- 1School of Municipal and Mapping Engineer, Hunan City University, Yiyang, Hunan, China
- 2School of Municipal and Environmental Engineering, Shenyang Jianzhu University, Shenyang, Liaoning, China
- 3Hunan Provincial Village Drinking Water Quality Safety Engineering Technology Research Center, Yiyang, Hunan, China
- 4Yiyang City Commodity Quality Supervision and Inspection Institute, Yiyang, Hunan, China
Phytic acid was investigated as an organophosphorus pollutant. Titanium dioxide (TiO2) doped with Ce and N was prepared using the sol-gel method and loaded onto a modified shell power to produce modified shell powder/Ce-N-TiO2 (Msp/CeNT). The combined effects of adsorption and photocatalysis on phytic acid were explored. The actual phytic acid degradation rate with the composite photocatalyst was higher than the sum of the adsorption removal rate of phytic acid using the modified shell powder and the photocatalytic degradation removal rate of phytic acid using the Ce-N-TiO2 photocatalyst. Msp/CeNT synergistically affected adsorption and photocatalytic degradation. The effects of different factors, such as reaction temperature, catalyst dosage, initial pH, stirring speed, and light intensity, on the combined effect were investigated. The results showed that the synergistic effect increases with the increase of light intensity. Increasing the reaction temperature, catalyst dosage, initial pH, and stirring speed first increased and then decreased the synergistic effect of the composite photocatalysts. Phytic acid (69.54%) was degraded within 4 h when the temperature, pH, catalyst dosage, stirring speed, and light intensity were 25 °C, 5, 1 g/L, 300 rpm, and 500 W, respectively. We investigated and prepared a composite photocatalytic material, developing a new theoretical method for degrading organophosphorus dissolved in water and providing a basis for treating lake eutrophication as a practical application.
1 Introduction
The eutrophication of lake water is a serious ecological problem. Limiting the input of nitrogen only without controlling the input of phosphorus stimulates the proliferation of nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria, which leads to continued algae growth in lake water, aggravating the eutrophication of water bodies (Wang and Jiang, 2016). Reducing the phosphorus input to water bodies can slow water body eutrophication (Suresh et al., 2023). In lake water, organic phosphorus accounts for up to 74% of the total phosphorus and is more likely to be adsorbed into particulate matter and transformed into particulate phosphorus than inorganic phosphorus, increasing the eutrophication degree (Cao et al., 2018). Therefore, suppressing excess organic phosphorus in lakes is key to controlling eutrophication.
Phytic acid is a dissolved organic phosphorus pollutant that usually accounts for 50%–80% of the total phosphorus content in plants (Wang and Guo, 2021). A large amount of metabolizable organophosphorus phytic acid is excreted in feces because humans and ruminants lack phytase for digesting phytic acid. A high concentration of phytic acid is thus released into the soil and discharged into rivers through leaching or surface runoff, which aggravates lake eutrophication (Gupta et al., 2015). Phytic acid easily combines with metal ions to form insoluble phytates, which the human body cannot absorb and use, reducing the use of minerals by the human body (Mingjing and Jaisi, 2018). Adopting suitable methods to degrade phytic acid in surface water bodies is essential for controlling the eutrophication of water bodies. Of these methods, adsorption is widely used because of its ease of operation and high removal efficiency (Zheng et al., 2023). Traditional adsorbents, such as alumina, iron oxide, and its water and oxide, differ in their organophosphorus removal effects; however, their high cost and complicated treatment processes hinder their practical application. As such, the preparation of new and green adsorbents from waste is a current research topic (Jiang et al., 2018). The oyster shells in freshwater contains large amounts of CaCO3 and are microporous, providing a natural material for the preparation of adsorbents (Zhou et al., 2022). Modification of the powdered clam shell substantially increases its specific surface area and adsorb organophosphorus in water (Raizq, 2020). However, modified shell powder can only adsorb phytic acid, which can still be released into water, causing environmental pollution. Therefore, appropriate methods must be used to remove phytic acid in subsequent steps.
Titanium dioxide (TiO2) photocatalytic oxidation is a water treatment method that strongly oxidizes TiO2 with low selectivity and high treatment efficiency that produces no secondary pollution (Zhang et al., 2021). The UV content of sunlight is less than 5%, so sunlight is less efficient for use and restricts the large-scale application of photocatalysts. The modification of TiO2 has been considered to overcome this drawback. The co-doping of TiO2 with metal and nonmetal ions effectively overcomes this drawback. The introduction of metal elements produces new impurity energy levels, thus reducing the bandgap energy; the introduction of nonmetal elements produces more oxygen vacancies, which reduces the bandgap and widens the light absorption range, thus strengthening the response to visible light.
The rare earth element Ce has a unique 4f electronic configuration. Doping nano-TiO2 increases the electron–hole separation efficiency and the quantum yield, reduces the bandgap so that TiO2 can respond to visible light, and inhibits the anatase-to-rutile transformation of TiO2 (Maarisetty et al., 2019). However, the doped nonmetallic element N enters the lattice of TiO2 to form Ti-O-N bond, which can shift the absorption red to the visible region (Yu et al., 2010). Therefore, co-doping TiO2 with Ce and N effectively increases photocatalytic efficiency. A large number of pollutants must be enriched on the surface of nano-TiO2 particles to further increase photocatalytic activity. Nano-TiO2 particles can be attached to modified clam shell powder for use as a pollutant adsorbent to achieve pollutant degradation through adsorption and photocatalysis.
In this study, modified shell powder/Ce-N-TiO2 was prepared using the sol-gel method. The morphological characteristics and physicochemical properties of the composite catalyst were explored using SEM, BET, and Raman spectroscopy. Phytic acid was the target material to be removed from water. The synergistic adsorption and photodegradation of phytic acid by the modified shell powder/Ce-N-TiO2 was explored; the effects of different factors, such as temperature, pH, composite photocatalyst dosage, stirring speed, and light intensity, on this synergistic effect were determined.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Materials
Tetrabutyl titanate (AR, Beijing Myrida Technology Co., Ltd.); Cerium nitrate hexahydrate (AR, Beijing Myrida Technology Co., Ltd.); Urea (AR Beijing Merida Technology Co., Ltd.); Anhydrous ethanol (AR, Beijing Myrida Technology Co., Ltd.); Phytic acid (70%, Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd.); Potassium persulfate (AR, Tianjin Fengchuan Chemical Reagent Technology Co., Ltd.); Potassium antimony tartrate (AR, Shanghai Zhanyun Chemical Technology Co., Ltd.); Ammonium molybdate (AR, Tianjin No.4 Chemical Reagent Factory). Concentrated sulfuric acid (AR, Hengyang Kaixin Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd.); Hydrochloric acid (AR, Hengyang Kaixin Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd.). All chemical reagents are analytically pure and can be used directly without treatment.
Main Instruments: CEL-S500 xenon lamp light source; HJ-6 multi-head constant temperature magnetic stirrer; UV-1800 UV-visible spectrophotometer; H2050R-1 high-speed tabletop freezing centrifuge; KSY-14-16 muffle furnace; GZ-WXJ-I microwave closed-type dissolver; DHG-9030A electric constant temperature blower drying oven; SEM test using ZEISS Sigma 300 from Germany, automatic specific surface and porosity analyzer (Micromeritics ASAP 2460 from the United States) at 200°C, N2 adsorption test BET. Horiba LabRAM HR Evolution Raman Spectrometer from Japan was used to record the Raman spectra of the samples, the exciter wavelength of 532 nm, testing Wave number range 50–900 cm−1.
2.2 Preparation of composite photocatalyst
2.2.1 Modification of shell powder
The oyster shells used in the laboratory were obtained from an agricultural product market. The surfaces of the clam shells were cleaned using detergent and a cleaning ball. The surfaces were polished until clean and then soaked in 0.5% dilute hydrochloric acid for 0.5 h to remove excess impurities. After cleaning with pure water, these pretreated shells were dried in a drying oven at 65°C; the shells were crushed to a powder with sealed sample pulverizer, and the shell powder was sieved through 200 mesh. Finally, the sieved powder was calcined in a muffle furnace at 900°C for 2 h, producing the modified shell powder, which was sealed and kept until further use.
2.2.2 Preparation of modified shell Powder/Ce-N-TiO2 composite photocatalyst
The Msp/CeNT composite photocatalyst was prepared using the sol-gel method. We mixed 30 mL of anhydrous ethanol with a certain amount of modified shell powder via ultrasonic vibration, and we added 8.5 mL of tetra-butyl titanate to produce solution A. We combined 20 mL of anhydrous ethanol, 1.5 mL of ultrapure water, and a certain amount of hydrochloric acid, which we fully mixed. We calculated the molar amounts of doped cerium and nitrogen. The cerium and nitrogen sources were cerium nitrate hexahydrate and urea, respectively, which were added into the mixed solution. The resulting solution was mixed to produce solution B. We combined 20 mL of anhydrous ethanol, 1.5 mL of ultrapure water, and a certain amount of hydrochloric acid, which we fully mixed. We calculated the molar amounts of doped cerium and nitrogen. The cerium and nitrogen sources were cerium nitrate hexahydrate and urea, respectively, which were added into the mixed solution. The resulting solution was mixed to produce solution B. Under vigorous stirring without bubbles, solution B was slowly dropped into solution A, after which the mixture was continuously stirred for 1.5–2 h to prepare the composite photocatalyst gel, which was dried in a vacuum-drying oven at 65°C for 12 h, and then ground and crushed with a mortar. Then, the modified shell powder/Ce-N-TiO2 was prepared via calcination at 600°C for 2 h in a muffle furnace. Ce-N-TiO2 was prepared without adding the modified shell powder using the same method.
2.3 Methods
2.3.1 Determination of combined effects of adsorption and photocatalysis
This experiment was performed using a xenon lamp as the light source and a double-layer beaker with a jacket as the reaction container. Phytic acid (100 mL) at a mass concentration of 50 mg/L was added to a double-layer beaker; 10 mg of modified shell powder, 90 mg of Ce-N-TiO2, and 100 mg of modified shell powder/Ce-N-TiO2 composite photocatalyst were added to the phytic acid. The phytic acid degradation rates of the modified shell powder, CeNT, and composite photocatalysts via adsorption and photocatalysis were investigated. Before the degradation test, the mixed modified shell powder/Ce-N-TiO2 solution was placed in a dark room, and an adsorption–desorption equilibrium test was conducted for 2 h in the dark. A magnetic stirrer was used under irradiation with a xenon lamp. Under the xenon lamp illumination, a small amount of liquid was measured with a sampler at 0.5, 1, 1.5, 2, 2.5, 3, 3.5, and 4 h, which was then centrifuged and filtered for the subsequent determination of the mass concentration of phosphate. The effects of the reaction temperature, initial pH, stirring speed, composite photocatalyst dosage, and light intensity on the synergistic effect were further analyzed using this method.
2.3.2 Phosphate determination method
Ammonium molybdate spectrophotometry was used for phosphate determination. We pipetted 1 mL of the solution to be measured into a 25 mL colorimeter tube, and we fixed the volume to 25 mL with distilled water. Ascorbic acid (1 mL) was added and shaken well, and 2 mL of the molybdate solution was added dropwise after 30 s. The solution was allowed to stand for 15 min and then measured colorimetrically at 700 nm using a UV–visible spectrophotometer. The phosphate concentration was determined according to the standard phosphate curve, and the degradation rate of the phytic acid solution was calculated as follows:
where, η is degradation rate (%) of organic phosphorus in phytic acid solution; Ct is the content of PO43- in the phytic acid solution at moment t; C0 is the total phosphorus content in phytic acid at the initial moment.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Characterization and analysis of Msp/CeNT composite photocatalysts
3.1.1 SEM characterization and analysis
Figure 1A shows a scanning electron micrograph of the modified shell powder at ×400 magnification, indicating a loose, porous, layered surface structure, which is suitable for photocatalyst loading. Figure 1B shows a scanning electron micrograph of the Ce-N co-doped TiO2 loaded with modified shell powder with a 1 μm scale bar. The modified TiO2 after doping was uniformly loaded in a thin layer on the surface of the modified shells. Figure 1C depicts the loaded Ce-N co-doped TiO2 in a 200 nm scanning electron microscope image, which shows that the particle distribution and size were relatively uniform, and loading on the surface of modified shell was uniform. Some areas showed particle agglomeration, which may have been caused by the high-temperature calcination. The results of the pore size analysis of a composite photocatalyst sample is shown in Figure 1D, which was analyzed using ImageJ. The particle size was 30.3787 nm, which is classified as mesoporous. Mesoporous structures are favorable for the diffusion of phytic acid in a catalyst and for the combination of phytic acid molecules with the catalyst, which promotes the photocatalytic reaction.

Figure 1. Scanning electron micrographs of different samples. (A) Modified shell powder. (B, C) Msp/CeNT SEM at different magnifications. (D) Composite catalyst particle size analysis.
3.1.2 BET specific surface area and pore size analysis
Figure 2 shows the N2 adsorption–desorption isothermal curves and pore size distribution curves of the CeNT and Msp/CeNT. The adsorption isothermal curves of both catalysts contain hysteresis loops inside the relative pressure region of 0.8–1.0, which indicates the fourth type of adsorption isothermal model and that the composite catalysts had a mesoporous structure (Lei et al., 2020). The average pore size of the composite photocatalyst decreased from 15.3216 nm before modification to 12.0106 nm after load modification. A composite photocatalyst with a mesoporous structure has a large specific surface area, which enables the increased mass transfer of pollutants in which the pollutants are subjected to less diffusion resistance, thus effectively increasing photocatalytic efficiency (Li et al., 2022). The specific surface area of Msp/CeNT increased from 45.5875 to 56.3615 m2/g after doping with the modified shell powder, an increase of 23.6%. The loaded modified shell helped enrich the phytic acid on the surface of the composite photocatalyst, which facilitated the synergistic adsorption and photocatalysis effects.
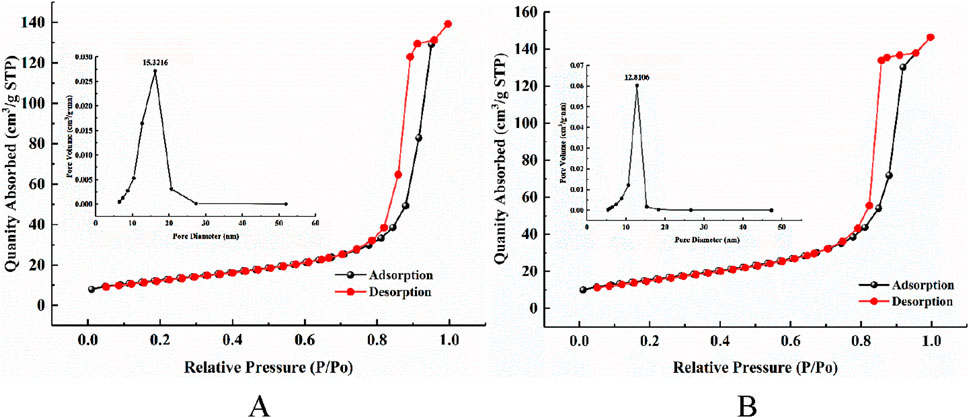
Figure 2. N2 adsorption–desorption isothermal and pore size distribution curves for different catalysts. (A) CeNT. (B) Msp/CeNT.
3.1.3 Raman spectroscopy characterization and analysis
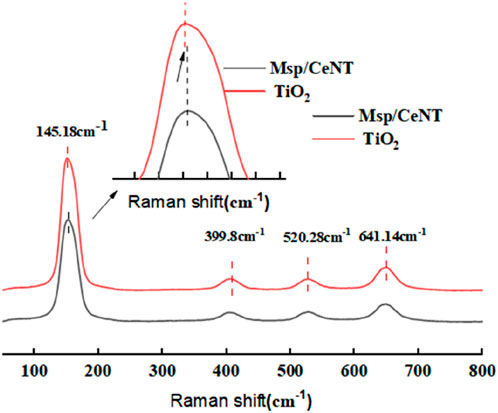
Figure 3 shows the Raman spectra of the different samples. Six peaks (A1g+2B1g+3Eg) can be observed in the Raman activity pattern of anatase TiO2 (Wang et al., 2015). The spectra of both samples showed strong vibrations at four bands: 145.18 cm−1 (Eg), 399.8 cm−1 (B1g), 520.28 cm−1 (A1g+B1g), and 641.14 cm−1 (Eg), indicating that the TiO2 in the composites was present as the anatase type (Ohsaka et al., 1978). The two characteristic peaks at 399.8 and 520.28 cm−1 represent the tensile vibration of the Ti-O bond; the peaks at 145.14 and 640 cm−1 indicate the bending vibration of the Ti-O bond. The peak value of the prepared sample shifted to a higher wavenumber, which may have been because of the presence of oxygen vacancies (Zhang et al., 2023). No Raman spectral peaks representing the rutile phase were found, indicating that no rutile TiO2 was present or that the content of the rutile phase in the sample was relatively low and did not reach the detection limit. Overall, the findings indicated that the composite catalyst was thoroughly crystallized and mainly consisted of anatase TiO2, which is suitable for photocatalysis.
The sizes of the particles and the defects in a nanomaterial are the two most important factors that affect the material’s intensity, peak width, and position of the Raman spectral peaks. Figure 3 shows a strong peak enhancement and a larger peak in the Raman spectra of the Ce and N co-doped composite catalysts compared with those of the pure TiO2 sample (Choudhury et al., 2013). Moreover, the Raman vibrational peak of the composite catalyst at 145.18 cm−1 (Eg) shifted toward a higher wavenumber compared with that of pure TiO2. This occurred because the ionic radius of Ce3+ is larger than that of Ti, and Ce3+, when doped in lattice interstitials, distorts the lattice and generates a large number of oxygen vacancy defects, which shifts the Eg mode toward a higher wavenumber (Zhang et al., 2023). The formation of O-Ti-N bonds via N doping decreased the strength of the Ti-O bonds and changed the intensity and width of the vibrational peaks. The Raman spectral peaks of the co-doped catalysts were stronger and wider than those of the single TiO2 Raman spectral peaks, suggesting that more oxygen vacancies were present on the surface, which strengthened photocatalytic performance.
3.1.4 X-ray characterization analysis
The XRD pattern shows that the composite catalyst sample was successfully doped with cerium and nitrogen (Zhang et al., 2023). The crystal size of the modified TiO2 sample was reduced because of the doping with metallic Ce and the nonmetallic B, which inhibited the phase transition of TiO2, thus maintaining the anatase phase, which is more conducive to photocatalysis. According to the calculations, the crystal size of the sample was notably smaller than that of the undoped sample.
3.2 Evaluation of synergistic effects of adsorption and photocatalysis
The phytic acid degradation rates of the modified shell powder via adsorption alone, via CeNT alone, and via adsorption and photocatalysis using the composite photocatalyst were investigated under the following conditions: an initial temperature of 25°C, a pH of 5, a light intensity of 400 W, a photocatalyst dosage of 0.8 g/L, and stirring speed of 400 rpm. The results are shown in Figure 8.
The actual degradation efficiency of phytic acid is greater than the sum of the theoretical superposition values of the adsorption efficiency of modified shell powder alone and the photocatalytic degradation efficiency of phytic acid by CeNT alone. The results of these three tests are shown in Figure 4. The actual degradation rate of phytic acid using the modified shell powder/Ce-N-TiO2 in the first 3 h was higher than the sum of the individual adsorption and photodegradation removal effects of the modified shell powder alone, indicating that the degradation of phytic acid using the composite photocatalyst was the result of the synergistic effects of adsorption and photocatalysis. The incorporation of modified shell powder was conducive to the adsorption of phytic acid molecules onto the surface of the CeNT photocatalysts, which resulted in a concentration effect of the pollutant because the specific surface area of the modified shell powder and CeNT increased after compositing (Xue et al., 2011),accelerated the reaction between the phytic acid molecules and active groups, and thus increased the efficiency of the composite catalysts in the photocatalytic degradation of phytic acid. The specific surface area of the composite photocatalysts increased from 46.5785 to 56.5875 m2/g after loading the modified shell powder with Ce-N-TiO2 which promoted the adsorption of phytic acid. After 3 h of reaction, although the values on the theoretical curve were lower than those from the synergistic degradation curve for the composite photocatalyst, the difference between the two gradually narrowed, indicating that the synergistic effect of the adsorption and photocatalytic degradation of phytic acid by Msp/CeNT gradually weakened. Moreover, the amount of pollutants that could react with the composite photocatalyst decreased as the phytic acid concentration decreased, although the photocatalytic performance remained strong, which led to a weakening of the synergistic adsorption–photocatalytic effect. Considering these findings with those in Figure 4B shows that Msp/CeNT also degraded the COD.

Figure 4. (A) Phytic acid adsorption using modified shell powder alone, photocatalysis using CeNT alone, theoretical superimposed values and the actual removal effect of phytic acid using Msp/CeNT. (B) Actual COD removal rate.
3.3 Influence of different factors on adsorption–photocatalytic synergy
3.3.1 Effect of temperature on Msp/CeNT synergy
The adsorption of phytic acid using the modified shell powder, the photodegradation of phytic acid using CeNT, and the degradation of phytic using by composite photocatalysts were investigated under an initial pH of 6, a light intensity of 400W, a catalyst dosage of 1 g/L, a stirring speed of 300 rpm, and at ambient temperatures of 15, 25, or 35°C. The experimental results are shown in Figure 5.
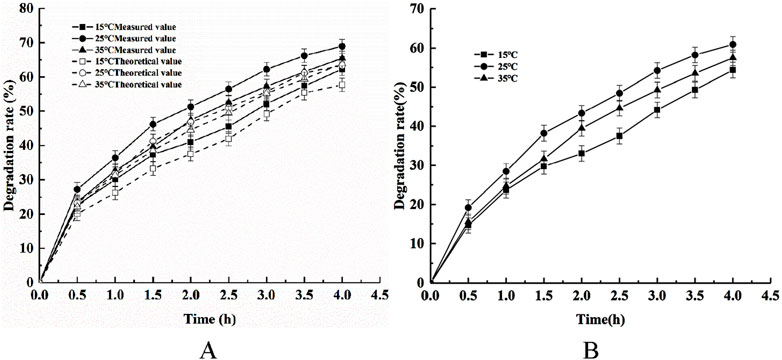
Figure 5. Effects of different temperatures on (A) the removal of phytic acid via catalytic adsorption and photocatalysis and (B) COD removal.
Figure 5 shows that the actual phytic acid degradation efficiency of the composite photocatalyst at different reaction temperatures was higher than the sum of the theoretically superimposed degradation efficiency of phytic acid via adsorption using modified shell powder alone and photocatalytic degradation with CeNT alone, which proves the synergistic effects of adsorption and photocatalysis in the degradation of phytic acid of the composite photocatalyst. Figure 5 also shows that temperature affects the synergistic effect: the composite photocatalytic degradation efficiency increased as the temperature increased, reaching a maximum at 25°C, after which the degradation rate gradually decreased. The main reason for this finding is that the movement of phytic acid molecules accelerates with the increase in temperature, which increases the effective collision efficiency between the active groups on the composite photocatalyst and phytic acid molecules. In addition, the process of the adsorption of phytic acid on the composite photocatalyst is an exothermic reaction; as such, an increase in temperature is favorable for the desorption of pollutants and phytic acid degradation intermediates from the composite catalyst (Zhang et al., 2022). As the reaction proceeded, the concentration of phytic acid in the system gradually decreased, and the intermediate products generated on the surface of the catalyst gradually desorbed with increasing temperature, providing more active sites for phytic acid molecules, which in turn increased their chance of being oxidized via photocatalysis. Phytic acid degradation rate decreased as the temperature further increased, which may have been because of the evaporation of water from the solution system. Part of the catalyst attached to the inner wall of the reaction vessel, which reduced the chance of contact with the catalyst and decreased the phytic acid degradation efficiency. The COD removal efficiency in phytic acid is also affected by temperature, and the degradation efficiency of COD is lower than that of phytic acid because phytic acid has six phosphate groups when COD is in the last stage of degradation.
3.3.2 Effect of catalyst dosage on Msp/CeNT synergy
The adsorption of phytic acid using modified shell powder alone, the photodegradation of phytic acid by CeNT alone, and the synergistic adsorption and photodegradation of phytic acid using the composite photocatalyst were investigated at an initial pH of 5, a light intensity of 500W, a temperature of 25°C, and a stirring speed of 300 rpm, and with different composite catalyst dosages of 0.8, 1, and 1.2 g/L. The phytic acid removal results are shown in Figure 6.
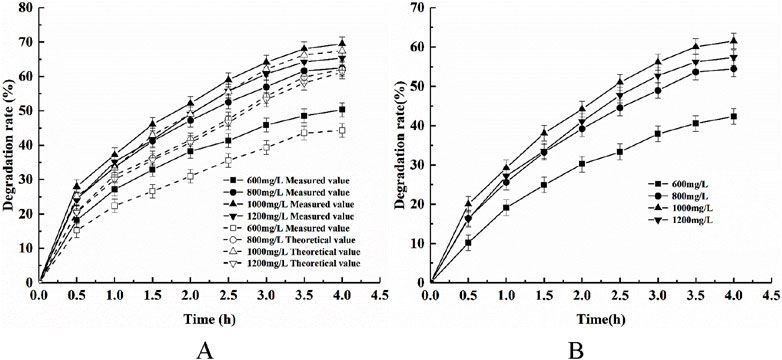
Figure 6. Effects of catalyst dosage on (A) the removal of phytic acid via the synergistic action of adsorption and photocatalysis and (B) COD degradation.
Figure 6 shows that the actual degradation efficiency of phytic acid was larger than the sum of the theoretically superimposed phytic acid degradation rates of the modified shell powder adsorption alone and CeNT photocatalysis alone for the different dosage conditions. The results indicated that the composite photocatalyst had a synergistic effect through the adsorption–photocatalytic degradation of phytic acid. Analyzing Figure 6 demonstrates the effect of dosage on this synergistic effect: the phytic acid degradation rate gradually increased with an increase in the photocatalyst dosage and reached a maximum value at a dosage of 1 g/L. More phytic acid was adsorbed onto the surface of the catalyst as the catalyst dosage increased, which increased the opportunity for contact with the active groups on the catalyst and thus the photocatalytic efficiency (Gusain et al., 2020). Moreover, the probability of photon absorption by CeNT increased with the gradual increase in the concentration of the composite catalyst in the solid–liquid system, which generated more photogenerated electrons and holes, leading to an increase in the phytic acid oxidation efficiency. However, the catalytic efficiency no longer increased but gradually decreased with further increases in the composite catalyst dosage, which was attributed to the suspended particles of the high-concentration catalyst having a scattering and masking effect on the light. In this situation, the photocatalysts could not be sufficiently excited by light energy, which ultimately weakening the effect of the photocatalyst (Nishiyama et al., 2018). Although the number of active sites in the solution increased with increasing photocatalyst dosage, the tendency for particle-to-particle agglomeration also increased when the photocatalyst dosage was too high, which gradually led to a decrease in the number of active sites and thus to a decrease in the photodegradation rate (Soto-Vazquez et al., 2016).
3.3.3 Effect of initial pH on Msp/CeNT synergy
The adsorption of phytic acid using modified shell powder alone, the photocatalytic degradation of phytic acid using CeNT alone, and the degradation of phytic acid using the composite photocatalyst were investigated at pH 3, 5, 7, and 9 under an initial temperature of 25°C, a light intensity of 500 W, a catalyst dosage of 1 g/L, and a stirring speed of 300 rpm. The results are shown in Figure 7.
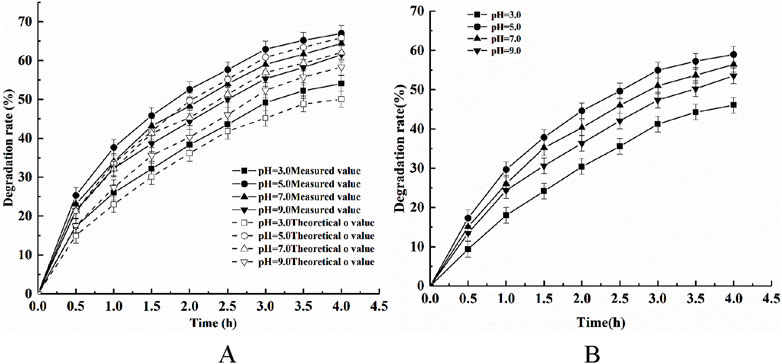
Figure 7. Effects of pH on (A) the removal of phytic acid via the synergistic action of adsorption and photocatalysis and (B) COD degradation.
Figure 7 shows that the actual degradation phytic acid rate was always higher than the sum of the theoretical values of phytic acid adsorption using the modified shell powder alone and phytic acid degradation using CeNT alone under different pH conditions, indicating that the composite photocatalyst synergistically affected the adsorption and photodegradation of phytic acid. Figure 7 also shows that when the initial pH of the solution increased from 3.0 to 9.0, the synergistic efficiency of the composite photocatalyst increased and then decrease. The maximum phytic acid degradation rate was reached at an initial pH of 5, potentially because the photocatalytic activity of TiO2 is higher under acidic conditions. The positively charged catalyst surface facilitates the process of photogenerated electron transfer to the catalyst surface, which favors the generation of reactive radicals, such as ⋅O2− and ⋅OH, in the presence of oxygen in aqueous media and slows the complexation of photogenerated electrons with holes. The degree of protonation on the surface of CeNT and the number of positive charges carried increase under lower pH conditions, which benefits the transfer of photogenerated electrons to the catalyst in the photocatalytic reaction, thus enhancing the adsorption–photodegradation efficiency. The degradation efficiency of phytic acid decreased as the pH of the reaction system was further increased. This could be attributed to the increase in the amount of hydroxide in water, which consumed the photogenerated vacancies generated on the catalyst surface and reduced the number of active groups accessible to phytic acid, thus degrading the catalytic efficiency. The COD removal efficiency in phytic acid was also affected by the pH, and the maximum removal rate was achieved at pH 5, which first increased and then decreased.
3.3.4 Effect of stirring speed on Msp/CeNT synergy
The phytic acid degradation rates using adsorption alone, the photocatalysis using Ce-N-TiO2 alone, and the synergistic adsorption and photodegradation using the composite photocatalyst were investigated under an initial pH of 5, a temperature of 25°C, a catalyst dosage of 1 g/L, and light intensity of 500W while varying the stirring speed: 100, 200, 300, or 400 rpm. The results are shown in Figure 8.
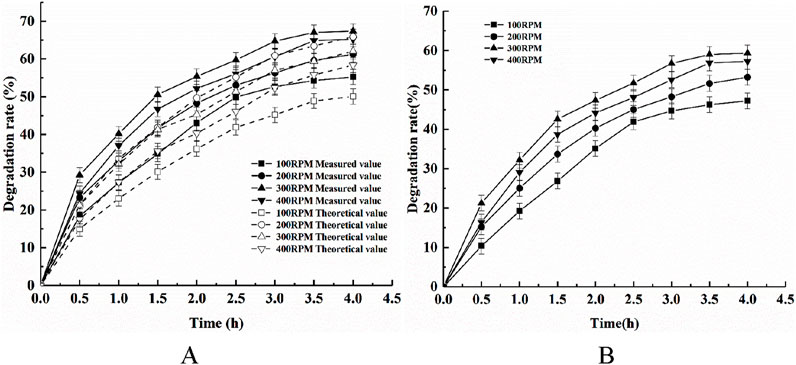
Figure 8. Effects of different stirring speeds on (A) the removal of phytic acid via the synergistic action of adsorption and photocatalysis and (B) COD degradation.
Figure 8 shows that the phytic acid degradation efficiency was higher using the composite photocatalyst than the sum of the adsorption of phytic acid using the modified shell powder alone and the photodegradation of phytic acid using CeNT alone under different stirring speeds, which indicated that the composite photocatalyst has a synergistic effect on the adsorption and photodegradation of phytic acid. The maximum synergistic efficiency of phytic acid adsorption and photocatalysis as well as the COD removal efficiency reached a maximum when the stirring speed was 300 rpm. The stirring speed affected the synergistic effect of the composite catalyst as follows: the phytic acid degradation rate increased and then decreased with increasing magnetic stirring rate, mainly because the rotational speed of the magnetic stirrer affected the dissolved oxygen content in the aqueous phytic acid solution. The higher the rotational speed, the larger the amount of dissolved oxygen, which is capable of reacting with photogenerated electrons to produce more superoxide radicals and increases the oxidative phytic acid degradation rate. Cerium ions use dissolved oxygen to generate superoxide radicals. In addition, the accelerated rotational speed of the magnetic stirrer increases the probability of collision between particles, which is conducive to the adsorption and desorption processes. However, too fast a rotational speed leads to the appearance of a central vortex in the container, resulting in powder photocatalysts being nonuniformly dispersed in the phytic acid solution, thus reducing the contact with the concentration of phytic acid. This results in a decrease in the degradation efficiency.
3.3.5 Effect of light intensity on Msp/CeNT synergy
The phytic acid degradation rate was investigated for the adsorption using the modified shell powder alone, via photocatalysis using Ce-N-TiO2 alone, and the synergistic photodegradation and adsorption using the composite photocatalyst under an initial pH of 5, a temperature of 25°C, a catalyst dosage of 1 g/L, and a stirring speed of 300 rpm, for various illumination intensities of 300, 400, and 500. The phytic acid degradation rate via adsorption and photodegradation with the composite photocatalyst is shown in Figure 9.
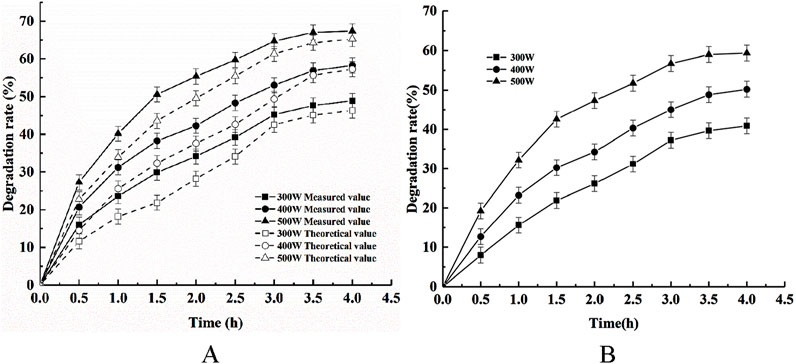
Figure 9. Effects of light intensity on (A) the removal of phytic acid via the synergistic action of adsorption and photocatalysis and (B) COD removal.
Figure 9 shows that the actual phytic acid degradation efficiency with the composite catalyst was higher than the sum of degradation efficiency of phytic acid phytic acid adsorbed by modified shell powder alone and degraded by CeNT light alone under different light intensities. We noted a synergistic effect of adsorption and photodegradation of phytic acid by Msp/CeNT under the different light intensity conditions. Moreover, Figure 9 shows that the phytic acid photodegradation efficiency increased with increasing light intensity, reaching a maximum when the light intensity was 500 W. This occurred because the light intensity determined the degree of light absorption of the Msp/CeNT composite photocatalyst at a given wavelength, and the rate of photogenerated electron–hole formation in the photocatalytic reaction depended on the light intensity. The higher the light intensity, the more photons are produced per unit time and area. This leads to an increase in the number of photogenerated carriers on the catalyst surface, resulting in the production of more photogenerated electrons and holes. The COD removal efficiency of phytic acid showed the same trend with increasing light intensity.
3.4 Free radical quenching experiment
Tert-butanol (TBA), 1,4-benzoquinone (BQ), and ammonium oxalate (AO) were selected as the bursting agents of ⋅OH, ⋅O2−, and h+, respectively, under the optimal experimental conditions to determine the types of active groups that play a role in the photocatalytic degradation of phytic acid using the Msp/CeNT composite photocatalyst. The effects of the different trapping agents on degradation are shown in Figure 10.
Catalysts are used in various applications. Four burst test experiments were conducted: a blank group and the three groups of experiments with molar concentrations of 10 mmol/L of tert-butanol, AO, and 0.2 mmol/LBQ solution under an ambient temperature of 25°C, an initial pH of 5, a catalyst dosage of 1 g/L, and a light intensity of 500 W. The results of the burst tests are shown in Figure 10. AO more strongly affected the phytic acid degradation rate of the composite photocatalysts, indicating that the holes or the active groups capable of interacting with the holes played a major role in the photocatalytic degradation of phytic acid. In contrast, the addition of p-benzoquinone and tert-butanol reduced the phytic acid degradation rate by 25.94% and 11.24%, respectively; which indicated that ⋅O2− and ⋅OH were the main active species playing a role in the phytic acid degradation process.
The adsorption–photocatalytic mechanism was determined based on the above characterization and free radical trapping experiment results. The doping of metallic Ce and nonmetallic N generated lattice defects on the surface of the composite, which increased the number oxygen vacancies, provided more active sites, and improved the photocatalytic oxidation performance of the catalyst. More contact sites were provided to adsorb phytic acid molecules onto the surface of the composite material through the loading of modified shell powder. Phytic acid was decomposed into small molecules such as PO43−, H2O, and CO2 under the action of ⋅O2− and ⋅OH.
4 Conclusion
The specific surface area of the photocatalyst increased from 45.5875 to 56.3615 m2/g after catalyst loading, which improved the adsorption performance of the modified TiO2 material and increased the number of active sites on the photocatalyst, favoring the synergistic effect of adsorption and photocatalysis on the degradation of phytic acid. This effect was strengthened by an increase in light intensity. Increases in reaction temperature, catalyst dosage, initial pH, and stirring speed tended to increase and then decrease the synergistic effect of the composite photocatalyst. The phytic acid degradation efficiency was 69.54% under the optimal experimental conditions: a reaction temperature of 25°C, an initial pH of 5, a catalyst dosage of 1 g/L, a stirring speed of 300 rpm, and a light intensity of 500 W. Superoxide and hydroxyl radicals were the main active species in the removal of phytic acid using the composite photocatalysts according to the results of the free radical burst experiment, which acted together in the photodegradation of phytic acid. In conclusion, it shows that Msp/CeNT is a green, efficient and stable photocatalyst, which has important theoretical significance and potential application value for controlling lake eutrophication. Next, we should explore the combination of photocatalyst and various physical and chemical methods to completely remove dissolved organic phosphorus, which is of great significance for protecting the health of the ecological environment.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
WZ: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. ZW: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing–original draft. JS: Writing–review and editing. AW: Data curation, Methodology, Writing–review and editing. HL: Formal Analysis, Validation, Writing–original draft. XY: Writing–original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. National Natural Science Foundation of China No.42071122.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Cao, X., Wan, L., Xiao, J., Chen, X., Zhou, Y., Wang, Z., et al. (2018). Environmental effects by introducing Potamogeton crispus to recover a eutrophic Lake. Sci. Total Environ. 621, 360–367. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.11.267
Choudhury, B., Borah, B., and Choudhury, A. (2013). Ce–Nd codoping effect on the structural and optical properties of TiO2 nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 178 (4), 239–247. doi:10.1016/j.mseb.2012.11.017
Gupta, R. K., Gangoliya, S. S., and Singh, N. K. (2015). Reduction of phytic acid and enhancement of bioavailable micronutrients in food grains. J. Food Sci. Technol. 52 (2), 676–684. doi:10.1007/s13197-013-0978-y
Gusain, R., Kumar, N., and Ray, S. S. (2020). Factors influencing the photocatalytic activity of photocatalysts in wastewater treatment. John Wiley and Sons, Ltd, 229–270.
Jiang, N., Shang, R., Rietveld, L. C., and Heijman, S. G. J. (2018). High-silica zeolites for adsorption of organic micro-pollutants in water treatment: a review. Water Res. 144 (NOV.1), 145–161. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2018.07.017
Lei, Z., Gao, W., Zeng, J., Wang, B., and Xu, J. (2020). The mechanism of Cu (II) adsorption onto 2, 3-dialdehyde nano-fibrillated celluloses. Carbohydr. Polym. 230, 115631. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115631
Li, H., Sun, B., Gao, T., Ren, Y., and Zhou, G. (2022). Ti3C2 MXene co-catalyst assembled with mesoporous TiO2 for boosting photocatalytic activity of methyl orange degradation and hydrogen production. Chin. J. Catal. 43 (2), 461–471. doi:10.1016/s1872-2067(21)63915-3
Maarisetty, D., Baral, S. S., Maarisetty, D., and Baral, S. S. (2019). Defect-induced enhanced dissociative adsorption, optoelectronic properties and interfacial contact in Ce doped TiO2: solar photocatalytic degradation of Rhodamine B. Ceram. Int. 45 (17), 22253–22263. doi:10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.07.251
Mingjing, S., and Jaisi, D. P. (2018). Distribution of inositol phosphates in animal feed grains and excreta: distinctions among isomers and phosphate oxygen isotope compositions. Plant Soil 430 (1-2), 1–15. doi:10.1007/s11104-018-3723-5
Nishiyama, NAOTO, Kozasa, , Okajima, T., Fujitsuka, M., Majima, T., and Yamazaki, S. (2018). Factors affecting photocatalytic activity of visible light-responsive titanium dioxide doped with chromium ions. Catal. Sci. and Technol. 8 (18), 4726–4733. doi:10.1039/c8cy01411f
Ohsaka, T., Izumi, F., and Fujiki, Y. (1978). Raman spectrum of anatase, TiO2. J. raman Spectrosc. 7 (6), 321–324. doi:10.1002/jrs.1250070606
Raizq, D. F. (2020). Modification strategies of TiO2 for potential applications in photocatalysis: a critical review. Green Chem. Lett. Rev.
Soto-Vazquez, L., Cotto, M., Duconge, J., Morant, C., and Márquez, F. (2016). Synthesis and photocatalytic activity of TiO2 nanowires in the degradation of p-aminobenzoic acid: a comparative study with a commercial catalyst. J. Environ. Manag. 167 (FEB.1), 23–28. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2015.11.006
Suresh, K., Tang, T., Vliet, M. V., Bierkens, M. F. P., Strokal, M., Sorger-Domenigg, F., et al. (2023). Recent advancement in water quality indicators for eutrophication in global freshwater lakes. Environ. Res. Lett. 18, 063004. doi:10.1088/1748-9326/acd071
Wang, C., and Jiang, H. L. (2016). Chemicals used for in situ immobilization to reduce the internal phosphorus loading from lake sediments for eutrophication control. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. and Technol. 46 (10), 947–997. doi:10.1080/10643389.2016.1200330
Wang, R., and Guo, S. (2021). Phytic acid and its interactions: contributions to protein functionality, food processing, and safety. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 20 (3), 2081–2105. doi:10.1111/1541-4337.12714
Wang, S., Pan, L., Song, J., Mi, W., Zou, J. J., Wang, L., et al. (2015). Titanium-defected undoped anatase TiO2 with p-type conductivity, room-temperature ferromagnetism, and remarkable photocatalytic performance. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 137 (8), 2975–2983. doi:10.1021/ja512047k
Xue, G., Liu, H., Chen, Q., Hills, C., Tyrer, M., and Innocent, F. (2011). Synergy between surface adsorption and photocatalysis during degradation of humic acid on TiO2/activated carbon composites. J. Hazard. Mater. 186 (1), 765–772. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.11.063
Yu, T., Tan, X., and Zhao, L. (2010). RETRACTED: characterization and mechanistic analysis of the visible light response of cerium and nitrogen co-doped TiO2 nano-photocatalyst synthesized using a one-step technique. J. Hazard. Mater. 176 (1-3), 829–835. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.11.111
Zhang, W., You, Q., Shu, J., Wang, A., Lin, H., and Yan, X. (2023). Photocatalytic degradation of glyphosate using Ce/N co-doped TiO2 with oyster shell powder as carrier under the simulated fluorescent lamp. Front. Environ. Sci. 11, 1131284. doi:10.3389/fenvs.2023.1131284
Zhang, W., He, H., Li, H., Duan, L., Zu, L., Zhai, Y., et al. (2021). Visible-light responsive TiO2-based materials for efficient solar energy utilization. Adv. Energy Mater. 11 (15), 2003303. doi:10.1002/aenm.202003303
Zhang, W., Liang, Z., Lin, H., Zhang, W., Liang, Z., Lin, H., et al. (2022). Adsorption performance of glyphosate on modified shell powder/Ce-N-Tio2. E3S Web Conf. EDP Sci. 350, 01016. doi:10.1051/e3sconf/202235001016
Zheng, Y., Wan, Y., Zhang, Y., Huang, J., Yang, Y., Tsang, D. C. W., et al. (2023). Recovery of phosphorus from wastewater: a review based on current phosphorous removal technologies. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 53 (11), 1148–1172. doi:10.1080/10643389.2022.2128194
Keywords: composite photocatalyst, phytic acid, adsorption, photodegradation, synergy
Citation: Zhang W, Wang Z, Shu J, Wang A, Lin H and Yan X (2025) Loading of Ce and n co-doped TiO2 composites onto modified shell powder synergism of adsorption and photocatalysis phytic acid removal: performance and mechanism. Front. Environ. Chem. 5:1511657. doi: 10.3389/fenvc.2024.1511657
Received: 22 October 2024; Accepted: 26 December 2024;
Published: 14 January 2025.
Edited by:
Vincenzo Vaiano, University of Salerno, ItalyReviewed by:
Ramadan Geioushy, Central Metallurgical Research and Development Institute (CMRDI), EgyptHari Mahalingam, National Institute of Technology, India
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Wang, Shu, Wang, Lin and Yan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Wei Zhang, emhhbmd3ZWlfd2F0ZXIyMDIyQDE2My5jb20=
 Wei Zhang
Wei Zhang Zheng Wang2
Zheng Wang2