- 1School of Finance and Business, Zhenjiang College, Zhenjiang, China
- 2Department of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering, University of Calgary, Calgary, AB, Canada
- 3School of Management, Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang, China
- 4Jingjiang College, Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang, China
Collaborative environmental governance (CEG) is increasingly advocated to address the environmental risk issues in the integrated development of urban agglomerations. Constructing an effective CEG network from the perspective of interdependent multilevel network plays a vital role in promoting the environmental governance of urban agglomerations. To investigate the structure characteristics and formation mechanism of CEG network, this paper takes the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration as the research area, and employes the social network analysis and Exponential Random Graph Model (ERGM) methods to analyze the CEG network, which consists of the collaborative network of cities, relationship network of topics, and affiliation network connecting cities to topics. Research results show that the CEG level in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration continues to improve, while the CEG network is still not in a tightly connected state. For the collaborative network of cities, it presents the small world characteristics and forms a cooperative trend of “central-subcentral-peripheral city.“For the relationship network of topics, the evolution of environmental governance topics is characterized by “from aspect to point.” For the affiliation network connecting cities to topics, as the diversity of environmental governance topics increases among cities, cities within the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration tend to share the similar topics. In addition, the interactive triangular structures, star structures, open triangular structures and closed triangular structures in the network can promote the formation of new cooperative relationships in CEG network.
1 Introduction
Reform and Opening Up have dramatically facilitated the process of industrialization and urbanization in China, which leads to the rising pollution problems (Duan et al., 2020). Chinese governments have attached great importance to environmental governance to achieve the sustainable and healthy development of economy. Environmental governance refers to the regulatory process that influence environmental management actions and results through different stakeholders (Candace, 2016). Due to the indivisibility of regional environment and the diffusion of environmental pollution, the traditional governance mode where a single government controls the local pollution does not play a significant role in environmental governance. Since the governance theory advocates multi-center governance and emphasizes cooperation (Mason et al., 2007; Sun and Wen, 2018), it is necessary to overcome the administrative boundaries and establish a collaborative governance mechanism with high participation of cities with respect to the environmental governance (Gunningham, 2009; Ulibarri, 2015).
Urban agglomeration is a highly developed spatial form of integrated cities (Fang and Yu, 2017). In 2006, China proposed the urban agglomeration as the main form of urbanization in the 11th Five-Year Plan. The Government Work Report in 2015 has emphasized the importance of constructing urban agglomeration for the regional harmonious development. In 2018, the Communist Party of China and the state council placed the construction of urban agglomeration to the national regional strategy. Currently, urban agglomerations in China have accounted for 22% of the total land area, 79% of the total economic output and 49% of the total population (Han et al., 2019). Urban agglomeration is characterized by strong radiation effect and plays a vital role in promoting the development of cities within the urban agglomeration. The spatial spillover and transferability of environmental pollution enable the urban agglomeration to become an important supporter and subject of environmental governance (Xu et al., 2020). Hence, considering the mobile and trans-regional characteristics of ecological pollution in urban agglomerations (Zhang G. et al., 2022), collaborative environmental governance (CEG) is increasingly advocated to address the environmental risk issues in the integrated development of urban agglomerations.
Since multiple governance subjects and stakeholders are involved in CEG of the urban agglomeration, together with the interconnected environmental issues across the cities, CEG of the urban agglomeration presents a complex network structure rather than a simple chain form. Figuring out the structure characteristics and formation mechanism of CEG network is conducive to the overall optimization of CEG network and the environment improvement in urban agglomerations, which contributes to a sustainable path for the green development. The Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration is the fifth-largest urban agglomeration in the world, and is one of the urban agglomerations with the most dynamic economy and the strongest innovation capacity in China (Miao and Sun, 2020). On November 2018, the integrated development of the Yangtze River Delta has become a national strategy. With the advent of great economic accomplishments in the Yangtze River Delta, CEG has become one of the important ways to realize the integrated development of the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration. Therefore, this study selects the Yangtze River Delta as the research area, and investigates the CEG network of the urban agglomeration.
The existing research on regional CEG mainly focuses on three aspects, which are summarizing the current development status of CEG (Fu et al., 2023; Avoyan, 2023), exploring the governance modes of CEG (Olvera-Garcia and Nei, 2020; Koebele, 2020), and evaluating the effect of CEG (Ge et al., 2023; Ulibarri et al., 2023), respectively. However, the research on CEG network of urban agglomerations has rarely been carried out before. The relevant literature just place emphasis on the actor network of CEG. For example, Wu and Feng (2021) take 11 cities in Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area (GBA) as the research area, and analyze the structure, internal characteristics and evolution relationship of the actor network of CEG with UCINET analysis. Yu and Zou (2022) construct an actor network of the water environmental governance cooperation in the Yangtze River Delta and propose that the constructed actor network is currently at the initial stage. In addition, many researchers have investigated the actor network of regional collaboration in different fields, including the studies of network structure and dynamic evolution of network, etc., which provides the reference for the current research on CEG network of the urban agglomeration. For example, Zhang w. et al. (2022) construct the public health emergency collaboration network (ECN) based on the joint publishing subject of emergency policies to investigate the evolution of ECN and optimize the emergency information collaboration. Pan et al., 2022 focus on the collaborative innovation network, and compare the network structure and spatial characteristics of synergy innovation among three urban agglomerations in China. Xie, Tai and Li (2022) take the Belt and Road as the research object, and explore the characteristics of transnational patent cooperation network and network evolution in the field of digital communication with the social network analysis, providing strategies for strengthening transnational patent cooperation among regions in the Belt and Road. Liu et al., 2021 apply the social network analysis to analyze the structure of medical service cooperation network in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration, and measure the structural attributes of the cooperation network.
The previous studies yield valuable information and insights for investigating the CEG network of the urban agglomeration. Nevertheless, there are two aspects that can be substantially improved. Firstly, the existing literature on regional CEG mainly focuses on the analysis of current situation, governance modes, and governance effects with the application of qualitative methods. It is generally believed that the inter-regional cooperation within the urban agglomerations has a positive effect on the environmental governance. However, there is a gap that exists in the related literature regarding the quantitative and empirical analysis methodologies applied to CEG in urban agglomerations. In particular, the systematic research on the overall structure, evolutionary logic and formation mechanism of CEG network in the urban agglomeration is very lacking. Secondly, existing literature on CEG network and the collaborative network in other fields place emphasis on the single-level network composed of actors, ignoring the impact of elements other than actors on the effectiveness of collaboration. Specifically, the effect of CEG in the urban agglomerations does not solely depend on the cooperation between governance actors, which are the cities within the urban agglomeration. The specific topics of environmental governance are also the crucial factors influencing the results of CEG in the urban agglomerations. The network of cities reflects the collaborations between environmental governance actors, while the network of topics explains the relationships of environmental governance issues. The network of cities in conjunction with the network of topics jointly determine the results of CEG in urban agglomerations.
In sum, research on the CEG network in urban agglomerations should not be confined to the cooperation between cities. Through incorporating the relationships between environmental governance topics, and taking into account the affiliation relationships between environmental governance cities and topics, together with the collaborative relationships between cities, the structural characteristics of CEG network in urban agglomerations can be explained comprehensively. Specifically, this research takes the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration as the research area, and focuses on the questions as follow:
(1) What entities are included in the CEG network of the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration?
(2) What are the structural characteristics of the CEG network of the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration?
(3) What is the formation mechanism of the CEG network of the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration? And which structures can promote the formation of new cooperative relationships in CEG network?
In view of above questions, drawing on the multilevel network structure proposed by Wang et al. (2013), the current paper integrates the collaborative network of cities, relationship network of topics, and affiliation network connecting cities to topics, to construct an interdependent multilevel network of CEG in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration. Firstly, we take the multilevel network of CEG in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration as the research object, and figure out the structure characteristics of the CEG network from multiple dimensions based on the social network analysis method. It is worth investigating the cooperative relationships between cities within the urban agglomeration, co-occurrence relationships between environmental governance topics, and the affiliation relationships between cities and topics, to clarify the structural characteristics of the CEG network in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration. Secondly, this paper strives to analyze the formation mechanism of the multilevel network of CEG, aiming to further promote the improvement of CEG network and collaborative governance efficiency. Given the advantages of Exponential Random Graph Model (ERGM) in analyzing the formation mechanism of network (Van der Pol, 2019), the current research employs the ERGM method to investigate the effect of network structure and node or edge-level attributes on the connection probability between nodes in the CEG network. From the perspective of interdependent multilevel network, we analyze the structural characteristics and formation mechanism of CEG network in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration, facilitating the optimization of CEG network in urban agglomerations and sustainable development of regional economic.
The contribution of this study is reflected in the following three aspects.
(1) From the perspective of interdependent multilevel network, the current research constructs the CEG network in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration, which includes collaborative network of cities, relationship network of topics, and affiliation network connecting cities to topics.
(2) With the application of social network analysis methods, the structural characteristics of CEG network in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration are analyzed. Additionally, the formation mechanism of the multilevel CEG network is obtained through employing ERGM method.
(3) In terms of constructing the network, the current research adopts the text mining technology to construct the relationship network of topics. To our best of knowledge, this paper is the first attempt to combine social network analysis, ERGM method and text mining technology, which offers insights for network analysis.
This paper is organized as follows. Framework of network, data collection, and research methodologies are given in Section 2. Section 3 is dedicated to constructing the multilevel CEG networks and analyzing the networks through social network analysis and ERGM methods. Section 4 presents the research conclusions and policy implications.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Framework of network
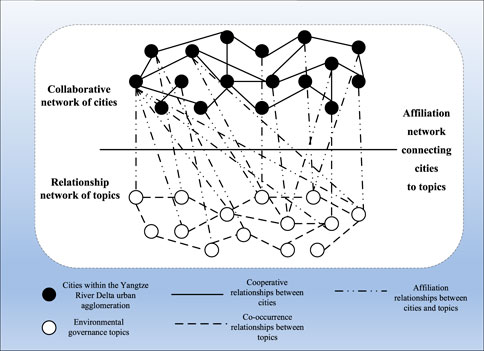
The interdependent multilevel network consists of multiple single-layer networks, overcoming the limitation in the single-layer network where nodes and edges must be homogeneous. Therefore, the current research constructs an interdependent multilevel CEG network, which can reflect the cooperative relationships between cities, co-occurrence relationships between environmental governance topics, and the affiliation relationships between cities and topics in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration. Based on the constructed network, a comprehensive analysis of the overall structure, internal characteristics, and evolution of the CEG network can be conducted. The framework of the multilevel CEG network is illustrated in Figure 1.
The specific steps for constructing the multilevel CEG network in the urban agglomeration are as follows:
Step 1: According to the theory of public goods and spillover effect (Lin et al., 2023; Huhe, et al., 2022), it can be learned that the environmental pollution exhibits distinct negative externalities, necessitating trans-regional collaborative governance among governments. Scholars and practitioners agree that collaboration among governments play a vital role in environmental governance. The collaborative matrix of cities is firstly constructed based on whether there are joint documents or joint actions between two local governments regarding the environmental governance issues. Then taking the cities within the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration as the nodes, and the collaboration relationships between two cities as the edges, a collaborative network of cities is finally built.
Step 2: In addition to the intergovernmental collaboration network, scholars regarding the social network analysis also pay attention to other network construction, such as knowledge network (Zhao et al., 2022; Chandra and Dong, 2022), patent network (Wang, et al., 2023; Akçomak et al., 2023) and topic network (Wang and Zhang, 2023). Previous studies have proved the significance of the role played by policy collaboration networks. Recently, the value of policy topic networks has gradually been revealed (Pan et al., 2018). According to the social network theory and complex network theory, topic network can reflect the interaction relationship between two topic nodes. Firstly, keywords with regards to the environmental governance are extracted from the relevant policy texts to serve as the topic nodes in the network. Secondly, With the application of word2vec algorithm, the associations between keywords are calculated, and the edges can be constructed between two keywords with the association greater than 0.8. Hence, a relationship network of topics regarding the environmental governance obtained.
Step 3: With reference to the research of Caschili, Medda and Wilson (2015) and Ahangar, Sullivan and Nurre (2020), we explore the affiliation relationship between environmental governance topics and cities from the perspective of interdependent multilayer network. The affiliation network connecting cities to topics is constructed as follows. Firstly, both the cities within the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration and the topics of environmental governance are taken as network nodes. Then the edges of the network are constructed through judging whether there is an affiliation relationship between the cities and topics. Thus, the affiliation network connecting cities to topics is finally obtained.
In sum, the multilevel CEG network in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration which consists of the collaborative network of cities, relationship network of topics, and affiliation network connecting cities to topics, is constructed.
2.2 Data collection
Based on the multilevel CEG network in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration, we will collect the data according to three sub-networks, which are the collaborative network of cities, relationship network of topics, and affiliation network connecting cities to topics.
2.2.1 Collaborative network of cities
In terms of the collaborative network of cities, we take 27 cities in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration as network nodes, which are Shanghai, Nanjing, Hangzhou, Suzhou, Yangzhou, Jiaxing, Wuxi, Ningbo, Shaoxing, Changzhou, Huzhou, Zhenjiang, Nantong, Yancheng, Ma’anshan, Hefei, Jinhua, Zhoushan, Wenzhou, Wuhu, Taizhou, Taizhou, Xuancheng, Chuzhou, Tongling, Anqing, Chizhou. The data collection method, primarily based on document retrieving and web searches, is employed to extract information about CEG among the 27 cities, and the collaborative information can serve as the basis for determining whether two nodes are connected. Specifically, the collection of collaborative information can be conducted from the following two aspects: firstly, collaborative information between governments can be retrieved from the legal regulations, policy texts, and other documents related to environmental governance on the official government websites of 27 cities. Secondly, taking authoritative news portals, China Environmental News, Ecological Journal, and city daily newspaper as the search objects and data sources, we conduct the information retrieval with the keywords of environmental governance, ecology, green, etc. along with the keywords of 27 city names, and the data pertaining to CEG among 27 cities in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration is extracted. In 2020, the State Council officially approved the implementation of the ”Regional Plan for the Yangtze River Delta Region”, which clarified the division and layout of the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration. The issue of the document indicates that the development of the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration has been elevated to a national strategy. Hence, the data collection period for the collaborative network of cities spans from 2010 to 2019.
To ensure the reliability and validity of the data, the data collection is carried out by two independent groups, and each group consists of one PhD candidate and one graduate. Through judging whether the policy texts, news reports or specific actions involve CEG among two cities, a total of 112 policy texts and collaborative actions are collected. Then the pre-processing of data is performed, and the duplicate policy texts and reports, or actions that do not involve the CEG are removed. After the pre-processing, 61 policy texts and 41 collaborative actions pertaining to CEG in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration are finally generated. According to the collected data, if there are joint documents or collaborative actions on environmental governance between two cities, the value of the cooperation relationship between two cities is assigned to 1. If there is no cooperation relationship established between two cities in terms of environmental governance, the value is assigned to 0. Thus, a collaborative matrix of cities is obtained, which can be employed to construct a collaborative network of cities in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration.
2.2.2 Relationship network of topics
In terms of relationship network of topics, we use text mining technology to collect data regarding environmental governance and construct the network. Text mining combines information retrieval and machine learning technology (Jung and Lee, 2020). Its main purpose is extracting information from large amounts of text data to satisfy users’ needs. Given that policy texts of environmental governance are lengthy and complex, relying solely on human labor to peruse such texts and extract the topics of environmental governance comes with a huge workload and is susceptible to subjectivity. Text mining technology can overcome these deficiencies, and assist in the collection of comprehensive topics and the construction of relationship network of topics. Therefore, the specific process of data collection and processing with the application of text mining technology is as follows:
(1) Constructing the original corpus to be mined. The annual National Conference on Ecological and Environmental Protection is held to outline key tasks of environmental governance for the year, reflecting the central government’s core ideas on the environmental governance. Additionally, proposals related to environmental protection from the annual Two Sessions (National People’s Congress and Chinese People’s Political Consultative Conference) also highlight key areas for environmental governance. Therefore, the content of the National Ecological and Environmental Protection Work Conference and the ecological and environmental protection proposals from the Two Sessions from 2010 to 2019 are separately incorporated into the corpus, aiming to extract the key topics with regards of environmental governance for each year by means of text mining.
(2) Conducting the text pre-processing. Text preprocessing is the first step in text mining. This study utilizes Python and the third-party library jieba to perform word segmentation and generate word frequency statistics for the texts in corpus. Firstly, Harbin Institute of Technology’s stopword dictionary is loaded to filter the common Chinese stopwords from the original corpus, which constitute large proportion in texts. Secondly, to improve the accuracy of text mining and eliminate the interference of irrelevant words that commonly used in the environmental governance field, we incorporate the irrelevant words such as “Development,” “Implementation,” “Country,” etc. Into the self-defined stopwords dictionary. Thirdly, we construct a customized dictionary pertaining to environmental governance to facilitate the efficiency of subsequent word frequency statistics. Finally, the precise mode of jieba utility is applied to segment words.
(3) Extracting keywords regarding environmental governance. The current research uses Term Frequency-Inverse Document Frequency (TF-IDF) algorithm to extract keywords from the constructed original corpus regarding the environmental governance. Compared to word frequency statistics, TF-IDF value can better reveal the distinction and importance of the words (Wan et al., 2024). Firstly, jieba. analysis library is imported in Python. Then, the TF-IDF value of each term can be calculated through applying the command of jieba. analyse.extract_tags. As a result of the above operations, the top 30 keywords sorted by TF-IDF value can be obtained, and these keywords are taken as the nodes of relationship network of topics.
(4) Constructing the relationship network of topics. Based on the extracted topic keywords, the word2vec algorithm is applied to calculate the correlation between two topic keywords. Pairs of nodes, that is, two topic keywords with a correlation greater than 0.8, are connected with edges (Zhu and Zhang, 2020). We firstly import Word2Vec from the genism library. Then the Word2Vec model can be trained and applied to calculate the correlation between two terms. Thus, the relationship networks of topics from 2010 to 2019 can be constructed.
2.2.3 Affiliation network connecting cities to topics
The relationship networks of topics from 2010 to 2019 represents the key issues in the field of environmental governance at the national level, while the affiliation network connecting cities to topics can deeply explore the specific environmental governance activities in different cities. To construct the affiliation network connecting cities to topics, this study pairs the names of 27 cities with 30 topic keywords in each year, together with the theme of “Environmental governance” to serve as the retrieve keywords in the software PKULAW, aiming to collect the policy texts and legal documents pertaining to the environmental governance in different cities. The 27 cities in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration and extracted topic keywords are taken as the nodes. Then affiliation networks connecting cities to topics from 2010 to 2019 can be constructed by judging whether the city has issued the environmental governance policies with regards to the corresponding topics.
2.3 Research methodologies
2.3.1 Social network analysis
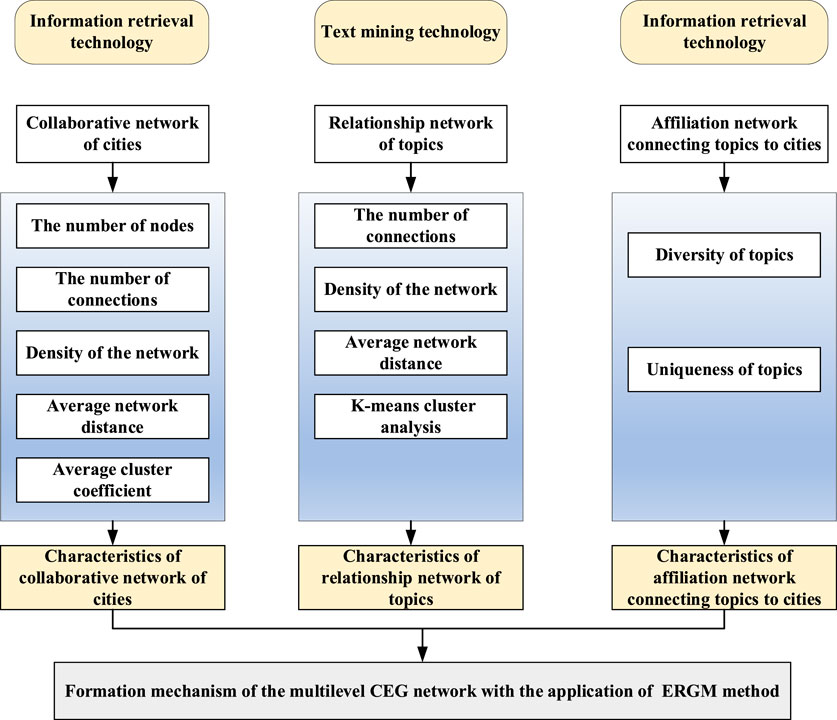
The current research investigates the CEG network in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration from the perspective of interdependent multilevel network. As shown in Figure 1, the CEG network is constructed by stacking different network layers to form a multilevel network. Hence, the traditional social network analysis method is still applicable for analyzing the interdependent multilevel network of CEG. Social network analysis is defined as a perspective that “includes theories, models, and applications that are expressed in terms of relationship concepts or process (Kothari et al., 2014).” Different from the traditional individualistic social theory, social network analysis method prioritizes the relationships between actors and focuses on the relational data. It is employed to characterize the structures of networks, where networks are composed of a variety of individual units that are linked by ties to one another (Hayat et al., 2017). Hence, social network analysis is an effective method for measuring and analyzing the characteristics of collaborative network of cities in the CEG network. It can not only clearly describe the overall structural features of the collaborative network of cities, but also can reveal the microstructure and internal relationships of the network.
For the collaborative network of cities in the CEG network, we select the number of nodes, the number of connections, the density of the network, the average network distance between nodes, and the average cluster coefficient (Leng et al., 2021; Parnell and Robinson, 2018) to depict the overall structure of the network. In terms of measuring the individual characteristics of one node in the collaborative network of cities, centrality is used to reflect the importance of one node within the entire network (Tanhapour et al., 2022). The current paper adopts three indicators which are degree centrality, betweenness centrality, and closeness centrality (Lu et al., 2010; Chong et al., 2017), to measure the position and role of each node in the collaborative network of cities.
For the relationship network of topics in the CEG network, the number of connections, the density of the network, the average network distance between nodes are selected as indicators to measure the overall structure of the relationship network of topics. Additionally, topic keywords in each year can be categorized into several clusters through K-means cluster analysis. K-means cluster analysis is an unsupervised machine learning method that does not require pre-training or the pre-categorization (Li and Wang, 2022). It can be adopted to characterize the clustering degree of the topic keywords, and further analyze the key focus areas in environmental governance for that year.
To describe the structural characteristics of the affiliation network connecting cities to topics in the CEG network, and explore the specific efforts that various cities make in the field of environmental governance, the current paper adopts the diversity and uniqueness of topics as indicators to measure the structural characteristics and evolutionary logic of the affiliation network in the CEG network.
2.3.2 Exponential random graph models
In order to ascertain the motivations for the entities (nodes) to create links and identify the global network structure, a more in-depth analysis is required. Exponential random graph model (ERGM) has increasingly become one of primary statistical methods for analyzing the social networks (Wasserman and Faust, 1994; Stewart et al., 2019). The dominant aim of an ERGM is to identify the process that influences link connection and figure out the formation mechanism of a network. ERGM treats the network structure as endogenous (Stewart et al., 2019). It is fundamentally a modified logistic regression that allows the connections between nodes to take into account the presence of other connections within the network, as well as other variables.
The researchers in the ERGM academia have incorporated various explanatory variables into the model that are hypothesized to explain the observed network, and the ERGM can provide the information pertaining to the statistical significance of the explanatory variables, much like a standard linear regression (Van der Pol, 2019). There are two types of explanatory variables in the ERGM, which are structural variables (endogenous variables) and node or edge-level variables (exogenous variables). ERGM method has been applied to a variety of fields, such as intellectual property protection network (Cao et al., 2019), collaborative innovation network (Guo and Xie, 2021), adolescent social network (Goodreau et al., 2009), political discussion network (Song, 2015), etc. The applications of ERGM in the field of CEG has rarely been carried out before. Hence, we adopt ERGM to further analyze the impact of network structure and node or edge-level variables on the probability of links creation in the CEG network, and investigate the formation mechanism of CEG network in urban agglomeration.
Generally, Equation 1 is the general formula for the ERGM.
Where
In sum, based on the perspective of interdependent multilevel network, this paper explores the structural characteristics and formation mechanism of CEG network in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration with the application of social network analysis and ERGM method. The overall research framework is illustrated as Figure 2.
3 Results and discussions
3.1 Collaborative network of cities
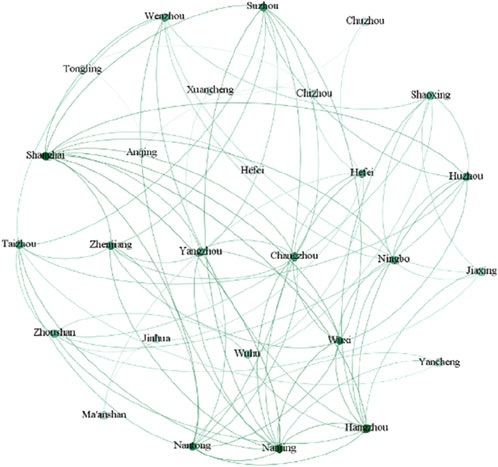
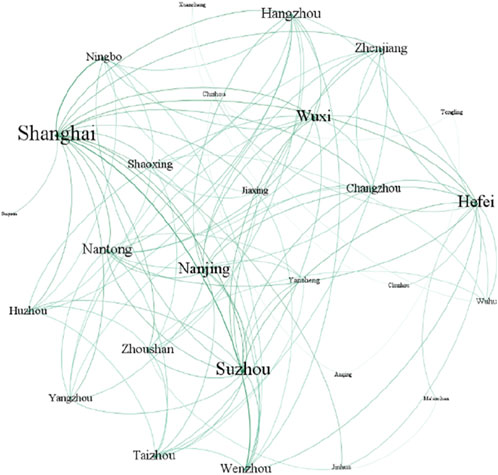
In accordance to the above data collection steps, the collaboration relationships between 27 cities in terms of environmental governance are achieved. Then the collaborative matrixes of cities from 2010 to 2019 are imported into the Gephi software, which leads to the construction of 10 collaborative networks of cities. The nodes in the network represents the cities within the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration, and the link connecting two nodes indicate that there is a cooperative relationship between cities in terms of CEG. The collaborative networks of cities in 2010 and 2019 are shown in Figures 3, 4.
3.1.1 Characteristic of network structure
Based on the constructed networks, Gephi software is employed to calculate various indicators which can reflect the overall structural characteristics of the collaborative network of cities. As introduced in the above section, five indicators are adopted. Specifically, the number of nodes represents the number of cities within the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration who participate in the CEG in that year. The larger value of the number of nodes indicates more cities are involved in CEG in that year. The number of connections reflects the number of links between nodes in the network. The greater value reflects that more cooperative relationships have been established among cities in terms of environmental governance. The density of the network and the average network distance between nodes can both be adopted to measure the cohesion of the overall network. The density of the network can reflect the closeness of relationships among nodes in the collaborative network of cities. It is equal to the ratio of the actual number of connections in the network to the total number of theoretical connections in the network. The greater the density of the network, the more frequent the connection among the nodes, the better the sustainability of the collaborative relationships between cities. The average network distance between nodes refers to the mean of the shortest path required to connect any two nodes in the network. It is an important indicator to measure the transmission efficiency and cohesion of the collaborative network of cities. The average cluster coefficient is the mean of the cluster coefficients of all nodes in the network. A node’s cluster coefficient is the ratio of its actual number of connections with its neighboring nodes to the theoretical connections with its neighboring nodes. The results of the indicators that measure the overall structural characteristics of the collaborative network of cities are listed in Table 1.
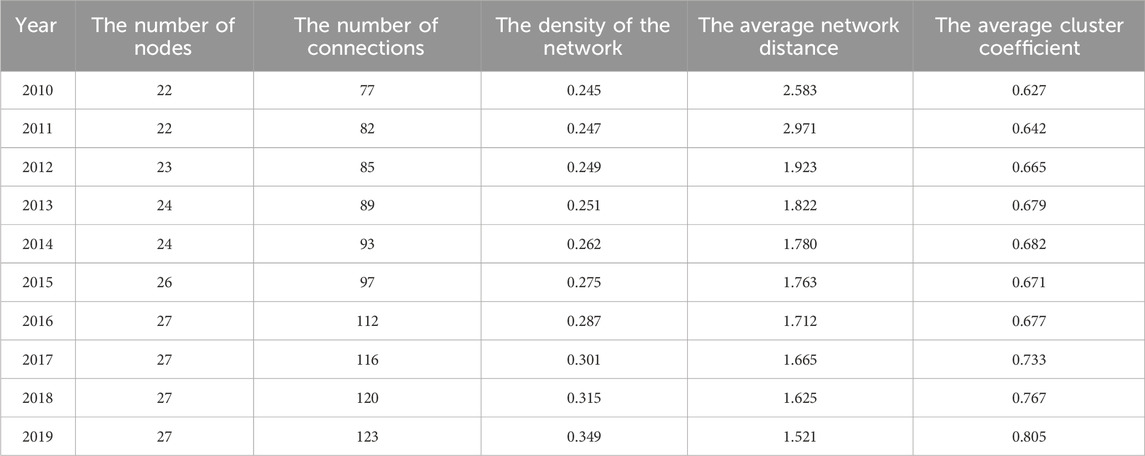
Table 1. Indicators for measuring the structural characteristics of the collaborative network of cities from 2010 to 2019.
As shown in Table 1, the number of nodes and the number of connections in the collaborative network of CEG in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration both continue to raise from 2010 to 2019. The results suggest that the cooperative relationships between cities within the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration are gradually established with regards to the environmental governance from 2010 to 2019, and the collaborative network of cities is expanding and becoming more stable. It is worth stating that overcoming the fragmented administrative boundaries and strengthening collaboration between cities have become one of the prominent ways to address the environmental pollution.
The density of the network characterizes the closeness of cooperation between cities in terms of CEG, and it can reflect the overall development level of the collaborative network of cities. Generally, a greater density of the collaborative network of cities indicates more interactions between cities. It can be learned from Table 1 that the density of the collaborative networks of cities regarding CEG within the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration shows an increasing trend annually. However, the density of the network in each year remains relatively low with a maximum value of only 0.349. The results indicate that the cooperation in terms of environmental governance among the cities of the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration is still not close and has not formed a mature cooperative relationship from an overall perspective. The results also reflect that, although the CEG in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration has improved, great efforts should be made to facilitate the further collaboration in environmental governance.
In the collaborative network of cities, the greater the average network distance, the more intermediate nodes are required for communication between nodes, which makes the information communication more difficult. As shown in Table 1, the average network distance of the collaborative network of cities is 2.583 in 2010 and 2.971 in 2011, respectively. It indicates that the during 2010–2011, the node cities in the CEG network of the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration have to pass through nearly three intermediate node cities on average to achieve cooperation, and the information transmission is inconvenient. From 2012 to 2019, the decreasing trend in the average network distance indicates that the accessibility between cities has improved in terms of environmental governance, facilitating the efficiency of information transmission and cooperation among cities within the network. Furthermore, the average clustering coefficient of the collaborative network remains between 0.627 and 0.805 from 2010 to 2019, which is relatively high. The high clustering coefficients of the networks suggest that the cities are relatively close-knit and clustered during this period. According to the social network theory, small world networks are characterized by the shorter average network distance and greater average clustering coefficient. In the collaborative network of cities in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration, the maximum average network distance is 2.917, and the maximum average clustering coefficient is 0.805, suggesting that the collaborative network of cities has the characteristics of small world.
3.1.2 Characteristic of individual node
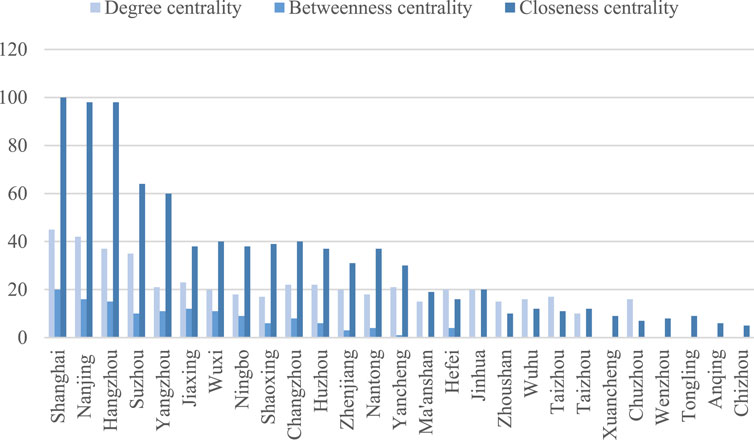
In terms of measuring individual characteristics of a certain node, several centrality indicators are adopted to reflect the position and role of node cities in the collaborative network of cities, which mainly includes degree centrality, betweenness centrality, and closeness centrality. The results of centrality indicators of cities within the network in 2010 and 2019 are shown in Figures 5, 6, respectively. It can be found that the centrality of each city generally shows an upward trend from 2010 to 2019. However, there are significant differences between cities in terms of the centrality indicators, forming a gradient distribution among cities and leading to a cooperative trend of “central-subcentral-peripheral city.”
Specifically, degree centrality is mainly used to explore the extent to which a city is at the central position of the collaborative network of cities. The greater the degree centrality of the city, the more resources of environmental governance the city has, and the greater its influence in the CEG among cities. The collaborative network of city tends to concentrate on a node city with a high degree centrality. It can be seen from Figures 5, 6 that the degree centrality of Shanghai, Nanjing, Hangzhou, and Suzhou is relatively high, indicating that these four cities are at the core position of the network and dominate the CEG in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration. Yangzhou, Jiaxing, Wuxi, Ningbo, Shaoxing, Changzhou, Nantong, Huzhou, Zhenjiang, Yancheng, and Hefei are located in the subcentral positions of the network. Cities such as Ma’anshan, Wuhu, Xuancheng, Chizhou, Tongling, etc. have low degree centrality and are in a peripheral position in the collaborative network of cities, indicating that they are not active in the environmental governance.
Betweenness centrality can be used to measure the position and power of a certain city. If the connection between other cities has to go through a city, the betweenness centrality of this city is high. The higher the value of betweenness centrality of a city, the more the city can control the interaction between other cites, and it is in the central position of the collaborative network and has greater power. Different from the degree centrality, betweenness centrality places emphasis on measuring a city’s ability to achieve information and resources. Hence, it can be learned from Figures 5, 6 that the betweenness centrality of Shanghai, Nanjing and Hangzhou is much greater than that of other cities, indicating that Shanghai, Nanjing and Hangzhou occupy a dominant position in the whole collaborative network of cities, and serve as crucial intermediaries for connecting various cities in CEG. The betweenness centrality of Suzhou, Jiaxing, Changzhou, Yangzhou, etc. Is slightly lower than that of Shanghai, Nanjing and Hangzhou, indicating that these cities are also important intermediaries in the collaborative network of cities. The betweenness centrality of the remaining cities are zero, thus these cities just play a supporting and auxiliary role in the collaborative network, and the cooperation with other cities in terms of CEG needs to be further improved.
Closeness centrality is adopted to measure the ability of a city not being controlled by other cities, reflecting the accessibility of the city in the collaborative network. If the distance between a certain city and all other cities in the collaborative network is very short, the city can be considered to have a high closeness centrality. In 2019, the closeness centrality of Shanghai, Hangzhou, and Nanjing reaches 100, significantly higher than other cities within the collaborative network. The results suggest that, as national central cities and provincial capitals, Shanghai, Nanjing and Hangzhou have much more synergistic associations with other cities, and higher efficiency in information transmission. The closeness centrality of Suzhou, Yangzhou, Shaoxing, Ningbo, etc. Is relatively high, indicating that they can quickly establish cooperation relationships with other cities. Due to the geographical limitations, the closeness centrality of Chizhou, Anqing, Tongling, etc. Is relatively low, resulting in their poor performance in resourcing sharing and cooperation efficiency in terms of CEG.
3.2 Relationship network of topics
The current paper constructs the relationship network of topics in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration with the application of text mining technology, investigating the key focus and evolution of the topics of environmental governance for each year. Taking the content of the National Ecological and Environmental Protection Work Conference and the ecological and environmental protection proposals in the Two Sessions from 2010 to 2019 as the corpus to be mined, we aim to extract the key topics about environmental governance in each year with TF-IDF algorithm. Then the correlation between two topic keywords can be calculated, and the links between two keywords with the correlation greater than 0.8 are established. Thus, the relationship networks of topics from 2010 to 2019 are constructed. To analyze the structural characteristics of the relationship network of topics in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration, we take the number of connections, the density of the network, and the average network distance as the indicators to measure the relationship network of topics from 2010 to 2019, and the results of indicators are listed in Table 2.
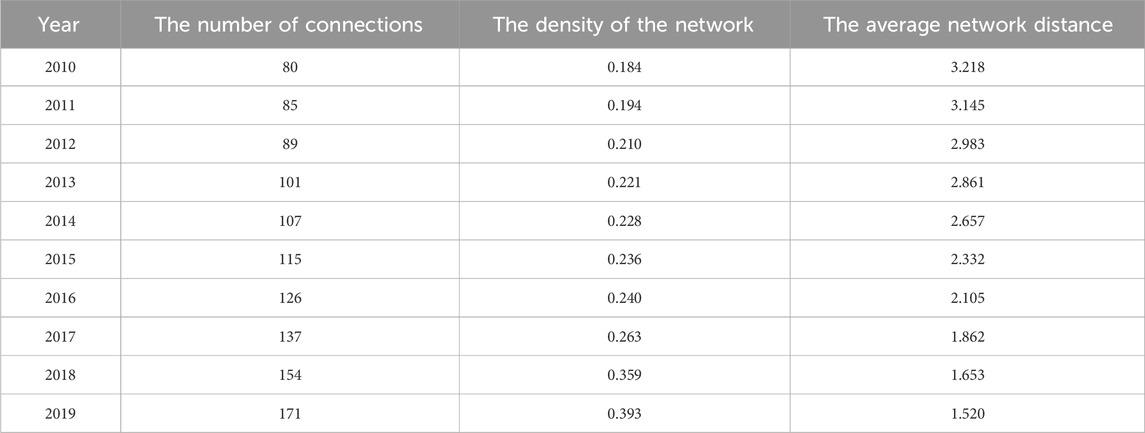
Table 2. Indicators for measuring the structural characteristics of the relationship network of topics from 2010 to 2019.
Since the current paper selects the top 30 keywords by TF-IDF value as the nodes of relationship network of topics, the number of the nodes, that is, the size of the network remains stable from 2010 to 2019. In addition, as shown in Table 2, the number of connections in the relationship network of topics increases from 80 to 171, indicating that the relationships of different topics about environmental governance is becoming closer and the combinations between different measures of environmental governance is more coordinated. The density of the relationship network of topics increases from 0.184 to 0.393, which shows an upward trend. However, the overall value of the density of network from 2010 to 2019 remains low, indicating that the relationship network of topics in terms of environmental governance is still a low-density network. The further configuration and integration of different topics will be beneficial for the environmental governance. The average network distance of the relationship network of topics shows a decreasing trend from 2010 to 2019. Therefore, the communication efficiency and the accessibility between topics of environmental governance improves constantly, but there is a great demand for further enhancement.
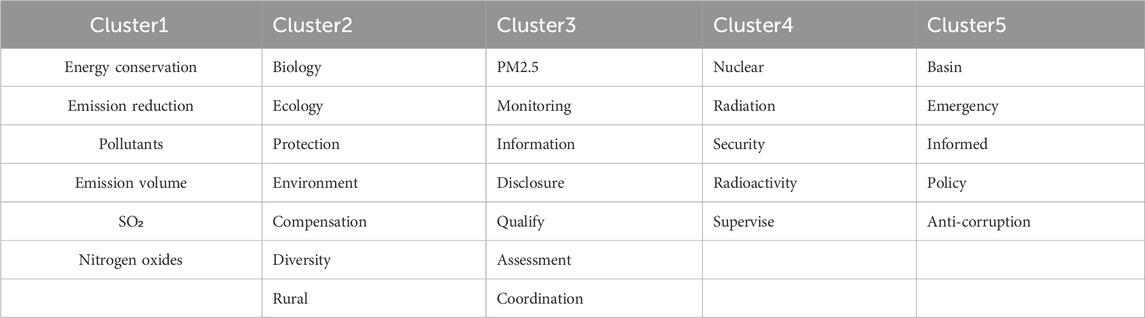
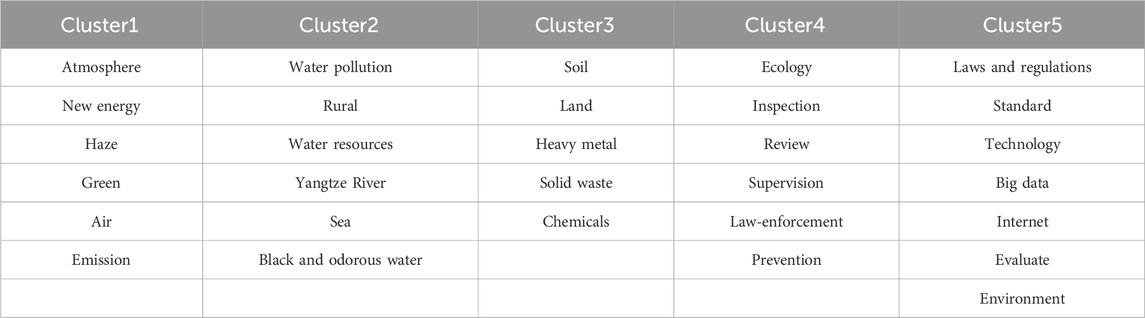
To clarify the cluster of topic keywords and further refine the theme of environmental governance in each year, the current paper adopts the K-means cluster analysis of the keywords in the relationship network of topics from 2010 to 2019. Due to the limitation of manuscript length, the current paper selects 2010 and 2019 as the representative years, and conduct the cluster analysis of topic keywords in the network of 2010 and 2019, aiming to figure out the evolution of environmental governance topics from 2010 to 2019. Specifically, the elbow method is firstly employed to determine the optimal number k of clusters. The core indicator of the elbow method is the sum of squares of errors (SSE) (Sinaga and Yang, 2020). When the value of k is close to the real number of clusters, the SSE will decrease to a much lesser extent, and its value tends to be flat with the continuous increase in k. Therefore, the graph depicting the relationship between SSE and k is elbow-shaped, and the k value that corresponds to the position of the elbow joint is the final number k of clusters in the K-means clustering analysis (Wang et al., 2019). With the help of Python software and the application of the elbow method, the number of clusters of topic keywords is five in both 2010 and 2019. Then, the K-means cluster analysis is adopted to cluster the topic keywords. Results of the K-means cluster analysis in 2010 and 2019 is listed is Tables 3, 4, respectively.
According to the clustering results of topic keywords in 2010 and 2019, it can be concluded that the evolution of environmental governance topics is characterized by optimization and integration, and the theme of environmental governance shows a development trend of “from aspect to point”. The specific explanation is as follows. As shown in Table 4, which is the clustering results of keywords in 2019, keywords in Cluster one include “atmosphere,” “haze,” “air,” etc. Hence, Cluster one is summarized as air pollution. Cluster two includes the keywords such as “water pollution,” “water resources,” “black and odorous water,” etc., thus Cluster two is classified as water resource pollution. Keywords such as “soil,” “land,” “heavy metal,” etc. are in the Cluster 3, which should be labelled as land pollution. The keywords in Cluster four include “inspection,” “review,” “supervision,” etc., thus Cluster four is categorized as inspection in environmental governance. Based on the keywords in Cluster 5, support in environmental governance is used to label Cluster 5. According to the keywords of relationship network of topics in 2010, which is listed in Table 3, Cluster one is summarized as pollution reduction, Cluster 2 as ecological protection, Cluster 3 as PM2.5 monitoring and information disclosure, Cluster 4 as regulation of nuclear and radiation, and the theme of Cluster five is not clearly defined. Through comparing the clustering results of topic keywords in the relationship network and the summarized theme of clusters in 2010 and 2019, it can be found that the themes of environmental governance in 2019 are more specific and detailed, clarifying the objects of environmental governance and emphasizing the inspection and law-enforcement of ecological protection. Improving the support and guarantee capabilities of environmental governance is also a crucial theme in 2019. However, the themes of environmental governance in 2010 are very broad, without specifying the particular areas of environmental governance or the concrete measures for environmental protection. Therefore, the evolution of environmental governance topics from 2010 to 2019 is characterized by optimization and integration, exhibiting a development pattern of “from aspect to point”.
3.3 Affiliation network connecting cities to topics
The collaborative network of cities in CEG network reflects the cooperation of 27 cities in terms of environmental governance, while the relationship network of topics in CEG network can clarify the configurations between different topics of environmental governance. Since the collaboration of cities and the relevant topics can jointly affect the results of CEG in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration, exploring the affiliation network connecting cities to topics and analyzing the specific environmental governance measures adopted by cities is of vital significance, which provides a comprehensive analysis of CEG network of Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration.
Through taking the environmental governance topics and cities in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration as the keywords, we can retrieve the relevant policies or laws with PUKLAW software, and determine whether a certain city has issued the environmental governance policies or laws pertaining to the topic keywords in a certain year. Then the affiliation networks connecting cities to topics from 2010 to 2019 are constructed by means of judging the affiliation relationships between cities and environmental governance topics. The results of indicators for measuring the structure of affiliation network connecting cities to topics are listed in Table 5.
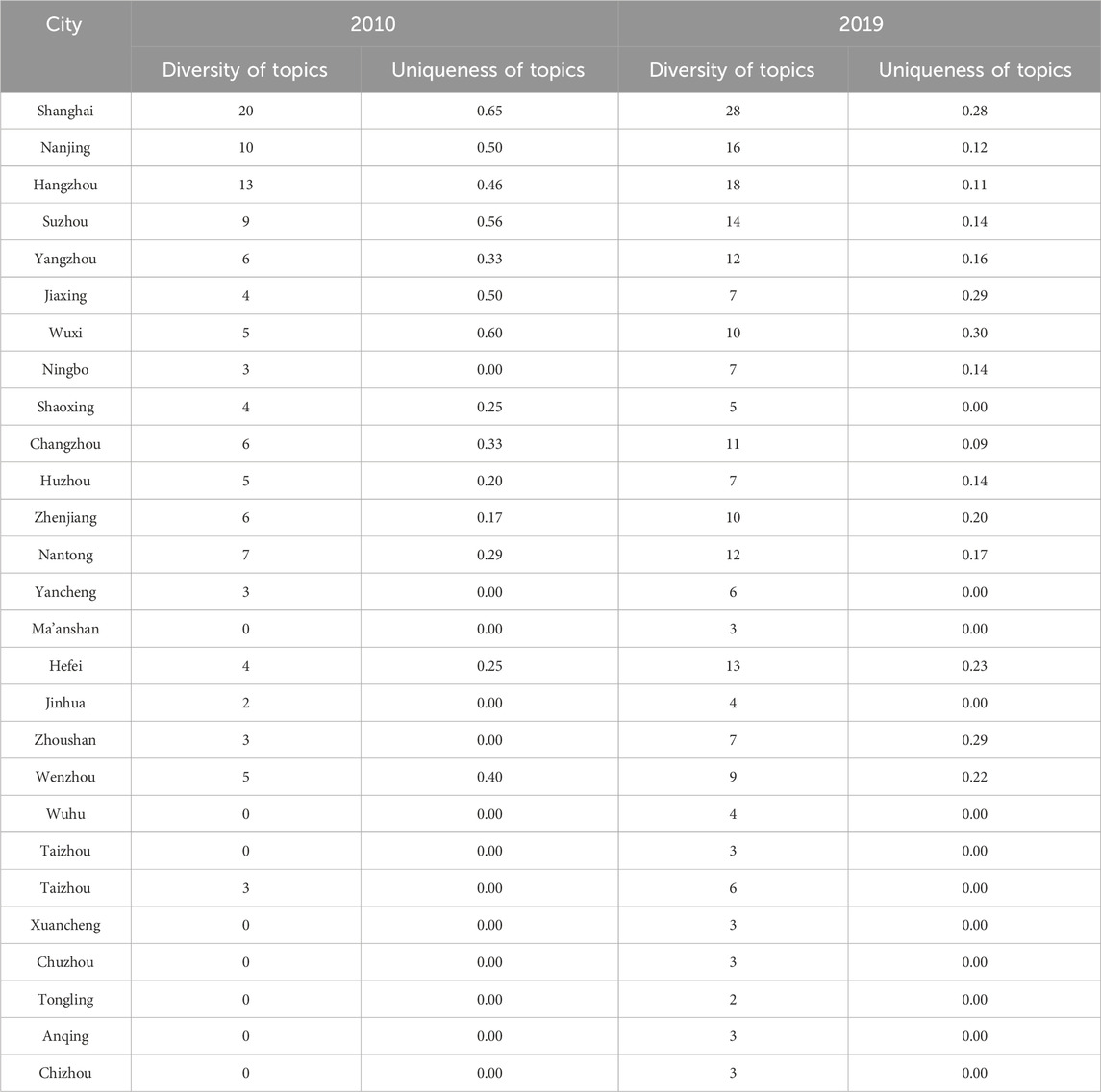
Table 5. Indicators for measuring the structural characteristics of the affiliation network connecting cities to topics in 2010 and 2019.
Diversity of topics refers to the number of environmental governance topics that the city involves. The greater the diversity of topics, the richer the topics regarding environmental governance that a city concerns, which is conducive to the effect of environmental governance. Uniqueness of topics refers to the ratio of the number of topics a city engages in that differ from those of its connected cities to the total number of environmental governance topics that the city involves. The uniqueness of topics measures the exclusivity of environmental governance issues that a city concerns. A higher value of uniqueness of topics represents that the city adopts more unique and exclusive environmental governance measures. It can be learned from Table 5 that the value of diversity of topics in 27 cities has raised from 2010 to 2019, indicating that the cities within the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration diversifies their focus on the environmental governance issues, and the capabilities of environmental governance of each city continue to strengthen. In addition, the uniqueness of topics in the affiliation network is relatively low in both 2010 and 2019. The possible reason for the result is as follows. In the early stage of CEG in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration, policies for CEG are very scarce, and the cities lack the proactive awareness to take the environmental governance measure. In this context, local governments tend to imitate the environmental governance measures of their neighboring cities. Hence, there is little innovative and unique environmental governance measures, and the value of uniqueness of topics is relatively low. With the improvement of economy and the advent of integrated development of urban agglomerations, cities within the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration tend to engage in the in-depth cooperation in terms of environmental governance. Since the promotion of integrated development of CEG in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration, the diversity of environmental governance topics has improved while the topics among cities become more similar. Therefore, the diversity of topics in the affiliation network connecting cities to topics remains relatively low from 2010 to 2019.
3.4 Formation mechanism of the CEG network
After constructing the CEG network of Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration from the perspective of multilevel network and analyzing its structure characteristics, it can be found that the CEG network is a complex system that involves the participation of different entities and the interaction of multiple elements. During the process of CEG in the urban agglomerations, the CEG network, composed of collaborative network of cities, relationship network of topics, and affiliation network connecting cities to topics, is influenced by various factors such as the endogenous network structure and the exogenous node-level attributes, making it difficult to achieve the desired collaborative effect. Identifying the formation mechanism of the CEG network and figuring out the factors affecting the formation of new cooperative relationships play an important role in facilitating the CEG efficiency. In view of this, the connection probability between nodes in the CEG network is taken as the dependent variable, and the structural variables (endogenous variables) and edge-level variables (exogenous variables) are taken as the independent variables, the formation mechanism of the CEG network is analyzed with ERGM method.
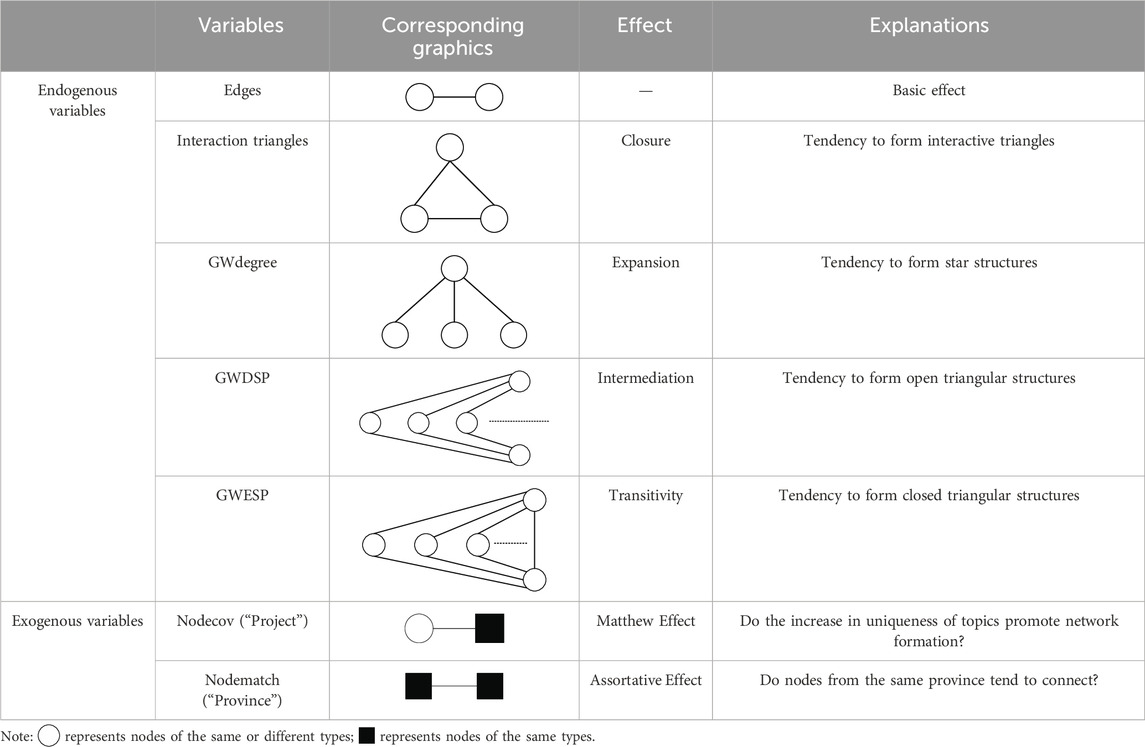
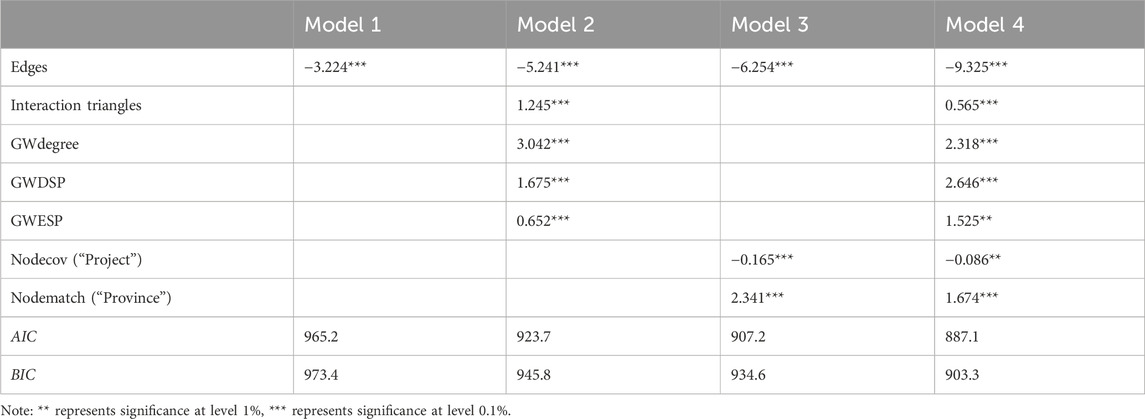
With reference to the research of Song (2015) and Wang et al. (2013), we select edge, interaction triangles, alternating k-stars (GWdegree), alternating k-2 path (GWDSP), and alternating k-triangle (GWESP) as the structural variables. Additionally, considering the feature of nodes themselves and their interaction characteristics, we select the uniqueness of topics (Nodecov) and matching of regions (Nodematch) as the exogenous variables to measure their influence on the formation of CEG network. Specific explanations of variables are listed in Table 6.
Based on the selected ERGM variables for the CEG network, the current paper constructs four models to empirically analyze the formation mechanism of the CEG network in Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration. Specifically, Model one is a basic ERGM model that only includes the variable of edges. The endogenous variables are added in Model two on the basis of Model 1, examining the influence of the star and triangle structures formed between nodes on the formation of CEG network. Model three is constructed based on Model 1, taking into account the exogenous variables to investigate whether uniqueness of topics and matching of regions affect the probability of relationship formation in CEG network. Model four is a comprehensive model that incorporates both endogenous structural variables and exogenous variables into the ERGM model.
This paper uses the Statenet package in R to construct the ERGM model, Monte Carlo maximum likelihood estimates for four models are shown in Table 7.
As shown in Table 7, the value of AIC and BIC, which are the model fit indicators, is the lowest in Model four compared with Model 1, Model 2, and Model 3, indicating that the model fitting degree of Model four is the highest. This suggests that the network, which takes into account both structural variables and node-level variables, is closer to the actual CEG network. In addition, compared with Model one that only considers edges, the decrease of AIC and BIC in Model three is greater than that in Model 2, suggesting that the influence of exogenous node-level variables on the formation of CEG network is more significant. Since the model fitting degree is the highest in Model 4, the specific formation mechanism of CEG network is analyzed with Model 4.
(1) The research results indicate that the formation of cooperative relationship in the CEG network is influenced by both endogenous variables and exogenous variables. Hence, in the practice of CEG among urban agglomerations, we should not only pay attention to the effect of structural variables on the formation of new cooperative relationship, but also the effect of node-level variables on CEG network.
(2) In terms of endogenous variables, the value of Monte Carlo maximum likelihood estimates of “Edges” is negative, indicating that an increase in the number of edges does not promote the establishment of new cooperative relationships in CEG network. Hence, the formation of CEG network exhibits the sparse effects (Yan and Ding, 2012). The possible reason for this phenomenon is as follows. The collaborative relationships in the CEG network such as the cooperation between cities are sporadic. Stable and trusting collaborative relationship have not been established in the CEG network, which cannot attract new partners to cooperative with them. Therefore, the occasional cooperation should be avoided during the process of establishing collaborative relationships in CEG network. Long-term and stable cooperative relationships are advocated to diminish the sparse effects in CEG network.
(3) While the values of Monte Carlo maximum likelihood estimates of “Interaction triangles,” “GWdegree,” “GWDSP,” “GWESP,” “GWESP” are all significantly positive, indicating that the interactive triangular structures, star structures, open triangular structures and closed triangular structures tend to emerge in the CEG network. The existence of these structures can promote the formation of new cooperative relationships in CEG network. The star structures in CEG network represent the network scalability and the center-edge characteristic, which can enable the central nodes to obtain more resources. The triangular structures in CEG network can promote the information exchange between cooperative nodes (Guan et al., 2015). Hence, the cities in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration who are involved in the environmental governance should focus on constructing the star-shaped and triangular-shaped cooperation relationship.
(4) In terms of exogenous variables, the value of Monte Carlo maximum likelihood estimates of “Nodecov” is significantly negative, indicating that the uniqueness of topics has a negative effect on the formation of cooperative relationships in the CEG network. In other words, the cities within the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration with the unique environmental governance issues are less likely to collaborate with other cities in terms of environmental governance. The possible reason for the results is as follows. The unique environmental governance topics are not universal and applicable for all cities whose natural or economic conditions are diverse. Hence, the cities with unique environmental governance topics tend to pay attention to themselves, rather than cooperate with other cities.
(5) In addition, the value of Monte Carlo maximum likelihood estimates of “Nodematch” is significantly positive. Hence, it is easier for cities within the same province to establish collaborative relationships in terms of environmental governance. Cities within the same province are more likely to establish cooperative relationships due to their closer geographical distance, lower cooperation costs, and lower risks. Therefore, relevant departments should take measures to provide a platform for cooperation between cities in different provinces, break the limitations caused by excessive matching effects, and promote technology exchange and knowledge sharing among different regions (Sun, 2016). Cities in the same province are encouraged to cooperate in terms of the environmental governance.
4 Conclusion and policy implications
4.1 Research conclusion
Investigating the structural characteristics and formation mechanism of the CEG network in the urban agglomerations plays a significant role in improving the CEG network and facilitating the sustainable development in the urban agglomerations. The existing research on CEG network aims to analyze the single-layer network which is composed of actors, neglecting the influence of other elements such as environmental governance topics on the effect of CEG. Hence, to depict the characteristics of the CEG network comprehensively, the current paper accounts for the collaborative network of cities, relationship network of topics, and affiliation network connecting cities to topics from the perspective of multilevel network. With the information retrieval and text mining technology, the CEG network which consists of several sub-networks in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration is constructed. Then the social network analysis method and ERGM method are applied to investigate the structural characteristics, evolution logics and formation mechanism of the CEG network. The research results are concluded as follows.
(1) From the overall perspective, the CEG level in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration continues to improve. However, the CEG network is still not in a tightly connected state. Specifically, the scale of the collaborative network of cities of CEG in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration expands continuously, and the network density raise from 2010 to 2019. For the relationship network of topics of CEG, both the number of connections and network density show an upward trend. From the analysis results of affiliation network connecting cities to topics, it can be learned that the environmental governance topics are gradually diversifying, and the coordination between different topics is becoming closer from 2010 to 2019, which indicates the improvement of CEG level in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration. However, the maximum value of network density of collaborative network of cities and relationship network of topics is only 0.349 and 0.393, suggesting that the networks are not closely connected, and the integration degree in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration should be enhanced.
(2) The collaborative network of cities of CEG in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration presents the characteristics of small world and the cooperation trend of “central-subcentral-peripheral city.” In terms of relationship network of topics, the evolution of environmental governance topics from 2010 to 2019 is characterized by optimization and integration, exhibiting a development pattern of “from aspect to point”. From the perspective of affiliation network connecting cities to topics, as the trend of regional integration in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration becomes pronounced, the diversity of environmental governance topics is increasing while the cities within the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration tend to share the similar environmental governance topics.
(3) The formation of the CEG network in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration is influenced by both endogenous structural variables and exogenous edge-level variables. In terms of endogenous structural variables, triangle and star structures among nodes play a vital role in the CEG network. In terms of Mathew effect, the uniqueness of environmental governance topics of a certain city within the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration has a restraining effect on the formation of the CEG network. In terms of the matching of regions, geographical proximity promotes the collaborative relationships in the CEG.
4.2 Policy implications
Based on the above research conclusions, the current paper proposes the following policy suggestions.
(1) Local governments should pay attention to promoting the development of CEG network in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration by means of enhancing the cooperation efforts among cities and increasing network density. The locational advantages of central cities such as Shanghai, Nanjing, and Hangzhou should be fully exploited. Cities with high degree centrality, betweenness centrality, and closeness centrality are supposed to strengthen the CEG with surrounding cities, radiating and guiding the environmental governance of the edge cities. Meanwhile, it is important to take advantage of the small world characteristics of the collaborative network of cities in the CEG. Breaking down the cooperation barriers between cities and strengthening the exchange of technology, information and knowledge in terms of environmental governance play a vital role in facilitating the flow of environmental governance resources and promoting the CEG in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration.
(2) It is notable that governments should strengthen the construction of relationship network of topics in CEG and diversify the environmental governance topics. The cities within the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration need to explore the scientific combinations of diverse environmental governance topics taking into account their actual conditions of ecological pollution. In addition, governments need to facilitate the cooperation and learning among cities regarding environmental governance measures, and emphasize the dual role of city collaboration and environmental governance topics in the CEG results, leading to the positive development of affiliation network connecting cities to topics in CEG.
(3) In the research and related practices of constructing CEG network, it is crucial to not only emphasize the effect of endogenous structural characteristics on the network formation, but also to focus on the role of matching of regions and uniqueness of topics in the formation of cooperative relationships in CEG. In the CEG network, establishing triangular and star-shaped structures should be prioritized, fully leveraging the advantages of two structures in the resource acquisition for environmental governance.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
YZ: Formal Analysis, Supervision, Writing–review and editing. XZ: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing–original draft. ZL: Software, Validation, Writing–original draft. DZ: Investigation, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study is funded by The Research Project of Zhenjiang College.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Ahangar, N. E., Sullivan, K. M., and Nurre, S. G. (2020). Modeling interdependencies in infrastructure systems using multi-layered network flows. Comput. and Operations Res. 117, 104883. doi:10.1016/j.cor.2019.104883
Akçomak, B. S., Çetinkaya, U. Y., Erdil, E., and Gossart, M. Ö. (2023). What drives network evolution? Comparing R&D project and patent networks in the EU. Industrial Corp. Change 32 (5), 1109–1134. doi:10.1093/icc/dtad044
Avoyan, E. (2023). Collaborative governance for innovative environmental solutions: qualitative comparative analysis of cases from around the world. Environ. Manag. 71 (3), 670–684. doi:10.1007/s00267-022-01642-7
Candace, K. (2016). Visibility and invisibility: structural, differential, and embedded power in collaborative governance of fisheries. Soc. Nat. Resour. 29 (7), 1–16. doi:10.1080/08941920.2015.1072257
Cao, W., Dong, Y., and Miao, J. (2019). Research on formation mechanism of regional intellectual property protection network based on exponential random graph models. Soft Sci. 11 (33), 131–137.
Caschili, S., Medda, F. R., and Wilson, A. (2015). An interdependent multi-layer model: resilience of international networks. Netw. and Spatial Econ. 15 (2), 313–335. doi:10.1007/s11067-014-9274-2
Chandra, P., and Dong, A. (2022). Knowledge network robustness: a new perspective on the appropriation of knowledge from patents. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 69 (6), 2806–2816. doi:10.1109/tem.2020.3016278
Chong, Z., Qin, C., and Ye, X. (2017). Environmental regulation and industrial structure change in China: integrating spatial and social network analysis. Sustainability 9 (8), 1465. doi:10.3390/su9081465
Duan, X., Dai, S., Yang, R., Duan, Z., and Tang, Y. (2020). Environmental collaborative governance degree of government, corporation, and public. Sustainability 12 (3), 1138. doi:10.3390/su12031138
Fang, C., and Yu, D. (2017). Urban agglomeration: an evolving concept of an emerging phenomenon. Landsc. Urban Plan. 162, 126–136. doi:10.1016/j.landurbplan.2017.02.014
Fu, C., Xu, Y., and Zhou, F. (2023). Environmental collaborative governance of urban agglomeration in China: influencing factors and drivers. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 30 (13), 38363–38379. doi:10.1007/s11356-022-24769-w
Ge, T., Chen, X., Geng, Y., and Yang, K. (2023). Does regional collaborative governance reduce air pollution? Quasi-experimental evidence from China. J. Clean. Prod. 419, 138283. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.138283
Goodreau, S., Kitts, J., and Morris, M. (2009). Birds of A Feather, or friend of A friend? Using exponential random graph models to investigate adolescent social networks. Demography 46 (1), 103–125. doi:10.1353/dem.0.0045
Guan, J., Zhang, J., and Yan, Y. (2015). The impact of multilevel networks on innovation. Res. Policy 44 (3), 545–559. doi:10.1016/j.respol.2014.12.007
Gunningham, N. (2009). The new collaborative environmental governance: the localization of regulation. J. Law Soc. 36 (1), 145–166. doi:10.1111/j.1467-6478.2009.00461.x
Guo, J., and Xie, F. (2021). An empirical study on the determinants of collaborative innovation network formation: based on the ERGM. Chin. J. Manag. 18 (1), 91–96. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1672-884x.2021.01.010
Han, J., Gao, M., and Sun, Y. (2019). Research on the measurement and path of urban agglomeration growth effect. Sustainability 11, 5179. doi:10.3390/su11195179
Hayat, T., Lesser, O., and Samuel-Azran, T. (2017). Gendered discourse patterns on online social networks: a social network analysis perspective. Comput. Hum. Behav. 77, 132–139. doi:10.1016/j.chb.2017.08.041
Huhe, N., Thomson, R., Arregui, J., and Naurin, D. (2022). Intergovernmental cooperation networks, national policy positions and partisan ideologies: longitudinal evidence from the Council of the European Union. J. Eur. Public Policy 29 (1), 78–96. doi:10.1080/13501763.2021.1991980
Jung, H., and Lee, B. (2020). Research trends in text mining: semantic network and main path analysis of selected journals. Expert Syst. Appl. 162, 113851. doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2020.113851
Koebele, E. (2020). Cross-coalition coordination in collaborative environmental governance processes. Policy Stud. J. 48 (3), 727–753. doi:10.1111/psj.12306
Kothari, A., Hamel, N., MacDonald, J., Meyer, M., Cohen, B., and Bonnenfant, D. (2014). Exploring community collaborations: social network analysis as a reflective tool for public health. Syst. Pract. Action Res. 27 (2), 123–137. doi:10.1007/s11213-012-9271-7
Leng, Z., Sun, H., Cheng, J., Wang, H., and Yao, Z. (2021). China’s rare earth industry technological innovation structure and driving factors: a social network analysis based on patents. Resour. Policy 73, 102233. doi:10.1016/j.resourpol.2021.102233
Li, H., and Wang, J. (2022). Collaborative annealing power k-means plus plus clustering. Knowledge-Based Syst. 255, 109593. doi:10.1016/j.knosys.2022.109593
Lin, J. Y., Tian, Y. H., Yao, Q., and Shi, Y. (2023). Structural characteristics of intergovernmental water pollution control cooperation networks using social network analysis and GIS in Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration, China. Sustainability 15 (18), 13655. doi:10.3390/su151813655
Liu, F., Fu, L., and Xu, K. (2021). Structure and effect measurement of inter-government and inter-city cooperation network of medical and health services: taking jingjinji metropolitan region as an example. J. Northeast. Univ. Soc. Sci. 4, 59–66. doi:10.15936/J.CNKI.1008-3758.2021.04.008
Lu, Y., Polgar, M., Luo, X., and Cao, Y. (2010). Social network analysis of A criminal hacker community. J. Comput. Inf. Syst. 51 (2), 31–41. doi:10.1080/08874417.2010.11645466
Mason, C., Kirkbride, J., and Bryde, D. (2007). From stakeholders to institutions: the changing face of social enterprise governance theory. Manag. Decis. 45 (2), 284–301. doi:10.1108/00251740710727296
Miao, L., and Sun, Y. (2020). Quantitative analysis of regional economic balance and sustainable development in Yangtze River Delta and pearl River Delta. J. Coast. Res. 115, 570–574. doi:10.2112/jcr-si115-153.1
Olvera-Garcia, J., and Nei, S. (2020). Examining how collaborative governance facilitates the implementation of natural resource planning policies: a water planning policy case from the Great Barrier Reef. Environ. Policy Gov. 30 (3), 115–127. doi:10.1002/eet.1875
Pan, C., Mu, A., and Zhai, W. (2022). The network structure and spatial characteristics of synergy innovation among three urban agglomerations in China——based on the comparative analysis of beijing-tianjin-hebei region, the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration and the Guangdong-Hong Kong. Reform Econ. Syst. 2, 50–58.
Pan, Z. Y., Liu, Y., Liu, G. J., and Guo, M. (2018). Topic network: topic model with deep learning for image classification. J. Electron. Imaging 27 (3), 1. doi:10.1117/1.jei.27.3.033009
Parnell, J., and Robinson, J. (2018). Social network analysis: presenting an underused method for nursing research. J. Adv. Nurs. 74 (6), 1310–1318. doi:10.1111/jan.13541
Sinaga, K., and Yang, M. (2020). Unsupervised K-means clustering algorithm. IEEE ACCESS 8, 80716–80727. doi:10.1109/access.2020.2988796
Song, H. (2015). Uncovering the structural underpinnings of political discussion networks: evidence from an exponential random graph model. J. Commun. 65 (1), 146–169. doi:10.1111/jcom.12140
Stewart, J., Scheweinberger, M., Bojanowski, M., and Morris, M. (2019). Multilevel network data facilitate statistical inference for curved ERGMs with geometrically weighted terms. Soc. Netw. 59, 98–119. doi:10.1016/j.socnet.2018.11.003
Sun, T. (2016). The structure and dynamics of intra- and inter-regional research collaborative networks: the case of China (1985–2008). Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 108, 70–82. doi:10.1016/j.techfore.2016.04.017
Sun, T., and Wen, X. (2018). Network analysis of regional environmental governance under inter-government cooperation: an example of the regional air governance in beijing-tianjin-hebei area. Chin. Public Adm. 5, 83–89. doi:10.3782/j.issn.1006-0863.2018.05.13
Tanhapour, M., Safaei, A., and Shakibian, H. (2022). Personal health record system based on social network analysis. Multimedia Tools Appl. 81 (19), 27601–27628. doi:10.1007/s11042-022-12910-3
Ulibarri, N. (2015). Tracing process to performance of collaborative governance: a comparative case study of federal hydropower licensing. Policy Stud. J. 43 (2), 283–308. doi:10.1111/psj.12096
Ulibarri, N., Imperial, M., Siddiki, S., and Henderson, H. (2023). Drivers and dynamics of collaborative governance in environmental management. Environ. Manag. 71, 495–504. early access. doi:10.1007/s00267-022-01769-7
Van der Pol, J. (2019). Introduction to network modeling using exponential random graph models (ERGM): theory and an application using R-project. Comput. Econ. 54 (3), 845–875. doi:10.1007/s10614-018-9853-2
Wan, Q., Xu, X., and Han, J. (2024). A dimensionality reduction method for large-scale group decision-making using TF-IDF feature similarity and information loss entropy. Appl. Soft Comput. 150, 111039. doi:10.1016/j.asoc.2023.111039
Wang, J. X., and Zhang, J. J. (2023). The impact of policy collaboration networks and policy topic networks on policy diffusion: empirical evidence from the energy field. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 197, 122883. doi:10.1016/j.techfore.2023.122883
Wang, P., Robins, G., Pattison, P., and Lazega, E. (2013). Exponential random graph models for multilevel networks. Soc. Netw. 35, 96–115. doi:10.1016/j.socnet.2013.01.004
Wang, W. T., Jian, L. R., Lei, Y. Y., and Liu, J. (2023). Measurement and prediction of the relationships among the patent cooperation network, knowledge network and transfer network of the energy storage industry in China. J. Energy Storage 67, 107467. doi:10.1016/j.est.2023.107467
Wasserman, S., and Faust, K. (1994). Social network analysis: methods and applications. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Wu, Y., and Feng, J. (2021). Environmental governance cooperation network in megacities: structure, characteristics and evolution——taking GBA as an example. Reform Econ. Syst. 4, 80–87.
Xie, G., Tai, J., and Li, W. (2022). Research on the characteristics of transnational patent cooperation and network evolution in the field of digital communication under the background of “Belt and Road”. J. Technol. Econ. 2, 15–25.
Xu, J., Yin, P., Hu, W., Fu, L., and Zhao, H. (2020). Assessing the ecological regime and spatial spillover effects of a reclaimed mining subsided lake: a case study of the Pan’an lake wetland in Xuzhou. PLoS One 15 (8), e0238243–243. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0238243
Yan, E., and Ding, Y. (2012). Scholarly network similarities: how bibliographic coupling networks, citation networks, cocitation networks, topical networks, coauthorship networks, and coword networks relate to each other. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 63 (7), 1313–1326. doi:10.1002/asi.22680
Yu, M., and Zou, F. (2022). Stimulating social vitality: the construction of an activist network in the coordinated governance of water environment in the Yangtze River Delta. Jiangsu Soc. Sci. 1, 45–51. doi:10.13858/j.cnki.cn32-1312/c.2022.01.005
Zhang, G., Lei, Y., Zhao, W., and Fu, C. (2022a). Evolution of emergency information collaboration network in public health events. Inf. Sci. 40 (12), 181–187. doi:10.13833/j.issn.1007-7634.2022.12.022
Zhang, w., Liu, G., Gonella, F., Xu, L., and Yang, Z. (2022b). Research on collaborative management and optimization of ecological risks in urban agglomeration. J. Clean. Prod. 372, 133735. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.133735
Zhao, R. Y., Li, D. Y., Wei, M. K., and Li, X. (2022). The contents and methods of knowledge network from the perspective of bibliometrics. Technol. Analysis and Strategic Manag. 34 (3), 245–257. doi:10.1080/09537325.2021.1894329
Keywords: collaborative environmental governance, multilevel network, social network analysis, ERGM, urban agglomeration
Citation: Zhang Y, Zhang X, Lu Z and Zhu D (2024) Structural characteristics and mechanism of collaborative environmental governance network of urban agglomerations: perspective of multilevel network. Front. Environ. Sci. 12:1478864. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2024.1478864
Received: 11 August 2024; Accepted: 08 November 2024;
Published: 25 November 2024.
Edited by:
Sílvia Jorge, Associação do Instituto Superior Técnico de Investigação e Desenvolvimento (IST-ID), PortugalCopyright © 2024 Zhang, Zhang, Lu and Zhu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiangwei Zhang, MTQyNzUwOTE0MUBxcS5jb20=
 Yuting Zhang
Yuting Zhang Xiangwei Zhang3,4*
Xiangwei Zhang3,4*