- 1School of Architecture, Inner Mongolia University of Technology, Hohhot, China
- 2Key Laboratory of Green Building at Universities of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, Hohhot, China
- 3College of Civil Engineering and Water Resources, Qinghai University, Xining, China
- 4State key laboratory of Remote Sensing Sciences, Aerospace Information Research Institute Chinese Academy of Science (AIRCAS), Beijing, China
- 5University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China
- 6College of Public Administration, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China
Population migration brings about many problems in villages. The Ji (几)-shape bend of the Yellow River is an important ecological sensitivity study area, and some progress exists in the study of villages, still has many problems. This article addresses the inadequacy of the existing research and mainly solves the problems in three areas. It primarily used the research method of Arc GIS10.8, the big data research methods such as imbalance index, Gini coefficient, geographic concentration index, Geodetector, and other methods were used, laying the groundwork for additional analysis of various factors. Hence, the subsequent study findings were attained. 1) The distribution pattern in the village system around the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River seems to be a positive spatial correlation, with the characteristics of random distribution, uneven spatial distribution, and low concentration, with Hohhot-Baotou serving as a center. 2) Natural factors are the most important factors in the distribution of villages. 3) Among the natural factors, elevation (0.244619), the value of slope (0.319805), and the aspect of slope (0.074089) appear to be the strongest explanatory power. Among the social factors, the rate of urbanization (0.019082), highway density (0.019082), and percentage of tertiary industry (0.018422) show the strongest explanatory power on socioeconomic factors. The natural and social characteristics of villages are important for the siting of villages. This paper put forward some suggestions for the protection and development of villages in ecologically sensitive areas.
1 Introduction
Understanding the clustering features and current distribution of villages and reasonably determining their layout and scale play a crucial role in coordinating urban and rural development space (Yang et al., 2023). With an increasing number of people relocating from rural to urban regions, it has resulted in societal issues including waste of land resources, ecological deterioration, and climate change (Liu and Xu, 2021; Zhang et al., 2024a). The changes in land use brought about by urbanization (Ul Din and Mak, 2021) have led to changes in the human settlements (Ye et al., 2022) and the ecological environment (Wang et al., 2024; Xie et al., 2024; Xu et al., 2020), profoundly affecting local, regional, and global development. The environment has also been degraded as a result of unplanned developmental activities, unchecked resource extraction, and accelerated rates of land-use and land-cover issues (Ramachandra et al., 2020). The sustainable development of villages is severely hampered by these issues.
The Yellow River originates in the Bayankala Mountains in Qinghai Province, China. The basin covers an area of approximately 795,000 square kilometers (307,000 square miles) and includes parts of nine provinces and autonomous regions. Traffic is highly variable, with large seasonal fluctuations. There are mainly alluvial soil, desert soil and ash soil, each of which has its own management challenges. In 2009, scientists from the Chinese Academy of Sciences first proposed the concept of the “Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River.” The “Strategic Concept for the Development of the Ji-shape Bends of the Yellow River” was submitted to the federal government in 2011 by the Regional Development Committee of the National Innovation and Promotion Commission and was subsequently approved. The 2019 concept of “ecological protection and high-quality development of the Yellow River Basin” offers a new strategic framework for planning (Du, 2023). This region is characterized by a diverse population, including ethnic minorities, as well as typical pastoral and agricultural areas, regions of extreme poverty, and areas rich in energy resources. Due to its low ecological carrying capacity and somewhat delicate ecological environment, the region has limited ability to adjust to changing climate conditions. The Yellow River Basin is a complex system where river dynamics, landforms, human settlements, climate factors, and anthropogenic activities are deeply interconnected. Rivers shape landforms and influence settlement patterns, while land use and human activities impact river systems and soil conditions. Climate variability and change affect water availability and agricultural productivity, while human actions such as deforestation, urbanization, and pollution interact with these environmental factors.
Ecologically sensitive areas refer to ecosystems’ responses to environmental changes caused by internal and external factors (Yilmaz et al., 2020). Today, environmental and resource issues have become serious challenges facing developing countries (Bai et al., 2016). These challenges include atmospheric pollution (Guo et al., 2015), carbon sequestration issues (Lal, 2005), soil pollution (Brookes, 1995), water pollution (Moss, 2008), and biodiversity loss (Pollock et al., 2020), among others. China has implemented policies to mitigate environmental damage. However, there are still environmental protection issues in ecologically sensitive areas. As a crucial factor in river basin development, the Yellow River represents an important target for environmental protection efforts. The Yellow River Basin in Inner Mongolia features several ecologically sensitive areas, including the Loess Plateau, floodplain regions, desert and semi-arid zones, highland areas, and protected nature reserves. These areas face challenges such as soil erosion, desertification, flooding, water scarcity, and biodiversity loss. Effective management and conservation efforts are essential to address these challenges, involving strategies like soil conservation, flood control, water management, habitat preservation, and strict protection measures. Ensuring the health of these ecologically sensitive areas is crucial for maintaining the overall environmental balance and supporting both natural ecosystems and human communities.
On the other hand, studies in humanities, politics, economics, society, and energy can be applied to the study of villages (Nash, 2013; Valera and Guardia, 2002; Chang and Wang, 1994; Hu and Wang, 1998). In the field of architecture, there are mainly the following aspects. 1. Research on the spatial form of villages (Nie et al., 2022; Zhu and Liu, 2023). 2. Research on the landscape of villages (Daoyong et al., 2020; Kowkabi, 2020). 3. Research on the factors that affect land use and how villages evolve spatially (Chen J. et al., 2021; Chen Z. et al., 2021). 4. Research on village protection (Wang and Zhu, 2022; Li, 2015). 5. Research on natural climate (Ogura et al., 2007; Hasegawa et al., 2007). Furthermore, in terms of research topics, some academics concentrate on the village environment (Xiao et al., 2022), local culture (Parameswara and Wulandari, 2020), and the evaluation system (Kim et al., 2014). In terms of research scope, some scholars have conducted certain research on the research area, like countries (Bian et al., 2022), provinces (Gao et al., 2023), cities (Lin and Ma, 2023), areas (Jin et al., 2022) and poverty-stricken regions (Mohammadi Yegane et al., 2014; Marcinko et al., 2022). There is a qualitative study on assessment systems in terms of research methodologies (Wang et al., 2020) and development strategies (Sebayang et al., 2019), as well as quantitative research using SPSS (Wang et al., 2020), ArcGIS (Adi and Suhartono, 2017), and space syntax (Lee et al., 2004). In addition, there are macro-level studies on such aspects, as well as micro-level studies on villages (Jia et al., 2023), and other studies on interactions with other factors (Momose, 2002; Kim et al., 2018). In summary, the research on villages has developed to multiple levels and fields, but there are still certain defects. On the one hand, there are few studies at the river basin level, and on the other hand, there are relatively few studies on ecologically sensitive areas. Past studies have only focused on single factors such as climate and land, and lacked comprehensive research on multiple factors.
In terms of the distribution of villages and their influencing factors, there are many analyses of the distribution characteristics of traditional Chinese villages and their influencing factors (Su et al., 2022; Bian et al., 2022), along with many analyses on the distribution factors of traditional villages in provinces (Yang et al., 2023). One example is an analysis of the spatiotemporal evolution characteristics and impacts of traditional villages in the Yellow River basin in Henan (Feng et al., 2023). In terms of methods, most of them are analyzed using techniques such as kernel density analysis, nearest neighbor index, Geodetector, imbalance index, spatial autocorrelation analysis, and others. These methods reveal the spatiotemporal features and geographical heterogeneity of villages, illustrating the interdependent interaction between the natural environment and human activities, exposing both internal and external driving forces, as well as macro-level determinants of development and renewal (Bian et al., 2022). Innovative urban development, livability, and smart cities play crucial roles in the development of villages (Chi and Mak, 2021; Zhang, 2022; Myeong et al., 2018). Social factors such as urbanization, transportation, GDP, and population, as well as natural factors such as topography, hydrology, ecology, and climate, influence the emergence, geographical distribution, development, and changes of villages (Gao et al., 2023).
Village research has advanced across a variety of domains and levels so far (Li et al., 2023). However, issues such as unequal research focus and reliance on single research techniques persist, largely due to specific regional disparities. Geographically speaking, most studies on villages were conducted in larger, more developed coastal towns and major cities (Zhang and Wang, 2023; Xiaoyue et al., 2022), and studies focusing on specific administrative units (Qianting et al., 2022) are more common, but research on river basins is scarce, with even fewer studies focusing specifically on the Yellow River Basin (Feng et al., 2023; Xu et al., 2023). A systematic comparison and selection of research parameters remain incomplete, particularly concerning the research substance. Since cities and villages differ significantly and these variations are strongly influenced by natural and human environments (Qianting et al., 2022). From a research standpoint, the majority of studies have concentrated on ecological villages and very few explicitly address villages in environmentally vulnerable locations (Mahlabani et al., 2016; Niren, 2003), research on villages in ecologically fragile areas is limited, with case studies often focusing primarily on factors influencing the distribution of traditional villages (Liu et al., 2023; Zhang, 2022). This study aims at the deficiencies in the existing research fields and adds research on specific realms. At the same time, it also conducts related research on ecologically sensitive areas. The objective is to provide an overview of urban planning and environmental protection implications in these areas.
Precisely identifying the various living and working areas within villages is crucial for their protection, management, and zoning (Zhang et al., 2023). This approach can also help reveal the natural resources and land use conditions of individual villages. This article have addressed three questions: 1. What is the distribution of villages around the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River? 2. What are the influencing factors? 3. What laws and procedures are in place to safeguard villages, and how can villages be protected? Using data from 5,409 villages around the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River in Inner Mongolia, this paper aims to analyze spatial distribution characteristics, summarize factors affecting climate change, precipitation, and temperature, and use ArcGIS 10.8 and other techniques to investigate ecologically sensitive villages in the region. The study seeks to reveal the development patterns of these villages, objectively analyze their current development dynamics and trends, clarify existing research conclusions, and deepen the understanding of future development patterns. Additionally, the findings have reference value for protecting traditional villages, classifying traditional villages, and informing China’s rural revitalization strategy.
2 Research area and research methods
2.1 Study area
The study area primarily encompasses the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River, which is located in the central and western part of Inner Mongolia. Ji-shaped bend in the Yellow River Basin presents a unique combination of geomorphological and climate characteristics. Its proximity to the Yellow River shapes its landscape through sediment deposition and erosion. The area experiences significant seasonal climate variations, with implications for water resources and agricultural productivity. The Inner Mongolia Yellow River region is very different from other regions in terms of topography, climate, soils, and land use. The Inner Mongolia Yellow River region is known for its unique geomorphic features, including loess and dynamic river systems. The climate is characterized by extreme seasonal variations and low precipitation, affecting agriculture and water resource management. Soil characteristics pose challenges due to erosion and potential desertification. Human settlements and land use are closely related to the river and its resources, and traditional practices are adapted to the environment. The geographical and social factors within the region are complex. The natural environment has significantly influenced the establishment of towns. The research shows that many civilizations historically relied on rivers for sustenance and expansion. Gathering water is one of the main factors that promotes population expansion and the development of a unique village culture. The distribution of villages and water systems are strongly correlated, as several studies have shown. The majority of villages are located near water flows and exhibit considerable hydrophilicity (Gao et al., 2023; Fu et al., 2021).
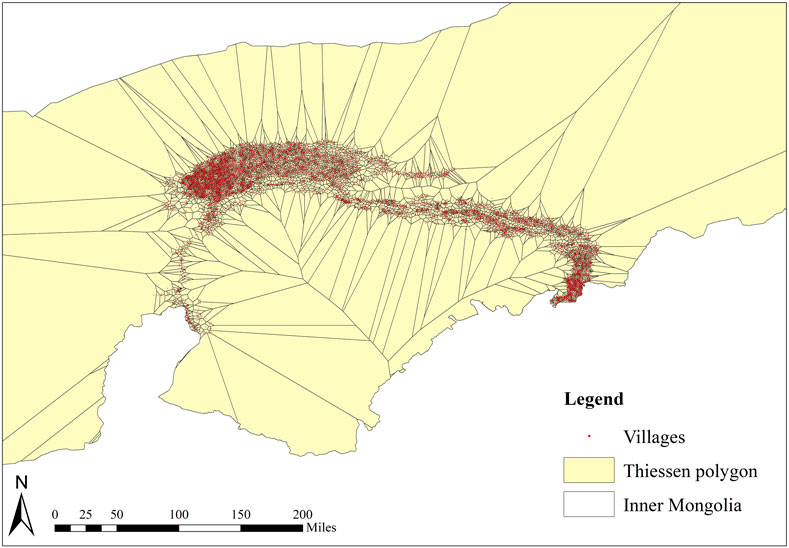
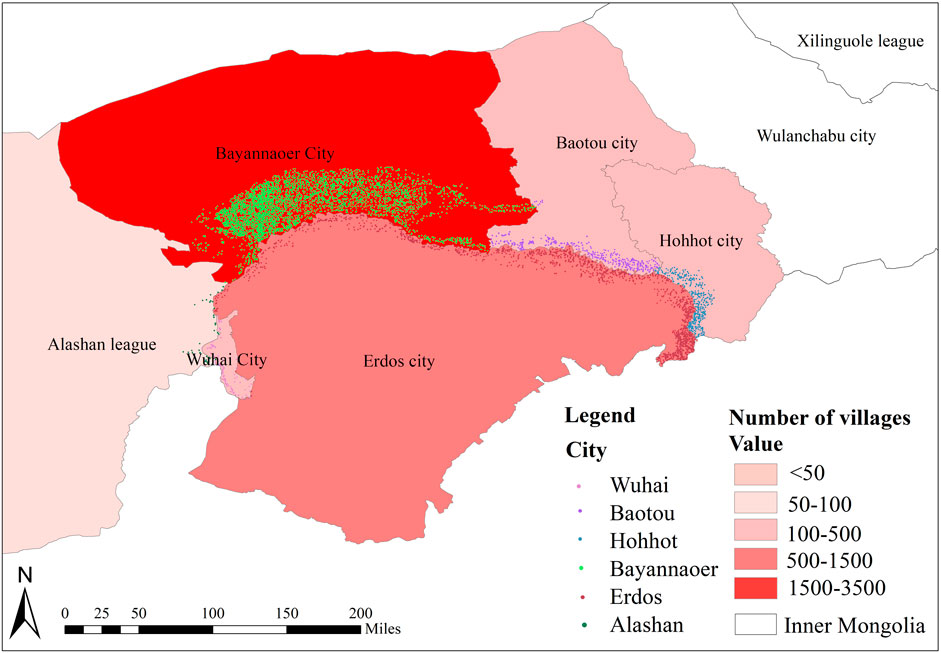
The northern area of the Ji-shape bend is a complex ecological zone, with the highest number of villages around the Yellow River Basin. In addition, due to its unique geographic location, this area features a diverse range of landscapes, including grasslands, mountains, and deserts. The study focuses on the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River in Inner Mongolia, covering the regions of Alashan, Wuhai, Bayannaoer, Hohhot, and Baotou, along with their subordinate districts and counties. The variation in geographical locations results in different village characteristics, allowing for a more comprehensive examination of village types, making village research more comprehensive (Table 1), in total, the study analyzed 5,409 villages in the surrounding areas (Figure 1).
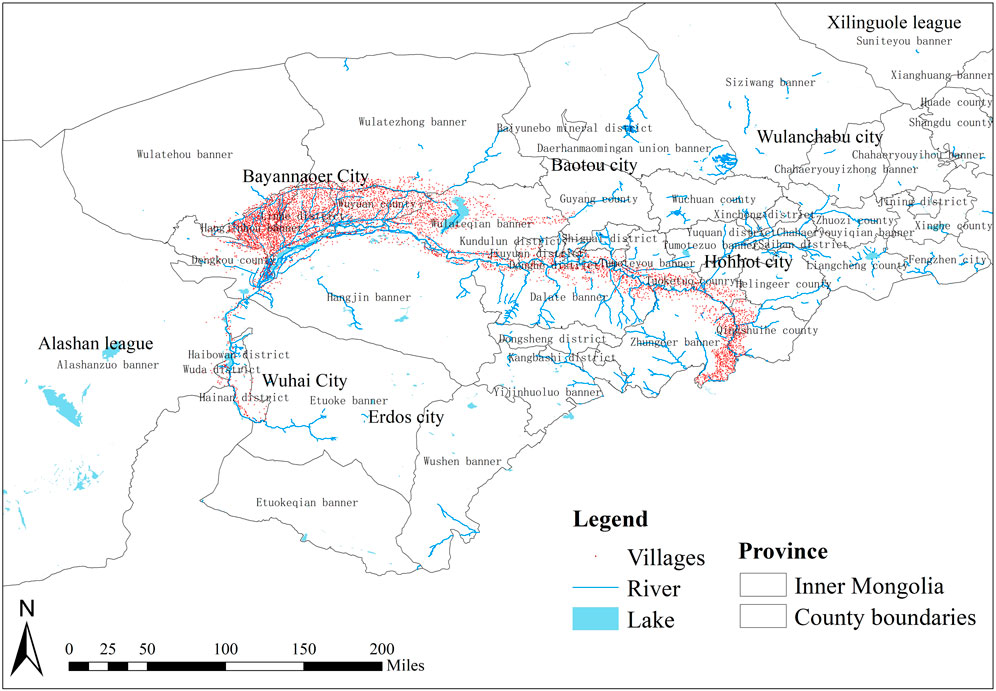
Figure 1. Spatial distribution map of villages around the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River in Inner Mongolia.
2.2 Data sources
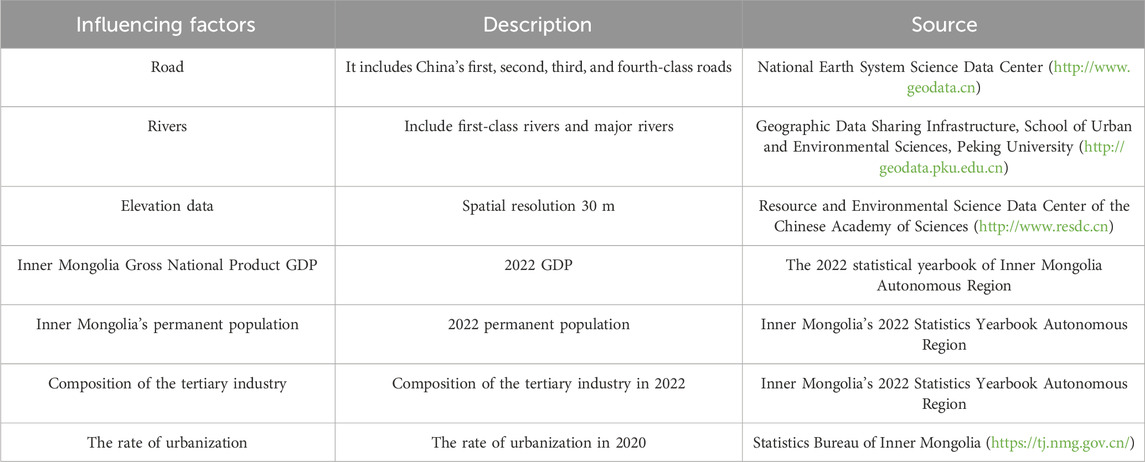
Village patches were treated as point elements. Geographic positions were identified and calibrated using Google Earth. The coordinates of these points were then obtained and imported into ArcGIS 10.8 for vectorization processing. Using the geospatial data cloud platform, we downloaded the 30-m resolution digital elevation model (DEM) data for Inner Mongolia and extracted slope and elevation data. Administrative borders and physical geographic data were sourced from the national 1:4 million basic geographical information database. Socioeconomic information for each city and county was obtained from the “Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region’s 2022 Statistics Yearbook” (Table 2).
2.3 Methods
This study used big data methods of the nearest neighbor index, spatial autocorrelation analysis, coefficient of variation, imbalance index, Gini coefficient, geographic concentration index, kernel density analysis, and Geodetector methods. Nearest Neighbor Index: Used to assess the degree of spatial distribution balance. Spatial Autocorrelation Analysis: Applied to evaluate spatial dispersion. Imbalance Index: Employed to investigate the extent of spatial dispersion. Gini Coefficient: Utilized to measure spatial dispersion. Geographic Concentration Index: Analyzed to understand the concentration of village distribution. Kernel Density Analysis: Used to assess the probability of an event occurring based on spatial distribution. Geodetector: Applied to identify driving factors influencing the spatial distribution. The overall analysis aims to perform overlay and linear regression to identify contributing factors. By using these geographical spatial analysis methods, the spatial characteristics of villages in Inner Mongolia are analyzed.
2.3.1 Imbalance index
The imbalance index measures the degree of harmony in the allocation of research items across different levels or fields (Li et al., 2020). In this study, it was used to quantify how evenly villages are distributed across various counties and cities. The imbalance index was calculated using a procedure similar to that used for the concentration index in the Lorenz curve Equation 1:
The number of regions is denoted by n, and the i-th position’s cumulative percentage is shown by
2.3.2 Gini Coefficient
In geography, the Gini coefficient is a useful tool for evaluating the spatial distribution of dispersed zones and regional geographical characteristics (Xu et al., 2021). It was used in this article to calculate the regional village distribution around the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River in Inner Mongolia. The equation used to calculate the Gini coefficient is Equations 2, 3:
The equation takes N as the number of regions, C as the evenness of distribution, and
2.3.3 Geographic concentration index
The GCI quantifies the extent to which villages are concentrated in specific geographic areas (Yang et al., 2023). The following is the calculating Equation (4):
2.3.4 Geodetector
The Geodetector is used to detect the heterogeneity of geographical data and reveal its underlying causes (Wang and Xu, 2017; Zhang et al., 2024a). This approach assumes that the independent variables should have comparable geographical distributions if they significantly affect the dependent variable.
2.3.4.1 Factor detection
In this study, the Geodetector was used to analyze the spatial distribution of the data Y and assess the extent to which each factor contributes to spatial differentiation (Zhang et al., 2024b). The degree of explanation was expressed by the q value, which had a range of 0–1. The explanatory factor for the geographical divergence increases with increasing value. The following is the calculating Equation (5):
Each factor’s explanatory capacity for spatial differentiation is denoted by q, the number of layers in each factor is represented by L, and N stands for the total number of samples. Nevertheless, the quantity of samples within the factor partition is shown by
2.3.4.2 Interaction detection
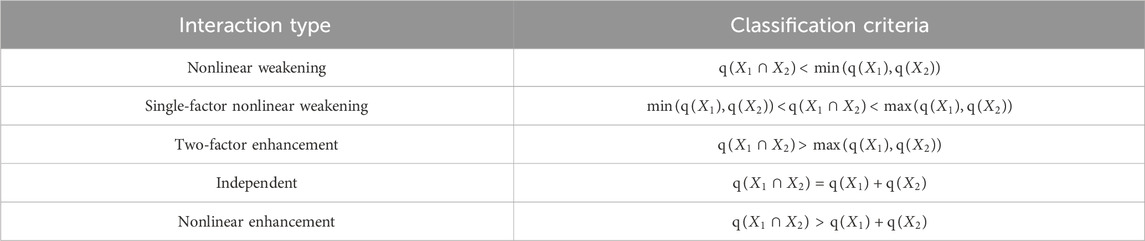
Determining whether two factors are independent of one another if they increase or decrease the dependent variable Y’s explanatory power when combined, or to assess how several factors interact. The evaluation factors are X1 and X2 (It can be found in 3.10.2). The judgment method was to compare the factor detection q value of the new layer formed by the superposition of two factors X1 and X2 with the q value of the single factor detection result. The particular evaluation standards are shown in Table 3.
3 Results
The factors were divided into two aspects: natural and social factors. For natural factors, topographic features, elevation, slope, slope direction, and hydrological features, including precipitation and temperature in climate. For the social factors, transport and demographic factors were considered, including GDP, the rate of urbanization, and the proportion of the tertiary industry for economic factors, as well as history and cultural heritage for human factors. The selection of these factors was made after comparing them with those used by previous scholars (Li et al., 2023).
3.1 Natural geographical factors
3.1.1 Topography and landform
It can be seen that the landforms around the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River are very complex, including plateaus, plains, and desert mountains. These landforms encompass the Erdos Plateau, the Hetao Plain, the Tumochuan Plain, the Ulan Buh Desert, and the Kubuqi Desert, several typical landforms such as which include several typical landforms such as deserts and mountains (Sun, 1959). ArcGIS 10.8 was used to overlay the villages and the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River topography and landform classification map to obtain the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River topography and landform distribution map (Figure 2). Villages are mostly found in the regions of the Tumochuan Plain and the Hetao Plain. More villages are spread out along the northern bank of the Yellow River than on the southern bank. Additionally, villages are widely scattered along the tributaries of the Yellow River.
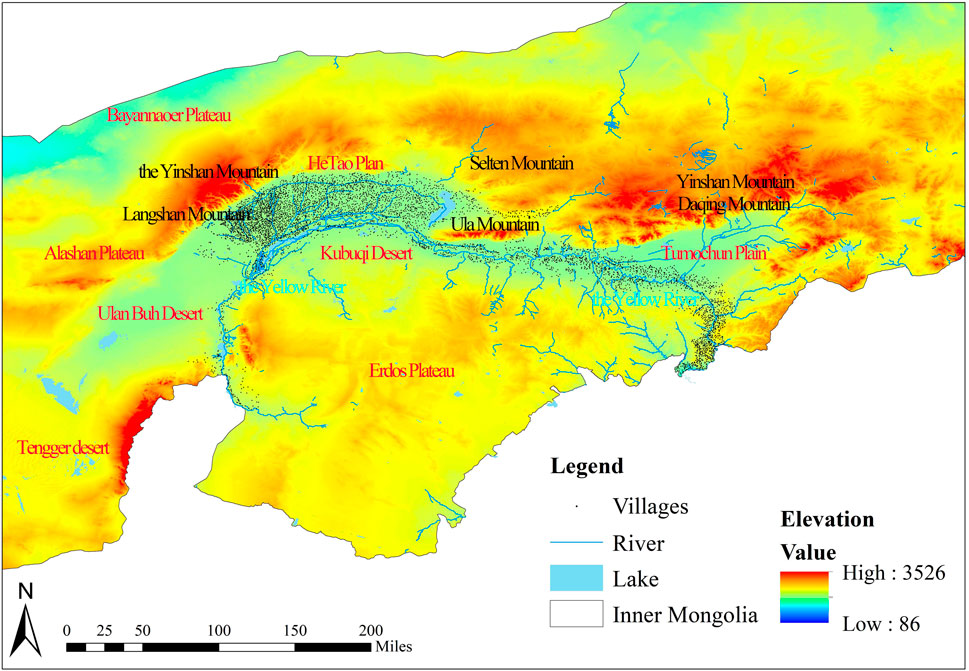
Figure 2. Map showing the topography and landform distribution around the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River.
3.1.2 Altitude
First, based on the DEM digital elevation data of the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River, using the extraction tool in ArcGIS 10.8 spatial analysis, the exact value of each village’s elevation was obtained, and resulted in an accurate elevation distribution map of the villages around the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River (Figure 3). The DEM elevation data of the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River were reclassified into five categories: ≤500 m, 501–800 m, 801–1,100 m, 1,101–1,400 m, ≥1,401 m. After gathering statistics on the number of villages in each category, the following conclusions were reached: 85.94% of the villages are located in the 801–1,100 m region. 13.70% in the 1,101–1,400 m sector, and 0.36% in the ≥1,401 m section. Villages are predominantly found at higher altitudes.
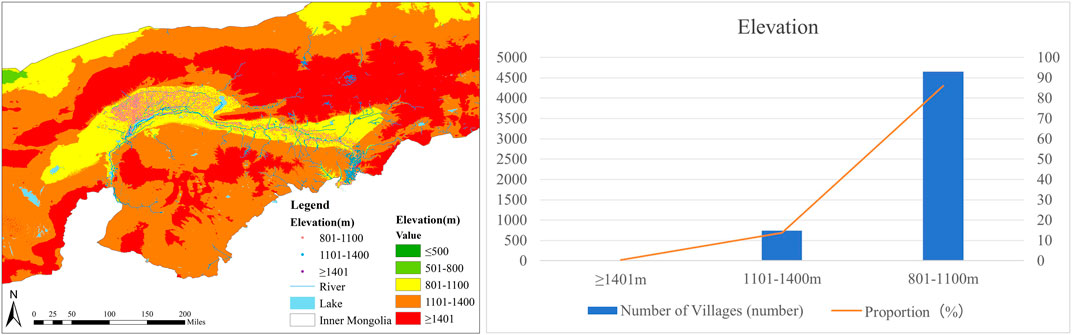
Figure 3. (A) Map showing village altitude distribution around the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River; (B) Statistical table of village elevations around the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River.
3.1.3 The value of slope
The value of slope is an important indicator that reflects the macroscopic terrain relief (Li et al., 2023). Around the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River in Inner Mongolia, in Inner Mongolia, and the terrain changes significantly. The slope value is a major factor influencing village distribution. Villages are dispersed over several slope ranges.
According to Figure 4, 322 villages, or 5.96% of the total, are located on mild slopes (6°–10°); 119, or 2.20% of the total, are placed on medium slopes (11°–15°); and 18, or 0.33% of the total, are situated on high slopes (16°–20°). 4,943 villages, which make up 91.39% of the total, are found on level slopes (≤5°), and 7 villages are located on very steep slopes (≥20°) that make up 0.13% of the total.
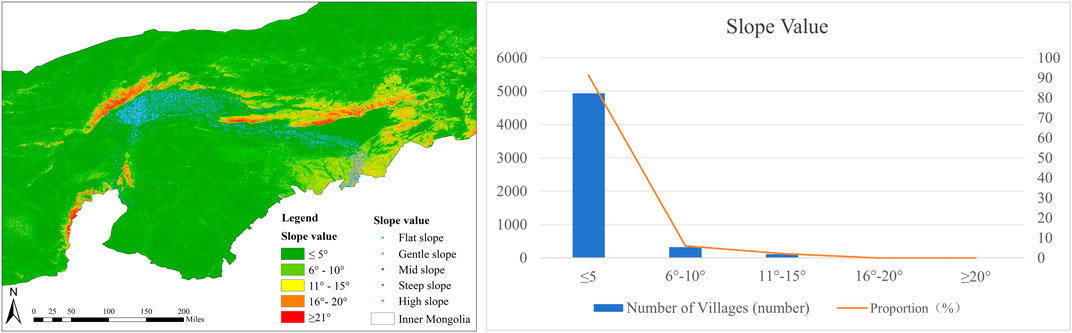
Figure 4. (A) Map showing village the value of slope distribution around the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River; (B) Statistical table of slope distribution around the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River.
Plains, low-lying landscapes, and river valleys are typically found on flat slopes, whereas hilly terrain is characterized by gentle to moderate slopes. High slopes and steep slopes are typically found in places like Daqing Mountain and Yinshan Mountain. In summary, the villages situated around the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River are primarily found in locations with mild topography. Villagers tend to build homes in areas with moderate topography for convenience and cost-effectiveness (Figure 4).
3.1.4 The aspect of slope
The slope of a village determines the amount and duration of sunshine it receives, as well as how the surrounding land surface is oriented in three dimensions. It is a major element influencing the distribution of villages and has a considerable influence on people’s everyday lives and production activities. The villages around the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River are mostly on the sunny hillsides. A substantial portion of the villages, 36.0%, are located on southern slopes, comprising 1,949 villages (including southeast, south, and southwest); the northern slope is home to the remaining 37.8% of the total number of villages, which consists of 2,046 villages (including northeast, north, and northwest). There are more villages on the northern slopes compared to the southern slopes. On the east slope are villages that makeup 13.1% of all the villages, with 709 villages, while 11.7% are located on the west slope, with 635 villages. There are more villages on the eastern slopes compared to the western slopes. Construction and development are prioritized in north-south oriented areas due to better natural lighting. To accommodate the intricate local natural environment, village construction has been integrated with the land throughout the building process (Figure 5).
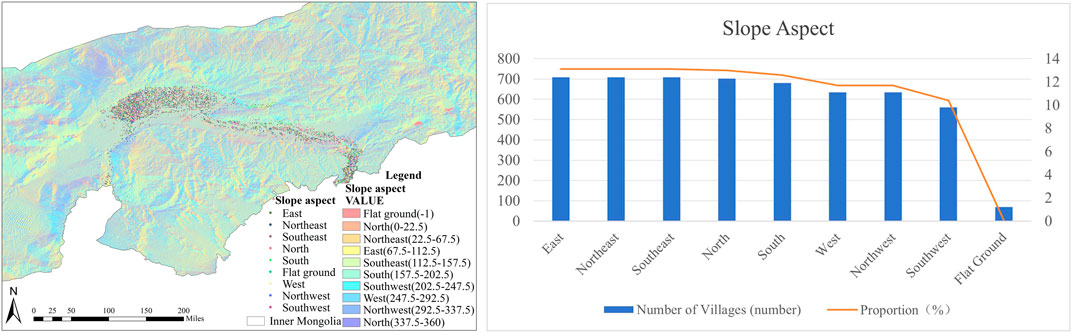
Figure 5. (A) Map showing village the aspect of slope distribution around the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River; (B) Statistical table of the aspect of slope distribution around the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River.
3.2 Hydrological
3.2.1 The classification of basin
Based on the DEM digital elevation data of the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River, hydrological analysis was performed using ArcGIS 10.8 spatial analysis tools to generate the river system and drainage area of the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River and to classify the drainage area. The drainage areas ≥1800 km2 are categorized as extra-large, areas between 1,601 km2 and 1800 km2 are considered large, and the drainage area between 1,601 km2 and 1800 km2 is considered large, the watershed area between 1,500 km2 and 1,600 km2 is medium, and the areas ≤1,300 km2 are categorized as small (Figure 6). It can be concluded that 4.71% is distributed outside the basin, 22.56% is distributed in large river basins, 0.24% is distributed in extra-large river basins, and 33.33% is distributed in small river basins. 51.72% of villages are situated within medium-sized watersheds, indicating a significant concentration of villages in medium-sized watersheds. Valjarević studied the impact of climate change and hydrology (Valjarević, 2024).
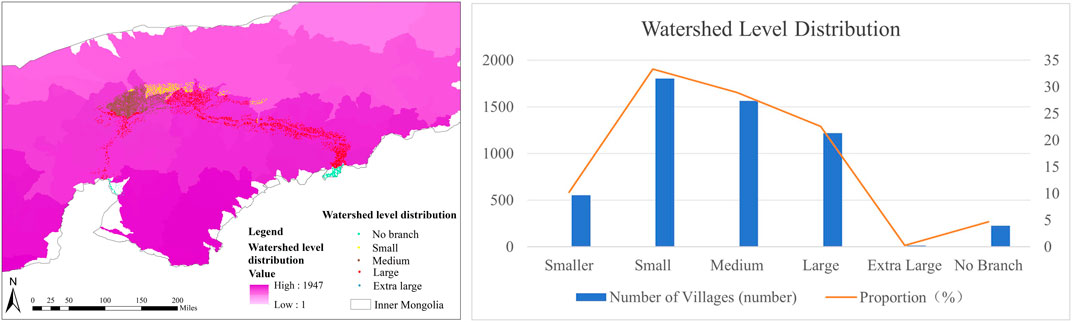
Figure 6. (A) Map showing village watershed level distribution around the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River; (B) Basin statistical table around the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River.
3.2.2 Relationships between the rivers
Using the DEM data of the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River, a detailed analysis of the relationships between villages and river sites was conducted. Initially, the river network of the Ji-shape bend was classified using a hydrological study utilizing the Arc GIS10.8 spatial analysis program. Then buffer zones of 1 km, 3 km, and 5 km were established around the rivers, and the values were set within 1 km. According to the “2020 Evaluation Criteria for Drinking Water Safety in Pastoral Areas” promulgated by Inner Mongolia, and 1 km, 3 km, and 5 km buffer zones were established for the rivers, and the values were set within 1 km. Finally, the villages and river buffer zones were superimposed to obtain an accurate distribution map of villages and rivers around the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River (Figure 7). Kamberis studied the correlation between the tectonic pattern of the region and the development of the hydrological network (Kamberis et al., 2012).
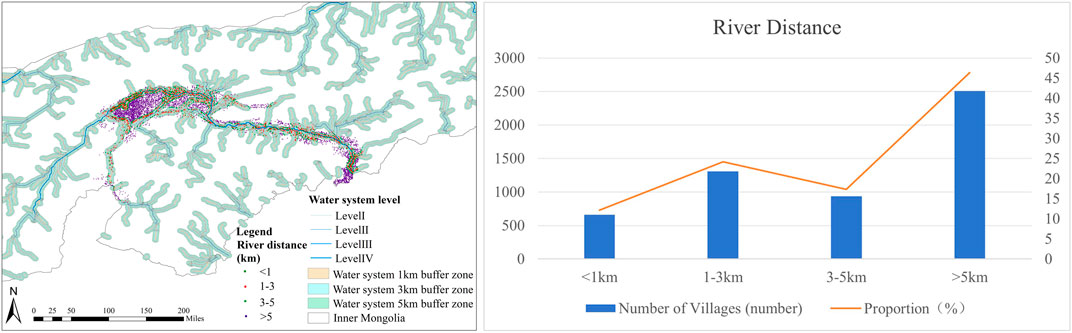
Figure 7. (A) Map showing village river relationships distribution around the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River; (B) Statistical table of river relationships around the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River.
Statistics on the relationship between villages around the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River and the river show that more than 53.67% of the villages are closely related to the river and are situated near the water. Among them, 659 villages are located within 1 km of the river, accounting for 12.18% of the total, and 1,308 villages are situated between 1 km and 3 km from the river, making up 24.18% of the total, 936 villages are found between 3 km and 5 km from the river, accounting for 17.30% of the villages, and the remaining 2,506 villages are more than 5 km away from the river, representing 46.33% of the total, accounting for 46.33% of the villages. The majority of villages are located in close proximity to the river. When planning and utilizing land, greater consideration should be given to locating residential areas near the rivers.
3.3 Climatic factors
3.3.1 Precipitation
Factors in a certain area interact with each other to form a micro-climate, which affects the shape, structure, and building height of villages, and indirectly changes their layout. The most common ways to describe a region’s climate are in terms of temperature and precipitation. For this study, the average annual precipitation for 2022 and the average temperature for 2010 were selected as the main evaluation indicators, the distribution of these indicators in relation to the villages was analyzed and overlaid with the village locations using ArcGIS 10.8, resulting in Figure 8. Figure 8 shows that precipitation decreases from east to west. Specifically, 2,610 villages experience annual precipitation ranging from 0 to 100 mm, while 2,799 villages have precipitation ranging from 100 to 200 mm, with precipitation levels gradually decreasing as indicated in the figure (Figure 8). Precipitation is an important factor that affects the distribution of villages.
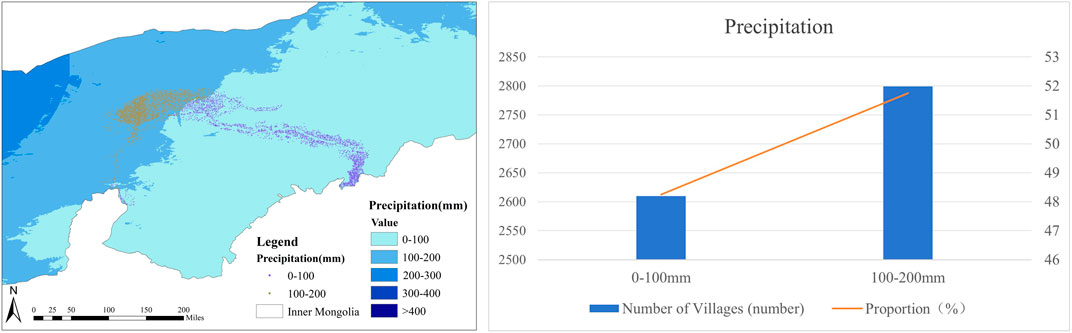
Figure 8. (A) Villages around the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River - precipitation distribution map; (B) Precipitation statistics table of villages around the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River.
3.3.2 Temperature
According to Figure 9, 401 villages experience an average temperature between 2°C and 5°C for 7.41% of the year, while 5,008 villages have an average temperature between −5 and −9°C for 92.59% of the year. These findings illustrate the impact of the environment on village distribution. The results indicate significant variations in village distribution across different climates. It is typical for people in Inner Mongolia to reside in plains with higher average annual temperatures and ample rainfall due to the region’s mild continental monsoon climate. As such, the spatial distribution of villages around the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River in Inner Mongolia is positively correlated with temperature and precipitation.
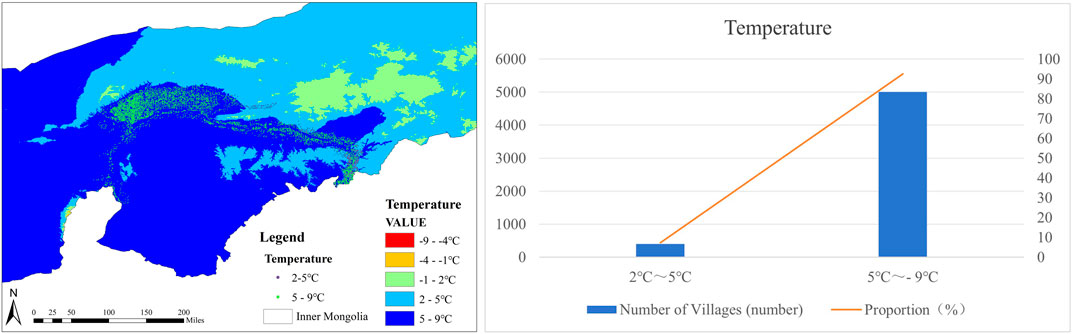
Figure 9. (A) Villages around the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River - temperature distribution map; (B) Temperature statistics table of villages around the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River.
3.4 Traffic factors
One of the key elements influencing the spatial layout of villages is their road system. This article evaluates the relationship between highway density and the number of villages in each city, using highway density as a proxy for transportation development. Figure 10 illustrates that, with only 429 villages, the dispersion of villages is relatively modest, with Hohhot and Wuhai having the highest road network density. Baotou and Erdos have the second densest road networks, with a combined total of 1,578 villages, accounting for 29.17% of the total. Bayannaoer, which has the third densest road network, contains the most villages, totaling 3,366 and accounting for 62.23%. Alashan, with the sparsest road network, has the fewest villages, numbering only 36. This sparse distribution indicates that villages in Alashan are relatively isolated. Villages are vulnerable to external damage due to their fragility and non-renewable nature. In areas with well-developed transportation infrastructure, the urbanization process tends to be faster, leading to greater potential damage to villages. Conversely, in areas with less developed transportation, the impact on villages can be mitigated, and the preservation and growth of village culture can be better supported.
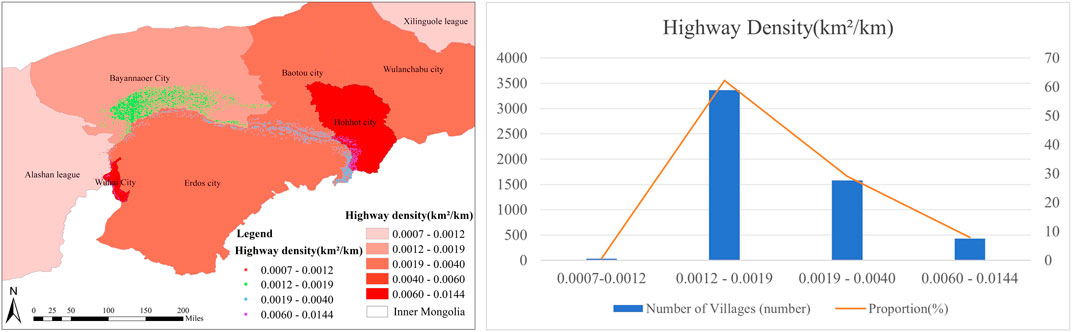
Figure 10. (A) Villages around the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River - highway density distribution map; (B) Traffic statistics table of villages around the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River.
3.5 Demographic factors
With 340 villages dispersed, or 6.29% of the total, Hohhot has the largest number of villages, as shown in Figure 11. Baotou has the second-largest population, with 327 villages spread, or 6.04% of the total. Bayannaoer and Erdos, each with 4,617 villages or 85.36% of the total, have both the highest number of villages and the third-largest population. Alashan, with only 2.31% of the total number of villages, has the smallest distribution.
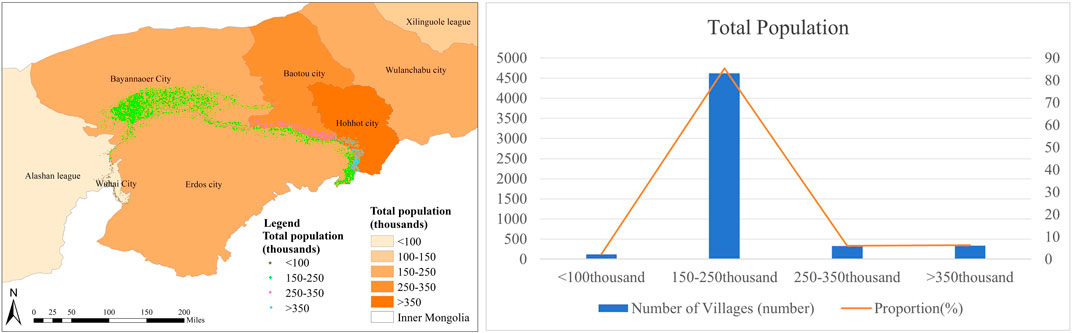
Figure 11. (A) Villages around the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River - population distribution map; (B) Demographic table of villages around the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River.
3.6 GDP
Figure 12 illustrates that Erdos has the highest GDP, with 1,251 villages, or 23.13% of the total. Erdos has the greatest GDP. Baotou and Hohhot, with 667 villages each, have the second-highest GDP, representing 12.33% of the total. Bayannaoer and Wuhai rank third in terms of GDP, with 3,455 villages, or 63.88% of the total. Alashan, with just 36 villages, has both the smallest dispersion of villages and the lowest GDP figure. The rate of urban economic growth affects village distribution: as a city develops, the number of villages tends to decrease.

Figure 12. (A) Villages around the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River - GDP distribution map; (B) GDP table of villages around the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River.
3.7 The rate of urbanization
Figure 13 illustrates that Wuhai has the highest rate of urbanization and the fewest number of villages—just 89, or 1.65% of the total. The second-highest rates of urbanization are found in Alashan and Baotou have the second-highest urbanization rates, with Alashan having the second-largest number of villages at 363, making up 6.71% of the total. Hohhot and Erdos exhibit the third-highest urbanization rates, with a combined total of 1,591 villages, or 29.41% of the total. Bayannaoer, with 62.23% of the total number of villages, shows the largest distribution of villages and the fewest urbanizations. This data indicates an inverse correlation between the rate of urbanization and the distribution of villages. The spread of villages decreases with the increase of the rate of urbanization. Inner Mongolia has long emphasized the importance of ecological protection and considers it a critical strategy. It has promulgated corresponding regulations to promote ecological construction and protect the environment. Compared to the baseline scenario, land use changes under the ecological protection priority scenario would favor the expansion of forest and grassland areas (Hasan et al., 2017).
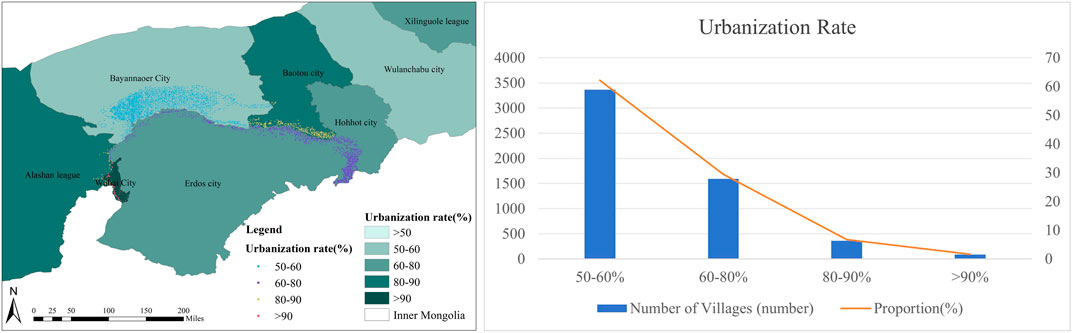
Figure 13. (A) Villages around the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River -the rate of urbanization distribution map; (B) The rate of urbanization table of villages around the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River.
3.8 The proportion of tertiary industry
With 340 villages, or 6.29% of the total, Hohhot has the highest percentage of tertiary industry, as shown in Figure 14. The second-highest percentage of tertiary industry is found in Baotou, with 327 villages, accounting for 6.05%. Bayannaoer, with 3,366 villages or 62.23% of the total, has the third-highest percentage of tertiary industry. Erdos, Alashan, and Wuhai, with 1,376 villages or 25.43%, have the lowest percentage of tertiary industry.
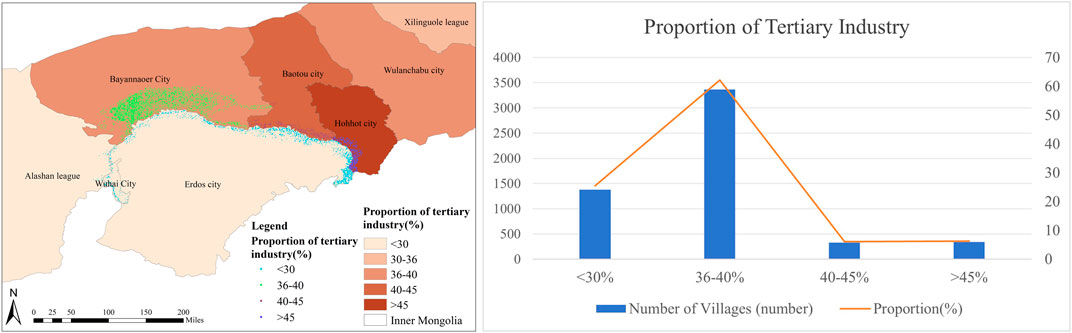
Figure 14. (A) Villages around the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River -distribution map of the proportion of the tertiary industry; (B) Proportion of tertiary industry table of villages around the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River.
Economic and demographic factors significantly influence village distribution. A visual analysis of Inner Mongolia’s total population, GDP, and urbanization rate has been conducted to explore the relationship between these factors and village distribution. Figure 15 illustrates the percentage of tertiary and primary industries. It shows that road density and the proportion of primary industry have a significant impact on village distribution. Bayannaoer has the most traditional villages and the highest proportion of primary industry. Road density is inversely proportional to the distribution of villages, as evidenced by Wuhai, which has the highest road density and the lowest village distribution.
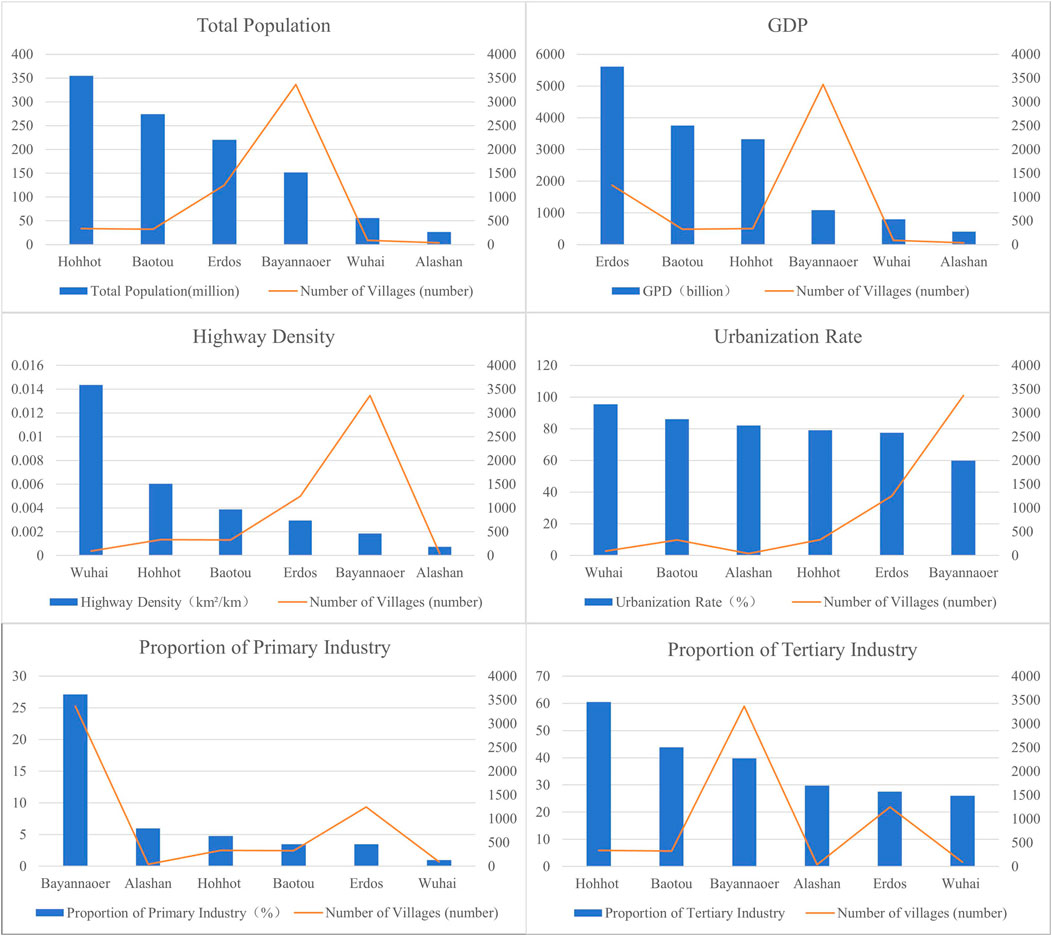
Figure 15. Distribution map of the number of villages and economic development levels around the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River.
3.9 History and cultural heritage
With a long history of ethnic diversity, Inner Mongolia has developed a vibrant nomadic society. The distribution of traditional villages significantly influences their historical context. As a result, one major determining aspect is the distribution features of traditional villages. Figure 16 shows that with 327 traditional villages—or 6.05% of all villages—Baotou has the greatest spread of traditional villages. Bayannaoer and Hohhot have the second-largest distribution of traditional villages, with 3,706 villages, or 68.52% of the total. Alashan and Erdos, with 1,287 villages, make up 23.79% of the total, ranking them third in terms of traditional village distribution. Wuhai, with only 89 traditional villages, represents the smallest distribution, making up 1.65% of the total. There is a strong correlation between the number of villages and the dispersion of traditional villages, with local government policies having a significant impact.

Figure 16. (A) Villages around the Ji-shape bend in the Yellow River -distribution map of traditional villages; (B) Traditional villages around the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River.
3.10 Factors affecting village distribution
3.10.1 Single factor detection
Among the numerous variables influencing the distribution of villages, this study focuses on both natural and social elements. Several natural elements impact the dispersal of villages, including temperature, precipitation, elevation, slope aspect, and proximity to rivers. In total, twelve social factors were examined, including total population, GDP, the rate of urbanization, highway density, number of traditional villages, and percentage of tertiary industry. The spatial differentiation of villages in Inner Mongolia was analyzed using GeoDetector2018 software to explain the extent to which each factor influences village distribution throughout the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River. The q-values for each factor are as follows: X10 the value of slope (0.319)>X12 elevation (0.245)>X1 the aspect of slope (0.074)>X9 river distance (0.026)>X7 road density (0.019) >X6 the rate of urbanization (0.019) >X3 proportion of tertiary industry (0.018)>X5 GDP (0.017)>X8 total population (0.010)>X4 number of traditional villages (0.009)>X11 precipitation (0.002)>X2 temperature (0.0001).
Among these, natural factors account for 0.668, while social factors account for 0.093. Therefore, the distribution of villages is significantly influenced by natural factors. In an agricultural society, favorable natural conditions, such as temperature and precipitation, facilitate village formation. Thus, villages are most affected by natural factor. Among natural factors, slope, elevation, and slope aspect have the greatest influence, affecting both site selection and village layout, as well as crop growth. Among social factors, economic aspects such as road density, urbanization rate, and the proportion of the tertiary industry are important in influencing village layout. In modern society, economic factors contributing to the decline of villages are also significant.
3.10.2 Multi-factor detection
Different influencing factors have varying degrees of correlation with one another, and the way two elements interact will determine how much of an explanatory power each has (Song et al., 2008). The primary factors influencing village distribution in Inner Mongolia, specifically along the Ji-shape bend area, were examined through interaction analysis to assess the capacity of various variables to interact and identify the significance of the two factors in village distribution. Test results are illustrated using heatmap features (Figure 17).
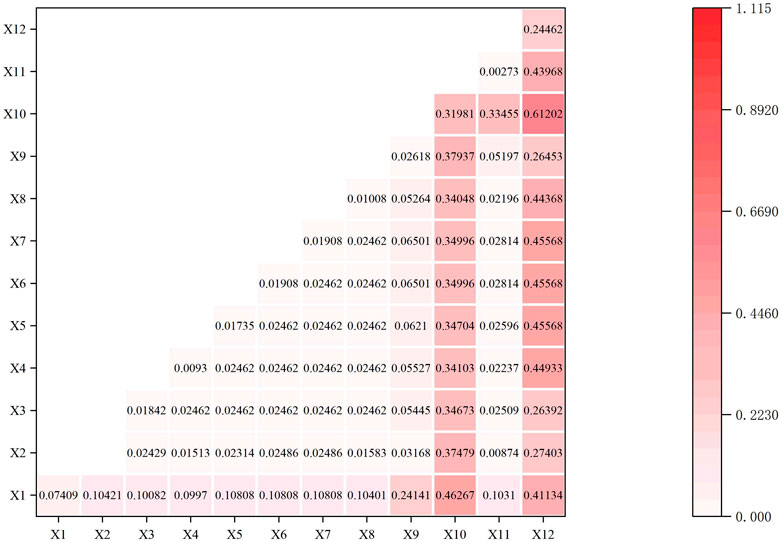
Figure 17. Heat map of geographical detection of villages around the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River.
The interaction results can be divided into double-factor increase and non-linear increase. Comparing the outcomes to that of a single impact factor, the combined influence of all interaction variables greatly increases the geographical heterogeneity of the dependent variable. The results show that the interaction factors of the slope and elevation group are the strongest, exceeding 0.6, followed by aspect and slope, GDP and elevation, the rate of urbanization and elevation, and road density and elevation, which are the four highest interaction factors showing double-factor enhancement. The elements that most effectively describe how villages are distributed throughout the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River of Inner Mongolia include height, the value of slope, the aspect of slope, GDP, the rate of urbanization, and highway density. This shows that the distribution of villages is not affected by a single result, but also interacts with multiple factors. Among them, natural factors such as the slope and elevation of topography have a significant impact on the distribution characteristics of villages, and social factors such as GDP, the rate of urbanization, and road density also have a certain impact on village distribution. In ancient times, the factors affecting the development of villages were mainly natural, influencing their farming and laboring as well as the layout of their houses, whereas, in modern times, they receive more influence from the role of the economy, which affects the sustainable development of villages.
4 Discussion
4.1 Spatial distribution characteristics
4.1.1 Type of spatial distribution
Using the ArcGIS 10.8 spatial statistics tool, it was calculated that the average nearest neighbor index actual distance between villages around the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River is 1.173 km, the theoretical closest neighbor distance is 2.312 km on average, where 0.507475 < 1 is the nearest neighbor index R, indicating a somewhat unequal geographical distribution of villages along the Yellow River in Inner Mongolia.
4.1.2 Balance to regional distribution
The following results are yielded: a z-score of 189.168622, Moran’s I > 0, indicating a substantial positive spatial correlation, and a spatial distribution pattern showing value aggregation with minimal spatial variation.
The following results are obtained, X = 1,563.26 km, M = 2,700.20 km, CV = 57.89%, with the coefficient of variation falling between 33% and 64%. The spatial distribution type is identified as random distribution (Figure 18).
Equation 1 can be used to determine the imbalance index S = 0.744, which indicates a generally balanced distribution of villages around the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River in Inner Mongolia. The distribution of each region is shown in the figure below (Figure 19).
Based on the calculations made using Equations 2, 3, the Gini coefficient is 0.17, which suggests a relatively low degree of concentration. Here, C = 0.83,
4.1.3 Spatial distribution agglomeration area
By using Equation 4, it can be calculated that the G value is 66.98 and 2.30,
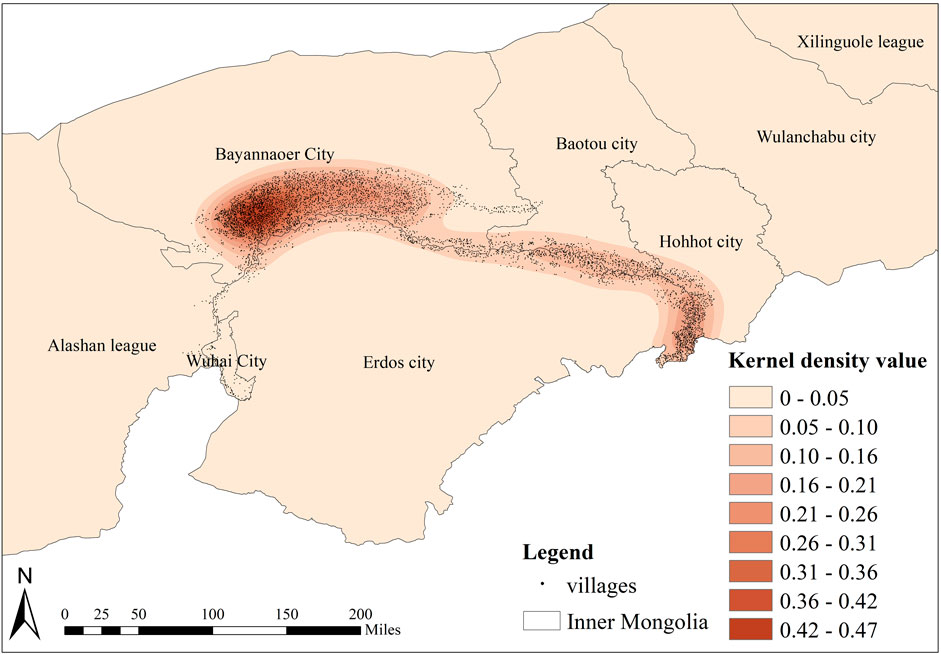
The villages were subjected to kernel density analysis using the Arc GIS10.8 spatial analysis tool. The outcome was a map of Inner Mongolian villages based on kernel density analysis, which contained the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River (Figure 21). According to analysis, the villages around the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River in Inner Mongolia show two high-density agglomeration areas, with Linhe in Bayannaoer and Hangjinhou and Zhungeer in Erdos City serving as the cores. This indicates a centripetal distribution of agglomeration. The density of the patch distribution gradually decreases from the center to the surrounding areas; it diminishes along the river route through Bayannaoer and Erdos, with the most secondary dense areas in Alashan and Wuhai.
In summary, the Yellow River basin of Inner Mongolia has a relatively uneven village spatial distribution, as indicated by the nearest neighbor index of 0.507475 (which is less than 1). Moran’s I for the distribution is 0.904158, indicating minimal geographic difference and a strong positive spatial association. The geographical distribution type is random, with a coefficient of variation (CV) between 33% and 64%, and a CV of 57.89%. According to the imbalance index S = 0.744, the distribution of villages around Inner Mongolia’s Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River is fairly balanced. The degree of concentration is not high, as indicated by the 0.17 Gini coefficient. There is a rather dense distribution of villages, as shown by the geographical concentration index G value of 66.98. After examining techniques such as spatial autocorrelation analysis, the geographical concentration index, kernel density analysis, the variation coefficient, the imbalance index, and the Gini coefficient, it can be concluded that the overall distribution trend of villages around the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River shows a significant positive spatial correlation. The spatial difference is small, and the spatial distribution is relatively balanced. The villages are randomly distributed but unevenly so, with a moderate degree of concentration. The villages around the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River are dispersed across Erdos, with a greater concentration in Bayannaoer and less distribution in Wuhai and Alashan. The cities of Hohhot and Baotou constitute the heart of the distribution agglomeration, forming a high-density agglomeration region with features of centripetal aggregation. The density of the patch distribution progressively decreases along the river route through Bayannaoer and Erdos, with secondary dense spots in Alashan and Wuhai.
4.2 Natural features of the village
This paper focuses on 5,409 village patches around the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River as the subject of study. The characteristics of the villages’ geographical distribution around the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River are explored through the examination of the present situation and map placement.
When analyzing the geographical environment of the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River, it can be concluded that the terrain is very complex, including mountains, rivers, deserts, plateaus, and plains. However, the Tumochuan Plain and Hetao Plain host the majority of villages. These plains have an average elevation above 1,000 m, making them conducive to village settlement. There are numerous mountains around the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River in Inner Mongolia, leading to significant terrain variations. One major factor influencing the distribution of villages is slope. Most villages are situated in areas with gentle slopes. Additionally, villages are more abundant on level slopes, with a higher concentration on northern and eastern slopes compared to southern and western slopes. The northern bank of the Yellow River has a denser distribution of villages compared to the southern bank. Villages are also widely dispersed along the Yellow River’s tributaries. Plains with moderate slopes and ample sunshine support extensive village dispersal, providing a favorable natural environment for crop cultivation and habitation in lowland areas. Most villages are located near aquatic vegetation or transportation hubs in rural areas (Yang et al., 2016).
Access to water is crucial for village livelihoods and productivity. Villages benefit from abundant water resources in their vicinity (Guo et al., 2012). The expansive Yellow River flows near most villages in the river basin. Villages are evenly distributed around the river basin, with approximately 58.9% of villages located within 5 km of the river. Villages maintain a certain distance from the river to avoid flooding during high tides and to facilitate convenient river transportation. This aligns with findings from other academic studies (Wang et al., 2021; Fu, 2021). Water resources significantly influence village location and layout.
Climate also influences village distribution. Temperature and precipitation in the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River in Inner Mongolia correlate with the spatial distribution of villages. Plain areas with sufficient rainfall and higher temperatures are favorable for crop growth, while desert regions with arid conditions have fewer villages.
Effective urban planning must comprehensively consider geographical factors, including topography, landforms, and proximity to water resources, as well as climate-related impacts. These factors are critical for conducting rational planning and layout based on terrain conditions in urban planning processes.
4.3 Social characteristics of the villages
At the same time, social conditions, such as population, economy, history, and other conditions also affect the distribution of villages (He et al., 2019). To begin with, transportation has the opposite effect on village growth. In areas with developed transportation, the urbanization process is relatively fast, and the damage to villages is greater. In areas with inconvenient transportation, it can alleviate the impact on villages, to facilitate the inheritance and development of village culture. The convenience of transportation has enabled the village’s economy to develop, making it easier to change the past production and lifestyle and develop in a more modern direction. Therefore, transportation has a counterproductive effect on the inheritance of the village. Secondly, the geographical distribution of villages is influenced by demographic considerations. Rural economic growth can benefit more from higher population densities. On the contrary, a small population size is less favorable for the development of economic activities. Regarding the influence of historical factors, the more economically developed the area is, the stronger the awareness of protecting traditional villages, which has an important relationship with economic development (Li et al., 2023). In conclusion, the rate of urban economic expansion impacts the allocation of villages. The spread of villages decreases as a city’s degree of development increases. Developed economic life has destroyed the production and lifestyle of traditional villages and affected the development and layout of villages (Li et al., 2023). The productivity and way of life of traditional villages have been destroyed by developed economies, which has also had an impact on the growth and design of villages. But it also has a dialectical effect. On the one hand, it encourages village growth while destroying the traditional village layout. However, it also fosters the development of the village’s features and preserves its traditional culture. Village development is a long-term spontaneous process with little influence from urban planning. Later planning can have a good impact on the development of the village, which requires the joint efforts of the government and villagers.
4.4 Factors affecting the distribution of villages
According to analysis, natural environment serve as the foundation for the geographical dispersion of villages (Li et al., 2022). According to the findings of study publications by Gao et al. (2023), Qu et al. (2017), and others, natural variables have a significant influence on village distribution. The exceptional natural surroundings can offer a wealth of natural resources, comfortable living arrangements, and easy access to transportation—all of which are essential for regional growth (Guanghui et al., 2007). The layout is significantly affected by natural features. The impacts of natural elements that have the highest explanatory power include height, the value of slope, and the aspect of slope (Zhang et al., 2018). In ancient times, people tended to choose plain areas with suitable climates and superior geographical conditions to develop agriculture and animal husbandry. Communication among the villagers along the river became more convenient, hence that is how the villages were formed, which is consistent with the traditional understanding.
In terms of social determinants, the highest explanatory power among socioeconomic variables is found in the rate of urbanization, highway density, and the percentage of tertiary industry. That is to say, the traffic factor is the strongest dominant factor affecting factors. This is consistent with the conclusions obtained by Gao et al. (2023), Li et al. (2023), and others (Zhe et al., 2022). Transportation affects communication between villages. Convenient transportation is conducive to foreign trade and ensures the accessibility of villages. Villages tend to choose places with more convenient transportation for development. In areas with underdeveloped economies and the lowest urbanization rates, there are more traditional villages in Bayannaoer City than anywhere else. The growth of villages has been impacted by economic activity, and as living standards have increased, the government has been able to preserve, restore, and pass down traditional villages, which in turn has helped to boost village development.
In conclusion, the distribution of villages is mostly influenced by the natural environment. Secondly, villages’ ability to flourish is somewhat hampered by the modernization process. However, this development is two-sided, and good economic conditions also bring more possibilities for the protection of villages. Villages are where culture is carried. Putting in place effective protective measures will influence village development and encourage further growth.
4.5 Social characteristics of the villages
The culture of site selection is tied to the village’s fundamental existence and future growth, although it is not very clear what cultural manifestations link to requirements that are developing and being unmet (Xie et al., 2022). Traditionally built villages are frequently found in regions with delicate natural settings (Yang et al., 2016). As a result, care should be taken to explore how villages’ unseen cultural elements are developing. As ecological civilization development and rural rejuvenation advance, village protection should carefully address the holistic preservation of traditional culture, the natural environment, and the social economy. There should be special protections for different kinds, locations, and characteristics of traditional villages (Zheng et al., 2021).
According to the studies aforementioned above, for rural development in environmentally vulnerable regions, the following suggestions are put forward to protect village development: 1. To boost financial investment in developing regions and offer financial assistance for the preservation of these regions’ economies and cultures; 2. To utilize existing historical and cultural resources, develop local cultural characteristics, enrich and develop local cultural industry construction, and provide certain support for rural revitalization; 3. To ensure the harmonious development of villages, give careful consideration to the establishment of rural cultural ecology and the preservation of the natural environment. Take note of rural regions’ ecological carrying capability, reject excessive commercial development of rural villages, develop diversified protection measures, properly handle the relationship between rural development and preservation, as well as facilitate the sensible and planned growth of rural regions; 4. Since the distribution of villages is uneven, account should be taken that the villages in different watersheds have different characteristics. Because of their aggregation, hydrophilicity, nationality, and political factors, integrating different villages into different watershed units can help build watershed units, aquatic ecosystems, and a focus on sustainable development. It can also help overcome the limitations of administrative units and protect the regional characteristics formed in different watersheds. Finally, it can enrich and protect the village’s content and create an effective protection mechanism.
The ecological, cultural, economic, and social environments that sustain traditional villages are inextricably linked. The primary cause of the current traditional village culture’s downfall is the fast changes in the village’s environment for survival and evolution, as well as the community’s incapacity to adjust to these changes (Ma and Tong, 2022). Therefore, paying attention to the environmental changes and self-development of villages is an eternal topic, and we are called upon to make unremitting efforts.
5 Conclusion
The research on the geographical distribution features and affecting elements of the 5,409 village patches around the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River is crucial for effective resource management, environmental preservation, socio-economic development, and informed policymaking. By providing insights into spatial patterns and their impacts, the research supports sustainable development practices, enhances villages wellbeing, and helps manage environmental and hydrological challenges in this region. The study found that social factors and natural factors affect the distribution of villages, among which natural factors are the main factors affecting the distribution of villages. Therefore, the influence of natural factors should be considered when planning the layout of villages. The research’s findings are as follows:
The overall distribution trend of villages around the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River is that the spatial distribution has a significant positive correlation, the spatial difference is small, the spatial distribution is relatively balanced, random distribution, uneven distribution, and the degree of concentration is not high. It has a relatively uneven village spatial distribution, as shown by the nearest neighbor index of 0.507475 < 1. The index of Moran’s I for the distribution is 0.904158, the geographic difference is minimal, and a strong positive association is present. The geographical distribution type is random, 33% < CV < 64%, is the variance coefficient, and the variance coefficient is CV = 57.89%. According to the imbalance index S = 0.744, the distribution of villages around Inner Mongolia’s Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River is fairly balanced. The degree of concentration is not high, as indicated by the 0.17 Gini coefficient. There is a rather dense distribution of villages, as shown by the geographical concentration index G value of 66.98; Regarding the factors affecting the distribution of villages around the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River, natural factors are an important factor affecting the spatial distribution of villages. The locations of villages are determined by natural environmental variables. Both social and environmental elements have a major impact on the layout. The rate of urbanization (0.019082), road density (0.019082), and the percentage of tertiary industry (0.018422) have the best explanatory power among socioeconomic factors, whereas elevation (0.244619), the value of slope (0.319805), and the aspect of slope (0.074089) have the strongest explanatory power among the impacts of natural elements; When protecting villages, corresponding protection methods should be selected based on different influencing factors. For village protection in ecologically sensitive areas, attention should be paid to the utilization of water resources in the basin, and protection areas should be divided. At the same time, ecological construction should be reasonably promoted and attention should be paid to the protection of the natural environment, rational utilization, and development of local resources. When planning, pay attention to the impact of natural factors, among which geographical and landform factors are very important. Based on this, the planning and layout of the site should be carried out. At the same time, the impact of social factors should be taken into consideration, and the effect of economic development on the village should be paid attention to. On the issue of atmosphere, we should enhance the climate adaptability of buildings. By considering climate change, we should enhance the climate adaptability of buildings and reduce air pollution caused by building construction; Land use has a very important impact on the development of villages. We should pay attention to land use and provide the public with a piece of relatively open information, to provide certain guidance for the sustainable development of cities and villages. The development of urbanization has brought about contradictions in land use. Reasonable allocation of land and improvement of land use efficiency will further improve the urban and rural living environment and meet the needs of residents for survival and development in the process of urbanization.
Only 12 natural and social components were chosen as the study’s influencing factors for investigation due to the article’s constraints. The analysis may not be comprehensive. In the future, it can be suggested that the next research focus on a deeper, micro-level research, such as on specific villages, exploring the laws of its development and evolution.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are publicly available. This data can be found here, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors. http://www.geodata.cn; http://geodata.pku.edu.cn; http://www.resdc.cn; https://tj.nmg.gov.cn/.
Author contributions
ZW: Writing–review and editing, Data curation, Investigation. SJ: Writing–original draft, Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Validation, Visualization. SX: Writing–review and editing, Resources, Supervision. JZ: Writing–review and editing, Data curation. FM: Writing–review and editing, Data curation. MZ: Writing–review and editing, Resources, Supervision.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was funded by the “Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region Key R&D and Achievements Transformation Program Project ‘Research and Development of Assembly Building Productization for Prefabricated Construction in Ecologically Sensitive Areas along the Yellow River in Inner Mongolia’ (2023YFHH0025)”; “Inner Mongolia Natural Science Foundation Project ‘Research on the Coupling Mechanism of Traditional Construction Techniques and Contemporary Modular Construction Mode of Residential Buildings around the Ji-shape Bend of the Yellow River in Inner Mongolia’ (2024MS05014)”; “National Natural Science Foundation of China Youth Fund Project ‘Research on Modular Construction Method of Grassland Grazing in Inner Mongolia under Fixed Grazing Mode’ (52408026)”.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region Key R&D and Achievements Transformation Program Project and Inner Mongolia Natural Science Foundation Project and National Natural Science Foundation of China Youth Fund Project for their support. They also thank all the authors for their hard work.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Adi, S., and Suhartono, J. (2017). “Smart village geographic information system (GIS) development in Indonesia and its analogous approaches, translated by IEEE,” in 2017 International Conference on Information Management and Technology (ICIMTech), Special Region of Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 15-17 November 2017 (IEEE), 65–70.
Bai, Y., Jiang, B., Wang, M., Li, H., Alatalo, J. M., and Huang, S. (2016). New ecological redline policy (ERP) to secure ecosystem services in China. Land Use Policy 55, 348–351. doi:10.1016/j.landusepol.2015.09.002
Bian, J., Chen, W., and Zeng, J. (2022). Spatial distribution characteristics and influencing factors of traditional villages in China. Int. J. Env. Res. Pub. He 19 (8), 4627. doi:10.3390/ijerph19084627
Brookes, P. (1995). The use of microbial parameters in monitoring soil pollution by heavy metals. Fertil. Soils 19, 269–279. doi:10.1007/BF00336094
Chang, C., and Wang, Y. (1994). The nature of the township-village enterprise. J. Comp. Econ. 19 (3), 434–452. doi:10.1006/jcec.1994.1111
Chen, J., Wang, C., Dai, R., Xu, S., Shen, Y., and Ji, M. (2021a). Practical village planning strategy of different types of villages—a case study of 38 villages in shapingba district, chongqing. Land 10 (11), 1143. doi:10.3390/land10111143
Chen, Z., Zhang, Q., Li, F., and Shi, J. (2021b). Comprehensive evaluation of land use benefit in the Yellow River Basin from 1995 to 2018. Land 10 (6), 643. doi:10.3390/land10060643
Chi, Y. L., and Mak, H. W. L. (2021). From comparative and statistical assessments of liveability and health conditions of districts in Hong Kong towards future city development. Sustainability 13 (16), 8781. doi:10.3390/su13168781
Daoyong, L., Mengge, L., and Junchen, L. (2020). Design strategy of rural settlement landscape: a case study of xinji village in beijing. J. Landsc. Res. 12 (2). doi:10.16785/j.issn1943-989x.2020.2.006
Du, J. (2023). Research on optimization of industrial spatial layout in jizi bay area of the Yellow River Basin. Front. Econ. Cult., 30–33.
Feng, Y., Wei, H., Huang, Y., Li, J., Mu, Z., and Kong, D. (2023). Spatiotemporal evolution characteristics and influencing factors of traditional villages: the Yellow River Basin in Henan Province, China. Sci 11 (1), 97. doi:10.1186/s40494-023-00939-y
Fu, J., Zhou, J., and Deng, Y. (2021). Heritage values of ancient vernacular residences in traditional villages in Western Hunan, China: spatial patterns and influencing factors. Build. Environ. 188, 107473. doi:10.1016/j.buildenv.2020.107473
Fu, X. L. (2021). Cognitive research on spatial morphology of traditional villages based on ecological perspective. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 30 (2 A), 2285–2289.
Gao, C., Wu, Y., Bian, C., and Gao, X. (2023). Spatial characteristics and influencing factors of Chinese traditional villages in eight provinces the Yellow River flows through. River Res. App 39 (7), 1255–1269. doi:10.1002/rra.3880
Guanghui, J., Fengrong, Z., Junwei, C., Zengqiang, D., and Ziyou, S. (2007). Analysis of the driving forces of change of rural residential areas in Beijing mountainous areas based on Logistic regression model. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 23 (5), 81–87.
Guo, L., Guo, X., Fang, C., and Zhu, S. (2015). Observation analysis on characteristics of formation, evolution and transition of a long-lasting severe fog and haze episode in North China. Sci. China Earth Sci. 58, 329–344. doi:10.1007/s11430-014-4924-2
Guo, X., Ma, L., and Zhang, Q. (2012). A GIS-based research on the spatial evolution characteristics and driving mechanism of the rural settlements in qin, an county. Econ. Geogr. 32 (7), 56–62.
Hasan, S. S., Deng, X., Li, Z., and Chen, D. (2017). Projections of future land use in Bangladesh under the background of baseline, ecological protection and economic development. Sustainability 9 (4), 505. doi:10.3390/su9040505
Hasegawa, H., Akata, N., Kawabata, H., Chikuchi, Y., Sato, T., Kondo, K., et al. (2007). Mechanism of 7 Be scavenging from the atmosphere through precipitation in relation to seasonal variations in Rokkasho Village, Aomori Prefecture, Japan. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 273, 171–175. doi:10.1007/s10967-007-0731-y
He, X. Q., Gong, S. S., Hu, J., and Xu, J. J. (2019). Spatial differentiation and it’s influence factors of traditional villages in hunan, hubei and jiangxi provinces at different scales. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 28, 2857–2866.
Hu, D., and Wang, R. (1998). Exploring eco-construction for local sustainability: an eco-village case study in China. Ecol. Eng. 11 (1-4), 167–176. doi:10.1016/S0925-8574(98)00032-9
Jia, A., Liang, X., Wen, X., Yun, X., Ren, L., and Yun, Y. (2023). GIS-based analysis of the spatial distribution and influencing factors of traditional villages in Hebei Province, China. Sustainability 15 (11), 9089. doi:10.3390/su15119089
Jin, L., Wang, Z., and Chen, X. (2022). Spatial distribution characteristics and influencing factors of traditional villages on the Tibetan plateau in China. Int. J. Env. Res. Pub. He 19 (20), 13170. doi:10.3390/ijerph192013170
Kamberis, E., Bathrellos, G., Kokinou, E., and Skilodimou, H. J. O. G. (2012). Correlation between the structural pattern and the development of the hydrographic network in a portion of the Western Thessaly Basin (Greece). Central Eur. J. Geosciences 4 (3), 416–424. doi:10.2478/s13533-011-0074-7
Kim, G., Kang, W., Park, C. R., and Lee, D. (2018). Factors of spatial distribution of Korean village groves and relevance to landscape conservation. Landsc. urban Plan. 176, 30–37. doi:10.1016/j.landurbplan.2018.03.015
Kim, Y.-T., Choi, S.-M., Kim, H.-G., and Im, S.-B. (2014). Development of evaluation indicators system by rural village types. J. Kor. Soc. Rural. Plan. 20 (1), 37–49. doi:10.7851/ksrp.2014.20.1.037
Kowkabi, L. (2020). The fundamental characteristics of the rural landscape through application of grounded theory (case study: historic village of Furg). J. Environ. Stud. 45 (4), 693–709. doi:10.22059/JES.2020.295707.1007968
Lal, R. (2005). Forest soils and carbon sequestration. For. Ecol. Manage 220 (1-3), 242–258. doi:10.1016/j.foreco.2005.08.015
Lee, H.-W., Kim, Y.-J., and Choi, S.-M. (2004). A study on spatial structure analysis for comprehensive rural clustered villages development area using the space syntax method technique. J. Korean Soc. Rural. Plan. 10 (4), 19–28.
Li, D., Gao, X., Lv, S., Zhao, W., Yuan, M., and Li, P. (2023). Spatial distribution and influencing factors of traditional villages in inner Mongolia autonomous region. Buildings 13 (11), 2807. doi:10.3390/buildings13112807
Li, J., Wang, X., and Li, X. (2020). Analysis of spatial distribution characteristics and influencing factors of traditional villages in China. Econ. Geogr. 40, 143–153.
Li, M., Ouyang, W., and Zhang, D. (2022). Spatial distribution characteristics and influencing factors of traditional villages in Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region. Sustainability 15 (1), 632. doi:10.3390/su15010632
Li, W. (2015). Research on the localization method of protecting traditional village landscape: a case study on tangyin. Int Arch Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 40, 289–294.
Lin, S., and Ma, Y. (2023). Creating spatial characteristics of traditional village entrances based on multivariate statistical analysis--taking zengcheng district, guangzhou as an example. Appl. Math. Nonlinear Sci. 9 (1). doi:10.2478/amns.2023.2.01188
Liu, C., and Xu, M. (2021). Characteristics and influencing factors on the hollowing of traditional villages—taking 2645 villages from the Chinese traditional village catalogue (Batch 5) as an example. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 18 (23), 12759. doi:10.3390/ijerph182312759
Liu, W., Xue, Y., and Shang, C. (2023). Spatial distribution analysis and driving factors of traditional villages in Henan province: a comprehensive approach via geospatial techniques and statistical models. Herit. Sci. 11 (1), 185. doi:10.1186/s40494-023-01038-8
Ma, H., and Tong, Y. (2022). Spatial differentiation of traditional villages using ArcGIS and GeoDa: a case study of Southwest China. Ecol. Inf. 68, 101416. doi:10.1016/j.ecoinf.2021.101416
Mahlabani, Y. G., Shahsavari, F., and Alamouti, Z. M. (2016). Eco-village, amodel of sustainable architecture. J. Fundam. Appl. Sci. 8 (3S), 1835–1847. doi:10.4314/jfas.v8i3s.312
Marcinko, C. L., Samanta, S., Basu, O., Harfoot, A., Hornby, D. D., Hutton, C. W., et al. (2022). Earth observation and geospatial data can predict the relative distribution of village level poverty in the Sundarban Biosphere Reserve, India. J. Environ. Manage 313, 114950. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.114950
Mohammadi Yegane, D. B., Cheraghi, M., and Yazdani, Z. (2014). Analysis of the factors affecting the spatial distribution of poverty in rural areas, by emphasizing on the economic-social characteristics, case study: mahmoudabad Village, Shahin Dej Town Ship. Geog. Terr. Spat. Arrange. 4 (13), 83–96. doi:10.22111/GAIJ.2014.1775
Momose, K. (2002). Environments and people of Sumatran peat swamp forests II: distribution of villages and interactions between people and forests. Jpn. J. Se. Asian. Stud. 40 (1), 87–108. doi:10.20495/tak.40.1_87
Moss, B. (2008). Water pollution by agriculture. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 363 (1491), 659–666. doi:10.1098/rstb.2007.2176
Myeong, S., Jung, Y., and Lee, E. (2018). A study on determinant factors in smart city development: an analytic hierarchy process analysis. Sustainability 10 (8), 2606. doi:10.3390/su10082606
Nash, C. J. (2013). The age of the “post-mo”? Toronto’s gay village and a new generation. Geoforum 49, 243–252. doi:10.1016/j.geoforum.2012.11.023
Nie, Z., Li, N., Pan, W., Yang, Y., Chen, W., and Hong, C. (2022). Quantitative research on the form of traditional villages based on the space gene—a case study of Shibadong village in western Hunan, China. Sustainability 14 (14), 8965. doi:10.3390/su14148965
Niren, T. (2003). Eco-village: a trial toward sustainable society. J. Environ. Conserv. Eng. 32 (10), 762–768. doi:10.5956/jriet.32.762
Ogura, C., Sukchan, S., and Narioka, H. (2007). Characteristics of precipitation in nong saeng village, khon kaen province, northeast Thailand. Jap. Agr. Res. Q. 41 (4), 325–332. doi:10.6090/jarq.41.325
Parameswara, A., and Wulandari, A. (2020). Sustaining local communities through cultural industries based on local wisdom in Tigawasa village. J. Sustain. Dev. 13 (6), 139. doi:10.5539/JSD.V13N6P139
Pollock, L. J., O’connor, L. M., Mokany, K., Rosauer, D. F., Talluto, M. V., and Thuiller, W. (2020). Protecting biodiversity (in all its complexity): new models and methods. Trends Ecol. Evol. 35 (12), 1119–1128. doi:10.1016/j.tree.2020.08.015
Qianting, C., Zhang, L., Yapeng, D., and Shiqi, F. (2022). Spatial-temporal pattern and evolution of traditional villages in Jiangxi province. Natl. Remote Sens. Bull. 25 (12), 2460–2471. doi:10.11834/jrs.2021119
Qu, Y., Jiang, G., Zhao, Q., Ma, W., Zhang, R., and Yang, Y. (2017). Geographic identification, spatial differentiation, and formation mechanism of multifunction of rural settlements: a case study of 804 typical villages in Shandong Province, China. J. Clean. Prod. 166, 1202–1215. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.08.120
Ramachandra, T., Bharath, S., and Bharath, A. H. (2020). Insights of forest dynamics for the regional ecological fragility assessment. J. Indian Soc. Remote 48 (8), 1169–1189. doi:10.1007/s12524-020-01146-z
Sebayang, S., Novalina, A., Nasution, A. P., and Panggabean, L. S. R. (2019). “An empirical investigation of the factors influencing village development: a confirmatory factor analysis,” in In Proceedings of the 2nd Padang International Conference on Education, Economics, Business and Accounting (PICEEBA-2 2018).
Song, S., Ju, Y., and Wang, H. (2008). Possible effects of land use change caused by orderly human activities on regional precipitation. Clim.Environ. Stud. 13, 759–774.
Su, H., Wang, Y., Zhang, Z., and Dong, W. (2022). Characteristics and influencing factors of traditional village distribution in China. Land 11 (10), 1631. doi:10.3390/land11101631
Ul Din, S., and Mak, H. W. L. (2021). Retrieval of land-use/land cover change (LUCC) maps and urban expansion dynamics of Hyderabad, Pakistan via Landsat datasets and support vector machine framework. Remote Sens. 13 (16), 3337. doi:10.3390/rs13163337
Valera, S., and Guardia, J. (2002). Urban social identity and sustainability: barcelona’s Olympic Village. Environ. Behav. 34 (1), 54–66. doi:10.1177/0013916502034001004
Valjarević, A. (2024). GIS-based methods for identifying river networks types and changing river basins. Water Resour. Manag., 1–19. doi:10.1007/s11269-024-03916-7
Wang, A., Zhang, M., Chen, E., Zhang, C., and Han, Y. (2024). Impact of seasonal global land surface temperature (LST) change on gross primary production (GPP) in the early 21st century. Sustain Cities Soc. 110, 105572. doi:10.1016/j.scs.2024.105572
Wang, P., Zhang, J., Sun, F., Cao, S., Kan, Y., Wang, C., et al. (2021). The spatial distribution characteristics and influencing mechanism of traditional villages in Southwest China. Econ. Geogr. 41, 204–213.
Wang, X., Chen, G., and Wang, X. (2020). Investigation and research on the cognition of traditional village landscape environment improvement strategy based on SPSS analysis. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 474, 072050. doi:10.1088/1755-1315/474/7/072050
Wang, X., and Zhu, Q. (2022). Influencing factors of traditional village protection and development from the perspective of resilience theory. Land 11 (12), 2314. doi:10.3390/land11122314
Xiao, C., Zhou, J., Shen, X., Cullen, J., Dobson, S., Meng, F., et al. (2022). Rural living environment governance: a survey and comparison between two villages in henan province of China. Sustainability 14 (21), 14136. doi:10.3390/su142114136
Xiaoyue, X., Chengcai, T., and Wenqi, L. (2022). Spatial distribution and cultural features of traditional villages in Beijing and influencing factors. J. Resour. Ecol. 13 (6), 1074–1086. doi:10.5814/j.issn.1674-764x.2022.06.012
Xie, G., Zhou, Y., and Liu, C. (2022). Spatial distribution characteristics and influencing factors of Hakka traditional villages in Fujian, Guangdong, and Jiangxi, China. Sustainability 14 (19), 12068. doi:10.3390/su141912068
Xie, H., Sun, Q., and Song, W. (2024). Exploring the ecological effects of rural land use changes: a bibliometric overview. Land 13 (3), 303. doi:10.3390/land13030303
Xu, C., Jiang, W., Huang, Q., and Wang, Y. (2020). Ecosystem services response to rural-urban transitions in coastal and island cities: a comparison between Shenzhen and Hong Kong, China. J. Clean. Prod. 260, 121033. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121033
Xu, J., Yang, M., Hou, C., Lu, Z., and Liu, D. (2021). RETRACTED ARTICLE: distribution of rural tourism development in geographical space: a case study of 323 traditional villages in Shaanxi, China. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 54, 318–333. doi:10.1080/22797254.2020.1788993
Xu, Y., Yang, X., Feng, X., Yan, P., Shen, Y., and Li, X. (2023). Spatial distribution and site selection adaptation mechanism of traditional villages along the Yellow River in Shanxi and Shaanxi. River. Res. Appl. 39 (7), 1270–1282. doi:10.1002/rra.3977
Yang, R., Xu, Q., and Long, H. (2016). Spatial distribution characteristics and optimized reconstruction analysis of China’s rural settlements during the process of rapid urbanization. J. Rural. Stud. 47, 413–424. doi:10.1016/j.jrurstud.2016.05.013
Yang, Z., Wang, S., Hao, F., Ma, L., Chang, X., and Long, W. (2023). Spatial distribution of different types of villages for the rural revitalization strategy and their influencing factors: a case of jilin province, China. Sci 33 (5), 880–897. doi:10.1007/s11769-023-1359-8
Ye, L., Wu, Z., Wang, T., Ding, K., and Chen, Y. (2022). Villagers’ satisfaction evaluation system of rural human settlement construction: empirical study of Suzhou in China’s rapid urbanization area. Int. J. Env. Res. Pub. He 19 (18), 11472. doi:10.3390/ijerph191811472
Yilmaz, F., Zengin, M., and Tekin Cure, C. (2020). Determination of ecologically sensitive areas in Denizli province using geographic information systems (GIS) and analytical hierarchy process (AHP). Environ. Monit. Assess. 192 (9), 589. doi:10.1007/s10661-020-08514-9
Zhang, H. (2022). The spatial distribution and evolution of traditional villages based on remote sensing technology. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2022, 1–14. doi:10.1155/2022/8022002
Zhang, J.-X., Cheng, J.-W., Philbin, S. P., Ballesteros-Perez, P., Skitmore, M., and Wang, G. (2023). Influencing factors of urban innovation and development: a grounded theory analysis. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 25 (3), 2079–2104. doi:10.1007/s10668-022-02151-7
Zhang, M., Tan, S., Chen, E., and Li, J. (2024b). Spatio-temporal characteristics and influencing factors of land disputes in China: do socio-economic factors matter? Ecol. Indic. 160, 111938. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2024.111938
Zhang, M., Tan, S., Zhang, C., and Chen, E. (2024a). Machine learning in modelling the urban thermal field variance index and assessing the impacts of urban land expansion on seasonal thermal environment. Sustain. Cities Soc. 106, 105345. doi:10.1016/j.scs.2024.105345
Zhang, Q., and Wang, J. (2023). Spatial differentiation and driving factors of traditional villages in jiangsu province. Sustainability 15 (14), 11448. doi:10.3390/su151411448
Zhang, X., He, J., Deng, Z., Ma, J., Chen, G., Zhang, M., et al. (2018). Comparative changes of influence factors of rural residential area based on spatial econometric regression model: a case study of Lishan Township, Hubei Province, China. Sustainability 10 (10), 3403. doi:10.3390/su10103403
Zhe, L., Si, H., Han, W., and Yan, L. (2022). Digital analysis of the water layout ecological wisdom in traditional Chinese rural settlements: a case study of liukeng village in jiangxi province. J. Resour. Ecol. 13 (3), 371–381. doi:10.5814/j.issn.1674-764x.2022.03.003
Zheng, X., Wu, J., and Deng, H. (2021). Spatial distribution and land use of traditional villages in southwest China. Sustainability 13 (11), 6326. doi:10.3390/su13116326
Keywords: spatial characteristics, influencing factors, land use, 5409 villages, Inner Mongolia, GIS
Citation: Wang Z, Jiang S, Xu S, Zhang J, Mumtaz F and Zhang M (2024) Spatial patterns and its influencing factors on villages around the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River. Front. Environ. Sci. 12:1477693. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2024.1477693
Received: 08 August 2024; Accepted: 19 September 2024;
Published: 02 October 2024.
Edited by:
Sawaid Abbas, University of the Punjab, PakistanReviewed by:
Aleksandar Valjarević, University of Belgrade, SerbiaXiang Wang, Northwest Normal University, China
Copyright © 2024 Wang, Jiang, Xu, Zhang, Mumtaz and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Shuang Xu, eHMyMDE5QGltdXQuZWR1LmNu; Maomao Zhang, c3Rhcl9temhhbmdAbWFpbHMuY2NudS5lZHUuY24=
 Zhiqiang Wang
Zhiqiang Wang Shuang Jiang
Shuang Jiang Shuang Xu
Shuang Xu Jianxun Zhang
Jianxun Zhang Faisal Mumtaz
Faisal Mumtaz Maomao Zhang
Maomao Zhang