- 1School of Resources and Environmental Engineering, Ludong University, Yantai, China
- 2Environmental Development Center of the Ministry of Ecology and Environment, Beijing, China
- 3College of Architecture and Urban Planning, Tongji University, Shanghai, China
Introduction: At the crucial stage of China’s transition from extensive expansion driven by external factors to intensive, connotation-focused development, scientifically optimizing the spatial form of new urban districts, promoting dynamic and adaptive spaces, and enhancing the quality and diversity of urban environments are issues of substantial importance.
Methods: Based on urban morphology, this study proposes that high street accessibility, appropriate building density and typology, and a sufficient degree of functional mixing are the foundations of spatial morphology for promoting sustainable urban development. Using spatial syntax, a spatial matrix, and mixed-function indices, this study measures urban spatial morphology elements and explores differences and rhythms in sustainable spatial morphology in new urban districts with varying development functions and cycles.
Results: The results of the study show that: 1) the overall synergy of the accessibility spatial network in the new urban districts of Yinzhou and Xianlin is high. The building typology was dominated by mid-rise slab and enclosed types, low-rise enclosed types, and high-rise slab types, while the multistory high-coverage forms were interspersed with intervals. 2) Development in new urban districts primarily adopted a large land plot development mode with a single function. The degree of multifunctional mixing was observed to be relatively low. The dual-functional mixing degree in the Yinzhou New Urban District is higher than that in the New Xianlin urban district. 3) A significant level of overlap was observed among functional mixing, accessibility, building density, and typology. Of the functional mixing units, 42.41% of the dual-function and 78.57% of multi-function types were clustered in high-value areas of urban vitality. Additionally, 50.25% of dual-function and 85.71% of multi-function units were aggregated in high-accessibility areas.
Discussion: The mixed-use of sites contributes to the creation of urban vitality and sustainability, and the effect of the correlation between mixed-functionality and accessibility is more pronounced when mixed units involve utility land. The research results provide a reference for evaluating the current sustainable challenges of spatial patterns and offer specific tools for optimizing new urban districts.
1 Introduction
Understanding the relation between urban spatial patterns and sustainability is crucial for the study of urbanization and global change. Urban planning and the resulting spatial patterns are essential for promoting sustainable urban development (Wei, 2016; Cao and Deng, 2021; Du et al., 2024). In 2015, all member states of the United Nations adopted the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, which included 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Buildings in cities play a critical role in achieving certain SDGs, such as making cities and human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient, and sustainable (SDG 11). After years of rapid urbanization and expansion, China’s economy is gradually transitioning to a “new normal”, establishing a new urbanization strategy that is people-oriented and emphasizes spatial quality and vitality (Ye et al., 2016; Chen M. et al., 2019; Chen M. X. et al., 2019; Meng and Xing, 2019). In this context, the paradox of medium- and high-intensity buildings coexisting with low-density human activity, common in China’s new cities and districts, has become prominent. Many new cities and districts have high development intensities and population densities, which theoretically create a strong foundation for urban vitality. However, achieving vitality in practice, remains a pressing challenge (Duan and Yin, 2011; Xia et al., 2020; Liu et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2022). In addition to the anticipated organic regeneration of historical cities, new towns and districts require transformation (Xue et al., 2013; Feng, 2018; He et al., 2018). As China transitions from extensive and rudimentary to more sophisticated and intensive development, it is crucial to scientifically optimize the spatial forms of new towns and districts. This includes creating dynamic spaces and enhancing the quality and diversity of urban areas—critical issues that merit further exploration. Simultaneously, exploring construction ideas and updating models with a focus on “sustainable spatial form” for new cities and districts holds long-term strategic importance for urban development.
Although a precise definition of sustainable spatial patterns has not been established in current research, scholars have concentrated on identifying the key features of sustainable urban spatial patterns. These include compactness, suitable density, high street connectivity, human-scale design, efficient public transportation systems, mixed land use, well-designed public spaces, diversity, rigorous environmental controls and urban governance (Song et al., 2018; Cao et al., 2019; Cai et al., 2021). Alberti (1996) proposed urban spatial form indicators, such as morphology, density, differentiation, and connectivity, within the context of urban sustainability (Alberti, 1996). Lynch (1981) suggested that a good urban form should include a range of elements, such as vitality, diversity, accessibility, controllability, ease of feeling, flexibility, and social equality (Lynch, 1981). Rogers (1998) proposed that a sustainable urban form should have seven characteristics: equity, ecology, aesthetic principles, creativity, compactness, richness, and functional complexity (Rogers 1997). By analyzing the basic concepts of different urban form development patterns, Jabareen (2006) refined the elements of sustainable urban form to include compactness, green space, sustainable transportation, high density, mixed urban use, and diversity (Jabareen, 2006). Yu et al. (2016) summarized sustainable spatial forms from the perspective of spatial morphology as good street accessibility, appropriate building density and typology, and a sufficient functional mixture (Ye et al., 2016). Behind these theoretical models of urban spatial form are some common elements for realizing the concept of sustainable urban development, whereas different models reflect varying emphases and combinations of these elements. However, the response strategies in current urban planning and architectural design are mostly aimed at high-density spaces, old urban areas, or new European and American cities (Ye et al., 2018; Zumelzu and Barrientos-Trinanes, 2019; Larkin et al., 2021; Zhang et al., 2022). And there are few systematic analyses of the morphology of new towns and districts in China, which hinders the scientific understanding of the process of sustainable new town regeneration and limits rational support for optimizing the scheme.
The results of the sustainability assessment of new urban districts in the Yangtze River Delta showed that the sustainability of these districts is influenced by urban planning and design, spatial form structure, urban vitality, and, specifically, by the core elements of high densities, sustainable transportation systems, and mixed land use (Li and Li, 2017; Huang et al., 2020; Wang, 2022). First, density is an intuitively important factor in determining urban form, and there is a consensus in the field of urban design that high-density development patterns have the advantages of conserving land, reducing transportation and energy consumption, encouraging people to socialize, and improving residents’ perceptions of the living environment (Talen, 2011; Usman and Abdullah, 2017; Wang and Shaw, 2018). Second, a sustainable transportation system is one of the factors that most substantially impacts environmental quality, and the impact of transportation planning on urban form is critical (Hui and Yu, 2013; Kashem et al., 2014; Liu et al., 2021; Haseli et al., 2024). Third, mixed land-use patterns are necessary for sustainable urban form and vitality, which can be understood as vibrant and engaging urban life shaped by the influence of the urban spatial form. In summary, drawing on the theoretical framework of urban sustainability, it is worthwhile to investigate methods for translating the concept of sustainability into actionable spatial strategies for improvement and to provide urban planners with more detailed spatial design guidelines. Consequently, this study selected two representative cases from the Yangtze River Delta, commencing with an examination of their urban form, and explored the relation between sustainable development and urban spatial form through a quantitative investigation of three core elements: street accessibility, building density and typology, and the degree of functional mixing. This study facilitates a more precise and meticulous investigation of the temporal evolution of sustainable urban spatial form characteristics and vitality levels within a new district.
2 Methods and data sources
2.1 Study area
The Xianlin New Urban District is located to the east of the main urban area in Nanjing, Jiangsu Province, China. It extends from the Ring Road in the west to the Qinhuai River in the east and from Ningzhen Road in the north to the Yangtze River in the south. The total land area is approximately 80 km2. The region is divided into four zones by natural mountainous terrain running from east to west through the central region, with rivers flowing from north to south. These zones are designated as university concentration zones, science and technology industrial zones, international exhibitions and exchange zones, and residential zones. The Yinzhou New Urban District is located in the southern part of the core area of central urban Ningbo, situated on both sides of the Fenghua River. It extends from the Ningbo Airport Expressway in the west to the Tongsan Expressway in the east, and from the Hangyong Expressway in the north to Yinzhou Avenue in the south. It is an important component of the Sanjiang Area in the central urban zone of Ningbo. The total study area is 30 km2 (Figure 1).
A sustainability assessment of 15 new districts in the Yangtze River Delta (Wang et al., 2017), was conducted, selecting these districts as case studies of urban areas with relatively superior levels of sustainable development and different development functions and cycles. The term “new districts” is defined as urban built-up zones that are rapidly developed and constructed within a short period following planned design. This includes extensions adjacent to existing built-up areas as well as leapfrog developments that possess a certain level of independence, such as new towns. The term “new” primarily refers to these areas in contrast to “old” cities, which have developed gradually over a long period. Yinzhou and Xianlin New Urban Districts belong to the first and third levels of sustainable development, respectively. The leading function of the Yinzhou New Urban District is industry, whereas the Xianlin New Urban District was developed for higher education. The development cycles of these districts fall under the categories of renewal and newly built areas. The Yinzhou New Urban District was constructed during the rapid urbanization phase, Xianlin New Urban District is an important hub for higher education resources in Jiangsu Province and nationwide. The selection of these two case study areas is representative, and the research results are significant for the transformation and upgrading of other new urban districts. To determine the fundamental spatial analysis unit, comprehensive consideration was given to the walkability of both the street network architecture and residents. Specifically, an overly small raster scale leads to the fragmentation of street network buildings, whereas an unduly large scale undermines the precision of the vector analysis. A 150 × 150 m2 grid was used as the analysis unit in this study. Subsequently, cells with a minimal land area or ambiguous functions were excluded, and the resulting sample comprised of 2,096 cells.
2.2 Methods
2.2.1 Accessibility indicators
In this study, we employed a line segment model analysis from Space Syntax, which introduces the concept of spatial scale into the axial analysis method. The accuracy of the analysis results was further improved and enhanced through the introduction of new accessibility measurements, “metric weighting” and “angular weighting” (Xiao et al., 2014). For the specific accessibility measure, we selected Hillier’s (1984) “normalized angular choice (NACH),” (Equation 1) which reflects the probability that a segment will be traversed during the process of interconnecting all segments. The formula is as follows:
where CH represents the global or local selectivity, and TD denotes the spatial depth.
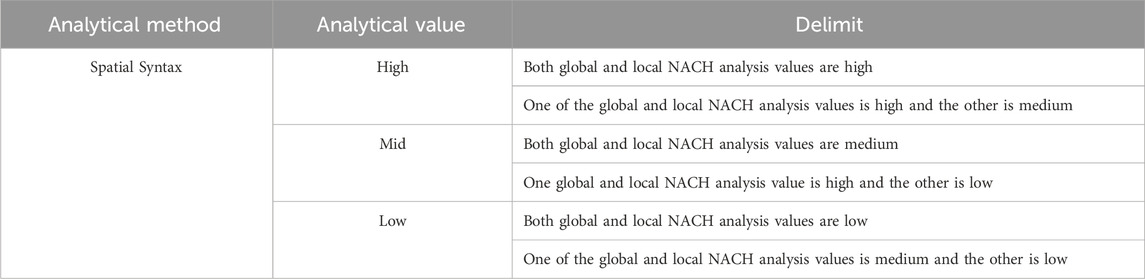
Spatial syntactic analysis can be divided into two categories—global and local—based on their different computational radii. At the global scale, major paths with high accessibility are effectively identified; at the local scale, neighborhood, residentia, and other places with small-scale accessibility can also be effectively identified (Van Nes and Stolk, 2012). Therefore, in this study, the NACH values at both global and local scales were considered. The NACH values of each road network were assigned to their corresponding parcels using the ArcGIS software, and the accessibility values were calculated. The global and local NACH values were classified as high, medium, and low through the natural breaks (jenks) method of the ArcGIS software and were then unified and integrated by overlay analysis (Table 1).
2.2.2 Building density and typology indicators
The Space Matrix proposed by Berghauser and Haupt, (2010) in the context of European urban planning is an analytical framework for the typological analysis of urban forms. It includes four indicators: the Floor Space Index (FSI), Ground Space Index (GSI), average number of building layers, and Open Space Ratio. This framework constructs a classification standard for urban forms based on quantitative data, thereby providing a more efficient way to differentiate between urban morphologies (Ye et al., 2018). Based on the different building heights within the parcels, they can be classified into three categories: low-rise (1–3 floors), mid-rise (4–7 floors), and high-rise (≥8 floors), reflecting variations in construction intensity. In addition, different building typologies within the parcels can be classified into point, slab, and enclosure forms, which reflect different morphological characteristics. The overall urban form was categorized into nine types based on these criteria (Figures 2A): low-rise point type (A), low-rise slab type (B), low-rise enclosure type (C), mid-rise point type (D), mid-rise slab type (E), mid-rise enclosure type (F), high-rise point type (G), high-rise slab type (H), and high-rise enclosure type (I). Van Nes and Stolk (2012) classified nine types of construction intensity and building typology in a Space Matrix framework into three broad categories based on their impact on urban spatial vitality: 1) high-value areas, including mid-rise slabs or enclosures and high-rise enclosures; 2) medium-value areas, including mid-rise points, high-rise points, and slabs; and 3) low-value areas, including low-rise points, slabs, and enclosures (Figures 2B).
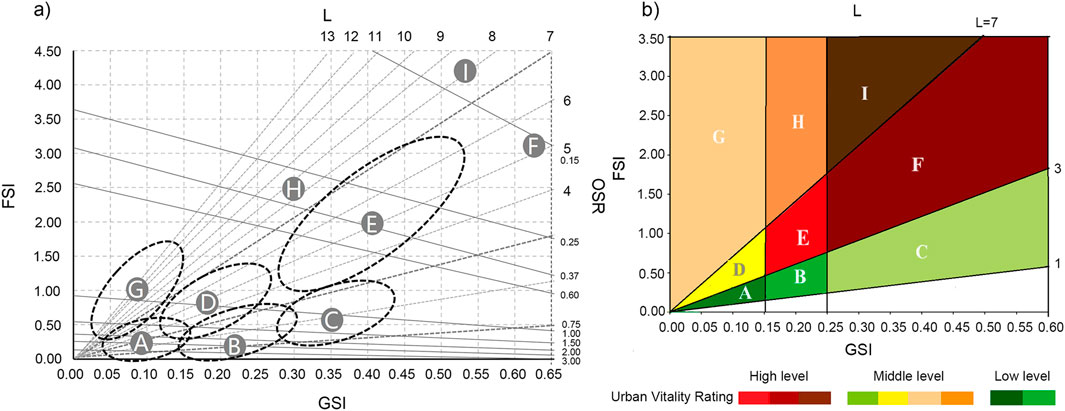
Figure 2. Space matrix model (A) and high-medium-low value partition of urban vitality analysis (B).
2.2.3 Mixed-use index (MIX)
The MXI was developed by Van den Hoek at Delft University in the Netherlands to measure the degree of functional mixing of urban land units (Ye and Nes, 2014). This index aims to analyze the quantification of functional mixing and define the degree of functional mixing of a site by the ratio of the floor area of the three main functions of the site: 1) residential (including pure residential, residential buildings with commercial premises, and community public buildings, etc.); 2) office (including administrative office buildings with service outlets and industrial plant, etc.); 3) commercial services (pure commercial areas, mixed commercial and administrative offices, and educational land such as primary and secondary schools and universities, etc.). If one of the functions accounts for more than 95%, it is called a single-function site. If two types of functional land use are mixed and the proportion of each type of land use is >5%, it is called a dual-function site. When three types of functional land use are mixed and the proportion of each type of land use is >5%, it is called a multifunctional site. This study adopts the MXI to characterize the degree of functional mixing of urban land units.
2.3 Data sources
2.3.1 Road data
Road data were obtained from OpenStreetMap (https://www.openstreetmap.org/) and, in conjunction with remote sensing imagery, were employed to extract expressways, main roads, secondary roads, side roads, residential roads, and district roads in the residential areas of the new urban district. Missing or incorrect parts of the road network were verified and corrected through field reconnaissance.
2.3.2 Building data
Building data were obtained from CNBH-1029 (https://wwanben1994.users.earthengine.app/view/cnbh10mtest). The building vector data were sourced from the AutoNavi Map and Tianditu Data Platform, and include information, such as the building footprint area and number of stories. Based on the aforementioned data, the following equations were used to calculate the floor area ratio (Equation 2) and building density indicators (Equation 3) for each parcel within the new urban district:
where
2.3.3 Functional mixture data
The functional mixture of each land-use unit in the new urban area was obtained through field investigations combined with the Nanjing and Ningbo Urban Master Plans of 2022. Among them, residential functions mainly include pure residences, residences with ground-floor commercial premises, and public buildings in residential areas. The production function mainly includes administrative office buildings with service outlets and industrial plants. The production-service function includes pure commercial areas, mixed commercial and administrative office areas, and educational land such as middle schools and universities. The survey results were marked in the building attribute table to obtain a functional mixture database.
3 Results and analysis
3.1 Spatial syntax-based accessibility analysis of street networks
3.1.1 Analysis of global and local standardized selectivity results
Global and local (500 m radius) standardized selectivity (NACH) distribution maps of the new urban district were obtained using a depth map. Global and local NACH values represent the accessibility of vehicular and pedestrian flows along different radii in a new urban district. As shown in Figure 3, the local NACH of Xianlin New Urban District was higher in Xianhemen, Dongchenghui, Gaoke Rongwei, Nanda Heyuan, and Yiyunxigu, with all values greater than 2.50. Other areas, such as higher education parks, exhibited cooler tones. The values of local NACH ranged from 1.25 to 1.85, and the tones became warmer on a global scale. The main roads of the new urban district showed higher accessibility, with all values greater than 2.55. Examples include Xianlin Avenue, which connects the new urban district to the central city, and Xuehai Road and Xianjing Road, which connect the center of Qixia to the new urban district. The overall level of local NACH in Yinzhou New Urban District was relatively low. On a global scale, the selectivity of each level is significant, and some urban trunk roads show high accessibility, such as Yinxian Avenue, which runs through the entire new urban district, connecting the eastern and western sides of the Fenghua River, and Tiantong Road, which connects the new urban district to the old city of Ningbo. Many public service facilities are clustered on both sides of the road.
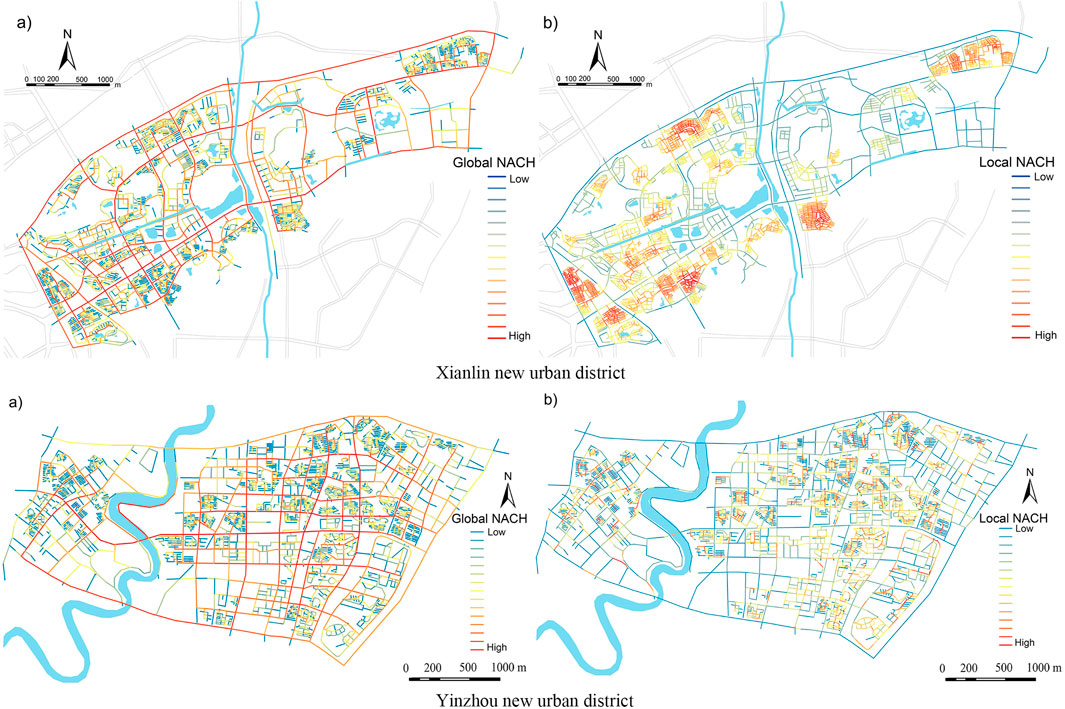
Figure 3. Spatial syntax global and local NACH results based on segment patterns of the case new urban district. Xianlin new urban district. Yinzhou new urban district. (A) Xianlin new urban district (B) Yinzhou new urban district.
Statistical analysis was conducted on the global and local NACH values of Yinzhou New Urban District. In Figure 4, the red dots represent the street-road network of the new urban district. Global NACH values correlated well with local NACH values, with a significant positive correlation. This indicates that the spatial network of Yinzhou New Urban District exhibits a strong overall synergy between the local spatial network and overall spatial network structure, demonstrating a high level of integration. By contrast, Xianlin New Urban District showed a poor correlation between the global and local NACH values. This is mainly because, although Xianlin has a certain scale of residential land and preliminary conditions to support high-level public facilities, the residential land is internally aggregated within each district. The new urban district level is fragmented by ecological corridors and university campuses and lacks a unified organization. This situation has led to the dispersal of public facilities to the central areas of each district, resulting in low integration between the local and global spatial network structures. Additionally, segments with high global and low local NACH values tended to perform more functions in connecting busy surrounding traffic.
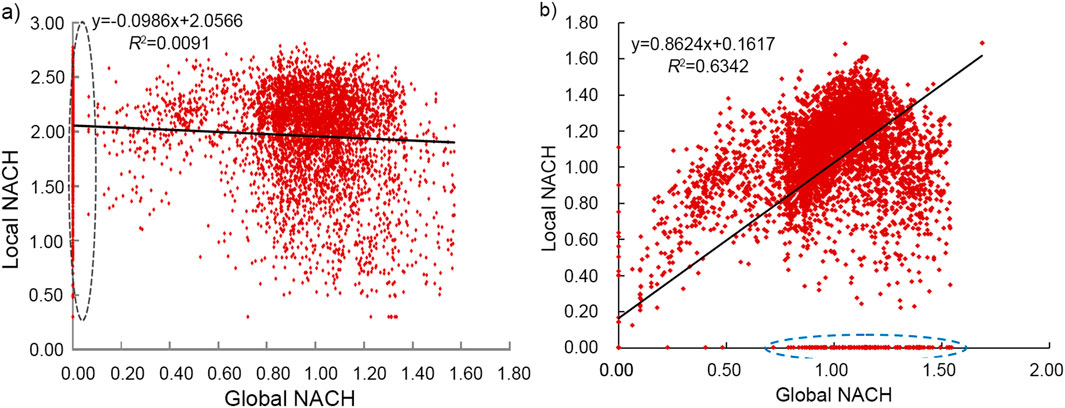
Figure 4. Correlation analysis of global and local NACH in Xianlin new urban district (A) and Yinzhou new urban district (B).
3.1.2 Street network accessibility analysis
The central area of the district showed high accessibility and relatively wide coverage, indicating the highest permeability for traffic and pedestrian flow in this area. Local accessibility was also high at points A, B, C, and D. However, areas farther from the center of the new urban district exhibited lower accessibility. In the analysis of street accessibility grid data for the new urban district (Figure 5), the proportions of high, medium, and low accessibility grid units in Xianlin New Urban District were 40.19%, 42.28%, and 17.53%, respectively, whereas in Yinzhou New Urban District, the proportions were 44.70%, 27.30%, and 28.00%, respectively. Overall, street network accessibility was relatively high.
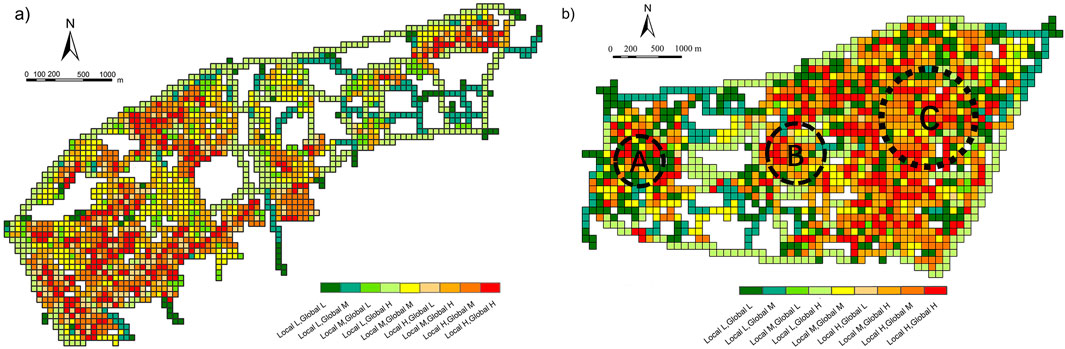
Figure 5. Analysis on the accessibility of Xianlin new urban district (A) and Yinzhou new urban district (B) street based on grid.
3.2 Spatial matrix-based analysis of construction intensity and morphology
3.2.1 Analysis of results for density indicators
Based on the building height, building base area, and parcel units, the distributions of the FSI and GSI were obtained at the grid scale in the new urban district (as shown in Figure 6). Quantitative analysis revealed the following: 1) statistical analysis revealed that the building density (GSI) values in the Xianlin New Urban District were primarily distributed between 0.10 and 0.30, whereas the floor area ratio (FSI) values were mainly distributed between 0.2 and 1.5. Grid units with low intensity (FSI <1.5) accounted for 87.15% of the total grid units, and grid units with low density (GSI <0.3) accounted for 96.31% of the total grid units. 2) In the Yinzhou New Urban District, the building density (GSI) values were primarily distributed between 0.10 and 0.40, and the floor area ratio (FSI) values were mainly distributed between 0.2 and 2.5. Grid units with low intensity (FSI <1.5) accounted for 59.62% of the total grid units, and grid units with low density (GSI <0.3) accounted for 68.97% of the total grid units. Yinzhou New Urban District has a higher development intensity than that of Xianlin New Urban District, which is mainly related to its development history and initial functions. Xianlin New Urban District has undergone development since the beginning. Land plots with large areas and low development intensities are mainly used for research and educational purposes. By contrast, the Yinzhou New Urban District was developed based on Yinzhou County, and the resettlement communities in the original Zhonggong Temple and Shiqi Old Town Center were of medium to high intensity (FSI >1.5). Industrial functions also led to the Yinzhou New Urban District having a higher density (GSI >0.4) of large-scale industrial buildings, including the Samsung Group, Youngo Clothing City, and Ningbo Textile City. 3) The new urban district’s high volume ratio (FSI >3.0) units were concentrated in areas with high accessibility, accounting for 64.54% of them. In the new Xianlin Urban District, owing to the weaker overall synergy between global and local structures, the relation between accessibility and urban density was significantly influenced by the network scale and exhibited significant characteristics in local structures with a smaller radius.
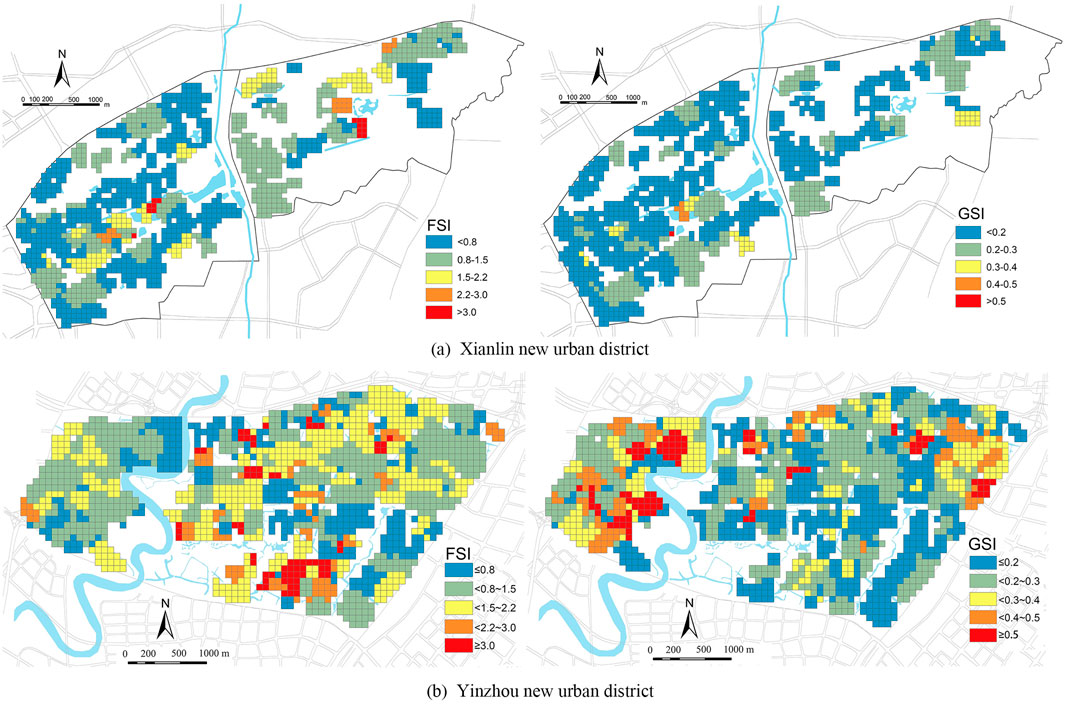
Figure 6. Spatial distribution of FSI and GSI of the case new urban district. (A) Xianlin new urban district. (B) Yinzhou new urban district.
3.2.2 Building density and typology analysis
Through field investigations and high-resolution imagery, nine urban morphologies corresponding to the spatial matrix model of the new urban district were obtained. Figures 7A shows the building density and distribution of building typology in the Xianlin New Urban District. The building types are relatively homogeneous, with mid-rise point-style and slab-style buildings dominating. The grid units of mid-rise buildings (4–7 floors) accounted for 55.25% of the total grid units, whereas high-rise buildings accounted for a smaller proportion (15.93%). The main reason for this distribution is that the early planning of the Xianlin New Urban District was based on ecological and landscape considerations, and a low-density development concept was required at the time. Garden villas, detached houses, townhouses, and stacked villas are the predominant building types in the Xianlin New Urban District, and the main public facilities are developed around higher education parks, with a focus on multistory slab-style buildings. According to the research results, in 2007, Xianlin New Urban District began to construct high-rise point-style, slab-style, and enclosed buildings. Figures 7B shows that, in the Yinzhou new urban district, the main building types are mid-rise slab-style and enclosed, low-rise enclosed, and high-rise slab-style, accounting for 74.27% of the total grid units. The main reason for this distribution in Yinzhou New Urban District was its focus on county-level industrial development. During the initial stages of construction, low-density rural settlement buildings, medium-density town-style multistory residential buildings, and large-span factory buildings were the primary focus areas. The land use and development patterns in new urban districts are similar to those of traditional town areas, which are characterized by extensive land use. Consequently, concentrated areas of rural settlements and urban villages persisted. The nine construction intensities and form types in the spatial matrix were divided into three levels (high, medium, and low) based on their impact on urban spatial vitality (Figures 7B). In the Xianlin New Urban District, the proportions of high- value, medium- value, and low-value areas were 32.44%, 50.09%, and 17.46%, respectively. In the Yinzhou New Urban District, these proportions were 37.26%, 54.42%, and 8.32%, respectively. Compared with those in the Xianlin New Urban District, the proportions of high-value areas, which have a greater impact on urban spatial vitality, are higher in the Yinzhou New Urban District. This indicates that the proportion of multistory slab-style, enclosed, and high-rise enclosed buildings, which are included in high-value areas, is higher in the Yinzhou New Urban District than the proportion of mid-rise point-style, high-rise point-style, or slab-style buildings included in medium-value areas.
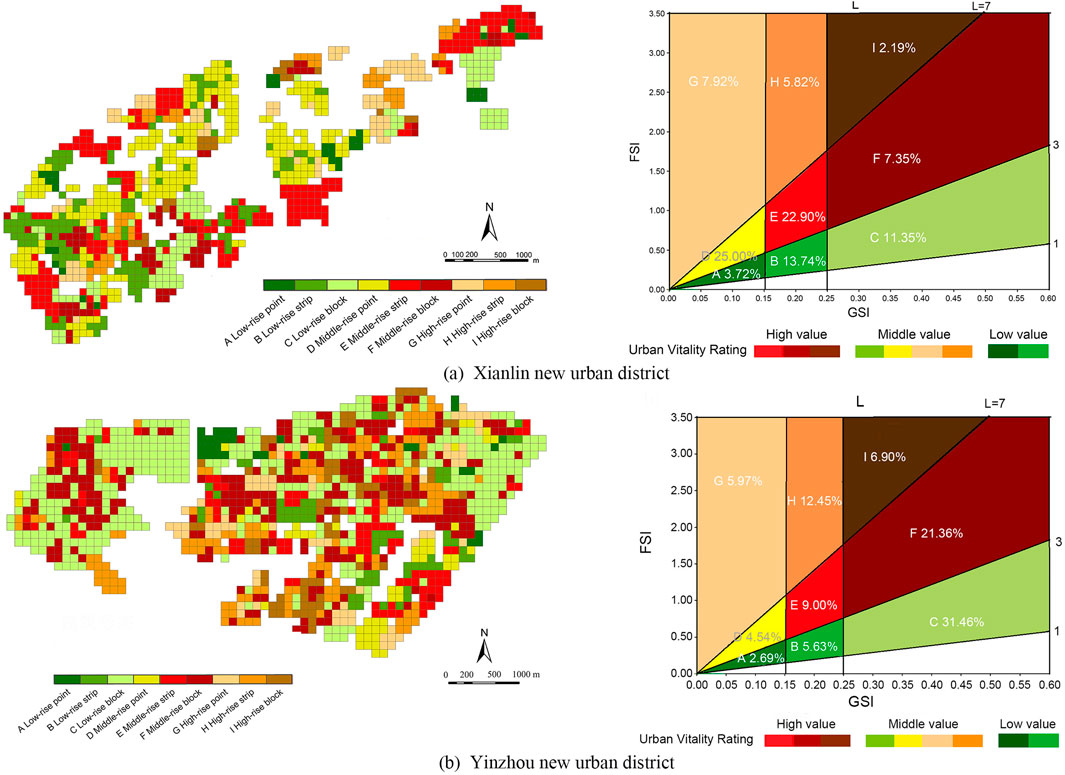
Figure 7. Spatial distribution of building type, building intensity and building morphology of case new urban district. (A) Xianlin new urban district. (B) Yinzhou new urban district.
3.3 Functional hybridity analysis based on hybrid functional indicators
Figures 8A shows that the high-mixed grid cells were mainly distributed in the main blocks of Xianhe in the Xianlin New Urban District, whereas the dual-function mixed grid cells were mainly distributed in areas such as the Nanjing Zhongke, Dongcheng Hui, and Xianhemen subway stations in Xianhe. Single-function grid cells are more widely distributed in the Xianlin New Urban District. From Figures 8B, high-mixed grid cells are distributed in the central area north of the “cross-axis” in the Yinzhou New Urban District, where commercial, residential, and office functions are more concentrated. Dual-function mixed grid cells were scattered in areas, such as the intersection of Songjiang Road and Qianhu Road, whereas single-function grid cells were mainly concentrated in the residential area north of Yinxian Avenue and in the higher education park area south of Yinxian Avenue. The MXI model of functional mixture proportion showed that the Xianlin New Urban District area had the largest share of single-service (A) land use, accounting for 44.96% of total grid cells (Figures 9A). The proportion of mixed-use land was 5.47%, which was much lower than the proportion of single-function (H, A, and W) land use (94.53%). The proportion of two-function mixed uses (H_A, H_W, A_W) was 4.42%, whereas the proportion of fully mixed use (H_A_W) was 1.05%. Owing to development sequence factors, the Xianhe area in Xianlin’s New Urban District had a higher level of mixing than the Baixiang area. In the Yinzhou new urban district area (Figures 9B), single residential (H) land use accounted for the highest proportion at 38.50%. Single-use land (H, A, and W) dominated with a proportion of 79.19%, whereas the proportion of mixed-use land was 20.81%. The proportion of two-function mixed uses (H_A, H_W, A_W) was 19.07%, whereas the proportion of fully mixed uses (H_A_W) was 1.73%.
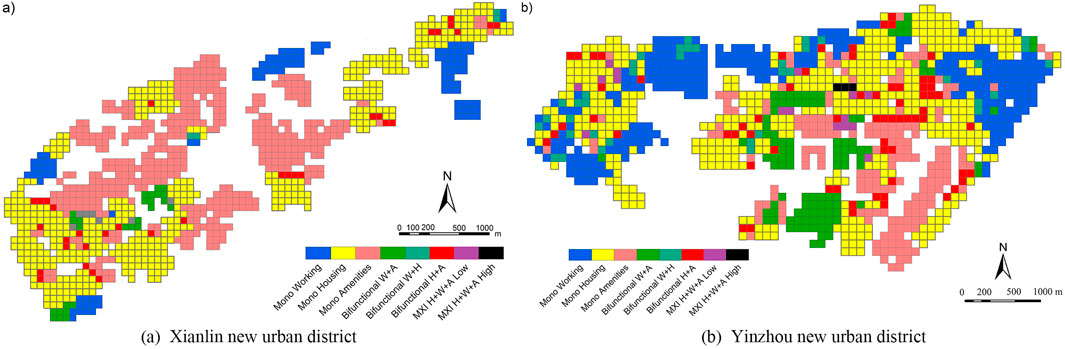
Figure 8. Spatial distribution of functional mix degree in Xianlin new urban district (A) and Yinzhou new urban district (B).
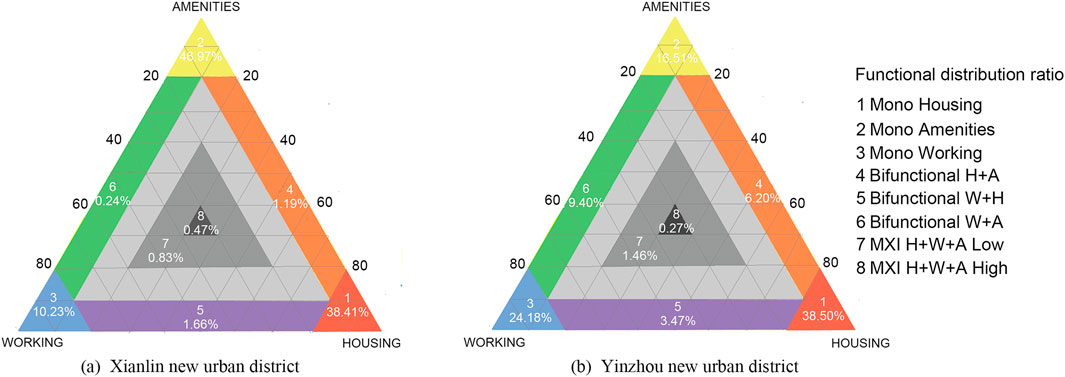
Figure 9. Code of urban Residential Areas Planning and Design (A) and density-shape interval diagram (B) in case new urban district. Note: a In the figure, green represents low-rise zones, blue represents multi-storey zones, yellow represents mid- to high-rise zones, and red represents high-rise zones.
4 Discussion
4.1 Correlation between residential density and form interval
According to the national standard for construction land floor area ratio (2012), the dominant building types in the Xianlin New Urban District are independent villas (floor area ratio: 0.2–0.5), townhouse villas (floor area ratio: 0.4–0.7) and multistory residential buildings below six floors (floor area ratio: 0.8–1.2). In the Yinzhou New Urban District, the dominant building types are independent villas (0.2–0.5), townhouse villas (0.4–0.7), multistory residential buildings below six floors (0.8–1.2), 11-story small high-rise residential buildings (1.5–2.0), and 18-story high-rise residential buildings (1.8–2.5). By combining the spatial matrix model with the principles of new urbanism, which advocate the creation and development of diverse, walkable, compact, and mixed-use communities—different combinations of density represent different urban forms in various locations, such as central areas and suburbs. Different residential forms also correspond to distinct density combinations, such as high-rise towers and densely enclosed blocks. Currently, the standards for residential area planning and design in China, known as the “Standard for Planning and Design of Urban Residential Areas” (GB50180-2018) (referred to as the Standard), reflect density regulations (China, 2021) regarding floor area ratio, building density, average number of floors, and open space ratio. Figure 10A of the spatial matrix model shows that a significant portion of the residential forms do not comply with or encourage normative standards. For instance, residential forms with low-rise buildings and high coverage, as well as multistory buildings with high coverage, are more common in Japan, Europe, and the United States. For example, in Tokyo, two-story housing accounts for over 40%, housing with fewer than seven floors accounts for over 80%, and housing with more than 15 floors accounts for 2.5%. In Barcelona’s expansion area, residential buildings are typically limited to five floors (Zhou and Wang, 2013; Xu and Huang, 2017).

Figure 10. Code of urban Residential Areas Planning and Design (A) and density-shape interval diagram (B) in case new urban district. Note: a In the figure, green represents low-rise zones, blue represents multi-storey zones, yellow represents mid- to high-rise zones, and red represents high-rise zones.
Compared to the residential forms reflected in the density regulations of the “Standard”, the case of the new urban district features residential distributions within the range of low-rise buildings with high coverage. However, the range of multiplestory buildings with high coverage is limited (Figure 10B). The residential forms in the new urban district are mainly concentrated in two types: 1) multistory panel buildings, which were common in the 1980 s and 1990 s, and 2) high-rise slabs and tower buildings, which have been widespread in Chinese cities over the past 20 years. The main reasons for this phenomenon are as follows: 1) The Code for Planning and Design of Urban Residential Areas (GB50180-9 referred to as the “Code”) stipulates that the green space ratio in residential areas in new urban districts should not be less than 30%, and in historic areas, it should not be lower than 25% (PRC, 2002). 2) The “Code” as the statutory basis for urban construction control planning, has long lacked consideration of morphological factors. The range of forms defined by the “Standard” is relatively broad. However, to maximize profits, the floor area ratio is pursued at the upper limit, and high-rise buildings are designed to achieve greater heights. This further narrows the range of options available for residential forms.
4.2 Degree of overlap between spatial form elements
The level of multiple-function high mixedness in the new urban district areas of Xianlin and Yinzhou was relatively low, at 0.38% and 0.27%, respectively. This indicates that the development pattern of large blocks with single functions leads to a lack of resilience in public spaces. This finding aligns with the comparison results of Yu et al. (2016) regarding the degree of functional mixture between the old and new areas of Songjiang (Ye et al., 2016). In the old area, multifunctional mixedness is not only concentrated in the historic center but also extends across the entire area. By contrast, in the new area, multifunctional mixedness is concentrated only in the central area, with single residential functions dominating the res. The main reasons for this phenomenon are as follows: 1) under the guidance of the Urban Land Classification and Planning Construction Land Standard (GBJ137-90) (PRC, 1991), land classification is rigidly determined based on land-use functions, where one land code corresponds to one type of land use. It is difficult to define mixed-use land, and large areas of land sold often result in single-function of usage. 2) The spatial form of new urban district areas is based on traditional land-use zoning and is influenced by “top-down” planning organizations. Because of the short development sequence, land control units were delineated within the framework of large-scale urban roads. This typically leads to the organization of functions such as residential and public buildings, without effective connections or complementarity, resulting in a lack of rational mixed-use. 3) Many multistory residential areas in new urban districts have undergone transformations from small-block old city renewals to large-scale comprehensive developments, resulting in low spatial integration and an overemphasis on single land use functions.
Two case studies of new urban districts were integrated to analyze the spatial relation between the degree of functional mixture, accessibility, and urban vitality factors. The following findings were observed: 1) single units with mixed functionality (H_A, H_W, A_W) and multifunctionality (H_A_W) were clustered at 42.41% and 78.57%, respectively, in areas with high urban vitality. This indicates that mixed-use land is more attractive, contributing to urban vitality and promoting sustainable development. 2) Single units with mixed functionality (H_A, H_W, A_W) and multifunctionality (H_A_W) clustered at 50.25% and 85.71%, respectively, in areas with high accessibility values. Furthermore, influenced by spatial functions with high transportation dependencies, such as offices and commercial areas, the interaction between land use and public facilities has become more evident. Multiscale accessibility plays a crucial role in maintaining urban vitality and spatial network density (Ye and Nes, 2014).
4.3 Optimization measures
In the context of urban and sustainable development, achieving a sustainable urban spatial form has become essential for China’s future urban development. This study analyzed the main factors influencing sustainable urban spatial forms from a new perspective, which is of great significance for future urban renewal and development in China. From a morphological perspective, sustainable urban spatial morphology is characterized by appropriate building density, typology, and a sufficient functional mixture. These elements gradually aggregate towards high street-level accessibility sites. Specifically, street-level accessibility tends to remain relatively stable during this process, whereas construction intensity, building typology, and functional mixtures change over time. Urban vitality is fundamental to the sustainable development of a city, and it naturally increases over several decades as a result of the alignment between spatial structure (accessibility) and other factors based on spatial structure (construction intensity and function). In this process, sites with high accessibility, owing to their convenience, spontaneously attract high-intensity redevelopment and functional adjustments, gradually achieving the spatial aggregation of these three morphological elements and cultivating urban vitality.
However, urban vitality does not necessarily increase gradually over time. Two factors determine its manifestation in terms of physical form: 1) the inherent factor of street-level accessibility is based on the characteristics of the road network, which is largely determined by planning and design and does not change significantly over time. 2) Morphological elements evolve gradually over time after construction. If new urban districts are characterized by closed communities, dead-end roads, and cul-de-sacs, the overall street-level accessibility of their spatial structures may be lower. Considering the relatively stable nature of street-level accessibility over a long period, if the fit between these morphological elements and high-density development is already poor, urban vitality may remain at a low level for a long time, making it difficult for it to evolve and become more vibrant. Currently, construction models of closed communities and large block layouts with cul-de-sacs are common in new urban districts in China (Sui et al., 2020). However, new urban districts with good street-level accessibility, such as Xianlin’s “Newly Built District” and Yinzhou’s “Renewal District,” built on a county scale, currently perform poorly in terms of building density, typology, and functional mixture. Nonetheless, the expected urban vitality may gradually increase over time as the fit between these morphological elements improves.
At present, urban planning practices can impede the natural process of urban maturity, resulting in new districts lacking economic vitality and vibrant street life. This is because of the conflict between planning goals and complex dynamics of urban development. Consequently, there is a need to rethink urban planning strategies that can support urban vitality and foster long-term sustainable developmen. Therefore, when planning and designing to promote urban sustainability and foster urban vitality, street-level accessibility should be considered a key starting point for the spatial structure. First, good overall street-level accessibility should be ensured. Second, the distribution of highly accessible streets should be used to organize factors, such as construction intensity and functionality. In the field of urban planning, it is important to establish scientifically determined standards for residential area density, promote density zoning at the city level, and refine density morphology in detail. This could include reducing barriers to appropriate building typologies, enriching the range of options for residential area forms, and promoting the aggregation of multiple urban form features with positive effects. This can be achieved by: 1) establishing density zoning in city-level plans, 2) refining density morphology in detailed plans, and 3) ensuring the rationality of urban form layout. Ultimately, these efforts assist in achieving high urban vitality and sustainable urban spatial development. The importance of implementing the “block system” and “open neighborhoods,” as proposed in the central urban work conference, is emphasized. Good street-level accessibility is essential to promote urban vitality and improve sustainability. Only by gradually dismantling the “Hutong system”, changing the development model dominated by closed blocks, and continuously promoting the connectivity of block road networks, can we fundamentally improve the overall accessibility of the urban street system. This will open up more possibilities for enhancing urban spatial quality and diversity. Finally, while emphasizing functional zoning, it is important to consider a moderate mixture of urban land uses, diversify and integrate office, commercial, residential, and recreational functions, and create diverse urban life to enhance urban spatial vitality and sustainability.
5 Conclusion
Based on urban morphology, it has been proposed that good street accessibility, appropriate building density and typology, and a diverse functional mixture are the foundations of spatial morphology for promoting sustainable urban development. Furthermore, at the grid level, various analytical tools such as space syntax, spatial matrices, and mixed-use indices were used to quantify and describe these three spatial morphological characteristics. The main conclusions of this study are as follows:
1) There are both similarities and differences in the sustainable morphologies of the case studies in the on new urban districts. In terms of accessibility, the proportion of high-value areas in terms of accessibility is relatively high in both new urban districts. The overall synergy of the spatial networks in Yinzhou New Urban District was stronger, with local spatial networks integrated into the global spatial network structure. In terms of urban density, Yinzhou New Urban District has a higher development intensity than that of Xianlin New Urban District, primarily because of its development history and functions. Good connectivity of the global structure in Xianlin New Urban District and insufficient local microcirculation are important factors influencing urban density in relation to small-scale spatial structures. Regarding functional mixture, both the Xianlin and Yinzhou New Urban Districts exhibited a predominant pattern of large-scale land development with single functions, and the degree of multifunctional mixture was relatively low. However, the degree of dual-functionality mix was higher in the Yinzhou New Urban District than in Xianlin New Urban District.
2) The architectural forms in the case studies of new urban districts were predominantly mid-rise panel and enclosure-type buildings, low-rise enclosure-type buildings, and high-rise panel buildings. In the low-rise, high-coverage ratio forms, there are residential areas, but they are less evident in the multistory, high-coverage-ratio forms. The proportion of high-value areas that influenced urban spatial vitality was relatively high in the Yinzhou New Urban District, indicating better urban vitality compared with that of the Xianlin New Urban District. On the one hand, these forms provide sufficient construction intensity, ensuring that a sufficient number of people use these plots. On the other hand, the panel or enclosure form of buildings ensures permeability and interaction between the buildings and streets, enabling possibilities for diverse urban living. Therefore, it is recommended to appropriately enrich the forms of multistory panels, enclosures, and high-rise enclosures, which have a strong positive effect on the vitality of new urban districts.
3) There is a considerable degree of overlap between spatial elements, such as accessibility, building density/typology, and functional mixture. Specifically, 42.41% and 78.57% of the dual-function and multifunction mixed units in the new urban districts are clustered in high-value areas of urban vitality, indicating that mixed land use contributes to urban vitality and sustainable development. Furthermore, 50.25% and 85.71% of the dual-function and multifunction mixed units, respectively, were clustered in areas of high accessibility. This effect was especially pronounced when mixed units included public facilities, strengthening the association between mixed functions and accessibility. Additionally, 64.54% of the high plot ratio units were clustered in areas of high accessibility, indicating a strong correlation between microlevel accessibility and plot ratio, with a significant influence on the composition of land functions. These findings suggest that mixed land use in new urban districts contributes to accessibility, spatial vitality, and sustainable development.
Currently, numerous urban spatial design principles have been proposed by different theorists, each with distinct focal points and varying descriptions of spatial characteristics, making it challenging to effectively guide urban design practices. Therefore, it is essential to delve deeper into the sustainable spatial forms that underlie urban vitality and utilize these insights to provide practical guidance for enhancing urban spatial vitality. In this context, this study approaches the principles of urban vitality creation from a morphological perspective, by extracting key morphological elements from existing complex principles. It integrates traditional qualitative theories of morphology with new quantitative methods, including space syntax, spatial matrices, and mixed-function indicators. This framework enables the analysis of sustainable urban morphological characteristics that represent urban spatial vitality. Traditionally, the creation of sustainable urban spaces has mostly relied on the intuition and experience of designers. However, based on the morphological understanding of spatial vitality, this study conducted a conducts visual analysis, presentation, and evaluation of urban spatial vitality and sustainable development—key objectives of urban design—on a geographic information system analysis platform. By combining a series of quantitative urban morphological analysis tools, such as space syntax, with traditional urban morphology and urban design theories, designers can conveniently conduct quantitative verification to create sustainable urban spatial vitality at multiple stages of urban design. This provides a series of new analytical tools for quantifying urban built environments and offers the potential for a more precise and detailed study of the spatial form characteristics of new areas, along with the evolution of their vitality over time.
Owing to the lack of detailed urban morphological data over an extended time span, it has become necessary to conduct comparative analyses using multiple similar cases. Although this is currently the only feasible approach, the representativeness of these cases remains debatable. Moreover, issues such as the adaptability of this morphological analysis to different built environments and the weighting of various morphological elements require further investigation. However, the current research methodology has already demonstrated a strong development framework, with substantial for further expansion of research content. In the future, with the development of new data environments and the extensive collection of urban morphological data from different time periods, more in-depth empirical studies can be conducted. Additionally, with support from new data environments and urban research techniques and methodologies, future studies on sustainable urban forms may consider incorporating the concept of human-scale urban forms. This will lead to a deepening of research on classical urban morphology and better address the requirements of rational urban planning and design.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
YZ: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Software, Writing–original draft. XW: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Validation, Writing–original draft. LW: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Validation, Writing–original draft. GL: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing–original draft. YZ: Data curation, Software, Writing–review and editing. YY: Investigation, Writing–review and editing. HJ: Investigation, Writing–review and editing. SZ: Writing–review and editing. JS: Investigation, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the Youth Innovation Team Project in Universities of Shandong Province (2022RW026); the National Natural Science Foundation of China (42377207, 42207553); the Shandong Provincial Humanities and Social Sciences Project (2022-YYGL-31); the general project of Undergraduate Teaching Reform in Shandong Province (Z2021177); the Shandong Taishan Scholar Young Expert Program (tsqn202306240); the Key project of Research and Development Program in Shandong Province (2022RKY07006); the Foundation of School and Land Integration Development in Yantai (2021XDRHXMQT18); the open foundation of State Key Laboratory of Lake Science and Environment (2022SKL005); the open foundation of State Key Laboratory of Loess and Quaternary Geology, Institute of Earth Environment, CAS (SKLLQG 2024); the Humanity and Social Science Foundation of Ministry of Education of China (19YJCZH171); the Youth Innovation Team Project for Talent Introduction and Cultivation in Universities of Shandong Province.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Alberti, M. (1996). Measuring urban sustainability. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 16 (4), 381–424. doi:10.1016/s0195-9255(96)00083-2
Berghauser, P. M., and Haupt, P. (2010). Spacematrix: space, density and urban form. Rotterdam, The Netherlands: NAI Publishers.
Cai, Z., Tang, Y., Liu, C., and Demuzere, M. (2021). Analyzing the transformation of 3D urban morphology and corresponding surface heat island effect in beijing. Urban Plan. Int. 36 (05), 61–68. doi:10.19830/j.upi.2021.407
Cao, K., and Deng, Y. (2021). Spatio-temporal evolution path and driving mechanisms of sustainable urban renewal: progress and perspective. Prog. Geogr. 40 (11), 1942–1955. doi:10.18306/dlkxjz.2021.11.012
Cao, X., Liang, F., and Chen, H. (2019). Influence of different spatial forms for metropolitans on transportation network efficiency. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 39 (01), 41–51. doi:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2019.01.005
Chen, M., Gong, Y., Lu, D., and Ye, C. (2019). Build a people-oriented urbanization: China’s new-type urbanization dream and Anhui model. Land Use Policy 80, 1–9. doi:10.1016/j.landusepol.2018.09.031
Chen, M. X., Ye, C., Lu, D. D., Sui, Y. W., and Guo, S. S. (2019). Cognition and construction of the theoretical connotations of new urbanization with Chinese characteristics. J. Geogr. Sci. 29 (10), 1681–1698. doi:10.1007/s11442-019-1685-z
Du, X., Zhou, J., and Xiao, C. (2024). Spatial effects and influencing factors of urban sustainable development: an analysis of urban agglomerations in China. Econ. Analysis Policy 81, 556–575. doi:10.1016/j.eap.2023.12.022
Duan, J., and Yin, M. (2011). Spatial evolution of contemporary new town in China: case follow-up study and future planning. Nanjing: Southeast University Press.
Feng, K. (2018). China new city new district development report: 2018. Beijing: Enterprise Management Press.
Haseli, G., Rahnamay Bonab, S., Hajiaghaei-Keshteli, M., Jafarzadeh Ghoushchi, S., and Deveci, M. (2024). Fuzzy ZE-numbers framework in group decision-making using the BCM and CoCoSo to address sustainable urban transportation. Inf. Sci. 653, 119809. doi:10.1016/j.ins.2023.119809
He, Q. S., He, W. S., Song, Y., Wu, J. Y., Yin, C. H., and Mou, Y. C. (2018). The impact of urban growth patterns on urban vitality in newly built-up areas based on an association rules analysis using geographical big data. Land Use Policy 78, 726–738. doi:10.1016/j.landusepol.2018.07.020
Hillier, B., and Hanson, J. (1984). The social logic of space. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Huang, Y. J., Zhang, J. Q., and Wu, J. Q. (2020). Integrating sustainability assessment into decoupling analysis: a focus on the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomerations. Sustainability 12 (19), 7872. doi:10.3390/su12197872
Hui, E. C. M., and Yu, K. H. (2013). Commuting patterns of residents within a high-density urban development: a study of Hong Kong. Habitat Int. 39, 201–213. doi:10.1016/j.habitatint.2012.12.008
Jabareen, Y. R. (2006) Sustainable Urban Forms: Their Typologies, Models, and Concepts. JPER 26 (1), 38–52. doi:10.1177/0739456x05285119
Joosten, V., and Van, N. A. (2005) How block types influences the natural movement economic process: micro-spatial conditions on the dispersal of shops and café in berlin in 5th international space syntax symposium. Delft. Netherlands: Techne Press.
Kashem, S. B., Irawan, A., and Wilson, B. (2014). Evaluating the dynamic impacts of urban form on transportation and environmental outcomes in US cities. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 11 (8), 2233–2244. doi:10.1007/s13762-014-0630-z
Larkin, A., Gu, X., Chen, L. Z., and Hystad, P. (2021). Predicting perceptions of the built environment using GIS, satellite and street view image approaches. Landsc. Urban Plan. 216, 104257. doi:10.1016/j.landurbplan.2021.104257
Li, C., and Li, J. X. (2017). Assessing urban sustainability using a multi-scale, theme-based indicator framework: a case study of the Yangtze River Delta region, China. Sustainability 9 (11), 2072. doi:10.3390/su9112072
Liu, H., Gou, P., and Xiong, J. (2022). Vital triangle: a new concept to evaluate urban vitality. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 98, 101886. doi:10.1016/j.compenvurbsys.2022.101886
Liu, J. M., Hou, X. H., Xia, C. Y., Kang, X., and Zhou, Y. J. (2021). Examining the spatial coordination between metrorail accessibility and urban spatial form in the context of big data. Land 10 (6), 580. doi:10.3390/land10060580
Meng, Y., and Xing, H. F. (2019). Exploring the relationship between landscape characteristics and urban vibrancy: a case study using morphology and review data. Cities 95, 102389. doi:10.1016/j.cities.2019.102389
Prc, M. (1991). Urban land classification and planning construction land standard: gbj 137-90. Beijing: China Planning Press.
Prc, M. (2002). GB50180-93 code for planning and design of urban residential areas. Beijing: China Architecture and Building Press.
Song, Y., Long, Y., Wu, P., and Wang, X. (2018). Are all cities with similar urban form or not? Redefining cities with ubiquitous points of interest and evaluating them with indicators at city and block levels in China. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 32 (12), 2447–2476. doi:10.1080/13658816.2018.1511793
Sui, H., Yang, X., Xu, S., and Zhou, D. (2020). Progress and hot research on urban functional space renewal in the new era. Trop. Geogr. 40 (06), 1150–1160. doi:10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.003291
Talen, E. (2011). Sprawl retrofit: sustainable urban form in unsustainable places. Environ. and Plan. B Plan. and Des. 38 (6), 952–978. doi:10.1068/b37048
Usman, A. S., and Abdullah, W. M. Z. B. W. (2017). Towards sustainable urban form: a comparative analysis of two urban neighbourhoods in kano, Nigeria. Adv. Sci. Lett. 23 (7), 6367–6371. doi:10.1166/asl.2017.9271
Van Nes, A., and Stolk, E. (2012). Degrees of sustainable location of railway stations: integrating space syntax and node place value model on railway sations in the province of North Holland's strategic plan for 2010-2040.
Wang, X. (2022). Study on the sustainability of new urban districts and measuring in dimension of urban morphology in the Yangtze River Delta. Beijing: China Social Press.
Wang, X., Chen, S., Yao, S., and Zhang, Y. (2017). Study on the assessment of resource utilization efficiency and environmental sustainability of new towns in Yangtze River Delta. Hum. Geogr. 32 (04), 68–77. doi:10.13959/j.issn.1003-2398.2017.04.010
Wang, X. X., Zhang, Y. J., Yu, D. L., Qi, J. H., and Li, S. J. (2022). Investigating the spatiotemporal pattern of urban vibrancy and its determinants: spatial big data analyses in Beijing, China. Land Use Policy 119, 106162. doi:10.1016/j.landusepol.2022.106162
Wang, Y., and Shaw, D. (2018). The complexity of high-density neighbourhood development in China: intensification, deregulation and social sustainability challenges. Sustain. Cities Soc. 43, 578–586. doi:10.1016/j.scs.2018.08.024
Wei, Y. D. (2016). Towards equitable and sustainable urban space: introduction to special issue on urban land and sustainable development. Sustainability 8 (8), 804. doi:10.3390/su8080804
Xia, C., Yeh, A.G.-O., and Zhang, A. (2020). Analyzing spatial relationships between urban land use intensity and urban vitality at street block level: a case study of five Chinese megacities. Landsc. Urban Plan. 193, 103669. doi:10.1016/j.landurbplan.2019.103669
Xiao, Y., Chiaradia, A., and Song, X. (2014). Limitations of space syntax in urban planning and ways to improve and expand it. Urban Plan. Forum (05), 32–38.
Xu, Y., and Huang, Y. (2017). Urban renewal of enclosed blocks in the Barcelona expansion area. Hous. Sci. 37 (10), 73–78. doi:10.13626/j.cnki.hs.2017.10.014
Xue, C. Q. L., Wang, Y., and Tsai, L. (2013). Building new towns in China – a case study of Zhengdong New District. Cities 30, 223–232. doi:10.1016/j.cities.2012.02.003
Ye, Y., Li, D., and Liu, X. J. (2018). How block density and typology affect urban vitality: an exploratory analysis in Shenzhen, China. Urban Geogr. 39 (4), 631–652. doi:10.1080/02723638.2017.1381536
Ye, Y., and Nes, A. v. (2014). Measuring urban maturation processes in Dutch and Chinese new towns: combining street network configuration with building density and degree of land use diversification through GIS. J. Space Syntax 4.
Ye, Y., Zhuang, Y., Lingzhu, Z., and Nes, A. V. (2016). Designing urban spatial vitality from morphological perspective: a study based on quantified urban morphology and activities’ testing. Urban Plan. Int. 31 (01), 26–33.
Zhang, A. Q., Xia, C., and Li, W. F. (2022). Relationships between 3D urban form and ground-level fine particulate matter at street block level: evidence from fifteen metropolises in China. Build. Environ. 211, 108745. doi:10.1016/j.buildenv.2021.108745
Zhou, J., and Wang, L. (2013). The content, characteristics, and enlightenment of Japan’s residential statistical survey. Famous Cities China 11, 25–30.
Keywords: sustainability, urban spatial form, grid scale, spatial vitality, New Urban
Citation: Zhang Y, Wang X, Wang L, Li G, Zhang Y, Ye Y, Jiang H, Zhong S and Song J (2024) Measurement and optimization of sustainable urban form elements in New Urban districts using multi-source data. Front. Environ. Sci. 12:1451903. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2024.1451903
Received: 20 June 2024; Accepted: 29 November 2024;
Published: 24 December 2024.
Edited by:
Pedro Cabral, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, ChinaReviewed by:
Adam Radzimski, Adam Mickiewicz University, PolandSubhanil Guha, National Institute of Technology Raipur, India
Vicente Tang, New University of Lisbon, Portugal
Copyright © 2024 Zhang, Wang, Wang, Li, Zhang, Ye, Jiang, Zhong and Song. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiaohui Wang, WGlhb2h1aXdhbmc4ODExMjRAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Guangyu Li, bGVlZ3Vhbmd5dUAxMjYuY29t
 Yanfeng Zhang
Yanfeng Zhang Xiaohui Wang
Xiaohui Wang Longsheng Wang
Longsheng Wang Guangyu Li
Guangyu Li Yige Zhang1
Yige Zhang1 Yu Ye
Yu Ye