- 1Center of Eco-environmental Monitoring and Scientific Research, Administration of Ecology and Environment of Haihe River Basin and Beihai Sea Area, Ministry of Ecology and Environment of People’s Republic of China, Tianjin, China
- 2State Key Laboratory of Hydraulic Engineering Intelligent Construction and Operation, Tianjin University, Tianjin, China
- 3Ecological Environment Monitoring Center of Hebei Province, Shijiazhuang, China
Introduction: Investigating and assessing native fish diversity and conducting regional assessments of threats are vital for the conservation of aquatic biodiversity. For this specific study, the Daqing River basin in China was chosen as the research area. Field surveys were carried out between 2018 and 2019, supplemented by a review of pertinent literature and other records.
Methods: To evaluate fish diversity, the following parameters are selected for analysis: Relative abundance (Pi), Frequency of occurrence (Fi), Margalef richness index (D) , Shannon Wiener diversity index (H′) , and Pielou evenness index (J′).Relative abundance levels are categorized as follows: dominant species make up more than 10%, common species account for 1%–10%, and occasional species constitute less than 1%. Canoco 5.0 software was utilized to conduct Redundancy Analysis (RDA) on the fish species composition and environmental factors at 34 sampling sites.
Results: The findings revealed that 85 fish species have been recorded in the basin, consisting of 78 freshwater species categorized into 8 orders, 17 families, and 59 genera, among which Cypriniformes comprised 64% of the total catch. The low proportion of threatened and endemic species was an important feature of the fish diversity of the Daqing River. Despite the theoretical presence of 85 species, field surveys managed to collect only 42 species, of which 33 were confirmed as naturally occurring within the basin. The average values of Margalef richness index, 22 Shannon Wiener diversity index and Pielou evenness index were 1.72, 2.04 and 0.80 respectively, signifying a low fish diversity with relatively uniform distribution across the sampled regions.
Discussion: This study found that the community structure and diversity of fish were closely related to environmental factors, particularly water quality. Among these factors, ammonia nitrogen emerged as a significant determinant of fish diversity. High concentrations of ammonia nitrogen inhibit fish growth, endanger health, and can even lead to death. Additionally, dams and other water infrastructure also impact fish community structure and diversity. This baseline study can provide a basis for the protection and ecological restoration of fish resources in the Daqing River.
1 Introduction
The Daqing River basin, situated mainly in the North China Plain, extends from the upstream of the Nanzhitang river to the estuary of the Duliujian river, covering a total length of 483 km (Chen et al., 2022; Cui et al., 2019). This basin encompasses four districts across Hebei province, Shanxi province, Beijing city, and Tianjin city, with a collective area of 43,060 km2 (Lu and Fu, 2010). The mountainous region within the basin spans 22,822 km2, while the plain area covers 20,238 km2, representing 53% and 47% of the total basin area, respectively. The mountainous area typically ranges from 1,000 to 1,500 m above sea level, while the plain area is situated below 50 m. The upstream of the Daqing River is divided into north and south branches, with a sector distribution, and is fed by major tributaries such as Juma, Yishui, Zhulong, Tang, Jie Fu, Cao, and Pu (Liu and Zhao, 2012). Baiyangdian Lake, the largest freshwater shallow wetland in the North China Plain, plays a crucial role in the Daqing River basin. Positioned in the middle reaches of the basin, Baiyangdian Lake controls a drainage area of 31,205 km2, which accounts for 72% of the total drainage area (Han et al., 2020).
In recent years, the rapid economic and social development of the Daqing River basin, along with the continuous improvement of urbanization, has led to the degradation of the ecology and environment of the river system. This degradation has resulted in rivers drying up, wetlands shrinking, and water quality deteriorating, significantly impacting the survival of aquatic organisms in the catchment area. The Daqing River basin currently hosts six large-scale junction projects, including Zaolinzhuang Junction, Xingaifang Junction, Wangcun Gate, Duliujian River Flood Gate Junction, Xihe Gate Junction, and Gongnongbing Tide Gate. Additionally, there are seven large-sized reservoirs and 12 medium-sized reservoirs in the catchment area, collectively providing a total storage capacity of 4.15 billion m3 (Committee of Tianjin Chorography Compilation, 2005). Despite these environmental challenges, existing research on the Daqing River primarily focuses on hydrology and water resources (Liu, 2009; Wang, 2019; Ye et al., 2020), water conservancy engineering (Zhang, 2019), and river regulation (Qiu and Zhang, 2018). The establishment of the Xiong’an New District in Hebei in April 2017 has garnered significant attention in the Daqing River basin. Given these developments, it is imperative to conduct a comprehensive investigation into the overall fish diversity of the Daqing River basin and analyze the factors contributing to changes in fish diversity.
The significance of studying fish diversity lies in gaining a comprehensive understanding of the health and function of river water ecosystems. Fish, as a crucial component of aquatic ecosystems, serves not only as a representation of biodiversity but also as a sensitive indicator of changes in water ecological environment quality (Gomes et al., 1995; Alkins-koom, 2000; Tzeng et al., 2002). The abundance and diversity of fish not only mirror the complexity of aquatic ecosystems but also directly and indirectly reflect the health status of aquatic ecosystems and the integrity of biological chains. These factors are vital indicators for assessing water quality and ecosystem health (Richter et al., 1996; Linde-Arias et al., 2008). Historically, research on fishes in the Daqing River basin has been fragmented and unsystematic (Xie et al., 2021). Previous studies, such as Liu et al. (1981) on fish resources and Li (1986) on freshwater fish fauna in Hebei province, only touched upon a portion of the fish distribution in the Daqing River basin. Other studies have been confined to the Baiyangdian area (Zheng et al., 1960; Wang and Gu, 1981; Han et al., 1991; Cao et al., 2003; Zhao et al., 2007; Xie and He, 2010). Currently, there is a lack of dedicated research on fish diversity in the Daqing River basin. To understand the fish diversity and resource information of the Daqing River basin, as well as to understand the fish community structure and spatial distribution characteristics, a systematic analysis was conducted from 2018 to 2019. The primary objective is to offer fundamental information for the ecological restoration and protection of fish diversity in the Daqing River basin. This information serves as a scientific foundation for the rational development of ecological resources and the formulation of policies for ecological environmental protection.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Sample collection and identification
In 2018 and 2019, we conducted a series of surveys on fish diversity in the Daqing River basin, spanning from May to September, December, and October to November, respectively. A total of 34 sampling locations were strategically chosen in the basin, taking into account factors such as water function area distribution, topography, and the representative, typicality, and consistency of the sites (Figure 1). Various collection methods, including cast nets, hand nets, and traps, were employed to ensure scientifically sound sampling. At each sampling site, approximately five specimens per species were collected and preserved by immersion in formaldehyde or alcohol. Specimens that posed identification challenges were carefully marked and transported to the laboratory for further analysis. Additionally, supplementary fish samples were obtained from fishermen, markets, restaurants, and other relevant sources. The classification and identification of fish species were primarily based on authoritative sources such as “Chinese Zoology” (Chen, 1998; Chu et al., 1999; Yue, 2000; Wu and Zhong, 2008), “Chinese Loach History” (Zhu, 1989), “Hebei Zoology·Fishes” (Wang et al., 2001), and “Fishes in Beijing and its adjacent areas” (Zhang and Zhao, 2013). The taxonomy and nomenclature of the fish species followed the guidelines outlined in “Inland China Fish Species and Distribution” (Zhang and Zhao, 2016).
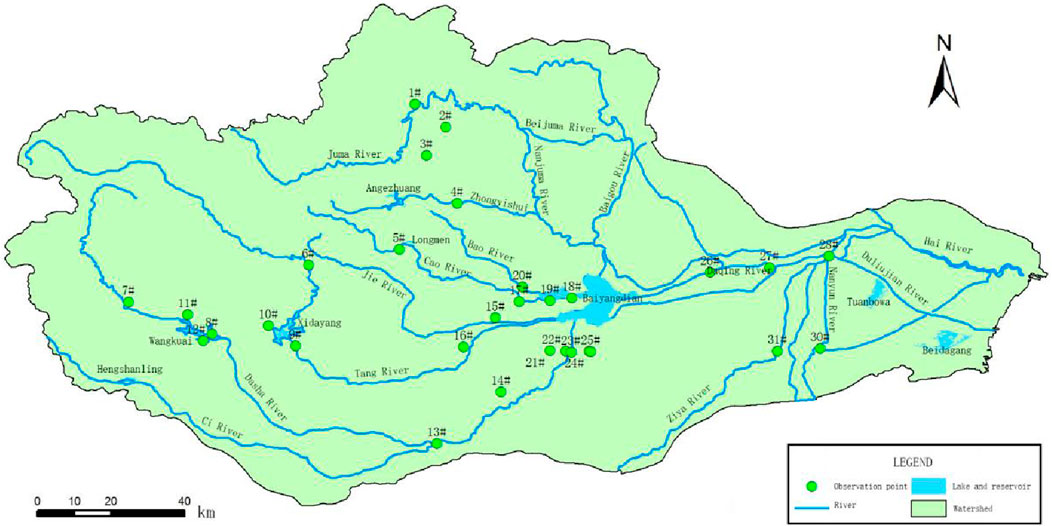
Figure 1. Location of observation points in the Daqing River system. The green dot represents the observation point; The blue line represents the river; The blue area represents the lake and reservoir.
When conducting fish surveys, environmental factors such as NH3-N, CODMn, BOD5 and DO were measured. Among them, DO was measured on-site with the United States YSI ProQuatro handheld multi-parameter water quality analyzer. At the same time, 2.5 L water samples were collected on site, stored in a 0°C–4°C constant temperature refrigerator, and brought back to the laboratory within 48 h to measure the mass concentration of NH3-N, CODMn and BOD5, following the GB 3838–2002″Environmental Quality Standard for Surface Water” and “Water and Wastewater Monitoring and Analysis Methods” (Editorial Board of Water and Wastewater Monitoring and Analysis Methods of State Environmental Protection Administration, 2002).
2.2 Statistical analysis
To evaluate fish diversity, the following parameters are selected for analysis: Relative abundance (Pi), Frequency of occurrence (Fi), Margalef richness index (D) (Ulanowicz R E, 2001), Shannon-Wiener diversity index (H′) (Shannon C E, 1966), and Pielou evenness index (J′) (Pielou E C, 1966).
in which,
Relative abundance levels are categorized as follows: dominant species make up more than 10%, common species account for 1%–10%, and occasional species constitute less than 1%.
Canoco 5.0 software was utilized to conduct Redundancy Analysis (RDA) on the fish species composition and environmental factors at 34 sampling sites.
3 Results
3.1 Fish composition and dominant species
After combining historical data, collection information from the herbarium, and conducting field surveys in the Daqing River basin (including Baiyangdian), it was found that there were a total of 85 species of fishes. These species belonged to 10 orders, 20 families, and 64 genera. Notably, among these species, Lateolabrax japonicus, Synechogobius ommaturus, Tridentiger trigonocephalus, Periophthalmus modestus, Takifugu obscurus, and Liza haematocheila were classified as estuary species. Additionally, Hypomesus olidus was identified as an imported exotic cultured species. Consequently, the natural distribution of freshwater fish in the Daqing River basin encompassed 8 orders, 17 families, 59 genera, and 78 species. During field investigations, a total of 7 orders, 40 genera, and 42 species were examined in the Daqing River. Noteworthy among these were Mylopharyngodon piceus, Ctenopharyngodon idellus, Hypophthalmichthys molitrix, and Aristichthys nobilis, which were identified as proliferated and released species in recent years. In contrast, Protosalanx hyalocranius and H. olidus were introduced breeding species. Furthermore, L. japonicus, S. ommaturus, and T. trigonocephalus were classified as estuarine fishes. Consequently, after excluding these species, the investigation revealed only 33 freshwater fish species. These species belonged to 5 orders, 13 families, and 31 genera, and were naturally distributed in the Daqing River (Supplementary Table S1).
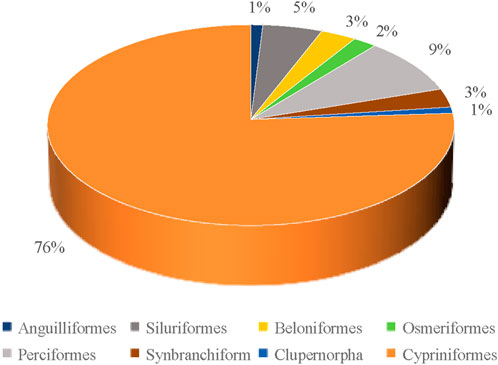
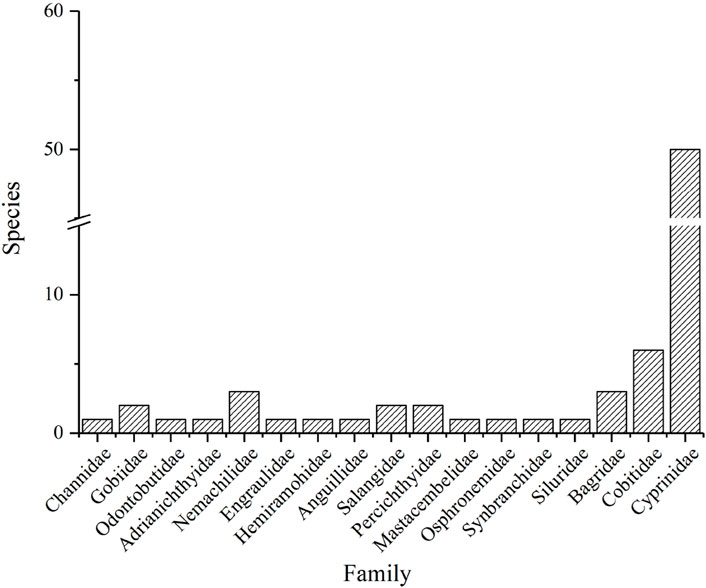
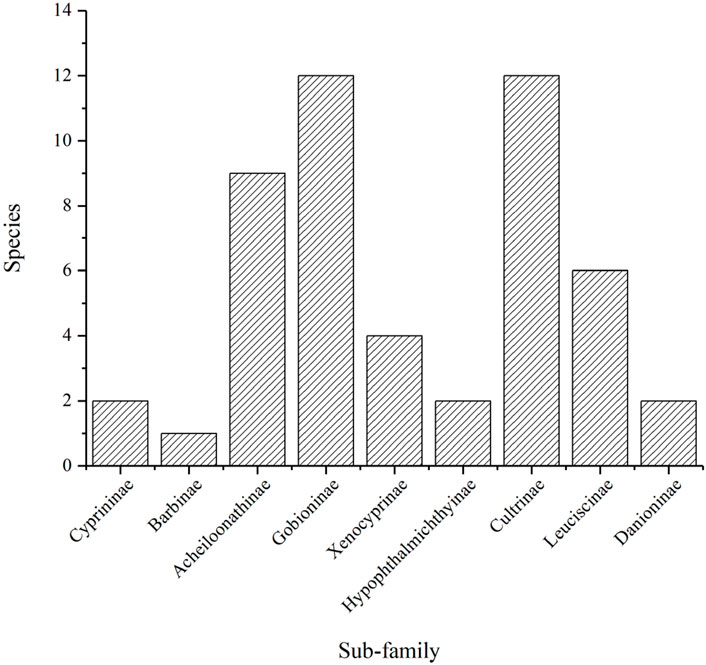
From the order level analysis, Cypriniformes stood out as the most diverse order, boasting 59 species which represented a significant 75.64% of the total number of freshwater fishes. In comparison, Perciformes and Siluriformes followed with 7 and 4 species, accounting for 8.97% and 5.13% of the total species, respectively. The remaining orders each contained no more than 2 species (Figure 2). Moving to the family level, Cyprinidae emerged as the dominant family with 50 species, making up 64.10% of the total number. Cobitidae came in second with 6 species, representing 7.70% of the total, while Nemachilidae and Bagridae each had 3 species, accounting for 3.85% respectively (Figure 3). Notably, Cyprinidae, Cobitidae, and Nemachilidae all belonged to the Cypriniformes order. Within Cyprinidae, there were 9 subfamilies identified in the Daqing River basin. Among these, Cultrinae and Gobioninae boasted the highest species numbers, each with 12 species, constituting 24% of the total. Additionally, Acheilognathinae comprised 9 species, making up 18% of the total species (Figure 4).
Through field investigation, a total of 747 fishes belonging to 34 species, 13 families, and 7 orders were captured. The current distribution of species under investigation represents only 42.31% of historical records. Among the captured species, Cypriniformes were the most abundant with 22 species, accounting for 66.67%, followed by Perciformes with 5 species, accounting for 15.15%. Siluriformes and Synbranchia each had 2 species, accounting for 6.06% respectively, while Needlefish was represented by only one species, accounting for 3.03%. The most frequently captured species were Pseudorasbora parva with 163 individuals and Carassius auratus with 118 individuals. The relative abundances of P. parva and C. auratus were 21.82% and 15.8% respectively, with a frequency of 0.7 for both species. These two species were identified as dominant and widely distributed in the Daqing River, consistent with a previous study by Xie et al. (2021). Additionally, Opsariicjthys bidens, Zacco platypus, Hemiculter leucisculus, Gnathopogon mantschuricus, Squalidus wolterstorffi, Abbottina rivularis, Paramisgurnus dabryanus, Misgurnus anguillicaudatus, Pelteobagrus fulvidraco, Hypseleotris swinhonis, Rhinogobius giurinus, S. ommaturus, Macropodus ocellatus, and Sinobdella sinensis were identified as common species, while the remaining 18 species were classified as occasional species. Regarding feeding habits, omnivorous fishes constituted 63.64% of the captured species, followed by carnivorous fishes at 33.33%, with only one herbivorous species identified. In terms of inhabiting water layers, demersal fish were the most prevalent, followed by pelagic and middle-lower layer fishes, accounting for 75.76% of the captured species (Supplementary Table S1).
3.2 Characteristics of fish community in Daqing River
Spatial analysis revealed that the upstream of the southern branch exhibited the highest species diversity, comprising 26 species, which accounted for 76.5% of the total species collected. In this region, a total of 253 fish were collected, with A. rivularis and P. parva emerging as the dominant species, representing relative abundances of 28.1% and 10.3%, respectively. Moving to the northern branch of the upper reaches, 20 fish species were identified, totaling 296 individuals. The dominant species in this area were P. parva, C. auratus, and Z. platypus, with relative abundances of 19.9%, 12.2%, and 10.8%, respectively. As for the middle and lower reaches, 17 fish species were recorded, amounting to 82 individuals, with C. auratus and S. ommaturus standing out as the dominant species, with relative abundances of 34.1% and 18.3%, respectively. Within the Baiyangdian area, a survey yielded 15 fish species, totaling 116 individuals, with C. auratus and P. parva dominating at relative abundances of 32.8% and 25%, respectively. Notably, eight fish species, namely P. parva, A. rivularis, C. auratus, P. dabryanus, H. swinhonis, R. giurinus, M. ocellatus, and Cyprinidae, were found distributed across all regions. S. sinensis was exclusively observed in the upstream of the Yishui River, while G. mantschuricus, Microphysogobio hsinglungshanensis, Barbatula nuda, and H. olidus were restricted to the southern branch of the upper reaches. H. olidus was specifically identified in the Pu River. Additionally, S. ommaturus, T. trigonocephalus, and L. japonicus were solely collected in the downstream of the Duliujian River.
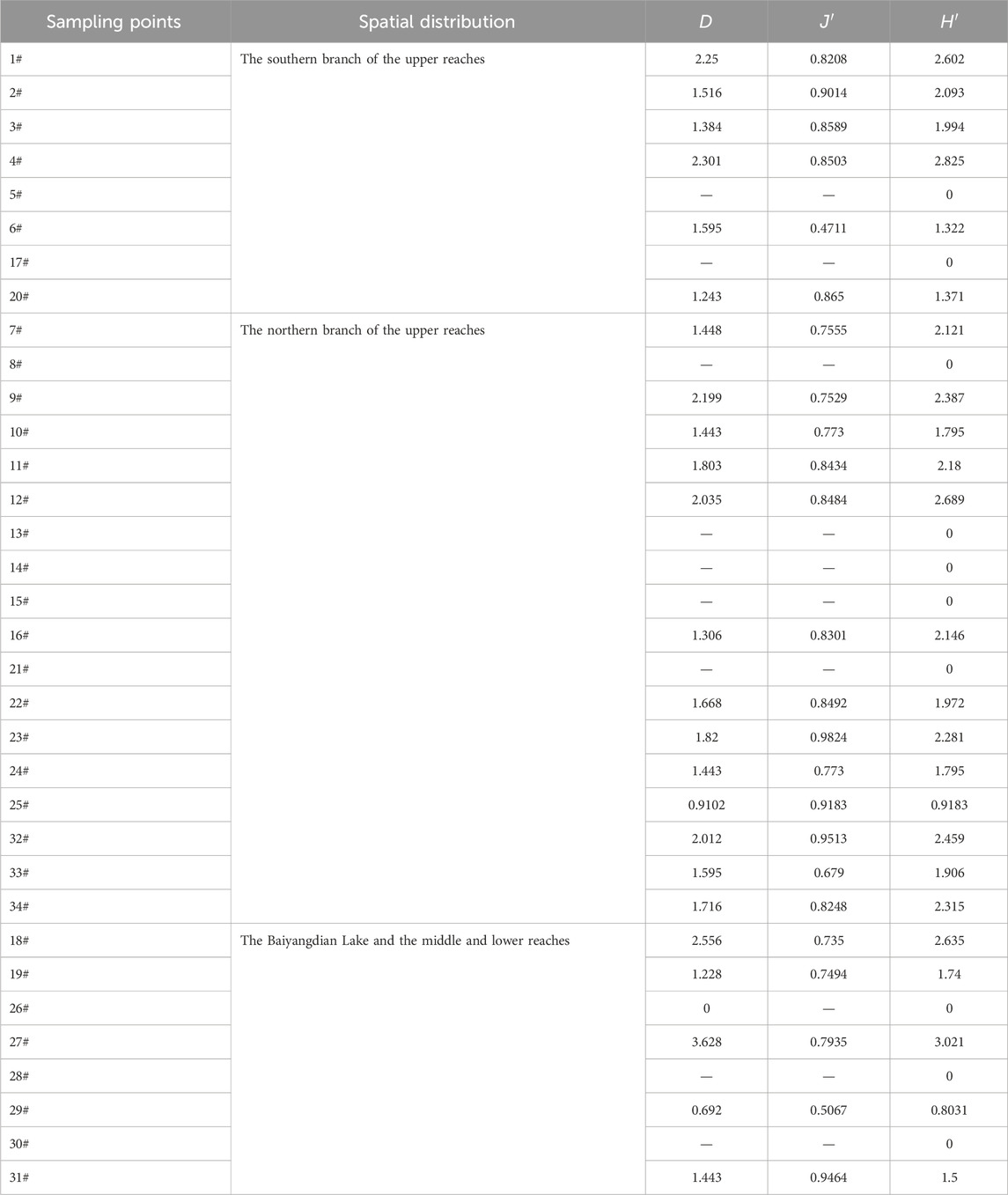
The fish species diversity, abundance, and uniformity of the Daqing River basin were assessed using the Shannon-Wiener diversity index (H′), Margalef richness index (D), and Pielou evenness index (J′). The calculated values were 1.72, 2.04, and 0.80, respectively, indicating an average level of species diversity in the Daqing River. Notably, Daqing Anlitun (27#) exhibited the highest H′ value of 3.02, while Duliujianhe Bridge (29#) had the lowest H′ value of 0.8. Daqing Anlitun (27#) also had the highest D value of 2.51, with Yishuihe Songshan Village (29#) recording the lowest D value of 0.43. The highest J′ value of 0.98 was observed at Zhulonghe Boshizhuang Village (23#), while the lowest J′ value of 0.47 was found at Tanghe Yunv Bridge (6#) (Table 1). Analyzing the regional perspective, the northern branch of the upper reaches displayed diversity, abundance, and uniformity indices of 2.15, 1.16, and 0.86, respectively. In comparison, the southern branch of the upper reaches had values of 1.88, 1.06, and 0.81, while the Baiyangdian area recorded indices of 2.06, 1.21, and 0.75. Moving to the middle and lower reaches, the indices were 1.89, 1.29, and 0.78, respectively. The northern branch of the upper reaches exhibited the highest diversity and uniformity indices but the lowest abundance, suggesting a relatively abundant species distribution with no dominant species. Conversely, the southern branch of the upper reaches had the lowest diversity and abundance indices but a relatively higher level of uniformity. The Baiyangdian area showed the lowest uniformity level, with higher diversity and abundance indices. In contrast, the middle and lower reaches had the highest abundance indices but lower diversity and uniformity levels, indicating a rich species composition with dominant groups, such as C. auratus, which accounted for 32.8% in Baiyangdian and 34.1% in the middle and lower reaches.
3.3 Relationship between fish community structure and environmental factors in Daqing River
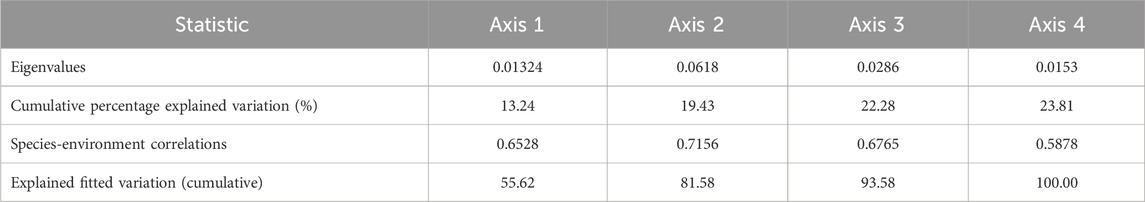
In the RDA analysis, the first and second axes were identified as the main component axes (Table 2). The first axis explained a change rate of 13.24%, contributing to a cumulative explanatory change rate of 19.43% for the first two axes. The correlation between species and the environment with the first two axes was found to be 65.28% and 71.56%, respectively. The results from the RDA ranking chart of the fish community and environmental factors in the Daqing River (Figure 5) indicated that ammonia nitrogen (NH3-N) exerted the most significant influence on the composition of the fish community, being a notable influencing factor (Monte Carlo test F = 2.3, P = 0.006). Furthermore, a strong correlation was observed between ammonia nitrogen and permanganate index (CODMn). Specifically, ammonia nitrogen exhibited a substantial impact on C. auratus, H. swinhonis, R. giurinus, Misgurnus anguillicaudats, and P. parva, suggesting a positive correlation with changes in ammonia nitrogen. Conversely, S. ommaturus, S. sinensis, P. fulvidraco, and O. bidens were negatively correlated with changes in ammonia nitrogen. Dissolved oxygen was found to have a significant influence on M. ocellatus, G. mantschuricus, A. rivularis, Z. platypus, and O. bidens. Notably, for the two dominant species, C. auratus and P. parva, dissolved oxygen had a greater impact on P. parva compared to C. auratus.
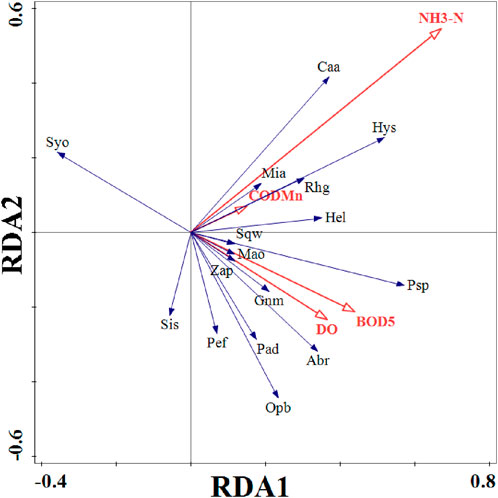
Figure 5. Redundancy analysis of fish community and environmental factors in the Daqing River. Caa, Carassius auratus; Mia, Misgurnus anguillicaudatus; Hys, Hypseleotris swinhonis; Rhg, Rhinogobius giurinus; Hel, Hemiculter leucisculus; Sqw, Squalidus wolterstorffi; Mao, Macropodus ocellatus; Psp, Pseudorasbora parva; Zap, Zacco platypus; Gnm, Gnathopogon mantschuricus; Abr, Abbottina rivularis; Pad, Paramisgurnus dabryanus; Opb, Opsariicjthys bidens; Pef, Pelteobagrus fulvidraco; Sis, Sinobdella sinensis; Syo, Synechogobius ommaturus.
Since the 1950s, numerous water conservancy projects have been constructed in the Daqing River water system. Currently, the system includes six large-scale hub projects: Zaolinzhuang Hub, Xingaifang Hub, Wangcun Gate, Duliu River Flood Reduction Gate Hub, Xihe Gate Hub, and Workers, Peasants and Soldiers Tide Gate. Additionally, there are seven large reservoirs and twelve medium-sized reservoirs within the basin, with a combined capacity of 4.15 billion m³ (Editorial Board of Water and Wastewater Monitoring and Analysis Methods of State Environmental Protection Administration, 2002). Beyond these major reservoirs, many small power stations and hydraulic facilities have been established on various tributaries. In recent years, urbanization in the Daqing River basin has surged, leading to the overexploitation of water resources. This overuse has caused severe ecological degradation, including the drying up of rivers and a sharp decline in groundwater levels. Consequently, the functionality of the water system has significantly diminished. Among the 67 water function areas in the Daqing River system, 19 have dried up, and only 14 meet the required standards, resulting in a compliance rate of just 20.9%. The ecological status of the river water has deteriorated markedly. A comparison of measured data from the past decade with the minimum ecological water volume specified in the Haihe River Basin Comprehensive Plan (2012–2030) (Haihe River Water Resources Commission of Ministry of Water Resources, 2009) reveals a significant shortfall. The Daqing River system requires an ecological water volume of 83 million m³, but the average measured volume over the past 10 years is only 45 million m³. This indicates that the current ecological water volume in the Daqing River system is insufficient, and the water required by Baiyangdian Lake is also inadequate.
4 Discussion
4.1 Current status of fish in the Daqing River
The Daqing River catchment area boasts a rich diversity of freshwater fish, with 8 orders, 17 families, 59 genera, and 78 species naturally distributed. Notably, the high classification levels, such as order and family, exhibit significant diversity. Specifically, the fish species in the Daqing River represent 47.06% and 36.17% of the Chinese classification at the order and family levels, respectively. Within the Cyprinidae family, which dominates the Daqing River and many other river catchment areas in China, there are 12 subfamilies in China and 9 in the Daqing River. However, some subfamilies like Schizothoracinae, Gobiobotinae, and Labeoninae are absent in the Daqing River due to their specific distributions and limited numbers. For instance, Schizothoracinae primarily inhabit the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, Gobiobotinae are predominantly warm-water fish, and Labeoninae are represented by only 15 species (Liu et al., 1981). Despite the high diversity at higher taxonomic levels, the fish diversity at the species level in the Daqing River catchment area remains relatively low, constituting only 5.73% of the total fish species diversity in China. Most species exhibit wide distributions, a key characteristic of fish diversity in the Daqing River. As a tributary of the Haihe River, the Daqing River holds a significant position within the entire Haihe River system. The Haihe River is home to 83 freshwater fish species (Xing et al., 2016), with the Daqing River hosting 78 species, representing 93.96% of the Haihe River’s fish diversity. This high representation underscores the importance of the Daqing River in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region and as one of the five major rivers in the Haihe River Basin (Sun et al., 2023; Chen et al., 2022). Consequently, the ecological status and threats faced by the Daqing River can serve as a microcosm reflecting the broader situation and challenges within the Haihe River Basin.
The Daqing River is home to a variety of endemic species, including Leptobotia flavolineata, which is exclusively found in the Juma River, and Triplophysa cuneicephala, an endemic species of the Haihe River Basin that also inhabits the Daqing River. Furthermore, the river hosts several Chinese endemic species such as Ponychostoma macrolepis and Leptobotia orientalis. Among the fish species in the Daqing River basin, only four are classified as threatened, with T. cuneicephala being categorized as critically endangered (CR), Anguilla japonica and L. flavolineata as endangered (EN), and P. macrolepis as vulnerable (VU) (Jiang et al., 2016). Interestingly, the endangered species make up just 5.13% of the total fish population in the basin, a figure significantly lower than the national average of 20.44% and the global average of 29% (Liang et al., 2016). This scarcity of rare endemic fish species stands out as a defining feature of the fish diversity in the Daqing River.
The fish community in Daqing River exhibits a predominance of omnivorous species, with carnivorous fish such as Culter erythropterus, P. fulvidraco, O. bidens, and S. sinensis following suit, and only one species of herbivorous fish present. This distribution can be attributed to the diverse food sources, broad ecological niche, and strong environmental adaptability of omnivorous fish. The carnivorous species primarily prey on small fish, shrimp, molluscs, and aquatic insects, indicating a lower trophic level within the fish community and a habitat more conducive to omnivorous species. Research has indicated that omnivorous fish constitute less than 20% of the community, while carnivorous fish make up over 45%, underscoring a poor community structure. Notably, 63.64% of omnivorous fish were observed in the Daqing River, further highlighting the community’s structural deficiencies (Karr, 1981; Karr et al., 1986). The phenomenon of fish miniaturization is prevalent in inland water bodies, with fish species attaining sexual maturity before the age of 2 years and reaching a maximum length of less than 24 cm classified as small fish (Zhang et al., 2016). In the Daqing River, the dominant species from 2018 to 2019, C. auratus and P. parva, fall under this category, indicating a trend towards miniaturization. This trend may be attributed to human encroachment on fish habitats and the impact of water pollution. Among these species, P. parva, as the dominant fish, possesses significant ecological advantages, including adaptability, high fecundity, and a broad diet. However, its competitive behavior, such as consuming fish eggs and disrupting spawning grounds, poses a substantial threat to the survival of indigenous fish species in the Daqing River. To address this challenge, regular monitoring of P. parva populations in affected river sections is recommended, with potential interventions to control their numbers if deemed necessary.
4.2 Changes in fish diversity in the Daqing River basin
In the survey of fish resources in Haihe River in 1979, Liu et al. (1981) identified 21 species of fish belonging to 5 orders and 6 families in Daqing River and Duliujian River. Li (1986) conducted research in Hebei Province and identified 54 fish species, including Myxocyprinus asiaticus and Ochetobius elongatus, which were believed to have been introduced from southern China. Yang et al. (2008) conducted three surveys of the Beijing section from the Juma River in 2004 and identified 24 fish species from 4 orders and 8 families. A more recent study by Xie and He, 2010 found a total of 24 fish species from 7 orders and 11 families in Baiyangdian between 2007 and 2009. The number of species investigated varied across different historical periods and catchment areas, providing valuable insights into the diversity and distribution of fish species in these regions.
In our field study of the Daqing River, a total of 33 species were identified as naturally distributed. Notably, Anguilliformes and Clupernorpha were absent in the current investigation. The undetected species primarily consisted of drifting egg fishes like Eloqjchthys bambusa and Acanthobrama simony, shellfish spawning fishes including seven species of Acheilognathus, and middle to lower layer or bottom-dwelling fishes such as Squaliobarbus curriculus, Hemibarbus maculatus, Xenocypris argentea, Pelteobagrus vachellii, and Cobitidae. Additionally, migratory or brackish water fishes like Colia ectenes were not observed. Regarding the feeding and habitat preferences of the fish species, the current composition mirrored historical records, with a ranking of omnivorous fishes, carnivorous fishes, herbivorous fishes, and bottom, middle, and upper layer fishes. However, there were notable declines in the proportions of certain species groups. The percentages of omnivorous fishes, carnivorous fishes, and herbivorous fishes decreased to 58.82%, 54.17%, and 66.67%, respectively. Similarly, the proportions of bottom-dwelling fishes, middle to lower layer fishes, middle to upper layer fishes, and upper layer fishes decreased to 37.50%, 55.00%, 55.56%, and 50.0%, respectively.
The diversity index (H′) and evenness index (J′) are important indicators for evaluating the stability of community structure (Xu et al., 2012). A higher species richness leads to a more evenly distributed number of individuals, resulting in a more stable community structure with greater diversity and evenness indices. Conversely, when species are under environmental stress, the community structure becomes unstable, leading to lower diversity indices. The diversity index was similar across regions, with the north branch of the upper reaches exhibiting the highest diversity and evenness, and the lowest richness. This suggests that the region had relatively rich species diversity with a uniform distribution of groups, without any dominant species. In contrast, the southern branch of the upper reaches had the lowest diversity and richness indices, but a relatively high level of uniformity. Although this region had more species, the population sizes between species were relatively small and uniform. Baiyangdian Lake showed the lowest uniformity index, but high diversity and richness indices. In comparison, the middle and lower reaches had the highest richness index, but relatively low diversity and evenness levels, indicating a high abundance of species with dominant groups present. For example, the relative abundance of C. auratus in Baiyangdian Lake was 32.8%, while in the middle and lower reaches, it reached 34.1%.
The integrity of the original fish fauna in the Daqing River has been compromised, as evidenced by the Shannon-Wiener diversity index (H′), Margalef richness index (D), and Pielou evenness index (J′) of fish communities, indicating a certain level of pollution in the water environment (Sun, 2017). There is a clear trend of fragmentation observed in the fish communities of the Daqing River, highlighting the impact of pollution on the ecosystem.
4.3 Effects of various environmental influencing factors on fish community structure in Daqing River
The spatial pattern of fish communities is influenced not only by their own living habits but also by the spatial heterogeneity of environmental factors, which vary depending on the characteristics of the water environment. Ammonia nitrogen is a crucial environmental factor that impacts fish diversity, with high concentrations of ammonia nitrogen inhibiting fish growth, posing health risks, and potentially leading to mortality (Sun et al., 2012; Schram et al., 2014). Species such as C. auratus, H. swinhonis, R. giurinus, M. anguillicaudats, and P. parva have been observed to increase with rising levels of ammonia nitrogen. This increase can be attributed to the tolerance exhibited by M. anguillicaudats, P. parva, and H. swinhonis, with the enhanced tolerance of these fish serving as an indicator of deteriorating water quality (Schleiger, 2000).
In addition, Kadye et al. (2008) demonstrated that dissolved oxygen plays a significant role in shaping river fish communities. Dissolved oxygen exerts a greater influence on P. parva compared to C. auratus. This discrepancy may be due to the distinct habitat preferences of the two species; C. auratus typically resides at the bottom of the water column with a lower oxygen demand, while P. parva inhabits the middle to lower layers where oxygen levels are relatively higher. Studies have indicated that the dissolved oxygen concentration at the ventricular point of C. auratus ranges from 0.10 to 0.15 mg/L, highlighting its strong tolerance to hypoxia (Abdel-Tawwab et al., 2019). Additionally, the Redundancy Analysis (RDA) revealed a strong correlation between dissolved oxygen and species such as M. ocellatus and O. bidens, aligning with the high oxygen consumption rates typically observed in carnivorous fish.
The community structure and diversity of fish are influenced not only by water quality but also by the construction of water infrastructure. In the Daqing River system, the shortage of ecological water is a primary factor affecting fish biodiversity and contributing to the decline in species diversity. Onychostoma macrolepis, the only Cyprinidae subfamily species distributed north of the Yangtze River, is primarily found in the Juma River within the Daqing River system, marking the northernmost limit of its distribution. However, the continuous decrease in water quantity has led to the disconnection of caves and rivers, resulting in the disappearance of many suitable habitats. Consequently, O. macrolepis has nearly vanished from the Daqing River. Historically, Anguilla japonica was a relatively common species in the Daqing River basin (Li, 1989). The construction of sluice gates and reservoirs, however, has blocked the migration channels between rivers and seas. As a result, Anguilla japonica has almost completely disappeared from the Daqing River. The completion of reservoirs has significantly altered the hydrological conditions, shifting the fish species composition from “river facies” to “lake facies.” Fish species adapted to sediment environments, such as those thriving in benthic jet streams and gravel, have been gradually replaced by species suited to slow-flowing or still water environments, including Cyprinus carpio, C. auratus, and Gobio rivuloides.
5 Conclusion
In this study, a total of 85 fish species belonging to 10 orders, 20 families, and 64 genera were identified in the Daqing River, enriching the existing species composition and providing essential data for both the utilization and conservation of fish resources in the area. The spatial distribution of fish in the Daqing River exhibited regional variations. The southern branch of the upper reaches was characterized by the dominance of A. rivularis and P. parva, while the northern branch of the upper reaches featured P. parva, C. auratus, and Z. platypus as the dominant species. In Baiyangdian Lake and the middle to lower reaches, C. auratus, S. ommaturus, and P. parva were the prevailing species, offering insights that could inform ecological restoration efforts and water management initiatives in the Daqing River. Analysis of the dominant species within the fish community revealed a prevalence of small fish species with high pollution tolerance, particularly P. parva and C. auratus, indicating a certain level of disturbance in the fish community structure. Redundancy analysis highlighted ammonia nitrogen as the primary environmental factor influencing fish distribution in the Daqing River. Given that the Daqing River serves as a crucial component of the Haihe River system, it is recommended that biodiversity conservation efforts in the basin be intensified in alignment with the water ecological conditions of the Daqing River. Given the current state of fish diversity in the Daqing River, various positive measures are strongly recommended to address the decline. Enforcing strict fishing regulations is crucial. Additionally, strategies such as improving water quality, maintaining ecological discharge, restoring river connectivity, and preventing biological invasions are essential. By effectively implementing these measures and protecting fish habitats, fish diversity in the area can be enhanced and maintained.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
XZ: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. YL: Supervision, Writing–original draft. JH: Methodology, Writing–original draft. YH: Visualization, Writing–original draft. FW: Investigation, Writing–original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was partially granted by the Water ecological monitoring project in Baiyangdian Basin (ZC-467004-2024003) and Construction and operation of the national ecological environment monitoring network (102144220490020009010).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fenvs.2024.1450903/full#supplementary-material
SUPPLEMENTARY TABLE S1 | Fish species list for the Daqing River system.
References
Abdel-Tawwab, M., Monier, M. N., Hoseinifar, S. H., and Faggio, C. (2019). Fish response to hypoxia stress: growth, physiological, and immunological biomarkers. Fish Physiology Biochem. 45 (3), 997–1013. doi:10.1007/s10695-019-00614-9
Alkins-koom (2000). Reproductive timing of fishes in a tropical intermittent stream. Environ. Biol. Fishes 57 (1), 49–66. doi:10.1023/a:1007566609881
Cao, Y. P., Wang, W., and Zhang, Y. B. (2003). Present situation of fish stocks in Baiyangdian Lake. Chin. J. Zoology (3), 66–70. doi:10.13859/j.cjz
Chen, L., Yang, M. X., Liu, Y., and Nan, L. J. (2022). Early warning and joint regulation of water quantity and quality in the daqing River Basin. Water 14, 3068. doi:10.3390/w14193068
Chu, X. L., Zheng, B. S., and Dai, D. (1999). Fauna sinica(osteichthyes): Siluriformes. Beijing: Science Press.
Committee of Tianjin Chorography Compilation (2005). General annals of tianjin:water conservancy Records. Tianjin: Tianjin Academy of social Sciences. Press.
Cui, H., Xiao, W., Zhou, Y., Hou, B., Lu, F., and Pei, M. (2019). Spatial and temporal variations in vegetation cover and responses to climatic variables in the Daqing River basin, North China. J. Coast Res. 93 (sp1), 450–459. doi:10.2112/si93-059.1
Editorial Board of Water and Wastewater Monitoring and Analysis Methods of State Environmental Protection Administration (2002). Analytical methods for water and wastewater monitoring. 4th edition. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press.
Gemes, M. C., Haedrich, R. L., and Villagarcia, M. G. (1995). Spatial and temporal changes in the groundfish assemblages on the north-east Newfoundland/Labrador Shelf, north-west Atlantic, 1978–1991. Fish. Oceanogr. 4 (2), 85–101. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2419.1995.tb00065.x
Haihe River Water Resources Commission of Ministry of Water Resources. (2009). The integrated planning and special research.
Han, Q., Tong, R., Sun, W., Zhao, Y., Yu, J., Wang, G., et al. (2020). Anthropogenic influences on the water quality of the Baiyangdian Lake in North China over the last decade. Sci. Total Environ. 701, 134929. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134929
Han, X. F., Wang, S. A., and Cao, Y. P. (1991). Ecological analysis of fish composition in Baiyangdian Lake after recharge. Fish. Hebei 12 (6), 8–11.
Jiang, Z. G., Jiang, J. P., Wang, Y. Z., Zhang, E., Zhang, Y. Y., and Li, L. L. (2016). Red list of China's vertebrates. Biodivers. Sci. 24, 500–551. doi:10.17520/biods.2016076
Kadye, W. T., Magadza, C. H. D., Moyo, N. A. G., and Kativu, S. (2008). Stream fish assemblages in relation to environmental factors on a montane plateau (Nyika Plateau, Malawi). Environ. Biol. Fishes 83 (4), 417–428. doi:10.1007/s10641-008-9364-4
Karr, J. R. (1981). Assessment of biotic integrity using fish communities. Fisheries 6 (6), 21–27. doi:10.1577/1548-8446(1981)006<0021:aobiuf>2.0.co;2
Karr, J. R., Fausch, K. D., and Angermeier, P. L. (1986). Assessing biological integrity in running waters: a method and its rationale. Ill. Nat. Hist. Surv. (Suppl. 5), 1–28.
Li, G. L. (1986). Discussion on freshwater fish fauna in Hebei Province. Chin. J. Zoology (4), 4–9. doi:10.13859/j.cjz.1986.04.00
Li, G. L. (1989). Preliminary study on geographical division of freshwater fishes in Hebei Province. Chin. J. Zoology (5), 13–16. doi:10.13859/j.cjz.1989.05.006
Liang, C., Zhang, E., Zang, C., and Cao, W. (2016). Evaluating the status of China's continental fish and analyzing their causes of endangerment through the red list assessment. Biodivers. Sci. 24 (5), 598–609. doi:10.17520/biods.2015331
Linde-Arias, A. R., Incaio, A. F., Novo, L. A., de Alburquerque, C., and Moreira, J. C. (2008). Multibiomarker approach in fish to assess the impact of pollution in a large Brazilian river, Paraiba do Sul. Environ. Pollut. 156, 974–979. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2008.05.006
Liu, K. (2009). Study on hydrological characteristics evolution and ecological response of wetlands in the lower reaches of Daqing River. Beijing: Capital Normal University.
Liu, W. J., and Zhao, W. J. (2012). Analysis on the influence of hydrological characteristics change of daqing River Basin on baiyangdian wetland. Ground water 34 (6), 101–102. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1004-1184.2012.06.038
Liu, X. Y., Wang, C. L., Yang, Z. F., and Li, G. L. (1981). Investigation of fish resources in Haihe River system freshwater fisheries, 2, 36–43.
Pielou, E. C. (1966). The measurement of diversity in different types of biological collections. J. Theor. Biol. 13, 131–144. doi:10.1016/0022-5193(66)90013-0
Qiu, L., and Zhang, Y. (2018). “Discussion on river regulation and rectification of Daqing River system based on xiong'an New area,” in Shanxi Agric. Econ. doi:10.16675/j.cnki.cn14-1065/f.2018.12.046
Richter, B. D., Baumgartner, J. V., Powell, J., and Braun, D. P. (1996). A method for assessing hydrologic alteration within ecosystems. Conserv. Biol. 10 (4), 1163–1174. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1739.1996.10041163.x
Schleiger, S. L. (2000). Use of an index of biotic integrity to detect effects of land uses on stream fish communities in west-central Georgia. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 129 (5), 1118–1133. doi:10.1577/1548-8659(2000)129<1118:uoaiob>2.0.co;2
Schram, E., Roques, J. A., Abbink, W., van de Heul, J., de Vries, P., and Bierman, S. (2014). The impact of elevated water ammonia and nitrate concentrations on physiology, growth and feed intake of pikeperch (Sander lucioperca). Aquaculture 420-421, 95–104. doi:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2013.10.027
Shannon, C. E. (1966). A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 27 (13), 379–423. doi:10.1002/j.1538-7305.1948.tb01338.x
Sun, H. J., Li, K., Chen, Y. F., Yang, Z., and Montagnes, D. J. (2012). Combined effects of ammonia and microcystin on survival, growth, antioxidant responses, and lipid peroxidation of bighead carp Hypophthalmythys nobilis larvae. J. Hazard. Mater. 221-222, 213–219. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.04.036
Sun, L., Shu, C., Ding, L., Tian, Z., and Liu, H. (2023). Zoning method of aquatic ecosystem functional management fourth-level region in the Daqing River Basin, China. J. Environ. Manag. 327, 116870. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.116870
Sun, X. (2017). The study on fish species diversity and analysis of influencing factors of Muling River watershed. Harbin: Northeast Forestry University.
Tzeng, W., Wang, Y., and Chang, C. (2002). Spatial and temporal variations of the estuarine larval fish community on the west coast of Taiwan. Mar. Freshw. Res. 53 (2), 419–430. doi:10.1071/mf01136
Ulanowicz, R. E. (2001). Information theory in ecology. Comput. and Chem. 25 (4), 393–399. doi:10.1016/s0097-8485(01)00073-0
Wang, K. (2019). Analysis on the change of water system connectivity in Daqing River Basin from 1980 to 2017. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University.
Wang, S. A., and Gu, J. L. (1981). Effects of environmental changes on fish composition and ecology in Baiyangdian Lake. J. zoology (4), 10–13. doi:10.13859/j.cjz.1981.04.004
Wang, S. A., Wang, Z. M., and Li, G. L. (2001). Animal of hebei:fishes. Shijiazhuang: Hebei Science and Technology Press.
Wu, H. L., and Zhong, J. S. (2008). Fauna sinica:Osteichthyes,Perciformes.V.gobioidei. Beijing: Science Press.
Xie, R., Zhao, G., Yang, J., Wang, Z., Xu, Y., Zhang, X., et al. (2021). eDNA metabarcoding revealed differential structures of aquatic communities in a dynamic freshwater ecosystem shaped by habitat heterogeneity. Environ. Res. 201, 1111602. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2021.111602
Xie, S., and He, H. D. (2010). Present condition analysis of Hebei Baiyangdian lake fish stocks after diversion from Yellow River to the lake. Sci. and Technol. Inf. (9), 439–497.
Xing, Y. C., Zhang, C. G., Fan, E. Y., and Zhao, Y. H. (2016). Freshwater fishes of China: species richness, endemism, threatened species and conservation. Divers. and Distributions 22 (3), 358–370. doi:10.1111/ddi.12399
Xu, K. D., Zhang, H. L., and Xie, H. Y. (2012). Resource density and community diversity of crustaceans in the waters of Zhongjieshan Islands. Mar. Fish. 34 (3), 308–315. doi:10.1007/s11783-011-0280-z
Yang, W. B., Li, J. L., and Li, X. X. (2008). Fish composition and species biodiversity of the Beijing section ofJuma River. J. Shanghai Fish. Univ. 17 (2), 175–181. doi:10.3724/SP.J.1035.2008.00038
Ye, L. Y., Liu, P., Huang, J. X., Liu, D. D., Li, C. Z., and Chen, L. (2020). Estimation of water consumption characteristics of typical ecosystems in the Daqing River basin using WAVES model. China Rural. Water Hydropower 8, 35–39.
Zhang, C. G., and Zhao, Y. H. (2013). Fishes in Beijing and adjacent areas. China.Beijing: Science Press.
Zhang, C. G., and Zhao, Y. H. (2016). Species diversity and distribution of inland fishes in. China.Beijing: Science Press.
Zhang, W. J. (2019). “The change of daqing River Water conservancy project and its impact on the construction of xiongan New area,” in Baoding. Hibei: Hebei Agricultural University.
Zhang, X. K., Yu, D. P., and Wang, H. L. (2016). Fish community structure in main habitat of the finless porpoise, the Anqing section of Yangtze River. Acta Ecol. Sin. 36 (7), 1832–1839.
Zhao, C. L., Xiao, G. H., and Luo, N. T. (2007). Analysis on current fish composition in Baiyangdian Lake. Hebei Fish. (11), 49–50.
Zheng, B. S., Fan, Q. D., and Dai, D. Y. (1960). Fish in Baiyangdian Lake. Tianjin: Hebei People’s publishing house.
Keywords: native fish, river basin, environmental influencing factors, biodiversity, fauna
Citation: Zhou X, Li Y, He J, Hou Y and Wang F (2024) The native fish diversity with environmental influencing factors in the Daqing River basin, China. Front. Environ. Sci. 12:1450903. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2024.1450903
Received: 18 June 2024; Accepted: 06 September 2024;
Published: 23 September 2024.
Edited by:
Shuping Wang, Chinese Research Academy of Environmental Sciences, ChinaReviewed by:
Guochen Zheng, Hebei University of Environmental Engineering, ChinaWenbin Liu, Tianjin Normal University, China
Xinyu Jiang, Henan Normal University, China
Copyright © 2024 Zhou, Li, He, Hou and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xushen Zhou, am5zc3picEAxNjMuY29t
 Xushen Zhou
Xushen Zhou Yanqing Li
Yanqing Li Jianwu He1
Jianwu He1