- 1Shanghai Collaborative Innovation Centre for WEEE Recycling, School of Resources and Environmental Engineering, Shanghai Polytechnic University, Shanghai, China
- 2Shanghai Academy of Environmental Sciences, Shanghai, China
Introduction: Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) have attracted widespread attention due to their adverse effects on human health. Photocatalytic oxidation is an effective technology for degrading VOCs under ambient conditions.
Methods: In order to better understand the trends and development of global trends in photocatalytic oxidation of VOCs, the analysis of 2493 articles or reviews from the Science Citation Index Expanded (SCIE) in the Web of Science Core Collection, covering the period from 1998 to 2023, was conducted using CiteSpace and VOSviewer software.
Results and Discussion: The findings indicate significant growth in papers concerning photocatalytic oxidation of VOCs. China emerges as the most active country among the main drivers. Principal sources publishing relevant research are Applied Catalysis B-Environmental, Chemical Engineering Journal, Journal of Hazardous Materials, and Environmental Science and Technology. A relatively well-established theoretical framework has been developed for the study of photocatalytic oxidation of VOCs. In the field of VOCs photocatalytic oxidation, the focus is on the development and optimization of advanced photocatalysts with efficient charge separation, better adsorption performance, and a wider light response range. In addition, the in-depth study of the charge generation and transfer mechanisms within the photocatalysts, as well as the comprehensive understanding of the reaction kinetics and catalytic oxidation process, the optimization of the reaction conditions, and the improvement of the catalytic efficiency are at the forefront of the research in this field. This research system is advancing and becoming more refined, with its theoretical propositions, research findings, and methodologies increasingly employed and confirmed.
1 Introduction
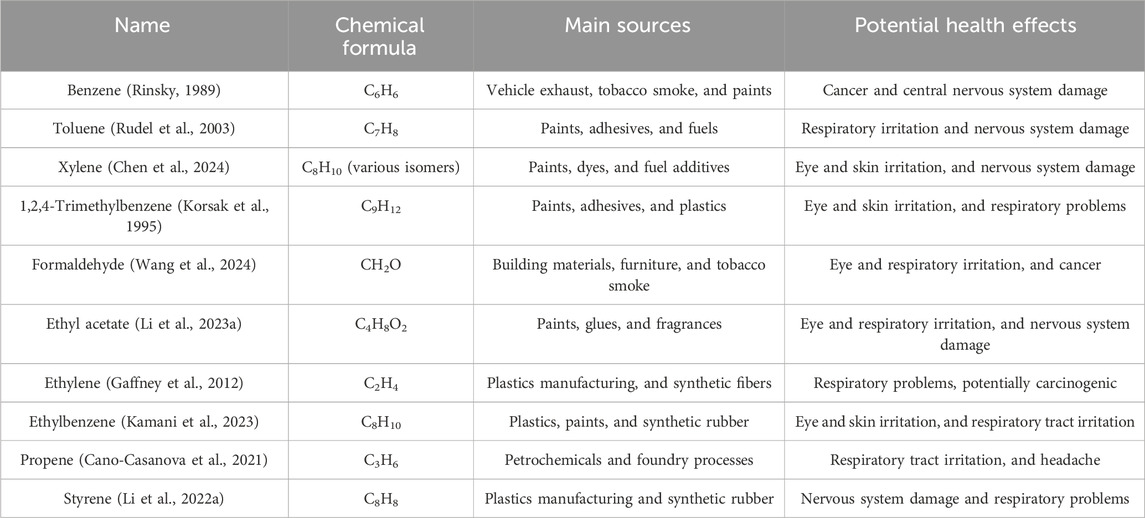
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are ubiquitous in the atmosphere and are key precursors of ground-level ozone (O3), secondary organic aerosols (SOA), peroxyacetyl nitrate (PAN), and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), affecting the atmospheric environment, human health, and vegetation growth (Ou et al., 2022; Liu et al., 2022a). It is defined as an organic pollutant with a boiling point in the environmental range of 50°C–260°C (ISO, 2011; Sui et al., 2024). VOCs are mainly produced by the chemical, pharmaceutical, and tobacco industries, as well as by fuel combustion, composting, building renovation, and other production and living processes (Halios et al., 2022; Zhang et al., 2022; Emran et al., 2022). The most common volatile organic compounds are benzene, toluene, xylene, and ethylbenzene, collectively known as BTEX. Benzene causes immune cells to produce excessive inflammatory factors, leading to inflammatory responses and damage to the bone marrow and other hematopoietic tissues. Benzene and its metabolites also activate the intrinsic apoptotic pathway within cells, promoting programmed cell death of hematopoietic cells and causing hematotoxicity (Li et al., 2024). In BTEX compounds, the concentration of toluene is the highest. Long-term exposure to toluene in the human body can damage the central nervous system (Filley et al., 2004) and respiratory system (Yoon et al., 2010). Kim et al. coupled ultraviolet light with a Pd/TiO2 photocatalyst to degrade toluene, with approximately 94.1% of toluene being converted into CO2 and CO, with most intermediate products being benzaldehyde and formic acid. Common BTEX also includes xylene. During the photocatalytic process of xylene, intermediate compounds such as aromatic hydrocarbons, alkanes, and carbonyl compounds are produced. The health risks of the secondary products generated during the process are at least 4.5 times lower than those of degraded xylene, but the secondary pollution and health risks of xylene photodegradation products cannot be ignored. These isomerization products not only contribute about 97% and 91% to the formation potential of O3 (OFP) and secondary organic aerosol (SOAFP) but also show obvious non-carcinogenic risks (Chen et al., 2024).
Other common VOC pollutants include ethyl acetate, styrene, and formaldehyde. Ethyl acetate (EA) is a colorless, transparent, fragrant liquid with low toxicity and sweet smell. It has a pungent odor and is highly volatile at high concentrations (Deng et al., 2021). Ethyl acetate is commonly used in the paint, ink, pharmaceutical, and automotive manufacturing industries. Intermediate products formed during the photodegradation of ethyl acetate include acetic acid, ethanol, and formaldehyde, which ultimately degrade into CO2 and H2O (Wang et al., 2023). Formaldehyde is the most representative indoor VOC pollutant, with a boiling point of only −19.5°C. As long as the indoor temperature is above −19.5°C, the free formaldehyde generated from decorative materials and furniture will continuously volatilize into the air, with a release period of 3–15 years, and cannot be removed in a short time. The diffusion speed of formaldehyde will be increased in high temperature and high humidity weather conditions, aggravating indoor air pollution. Released formaldehyde enters the body through breathing, dietary intake, or skin contact. Formaldehyde that enters the body is usually converted into a non-toxic chemical substance called formate, which is excreted through urine and exhaled as carbon dioxide. Unreacted formaldehyde will adhere to DNA or proteins in the body (Kim et al., 2011). Formaldehyde can cause neurotoxicity (Songur et al., 2010), respiratory system damage, and reproductive and genetic toxicity (Jakab et al., 2010). Formaldehyde also has carcinogenicity, and the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) classifies formaldehyde as a human carcinogen that can cause nasopharyngeal cancer. Styrene is commonly used in automotive and motorcycle maintenance and repair services, the manufacture of other chemical products, ship and boat manufacturing, basic chemical manufacturing, and the manufacture of plastic products (Hahm et al., 2016); long-term exposure to styrene can cause serious health problems. Styrene has ear toxicity and may cause hearing loss, which may increase the likelihood of ear toxicity in combination with exposure to multiple chemicals and noise (Chen et al., 2009). Styrene also has lung function impairment effects, with studies showing that the average level of serum cytochrome c in styrene-exposed workers was 1.1 ng/mL (0.89–1.89), while the control group had levels below the detection limit (0.05 ng/mL), indicating that workers exposed to styrene have increased oxidative stress levels, which should be the cause of lung injury (Sati et al., 2011). Multiple reports have also verified the cancer-inducing risk of styrene exposure. In the photocatalytic degradation process, styrene is converted into intermediate products such as benzene, benzaldehyde, and benzoic acid, thereby reducing health risks (Hamada et al., 2022). The common VOCs in human production and life and their main sources and hazards are shown in Table 1. In recent years, adsorption, thermal oxidation, and photocatalytic oxidation have been researched and developed for the effective and rapid removal of VOCs (Rong et al., 2023; Sun et al., 2019; Song et al., 2020; Qian et al., 2021; Enesca, 2020; Le et al., 2021).
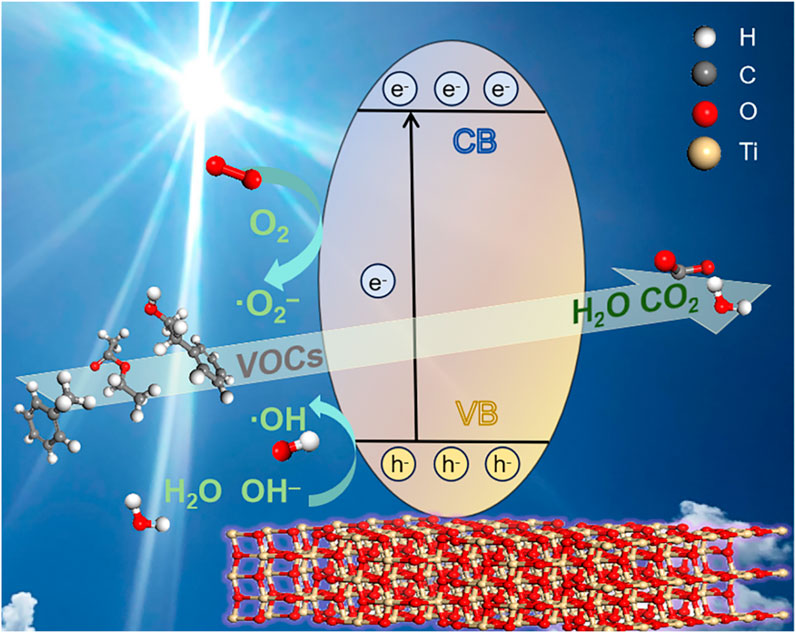
Photocatalysts are typically triggered through the absorption of light, leading to the excitation of electrons from the occupied valence band (VB) to the unoccupied conduction band (CB), resulting in the generation of positive holes within the VB. The resultant electrons and positive holes serve as pivotal agents in driving the reduction and oxidation processes of molecules adsorbed onto the surface of the photocatalyst, respectively (Ohtani, 2008; Carp et al., 2004; Pelaez et al., 2012; Montini et al., 2016). These active electrons and holes will interact with oxygen to generate reactive oxygen species, such as hydroxyl radicals (⋅OH) and superoxide radicals (⋅O2−). The VOC pollutant molecules will come into contact with the generated reactive species and decompose into lower molecular weight products, ultimately into CO2, H2O, and other by-products (Mamaghani et al., 2017; Shayegan et al., 2018), as shown in Figure 1. Notable features of this technology include operation at ambient temperature without significant energy input, environmental friendly end products (CO2 and H2O), and applicability to different types of pollutants (water and microplastics) (Mamaghani et al., 2017; Zhong et al., 2010; Ollis, 2000; Zhang et al., 2022; Moura et al., 2022). Taken together, the treatment of VOC pollution by photocatalytic technology has a broad and long-term impact on the management of the atmospheric environment, and the development and research trends in this field of study have a bearing on human safety and global environmental sustainability. Therefore, it is crucial to analyze the current status of this field. Mathematics and statistics are the main methods used in bibliometrics to analyze literature data, using knowledge mapping as an analytical tool to show the visual results of scientific knowledge and its relationship with each other more intuitively, quantitatively, and objectively, which is widely used in the field of scientometrics (Ni et al., 2022). The bibliometric analysis of VOC photocatalytic oxidation research is to use knowledge mapping as an analytical tool to study the trend of VOC photocatalytic oxidation research, the knowledge base, the hot frontiers, and their dynamic evolution relationship.
In this study, scientific knowledge mapping and comprehensive analysis of relevant literature information within the scope, including publication trends, source journals, authors’ contributions and collaborations, keywords, research frontiers, and hotspots, were conducted with the help of software such as VOSviewer and CiteSpace. The analytical work identified and tracked research frontiers and hotspots in the field, captured the dynamic evolution of research topics and scientific priorities in the field, and highlighted established and emerging research directions. In addition, the analytical work contributes to a deeper understanding of the knowledge structure and developmental trajectory of the field and provides an intuitive scientific basis for subsequent research on photocatalytic oxidation of VOCs.
2 Data and methods
2.1 Data retrieval
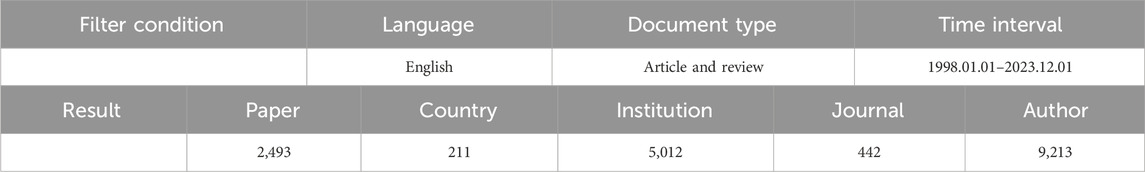
The Web of Science Core Collection (WoSCC) database was used to collect data from articles on photocatalytic VOC oxidation studies. It is an important data source for bibliometric studies and the assessment of scientific papers and is considered to be highly reliable and widely used in the field of scientific metrics (Chen et al., 2023; Cheng et al., 2019). “Topic” (TS) as the search field: TS = (“photochemical catalysis” OR Photocatalysis OR photocatalytic OR photocatalyst OR “light cataly*” OR “photoredox catalysis” OR photodegradation OR photolytic OR photo-cataly* OR photooxidation OR “ultraviolet catalyzing” OR photoinduced OR “photo-assisted catalysis” OR “light catalyzing” OR “visible-light catalysis”) AND TS = (VOCs OR VOC OR “volatile organic compounds” OR “volatile organics” OR “volatile organic components” OR “volatile organic matter” OR “volatility organic compounds” OR “volatile organic contaminants” OR “volatile organic matters”). The specific screening conditions are shown in Table 2, and the screening results were scrutinized to exclude irrelevant research topics and directions such as “Endocrinology Metabolism” and “Agronomy,” and the final data are shown in Table 2.
2.2 Methods
The bibliometric analysis of data collected from the core WoS repositories, especially the number of publications, authors, institutions, countries/regions, citations, etc., using mathematical and statistical methods, and visualization, often using CiteSpace and VOSviewer software (van Eck and Waltman, 2010; Pan et al., 2018; Chen, 2004; ŞEnocak and Arpaci, 2023). To determine the major contributions in the literature on photocatalytic oxidation of VOCs, we restricted our focus to authors, institutions, and countries with five or more publications, yielding 268 nodes, 245 nodes, and 49 nodes, respectively. The literature co-citation analysis considered works with a minimum of 50 citations and produced 83 nodes. Journals with more than 100 total citations were examined for co-citation, resulting in 184 nodes. In addition, 8,202 keywords were extracted from the WoSCC. The 163 keyword nodes were selected for visual analysis by selecting keywords with more than 25 occurrences. Furthermore, CiteSpace software was utilized to analyze the “20 most cited keywords” and the “keyword timeline”.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Trends in quantitative changes in research outputs
By statistically analyzing the number of papers published from 1998 to 2023, the development trend and the development and maturity of the scientific research results of VOC photocatalytic oxidation technology can be clearly understood. Figure 2 shows the distribution of research results on photocatalytic oxidation of VOCs based on time series. Between 1998 and 2000, less than 10 articles per year were published on the photocatalytic oxidation of VOCs. From 2001 to 2015, the overall trend of this field showed a slow growth, and in 2015, the annual number of articles in this field exceeded 100 for the first time. The research related to VOC photocatalytic oxidation has gradually become a hotspot, which is inseparable from the environmental protection policies of many countries. From 2016 to 2020, the number of published articles increased significantly, and the annual publication volume of 200 articles has been achieved in 5 years. By 2023, there have been 2,493 publications in the research area of photocatalytic oxidation of VOCs. The increasing volume of the literature in this domain implies that researchers are paying more attention to the photocatalytic oxidation of VOCs.
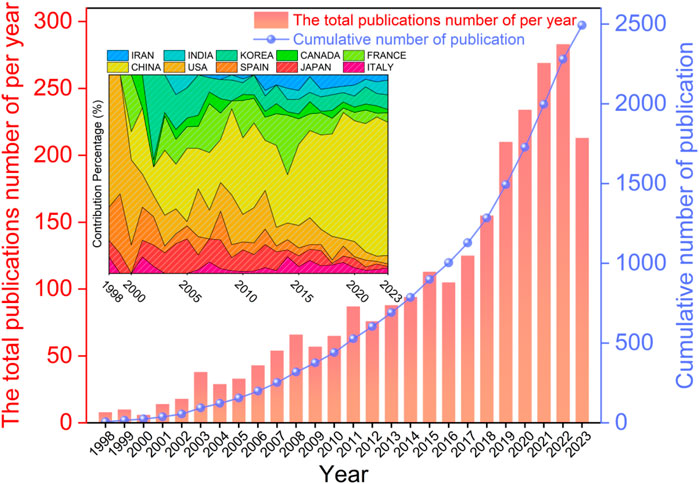
Figure 2. Annual and cumulative number of publications (inset: ratio of contributions from the top 10 countries in terms of number of publications per year).
Figure 2 (inset) shows the contribution of the top 10 countries in terms of the number of articles published annually in the field of photocatalytic oxidation of VOCs. In 1998 and 2000, the United States, Spain, and Japan were among the top three countries in terms of contributing significantly to basic research on photocatalytic oxidation of VOCs. It should be noted that the number of relevant articles from China has increased significantly since 2001. Over the past 2 decades, Chinese researchers have made significant contributions to the study of VOC photocatalytic oxidation. Currently, the number of articles published by Chinese researchers has exceeded 40 percent and continues to increase, indicating their active participation and meaningful results. The increase could potentially be attributed to China’s emphasis on air pollution control starting in the early 21st century.
3.2 Analysis of journals published
Research field journals aid researchers in comprehending the primary scholarly resources and avenues of knowledge distribution in their field. The h-index is a hybrid quantitative metric that can be used to assess the volume and level of academic output, proposed in 2005 by George Hirsch, a physicist at the University of California, San Diego (Cheng et al., 2019). As shown in Table 3, the analysis of the journals resulted in the top 10 publications with the highest h-index on photocatalytic oxidation of VOCs.
Applied Catalysis B-Environmental (Appl. Catal. B-Environ.) is the most influential journal in the field (H = 76), focusing on the reaction mechanisms of photocatalytic processes and the fundamental understanding of photocatalysts, as applied to environmental problems. Moreover, Appl. Catal. B-Environ. published 181 papers on the research of photocatalytic oxidation of VOCs, with the highest number of papers. The second ranked journal is Chemical Engineering Journal (Chem. Eng. J., 176 papers, H = 48), which mainly researches about the synthesis and modification of photocatalyst materials in the field of photocatalytic oxidation of VOCs, as well as the mechanism of chemical reactions involved in the setup. The third ranked journal is Journal of Hazardous Materials (J. Hazard. Mater., 98 papers, H = 47), which is involved in the study of the development and modification of photocatalytic materials, the design of the light source, and the reactor. Other core journals also focus on the reaction mechanism, catalyst preparation, engineering design, and reaction products of photocatalytic oxidation of VOCs. Journal impact analysis in the field of photocatalytic oxidation technology for VOCs is pivotal for researchers and scholars as it illuminates the most influential and high-quality journals, thereby informing their publication choices and research trajectories, as well as significantly influencing the evolution of trends and the distribution of resources in this specialized domain.
3.3 Analysis of authors’ contributions and collaborations
3.3.1 Author partnerships
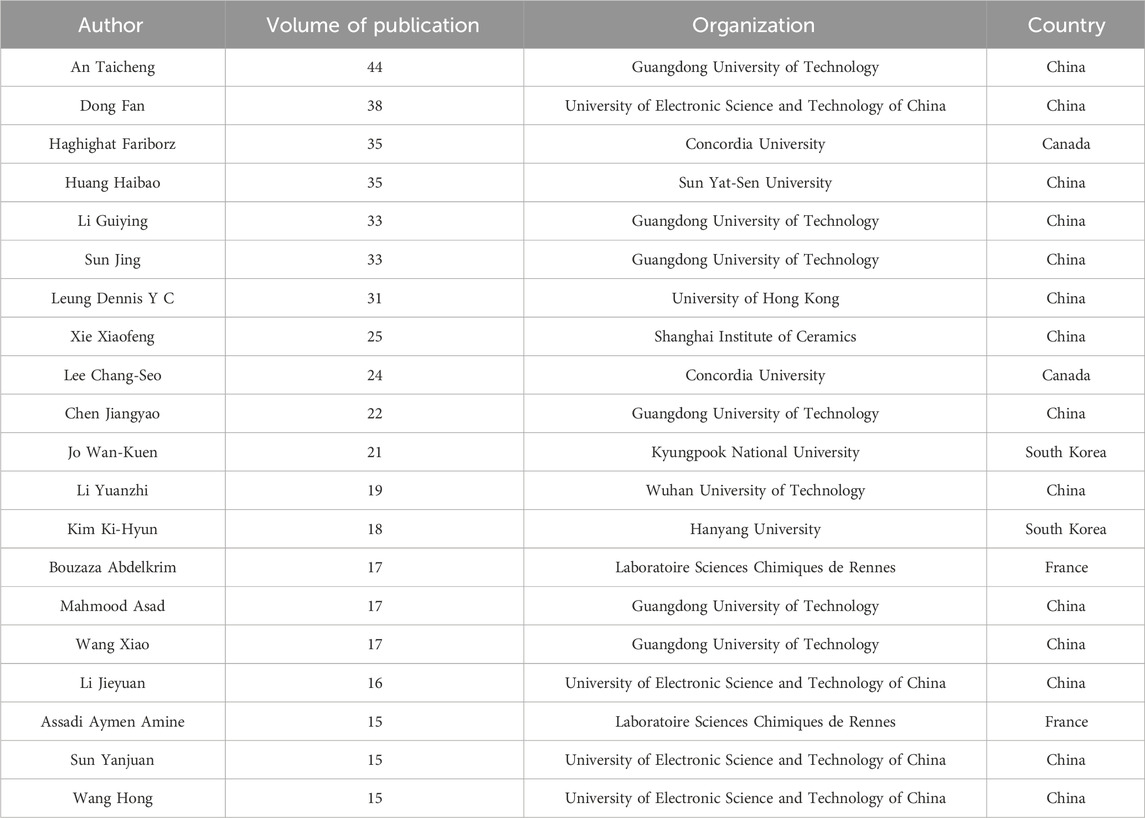
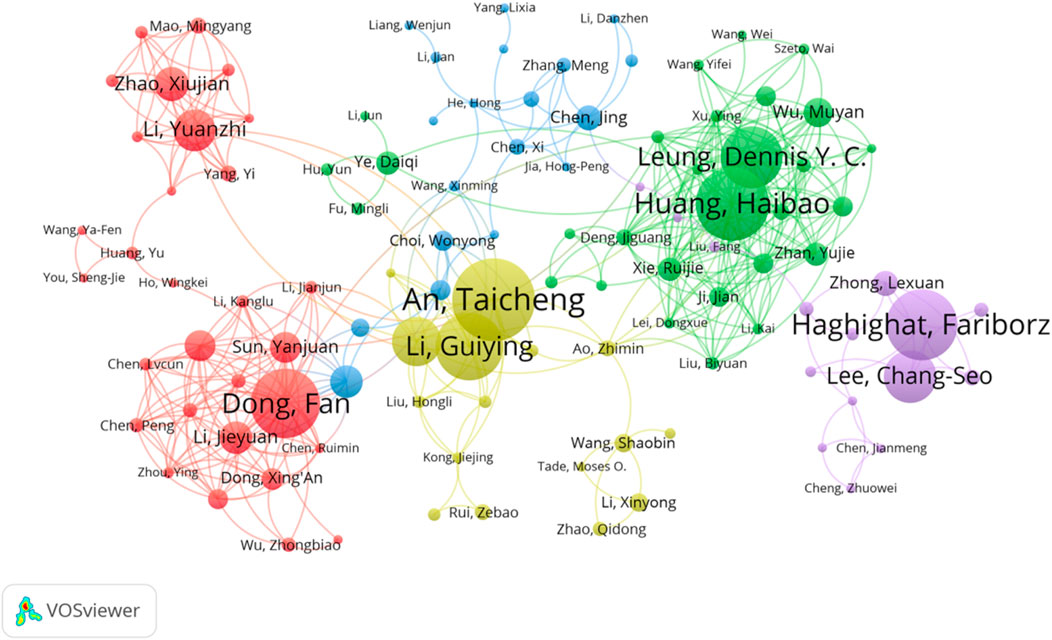
Authors in a field of research and the collaborations between them are key elements in advancing scholarship and disseminating knowledge, and bibliometric analyses identify authors and their collaborations that contribute to a particular field of research (Kholidah et al., 2022). The 20 authors with the most publications in the field of photocatalytic oxidation of VOCs are shown in Table 4. Among them, 14 authors are from China, reflecting China’s contribution to the field. An Taicheng from the Guangdong University of Technology, China, has the highest number of publications with 44 papers. One of his most influential papers was on the development of a modified ordered porous catalyst with high anti-coking properties by introducing oxygen vacancies into CeO2 via simple redox and steam treatment (ARCeO2) and its application to the efficient photothermal catalytic degradation of VOCs (Kong et al., 2020). This work highlights the importance of oxygen vacancy engineering in improving photothermal catalytic performance for VOC degradation and provides a facile and cost-effective strategy for the design and fabrication of CeO2 catalysts with strong anti-coking potential. Dong Fan of Zhejiang University, China, came in second with 38 articles. The representative study of the second influential author involved the first preparation of mesoporous c-doped TiO2 nanomaterials with the anatase phase using sucrose as the carbon doping source by green synthesis, thus improving the photocatalytic activity of the catalyst (Dong et al., 2011).
The distribution map of authors’ collaboration can better reflect the collaboration and co-research among scholars in the field of photocatalytic oxidation of VOCs (Figure 3). The size of each node in the graph indicates the author’s publication volume (the larger the node, the more productive the author), while the connecting lines indicate the collaborative relationship between authors. Figure 3 indicates the degree of author collaboration, with several clusters of authors working closely together appearing as shown, including An Taicheng, Dong Fan, Sun Jing, Li Guiying, and Huang Haibao. Moreover, they are the authors with the largest volume of articles. The strength of the linkages between the different authors is shown in Supplementary Figure S1 (Supplementary Material), indicating that international collaboration in this area currently needs to be strengthened. It is important to analyze the level of collaboration between researchers as such a collaboration not only helps pool expertise from different disciplines and promote innovation and progress but also improves the efficiency, quality, and reliability of research through the sharing of resources, transfer of knowledge, and peer review. In addition, the collaboration promotes the internationalization of scientific research, helps address complex interdisciplinary issues, and accelerates the translation of research results into practical applications, in particular in the field of environmental protection and pollution control.
3.3.2 Analysis of institutions
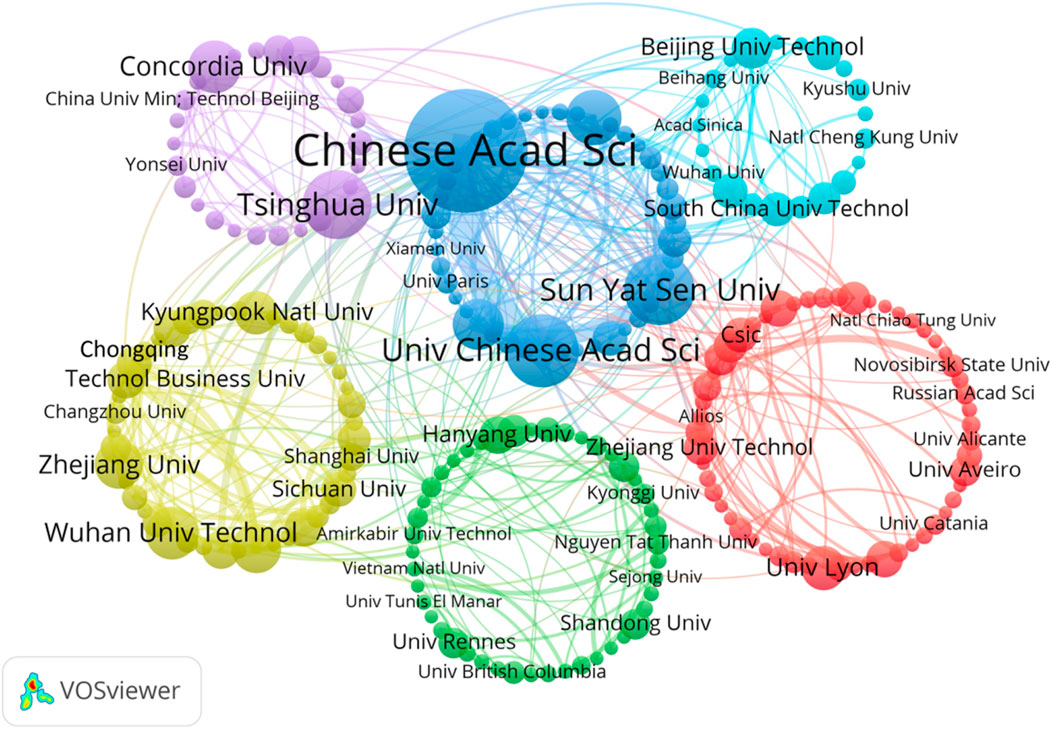
The analysis of research institutions, which provides information on the research institutions with the greatest impact and highest research output in a given field of research, can help researchers better understand the state and trends of the field and provide guidance on how to address important issues and drive innovation (Li et al., 2023). Figure 4 illustrates a graph displaying the knowledge domains of collaborating organizations utilizing VOSviewer software. Each circular node denotes an organization, and the circle’s dimensions indicate the number of papers published. Inter-institutional cooperation is indicated by a line between two nodes: the thicker the line, the closer the institutional cooperation. The Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) ranks the highest in terms of total linkage strength, boasting the largest number of publications and suggesting an expansive collaborative network and highly significant academic influence. The promotion of photocatalytic oxidation of gaseous pollutants on g-C3N4 is one of the most influential articles (Li et al., 2016). This strategy provides an easy and promising solution for combating air pollution through solar energy. In addition, as shown in Figure 4, there is a relatively close cooperation between CAS, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (CASU), and Guangdong University of Technology. Their works mainly study the change in atmospheric carbonyl compounds in cities under light with time and the use of a polymer photocatalyst to decompose water.
3.3.3 Analysis of productivity and impact among countries
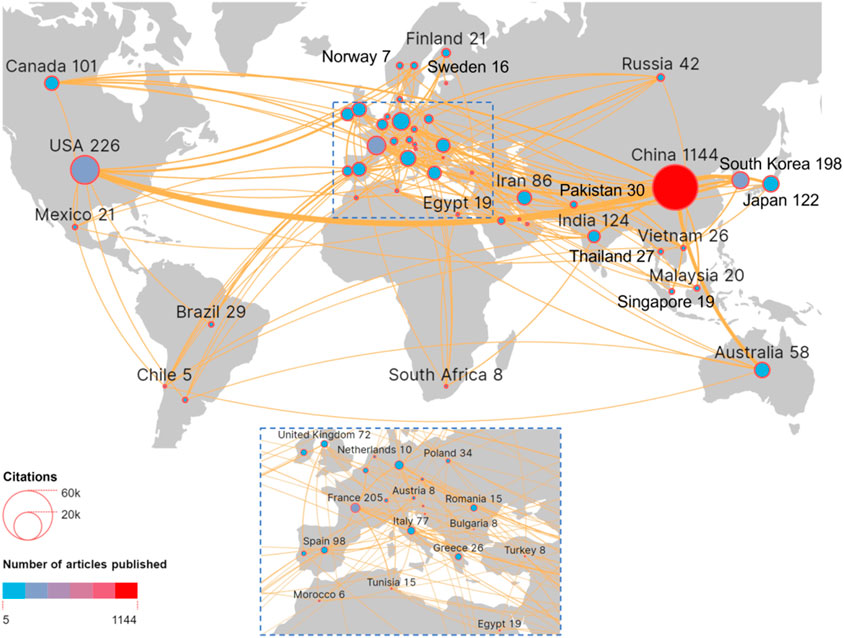
The problem of VOC air pollution is a global environmental issue; therefore, the analysis of international research cooperation in the field of photocatalytic oxidation of VOCs is of far-reaching importance for promoting global scientific progress, improving the quality and feasibility of research, and contributing to the sustainable development of global society (Zhang et al., 2023). China, the United States, France, South Korea, and India are the top five countries/regions with 1,144 (45.89%), 226 (9.07%), 205 (8.22%), 198 (7.94%), and 124 (4.79%) publications, respectively. Figure 5 shows the knowledge domains of the co-author countries, with the size of the nodes representing the number of national publications and the width of the connecting lines representing the strength of the links between the two countries. Through Figure 5 and Supplementary Table S1, it can be found that China, the United States, France, South Korea, and India have strong co-authorship links with other countries, with China working most closely with the United States, followed by Australia working with China.
3.4 Analysis of co-citation
To explore the links between academic publications and papers in the field of VOC photocatalytic oxidation research and to analyze the dynamics and direction of the field, journal co-citation and article co-citation analyses were performed (Farideh, 1996).
3.4.1 Analysis of journal co-citation
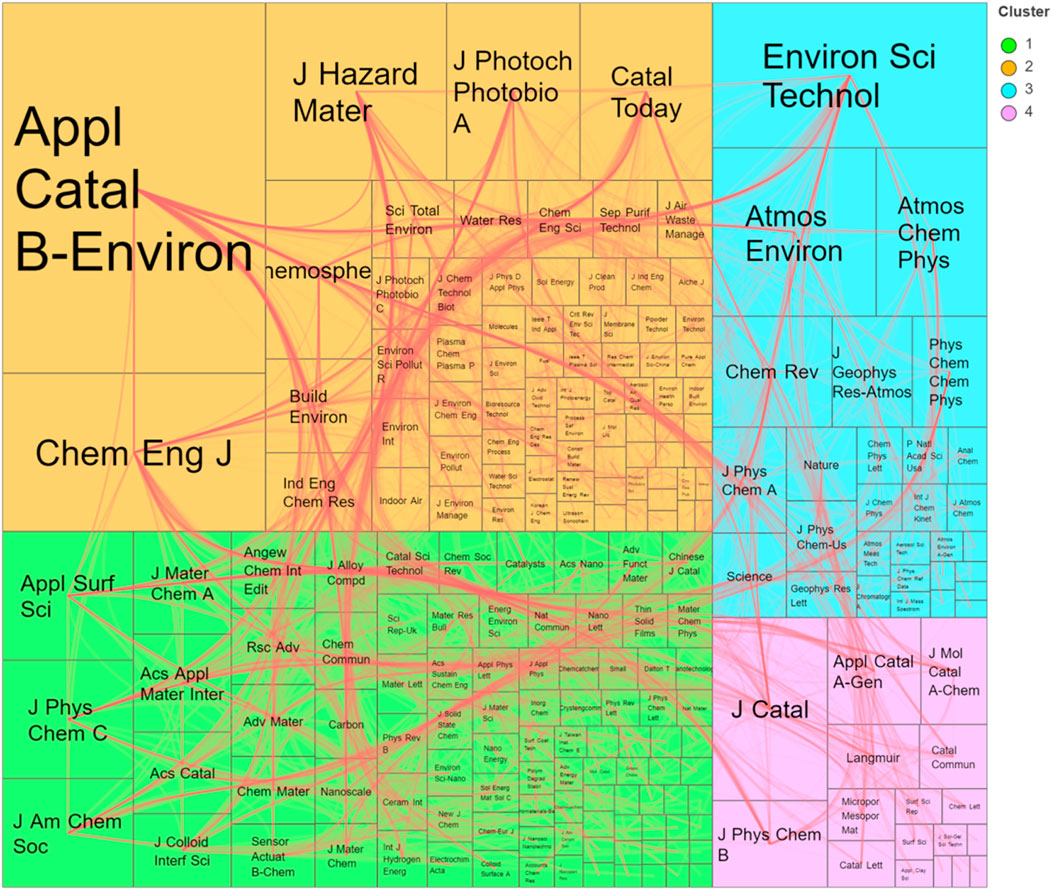
The research depicted in Figure 6 displays the journal co-citation mapping of the knowledge domain in the area of photocatalytic oxidation of VOCs, and the greater the number of connecting lines, the stronger the co-citation relationship between the two journals.
The orange cluster in Figure 6 mainly focuses on experimental and theoretical studies of photocatalytic oxidation of VOCs, including but not limited to the areas of photocatalyst characterization and VOC degradation, as represented by Appl. Catal. B-Environ., Catalysis Today, Chemosphere, Chem. Eng. J., and J. Hazard. Mater. In the latest research of this clustered journal, the main focus is on the latest hotspots of VOC photooxidation technology, with a major emphasis on the photocatalytic effects of modified porous materials and composite catalyst combination strategies. In recent studies, the focus is on the research of metal–organic frameworks (MOFs), with the study in Appl. Catal. B-Environ. focusing on the catalytic degradation mechanism of MOFs materials. Qin, JX. et al. prepared Fe-MOF derivatives with the MIL-100(Fe) precursor through thermal treatment, exposing the unsaturated Fe2+ active sites that could significantly promote the transfer of photoelectrons, enhancing the oxidation–reduction reaction and improving the photocatalytic performance (Qin et al., 2023). Chen, L. et al. designed the local charge imbalance of carboxylate ligands to regulate the Lewis acid–base sites in NaFe bimetal MOXs, thereby improving the adsorption of acetaldehyde or xylene and enhancing the production of oxidizing free radicals, thereby improving the photocatalytic performance (Chen et al., 2023). Research provided in Chem. Eng. J. primarily modifies MOF porous materials through pretreatment methods to enhance their photocatalytic performance while maintaining their adsorption effect for VOCs. Yu, X. et al. utilized the hotspot effect of MXene’s absorption, designing an MXene/MOF high-performance photocatalytic performance aerogel, achieving a TOC removal rate of approximately 95% for acetone vapor within 60 min and demonstrating good stability (Yu et al., 2023). Chem. Eng. J. also focuses on composite catalyst combination strategies, and the S-scheme heterojunction is a recent research hotspot. Zhou, X. et al. synthesized an S-type TiO2/BaTiO3 heterojunction, where electrons pass through the Ti-O chain from BaTiO3 to TiO2 and form an internal electric field; it improved the efficiency of photogenerated carrier separation and electron transfer.
The Journal of the American Chemical Society (J. Am. Chem. Soc.), Journal of Physical Chemistry C (J. Phys. Chem. C), Applied Surface Science (Appl. Surf. Sci.), and ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces (ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces) are affiliated with the Green Cluster. The cluster is dedicated in examining newly discovered catalyst materials, anticipating and observing new materials and surface properties, and studying material properties at a molecular and atomic level using specialized surface analysis techniques and computational methods. In this cluster of journals, the importance of material adsorption capacity and the formation and role of surface oxygen vacancies are emphasized. Appl. Surf. Sci. focuses on the adsorption of VOCs gases by catalysts. Zhao, SF. et al. used DFT calculations to simulate the adsorption ability of five prototype VOCs on transition metal-deposited graphene adsorbents and compared the enhancement effects of different metal depositions (Kunaseth et al., 2017). Kim, S. et al. modified activated carbon surfaces with polyethyleneimine (PEI) and MgO to regulate the adsorbent surface acidity and improve the adsorption of polar VOCs (Kim et al., 2023). Lin, ZF. et al. explored the impact of intermediate products on benzene photocatalytic oxidation in pulp mills, revealing the mechanism and cause of catalyst inactivation (Lin et al., 2020). ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. focuses on the activation of surface lattice oxygen and the formation of oxygen vacancies in its latest research. Chen, LC. et al. proved that Sr2Sb2O7 is highly efficient and stable in photocatalytic oxidation of toluene compared to TiO2, which is attributed to the large activation of surface lattice oxygen. The lattice oxygen promotes the adsorption and activation of O2 and H2O molecules, producing high-activity free radicals and enhancing the catalytic efficiency.
The blue cluster journals concentrate on the effects of chemical processes that form the foundation of photocatalytic VOC oxidation on human wellbeing, air quality, climate variation, and ecosystems such as Environmental Science & Technology (Environ. Sci. Technol.), Atmospheric Environment (Atmos. Environ.), and Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics (Atmos. Chem. Phys.). Environ. Sci. Technol. primarily focuses on solving real-world environmental problems. In recent studies, there has been a great interest in the environmental pollution caused by volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in solar evaporators. Ma, JX. et al. used a BiOBrI nanoflake with oxygen-rich vacancies to prepare porous sponges and used them as light-permeable solar evaporators with three-dimensional photocatalytic sites to boost VOC rejection for water purification (Ma et al., 2022). Zhou, S. et al. used Ag/AgCl particles to efficiently activate H2O2 to generate hydroxyl radicals, which rapidly degraded VOCs during steam generation, solving the VOC pollution problem in solar evaporators (Zhou et al., 2022). Atmos. Chem. Phys., on the other hand, primarily reveals some photochemical oxidation processes in the natural atmosphere. Wang, Y et al. studied the photochemical oxidation of α-pinene, isoprene, and o-cresol on hygroscopic ammonium sulfate seeds to reveal the trend of aerosol rebound (Wang et al., 2021). Li, JL. et al. studied the secondary organic aerosol production process from the photooxidation of mixed anthropogenic volatile organic compounds (Li et al., 2021).
The Purple Cluster, spearheaded by the Journal of Catalysis (J. Catal.), Journal of Physical Chemistry B (J. Phys. Chem. B), and Catalysis Communications (Catal. Commun.), concentrates on the preparation, combination, and kinetic analysis of photocatalytic materials, along with employing spectroscopic techniques for catalyst characterization and theoretical models to explore probe–catalyst interactions and various theoretical methods. J. Catal. is dedicated to the study of the mechanism of VOC gas degradation. Song, BY. et al. explored the photocatalytic oxidation performance and mechanism of isoprene over titanium oxide by UV-Vis lights (Song et al., 2024). Krauter, J. et al. proved that partial photooxidation of 2-propanol not only is possible in the presence of oxygen but also in the absence of adsorbed water or even at room temperature below (Kräuter et al., 2022). The main research direction of Catal. Commun. in recent times is the modification strategy for titanium dioxide photocatalysts for the decomposition of VOCs (Higashimoto et al., 2020; Kovalevskiy et al., 2020).
As shown in Figure 6, Appl. Catal. B-Environ. has the largest share of area and is the most co-cited journal of all journals. Its significant impact on VOC photocatalytic oxidation research is mainly attributed to the journal prestige and the quantity of published articles. The journal has published 181 studies with photocatalytic oxidation of VOC topic, which is the largest number among all. Among the four clusters, Appl. Catal. B-Environ. and Chem. Eng. are included. Journals such as J. Catal. and Environ. Sci. Technol. are more widely cited, suggesting that journals dealing with the chemical processes involved in the photocatalytic oxidation of VOCs generally have a broader reach. Moreover, the connecting lines linking the aforementioned three journals are bolder, indicating a greater occurrence of co-citations among them.
In summary, studies on photocatalytic oxidation of VOCs have been published mainly in journals focusing on research and development of photocatalytic materials, analysis of VOC degradation processes, interfacial reactions, microscopic theoretical calculations, and macroscopic atmospheric environment. Journal co-citation analysis significantly reveals the network of key research and scholarly communication in the field of photocatalytic oxidation of VOCs, helping researchers to identify major trends, the core literature, and potential opportunities for interdisciplinary collaboration in the field.
3.4.2 Literature co-citation analysis
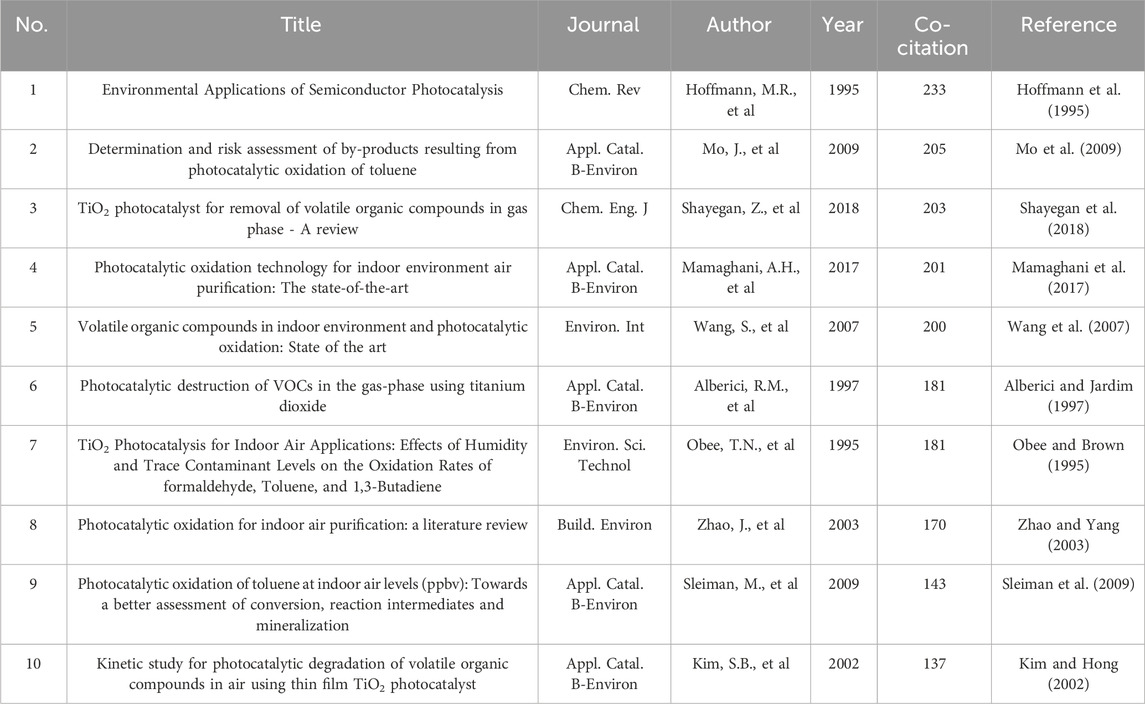
Both the number of co-citations and the number of citations are important indicators of the impact of scholarly articles, but there are differences in the emphasis and information reflected. Articles with a high number of co-citations (Table 5) emphasize the relevance of different studies and the concentration of research interests, whereas articles with a high number of citations (Supplementary Table S2) are more likely to highlight the broader impact and scientific contribution of an individual article. Table 5 displays the co-citations of the 10 most prominent papers in the scientific study of photocatalytic oxidation of VOCs. Seven of the top 10 most cited articles were published post-2000, indicating a remarkable advancement in the field over the last 2 decades. Of the 10 papers, five are reviews of photocatalytic oxidation of VOCs, two relate to the by-products of this process, and three discuss the degradation mechanism of photocatalytic oxidation, and titanium dioxide (TiO2) was the photocatalyst used in their study.
The most co-cited paper was “Environmental Applications of Semiconductor Photocatalysis” by Hoffmann, et al., being co-cited 233 times. The aim of this review is to provide an overview of the fundamentals of semiconductor photocatalysis and its potential applications in environmental control technologies (Hoffmann et al., 1995). The analysis shows that semiconductor photocatalysis has extensive usage in environmental systems, including air purification. Furthermore, advancing research for this technology requires a new comprehension of the non-uniform photochemistry complexity of metal oxide systems in multiphase environments. The second ranked article is “Determination and risk assessment of by-products resulting from photocatalytic oxidation of toluene” (205 times). The article investigated the ppb-grade by-products generated during the photocatalytic oxidative decomposition of toluene using TiO2 as a catalyst and concluded that the concentration of undesirable by-products generated during the photocatalytic oxidation process was low and would not have a negative impact on human health (Mo et al., 2009). Also of note are two research papers on the photocatalytic oxidation of VOCs by TiO2, published before 2000, which provide a research base for the development of research in this field. “Photocatalytic destruction of VOCs in the gas-phase using titanium dioxide” has been co-cited 181 times and is ranked sixth. The gas-phase photocatalytic degradation of 17 VOCs by TiO2 was investigated in this paper, and the results indicate the potential application of multiphase photocatalysis in the reduction of different classes of VOCs (Alberici and Jardim, 1997). The seventh-ranked article is “TiO2 Photocatalysis for Indoor Air Applications: Effects of Humidity and Trace Contaminant Levels on the Oxidation Rates of Formaldehyde, Toluene, and 1,3-Butadiene” (181 times), which outlines how humidity and pollutant concentration impact the oxidation rate of VOCs in indoor air for TiO2 photocatalytic applications (Obee and Brown, 1995). It attributes this relationship to the competitive adsorption to hydroxyl adsorption sites, as well as to changes in the quantity of hydroxyl radicals.
The four other articles reviewed the current state-of-the-art photocatalytic oxidation of VOCs in indoor air using TiO2 as a photocatalyst (Wang et al., 2007), investigated the dependence of the reaction rate on key factors through kinetic experiments and developed a kinetic model to assist in optimizing the reactor design (Zhao and Yang, 2003), and reviewed the removal of airborne VOCs by commercial TiO2 photocatalysts for VOCs and reporting the results of a comprehensive literature review on TiO2 modification technologies, including methods to overcome the inherent limitations of TiO2 and improve the photocatalytic degradation of VOCs (Mamaghani et al., 2017; Shayegan et al., 2018). By synthesizing and analyzing research results on photocatalytic oxidation of VOCs, a comprehensive knowledge framework can be provided to researchers to help them understand the progress and challenges in the field. The study of the relationship between the reaction rate and key factors, as well as the development of kinetic models, can provide practical guidance for optimizing reactor design and further promote the application of this technology in production.
“Kinetic study for photocatalytic degradation of volatile organic compounds in air using thin film TiO2 photocatalyst” and “Photocatalytic oxidation of toluene at indoor air levels (ppbv): Towards a better assessment of conversion, reaction intermediates, and mineralization” indicate that the degradation effect of photocatalytic oxidation of VOCs is impacted by various factors, including the initial concentration of VOCs, water vapor content, and photon flux of ultraviolet light (Sleiman et al., 2009; Kim and Hong, 2002). The thorough examination of the kinetics of the photocatalytic degradation process yields crucial insights into the degradation mechanism of VOCs on the catalyst surface. This information can be utilized to enhance the reaction conditions and enhance the efficiency of degradation. Furthermore, doing a comprehensive analysis of the intermediates generated throughout the reaction and the ultimate mineralization can provide valuable insights into the photocatalytic process, its safety implications, and its environmental effects.
3.5 Analysis of keyword co-occurrence
Keyword co-occurrence analysis facilitates comprehension of essential themes and concepts in the literature or dataset. It assists researchers in orientating their research, decision-making, and collaboration to achieve a fuller understanding of the challenges and opportunities of a specific field or topic.
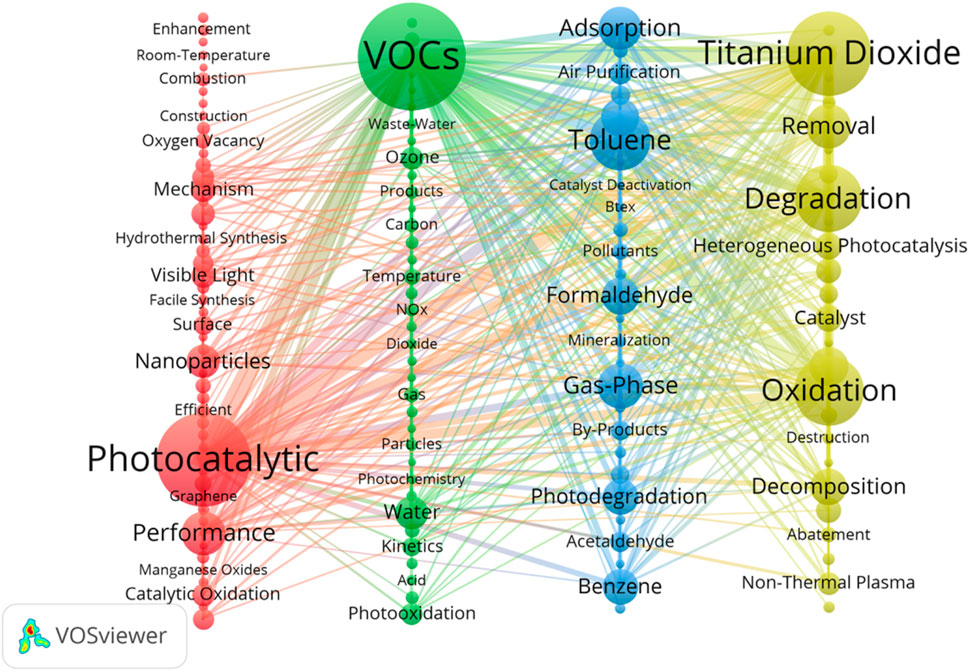
From the results displayed in Figure 7, the analysis software application produced four clusters. Cluster 1 (red): as shown in Figure 7, the main nodes in the red cluster include “Photocatalytic,” “Performance,” “Nanoparticles,” “Oxygen Vacancy,” “Manganese Oxides,” “Graphene,” and “Hydrothermal Synthesis.” Hence, the advancement of effective photocatalysts is a significant field of study in the research of photocatalytic oxidation of VOCs. This can be accomplished by altering the structure of nanomaterials like TiO2, manganese oxides, and graphene through straightforward and efficient techniques such as hydrothermal synthesis. For instance, the introduction of oxygen vacancies can enhance the catalysts’ capability to perform photocatalytic oxidation reactions at ambient temperature. Supplementary Table S3 presents a concise overview of various photocatalysts, together with their associated modifying reagents, bandgaps, and target pollutants. Cluster 2 (green) with “VOCs,” “Kinetics,” “Acid,” “Temperature,” “Water,” and “Dioxide” as the representative keyword indicates that photocatalytic oxidation of VOC technology is environmentally important in theory and practice and is an effective means of controlling air pollution and improving indoor and outdoor air quality. Photocatalysts catalyze the oxidative decomposition of VOCs under light conditions, converting them into more harmless substances such as carbon dioxide and water. Key factors in the treatment process include temperature, humidity, and pH conditions, which affect the reaction kinetics, the conversion efficiency of the pollutants, and the final degradation products. Cluster 3 (blue) of the keywords “Toluene,” “Gas-Phase,” “Benzene,” “Formaldehyde,” “By-Products,” “Btex,” “Catalyst Deactivation,” and “Mineralization” indicates that photocatalytic technology is commonly used to remove Btex such as formaldehyde, acetaldehyde, benzene, and toluene from the air (Kamani et al., 2023). However, catalyst deactivation can occur due to the adsorption properties of the catalytic materials, and the photodegradation process can produce by-products that prevent complete mineralization of the pollutants. This requires a thorough understanding of the reaction mechanism in order to optimize reaction conditions and select suitable photocatalysts. Cluster 4 (yellow) represents the keywords “Titanium Dioxide,” “Removal,” “Degradation,” “Oxidation,” “Decomposition,” and “Non-Thermal Plasma.” Titanium dioxide is one of the most studied photocatalysts. The traditional titanium dioxide catalyst has a bandgap of 3.2 eV and can be excited by ultraviolet light to produce photogenerated electron hole pairs, which is the earliest discovered photocatalyst. However, because it can only be excited by ultraviolet light and the ultraviolet component of ambient sunlight only accounts for 5%, so it needs to be modified. Modified TiO2 can effectively promote the degradation and mineralization of organic and inorganic pollutants. This process involves not only the direct decomposition of pollutants but also the in-depth treatment of their secondary decomposition products to ensure their complete harmlessness. On the other hand, non-thermal plasma technology, which decomposes pollutants by generating high-energy electrons, is particularly suitable for treating compounds that are difficult to degrade (Mu and Williams, 2022). This technology achieves efficient pollutant control at low temperatures, demonstrating unique advantages for treating low concentrations or stubborn pollutants. Combining these two technologies, the current research is not only focused on improving the efficiency and rate of pollutant treatment but also on optimizing the reaction conditions, lowering the operating costs, and reducing the generation of secondary pollutants. In addition, a deeper understanding and improvement of these technologies is scientifically and practically important for achieving more environmental friendly and cost-effective pollutant treatment methods.
3.6 Identification of research frontiers
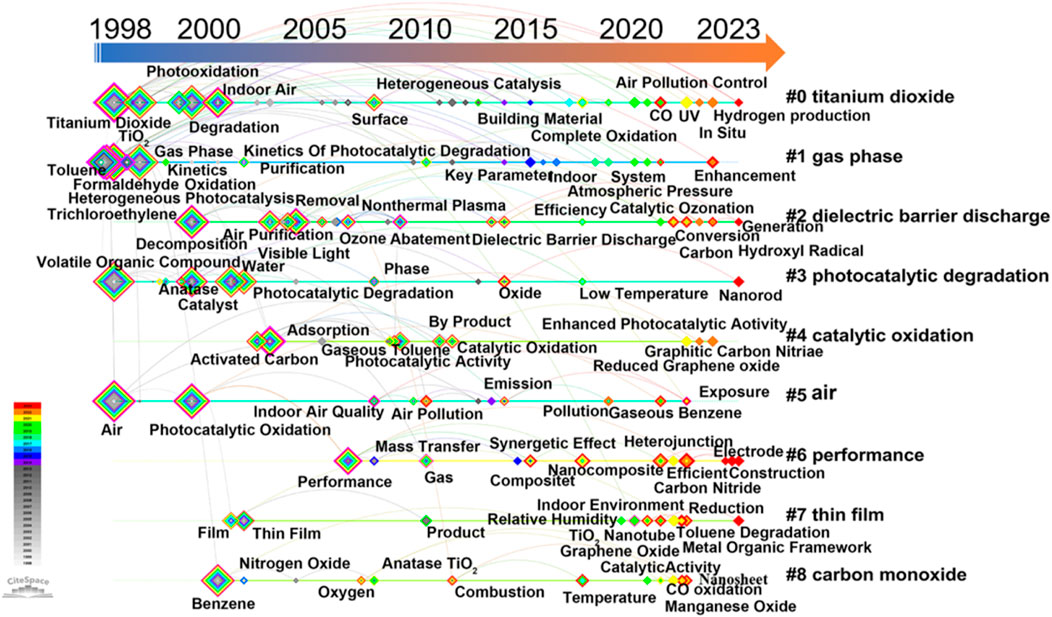
As shown in Figure 8 , the keywords represent a node; the larger the node means that the keyword is more heavily researched, and some nodes means the keyword has high explosive power (Table 6); however, links between them indicate co-occurrence relationships (van Eck and Waltman, 2010). CiteSpace software was used to obtain nine clustering labels by the LLR (log-likelihood ratio) method: “#0 titanium dioxide,” “#1 gas phase,” “#2 dielectric barrier discharge,” “#3 photocatalytic degradation,” “#4 catalytic oxidation,” “#5 air,” “#6 performance,” “#7 thin film,” and “#8 carbon monoxide.” The timeline clearly illustrates the development of the keywords within each of the representative clusters in the literature on the photocatalytic oxidation of VOCs over this time period (Seltenrich, 2015).
The keywords “Titanium Dioxide,” “Formaldehyde,” “Heterogeneous Photocatalysis,” “Volatile Organic Compound,” and “Air” appear in the 1998 timeline. From 2001 to 2003, the keywords include “Degradation,” “Decomposition,” “Photocatalytic Oxidation,” “Indoor Air,” “Activated Carbon,” “Benzene,” and “Thin-Film.” In 2015, “Hydrothermal Synthesis,” “Efficiency,” “Low-Temperature,” and “Nanocomposite” appeared. During 2020 to 2023, keywords involved “UV,” “synergistic effect,” “Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity,” “Manganese Oxide,” “Metal Organic Framework,” “Efficient,” “Charge Separation,” “Hydrogen Production,” “Carbon Nitride,” and “Nanorod.” Collectively, these keywords reflect the latest trends and advances in the field of inhomogeneous photocatalysis and provide directions for future research in material science, energy conversion, and environmental protection. Further progress in the efficiency and application of photocatalytic technology is expected through in-depth research in these key areas.
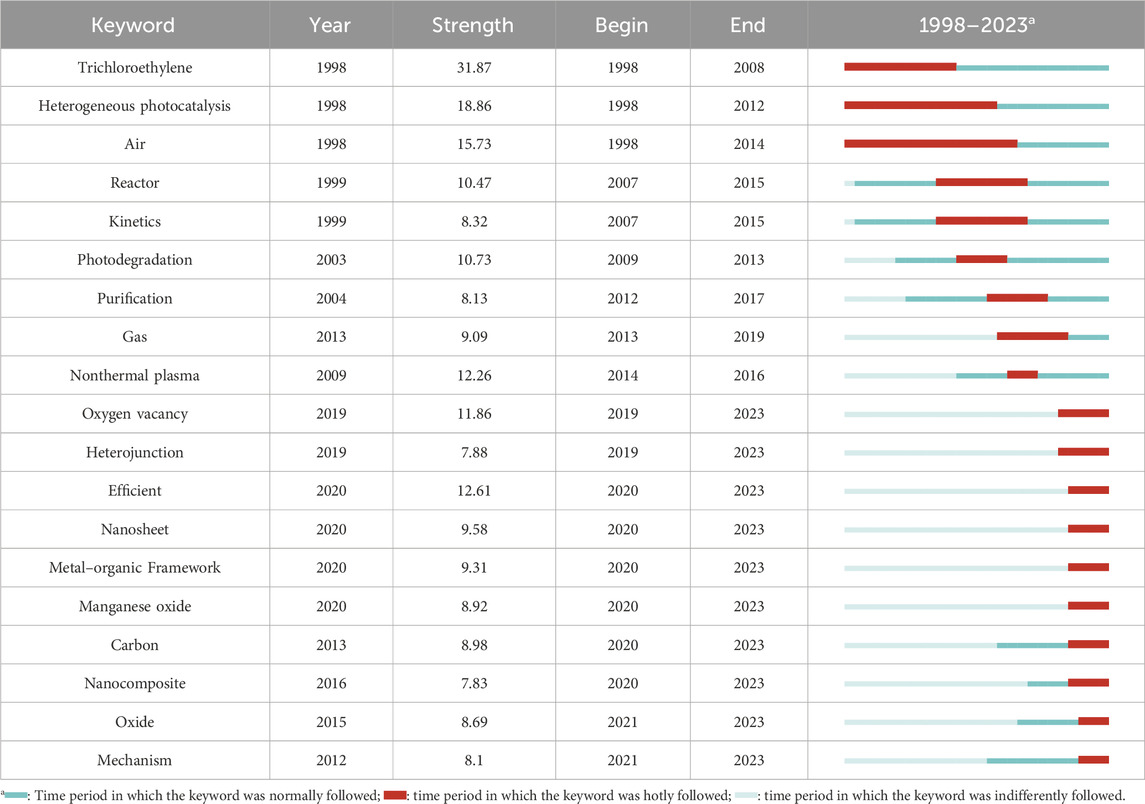
CiteSpace software counts the frequency of words in the identifiers of titles, abstracts, keywords, and bibliographic records of papers in related fields and identifies hot words based on the growth rate of word frequency of these words to reveal the research trend of photocatalytic oxidation of VOCs. As shown in Table 6, “Trichloroethylene,” “Titanium Dioxide,” “Heterogeneous,” “Photocatalysis,” “Air,” and “Kinetics” have been a research buzzword from 1998 to 2015. In this stage, most of the studies used trichloroethylene as the target pollutant and TiO2 as the photocatalyst to investigate the efficacy and kinetics of photocatalytic oxidation technology for VOCs. TiO2, the cornerstone of photocatalysts, is the most popular photocatalyst, and its composites, with the combined advantages of their respective components, play an important role in different areas of pollution control (Belessiotis et al., 2022). Silvia Suárez et al. prepared hybrid-structured photocatalysts based on the adsorbents seafoam and TiO2 by extruding ceramic dough and tested them for the photocatalytic degradation of the target volatile organic compound molecule trichloroethylene (Suárez et al., 2008). Khurram Shahzad Ayub et al. selected Co and Cu bimetallic oxides with high catalytic activity dispersed on TiO2 and successfully prepared Co-Cu/TiO2 catalysts, which were used in post-plasma catalysis for effective degradation of toluene (Ayub et al., 2022). The effects of TiO2 content, zeolite structure, and silica/aluminum ratio on the textural properties, adsorption capacity, and photodegradation activity of zeolite/TiO2 composites were investigated using formaldehyde and chlorinated hydrocarbon trichloroethane as model VOCs by Jansson et al. (2015). Xiaoqing Qiu et al. reported here that grafting nano-sized CuxO clusters onto TiO2 produces an excellent indoor environmental risk reduction material. By controlling the balance of Cu-I and Cu-II in CuxO, the CuxO/TiO2 hybrid nanocomposites achieved efficient decomposition and anti-pathogenic activity (Qiu et al., 2012). Shuang Cao et al. prepared bimodal mesoporous TiO2 catalysts doped with platinum, palladium, and ruthenium by wet impregnation for the catalytic combustion of dichloromethane, and the deactivation of Ru/TiO2 catalysts was suppressed due to the fact that carbon and chlorine could be removed by RuO2, which resulted in excellent catalytic activity (Cao et al., 2018). The research field of photocatalytic oxidation of VOCs has developed rapidly in the last 2 decades, and research on modified catalysts with TiO2 catalysts as the cornerstone continues to be hot, with a deeper understanding of the photochemical mechanism and optimization of photocatalyst design, contributing to the reduction of air pollutants.
“Oxygen vacancies,” “heterojunctions,” “high efficiency,” “nanosheets,” “metal-organic frameworks,” “manganese oxide,” “carbon,” “nanocomposites,” “oxides,” and “mechanism” are the burst keywords from 2019 to 2023.
3.6.1 Burst keyword “heterojunctions”
By adding the keyword “Heterojunction” to the Boolean operation search formula and conducting keyword analysis, Supplementary Figure S2 was obtained. It can be seen from the figure that the three keywords distributed over time, “p-n Heterojunction,” “Z-scheme Heterojunction,” and “S-scheme Heterojunction,” imply the development of composite photocatalysts in the field of photocatalytic degradation of VOCs. According to the different positions of the energy band, the coupling of semiconductors can be divided into three types: broken gap, cross-border gap, and staggered gap (Che et al., 2023). In fact, only the heterojunction with staggered gaps can improve the charge transfer at the interface, thus attracting the attention of scholars. “p-n heterojunction” is a typical strategy of staggered-gap heterojunction. Since the main carriers of p-type semiconductors are positive charges and the main carriers of n-type heterojunctions are negative charges, the interface of p-n heterojunctions contains a built-in electric field and suppresses the recombination of carriers by separating the photogenerated electrons (eCB−) and holes (hVB+) (Zou et al., 2020). The formed heterojunction makes the spatial separation of photoinduced carriers possible and effectively inhibits the possibility of charge recombination. However, the separation efficiency of photogenerated electron–hole pairs is at the cost of reducing the oxidation ability of the two semiconductor photocatalysts.
The photocatalyst modified by the “Z-scheme Heterojunction” strategy not only has a strong redox ability to drive photocatalytic reactions but can also effectively separate photogenerated electrons and holes. The Z-type photocatalyst can help ensure the improvement of the utilization efficiency of solar energy while enhancing the redox ability of the photocatalyst and promoting the separation of charge carriers through its unique electron transfer (Li et al., 2022). In the Z-scheme heterojunction, electrons on the semiconductor with a lower CB move to the higher VB of the other semiconductor to combine with holes, thereby preventing the recombination of photogenerated carriers and maintaining the original maximum redox potential (Jia et al., 2023). The formation of Z-scheme heterojunctions can be proved by the production of high-energy free radicals. Yang, J. et al. coupled BiOCl with Bi2WO6 to form a heterojunction for efficient photocatalytic degradation of toluene; theoretically, the conduction band of BiOCl cannot reach the band condition for oxygen activation to superoxide radical (−0.33 eV). After the formation of composite free radicals, the existence of superoxide radicals was detected by EPR, proving that high-energy electrons can be retained on the conduction band of Bi2WO6 and form a Z-scheme heterojunction, effectively separating high-energy electrons from holes to improve the photocatalytic efficiency (Yang et al., 2023a). Based on the fact that Z-scheme heterojunctions can produce high-energy electrons or holes, many studies have adopted this approach to more efficiently generate free radicals. Li, X. et al. constructed a Z-scheme heterojunction formed by MnO2 and C3N4, where low-energy electrons from the conduction band of C3N4 combine with holes on the valence band of MnO2, retaining high-energy electrons on the low-conduction band of MnO2, which is more conducive to the production of superoxide radicals, and improving the photocatalytic efficiency (Li et al., 2022). To further improve the photocatalytic efficiency of Z-scheme heterojunctions, researchers have proposed many modification strategies. Experimental evidence has shown that the surface plasmon resonance effect of Ag nanoparticles can assist in producing large amounts of active oxygen. Chen, JY. et al. introduced Ag nanoparticles into the heterojunction system of CuxO and SrTiO3, achieving highly efficient degradation of toluene while also exhibiting excellent antibiosis against E. coli due to the chemical disinfection action of Cu and Ag (Chen et al., 2023). Yang, J. et al. chemically deposited AgCl on the surface of Bi2WO6 and synthesized Ag/AgCl/Bi2WO6 photocatalysts by photoreduction of Ag-0 nanoparticles under UV light, achieving nearly 100% toluene degradation efficiency under visible light irradiation (Yang et al., 2023b). There are also studies that combine three semiconductor materials to form a double Z-type heterojunction with overlapping band structures. Shi, L. et al. synthesized a tri-component Z-type heterojunction photocatalyst BiPO4/BiVO4/g-C3N4 by a one-step sol–gel method, exhibiting high catalytic performance (Shi et al., 2022).
The basic condition for the formation of the “S-scheme Heterojunction” strategy is that the conduction band (CB) position and Fermi level (Ef) of the reducing semiconductor (RP) should be higher than those of the oxidizing semiconductor (OP) (Li et al., 2023). Under illumination, the low-energy photoelectrons generated in the conduction band of OP are driven by the internal electric field to cross the interface, where they recombine with the photogenerated holes in the valence band of RP. Therefore, the photogenerated carriers with strong redox ability can accumulate at the high conduction band position of RP and the low valence band position of OP, respectively. This leads to the spatial separation of oxidation and reduction sites on both sides of the connection, greatly improving the utilization rate of photoinduced carriers and thereby greatly enhancing the production efficiency of photooxidation active substances for VOCs (Xu et al., 2022). The formation of S-scheme heterojunctions can be analyzed by photo-irradiating a Kelvin probe and in situ X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Li. YW et al. synthesized BiVO4/tubular g-C3N4 S-scheme heterojunction photocatalysts for formaldehyde degradation, and the elemental binding energy changes were observed through in situ X-ray irradiation. The surface morphology and potential were observed using a Kelvin probe force microscope, showing that electrons migrated from g-C3N4 to BiVO4 in the dark, while electrons migrated from BiVO4 to g-C3N4 in the light, thus proving the formation of the S-scheme heterojunction (Li et al., 2023). The regulation of the interface charge transfer in S-scheme heterojunctions is of great importance, and recent research has used DFT (density functional theory) calculations to predict the formation strategies of S-scheme heterojunctions. Dong, YP. et al. predicted the formation of an S-scheme heterojunction by combining Cds with InVO4 through DFT calculations and successfully loaded Cds quantum dots onto InVO4. The transfer of electrons between Cds and InVO4 was observed using a Kelvin probe force microscope, verifying the existence of the S-scheme heterojunction and achieving high-efficiency photocatalytic degradation of C2H4 (Dong et al., 2024). Xu, XY. et al. used DFT calculations to predict that an S-scheme heterojunction can be formed between CdS quantum dots and Bi2MoO6 monolayers and successfully fabricated the catalyst through in situ hydrothermal synthesis for highly efficient photocatalytic degradation of C2H4 under visible light (Xu et al., 2022).The high efficiency of charge separation and electron transfer in the S-scheme heterojunction is due to the bonding form between the semiconductors, which enhances the efficiency of electron transfer and inhibits the accumulation of degradation intermediates. Recent studies have reported that exposing more oxygen vacancies by forming S-scheme heterojunctions can enhance the catalyst’s adsorption ability for VOC gases. Ying, TT. et al. prepared CeO2/Cu2O through a simple wet chemical method and found that the large number of oxygen vacancies on CeO2 enhances the adsorption capacity for pollutants. The built-in electric field formed by the S-scheme heterojunction can improve the separation of photogenerated charges, enhancing the photocatalytic performance (Ying et al., 2024).
In Supplementary Table S4, the works of the above three heterojunction strategies including the S-type heterojunction in the field of modified photocatalytic degradation of VOCs are listed. The construction of heterojunctions is an effective strategy to improve the performance of photocatalysts by combining different semiconductor materials, which can achieve better charge separation and a wider range of light response.
In summary, monolithic semiconductor catalysts often exhibit poor photocatalytic activity due to limited light response, rapid photoinduced charge recombination, and weak oxidation–reduction ability. Therefore, designing heterojunctions between different semiconductors can overcome the disadvantages of monolithic semiconductor catalysts. By designing Z-scheme or S-scheme inhibition junctions, it is possible to effectively separate the photoelectron–hole pairs and enhance the oxidation–reduction ability of the electron and hole. However, the characterization techniques for Z-scheme heterojunctions are insufficient, and the charge transfer pathway between the semiconductors is still unclear. The synthesis requirements for S-scheme heterojunctions are certain, and there are sufficient characterization techniques, but there is still a need to explore efficient and unobstructed charge transfer pathways, and the stability and deactivation issues of the composite catalyst also need further research.
(1) Composite heterojunction photocatalysts can generate high oxidation–reduction potentials and rich photogenerated charges to enable various oxidation and reduction reactions. It is necessary to adjust the band structure and active centers of the semiconductor through targeted optimization to enhance specific oxidation–reduction reactions and improve the photocatalytic degradation efficiency.
(2) Building unobstructed and directed transfer channels at the interface of the heterojunction material is a top priority, and establishing stable chemical bonds is a reliable strategy. It is crucial to clarify the charge transfer pathway between different catalysts for the design of composite catalysts.
(3) For composite heterojunctions, it is necessary to consider the catalyst’s activity and material stability. Therefore, composite catalysts with stronger interactions can be designed, such as chemical bonding, in situ growth, and high-temperature calcination, to ensure that the different semiconductor catalysts are in close contact.
3.6.2 Burst keyword “Metal Organic Framework”
MOFs have shown great potential in the design and synthesis of photocatalysts. Supplementary Figure S3 was obtained by adding the keyword “Metal Organic Framework” to the Boolean operation retrieval formula and conducting keyword analysis. It can be found in the figure that keywords such as “UiO-66,″ “ZIF-8,” “Cu-btc,” and “Mil-100(Fe)” are presented. These keywords represent different structural classifications of MOFs. “Uio-66″ is composed of [Zr6O4(OH)4] coordinated with 12 terephthalic acid ligands to form a regular octahedral crystal structure. UiO (Universitetet i Oslo) belongs to coordination pillar layer (CPL) materials. Its synthesis method is simple, the material structure is flexible, and the pore size is adjustable. It has been widely applied in the fields of gas adsorption and energy storage (Marks et al., 2020). Zeolitic imidazolate frameworks (ZIFs) are self-assembled by Zn or Co ions bonded in a tetracoordinated manner to the N sites of the imidazole (or imidazole derivatives) ring. As a subclass of MOFs, ZIFs combine the advantages of zeolites and MOFs. Moreover, ZIFs also have higher chemical and thermal stability (Li et al., 2018). MIL (Materials Institute Lavoisier) is coordinated by trivalent transition metal ions (such as Fe, Al, and Cr) and carboxylic acid ligands (such as terephthalic acid and trimellitic acid), and usually has a high specific surface area and rich porosity. In conclusion, MOFs are a kind of porous crystalline multifunctional materials, which have received increasing attention due to their ultrahigh specific surface area. MOFs with different configurations have been studied and applied in photocatalytic degradation of VOCs (Zhao et al., 2020).
The structure of MOFs is adjustable, which is conducive to the implementation of modification strategies. Different functional groups (Yao et al., 2018; Zhang et al., 2020), metal clusters (Man et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2018), and nanoparticles (Zhang et al., 2022) can be incorporated through methods such as heat treatment and solvent exchange to improve the functionality and selectivity of the catalyst. The heterogeneous junction strategy can effectively separate photogenerated carriers to improve light utilization efficiency and photocatalytic performance (Chen et al., 2021). Atomic doping strategies can alter the bandgap of materials, improve light absorption ability, promote charge separation, and provide adsorption sites to enhance the adsorption capacity for specific pollutants. Wang, X. et al. prepared MOF-derived Pd, N-co-doped TiO2, where the incorporation of N and the loading of Pd nanoparticles reduced the bandgap and enhanced the light absorption efficiency, enhanced charge separation and charge transfer ability, resulting in high photocatalytic oxidation activity and exhibiting strong adsorption and degradation efficiency for ethyl acetate (Wang et al., 2023). Liu, Y. et al. successfully introduced Pt ions into MOFs, forming abundant atomic Pt and oxygen vacancy content on the surface, and maintained the selectivity of toluene and CO2 products at 100% (Liu et al., 2022b). Metal nanoclusters and MOF materials can be combined to form MOF-nanoparticle composite materials, in which the metal nanoclusters can effectively separate charges and enhance the material’s regenerative ability. Lin, LY. et al. successfully loaded Ti-based nanoclusters onto NH2-UiO-66(Zr), not only providing extended visible light absorption and high charge mobility but also effectively converting key intermediates in the toluene degradation process (Lin et al., 2023). Carbon-based porous materials have stable structures and contain abundant mesopores and macropores, which can provide excellent diffusion channels for gas molecules when combined with MOFs, thereby significantly enhancing the material’s gas adsorption capacity. Tan, HC. et al. successfully composite graphene aerogels with MOF materials; the open mesoporous structure of graphene aerogels helps molecules of reactants and products enter and exit, showing extremely strong formaldehyde adsorption capacity (Tan et al., 2019).
In summary, MOF is a porous crystalline multifunctional material that is increasingly gaining attention due to its ultrahigh specific surface area. However, truly efficient and highly selective catalytic effects achieved by MOF materials are still very limited. It is still necessary to design highly efficient MOF materials that can respond to visible light. The morphology design and surface microstructure control of MOFs are of great significance for exploring the crystal growth mechanism and developing novel nanomaterials with excellent performance and prospects for applications.
The applications of different configuration MOF modification strategies in the field of photocatalytic degradation of VOCs are listed in Supplementary Table S5.
3.6.3 Burst keyword “oxygen vacancy”
“Oxygen Vacancy”: In photocatalytic materials, oxygen vacancies are essential for improving photocatalytic activity as they can act as electron capture centers, thus improving charge separation efficiency and enhancing the catalytic response (Zhou et al., 2023). The formation of oxygen vacancies is due to the destruction of oxygen atoms in the crystal lattice, with oxygen atoms being removed from their original lattice positions. In Supplementary Figure S4, the keywords “doping,” “etching,” and “combustion” can be found, which suggest different strategies for forming oxygen vacancies. Ion doping breaks the long-term periodicity of the crystal lattice oxygen by replacing existing atoms with cations or anions, thus producing oxygen vacancies and ensuring charge balance (Dong et al., 2020). Dong, C. et al. obtained two-dimensional MnO2 catalysts with different oxygen vacancy concentrations by doping Cu2+, and the oxygen vacancies enhanced the catalyst’s reducibility and oxygen species activity, thereby improving the catalytic activity for toluene oxidation. Acid–base etching uses the corrosive action of strong acids or strong bases to dissolve metal elements, thereby forming many vacancy defects (Liu et al., 2019). Liu, Y. et al. used 0.2 M HNO3 to modify MnO2, and the increased acid sites and acidity on the catalyst surface after acid treatment promoted the adsorption and activation of gaseous benzene. The efficiency of benzene-related compound degradation was improved by the increased oxygen vacancies in the crystal lattice and surface-adsorbed oxygen due to the acid treatment-induced active oxygen species. Reduction strategies can produce oxygen vacancies by inducing oxygen atoms to escape from the material surface (Xu et al., 2021). Xu, Y. et al. synthesized Cu-Mn composite oxide catalysts by the hydrothermal method and then modified them by a solid-phase reaction with urea for improvement. The photocatalyst obtained has a large number of oxygen vacancies, which increases the number of surface-adsorbed oxygen and enhances the mobility of lattice oxygen, thereby improving the catalyst’s reducibility and oxygen activity. High-temperature calcination causes the surface atoms of the material to vibrate violently, and surface lattice oxygen is easily diffused out, leading to the formation of oxygen vacancies (Liu et al., 2003). Liu, H. et al. pretreated TiO2 with H2 gas at a high temperature of 500°C–600°C and detected the presence of oxygen vacancies through the intensity of the electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) signal. They found that the presence of oxygen vacancies enhanced the photocatalytic activity and facilitated the degradation of phenol.
In summary, oxygen vacancies play an important role in adsorption and catalysis in the field of photocatalytic VOCs. It is crucial to clarify the generation mechanism and distribution conditions of oxygen vacancies. Since oxygen vacancies can exist in different catalyst positions, such as the surface, lattice, or other positions, clarifying their distribution locations can help analyze their catalytic oxidation mechanism. Second, it is necessary to clarify the formation process and form change of oxygen vacancies in the catalytic process and clarify their catalytic role. Finally, it is necessary to clarify the role of different schemes of oxygen vacancies in the catalytic oxidation of VOCs, such as promoting adsorption and activation, promoting lattice oxygen and electron transfer, anchoring precious metals, and providing Lewis acid sites.
“Efficient”: Improving photocatalytic efficiency is a central goal of the current research, especially in the fields of energy conversion and environmental remediation. “Nanosheet”: Nanosheets with two-dimensional structure are promising materials for improving photocatalytic efficiency due to their high specific surface area and unique electronic properties (Ou et al., 2022). These keywords reflect the latest research trends in photocatalysis, highlighting innovations in material synthesis, structural design, and understanding of reaction mechanisms. These studies are of great significance for future applications in fields such as energy conversion, environmental remediation, and chemical synthesis.
4 Conclusion
(1) A bibliometric study was conducted on the WoSCC database for VOC photocatalytic oxidation research from 1998 to 2023. Using information visualization analysis, we generated a knowledge map. From 2000 to 2015, research on VOC photocatalytic oxidation showed a gradual increase trend and then rapidly upgraded after 2016. The most studied VOC gases are still benzene derivatives and formaldehyde, while alkanes and ethyl acetate are also relatively popular VOC gases.
(2) The basic information relationship diagram can help researchers identify the countries that have made major contributions to the field, as well as the authors and institutions. It can be seen that China has the most prolific authors, with the most papers published, with the Guangdong University of Technology’s An Taicheng team being the most productive team in China, focusing on the degradation effects and mechanisms of ring-shaped VOCs using modified photocatalysts. Canada has a relatively concentrated research force in this field, with 106 papers published, with Concordia University’s Haghighat Fariborz and Lee Chang-Seo team publishing 59 papers, focusing on the modification strategies of TiO2 photocatalysts. Some countries, such as China and the United States, have close cooperation in this field. However, the research cooperation of other countries is relatively independent, highlighting the potential for enhanced global cooperation.
(3) The journal map shows that different journals have different emphases. From the current journal publication information, the development of catalysts is a top priority, especially the modification strategies and design of composite catalysts, while the development of new materials is relatively less emphasized. In terms of the degradation of pollutants, more attention is paid to pollutants that have a significant impact on human health, while less attention is paid to the natural oxidation of volatile organic compounds. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. and similar journals mainly report on the photocatalytic effects of porous materials and the combination strategies of composite catalysts. Appl. Surf. Sci. and other journals focus on the adsorption of VOC gases by catalysts. Journals such as Environ. Sci. Technol. are mainly dedicated to solving real-world environmental problems. If readers want to understand the mechanism of VOC gas degradation, they can refer to related journals such as J. Catal. Analyzing the most highly cited research, it was determined that following research must be conducted in this field: the catalyst’s adsorption capacity, the catalyst’s degradation efficiency, and the analysis of intermediate products and their harmfulness.
(4) In the field of VOC photocatalytic oxidation, the focus of front-end development is on developing and optimizing advanced photocatalysts with a high charge separation efficiency, improved adsorption performance, and expanded light response range. In-depth research on the VOC degradation process focuses on the mechanisms of charge generation and transfer within the photocatalyst and the detailed mechanism of catalytic oxidation, which is crucial for optimizing reaction conditions and improving catalytic efficiency. At the same time, research has been conducted on the stability and durability of the photocatalyst in long-term use, as well as the secondary pollutants that may arise during the photocatalytic process, to ensure the environmental friendliness and sustainability of the technology. TiO2 remains the most studied catalyst. In terms of catalyst modification strategies, emphasis has been placed on designing novel material structures, such as MOFs, heterojunctions, manganese oxides, and nanocomposites, to improve the photocatalytic oxidation efficiency of VOCs. It is worth noting that the surface engineering and adsorption capacity of the catalyst are also research priorities in this field, with oxygen vacancies being a major research topic. Of course, the key step toward commercialization and large-scale application of photocatalytic VOC oxidation technology is to transform laboratory research results into practical applications and conduct comprehensive evaluations of environmental impact and cost-effectiveness.
Despite the development of many methods to enhance the photocatalyst’s degradation of VOCs, the application of photocatalysis in removing VOCs still faces significant challenges. First, a composite of multiple materials needs to be developed to produce a synergistic effect, which may result in better photocatalytic performance than that of a single semiconductor material. Second, the adsorption effect of gaseous organic compounds on the catalyst surface and its mechanism also need to be explored. Another challenge is to develop efficient photocatalysts to solve the real difficulties at industrial scale. To solve the problem of scaling up, more collaboration is needed between researcher groups from different disciplines to bridge the gap between laboratory testing and actual application. In addition, a series of strategies need to be developed to effectively utilize visible light photocatalysts and improve new materials or design structures to degrade toxic intermediates/by-products generated during the photocatalytic degradation of VOCs. Therefore, further research should be conducted to identify these created materials.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
XZu: Writing–original draft, Visualization, Investigation. YS: Software, Methodology, Writing–original draft, Investigation. XL: Writing–original draft, Methodology, Investigation. JG: Writing–review and editing, Resources, Funding acquisition. XZg: Writing–review and editing, Supervision. GZ: Writing–original draft, Methodology. YG: Writing–review and editing, Supervision, Investigation, Funding acquisition.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. The present work was financially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (52270129, 52070127, and 52370142), Oriental Talent Youth Program, Shanghai Shuguang Program (23SG52), and Guizhou Provincial Key Technology R&D Program (QKHZC(2024)153). Dr. Guo also thanks the financial support of Science and Technology Development Fund of Pudong New Area (PKJ2022-C07 and PKJ2022-C10).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors, and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fenvs.2024.1482766/full#supplementary-material
References
Alberici, R. M., and Jardim, W. F. (1997). Photocatalytic destruction of VOCs in the gas-phase using titanium dioxide. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 14, 55–68. doi:10.1016/S0926-3373(97)00012-X
Ayub, K. S., Zaman, W. Q., Miran, W., Ali, M., Abbas, Z., Mushtaq, U., et al. (2022). Efficient post-plasma catalytic degradation of toluene via series of Co–Cu/TiO2 catalysts. Res. Chem. Intermed. 48, 4227–4248. doi:10.1007/s11164-022-04805-7
Belessiotis, G. V., Falara, P. P., Ibrahim, I., and Kontos, A. G. (2022). Magnetic metal oxide-based photocatalysts with integrated silver for water treatment. Materials 15, 4629. doi:10.3390/ma15134629
Cano-Casanova, L., Amorós-Pérez, A., Ouzzine, M., Román-Martínez, M. C., and Lillo-Ródenas, M. A. (2021). Enhancement of the TiO2 photoactivity for propene oxidation by carbon incorporation using saccharose in hydrothermal synthesis. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 9, 104941. doi:10.1016/j.jece.2020.104941
Cao, S., Fei, X., Wen, Y., Sun, Z., Wang, H., and Wu, Z. (2018). Bimodal mesoporous TiO2 supported Pt, Pd and Ru catalysts and their catalytic performance and deactivation mechanism for catalytic combustion of Dichloromethane (CH2Cl2). Appl. Catal. A General 550, 20–27. doi:10.1016/j.apcata.2017.10.006
Carp, O., Huisman, C. L., and Reller, A. (2004). Photoinduced reactivity of titanium dioxide. Prog. Solid State Chem. 32, 33–177. doi:10.1016/j.progsolidstchem.2004.08.001
Che, L., Pan, J. L., Cai, K. X., Cong, Y. Q., and Lv, S. W. (2023). The construction of p-n heterojunction for enhancing photocatalytic performance in environmental application: a review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 315, 123708. doi:10.1016/j.seppur.2023.123708
Chen, C. (2004). Searching for intellectual turning points: progressive knowledge domain visualization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 101, 5303–5310. doi:10.1073/pnas.0307513100
Chen, C. C., Duh, Y. S., and Shu, C. M. (2009). Thermal polymerization of uninhibited styrene investigated by using microcalorimetry. J. Hazard. Mater. 163, 1385–1390. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.07.151
Chen, J. Y., Guo, X. M., Lang, L., Yin, X. L., Wang, A. M., and Rui, Z. B. (2023c). Multifunctional Z-scheme CuxO/Ag/SrTiO3 heterojunction for photothermocatalytic VOCs degradation and antibiosis. Appl. Surf. Sci. 618, 153275. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2022.153275
Chen, L., Wang, X., Rao, Z. P., Tang, Z. X., Wang, Y., Shi, G. S., et al. (2021). In-situ synthesis of Z-Scheme MIL-100(Fe)/α-Fe2O3 heterojunction for enhanced adsorption and Visible-light photocatalytic oxidation of O-xylene. Chem. Eng. J. 416, 129112. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2021.129112
Chen, L., Wang, X., Shi, G. S., Lu, G. H., Wang, Y., Xie, X. F., et al. (2023b). The regulation of Lewis acid/basic sites in NaFe bimetal MOXs for the controllable photocatalytic degradation of electron-rich/deficient VOCs. Appl. Catal. B-Environmental 334, 122850. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2023.122850
Chen, X. Y., Zhu, W. K., Feng, S. F., and Chen, J. Y. (2024). Photodegradation of xylene isomers: kinetics, mechanism, secondary pollutant formation potential and health risk evaluation. J. Environ. Sci. 136, 658–669. doi:10.1016/j.jes.2022.12.034
Chen, Y.-H., Yin, M.-Q., Fan, L.-H., Jiang, X.-C., Xu, H.-F., Zhang, T., et al. (2023a). Bibliometric analysis of traditional Chinese medicine research on heart failure in the 21st century based on the WOS database. Heliyon 9, e12770. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e12770
Cheng, S., Chang-Chien, G.-P., Huang, Q., Zhang, Y.-B., Yan, P., Zhang, J., et al. (2019). Global research trends in health effects of volatile organic compounds during the last 16 Years: a bibliometric analysis. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 19, 1834–1843. doi:10.4209/aaqr.2019.06.0327
Deng, X., Zhang, D. Y., Lu, S. H., Bao, T., Yu, Z. M., and Deng, C. X. (2021). Green synthesis of Ag/g-C3N4 composite materials as a catalyst for DBD plasma in degradation of ethyl acetate. Mater. Sci. Eng. B-Advanced Funct. Solid-State Mater. 272, 115321. doi:10.1016/j.mseb.2021.115321
Dong, C., Qu, Z. P., Jiang, X., and Ren, Y. W. (2020). Tuning oxygen vacancy concentration of MnO2 through metal doping for improved toluene oxidation. J. Hazard. Mater. 391, 122181. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122181
Dong, F., Guo, S., Wang, H., Li, X., and Wu, Z. (2011). Enhancement of the visible light photocatalytic activity of C-doped TiO2 nanomaterials prepared by a green synthetic approach. J. Phys. Chem. C 115, 13285–13292. doi:10.1021/jp111916q
Dong, Y. P., Ji, P. Z., Xu, X. Y., Li, R., Wang, Y., Homewood, K. P., et al. (2024). Rational design and construction of a CdS QDs/InVO4 atomic-layer (110)/(110) facet S-scheme heterojunction for highly efficient photocatalytic degradation of C2H4. Energy and Environ. Mater. 7. doi:10.1002/eem2.12643
Emran, M. Y., Miran, W., Gomaa, H., Ibrahim, I., Belessiotis, G. V., Abdelwahab, A. A., et al. (2022). “Biowaste materials for advanced biodegradable packaging technology,” in Handbook of biodegradable materials. Editors G. A. M. Ali, and A. S. H. Makhlouf (Cham: Springer International Publishing), 1–37.
Enesca, A. (2020). Enhancing the photocatalytic activity of SnO2-TiO2 and ZnO-TiO2 tandem structures toward indoor air decontamination. Front. Chem. 8, 583270. doi:10.3389/fchem.2020.583270
Farideh, OSAREH (1996). Bibliometrics, citation analysis and Co-citation analysis: a review of literature I. Libri 46. doi:10.1515/libr.1996.46.3.149
Filley, C. M., Halliday, W., and Kleinschmidt-DeMasters, B. K. (2004). The effects of toluene on the central nervous system. J. Neuropathology Exp. Neurology 63, 1–12. doi:10.1093/jnen/63.1.1
Gaffney, J. S., Marley, N. A., and Blake, D. R. (2012). Baseline measurements of ethene in 2002: implications for increased ethanol use and biomass burning on air quality and ecosystems. Atmos. Environ. 56, 161–168. doi:10.1016/j.atmosenv.2012.04.002
Hahm, M., Lee, J., Lee, M. Y., and Byeon, S. H. (2016). Health risk assessment of occupational exposure to styrene depending on the type of industry: data from the Workplace Environmental Monitoring Program in Korea. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 22, 1312–1322. doi:10.1080/10807039.2016.1168691
Halios, C. H., Landeg-Cox, C., Lowther, S. D., Middleton, A., Marczylo, T., and Dimitroulopoulou, S. (2022). Chemicals in European residences – Part I: a review of emissions, concentrations and health effects of volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Sci. Total Environ. 839, 156201. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.156201
Hamada, K., Ochiai, T., Aoki, D., Akutsu, Y., and Hirabayashi, Y. (2022). Decomposition of gaseous styrene using photocatalyst and ozone treatment. Catalysts 12, 316. doi:10.3390/catal12030316
Higashimoto, S., Katsuura, K., Yamamoto, M., and Takahashi, M. (2020). Photocatalytic activity for decomposition of volatile organic compound on Pt-WO3 enhanced by simple physical mixing with TiO2. Catal. Commun. 133, 105831. doi:10.1016/j.catcom.2019.105831
Hoffmann, M. R., Martin, S. T., Choi, W., and Bahnemann, D. W. (1995). Environmental applications of semiconductor photocatalysis. Chem. Rev. 95, 69–96. doi:10.1021/cr00033a004
Iso, I. (2011). 16000–6: 2011 indoor air—part. 6: determination of volatile organic compounds in indoor and test chamber air by active sampling on tenax TA sorbent, thermal desorption and gas chromatography using MS or MS-FID. Therm. Desorption Gas Chromatogr. Using MS or MS-FID.
Jakab, M. G., Klupp, T., Besenyei, K., Biró, A., Major, J., and Tompa, A. (2010). Formaldehyde-induced chromosomal aberrations and apoptosis in peripheral blood lymphocytes of personnel working in pathology departments. Mutat. Research-Genetic Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 698, 11–17. doi:10.1016/j.mrgentox.2010.02.015
Jansson, I., Suárez, S., Garcia-Garcia, F. J., and Sánchez, B. (2015). Zeolite–TiO2 hybrid composites for pollutant degradation in gas phase. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 178, 100–107. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.10.022
Jia, Y., Zhang, X., Wang, R. Y., Yuan, J., Zheng, R. Z., Zhang, J. Q., et al. (2023). Energy band engineering of WO3/Bi2WO6 direct Z-scheme for enhanced photocatalytic toluene degradation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 618, 156636. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2023.156636
Kamani, H., Baniasadi, M., Abdipour, H., Mohammadi, L., Rayegannakhost, S., Moein, H., et al. (2023). Health risk assessment of BTEX compounds (benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene and xylene) in different indoor air using Monte Carlo simulation in zahedan city, Iran. Heliyon 9, e20294. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e20294
Kholidah, H., Hijriah, H. Y., Mawardi, I., Huda, N., Herianingrum, S., and Alkausar, B. (2022). A Bibliometric mapping of peer-to-peer lending research based on economic and business perspective. Heliyon 8, e11512. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e11512
Kim, K. H., Jahan, S. A., and Lee, J. T. (2011). Exposure to formaldehyde and its potential human health hazards. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part C-Environmental Carcinog. and Ecotoxicol. Rev. 29, 277–299. doi:10.1080/10590501.2011.629972
Kim, S., Kim, S., and Lee, S. (2023). Activated carbon modified with polyethyleneimine and MgO: better adsorption of aldehyde and production of regenerative VOC adsorbent using a photocatalyst. Appl. Surf. Sci. 631, 157565. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2023.157565
Kim, S. B., and Hong, S. C. (2002). Kinetic study for photocatalytic degradation of volatile organic compounds in air using thin film TiO2 photocatalyst. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 35, 305–315. doi:10.1016/S0926-3373(01)00274-0
Kong, J., Xiang, Z., Li, G., and An, T. (2020). Introduce oxygen vacancies into CeO2 catalyst for enhanced coke resistance during photothermocatalytic oxidation of typical VOCs. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 269, 118755. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.118755
Korsak, Z., Rydzynski, K., Stetkiewicz, J., Świercz, R., and Jajte, J. (1995). Toxic effects of 1,2,4-trimethylbenzene (pseudocumene) after acute and subchronic inhalation exposure. Toxicol. Lett. 78, 49. doi:10.1016/0378-4274(95)94806-R
Kovalevskiy, N., Selishchev, D., Svintsitskiy, D., Selishcheva, S., Berezin, A., and Kozlov, D. (2020). Synergistic effect of polychromatic radiation on visible light activity of N-doped TiO2 photocatalyst. Catal. Commun. 134, 105841. doi:10.1016/j.catcom.2019.105841
Kräuter, J., Franz, E., Waidhas, F., Brummel, O., Libuda, J., and Al-Shamery, K. (2022). The role of defects in the photoconversion of 2-propanol on rutile titania: operando spectroscopy combined with elementary studies. J. Catal. 406, 134–144. doi:10.1016/j.jcat.2021.12.025
Kunaseth, M., Poldorn, P., Junkeaw, A., Meeprasert, J., Rungnim, C., Namuangruk, S., et al. (2017). A DFT study of volatile organic compounds adsorption on transition metal deposited graphene. Appl. Surf. Sci. 396, 1712–1718. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.11.238
Le, M. C., Le, T. H., Thi, T. H. B., Nguyen, Q. D., Thi, T. H., and Thi, M. N. T. (2021). Synthesizing and evaluating the photocatalytic and antibacterial ability of TiO2/SiO2 nanocomposite for silicate coating. Front. Chem. 9, 738969. doi:10.3389/fchem.2021.738969
Li, H., Sun, Q. Y., Li, F., Wang, B. S., and Zhu, B. L. (2024). Metabolomics of benzene exposure and development of biomarkers for exposure hazard assessment. Metabolites 14, 377. doi:10.3390/metabo14070377
Li, J., Mo, S., Ding, X., Huang, L., Zhou, X., Fan, Y., et al. (2023a). Hollow cavity engineering of MOFs-derived hierarchical MnOx structure for highly efficient photothermal degradation of ethyl acetate under light irradiation. Chem. Eng. J. 464, 142412. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2023.142412
Li, J. L., Li, H., Li, K., Chen, Y., Zhang, H., Zhang, X., et al. (2021). Enhanced secondary organic aerosol formation from the photo-oxidation of mixed anthropogenic volatile organic compounds. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 21, 7773–7789. doi:10.5194/acp-21-7773-2021
Li, M., Ma, L., Luo, L., Liu, Y., Xu, M., Zhou, H., et al. (2022a). Efficient photocatalytic epoxidation of styrene over a quantum-sized SnO2 on carbon nitride as a heterostructured catalyst. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 309, 121268. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2022.121268
Li, X., Fang, G. G., Qian, X. R., and Tian, Q. W. (2022b). Z-scheme heterojunction of low conduction band potential MnO2 and biochar-based g-C3N4 for efficient formaldehyde degradation. Chem. Eng. J. 428, 131052. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2021.131052
Li, X. Y., Li, J. A., Shi, Y., Zhang, M. M., Fan, S. Y., Yin, Z. F., et al. (2018). Rational design of cobalt and nitrogen co-doped carbon hollow frameworks for efficient photocatalytic degradation of gaseous toluene. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 528, 45–52. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2018.05.067
Li, Y., Du, Q., Zhang, J., Jiang, Y., Zhou, J., and Ye, Z. (2023b). Visualizing the intellectual landscape and evolution of transportation system resilience: a bibliometric analysis in CiteSpace. Dev. Built Environ. 14, 100149. doi:10.1016/j.dibe.2023.100149
Li, Y., Ouyang, S., Xu, H., Wang, X., Bi, Y., Zhang, Y., et al. (2016). Constructing solid–gas-interfacial fenton reaction over alkalinized-C3N4 photocatalyst to achieve apparent quantum yield of 49% at 420 nm. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138, 13289–13297. doi:10.1021/jacs.6b07272
Li, Y. W., Li, S. Z., Zhao, M. B., and Ma, W. L. (2023c). Decahedral BiVO4/tubular g-C3N4 S-scheme heterojunction photocatalyst for formaldehyde removal: charge transfer pathway and deactivation mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 327, 124966. doi:10.1016/j.seppur.2023.124966
Lin, L. Y., Liu, C. H., Dang, V. D., and Fu, H. T. (2023). Atomically dispersed Ti-O clusters anchored on NH2-UiO-66(Zr) as efficient and deactivation-resistant photocatalyst for abatement of gaseous toluene under visible light. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 635, 323–335. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2022.12.147
Lin, Z. F., Shen, W. H., Chen, X. Q., Corriou, J. P., and Xi, H. X. (2020). Impact of intermediate products on benzene photocatalytic oxidation in pulp mills: experimental and adsorption simulation study. Appl. Surf. Sci. 529, 147130. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.147130
Liu, H., Ma, H. T., Li, X. Z., Li, W. Z., Wu, M., and Bao, X. H. (2003). The enhancement of TiO2 photocatalytic activity by hydrogen thermal treatment. Chemosphere 50, 39–46. doi:10.1016/s0045-6535(02)00486-1
Liu, Y., Chen, G. D., Chen, J. J., and Niu, H. J. Y. (2022b). Excellent catalytic performance of Ce-mof with abundant oxygen vacancies supported noble metal Pt in the oxidation of toluene. Catalysts 12, 775. doi:10.3390/catal12070775
Liu, Y., Cheng, Z., Liu, S., Ren, Y., Yuan, T., Zhang, X., et al. (2022a). A quantitative structure activity relationship (QSAR) model for predicting the rate constant of the reaction between VOCs and NO3 radicals. Chem. Eng. J. 448, 136413. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2022.136413
Liu, Y., Zhou, H., Cao, R. R., Liu, X. Y., Zhang, P. Y., Zhan, J. J., et al. (2019). Facile and green synthetic strategy of birnessite-type MnO2 with high efficiency for airborne benzene removal at low temperatures. Appl. Catal. B-Environmental 245, 569–582. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.01.023
Ma, J. X., An, L. Q., Liu, D. M., Yao, J. X., Qi, D. P., Xu, H. B., et al. (2022). A light-permeable solar evaporator with three-dimensional photocatalytic sites to boost volatile-organic-compound rejection for water purification. Environ. Sci. and Technol. 56, 9797–9805. doi:10.1021/acs.est.2c01874
Mamaghani, A. H., Haghighat, F., and Lee, C.-S. (2017). Photocatalytic oxidation technology for indoor environment air purification: the state-of-the-art. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 203, 247–269. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.10.037
Man, Z., Meng, Y., Lin, X. C., Dai, X. R., Wang, L. P., and Liu, D. Z. (2022). Assembling UiO-66@TiO2 nanocomposites for efficient photocatalytic degradation of dimethyl sulfide. Chem. Eng. J. 431, 133952. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2021.133952
Marks, S. D., Riascos-Rodriguez, K., Arrieta-Pérez, R. R., Yakovenko, A. A., Exley, J., Evans, P. G., et al. (2020). Lattice expansion and ligand twist during CO2 adsorption in flexible Cu bipyridine metal-organic frameworks. J. Mater. Chem. A 8, 18903–18915. doi:10.1039/d0ta03298k
Mo, J., Zhang, Y., Xu, Q., Zhu, Y., Lamson, J. J., and Zhao, R. (2009). Determination and risk assessment of by-products resulting from photocatalytic oxidation of toluene. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 89, 570–576. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2009.01.015
Montini, T., Melchionna, M., Monai, M., and Fornasiero, P. (2016). Fundamentals and catalytic applications of CeO2-based materials. Chem. Rev. 116, 5987–6041. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00603
Moura, L., and Picão, R. C. (2022). “Chapter 23 - removal of antimicrobial resistance determinants from wastewater: a risk perspective on conventional and emerging technologies,” in Emerging contaminants in the environment. Editors H. Sarma, D. C. Dominguez, and W.-Y. Lee (Elsevier), 603–642.
Mu, Y., and Williams, P. T. (2022). Recent advances in the abatement of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and chlorinated-VOCs by non-thermal plasma technology: a review. Chemosphere 308, 136481. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.136481
Ni, Q., Amalfitano, N., Biasioli, F., Gallo, L., Tagliapietra, F., and Bittante, G. (2022). Bibliometric review on the volatile organic compounds in meat. Foods 11, 3574. doi:10.3390/foods11223574
Obee, T. N., and Brown, R. T. (1995). TiO2 photocatalysis for indoor air applications: effects of humidity and Trace contaminant levels on the oxidation rates of formaldehyde, toluene, and 1,3-butadiene. Environ. Sci. and Technol. 29, 1223–1231. doi:10.1021/es00005a013
Ohtani, B. (2008). Preparing articles on photocatalysis—beyond the illusions, misconceptions, and speculation. Chem. Lett. 37, 216–229. doi:10.1246/cl.2008.216
Ollis, D. F. (2000). Photocatalytic purification and remediation of contaminated air and water. Comptes Rendus l'Académie Sci. - Series IIC - Chemistry 3, 405–411. doi:10.1016/S1387-1609(00)01169-5
Ou, K., Liu, J., Dou, Q., Zhou, Y., Zeng, Y., and Zhang, J. (2022). High-pressure modified mesoporous Zr-BTB nanosheets with enhanced photocatalyst activity. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 649, 129511. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2022.129511
Pan, X., Yan, E., Cui, M., and Hua, W. (2018). Examining the usage, citation, and diffusion patterns of bibliometric mapping software: a comparative study of three tools. J. Inf. 12, 481–493. doi:10.1016/j.joi.2018.03.005
Pelaez, M., Nolan, N. T., Pillai, S. C., Seery, M. K., Falaras, P., Kontos, A. G., et al. (2012). A review on the visible light active titanium dioxide photocatalysts for environmental applications. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 125, 331–349. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.05.036
Qian, Y. H., Ma, D. G., and Zhong, J. B. (2021). Metal-organic frameworks with variable valence metal-photoactive components: emerging platform for volatile organic compounds photocatalytic degradation. Front. Chem. 9, 749839. doi:10.3389/fchem.2021.749839
Qin, J. X., Pei, Y., Zheng, Y., Ye, D. Q., and Hu, Y. (2023). Fe-MOF derivative photocatalyst with advanced oxygen reduction capacity for indoor pollutants removal. Appl. Catal. B-Environmental 325, 122346. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2022.122346
Qiu, X., Miyauchi, M., Sunada, K., Minoshima, M., Liu, M., Lu, Y., et al. (2012). Hybrid CuxO/TiO2 nanocomposites as risk-reduction materials in indoor environments. ACS Nano 6, 1609–1618. doi:10.1021/nn2045888
Rinsky, R. A. (1989). Benzene and leukemia: an epidemiologic risk assessment. Environ. Health Perspect. 82, 189–191. doi:10.1289/ehp.8982189
Rong, X., Cao, Q., Gao, Y., Du, X., Dou, H. W., Yan, M., et al. (2023). Performance optimization and kinetic analysis of HNO3 coupled with microwave rapidly modified coconut shell activated carbon for VOCs adsorption. Front. Energy Res. 10. doi:10.3389/fenrg.2022.1047254
Rudel, R. A., Camann, D. E., Spengler, J. D., Korn, L. R., and Brody, J. G. (2003). Phthalates, alkylphenols, pesticides, polybrominated diphenyl ethers, and other endocrine-disrupting compounds in indoor air and dust. Environ. Sci. and Technol. 37, 4543–4553. doi:10.1021/es0264596
Sati, P. C., Khaliq, F., Vaney, N., Ahmed, T., Tripathi, A. K., and Banerjee, B. D. (2011). Pulmonary function and oxidative stress in workers exposed to styrene in plastic factory: occupational hazards in Styrene-exposed plastic factory workers. Hum. and Exp. Toxicol. 30, 1743–1750. doi:10.1177/0960327111401436
Seltenrich, N. (2015). New link in the food chain? Marine plastic pollution and seafood safety. Environ. Health Perspect. 123, A34–A41. doi:10.1289/ehp.123-A34
Şenocak, E., and Arpaci, İ. (2023). A bibliometric analysis on nanoscience and nanotechnology education research. Turk. Kim. Dernegi Derg. Kısım C. Kim. Egitimi 8, 1–30. doi:10.37995/jotcsc.1202851
Shayegan, Z., Lee, C.-S., and Haghighat, F. (2018). TiO2 photocatalyst for removal of volatile organic compounds in gas phase – a review. Chem. Eng. J. 334, 2408–2439. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2017.09.153
Shi, L., Xue, J. Q., Xiao, W., Wang, P., Long, M. Y., and Bi, Q. (2022). Efficient degradation of VOCs using semi-coke activated carbon loaded ternary Z-scheme heterojunction photocatalyst BiVO4-BiPO4-g-C3N4 under visible light irradiation. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 24, 22987–22997. doi:10.1039/d2cp03606a
Sleiman, M., Conchon, P., Ferronato, C., and Chovelon, J.-M. (2009). Photocatalytic oxidation of toluene at indoor air levels (ppbv): towards a better assessment of conversion, reaction intermediates and mineralization. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 86, 159–165. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2008.08.003
Song, B. Y., Wang, Z. C., Ma, W., Zhou, W. S., Tang, Q., Bao, X. L., et al. (2024). Photocatalytic oxidation mechanism of isoprene over titanium oxide by UV-Vis lights. J. Catal. 430, 115362. doi:10.1016/j.jcat.2024.115362
Song, S. N., Zhang, S. Y., Zhang, X. L., Verma, P., and Wen, M. C. (2020). Advances in catalytic oxidation of volatile organic compounds over Pd-supported catalysts: recent trends and challenges. Front. Mater. 7. doi:10.3389/fmats.2020.595667
Songur, A., Ozen, O. A., and Sarsilmaz, M. (2010). The toxic effects of formaldehyde on the nervous system, Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 203, 105–118. doi:10.1007/978-1-4419-1352-4_3
Suárez, S., Coronado, J. M., Portela, R., Martín, J. C., Yates, M., Avila, P., et al. (2008). On the preparation of TiO2−Sepiolite hybrid materials for the photocatalytic degradation of TCE: influence of TiO2 distribution in the mineralization. Environ. Sci. and Technol. 42, 5892–5896. doi:10.1021/es703257w
Sui, Y., Lu, D., Zhu, X., Guan, J., Li, F., Shen, J., et al. (2024). Insight into recycling spent power ternary cathode materials: towards preparation of Mn-based catalyst for efficient toluene removal. Surfaces Interfaces 46, 104086. doi:10.1016/j.surfin.2024.104086
Sun, X. J., Gu, X. L., Xu, W. T., Chen, W. J., Xia, Q. B., Pan, X. Y., et al. (2019). Novel hierarchical Fe(III)-Doped Cu-MOFs with enhanced adsorption of benzene vapor. Front. Chem. 7, 652. doi:10.3389/fchem.2019.00652
Tan, H. C., Chen, D. Y., Li, N. J., Xu, Q. F., Li, H., He, J. H., et al. (2019). Platinum-supported zirconia nanotube arrays supported on graphene aerogels modified with metal-organic frameworks: adsorption and oxidation of formaldehyde at room temperature. Chemistry-a Eur. J. 25, 16718–16724. doi:10.1002/chem.201904426
van Eck, N. J., and Waltman, L. (2010). Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics 84, 523–538. doi:10.1007/s11192-009-0146-3
Wang, D. W., Li, Z. W., Zhou, J., Fang, H., He, X., Jena, P. R., et al. (2018). Simultaneous detection and removal of formaldehyde at room temperature: janus Au@ZnO@ZIF-8 nanoparticles. Nano-Micro Lett. 10, 4. doi:10.1007/s40820-017-0158-0
Wang, L., Tang, M., Jiang, H., Dai, J., Cheng, R., Luo, B., et al. (2024). Sustainable, efficient, and synergistic photocatalytic degradation toward organic dyes and formaldehyde gas via Cu2O NPs@wood. J. Environ. Manag. 351, 119676. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.119676
Wang, S., Ang, H. M., and Tade, M. O. (2007). Volatile organic compounds in indoor environment and photocatalytic oxidation: state of the art. Environ. Int. 33, 694–705. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2007.02.011
Wang, X., Wu, L. K., Wang, Z. W., Feng, Y., Liu, Y. X., Dai, H. X., et al. (2023). Photothermal synergistic catalytic oxidation of ethyl acetate over MOFs-derived mesoporous N-TiO2 supported Pd catalysts. Appl. Catal. B-Environmental 322, 122075. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2022.122075
Wang, Y., Voliotis, A., Shao, Y. Q., Zong, T. M., Meng, X. X. Y., Du, M., et al. (2021). Phase state of secondary organic aerosol in chamber photo-oxidation of mixed precursors. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 21, 11303–11316. doi:10.5194/acp-21-11303-2021
Xu, X. Y., Su, Y. H., Dong, Y. P., Luo, X., Wang, S. H., Zhou, W. Y., et al. (2022). Designing and fabricating a CdS QDs/Bi2MoO6 monolayer S-scheme heterojunction for highly efficient photocatalytic C2H4 degradation under visible light. J. Hazard. Mater. 424, 127685. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127685
Xu, Y., Qu, Z. P., Ren, Y. W., and Dong, C. (2021). Enhancement of toluene oxidation performance over Cu-Mn composite oxides by regulating oxygen vacancy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 560, 149983. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.149983
Yang, J., Li, L., Fu, F., Xu, H., Da, K., Cao, S. B., et al. (2023b). Construction of Z-scheme Ag/AgCl/Bi2WO6 photocatalysts with enhanced visible-light photocatalytic performance for gaseous toluene degradation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 610, 155598. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2022.155598
Yang, J., Yang, L., Fang, M., Li, L., Fu, F., Xu, H., et al. (2023a). A compact Z-scheme heterojunction of BiOCl/Bi2WO6 for efficiently photocatalytic degradation of gaseous toluene. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 631, 44–54. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2022.11.023
Yao, P. Z., Liu, H. L., Wang, D. T., Chen, J. Y., Li, G. Y., and An, T. C. (2018). Enhanced visible-light photocatalytic activity to volatile organic compounds degradation and deactivation resistance mechanism of titania confined inside a metal-organic framework. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 522, 174–182. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2018.03.075
Ying, T. T., Liu, W., Yang, L. X., Zhang, S. Q., Wu, Z. Y., Li, J. Y., et al. (2024). S-scheme construction boosts highly active self-supporting CeO2/Cu2O photocatalyst for efficient degradation of indoor VOCs. Sep. Purif. Technol. 330, 125272. doi:10.1016/j.seppur.2023.125272
Yoon, H. I., Hong, Y. C., Cho, S. H., Kim, H., Kim, Y. H., Sohn, J. R., et al. (2010). Exposure to volatile organic compounds and loss of pulmonary function in the elderly. Eur. Respir. J. 36, 1270–1276. doi:10.1183/09031936.00153509
Yu, X., Hu, Y., Luan, X. Q., Shah, S. J., Liu, L. M., Li, C. H., et al. (2023). Microwave-assisted construction of MXene/MOF aerogel via N-metal bonds for efficient photodegradation of vapor acetone under high humidity. Chem. Eng. J. 476, 146878. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2023.146878
Zhang, J. H., Hu, Y., Qin, J. X., Yang, Z. X., and Fu, M. L. (2020). TiO2-UiO-66-NH2 nanocomposites as efficient photocatalysts for the oxidation of VOCs. Chem. Eng. J. 385, 123814. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2019.123814
Zhang, X., Xiang, W., Miao, X., Li, F., Qi, G., Cao, C., et al. (2022a). Microwave biochars produced with activated carbon catalyst: characterization and sorption of volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Sci. Total Environ. 827, 153996. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153996
Zhang, X. D., Yue, K., Rao, R. Z., Chen, J. F., Liu, Q., Yang, Y., et al. (2022c). Synthesis of acidic MIL-125 from plastic waste: significant contribution of N orbital for efficient photocatalytic degradation of chlorobenzene and toluene. Appl. Catal. B-Environmental 310, 121300. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2022.121300
Zhang, Z., Wu, X., Liu, H., Huang, X., Chen, Q., Guo, X., et al. (2023). A systematic review of microplastics in the environment: sampling, separation, characterization and coexistence mechanisms with pollutants. Sci. Total Environ. 859, 160151. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.160151
Zhang, Z., Wu, X., Zhang, J., and Huang, X. (2022b). Distribution and migration characteristics of microplastics in farmland soils, surface water and sediments in Caohai Lake, southwestern plateau of China. J. Clean. Prod. 366, 132912. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.132912
Zhao, C., Wang, Z. H., Chen, X., Chu, H. Y., Fu, H. F., and Wang, C. C. (2020). Robust photocatalytic benzene degradation using mesoporous disk-like N-TiO2 derived from MIL-125(Ti). Chin. J. Catal. 41, 1186–1197. doi:10.1016/s1872-2067(19)63516-3
Zhao, J., and Yang, X. (2003). Photocatalytic oxidation for indoor air purification: a literature review. Build. Environ. 38, 645–654. doi:10.1016/S0360-1323(02)00212-3
Zhong, L., Haghighat, F., Blondeau, P., and Kozinski, J. (2010). Modeling and physical interpretation of photocatalytic oxidation efficiency in indoor air applications. Build. Environ. 45, 2689–2697. doi:10.1016/j.buildenv.2010.05.029
Zhou, H., Wang, Y., Wu, J., Zhou, W., Qi, Y., Liu, Q., et al. (2023). Enhanced photocatalytic reduction of CO2 using a novel 2D/0D SnS2/CeO2 binary photocatalyst with Z-scheme heterojunction and oxygen vacancy. J. CO2 Util. 76, 102591. doi:10.1016/j.jcou.2023.102591
Zhou, S., He, R. H., Pei, J. C., Liu, W. P., Huang, Z. H., Liu, X. G., et al. (2022). Self-Regulating solar steam generators enable volatile organic compound removal through in situ H2O2 generation. Environ. Sci. and Technol. 56, 10474–10482. doi:10.1021/acs.est.2c02067
Keywords: volatile organic compounds, photocatalytic oxidation, advanced photocatalysts, software, bibliometric analysis
Citation: Zhu X, Sui Y, Li X, Guan J, Zhang X, Zhang G and Guo Y (2024) Bibliometric analysis of photocatalytic oxidation of volatile organic compounds from 1998 to 2023. Front. Environ. Sci. 12:1482766. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2024.1482766
Received: 18 August 2024; Accepted: 09 October 2024;
Published: 30 October 2024.
Edited by:
Nnanake-Abasi O. Offiong, Topfaith University, NigeriaReviewed by:
Fei He, Korea Institute of Energy Technology, Republic of KoreaShreya Singh, Cornell University, United States
Copyright © 2024 Zhu, Sui, Li, Guan, Zhang, Zhang and Guo. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiaojiao Zhang, eGp6aGFuZ0Bzc3B1LmVkdS5jbg==; Yaoguang Guo, eWdndW9Ac3NwdS5lZHUuY24=
 Xinjie Zhu
Xinjie Zhu Yifan Sui
Yifan Sui Xiuli Li1
Xiuli Li1 Yaoguang Guo
Yaoguang Guo