- 1Faculty of Mathematics and Statistics, SuZhou University, SuZhou, Anhui, China
- 2Department of Mathematics, College of Basic Education, University of Duhok, Duhok, Iraq
- 3Department of Mathematics, College of Computer Science and Mathematics, University of Mosul, Mosul, Iraq
- 4Department of Mathematics, COMSATS University Islamabad, Vehari Campus, Vehari, Pakistan
- 5Department of Mathematics, Division of Science and Technology, University of Education, Lahore, Pakistan
Watershed system models are tools used to study and simulate the behavior of watersheds, which are areas of land where all the water drains to a common outlet, typically a river, lake, or ocean. These models are essential for understanding and managing water resources, predicting flood events, and assessing the impact of land use and climate changes on the environment. Moreover, these advanced models should also help in making better decisions about the watersheds. This paper presents an integrated novel approach for decision-making in the selection of a watershed system model called decision-making trial and evaluation laboratory (DEMATEL)-multi-objective optimization based on the ratio analysis (MOORA) framework. The proposed method employs the 2-tuple linguistic
1 Introduction
In hydrology and environmental research, a watershed system model (WSM) is a complex and all-encompassing analytical framework. It is a useful resource for figuring out how water moves around a certain area, or watershed, where all the precipitation and runoff from that region eventually meets up and empties into a larger body of water. The purpose of this model is to simulate and anticipate how water will behave throughout the watershed given a variety of conditions. The WSM, at its heart, incorporates multiple critical components to provide a comprehensive analysis of the hydrological cycle in a specific area. Among these factors is meteorological information, such as rainfall and temperature patterns, which is crucial for comprehending the system’s water supply. Things like land use and land cover have a significant impact on how water moves through the landscape. Urban areas, farms, woods, and wetlands all have different impacts on water penetration, surface runoff, and pollution transfer. Because soil type and features effect water retention and infiltration rates, which in turn effect groundwater recharge and the water balance within the watershed, they are also accounted for in the model. Variations in runoff rates and possible flood-risk areas are directly influenced by the topography of the area, which includes slopes and elevation changes. Additionally, agriculture, industry, and urban expansion within the watershed can introduce toxins and change the natural flow of water. The WSM must take into account these human-caused issues because of their significant effects on water quality, habitat protection, and ecosystem health. The WSM is used primarily to anticipate and analyze the flow of water within the system under varying conditions. This data is crucial for numerous uses, such as flood forecasting and management, water resource administration, pollution avoidance, and urban development strategies. It equips politicians, environmental scientists, and other decision-makers (DMs) with the fundamental information they require to make educated decisions on land use, conservation, and infrastructure development. The WSM is essentially a potent instrument that connects a theoretical understanding of environmental processes with real-world decision-making.
It helps us safeguard and sustainably manage our essential water resources while reducing our overall environmental impact by modeling the interplay between natural and human-induced elements within a watershed. The WSM continues to be an invaluable tool in our fight to preserve the world’s water supplies and secure a sustainable future for future generations in the face of mounting environmental problems and climate change. Earth system modeling, a fundamental research approach in Earth system science, is considered as the second Copernican revolution. Modeling may be seen of as a synthesis strategy to formalizing existing knowledge in Earth system science. The only way to simulate the evolution and interactions between the spheres of the complex and massive Earth system is through numerical modeling. The qualitative understanding of the Earth system may be transformed into a quantitative understanding via numerical modeling. Models can reproduce the previous state of the Earth system and anticipate its future condition. Moreover, models can assist academics, stakeholders, and DMs in proposing responses in advance of potential future changes based on real and hypothetical circumstances. In this light, numerical modeling is a critical tool for attaining sustainability. The watershed is the fundamental unit of the land-surface system on Earth. To better understand complex watershed processes and to promote the implementation of integrated river basin management, scientists have developed what is known as a watershed model, which is an all-encompassing Earth system model at the basin measurement. Similar to Earth system modeling, watershed modeling necessitates the simulation of energy, water, and geochemical cycles within the natural system. A watershed model must also be adequately detailed because the size of watershed research is significantly smaller than that of the entire Earth system. A wide range of phenomena, which are typically not accounted for in global-scale models, need to be incorporated into a WSM. These include three-dimensional groundwater dynamics, variations in plant distribution, seasonal changes in land use, and patterns of water demand. A WSM should also contain human activity simulation to better understand human impacts on hydrologic and biological processes and to propose solutions for river basin management.
1.1 Motivation
Although multiple multi-attribute decision-making strategies are employed to handle different decision-making problems, there is no study in which 2TL
The proposed study is driven by the following motivations:
1. The 2TL
2. The WPMM AO is a versatile and effective decision-making tool. This operator is very useful for aggregating data in MAGDM problems. As a result of these assertions, we are inspired to utilize WPMM AO for the 2TL
3. The DEMATEL-MOORA approach is capable of handling various MAGDM situations and provides a unique way to compute attribute weights and alternatives’ ranking values. This integrated method has received very little attention thus far. Apart from that, it has been noted to be a highly thorough, easy, and reliable way to determine the optimal choice in decision-making with the calculation of attribute weights. Nevertheless, this integrated method has not yet been expanded in the context of 2TL
1.2 Contribution
We begin our study by utilizing some fundamental WPMM AO for 2TL
The contributions of this study are as follows:
• The objective of this study is to employ the WPMM AO methodology within the context of the 2TL
• The subsequent objective is to formulate an enhanced DEMATEL-MOORA methodology in order to tackle the MAGDM problem. The DEMATEL-MOORA approach is implemented within the framework of 2TL
• To show the efficacy of the proposed method, it is applied to the problem of choosing a WSM. In addition, we analyze how varying inputs affect the outcomes.
• We compare the proposed technique to other existing approaches in order to demonstrate the reliability of the proposed method.
1.3 Structure
The article is structured as follows: In Section 2, a brief literature review is provided. Section 3 goes through some fundamental notions and definitions of existing concepts. Based on the 2TL
2 Literature review
In this section, we discuss about the literature review of
2.1
A key challenge is defining assessment values in decision-making due to unclear and unpredictable information. As a result, the FS was defined by Zadeh (1965). Later that year, FS extensions and FS-based MAGDM approaches were created (He and Wang, 2023; Denoeux, 2023; Al-shami and Mhemdi, 2023). However, FS only identifies the membership degree (MD) when representing uncertain information and completely ignores the non-membership degree (NMD). In order to characterize each element by two elements of MD
2.2 2-Tuple linguistic representation model
It is common practice to consider multiple alternatives to a problem and pick the best one based on the results of these comparisons. MAGDM is a cutting-edge field of study in the field of management science. The ability to make decisions is crucial in many contexts. The majority of individuals are obliged to convey their opinions in language because qualitative attributes are subjective or because exact numerical data collection is expensive. Significant improvements have been achieved in a variety of fields, including business strategy planning, quality evaluation, investment strategy selection, and linguistic decision-making, which evaluates linguistic data as the values of linguistic variables. DMs can communicate their preferences for different options in real-world decision-making situations. This can be done through the use of linguistic phrases such as good, fair, or poor. By employing appropriate decision-making processes, DMs can then identify and choose the most optimal alternative. In the context of analyzing the viability of a company’s investment strategy, professionals may articulate their assessments by employing a set of seven linguistic phrases derived from the linguistic term set (LTS) S = {
Owing to its advanced linguistic information processing capability, the language model effectively mitigates the issues of data loss and misrepresentations that were prevalent in previous models of language. According to Herrera and Martinez, a 2TL information processing method can successfully prevent information loss and deformation. To deal with scenarios where linguistic labels are applied to given data, Akram et al. (2023b) created a novel decision-making technique based on the 2TL Fermatean FS. That study’s key objective was to explore and clarify the use of the ELECTRE II method for group decision-making in a 2TL Fermatean fuzzy context. They investigated and expanded the 2TL
2.3 Power Muirhead mean aggregation operator
In the field of mathematical aggregation, the PMM operator is a strong synthesis of elegance and adaptability. Using its power parameter to add a dynamic twist on top of the classical Muirhead mean (MM), the PMM operator lets it naturally adapt to many situations. See it as a symphony conductor harmonizing individual parts to capture their interconnections and produce a balanced and subtle result. In multi-attribute decision-making, where complexity abounds and easily balances importance and correlation among inputs, this operator shines the most. The PMM operator creates a real masterpiece of mathematical creativity by combining the individual and group traits of data, transforming complex problems into clear, practical insights. Li et al. (2018) introduced new operators for aggregating PF information, including the PMM operator. These operators considered relationships between fused data and aggregated values, providing more information for multi-attribute decision-making. Linguistic
2.4 DEMATEL method
In order to more effectively boost the competency development of global managers, Wu and Lee (2007) created an efficient method combining fuzzy logic and the DEMATEL method. To evaluate the relationships between factors in different areas in an uncertain and fuzzy environment, the fuzzy DEMATEL approach is widely used. Zhang et al. (2023) developed a novel fuzzy DEMATEL approach based on alpha-level sets for managing fuzzy information, as well as recognizing experts’ hesitation from the qualitative context in an uncertain and fuzzy environment. Most modern DEMATEL approaches are only appropriate for small and simple systems, and they do not determine whether expert consensus has been reached. For achieving consensus in complex systems, Du and Shen (2023) proposed a group hierarchical DEMATEL approach. The decision-making process of the hierarchical DEMATEL approach was examined as it was expanded from individual decisions to group decisions. Based on a fuzzy DEMATEL approach, Priyanka et al. (2023) studied the critical challenges in selecting the best human resources practices for start-ups. Because the DEMATEL method on human assessments is inaccurate and subjective, the fuzzy DEMATEL approach was proposed to investigate the significance of identified challenges and the cause-effect relationships between them. Yilmaz et al. (2023) proposed the fuzzy DEMATEL approach to improve performance. The proposed approach evaluated and ranked the most important indicators for boosting an enterprise’s overall maintenance performance. Using a
2.5 MOORA method
Several objectives are handled through multi-objective optimization, with each objective maintaining its units. It is suggested to use a ratio system’s internal mechanical solution, which generates dimensionless numbers. The ratio system makes it possible to use a second method called a Reference Point Theory, which makes use of the ratios in the ratio system. Brauers and Zavadskas (2012) were the creators of the general theory known as the MOORA method. Sevim and Kurtaran (2023) used MOORA, a MAGDM method based on ratio analysis, to evaluate Turkey’s performance in the field of health tourism and to show the current situation in the interest of improving the field. In that study, the MOORA-Ratio method and the MOORA-Reference Point method were combined. To choose the best alternatives, Kumar et al. (2023) applied the decision-making methods AHP and MOORA, which combined minimization and maximization attributes. AHP and MOORA have been merged and used in that study to optimize the outcomes. When selecting phase change materials, Wankhede et al. (2023) used the GRA, COPRAS, and MOORA approaches while considering the technical requirements of the materials. The failure mode and effects analysis method have some disadvantages, including incomplete prioritization and the lack of ability to assess the relative importance of risk factors in an uncertain environment. To solve these problems, Ghiaci and Ghoushchi (2023) developed a new integrated approach based on SWARA and MOORA in the field of PFS. Shahzadi et al. (2022) explored the intelligent manufacturing system, a framework that boosted productivity by integrating the logical aspects of manufacturing. The applicability of the MOORA method has been investigated in that paper to choose the intelligent manufacturing system utilizing Fermatean FS. For the contemporary era’s growing energy demand, a movement towards clean and natural energy sources is essential. Basaran and Tarhan (2022) used the MOORA approach, one of the MAGDM methods, to determine the best location for offshore wind turbines. Due to the Dombi generalized structure, the Dombi operators provide a versatile structure with their adjustable parameters. On
2.6 Abbreviations and descriptions
Different abbreviations and their descriptions used in this article are given in Table 1.
3 Review of fundamental concepts
To facilitate a better understanding of the subject matter, this section presents a concise summary of fundamental principles, encompassing the
Definition 1. (Yager, 2016) Let
in which
Definition 2. (Naz et al., 2022a) Consider a LTS denoted as
where
Definition 3. (Naz et al., 2022a) Consider the 2TL
and its accuracy function
Definition 4. (Naz et al., 2022a) Let
(1) If
(2) If
(3) If
• If
• If
• If
Definition 5. (Naz et al., 2022a) Let
1.
2.
3.
4.
Definition 6. (Naz et al., 2022a) Let
Definition 7. (Muirhead, 1902) Let
where
3.1 Terminologies and notations
The terminologies and notations used in this article are listed in Table 2.
4 Decision analysis with a 2TL
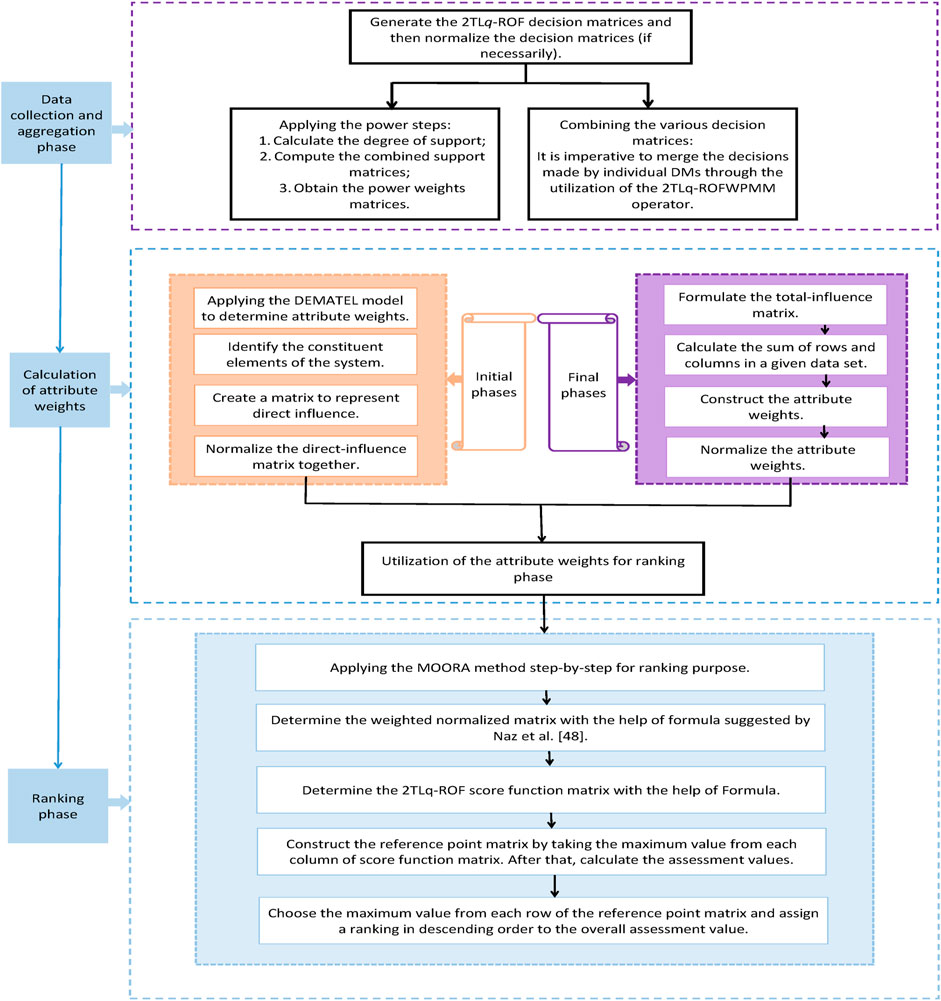
Research methodology plays a crucial role in scientific investigations as it provides a systematic framework for conducting research and generating reliable results. The combination of 2TL
Step 1. Establish the 2TL
Let us consider a set of
Step 2. Normalize the decision matrices:
where
Step 3. Calculate the degree of support denoted as
The dissimilarity between
Step 4. Compute the combined support matrices
Step 5. The power weights matrices, denoted as
Step 6. Combining the various decision matrices.
In order to construct an aggregated 2TL
Step 7. Applying the DEMATEL model to determine attribute weights.
Step 7.1. Identify the constituent elements of the system. This approach can be achieved through several methodologies, such as conducting a comprehensive review of pertinent scholarly sources, engaging in collaborative group deliberations regarding practical obstacles, and seeking insights from authoritative subject matter specialists. Let
Step 7.2. Create a matrix to represent direct influence by conducting pairwise assessments of the causal impact among
Step 7.3. Normalize the direction-influence matrix together. The formula for calculating the normalized direct-influence matrix in Equations 12:
where in Equations 13
And,
Step 7.4. Use an iterative method to compute the complete influence matrix. Matrix inversion converges if and only if the system’s indirect effects, as well as the powers of
Step 7.5. Use the following formulas to find the total number of rows
The transposed value of the
Step 7.6. The construction of attribute weights is determined by the following Equation 18:
Finally, the normalized attribute weights are defined in Equation 19:
Step 8. Determine the weighted normalized matrix
Step 9. Determine the 2TL
Step 10. Construct the reference point matrix
Step 11. Choose the maximum value from each row of the reference point matrix
4.1 Pseudocode framework
The pseudocode framework of the proposed approach is as follows:
Step 1. Establish the 2TL
Let us consider a set of
Step 2. Normalize the decision matrices:
Step 3. Calculate the degree of support
The dissimilarity is quantified by the normalized Hamming distance.
Step 4. Compute the combined support matrices:
Step 5. Compute the power weight matrices:
Step 6. Combine the decision matrices using the 2TL
Step 7. Apply the DEMATEL model to determine attribute weights. Perform the following sub-steps:
7.1. Identify the constituent elements of the system.
7.2. Create and aggregate direct influence matrices:
7.3. Normalize the direct influence matrix:
7.4. Compute the total influence matrix:
7.5. Calculate row and column sums:
7.6. Construct normalized attribute weights:
Step 8. Compute the weighted normalized matrix
Step 9. Determine the 2TL
Step 10. Construct the reference point matrix
where
Step 11. Rank alternatives based on the maximum values from
The steps of the proposed approach are visually depicted in Figure 1.
4.2 Complexity analysis
The complexity of the proposed approach is analyzed as follows:
The complexity analysis of the proposed approach involves evaluating each step in the decision-making process. Constructing the decision matrix for all DMs and normalizing it has a time complexity that grows linearly with the number of alternatives, attributes, and DMs. The calculation of the degree of support involves pairwise comparisons, which adds a quadratic factor concerning the number of DMs. Aggregating these support values and computing power weights also scale linearly. The DEMATEL model, used to analyze relationships among attributes, includes matrix inversion and multiplication, leading to a cubic complexity with respect to the number of attributes. Ranking alternatives requires sorting, which is logarithmic in complexity relative to the number of alternatives. Combining all steps, the dominant factors are the quadratic dependency on the number of DMs for degree of support and the cubic dependency on the number of attributes in the DEMATEL model, resulting in the overall complexity being the sum of these terms.
5 Numerical illustration
WSMs are highly advanced instruments that serve a crucial function in comprehending, evaluating, and governing the intricate hydrological and environmental dynamics within watersheds, which are fundamental constituents of our natural ecosystems. These models function as comprehensive frameworks for analyzing the complex interrelationships among different elements of a watershed, encompassing precipitation, surface water, groundwater, soil, vegetation, and human activities. WSMs offer significant insights into the dynamics of water movement, pollutant dispersion, and the influence of factors such as land use alterations, climate fluctuations, and infrastructure advancements on the overall wellbeing and sustainability of a watershed. These models effectively simulate intricate interactions within the system, thereby facilitating a comprehensive understanding of the aforementioned processes. One of the principal purposes of these models is to accurately forecast and efficiently administer water resources. Water resource managers can make well-informed decisions regarding the allocation, distribution, and conservation of water by utilizing estimates of both the quantity and quality of water present within a given watershed. Moreover, watershed models provide significant value in the realm of flood prediction and management. In addition, WSMs are critical resources for these aims. Water quality and ecosystem health can be evaluated concerning human activities, including agriculture, urbanization, and industrial development. This data is crucial for planning strategies that reduce pollution and maintain watershed ecosystem health. WSMs are becoming increasingly important in a fast-evolving world where climate change presents formidable threats to water resources and ecosystems. They help us learn more about the possible implications of climate change on rainfall, temperature, and hydrological cycles, which is crucial for planning adaptation methods to lessen the severity of these effects. Models of the watershed system are multi-purpose tools that help bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and real-world watershed management. Ultimately, they ensure the sustainable use and protection of one of our most precious natural resources, water, by equipping scientists, policymakers, and stakeholders to make educated decisions about water resource management, environmental conservation, and disaster preparedness. For the sake of present and future generations, these models are vital parts of our toolset for creating sustainable and robust communities.
A concise overview of the alternatives that have to be assessed is provided below: (1) Physically-based models
WSMs can simulate the potential impacts of excessive precipitation or snowmelt on downstream regions, thereby facilitating the provision of timely warnings and the implementation of effective disaster preparedness measures. Therefore, WSMs in the environment could be categorized as a classical MAGDM problem. Based on the discussion above, the 2TL
5.1 Decision analysis
This subsection outlines the evaluation approach employed for the selection of WSMs. The 2TL
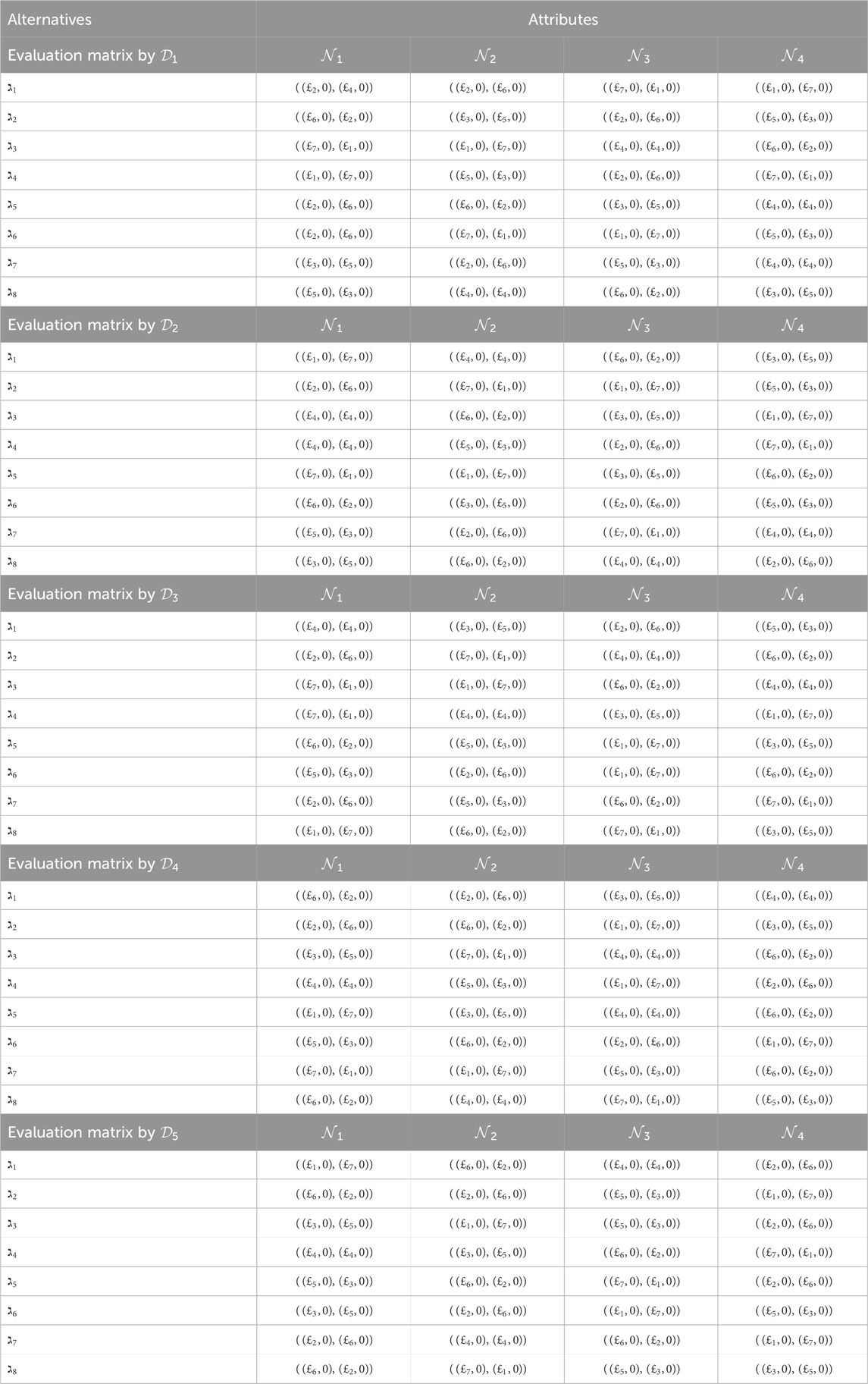
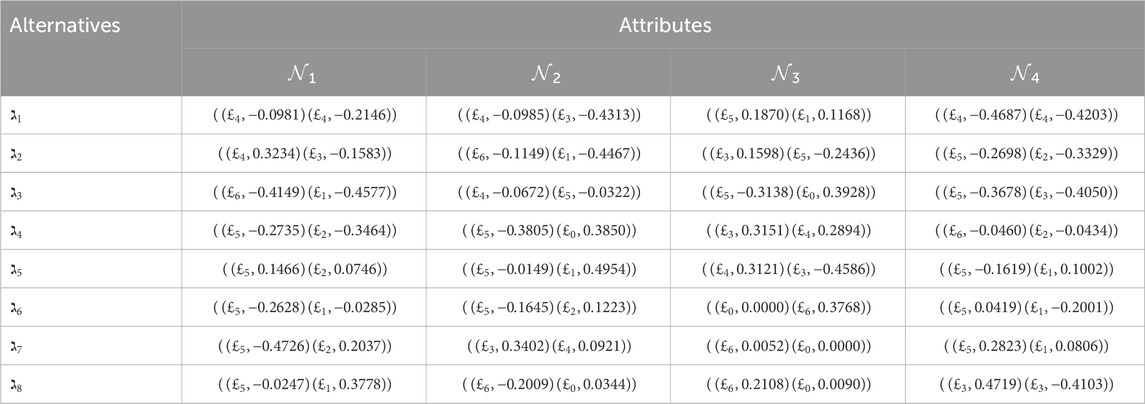
Step 1. Formulate the 2TL
Step 2. The utilization of Equation 7 serves the goal of normalizing the decision matrices. Given that all attributes exhibit advantageous characteristics, it can be shown that the five choice matrices remain unaltered.
Step 3. Using Equation 8, we can compute the support










Step 4. Utilizing Equation 9, we can determine the comprehensive support matrices










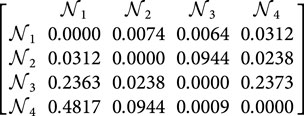
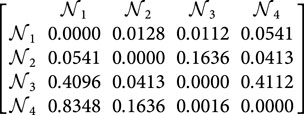
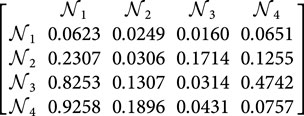
Step 5. By utilizing Equation 10, we are able to calculate the power weight matrix for the judgment
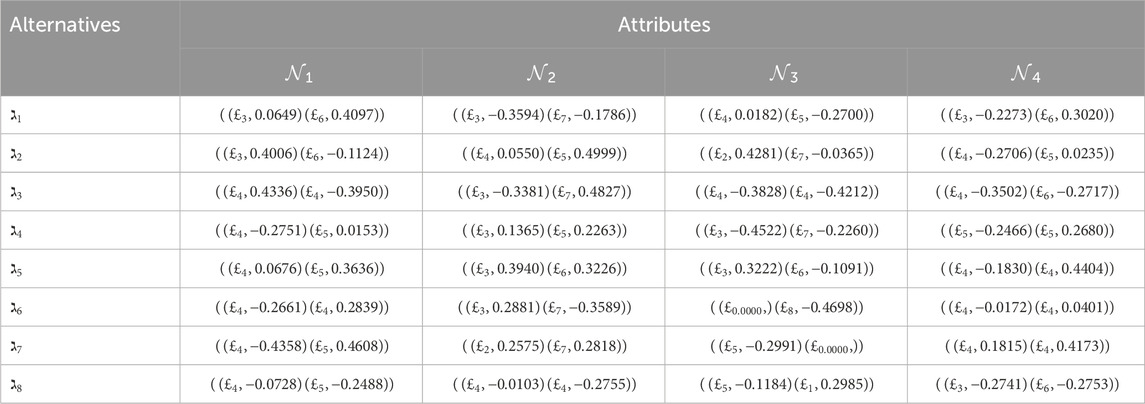
Step 6. To aggregate the values from the overall
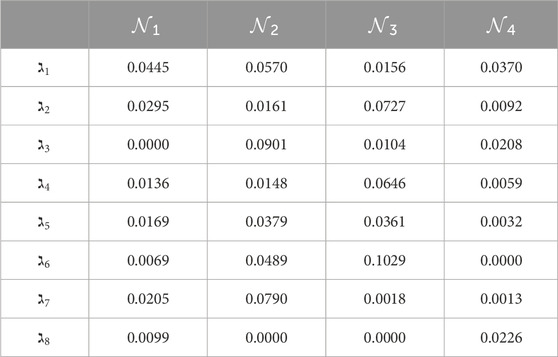
Step 7. The DEMATEL model is utilized for the determination of attribute weights.
Step 7.1. The identification of the system’s components can be accomplished by several methods, such as conducting a comprehensive review of pertinent literature, engaging in group deliberations focused on practical obstacles encountered in real-life scenarios, and seeking input from domain experts.
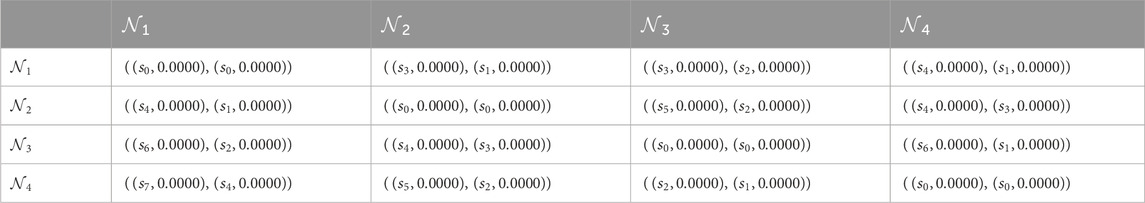
Step 7.2. The construction of the direct influence matrix involves conducting pairwise comparisons of qualities with DMs, as seen in Table 5.
Step 7.3. Acquire a matrix that represents the direction and influence of a single value. The matrix values are presented below:
Then normalized the single valued direct-influence matrix. Normalized direct-influence matrix is given below:
Step 7.4. The total influence matrix is constructed according to the format presented below:
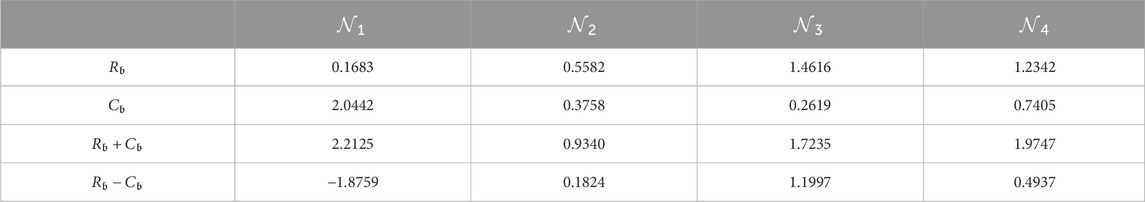
Step 7.5. The calculation of the row sums
Step 7.6. So, the normalized representation of the weight vector is as follows:
Step 8. Determine
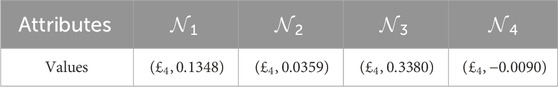
Step 9. Determine the 2TL
Step 10. Construct
Step 11. Choose the maximum value from each row of
And the ranking of alternatives is as follows:
Therefore,
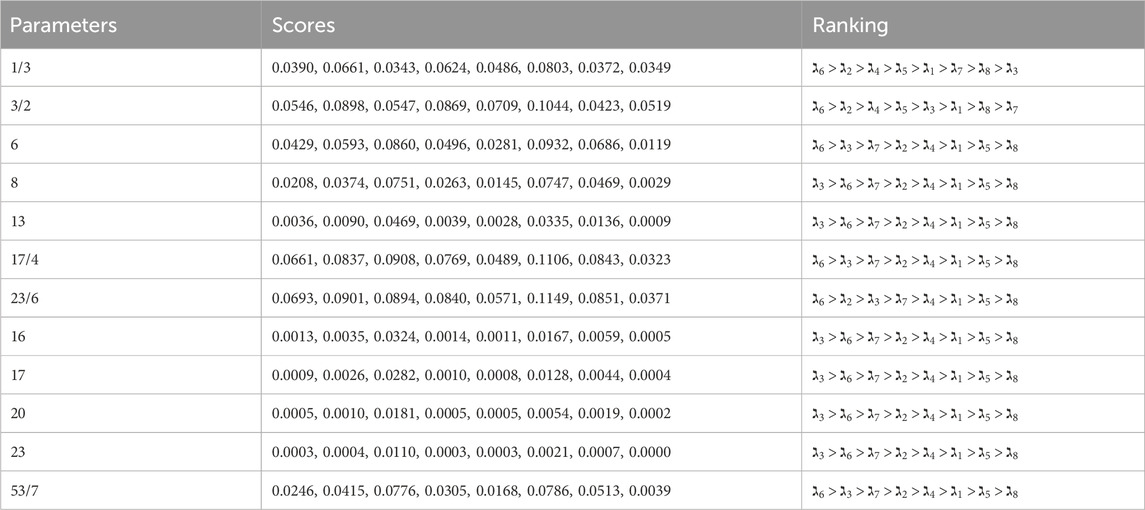
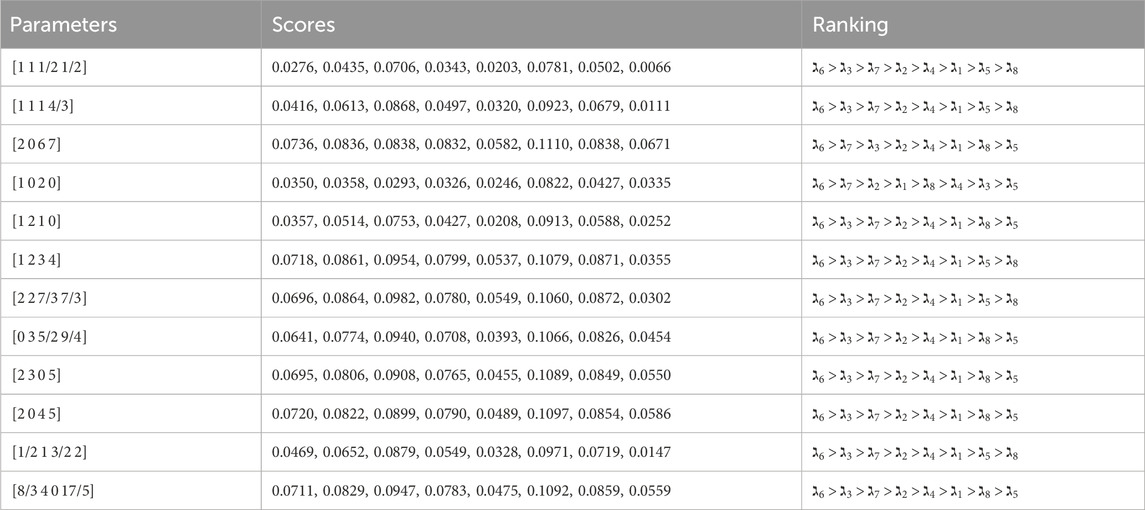
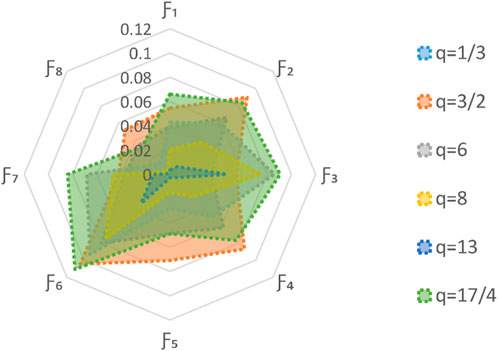
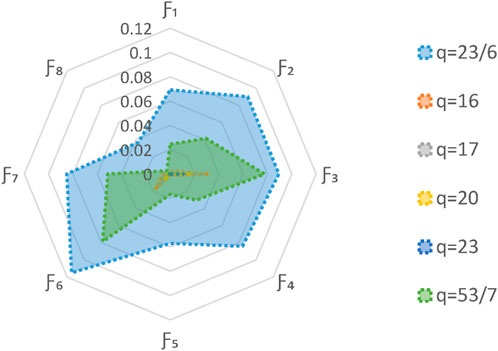
5.2 Parameter analysis
In this subsection, a thorough parameter analysis is conducted utilizing the parameters
5.2.1 The effect of parameter
The parameter
5.2.2 The effect of parameter
The present study evaluates the impact of parameter
This consistency in the optimal choice, regardless of different
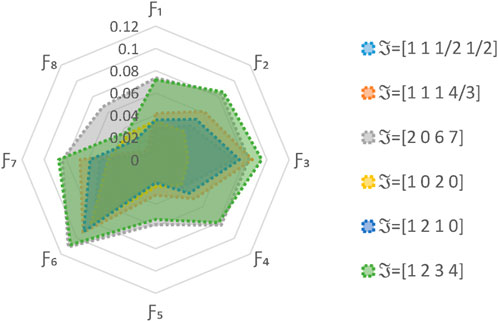
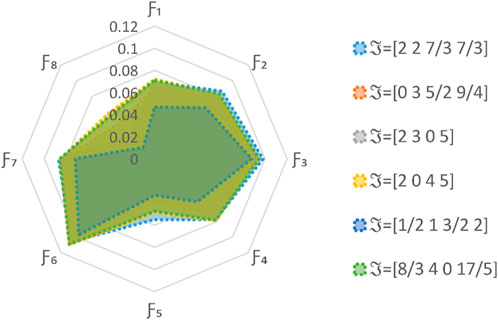
5.3 Comparative analysis
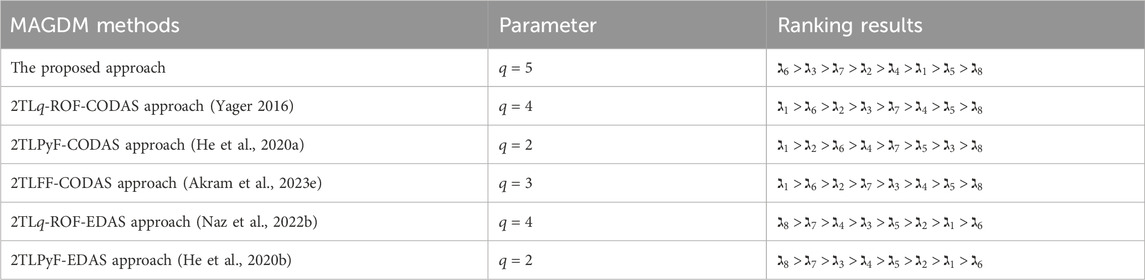
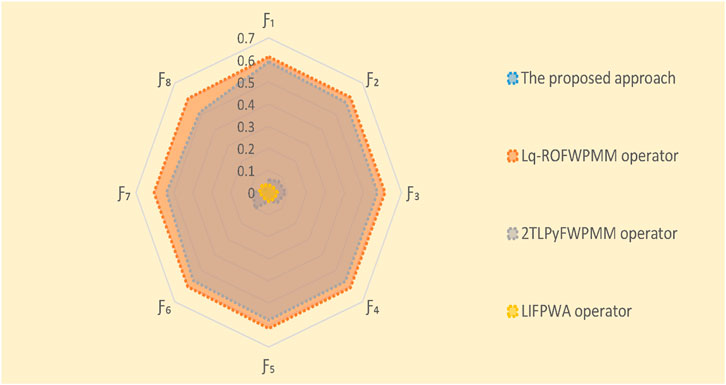
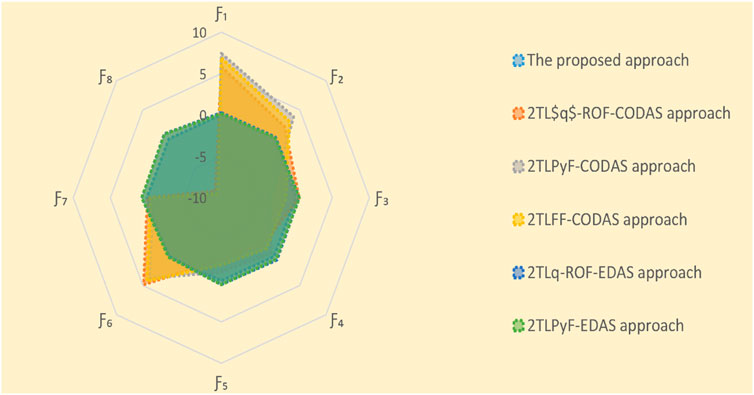
In this subsection, we employ validated methodologies to address the proposed MAGDM problem and evaluate the results using our framework to assess its practicality and efficacy. The proposed technique is subjected to a comparative study using several AOs and ranking systems. The evaluation outcomes for the selection of the best choice are computed meticulously through the implementation of these procedures. Hence, we solve the concerned problem for these approaches and ranked the results in Tables 14–17. The visual depiction of comparative analysis is given in Figures 6, 7.
5.3.1 Comparative analysis with different AOs
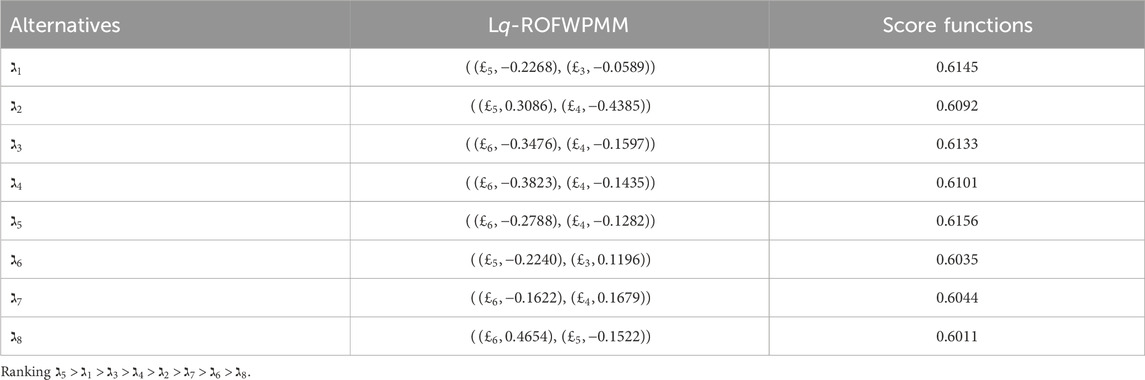
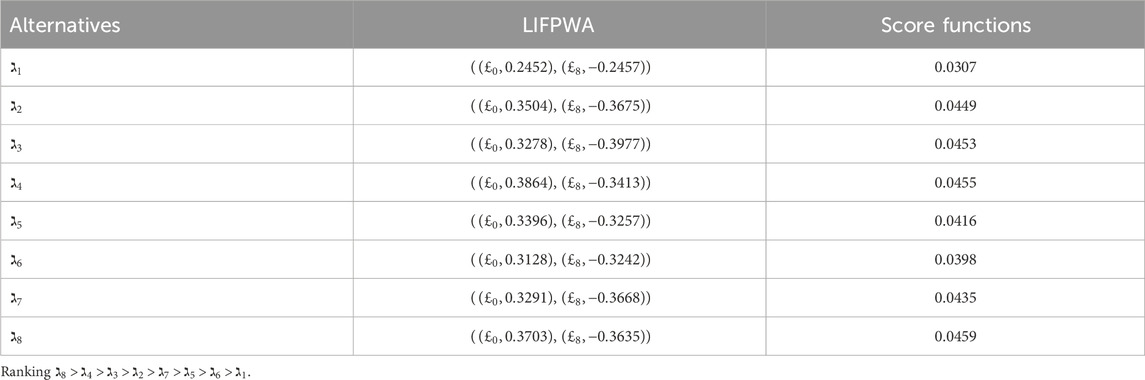
In this study, we compare our proposed method to three existing AOs: the L
5.3.2 Comparative analysis with different ranking methods
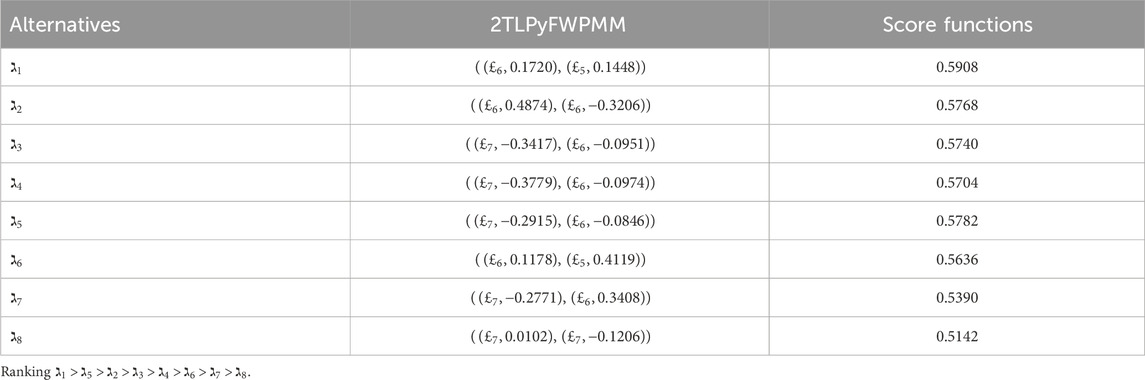
In this analysis, we compare our proposed approach with the 2TL
Our analysis involves a comprehensive comparison of our proposed methodology with different AOs and ranking methods. The primary objective is to rigorously validate the effectiveness and rationale of our novel approach presented in this research paper. By conducting thorough computations and rankings, we aim to discern the most optimal alternative. To achieve this, we employed a range of datasets and scenarios to test the adaptability and robustness of our method under various conditions. Ultimately, this comprehensive evaluation seeks to establish the reliability and practical utility of our approach in addressing real-world decision-making problems.
6 Conclusion
To better understand the complex dynamics of watersheds, which are vital parts of our natural landscape, hydrologists and environmental scientists rely on WSMs. A WSM is a computational depiction of the complex processes that occur within a watershed, such as the flow of water, the distribution of precipitation, the actions of soil and plants, and the effects of human activities. These models are based on the idea of simulating a watershed’s behavior under different conditions, which provides researchers, scientists, and policymakers with invaluable insights into water flow across the landscape, the transport of pollutants, and the impact of factors like land use change, climate variation, or infrastructure development on the watershed’s health and sustainability. Management of water supplies is a fundamental use case for WSMs. They allow for accurate forecasting and control of a watershed’s water supply. This is of critical importance in areas where water is scarce or when water is used for multiple purposes. These models help with water allocation, conservation policies, and infrastructure construction by providing realistic estimates of water availability and demand. In addition, watershed models assume a critical role in the prediction and management of floods. Through the simulation of a watershed’s reaction to intense precipitation or the melting of snow, these models can offer early notification of the likelihood of flooding occurrences. This aids communities in their preparedness and enables them to respond efficiently, thereby mitigating harm and safeguarding human lives. WSMs are also highly advantageous for environmental conservation and protection.
These tools provide an evaluation of the influence of human activities, such as agriculture, urbanization, or industrial operations, on the quality of water and the overall wellbeing of ecosystems within a given watershed. Understanding this information is crucial for formulating policies and implementing strategies that effectively address pollution and uphold the integrity of ecological equilibrium. In the context of a dynamic climate, the significance of WSMs is progressively escalating. These studies aid in comprehending the influence of climate change on precipitation patterns, temperature variations, and hydrological cycles within a specific watershed. Consequently, they furnish useful empirical evidence for the formulation of policies aimed at adapting to and mitigating the aforementioned impacts. WSMs are highly adaptable and essential instruments that serve to connect the divide between scientific comprehension and the implementation of effective watershed management strategies. These tools provide individuals with the ability to make well-informed choices regarding water resources, environmental preservation, and readiness for disasters, guaranteeing the sustainable utilization and safeguarding of one of the Earth’s most valuable assets water. These models play a crucial role in our repertoire for constructing resilient and ecologically sustainable communities that cater to the needs of both current and future generations. The use of integrated watershed models to examine complex watershed systems and facilitate integrated river basin management is on the rise. We think that improved watershed management and scientific understanding can both benefit from integrated watershed modeling.
The water, land, air, plant, and human nexus within the watershed should be modeled to accurately reflect its dynamics and coevolution. As a stand-in for models of watershed systems that incorporate decision-making algorithms, the management-focused model is useful. The explicit linkage of attribute values in the modern environment means that the generalized WPMM AO can address problems in MAGDM that arise in the real-world. So, we suggested forming a group AO to combine 2TL
Moreover, the method’s effectiveness in predicting real-world watershed dynamics may be influenced by the limitations of the available data and the assumptions made during model development, such as the simplification of environmental processes and human behaviors. Furthermore, the approach may require more extensive validation under diverse environmental and socio-economic conditions to fully establish its generalizability and robustness across different geographical regions. In the future, we will plan to broaden our scope to encompass cases involving two variables. Our initial goal is to see if the method we have proposed can be applied to other typical MAGDM situations, such as supplier selection, medical diagnostics, and so on. The rest of the study will examine prospective alternative AOs for 2TL
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
JL: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. HS: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. AS: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. MR: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. MB: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. NS: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. Educational Fund: Doctoral, and Scientific Research Start up Fund (Project No: 2019jb25).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Akram, M., Bibi, R., and Deveci, M. (2023b). An outranking approach with 2-tuple linguistic Fermatean fuzzy sets for multi-attribute group decision-making. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 121, 105992–992. doi:10.1016/j.engappai.2023.105992
Akram, M., Khan, A., Luqman, A., Senapati, T., and Pamucar, D. (2023c). An extended MARCOS method for MCGDM under 2-tuple linguistic q-rung picture fuzzy environment. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 120, 105892. doi:10.1016/j.engappai.2023.105892
Akram, M., Muhammad, G., and Ahmad, D. (2023a). Analytical solution of the Atangana-Baleanu-Caputo fractional differential equations using Pythagorean fuzzy sets. Granul. Comput. 8 (4), 667–687. doi:10.1007/s41066-023-00364-3
Akram, M., Naz, S., Feng, F., Ali, G., and Shafiq, A. (2023d). Extended MABAC method based on 2-tuple linguistic T-spherical fuzzy sets and Heronian mean operators: an application to alternative fuel selection. AIMS Math. 8 (5), 10619–10653. doi:10.3934/math.2023539
Akram, M., Niaz, Z., and Feng, F. (2023e). Extended CODAS method for multi-attribute group decision-making based on 2-tuple linguistic Fermatean fuzzy Hamacher aggregation operators. Granul. Comput. 8 (3), 441–466. doi:10.1007/s41066-022-00332-3
Al-shami, T. M., and Mhemdi, A. (2023). Generalized frame for orthopair fuzzy sets: (m, n)-fuzzy sets and their applications to multi-criteria decision-making methods. Information 14 (1), 56. doi:10.3390/info14010056
Arora, R., Dhankhar, C., Yadav, A. K., and Kumar, K. (2023). “A TOPSIS method based on Entropy measure for q-rung orthopair fuzzy sets and its application in MADM,” in In soft computing for problem solving: proceedings of the SocProS. Singapore: springer nature Singapore, 709–718. doi:10.1007/978-981-19-6525-8-54
Atanassov, K. T. (1986). Intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 20 (1), 87–96. doi:10.1016/s0165-0114(86)80034-3
Aydemir, S. B., and Yilmaz Gunduz, S. (2020). Extension of multi-Moora method with some q-rung orthopair fuzzy Dombi prioritized weighted aggregation operators for multi-attribute decision making. Soft Comput. 24 (24), 18545–18563. doi:10.1007/s00500-020-05091-4
Basaran, H. H., and Tarhan, I. (2022). Investigation of offshore wind characteristics for the northwest of Turkiye region by using multi-criteria decision-making method (MOORA). Results Eng. 16, 100–757.
Brauers, W. K. M., and Zavadskas, E. K. (2012). Robustness of MULTIMOORA: a method for multi-objective optimization. Informatica 23 (1), 1–25. doi:10.15388/informatica.2012.346
Deng, X., Wang, J., and Wei, G. (2020). Multiple attribute decision making based on power muirhead mean operators under 2-tuple linguistic pythagorean fuzzy environment. Cogn. Comput. 12 (6), 1276–1298. doi:10.1007/s12559-020-09756-y
Denoeux, T. (2023). Reasoning with fuzzy and uncertain evidence using epistemic random fuzzy sets: general framework and practical models. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 453, 1–36. doi:10.1016/j.fss.2022.06.004
Du, Y. W., and Shen, X. L. (2023). Group hierarchical DEMATEL method for reaching consensus. Comput. and Industrial Eng. 175, 108842–842. doi:10.1016/j.cie.2022.108842
Eti, S., Dincer, H., Gokalp, Y., Yuksel, S., and Kararoglu, D. (2023). Identifying key issues to handle the inflation problem in the health care industry caused by energy prices: an evaluation with decision-making models. Manag. Inflat. Supply Chain Disruptions Glob. Econ., 162–178. doi:10.4018/978-1-6684-5876-1.ch011
Ghiaci, A. M., and Ghoushchi, S. J. (2023). Assessment of barriers to IoT-enabled circular economy using an extended decision-making-based FMEA model under uncertain environment. Internet Things 22, 100–719.
Guneri, B., and Deveci, M. (2023). Evaluation of supplier selection in the defense industry using q-rung orthopair fuzzy set based EDAS approach. Expert Syst. Appl. 222, 119846–846. doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2023.119846
He, S., and Wang, Y. (2023). Evaluating new energy vehicles by picture fuzzy sets based on sentiment analysis from online reviews. Artif. Intell. Rev. 56 (3), 2171–2192. doi:10.1007/s10462-022-10217-1
He, T., Wei, G., Lu, J., Wu, J., Wei, C., and Guo, Y. (2020b). A novel EDAS based method for multiple attribute group decision making with Pythagorean 2-tuple linguistic information. Technol. Econ. Dev. Econ. 26 (6), 1125–1138. doi:10.3846/tede.2020.12733
He, T., Zhang, S., Wei, G., Wang, R., Wu, J., and Wei, C. (2020a). CODAS method for 2-tuple linguistic Pythagorean fuzzy multiple attribute group decision making and its application to financial management performance assessment. Technol. Econ. Dev. Econ. 26 (4), 920–932. doi:10.3846/tede.2020.11970
Herrera, F., and Martinez, L. (2001). A model based on linguistic 2-tuples for dealing with multigranular hierarchical linguistic contexts in multi-expert decision-making. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man, Cybern. Part B Cybern. 31 (2), 227–234. doi:10.1109/3477.915345
Ihsan, M., Saeed, M., Khan, K. A., and Nosheen, A. (2023). An algebraic approach to the variants of convexity for soft expert approximate function with intuitionistic fuzzy setting. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 17 (1), 2182144. doi:10.1080/16583655.2023.2182144
Jin, F., Guo, S., Cai, Y., Liu, J., and Zhou, L. (2023). 2-Tuple linguistic decision-making with consistency adjustment strategy and data envelopment analysis. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 118, 105671. doi:10.1016/j.engappai.2022.105671
Komsiyah, S., and Balqis, D. A. (2023). Analysis of decision support system for determining industrial sub-district using DEMATEL-MABAC methods. Procedia Comput. Sci. 216, 499–509. doi:10.1016/j.procs.2022.12.162
Kumar, R., Mishra, A. K., Dutta, S., Singh, A. K., and Kumar Singh, A. (2023). Optimization and prediction of response characteristics of electrical discharge machining using AHP-MOORA and RSM. Mater. Today Proc. 80, 333–338. doi:10.1016/j.matpr.2023.02.138
Li, L., Zhang, R., Wang, J., Zhu, X., and Xing, Y. (2018). Pythagorean fuzzy power Muirhead mean operators with their application to multi-attribute decision making. J. Intelligent and Fuzzy Syst. 35 (2), 2035–2050. doi:10.3233/jifs-171907
Liu, P., Khan, Q., and Mahmood, T. (2019a). Some single-valued neutrosophic power muirhead mean operators and their application to group decision making. J. Intelligent and Fuzzy Syst. 37 (2), 2515–2537. doi:10.3233/jifs-182774
Liu, P., Khan, Q., Mahmood, T., and Hassan, N. (2019b). T-spherical fuzzy power Muirhead mean operator based on novel operational laws and their application in multi-attribute group decision making. IEEE Access 7, 22613–22632. doi:10.1109/access.2019.2896107
Liu, P., and Liu, W. (2019). Multiple-attribute group decision-making method of linguistic q-rung orthopair fuzzy power Muirhead mean operators based on entropy weight. Int. J. Intelligent Syst. 34 (8), 1755–1794. doi:10.1002/int.22114
Liu, P., and Qin, X. (2017). Power average operators of linguistic intuitionistic fuzzy numbers and their application to multiple-attribute decision making. J. Intelligent and Fuzzy Syst. 32 (1), 1029–1043. doi:10.3233/jifs-16231
Mahmood, T., Haleemzai, I., Ali, Z., Pamucar, D., and Marinkovic, D. (2021). Power Muirhead mean operators for interval-valued linear Diophantine fuzzy sets and their application in decision-making strategies. Mathematics 10 (1), 70. doi:10.3390/math10010070
Muirhead, R. F. (1902). Some methods applicable to identities and inequalities of symmetric algebraic functions of n letters. Proc. Edinb. Math. Soc. 21, 144–162. doi:10.1017/s001309150003460x
Namburu, A., Mohan, S., Chakkaravarthy, S., and Selvaraj, P. (2023). Skin Cancer segmentation based on triangular intuitionistic fuzzy sets. SN Comput. Sci. 4 (3), 228. doi:10.1007/s42979-023-01701-8
Naz, S., Akram, M., Al-Shamiri, M. M. A., Khalaf, M. M., and Yousaf, G. (2022a). A new MAGDM method with 2-tuple linguistic bipolar fuzzy Heronian mean operators. Math. Biosci. Eng. 19 (4), 3843–3878. doi:10.3934/mbe.2022177
Naz, S., Akram, M., Fatima, A., and Nadeem, A. (2022b). Q-rung orthopair fuzzy 2-tuple linguistic hamy mean operators for MAGDM with modified EDAS method. In real life applications of multiple criteria decision making techniques in fuzzy domain. Singap. Springer Nat. Singap., 369–415. doi:10.1007/978-981-19-4929−618
Naz, S., Akram, M., Shafiq, A., and Akhtar, K. (2024). Optimal airport selection utilizing power Muirhead mean based group decision model with 2-tuple linguistic q-rung orthopair fuzzy information. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern. 15 (2), 303–340. doi:10.1007/s13042-023-01911-9
Naz, S., Shafiq, A., Butt, S. A., and Ijaz, R. (2023). A new approach to sentiment analysis algorithms: extended SWARA-MABAC method with 2-tuple linguistic q-rung orthopair fuzzy information. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 126, 106943–943. doi:10.1016/j.engappai.2023.106943
Ozdemirci, F., Yuksel, S., Dincer, H., and Eti, S. (2023). An assessment of alternative social banking systems using T-spherical fuzzy TOP-DEMATEL approach. Decis. Anal. J. 6, 100184–184. doi:10.1016/j.dajour.2023.100184
Pan, L., Deng, Y., and Cheong, K. H. (2023). Quaternion model of Pythagorean fuzzy sets and its distance measure. Expert Syst. Appl. 213, 119222–222. doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2022.119222
Priyanka, R., Ravindran, K., Sankaranarayanan, B., and Ali, S. M. (2023). A fuzzy DEMATEL decision modeling framework for identifying key human resources challenges in start-up companies: implications for sustainable development. Decis. Anal. J. 6, 100192–192. doi:10.1016/j.dajour.2023.100192
Rao, F., and Xiao, M. (2023). A novel MADM algorithm for physical education teaching quality evaluation based on 2-tuple linguistic neutrosophic numbers power Heronian mean operators. Plos One 18 (2), e0279534. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0279534
Razzaque, A., Razaq, A., Alhamzi, G., Garg, H., and Faraz, M. I. (2023). A detailed study of mathematical rings in q-rung orthopair fuzzy framework. Symmetry. 15 (3), 697. doi:10.3390/sym15030697
Saeed, M., Ahmad, M. R., and Rahman, A. U. (2023). Refined Pythagorean fuzzy sets: properties, set-theoretic operations and axiomatic results. J. Comput. Cognitive Eng. 2 (1), 10–16. doi:10.47852/bonviewjcce2023512225
Sarkar, A., Deb, N., and Biswas, A. (2023). Weighted dual hesitant $$q$$-rung orthopair fuzzy sets and their application in multicriteria group decision making based on Hamacher operations. Comput. Appl. Math. 42 (1), 40. doi:10.1007/s40314-022-02160-2
Sevim, F., and Kurtaran, A. T. (2023). Evaluation of Turkey’s health tourism performance with the MOORA method. Gumushane Univ. Sos. Bilim. Derg. 14 (1), 99–109.
Shahzadi, G., Luqman, A., and Ali Al-Shamiri, M. M. (2022). The extended MOORA method based on Fermatean fuzzy information. Math. Problems Eng. 2022 (1), 7595872.
Wan, B., Hu, Z., Garg, H., Cheng, Y., and Han, M. (2023). An integrated group decision-making method for the evaluation of hypertension follow-up systems using interval-valued q-rung orthopair fuzzy sets. Complex and Intelligent Syst. 9 (4), 4521–4554. doi:10.1007/s40747-022-00953-w
Wankhede, S., Pesode, P., Pawar, S., and Lobo, R. (2023). Comparison study of GRA, COPRAS and MOORA for ranking of phase change material for cooling system. Mater. Today Proc. doi:10.1016/j.matpr.2023.02.437
Wu, W. W., and Lee, Y. T. (2007). Developing global managers’ competencies using the fuzzy DEMATEL method. Expert Syst. Appl. 32 (2), 499–507. doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2005.12.005
Yager, R. R. (2013). Pythagorean membership grades in multicriteria decision making. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 22 (4), 958–965. doi:10.1109/tfuzz.2013.2278989
Yager, R. R. (2016). Generalized orthopair fuzzy sets. IEEE trans. Fuzzy syst., IEEE transactions on fuzzy systems, 25(5), 1222–1230. doi:10.1109/tfuzz.2016.2604005
Yilmaz, I., Erdebilli, B., Naji, M. A., and Mousrij, A. (2023). A fuzzy DEMATEL framework for maintenance performance improvement: a case of Moroccan chemical industry. J. Eng. Res. 11 (1), 100019–019. doi:10.1016/j.jer.2023.100019
Yue, Q., Zou, W., and Hu, W. (2023). A new theory of triangular intuitionistic fuzzy sets to solve the two-sided matching problem. Alexandria Eng. J. 63, 57–73. doi:10.1016/j.aej.2022.07.018
Zeng, S., Ali, Z., Mahmood, T., and Jin, H. (2022). Complex interval-valued q-rung orthopair 2-tuple linguistic aggregation operators and their application in multi-attribute decision-making. Appl. Artif. Intell. 36 (1), 2033471. doi:10.1080/08839514.2022.2033471
Keywords: 2TLq-ROFWPMM operator, DEMATEL method, MOORA method, watershed system models, Muirhead mean
Citation: Li J, Saleh HY, Salih AA, Rasheed MW, Bilal M and Shabbir N (2025) Fuzzy-based group decision-making approach utilizing a 2-tuple linguistic q-rung orthopair set for the selection of optimal watershed system model. Front. Environ. Sci. 12:1502216. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2024.1502216
Received: 27 September 2024; Accepted: 30 December 2024;
Published: 16 April 2025.
Edited by:
Zhen Zhang, Dalian University of Technology, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Li, Saleh, Salih, Rasheed, Bilal and Shabbir. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: M. Waheed Rasheed, cmFzaGVlZHc2NzRAZ21haWwuY29t
 Jie Li1
Jie Li1 Hind Y. Saleh
Hind Y. Saleh M. Waheed Rasheed
M. Waheed Rasheed