- 1School of Business, Central South University of Forestry and Technology, Changsha, China
- 2School of Business, Wuchang University of Technology, Wuhan, China
- 3Institute of Quantitative Economics and Statistics, Huaqiao University, Xiamen, China
Introduction: The agricultural sector is the second largest emitter of greenhouse gases, accounting for 23% of global anthropogenic carbon emissions. Analysis of the basic state of carbon emissions from China's agriculture is helpful to achieve carbon reduction targets.
Methods: Agricultural carbon emissions were calculated using the emission factor method, based on data from the China Rural Statistical Yearbook and various provincial statistical yearbooks. To analyze spatial patterns, the standard deviation ellipse method and the center of gravity migration model were employed, uncovering the migration path of agricultural carbon emissions. Regional disparities and the driving factors of agricultural carbon emissions were further examined using the Theil index and the Logarithmic Mean Divisia Index (LMDI) model.
Results: The analysis indicated that the emissions center has gradually shifted towards the central and western regions, reflecting changes in agricultural production activity areas. Intraregional differences are the primary contributors to the imbalance in agricultural carbon emissions, with pronounced disparities in grain production and consumption balance regions. Key influencing factors include agricultural production efficiency, adjustments in agricultural industrial structure, economic structure and output, and urbanization levels. The economic output effect and urbanization effect are identified as the main drivers of increased carbon emissions, while declining production efficiency has hindered emission reduction efforts.
Conclusion: The findings provide valuable insights for regional management and policymaking in China's agricultural sector, highlighting the need to enhance production efficiency and optimize agricultural structure to reduce emissions.
1 Introduction
Climate change has emerged as one of the most pressing global environmental issues, garnering significant attention worldwide. The large-scale emissions of greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide and methane, are recognized as primary contributors to the rise in global temperatures (Dong et al., 2018a). In response to climate change, the international community, under frameworks like the Paris Agreement, has committed to mitigating global temperature increases to within 1.5°C through measures such as emission reductions and carbon neutrality (Dai et al., 2017; Liu et al., 2022). Against this backdrop, countries have increasingly prioritized and implemented active carbon emission control measures, with agriculture becoming a focal point for both academia and policymakers (Liu and Yang, 2021). Agricultural carbon emissions mainly stem from the use of agricultural inputs such as fertilizers, pesticides, and plastic mulch, as well as from the release of methane and nitrous oxide during livestock production and soil tillage. These emissions not only have environmental consequences but also hinder sustainable agricultural development (Yang et al., 2022). Consequently, effectively controlling agricultural carbon emissions and achieving a green transformation in agriculture have become significant global challenges.
As the largest developing country and agricultural producer in the world, China has experienced rapid agricultural economic growth, which has also led to substantial CO2 emissions. It is estimated that China’s agricultural carbon emissions account for approximately one-eighth of the global total and constitute a significant portion of the country’s overall carbon emissions (Zhu and Huo, 2022). In line with the Chinese government’s “dual carbon” goals of carbon peaking and carbon neutrality, promoting green agricultural development has become a critical objective. Therefore, effectively assessing the spatiotemporal evolution of agricultural carbon emissions and identifying the driving factors in different regions are essential for formulating precise emission reduction policies.
Current research on agricultural carbon emissions primarily focuses on the calculation methods, spatiotemporal evolution, and influencing factors of these emissions. The calculation of agricultural carbon emissions serves as the foundation of related studies, primarily achieved by estimating greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide (CO₂), methane (CH₄), and nitrous oxide (N₂O) produced during agricultural production. Commonly used calculation methods in academia include the emission factor method (Zhang H. et al., 2022; Li et al., 2022; Wu et al., 2022), life cycle assessment (LCA) (Wang et al., 2022; Bian et al., 2022; Ding et al., 2022), and energy input-output analysis (Jiang et al., 2022; Zha et al., 2022; Pan et al., 2022). The emission factor method recommended by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) is widely applied due to its simplicity, relying on carbon emission factors associated with different agricultural activities. However, the accuracy of this method is contingent upon the selection of emission factors, which may introduce biases in the results. Life cycle assessment, on the other hand, offers greater precision by thoroughly analyzing carbon emissions throughout the agricultural production process, though it involves complex data acquisition and processing. Energy input-output analysis indirectly estimates carbon emissions based on the energy consumed in agricultural production, offering practicality but neglecting non-energy-related factors.
Research on the spatiotemporal evolution of agricultural carbon emissions mainly investigates the changing trends of emissions across different regions and time periods. By utilizing Geographic Information System (GIS) technologies and spatial econometric methods, researchers have analyzed the spatial clustering phenomena, regional disparities, and dynamic evolution of agricultural carbon emissions. Spatial autocorrelation analysis and Moran’s I index are commonly employed spatial statistical tools (He et al., 2022) to reveal the spatial distribution patterns of agricultural carbon emissions. Findings indicate that China exhibits significant spatial clustering of agricultural carbon emissions, with higher levels observed in the developed eastern regions and major grain-producing areas (Wen et al., 2022). Furthermore, the regional disparities in agricultural carbon emissions have shown varying trends, either narrowing or widening over different periods, with faster emission growth observed in underdeveloped western regions. Spatiotemporal evolution studies suggest that with the adjustment of national agricultural policies and the promotion of green development concepts, some regions have experienced a slowdown in carbon emission growth or even a downward trend (Han et al., 2018; Li et al., 2023). Nevertheless, the heavy reliance on environmental resources in agricultural production and the increasing degree of agricultural mechanization have continued to exert significant pressure on carbon emissions in certain areas (Li and Wang, 2023).
In the study of factors influencing agricultural carbon emissions, commonly used analytical tools include the Kaya identity (Hao et al., 2022a; Zeng and He, 2023; Peng and Liu, 2022), the Logarithmic Mean Divisia Index (LMDI) model (Zhao et al., 2022; Huang et al., 2022; Luo et al., 2023), and the STIRPAT model (Sun et al., 2022; Cui et al., 2022; Gu et al., 2022). These methods have demonstrated strong explanatory power in analyzing the driving factors of carbon emissions, yielding significant results at both the national and provincial levels. While considerable research has been conducted on the influencing factors of agricultural carbon emissions at these levels, there is still a relative scarcity of studies analyzing the differences in emission drivers across various regions, particularly among China’s three major grain-producing zones—primary grain production regions, grain consumption regions, and grain production-consumption balance regions1. The significant disparities in natural conditions, agricultural practices, and policy environments across these regions suggest that the contributions of carbon emission drivers may vary greatly among different areas and provinces.
This paper employs the standard deviation ellipse, Theil index, and LMDI decomposition models to analyze the spatiotemporal evolution characteristics and influencing factors of agricultural carbon emissions in China from 2000 to 2022. By revealing the regional distribution and migration patterns of agricultural carbon emissions, the primary driving factors in each region are identified, providing a foundation for informed decision-making to promote green agricultural development in China.
The contributions of this paper are outlined as follows: First, while much of the existing literature emphasizes calculation methods and the spatiotemporal evolution of emissions, this study offers a more in-depth analysis of regional disparities and emission migration patterns across China’s three major grain-producing zones: primary grain production regions, grain consumption regions, and production-consumption balance regions. Spatial shifts in emission patterns are revealed within various agricultural contexts, providing a more nuanced perspective compared to previous national or provincial-level studies. Second, although many studies have analyzed the drivers of agricultural carbon emissions at national or provincial levels, this research employs advanced spatial and econometric techniques, including the standard deviation ellipse, center of gravity migration models, and the Theil index, to identify significant regional differences in emission drivers. These differences are particularly important given the diverse natural conditions, agricultural practices, and policy environments across China, which have been inadequately addressed in prior research. Finally, by applying the Logarithmic Mean Divisia Index (LMDI) model to decompose the factors influencing emissions, the study offers a detailed understanding of the contributions of variables such as agricultural production efficiency, structural adjustments, and urbanization in different regions. This approach provides a clearer view of how emission drivers vary regionally, enabling more targeted policy recommendations. In conclusion, the integration of spatial analysis with regional decomposition models offers new insights into the dynamic migration of agricultural carbon emissions and regional disparities in emission drivers, facilitating the development of more effective policies for green agricultural development in China.
The structure of this paper is as follows: First, the methods of calculating agricultural carbon emissions and the data sources are introduced. Next, the spatiotemporal evolution characteristics of agricultural carbon emissions are analyzed using the standard deviation ellipse model. Then, regional differences in agricultural carbon emissions are examined through the Theil index. Finally, the LMDI model is utilized to decompose the influencing factors of agricultural carbon emissions, followed by corresponding policy recommendations.
2 Research design
This study employs a combination of the Standard Deviation Ellipse (SDE), Theil index, and Logarithmic Mean Divisia Index (LMDI) to analyze the spatiotemporal dynamics and regional disparities of agricultural carbon emissions in China. Understanding how agricultural production activities and their associated emissions have shifted is critical in the context of China’s rapid economic development and agricultural transformation. The SDE method is used to visually and quantitatively capture spatial changes in emission patterns, aiding in the identification of changes in the geographic concentration and directional movement of emissions over time. The Theil index is particularly effective for decomposing inequality into within-region and between-region components, making it highly relevant for assessing regional disparities in emissions. This approach enables a more detailed analysis of emission inequalities across different agricultural regions in China, helping to identify areas where disparities are most pronounced. Lastly, the LMDI model is applied to decompose the driving factors behind agricultural carbon emissions, such as changes in agricultural production efficiency, structural adjustments, and urbanization. This model precisely attributes changes in emissions to specific drivers, offering region-specific insights into the impact of policy and economic changes on emission patterns. The combined application of these methods provides a comprehensive analysis of the spatial and temporal dynamics of emissions and offers a robust framework for understanding the regional factors driving agricultural carbon emissions, thereby contributing to the development of more targeted emission reduction policies.
2.1 Agricultural carbon emission estimation
Agriculture, as a source of carbon emissions, generates direct or indirect greenhouse gas emissions through material inputs in land use, soil disruption caused by crop planting and tilling, and enteric fermentation and manure management in livestock farming. Due to its simplicity, practicality, and ease of application, the emission factor method has been widely used for carbon emission estimation at both national and provincial levels. Drawing on the existing studies by Chen et al. (2019) and Guo et al. (2016), and considering the actual agricultural production conditions in China, this study identifies the primary sources of agricultural carbon emissions in China as stemming from the use of fertilizers, pesticides, agricultural plastic films, agricultural diesel, and irrigation during land use. To ensure consistency in data units for comparative analysis, the conversion factors from the IPCC Fourth Assessment Report are applied, with 1 ton of CH₄ equivalent to 6.82 tons of carbon (C), and 1 ton of N₂O equivalent to 81.27 tons of carbon (C). The specific formula for calculating agricultural carbon emissions is as follows:
In Equation 1, E represents the total agricultural carbon emissions (measured in ten thousand tons), Ti denotes the quantity of the ith carbon emission source, and
2.2 Standard deviation ellipse
The Standard Deviation Ellipse (SDE) is a statistical tool widely used in spatial analysis to describe the central tendency and dispersion characteristics of a set of spatial points (Zhao and Zhao, 2014). By constructing an ellipse, the SDE can visually represent the spatial distribution and directional trends of data points relative to their mean center. The ellipse’s major and minor axes correspond to the standard deviations of the data in the primary and secondary directions, respectively. The major axis indicates the direction of maximum variance, while the minor axis, orthogonal to the major axis, represents the direction of minimum variance (Zhong et al., 2020). The orientation of the ellipse reflects the dominant distribution trend of the data, and its size indicates the degree of spatial dispersion. The following are the formulas for calculating the SDE for provincial data:
For a given year, the centroid coordinates
The carbon emissions of the jth province are represented by
The orientation of the major axis, θ can be expressed as follows:
Equation 3 describes the orientation of the ellipse’s major axis, which is based on the carbon emission weights and coordinates of each province. The standard deviation along the x-axis is expressed as follows:
Equation 4 represents the degree of dispersion of data points along the major axis. The standard deviation along the y-axis is expressed as follows:
Equation 5 represents the degree of dispersion of data points along the minor axis.
2.3 Theil Index
The Theil Index is a measure of distributional inequality, commonly used to evaluate disparities in income or economic development (Fan and Sun, 2008; Dong and Hao, 2018). The Theil Index ranges between 0 and 1, where 0 represents complete equality and one denotes maximum inequality. Due to its decomposability, the Theil Index is particularly suitable for analyzing the contributions of within-group and between-group differences to total inequality.
By applying the Theil Index to the agricultural carbon emissions data of various provinces (j), it becomes possible to measure the distributional imbalance of carbon emissions across provinces. Let
To further analyze the sources of inequality, the Theil Index can be decomposed into two components: within-group inequality and between-group inequality.
Within-group inequality
In Equation 7, Tk represents the Theil Index of the kth group, and Yk denotes the total carbon emissions of the kth group.
Between-group inequality Tb captures the distributional differences of carbon emissions across different groups. The formula is as follows:
In Equation 8, nk represents the number of provinces in the kth group.
Through the calculation and decomposition of the Theil Index, the agricultural carbon emissions imbalance among provinces can be comprehensively analyzed, allowing for a clear understanding of the contribution of within-group and between-group disparities to overall inequality.
2.4 LMDI model
The Logarithmic Mean Divisia Index (LMDI) model is a widely applied decomposition method for analyzing the driving factors of carbon emissions. It is particularly well-suited for decomposition problems that require no residuals (Ang, 2005; Ma and Stern, 2008; Ma et al., 2019). This model allows for the decomposition of changes in agricultural carbon emissions into the effects of various driving factors, such as production efficiency, industrial structure, economic output, and urbanization levels. Drawing on the identity principle of both sides of the Kaya Identity, the carbon emissions of China’s agriculture can be decomposed as follows:
In Equation 9, CE represents the total agricultural carbon emissions in China; CEj denotes the agricultural carbon emissions of province j; BGDPj refers to the gross output value of agriculture and animal husbandry in province j; AGDPj represents the total output value of agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry, and fisheries in province j; GDPj is the total economic output of province j; FPj indicates the total population of province j; Pj refers to the rural population of province j; Bj stands for production efficiency in province j; Aj represents the agricultural industrial structure of province j; Sj denotes the economic structure of province j; Ej signifies the economic development level of province j; and Uj represents the urbanization level of province j.
The influencing factors are further decomposed using the additive decomposition method, as follows:
In Equation 10,
In Equations 11–16,
2.5 Data sources and processing
The empirical analysis in this study relies on data related to fertilizer use (in pure form), agricultural film consumption, pesticide usage, diesel for agricultural machinery, crop planting area, effective irrigation area, total output value of planting, total output value of agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry, and fisheries, and agricultural labor force size. These data were sourced from the China Rural Statistical Yearbook (2000-2022) and provincial statistical yearbooks of 31 provinces, municipalities, and autonomous regions in mainland China.
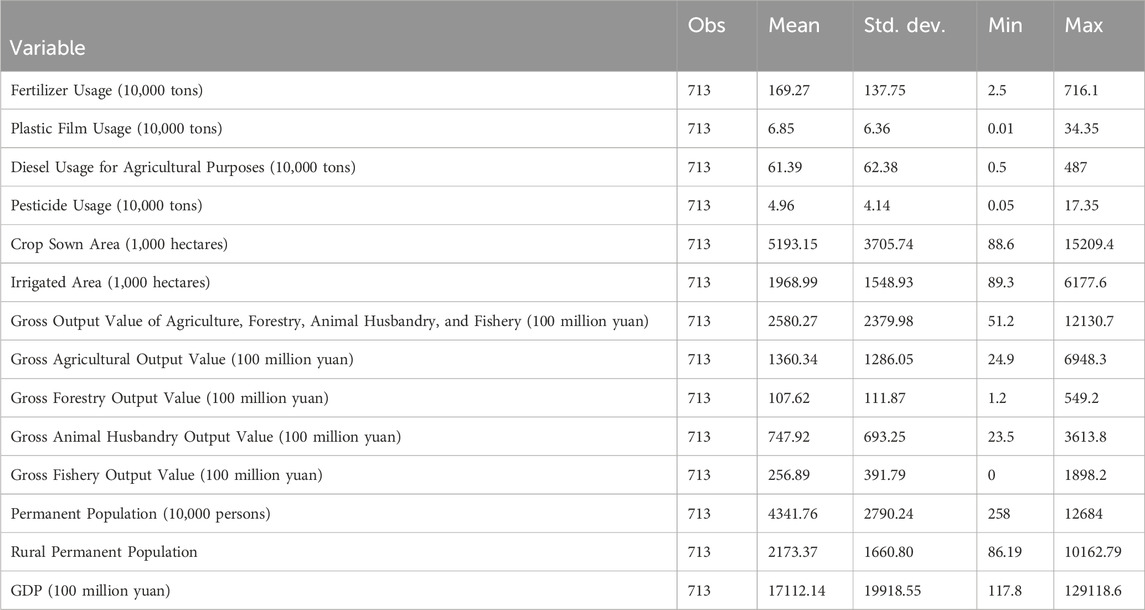
The descriptive statistics of the key variables used in this study are presented in Table 1. Fertilizer usage averages 169.27 (10,000 tons) with a standard deviation of 137.75, indicating significant differences across regions. Similarly, diesel usage for agricultural purposes exhibits a mean of 61.39 (10,000 tons) and a broad range from 0.5 to 487 (10,000 tons). The crop sown area and irrigated area display substantial variation, with mean values of 5193.15 and 1968.99 (1,000 ha), respectively, reflecting diverse land use patterns. Economic indicators show that the gross output value of agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry, and fishery averages 2580.27 (100 million yuan), while GDP records a mean of 17,112.14 (100 million yuan), highlighting economic disparities across regions. Population data further demonstrate a permanent population mean of 4341.76 (10,000 persons), with rural populations averaging 2173.37 (10,000 persons).
3 Analysis of Agricultural carbon emission results
3.1 Spatiotemporal evolution characteristics
3.1.1 Temporal Variation characteristics
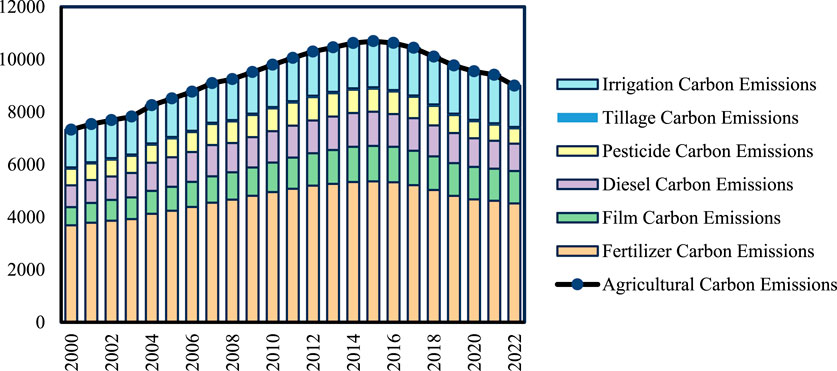
The estimated total agricultural carbon emissions in China from 2000 to 2022 are illustrated in Figure 1. As shown, agricultural carbon emissions in China exhibited a fluctuating upward trend during this period. By 2022, total agricultural carbon emissions reached 89.99 million tons, representing an increase of approximately 22.88% compared to 73.25 million tons in 2000. This reflects a continuous rise in carbon emissions associated with agricultural activities. However, the growth in emissions was not linear, with various phases of change observed over time.
From 2000 to 2007, carbon emissions experienced continuous growth, marked by a steady upward trend. During this period, the use of fertilizers, plastic films, and diesel significantly increased. The modernization of agriculture, characterized by the widespread use of fertilizers and pesticides, contributed to increased agricultural yields but also led to a rise in carbon emissions. From 2008 to 2014, carbon emissions fluctuated at high levels. After peaking in 2008, agricultural carbon emissions remained elevated for several years. During this stage, the continued adoption of mechanized farming and improvements in irrigation technology kept emissions at a high but volatile level. From 2015 to 2022, emissions gradually declined. Starting in 2015, a downward trend in emissions emerged, particularly due to noticeable reductions in emissions from plastic films and diesel. This decline may be attributed to national policies and technological advancements, such as initiatives promoting fertilizer efficiency, pesticide reduction, and optimized rural energy structures, all contributing to the gradual decrease in agricultural carbon emissions.
The different components of carbon emissions also exhibited varying behaviors within the overall trend. Fertilizer emissions increased from 36.91 million tons in 2000 to 45.20 million tons in 2022, reflecting a growth of 22.47%. Fertilizer emissions followed a general upward trajectory throughout the period, making it a significant source of agricultural carbon emissions. Diesel emissions rose from 8.29 million tons in 2000 to 10.44 million tons in 2022, indicating the advancement of agricultural mechanization. Irrigation-related emissions also showed substantial growth, increasing from 14.34 million tons in 2000 to 15.66 million tons in 2022, highlighting the expansion of irrigation technology and coverage. Although agricultural carbon emissions in China increased over the entire period, recent mitigation efforts have had some success, with a decline in carbon intensity observed. This suggests progress in China’s pursuit of green agricultural development.
3.1.2 Spatial shift path
To further reveal the migration patterns of agricultural carbon emissions in China, an analysis was conducted using the standard deviation ellipse and centroid shift model (see Table 2; Figure 2). Figure 2 shows that the centroid of the ellipse is primarily concentrated in the central region of China. Overall, from 2001 to 2022, the centroid exhibited a northwestward shift, particularly evident between 2001 and 2015, during which the centroid migrated significantly, covering a cumulative distance of 153.23 km. This trend may reflect the increasing agricultural activities in the central and western regions, leading to a more concentrated distribution of related carbon emissions.
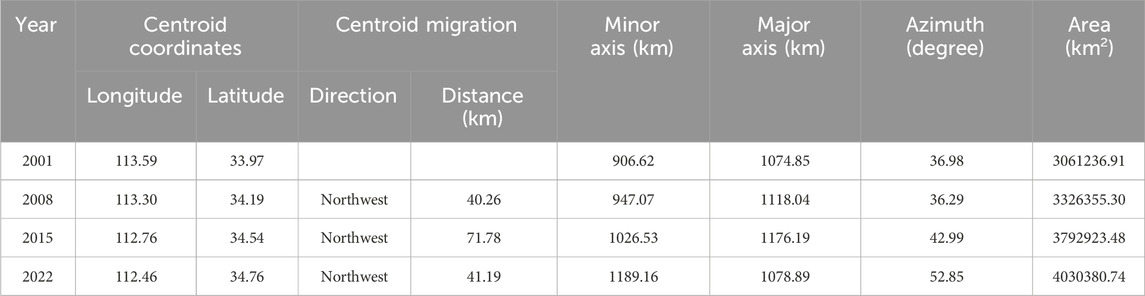
Table 2. Changes in the standard deviation ellipse parameters of China’s agricultural carbon emissions.
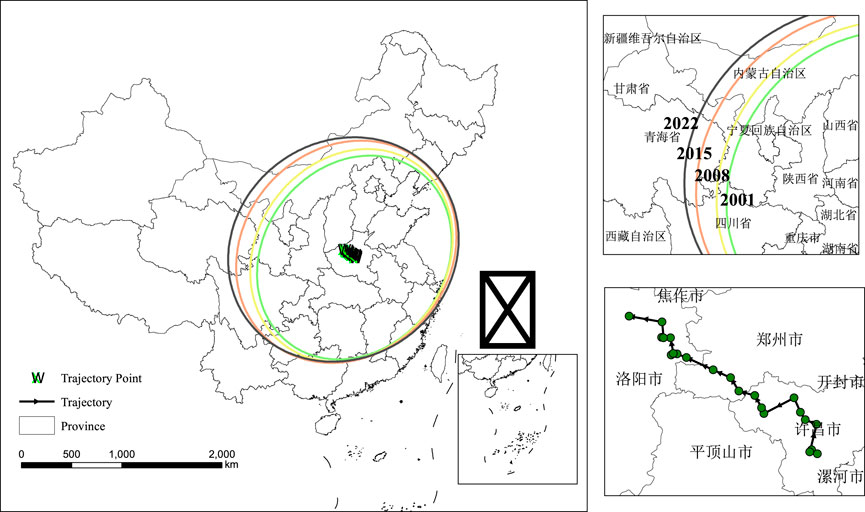
Figure 2. Changes in the Standard Deviation Ellipse of China’s Agricultural Carbon Emissions. Note: The top-right inset in Figure 2 provides a magnified view of the outer region of the main ellipse, illustrating the specific locations and trajectories of the agricultural carbon emission centroids for the years 2001, 2008, 2015, and 2022. The bottom-right inset details the migration path of the agricultural carbon emission centroid.
Table 2 shows the changes in the standard deviation ellipse parameters for China’s agricultural carbon emissions. The minor and major axes reflect the spread of emissions in the north-south and east-west directions, respectively. The minor axis increased from 906.62 km in 2001 to 947.07 km in 2008 and continued expanding to 1,189.16 km by 2022, indicating a widening spatial distribution in the north-south direction. Meanwhile, the major axis grew from 1,074.85 km in 2001 to 1,078.89 km in 2022, indicating relatively stable expansion in the east-west direction over the period.
In terms of the centroid migration path, the ellipse’s centroid experienced a southeast-to-northwest shift between 2001 and 2022. Notably, during the period from 2008 to 2015, the migration distance was substantial, reaching 71.78°km, followed by a deceleration in migration speed. This shift in the centroid reflects a gradual concentration of agricultural carbon emissions towards the central and western regions, closely linked to adjustments in agricultural production layouts and regional policy changes. As shown in Table 2, the azimuth angle increased from 36.98° in 2001° to 52.85° in 2022, indicating that the primary direction of agricultural carbon emissions shifted from a northeast-southwest axis to a more northern orientation. Additionally, the area of the ellipse expanded from 3.06 million km2 in 2001 to 4.03 million km2 in 2022.
3.2 Regional disparity analysis
The Theil index serves as an effective tool for quantifying disparities in carbon emissions distribution by evaluating the contributions of various regions or functional areas. In this study, the index is decomposed into two primary components: within-group disparity and between-group disparity. The within-group disparity measures the extent of inequality in carbon emissions within each of the three functional grain areas—major grain-producing, major grain-consuming, and grain production-consumption balanced areas. A lower within-group Theil index indicates a more uniform distribution of emissions within a specific group, while a higher index suggests greater variation.
Conversely, the between-group disparity captures the differences in emissions intensity between the three functional grain areas. A high between-group Theil index reflects significant disparities in emissions patterns across regions, whereas a lower index indicates that regional differences are diminishing.
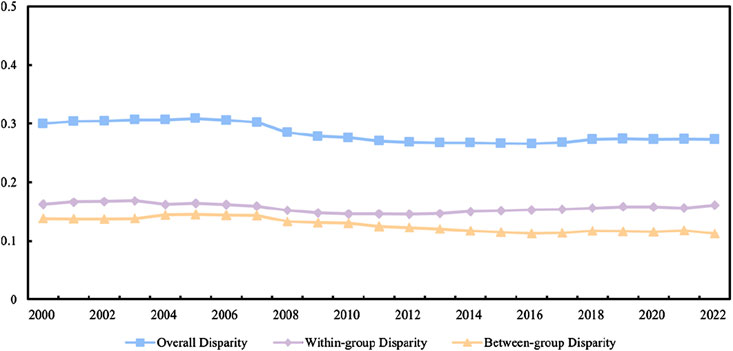
By analyzing the trends in overall, within-group, and between-group disparities presented in Figure 3, the general evolution of emissions inequality across the country can be observed, alongside the specific contributions of disparities within and between the grain regions. Figure 4 provides a deeper examination of the dynamics within the functional grain areas, illustrating how disparities in emissions evolve distinctly across these regions over time.
As illustrated in Figure 3, the overall Theil index remained relatively stable between 2000 and 2006, followed by an increase during the 2006-2008 period, peaking at 0.30575 in 2008. After 2008, the overall Theil index steadily declined, reaching 0.27331 in 2022, indicating a gradual reduction in carbon emission intensity disparities among provinces. This trend may be closely linked to national policy regulations, industrial restructuring, and the implementation of energy conservation and emission reduction measures (Li et al., 2021; Dong et al., 2018b; Shuai et al., 2017). The intra-group Theil index exhibited a similar trend to the overall Theil index, showing relative stability between 2000 and 2007, and gradually decreasing after 2008. This suggests that disparities in carbon emission intensity within provinces have diminished, particularly as coordinated development within certain regions has been strengthened. The inter-group Theil index showed an overall downward trend, with a particularly noticeable decline after 2008, indicating that differences in carbon emission intensity among different regions have gradually narrowed.
As shown in Figure 4, the inter-group disparities in the major grain-producing regions declined significantly between 2000 and 2022. In contrast, the inter-group disparities in the major grain-selling regions remained relatively stable, albeit with slight fluctuations. The grain balance regions, however, maintained higher levels of inter-group disparities, with a noticeable increase after 2020.
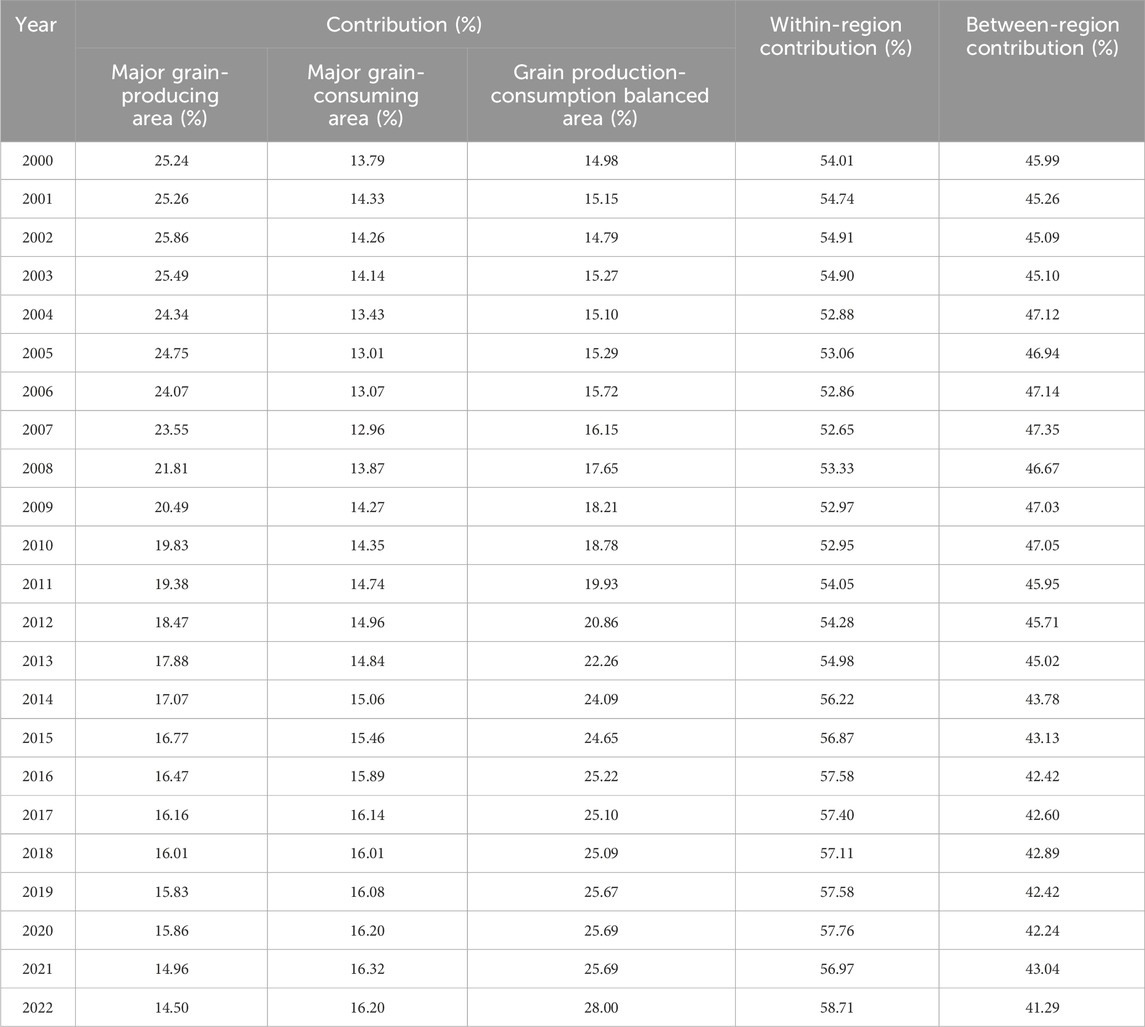
Table 3 reveals that from 2000 to 2022, the regional contribution of agricultural carbon emissions displayed a clear trend where the contribution of intra-regional differences significantly outweighed that of inter-regional differences. This indicates that intra-regional variations were the primary factor driving disparities in carbon emission intensity. Among the three major grain functional areas, the Grain Production and Consumption Balanced Zone contributed the most to intra-regional differences, with an average contribution rate of approximately 57%. The Grain Production Zone followed, with an average contribution rate of 16.8%, while the Grain Consumption Zone contributed the least, with an average of only 14.5%. This phenomenon suggests that carbon emission differences were more pronounced within regions rather than between them.
Specifically, the intra-regional contribution of the Grain Production and Consumption Balanced Zone showed a gradual increase throughout the analysis period, particularly after 2014, rising from around 24% in 2014 to approximately 28% in 2022. This growth may be attributed to advancements in agricultural technology, improvements in resource utilization efficiency, and differentiated regional economic development. In contrast, the intra-regional contribution of the Grain Production Zone and the Grain Consumption Zone remained relatively stable. The contribution of the Grain Production Zone has hovered around 16% since 2000 and slightly declined after 2020, likely influenced by policy directives and the optimization of production methods. The contribution of the Grain Consumption Zone increased from 13.87% in 2008 to 16.2% in 2022, but the overall growth was relatively modest, reflecting a more stable pattern of carbon emissions within this region.
3.3 Factor analysis
3.3.1 National-level factor analysis
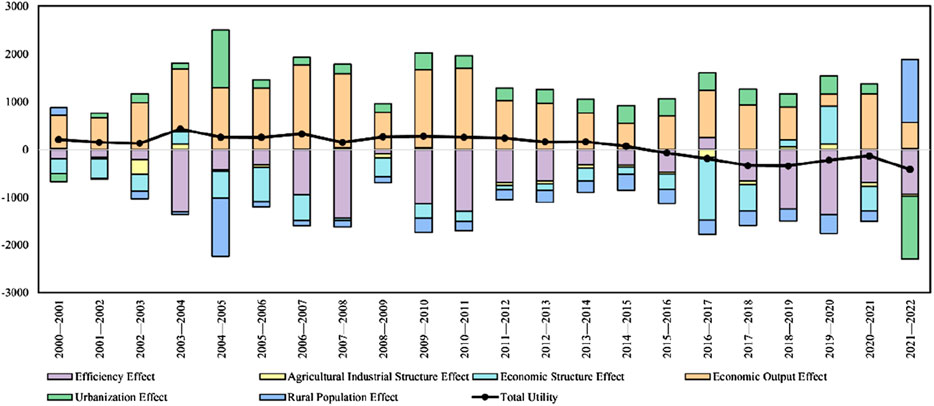
Based on the LMDI model and calculated data on agricultural carbon emissions, the factors influencing China’s agricultural carbon emissions from 2000 to 2022 were decomposed, as shown in Figure 5. The results indicate a clear fluctuation in both the overall effect of agricultural carbon emissions and its influencing factors over time. On the whole, the impact of various factors on carbon emissions was uneven.
From 2000 to 2014, agricultural carbon emissions exhibited a continuous upward trend, with the most significant increase occurring in 2003–2004 when the total effect reached 4.33 million tons. This growth was primarily driven by the economic output effect. Starting in 2008, the total effect showed noticeable fluctuations, particularly in 2016–2017 when it turned negative, reaching −1.87 million tons. This reduction in carbon emissions during this period was mainly attributed to improvements in efficiency. However, in 2022, the total effect again displayed a large negative value (−4.12 million tons), indicating the strong influence of various emission-reduction factors that year.
The efficiency effect has consistently been one of the main factors suppressing agricultural carbon emissions. In most years, it contributed to reducing emissions. Notably, in 2003–2004 and 2007-2008, the efficiency effect reached −13.07 million tons and −14.49 million tons, respectively, demonstrating its substantial role in mitigating emissions during these periods. These reductions suggest that improvements in agricultural technology and resource-use efficiency greatly curtailed carbon emissions. However, in some years, such as 2016-2017 (252.57 thousand tons), the efficiency effect was positive, indicating a decline in production efficiency or increased energy consumption in agricultural activities, warranting further investigation into the factors behind these fluctuations.
The agricultural structural effect generally had a smaller impact on carbon emissions, but notable fluctuations were observed in certain years. For instance, in 2000–2001, the agricultural structural effect was 237.1 thousand tons, contributing to emission increases, whereas in 2008–2009, it was −915.4 thousand tons, indicating that internal adjustments in the agricultural sector helped reduce emissions. This highlights that changes in agricultural structure do not consistently promote emission reductions, and their effects vary depending on specific policies and timeframes.
The economic structural effect typically contributed to emission reductions. From 2004 to 2007, the economic structural effect accounted for reductions of 5.65 million tons, 7.11 million tons, and 5.45 million tons, respectively. These reductions were driven by shifts in the economy, such as the declining share of agriculture and the increasing dominance of the industrial and service sectors. However, in some years, such as 2022 (216.5 thousand tons), the economic structural effect led to emission increases, which may have been caused by imbalanced structural adjustments or a temporary resurgence in agricultural activity.
The economic output effect remained one of the primary drivers of increased agricultural carbon emissions throughout the study period. It contributed significantly to emission increases in 2002–2003 (9.80 million tons), 2006-2007 (17.54 million tons), and 2020-2021 (11.65 million tons). This reflects how the expansion of agricultural production and economic activities directly resulted in higher resource consumption and, consequently, increased carbon emissions. The persistent trend of rising emissions driven by economic output underscores the need for future strategies to balance agricultural economic growth with enhanced production efficiency and reduced resource consumption to mitigate emissions.
Urbanization effects also contributed to emission increases in several years. For example, in 2009–2010 (3.46 million tons) and 2019-2020 (3.87 million tons), the acceleration of urbanization led to higher emissions, likely due to changes in land use, shifts in agricultural production methods, and increased demand for agricultural products.
The rural population effect, conversely, acted as a mitigating factor for emissions. In 2004-2005 and 2008-2009, it contributed to reductions of 12.36 million tons and 1.20 million tons, respectively, indicating that population decline in rural areas reduced the intensity of agricultural activity and, as a result, lowered carbon emissions.
3.3.2 Analysis of influencing factors in functional grain zones
Figure 6 presents the decomposition of agricultural carbon emissions using the LMDI model reveals distinct patterns across China’s grain functional zones: the main grain-producing area, the main grain-consuming area, and the grain production-consumption balance area.
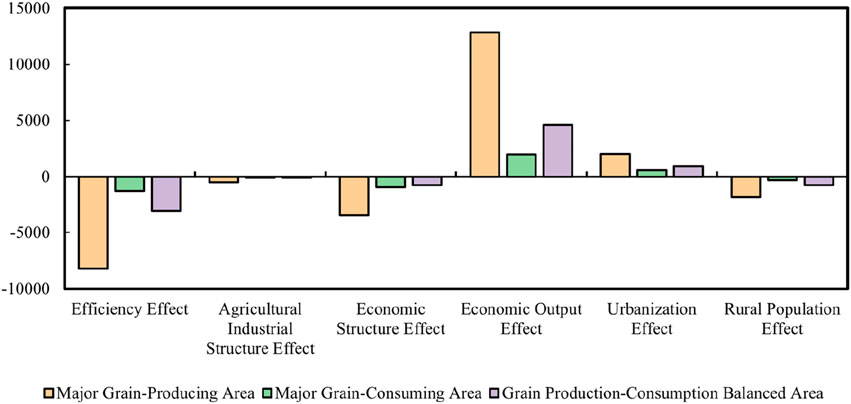
Figure 6. Overall decomposition results of the influencing factors of agricultural carbon emissions in the three major grain functional zones.
In the main grain-producing area, the total effect is a net increase of 836.67 million tons of carbon emissions. This growth is primarily driven by the economic output effect, which adds 12,846.39 million tons, reflecting the strong influence of agricultural production expansion on emissions. However, substantial mitigating effects are observed in the efficiency effect (−8,221.94 million tons), the economic structural effect (−3,474.46 million tons), and the agricultural structural effect (−501.08 million tons), highlighting the role of improved efficiency and structural changes in reducing emissions. Additionally, the urbanization effect contributes 2,019.67 million tons to emissions, while the rural population effect reduces emissions by −1,831.91 million tons, suggesting that rural depopulation helped curb emissions.
In contrast, the main grain-consuming area exhibits a slight net decrease in emissions, with a total effect of −14.97 million tons. The efficiency effect (−1,278.18 million tons), economic structural effect (−944.54 million tons), and agricultural structural effect (−78.10 million tons) all contribute to reducing emissions. However, these reductions are partially offset by the economic output effect, which increases emissions by 1,990.81 million tons. The urbanization effect adds 585.86 million tons to emissions, while the rural population effect further reduces emissions by −290.82 million tons.
In the grain production-consumption balance area, the total effect is a net increase of 852.57 million tons of emissions. Similar to other regions, the economic output effect plays a dominant role, contributing 4,596.06 million tons to emissions. Meanwhile, the efficiency effect (−3,088.96 million tons), economic structural effect (−764.61 million tons), and agricultural structural effect (−91.97 million tons) act to mitigate emissions. The urbanization effect increases emissions by 954.08 million tons, while the rural population effect contributes a reduction of −752.04 million tons.
Overall, the findings emphasize that while economic output and urbanization drive emission increases, improvements in efficiency and structural adjustments in both the economy and agriculture play crucial roles in mitigating carbon emissions across all regions. These results suggest the importance of targeted policy measures to balance economic growth with sustainability in agricultural practices.
4 Conclusion and recommendations
This paper analyzes the spatiotemporal evolution and influencing factors of agricultural carbon emissions in China from 2000 to 2022 using the Standard Deviation Ellipse, Theil Index, and LMDI model. The findings are as follows:
First, spatiotemporal evolution characteristics: Between 2000 and 2022, China’s agricultural carbon emissions exhibited a fluctuating upward trend, particularly during 2000–2007, where emissions consistently increased, followed by a decline post-2015. Spatially, the center of agricultural carbon emissions gradually shifted northwest, indicating that agricultural production activities are increasingly concentrated in the central and western regions of China. Second, regional differences: The overall Theil Index reveals that the disparity in agricultural carbon emissions intensity among Chinese provinces gradually diminished between 2000 and 2022. This change is closely linked to national policies, industrial restructuring, and the implementation of energy-saving and emission reduction measures. The contribution of intra-regional differences significantly surpassed that of inter-regional differences, with the grain production-consumption balance zone contributing the most to intra-regional differences. This indicates that the heterogeneity of carbon emissions within this zone is more pronounced. Third, factor decomposition: The decomposition results from the LMDI model indicate that the economic output effect and urbanization effect were the primary drivers of increased agricultural carbon emissions. Conversely, production efficiency, agricultural industrial structure adjustments, and economic structural changes played a significant role in reducing carbon emissions. Notably, carbon emissions increased more prominently in the grain-producing areas and the grain production-consumption balance zones, while emissions in the grain-consuming areas showed a decline.
The shift of agricultural carbon emissions toward the northwest aligns with broader agricultural policy trends in China. Policies such as the “Western Development” strategy and incentives to promote agricultural production in central and western China have stimulated growth in these regions. This finding is consistent with previous studies (Liu et al., 2021), which highlight the expansion and improvement of agricultural productivity in central and western China. However, while this expansion has contributed to food security and regional development, it has also increased carbon emissions due to intensive land use and mechanization. The decline in emissions after 2015 can be attributed to the implementation of stricter environmental policies, such as the promotion of sustainable agricultural practices and the reduction of fertilizer use, a trend echoed in earlier research.
The Theil index reveals that the reduction in disparities among provinces reflects the impact of nationwide efforts to standardize agricultural practices and improve production efficiency. Policies focused on narrowing regional economic gaps and supporting rural development have likely played a significant role in reducing carbon emissions disparities between provinces. Previous research similarly emphasizes how national energy-saving and emission-reduction policies have contributed to regional convergence in environmental indicators (Huisingh et al., 2015; Zhang L. et al., 2022). Notably, intra-regional disparities, particularly within the grain production-consumption balance zones, indicate that while regional policies have been effective in reducing inter-provincial disparities, local factors such as land management practices, resource availability, and stages of economic development still lead to significant heterogeneity in emissions.
The LMDI decomposition results highlight that economic output and urbanization are the primary contributors to carbon emissions, aligning with broader economic trends in China. As agriculture becomes increasingly mechanized and commercialized, economic growth inevitably leads to higher energy consumption and emissions. Urbanization has also driven demand for agricultural products, further boosting production. This supports previous findings that urbanization is associated with growing agricultural demand and subsequent emissions increases (Sun and Huang, 2020; Wang et al., 2016). On the other hand, improvements in production efficiency and structural adjustments have counteracted these pressures, contributing to emissions reductions. These factors are widely recognized in the literature as key components for achieving emissions reductions (Shuai et al., 2018; Hao et al., 2022b), particularly as the nation invests in green technology and sustainable agricultural practices.
To promote low-carbon agricultural development, more refined regional carbon reduction strategies need to be developed based on specific regional conditions.
First, strengthening differentiated regional management: In major grain-producing areas, it is essential to promote low-carbon agricultural technologies, such as precision fertilization and water-saving irrigation techniques, while further optimizing mechanized agricultural operations to reduce carbon emissions from agricultural production. Governments can offer economic incentives, such as subsidies, to encourage farmers to adopt green agricultural practices, gradually reducing dependence on fertilizers and pesticides. In grain-consuming regions, where agricultural production activities are relatively limited, urbanization has a significant impact on carbon emissions. It is recommended to optimize urban planning, promote energy-efficient buildings, and encourage the use of renewable energy to reduce carbon emissions resulting from urban expansion. Additionally, the development of ecological agriculture in surrounding areas can help reduce the carbon footprint of urban food supply chains. Given the high heterogeneity of agricultural carbon emissions in grain production-consumption balance zones, it is advisable to strengthen carbon emission monitoring within these regions. In areas with higher agricultural carbon emissions, implementing carbon emission trading mechanisms could incentivize enterprises and farmers to adopt emission reduction measures.
Second, enhancing agricultural production efficiency and optimizing resource allocation: Governments should support efforts to improve agricultural production efficiency by promoting agricultural mechanization and smart agriculture, as well as upgrading farmland infrastructure to reduce resource waste and optimize resource allocation. Additionally, agricultural technical training can be enhanced to improve farmers’ operational skills, thereby reducing unnecessary carbon emissions during production. Precision agriculture should be advanced by utilizing big data and IoT technology for precision fertilization and irrigation, further improving resource utilization efficiency and reducing the environmental burden and carbon emissions caused by excessive use.
Third, establishing long-term monitoring and evaluation mechanisms for agricultural carbon emissions. A national or regional agricultural carbon emission monitoring system should be established to regularly assess carbon emissions in different regions and adjust related policies based on monitoring results. Moreover, research and promotion of agricultural carbon reduction technologies suitable for China’s diverse regional characteristics should be accelerated, providing scientific support for managing agricultural carbon emissions.
Data availability statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found here: The data used in this study are publicly available and have been correctly cited. Data sets used or analysed in the current study are available from corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Author contributions
XH: Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing–original draft. XW: Formal Analysis, Methodology, Software, Supervision, Writing–original draft. XG: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Software, Validation, Writing–original draft. YS: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Resources, Supervision, Visualization, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. Mention of trade names or commercial products in this article is solely for the purpose of providing scientific information and does not imply recommendation or endorsement by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA). USDA is an equal employment provider and employer.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Footnotes
1China’s current grain production layout was established between 2003 and 2004. The 31 provinces are classified into main production areas, production-consumption balance areas, and main consumption areas based on indicators such as grain output, per capita availability, and commercial grain reserves. Thirteen provinces (or autonomous regions)—Hebei, Inner Mongolia, Jilin, Heilongjiang, Liaoning, Jiangsu, Anhui, Jiangxi, Shandong, Henan, Hubei, Hunan, and Sichuan—are designated as the main production areas. The main consumption areas include seven provinces (or municipalities) with large grain inflows: Beijing, Tianjin, Shanghai, Zhejiang, Fujian, Guangdong, and Hainan. Eleven provinces (or autonomous regions and municipalities)—Shanxi, Guangxi, Guizhou, Yunnan, Chongqing, Tibet, Shaanxi, Gansu, Qinghai, Ningxia, and Xinjiang—are categorized as production-consumption balance areas. In the main production areas, grain production is to be stabilized and gradually increased. The main consumption areas are tasked with maintaining sufficient grain planting areas to ensure a necessary level of self-sufficiency. The production-consumption balance areas are to continue stabilizing the balance between grain supply and demand.
References
Ang, B. W. (2005). The LMDI approach to decomposition analysis: a practical guide. Energy policy 33 (7), 867–871. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2003.10.010
Bian, R., Chen, J., Zhang, T., Gao, C., Niu, Y., Sun, Y., et al. (2022). Influence of the classification of municipal solid wastes on the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions: a case study of Qingdao City, China. J. Clean. Prod. 376, 134275. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.134275
Chen, Y., Li, M., Su, K., and Li, X. (2019). Spatial-temporal characteristics of the driving factors of agricultural carbon emissions: empirical evidence from Fujian, China. Energies 12 (16), 3102. doi:10.3390/en12163102
Cui, Y., Khan, S. U., Sauer, J., and Zhao, M. (2022). Exploring the spatiotemporal heterogeneity and influencing factors of agricultural carbon footprint and carbon footprint intensity: embodying carbon sink effect. Sci. Total Environ. 846, 157507. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.157507
Dai, H. C., Zhang, H. B., and Wang, W. T. (2017). The impacts of US withdrawal from the Paris Agreement on the carbon emission space and mitigation cost of China, EU, and Japan under the constraints of the global carbon emission space. Adv. Clim. Change Res. 8 (4), 226–234. doi:10.1016/j.accre.2017.09.003
Ding, Y., Duan, H., Xie, M., Mao, R., Wang, J., and Zhang, W. (2022). Carbon emissions and mitigation potentials of 5G base station in China. Resour. Conservation Recycl. 182, 106339. doi:10.1016/j.resconrec.2022.106339
Dong, F., Yu, B., Hadachin, T., Dai, Y., Wang, Y., Zhang, S., et al. (2018a). Drivers of carbon emission intensity change in China. Resour. Conservation Recycl. 129, 187–201. doi:10.1016/j.resconrec.2017.10.035
Dong, F., Yu, B., Hadachin, T., Dai, Y., Wang, Y., Zhang, S., et al. (2018b). Drivers of carbon emission intensity change in China. Resour. Conservation Recycl. 129, 187–201. doi:10.1016/j.resconrec.2017.10.035
Dong, X. Y., and Hao, Y. (2018). Would income inequality affect electricity consumption? Evidence from China. Energy 142, 215–227. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2017.10.027
Fan, C. C., and Sun, M. (2008). Regional inequality in China, 1978-2006. Eurasian Geogr. Econ. 49 (1), 1–18. doi:10.2747/1539-7216.49.1.1
Gu, R., Li, C., Li, D., Yang, Y., and Gu, S. (2022). The impact of rationalization and upgrading of industrial structure on carbon emissions in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 19 (13), 7997. doi:10.3390/ijerph19137997
Guo, X., Zhang, L., Hu, R., and Song, M. (2016). Influencing factor decomposition of planting carbon emission in central China. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 25 (5), 695–701. doi:10.11870/cjlyzyyhj201605001
Han, H., Zhong, Z., Guo, Y., Xi, F., and Liu, S. (2018). Coupling and decoupling effects of agricultural carbon emissions in China and their driving factors. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 25, 25280–25293. doi:10.1007/s11356-018-2589-7
Hao, J., Gao, F., Fang, X., Nong, X., Zhang, Y., and Hong, F. (2022a). Multi-factor decomposition and multi-scenario prediction decoupling analysis of China's carbon emission under dual carbon goal. Sci. Total Environ. 841, 156788. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.156788
Hao, J., Gao, F., Fang, X., Nong, X., Zhang, Y., and Hong, F. (2022b). Multi-factor decomposition and multi-scenario prediction decoupling analysis of China's carbon emission under dual carbon goal. Sci. Total Environ. 841, 156788. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.156788
He, Q., Deng, X., Li, C., Yan, Z., Kong, F., and Qi, Y. (2022). The green paradox puzzle: fiscal decentralisation, environmental regulation, and agricultural carbon intensity in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 29 (51), 78009–78028. doi:10.1007/s11356-022-21149-2
Huang, W., Wu, F., Han, W., Li, Q., Han, Y., Wang, G., et al. (2022). Carbon footprint of cotton production in China: composition, spatiotemporal changes and driving factors. Sci. Total Environ. 821, 153407. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153407
Huisingh, D., Zhang, Z., Moore, J. C., Qiao, Q., and Li, Q. (2015). Recent advances in carbon emissions reduction: policies, technologies, monitoring, assessment and modeling. J. Clean. Prod. 103, 1–12. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.04.098
Jiang, J., Ye, B., Xie, D., and Tang, J. (2017). Provincial-level carbon emission drivers and emission reduction strategies in China: combining multi-layer LMDI decomposition with hierarchical clustering. J. Clean. Prod. 169, 178–190. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.03.189
Jiang, T., Li, S., Yu, Y., and Peng, Y. (2022). Energy-related carbon emissions and structural emissions reduction of China’s construction industry: the perspective of input–output analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 29 (26), 39515–39527. doi:10.1007/s11356-021-17604-1
Li, J., Li, S., Liu, Q., and Ding, J. (2022). Agricultural carbon emission efficiency evaluation and influencing factors in Zhejiang province, China. Front. Environ. Sci. 10, 1005251. doi:10.3389/fenvs.2022.1005251
Li, L., Han, J., and Zhu, Y. (2023). Does environmental regulation in the form of resource agglomeration decrease agricultural carbon emissions? Quasi-natural experimental on high-standard farmland construction policy. J. Clean. Prod. 420, 138342. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.138342
Li, S., and Wang, Z. (2023). The effects of agricultural technology progress on agricultural carbon emission and carbon sink in China. Agriculture 13 (4), 793. doi:10.3390/agriculture13040793
Li, Z. Z., Li, R. Y. M., Malik, M. Y., Murshed, M., Khan, Z., and Umar, M. (2021). Sustain. Prod. Consum. 27, 392–401. doi:10.1016/j.spc.2020.11.008
Liu, M., and Yang, L. (2021). Spatial pattern of China’s agricultural carbon emission performance. Ecol. Indic. 133, 108345. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.108345
Liu, S., Lin, Z., Jiang, Y., Zhang, T., Yang, L., Tan, W., et al. (2022). Modelling and discussion on emission reduction transformation path of China's electric power industry under“ double carbon” goal. Heliyon 8 (9), e10497. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e10497
Liu, W., Xu, R., Deng, Y., Lu, W., Zhou, B., and Zhao, M. (2021). Dynamic relationships, regional differences, and driving mechanisms between economic development and carbon emissions from the farming industry: empirical evidence from rural China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 18 (5), 2257. doi:10.3390/ijerph18052257
Luo, X., Liu, C., and Zhao, H. (2023). Driving factors and emission reduction scenarios analysis of CO2 emissions in Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area and surrounding cities based on LMDI and system dynamics. Sci. Total Environ. 870, 161966. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.161966
Ma, C., and Stern, D. I. (2008). China's changing energy intensity trend: a decomposition analysis. Energy Econ. 30 (3), 1037–1053. doi:10.1016/j.eneco.2007.05.005
Ma, X., Wang, C., Dong, B., Gu, G., Chen, R., Li, Y., et al. (2019). Carbon emissions from energy consumption in China: its measurement and driving factors. Sci. total Environ. 648, 1411–1420. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.183
Pan, X., Wang, Y., Shen, Z., and Song, M. (2022). Technological progress on embodied carbon emissions in G7 countries’ exports: a structural decomposition analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 372, 133800. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.133800
Peng, D., and Liu, H. (2022). Measurement and driving factors of carbon emissions from coal consumption in China based on the Kaya-LMDI Model. Energies 16 (1), 439. doi:10.3390/en16010439
Quan, C., Cheng, X., Yu, S., and Ye, X. (2020). Analysis on the influencing factors of carbon emission in China's logistics industry based on LMDI method. Sci. Total Environ. 734, 138473. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138473
Ren, S., Yin, H., and Chen, X. H. (2014). Using LMDI to analyze the decoupling of carbon dioxide emissions by China's manufacturing industry. Environ. Dev. 9, 61–75. doi:10.1016/j.envdev.2013.11.003
Shuai, C., Chen, X., Wu, Y., Tan, Y., Zhang, Y., and Shen, L. (2018). Identifying the key impact factors of carbon emission in China: results from a largely expanded pool of potential impact factors. J. Clean. Prod. 175, 612–623. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.12.097
Shuai, C., Shen, L., Jiao, L., Wu, Y., and Tan, Y. (2017). Identifying key impact factors on carbon emission: evidences from panel and time-series data of 125 countries from 1990 to 2011. Appl. energy 187, 310–325. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.11.029
Sun, L. L., Cui, H. J., and Ge, Q. S. (2022). Will China achieve its 2060 carbon neutral commitment from the provincial perspective? Adv. Clim. Change Res. 13 (2), 169–178. doi:10.1016/j.accre.2022.02.002
Sun, W., and Huang, C. (2020). How does urbanization affect carbon emission efficiency? Evidence from China. J. Clean. Prod. 272, 122828. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122828
Wang, R., Wen, X., Wang, X., Fu, Y., and Zhang, Y. (2022). Low carbon optimal operation of integrated energy system based on carbon capture technology, LCA carbon emissions and ladder-type carbon trading. Appl. Energy 311, 118664. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2022.118664
Wang, Y., Li, L., Kubota, J., Han, R., Zhu, X., and Lu, G. (2016). Does urbanization lead to more carbon emission? Evidence from a panel of BRICS countries. Appl. Energy 168, 375–380. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.01.105
Wen, S., Hu, Y., and Liu, H. (2022). Measurement and spatial–temporal characteristics of agricultural carbon emission in China: an internal structural perspective. Agriculture 12 (11), 1749. doi:10.3390/agriculture12111749
Wu, Q., Zhang, Y. Y., and Zhang, M. Y. (2022). Quantitative assessment, temporal and spatial characteristics and dynamic evolution of China’s animal husbandry carbon emissions. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 36 (6), 65–71. doi:10.13448/j.cnki.jalre.2022.148
Yang, H., Wang, X., and Bin, P. (2022). Agriculture carbon-emission reduction and changing factors behind agricultural eco-efficiency growth in China. J. Clean. Prod. 334, 130193. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.130193
Zeng, Q. H., and He, L. Y. (2023). Study on the synergistic effect of air pollution prevention and carbon emission reduction in the context of“ dual carbon”: evidence from China's transport sector. Energy Policy 173, 113370. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2022.113370
Zha, D., Chen, Q., and Wang, L. (2022). Exploring carbon rebound effects in Chinese households’ consumption: a simulation analysis based on a multi-regional input–output framework. Appl. Energy 313, 118847. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2022.118847
Zhang, H., Feng, C., and Zhou, X. (2022b). Going carbon-neutral in China: does the low-carbon city pilot policy improve carbon emission efficiency? Sustain. Prod. Consum. 33, 312–329. doi:10.1016/j.spc.2022.07.002
Zhang, L., Yan, Y., Xu, W., Sun, J., and Zhang, Y. (2022a). Carbon emission calculation and influencing factor analysis based on industrial big data in the “double carbon” era. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022 (1), 1–12. doi:10.1155/2022/2815940
Zhang, W., Li, K., Zhou, D., and Gao, H. (2016). Decomposition of intensity of energy-related CO2 emission in Chinese provinces using the LMDI method. Energy Policy 92, 369–381. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2016.02.026
Zhao, L., and Zhao, Z. Q. (2014). Projecting the spatial variation of economic based on the specific ellipses in China. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 34 (8), 979–986. doi:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2014.08.979
Zhao, Y., Su, Q., Li, B., Zhang, Y., Wang, X., Zhao, H., et al. (2022). Have those countries declaring “zero carbon” or “carbon neutral” climate goals achieved carbon emissions-economic growth decoupling? J. Clean. Prod. 363, 132450. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.132450
Zhong, Y., Lin, A., He, L., Zhou, Z., and Yuan, M. (2020). Spatiotemporal dynamics and driving forces of urban land-use expansion: a case study of the Yangtze River economic belt, China. Remote Sens. 12 (2), 287. doi:10.3390/rs12020287
Keywords: agricultural carbon emissions, standard deviation ellipse, theil index, LMDI decomposition, carbon neutral
Citation: Huang X, Wu X, Guo X and Shen Y (2024) Agricultural carbon emissions in China: measurement, spatiotemporal evolution, and influencing factors analysis. Front. Environ. Sci. 12:1488047. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2024.1488047
Received: 29 August 2024; Accepted: 15 October 2024;
Published: 29 October 2024.
Edited by:
Sufyan Ullah Khan, University of Stavanger, NorwayCopyright © 2024 Huang, Wu, Guo and Shen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yang Shen, eWFuZ3M5OTZAZm94bWFpbC5jb20=
 Xiujing Huang
Xiujing Huang Xinyu Wu2
Xinyu Wu2 Xiaoyang Guo
Xiaoyang Guo Yang Shen
Yang Shen