- 1School of Business, Henan Institute of Economics and Trade, Zhengzhou, Henan, China
- 2School of Political Science and Public Administration, Henan Normal University, Xinxiang, China
As a high-intensity, high-standard institutional mechanism in land supervision and management, the State Land Supervision System (SLSS) plays a crucial role in deterring land-related violations, enforcing farmland protection, ensuring national food security, and facilitating sustainable agricultural development. However, previous research has seldom examined how the SLSS contributes to the low-carbon transformation of agriculture (LCTA). This study treats China’s routine land inspections as a quasi-natural experiment, utilizing panel data from 283 prefecture-level and higher cities from 2005 to 2016 to empirically analyze whether and how the SLSS supports LCTA. The findings reveal that the SLSS significantly advances LCTA, with the low-carbon agricultural development level in inspected cities increasing by approximately 2.17%. The SLSS promotes LCTA primarily through enhancing agricultural technological progress and encouraging agricultural scale operations. Compared to major grain-producing regions, high-poverty areas, and regions under significant fiscal pressure, the SLSS more effectively fosters LCTA in non-grain-producing areas, regions with lower poverty rates, and areas facing less fiscal strain. Furthermore, the SLSS has a more pronounced effect on advancing low-carbon agricultural development in cities that already demonstrate higher levels of low-carbon progress. This study provides novel empirical evidence regarding the environmental impacts of SLSS in the agricultural sector, offering insights relevant to the pursuit of agricultural modernization.
1 Introduction
Agriculture functions both as a major carbon sink and as the world’s second-largest source of carbon emissions (Cui et al., 2021). In 2017, agricultural activities contributed approximately 20% of global carbon emissions (Wang et al., 2022), making agriculture a significant factor in global climate warming (Paustian et al., 1998). Both the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) have identified the agricultural sector as the second-largest source of global greenhouse gas emissions. China’s Second National Communication on Climate Change further highlights that agricultural production is a major contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, with profound implications for climate change. Consequently, achieving carbon reduction in agriculture while maintaining food security and productivity has emerged as a central issue for sustainable agricultural development worldwide.
As a major global agricultural producer, China’s efforts in reducing agricultural carbon emissions and enhancing carbon sequestration are critically important for global climate governance. Although China’s total agricultural carbon emissions are relatively modest compared to those from industry, they still account for approximately 17% of the country’s total emissions (Liu and Yang, 2021), exceeding the global average of 13.5% (Cui et al., 2021). Projections suggest that by 2050, agriculture could become China’s largest source of carbon emissions. In response, the Chinese government has implemented a series of policy initiatives aimed at advancing agricultural carbon reduction and carbon sequestration. In 2015, the Ministry of Agriculture introduced the “One Control, Two Reductions, Three Basics” policy, which focuses on strategies such as preventing agricultural water pollution, reducing the use of fertilizers and pesticides, and comprehensively utilizing agricultural waste. In 2021, the government issued the Opinions on Fully and Accurately Implementing the New Development Concept for Carbon Peaking and Carbon Neutrality, explicitly calling for “accelerating green agricultural development to enhance carbon sequestration and efficiency in agriculture.” In 2024, the Third Plenary Session of the 20th Central Committee of the Chinese Communist Party introduced significant reforms to strengthen the ecological civilization system, outlining three primary goals: “enhancing the foundational system for ecological civilization,” “reinforcing environmental governance structures,” and “establishing mechanisms for green and low-carbon development.” This provides a comprehensive policy framework for the Low-Carbon Transformation of Agriculture (LCTA). Thus, establishing and refining institutional mechanisms for LCTA is of considerable theoretical and practical significance, advancing sustainable agricultural development in China and globally and contributing to the achievement of the “dual carbon” targets.
Amid China’s rapid economic growth, demand for land has steadily increased, leading local governments to adopt a “land-driven development” model characterized by land financing and revenue generation. Under China’s dual urban-rural land management system, local governments are typically able to transfer land only by converting agricultural land into construction land (Liu et al., 2024). Driven by this model, local governments have engaged in large-scale expansion and frequent land transfers, resulting in construction land areas in many provinces prematurely exceeding established land use planning limits. This process has led to the permanent conversion of substantial areas of rural farmland into urban construction land, making it difficult to revert these lands to their original agricultural purpose and intensifying the pressures on farmland preservation (Jiang et al., 2013). The reduction and repurposing of farmland have raised significant concerns within the central government regarding food security. The report from the 20th National Congress of the Communist Party of China explicitly calls for a “bottom-line mentality” to be maintained, emphasizing the need to secure the foundations of food security comprehensively and to firmly uphold the red line of 1.8 billion mu of farmland. Farmland forms the basis of food production, and its protection is essential for ensuring national food security. The widespread occupation of farmland not only undermines food production capacity but also has the potential to damage the ecological environment, posing challenges to the Low-Carbon Transformation of Agriculture (LCTA) (Liu et al., 2022a). Thus, strengthening the rational management and protection of farmland and preventing illegal occupation are crucial measures to support the low-carbon, sustainable development of agriculture. To regulate local government practices in land transfers and prevent excessive encroachment on farmland, the central government has consistently enforced strict land control policies (Hou et al., 2019) and has progressively established a series of institutional measures to safeguard farmland resources, including the construction land permitting system (Wu et al., 2017). Among these policy frameworks, the State Land Supervision System (SLSS) stands out as a highly authoritative and influential institution, designed to oversee and regulate various forms of land violations associated with economic development. SLSS rigorously supervises and inspects activities such as the illegal occupation of prime farmland and unauthorized approvals of construction land, thereby reinforcing compliance with land use regulations (Yang et al., 2024).
In 2004, the Chinese government issued the Decision on Deepening Reform and Strict Land Management, marking the first proposal to establish the SLSS. This decision explicitly required that “for all non-agricultural construction projects approved to occupy farmland, the construction entity must compensate with farmland of equivalent quantity and quality,” thus laying an institutional foundation for farmland protection. To further strengthen this framework, the government issued the Notice on Issues Related to Establishing the National Land Supervision System in 2006, formally initiating the land supervision system. Under this system, the Ministry of Land and Resources created the role of Chief National Land Inspector and established National Land Supervision Bureaus in local regions to oversee and inspect land use and management nationwide. Over time, the land supervision system has been continuously refined and has gradually taken effect in practice. In 2019, the Chinese government revised the Land Management Law, officially incorporating the land supervision system into the legal framework for the first time. This revision introduced essential principles for comprehensive land use planning, including “the strict protection of permanent basic farmland, stringent controls on the use of agricultural land for non-agricultural construction, ensuring a balance in quantity and equivalence in quality between farmland occupied and reclaimed, protecting and improving the ecological environment, and guaranteeing the sustainable use of land.” In 2021, the newly amended Regulations for the Implementation of the Land Management Law further specified the scope of land supervision and clarified the responsibilities of institutions at various levels. These regulations emphasize a coordinated approach to planning functional spaces for agriculture, ecology, and urban development, establishing land consolidation plans to enhance farmland protection and promote efficient, intensive land use. The regulations also encourage social entities to participate in land consolidation legally, to prevent and manage soil erosion and pollution on farmland, to systematically transform low- and medium-yield fields, and to construct high-standard farmland to improve farmland quality.
Land is a vital input in agricultural production and serves as a key driver of agricultural productivity (Dumortier and Elobeid, 2021). Farmland systems are among the major sources of carbon emissions (Xia et al., 2023; Chen et al., 2024), and the ways in which farmland is utilized significantly impact agricultural carbon emissions (Zhou et al., 2024). In China’s traditional agricultural production model, issues such as extensive land management, excessive exploitation of farmland, and improper usage are prevalent. These practices not only lead to a continuous increase in agricultural carbon emissions but also have serious adverse effects on the ecological environment. Within the NLSS, routine land inspections are the core, most representative, and most effective form of oversight (Yang et al., 2024). Since 2008, China’s National Land Supervision Bureau has piloted routine inspections in 16 administrative regions, including Cangzhou in Hebei Province, Fushun in Liaoning Province, Yuxi in Yunnan Province, and Xi’an in Shaanxi Province. By 2017, these inspections had achieved nationwide coverage across all 31 provincial-level administrative regions.
In this context, can an effective SLSS curb the over-exploitation and improper utilization of farmland, thereby promoting the LCTA? If so, what are the specific mechanisms through which SLSS achieves this? Additionally, does the effect of SLSS vary across different regions? Exploring these questions in depth not only contributes to the theoretical framework within the fields of land management and environmental protection but also offers valuable empirical evidence from China that can inform other developing countries seeking to optimize land policies and promote low-carbon, sustainable agricultural development. This study aims to provide significant theoretical insights and practical references for global efforts to address environmental and resource pressures, reduce agricultural carbon emissions, and promote sustainable development.
The structure of this study is organized as follows: Section 2 presents a literature review and theoretical analysis. Section 3 describes the models and methods employed, along with the data sources. Section 4 reports the results of the empirical analysis. Section 5 discusses the implications of the findings. Finally, Section 6 provides a summary of the study’s conclusions.
2 Literature review and theoretical analysis
2.1 Literature review
The literature closely related to this study centers on three main areas: factors influencing the LCTA, the environmental impacts of land use, and the economic and environmental effects of the SLSS.
First, on the factors influencing LCTA, most studies indicate that urban expansion leads to the continuous loss of agricultural land (Beckers et al., 2020), adversely affecting food security and agricultural production (Gardi et al., 2015; Shi et al., 2016). Moreover, increases in the urban population and the share of secondary and tertiary industries have intensified pesticide usage and led to a U-shaped trend in fertilizer application intensity (You, 2016), both of which negatively impact LCTA. However, some studies suggest that urbanization supports large-scale agricultural production in China (Wang et al., 2021), enhances rural clean energy use (Han et al., 2022), and significantly improves agricultural green water utilization efficiency (Ding et al., 2021). Under the “dual carbon” framework, agricultural carbon emission intensity has become a key metric for assessing sustainable agricultural development, drawing increasing attention from researchers. Studies have examined factors influencing agricultural carbon emissions from various angles, including rural energy poverty alleviation (Li et al., 2023), agricultural specialization (Wang et al., 2022), agricultural insurance (Ma and Cui, 2021), fiscal policy (Xu et al., 2023), and water and soil resource development (Zhao et al., 2018).
Second, on the environmental impacts of land use, research indicates that land intensification can effectively reduce carbon emissions (Xie et al., 2018; Wu et al., 2022; Ling et al., 2023). Studies also explore how industrial land transfer preferences affect carbon emission efficiency and the mechanisms involved (Huang and Song, 2023). Other research examines the impact of land marketization and resource misallocation on carbon emissions (Ma et al., 2021; Liu et al., 2022b;Li et al., 2023b; Li et al., 2023c). In terms of farmland use and LCTA, some studies analyze the effects of farmland changes on carbon emissions, focusing on aspects such as farmland transfer (Ji et al., 2023), high-standard farmland construction (Li L. et al., 2023), and crop rotation and fallow practices (Zhang et al., 2024). Together, these studies provide a comprehensive view of the multiple environmental impacts of land use, offering valuable references for achieving LCTA.
Third, on the economic and environmental impacts of SLSS, studies have evaluated SLSS’s economic consequences from various perspectives, including land marketization (Zhao et al., 2012), suppression of illegal land use (Lü et al., 2012), local government land finance (Liu and Peng, 2022), and urban expansion (Yang et al., 2024). On environmental effects, some research has focused on the establishment of national land supervision bureaus in nine Chinese provinces in 2006, using panel data from 30 provinces to assess the environmental outcomes of SLSS (Ma and Zhang, 2024).
Building on this foundation, the present study extends the existing literature in four significant ways. First, from a research perspective, unlike studies focused on high-standard farmland construction (Li F. et al., 2023) and crop rotation practices (Zhang et al., 2024), this study examines SLSS—a high-intensity, high-standard land supervision system—as a novel framework for exploring LCTA drivers. By investigating SLSS’s role in curbing farmland over-exploitation and improper land use, this study broadens the scope of research on LCTA determinants, offering new theoretical and empirical insights into the relationship between land institutions and sustainable agricultural development. Second, at the research level, since routine land inspections began in 2008 across 16 cities and counties, including Cangzhou in Hebei Province, the inspection scope has expanded annually, achieving nationwide coverage by 2017. Unlike studies that use provincial-level data (Ma and Zhang, 2024), this study treats city- and county-level routine land inspections as a quasi-natural experiment, using panel data from 283 Chinese cities (2005–2016) to examine SLSS’s impact on LCTA from a city-level perspective. This more granular longitudinal analysis deepens the understanding of land supervision policies, providing a unique lens through which to evaluate SLSS’s role in promoting LCTA. Third, in terms of research content, this study unveils the mechanisms by which SLSS affects LCTA by focusing on agricultural technological progress and large-scale farming operations, thus revealing the “black box” of SLSS’s impact on LCTA for the first time. Additionally, the study examines the heterogeneous effects of SLSS on LCTA across various dimensions, including food production capacity, urban scale, agricultural low-carbon development levels, regional poverty rates, and fiscal constraints. This multi-dimensional analysis further clarifies the differential impacts of SLSS under varying conditions.
2.2 Theoretical analysis
Land consolidation is considered an effective strategy for optimizing the spatial distribution of farmland (Jin et al., 2022), and the implementation of the SLSS has further motivated local governments to pursue land consolidation initiatives. This process not only increases the total area of farmland but also promotes more intensive use, improving farmland utilization efficiency by maximizing the potential of existing land resources and thereby reducing carbon emissions associated with farmland use Wang et al. (2024). Agricultural land-use patterns significantly impact the environment (Foley et al., 2005; Hamidov et al., 2016). Land fragmentation, for example, can heighten farmers’ dependence on fertilizers and pesticides, increase environmental pollution (Yu et al., 2019), and limit agricultural productivity and profitability (Uyan et al., 2015), all of which hinder the LCTA. Through scientific planning and rational land allocation, SLSS directs construction projects away from high-quality farmland to minimize encroachment on agricultural land. SLSS also actively promotes a balance between farmland occupation and compensation, along with land consolidation efforts, to prevent land fragmentation and support LCTA.
Illegal occupation of farmland has multiple adverse effects on LCTA. First, such occupation leads to the segmentation and fragmentation of farmland, disrupting its integrity and continuity. This fragmentation raises the costs associated with environmentally friendly technologies, limiting the benefits of low-carbon management practices and directly hindering their application and expansion in agriculture (Kuang and Zhang, 2024). Furthermore, secure and stable land use rights are essential for agricultural innovation and capital investment. When land use rights are insecure or threatened by illegal occupation, farmers and agricultural enterprises are less likely to invest in advanced agricultural technologies. This uncertainty elevates the risks of agricultural technology investment, reducing the adoption of low-carbon practices in agriculture. In contrast, stable land use rights enhance farmers’ confidence in investing, particularly in the adoption of modern, intensive, low-carbon agricultural technologies such as precision fertilization, smart irrigation, and biological pest control. By enforcing strict land management policies, SLSS ensures the protection and rational use of farmland, significantly enhancing the stability of land use rights. Through regulating illegal occupation and implementing a comprehensive land use monitoring system, SLSS provides institutional safeguards for agricultural land, ensuring effective farmland protection and establishing an orderly framework for land management. This institutional protection enhances the security of land use, boosting the long-term investment confidence of farmers and agricultural enterprises and encouraging them to apply green, low-carbon agricultural technologies in their production practices. By adopting these technologies, farmers can reduce fertilizer and pesticide use, optimize water resource management, and mitigate soil erosion, thereby effectively reducing agricultural carbon emissions (Xie and Liu, 2021).
Large-scale agricultural operations contribute to a more systematic and standardized production process, helping to reduce resource waste and improve production efficiency. Additionally, the expansion of large-scale operations accelerates mechanization and optimizes pesticide and fertilizer usage (Song et al., 2021), thus lowering agricultural carbon emissions. Large-scale operations not only improve resource use efficiency but also enable agricultural entities to more effectively leverage capital, land, and management resources, allowing for greater investment in advanced green agricultural equipment and technology, which further reduces carbon emissions in agricultural activities (Li et al., 2015). Through rigorous land use planning and oversight, SLSS establishes a stable land resource base for large-scale agricultural operations. SLSS effectively prevents farmland from being illegally occupied or converted to non-agricultural purposes, ensuring both the quantity and quality of farmland and providing essential land resources for large-scale operations. Moreover, SLSS conducts regular inspections and evaluations of land use practices, promptly identifying and correcting improper land use, thereby promoting the intensive and large-scale utilization of farmland. Under the stringent management framework of SLSS, rational land consolidation and intensive use further accelerate the expansion of large-scale agricultural operations, enabling more efficient and concentrated allocation of agricultural resources. By reducing land fragmentation, SLSS provides favorable conditions for large agricultural operators, maximizing the benefits of resource economies of scale. This model of large-scale operations not only improves agricultural production efficiency but also creates conducive conditions for the adoption of low-carbon agricultural technologies, supporting sustainable development and the low-carbon transition in agriculture.
3 Research design
3.1 Model specification
In this study, a Difference-in-Differences (DID) model was constructed to examine the effect of the SLSS on the LCTA. This analysis compares LCTA changes in treatment and control cities before and after the implementation of SLSS inspections. The specific DID model is presented as follows:
According to Equation 1, LCTAit represents the low-carbon transformation of agriculture in city i at time t. SLSSit is a dummy variable for routine land inspections. Controlsit is a series of control variables.
3.2 Variable definitions
(1) Dependent variable: Total Factor Carbon Emission Efficiency is a comprehensive metric for assessing CO₂ emission efficiency (Gao and Wang, 2023). Drawing on existing literature Zhou et al. (2024), this study employs a non-oriented, variable returns to scale Super-Efficiency EBM (epsilon-based measure) model to calculate an index of agricultural total factor carbon production efficiency, which serves as an indicator of LCTA. The measurement of agricultural total factor carbon production efficiency involves both input and output indicators.
For input indicators, this study includes seven variables: land (total sown area of crops), fertilizer (effective amount of fertilizer used), agricultural film (use of agricultural plastic film), pesticides (amount of pesticide used), irrigation (effective irrigated area), machinery (total horsepower of agricultural machinery), and labor (number of employees in the primary industry). For output indicators, the desired output is represented by the total output value of the agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry, and fishery sectors, while the undesired output is agricultural carbon emissions.
Due to the unavailability of accurate city-level data on pesticide usage, agricultural plastic film usage, and agricultural diesel usage, this study estimates these values at the city level by referencing provincial-level data on pesticide, agricultural plastic film, and agricultural diesel usage per unit of farmland area, combined with each city’s year-end farmland area (Zhou et al., 2024). Subsequently, carbon emissions from the effective amount of fertilizer applied, pesticide usage, agricultural plastic film usage, agricultural diesel usage, total sown area of crops, and effective irrigated area are calculated using appropriate emission coefficients, providing a more precise assessment of LCTA.
(2) Core explanatory variable: The primary explanatory variable in this study is the SLSS, which encompasses three main forms of inspection: review inspections, special inspections, and routine inspections. Among these, routine inspections are the most central, representative, and effective operational form. Since 2008, pilot cities for routine land inspections have been widely distributed across the country, providing a broad sample that helps to mitigate potential selection bias. Additionally, the batch implementation of routine inspections aligns well with the assumptions underlying a “quasi-natural experiment” (Yang et al., 2024). Therefore, this study uses routine land inspections as the operational measure for SLSS. Specifically, if a city (including counties within its jurisdiction) is designated as a routine inspection target in a given year, the SLSS variable for that city is assigned a value of 1 for that year and all subsequent years. If it is not designated for routine inspection, the SLSS variable is assigned a value of 0. This coding approach allows for a more accurate capture of the impact of SLSS on LCTA, thereby enhancing the scientific rigor and reliability of the study’s findings.
(3) Control variables: This study incorporates the following control variables that may influence the LCTA:
Industrial Agglomeration (AGG) facilitates the flow of information and knowledge, making it easier for agricultural producers to access the latest low-carbon technologies, environmental standards, and changes in market demand. This helps agricultural enterprises to flexibly adjust production strategies and improve carbon production efficiency. Referring to existing literature Wu et al. (2020), this study measures AGG using the location quotient of the total output value of agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry, and fishery in each city.
High-quality human capital (HUMAN) can accelerate the promotion and adoption of low-carbon technologies, enabling advanced low-carbon production methods to achieve scale and intensification in agricultural production, thereby promoting LCTA. Referring to existing literature Shahbaz et al. (2022), this study uses the average years of education per capita in rural areas as the indicator for HUMAN.
Regions with high poverty rates (POV) often lack sufficient funds and resources to support the promotion of low-carbon technologies. Low-income farmers tend to prioritize basic living needs, making it difficult to afford the initial investment for low-carbon technologies (such as water-saving irrigation, modern machinery, and biomass energy equipment), which limits the realization of low-carbon production. Referring to existing literature Jiang et al. (2024), this study uses a comprehensive index synthesized by the entropy method, which includes six indicators: per capita net income of rural residents, the proportion of full-time teachers with bachelor’s degrees in rural compulsory education, the number of healthcare technicians per capita in rural areas, safe drinking water coverage, per capita housing area of rural residents, and the proportion of administrative villages with broadband internet access, to measure POV.
Agricultural Mechanization (MACH) achieves precision in cultivation, sowing, fertilization, and harvesting through high-efficiency equipment replacing manual labor, effectively reducing resource waste, and thus influencing LCTA. Referring to existing literature Guan et al. (2023), MACH is measured by the logarithm of the per capita total horsepower of agricultural machinery.
Improved transportation infrastructure (INFRA) makes the transportation of agricultural products more convenient and efficient, reducing carbon emissions during transportation and facilitating the circulation of low-carbon technologies and equipment, thereby making advanced low-carbon agricultural technologies more accessible in rural areas. Referring to existing literature Xie et al. (2017), this study measures INFRA by the per capita road area in rural areas.
A higher level of economic development (AGDP) implies sufficient financial resources to support the research, promotion, and application of low-carbon agricultural technologies. Referring to existing literature Xu et al. (2022), this study measures AGDP using the logarithm of per capita GDP.
Urbanization (URB) aids in the diffusion of technology and knowledge, as research institutions and technical personnel concentrated in cities transfer low-carbon technologies and innovative concepts to rural areas through various channels, driving the development of low-carbon agricultural technology. Referring to existing literature Xu et al. (2022), this study measures URB by the ratio of the year-end urban population to the total resident population at year-end in each city.
3.3 Sample selection and data sources
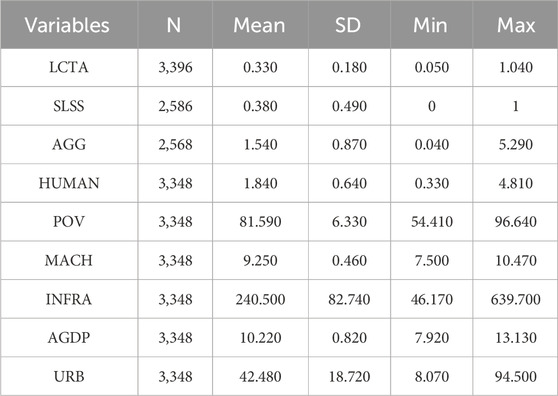
In 2017, routine land inspections achieved full coverage across all 31 provincial-level administrative regions in China. To ensure an adequate sample of treatment and control cities before and after the policy implementation, this study selected a time span from 2005 to 2016, initially encompassing 283 prefecture-level and above cities. Data on national land inspections were sourced from the official website of the Ministry of Natural Resources of the People’s Republic of China and manually compiled. Due to substantial data gaps in some cities, the final study sample includes panel data from 210 Chinese cities over the period 2005–2016. The original data for the study’s variables were obtained from multiple authoritative yearbooks, including the China Statistical Yearbook, China Rural Statistical Yearbook, China Agricultural Yearbook, China Agricultural Statistical Data, China City Statistical Yearbook, China Energy Statistical Yearbook, and the China Rural Poverty Alleviation Report, as well as the EPS data platform. For certain missing data, linear interpolation was employed to ensure data completeness and continuity. Table 1 provides a statistical description of the variables.
4 Empirical analysis
4.1 Parallel trend test
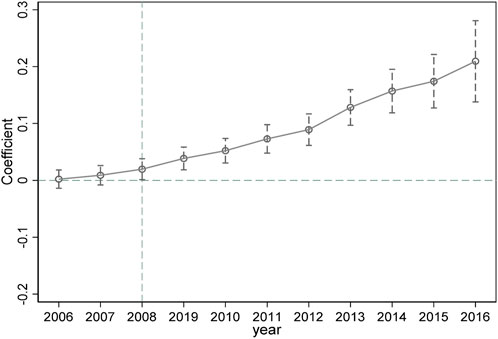
The parallel trends assumption requires that, prior to policy implementation, the LCTA trends in the treatment group (i.e., pilot cities) and the control group (non-pilot cities) are similar. Figure 1 indicates that, in 2008 and earlier, there was no significant difference in the LCTA trends between pilot and non-pilot cities, suggesting that the trends in both groups were parallel before the policy took effect. This finding supports the validity of the parallel trends assumption, providing a solid basis for using the DID method for causal inference.
Following the policy implementation in 2008, Figure 1 shows a significantly positive effect of SLSS on LCTA, with this positive impact exhibiting increasing fluctuations over time. This positive effect can be attributed to SLSS, as a high-standard land supervision system, which effectively curtailed illegal and improper land use through stringent land use oversight and management, thereby ensuring the rational use and effective protection of farmland. Additionally, SLSS promoted scientific planning and rational land allocation, guiding construction projects to avoid high-quality farmland and supporting the implementation of farmland occupation-compensation balance and land consolidation projects. These efforts not only strengthened farmland resource protection but also improved the efficiency of intensive and economical land use, ultimately reducing agricultural carbon emissions.
As SLSS was gradually promoted and implemented nationwide, its supervisory and enforcement intensity increased across different regions. With the deepening of policy implementation, various regions adopted more stringent land management measures, which may have led to noticeable increases and fluctuations in the positive effects on LCTA in certain regions.
4.2 Benchmark regression analysis
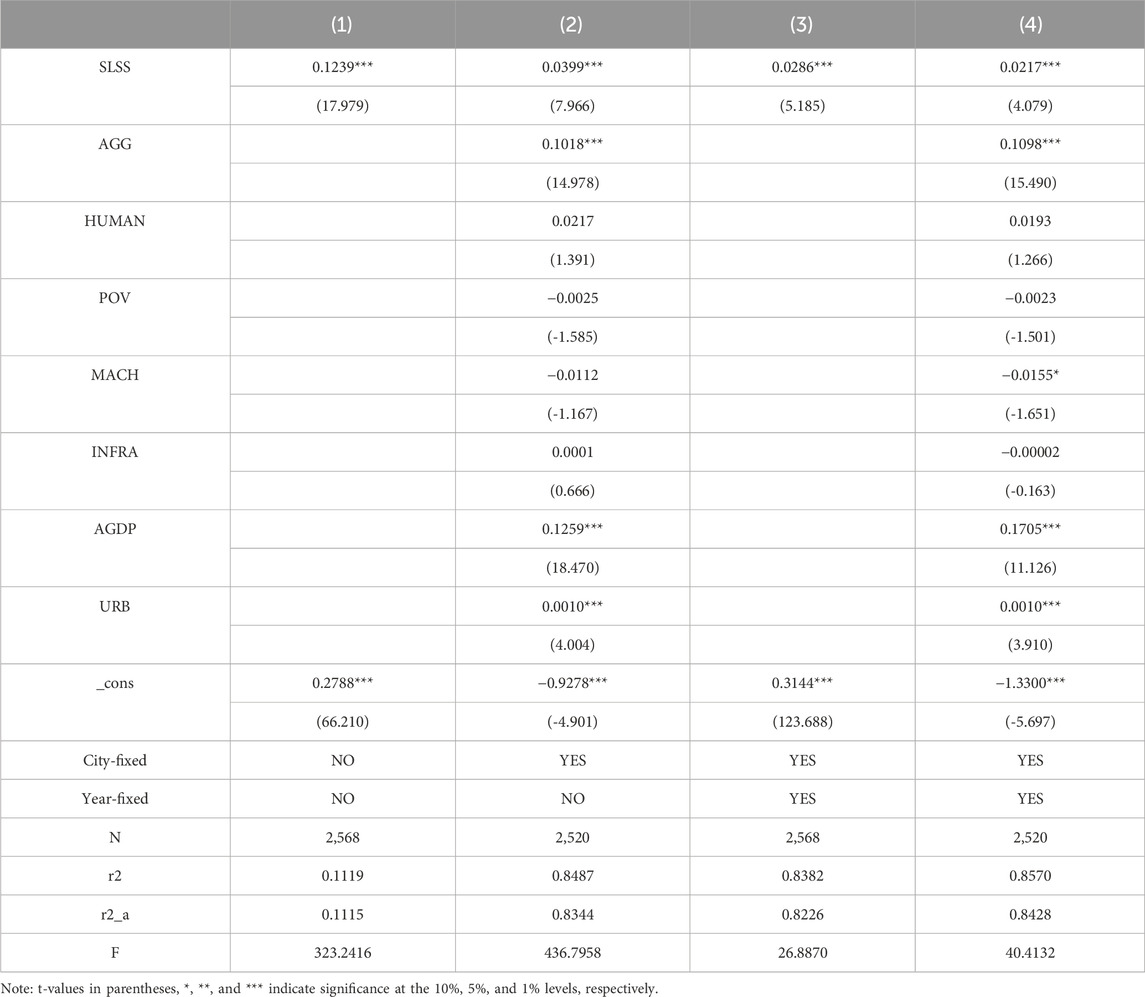
Table 2 presents the baseline regression results on the impact of SLSS on LCTA. The findings indicate that SLSS significantly promotes LCTA, regardless of whether control variables are included or whether city fixed effects and time fixed effects are controlled. Taking column (4) as an example, cities that implement routine land inspections show an average increase of 2.17% in their agricultural low-carbon development level compared to cities that do not implement such inspections.
The rationale behind this effect lies in the importance of rational management and utilization of farmland as a cornerstone for low-carbon sustainable agricultural development. Illegal occupation of farmland, along with the resulting land-use changes and improper development, tends to increase carbon emissions and heighten environmental stress. The conversion of farmland to construction land or other uses releases soil carbon, thereby increasing greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, improper land use often leads to a higher reliance on fertilizers and pesticides, further exacerbating environmental pollution and carbon emissions.
Through stringent land use regulation, SLSS ensures the effective protection and rational utilization of farmland, encouraging local governments to prioritize farmland protection and to prevent illegal occupation and degradation. This mechanism not only safeguards farmland quantity but also enhances land use efficiency, promoting the sustainable development of agricultural production. Through scientific planning and rational land allocation, the SLSS system directs construction projects to avoid high-quality farmland wherever possible and supports the implementation of farmland occupation-compensation balance and land consolidation projects. These efforts help to maintain both the quantity and quality of farmland, promote intensive and economical land use, and ultimately improve the low-carbon development level of agriculture.
From the control variables, it can be concluded that AGG, AGDP, and URB significantly promote LCTA, while HUMAN, POV, and INFRA do not have a significant impact on LCTA. Additionally, MACH significantly inhibits LCTA.
4.3 Robustness analysis
4.3.1 Placebo test
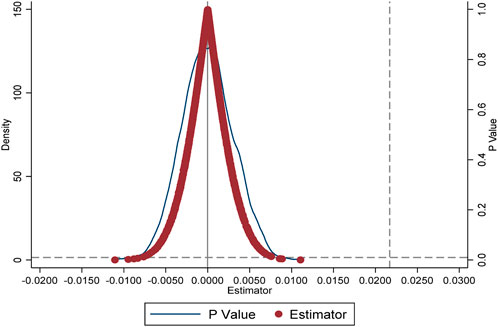
In this study, a placebo test was conducted by randomly assigning treatment and control groups and randomizing the implementation timing of routine land inspections. This approach involved constructing pseudo-treatment group dummy variables and pseudo-policy timing dummy variables to simulate the experimental and control groups under random conditions, thus helping to rule out the influence of other unobservable factors on the results. Specifically, an interaction term between the randomly generated pseudo-treatment group and pseudo-policy timing variables was included in the baseline regression analysis to test whether SLSS would still exhibit a significant impact on LCTA under randomized conditions.
To ensure the robustness of the findings, this process was repeated 1,000 times. In each iteration, new interaction terms for the pseudo-treatment group and pseudo-policy timing were generated, yielding 1,000 regression coefficients for these interactions. Figure 2 displays the distribution of p-values and the kernel density of these randomly generated coefficients. The results in Figure 2 show that most of the randomly generated coefficients are concentrated around 0, with p-values predominantly above 0.1, which is significantly different from the actual baseline regression estimate of 0.0217. This result further validates the reliability of the significant positive impact of SLSS on LCTA.
4.3.2 Other robustness tests
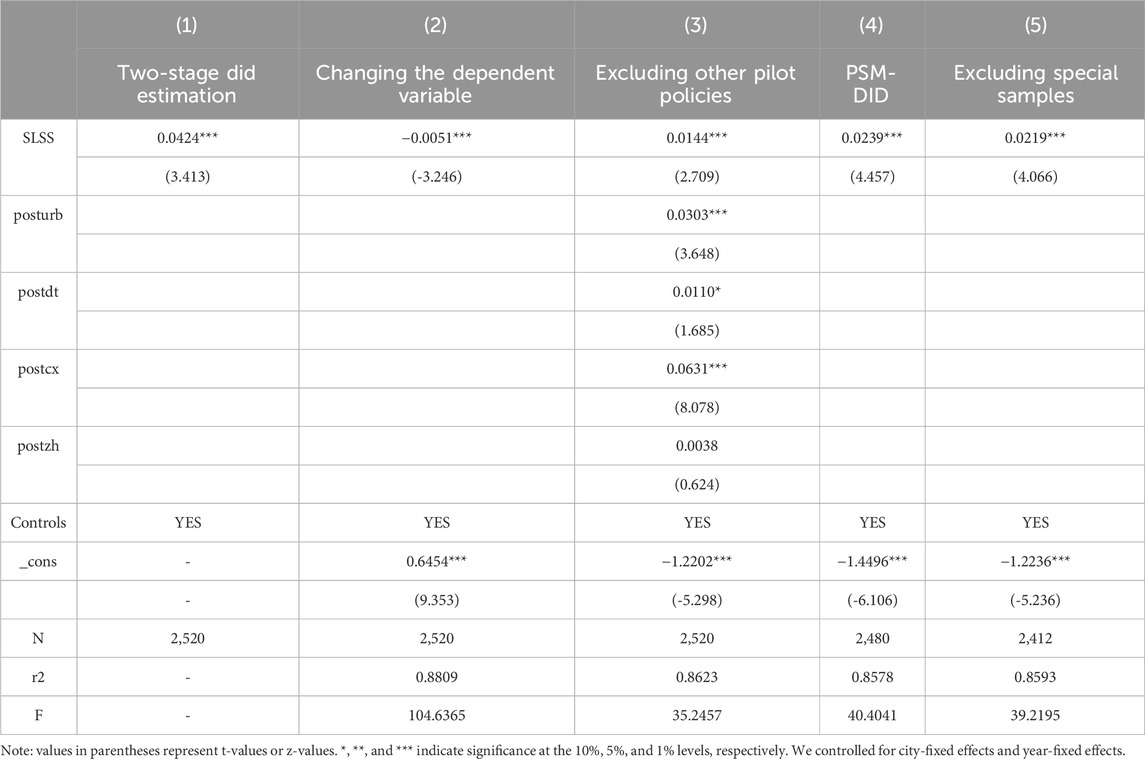
(1) Two-stage did estimation. The two-way fixed effects model can introduce bias when addressing heterogeneous treatment effects, necessitating the use of more advanced estimation methods, such as the two-stage difference method, to correct for these biases. This approach not only improves the model’s explanatory power but also enables a more accurate identification of the policy’s true impact. As shown in column (1) of Table 3, after correcting for the bias associated with the two-way fixed effects model, the coefficient for the core explanatory variable in this study (0.0424) is higher than the baseline regression coefficient (0.0217).
(2) Changing the dependent variable. We use agricultural carbon emissions per unit of GDP as a measure of LCTA and re-estimate the baseline regression model. The regression results are presented in column (2) of Table 4. The findings indicate that SLSS significantly reduces agricultural carbon emissions per unit of GDP, thereby confirming that SLSS contributes to LCTA.
(3) Excluding other pilot policies. To account for the potential influence of other policy initiatives, such as the new urbanization pilot policy (posturb), the smart city pilot policy (postzh), the low-carbon city pilot policy (postdt), and the innovation city pilot policy (postcx), this study incorporates these variables into the baseline regression model. The results in column (3) of Table 4 indicate that, even after controlling for these additional policy factors, the coefficient for SLSS remains significantly positive. This finding suggests that, even when considering the effects of other policies, SLSS still exerts a significant positive impact on LCTA, further affirming SLSS’s unique and essential role in advancing LCTA.
(4) Propensity score matching did. Cities undergoing routine land inspections tend to exhibit higher levels of low-carbon agricultural development, which may introduce selection bias in the choice of cities. To address this issue, this study employs propensity score matching (PSM) to match the treatment and control group samples, thereby mitigating the impact of systematic differences between the two groups on the model. Specifically, a 1:1 nearest-neighbor matching approach is applied annually to match samples, and baseline analysis is subsequently conducted on the matched samples. The empirical results in column (4) of Table 4 show that, even after controlling for selection bias, SLSS continues to have a significant positive impact on LCTA. This finding further validates the crucial role of SLSS in promoting LCTA, demonstrating that its effect is both robust and credible.
(5) Excluding special samples. To further eliminate the potential influence of municipalities and sub-provincial cities on the baseline regression results, particularly in terms of economic development and policy implementation, this study excludes these cities from the analysis to enhance the robustness and accuracy of the findings. Due to their higher administrative status, superior resource allocation, and stronger policy enforcement capabilities, municipalities and sub-provincial cities may exhibit more favorable LCTA outcomes, potentially biasing the assessment of SLSS’s effectiveness. To address this potential bias, we exclude these cities and re-estimate the regression model. The empirical results, shown in column (5) of Table 4, indicate that even after excluding cities with these special advantages, the positive effect of SLSS on LCTA remains significant, with the coefficient continuing to be positive. This finding demonstrates that the positive impact of SLSS on LCTA is consistent and broadly applicable across different types of cities, further confirming the effectiveness and robustness of SLSS as a key policy instrument for advancing the low-carbon transformation of agriculture.
4.4 Transmission mechanism test
Building on the theoretical analysis and the foundation of model (1), this study further investigates the transmission mechanism through which SLSS affects LCTA. The model is constructed as follows:
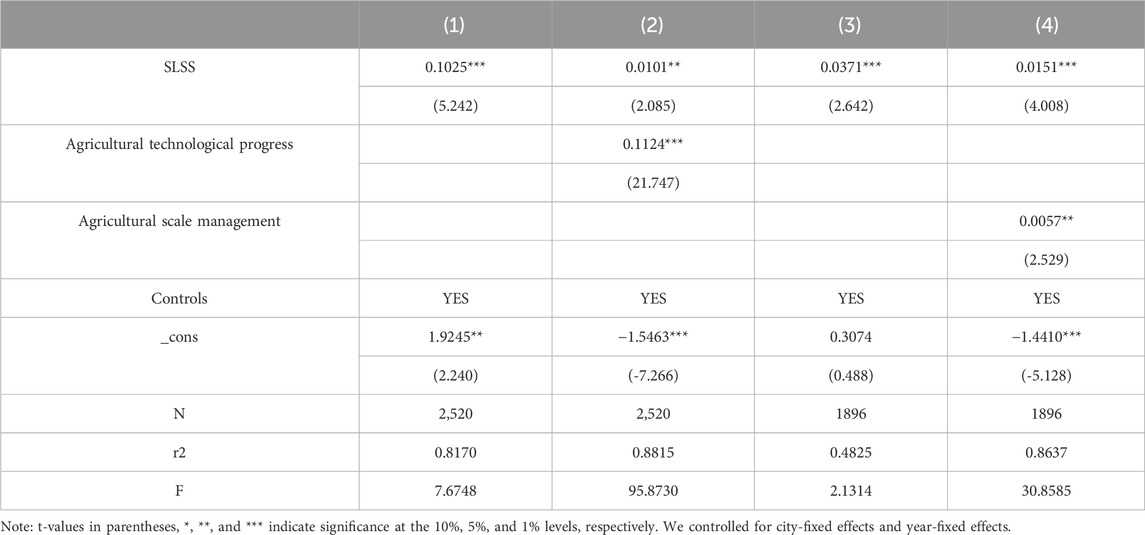
In Equations 2 and 3, M is the conduction mechanism variable.
Table 4 presents the results of the transmission mechanism analysis of SLSS’s impact on LCTA. Columns (1) and (2) in Table 4 indicate that SLSS significantly promotes agricultural technological progress, and that technological progress, in turn, contributes to LCTA. This finding suggests that SLSS advances LCTA by fostering agricultural technological progress. Similarly, columns (3) and (4) reveal that SLSS significantly encourages agricultural scale operations, which are beneficial for LCTA. This implies that SLSS supports LCTA through the promotion of agricultural scale operations.
4.5 Heterogeneity analysis
4.5.1 Grain production capacity and city size
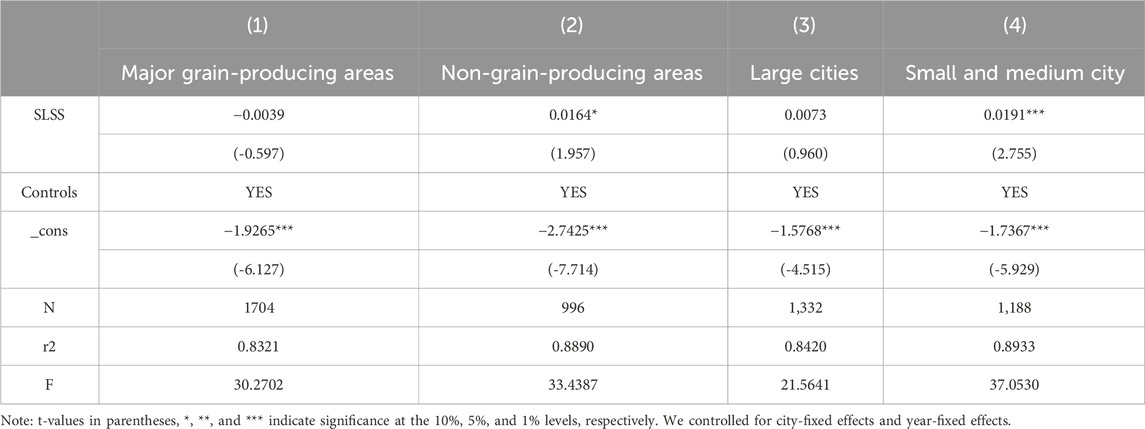
Table 5 presents the empirical results of SLSS’s impact on LCTA across regions with varying grain production capacities and city sizes. The findings indicate that SLSS has a more pronounced effect on promoting LCTA in non-grain-producing regions compared to major grain-producing areas. This difference can be attributed to the more diversified land use patterns typically found in non-grain-producing regions, where land can be more readily reallocated and adjusted for activities such as cash crop cultivation, forestry, and animal husbandry. By enforcing strict land regulation and promoting relevant policies, SLSS encourages non-grain-producing areas to optimize land allocation and adopt diversified cropping structures, which enhances land use efficiency and reduces greenhouse gas emissions. Moreover, non-grain-producing areas often emphasize restructuring and upgrading the agricultural industry. In these regions, SLSS has accelerated agricultural modernization and the expansion of large-scale operations, facilitating land transfer and concentration, which improves agricultural productivity and resource efficiency. For instance, non-grain-producing regions are more likely to adopt large-scale farming practices and advanced agricultural technologies, thereby effectively minimizing resource waste and environmental pollution.
Regarding city size, SLSS has a more significant impact on LCTA in smaller cities than in larger ones. Small cities tend to have relatively concentrated resources, and land management and allocation are simpler. Through stringent land regulation and policy guidance, SLSS can more effectively channel resources toward agricultural development, reducing land wastage and inefficient use. In contrast, large cities face greater challenges due to rapid urbanization, resulting in more dispersed land resources, increased management complexity, and relatively weaker resource integration. Additionally, smaller cities often exhibit greater flexibility and efficiency in policy implementation compared to larger cities. With fewer administrative layers and shorter decision-making chains, small cities can swiftly respond to and implement SLSS requirements. In contrast, large cities, with more complex administrative structures, may experience delays in information transmission and challenges in effective policy execution, which can weaken the policy’s overall impact.
4.5.2 Agricultural low-carbon development level
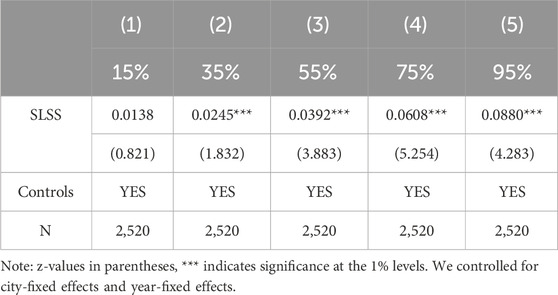
Table 6 presents the heterogeneity analysis results for low-carbon agricultural development levels. The findings indicate that at the 15%, 35%, 55%, 75%, and 95% quantiles of LCTA, the impact of SLSS on promoting LCTA is 0.0138, 0.0245, 0.0392, 0.0608, and 0.0880, respectively, showing an upward trend. This suggests that SLSS has a more substantial effect in cities with higher levels of low-carbon agricultural development.
The underlying reason is that cities with higher levels of low-carbon agricultural development generally possess greater experience in policy formulation and stronger administrative capabilities. Local governments in these cities are better equipped to effectively implement SLSS requirements, promoting large-scale and intensive agricultural practices, optimizing land use, and reducing resource waste and carbon emissions. Consequently, a supportive policy environment and robust management experience make the impact of SLSS more significant in these cities. Additionally, in cities with higher levels of low-carbon agricultural development, public environmental awareness tends to be stronger, and there is greater societal support for low-carbon agricultural practices. This positive social atmosphere facilitates the smooth implementation of SLSS and enhances its effectiveness. High levels of public awareness and social support further promote the adoption of green agricultural technologies, strengthening the effectiveness of policy execution and thus advancing LCTA.
Moreover, these cities typically enjoy better environmental and ecological conditions, allowing for more efficient use of natural resources and reduced environmental impact. In such favorable conditions, SLSS—through stringent land regulation and resource management—can more effectively enhance the sustainability and low-carbon orientation of agricultural production. Therefore, in cities with higher levels of low-carbon agricultural development, the impact of SLSS is more pronounced, further driving the progress of LCTA.
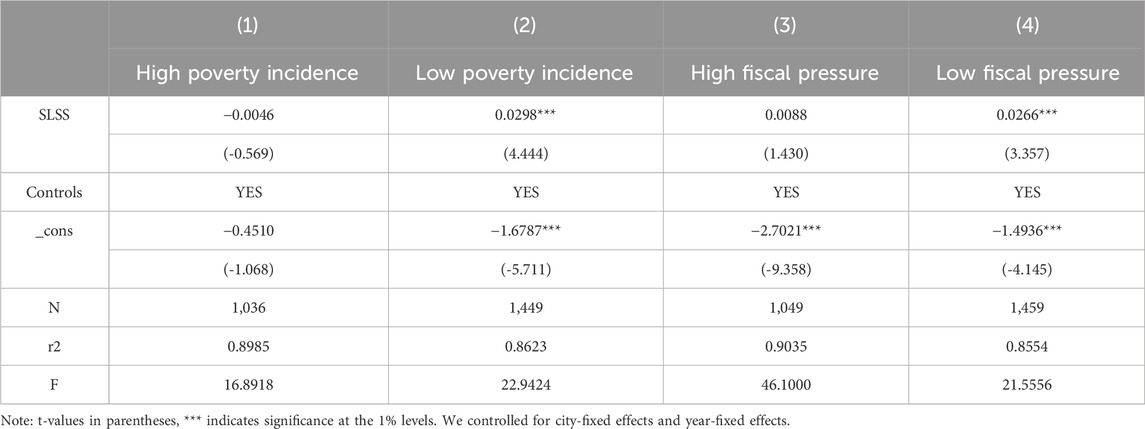
4.5.3 Poverty incidence and fiscal pressure
Table 7 presents the heterogeneity analysis results for poverty rate and fiscal pressure. The findings indicate that SLSS has a more pronounced impact on promoting LCTA in regions with low poverty rates compared to regions with high poverty rates. This may be because regions with lower poverty rates generally possess stronger policy implementation capabilities and higher levels of management. Local governments in these areas are better able to fulfill the requirements of SLSS, advancing large-scale and intensive agricultural operations and optimizing land use. Higher management standards and more efficient resource coordination and allocation in these regions further contribute to the promotion of LCTA.
This study measures fiscal pressure by calculating the ratio of the difference between local fiscal expenditure and revenue to local fiscal revenue, and then examines the impact of SLSS on LCTA under conditions of high and low fiscal pressure. The results reveal that SLSS has a more significant effect on LCTA in regions with low fiscal pressure compared to those with high fiscal pressure. Regions with lower fiscal pressure generally have greater financial resources and a more stable economic foundation, which better supports the implementation of SLSS. Adequate funding and a strong economic base not only facilitate the adoption and application of low-carbon agricultural technologies but also support the construction and maintenance of infrastructure, ensuring smooth policy execution and expansion.
5 Discussion
5.1 Result interpretation
Using panel data from 283 Chinese cities over the period 2005–2016, this study empirically analyzes whether and how the SLSS promotes the LCTA. The findings indicate that SLSS effectively promotes LCTA, with cities under inspection experiencing an average increase of approximately 2.17% in low-carbon agricultural development. This empirical result offers a new theoretical perspective on the role of land management policies in environmental protection and sustainable development. By demonstrating the significant impact of SLSS in advancing low-carbon agricultural development, this study contributes to the academic discourse on the relationship between land management and environmental protection.
Additionally, the study provides critical empirical evidence for policymakers, showing that strict land management and supervision can effectively drive the low-carbon transformation of agriculture. Based on this insight, policymakers can further refine land management policies to foster sustainable agricultural development. Unlike studies focused on evaluating the carbon reduction effects of high-standard farmland construction (Li et al., 2023b), SLSS’s primary objective is to protect farmland, prevent illegal occupation and improper use, and safeguard national food security and ecological integrity. SLSS emphasizes the enforcement and oversight of land management policies, establishing dedicated inspection agencies to regularly monitor land use practices across regions, thereby ensuring effective policy implementation. This rigorous enforcement mechanism grants SLSS a notable advantage in terms of policy efficacy and real-world impact.
Moreover, SLSS has established a long-term land supervision mechanism to ensure the sustained implementation and effectiveness of land management policies. This enduring framework helps prevent short-term exploitation and regulatory violations in land use, providing institutional support for the long-term low-carbon transformation and sustainable development of agriculture. Unlike previous studies that used panel data from 30 Chinese provinces to assess the environmental effects of land supervision (Ma and Zhang, 2024), this study leverages panel data from 283 cities, offering a more granular evaluation of SLSS’s impact on LCTA and expanding the applicability of SLSS in environmental impact research.
The impact of SLSS on promoting LCTA is primarily achieved through facilitating agricultural technological progress and encouraging large-scale farming operations. Agricultural technological advancement and large-scale operations are widely recognized as critical drivers for achieving LCTA, with numerous studies confirming their importance from various policy and developmental perspectives (Guan et al., 2023; Li and Wang, 2023). For example, research has examined these factors through lenses such as the new urbanization pilot policy (Zhou et al., 2024), the digital economy (Zhong et al., 2022), and urban-rural integration (Xie et al., 2018). By focusing on land institutions, this study validates the effectiveness of SLSS in promoting LCTA through the advancement of agricultural technology and the expansion of large-scale operations, providing a novel perspective to the academic community and expanding the scope of research on this topic. To achieve LCTA objectives, it is essential to coordinate land management policies with other related policies. For instance, agricultural technology, environmental, and rural development policies should work synergistically to promote low-carbon transformation and sustainable development in agriculture. Such policy coordination not only enhances the effectiveness of SLSS but also systematically accelerates the agricultural sector’s transition toward low-carbon practices.
Compared to major grain-producing regions, high-poverty areas, and high-fiscal-pressure regions, SLSS has a more pronounced effect on LCTA in non-grain-producing regions, low-poverty areas, and low-fiscal-pressure areas. Furthermore, SLSS has a stronger impact in cities with higher existing levels of low-carbon agricultural development. These findings not only enrich the theoretical framework for evaluating policy effectiveness but also provide scientific guidance for designing differentiated and refined land management policies. When developing and implementing land management policies, the government should adopt region-specific strategies. Non-grain-producing and low-fiscal-pressure areas may be more amenable to strict land management policies, while high-poverty and high-fiscal-pressure areas may require supplementary supportive policies to foster LCTA. This insight offers a new approach to achieving balanced regional development—by implementing stricter land management in non-grain-producing and low-poverty areas, LCTA can be promoted in these regions, helping to narrow regional development gaps. At the same time, diverse policy tools to support high-poverty and high-fiscal-pressure areas can help facilitate balanced development across regions.
These conclusions also offer valuable insights for other developing countries. The successful implementation of SLSS demonstrates that land management policies can effectively promote LCTA by advancing agricultural technology and supporting large-scale farming operations. Developing countries can draw on this experience to design appropriate land supervision systems that align with their specific national contexts, thereby fostering low-carbon and sustainable agricultural development. Additionally, when promoting similar policies, it is important to consider regional disparities and develop differentiated policies that are tailored to local conditions, thereby promoting green development and environmental protection. This study provides empirical support for the international promotion of SLSS, facilitating the sharing of successful practices through international collaboration. Developing countries can utilize international conferences, collaborative research, and knowledge-sharing platforms to learn from SLSS’s implementation, thereby enhancing their land management capabilities and accelerating LCTA.
5.2 Policy recommendations
The government should continue to support and reinforce SLSS, especially in key agricultural regions, to ensure the long-term effective implementation of policies concerning farmland protection and the regulation of land use. Building on this foundation, it is important to gradually establish and promote standardized procedures for land inspections, enabling a stable role in advancing low-carbon development across a wider range of areas. SLSS can increase local governments’ accountability and transparency in land management by making land inspection information publicly accessible and instituting a performance evaluation system for land use. The regular publication of routine land inspection results not only enhances the transparency of policy enforcement but also boosts public trust and encourages active oversight, thereby better ensuring the sustained positive impact of SLSS on LCTA.
Moreover, the government should implement differentiated land regulatory policies tailored to the agricultural conditions, fiscal situations, and poverty levels of various regions to improve the adaptability and effectiveness of SLSS. For instance, in non-major grain-producing regions, areas with low poverty rates, and regions with low fiscal pressure, efforts in land management can be intensified to support large-scale and intensive agricultural practices, facilitating the optimal allocation of land resources. In regions with high poverty rates and high fiscal pressure, additional supportive measures, such as technical assistance and financial subsidies, can be integrated within the SLSS framework to enhance the practicality and adaptability of land management policies. This differentiated policy approach ensures the broad applicability of land management while also enhancing policy precision to meet the specific needs of different regions.
Through monitoring land use data within the SLSS framework, the government can track the real-time effectiveness of low-carbon agricultural technologies, identify areas where the promotion of these technologies is lacking, and provide a scientific basis for technological improvements and resource distribution. Within the SLSS framework, tax incentives for large-scale agricultural enterprises can be introduced to reduce operational costs, thereby encouraging more agricultural businesses and cooperatives to engage in large-scale operations and further promoting the adoption of low-carbon technologies. This tax incentive mechanism underpinned by SLSS not only supports the expansion of large-scale agriculture but also ensures the widespread adoption of low-carbon technologies, thus accelerating the LCTA process.
5.3 Limitations and future research
This study offers significant insights into the impact of SLSS on LCTA, drawing a range of conclusions with both practical and theoretical implications. By broadening the understanding of LCTA’s impact mechanisms, this research contributes a new perspective to existing land management and environmental economics theories. However, several limitations should be acknowledged. First, since 2017, routine land inspections have achieved full coverage across all 31 provincial-level administrative regions in China, rendering data from subsequent years unsuitable for DID analysis. To ensure an adequate sample of control group cities before and after policy implementation, this study focused on the period from 2005 to 2016. The data from this timeframe in China is relatively complete and reliable, providing a stable foundation for analysis and enhancing the continuity and reliability of the findings. Nonetheless, future studies could consider using more recent data to capture new policy impacts and reveal the latest developments in LCTA. Additionally, the spatial spillover effects of SLSS warrant further investigation, particularly regarding its potential influence on low-carbon agricultural development in neighboring regions, which may exhibit additional spillover effects. This study is centered on SLSS within the Chinese context and lacks an international perspective. Future research could incorporate cross-country comparisons to examine how different nations’ land management policies affect LCTA, thereby offering broader insights and references for LCTA policy formulation on a global scale.
6 Conclusion
This study uses China’s routine land inspections as a quasi-natural experiment, analyzing panel data from 283 Chinese cities from 2005 to 2016 to assess the impact of the State Land Supervision System (SLSS) on the Low-Carbon Transformation of Agriculture (LCTA). The main findings are as follows:
(1) SLSS significantly enhances LCTA, as confirmed by a series of robustness checks. On average, cities that implemented routine land inspections experienced a 2.17% increase in their low-carbon agricultural development levels compared to cities without such inspections.
(2) The positive effect of SLSS on LCTA is primarily achieved through the promotion of agricultural technological progress and the expansion of large-scale agricultural operations. SLSS has a stronger impact on LCTA in non-grain-producing areas, regions with low poverty rates, and areas with low fiscal pressure, compared to major grain-producing areas, high-poverty regions, and high-fiscal-pressure areas.
(3) SLSS has a greater impact on LCTA in cities with higher baseline levels of low-carbon agricultural development.
Data availability statement
The data analyzed in this study is subject to the following licenses/restrictions: Data can be obtained from the corresponding author. Requests to access these datasets should be directed to MjAyMTE5OUBodHUuZWR1LmNu.
Author contributions
JQ: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. NX: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Beckers, V., Poelmans, L., Van Rompaey, A., and Dendoncker, N. (2020). The impact of urbanization on agricultural dynamics: a case study in Belgium. J. Land Use Sci. 15 (5), 626–643. doi:10.1080/1747423x.2020.1769211
Chen, L. G., Wang, X. Y., Yang, X. Y., Wu, H. Q., Lin, Y., and Chen, L. Q. (2024). The carbon effect of cultivated land change and the spatial-temporal differentiation of its driving forces: a case study of Jiangsu. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 33 (9), 1953–1968.
Chen, S. Y. (2010). China’s green industrial revolution: an explanation from the perspective of environmental total factor productivity (1980–2008). Econ. Res. J. 45 (11), 21–34.
Chen, Z. W., Tang, C., Liu, B., Liu, P., and Zhang, X. Y. (2022). Can socialized services reduce agricultural carbon emissions in the context of appropriate scale land management? Front. Environ. Sci. 10. doi:10.3389/fenvs.2022.1039760
Cui, Y., Khan, S. U., Deng, Y., and Zhao, M. (2021). Regional difference decomposition and its spatiotemporal dynamic evolution of Chinese agricultural carbon emission: considering carbon sink effect. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 28 (29), 38909–38928. doi:10.1007/s11356-021-13442-3
Ding, X., Cai, Z., and Fu, Z. (2021). Does the new-type urbanization construction improve the efficiency of agricultural green water utilization in the yangtze river economic belt? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 28 (45), 64103–64112. doi:10.1007/s11356-021-14280-z
Dumortier, J., and Elobeid, A. (2021). Effects of a carbon tax in the United States on agricultural markets and carbon emissions from land-use change. Land use policy 103, 105320. doi:10.1016/j.landusepol.2021.105320
Feng, Y., Yuan, H., Liu, Y., and Zhang, S. (2023). Does new-type urbanization policy promote green energy efficiency? Evidence from a quasi-natural experiment in China. Energy Econ. 124, 106752. doi:10.1016/j.eneco.2023.106752
Foley, J. A., DeFries, R., Asner, G. P., Barford, C., Bonan, G., Carpenter, S. R., et al. (2005). Global consequences of land use. Science 309 (5734), 570–574. doi:10.1126/science.1111772
Gao, D., and Wang, G. (2023). Does the opening of high-speed rails improve urban carbon efficiency? Evidence from a spatial difference-in-difference method. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 30 (45), 101873–101887. doi:10.1007/s11356-023-29454-0
Gardi, C., Panagos, P., Van Liedekerke, M., Bosco, C., and De Brogniez, D. (2015). Land take and food security: assessment of land take on the agricultural production in europe. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 58 (5), 898–912. doi:10.1080/09640568.2014.899490
Guan, N., Liu, L., Dong, K., Xie, M., and Du, Y. (2023). Agricultural mechanization, large-scale operation and agricultural carbon emissions. Cogent Food Agr 9 (1), 2238430. doi:10.1080/23311932.2023.2238430
Hamidov, A., Helming, K., and Balla, D. (2016). Impact of agricultural land use in central asia: a review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 36, 6–23. doi:10.1007/s13593-015-0337-7
Han, J., Yang, Q., and Zhang, L. (2022). What are the priorities for improving the cleanliness of energy consumption in rural China? Urbanisation advancement or agriculture development? Energy Sustain Dev. 70, 106–114. doi:10.1016/j.esd.2022.07.011
Hou, X., Liu, J., Zhang, D., Zhao, M., and Xia, C. (2019). Impact of urbanization on the eco-efficiency of cultivated land utilization: a case study on the yangtze river economic belt, China. J. Clean. Prod. 238, 117916. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.117916
Huang, Z., and Song, M. (2023). The influence of industrial land transfer structure tendency on carbon emission efficiency and its transmission mechanism:based on the intermediary perspective of green technology innovation. Econ. Geogr. 43 (7), 65–76.
Ji, X., Li, Z., and Zhang, Y. (2023). Influence of rural land transfer on agricultural carbon emissions and its spatial characteristics. Resour. Sci. 45 (1), 77–90. doi:10.18402/resci.2023.01.06
Jiang, L., Deng, X., and Seto, K. C. (2013). The impact of urban expansion on agricultural land use intensity in China. Land use policy 35, 33–39. doi:10.1016/j.landusepol.2013.04.011
Jiang, X. L., Sun, Y., Shen, M., and Tang, L. X. (2024). How does developing green agriculture affect poverty? Evidence from China's prefecture-level cities. Agriculture-Basel 14 (3), 402. doi:10.3390/agriculture14030402
Jin, X., Luo, X., and Zhou, Y. (2022). Basic logic, key issues and main relations of comprehensive land consolidation. China Land Sci. 36 (11), 1–12.
Kuang, Y. P., and Zhang, H. P. (2024). Has farmland transfer improved agricultural green total factor productivity? World Agric. (2), 59–71. doi:10.13856/j.cn11-1097/s.2024.02.006
Li, F., Ma, R., Du, M., Ding, X., Feng, J., and Jing, Y. (2023a). The impact of land resource mismatch and environmental regulation on carbon emissions: evidence from China. J. Environ. Plan. Manag., 1–22. doi:10.1080/09640568.2023.2276063
Li, J., Gao, M., Luo, E., Wang, J., and Zhang, X. (2023b). Does rural energy poverty alleviation really reduce agricultural carbon emissions? The case of China. Energy Econ. 119, 106576. doi:10.1016/j.eneco.2023.106576
Li, J., Jiao, L., Li, R., Zhu, J., Zhang, P., Guo, Y., et al. (2023c). How does market-oriented allocation of industrial land affect carbon emissions? Evidence from China. J. Environ. Manage. 342, 118288. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.118288
Li, L., Han, J., and Zhu, Y. (2023d). Does environmental regulation in the form of resource agglomeration decrease agricultural carbon emissions? Quasi-natural experimental on high-standard farmland construction policy. J. Clean. Prod. 420, 138342. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.138342
Li, S., and Wang, Z. (2023). The effects of agricultural technology progress on agricultural carbon emission and carbon sink in China. Agriculture 13 (4), 793. doi:10.3390/agriculture13040793
Li, W. M., Luo, D., Chen, J., and Xie, Y. (2015). Moderate scale operation in agriculture: scale efficiency, output level, and production cost—based on survey data from 1,552 rice farmers. China Rural. Econ. (3), 4–17.
Ling, X., Gao, Y., and Wu, G. (2023). How does intensive land use affect low-carbon transition in China? New evidence from the spatial econometric analysis. Land 12 (8), 1578. doi:10.3390/land12081578
Liu, J., and Peng, J. (2022). Does the land regulatory talks restrain the local government's land finance? An empirical analysis based on multi-period difference-in-difference model. China Land Sci. 36 (7), 34–42.
Liu, J., Zhu, S., and Peng, J. (2024). The impact and mechanism of central land inspections on local land transfers: a quasi-experimental study based on routine inspections. Public Adm. Policy Rev. 13 (3), 93–115.
Liu, M., and Yang, L. (2021). Spatial pattern of China’s agricultural carbon emission performance. Ecol. Indic. 133, 108345. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.108345
Liu, X., Wang, S., Zhuang, Q., Jin, X., Bian, Z., Zhou, M., et al. (2022a). A review on carbon source and sink in arable land ecosystems. Land 11 (4), 580. doi:10.3390/land11040580
Liu, X., Xu, H., and Zhang, M. (2022b). Impact and transmission mechanism of land leasing marketization on carbon emissions:based on the mediating effect of industrial structure. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 32 (6), 12–21.
Lü, X., Zhong, T. Y., Zhang, X. L., Huang, X. J., and Tian, X. (2012). Evaluating the deterrent effect of land inspections on land violations. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 22 (8), 121–127.
Ma, A., He, Y., and Tang, P. (2021). Understanding the impact of land resource misallocation on carbon emissions in China. Land 10 (11), 1188. doi:10.3390/land10111188
Ma, J., and Cui, H. (2021). Effect and mechanism of agricultural insurance on agricultural carbon emission reduction. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 31 (10), 79–89.
Ma, S., and Zhang, Y. (2024). Will the central land inspection affect the intensity of local environmental protection? Evidence from China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 31, 46739–46751. doi:10.1007/s11356-023-31672-5
Paustian, K., Cole, C. V., Sauerbeck, D., and Sampson, N. (1998). Co2 mitigation by agriculture: an overview. Clim. Change 40 (1), 135–162. doi:10.1023/A:1005347017157
Shahbaz, M., Song, M., Ahmad, S., and Vo, X. V. (2022). Does economic growth stimulate energy consumption? The role of human capital and r&d expenditures in China. Energy Econ. 105, 105662. doi:10.1016/j.eneco.2021.105662
Shi, K., Chen, Y., Yu, B., Xu, T., Li, L., Huang, C., et al. (2016). Urban expansion and agricultural land loss in China: a multiscale perspective. Sustainability 8 (8), 790. doi:10.3390/su8080790
Song, H., Jiang, H., Zhang, S., and Luan, J. (2021). Land circulation, scale operation, and agricultural carbon reduction efficiency: evidence from China. Discrete Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2021, 1–12. doi:10.1155/2021/9288895
Uyan, M., Cay, T., Inceyol, Y., and Hakli, H. (2015). Comparison of designed different land reallocation models in land consolidation: a case study in konya/Turkey. Comput. Electron. Agric. 110, 249–258. doi:10.1016/j.compag.2014.11.022
Wang, M., Dong, Y., Lin, N., Qi, X., and Huang, X. (2024). Impact of farmland use transition on farmland use carbon emissions and its spatial spillover effects under the double carbon background: a case study of huang-huai-hai plain. J. Nat. Resour. 39 (2), 352–371. doi:10.31497/zrzyxb.20240208
Wang, R., Zhang, Y., and Zou, C. (2022). How does agricultural specialization affect carbon emissions in China? J. Clean. Prod. 370, 133463. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.133463
Wang, S. T., Bai, X. M., Zhang, X. L., Reis, S., Chen, D. L., Xu, J. M., et al. (2021). Urbanization can benefit agricultural production with large-scale farming in China. Nat. Food 2 (3), 183–191. doi:10.1038/s43016-021-00228-6
Wei, M. S., Yan, T. W., and Luo, X. (2023). The impact of scale operation and technological progress on green and low-carbon agricultural development: a quasi-natural experiment based on the establishment of major grain-producing areas. China Rural. Econ. (2), 41–65.
Wu, H., Qiu, Y., Yin, L., Liu, S., Zhao, D., and Zhang, M. (2022). Effects of China’s land-intensive use on carbon emission reduction: a new perspective of industrial structure upgrading. Front. Environ. Sci. 10, 1073565. doi:10.3389/fenvs.2022.1073565
Wu, J., Ge, Z., Han, S., Xing, L., Zhu, M., Zhang, J., et al. (2020). Impacts of agricultural industrial agglomeration on China’s agricultural energy efficiency: a spatial econometrics analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 260, 121011. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121011
Wu, Y., Shan, L., Guo, Z., and Peng, Y. (2017). Cultivated land protection policies in China facing 2030: dynamic balance system versus basic farmland zoning. Habitat Int. 69, 126–138. doi:10.1016/j.habitatint.2017.09.002
Xia, L., Cao, L., Yang, Y., Ti, C., Liu, Y., Smith, P., et al. (2023). Integrated biochar solutions can achieve carbon-neutral staple crop production. Nat. Food 4 (3), 236–246. doi:10.1038/s43016-023-00694-0
Xie, H., and Wu, X. (2023). Impact and its mechanism of urban-rural integration on the efficiency of agricultural carbon emissions in China. Resour. Sci. 45 (1), 48–61. doi:10.18402/resci.2023.01.04
Xie, H., Zhai, Q., Wang, W., Yu, J., Lu, F., and Chen, Q. (2018). Does intensive land use promote a reduction in carbon emissions? Evidence from the Chinese industrial sector. Resour. Conservation Recycl. 137, 167–176. doi:10.1016/j.resconrec.2018.06.009
Xie, R., Fang, J., and Liu, C. (2017). The effects of transportation infrastructure on urban carbon emissions. Appl. Energy 196, 199–207. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.01.020
Xie, W., and Liu, G. (2021). Study on farmers' technology adoption of mechanical residual film recycling under farmland circulation in xinjiang. J. China Agric. Resour. Regional Plan. 42 (4), 90–98.
Xu, N., Zhang, H., Li, T., Ling, X., and Shen, Q. (2022). How big data affect urban low-carbon transformation-a quasi-natural experiment from China. Int. J. Environ. Res. public health 19 (23), 16351. doi:10.3390/ijerph192316351
Xu, N., Zhang, W., Li, H., and Chen, W. (2023). Fiscal support and carbon productivity of agriculture-empirical evidence from China. Energy Environ. 35, 2451–2475. doi:10.1177/0958305X231151683
Yang, M. Y., Tang, B. S., and Liu, Y. N. (2024). Passive response and active choice: how national land inspections curb urban expansion. China Rural. Econ. (2), 131–154.
You, H. (2016). Impact of urbanization on pollution-related agricultural input intensity in hubei, China. Ecol. Indic. 62, 249–258. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2015.11.002
Yu, W., Luo, X., Tang, L., and Huang, Y. (2019). Impact of grain growing objectives on the application of bio-pesticides of rice farmers from the perspective of land fragmentation. Resour. Sci. 41 (12), 2193–2204. doi:10.18402/resci.2019.12.04
Zhang, X., Sun, H., Xia, X., Yang, Z., and Zhu, S. (2024). Can a crop rotation and fallow system reduce the carbon emission intensity of agriculture? Land 13, 293. doi:10.3390/land13030293
Zhao, Y., Huang, X., Zhong, T., Zhang, X., Peng, J., Du, G., et al. (2012). Effects of land supervision on land marketization in China. J. Nat. Resour. 27 (6), 901–911.
Zhao, R., Liu, Y., Tian, M., Ding, M., Cao, L., Zhang, Z., et al. (2018). Impacts of water and land resources exploitation on agricultural carbon emissions: the water-land-energy-carbon nexus. Land use policy 72, 480–492. doi:10.1016/j.landusepol.2017.12.029
Zhong, R., He, Q., and Qi, Y. (2022). Digital economy, agricultural technological progress, and agricultural carbon intensity: evidence from China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 19 (11), 6488. doi:10.3390/ijerph19116488
Zhou, J., Xu, N., Zhang, W., and Ning, X. (2024). Can agricultural low-carbon development benefit from urbanization? Empirical evidence from China's new-type urbanization pilot policy. J. Clean. Prod. 435, 140388. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.140388
Keywords: state land supervision system, low-carbon transformation of agriculture, agricultural technological advancement, agricultural scale operations, quasi-natural experiment
Citation: Qian J and Xu N (2024) State land supervision system and low-carbon transformation of agriculture: a quasi-natural experiment from China’s routine land inspections. Front. Environ. Sci. 12:1499329. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2024.1499329
Received: 23 September 2024; Accepted: 11 November 2024;
Published: 21 November 2024.
Edited by:
Merja H. Tölle, University of Kassel, GermanyReviewed by:
Yanqi Sun, University of Waikato, New ZealandDa Gao, Wuhan Institute of Technology, China
Copyright © 2024 Qian and Xu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ning Xu, MjAyMTE5OUBodHUuZWR1LmNu
 Jingjing Qian1
Jingjing Qian1 Ning Xu
Ning Xu