- 1School of Economics, Guizhou University of Finance and Economics, Guiyang, China
- 2Business School, Qilu Institute of Technology, Jinan, China
The construction of smart cities plays a pivotal role in promoting regional sustainability by utilizing technology-driven urban development in the digital era. This study employs the difference-in-differences model to empirically analyze the impact of the smart city pilot policy on corporate carbon intensity, using data from Chinese A-share listed corporates from 2009 to 2021. The findings are as follows: First, the smart city pilot policy significantly reduces corporate carbon intensity in pilot cities, and this conclusion remains robust after a series of sensitivity tests. Second, the policy exhibits heterogeneous effects on corporate carbon intensity across different industries and city locations, with more pronounced effects observed in central cities, traditional industries, and heavily polluting industries. Third, mechanism analysis reveals that the policy reduces corporate carbon intensity through three channels: promoting technological innovation, increasing external market attention, and providing ex-ante government subsidies.
1 Introduction
Climate change presents an urgent and persistent threat to humanity. The continued rise of greenhouse gas emissions is generating widespread and significant adverse effects on global agricultural yields, socioeconomic stability, and human well-being, ultimately jeopardizing the sustainable development of human society. At present, the Chinese government attaches great importance to addressing climate change and is actively implementing measures to conserve energy and reduce emissions. Enterprises are not only the main body of market economic activities, but also the main implementors of energy saving and carbon emission reduction (Haney, 2017; Chen et al., 2022). As a key factor for enterprises to achieve carbon emission reduction breakthrough, green technology innovation is significantly affected by urban strategy (Xie et al., 2021; Feng et al., 2024). Smart city pilots promote sustainable urban development by building digital infrastructure and knowledge ecosystems (Shen et al., 2023). The policy promotes green technology innovation in enterprises by enhancing the level of digitization in enterprises. In 2008, IBM introduced the concept of a “Smarter Planet,” which significantly influenced China’s approach to urban development. On 5 December 2012, the General Office of China’s Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development formally issued the “Notice on Launching Pilot Projects for National Smart Cities”, along with the “Interim Management Measures for the Pilot Projects of National Smart Cities” and the “Indicator System for the Pilot Projects of National Smart Cities (Trial)”. Between 2012 and 2015, China launched three batches of pilot smart cities involving over 300 counties and cities. The pilot program clearly required that cities applying for pilot status should use the indicator system as a reference to develop achievable goals and implementation plans tailored to their local context. The indicator system encompasses various aspects such as security systems, network infrastructure, public platforms and databases, intelligent construction and livability, smart management and services, as well as smart industries and economy. In 2014, the State Council issued the “National New Urbanization Plan (2014–2020)”, elevating smart city development to a strategic level and outlining six key directions: broadband information networks, informatized planning and management, intelligent infrastructure, convenient public services, modernized industrial development, and refined social governance. This research examines the intersection of smart city initiatives and corporate sustainability: Do smart city pilot programs, implemented alongside global energy and emissions reduction goals, tangibly influence corporate carbon reduction endeavors? What policy levers drive this relationship?
Mitigating carbon dioxide emissions presents a pressing challenge for both contemporary society and the corporate sector. The escalating concentration of carbon dioxide, a key driver of global warming, presents a multitude of challenges to human development. These include economic stagnation, adverse health impacts, a heightened frequency of extreme weather events, and rising sea levels (Mora et al., 2018; Dahlmann et al., 2019; Liu L. et al., 2022). The topic of corporate carbon reduction has attracted widespread attention from scholars, with numerous studies exploring its various aspects. A substantial body of research examines the influence of firm-level characteristics on corporate carbon performance, with studies highlighting the roles of firm size, stakeholder pressure, and export behavior, among other factors (Sadler, 2016; Kumarasiri, 2017; Cui et al., 2016; Richter and Schiersch, 2017). Other studies examine external factors, finding that internationalization level, financial support, pollution prevention actions and institutional regulations all influence corporate participation in carbon reduction (Sadler, 2016; Wang et al., 2019; Niu et al., 2023; Feng et al., 2023).
Researchers have employed various methodologies, including double difference model, panel quantile regression model, and synthetic control method, to validate the inhibitory effect of smart city construction on carbon emissions in pilot cities (Zawieska and Pieriegud, 2018; Wang et al., 2021; Guo et al., 2022). In terms of mechanisms, smart cities foster digital technology innovation that directly contributes to reducing carbon emissions (Jiang et al., 2021), while also facilitating urban carbon reduction through industrial upgrading, enhancing energy efficiency, bolstering carbon absorption capacity among other measures (Caragliu and Del Bo, 2019; Chu et al., 2021; Shen et al., 2024). Smart city construction not only promotes inclusive financial development and addresses energy poverty issues within enterprises to curtail enterprise-level carbon emissions (Gao and Yuan, 2022), but also reduces household transportation and education-related emissions through the development of smart technology (Wu, 2022). Some scholars categorize smart city pilot policies into three types: smart governance, smart industry, and smart livelihood, suggesting that smart industry policies reduce carbon emissions by driving data aggregation and optimizing industrial structures, while smart governance and smart livelihood policies promote carbon reduction by stimulating green technology innovation and enhancing energy efficiency (Nicolas et al., 2021). It is evident that existing research still requires further exploration in several areas. First, the existing literature lacks a comprehensive framework that integrates both smart city development and corporate carbon emissions intensity. There is a notable absence of research exploring the theoretical underpinnings and inherent mechanisms through which smart city initiatives influence a firm’s carbon footprint. Second, current studies predominantly focus on the construction of smart cities themselves, with insufficient theoretical research on how smart city construction affects corporate carbon emissions. Third, there is a dearth of empirical research that delves into the relationship between smart city development and corporate carbon emission intensity using granular, micro-level data.
The contributions of this study are threefold: Firstly, while previous studies have often relied on aggregate or per capita carbon emission data, this research adopts carbon emission intensity as a more precise indicator of corporate-level performance, especially given the unique dynamics of developing economies. Secondly, starting from the smart city pilot policy, a rigorous quasi-natural experimental design is employed to identify its net policy effect on corporate carbon emission intensity. This clarifies the mechanism by which the smart city pilot policy helps reduce corporate carbon emission intensity, revealing specific pathways through green technology innovation, external attention, and government subsidies. Specifically, smart city development promotes the digital economy, improves the efficiency of resource allocation such as talent, capital, and land, increases R&D investment, and fosters corporate green technology innovation (Yang et al., 2024; Guo et al., 2024). It also enhances investors’ environmental awareness (Guo et al., 2024), improves corporate information transparency (Mahmood et al., 2020), and strengthens market external supervision capabilities (Liu et al., 2020), thereby increasing market external attention to enterprises. Carbon emission is an important aspect of smart city development (Li, 2022), and the improvement of urban digitalization and informatization levels also enhances the efficiency of government subsidies, thereby reducing corporate carbon emission intensity. Thirdly, to ensure robust findings, this study carefully accounts for potential confounding effects arising from other policy interventions.
The remainder of this study is organized as follows: Section 2 establishes the theoretical framework and research hypotheses. Section 3 outlines the data sources and research design employed. Section 4 presents the empirical analysis. Section 5 explores potential avenues for further research. Finally, Section 6 concludes the study.
2 Theoretical analysis
2.1 Smart city construction and corporate carbon intensity
Smart cities represent an advanced stage of urban digitalization, where pilot policies focus primarily on leveraging information technology transformations to elevate urban governance models, fostering innovation in resource allocation, emerging industries, and related technologies and products (Xin and Qu, 2019). Essentially, this involves providing support and assurance for environmental governance and emission control through technological innovation. The construction of smart cities enables local governments to enforce environmental laws using modern information technology methods. Given the emphasis on environmental sustainability in smart cities, the environmental requirements imposed by the government are often stricter than those in other ordinary cities. For instance, China’s “National Smart City Pilot Indicator System” explicitly mandates that smart cities must achieve intelligent management of urban ecological environments, build city-level carbon emission monitoring platforms based on smart city infrastructure, and collect carbon emission and energy usage data accurately and in real-time. By interconnecting data across various stages and employing visualization techniques, real-time carbon emission monitoring is enabled, thereby enhancing governmental decision-making capabilities and strengthening institutional-level environmental supervision (Xu et al., 2023). Smart city pilot policies have driven enterprises towards a green and low-carbon transformation. The development of smart cities enhances digital infrastructure, allowing enterprises to access and share big data resources more conveniently, optimize production processes and resource allocation, and reduce energy consumption and waste emissions. Smart city policies also promote the formation of smart industrial clusters, providing companies with more opportunities for collaboration and innovation, facilitating industrial structure optimization and upgrading, and lowering corporate carbon emission intensity. Additionally, in policy implementation, there is a focus on developing new models of digital industrialization and industrial digitalization, encouraging enterprises to continuously explore these innovative models to enhance production and resource efficiency, thereby aiding in reducing corporate carbon emissions.
Hypothesis 1. Smart city development contributes to a decline in corporate carbon intensity.
2.2 The role of green technological innovation
The pilot policies for smart cities have provided enterprises with the motivation and opportunities for innovation by promoting green technology innovation, effectively reducing corporate carbon emissions. These policies aim to integrate advanced information technology and intelligent systems to enhance urban digitalization, improve the allocation efficiency of labor, land, and capital, and drive green technology innovation (Yang et al., 2024). In the process of building smart cities, government environmental subsidies, corporate environmental awareness, and R&D investment have facilitated green technology innovation in enterprises (Guo et al., 2024). For instance, the “smart city” pilot index system explicitly includes elements such as digital management, smart environmental protection, and innovation investment. The level of digitalization (Han et al., 2021), R&D investment (Wang et al., 2016), and environmental expenditure (Chen et al., 2020) are crucial factors influencing green technology innovation in enterprises. The 14th Five-Year Plan mentions that “smart city” pilots need to advance the construction of new technology infrastructure, the transformation and upgrading of traditional industries, and the establishment of a new generation of information infrastructure systems. This trend has accelerated the iteration of information technology, providing a favorable external environment for enterprise technology R&D (Zhan and Li, 2022). In the Pidu District of Chengdu, Sichuan Province, China, the implementation of the “149” smart construction project has comprehensively promoted the digital transformation of Chengdu enterprises, facilitating the integration of new-generation information technology with traditional enterprises. Green technology innovation can boost clean production in enterprises, enhance energy-saving efforts, reduce resource consumption from the production side, and foster new energy consumption methods. It empowers the optimization and upgrading of industrial structures, aiding the transition to low-carbon green industries, and reducing corporate production carbon emissions, thereby achieving source control of carbon emissions (Liu et al., 2020). The use of green technology innovation in the energy sector can accelerate the development of photovoltaics, wind power, and renewable energy, effectively promoting the development of the new energy sector. It facilitates the transition of the energy consumption structure towards green, low-carbon, and clean energy, directly reducing carbon dioxide emissions. Green technology innovation can effectively control decarbonization costs and provides technical support for the research and large-scale application of carbon dioxide utilization, capture, and storage technologies, creating a “technology dividend” effect that enhances carbon emission performance. In summary, this paper proposes research Hypothesis 2.
Hypothesis 2. By encouraging the adoption of green technologies, smart city initiatives contribute to lowering corporate carbon intensity.
2.3 The role of external market attention
Smart city pilot policies provide significant external impetus for enterprises to reduce carbon intensity by guiding public attention, particularly the scrutiny of investors and media. Market investors are not only concerned with short-term economic returns but are also beginning to incorporate environmental responsibility into their investment considerations. This green investment preference encourages enterprises to pay more attention to their own green development and reduce carbon emissions. In addition, as important supervisors in the capital market, media coverage creates a “watchdog effect”, increasing the pressure on enterprises to expose their environmentally polluting behaviors. This effect compels non-compliant enterprises to enhance their environmental awareness and reduce carbon emissions (Ahern and Sosyura, 2015). Moreover, intelligent interconnected platforms utilizing digital technologies enhance enterprise information transparency. This enables external market players to conveniently access enterprise information and improves supervision effectiveness. Digital technologies represented by digital supply chain platforms can extend outwards, bringing efficient communication models to enterprises and increasing the level of integration with external stakeholders (Ivanov et al., 2022). For example, Liu et al. (2023) utilized the textual content of government environmental attention to empirically examine the impact of government oversight on corporate emissions, finding that government environmental attention significantly reduced corporate carbon emissions.
Hypothesis 3. By attracting the interest of environmentally conscious investors and consumers, smart city construction encourages enterprises to embrace sustainable practices and reduce their carbon intensity.
2.4 The role of government subsidies
The smart city pilot policy effectively reduces corporate carbon emission intensity by increasing government subsidies, thereby stimulating companies’ intrinsic motivation and environmental awareness. Firstly, the smart city policy considers urban carbon emissions as a crucial standard for performance assessment and governance capability evaluation (Li, 2022). As the leader in environmental governance, the government transfers part of the economic benefits to micro-market entities through financial subsidies, effectively stimulating companies’ intrinsic motivation to reduce pollution and emissions (Peng and Liu, 2018). Ex-ante subsidies can be used for environmental initiatives such as upgrading environmental technologies and purchasing energy-saving and emission-reducing equipment, thereby lowering the economic costs for companies in implementing environmental measures and enhancing their enthusiasm and initiative for emission reduction. Secondly, smart city development enhances the transparency of corporate environmental information, enabling the government to more accurately monitor and assess corporate environmental performance and provide targeted ex-ante subsidies to companies with good environmental performance. Through real-time monitoring and data analysis enabled by smart city technologies, the government can more precisely identify and reward companies actively taking emission reduction measures, further incentivizing them to lower carbon emissions.
Hypothesis 4. Government subsidies provided as part of smart city construction initiatives help reduce corporate carbon intensity.
3 Methodology
3.1 Model
This paper investigates whether and to what extent smart city development influences the carbon emission intensity of enterprises. To address this question, we employ a difference-in-differences (DID) methodology, exploiting the phased roll out of the smart city pilot program. Building upon the work of Yao et al. (2020), we construct the multi-period DID model (Equation 1).
where the subscripts i, j and t represent the city, enterprise and time, respectively. The dependent variable Intensity denotes the carbon emission intensity of enterprise. The explanatory variable, denoted by DID, measures the implementation of the smart city pilot policy. Controls represents a series of control variables, whose selection will be explained in detail below. εijt is the random error term. β0 is the constant term and β1 is the coefficient of the core explanatory variable, which indicates the specific impact of the smart city pilot policy on the carbon emission intensity of enterprises in the pilot areas.
3.2 Variables
3.2.1 The explained variable
The dependent variable analyzed in this study is corporate carbon emission intensity (Intensity). To construct this metric, we first collect data on firm’s reported annual carbon emissions (direct, indirect, and total) from publicly accessible sources such as annual reports, social responsibility reports, and environmental reports. For firms without explicit emissions disclosures, we estimate their emissions by multiplying their reported coal consumption by corresponding industry-specific carbon emission coefficients. In reference to Chapple et al. (2013), carbon emission intensity is operationalized as carbon dioxide emissions scaled by the firm’s primary business revenue.
3.2.2 The core explanatory
Our primary variable of interest is the DID estimator, operationalized as the interaction term between the treatment group dummy (Treat) and the post-policy time dummy (Post). Treat equals 1 for enterprises in cities designated as smart city pilot zones and 0 otherwise. Post takes a value of 1 for the year of policy implementation and subsequent years within the respective city, and 0 for pre-policy years.
3.2.3 The control variables
Referring to Yu et al. (2015), Wang et al. (2017), and Chen et al. (2023), this paper controls for firm-level and region-level variables that influence corporate carbon emission intensity, including firm size (Size) measured by the logarithm of total assets, leverage ratio (Lev) measured as the ratio of total liabilities to total assets, return on assets (ROA) measured as the ratio of net profit to total assets, board size (Board) measured by the logarithm of the number of board members, book-to-market ratio (BM) measured as the ratio of book value to market value, firm age (Age) represented by years since going public, growth rate of operating income (Growth) calculated as the increase in current operating income relative to previous operating income, regional economic development level (LnperGDP) indicated by logarithm per capita GDP, and regional financial development level (RFDL) expressed as loans balance from financial institutions relative to GDP.
3.2.4 The mediating variables
The level of green technology innovation (Innovation) is measured by the logarithm of the number of green patents obtained by enterprises. This paper examines the role of external market attention from two aspects: investors and media. Specifically, investor attention (Investor-attention) is measured by the logarithm of the median value of the Baidu search index for the year, which is mainly derived from the search volume of listed companies in Baidu search keywords; media attention (Media-attention) is measured by the total number of times the company was reported in online media news throughout the year. The research by Peng and Liu (2018) classifies government subsidies into two types: ex-ante and ex-post subsidies. Ex-ante government subsidies refer to subsidies that the government provides to enterprises without compensation, which is a form of ex-ante incentive. Ex-post government subsidies refer to the subsidy policy in which the government returns a certain amount of money to enterprises through tax reduction after the project reaches the expected effect or is completed, which is a form of ex-post incentive. This paper measures government ex-ante subsidies using various direct subsidies to enterprises and measures government ex-post subsidies using post-tax returns to enterprises.
3.3 Data sources
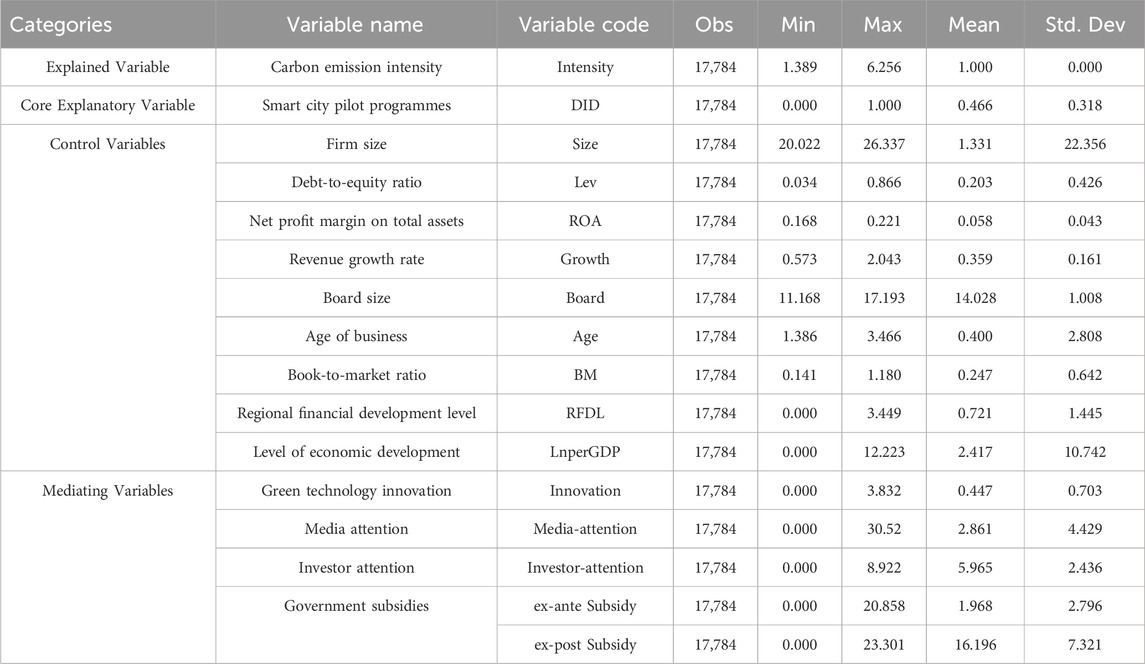
This study draws upon data from A-share listed companies on both the Shanghai and Shenzhen Stock Exchanges covering the period from 2009 to 2021. Firm-level data, including carbon emissions sourced from annual reports, environmental disclosures, and social responsibility reports, are supplemented by information from the CSMAR and Wind databases. City-level data is sourced from the China City Statistical Yearbook and the EPS database. The following data pre-processing steps were undertaken: (1) removal of companies marked as ST, ST* or PT; (2) excluding of samples from the financial sector, including banking and insurance; (3) elimination of samples with less than 3 years of data or missing values for key variables; (4) and winsorization of all continuous variables at the 1% level at both tails. The final sample comprises 1,368 listed companies, yielding a total of 17,784 observations. Among them, the manufacturing industry accounts for 14,488 observations, which is 81.47%; the mining industry accounts for 606 observations, which is 3.4%; the electricity, heat, gas, and water production and supply industries account for 881 observations, which is 4.95%; the transportation, storage, and postal services industries account for 864 observations, which is 4.86%; and other industries account for 945 observations, which is 5.31%. The descriptive statistical analysis of the data for the aforementioned variables is presented in Table 1.
4 Results
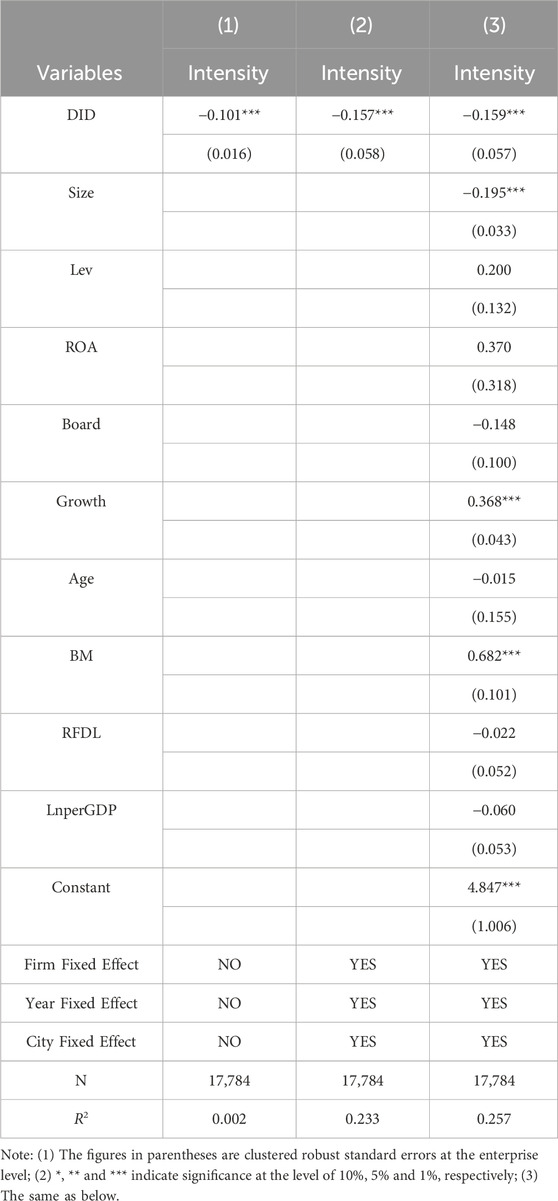
4.1 Benchmark results
We use Stata 17 as the econometric analysis tool in this paper. Table 2 presents the results of the difference-in-differences (DID) estimation. Column 1 provides a baseline estimate of the smart city pilot policy’s impact on firm carbon intensity without controlling for other factors. Column 2 introduces firm, year, and city fixed effects to address potential unobserved heterogeneity across these dimensions. Column 3 builds upon this specification by incorporating both company-level and city-level control variables that may influence firm carbon intensity. The regression results consistently demonstrate a statistically significant negative relationship between the smart city pilot policy and firm carbon intensity. This finding holds across all three model specifications, regardless of the inclusion of control variables. This robust result suggests that the implementation of the smart city pilot policy has contributed to a significant reduction in carbon emission intensity among firms located within the pilot cities. From an economic standpoint, using the comprehensive set of control variables in Column 3, we observe an average reduction of 15.9% in the carbon intensity of firms due to the implementation of the policy. Simultaneously, the econometric results reveal that firm size (Size), revenue growth rate (Growth), and book-to-market ratio (BM) all have significant impacts on reducing corporate carbon emission intensity. Specifically, firm size (Size) significantly reduces carbon emission intensity, possibly because larger firms face stricter environmental regulations, higher requirements for environmental information disclosure, and have greater capacity to adopt green technologies for emission reduction, ultimately promoting a decrease in carbon emission intensity. Conversely, a higher revenue growth rate (Growth) is associated with higher carbon emission intensity, indicating that Chinese companies have not yet completed their green transition, which aligns with China’s current stage of reaching peak carbon emissions. The book-to-market ratio (BM) has a positive impact on carbon emission intensity, suggesting that the higher the market value of a listed company (i.e., the lower the BM ratio), the more the company values green and low-carbon development and is more capable of adopting green and low-carbon technologies to transform its production model and reduce carbon emission levels.
4.2 Parallel trend test
Following Imbens and Wooldridge (2009), we construct model (Equation 2).
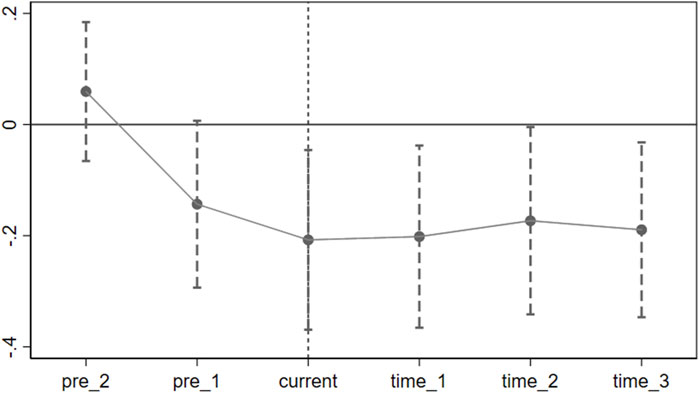
where Intensityijt is the explained variable in this paper, the variable t < 0 denotes the number of years preceding the implementation of the smart city pilot policy in city i, where enterprise j is located. During this period, the reformit variable takes on a value of 0. Similarly, when t = 0, it signifies the year of policy implementation. Subsequently, for t > 0, it indicates the number of years following the introduction of the smart city pilot policy, with the reformit variable assigned a value of 1. Given the extended sample period, this study focuses on illustrating the trend of the policy’s effect within the initial 2–3 years following its implementation. To mitigate concerns regarding perfect multicollinearity, the third year prior to policy implementation serves as the base year, maintaining consistency throughout the remaining model specifications.
Prior to the smart city pilot policy, there was no significant difference in carbon emission intensity between enterprises in pilot and non-pilot cities (Figure 1). This confirms the necessary assumption for a valid difference-in-differences analysis. Notably, the coefficients for the year of policy implementation and subsequent years are significantly negative, indicating that the policy has had a noticeable impact on carbon emission intensity within pilot areas. This suggests that developing smart cities can contribute to long-term and sustainable reductions in local business carbon emissions.
4.3 Placebo test
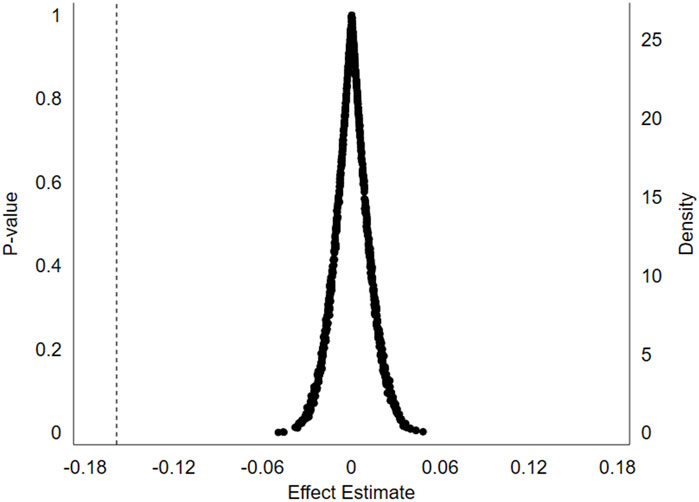
To further validate our baseline regression analysis, we conduct a placebo test using a non-parametric permutation approach (Cai et al., 2016). This involves randomly assigning cities to a simulated treatment group, effectively mimicking the implementation of the smart city pilot policy in a randomly selected subset of cities instead of the designated pilot cities. By evaluating this counterfactual scenario, we can assess the sensitivity of our initial findings to the specific selection of pilot cities and strengthen the causal relationship between the policy and observed reductions in carbon emission intensity.
Figure 2 presents the results of the placebo test, which encompassed 1,000 Monte Carlo simulations. The vertical dashed line in the figure represents the estimated DID coefficients from our baseline regression. As evident from the figure, the estimated coefficient probability density within the placebo test exhibits an approximately normal distribution. Importantly, these estimated coefficients are consistently situated far from the baseline regression results. Furthermore, a substantial majority of the p-values obtained from the placebo test surpass the p-values associated with the DID estimated coefficients in our baseline regression.
Therefore, we can confidently conclude that the baseline regression results of our study have successfully passed the placebo test. This outcome strongly supports the reliability and robustness of our findings, effectively mitigating concerns regarding spurious correlations or random fluctuations as potential drivers of our observed results. The placebo test serves as compelling evidence that our findings are likely to be genuine and not artifacts of our research design.
4.4 Robustness checks
4.4.1 Bacon decomposition
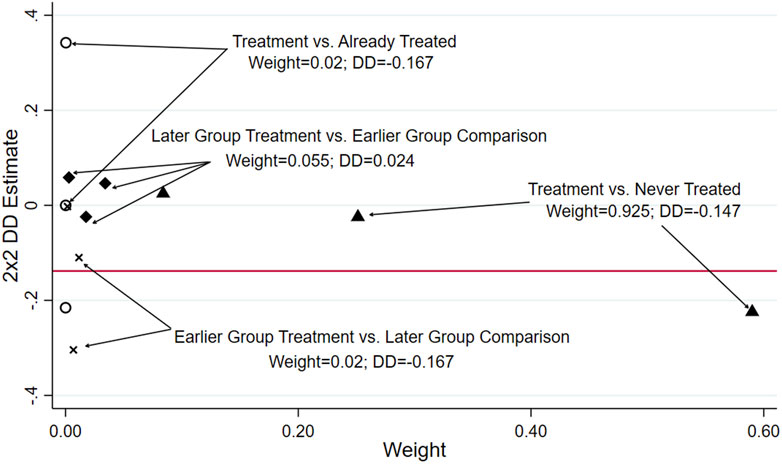
For staggered DID models, Goodman-Bacon (2021) points out that earlier treatment groups are not good control groups (also called “bad control groups”) because their pre-trends changed compared with later-treatment groups or never-treated groups (also called “good control groups”). The traditional two-way fixed effects model can produce potential bias when conducting staggered DID estimations precisely because of the existence of these “bad control groups”. Therefore, this paper adopts the Bacon decomposition method to decompose the estimator into weighted values of each part to test this issue.
The decomposition of the estimated treatment effect is visually represented in Figure 3. The figure reveals that the policy has a significant net effect on reducing carbon intensity in pilot cities, accounting for 94.5% of the total estimated effect. In contrast, only 5.5% can be attributed to “bad control groups”. This stark contrast highlights the high credibility of our baseline regression results. In our analysis, we utilize a “never-treated” group as the control for the period under examination. This makes our estimates of the policy’s effects more reliable and helps us accurately measure the overall impact of the policy over time.
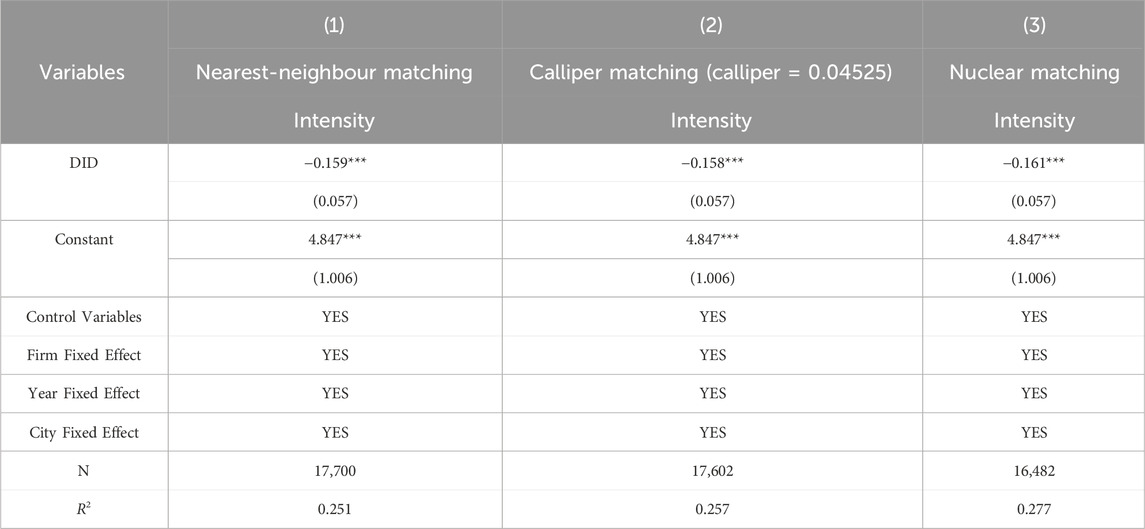
4.4.2 PSM-DID
To address potential sample selection bias, we employed a Propensity Score Matching-Difference-in-Differences (PSM-DID) approach, utilizing three matching techniques (1:2 nearest-neighbor, caliper, and kernel density) to refine the control group. This ensured comparability between treatment and control groups.
Subsequent PSM-DID estimation confirmed a statistically significant and negative impact of smart city pilot policies on corporate carbon intensity, consistent with our baseline regression findings (Table 3). This result suggests minimal sample selection bias, further strengthening the robustness of our initial conclusions.
4.4.3 Controlling competitive policy interference
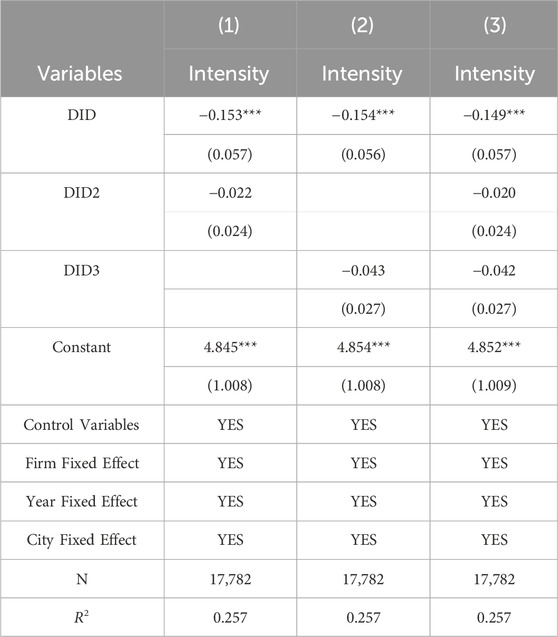
During the sample selection period, the implementation of other related policies could lead to coefficient bias in the core explanatory variables. Many policies across different regions occurred simultaneously or overlapped with the smart city pilot policy, causing a certain degree of policy overlap effect and potentially undermining the validity of regression results. Through researching and collecting relevant information, it was found that the implementation of the low-carbon city pilot policy and the carbon emissions trading pilot policy overlapped in time with the smart city pilot policy, which may affect the estimation results of the model in this paper. Regarding the low-carbon city pilot policy, the “National Low-Carbon City Pilot Progress Assessment Report” published by China’s Ministry of Ecology and Environment states that since 2010, China has conducted 81 national low-carbon city pilot projects in three batches. These projects have boldly explored five aspects: model innovation, system innovation, technological innovation, engineering innovation, and collaborative innovation, achieving positive results. As for the carbon emissions trading pilot policy, based on China’s 12th Five-Year Plan, the carbon emissions trading pilot program was launched in 2011 in seven provinces (municipalities), including Beijing. The first carbon trading market went online in June 2013 (Shenzhen), and by June 2014, the carbon trading markets of all the pilot cities in the plan had begun operation, establishing the basic framework of China’s carbon trading pilot markets. The timing for announcing emission control standards and lists of controlled enterprises across the pilot areas was concentrated in 2012–2013, with the actual opening of the carbon trading markets occurring mainly between 2013 and 2014. The implementation of the pilot policies effectively reduced carbon emissions of enterprises in the pilot regions (Li et al., 2023). To avoid interference from these policies, dummy variables for the corresponding policies are added in the regression analysis to control for the potential impact on the estimation results.
To account for the potential impact of other climate-related policies, our regression model includes variables representing low-carbon city initiatives (DID2) and carbon emission trading schemes (DID3). Even after accounting for other policies, our key finding holds true: the smart city pilot policy is linked to a significant decrease in corporate carbon emissions, as shown in Table 4.
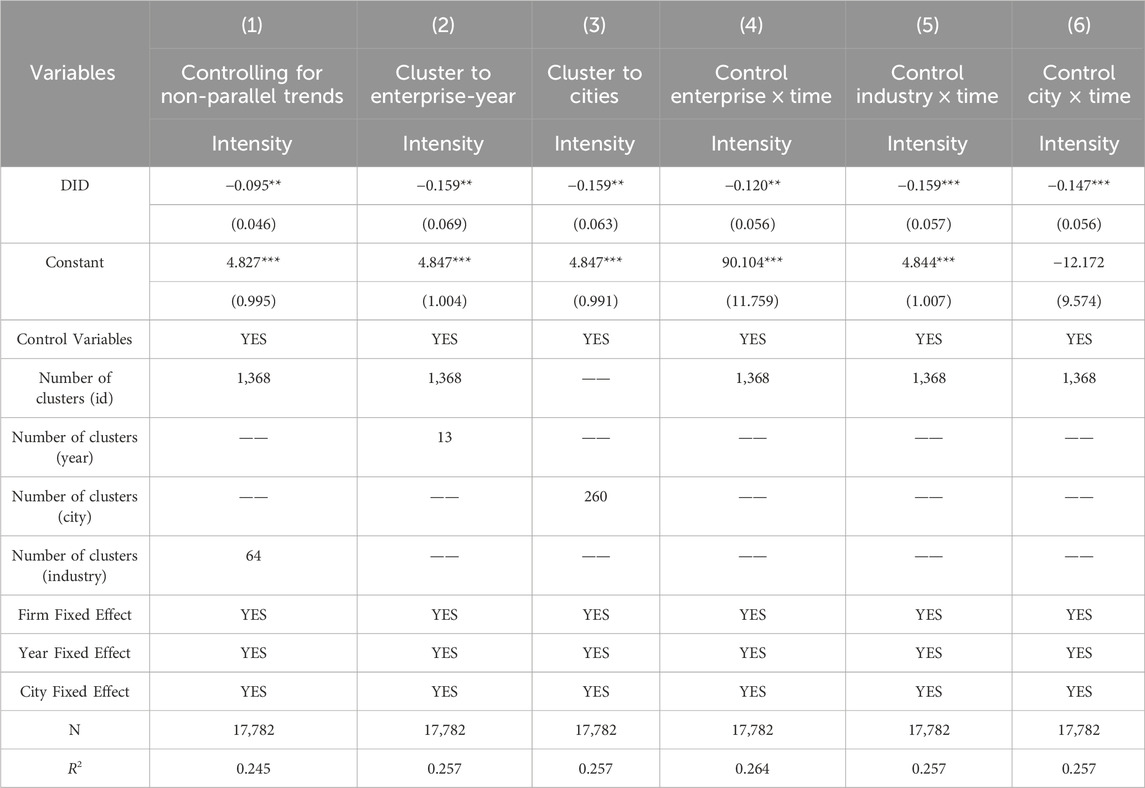
4.4.4 Controlling non-parallel trends and adjusting clustering standard errors
Following the methodology of Liu X. et al. (2022), we included linear, quadratic, and cubic time trend terms to capture the influence of time-dependent factors on firms. This is shown in Column 1 of Table 5. We also addressed potential issues related to standard error clustering. To address potential serial correlation, we initially clustered our data at the firm level. However, to address potential time-based variations within firms, we further clustered at the firm-year level (Column 2) and, considering the city-level implementation of the policy, at the city level (Column 3). Finally, to control for unobserved time-varying confounding factors, we included firm-year, industry-year, and city-year interaction terms in our DID model (Columns 4, 5, and 6).
The regression results consistently demonstrate a statistically significant and negative coefficient for our core explanatory variable, even after implementing various robustness checks. These checks include controlling for non-parallel trends, adjusting clustered standard errors at different levels, and incorporating fixed effects. This consistent finding strongly supports the robustness of our baseline regression results.
5 Further analysis
5.1 Heterogeneity analysis
5.1.1 Heterogeneity across high-tech and traditional industries
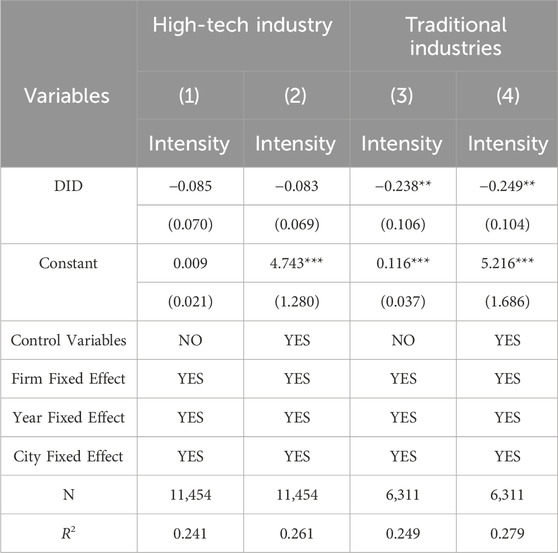
Companies in high-tech industries typically employ advanced technologies and production methods, characterized by strong innovation capabilities, high growth potential, and significant value (Cui and Mak, 2002). In contrast, traditional industries may rely more on resource-intensive sectors and outdated technologies, with policies potentially varying in terms of environmental and emission reduction measures for different industries. Given the significant differences in technological level and innovation capabilities, this paper conducts a heterogeneity analysis by categorizing companies into high-tech and traditional industries, referencing the approaches of Li and Peng (2022), to more accurately assess the impact of smart cities on corporate carbon emissions. Specifically, according to the 2012 classification guidelines for Chinese listed companies by the China Securities Regulatory Commission, companies with classification codes C25-C29, C31-C32, C34-C41, I63-I65, and M73 are defined as high-tech industry companies. After classification, there are 934 companies and 11,462 observations in the high-tech industry group, and 434 companies and 6,322 observations in the traditional industry group.
As shown in Table 6, smart city pilot policies demonstrate a statistically significant impact on carbon emission reduction within traditional industries. However, the same policies do not yield a statistically significant effect on the carbon intensity of high-tech enterprises. The primary reason for this disparity is that traditional industries are more susceptible to the direct influence of technological and management innovations associated with smart cities. Traditional industries often employ more conventional production processes and management methods, making it easier to implement and apply smart city policy measures such as intelligent production monitoring systems and energy utilization optimization technologies. In contrast, high-tech industries already possess advanced production technologies and management practices, resulting in relatively low carbon emissions. Therefore, the impact of smart city policies on their carbon emission intensity is less pronounced.
5.1.2 Heterogeneous effects across industries with varying pollution levels
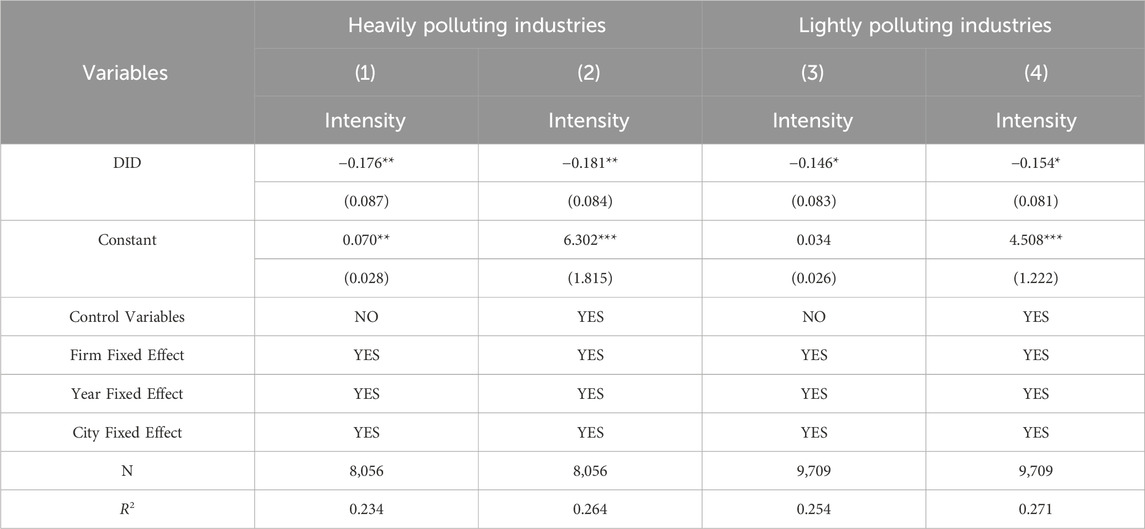
Industries characterized by heavy pollution typically use energy-intensive production processes and have higher carbon emissions, whereas light industries tend to adopt cleaner production technologies resulting in relatively lower carbon emissions. Considering the significant differences in carbon emission levels, production processes, and energy consumption between them, this paper conducts a heterogeneity analysis by categorizing companies into heavy pollution and light pollution industries. This aims to more accurately evaluate the impact of smart city policies on the carbon emission intensity of different types of enterprises and to develop targeted emission reduction measures and policy support. According to the definitions of heavily polluting industries from the “Notice on Issuing the Classified Directory of Environmental Inspection Industries for Listed Companies” by the Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China (formerly the Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China), combined with the “Industry Classification Guidelines for Listed Companies” revised by the China Securities Regulatory Commission in 2012, and following the approach of Pan et al. (2019), the codes for heavily polluting industries are specified as B06, B07, B08, B09, C17, C19, C22, C25, C26, C28, C29, C30, C31, C32, and D44. Based on this classification, the study samples are divided into two groups: heavy pollution and light pollution industries, for grouped regression analysis, with the regression results shown in Table 7.
The regression results reveal that the coefficient of DID is negative in both groups of samples. The coefficient has a larger absolute value and higher significance level in the sample of heavily polluting industry enterprises. This suggests that the pilot policy has a greater and more significant impact on reducing carbon emission intensity in these industries.
The primary reason for this disparity lies in production processes in heavily polluting industries. These industries typically employ traditional energy-intensive processes with high emission levels. The measures promoted by smart city policies, such as intelligent monitoring systems and resource utilization optimization technologies, can be more directly applied to heavily polluting industries. Consequently, these policies enhance production efficiency and optimize energy use, ultimately lowering carbon emission intensity in heavily polluting industries. Conversely, lightly polluting industries, having already adopted cleaner production processes with inherently lower emissions, experience a less pronounced impact on their carbon intensity from smart city initiatives.
5.1.3 Heterogeneity across central and non-central city enterprises
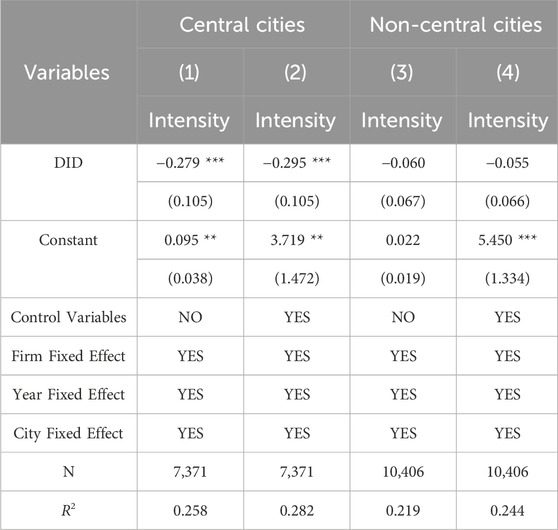
This paper also conducts a heterogeneity analysis by distinguishing between central and non-central cities to examine the heterogeneous impact of smart city pilot policies on enterprise location. Central cities typically have more concentrated economic activities and population density, with a larger number and scale of enterprises. Their carbon emission intensity is significantly influenced by factors such as transportation, buildings, and industry. In practice, provincial and sub-provincial cities in China are selected as central cities. Non-central cities, on the other hand, may have different industrial structures and development models, with relatively smaller enterprise scales but unique characteristics in energy utilization and transportation organization. In practice, prefecture-level cities, excluding central cities, are chosen as the statistical standard for non-central cities.
Table 8 demonstrates that smart city pilot policies effectively curb carbon emission intensity among enterprises situated in central cities, while the same impact remains statistically insignificant in non-central cities. This divergence likely stems from the distinct characteristics inherent to central urban environments. These cities typically boast denser economic landscapes, sophisticated infrastructure, and heightened levels of technological integration. Such attributes facilitate greater accessibility and adoption of cutting-edge energy efficiency and emission reduction technologies, enabling enterprises to streamline production processes and ultimately diminish their carbon footprint. However, in non-central cities, factors such as relatively simple industrial structures, smaller enterprise sizes and lagging technological levels may limit the impact of pilot policies. This condition could be attributed to a lack of advanced technological support, insufficient resource allocation and limitations in policy implementation.
5.2 Mechanism analysis
Based on the above analysis, the pilot policies primarily operate through these three channels: promoting green technology innovation, increasing external market attention and increasing government subsidies. In mechanism analysis, most scholars use the mediating effect model. However, this method may lead to unreliable results due to endogeneity bias and other issues. This study draws on the research method of Liu and Mao (2019) to explore the impact of mechanism variables on the treatment effect of pilot policies from the perspective of moderating effect.
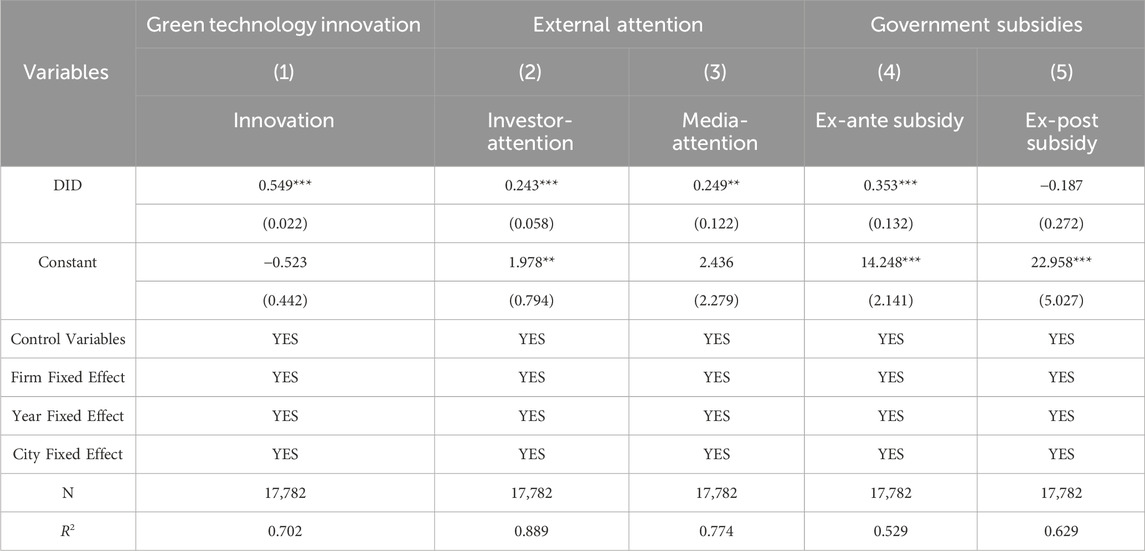
Findings from Table 9 demonstrate that smart city pilot policies effectively reduce enterprise carbon emission intensity, with a statistically significant positive coefficient for the policy dummy variable (DID) at the 1% level. This effect is achieved by promoting green technology innovation. The pilot policy is committed to integrating advanced information technology, intelligent systems and sustainable development concepts to improve urban operation efficiency, resource utilization efficiency and environmental quality. As smart cities develop, enterprises are increasingly driven to invest in green technology innovation. This trend is propelled by escalating environmental pressures and stricter carbon emission regulations. By introducing efficient energy-saving technologies and clean production processes, green technology innovation can effectively reduce energy consumption and carbon emissions during the production process, achieving cleaner and low-carbon production. Green technology innovation not only addresses environmental pressures but also offers tangible operational benefits. By optimizing resource utilization efficiency, it directly contributes to reducing the carbon footprint of enterprise production processes. Thus, Hypothesis 2 is verified.
Regression results presented in columns 2 and 3 of Table 6 indicate that smart city pilot policies demonstrably increase both investor and media attention towards enterprises. The pilot policy, by guiding external market attention, especially the supervisory pressure from investors and the media, provides an important external driving force for enterprises to reduce carbon emission intensity. The attention of investors and the media to corporate environmental protection and sustainable development encourages enterprises to pay more attention to emission reduction. Firstly, the increased attention of investors has improved the environmental transparency and sustainable development evaluation standards of enterprises. To maintain good investor relations and attract more investment, enterprises tend to take more proactive emission reduction measures to enhance their environmental image and investment attractiveness. Secondly, continuous media attention can increase the exposure and public awareness of enterprises. It often increases public attention to corporate environmental actions, thereby shaping the social image and reputation of enterprises. Under the pressure of public attention, enterprises will take more proactive emission reduction measures to maintain their image and reputation. Therefore, the smart city pilot policy effectively reduces the carbon emission intensity of enterprises by increasing the attention of investors and the media, encouraging enterprises to take more active emission reduction measures. Thus, Hypothesis 3 is verified.
The fourth column’s DID coefficient demonstrates that the smart city pilot policy, by increasing government subsidies, effectively reduces enterprise carbon emission intensity. These subsidies, a key fiscal policy tool, lower the cost for businesses investing in green technology adoption and energy-efficient, emission-reducing equipment. This financial incentive stimulates companies to proactively pursue emission reduction measures. In addition, government subsidies can be used to support enterprises in carrying out carbon emission monitoring and reporting. By providing subsidies or rewards to enterprises, they are encouraged to establish and implement carbon emission monitoring and reporting systems, strengthen the supervision and management of enterprise carbon emissions, and encourage enterprises to take proactive emission reduction measures to reduce carbon emission intensity. Therefore, the smart city pilot policy effectively promotes enterprise emission reduction actions and reduces the carbon emission intensity of enterprises by increasing government subsidies. Thus, Hypothesis 4 is verified.
6 Conclusion and policy implications
This paper uses data from Chinese A-share listed companies from 2009 to 2021 as a research sample to deeply analyze the theoretical logic and underlying mechanisms by which smart city construction affects corporate carbon emission intensity. Based on this analysis, a multi-period differences-in-differences model is constructed to empirically examine the impact of smart city pilot policies on corporate carbon emission intensity. The study finds that: ① Smart city pilot policies significantly reduce the carbon emission intensity of enterprises in pilot cities, and this conclusion remains robust after controlling for competitive policies and non-parallel trends. ② The impact of smart city pilot policies on corporate carbon emission intensity varies across different industries and cities, with more pronounced effects observed in central cities, traditional industries, and heavily polluting industries. ③ Further mechanism analysis indicates that smart city pilot policies reduce corporate carbon emission intensity through three mechanisms: promoting green technological innovation, increasing external market attention, and enhancing pre-emptive government subsidies.
Based on the above conclusions, this paper offers the following policy implications: First, continued investment and development of smart cities will create significant opportunities for reducing corporate carbon emissions. By providing targeted support to enterprises and fostering a sustainable ecosystem, smart city initiatives can effectively lower carbon intensity, encouraging businesses to embrace low-carbon development models and promoting a virtuous cycle of economic growth and environmental protection. Local governments should prioritize the development of robust smart infrastructure and promote data sharing and transparency. Establishing cross-sector and cross-industry data sharing mechanisms will be crucial. This will facilitate information flow and cross-border collaboration, ultimately providing enterprises with enhanced opportunities and support for carbon emission reduction initiatives. At the same time, policy guidance and incentive measures should be strengthened to encourage enterprises to adopt more environmentally friendly and energy-saving production methods, cooperation and exchanges between smart city construction and enterprises should be enhanced, and enterprises should be encouraged to participate in smart city planning, construction and operation to jointly promote low-carbon development.
Second, the government should implement differentiated smart city pilot policies tailored to enterprises across various industries and cities, taking into full account their unique characteristics and needs to promote green and low-carbon development. For central cities, it is essential to continue implementing smart city pilot policies, focusing on enhancing the intelligence level of environmental protection public facilities, leveraging economies of scale, and reducing the costs of emission reduction and carbon abatement for enterprises. In contrast, for non-central cities, it is crucial to promptly adjust smart city pilot construction plans, considering challenges such as relatively lagging economic development, inadequate information infrastructure, and weak green transition capabilities. Emphasis should be placed on leveraging the networked and shared characteristics of modern information systems to actively develop green and intelligent network service facilities with cross-regional service functions, thereby reducing the costs of green development in non-central cities. For traditional and heavily polluting industries, where pilot policies have shown significant effects on corporate carbon reduction, it is important to continue implementing these policies while emphasizing the application and secondary innovation of modern information technology in these sectors. Through intelligent construction, enterprises can enhance their green technology innovation capabilities. For high-tech and low-pollution industries, where the potential for carbon reduction through pilot policies is limited, it is necessary to strengthen industrial technology exchanges. This approach can drive the update of green production technologies and improve energy-saving and emission-reduction efficiency in traditional and heavily polluting industries through the development of high-tech industries.
Third, enhancing smart city development and effectively reducing the carbon emission intensity of enterprises require collaborative efforts from the government, businesses, investors, and the media. The government should establish a comprehensive policy framework that includes specific incentives and guiding policies to encourage increased investment in green technology innovation by enterprises. Various government subsidy types play distinct roles in promoting corporate carbon reduction within low-carbon city initiatives. Therefore, the government should strengthen the implementation of pre-subsidy policies, rigorously monitor and evaluate the use of subsidy funds, and further amplify the impact of pilot programs on corporate carbon reduction. Additionally, the government should utilize modern communication tools and social media platforms to promote and guide sustainable development concepts, such as green development and lifestyles, facilitating the transition of businesses to green production methods and encouraging residents to adopt greener lifestyles. The government must fulfill its environmental oversight responsibilities by enhancing environmental protection laws and regulations, strengthening the supervision of carbon reduction efforts in polluting enterprises, and reducing the carbon emission intensity of businesses.
Fourth, the effectiveness of smart city pilot policies depends on the specific developmental stage and politico-economic conditions of a region. As a government-led initiative, smart city pilot policies represent a significant urban intelligence construction project. Given that China is at a critical juncture as a developing country aiming for carbon peaking, it faces the dual challenges of carbon reduction and economic development. Successfully achieving a green and low-carbon economic transition requires fully leveraging the government’s regulatory role in the economy while respecting market principles, technological advancement, and sustainable development. The study’s conclusions and policy recommendations are applicable to other developing countries at a similar stage of development, facing the dual challenges of economic growth and carbon peaking. Additionally, ensuring the scientific formulation and effective implementation of smart city pilot policies necessitates a strong and incorruptible government.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
WP: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. JL: Data curation, Investigation, Validation, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. XR: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by National Social Science Foundation, grant number 21BJL078.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fenvs.2024.1457801/full#supplementary-material
References
Ahern, K. R., and Sosyura, D. (2015). Rumor has it: sensationalism in financial media. Rev. Financial Stud. 28, 2050–2093. doi:10.1093/rfs/hhv006
Cai, X., Lu, Y., Wu, M., and Yu, L. (2016). Does environmental regulation drive away inbound foreign direct investment? Evidence from a quasi-natural experiment in China. J. Dev. Econ. 123, 73–85. doi:10.1016/j.jdeveco.2016.08.003
Caragliu, A., and Del Bo, C. F. (2019). Smart innovative cities: the impact of smart city policies on urban innovation. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 142, 373–383. doi:10.1016/j.techfore.2018.07.022
Chapple, L., Clarkson, P. M., and Gold, D. L. (2013). The cost of carbon: capital market effects of the proposed emission trading scheme (ETS). Abacus 49, 1–33. doi:10.1111/abac.12006
Chen, H., Wang, R., Liu, X., Du, Y., and Yang, Y. (2023). Monitoring the enterprise carbon emissions using electricity big data: a case study of Beijing. J. Clean. Prod. 396, 136427. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.136427
Chen, Q., Jiao, J., Wang, Y., Mai, Z., Ren, J., He, S., et al. (2020). Egr-1 mediates low-dose arecoline induced human oral mucosa fibroblast proliferation via transactivation of Wnt5a expression. Nankai Econ. Stud. 21 (6), 80–100. doi:10.1186/s12860-020-00325-7
Chen, S., Mao, H., and Sun, J. (2022). Low-carbon city construction and corporate carbon reduction performance: evidence from a quasi-natural experiment in China. J. Bus. Ethics 180, 125–143. doi:10.1007/s10551-021-04886-1
Chu, Z., Cheng, M., and Yu, N. N. (2021). A smart city is a less polluted city. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 172, 121037. doi:10.1016/j.techfore.2021.121037
Cui, H., and Mak, Y. T. (2002). The relationship between managerial ownership and firm performance in high R&D firms. J. Corp. Finance 8 (4), 313–336. doi:10.1016/s0929-1199(01)00047-5
Cui, J., Lapan, H., and Moschini, G. (2016). Productivity, export, and environmental performance: air pollutants in the United States. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 98, 447–467. doi:10.1093/ajae/aav066
Dahlmann, F., Branicki, L., and Brammer, S. (2019). Managing carbon aspirations: the influence of corporate climate change targets on environmental performance. J. Bus. Ethics 158, 1–24. doi:10.1007/s10551-017-3731-z
Feng, Y., Gao, Y., Meng, X., Shi, J., Shi, K., Hu, S., et al. (2023). The impacts of casual environmental regulation on carbon intensity in China: dual mediating pathways of energy low-carbon reconstitution and industrial structure upgrading. Environ. Res. 238, 117289. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2023.117289
Feng, Y., Sun, M., Pan, Y., and Zhang, C. (2024). Fostering inclusive green growth in China: identifying the impact of the regional integration strategy of Yangtze River economic belt. J. Environ. Manag. 358, 120952. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2024.120952
Gao, K., and Yuan, Y. (2022). Is the sky of smart city bluer? Evidence from satellite monitoring data. J. Environ. Manag. 317, 115483. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.115483
Goodman-Bacon, A. (2021). Difference-in-differences with variation in treatment timing. J. Econ. 225, 254–277. doi:10.1016/j.jeconom.2021.03.014
Guo, C., Wang, Y., Hu, Y., Wu, Y., and Lai, X. (2024). Does smart city policy improve corporate green technology innovation? Evidence from Chinese listed companies. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 67 (6), 1182–1211. doi:10.1080/09640568.2022.2157708
Guo, Q., Wang, Y., and Dong, X. (2022). Effects of smart city construction on energy saving and CO2 emission reduction: evidence from China. Appl. Energy 313, 118879. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2022.118879
Han, L., Chen, S., and Liang, L. L. (2021). Digital economy, innovation environment and urban innovation capabilities. Sci. Res. Manag. 42 (4), 35–45. doi:10.19571/j.cnki.1000-2995.2021.04.004
Haney, A. B. (2017). Threat interpretation and innovation in the context of climate change: an ethical perspective. J. Bus. Ethics 143, 261–276. doi:10.1007/s10551-015-2591-7
Imbens, G. W., and Wooldridge, J. M. (2009). Recent developments in the econometrics of program evaluation. J. Econ. Literature 47 (1), 5–86. doi:10.1257/jel.47.1.5
Ivanov, D., Dolgui, A., and Sokolov, B. (2022). Cloud supply chain: integrating industry 4.0 and digital platforms in the supply chain-as-a-service. Logist. Transp. Rev. 160, 102676. doi:10.1016/j.tre.2022.102676
Jiang, H., Jiang, P., Wang, D., and Wu, J. (2021). Can smart city construction facilitate green total factor productivity? A quasi-natural experiment based on China’s pilot smart city. Sustain. Cities Soc. 69, 102809. doi:10.1016/j.scs.2021.102809
Kumarasiri, J. (2017). Stakeholder pressure on carbon emissions: strategies and the use of management accounting. Australas. J. Environ. Manag. 24, 339–354. doi:10.1080/14486563.2017.1350210
Li, B. (2022). Effective energy utilization through economic development for sustainable management in smart cities. Energy Rep. 8, 4975–4987. doi:10.1016/j.egyr.2022.02.303
Li, W., and Peng, H. (2022). The situation and reflections on technological innovation investment of Chinese listed companies: also on the enhancement of the main position of enterprise innovation. Quantitative Technol. Econ. Res. (06), 100–119. doi:10.13653/j.cnki.jqte.2022.06.001
Li, Z., Che, S., and Wang, J. (2023). Analysis of the policy effectiveness of the implementation of China’s carbon emissions trading pilot: new evidence from PSM-DID and SCM. Manag. Rev. 35 (12), 308–318. doi:10.14120/j.cnki.cn11-5057/f.2023.12.011
Liu, K., Tao, Y., Wu, Y., and Wang, C. (2020). How does ecological civilization construction affect carbon emission intensity? Evidence from Chinese provinces’ panel data. Chin. J. Popul. Resour. Environ. 18, 97–102. doi:10.1016/j.cjpre.2019.10.002
Liu, L., Wang, Y., and Xu, Y. (2022). A practical guide to counterfactual estimators for causal inference with time-series cross-sectional data. Am. J. Political Sci. 68, 160–176. doi:10.1111/ajps.12723
Liu, X., Cifuentes-Faura, J., Zhao, S., and Wang, L. (2023). Government environmental attention and carbon emissions governance: firm-level evidence from China. Econ. Analysis Policy 80, 121–142. doi:10.1016/j.eap.2023.07.016
Liu, X., Zhang, K., and Ren, Y. (2022). Does climate warming affect labour productivity in emerging economies? Evidence from Chinese-listed firms. Appl. Econ. 55 (24), 2801–2814. doi:10.1080/00036846.2022.2106033
Liu, Y., and Mao, J. (2019). How do tax incentives affect investment and productivity? Firm-level evidence from China. Am. Econ. J. Econ. Policy 11, 261–291. doi:10.1257/pol.20170478
Mahmood, H., Alkhateeb, T. T. Y., and Furqan, M. (2020). Industrialization, urbanization and CO2 emissions in Saudi Arabia: asymmetry analysis. Energy Rep. 6, 1553–1560. doi:10.1016/j.egyr.2020.06.004
Mora, C., Spirandelli, D., Franklin, E. C., Lynham, J., Kantar, M. B., Miles, W., et al. (2018). Broad threat to humanity from cumulative climate hazards intensified by greenhouse gas emissions. Nat. Clim. Change 8, 1062–1071. doi:10.1038/s41558-018-0315-6
Nicolas, C., Kim, J., and Chi, S. (2021). Natural language processing-based characterization of top-down communication in smart cities for enhancing citizen alignment. Sustain. Cities Soc. 66, 102674. doi:10.1016/j.scs.2020.102674
Niu, S., Chen, Y., Zhang, R., and Feng, Y. (2023). How does the air pollution prevention and control action plan affect sulfur dioxide intensity in China? Front. Public Health 11, 1119710. doi:10.3389/fpubh.2023.1119710
Pan, A., Liu, X., Qiu, J., and Shen, Y. (2019). Can green mergers and acquisitions under media pressure promote substantial transformation of heavily polluting enterprises? China Ind. Econ. (02), 174–192. doi:10.19581/j.cnki.ciejournal.20190131.005
Peng, H., and Liu, Y. (2018). How government subsidies promote the growth of entrepreneurial companies in clean energy industry: an empirical study in China. J. Clean. Prod. 188, 508–520. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.03.126
Richter, P. M., and Schiersch, A. (2017). CO2 emission intensity and exporting: evidence from firm-level data. Eur. Econ. Rev. 98, 373–391. doi:10.1016/j.euroecorev.2017.07.011
Sadler, T. R. (2016). Institutional pressures and organizational characteristics: the case of polluting emissions and the toxics release inventory. J. Interdiscip. Econ. 28, 1–23. doi:10.1177/0260107915609826
Shen, Q., Wu, R., Pan, Y., and Feng, Y. (2023). The effectiveness of smart city policy on pollution reduction in China: new evidence from a quasi-natural experiment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 30, 52841–52857. doi:10.1007/s11356-023-26010-8
Shen, Q., Wu, R., Pan, Y., and Feng, Y. (2024). Explaining and modeling the impacts of inclusive finance on CO2 emissions in China integrated the intermediary role of energy poverty. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 11, 82–19. doi:10.1057/s41599-023-02595-w
Wang, C., Wang, W., and Huang, R. (2017). Supply chain enterprise operations and government carbon tax decisions considering carbon emissions. J. Clean. Prod. 152, 271–280. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.03.051
Wang, F., Sun, J., and Liu, Y. S. (2019). Institutional pressure, ultimate ownership, and corporate carbon reduction engagement: evidence from China. J. Bus. Res. 104, 14–26. doi:10.1016/j.jbusres.2019.07.003
Wang, H., Wang, S., Miao, Z., et al. (2016). Heterogeneity threshold effect of R&D investment on green innovation efficiency: based on Chinese high-tech industries. Sci. Res. Manag. 37 (2), 63–71. doi:10.19571/j.cnki.1000-2995.2016.02.008
Wang, L., Chen, Y., Ramsey, T. S., and Hewings, G. J. (2021). Will researching digital technology really empower green development? Technol. Soc. 66, 101638. doi:10.1016/j.techsoc.2021.101638
Wu, S. (2022). Smart cities and urban household carbon emissions: a perspective on smart city development policy in China. J. Clean. Prod. 373, 133877. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.133877
Xie, Z., Wu, R., and Wang, S. (2021). How technological progress affects the carbon emission efficiency? Evidence from national panel quantile regression. J. Clean. Prod. 307, 127133. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.127133
Xin, B., and Qu, Y. (2019). Effects of smart city policies on green total factor productivity: evidence from a quasi-natural experiment in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 16, 2396. doi:10.3390/ijerph16132396
Xu, A., Wang, W., and Zhu, Y. (2023). Does smart city pilot policy reduce CO2 emissions from industrial firms? Insights from China. J. Innovation Knowl. 8 (3), 100367. doi:10.1016/j.jik.2023.100367
Yang, S., Jahanger, A., and Usman, M. (2024). Examining the influence of green innovations in industrial enterprises on China’s smart city development. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 199, 123031. doi:10.1016/j.techfore.2023.123031
Yao, T., Huang, Z., and Zhao, W. (2020). Are smart cities more ecologically efficient? Evidence from China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 60, 102008. doi:10.1016/j.scs.2019.102008
Yu, F., Han, F., and Cui, Z. (2015). Reducing carbon emissions through industrial symbiosis: a case study of a large enterprise group in China. J. Clean. Prod. 103, 811–818. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.05.038
Zawieska, J., and Pieriegud, J. (2018). Smart city as a tool for sustainable mobility and transport decarbonisation. Transp. Policy 63, 39–50. doi:10.1016/j.tranpol.2017.11.004
Keywords: smart city, sustainability, corporates carbon intensity, difference-in-differences, mechanism
Citation: Peng W, Li J and Ren X (2024) Can smart city construction be the answer to sustainable development? Evidence from Chinese corporates. Front. Environ. Sci. 12:1457801. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2024.1457801
Received: 01 July 2024; Accepted: 29 October 2024;
Published: 11 November 2024.
Edited by:
Sayali Apte, Symbiosis International University, IndiaReviewed by:
Carmen Cantuarias-Villessuzanne, ESPI2R Research in Real Estate, FranceGautam Siddharth Kashyap, Jamia Hamdard University, India
Copyright © 2024 Peng, Li and Ren. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiang Ren, cngxNzMxMTk4NjYzNkBxbGl0LmVkdS5jbg==
 Weihui Peng
Weihui Peng Jie Li
Jie Li Xiang Ren
Xiang Ren