- 1Department School of Environmental and Municipal Engineering, Organization Lanzhou Jiaotong University, Lanzhou, China
- 2Department School of Architecture and Urban Planning, Organization Lanzhou Jiaotong University, Lanzhou, China
Implementing Territorial Ecological Restoration is a crucial approach to achieving ecological stability and regional sustainable development, and it also serves as an important measure for promoting the coordinated development of socioeconomic and ecological environments in the Yellow River Basin. However, effective identification of key areas for Territorial Ecological Restoration remains challenging in planning ecological restoration projects. This study focuses on ecological security and restoration potential, taking Linxia Prefecture in the ecologically fragile area of the upper Yellow River as an example. By evaluating six types of ecosystem services in this area, utilizing morphological spatial pattern analysis models and circuit theory, we identified the structural elements of ecological security patterns and assessed the potential for ecological restoration, identifying key areas for regional ecological restoration.The findings indicated that (1) 13 ecological patches were identified in total, predominantly distributed in the southwest and central regions of Linxia Prefecture. 25 ecological corridors were identified, demonstrating a high level of spatial coherence in terms of significance and connectivity, establishing a closely integrated ecological security network primarily in the southwest of Linxia Prefecture. (2) Thirteen ecological pinch points and seventeen ecological barrier points have been identified, concentrated in the central and southwestern regions of Linxia Prefecture. (3) Based on the characteristics and urgency of key areas for Territorial Ecological Restoration, they are classified and graded as “point-line-surface” and “primary-very important-important.” The primary restoration areas of the point type are mainly located in the central part of Linxia Prefecture, while the primary restoration areas of the line and plane types are mainly in the southwestern part of Linxia Prefecture. This paper emphasizing a holistic approach that prioritizes ecosystem integrity and social support to guide targeted restoration strategies across various ecological features, ultimately aiming for sustainable regional development and maximizing restoration benefits in ecologically fragile areas.
1 Introduction
The rapid expansion of worldwide socio-economic advancements hastened urbanization trends, concentrated land developments, and human activities’ repercussions have resulted in ecosystem deterioration (Cumming et al., 2014; Kowe et al., 2020), imbalances in ecological functions (Hooper et al., 2017), and fragmentation of landscape patterns (Li et al., 2017), among other ecological environmental issues. There is no doubt that China also faces similar challenges in ecological security, such as regional loss of biodiversity (Peng et al., 2018a), land erosion, and water resources shortage (He et al., 2014; Qiu et al., 2017). Territorial Ecological Restoration (TER) offers a spatially focused approach to addressing ecological issues at the regional level (Li et al., 2011; Peng et al., 2018b). The concept of TER, originating from Putwain (Putwain and Cairns, 1981), pertains to the restoration and reconstruction of impaired and deteriorated ecosystems within terrestrial habitats (Ran et al., 2022). Unlike landscape restoration, TER has significant differences in focus and scope. TER places greater emphasis on the recovery of local ecosystems and specific ecological functions, while landscape restoration focuses on the health and sustainable development of the overall landscape, ecosystems, and human activities. urrently, it has evolved into a significant research domain within ecology, encompassing various directions such as TER zoning (Li et al., 2014; Lv et al., 2023; Omernik and Griffith, 2014), territorial ecosystem service benefits (Bullock et al., 2011; Elmqvist et al., 2015; Strassburg et al., 2020), and TER technologies (Breed et al., 2019; Song et al., 2015; Zhen et al., 2020). Recognizing the essential regions for ecological restoration within territories serves as an important strategy for addressing regional environmental issues and enhancing ecological security. This involves determining the spatial patterns and quantitative extent of significant ecological elements that play a vital role in facilitating ecological processes and safeguarding ecological security in the area (Fang H. et al., 2020; Ran et al., 2022). Identifying essential areas for TER is pivotal in tackling ecological challenges, enhancing ecological security, and driving sustainable development regionally. However, effectively identifying these key areas remains a pivotal challenge in the current stage of TER (Zhang et al., 2022).
In light of this, TER, stemming from landscape ecology theory, has progressively risen as a focal point of research interest. It identifies ecological barrier points, pinch points as key areas for TER intervention. Nevertheless, this model primarily concentrates on specific nodes of individual elements within the TER areas, failing to establish a comprehensive ecological restoration system (Peng et al., 2018b). For instance, in China, the formal proposal of exploring ecological security was introduced in the 1990s (Yu, 1996), with the goal of securing regional sustainable development by analyzing ecological processes (Kong et al., 2010). Currently, the focus of TER typically includes ecological patches and corridors. Generally, the framework of “ecological patch-ecological corridor” is utilized as a strategy for pinpointing and establishing an Ecological Security Pattern (ESP):
(1) Identifying ecological patches constitutes the initial step in constructing an ESP. There are two approaches to identifying ecological patches. One approach is involved in selecting nature reserves or land cover types as ecological patches, overlooking the different ecosystem service functions brought about by various habitats (Yan et al., 2021). An alternative approach involves creating a comprehensive evaluation index system to identify ecological patches. Due to the diverse ecological characteristics across different regions, the generally adopted index system typically includes dimensions such as ecological sensitivity (Gao et al., 2020), importance of ecosystem services (Peng et al., 2018a), and connectivity of landscapes (Wang et al., 2022).
(2) The subsequent phase in developing an ESP consists of pinpointing ecological corridors through the utilization of the minimum cumulative resistance (MCR) model. The MCR model simulates how landscapes impede species migration, enhancing the depiction of the interplay between ecological processes and landscape patterns (Yu, 1996). Central to this approach is the establishment of ecological resistance surfaces, which primarily entails two approaches. One approach gets involved in scoring land cover types to determine resistance surfaces (Savary et al., 2021), though this method only analyzes resistance from a single-factor and angle perspective. Another approach is designed to construct ecological resistance surfaces based on dimensions such as terrain topography (Wei et al., 2022), ecological environment (Jia et al., 2023), and human activities (Fan et al., 2022), thereby offering greater scientific rigor and accuracy. By delineating ecological patches and corridors for establishing an ESP, fragmented landscape components are linked, enhancing the spatial configuration of local ecosystems to attain holistic ecological, social, and economic advantages (Fan et al., 2020).
Ecological Restoration Potential (ERP) serves as a crucial criterion for delineating the ESP and TER. It refers to the ability of ecosystems to restore, recover, or reconstruct degraded systems through specific technical interventions, thereby reinstating their structural and functional aspects to their original or even heigh tened potential levels. It also represents the latent capability of enhancing ecosystem service functions post-TER implementation. ERP is typically utilized to gauge the proximity between habitats and reference targets (Laughlin, 2014). Historically, research on potential has predominantly focused on rural settlement potential (Zhou et al., 2023), land reclamation potential (Jiang et al., 2017), and vegetation restoration potential (Xu et al., 2020). However, Lately, there has been an increasing interest in investigating ERP, integrating approaches such as historical landscape analysis (Bolliger et al., 2004), remote sensing indices (Zhang Y. et al., 2021), and similar habitats (Niu et al., 2023). Nevertheless, these approaches are confined to singular methods of evaluating ecological functional potential within TER, failing to comprehensively depict the overall regional ERP. Typically, ERP is grounded in Ecological Restoration Natural Potential (ERNP), requiring a thorough examination of regional ecological factors including topography, vegetation status, and climatic components. Supported by geological and climatic variables, ERP can be consolidated through ecological restoration measures to bolster ecosystem service capabilities, aligning with the objective of constructing an ESP to enhance regional ecosystem service capacities. The ESP perceives the area as an entity, emphasizing the unity and coherence of ecological processes (Gao et al., 2020), thereby complementing the systemic perspective of regional TER (Tong and Shi, 2020). ERP and the ESP complement each other in TER projects across different regions, with ecological patches and ecological corridors being focal points for protection and restoration. Therefore, by jointly identifying key areas for TER through combining ESP and ERP, and by implementing restoration strategies, this method addresses the deficiency of extensive ecological understanding in ecological restoration studies. It establishes overall regional ecological security from a holistic sustainable development perspective.
The Yellow River Basin (YRB) serves as a biodiversity corridor connecting the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, the Loess Plateau area, and the Northern China Plain. It functions as a crucial environmental safeguard and a strategic zone for human activities and socio-economic advancement in China (Liu et al., 2022). The upper reaches of the YRB constitute vital areas for water conservation and ecological provisioning, fulfilling essential ecosystem services. However, due to factors such as overgrazing and excessive groundwater exploitation, In the upper reaches of the Yellow River, there is a noticeable decrease in runoff (Su et al., 2021), with certain areas exhibiting extreme ecological fragility (Fang F. et al., 2020; Liu et al., 2017). Within these areas, the Linxia Prefecture (LX) region is situated at the juncture of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and the Loess Plateau, within the upper reaches of the YRB. Consequently, enhancing ecological preservation and restoration initiatives in the LX area is beneficial for advancing the sustainable development of the entire YRB and strengthening its national ecological security measures. Currently, research on the ecosystem of the YRB predominantly concentrates on alterations in land use (Wang et al., 2010), fluctuations in precipitation (Liu et al., 2008) and level of vegetation change (Jiang et al., 2015). Although these studies shed light on the ecological environmental changes in the YRB, there has been scant research on regional ecological potential assessment, and existing efforts remain predominantly qualitative, lacking a comprehensive quantitative assessment framework for ERP. Given the ecological vulnerability in the upper reaches of the YRB and the emergence of various ecological challenges, it is essential to effectively identify critical areas for Total Ecosystem Recovery in the region.
In the context of this research, the focus is on the LX region, positioned in the environmentally vulnerable region of the upper YRB, and establishes a framework for delineating crucial areas for TER utilizing the ESP and ERP. The nearer the landscape elements are to the ecological sources and corridors within a region, the more critical the role of Total Ecosystem Recovery, warranting prioritized focus. The Ecological Restoration Plan in this area is a vital marker for the logical planning of Total Ecosystem Recovery initiatives and achieving sustainable regional development. The identification of key areas for TER is of considerable importance in enhancing the ecological environment and safeguarding natural resources in the YRB. In detail, the main contents of this paper encompassed the following aspects: (1) Utilize the Morphological Spatial Pattern Analysis (MSPA) model alongside ecosystem service value evaluation to identify and extract ecological patches, followed by employing the MCR model to delineate ecological corridors and assess their significance and connectivity through gravity models and landscape connectivity analyses. Identify critical zones for TER by recognizing ecological bottleneck points and barriers with the Linkage Mapper tool. (2) Evaluate the ERP using the potential similar habitat method, enhanced by social support for restoration potential adjustments. (3) Identify key areas for TER by integrating various elements from the ESP and ERP surfaces, and prioritize restoration efforts in these areas based on the importance and connectivity of ecological corridors in relation to the ERP. This research provides a reference for implementing TER projects, guiding the prioritization of limited funds and resources towards the “primary” key areas for national restoration. By doing so, it maximizes the efficiency and effectiveness of ecological restoration efforts. Additionally, it provides technical methods for pinpointing crucial areas for regional ecological restoration. This is critically significant for safeguarding ecological security in the ecologically sensitive upstream regions of the Yellow River Basin and for fostering sustainable growth in the area. Additionally, it fosters the integrated development of socio-economic and ecological environments in the YRB.
2 Study area and data
2.1 Study area
The geographical coordinates of LX are situated between 102°41′—103°40′E longitude and 34°57′—36°12′N latitude (Figure 1A). Located in the upper reaches of the Yellow River Basin, it is positioned at the junction between the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and the Loess Platea (Figure 1B), characterized by fragmented terrain, comprising mountainous hills and valleys, rendering its ecological environment sensitive and fragile. LX governs one city and seven counties, covering a total area of 8,169 km2. The terrain descends from southwest to northeast, forming a tilted basin, with elevations ranging from 1575 m to 4548 m (Figure 1C). Numerous rivers such as the Yellow River, Tao River, and Huangshui River flow through this area, among which, both the Tao River and Huangshui River are tributaries of the Yellow River. National-level nature reserves, including Mengda Heavenly Lake and Taizi Mountain, are situated here, characterized by rich natural resources,and a pristine ecological environment. Notably, the Liujiaxia Reservoir, one of the key water conservancy projects on the Yellow River, is also located within LX.
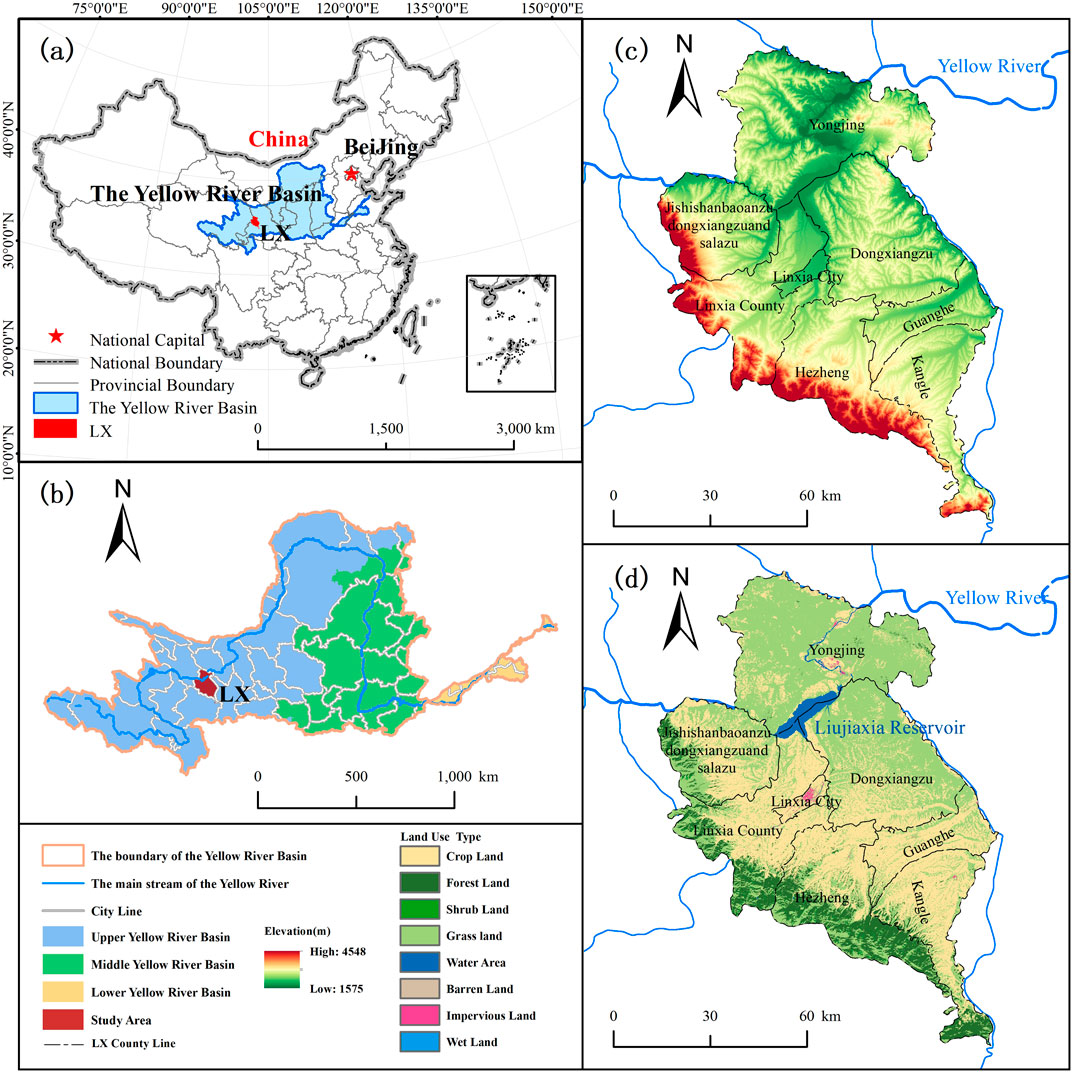
Figure 1. Location of LX. (A) Geographical location; (B) Location of the upper, middle, and lower reaches of the Yellow River, as well as the position of LX; (C) Elevation; (D) Land use.
The Linxia Hui Autonomous Prefecture is completely within the Yellow River basin, receiving an average annual precipitation of 537 mm and an evaporation rate between 1,198 and 1,745 mm; Most areas of Linxia Prefecture have a temperate semi-arid climate, with an average annual temperature of 6.3°C, where the southwestern mountainous area is cold and damp, while the northeastern part is dry, and the river valley plains are mild. The soil texture in the basin is mainly loamy or clay loam,due to the area’s classification as part of the loess plateau hilly ravine region, characterized by steep terrain and significant erosion, leading to serious soil erosion and loss of water in the basin. Bounded by mountains to the west and south, with Taizi Mountain designated as a national nature reserve, and flanked by rivers to the east and north, all of which are significant tributaries of the YRB, the entirety of the region lies within the YRB. Historically, it has functioned as a vital area for water source replenishment and an eco-safety barrier in the upper reaches of the YRB. Predominantly characterized by grassland and forest land, which account for 49.98% and 37.63% of the total area, respectively (Figure 1D), LX’s primary industries include agriculture, animal husbandry, and tourism, fostering socio-economic development in the region. However, these industries have also precipitated ecological environmental issues such as overgrazing, land reclamation, excessive exploitation of water resources, and industrial pollution, making TER imperative within the region.
2.2 Data sources
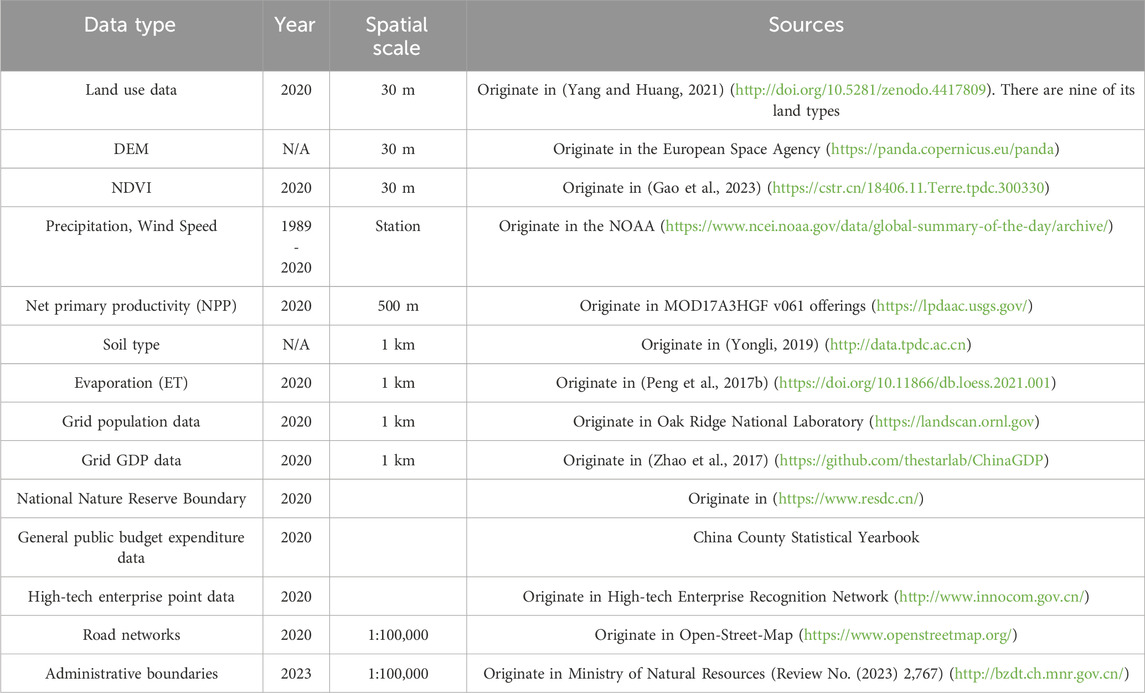
The data used in this research encompassed statistical, vector, and raster formats. Specific details concerning the data types, years, and sources are outlined in Table 1. All statistical and vector data were uniformly converted to raster data for computational purposes. The spatial resolution is 30 m × 30 m, At the same time, a uniform projection to CGCS 2000_3_Degree_GK_Zone_35.
3 Methods
The framework for identifying key areas for TER based on the ESP and ERP is illustrated in Figure 2. This paper was divided into three steps. Initially, ecosystem service categories were selected based on the topography, hydrology, and soil conditions of the environmentally fragile region upstream of the YRB. What’s more, the ecosystem service values of each ecosystem service type were calculated to construct the ESP and assess the ERP. In the end, by integrating the ESP with the ERP, key areas for TER were identified, and the priority order for ecological restoration was determined.
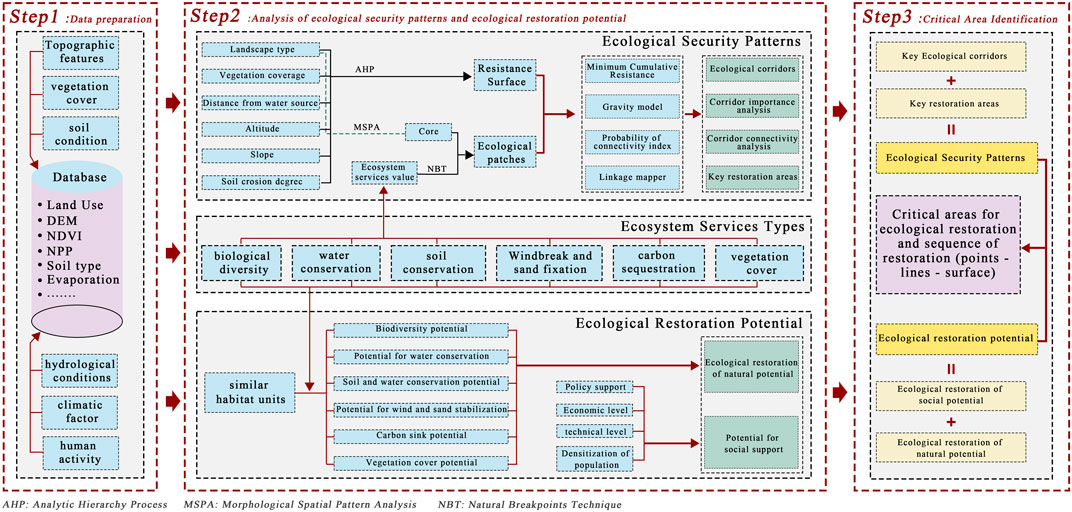
Figure 2. A research framework for identifying key areas of Territorial Ecological Restoration in linxia prefecture.
3.1 Ecological patch identification
The ecological patches provide ecosystem services to biological species, serving as the primary activity range and vital habitats for species, thereby ensuring their survival and reproduction (Ran et al., 2022). The identified ecological patches in this paper consist of three components: patches with high comprehensive ecosystem service values, core areas from the MSPA results, and national-level nature reserves and important water sources within LX.
3.1.1 MSPA method
The MSPA model, suggested by Vogt et al. (2009) and Soille and Vogt (2009), is employs principles of mathematical morphology, such as erosion, dilation, opening, and closing operations. It is utilized to measure, pinpoint, and segment spatial configurations within raster imagery. This method is commonly applied in the analysis of ecological networks (Shen et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2021) and effectively identifies and segments spatial patterns while determining their patch types and structures. Following previous studies (Liu H. et al., 2023; Wei et al., 2022), and taking into account the pertinent attributes of LX, Water and forests were classified as primary data and assigned a value of 2 for MSPA. Concurrently, other land use categories like impervious surfaces, farmland, and barren, is employed to quantitatively assess, precisely identify, and delineate spatial patterns in raster-format images.
3.1.2 Valuation of ecological services
The ecological patch identification process aligns with the ecosystem service categorization framework as described in the Millennium Ecosystem Assessment (MA) by the United Nations (Carpenter et al., 2009). Evaluation of the significance of six essential ecosystem services that are closely associated with hydrological functions, soil, and climatic geographical elements in LX—namely, biodiversity, water conservation, and soil conservation—yielded comprehensive ecosystem service value results. The results were categorized into five tiers using the natural breakpoints technique (NBT), where the highest two tiers were identified as ecological patches. Subsequently, through spatial overlay with core areas from the MSPA results and LX’s national-level nature reserves and important water sources, the final ecological patches were derived.
3.1.2.1 Biodiversity (Q)
Q is defined as the abundance of different species, genetic diversity, species richness, and the various interrelationships and dependencies among organisms within a given region. Habitat quality acts as a representative indicator for Q (Gong et al., 2019). In this research, the habitat quality was assessed using the InVEST model to determine habitat quality in the study area. The degree of habitat quality indicates the provisioning of Q. The specific formula used is as follows (Equations 1, 2):
In the formula,
In the formula, R indicates the count of stressors; r symbolizes a specific stressor; y denotes the number of grids impacted by stressor r;
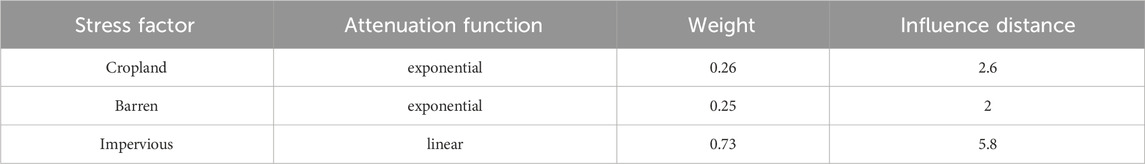
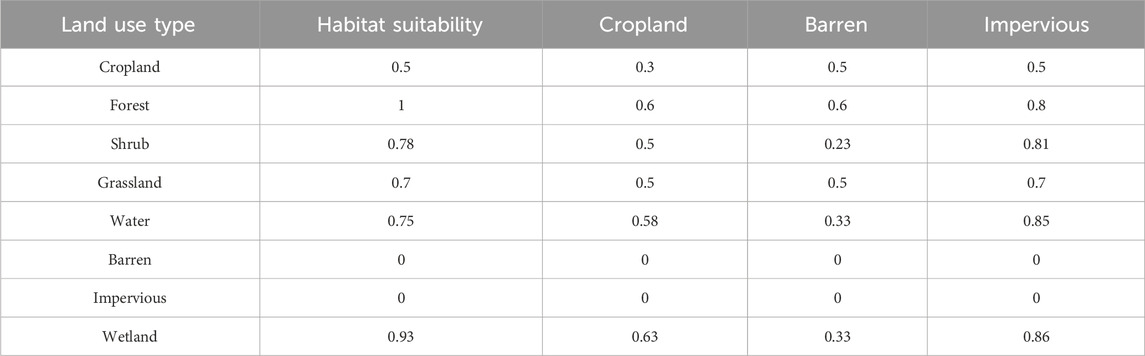
In this paper, three land use types, namely cropland, impervious surface, and bare land, were selected as stress factors. Combining relevant research with the actual situation in LX, the maximum influence distance, impact weights, and types of stress factors were determined (Table 2). Furthermore, the habitat suitability and relative vulnerability habitat for each land cover category were defined in Table 3. The habitat quality across the region was evaluated using the InVEST model.
3.1.2.2 Water conservation (TQ)
TQ concerns the capacity of ecosystems to capture, assimilate, and retain rainfall by virtue of their distinct configurations and interactions with water, consequently managing water movement and the hydrological process via evapotranspiration. The measurement of water conservation capacity or volume typically considers factors such as catchment characteristics, climate, land cover, and topography. The specific calculation formula is presented as follows (Equations 3, 4):
In the formula,
3.1.2.3 Soil conservation (SC)
SC denotes the ecological mechanism through which ecosystems mitigate soil erosion induced by water runoff via their intrinsic structures and functionalities. The assessment standard for soil conservation commonly relies on the conservation quantity, The calculation is based on subtracting the potential soil erosion from the observed soil erosion. The RUSLE model (Renard, 1997) is often utilized to perform this calculation. Below is the specific formula used for this computation (Equation 5):
In the formula,
3.1.2.4 Windbreak and sand fixation(SR)
SR denotes the ecological mechanism through which ecosystems alleviate soil erosion stemming from wind erosion via their intrinsic structures and functions. The assessment standard for SR primarily depends on the magnitude of SR, The calculation is derived from the difference between potential wind erosion and actual wind erosion. The precise formula for this calculation is outlined below (Equations 6–8):
In the formula, SR denotes the quantity of windbreak and sand stabilization. (t/km2·a);
3.1.2.5 Carbon sequestration (CS)
CS refers to the mechanism through which ecosystems uptake and sequester carbon dioxide. NPP of vegetation is widely utilized as a metric to evaluate carbon sequestration potential (He et al., 2022), with the specific calculation formula outlined below (Equation 9):
In the formula,
3.1.2.6 Fraction of Vegetation Cover (FVC)
FVC serves as a pivotal indicator for assessing the condition of surface vegetation, providing fundamental data for gauging environmental changes within regional ecosystems. Its computation can be facilitated through the employment of pixel-based binary models, with the specific calculation formula outlined below (Equation 10):
In the formula, FVC denotes vegetation cover; NDVI stands for the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index;
3.1.3 Correlation analysis between ecological services
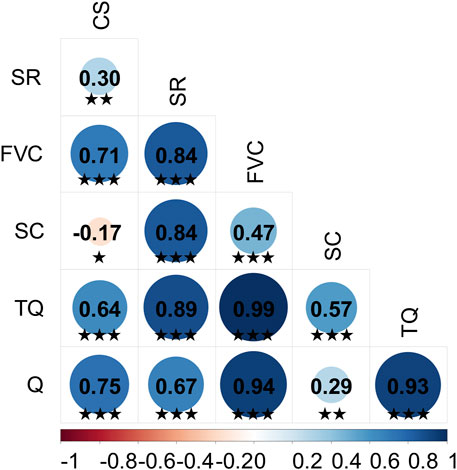
To avoid redundancy between basic ecosystem services, we used Spearman’s non-parametric correlation analysis to determine the trade-offs/synergies between pairs of ecosystem services. This is a popular quantitative method for identifying the direction and strength of these interactions (Dou et al., 2020; Xia et al., 2023), where a positive correlation between ecosystem services indicates synergy, while a negative correlation indicates trade-off. We conducted the Spearman correlation analysis using the “corrplot” package in R 4.0 software.
3.2 Determination of the ecological resistance surface
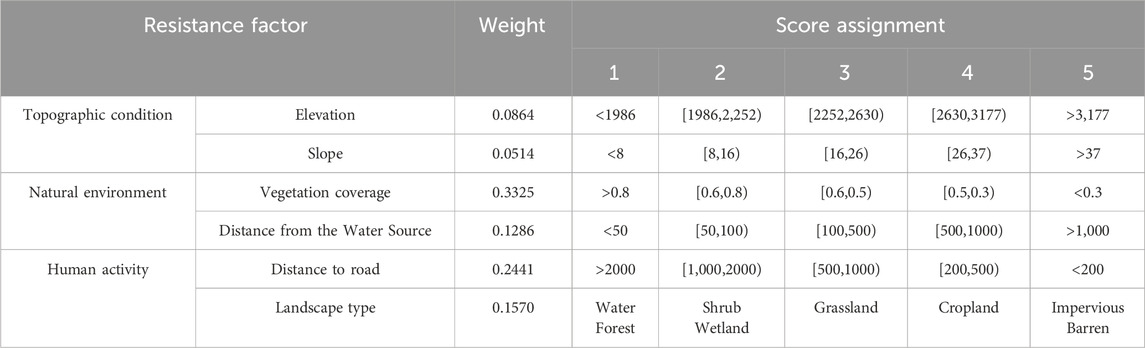
The ecological resistance surface quantifies the terrestrial landscape’s resistance to the spatial dispersion and migration of species and ecological components (Li et al., 2022). Drawing upon previous scholarly investigations and considering the natural geographical conditions of LX, six resistance factors were chosen from three primary indicators encompassing terrain conditions, natural environment, and human activities. The weighting of each factor was determined through the AHP (Table 5), which was then followed by a weighted overlay procedure conducted in ArcGIS10.8 software to generate the comprehensive resistance surface.
3.3 Identification of ecological corridors
Ecological corridors serve as essential conduits for the movement of species and energy, improving the connectivity between ecological sources and their conservation roles (Peng J. et al., 2017). In this research, the MCR model was employed to delineate ecological corridors, utilizing ecological patches and ecological resistance surfaces as input variables. The MCR model has been extensively utilized in the research on ESPs (Han et al., 2021). The formula for calculating the MCR model is presented below (Equation 11):
In the equation,
3.4 Corridor importance analysis
The effectiveness of potential ecological corridors and the significance of linking patches can be evaluated by examining the intensity of interactions between origins and destinations. By utilizing the gravity model to construct an interaction matrix among ecological patches, one can quantitatively assess the level of interactions between these patches. This analysis assists in assessing the relative significance of ecological corridors and identifying crucial ecological corridors (Zhao et al., 2019). The gravity model calculation formula is as follows (Equation 12):
In the formula,
3.5 Corridor connectivity analysis
Landscape connectivity pertains to the extent of linkage between biodiversity and ecosystem functionality among distinct geographic areas. The Probability Connectivity (PC) effectively quantifies the connectivity characteristics of patches (Pascual-Hortal and Saura, 2008). In this paper, the magnitude of connectivity change was employed to pinpoint significant ecological corridors and prioritize them. The formulas for calculating PC and values are outlined as follows (Equations 13, 14):
In the formula, PC represents the Potential Connectivity Index;
In the formula,
3.6 Identification of crucial restoration areas
3.6.1 Ecological pinch points
Ecological pinch points are solitary areas with unique ecological characteristics, serving as crucial points for ecological restoration efforts (Jie et al., 2020). This research utilized the Pinchpoint Mapper tool provided in the Linkage Mapper toolbox, applying the Circuitscape algorithm to identify small areas where local losses could severely impact landscape connectivity. Drawing from (Li et al., 2022), a cutoff distance of 1 km was set, and an “all to one” mode was selected for iterative calculations to produce the current density map of ecological pinch points. Subsequently, the natural breakpoint method was used to identify areas with the highest density as ecological pinch points.
3.6.2 Ecological barrier points
Ecological barrier points are regions where species encounter substantial resistance when moving between ecological patches, and restoring these regions can improve connectivity among source habitats (Jie et al., 2020). To identify ecological barrier points, this study employed the Barrier Mapper tool provided within the Linkage Mapper toolbox. Through exploration with various search radii, it could be found that setting the search radius to 500 m yielded optimal results. Additionally, this paper established the minimum and maximum detection radii to 500 m and 1,500 m, respectively, and chose the “maximum value” mode for execution. In the results, the maximum improvement score for each area was displayed within the channels. A higher area score indicated that restoring that area would greatly enhance the connectivity of ecological corridors. Furthermore, the natural breakpoint method was applied to select the area with the most significant enhancement score as the primary zone for ecological restoration. The improvement score formula is illustrated below Equations 15, 16:
In the formula,
3.7 Comprehensive ERP
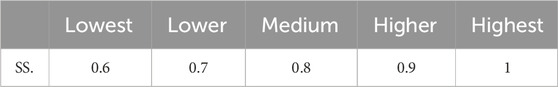
The calculation of ERP is conducted based on both the natural potential for ecological restoration and the social support potential. After computing the ERNP via the potential similar habitat method, a correction for social support potential is incorporated to formulate the ERP surface (Table 6). The equation for computing ERP is as follows (Equations 17, 18):
The variables in the formula are defined as follows: ERNP represents Ecological Restoration Natural Potential;
3.7.1 Calculation of ERNP
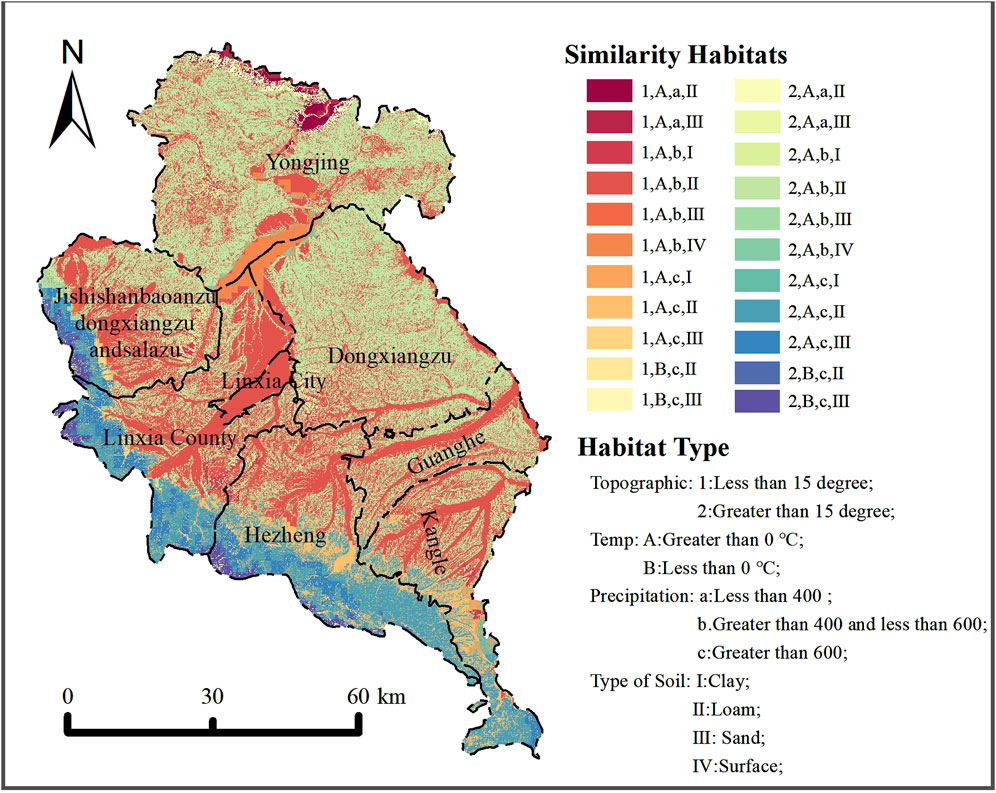
Following the assessment of various ecosystem service values in LX, ERNP is calculated based on this foundation. Similar habitat units refer to regions with analogous natural geographical, climatic, and soil conditions (Liu et al., 2022), where ecosystem service values should also be commensurate. To determine the ERP within LX, this paper delineated similar habitat units based on slope, precipitation, mean annual temperature, and soil texture, resulting in 23 categories and 294 partitions (Figure 3). The ecosystem service values within each partition were computed, and the discrepancy between the maximum and existing values represents the ecological natural restoration potential, calculated by the following Equation 19:
In the formula,
3.7.2 Calculation of social support potential
Public funding allocations for energy preservation and environmental safeguarding are vital for enabling the execution of TER and environmental management (Liu M. et al., 2023). This paper, integrating human needs (Guo et al., 2022) and socio-economic development (Liu M. et al., 2023), selected economic level, population density, policy support, and technological level as four indicators to measure social support (SS) potential. Utilizing GDP as an indicator of regional economic levels,a higher economic status generally indicates that both government and businesses can allocate more financial resources towards ecological restoration initiatives; In regions with high population density, the residents show greater concern for ecological issues, facilitating the establishment of community-participatory ecological restoration projects; Utilizing general public budget expenditures as a measure of policy support, clear policy frameworks and fiscal incentives can bolster ecological restoration activities; The distribution of technology-oriented SMEs and high-tech firms serves as a representation of technological capabilities, advanced technology can offer more efficient and viable ecological restoration strategies. The calculation formula is elaborated below (Equation 20):
In the formula,
3.8 Identification of key areas for TER and restoration priority
3.8.1 Identifying critical areas for TER
In this paper, key areas for TER were constructed jointly by the various structural elements of the ESP and ERP. These areas could be classified as key areas for TER, characterized by “point-line-surface.” Among them, ecological bottlenecks and ecological barriers are identified as the most critical regions in TER, represent the key areas for TER featured with the “point.” Ecological corridors represent the key areas for TER featured with the “line.” The key areas for TER featured with “surface” can be subdivided into two types: one is ecological patches, and the other is the key areas for TER identified jointly by the ESP and ERP.
3.8.2 Identification of priorities for ecological restoration
To guarantee the successful execution of ecological restoration strategies, it is crucial to prioritize restoration efforts in key areas identified for (Ran et al., 2022). The high-value areas of ERP represent critical domains requiring restoration efforts. Hence, implementing TER projects in these regions is more conducive to local ecological restoration. Therefore, through evaluating the ERP of ecological points and ecological barriers, the restoration priority for the key areas in TER characterized by the “point” aspect can be established. Likewise, by evaluating ecological corridors through gravity models and landscape connectivity, the priority for the key areas for TER featured with the “line” can be ascertained. Ecological patches, as one of the core elements in the ESP, represent the most critical regions in TER. By calculating ERP of ecological patches, the priority for their restoration can be established. Additionally, in TER projects, areas closer to ecological patches and ecological corridors hold greater significance for TER (Liu M. et al., 2023). Adhering to this principle, conducting buffer analysis on the ESP, overlaying it with the ERP surface, classifying the results based on natural breakpoints, extracting high-value areas, and overlaying them with ecological patches, facilitates the determination of the priority for the key areas for TER featured with the “surface.”
4 Results
4.1 Correlation analysis of ESs and the identification of ecological patches
A total of 15 correlations were determined through the correlation analysis among six ecosystem services, and all 15 analyses were statistically significant (P < 0.05) (Figure 4). Results show that, apart from a weak trade-off relationship between CS-SC, the other 14 correlations represent synergies, with weak synergies observed for Q-SC and SR-CS, whereas TQ-FVC displayed the highest synergy. In summary, there is a synergistic relationship among the six ecosystem services in LX. Subsequently, Using the MSPA model, the central region of LX encompasses an area of 1,708.58 km2, accounting for 20.96% of the total landmass, with significant concentrations in the southwestern and watershed zones (Figure 5A). The assessment of habitat quality reveals that biodiversity services are relatively low throughout LX, with high-value areas primarily situated in the southwestern sector, which is characterized by substantial forest cover and exhibits a distinct “southwestern prominence” amidst considerable spatial variability. The InVEST model underscores that biodiversity services are closely tied to land cover types, with the southwestern region demonstrating the highest capacity for such services (Figure 5B). Furthermore, water retention capacity correlates directly with precipitation and evapotranspiration rates, with high-value regions again clustered in the southwestern sector, highlighting a gradual decrease from southwest to northeast, reflective of enhanced rainfall patterns (Figure 5C). Soil conservation services are predominantly found in the northern sector, influenced by soil properties, topography, and climate, displaying a notable prominence in this area (Figure 5D). Windbreak and sand fixation services are most pronounced in the central region, exhibiting a central prominence, while these services decline in both the northern and southern sectors (Figure 5E). The average carbon sequestration capacity across the study area is 0.50, with high-value regions concentrated in the southern sector, illustrating a gradual decline from south to north, driven by land use types, particularly forests and shrublands (Figure 5F). Additionally, surface vegetation conditions yield an average score of 0.62, with high-value regions located in the southern and southwestern areas, whereas low-value zones are linked to urban development and arid northern regions, reflecting a gradual decrease from southwest to northeast due to extensive human activities and urbanization (Figure 5G). In conclusion, the southwestern region of LX demonstrates superior capacities in biodiversity, water conservation, carbon sequestration, and vegetation coverage, attributed to favorable soil and climatic conditions. Nevertheless, topographical features pose risks for soil erosion, consequently diminishing soil conservation capabilities. Finally, by overlaying patches with high comprehensive ecosystem service values identified through the MSPA model, we delineated ecological patches within LX, considering the boundaries of national nature reserves and critical water sources. Previous studies (Li et al., 2022) facilitated the identification of ecological patches larger than 2 km2. A total of 13 ecological patches, covering 1,206.56 km2 and constituting 14.77% of the total study area, were identified (Figure 5H).

Figure 5. Ecological patch identification process in LX. [(A) MSPA core area; (B) Normalization of biodiversity; (C) Normalization of water conservation; (D) Normalization of soil conservation; (E) Normalization of windbreak and sand fixation; (F) Normalization of carbon sequestration; (G) Fraction of Vegetation Cover; (H) Final Ecological Patch].
4.2 Constructing the ecological resistance surface
The spatial distribution of elevation (Figure 6A) and slope (Figure 6B) in LX reveals significant patterns influencing ecological resistance. Notably, higher altitudes and steeper slopes are predominantly located in the southwestern and northeastern regions, contributing to elevated resistance values. The Jishi Mountains in the west and the Taizi Mountains in the south characterize these areas, whereas the northeastern sector features the hilly terrain of the Loess Plateau. In contrast, the northern region’s arid conditions foster greater vegetation cover, enhancing ecological resistance (Figure 6C). Water sources and river distributions are relatively uniform, with higher resistance values concentrated in this northern area due to accessibility constraints (Figure 6D). The influence of terrain on transportation is evident, as regions with pronounced elevation and slope gradients exhibit lower ecological resistance under disturbance (Figure 6E). Urban development in central LX further complicates resistance dynamics; while urban areas demonstrate lower resistance due to milder terrain, the dense distribution of urban land and transportation networks ultimately increases overall resistance. Conversely, forested areas in the southwest exhibit superior ecological conditions and lower resistance values (Figure 6F). This comprehensive assessment indicates a gradual increase in ecological resistance from the southwestern to the northeastern regions (Figure 6G), highlighting the intricate interplay between topography, land use, and ecological attributes.
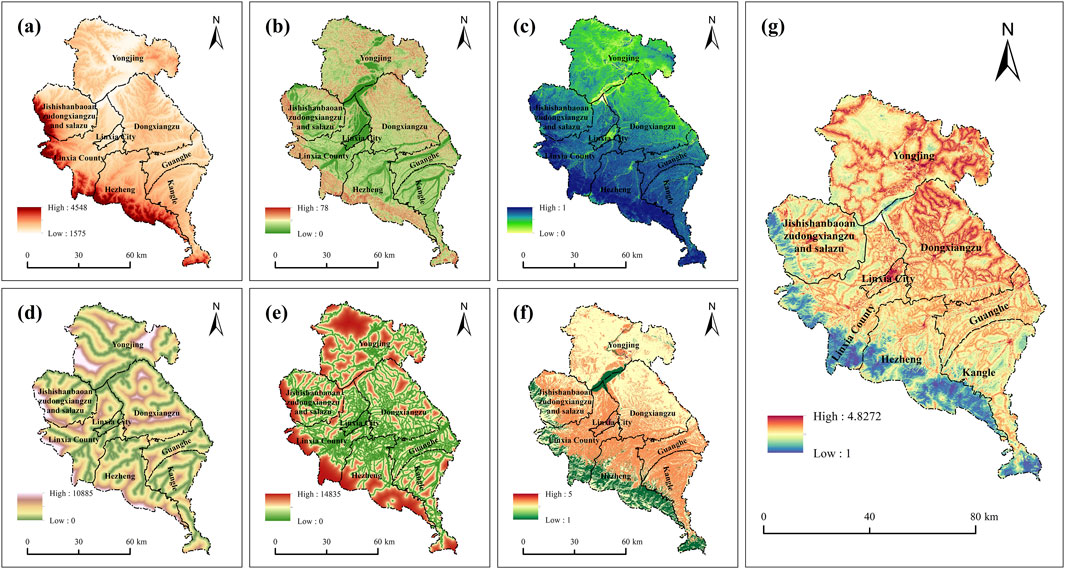
Figure 6. Resistance factors in LX. [(A) Dem; (B) Slope; (C) FVC; (D) Distance to water source; (E) Distance to road; (F) Resistance values of land use types; (G) Combined resistance surfaces].
4.3 Extraction of ecological corridors and analysis of corridor importance and connectivity
This research utilized the MCR framework to delineate 25 prospective ecological connectivity pathways in LX, encompassing a cumulative length of 791.78 km, predominantly situated in the mountainous regions of the west and south, as well as central-western territories (Figure 7A). The significance of ecological corridors is evident through the interactions of ecosystem services between various ecological patches. These interactions can be analyzed using a gravitational model, alongside comprehensive assessments of ecosystem service values. The identification of ten prominent ecological corridors, assessed through a gravity model, revealed a total coverage of 217.48 km, primarily concentrated in the southwestern area (Figure 7C), which facilitates connections among various small-scale ecological patches. Additionally, Conefor software analysis identified 13 highly interconnected corridors spanning 271.95 km, all located within the southwestern region (Figure 7D). The longest corridor measures 53.91 km, linking patches in the southwest and south, whereas the shortest spans 1.98 km, connecting adjacent patches in the west. Ecological patches situated at considerable distances can still interact, facilitating the movement of ecological factors across the landscape of LX. There are few corridors with high connectivity, and these are predominantly found in regions characterized by low resistance values. Notably, the lack of significant, highly connected ecological corridors in the north and east suggests an urgent need to optimize the integrity of the LX ecosystem.
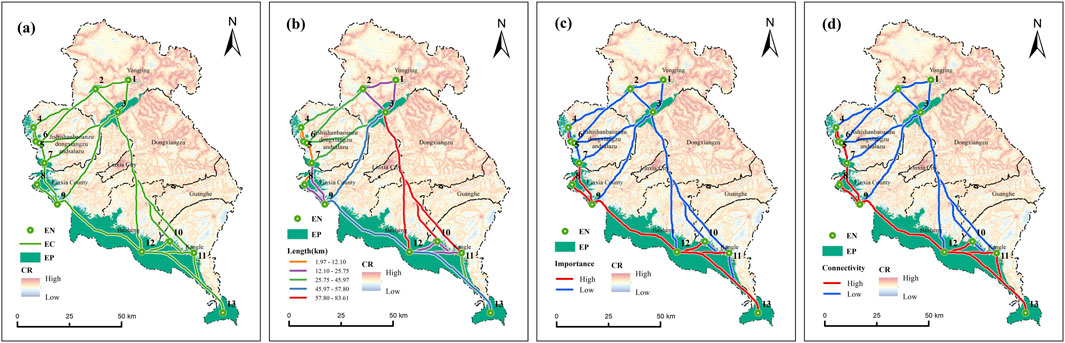
Figure 7. Ecological corridors in LX. [(A) Distribution; (B) Corridor length; (C) Corridor importance; (D) Corridor connectivity; EN, ecological nodes; EC, ecological corridors; EP, ecological patches; CR, cumulative resistance].
4.4 Identifying primary areas for ecological protection and restoration
Employing the natural break method on the current density map, 13 pinch points were identified in LX, predominantly located in the central and southwestern regions, with a higher concentration in the central area (Figure 8A). These pinch points are critical for maintaining ecological stability, as they frequently occur at the intersections of ecological corridors and are primarily characterized by forest and grassland land use. To safeguard these vital areas, it is imperative for relevant government departments to enhance protective policies and prioritize conservation efforts around pinch points. Additionally, 17 ecological barrier points were identified, mainly dispersed along the intermediate sections of various ecological corridors (Figure 8B). These barrier points are essential for restoring connectivity within the corridors, with predominant land use types including farmland, grassland, and urban land. Effective conservation strategies such as reforestation of agricultural land, vegetation restoration, and optimization of urban land use will be necessary to promote ecological restoration.
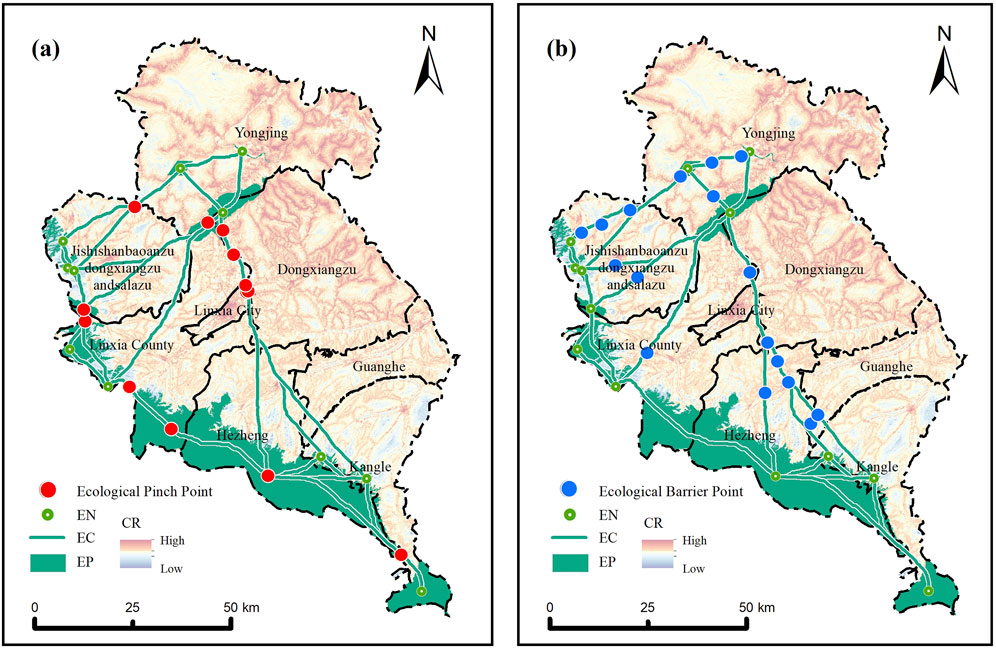
Figure 8. Priority areas for ecological protection and restoration in LX include: (A) Ecological PinchPoints; (B) Ecological Barrier Points; EN, Ecological Nodes; EC, Ecological Corridors; EP, Ecological Patches; CR, Cumulative Resistance.
4.5 ERP
4.5.1 ERNP
The calculation and standardization of the ENP for various ecological service types in LX indicate that the Q potential index is particularly high in the plateau regions of Yongjing County and Dongxiang County in northern LX, which are characterized by significant human activity and population density (Figure 9A). Despite their biological potential, these areas suffer from low biodiversity due to species homogenization, suggesting substantial restoration opportunities. The TQ potential displays a marked spatial distribution, with lower values in the southern region and higher values in the north, influenced by precipitation and evaporation rates, particularly evident in Yongjing County (Figure 9B). SC potential also exhibits considerable spatial variation, with elevated values concentrated in the loess hilly terrain of Yongjing County, an area affected by high soil erosion rates resulting from intense human activities (Figures 9C, D). The overall SR potential index in LX is relatively low, with higher-value areas located in urban built-up regions within the central area, indicating that enhancing urban green spaces could improve SR capabilities (Figure 9E). Additionally, both CS potential and FVC potential reveal consistent spatial distributions, exhibiting lower values in the southern regions and elevated values in the north (Figure 9F).
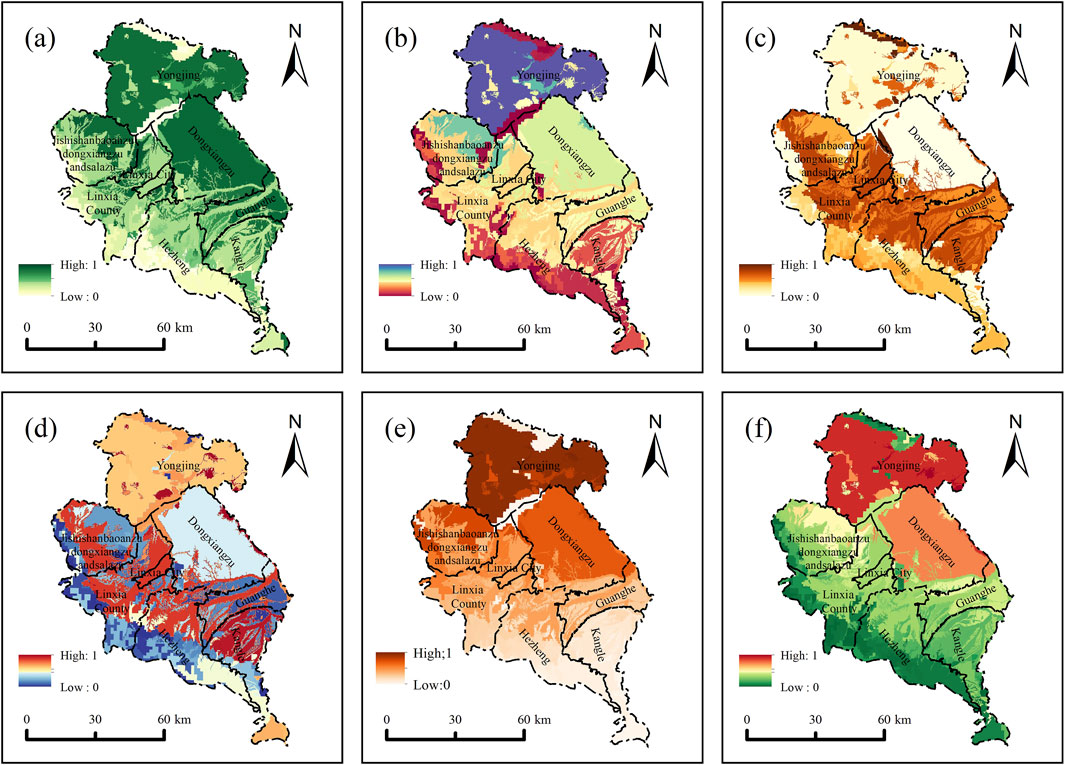
Figure 9. Natural ERP of LX. [(A) Standardization of biodiversity potential; (B) Standardization of water conservation potential; (C) Standardization of soil conservation potential; (D) Standardization of windbreak and sand fixation potential; (E) Standardization of carbon sequestration potential; (F) Standardization of FVC potential].
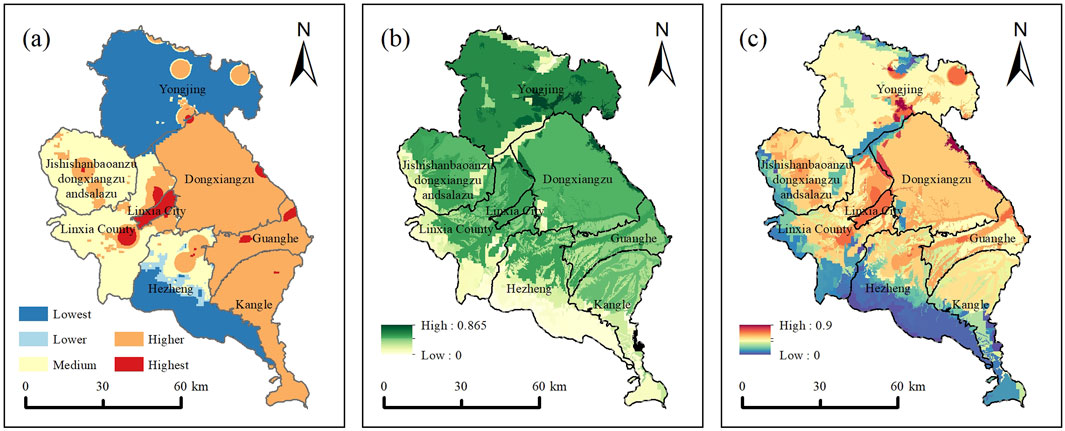
4.5.2 Social support potential and comprehensive ERP
This study assesses the level of social support for TER in LX by analyzing four critical factors: economic status, population density, policy support, and technological advancement. The findings indicate a spatial distribution of social support that is high in the central region and low in the northern and southern regions, with particularly low values observed in Yongjing County and Hezheng County (Figure 10A). In contrast, the ecological restoration network potential (ERNP) reveals lower values in the southern region and higher values in the north, predominantly concentrated in Yongjing County (Figure 10B). By integrating the social support levels into the ERNP analysis, the ERP for LX was derived, illustrating a distinct spatial distribution pattern with elevated values primarily located in Linxia City, Yongjing County, and Dongxiang Autonomous County, while exhibiting concave patterns in the northern and southern areas (Figure 10C).
4.6 Key areas for ecological restoration
4.6.1 Key areas for TER featured with the “point”
Ecological pinch points and barrier points are essential for enabling optimal biological flow within the ecosystem. Restoration of these key locations can significantly enhance the integrity of the regional ecological network and stabilize the ecological matrix and spatial configuration in LX, leading to an increased capacity for ecosystem service provision. By categorizing the key areas for TER based on the “point” feature, they are categorized into three types of restoration: “primary-very important-important.” (Figure 11A). Among these, there are 12 primary restoration sites, primarily located in the central and western areas of LX, there are 10 highly significant restoration zones found in the northern and central-southern regions, along with 8 notable restoration areas concentrated in the central and southwestern regions of LX.
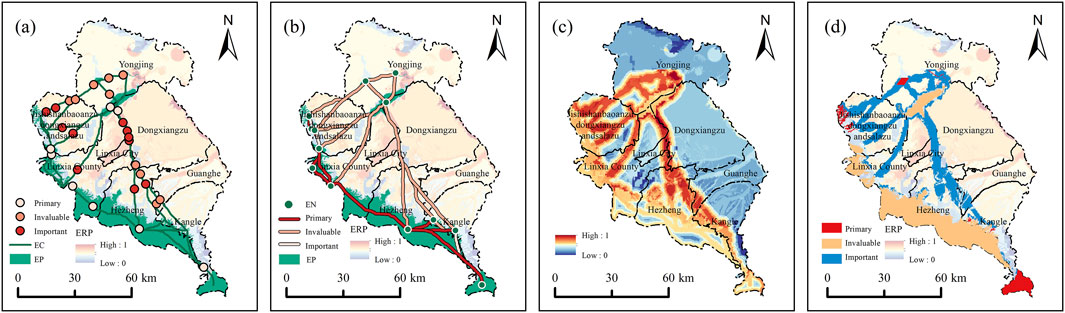
Figure 11. Critical areas for ecological restoration of LX. [(A) Point; (B) Line; (C) ESP and ERP overlay results; (D) Polygon; EC, ecological corridors; EP, ecological patches].
4.6.2 Key areas for TER featured with the “line”
After evaluating the ecological corridors through gravity modeling and landscape connectivity assessment, the priority of key areas for TER featured with the “line” can be determined (Figure 11B). Among these, there are 10 main restoration areas Covering a combined distance of 217.48 km, all situated in the southwestern region of LX. Additionally, there are 3 very important restoration areas spanning 54.47 km, located in the southern and western regions. Furthermore, 12 important restoration areas covering 519.83 km are predominantly positioned in the central-western areas of LX, Most of these restoration zones function as ecological corridors, linking the ecological patches from the southwestern to the central regions.
4.6.3 Key areas for TER featured with the “surface”
Ecological patches, fundamental components of ecological networks, represent relatively stable areas within ecosystems with significant landscape value (Chen et al., 2023). Ecological patches are fundamental to regional ecological processes and functions, exemplifying the core principles of ecological conservation (Liquete et al., 2015). Therefore, this paper assessed the ERP of each ecological patch, categorizing them into “primary” and “very important” restoration types. Subsequently, employing buffer analysis on various elements of the ESP at intervals of 1 km, 2 km, 3 km, and 4 km or more, and overlaying them with the ERP surface, this paper identified key ecological restoration areas classified as “important” restoration types (Figure 11C). Further integration of patch maps from each restoration type allowed delineation of key areas for TER featured with the “surface” (Figure 11D). The results revealed 8 primary restoration areas spanning a total area of 164.58 km2, spatially dispersed across the southern, western, and northern regions of LX. Moreover, there were 5 highly significant restoration areas spanning a combined area of 1,040.24 km2, predominantly situated in the central and southwestern regions. The important restoration areas, totaling 1,043.45 km2, were dispersed in a belt-like configuration throughout the central-western region of LX.
5 Discussion
5.1 Methodological advantages
This paper utilizes the theories and methodologies of ESP and ecological restoration potential ERP to identify crucial areas for TER and establish their prioritization based on ecosystem integrity and restoration potential. In contrast to traditional approaches that focus on single elements, this study adopts a holistic and systematic perspective to achieve sustainable regional development. The ESP was constructed using the MSPA landscape elements to evaluate comprehensive ecosystem service values and national nature reserves, mitigating subjective bias and landscape fragmentation (Wenbin et al., 2021). Additionally, the comprehensive resistance surface incorporated factors related to terrain, natural environments, and human activities. Employing the MCR model allowed for accurate identification of ecological corridors, thereby enhancing the preservation of regional ecological structures and functions (Li et al., 2020; Yang et al., 2020). The spatial distribution of restoration potential reveals lower values in the southern region and higher values in the north, particularly concentrated in Yongjing County. By integrating social support into the assessment of ecological restoration potential, this study highlights key areas for TER, promoting synchronized development of human communities and natural ecosystems within the YRB. The findings contribute to addressing the integration of ecological elements in restoration research and offer a framework for optimizing and systematically restoring territorial spatial patterns. Ultimately, this method provides guidance for implementing TER projects effectively, ensuring that limited resources are directed toward “first order” key areas, thereby maximizing ecological restoration benefits. This approach is applicable to other ecologically fragile regions in the upper YRB and offers viable planning solutions for sustainable regional development.
5.2 Ecosystem services and ERP
In establishing the ESP, the primary task is involved in assessing the ecosystem services to identify ecological patches. The functionality of ecosystem services is intricately connected to ERP, as illustrated by the spatial distribution patterns of areas with high-value ecosystem services and low-value ERP areas in Figures 4H, 9C, respectively. It is observed that there exists a negative correlation between ecosystem services and ERP, with low-value regions for ERP exhibiting a more extensive distribution. Additionally, a variety of ecosystem services within the LX study area are impacted by both human activities and natural environments., displaying a negative correlation between ecosystem services and human activity impacts. This is manifested in the degradation of ecological environments and habitat quality, as well as an increase in breakpoints within ecological corridors (Li et al., 2022). Nevertheless, the enlargement of urban built-up regions typically suggests an escalation in regional economic indicators and population growth, thereby providing social support for ERP. To sum up, there exists a negative correlation between ecosystem service functionality and ERP, coupled with the impacts of human activities.
5.3 Ecological restoration strategies in key areas
Optimizing the components within the Ecological Sensitivity Profile (ESP) is beneficial for improving the security and stability of regional ecosystems, facilitating habitat expansion, species migration, and other ecological processes. Based on the identification of crucial areas for TER in this study, subsequent restoration strategies and recommendations have been proposed:
1. Regarding the key areas for TER featured with the “point,” investigations and assessments should be conducted on these punctiform regions to formulate restoration planning routes, clarify restoration objectives and pathways. For example, initiatives may include the construction of small wetland parks and forest parks, strengthening land consolidation projects, protective afforestation projects, and ecological riverbank protection forest projects.
2. In terms of the key areas for TER featured with the “line,” rational planning of corridor widths should be adopted. Focus should be directed towards safeguarding vital connection corridors, merging land-based ecological pathways with aquatic corridors to enhance the cohesiveness of the ecological network, proactively rehabilitating ecologically sensitive zones such as ecological pinch points and barriers, and applying management and regulatory strategies within these corridor areas.
3. Concerning the key areas for TER featured with the “surface,” measures such as enriching the structure of vegetation communities in large ecological source areas, improving habitat quality in small patches, enhancing regional farmland quality, increasing green spaces and parks, and integrating ecological engineering techniques with natural restoration mechanisms should be adopted to accelerate the pace of ecosystem restoration.
4. As formulating ecological restoration plans, relevant land management authorities should implement targeted restoration measures for different types of the key areas for TER. Moreover, considering the priority of TER is conducive to maximizing the efficiency of restoration efforts, achieving high-level ecological value restoration at minimal economic cost. For instance, in priority restoration areas with forests, efforts should focus on maximizing forest protection, potentially designating them as ecological conservation redlines. This can be achieved through planting or introducing locally adapted vegetation to increase the fraction of vegetation cover and restore ecological diversity. Similarly, in priority restoration areas with water bodies, measures such as restoring riverbank water bodies and implementing ecological compensation mechanisms should be undertaken.
5.4 Limitations and directions for future research
This paper identified the key areas for TER through the recognition of the ESP and ERP. Nevertheless, this paper has been subject to limitations. Initially, this study oversimplified ecological corridors as linear elements; however, they are more accurately characterized as distinct landscape features that possess specific widths, which facilitate the connectivity between various ecological patches s (Li et al., 2022). The determination of corridor width is critical yet remains underexplored in current research, with methodologies still in their infancy. An effective corridor width should be tailored to accommodate the unique characteristics of each landscape, the biodiversity requirements of species utilizing these corridors, and overarching conservation objectives. Factors such as habitat type, species dispersal behaviors, and ecological interactions must be considered to ensure the corridors function effectively in promoting connectivity and enhancing ecosystem resilience. Consequently, establishing scientifically grounded and contextually appropriate widths for ecological corridors will be a primary focus for future research, as it is essential for optimizing their role in ecological restoration and conservation efforts. Secondly, due to the complexity of spatial flow of multiple types of ecosystem service values (Fisher et al., 2009), Determining the appropriate spatial scale for assessing ecosystem service values presents a challenge, for evaluating ecosystem service values, which in turn affects the identification of ecological patches. Thus, determining a reasonable scale for evaluating ecosystem service values is a key research direction for future construction of the ESP. Thirdly, in evaluating ecosystem service values, the reesarch’s reliance on data availability means that the precision of some data may vary, potentially leading to rough results. Additionally, in identifying ecological pinch points, the threshold setting was based on previous studies (Li et al., 2022; Qi and Fan, 2016) rather than field surveys. Therefore, conducting field surveys to determine species dispersal distances and setting thresholds reasonably is a key focus of future research.
6 Conclusion
To promote the sustainable development of socio-economic and ecological environments in the region, this study utilizes the “ecological patch-resistance surface-corridor” model to establish the ecological security pattern for LX. Based on the theories and methodologies of ESP and ERP, and considering the integrity of ecosystems and their restoration potential, key areas for TER have been identified, along with the prioritization sequence for restoration within these critical areas. This establishes a definitive strategy for the site selection, execution, and building of ecological restoration initiatives. This paper takes an integrated approach to sustainable development, seeking to improve ecosystem services and ensure synchronized progress of socio-economic and ecological settings in the upper reaches of the YRB. This approach holds practical significance for regional sustainable development.
The research findings indicated that (1) There were significant spatial disparities in the ecosystem service values across different types in LX. Based on the comprehensive ecosystem service values, 13 ecological patches were identified, Covering a combined land area of 1,206.56 km2, which constitutes 14.77% of the total study region. Moreover, utilizing the comprehensive resistance surface approach, 25 ecological corridors with a cumulative length of 791.78 km were identified, with a concentration in the southwest of LX, forming a cohesive ecological security network in conjunction with the ecological patches. (2) A total of 13 ecological pinch points and 17 ecological barrier points were recognized, crucial for optimizing regional biotic flow circulation. Restoration of these ecological breakpoints could significantly enhance landscape connectivity within the region. (3) Applying the potential similar habitat approach, LX’s similar habitat units were categorized into 23 types across 294 zones. Furthermore, the combined identification of LX’s ERP surface, considering both ERNP and social support potentials, displayed a spatial pattern marked by a prominence in the central region and depressions in the north and south. (4) This paper categorized the key areas for TER into three dimensions: characterized by “point-line-surface” and identified the priority of TER for each type of key areas, classified as “primary-very important-important.”
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
SD: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Software, Validation, Writing–review and editing. DX: Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, Visualization, Writing–original draft. FS: Conceptualization, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing–original draft. XD: Conceptualization, Data curation, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Software, Writing–original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the China Academy of Engineering Strategic Research and Consulting Program Project (GS2022ZDI02), Gansu Provincial Natural Science Foundation (22JR5RA316), Key Research and Development Program Project in Gansu Province (23YFFA0058), Lanzhou Philosophy and Social Science Planning Project (23-A06).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fenvs.2024.1463683/full#supplementary-material
References
Bolliger, J., Schulte, L. A., Burrows, S. N., Sickley, T. A., and Mladenoff, D. J. (2004). Assessing Ecological Restoration Potentials of Wisconsin (U.S.A.) Using Historical Landscape Reconstructions. Restor. Ecol. 12, 124–142. doi:10.1111/j.1526-100x.2004.00285.x
Breed, M. F., Harrison, P. A., Blyth, C., Byrne, M., Gaget, V., Gellie, N. J. C., et al. (2019). The potential of genomics for restoring ecosystems and biodiversity. Nat. Rev. Genet. 20, 615–628. doi:10.1038/s41576-019-0152-0
Bullock, J. M., Aronson, J., Newton, A. C., Pywell, R. F., and Rey-Benayas, J. M. (2011). Restoration of ecosystem services and biodiversity: conflicts and opportunities. Trends Ecol. Evol. 26, 541–549. doi:10.1016/j.tree.2011.06.011
Carpenter, S. R., Mooney, H. A., Agard, J., Capistrano, D., DeFries, R. S., Díaz, S., et al. (2009). Science for managing ecosystem services: Beyond the Millennium Ecosystem Assessment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 106, 1305–1312. doi:10.1073/pnas.0808772106
Chen, X., Kang, B., Li, M., Du, Z., Zhang, L., and Li, H. (2023). Identification of priority areas for territorial ecological conservation and restoration based on ecological networks: A case study of Tianjin City, China. Ecol. Indic. 146, 109809. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.109809
Cumming, G. S., Buerkert, A., Hoffmann, E. M., Schlecht, E., von Cramon-Taubadel, S., and Tscharntke, T. (2014). Implications of agricultural transitions and urbanization for ecosystem services. Nature 515, 50–57. doi:10.1038/nature13945
Dou, H., Li, X., Li, S., Dang, D., Li, X., Lyu, X., et al. (2020). Mapping ecosystem services bundles for analyzing spatial trade-offs in inner Mongolia, China. J. Clean. Prod. 256, 120444. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120444
Elmqvist, T., Setälä, H., Handel, S. N., van der Ploeg, S., Aronson, J., Blignaut, J. N., et al. (2015). Benefits of restoring ecosystem services in urban areas. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 14, 101–108. doi:10.1016/j.cosust.2015.05.001
Fan, F., Liu, Y., Chen, J., and Dong, J. (2020). Scenario-based ecological security patterns to indicate landscape sustainability: a case study on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Landsc. Ecol. 36, 2175–2188. doi:10.1007/s10980-020-01044-2
Fan, F., Wen, X., Feng, Z., Gao, Y., and Li, W. (2022). Optimizing urban ecological space based on the scenario of ecological security patterns: The case of central Wuhan, China. Appl. Geogr. 138, 102619. doi:10.1016/j.apgeog.2021.102619
Fang, F., Ma, L., Fan, H., Che, X., and Chen, M. (2020a). The spatial differentiation of quality of rural life based on natural controlling factors: A case study of Gansu Province, China. J. Environ. Manag. 264, 110439. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110439
Fang, H., Feng, Y., Zhang, L., Su, M., and Yang, H. (2020b). “A Long Short-Term Memory Neural Network Model for Predicting Air Pollution Index Based on Popular Learning,” in Database systems for advanced applications. DASFAA 2020 international workshops. Editors Y. Nah, C. Kim, S.-Y. Kim, Y.-S. Moon, and S. E. Whang (Cham: Springer International Publishing), 190–199.
Fisher, B., Costanza, R., Turner, R., and Morling, P. (2009). Defining and classifying ecosystem services for decision making. Ecol. Econ. 68, 643–653. doi:10.1016/j.ecolecon.2008.09.014
Gao, J., Shi, Y., Zhang, H., Chen, X., Zhang, W., Shen, W., et al. (2023). “China regional 250m fractional vegetation cover data set (2000-2022),” in National Tibetan plateau data center.
Gao, J., Zou, C., Zhang, K., Xu, M., and Wang, Y. (2020). The establishment of Chinese ecological conservation redline and insights into improving international protected areas. J. Environ. Manag. 264, 110505. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110505
Gong, J., Xie, Y., Cao, E., Huang, Q., and Li, H. (2019). Integration of InVEST-habitat quality model with landscape pattern indexes to assess mountain plant biodiversity change: A case study of Bailongjiang watershed in Gansu Province. J. Geogr. Sci. 29, 1193–1210. doi:10.1007/s11442-019-1653-7
Guo, Y., Fu, B., Wang, Y., Xu, P., and Liu, Q. (2022). Identifying spatial mismatches between the supply and demand of recreation services for sustainable urban river management: a case study of Jinjiang River in Chengdu, China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 77, 103547. doi:10.1016/j.scs.2021.103547
Han, Y., Yu, C., Feng, Z., Du, H., Huang, C., and Wu, K. (2021). Construction and Optimization of Ecological Security Pattern Based on Spatial Syntax Classification—Taking Ningbo, China, as an Example. Land 10, 380. doi:10.3390/land10040380
He, C., Liu, Z., Tian, J., and Ma, Q. (2014). Urban expansion dynamics and natural habitat loss in China: a multiscale landscape perspective. Glob. Chang. Biol. 20, 2886–2902. doi:10.1111/gcb.12553
He, Q., Wei, F., Deng, X., Kong, F., Li, C., Yan, Z., et al. (2022). Spatiotemporal pattern of carbon productivity and carbon offset potential in Chinese counties. Sci. Total Environ. 846, 157153. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.157153
Hooper, T., Beaumont, N., Griffiths, C., Langmead, O., and Somerfield, P. J. (2017). Assessing the sensitivity of ecosystem services to changing pressures. Ecosyst. Serv. 24, 160–169. doi:10.1016/j.ecoser.2017.02.016
Jia, L., Deng, Y., Hou, M., Li, Y., Ding, Z., and Yao, S. (2022). Pathways from the payment for ecosystem services program to ecological and socio-economic outcomes. Ecol. Indic. 144, 109534. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.109534
Jia, Q., Jiao, L., Lian, X., and Wang, W. (2023). Linking supply-demand balance of ecosystem services to identify ecological security patterns in urban agglomerations. Sustain. Cities Soc. 92, 104497. doi:10.1016/j.scs.2023.104497
Jiang, G., Zhang, R., Ma, W., Zhou, D., Wang, X., and He, X. (2017). Cultivated land productivity potential improvement in land consolidation schemes in Shenyang, China: assessment and policy implications. Land Use Policy 68, 80–88. doi:10.1016/j.landusepol.2017.07.001
Jiang, W., Yuan, L., Wang, W., Cao, R., Zhang, Y., and Shen, W. (2015). Spatio-temporal analysis of vegetation variation in the Yellow River Basin. Ecol. Indic. 51, 117–126. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2014.07.031
Jie, Z. H. U., Jie, S. U., Hai-wei, Y. I. N., and Fan-hua, K. (2020). Construction of Xuzhou ecological network based on comprehensive sources identification and multi-scale nesting. J. Nat. Resour. 35, 1986. doi:10.31497/zrzyxb.20200817
Kong, F., Yin, H., Nakagoshi, N., and Zong, Y. (2010). Urban green space network development for biodiversity conservation: Identification based on graph theory and gravity modeling. Landsc. Urban Plan. 95, 16–27. doi:10.1016/j.landurbplan.2009.11.001
Kowe, P., Mutanga, O., Odindi, J., and Dube, T. (2020). A quantitative framework for analysing long term spatial clustering and vegetation fragmentation in an urban landscape using multi-temporal landsat data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Observation Geoinformation 88, 102057. doi:10.1016/j.jag.2020.102057
Laughlin, D. C. (2014). Applying trait-based models to achieve functional targets for theory-driven ecological restoration. Ecol. Lett. 17, 771–784. doi:10.1111/ele.12288
Li, F., Pan, B., Wu, Y., and Shan, L. (2017). Application of game model for stakeholder management in construction of ecological corridors: A case study on Yangtze River Basin in China. Habitat Int. 63, 113–121. doi:10.1016/j.habitatint.2017.03.011
Li, F., Xu, M., liu, Q., Wang, Z., and Xu, W. (2014). Ecological restoration zoning for a marine protected area: A case study of Haizhouwan National Marine Park, China. Ocean and Coast. Manag. 98, 158–166. doi:10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2014.06.013
Li, J., Song, C., Cao, L., Zhu, F., Meng, X., and Wu, J. (2011). Impacts of landscape structure on surface urban heat islands: A case study of Shanghai, China. Remote Sens. Environ. 115, 3249–3263. doi:10.1016/j.rse.2011.07.008
Li, Q., Zhou, Y., and Yi, S. (2022). An integrated approach to constructing ecological security patterns and identifying ecological restoration and protection areas: A case study of Jingmen, China. Ecol. Indic. 137, 108723. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.108723
Li, S., Xiao, W., Zhao, Y., and Lv, X. (2020). Incorporating ecological risk index in the multi-process MCRE model to optimize the ecological security pattern in a semi-arid area with intensive coal mining: A case study in northern China. J. Clean. Prod. 247, 119143. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119143
Liquete, C., Kleeschulte, S., Dige, G., Maes, J., Grizzetti, B., Olah, B., et al. (2015). Mapping green infrastructure based on ecosystem services and ecological networks: A Pan-European case study. Environ. Sci. and Policy 54, 268–280. doi:10.1016/j.envsci.2015.07.009
Liu, H., Wang, Z., Zhang, L., Tang, F., Wang, G., and Li, M. (2023a). Construction of an ecological security network in the Fenhe River Basin and its temporal and spatial evolution characteristics. J. Clean. Prod. 417, 137961. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.137961
Liu, J., Zhang, G., Zhuang, Z., Cheng, Q., Gao, Y., Chen, T., et al. (2017). A new perspective for urban development boundary delineation based on SLEUTH-InVEST model. Habitat Int. 70, 13–23. doi:10.1016/j.habitatint.2017.09.009
Liu, M., Liu, X., Huai, H., and Tang, X. (2023b). Evaluation of the Potential for Territorial Ecological Restoration: A Case Study of Zhaoping County, China. Land 12, 1966. doi:10.3390/land12111966
Liu, Q., Yang, Z., and Cui, B. (2008). Spatial and temporal variability of annual precipitation during 1961–2006 in Yellow River Basin, China. J. Hydrology 361, 330–338. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2008.08.002
Liu, S., Shao, Q., Ning, J., Niu, L., Zhang, X., Liu, G., et al. (2022). Remote-Sensing-Based Assessment of the Ecological Restoration Degree and Restoration Potential of Ecosystems in the Upper Yellow River over the Past 20 Years. Remote Sens. 14, 3550. doi:10.3390/rs14153550
Lv, T., Zeng, C., Lin, C., Liu, W., Cheng, Y., and Li, Y. (2023). Towards an integrated approach for land spatial ecological restoration zoning based on ecosystem health assessment. Ecol. Indic. 147, 110016. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2023.110016
McRae, B. H., Dickson, B. G., Keitt, T. H., and Shah, V. B. (2008). Using Circuit Theory To Model Connectivity In Ecology, Evolution, And Conservation. Ecology 89, 2712–2724. doi:10.1890/07-1861.1
Niu, L.-n., Shao, Q.-q., Ning, J., Yang, X.-q., Liu, S.-c., Liu, G.-b., et al. (2023). Evaluation on the degree and potential of ecological restoration in Loess Plateau. J. Nat. Resour. 38, 779. doi:10.31497/zrzyxb.20230314
Omernik, J. M., and Griffith, G. E. (2014). Ecoregions of the Conterminous United States: Evolution of a Hierarchical Spatial Framework. Environ. Manag. 54, 1249–1266. doi:10.1007/s00267-014-0364-1
Pascual-Hortal, L., and Saura, S. (2008). Integrating landscape connectivity in broad-scale forest planning through a new graph-based habitat availability methodology: application to capercaillie (Tetrao urogallus) in Catalonia (NE Spain). Eur. J. For. Res. 127, 23–31. doi:10.1007/s10342-006-0165-z
Peng, J., Pan, Y., Liu, Y., Zhao, H., and Wang, Y. (2018a). Linking ecological degradation risk to identify ecological security patterns in a rapidly urbanizing landscape. Habitat Int. 71, 110–124. doi:10.1016/j.habitatint.2017.11.010
Peng, J., Yang, Y., Liu, Y., Hu, Y., Du, Y., Meersmans, J., et al. (2018b). Linking ecosystem services and circuit theory to identify ecological security patterns. Sci. Total Environ. 644, 781–790. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.06.292
Peng, J., Zhao, H., and Liu, Y. (2017a). Urban ecological corridors construction: A review. Acta Ecol. Sin. 37, 23–30. doi:10.1016/j.chnaes.2016.12.002
Peng, S., Ding, Y., Wen, Z., Chen, Y., Cao, Y., and Ren, J. (2017b). Spatiotemporal change and trend analysis of potential evapotranspiration over the Loess Plateau of China during 2011–2100. Agric. For. Meteorology 233, 183–194. doi:10.1016/j.agrformet.2016.11.129
Putwain, P. D., and Cairns, J. (1981). The Recovery Process in Damaged Ecosystems. J. Ecol. 69, 1062. doi:10.2307/2259654
Qi, K., and Fan, Z. (2016). Evaluation method for landscape connectivity based on graph theory: a case study of natural forests in Minqing County, Fujian Province. Acta Ecol. Sin. 36, 7593. doi:10.5846/stxb201507301599
Qiu, T., Song, C., and Li, J. (2017). Impacts of Urbanization on Vegetation Phenology over the Past Three Decades in Shanghai, China. Remote Sens. 9, 970. doi:10.3390/rs9090970
Ran, Y., Lei, D., Li, J., Gao, L., Mo, J., and Liu, X. (2022). Identification of crucial areas of Territorial Ecological Restoration based on ecological security pattern: A case study of the central Yunnan urban agglomeration, China. Ecol. Indic. 143, 109318. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.109318
Renard, K. G. (1997). “Predicting soil erosion by water: A guide to conservation planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss equation (RUSLE),” in Predicting soil erosion by water: a guide to conservation planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss equation (RUSLE).
Savary, P., Foltête, J. C., and Garnier, S. (2021). Cost distances and least cost paths respond differently to cost scenario variations: a sensitivity analysis of ecological connectivity modeling. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 36, 1652–1676. doi:10.1080/13658816.2021.2014852
Shen, Z., Wu, W., Tian, S., and Wang, J. (2022). A multi-scale analysis framework of different methods used in establishing ecological networks. Landsc. Urban Plan. 228, 104579. doi:10.1016/j.landurbplan.2022.104579
Soille, P., and Vogt, P. (2009). Morphological segmentation of binary patterns. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 30, 456–459. doi:10.1016/j.patrec.2008.10.015
Song, G., Li, Z., Yang, Y., Semakula, H. M., and Zhang, S. (2015). Assessment of ecological vulnerability and decision-making application for prioritizing roadside ecological restoration: A method combining geographic information system, Delphi survey and Monte Carlo simulation. Ecol. Indic. 52, 57–65. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2014.11.032
Strassburg, B. B. N., Iribarrem, A., Beyer, H. L., Cordeiro, C. L., Crouzeilles, R., Jakovac, C. C., et al. (2020). Global priority areas for ecosystem restoration. Nature 586, 724–729. doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2784-9
Su, X., Li, X., Niu, Z., Wang, N. A., and Liang, X. (2021). A new complexity-based three-stage method to comprehensively quantify positive/negative contribution rates of climate change and human activities to changes in runoff in the upper Yellow River. J. Clean. Prod. 287, 125017. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.125017
Tong, H.-l., and Shi, P.-j. (2020). Using ecosystem service supply and ecosystem sensitivity to identify landscape ecology security patterns in the Lanzhou-Xining urban agglomeration, China. J. Mt. Sci. 17, 2758–2773. doi:10.1007/s11629-020-6283-0
Vogt, P., Ferrari, J. R., Lookingbill, T. R., Gardner, R. H., Riitters, K. H., and Ostapowicz, K. (2009). Mapping functional connectivity. Ecol. Indic. 9, 64–71. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2008.01.011
Wang, S., Wu, M., Hu, M., Fan, C., Wang, T., and Xia, B. (2021). Promoting landscape connectivity of highly urbanized area: An ecological network approach. Ecol. Indic. 125, 107487. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.107487
Wang, S., Wu, M., Hu, M., and Xia, B. (2022). Integrating ecosystem services and landscape connectivity into the optimization of ecological security pattern: a case study of the Pearl River Delta, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 29, 76051–76065. doi:10.1007/s11356-022-20897-5
Wang, S.-Y., Liu, J.-S., and Ma, T.-B. (2010). Dynamics and changes in spatial patterns of land use in Yellow River Basin, China. Land Use Policy 27, 313–323. doi:10.1016/j.landusepol.2009.04.002
Wei, Q., Halike, A., Yao, K., Chen, L., and Balati, M. (2022). Construction and optimization of ecological security pattern in Ebinur Lake Basin based on MSPA-MCR models. Ecol. Indic. 138, 108857. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.108857
Wenbin, N., Yan-hua, S., Martin John, S., Yang, F., Renwu, W., Xukun, W., et al. (2021). Constructing and optimizing ecological network at county and town Scale: The case of Anji County, China. Ecol. Indic. 132, 108294. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.108294
Xia, H., Yuan, S., and Prishchepov, A. V. (2023). Spatial-temporal heterogeneity of ecosystem service interactions and their social-ecological drivers: Implications for spatial planning and management. Resour. Conservation Recycl. 189, 106767. doi:10.1016/j.resconrec.2022.106767
Xu, X., Zhang, D., Zhang, Y., Yao, S., and Zhang, J. (2020). Evaluating the vegetation restoration potential achievement of ecological projects: A case study of Yan’an, China. Land Use Policy 90, 104293. doi:10.1016/j.landusepol.2019.104293
Yan, Y., Jarvie, S., Zhang, Q., Zhang, S., Han, P., Liu, Q., et al. (2021). Small patches are hotspots for biodiversity conservation in fragmented landscapes. Ecol. Indic. 130, 108086. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.108086
Yang, G., Yuexin, L., Jianli, Q., Youxia, G., and Yingshan, H. (2020). Improving ecological security pattern based on the integrated observation of multiple source data: A case study of Wannian County, Jiangxi Province. Resour. Sci. 42, 2010–2021. doi:10.18402/resci.2020.10.17
Yang, J., and Huang, X. (2021). The 30 m annual land cover dataset and its dynamics in China from 1990 to 2019. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 13, 3907–3925. doi:10.5194/essd-13-3907-2021
Yongli, H. E. (2019). “Pan-TPE soil map based on Harmonized World Soil Database (V1.2),” in National Tibetan plateau data center.
Yu, K. (1996). Security patterns and surface model in landscape ecological planning. Landsc. Urban Plan. 36, 1–17. doi:10.1016/s0169-2046(96)00331-3
Zhang, B., Wang, S., Li, Q., and Xie, G. (2021a). Spatio-temporal changes of water conservation service in the Beijing-Tianjin sandstorm source control project area. Acta Ecol. Sin. 41. doi:10.5846/stxb202005111181
Zhang, H., Li, J., Tian, P., Pu, R., and Cao, L. (2022). Construction of ecological security patterns and ecological restoration zones in the city of Ningbo, China. J. Geogr. Sci. 32, 663–681. doi:10.1007/s11442-022-1966-9
Zhang, Y., Du, J., Guo, L., Sheng, Z., Wu, J., and Zhang, J. (2021b). Water Conservation Estimation Based on Time Series NDVI in the Yellow River Basin. Remote Sens. 13, 1105. doi:10.3390/rs13061105
Zhao, N., Liu, Y., Cao, G., Samson, E. L., and Zhang, J. (2017). Forecasting China’s GDP at the pixel level using nighttime lights time series and population images. GIScience and Remote Sens. 54, 407–425. doi:10.1080/15481603.2016.1276705
Zhao, S.-m., Ma, Y.-f., Wang, J.-l., and You, X.-y. (2019). Landscape pattern analysis and ecological network planning of Tianjin City. Urban For. and Urban Green. 46, 126479. doi:10.1016/j.ufug.2019.126479
Zhen, L., Ishwaran, N., Luo, Q., Wei, Y., and Zhang, Q. (2020). Role and significance of restoration technologies for vulnerable ecosystems in building an ecological civilization in China. Environ. Dev. 34, 100494. doi:10.1016/j.envdev.2020.100494
Keywords: Territorial Ecological Restoration, ecological restoration potential, ecological security pattern, potential similar habitat method, ecologically fragile areas in the YRB
Citation: Du S, Xu D, Sun F and Dong X (2024) Identification of key areas for Territorial Ecological Restoration: focusing on ecological security and restoration potential. Front. Environ. Sci. 12:1463683. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2024.1463683
Received: 12 July 2024; Accepted: 16 October 2024;
Published: 29 October 2024.
Edited by:
Marinés De La Peña-Domene, Instituto Tecnológico y de Estudios Superiores de Occidente, MexicoReviewed by:
Moisés Mendez-Toribio, Instituto de Ecología (INECOL), MexicoJose Flavio Marquez Torres, Centro de Investigación en Biodiversidad y Conservación (CIByC), Mexico
Copyright © 2024 Du, Xu, Sun and Dong. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Sen Du, ZHVzZW5AbWFpbC5semp0dS5jbg==
 Sen Du
Sen Du Deze Xu
Deze Xu Foyou Sun
Foyou Sun Xiaoyuan Dong
Xiaoyuan Dong