistan: a social analysis applied through multiple linear regression. Sustainability 16 (7), 2630–2642. doi:10.3390/su16072630
Barlin, O. O., Julio, C., Juan, C. R., Deyanira, L., Blanca, B. L., and José, A. G. (2021). Correlation of banana productivity levels and soil morphological properties using regularized optimal scaling regression. Catena 208, 1–11. doi:10.1016/j.catena.2021.105718
Chen, M. X., Zhou, Y., Huang, X. R., and Ye, C. (2021). The integration of new-type urbanization and rural revitalization strategies in China: origin, reality and future trends. Land 10 (2), 207–217. doi:10.3390/land10020207
Chen, Y., Liao, Y., and Wen, C. H. (2023). A novel evaluation system of green development level in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area and its spatial–temporal pattern. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 30, 110744–110763. doi:10.1007/s11356-023-29591-6
Chen, Y. G. (2023). Spatial autocorrelation equation based on Moran’s index. Sci. Rep. 13 (1), 19296. doi:10.1038/s41598-023-45947-x
Cui, H. (2022). Evaluation and analysis model of economic development level for Latin American countries. Math. Problems Eng. 2022 (1), 1–9. doi:10.1155/2022/7315059
Cui, X. L., Shen, Z., Li, Z. H., and Wu, J. (2021). Spatiotemporal evolutions and driving factors of green development performance of cities in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Ecol. Inf. 66, 101476. doi:10.1016/j.ecoinf.2021.101476
Fan, J. J., Wang, D. N., Zhao, Y., Zhou, X., Cheng, Y., Xu, F. F., et al. (2024). Spatiotemporal geographically weighted regression analysis for runoff variations in the Weihe River Basin. J. Environ. Manag. 366, 121908. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2024.121908
Fan, M. (2017). Economic development evaluation model based on entropy AHP. J. Discrete Math. Sci. Cryptogr. 20 (4), 873–884. doi:10.1080/09720529.2017.1359374
Fang, C. L. (2022). On integrated urban and rural development. J. Geogr. Sci. 32 (8), 1411–1426. doi:10.1007/s11442-022-2003-8
Grzebyk, M., and Stec, M. (2015). Sustainable development in EU countries: concept and rating of levels of development. Sustain. Dev. 23 (2), 110–123. doi:10.1002/sd.1577
Han, M. S., Yuan, Q. Q., Fahad, S., and Ma, T. C. (2022). Dynamic evaluation of green development level of ASEAN region and its spatio-temporal patterns. J. Clean. Prod. 362, 132402. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.132402
Huang, A., Xu, Y. Q., Lu, L. H., Liu, C., Zhang, Y. B., Hao, J. M., et al. (2020). Research progress of the identification and optimization of production-living-ecological spaces. Prog. Geogr. 39 (03), 503–518. doi:10.18306/dlkxjz.2020.03.014
Huang, J., Shangguan, Z. H., Gui, T. T., and Liu, J. P. (2023). How urban development affects green development efficiency in China: taking the city cluster of Yangtze river economic belt as an example. Front. Environ. Sci. 11, 1–17. doi:10.3389/fenvs.2023.1169226
Lee, H. S., and Park, E. Y. (2020). Developing a landscape sustainability assessment model using an analytic hierarchy process in korea. Sustainability. 12 (1). doi:10.3390/su12010301
Li, G. (2023). Urban - rural relations: problems, evolution and development. The Frontiers of Society. Sci. Technol. 5 (1), 1–24. doi:10.25236/fsst.2023.050104
Li, H. C., Zhou, M. L., and Shi, X. Y. (2023). The Study on the impact of clean energy development on green economy. Highlights in Business, 5. Economics and Management, 515–521. doi:10.54097/hbem.v5i.5138 Available at: https://drpress.org/ojs/index.php/HBEM/index.
Li, H. Y., Weng, G. M., and Wang, D. P. (2024). Assessing the sustainable development level of the tourism eco-security system in the chengdu-chongqing urban agglomeration: a comprehensive analysis of dynamic evolution characteristics and driving factors, 1–25. doi:10.3390/su16166740
Liu, J. P., Zhang, W. C., and Nie, N. (2018). Spatial downscaling of TRMM precipitation data using an optimal subset regression model with NDVI and terrain factors in the yarlung zangbo river basin, China. Adv. Meteorology 2018 (1), 1–13. doi:10.1155/2018/3491960
Liu, L., Zhao, Y. T., Yang, Y. R., Liu, S., Gong, X. J., and Jiang, P. (2023a). Study on the measurement of industrial eco-efficiency, spatial distribution and influencing factors in Yangtze River Economic Belt. PLOS ONE 18 (4), 02839644–e284023. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0283964
Liu, N., Chen, Y., and Su, F. (2023b). Research on the spatial differences and influencing factors of integrated urban-rural development in the Yangtze River Delta. Front. Sustain. cities 4, 1–20. doi:10.3389/frsc.2022.1077653
Liu, T., and Zhou, B. Y. (2023). Research on the optimization path of green development in Shaanxi province based on the OECD’s perspective. doi:10.3390/su151612588
Meng, R. L., and Shao, J. (2022). Measurement, influencing factors and spatial spillover effect of China's green economy development level. BCP Bus. and Manag. 25, 480–494. doi:10.54691/bcpbm.v25i.1859
Myeong, S., Jung, Y., and Lee, E. (2018). A study on determinant factors in smart city development: an analytic hierarchy process analysis. Sustainability 10 (8), 2606–2622. doi:10.3390/su10082606
Phoochinda, W. (2019). Development of community network for sustainable tourism based on the green economy concept. J. Environ. Manag. Tour. 9 (6), 1236–1243. doi:10.14505//jemt.9.6(30).13
Qin, M. M., and Huang, Z. Y. (2023). A study on the differences in the synergistic development level of digitalization and greenization in the eastern and central regions of China. Sustainability 15 (24), 16688–16708. doi:10.3390/su152416688
Rousta, I., Doostkamian, M., Haghighi, E., Ghafarian Malamiri, H. R., and Yarahmadi, P. (2017). Analysis of spatial autocorrelation patterns of heavy and super-heavy rainfall in Iran. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 34 (9), 1069–1081. doi:10.1007/s00376-017-6227-y
Sharma, S., Kumar, S., and Singh, A. (2023). Assessment of Green Infrastructure for sustainable urban water management. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 23, 1–10. doi:10.1007/s10668-023-03411-w
Shen, Z. Y., Zhao, Q. Q., and Fang, Q. M. (2021). Analysis of green traffic development in zhoushan based on entropy weight TOPSIS 13, 8109. doi:10.3390/su13148109
Sun, Y. S., Tong, L. J., and Liu, D. Q. (2020). An empirical study of the measurement of spatial-temporal patterns and obstacles in the green development of northeast China 12, 10190. doi:10.3390/su122310190
Tang, Y., Yuan, Y. B., and Tian, B. Q. (2023). Assessment of spatio-temporal evolution trends and driving factors of green development in Harbin-Changchun urban agglomeration. Sci. Rep. 13 (1), 16785. doi:10.1038/s41598-023-44091-w
Topi, C., Esposto, E., and Valentino, M. G. (2016). The economics of green transition strategies for cities: can low carbon, energy efficient development approaches be adapted to demand side urban water efficiency? Environ. Sci. and Policy 58, 74–82. doi:10.1016/j.envsci.2016.01.001
Wang, G. W. (2020). Research on the measurement and influencing factors of green development capability in provincial regions of China from the perspective of three dimensional space: a case study of inner Mongolia. west forum Econ. Manag. Sichuan Econ. Manag. Inst. 31 (6), 15–26. doi:10.12181/jjgl.2020.06.03
Wang, H. J., and Zhang, J. X. (2023). Spatio-temporal patterns and driving factors of green development level of urban agglomerations in the yellow river basin. Emerg. Mark. Finance Trade 60 (4), 724–743. doi:10.1080/1540496x.2023.2253979
Wang, L., Yu, B., Chen, F., Wang, N., and Li, C. R. (2022). An analysis of eco–environmental changes in rural areas in China based on sustainability indicators between 2000 and 2015. Land 11 (8), 1321–1336. doi:10.3390/land11081321
Wang, M. Y., Wang, Y. C., Yang, Z. Y., and Guo, B. N. (2024). Does energy-consuming rights trading policy achieve urban pollution and carbon reduction? A quasi-natural experiment from China. Front. Environ. Sci. 12, 1–15. doi:10.3389/fenvs.2024.1430031
Wu, X. X., Liu, H., and Liu, W. (2023). Exploring the spatiotemporal evolution dynamic and influencing factor of green ecology transition for megacities: a case study of Chengdu, China. Ecol. Indic. 158, 111285–111314. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2023.111285
Xie, X. J., Zhang, N., and Zhao, Z. X. (2019). Research progress on spatial identification and optimization of “production life ecology”: the level of coordinated development of rural production, life, and ecology under the green growth strategy. J. Environ. Econ. 4 (04), 78–95. doi:10.19511/j.cnki.jee.2019.04.006
Xue, H. L., Lan, X., Zhang, Q., Liang, H. G., and He, Z. X. (2021). RETRACTED ARTICLE: assessment of the green development level for participating countries in the Belt and Road initiative. Ann. Operations Res. 326, 125. doi:10.1007/s10479-021-04440-2
Yang, Y. P., Liu, Z. Q., Chen, H. M., Wang, Y. Q., and Yuan, G. H. (2020). Evaluating regional eco-green cooperative development based on a heterogeneous multi-criteria decision-making model: example of the Yangtze River Delta region. Sustainability 12 (7), 3029–3048. doi:10.3390/su12073029
Yu, J., Shen, H. Y., Gou, J., and Zhang, X. Q. (2020). The green environment measurement by entropy method: a study based on minnan coastal area in China. J. Coast. Res. 103, 442–446. doi:10.2112/si103-090.1
Yuan, Q. Q., Yang, D. W., Yang, F., Ralph, A. L., Saieed, A., and Wang, K. (2020). Green industry development in China: an index based assessment from perspectives of both current performance and historical effort. J. Clean. Prod. 250, 119457–119516. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119457
Zhong, L., Liu, X. S., and Yang, P. (2020). Regional development gap assessment method based on remote sensing images and weighted Theil index. Arabian J. Geosciences 13, 1176–1189. doi:10.1007/s12517-020-06043-w
Zhu, K. W., He, J., Tian, X. S., Hou, P., Wu, L. J., Guan, D. J., et al. (2024). Analysis of evolving carbon stock trends and influencing factors in chongqing under future scenarios. Land 12, 421–517. doi:10.3390/land13040421
Keywords: green development level, theil index, GIS, environmental management, Chengdu-Chongqing economic zone
Citation: Zhu K, Wang T, He J, Song D, Wu L, Wu D, Huang S, Zhou L and Liu J (2024) Green development in the Chengdu-Chongqing economic zone: evolution and drivers from a “production-living-ecology” perspective. Front. Environ. Sci. 12:1506618. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2024.1506618
Received: 05 October 2024; Accepted: 02 December 2024;
Published: 18 December 2024.
Edited by:
Zhisong Chen, Nanjing Normal University, ChinaReviewed by:
Yang Wang, Yunnan Normal University, ChinaBingnan Guo, Jiangsu University of Science and Technology, China
Copyright © 2024 Zhu, Wang, He, Song, Wu, Wu, Huang, Zhou and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jun He, aGVqdW43MTAxQDE2My5jb20=; Dan Song, c2QuY3FlZUBnbWFpbC5jb20=
 Kangwen Zhu
Kangwen Zhu Tianyu Wang
Tianyu Wang Jun He2*
Jun He2*