- 1School of Economics, Beijing Wuzi University, Beijing, China
- 2School of International Trade and Economics, Central University of Finance and Economics, Beijing, China
Green development, as a key link in the philosophy of new development, is the only way to achieve sustainable development. However, how science and technology (S&T) finance affects green development remains unclear. Based on panel data of 284 cities in China from 2007 to 2020, the multi-time-point difference-in-differences (DID) model and the mediation model were utilized to analyze the influencing mechanisms and paths of the S&T financial pilot policy on green development. The results show that S&T financial policy can significantly promote green development, for which green innovation (GI) capability, industrial structure advancement (ISA), and industrial structure rationalization (ISR) are important paths. Moreover, the effects of S&T financial policy on green development are heterogeneous: the policy exerts a stronger effect on the central region than on the eastern and western regions, a stronger effect on large cities than on small- and medium-sized cities, and a stronger effect on key cities than on general cities. Therefore, relevant governmental departments should continually optimize S&T financial policy; pay more attention to cities in the western region, small- and medium-sized cities, and general cities; actively foster GI capability; facilitate industrial structure transformation and upgrading; and vigorously support cross-regional exchange and cooperation to jointly realize green development. This study sheds new light on how the S&T finance related policy reform promotes sustainable growth and socio-economic welfare in developing countries.
1 Introduction
The promotion of green and low-carbon economies is a key factor in achieving sustainable development. However, economic growth is rapid in many developing countries, such as China, which relies on large-scale resource inputs and energy consumption. The subsequent extensive development modes of “GDP worship”1 and “treatment after pollution” have given rise to environmental issues that seriously hinder sustainable development. Against the backdrop of global climate change, extreme weather and natural disasters are occurring frequently, and problems such as resource depletion and environmental pollution caused by extensive production are becoming increasingly prominent. In the face of the contradiction between human survival and development needs and the limited supply of natural resources, it is imperative to promote green development (Xu and Zhu, 2022). However, enterprises usually carry out green transformation through green innovation with high-risk characteristics such as high starting points, large investments and long cycles. There is a serious phenomenon of “market failure” in innovation investment and transformation. Therefore, in the process of the leapfrog development of green transformation, policy support and guidance are required. It also requires effective integration of S&T innovation and the financial systems. The development of S&T finance is of great significance for alleviating the financing difficulties of S&T-based SMEs and promoting green technology innovation. S&T financial policy allocates more financial resources to S&T enterprises to enhance the competitiveness of low-carbon sectors, including the high-tech sectors, by reversing the misallocation of financial resources. This improves the fit between S&T finance and environmental governance, thereby boosting green development (Wang and Jiang, 2022).
The pilot program promoting the integration of science, technology, and finance (S&T financial policy) provides a good policy guarantee for building an innovative country and a strong country in S&T. However, could the pilot program provide institutional arrangements and guarantees for the rational allocation of S&T and financial resources through the innovation in public policy tools? What are the exact effects of S&T financial policies on green development? What are the relevant mechanisms and pathways involved? Are the effects of S&T financial policy heterogeneous across different regions and cities types? Solving these problems is of great theoretical and practical significance for seeking new paths to improve the level of green development and optimize the future S&T financial policy systems.
Green development has always been a popular topic in academic research. Scholars have mainly focused on the connotations and influencing factors of green development. Green development is derived from the concept of sustainable development. This can be traced back to the green economic growth proposed by Pearce et al. (1989) and the ecological economic development proposed by Costanza (1989). Over time, green development has not yet formed a unified concept, but its connotation is more diversified and inclusive. Liang et al. proposed that green development refers to promoting economic growth while minimizing resource consumption and environmental pollution to achieve sustainable development of the economy, society, and ecosystem. It emphasizes the realization of harmonious coexistence between humans and nature through the adoption of clean energy, energy-saving technologies, and ecological protection measures (Liang et al., 2022).
In addition, a large number of studies exploring the factors influencing green development have shown that green development is affected by digitalization, urbanization, industrial structure, population size, human capital, and environmental regulation (Lee et al., 2023; Zhang, 2021; Ma et al., 2022; Hu et al., 2020). Feng et al. (2017) believe that technological innovation is the most critical factor. S&T progress can effectively improve energy utilization efficiency and pollution control ability, reduce energy waste and pollutant emissions, and thus achieve green development (Mensah et al., 2019; Popkova et al., 2021; Liu et al., 2016). However, some researchers consider that S&T progress may impede green development. They stated that S&T progress is mainly a result of pursuing production efficiency, and such profit-seeking psychology drives enterprises to blindly expand their production scale and thus get trapped in a production mode of the “green dilemma.” This may aggravate environmental pollution and hinder green development (Khattak et al., 2020). In recent years, financial development has provided new ideas and methods for realizing green development with a continuous shift in investment from a real economy2 to a virtual economy. Numerous scholars have studied the underlying mechanisms and paths of such developments from various perspectives. Generally, the vast majority of scholars consider that financial development helps improve the regional green development level (Tian et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2021; Zhang et al., 2021; Yuan et al., 2020), to which the industrial structure (Feng et al., 2022), environmental regulation (Han et al., 2023), and technological innovation (Xiong and Dai, 2023) are main paths. However, there are still disputes regarding the relationship between financial development and environmental pollution (Tamazian et al., 2009; Elheddad et al., 2021). In particular, Canh et al. (2021) found that financial development significantly promotes environmental pollution accompanied by rapid economic growth in China. Mesagan et al. (2022) also proved that despite the lack of a significant relationship between financial development and environmental pollution in the short term, financial development significantly aggravates regional environmental pollution in the long run.
In summary, the relationships among financial development, S&T progress, and green development have been widely recognized, but the disputes therein have not been well resolved. In this context, S&T financial policy provides a new perspective for solving disputes between financial development, S&T progress, and green development by integrating financial development and S&T progress.
In the late 20th century, China began combining S&T with finance. Since the Shenzhen S&T Bureau proposed the “science and technology finance” in 1993, the synergy between S&T finance has gradually attracted the attention of the public and government (Zhang et al., 2019). S&T financial policy supports scientific research, transformation of achievements, and the development of technology-based enterprises through financial services, such as banking, securities, insurance, venture capital, mortgages, and guarantees (Julaiti, 2023). S&T finance is different from fintech, which focuses on using advanced technologies such as big data, cloud computing, and artificial intelligence to deeply innovate traditional financial services, thereby providing more convenient, efficient and inclusive financial services (Abis et al., 2024). In 2011 and 2016, the Chinese government implemented the pilot program to promote the integration of S&T and finance policies in batches. However, most existing studies only explore the effects of S&T financial policy on green innovation (GI) (Wang et al., 2022), environmental pollution (Liu et al., 2023), and carbon emissions (Xu et al., 2022). Although these studies are all related to green development, they only focus on a single aspect and therefore cannot be generalized.
Therefore, the multi-time-point DID and the mediation model were utilized to analyze the impact of S&T financial policy on green development based on panel data of 284 cities in China from 2007 to 2020. Compared with the existing research, this study’s contributions include the following three aspects. First, this study fills an important research gap in the literature, which is the lack of empirical evidence on the causal relationship between S&T financial policies and green development in China. Based on the analysis of historical evolution and characteristics of the development of S&T financial policies in China, this study seeks to unpack the mechanisms through which S&T financial policies affect green development, i.e., green innovation and industrial structure upgrading. Second, this study constructs a quasi-experimental analysis framework based on a multi-period DID model and uses the instrumental variable method to test the impact of S&T financial policies on green development, effectively solving possible endogeneity concerns. Third, this study conducts a heterogeneity analysis to delve deeper into the variations in the effects of S&T financial policies on green development based on different locations, sizes, and administrative levels, which allows policymakers to utilize targeted policies to enhance green development under diverse conditions.
2 Policy background and research hypotheses
2.1 Policy background
Literature review shows that a fairly large amount of research considers that the S&T finance in China emerged in 1985 (Zhang and Wang, 2023; Xu and Guo, 2023). In fact, as early as 1979, Deng Xiaoping had proposed that “Banks should develop to a leverage for economic development and technological innovation. We should develop real banks.” This implies the connotation of S&T finance (Zhang et al., 2019). In 1980, Zhejiang Province took the lead in exploring S&T finance through the trial implementation of compensated scientific research funds (Gu and Zhou, 1986), which has been regarded as the first year of S&T finance in China. Subsequently, cities (provinces) including Xiangtan City, Xiangfan City, and Qinghai Province also explored S&T finance. In 1985, the People’s Bank of China and State Council issued a Joint Notice on Actively Developing Lending for Science and Technology. They stated that banks and other financial institutions should allocate some loans to support S&T development, which was the first national-level S&T financial policy introduced in China and has forcefully driven S&T development (Zhu et al., 2012). This was closely followed by the formulation of the Law of the People’s Republic of China on Science and Technology Progress in 1993 and the Law of the People’s Republic of China on Promoting the Transformation of Scientific and Technological Achievements in 1996, which laid a solid legal foundation for S&T development. In 2006, the State Council issued the Outline of the National Medium- and Long-Term Science and Technology Development Program (2006–2020) and several supporting policies, in which it was proposed that financial policies that facilitate technological innovation should be implemented. This accelerated the development of S&T finance in China.
To lead social capitals to actively take part in the independent innovation and drive the cooperation of S&T and financial resources, the Ministry of Science and Technology, together with the People’s Bank of China, China Banking Regulatory Commission, China Securities Regulatory Commission and China Insurance Regulatory Commission issued the Notice on the Issuance of a Pilot Implementation Plan to Promote the Integration of Science, Technology and Finance in 2010. Note that the government should build pilots to drive demonstrations and guide and promote various financial institutions to innovate their financial services to provide reliable financial support for S&T development. In 2011, 16 regions (including Zhongguancun Science Park) were selected as the first batch of pilots to promote S&T and finance integration, which marks the formal implementation of S&T financial policy. Based on a summary of the experiences of the first group of pilots, nine cities, including Zhengzhou, were selected as the second group of pilots in 2016.
Generally, S&T financial policies highlight the effects of governments and markets simultaneously. Policy implementation involves two stages: practical exploration and further development (Xu and Guo, 2023). In the practical exploration stage, the implementation of S&T financial policy merely adopts financial subsidies and low-interest loan. The financing channels are single and the threshold is high. Therefore, the government’s investment in S&T innovation is limited, making it difficult to produce a large amplification and pulling effect and unable to fully meet the innovation funding needs of technology-based enterprises. In the further development stage, S&T financial policy has shifted its focus to improving the financial efficiency of the market and guiding social capital. Multiple policies for bank credit, capital markets, technology insurance, venture capital, bonds, and fiscal guidance are linked, thereby realizing the marketized operation of S&T finance and facilitating the in-depth integration of S&T and finance.
2.2 Research hypotheses
2.2.1 Direct effects of the S&T financial policy on green development
The S&T financial policy directly affects the regional innovation of investment and financing mechanisms in S&T. It may increase corporate R&D investment in green innovation, improve the efficiency of transformation of S&T innovation achievements, and promote the regional green development through government financial support and financial market capital allocation. On one hand, as the primary advocate of green development, the government can promote green development through policy tools such as green finance and environmental regulation. First, under the promotion of policy pilots, local governments pay more attention to local S&T financial innovation activities and encourage enterprises to conduct green technology R&D and application by providing subsidies or tax incentives to high-tech enterprises (Huang et al., 2017). Second, pilot cities will further improve urban greening, public services and infrastructure construction with the advantages of S&T finance to better play a leading role in demonstration, thereby increasing urban green welfare. Third, the government will try its best to collect relevant information about enterprises and build an information-sharing platform for financial institutions and enterprises to effectively evaluate their qualifications. Simultaneously, environmental supervision systems are built to control the excessive emission of pollutants for enterprises through credit quotas and the collection of pollution taxes (Ma et al., 2018).
On the other hand, the financial market has the advantage of information collection and plays an important role in optimizing resource allocation and accelerating the transformation of S&T achievements. Through efficient project screening, the financial market guides financial resources to technology companies with high innovation capabilities, improves the allocation efficiency of credit funds (Lubo and Veronesi, 2009; Kerr and Nanda, 2014), promotes the promotion of advanced technologies, accelerates the industrialization of high-tech, and stimulates the R&D motivation and innovation potential of enterprises. Simultaneously, based on the functions of capital allocation and information identification, the market will prioritize the allocation of financial resources to environmentally friendly projects with advanced technology and promote the green transformation of traditional industries and the development of emerging green industries (Li et al., 2022), thereby improving green innovation. Based on the above analysis, we propose the following hypotheses.
Hypothesis 1. The S&T financial policy can promote green development.
2.2.2 Influencing paths of the S&T financial policy on green development
Nobel Prize winner Hicks (1969) in economics once pointed out that “finance can offer huge financial support for the emergence of new technologies.” However, because of the long capital recovery cycle and large financing risk of S&T enterprises, a large number of small- and medium-sized S&T enterprises face financing difficulties. S&T financial policy leads and promotes all kinds of financial institutions to innovate financial products, improve service modes, and establish service platforms to offer differentiated financial services for S&T enterprises in different stages, from start-up to maturity. This effectively eases the financing constraints of S&T enterprises, especially those that are small, and significantly enhances regional GI capabilities (Yang and Shen, 2021). Technological innovation is also an important driver of green development (Wang et al., 2023a). Technological innovation can optimize production procedures, improve production and resource utilization efficiency, and reduce resource consumption and pollutant emissions, thereby achieving green development. Based on this, we propose the following hypothesis is put forward.
Hypothesis 2. S&T financial policies can promote green development by improving GI capabilities.
Apart from promoting green development by improving GI capability, S&T financial policy also facilitates green development by driving industrial structure upgrades. According to the research idea in existing research, industrial structure upgrading includes industrial structure advancement (ISA) and industrial structure rationalization (ISR) (Xue et al., 2022). Regarding ISA, the focus of economic development follows an evolutionary trend of shifting from the primary to the secondary industry first and then to the tertiary industry according to the Petty-Clark theorem. Considering this, implementing S&T financial policy can promote the reasonable allocation of financial resources and improve financial efficiency, which is actually the development of the tertiary industry (Zhou, 2011). ISR refers to the reasonable allocation and effective utilization of production factors in different industries (Gan et al., 2011). In general, the profit-seeking nature of capital drives financial resources to flow to high-return industries, giving rise to an imbalance in the industrial structure. However, S&T financial policy can allocate financial resources based on development prospects and investment risk and adjust the unreasonable industrial structure, thus achieving ISR (Feng and Qiu, 2021). Moreover, the traditional industrial structure school believes that industrial structure adjustment can bring “structural dividend” (Liu et al., 2022), that is, industrial structure upgrading can promote the transformation of high-pollution, high-energy-consuming industries into low-carbon, green, clean ones. Most green industries are high-tech industries that generally feature high production efficiency. Therefore, industrial structure transformation and upgrading can not only improve production efficiency but also reduce energy consumption and pollutant emissions, thus driving green economic development (Xie and Hu, 2023). In summary, the following hypotheses are proposed.
Hypothesis 3. S&T financial policies can promote green development by improving ISA levels.
Hypothesis 4. S&T financial policies can promote green development by improving ISR levels.
3 Research design
3.1 Variable selection
3.1.1 Dependent variable
Green Development(GTFP): Using the research method proposed by Zhan et al. (2022), the SBM-GML index is utilized to measure the green development level. The input indicators include labor input, capital input, built-up area, and energy consumption, whereas the output indicators include the expected output indicator (regional GDP) and unexpected output indicators (industrial wastewater, sulfur dioxide, and smoke and dust emissions).
3.1.2 Independent variable
S&T financial policy(DID): The independent variable is the dummy variable
3.1.3 Control variables
Four control variables were determined by referring to previous research results (Lee et al., 2023; Zhang, 2021; Ma et al., 2022; Hu et al., 2020). These include human capital, economic development, informationization, and population density.
Human Capital (HC): The human capital is measured by the proportion of college students in the local permanent population. People receiving a good education are more aware of the importance of environmental protection and are more likely to adopt environmentally friendly technologies and sustainable development modes to effectively utilize resources, reduce energy consumption and waste, and drive green development.
Economic Development (ED): The economic development level is measured by the logarithm of per capita regional GDP. A high level of economic development is generally accompanied by more effective resource allocation. As the level of economic development increases, people are generally more likely to use more advanced and efficient technologies and management methods to obtain more output with lower resource input, thus achieving green development and sustainable development.
Informationization Level (IL): The informationization level is measured by the proportion of the overall sales of postal and telecommunications services in the regional GDP. Increasing the informationization level contributes to more efficient and faster information transfer and allows enterprises to effectively acquire information about resource utilization, accurately allocate resources, reduce waste, and improve utilization and production efficiency.
Population Density (PD): Population density is measured as the population per unit area. Resource utilization is more strained in regions with a higher population density; therefore, efficient resource allocation methods should be used in these regions. In addition, densely populated regions are generally found to have a higher consumption demand, which drives enterprises to adopt environmentally friendly production modes to meet market demand.
3.2 Model specification
To empirically analyze the effects of S&T financial policy on green development, the following baseline regression model is established:
where
3.3 Data collection and descriptive statistics
The DID model was adopted to discuss the effects of S&T financial policies on the green development of cities. Additionally, a mediation model was built to verify the influencing paths. The research samples are panel data of 2843 cities in China from 2007 to 2020, based on the idea of Wang and Jiang (2022). Among these cities, the pilot cities for S&T financial policy are classified into the experimental group, and the remaining are the control group. The policy was implemented in the first batch of pilot cities in 2011, and in the second batch in 2016.
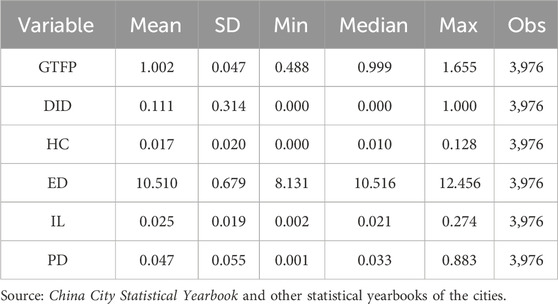
All data were derived from the China City Statistical Yearbooks and statistical yearbooks of the cities. Some of the missing values were interpolated. The descriptive statistics of the relevant variables are listed in Table 1.
As shown in the table, the mean, maximum, minimum, and standard deviation of green development levels in various cities were 1.002, 0.488, 1.655, and 0.047, respectively. This indicates a large gap between the various regions in terms of the green development level. In addition, different regions differ in human capital, economic development level, informationization level, and population density.
4 Results
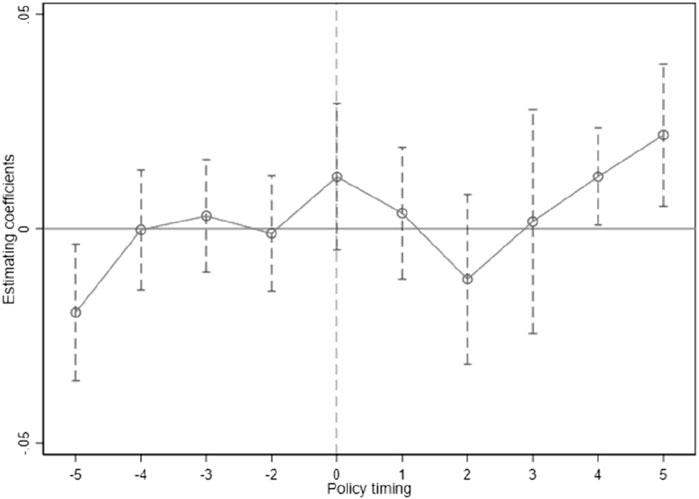
4.1 Parallel trend test
Because many variables are selected, it is necessary to check whether the variables are multicollinear before performing the regression analysis. The variance inflation factors (VIFs) of various variables are calculated, and all are smaller than 3, which means that the variables do not have serious multicollinearity. In addition, because the DID model is used here, parallel trend tests are also needed before conducting the regression analysis. Specifically, the method proposed by Alder et al. (2016) was used to establish the following model:
where
The test results suggest that before implementing the S&T finance pilot policy, the pilot and non-pilot cities do not show a significant difference in the green development level. The difference between the two begins to become significant from the fourth year after implementing the policy, so it passes the parallel trend test.
4.2 Baseline test
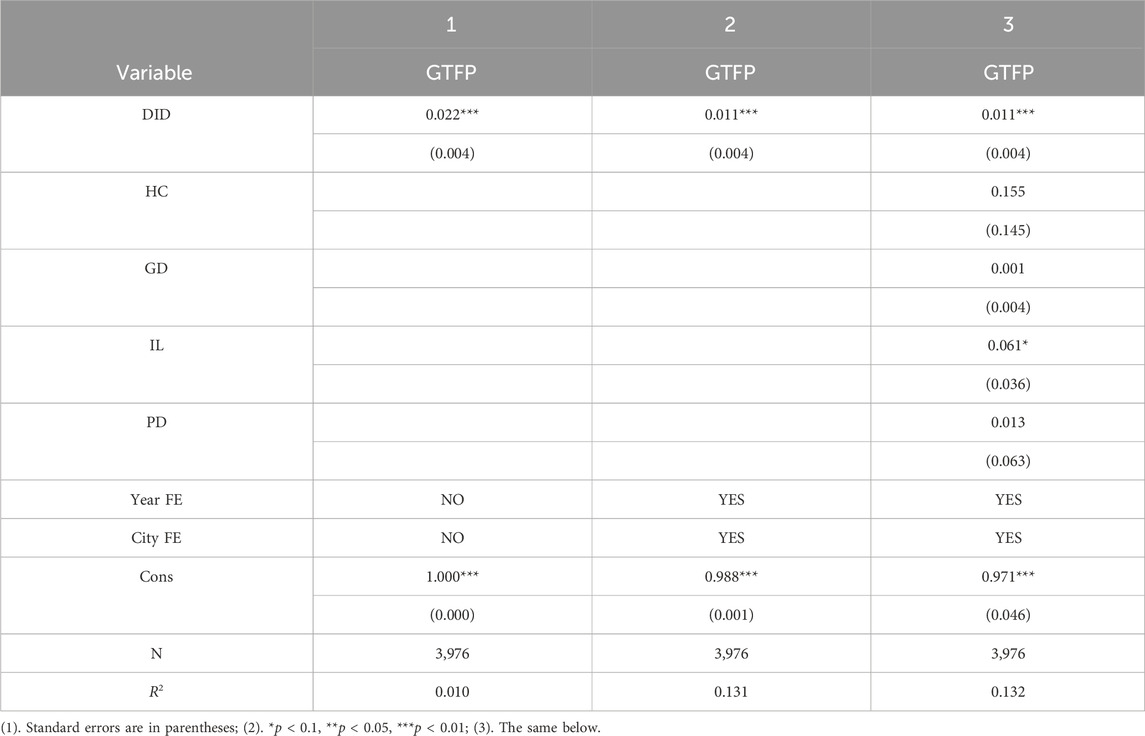
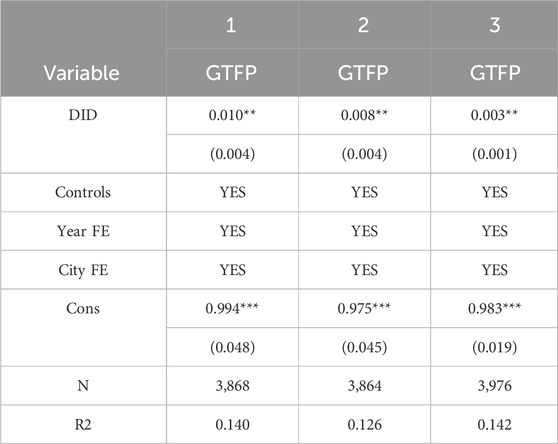
Hausman tests of the data show that the p-value is lower than 0.01, so the fixed effects model is employed for regression analysis. The results are displayed in Table 2.
To ensure the robustness of the regression results, the effects of S&T financial policy on green development were first subjected to a regression analysis. Then, the individual fixed effect and time fixed effect are added to the regression. Finally, the control variables are added to the regression. Obviously, S&T financial policy always exerts a significant promotion effect on green development, that is, the policy is able to promote green development, thus validating Hypothesis 1. This is inconsistent with previous studies (Canh et al., 2021; Mesagan et al., 2022). This is because S&T financial policy allocates more financial resources to low-carbon sectors including the high-tech sector by reversing the misallocation of financial resources, thereby boosting green development (Wang and Jiang, 2022; Li et al., 2022).
Except for S&T financial policy, the informationization level also exerts a significant positive effect on green development, which conforms to previous analysis results (Lee et al., 2023; Zhang, 2021). In addition, despite the insignificant coefficients of human capital, the economic development level, and population density, they are all positive. This indicates that they can promote green development to a certain extent. The causes for the insignificant coefficients include the following: 1) Although the proportion of college students in the local permanent population can, to some extent, reflect the amount of human capital input, the quality of human capital is equally important. Even though there are many college students, labor quality cannot be fully improved at low training and education levels, which influences their role in green development. 2) An increase in the level of economic development can facilitate green development to some extent. Despite this, the economy cannot realize green development unless inputting lots of time and resources to practice industrial structure transformation and upgrading if the local economy depends too much on energy-intensive industries (coal and petrochemical engineering). 3) Although a dense population can promote green development to some extent, a population density that is too high is generally accompanied by accelerated industrialization and urbanization. This may result in the discharge of large amounts of industrial waste, sewage, and garbage, seriously damaging the ecological environment and hindering green economic development.
4.3 Endogenous processing
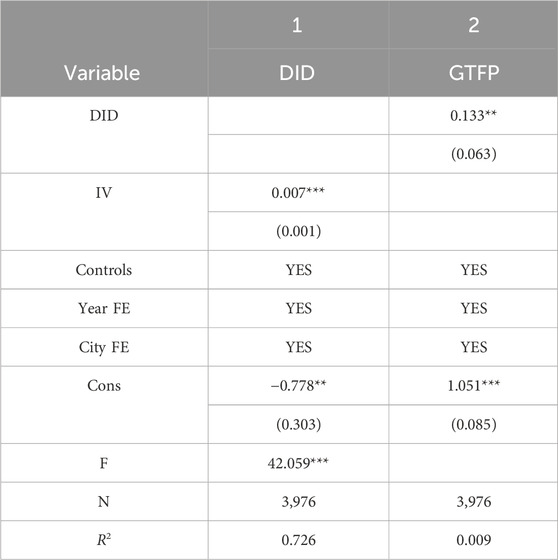
The instrumental variables method was used to further solve the possible endogeneity problem. Considering that existing historical events do not affect current green development, it is common practice in existing research to search for instrumental variables from historical data. Ma and Tao (2019) found that the number of Chinese time-honored enterprises in a region epitomizes the historical inheritance of entrepreneurship, which can significantly promote technological innovation in cities. Therefore, the number of Chinese time-honored enterprises in a region influences on whether a city is selected as a pilot of S&T financial policy, which meets the correlation requirement of instrumental variables. In the meantime, the number of Chinese time-honored enterprises is a historical datum and therefore does not affect current green development, which meets the exogenous condition of instrumental variables. However, the number of Chinese time-honored enterprises is a cross-sectional data that cannot be incorporated into panel data for regression. In view of this, the interaction term of the number of Chinese time-honored enterprises and the national R&D expenditure in the previous year is used as the proxy variable of S&T financial policy for instrumental variable analysis by referring to the research idea of Nunn and Qian (2014). The results are presented in Table 3.
It can be seen that the coefficient of instrumental variables is significantly positive at the 1% level in the first-stage regression results. This indicates that the more Chinese time-honored enterprises are, the higher the possibility of selecting the corresponding city as a pilot of the S&T financial policy; that is, the two have a close correlation. Additionally, the F value in the first stage is larger than 10, which rejects the hypothesis of weak instrumental variables. In the second stage, the coefficient of S&T financial policy is significantly positive, indicating that after controlling for endogeneity, S&T financial policy still exerts a significantly positive effect on green development, thus verifying the baseline regression results again.
4.4 Robustness tests
4.4.1 PSM-DID test
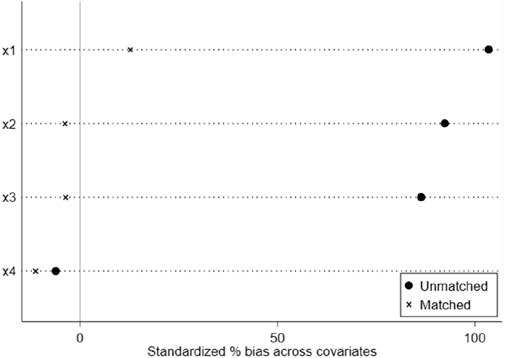
The PSM-DID method was adopted to guarantee the reliability of the research results. Before processing, a PSM-DID suitability test was conducted to determine whether the experimental and control groups had significant differences after matching. The results are shown in Figure 2.
As displayed in Figure 2, the difference between the experimental and control groups declines remarkably after matching, indicating that the PSM-DID method can be used to test the implementation effects of S&T financial policies.
Neighbor matching was adopted, and the matched data were substituted into Equation 1 for the regression. The results are presented in the first column of Table 4. It can be seen that the S&T financial policy exerts a significant effect in promoting green development, which also passes the significance test at 5%. This finding is consistent with the results of the baseline regression.
4.4.2 Eliminating pilot cities selected in 2016
Because the S&T financial policy implemented in pilot cities selected in 2016 only acted for a short time over the sample period, and the number of cities was so small that the policy effect probably had not been fully embodied, pilot cities selected in 2016 were eliminated, and regression was performed again. The results are listed in the second column of Table 4.
The results show that, after eliminating the pilot cities selected in 2016, S&T financial policy still exerts a significant promotion effect on green development. This result indicates that the baseline regression results are robust.
4.4.3 Substituting dependent variable
Apart from the SBM-GML index, the SBM-DDF index is also commonly used to calculate the green development level (He et al., 2020; Tu et al., 2023). Hence, the SBM-DDF index is adopted to calculate the green development level again on the premise of not changing the input and output indicators. The results are then substituted into Equation 1 for the regression. The results are presented in the third column of Table 4.
It can be seen that after substituting the explained variable, the S&T financial policy still significantly promotes green development at the 5% level, which is aligned with the baseline regression results.
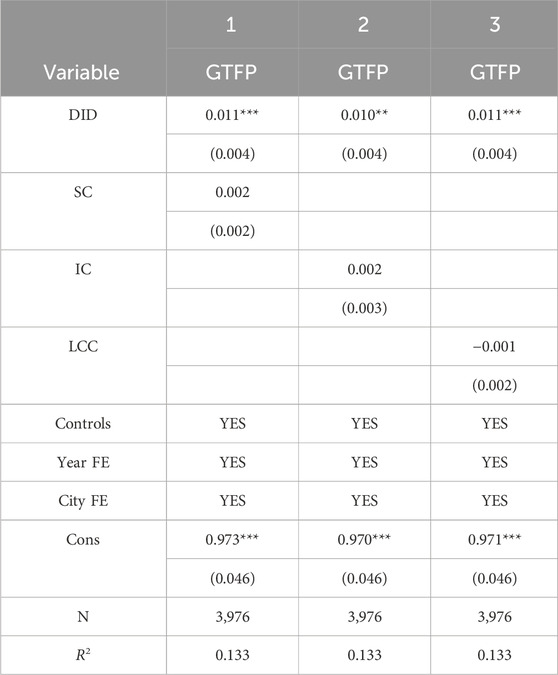
4.4.4 Eliminating interference of other policies
To eliminate other policies that may influence green development during the research period, the method proposed by Gong et al. (2023) is used to separately control smart cities, innovation-oriented cities, and low-carbon city pilot policies. The first, second, and third columns in Table 5 list the regression results. As shown in the table, the regression coefficient of the variables for S&T financial policy is still significantly positive after adding variables for the smart city, innovation-oriented city, and low-carbon city pilot policies.
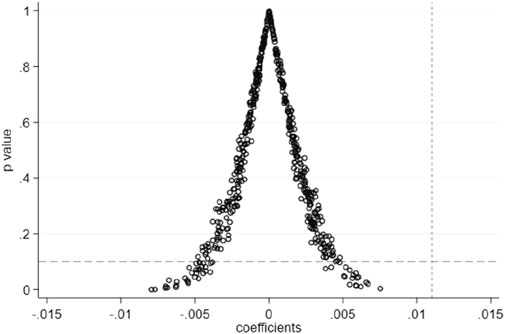
4.5 Placebo test
To further ensure the robustness of the regression results, placebo tests were conducted through random sampling 500 times, referring to the practice of Wang et al. (2023b). The results are shown in Figure 3.
The results show that most p-values are higher than 0.1, and the regression coefficients are concentrated near 0, which suggests that the sample combination of regression sampling does not affect green development. This result proves the robustness of the baseline regression.
4.6 Heterogeneity analysis
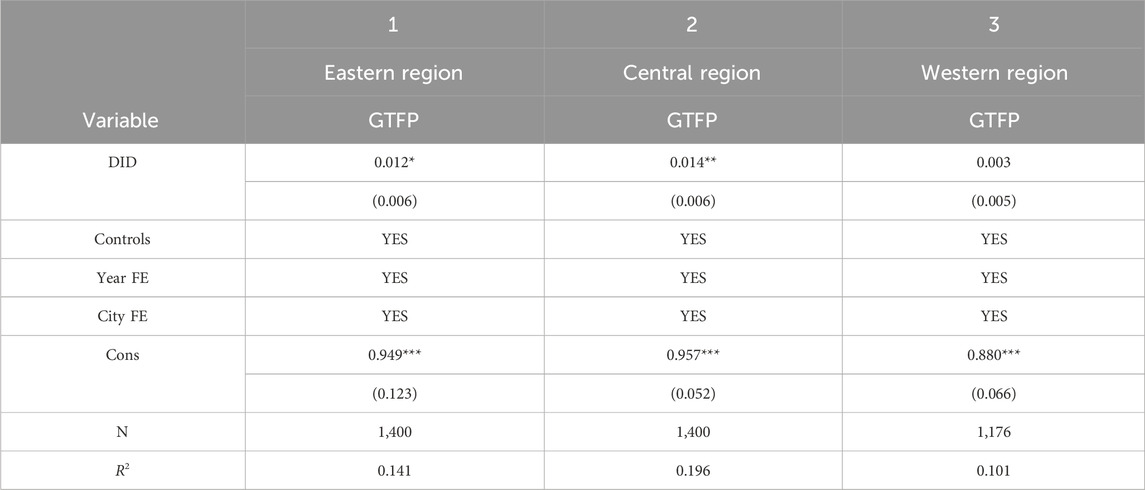
4.6.1 Location heterogeneity in cities
To test the effects of S&T financial policy on the green development of cities in different regions, samples are divided into those in the eastern, central, and western regions and then separately subjected to regression analysis. Table 6 shows the regression results. It can be seen that the S&T financial policy significantly promotes green development in the central region, followed by that in the eastern region, while insignificantly in the western region. This is probably because the geological location, population, and market scale of the eastern and central regions are obviously better than those of the western region. The implementation of the policy in the eastern and central regions releases great potential in the labor, capital, and market, thus promoting the improvement of green development levels. Moreover, compared to the eastern region, which has a developed economy, high technological level, dense population, and highly agglomerated industries, the central region has great room for improvement in green development. Therefore, the green development level in the central region is greatly improved by S&T financial policies.
4.6.2 Heterogeneity analysis of city sizes
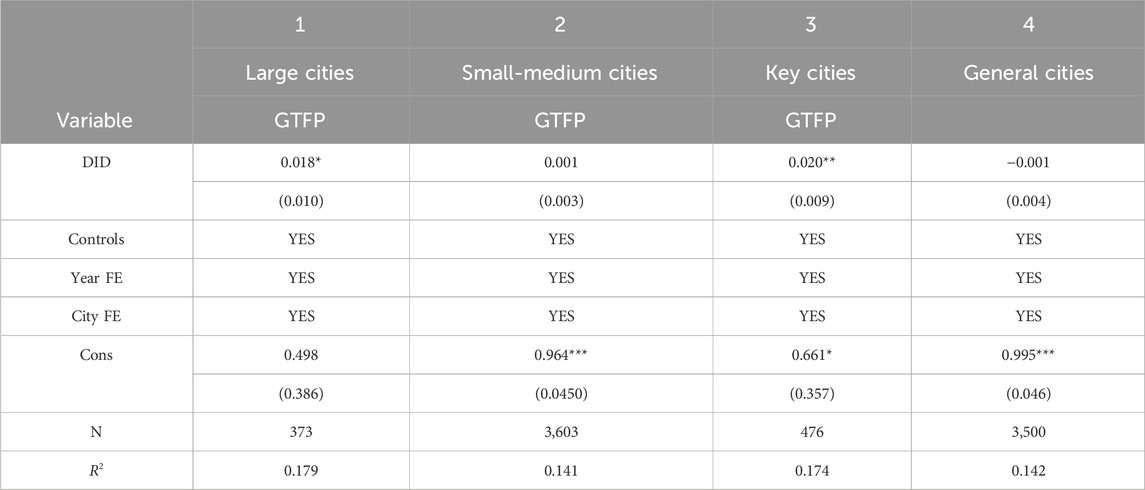
Generally, cities of different scales differ greatly in terms of labor, capital, and markets, and such heterogeneity may affect the influence of S&T financial policies on stimulating green development. Aiming at this, the classification method proposed by He et al. (2021) is used to classify cities with local permanent populations of five million and above as large cities and those smaller than five million as small- and medium-sized cities, followed by grouped regression. The results are presented in the first and second columns of Table 7, respectively.
The results show that implementing S&T financial policy can significantly promote green development in large cities, whereas the effect of the policy is insignificant in small- and medium-sized cities. A possible cause is that the infrastructure is poor and S&T is undeveloped in small- and medium-sized cities; thus, S&T financial policy cannot powerfully promote green development. In comparison, large cities have a perfect S&T base, many universities and colleges, research institutions, and high-tech enterprises, and can therefore perform large-scale technical research and development. Research production thereof is conducive to improving the green development level.
4.6.3 Heterogeneity analysis of political statuses of cities
In the administrative management system, differences in political status directly affect urban development. Therefore, the samples were divided into key and general cities according to their political status. Key cities include municipalities directly under the central government, sub-provincial cities, and provincial capitals. General cities are other cities, except for key cities. This was followed by a grouped regression, and the regression results are listed in the third and fourth columns of Table 7. It can be seen that the S&T financial policy can significantly promote green development in key cities, while the effect is insignificant in general cities. This is probably because key cities possess the resource allocation ability of higher authority, can take more flexible policies and measures according to their own conditions, improve government management and service efficiency, and therefore better utilize the benefits of the policy.
5 Further analysis
According to the above hypotheses, S&T financial policy promotes green development at the GI, ISA, and ISR levels. To verify the hypotheses, the following mediation model was built by referring to the theories on mediating effects (Baron and Kenny, 1986; Wen and Ye, 2014).
where
With regard to data sources, the research methods proposed by Gong et al. (2023), Li et al. (2021) are utilized. The number of patent applications for green inventions per ten thousand people is adopted to characterize GI capability, the ratio of the added value of the tertiary industry to those of the primary and secondary industries is utilized to characterize the ISA level, and the degree of deviation of the industrial structure is used to characterize the ISR level, as expressed in Equation 5:
Where
According to the hypothesis of classical economics, the productivity level of each industrial sector is the same, that is,
It is worth noting that the data for 2020 are deleted when testing the mediating effects of the ISR level because the number of employees in the primary, secondary, and tertiary industries is absent in the China City Statistical Yearbooks.
Table 8 reports the test results of mediating effects of the GI capability and ISA level. It can be seen that the S&T financial policy exerts significant promotion effects on both the GI capability and ISA level, which conforms to previous studies (Yang and Shen, 2021; Zhou, 2011). Meanwhile, technological innovation is also an important driver of green development (Wang et al., 2023a) and industrial structure upgrading can promote green economic development (Xie and Hu, 2023). After incorporating the S&T financial policy and GI capability together, as well as the policy and ISA level together into the regression equation, they also exert a significant positive effect on green development. Further comparison with the baseline regression results in the first column shows that the coefficient and significance level of the S&T financial policy both decline, which indicates that the promotion effect of the policy on green development is partially attributed to GI capability and ISA level, thus verifying hypotheses 2 and 3.
Table 9 summarizes the test results for the mediating effects of the ISR level. The results suggest that S&T financial policy significantly improves ISR levels. This is consistent with a previous study (Feng and Qiu, 2021). When separately incorporating policy and ISR levels into the regression equation, they both significantly promote green development. It has been demonstrated in the literature that optimization and upgrading of industrial structures can promote green development in cities (Xu and Zhou, 2023). Additionally, a comparison with the baseline regression results in the first column reveals that both the coefficient and significance level of the policy decrease, thus validating the mediating effect of the ISR level. Therefore, Hypothesis 4 is verified.
6 Discussions and conclusion
6.1 Conclusion
This study aimed to provide insights into the impact of S&T financial policies on green development in China. By taking the policy of “pilots to promote integration of science and technology with finance” in China as a quasi-experiment and constructing the difference-in-differences model and the mediating effect model, the empirical results have yielded compelling insights into the impact of the policy on green development. First, our findings consistently indicate that policies have a statistically significant, positive impact on green development. This conclusion is valid after the robustness test. Second, the impact of S&T financial policy on green development varies based on the localities, population sizes, and political status of cities. The impact of central cities is greater than that of eastern and western cities, the impact of large cities is stronger than that of small and medium-sized cities, and the impact of large cities is more obvious than that of small and medium-sized cities. Third, GI capability, ISA level, and ISR level have mediating effects between S&T financial policy and green development.
6.2 Policy implications
Our analysis has practical implications that can provide valuable guidance for policymakers and urban planners.
First, cities in China and beyond can consider adopting similar S&T financial policy development initiatives to stimulate green development. It is noteworthy that science and technology finance plays an important role in promoting green innovation. Thus, the government should strengthen its support for green innovation. Establishing special government funds and strengthening the protection of intellectual property rights can encourage innovation enthusiasm. However, optimizing the business environment and simplifying administrative approval procedures may stimulate entrepreneurial vitality. In addition, the government should invest in constructing innovation bases and incubators for technology enterprises and high-tech industrial parks, thus encouraging more high-tech firms and R&D institutions to station in.
Second, S&T financial policy plays a significant role in promoting the green transformation of industrial structures. Therefore, the government should establish a digital service platform to provide services such as green industrial policy interpretation, financial support, and approval process optimization to reduce the threshold of entrepreneurship in the green industry. Simultaneously, it is necessary for the government to use digital technologies such as big data to assess market demand and industrial trends, which can provide market information for firms.
Third, the findings of this study on locality heterogeneity underscore the importance of tailored strategies for different regions. The program’s stronger effectiveness in central regions, large cities, and key cities could potentially widen the gap between different regions. Addressing this imbalance requires comprehensive policy approaches that are inclined toward western cities, small cities, and general cities to fully release policy dividends. In addition, the government should encourage inter-regional collaboration and construct a cross-regional cooperation platform. It is more convenient for relevant economic entities to exchange resources and expertise.
6.3 Limitations and future research directions
The limitations of our analysis and future research directions are as follows: First, although the sample size is large, it may still be incomplete owing to data limitations. For example, this study involves fewer ethnic autonomous areas and some remote areas are excluded. In the future, more micro-level data and enterprise cases will be collected through field research. Second, because the study is mainly based on a sample of Chinese cities, the applicability of the conclusions to other countries or regions may be limited, especially in places where there are large differences in the level of green innovation, industrial structure, and degree of green development. Future research should conduct studies on other representative developing countries and comparative studies between developed and developing countries. Third, the time span of the study could be extended to analyze the sustained impact of S&T financial policy on green development over a longer period. Future studies could analyze whether new S&T financial policies have been introduced since 2016 and their overlapping effects with the present S&T financial policy.
Data availability statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found here: The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
XZ: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Writing–review and editing. JM: Formal Analysis, Software, Writing–original draft. SM: Funding acquisition, Methodology, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the Social Sciences General Program of the Beijing Municipal Education Commission (No. SM202310037005) and the Humanities and Social Science Fund of the Ministry of Education of China (No. 23YJA790056).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Footnotes
1GDP worship refers to the one-sided pursuit of absolute GDP growth while ignoring other factors, such as the balance of economic structure, environmental costs, social welfare, etc.
2The real economy refers to the production, purchase and flow of goods and services (like oil, bread and labour) within an economy.
3Limited by data availability, cities in Hong Kong, Macao, Taiwan, and Tibet Autonomous Region of China are not included.
References
Abis, D., Pia, P., and Limbu, Y. (2024). FinTech and consumers: a systematic review and integrative framework. Manag. Decis. ahead-of-print. doi:10.1108/md-07-2023-1136
Alder, S., Shao, L., and Zilibotti, F. (2016). Economic reforms and industrial policy in a panel of Chinese cities. J. Econ. Growth 21 (4), 305–349. doi:10.1007/s10887-016-9131-x
Baron, R. M., and Kenny, D. A. (1986). The moderator-mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. J. Personality Soc. Psychol. 51 (6), 1173–1182. doi:10.1037//0022-3514.51.6.1173
Canh, N. P., Hao, W., and Wongchoti, U. (2021). The impact of economic and financial activities on air quality: a Chinese city perspective. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 28 (7), 8662–8680. doi:10.1007/s11356-020-11227-8
Costanza, R. (1989). What is ecological economics? Ecol. Econ. 1 (1), 1–7. doi:10.1016/0921-8009(89)90020-7
Elheddad, M., Benjasak, C., Deljavan, R., Alharthi, M., and Almabrok, J. M. (2021). The effect of the fourth industrial revolution on the environment:The relationship between electronic finance and pollution in OECD countries. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 163, 120485. doi:10.1016/j.techfore.2020.120485
Feng, T., Zhang, H. Q., Hu, J., and Xia, X. (2017). Dynamics of green productivity growth for major Chinese urban agglomerations. Appl. Energy 196, 170–179. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.12.108
Feng, Y., Zou, L., Yuan, H., and Dai, L. (2022). The spatial spillover effects and impact paths of financial agglomeration on green development: evidence from 285 prefecture-level cities in China. J. Clean. Prod. 340, 130816. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.130816
Feng, Y. Q., and Qiu, J. J. (2021). Analysis of industrial structure upgrading effect and heterogeneity of science and technology financial policies: a quasi-experiment based on the science and technology and finance combination pilot. Industrial Econ. Res. (02), 128–142. doi:10.13269/j.cnki.ier.2021.02.010
Gan, C. H., Zheng, R. G., and Yu, D. F. (2011). The impact of industrial structure change on economic growth and volatility in China. Econ. Res. 46 (05), 4–16.
Gong, R. Z., Li, Q., and Liu, X. L. (2023). Impact of science and technology finance on urban green innovation: a quasi-experiment based on the policy of promoting the combination of science and technology and finance. J. Hunan Univ. Sci. Technol. Soc. Sci. Ed. 26 (04), 80–88. doi:10.13582/j.cnki.1672-7835.2023.04.011
Gu, X., and Zhou, D. W. (1986). Carrying out science and technology loans and establishing China's science and technology development bank. Sci. Manag. Res. (01), 24–28. doi:10.19445/j.cnki.15-1103/g3.1986.01.007
Han, Y. Q., Lin, L. M., and Li, Y. S. (2023). The impact of digital finance on the efficiency of green development under environmental regulation constraints: an examination based on provincial panel data from 2011-2020. J. Hunan Agric. Univ. Soc. Sci. Ed. 24 (04), 81–90. doi:10.13331/j.cnki.jhau(ss).2023.04.010
He, L. Y., Ma, Q. S., and Zhang, Y. M. (2021). The impact of smart city pilots on attracting FDI - evidence from a quasi-experiment. Int. Bus. (06), 69–84. doi:10.13509/j.cnki.ib.2021.06.005
He, W. J., Liang, X. H., and Chen, H. H. (2020). Analysis of the effect of green tax on green transformation of manufacturing industry: based on SBM-DDF model and Luenberger index measurement. Ecol. Econ. 36 (09), 58–66.
Hu, J. F., Pan, X. X., and Huang, Q. H. (2020). Quantity or quality?: the impacts of environmental regulationon firms’ innovation quasi-experiment based on China’s carbon emissions trading pilot. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 158, 1–12. doi:10.1016/j.techfore.2020.120122
Huang, C., Yue, X. X., Yang, M. Q., Su, J., and Chen, J. (2017). A quantitative study on the diffusion of public policy in China: evidence from the S&T finance sector. J. Chin. Gov. 2 (3), 235–254. doi:10.1080/23812346.2017.1342381
Julaiti, J. (2023). Research on the impact of China S&T finance on technology innovation. Financial Eng. Risk Manag. 6, 25–34. doi:10.23977/ferm.2023.060504
Khattak, S. I., Ahmad, M., Khan, Z. U., and Khan, A. (2020). Exploring the impact of innovation, renewable energy consumption, and income on CO2 emissions: new evidence from the BRICS economies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 27 (12), 13866–13881. doi:10.1007/s11356-020-07876-4
Lee, C. C., He, Z. W., and Yuan, Z. (2023). A pathway to sustainable development: digitization and green productivity. Energy Econ. 124, 106772. doi:10.1016/j.eneco.2023.106772
Li, J., Min, Y., and Wang, X. (2021). Can the opening of China-European liner train promote the upgrading of industrial structure? --A quasi-experimental study from 285 prefecture-level cities in China. Industrial Econ. Res. (03), 69–83. doi:10.13269/j.cnki.ier.2021.03.006
Li, Z., Li, H., Wang, S., and Lu, X. (2022). The impact of science and technology finance on regional collaborative innovation: the threshold effect of absorptive capacity. Sustainability 14 (23), 15980. doi:10.3390/su142315980
Liang, J., Bai, W., Li, Q., Zhang, X., and Zhang, L. (2022). Dynamic mechanisms and institutional frameworks of China’s green development: an analysis from the perspective of collaboration. Sustainability 14 (11), 6491. doi:10.3390/su14116491
Liu, G., Wang, B., and Zhang, N. (2016). A coin has two sides: which one is driving China's green TFP growth? Econ. Syst. 40 (3), 481–498. doi:10.1016/j.ecosys.2015.12.004
Liu, X., Chai, J., Luo, Y., Wang, S., and Liu, B. (2023). How to achieve sustainable development: from the perspective of science and technology financial policy in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 30 (10), 26078–26093. doi:10.1007/s11356-022-23874-0
Liu, Y., Yang, Y. L., Li, H. H., and Zhong, K. (2022). Digital economy development, industrial structure upgrading and green total factor productivity: empirical evidence from China's cities. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 19 (4), 2414. doi:10.3390/ijerph19042414
Lubo, P., and Veronesi, P. (2009). Technological revolutions and stock prices. Am. Econ. Rev. 99 (4), 1451–1483. doi:10.1257/aer.99.4.1451
Ma, Y., Lin, T., and Xiao, Q. (2022). The relationship between environmental regulation, green-technology innovation and green total-factor productivity—evidence from 279 cities in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 19 (23), 16290. doi:10.3390/ijerph192316290
Ma, Y., Xin, B., Pan, Y., Hou, G., and Yin, Q. (2018). The sources of green management innovation: does internal efficiency demand pull or external knowledge supply push. J. Clean. Prod. 202 (20), 582–590. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.08.173
Ma, Z. X., and Tao, Y. T. (2019). The impact of entrepreneurship on economic growth. Econ. Dyn. (08), 86–98.
Mensah, C. N., Long, X., Dauda, L., Boamah, K. B., Salman, M., Appiah-Twum, F., et al. (2019). Technological innovation and green growth in the organization for economic cooperation and development economies. J. Clean. Prod. 240, 118204. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118204
Mesagan, E. P., Adewuyi, T. C., and Olaoye, O. (2022). Corporate finance, industrial performance and environment in Africa: lessons for policy. Sci. Afr. 16, E01207. doi:10.1016/j.sciaf.2022.e01207
Nunn, N., and Qian, N. (2014). US food aid and civil conflict. Am. Econ. Rev. 104 (6), 1630–1666. doi:10.1257/aer.104.6.1630
Pearce, D., Markanday, A. A., and Barbier, E. B. (1989). Blueprint for a green economy. London: Earthscan Publications Limited, 177–198.
Popkova, E. G., Inshakova, A. O., Bogoviz, A. V., and Lobova, S. V. (2021). Energy efficiency and pollution control through ICTs for sustainable development. Front. Energy Res. 9, 735551. doi:10.3389/fenrg.2021.735551
Tamazian, A., Chousa, J. P., and Vadlamannati, K. C. (2009). Does higher economic and financial development lead to environmental degradation: evidence from BRIC countries. Energy Policy 37 (1), 246–253. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2008.08.025
Tian, Y., Wang, R., Liu, L., and Ren, Y. (2021). A spatial effect study on financial agglomeration promoting the green development of urban agglomerations. Sustain. Cities Soc. 70, 102900. doi:10.1016/j.scs.2021.102900
Tu, N. S., Zheng, Y. Z., and Guan, B. (2023). Impact of technological complexity of manufacturing exports on green total factor productivity. China Bus. Mark. 37 (08), 78–89. doi:10.14089/j.cnki.cn11-3664/f.2023.08.007
Wang, D., Li, J., and Liu, Y. (2023a). Evaluating barriers and strategies to green energy innovations for sustainable development: developing resilient energy systems. Front. Energy Res. 11, 1201692. doi:10.3389/fenrg.2023.1201692
Wang, K. L., and Jiang, W. (2022). Can science and technology financial policies reduce environmental pollution? --A quasi-experiment based on the Pilot Program to Promote the Integration of Science, Technology and Finance. Technol. Econ. 41 (10), 109–121.
Wang, W. L., Wang, J. L., and Li, Z. F. (2023b). Has urban renewal improved the efficiency of urban metabolism? --Test evidence from double difference method and spatial Durbin model. Soft Sci., 1–13. doi:10.13956/j.ss.1001-8409.2024.02.08
Wang, X., Sun, X., Zhang, H., and Xue, C. (2022). Does green financial reform pilot policy promote green technology innovation? Empirical evidence from China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 29 (51), 77283–77299. doi:10.1007/s11356-022-21291-x
Wang, Y., Zhao, N., Lei, X., and Long, R. (2021). Green finance innovation and regional green development. Sustainability 13 (15), 8230. doi:10.3390/su13158230
Wen, Z. L., and Ye, B. J. (2014). Analyses of mediating effects: the development of methods and models. Adv. Psychol. Sci. 22 (05), 731–745. doi:10.3724/sp.j.1042.2014.00731
Xie, D. J., and Hu, S. H. (2023). Green finance, industrial structure and green total factor productivity in urban industries. Int. Financ. Stud. (05), 46–56. doi:10.16475/j.cnki.1006-1029.2023.05.005
Xiong, Y., and Dai, L. (2023). Does green finance investment impact on sustainable development: role of technological innovation and renewable energy. Renew. Energy 214, 342–349. doi:10.1016/j.renene.2023.06.002
Xu, H., Liu, B., Lin, K., Zhang, Y., and Xie, M. (2022). Towards carbon neutrality: carbon emission performance of science and technology finance policy. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 19 (24), 16811. doi:10.3390/ijerph192416811
Xu, J. Y., and Guo, F. C. (2023). Research on the innovation support effect of China's science and technology financial policy under the perspective of green development. Zhejiang Soc. Sci. (04), 21–31. doi:10.14167/j.zjss.2023.04.014
Xu, S., and Zhou, Y. (2023). OFDI, industrial structure upgrading and green development—spatial effect based on China’s evidence. Sustainability 15 (3), 2810. doi:10.3390/su15032810
Xu, S., and Zhu, H. (2022). Does green governance efficiency and green finance polices matters in sustainable environment: implications for public health. Front. Public Health 10, 861349. doi:10.3389/fpubh.2022.861349
Xue, L., Li, H., Xu, C., Zhao, X., Zheng, Z., Li, Y., et al. (2022). Impacts of industrial structure adjustment, upgrade and coordination on energy efficiency: empirical research based on the extended STIRPAT model. Energy Strategy Rev. 43, 100911. doi:10.1016/j.esr.2022.100911
Yang, K. R., and Shen, S. (2021). Evolution of China's science and technology finance policy since reform and opening up and its revelation: based on the analysis of the co-words of central government policy texts. China Sci. Technol. Forum (06), 105–118. doi:10.13580/j.cnki.fstc.2021.06.019
Yuan, H., Feng, Y., Lee, J., Liu, H., and Li, R. (2020). The spatial threshold effect and its regional boundary of financial agglomeration on green development: a case study in China. J. Clean. Prod. 244, 118670. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118670
Zhan, X., Li, R. Y. M., Liu, X., He, F., Wang, M., Qin, Y., et al. (2022). Fiscal decentralisation and green total factor productivity in China: SBM-GML and IV model approaches. Front. Environ. Sci. 10, 989194. doi:10.3389/fenvs.2022.989194
Zhang, C., and Wang, M. C. (2023). Research on the impact of science and technology finance on the upgrading of urban industrial structure--a quasi-experiment based on the policy of promoting the combination of science and technology and finance pilot. Econ. Probl. Explor. (01), 73–86.
Zhang, H. (2021). Trade openness and green total factor productivity in China: the role of ICT-based digital trade. Front. Environ. Sci. 9, 809339. doi:10.3389/fenvs.2021.809339
Zhang, M. X., Guo, T. D., and Zhang, J. F. (2019). Development of science and technology finance for 40 Years: analysis based on evolutionary perspective. China Soft Sci. (03), 20–33.
Zhang, S., Wu, Z., Wang, Y., and Hao, Y. (2021). Fostering green development with green finance: an empirical study on the environmental effect of green credit policy in China. J. Environ. Manag. 296, 113159. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113159
Zhou, C. F. (2011). Guarantee mechanism of science and technology financial development. China Soft Sci. (03), 72–81.
Keywords: science and technology, finance, green development, green innovation, industrial structure
Citation: Zou X, Min J and Meng S (2024) The green development effect of science and technology financial policy in China . Front. Environ. Sci. 12:1463679. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2024.1463679
Received: 12 July 2024; Accepted: 03 September 2024;
Published: 13 September 2024.
Edited by:
Huwei Wen, Nanchang University, ChinaReviewed by:
Xiaojing Jiang, Jiangxi Normal University, ChinaWenxiao Wang, Zhongnan University of Economics and Law, China
Copyright © 2024 Zou, Min and Meng. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Shuang Meng, bWVuZ3NodWFuZ0BjdWZlLmVkdS5jbg==
 Xuxin Zou
Xuxin Zou Jiadi Min1
Jiadi Min1 Shuang Meng
Shuang Meng