- School of Surveying and Testing, Shaanxi Railway Institute, Weinan, Shaanxi, China
Water transparency, as indicated by the Secchi disk depth (Zsd), is a key parameter for assessing the quality of aquatic environments, reflecting the ability of light to penetrate through the water column. In the Tibetan Plateau (TP), where lakes are abundant yet remote and challenging to access, remote sensing techniques offer a promising approach for monitoring Zsd over large spatial scales. In this study, we used the semianalytical -based Zsd algorithm to study the temporal and spatial dynamics of water transparency over TP during the period from 2003 to 2022. The results show that the 173 lakes have a mean value of Zsd is 3.64 ± 2.4 m for long term, and generally with the significantly increasing change trends in the past 20 years. In the central Tibetan Plateau (CTP) region, lake transparency showed a positive correlation with lake surface temperature (r = 0.73) and a negative correlation with precipitation (r = −0.54), highlighting the region’s heightened sensitivity to meteorological changes compared to other areas. The spike in water clarity observed in the CTP region may be linked to alterations in lake hydrodynamics driven by the extremely climate events (i.e., El Niño). These results indicated the importance of considering regional climatic factors when interpreting fluctuations in water transparency.
1 Introduction
The Tibetan Plateau (TP), often referred to as the “Third Pole” of the world, is notable for its significant ecological value, with numerous lakes distributed across the region, covering a total area of ∼47,000 km2 (Zhang et al., 2014). As one of the most climate-sensitive regions, the Tibetan Plateau has experienced significant regional environmental and climatic changes, including persistent warming (Gao et al., 2015), increased precipitation (Rangwala et al., 2009), and decreased wind speed (Yang et al., 2011). These changes have the potential to alter the aquatic environment and water quality of high-altitude lakes. Consequently, long-term assessments of water quality changes are a crucial approach for exploring how lakes respond to climate change. Investigations into how water quality responds to climate change have profound implications for both lake ecology and climate science.
Secchi disk depth (Zsd) records the ability of light to penetrate through water and is one of the important parameters for measuring water quality. It is closely related to the content of dissolved, particulate matter and phytoplankton in water (Lee et al., 2015) widely used to study the spatial-temporal changes in the underwater light environment and phytoplankton content in water bodies (Carlson, 1977; Lee et al., 2015). It is considered to be a good indicator of the health of lake ecosystems (Cuffney et al., 2000; Shang et al., 2016). Typically, the Secchi disk is widely used as the primary method for measuring transparency. However, most lakes in the Tibetan Plateau are located in sparsely populated and cold high altitude areas, and the cost of in-situ measurement of water transparency in such harsh environments is prohibitive.
Remote sensing techniques can provide data for observing Zsd at a large spatial scale. Commonly used satellite for monitoring water quality parameters include the Sea-Viewing Wide Field-of-View Sensor (SeaWiFS), Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS), and the Landsat satellite series. Due to the wide coverage and high revisit frequency of MODIS data, it can provide daily Earth observation data, and thus has been widely applied in spatiotemporal monitoring studies of various water quality parameters (Shang et al., 2016; Shi et al., 2018; Wu et al., 2008). To date, various Zsd retrieval models have been proposed for water quality monitoring. For example, many scholars have developed empirical algorithms to estimate Zsd by exploring the correlation between radiometric information of satellite imagery such as apparent reflectance and surface reflectance and measured Zsd data (Duan et al., 2009; Olmanson et al., 2008; Ren et al., 2018; Shi et al., 2018; Yu et al., 2014). Lee et al. (2015) proposed a new Zsd retrieval algorithm based on the new underwater visibility theory. This new Zsd inversion model has been widely assessed using in situ measurements and successfully applied to analyze water transparency changes over time in the TP region (Liu et al., 2021). However, remote sensing studies on water transparency in the lakes of the TP have mainly focused on spatiotemporal variation characteristics, leaving the response of these lakes to extreme climate changes largely unexplored. Given the necessity to comprehensively investigate the long-term spatiotemporal evolution patterns of Zsd in the TP region and its responses to climate change, this study aims to document these evolution patterns in TP lakes from 2003 to 2022 using MODIS data and mechanism-based Zsd retrieval algorithms, and to explore how water quality has responded to the extreme climate conditions (i.e., El Niño).
2 Dataset and method
2.1 Study area
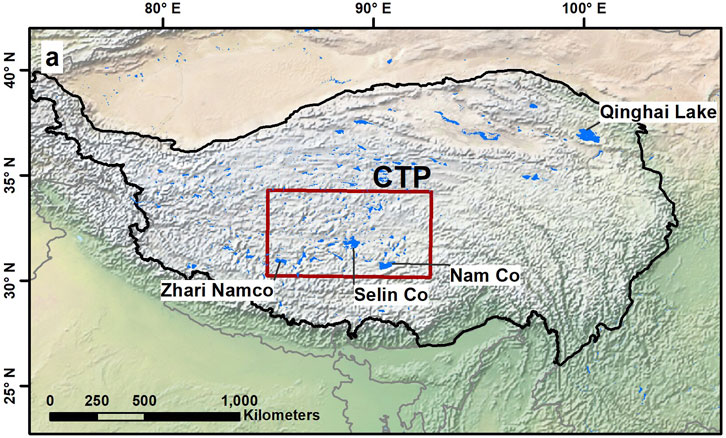
The Tibetan Plateau, often referred to as the “Roof of the World,” is a vast high-altitude plateau situated in central Asia. With the highest average elevation globally, it spans across southwestern China (26°00′N - 39°47′N, 73°19′E − 104°47′E), covering an approximate area of 2.9 million square kilometers (Figure 1). Characterized by its unique geography and challenging climatic conditions, the TP features a myriad of lakes, each manifesting distinctive attributes shaped by the plateau’s complex terrain and climate. Notable among these lakes are Qinghai Lake, Nam Co, and Selin Co, prominent large bodies of water that play a crucial role in the broader context of global climate change, water resource dynamics, and ecosystem evolution.
The Central Region of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau (CTP), encompassing 30°N to 34°N and 85°E to 92°E, represents a vital segment of the plateau, distinguished by its diverse and unique topography. The CTP is notably sensitive to climate fluctuations, making it a critical area for studying environmental and climatic changes (Lei et al., 2019). This sensitivity provides an invaluable opportunity to examine the impacts of these changes on local ecosystems and water bodies.
2.2 Satellite imagery
Rrs products from MODIS Aqua were used in this study to obtain Zsd properties and that of spatial-temporal variation over research area. Aqua satellite mainly carried on the MODIS ocean color bands (i.e., Band 8–16), which also can be applied to inland water color research. Specifically, the level-2 Rrs products in the period of 2003–2022 were acquired from NASA’s Ocean Color Web (https://oceancolor.gsfc.nasa.gov). The standard level-2 Rrs products were generated using the NIR-based atmospheric correction method, with detailed description on the Web Book (https://www.oceanopticsbook.info/view/introduction/overview). Since the accuracy of MODIS observation is frequently affected by unfavorable observation conditions, such as clouds, straylight and pixel noise, quality control flags (i.e., l2_flags) were applied to mask the problematic pixels.
2.3 Environmental dataset
Data related to perception were acquired from the NASA Giovanni website (https://giovanni.gsfc.nasa.gov/giovanni/). We obtained the Multi-satellitE Retrievals for Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) (IMERG) products, which provide the global surface precipitation rates at a high resolution of 0.1° every half-hour beginning 2000. Lake surface temperature (LST) data were derived from the MODIS Aqua Level-3 daily product for water surface temperature (https://oceancolor.gsfc.nasa.gov/), with a spatial resolution of 4 km. This dataset was produced by combining remote sensing and measured data, and it has been widely used on the inland lakes variation studies (O’Reilly et al., 2015; Schneider and Hook, 2010). For this study, spatial resolution of temperature and precipitation data of the lake watersheds were resampled to 0.1°.
2.4 Water transparency model
In order to accurately obtain the transparency of different types of water bodies, a semi-analytical method was used to calculate the Zsd. The approach represents an advancement of the Zsd methodology initially proposed by Lee et al. (2015), building upon the quasi-analytical algorithm (QAA) (Lee et al., 2002). The method has been validated by related studies using in situ measurements, proving its suitability for accurately estimating water transparency in the TP region (Liu et al., 2021). Therefore, we can accurately estimate the water transparency for the TP lakes using the semi-analytical method.
It encompasses three primary procedural steps. Initially, the QAA_v6 algorithm is employed to extract absorption (a) and backscattering (bb) coefficients from Rrs at various wavelengths. In QAA_v6, the choice of the reference band depends on the value of Rrs (667); if rrs (667) is less than 0.0015sr−1, 555 nm is utilized as the reference band, otherwise, the reference band shifts to 670 nm. Subsequently, the diffuse attenuation coefficient (kd) is estimated from a and bb using the Equation 1 (Lee et al., 2013):
where
Finally, the Zsd is estimated from
where
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Spatial and temporal dynamics of water transparency
Figure 2A showed the spatial distribution of the long-term annual mean (2003–2022) Zsd for TP region, totally 173 lakes. The Zsd values differed greatly among lakes, where the lowest values is 0.18 (MargogCaka, 87.01°E, 33.86°N), and the highest values is 12.1 (Mucuobingni Lake). The mean of water transparency over TP region is 3.64 ± 2.4 m, which is similarly with the Landsat-based mean Zsd retrievals by Song et al. (2020) (mean Zsd = 4.21m, median Zsd = 3.54 m). According to the subpanel, 28.3% of lakes have mean water transparency lower than 2m, with 13.4% of total lake areas. And 10.4% of lakes showed the Zsd values of higher than 7m, with the approximately 1/5 of the lake areas over TP. Note that the largest proportion of the lake areas is the Zsd values between 5 and 7m, with around 38.1%. The lower values of Zsd retrievals generally exhibited in the lakes with small areas, such as MargogCaka, and Rola Co. On the contrast, the large lakes showed the higher water transparency values easily.
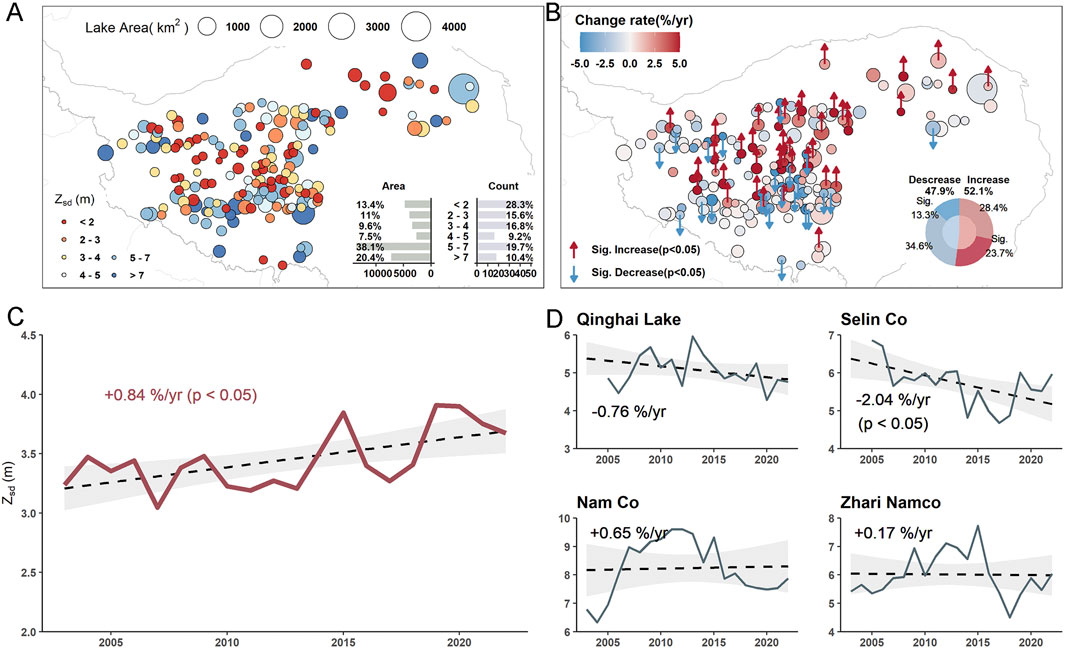
Figure 2. (A) Distributions of long-tern annual mean Zsd covering TP over 2003 to 2022 period. The subplot indicated the count and lake area for different Zsd level. (B) Distributions of interannual Zsd trend covering the TP. Lakes with a statistically significant increasing and decreasing trend at a significance level of 0.05 were annotated with “↑” and “↓”, respectively. The subplot represented the preparation of significant increasing and decreasing, as well as non-significant increasing and decreasing. (C) Interannual variability and trends of TP Zsd between 2003 and 2022. (D) Interannual variability and trends of Zsd for the top four largest lake covering TP are as follows: Qinghai Lake, Selin Co, Nam Co, and Zhari Namco.
Figure 2B demonstrated the interannual Zsd trend and significance over TP region. In terms of statistics, the number of lakes that lied into ranges of <0%/yr and >0%/yr accounted for 47.9% and 52.1%, which represented the decrease and increase trend. An analysis of trend significance showed that 13.3% and 23.7% of lakes experienced statistically significant (p < 0.05) decreasing and increasing trends, respectively. Spatially, the lakes located in the northern part generally dominated by the increasing trend. The total trend of the water transparency during the period between 2003 and 2022 over TP area showed the significance increasing trend, with the 0.84%/yr (see Figure 2C). It is note that there were two peaks appeared around 2015 and 2022, with the Zsd values of 4.09 m and 4.23 m, respectively. Specifically, for the top four largest lakes, only Selin Co dominated by the significance decreasing trend (−2.04%/yr) (Figure 2D). While other three lakes showed the slightly fluctuation trend (p > 0.05).
3.2 Correlation analysis of lake clarity and meteorological factors
Research indicated that lakes in the central region of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau (CTP, 30–34°N, 85–92°E, geographical location is shown in Figure 1) are more sensitive to the climate change than other regions of the plateau (Lei et al., 2019). Therefore, we conducted a correlation analysis of Zsd variations with meteorological data (including lake surface temperature and precipitation) separately for the CTP region and other regions of the plateau (non-CTP) (Figures 3A–D). Analysis of the correlation between lake clarity and meteorological parameters showed that lake surface temperature had a relatively remarkable impact on the clarity of lakes. This was illustrated by the finding: the clarity was mainly positively correlated with the LST both in CTP (r = 0.73, p < 0.01) and Non-CTP (r = 0.61, p < 0.05) regions. Therefore, from our analysis we concluded that the water transparency on the TP is linked with LST. The increase of lake surface temperature may reduce the vertical mixing ability of the water body (Carey et al., 2012), thereby enhancing the internal stability of the lake and maintaining the water clarity. The result of the correlation analysis between the Zsd retrievals and precipitation revealed a negative relationship in the CTP region (r = −0.54, p < 0.05). This may be attributed to increased runoff during precipitation events, which introduces more sediments and nutrients into the lakes, as well as enhanced mixing of the water column, both of which contribute to reduced water clarity. The similar correlation between precipitation and water clarity also existed in TP and other regions (Liu et al., 2021; Pilla et al., 2018; Rose et al., 2017). However, in the Non-CTP region, the correlation between Zsd and precipitation was weaker. This suggested that water transparency in the Non-CTP region might be less influenced by rainfall, whereas lakes in the CTP region demonstrated greater sensitivity to changes in meteorological conditions. Furthermore, other factors, such as lake expansion, could probably influence Zsd.
3.3 Speculation on the anomalous fluctuations in water transparency in 2015 for TP
In 2015, there was an anomalous peak in the water transparency of lakes in TP region, as shown in particular in Figure 2C. By analyzing the changes in water transparency in different regions (see Figure 3E), we found that lakes in the central region of the TP had anomalous transparency in 2015, while lakes in other regions generally maintained stable transparency levels. Therefore, the anomalous peak of water transparency in TP region in 2015 was mainly caused by the exceptional transparency of lakes in the central region. In 2015, several typical lakes in the CTP also showed similar anomalous peaks in water transparency (Figure 3E), including Nam Co, Zhari Namco, Dazeg Co, Bam Co, Pung Co, and Dawa Co.
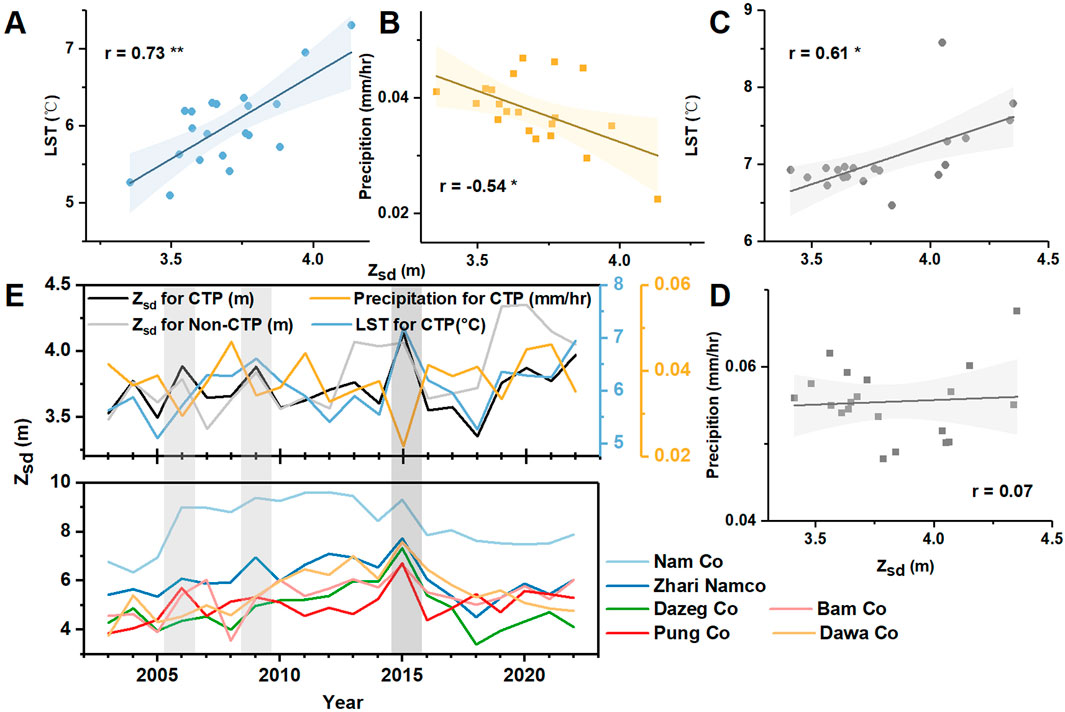
Figure 3. (A, B) Correlationship between annually mean Zsd and lake surface temperature and precipitation over CTP region, respectively. (C, D) Correlationship between annually mean Zsd and lake surface temperature and precipitation over Non-CTP regions, respectively. (E) Time series of the annually mean Zsd retrievals for CTP and Non-CTP, and the precipitation and lake surface temperature. Also, annually mean Zsd values were presented for typical lakes in CTP, including Nam Co, Zhari Namco, Dazeg Co, Bam Co, Pung Co, and Dawa Co. Note that statistically significant correlations at a significance level of 0.05 and 0.01 were annotated with “*” and “**”, respectively. The grey stripes indicate El Niño years.
Due to the sensitivity of water clarity of the CTP region to meteorological changes, including lake surface temperature and precipitation (Figures 3A, B), we speculated that the sharp increase in Zsd observed in 2015 might be linked to global extreme climate events (Zhang et al., 2020). In 2015/2016, the world experienced one of the strongest El Niño events on record, with significant impacts on global climate (Wang et al., 2017; Xue and Kumar, 2017). The El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO) is the primary mode of interannual climate variability in the tropical Pacific Ocean, characterized by periodic warming (El Niño) and cooling (La Niña) of sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern equatorial Pacific (Nicholls, 2015).
During strong El Niño events, the presence of anomalous meridional dry advection over the western TP and the intensification of the Indian-Myanmar monsoon trough lead to a weakening of the Indian summer monsoon dynamic system. This weakening reduced the moisture transport dynamics eastward and southward across the TP, resulting in decreased humidity and reduced precipitation in the region (Hu et al., 2021). In 2015, during the El Niño period, the precipitation in the CTP area decreased by 35% compared to previous years (Lei et al., 2019). Due to the reduced precipitation and global temperature increase, the lake surface temperature in the CTP region was higher than usual (Figure 3E). During strong El Niño events, the anomalous increase in lake surface temperature at the CTP during strong El Niño events leaded to greater vertical temperature differences, which in turn leaded to increased density contrasts between the upper and lower water column. As the temperature of the overlying water body increases, its density decreases, causing it to stably float above the denser water below (Bonan, 1995). Therefore, the increased vertical temperature difference in the CTP lake hydrological system leaded to a larger density difference between the upper and lower water bodies, promoting the formation of thermal stratification within the lake system and stabilizing the internal structure of the lake. This stability reduces the redistribution of substances within the lake due to vertical disturbances, thereby increasing the transparency of the lake water and consequently increasing the water transparency. Additionally, the weakening of the Indian summer monsoon dynamic system during El Niño periods further decreased the likelihood of vertical disturbances caused by wind-induced lake motion (Monismith and MacIntyre, 2009), and stabilizing the internal hydrological system of the lake and increasing water transparency. Additionally, during periods of historically lower El Niño intensity, such as in 2006 and 2009, a slight increase in Zsd was observed in the CTP region, which coincided with rising LST and reduced precipitation (Figure 3E).
4 Conclusion
This study investigated the spatiotemporal dynamics of water transparency in the TP region and its response to global climate change. The spatial distribution of lake Zsd varied markedly across the TP, with most lakes exhibiting Zsd values between 5 and 10 m. The mean Zsd of the 173 lakes significantly increased at a rate of 0.84%/yr (p < 0.05) from 2002 to 2022. In the CTP region, there was a positive correlation between lake transparency and lake surface temperature (r = 0.73) and a negative correlation between transparency and precipitation (r = −0.54). The CTP area exhibited greater sensitivity to meteorological changes in terms of water transparency compared to other regions. Notably, the anomalous spike in water clarity observed in the CTP area in 2015 may be related to changes in the lake hydrodynamic system driven by strong El Niño events. Furthermore, during periods of historically lower El Niño intensity, such as in 2006 and 2009, a slight increase in Zsd was observed in the CTP region, which coincided with rising LST and reduced precipitation. These findings emphasized the importance of considering regional climatic factors (e.g., El Niño) when understanding anomalous fluctuations in water transparency.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
WL: Writing–original draft, Validation, Software, Resources, Methodology, Data curation, Conceptualization. HX: Writing–review and editing, Supervision, Project administration, Investigation, Funding acquisition. GH: Writing–review and editing, Visualization, Investigation, Formal Analysis.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the financial support for this study was jointly provided by 2023 Youth Innovation Team Scientific Research Program of Shaanxi Provincial Department of Education (23JP027), the Scientific Research Foundation Project of Shaanxi Railway Institute (KY2022-03), the Young and Middle-aged Talents in Technological Innovation of Shaanxi Railway Institute (KJRC202105), and the Practical Project of Shaanxi Railway Institute (SYX2022-02).
Acknowledgments
We thank NASA for providing global MODIS Aqua Level-2 data (via https://oceancolor.gsfc.nasa.gov/), and environmental data include lake surface temperature data (MODIS Aqua Level-3 products, https://oceancolor.gsfc.nasa.gov/) and perception data (https://giovanni.gsfc.nasa.gov/giovanni/) provided by NASA. We also thank the reviewers for providing comments and suggestions to improve the writing.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Blackwell, H. R. (1946). Contrast thresholds of the human eye. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 36, 624–643. doi:10.1364/JOSA.36.000624
Bonan, G. B. (1995). Sensitivity of a GCM simulation to inclusion of inland water surfaces. J. Clim. 8, 2691–2704. doi:10.1175/1520-0442(1995)008<2691:SOAGST>2.0.CO;2
Carey, C. C., Ibelings, B. W., Hoffmann, E. P., Hamilton, D. P., and Brookes, J. D. (2012). Eco-physiological adaptations that favour freshwater cyanobacteria in a changing climate. Water Qual. Manag. 46, 1394–1407. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2011.12.016
Carlson, R. E. (1977). A trophic state index for lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 22, 361–369. doi:10.4319/lo.1977.22.2.0361
Cuffney, T. F., Meador, M. R., Porter, S. D., and Gurtz, M. E. (2000). Responses of physical, chemical, and biological indicators of water quality to a gradient of agricultural land use in the yakima river basin, Washington. Environ. Monit. Assess. 64, 259–270. doi:10.1023/A:1006473106407
Duan, H., Ma, R., Zhang, Y., and Zhang, B. (2009). Remote-sensing assessment of regional inland lake water clarity in northeast China. Limnology 10, 135–141. doi:10.1007/s10201-009-0263-y
Gao, Y., Li, X., Ruby Leung, L., Chen, D., and Xu, J. (2015). Aridity changes in the Tibetan Plateau in a warming climate. Environ. Res. Lett. 10, 034013. doi:10.1088/1748-9326/10/3/034013
Hu, S., Zhou, T., and Wu, B. (2021). Impact of developing ENSO on Tibetan plateau summer rainfall. J. Clim. 34, 3385–3400. doi:10.1175/JCLI-D-20-0612.1
Lee, Z., Carder, K. L., and Arnone, R. A. (2002). Deriving inherent optical properties from water color: a multiband quasi-analytical algorithm for optically deep waters. Appl. Opt. 41, 5755–5772. doi:10.1364/AO.41.005755
Lee, Z., Hu, C., Shang, S., Du, K., Lewis, M., Arnone, R., et al. (2013). Penetration of UV-visible solar radiation in the global oceans: insights from ocean color remote sensing. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 118, 4241–4255. doi:10.1002/jgrc.20308
Lee, Z., Shang, S., Hu, C., Du, K., Weidemann, A., Hou, W., et al. (2015). Secchi disk depth: a new theory and mechanistic model for underwater visibility. Remote Sens. Environ. 169, 139–149. doi:10.1016/j.rse.2015.08.002
Lei, Y., Zhu, Y., Wang, B., Yao, T., Yang, K., Zhang, X., et al. (2019). Extreme Lake level changes on the Tibetan plateau associated with the 2015/2016 El Niño. Geophys. Res. Lett. 46, 5889–5898. doi:10.1029/2019GL081946
Liu, C., Zhu, L., Li, J., Wang, J., Ju, J., Qiao, B., et al. (2021). The increasing water clarity of Tibetan lakes over last 20 years according to MODIS data. Remote Sens. Environ. 253, 112199. doi:10.1016/j.rse.2020.112199
Monismith, S. G., and MacIntyre, S. (2009). “The surface mixed layer in lakes and reservoirs,” in Encyclopedia of inland waters. Editor G. E. Likens (Oxford: Academic Press), 636–650. doi:10.1016/B978-012370626-3.00078-8
Morel, A. (1974). Optical properties of pure water and pure sea water, 1–24. No Source Information Available.
Nicholls, N. (2015). “TROPICAL METEOROLOGY and CLIMATE | El Niño and the southern oscillation: observation,” in Encyclopedia of atmospheric sciences. Editors G. R. North, J. Pyle, and F. Zhang Second Edition (Oxford: Academic Press), 91–96. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-382225-3.00148-1
Olmanson, L. G., Bauer, M. E., and Brezonik, P. L. (2008). A 20-year Landsat water clarity census of Minnesota’s 10,000 lakes. Remote Sens. Environ. 112, 4086–4097. doi:10.1016/j.rse.2007.12.013
O’Reilly, C. M., Sharma, S., Gray, D. K., Hampton, S. E., Read, J. S., Rowley, R. J., et al. (2015). Rapid and highly variable warming of lake surface waters around the globe. Geophys. Res. Lett. 42, 10773–10781. doi:10.1002/2015GL066235
Pilla, R. M., Williamson, C. E., Zhang, J., Smyth, R. L., Lenters, J. D., Brentrup, J. A., et al. (2018). Browning-related decreases in water transparency lead to long-term increases in surface water temperature and thermal stratification in two small lakes. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosciences 123, 1651–1665. doi:10.1029/2017JG004321
Rangwala, I., Miller, J. R., and Xu, M. (2009). Warming in the Tibetan Plateau: possible influences of the changes in surface water vapor. Geophys. Res. Lett. 36. doi:10.1029/2009GL037245
Ren, J., Zheng, Z., Li, Y., Lv, G., Wang, Q., Lyu, H., et al. (2018). Remote observation of water clarity patterns in three gorges reservoir and dongting lake of China and their probable linkage to the three gorges dam based on Landsat 8 imagery. Sci. Total Environ. 625, 1554–1566. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.01.036
Rose, K. C., Greb, S. R., Diebel, M., and Turner, M. G. (2017). Annual precipitation regulates spatial and temporal drivers of lake water clarity. Ecol. Appl. 27, 632–643. doi:10.1002/eap.1471
Schneider, P., and Hook, S. J. (2010). Space observations of inland water bodies show rapid surface warming since 1985. Geophys. Res. Lett. 37. doi:10.1029/2010GL045059
Shang, S., Lee, Z., Shi, L., Lin, G., Wei, G., and Li, X. (2016). Changes in water clarity of the bohai sea: observations from MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 186, 22–31. doi:10.1016/j.rse.2016.08.020
Shi, K., Zhang, Y., Zhu, G., Qin, B., and Pan, D. (2018). Deteriorating water clarity in shallow waters: evidence from long term MODIS and in-situ observations. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinformation 68, 287–297. doi:10.1016/j.jag.2017.12.015
Song, K., Liu, G., Wang, Q., Wen, Z., Lyu, L., Du, Y., et al. (2020). Quantification of lake clarity in China using Landsat OLI imagery data. Remote Sens. Environ. 243, 111800. doi:10.1016/j.rse.2020.111800
Wang, B., Li, J., and He, Q. (2017). Variable and robust East Asian monsoon rainfall response to El Niño over the past 60 years (1957–2016). Adv. Atmos. Sci. 34, 1235–1248. doi:10.1007/s00376-017-7016-3
Wu, G., De Leeuw, J., Skidmore, A. K., Prins, H. H. T., and Liu, Y. (2008). Comparison of MODIS and Landsat TM5 images for mapping tempo–spatial dynamics of Secchi disk depths in poyang lake national nature reserve, China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 29, 2183–2198. doi:10.1080/01431160701422254
Xue, Y., and Kumar, A. (2017). Evolution of the 2015/16 El Niño and historical perspective since 1979. Sci. China Earth Sci. 60, 1572–1588. doi:10.1007/s11430-016-0106-9
Yang, K., Ye, B., Zhou, D., Wu, B., Foken, T., Qin, J., et al. (2011). Response of hydrological cycle to recent climate changes in the Tibetan Plateau. Clim. Change 109, 517–534. doi:10.1007/s10584-011-0099-4
Yu, D. F., Xing, Q. G., Lou, M. J., and Shi, P. (2014). Retrieval of Secchi disk depth in the yellow sea and east China sea using 8-day MODIS data. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 17, 012112. doi:10.1088/1755-1315/17/1/012112
Zhang, G., Yao, T., Xie, H., Yang, K., Zhu, L., Shum, C. K., et al. (2020). Response of Tibetan Plateau lakes to climate change: trends, patterns, and mechanisms. EARTH-Sci. Rev. 208, 103269. doi:10.1016/j.earscirev.2020.103269
Keywords: water transparency, MODIS, Tibetan Plateau, alpine lakes, climate change
Citation: Liu W, Xu H and He G (2024) Long-term trends in water transparency of Tibetan Plateau lakes and the response to extreme climate events. Front. Environ. Sci. 12:1450320. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2024.1450320
Received: 17 June 2024; Accepted: 03 September 2024;
Published: 17 September 2024.
Edited by:
Zhuosen Wang, University of Maryland, United StatesReviewed by:
Shaohua Zhao, Ministry of Ecology and Environment Center for Satellite Application on Ecology and Environment, ChinaLiu Chong, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), China
Copyright © 2024 Liu, Xu and He. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Huan Xu, c3h0bGNoeHlsd21AMTYzLmNvbQ==
 Wangming Liu
Wangming Liu Huan Xu
Huan Xu