- 1Department of Applied Chemistry, Adama Science and Technology University, Adama, Ethiopia
- 2Department of Chemistry, Kotebe University of Education, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia
- 3Department of Chemistry, Department of Chemistry Engineering and Applied Chemistry, Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Republic of Korea
- 4Research Institute of Materials Chemistry, Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Republic of Korea
- 5Department of Environmental Science, Adis Ababa University, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia
Organic-based pollutants are extensively released from various industries and they potentially harm the environment and human health. Photocatalysis is regarded as one of the most promising techniques for removal of organic contaminants from wastewater. Therefore, in this study, iron oxide-based nanocomposites were synthesized by an emerging green and sustainable method using Ethiopian endemic plant extract, Echinops kebericho M. as a capping and stabilizing agent. The phytoextract-assisted synthesized nanoparticles (NPs) α-Fe2O3 and nanocomposites (NCs) α-Fe2O3/MgO calcinated at a temperature of 400°C were characterized and used for their photocatalytic activities toward gentian violet (GV) dye degradation using ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy (UV-vis) at optimized catalyst dose, initial GV concentration, pH, and time conditions. The X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis result revealed that the mean crystal size of α-Fe2O3 and α-Fe2O3/MgO is 11.2 and 15.4 nm, respectively. Characterization results of scanning electron microscopy coupled with energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (SEM-EDS), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) clearly showed the successful deposition of MgO on α-Fe2O3. The maximum degradation of GV, 96.2%, was observed by using α-Fe2O3/MgO after 60 min under visible light irradiation. Thus, synthesized NCs were shown to have better GV degradation efficiency in a shorter time as compared to the previously reported nanomaterials. The results revealed photocatalytic degradation using endemic plant extract-assisted synthesized NCs, α-Fe2O3/MgO, is considered a greener, simple, and more efficient method for the removal of organic dyes.
1 Introduction
Currently, environmental pollution is a severe problem across the world. Specifically, persistent organic pollutants in aquatic ecosystems cause harmful effects on both the environment and human health worldwide (Kezzim et al., 2017; Kurniawan et al., 2020). Numerous classes of lethal water pollutants are generated by the textile, pharmaceutical, food, printing, and paint industries. These contaminants can persist for a long period of time in the environment, and they can accumulate and relocate from one place to the other through different means (Ritter et al., 2001). Discharging of colored effluents containing gentian violet (GV) into the environment causes a potential threat to living things and the environment. GV is a triphenylmethane cationic dye widely used for paper printing and Gram staining, in detergents and antiseptics, and as anti-freezer and fertilizer agents. Its complex aromatic structure makes it recalcitrant to biodegradation and stable to light, heat, and oxidizing agents (Kanagamani et al., 2019). Hence, it is persistent in the environment, and exposure to GV causes eye irritation and respiratory tract inflammation; long-term exposure leads to kidney damage, permanent blondness, cancer, and gastrointestinal tract problems (Abdi et al., 2020; Kanagamani et al., 2019). Moreover, the presence of trace quantities of the GV dye (>1.0 mg/L) affect the aesthetic quality and transparency of water bodies, rendering the receiving water body unfit for use (Nayak and Pal, 2021).
Over the past years, different techniques for efficient removal and degradation of organic dyes from wastewater have been studied (Fakhri et al., 2015; Huang et al., 2020; Wang et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2020), such as coagulation–flocculation (Lau et al., 2014), advanced oxidation processes (Zhou and He, 2007), membrane filtration (Nikooe and Saljoughi, 2017), chemical reduction (Chowdhury et al., 2018), photocatalysis (Bozkurt Çırak et al., 2019; Chen et al., 2020; Linsebigler et al., 1995; Priya et al., 2020), and adsorption (Rashid et al., 2017; Yang et al., 2016; Zhang et al., 2021; Zhou S. et al., 2021). Indeed, photocatalytic degradation is a highly promising and applicable technique for the removal of organic-based pollutants from wastewater. For removal and elimination of organic contaminants, photocatalytic degradation offers several advantages, including ease of operation, flexibility of material design, and the capability to produce high-class treated effluents (Zhou S. et al., 2021). The method is cost-effective, environmentally friendly, and able to operate at low temperatures, making it a suitable technology for wastewater treatment (Nguyen et al., 2018). Furthermore, photocatalytic degradation does not leave any harmful residues and can be applied immediately to diverse organic pollutant mixtures (Ahmad et al., 2021; Kanagamani et al., 2019; Khurram et al., 2020; Sarma et al., 2019).
Photocatalytic degradation is a technology that uses active photocatalysts, mainly metal oxides, in UV or visible irradiation to degrade organic substances through photodegradation mechanisms (Chen et al., 2020; Zhou Y. et al., 2021). The energy source for photocatalytic degradation is abundant and nonpolluting light (Zhou S. et al., 2021). Currently, a number of metal oxide semiconductors have been studied and applied for photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants, such as CuO (Weldegebrieal, 2020), ZnO (Sun et al., 2020), SnO2 (Luque et al., 2020), and TiO2 (Nguyen et al., 2018). Among the large family of metal oxides, hematite (α-Fe2O3) is one of the most effective visible-light-driven photocatalysts with better chemical stability, high crystallinity, cost-effectiveness, eco-friendliness, and absorbance of the majority of visible light (1.9–2.2 eV) (An et al., 2022). However, its single component reveals less light absorption and a fast electron–hole pair recombination rate due to the lesser band gap that limits its use in photocatalytic application (Schöttner et al., 2019), which has been improved by combining it with other metal oxides (Allawi et al., 2020).
A number of reported hematite-based hetero-structured materials, such as α-Fe2O3@ZnO (Suresh et al., 2018), α-Fe2O3/g-C3N4 (Yang et al., 2022), SnFe2O4/α-Fe2O3 (Jia et al., 2020), SnO2/α-Fe2O3 (Ma et al., 2021), and BiVO4/α-Fe2O3 (Ma et al., 2021), have shown enhanced photocatalytic efficiency than a single α-Fe2O3 oxide. MgO has shown remarkable potential in combination with various semiconductors to create binary heterojunctions with excellent photocatalytic activity. Specifically, at the interface of these heterojunctions, the photoinduced electrons can efficiently transfer from MgO to the other semiconductor. This electron transfer process enhances the lifetime of light-generated charge carriers and increases the overall light absorption. The primary significance of coupling α-Fe2O3 with MgO is to enhance the surface area development of α-Fe2O3 and reduce the recombination of photoinduced electron–hole pairs in α-Fe2O3 (Allawi et al., 2020; An et al., 2022). Combining α-Fe2O3 with MgO not only enhances the photocatalytic degradation activity but also favors creating eco-friendly nanocomposites with reduced toxicity. These nanocomposites have shown promising potential in various applications, particularly in the field of environmental remediation. By utilizing this combination, we can effectively degrade pollutants and contaminants while minimizing the environmental impact and promoting sustainable practices (Weldegebrieal, 2020; Xue et al., 2021).
Currently, great attention is being paid to using eco-friendly methods for the synthesis of nanoparticles. This is achieved mostly by the use of plant extracts. The method provides numerous advantages, including high yields, simplicity, short reaction times, easy inspection, and mild reaction conditions (Hatamifard et al., 2016; Nair et al., 2022). These favorable features enable the formation of crystalline nanoparticles with diverse shapes and morphology. The photocatalytic activity of nanomaterials is known to be influenced by various properties such as size, morphology, chemical composition, and surface structure. It is worth noting that these critical characteristics are directly affected by the synthesis methods employed (Kianfar and Universitesi, 2020). Moreover, various studies have reported the use of plant extracts during the synthesis of metal oxide nanocomposites for improving their catalytic properties (Chandran et al., 2014; Song et al., 2020; Wang et al., 2016; Wu et al., 2017; Xue et al., 2021). In line with these approaches, the specific plant material utilized in our study is Echinops kebericho M., an endemic plant found in Ethiopia and belonging to the Asteraceae family. This plant contains various phytochemicals, including alkaloids, flavonoids, and terpenoids, which are responsible for its therapeutic properties (Deyno et al., 2021).
By incorporating the Echinops kebericho M. plant extract in the synthesis process, we aim to leverage its unique phytochemical composition to enhance the catalytic properties of the resulting nanocomposites. This plant extract holds promise for providing additional benefits and functionalities to the synthesized nanoparticles, thereby contributing to the expanding field of eco-friendly and sustainable nanoparticle synthesis.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Chemicals used for green synthesis
Ferric nitrate (Fe(NO3)3·9H2O 98%), magnesium nitrate (Mg(NO3)2·6H2O 98%), and methanol (CH3OH 99.9%) obtained from Loba Chemie Pvt Ltd. and gentian violet (C25N3H30Cl 99.9% Sigma Aldrich) from Fine Chemical General Trading PLC in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, were used for the synthesis of the composites. All the chemicals used were of analytical grade and applied without further purification.
2.2 Preparation of Echinops kebericho M. crude extract
The plant sample was collected from Bole Arabsa, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia (located 8.97202° 8° 58′19″ north 38° 53′26″ east). Echinops kebericho M. tuber (20 g) was thoroughly washed with tap water and then with distilled water to remove dirt and other contaminants. After air-drying, the tuber was finely cut into small pieces and ground using a pulverizer (051701, B0B1HYP8VP, MYFULLY). The powder was extracted using distilled water in which the flask containing the powder and distilled water in a 1:5 ratio was refluxed at 100°C for 3 h. The obtained crude extract was filtered via Whitman Filter paper and cooled for further use (Beressa et al., 2020; Deyno et al., 2021; Navada et al., 2021).
2.3 Synthesis of Fe2O3 and Fe2O3/MgO nanocomposites
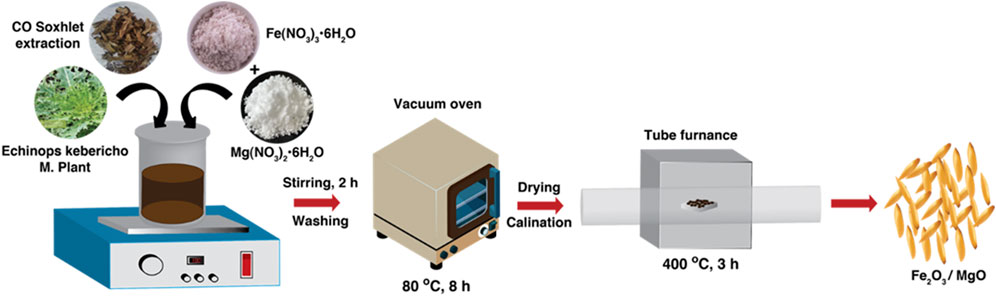
Prior to the synthesis of α-Fe2O3/MgO, a bare α-Fe2O3 control was prepared as follows: 0.05 M precursor solution of Fe(NO3)3·9H2O (100 mL) was stirred using a magnetic stirrer. Subsequently, 10 mL of Echinops kebericho M. extract was added dropwise with vigorous stirring at room temperature (See Figure 1). This gradual addition of the plant extract induced a remarkable transformation in the precursor solution, turning it into a deep brown color and resulting in the formation of a precipitate. To allow for complete reaction and precipitation, the resulting mixture was left undisturbed overnight. Then, the mixture was carefully separated to isolate the precipitate. To ensure the removal of any impurities, the separated precipitate was washed multiple times with double-distilled water and methanol. This rigorous washing procedure aimed to achieve a high purity level for the final product. Following the washing steps, the precipitate was subjected to a drying process to eliminate the residual moisture in an oven set to a temperature of 80°C for 8 h. To complete the synthesis of the desired nanocomposites, the powdered product obtained from the previous steps was subjected to annealing. The product was annealed at an optimized temperature of 400°C for a duration of 3 h. This annealing process played a crucial role in the formation and stabilization of the α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles. In a typical experimental setup, phytoextract-assisted α-Fe2O3/MgO nanoparticles with a molar composition of 2:1 were prepared using the homogenous co-precipitation method. This method ensured the formation of a well-dispersed and uniform nanocomposite structure, leveraging the use of the Echinops kebericho M phytoextract. The aforementioned detailed procedure aimed to achieve precise control in the synthesis of α-Fe2O3 as a basis for the subsequent synthesis of α-Fe2O3/MgO nanocomposites (Azhari et al., 2010). To synthesize α-Fe2O3/MgO NCs, a 0.05 M precursor solution (100 mL) of iron nitrate (Fe(NO3)3·9H2O) salt was prepared in a 500-mL beaker. A 0.025 M Mg (II) nitrate (Mg(NO3)2·6H2O) solution was added into the beaker containing ferric nitrate aqueous solution, followed by dropwise addition of 10 mL of Echinops kebericho M. extracts with vigorous stirring at room temperature to ensure a homogenous reaction. The precursor solution turned to deep brown, and a precipitate was formed after the addition of the plant extract, which reveals the development of heterojunction metal oxides. The resulting mixture was kept undisturbed for the whole night in order to allow the precipitate to settle down. The precipitate was separated and washed several times with double-distilled water (DDW) and methanol for removing the impurities. The obtained precipitate was oven-dried for 8 h at 80°C and ground by using a mortar and pestle. Finally, the obtained product was annealed at 400°C for 3 h to form α-Fe2O3/MgO nanocomposites for the photodegradation of GV (Hao et al., 2015; Munawar et al., 2021; Naga et al., 2019; Suresh et al., 2018).
2.4 Characterization of α-Fe2O3/MgO NCs
The structural analysis of α-Fe2O3/MgO NCs was carried out using the X-ray diffraction machine (XRD-7000S Shimadzu, Japan) with a nickel-filtered Cu radiation (CuKα, λ = 1.54056 Å). The scanning 2θ range was 10–80 and the accelerating voltage and filament current were maintained at 40 kV and 30 mA, respectively (Fierro and Spivey, 2015). The diffraction data pattern was analyzed by search match against the International Center for Diffraction Database (ICDD) using the software X'Pert HighScore Plus (Ekow et al., 2020).
Sizes of the NCs were calculated by Scherrer’s equation using the (101) reflection of α-Fe2O3/MgO (Hao et al., 2015). The morphology of the solids and particle size distribution were determined by scanning electron microscopy coupled with electron-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy SEM-EDS (Hitachi, TM1000) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM, FEI Tecnai G20, United States). The X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) method was applied to inspect the elemental composition of the synthesized NCs. The Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) micromeritics (ASAP 2420, United States) method was used for surface area measurements. The functional group analysis of the prepared sample was conducted using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR-8400S/Shimadzu, Japan). The FTIR analysis was performed over a frequency range of 400–4,000 cm−1, with a resolution of 2 cm−1. The band gaps of the synthesized nanocomposites were determined using UV–vis absorption spectrophotometry (Jenway 67, United Kingdom).
2.5 Photocatalytic activity of α-Fe2O3/MgO
The photocatalytic activity of the synthesized materials was assessed by measuring the rate of GV removal in an aqueous solution under visible light irradiation emitted by an LED lamp (58 W, λmax = 546 nm), within a photoreactor (Hu et al., 2019). The effects of catalyst load, pH, initial GV concentration, and time that control the photocatalytic efficiency of the nanocomposite were also optimized. Reaction suspensions were prepared by adding the required amount of the photocatalyst (50–125 mg L−1) with 100 mL of the GV solution, which had varying initial concentrations (ranging from 5 to 20 mgL−1) in the range of 5 mL, and adjusted to different pH levels within the range of 3–10. The photocatalytic reactions were then conducted under irradiation for specific time intervals of 20, 40, and 60 min. To establish adsorption/desorption equilibrium, the GV solution containing α-Fe2O3/MgO NCs was stirred in the dark for 30 min prior to irradiation. Subsequently, the solution was subjected to visible light illumination, while being continuously stirred (Zhou Y. et al., 2021). At regular time intervals, 5-mL aliquots were collected from each sample, followed by centrifugation and filtration to remove any particulate matter. The absorbance of the treated samples was then measured using a UV–vis spectrophotometer (Jenway 67, United Kingdom) to analyze the photodegradation of GV. The percent degradation of each sample was calculated using Equation 1. The relation given by Peng et al. (2019):
where A0 and At are the initial absorbance and the absorbance of the sample at time t, respectively.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Characterization of α-Fe2O3 and α-Fe2O3/MgO NCs
3.1.1 XRD analysis result
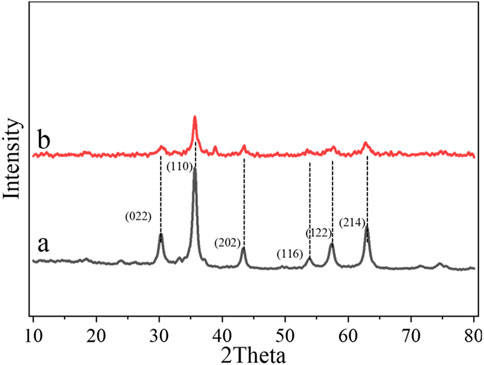
Figures 2A, B show the XRD patterns of Echinops kebericho M. extract-assisted α-Fe2O3 and α-Fe2O3/MgO. The diffraction peaks at 24.138 (012), 33.153 (104), 35.612 (110), 43.473 (202), 54.005 (116), 57.508 (122), and 62.385 (214) lattice planes in Figure 2A indicate the formation of rhombohedral (hexagonal) α-Fe2O3 NPs (JCPDS card no. 00-024–0072) (Saima et al., 2022). The diffraction peaks at 30.195 (022), 35.566 (131), 37.204 (222), 43.227 (040), 53.632 (242), 57.174 (151), and 62.788 (044) lattice planes in Figure 2B confirm the formation of cubic α-Fe2O3/MgO NCs (JCPDS card no. 96-900-3785) (Azhari et al., 2010). XRD analysis of α-Fe2O3/MgO showed that the peaks at angles 30.195o, 35.612o, 43.473o, 54.005o, 57.508o, and 62.385o correspond to the peaks of α-Fe2O3, confirming successful formation of α-Fe2O3/MgO NCs, as shown in Figure 2B. The existence of some weak peaks may be due to residuals from the synthesis processes of the NCs. The addition of MgO to α-Fe2O3 introduces a foreign material into the lattice structure of α-Fe2O3, leading to lattice strain and lattice parameter modifications. These changes can affect the diffraction pattern observed in XRD, resulting in altered peak intensities and shifts in the theta angle. This effect confirms the deformities of a crystalline lattice characteristic of the host metal oxide due to a combination with another material (Panchal et al., 2019). Therefore, the observed changes in the peak characteristics of the nanocomposites suggest the presence of deformities or distortions in the crystalline lattice of α-Fe2O3 caused by the combination with MgO. By applying (Equation 2) the Debye–Scherrer equation, the crystalline sizes of the synthesized α-Fe2O3 and α-Fe2O3/MgO were determined to be 11.2 and 15.4 nm, respectively. These results indicate that the nanocomposites were successfully synthesized with small particle sizes, resulting in a notable enhancement of the surface area-to-volume ratio. As a result, the photocatalytic activity of the NCs was greatly enhanced. Moreover, the formation of aggregates between α-Fe2O3 and MgO contributed to the improved surface porosity and enhanced photocatalytic activity of α-Fe2O3. The Debye–Scherrer equation is a fundamental equation used to estimate the average crystalline size of nanoparticles or nanocrystalline materials based on X-ray diffraction data. It relates the size of the crystalline domains (D) to the peak broadening (β), the wavelength of the X-ray radiation (λ), and the scattering angle (θ) using the following equation:
where D represents the crystalline size, K is the shape factor (usually taken as 0.9), λ is the X-ray wavelength, β is the full-width at half maximum (FWHM) of the diffraction peak, and θ is the Bragg angle.
3.1.2 FTIR analysis
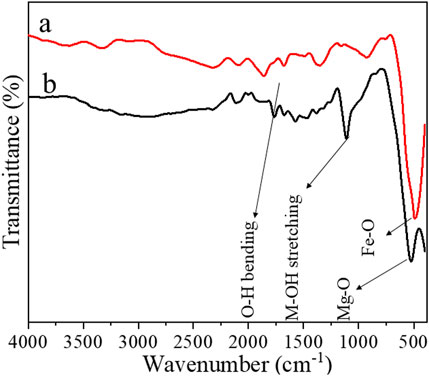
Figures 3A, B present the FTIR spectra of α-Fe2O3 and α-Fe2O3/MgO NCs in the wavenumber range of 400–4,000 cm−1, respectively. The bands observed at 434 cm−1 in Figure 3A and 520 cm−1 in Figure 3B correspond to the stretching vibrations of Fe-O and Mg-O bonds, respectively (Allawi et al., 2020). These bands provide information about the chemical bonding between α-Fe2O3 and MgO in the nanocomposites. A notable observation is that the relative intensity of these bands decreases when transitioning from α-Fe2O3 to α-Fe2O3/MgO, indicating changes in the bonding environment. The decrease in intensity suggests reduced abundance or strength of the Fe-O and Mg-O bonds in the nanocomposites compared to pure α-Fe2O3. This change in intensity can be attributed to the incorporation of MgO, which alters the chemical composition and bonding characteristics of the nanocomposites. Furthermore, the band positions for these vibrations exhibit a shift toward higher wavenumbers in the α-Fe2O3/MgO nanocomposites compared to α-Fe2O3. The shift in wavenumber suggests changes in the bond strength or bond lengths associated with the Fe-O and Mg-O stretching vibrations. The incorporation of MgO into the α-Fe2O3 lattice introduces structural modifications, which affect the vibrational properties and result in observed shifts in the FTIR spectra. In addition to the Fe-O and Mg-O stretching vibrations, bands in the range of 1700–1,650 cm−1 and 1,114–1,100 cm−1 are also observed. These bands correspond to specific molecular vibrations: the O-H bending vibration and the M-OH stretching vibration, respectively (Allawi et al., 2020; Sughra et al., 2022), altogether confirming the successful deposition of MgO on α-Fe2O3 and the successful development of α-Fe2O3 and α-Fe2O3/MgO. The presence of these bands confirms the existence of hydroxyl (OH) groups in the nanocomposites, which may be attributed to the adsorbed moisture or surface hydroxyl species. Taken together, the FTIR analysis provides valuable information about the chemical bonding and structural characteristics of α-Fe2O3 and α-Fe2O3/MgO nanocomposites. The observed changes in band intensity, shifts in wavenumber, and the presence of specific vibrational bands indicate the successful deposition of MgO on α-Fe2O3, as well as the successful development of α-Fe2O3 and α-Fe2O3/MgO nanocomposites.
3.1.3 SEM-EDS and TEM analysis results
Figures 4A–L show the SEM and TEM images of α-Fe2O3 and α-Fe2O3/MgO, as well as the corresponding EDS of α-Fe2O3/MgO NCs. In Figure 4A, the SEM micrograph reveals the formation of plate-shaped nano-clusters with a uniform and stable morphology in α-Fe2O3 powder. This demonstrates the successful development of α-Fe2O3 with desirable structural characteristics. Moving to Figure 4E, the SEM micrograph of α-Fe2O3/MgO exhibits the growth of ultrafine particles on the surface of α-Fe2O3, resulting in a nanoplate–road composite structure. The distortion of the plate-shaped nano-clusters of α-Fe2O3 into the nanoplate–road-like structure is attributed to the introduction of ultrafine MgO particles and the formation of a strong interface between the two materials. This observation is supported by the X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis presented in Figure 2B. The close interface between α-Fe2O3 and MgO in the nanocomposite facilitates efficient electron transfer, thereby enhancing the lifetime of light-generated charge carriers. This characteristic contributes to improved photocatalytic degradation performance. The presence of MgO not only alters the morphology but also enhances the electron transfer properties of α-Fe2O3, leading to better photocatalytic activity. Furthermore, the EDS mapping shown in Figures 4O–Q provides clear evidence of the presence and distribution of the targeted elements (Fe, Mg, and O) throughout the microstructure of the composite. This confirms the successful incorporation of both Fe and Mg elements within the composite, further supporting the formation of the α-Fe2O3/MgO nanocomposite.
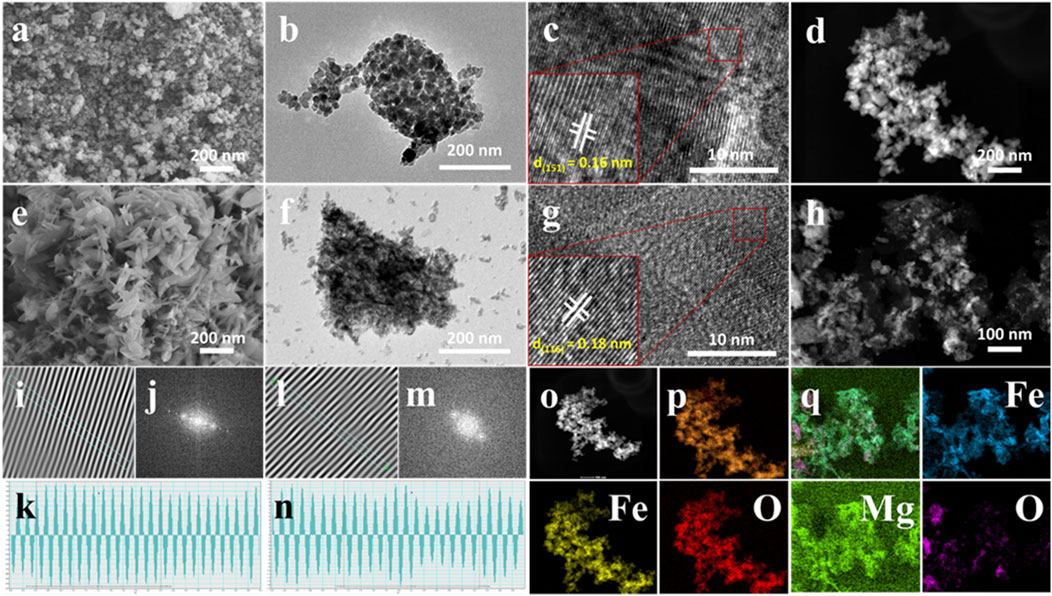
Figure 4. SEM (A), TEM (B), HRTEM (C, I–K), and STEM (D) profile/micrographs of α-Fe2O3 and SEM (E), TEM (F), HRTEM (G, L–N), and STEM (H) profile/micrographs of α-Fe2O3/MgO, as well as the EDS profile (O–Q) of α-Fe2O3/MgO.
The TEM analysis of α-Fe2O3 and α-Fe2O3/MgO nanocomposites, depicted in Figures 4B, F, provides detailed insights into their morphological and structural characteristics. The TEM image in Figure 4B reveals the hexagonal rhombohedral morphology of α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles. The well-defined shapes and uniformity of the particles indicate a high degree of crystallinity and stability in the structure. The TEM image in Figure 4F illustrates a cubic asymmetry morphology of α-Fe2O3/MgO, indicating the influence of MgO on the overall structure of the nanocomposite. The introduction of MgO leads to changes in the particle shape and arrangement within the α-Fe2O3 matrix, resulting in a modified morphology. The particle size distribution as analyzed from TEM by ImageJ software was 8–28 and 11–36 nm with a respective average size of 11.6 and 15.9 nm for α-Fe2O3 and α-Fe2O3/MgO, respectively, which is in agreement with the calculated values from XRD analysis using the Debye–Scherrer equation. Furthermore, HRTEM profiles were used to determine the d-spacing, which represents the space between each unit cell or particle. The HRTEM analysis, performed using ImageJ software, yielded d-spacing values of 0.12 nm for pure α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles and 0.16 nm for α-Fe2O3/MgO nanocomposites. These values indicate the presence of surface porosity and suggest the formation of aggregates between α-Fe2O3 and MgO. The increased d-spacing in the nanocomposite further supports the enhanced surface area and photocatalytic activity of α-Fe2O3 due to the presence of MgO (Albouchi et al., 2023).
3.1.4 XPS analysis results
The X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) method was applied to inspect the elemental composition information of the synthesized NC products. The wide-scan survey XPS profile in Figure 5A revealed the existence of Fe, Mg, and O elements in synthesized α-Fe2O3/MgO NCs. This implies the successful deposition of MgO on Fe2O3. The high-resolution XPS spectra of Fe 2p in Figure 5B displayed two high-intensity peaks at 711.8 and 726.1 eV, which were allotted to Fe 2p3/2 and Fe 2p1/2, respectively (Zhang et al., 2019). Moreover, a satellite peak at ∼719.2 eV confirmed the presence of Fe (III) of α-Fe2O3 (An et al., 2022). The high-resolution O 1s spectrum in Figure 5C shows an intense peak at 529.4 eV, which corresponds to the lattice oxygen atom in the NCs, which indicates that the valence state of O is (−2) (consistent with metal–oxygen bonds) oxygen defect sites (Khurram et al., 2020). The intense peak at 1,303.9 eV in Figure 5D is typical to Mg2+ species in the synthesized nanocomposite (Kumar et al., 2020; Bagus et al., 2020; Xu et al., 2021).
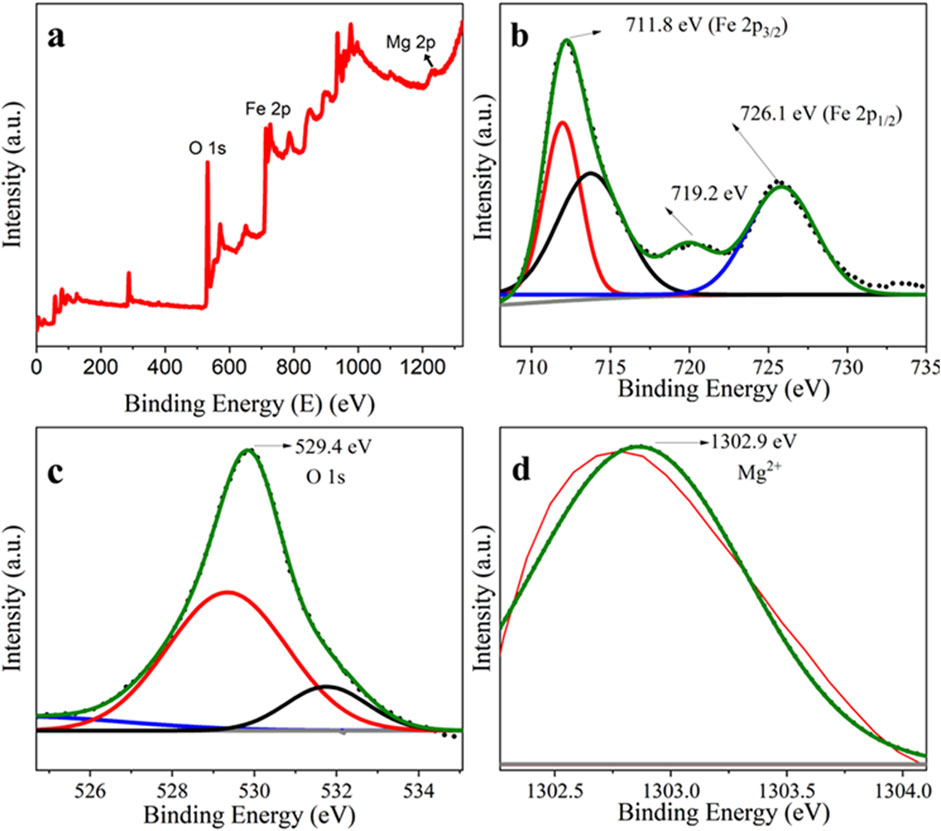
Figure 5. XPS profile of the full-scan survey of (A) α-Fe2O3/MgO, (B) core level bands of Fe 2p, (C) O 1 s, and (D) Mg 1 s.
3.1.5 UV–visible absorption spectra of α-Fe2O3 and α-Fe2O3/MgO NCs
The absorption spectra were used to study the energy band and the type of electronic transition. The UV–visible absorption spectra of α-Fe2O3 and α-Fe2O3/MgO NCs are shown in Figure 6. The UV–visible absorption spectra of α-Fe2O3 and α-Fe2O3/MgO in Figure 6 exhibit prominent peak regions between 340–376 and 470–570 nm, on the bases of the type of possible transitions responsible for producing the absorption band. These implies that the plant extract was stabilized and capped the surface of nanoparticles without the effect of surface plasmon resonance (Warren and Grzybowski, 2012; Ullah et al., 2018). The first absorption band region is formed due to the charge transfer of non-bonded electrons from O (2p) to the metal Fe (III) and Mg (II). This is responsible for the absorption of hematite in the visible region (Khurram et al., 2020). The second absorption band region is formed due to the d-d transition of the two magnetically coupled ions (Wang et al., 2005). Based on the spin selection rule, these transitions are allowed transitions. The absorption peak of α-Fe2O3 was shifted to the higher wavelength for α-Fe2O3/MgO. This is due to the incorporation of metal oxide in the α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles, which causes a variation in the band gap energy (Eg). The red-shift indicated increased absorption intensity within the visible region, which implied these composites can make excellent application in the visible irradiation. The spectra allowed observing the red-shift in the location or wavelength from the α-Fe2O3 nanoparticle which was annealed at 400°C (Hao et al., 2015; Mallick and Dash, 2013).
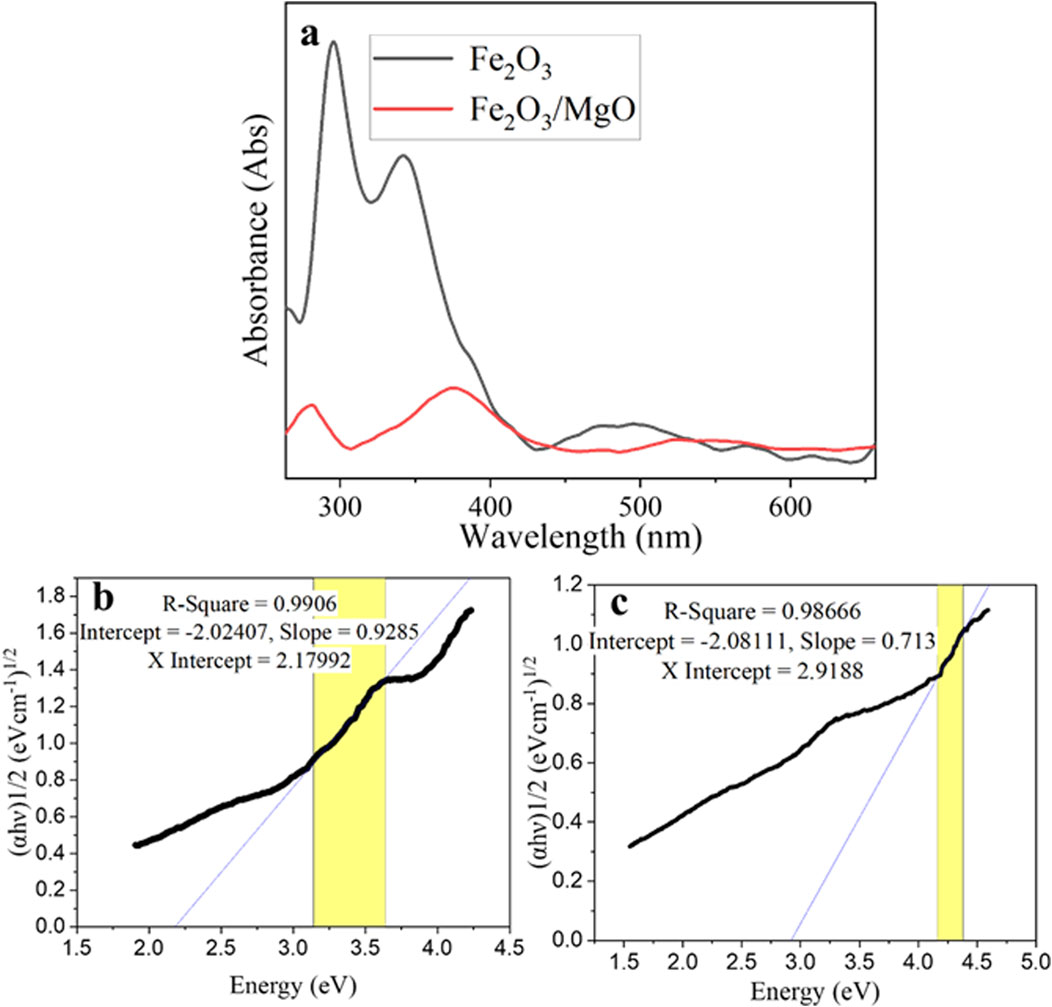
Figure 6. UV–vis spectra of: (A) α-Fe2O3 and α-Fe2O3/MgO, Tauc’s plot of (B) α-Fe2O3 and (C) α-Fe2O3/MgO.
The band gap energy of the synthesized material can be calculated by Tauc’s plot method through Equation 3 given below:
where
3.1.6 BET surface analysis
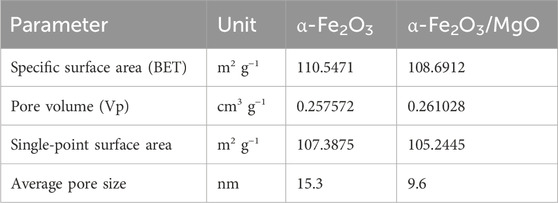
The specific surface area and porous nature of the green-synthesized α-Fe2O3 and α-Fe2O3/MgO nanocomposites were characterized using the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) and Barrett–Joyner–Halenda (BJH) methods, as shown in Figures 7A, B, respectively. The specific area and porous nature/surface characteristics of the green-synthesized α-Fe2O3 and α-Fe2O3/MgO NCs examined by BET and BJH methods are presented in Figures 7A, B, respectively. The BET pattern confirmed that both nanomaterials exhibit a mesoporous nature of a type IV sorption isotherm plot with H2 hysteresis loop (P/P0 > 0.4) (Rouquerol et al., 2013). The presence of the hysteresis loop suggests the existence of percolation phenomena, characterized by narrow ink-bottle-like pores within the nanomaterials. The particle size, pore volume, and BET surface area of α-Fe2O3 and α-Fe2O3/MgO nanocomposites are summarized in Table 1. These parameters provide further confirmation of the catalytic activity of the nanomaterials. Overall, the BET and BJH analyses of the α-Fe2O3 and α-Fe2O3/MgO nanocomposites demonstrate their mesoporous nature and confirm the presence of percolation phenomena. The particle size, pore volume, and BET surface area measurements provide valuable insights into the catalytic activity and surface characteristics of the nanomaterials.
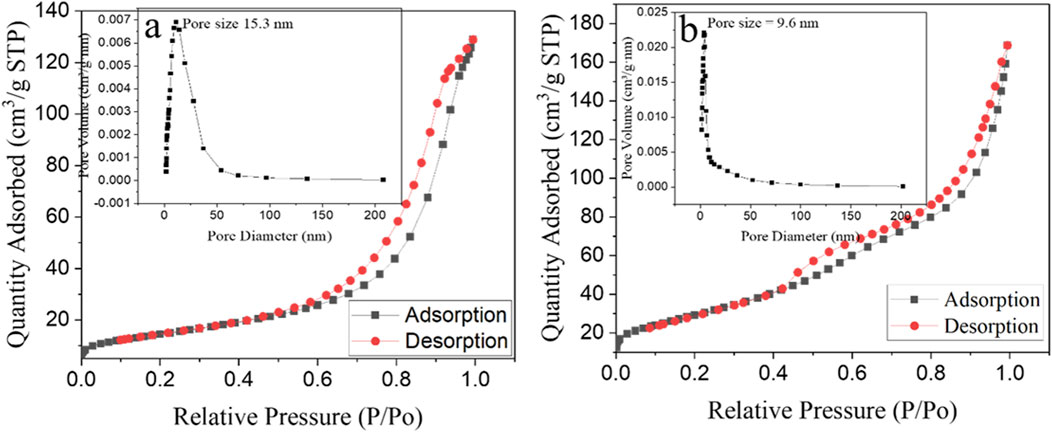
Figure 7. N2 adsorption/desorption isotherms with inset corresponding to the BJH plot of α-Fe2O3 (A) and α-Fe2O3/MgO (B) nanocomposite.
3.2 Photocatalytic activities of the synthesized NCs
The photocatalytic degradation activity of the synthesized materials was evaluated by measuring the rate of removal of GV in an aqueous solution under optimized conditions of catalyst dosage, pH, GV concentration, and time. The results of this evaluation are presented in Figures 8A–E.
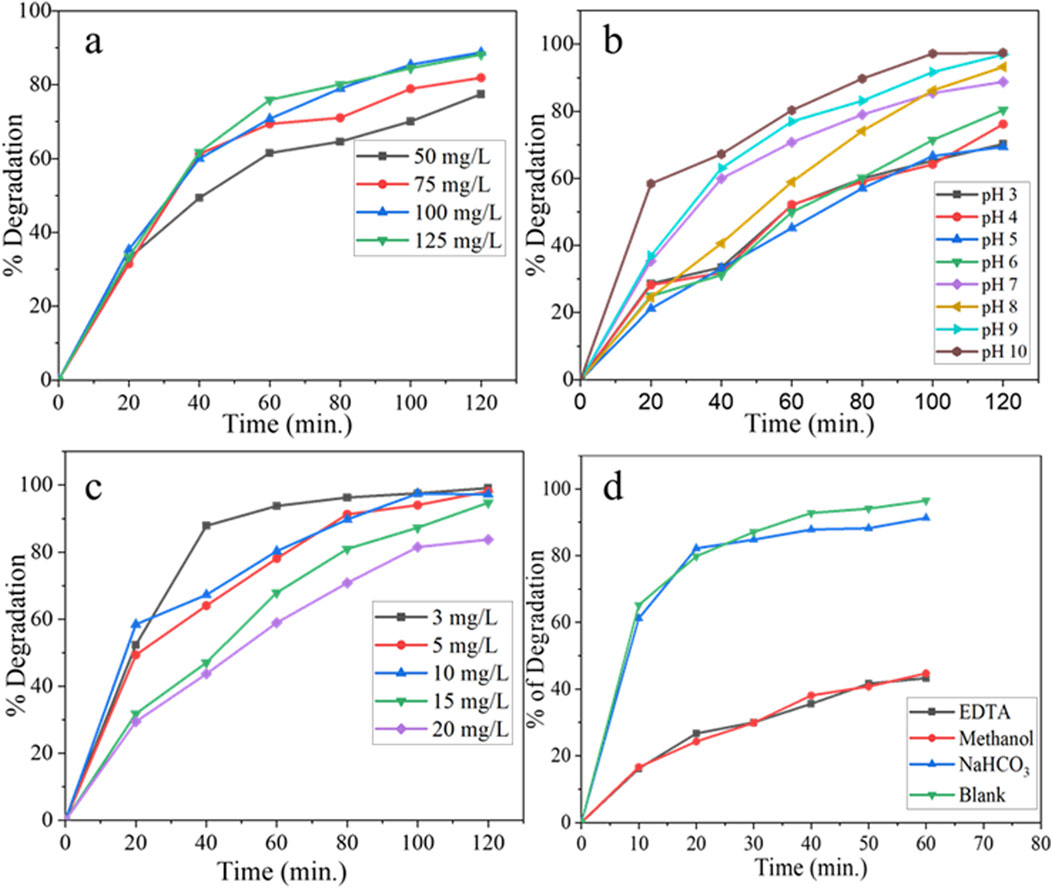
Figure 8. UV–visible spectra of photodegradation of GV at different (A) catalyst dose, (B) pH, (C) initial GV concentration, and (D) effect of different scavengers on the photocatalytic degradation of GV.
3.2.1 Effect of catalyst load
The optimal dosage of the photocatalyst for achieving efficient degradation was determined through a systematic variation in the photocatalyst amount within the range of 50–125 mgL−1 and evaluated in the presence of an initial dye concentration of 10 mgL−1, an irradiation time of 120 min, and at pH of 7. The results indicate that there was a noticeable increment in the photodegradation efficiency up to a photocatalyst dosage of 100 mgL−1. However, beyond this optimal value, the efficiency remained relatively constant. The maximum photocatalytic degradation efficiency of the NC observed at 100 mgL−1 catalyst load was 88.8% of the GV. The experimental trend can be attributed to the presence of an increased number of active sites as the photocatalyst dosage is increased within a given reactor design. However, further increases in the dosage led to a decline in the photodegradation efficiency due to the aggregation of particles, which repressed the availability of active sites. Additionally, when the dosage exceeded the optimal value, it resulted in a light screening effect that reduced the surface area of the nanocomposite exposed to light illumination, consequently diminishing the photocatalytic efficiency (Ahmad et al., 2021; Sajid et al., 2018; Sanakousar et al., 2021).
3.2.2 Effect of pH
The pH of the solution plays a crucial role in the photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants as it directly affects the surface-charge properties of the photocatalysts (Hanafi and Sapawe, 2020). The efficiency of the synthesized photocatalyst in degrading GV from the aqueous solution was evaluated at a dye concentration of 10 mgL−1, utilizing an optimized catalyst load of 100 mgL−1, an irradiation time of 120 min, and a pH range of 3–10, and the results are presented in Figure 8B. The synthesized phytoextract-assisted NC exhibited high activity for GV photodegradation in alkaline solutions, and more than 97% of GV was degraded. Alternatively, the degradation efficiency decreased with decreasing pH of the solution. The lower removal efficiency at lower pH might be allied with the GV adsorption capacity of the photocatalyst. At different pH values, GV will have different forms. The photocatalyst surface is negatively charged at higher pH, and the GV cations were electrostatically drawn further toward the catalyst surface, resulting in GV dye degradation. The maximum degradation efficiency of the synthesized material 97.4% was observed at pH 10 (Sanakousar et al., 2021).
3.2.3 Effect of initial GV load
The impact of the initial dye concentration on the efficiency of photocatalytic degradation was investigated within a concentration range of 3–20 mgL−1 for the GV solution. The experiment utilized an optimized catalyst load of 100 mgL−1, an irradiation time of 120 min, and an optimized pH of 10. The result depicted in Figure 8C demonstrates that as the concentration of the solution increases, the efficiency of photocatalytic degradation by the catalyst tends to decrease. This observation confirms the existence of an optimal dye coverage level that facilitates efficient reactions at the active sites. At an initial concentration of 3 mgL−1, the GV exhibited the highest percentage degradation (99.1%). Above that, due to inefficient adsorption on the surface of the photocatalyst, GV exhibits limited interactions with photons from the light source. Consequently, this leads to a decrease in the overall efficiency of the photodegradation process (Sanakousar et al., 2021). As the concentration levels increase, the probability of photocatalyst excitation weakens, and the dominant effect becomes the screening effect. Consequently, this leads to a decrease in the efficiency of degradation.
The percent photocatalytic degradation efficiency of α-Fe2O3/MgO as a function of time was monitored and compared with that of pure α-Fe2O3 under optimized conditions of catalyst load 100 mgL−1, GV concentration of 3 mgL−1, and pH of 10 (Figures 9A–D). The maximum degradation efficiency of GV (96.5%) was obtained using α-Fe2O3/MgO NC after 60 min of irradiation Figures 9A–D. The degradation rate for photocatalytic performance has followed a pseudo-first-order kinetic model with the rate of 0.025 min−1 and 0.05 min−1 for α-Fe2O3 and α-Fe2O3/MgO, respectively. Even though the observed results confirmed a higher photocatalytic degradation efficacy of the composite than that of bare α-Fe2O3 against GV, compared to previously reported values of NCs (Kossar et al., 2020; Sanakousar et al., 2021), both α-Fe2O3 and α-Fe2O3/MgO showed better degradation efficiency in a shorter period of visible light irradiation (Abdi et al., 2020; Kossar et al., 2020; Sanakousar et al., 2021). The observed difference in the degradation efficiency may be due to the Echinops kebericho M. plant extract used in the preparation of nanomaterials, which has contributed to its enhanced efficiency by producing special surface characteristics.
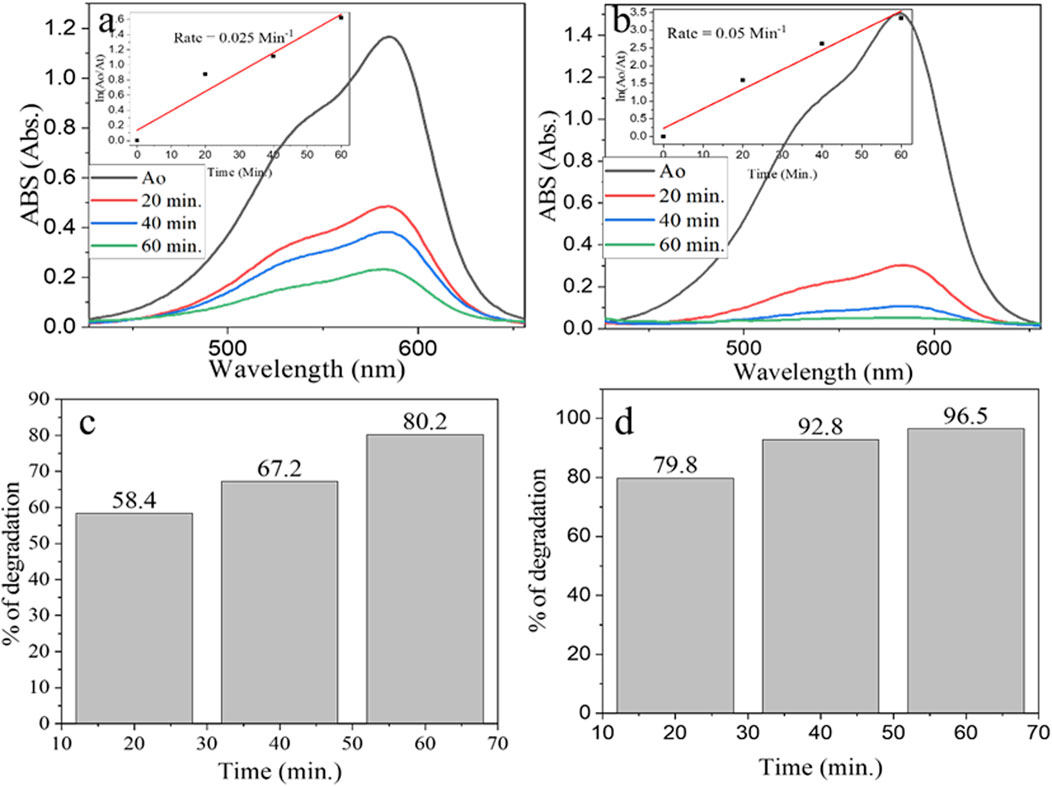
Figure 9. UV–visible spectra for degradation of GV by (A) α-Fe2O3 and (B) α-Fe2O3/MgO and % degradation efficiency of (C) α-Fe2O3 and (D) α-Fe2O3/MgO.
3.2.4 Effect of scavengers
The graph (Figure 8D) shows the degradation efficiency of GV in the presence of different scavengers (EDTA, methanol, and sodium bicarbonate) compared to a blank (control experiment with no scavenger). We investigated the effect of free radical scavengers on the degradation of GV. The results indicate that the addition of EDTA and methanol to the reaction mixture significantly inhibits the degradation of GV. The degradation efficiency of GV in the presence of EDTA was 43.3%, and in the presence of methanol, it was 44.3%. On the other hand, sodium bicarbonate had no effect on the degradation of GV. The decline in oxidation in the presence of scavengers is related to their higher affinity to react with free radicals. Therefore, the scavenger agents EDTA and methanol were found to have a higher affinity for free radicals, which led to a decrease in the degradation efficiency of GV. Overall, the result indicates that the addition of certain scavengers can affect the degradation efficiency of GV, which is important information for further research and development of methods to control the degradation of organic-based pollutants.
3.2.5 Mechanism of photocatalytic degradation of the GV dye
The photocatalytic degradation mechanism of α-Fe2O3/MgO can be further elucidated to provide a detailed understanding of the processes involved. When the surface of α-Fe2O3/MgO is exposed to visible light, it activates the excitation of electrons from the valence band (VB) to the conduction band (CB), as described by Equation 4. This excitation process leads to the formation of electron–hole pairs, which are crucial for the subsequent degradation reactions.
Once an electron is excited and occupies the CB, it can react with oxygen molecules (O2) present in the surrounding environment, resulting in the formation of superoxide radical anions (O2·−), as shown in Equation 5.
Furthermore, the superoxide radical anion can undergo protonation to form hydroperoxyl radicals (HOO·), as shown in Equation 6.
On the other hand, the positively charged hole (h+) in the VB can react with hydroxide ions (OH−) or water molecules (H2O), leading to the generation of hydroxyl radicals (OH·) as shown in Equation 7.
The superoxide radical anion (O2·-), hydroperoxyl radical (HOO·), and hydroxyl radical (OH·) formed in the previous steps can then react with the GV dye molecules, initiating their degradation. This degradation process involves various reactions and leads to the formation of several byproducts, as depicted in Equation 8 (Kanagamani et al., 2019; Kossar et al., 2021).
The enhanced surface characteristics and band gap energy of α-Fe2O3/MgO, which has been adjusted from 2.1 to 2.9 eV, play a vital role in the photocatalytic degradation. The increased band gap energy allows for improved light absorption, enabling the nanocomposite to harness a broader range of visible light for photocatalysis. Additionally, the optimized surface characteristics of α-Fe2O3/MgO contribute to efficient electron–hole pair separation, minimizing their recombination rates. This prolonged lifetime of the electron–hole pairs enhances the availability of reactive species, thereby facilitating the efficient degradation of the GV dye.
The photocatalytic degradation mechanism of α-Fe2O3/MgO involves the excitation of electrons, generation of superoxide radical anions and hydroxyl radicals, and subsequent reaction with the GV dye molecules. The enhanced surface characteristics and band gap energy of α-Fe2O3/MgO enable effective light absorption and decline of electron–hole pair recombination, thereby facilitating the efficient degradation of the GV dye.
4 Conclusion
The synthesis of phytoextract-assisted α-Fe2O3 and α-Fe2O3/MgO nanocomposites using the Echinops kebericho M. plant, endemic to Ethiopia, via the co-precipitation method, followed by calcination at 400°C, allowed for a comprehensive investigation of their structural, morphological, elemental, optical, and photocatalytic properties. The morphological analysis revealed that both α-Fe2O3 and α-Fe2O3/MgO nanocomposites exhibited a hexagonal structural arrangement, with the band gap energy of α-Fe2O3 and α-Fe2O3/MgO measured to be 2.1 and 2.9 eV, respectively. The results of the structural and elemental analysis confirmed that the deposition of MgO on α-Fe2O3 led to improved crystal size and pore properties. This successful deposition of MgO on α-Fe2O3 is of crucial importance as it contributes to the enhanced photocatalytic activity observed in the nanocomposite. In particular, the α-Fe2O3/MgO nanocomposite demonstrated a significantly higher photocatalytic degradation efficiency (96.2%) of GV dye from aqueous solution compared to bare α-Fe2O3 (80.2%). This improvement in degradation performance can be attributed to the elongated lifespan of light-induced charge carriers and a higher amount of light absorbed on the semiconductor surfaces, facilitated by the presence of MgO. The photocatalytic degradation reactions of the synthesized nanocomposites followed a pseudo-first-order kinetics model. Moreover, it is remarkable that both α-Fe2O3 and α-Fe2O3/MgO exhibited improved degradation efficiency within a shorter period of visible light irradiation compared to previously reported values. These findings highlight the promising application of Echinops kebericho M. plant extract-assisted nanocomposites in wastewater treatment. Considering the future directions for research, it is recommended to focus on the development of photocatalysts that efficiently degrade organic pollutants in wastewater, especially those that may contain radical scavengers. It is important to ensure that the photocatalysts possess improved stability and resistance to radical scavengers, thereby ensuring efficient and sustainable wastewater treatment. In summary, phytoextract-assisted α-Fe2O3 and α-Fe2O3/MgO nanocomposites exhibited favorable structural, morphological, elemental, optical, and photocatalytic properties. The incorporation of MgO resulted in enhanced photocatalytic degradation efficiency, making the nanocomposite a promising candidate for wastewater treatment applications. Further study should consider the development of photocatalysts that efficiently degrade organic pollutants from a wastewater that might contain radical scavengers that possess improved stability and resistance to radical scavengers, ensuring efficient and sustainable wastewater treatment.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
HT: conceptualization, data curation, investigation, methodology, supervision, writing–original draft, writing–review and editing, formal analysis, and software. MG: conceptualization, data curation, investigation, methodology, resources, writing–review and editing, and software. EW: conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, methodology, project administration, resources, supervision, validation, visualization, writing–review and editing, and investigation. LT: data curation, resources, software, conceptualization, methodology, writing–review and editing, formal analysis, funding acquisition, project administration, supervision, validation, and visualization. AM: resources, conceptualization, writing–review and editing, methodology, and supervision. JL: resources, conceptualization, writing–review and editing, and validation.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to Adama Science and Technology University for the financial support and Department of Chemical Engineering and Applied Chemistry, Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Republic of Korea, for all advanced instrumental characterization techniques.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors, and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fenvc.2024.1323752/full#supplementary-material
References
Abdi, M., Balagabri, M., Karimi, H., Hossini, H., and Rastegar, S. O. (2020). Degradation of crystal violet (CV) from aqueous solutions using ozone, peroxone, electroperoxone, and electrolysis processes: a comparison study. Appl. Water Sci. 10 (7), 168–210. doi:10.1007/s13201-020-01252-w
Ahmad, W., Khan, A., Ali, N., Khan, S., Uddin, S., Malik, S., et al. (2021). Photocatalytic degradation of crystal violet dye under sunlight by chitosan-encapsulated ternary metal selenide microspheres. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 28, 8074–8087. doi:10.1007/s11356-020-10898-7
Albouchi, W., Meftah, M., Ben, A., Amara, H., and Oueslati, W. (2023). Applied Surface Science Advances Effect of reactant ratio and nanofillers type on the microstructural properties, porosity fluctuations and heavy metal removal ability of chitosan-clay hybrid materials. Appl. Surf. Sci. Adv. 13, 100387. doi:10.1016/j.apsadv.2023.100387
Allawi, F., Juda, A. M., and Radhi, S. W. (2020). Photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue over MgO/α- Fe 2 O 3 nano composite prepared by a hydrothermal method. AIP Conf. Proc 2290, 030020. doi:10.1063/5.0029461
An, X., Chen, Y., Ao, M., Jin, Y., Zhan, L., Yu, B., et al. (2022) “Sequential photocatalytic degradation of organophosphorus pesticides and recovery of orthophosphate by biochar/α -Fe 2 O 3/MgO composite: A new enhanced strategy for reducing the impacts of organophosphorus from wastewater J. Chem. Eng 435, 135087. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2022.135087
Azhari, A., Sh, M. S., Golestanifard, F., and Saberi, A. (2010). Phase evolution in Fe 2 O 3/MgO nanocomposite prepared via a simple precipitation method. Mater. Chem. Phys. 124 (1), 658–663. doi:10.1016/j.matchemphys.2010.07.030
Beressa, T. B., Deyno, S., and Alele, P. E. (2020). Antifungal activity of the essential oil of Echinops kebericho mesfin: an in vitro study. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 3101324, doi:10.1155/2020/3101324
Bozkurt Çırak, B., Caglar, B., Kılınç, T., Morkoç Karadeniz, S., Erdoğan, Y., Kılıç, S., et al. (2019). Synthesis and characterization of ZnO nanorice decorated TiO2 nanotubes for enhanced photocatalytic activity. Mater. Res. Bull. 109, 160–167. doi:10.1016/j.materresbull.2018.09.039
Bagus, P. S., Nelin, C. J., and Brundle, C. R. (2020). Analysis of the Fe 2p XPS for hematite Fe 2 O 3: consequences of covalent bonding and orbital splittings on multiplet splittings. J. Chem. Phys, 014704. doi:10.1063/1.5135595
Chandran, P., Netha, S., and Sudheer Khan, S. (2014). Effect of humic acid on photocatalytic activity of ZnO nanoparticles. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 138, 155–159. doi:10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2014.05.013
Chen, M., Wang, H., Chen, X., Wang, F., Qin, X., Zhang, C., et al. (2020). High-performance of Cu-TiO2 for photocatalytic oxidation of formaldehyde under visible light and the mechanism study. Chem. Eng. J. 390, 124481. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2020.124481
Chowdhury, R., Mollick, M. M. R., Biswas, Y., Chattopadhyay, D., and Rashid, M. H. (2018). Biogenic synthesis of shape-tunable Au-Pd alloy nanoparticles with enhanced catalytic activities. J. Alloys Compd. 763, 399–408. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.05.343
Deyno, S., Asefa, M., Bazira, J., Makonnen, E., and Alele, P. E. (2021). Acute and repeated-dose toxicity of Echinops kebericho Mesfin essential oil. Toxicol. Rep. 8, 131–138. doi:10.1016/j.toxrep.2020.12.027
Ekow, E., Azis, S., Azowa, N., Mamoun, A., and Mohammad, D. (2020). Complex permittivity and power loss characteristics of α -Fe 2 O 3/polycaprolactone (PCL) nanocomposites: effect of recycled α -Fe 2 O 3 nano fi ller. Heliyon 6, e05595. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e05595
Fakhri, A., Rashidi, S., Tyagi, I., Agarwal, S., and Kumar, V. (2015). Photodegradation of Erythromycin antibiotic by γ -Fe 2 O 3/SiO 2 nanocomposite: response surface methodology modeling and optimization. J. Mol. Liq. 214, 378–383. doi:10.1016/j.molliq.2015.11.037
Fierro, J. L. G., and Spivey, J. J. (2015). Cu-promoted Fe 2 O 3/MgO-based fischer − tropsch catalysts of biomass-derived syngas. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 54, 911–921. doi:10.1021/ie504473a
Hanafi, M. F., and Sapawe, N. (2020). Materials Today: proceedings Influence of pH on the photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange using nickel catalyst. Mater. Today Proc. 31, 339–341. doi:10.1016/j.matpr.2020.06.094
Hao, C., Shen, Y., Wang, Z., Wang, X., Feng, F., Ge, C., et al. (2015). Preparation and characterization of Fe 2 O 3 nanoparticles by solid- phase method and its hydrogen peroxide sensing properties. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 4, 1069–1077. doi:10.1021/acssuschemeng.5b01150
Hatamifard, A., Nasrollahzadeh, M., and Sajadi, S. M. (2016). Biosynthesis, characterization and catalytic activity of an Ag/zeolite nanocomposite for base- and ligand-free oxidative hydroxylation of phenylboronic acid and reduction of a variety of dyes at room temperature. New J. Chem. 40 (3), 2501–2513. doi:10.1039/c5nj02909k
Hu, X., Zhao, H., Liang, Y., and Chen, R. (2019). Applied Catalysis B: Environmental Energy level mediation of (BiO) 2 CO 3 via Br doping for e ffi cient molecular oxygen activation and cipro fl oxacin photodegradation. Appl Catal. B, 258, 117966. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.117966
Huang, Y., Nengzi, L., Li, X., Meng, L., Song, Q., and Cheng, X. (2020). Fabrication of Cu2O/Bi25FeO40 nanocomposite and its enhanced photocatalytic mechanism and degradation pathways of sulfamethoxazole. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 109, 104932. doi:10.1016/j.mssp.2020.104932
Saima, Q., Duncan, G., Asif, A. T., and Safeer, A. (2022). Improved photoelectrochemical performance of chemically grown pristine hematite thin films. J Electron Mater 51, 652–669. doi:10.1007/s11664-021-09319-3
Jia, Y., Zhang, W., Yeon, J., Kang, M., and Liu, C. (2020). Z - scheme SnFe 2 O 4/α -Fe 2 O 3 micro-octahedron with intimated interface for photocatalytic CO 2 reduction. Chem. Eng. J. 402, 126193. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2020.126193
Kanagamani, K., Muthukrishnan, P., Saravanakumar, K., Shankar, K., and Kathiresan, A. (2019). Photocatalytic degradation of environmental perilous gentian violet dye using leucaena-mediated zinc oxide nanoparticle and its anticancer activity. Rare Met. 38 (4), 277–286. doi:10.1007/s12598-018-1189-5
Kezzim, A., Boudjemaa, A., Belhadi, A., and Trari, M. (2017). Photo-catalytic degradation of ibuprofen over the new semiconducting catalyst α-(Cu,Fe)2O3 prepared by hydrothermal route. Res. Chem. Intermed. 43 (7), 3727–3743. doi:10.1007/s11164-016-2837-8
Khurram, R., Wang, Z., Ehsan, F., Peng, S., Shafiq, M., and Khan, B. (2020). Synthesis and characterization of an a-Fe2O3/ZnTe heterostructure for photocatalytic degradation of Congo red, methyl orange and methylene blue. RSC Adv. 10, 44997–45007. doi:10.1039/d0ra06866g
Kianfar, E., and Universitesi, I. M. (2020). Catalytic properties of nanomaterials and factors affecting it. MedDocs.
Kossar, S., Banu, I. B. S., Aman, N., and Amiruddin, R. (2020). Investigation on photocatalytic degradation of crystal violet dye using bismuth ferrite nanoparticles. J. Dispersion Sci. Technol. 0, 2053–2062. doi:10.1080/01932691.2020.1806861
Kossar, S., Banu, I. B. S., Aman, N., and Amiruddin, R. (2021). Investigation on photocatalytic degradation of crystal violet dye using bismuth ferrite nanoparticles. J. Dispersion Sci. Technol. 42 (14), 2053–2062. doi:10.1080/01932691.2020.1806861
Kumar, N., Ghaffari, Y., Bae, J., and Soo, K. (2020). Synthesis of coral-like α -Fe 2 O 3 nanoparticles for dye degradation at neutral pH. J. Mol. Liq. 301, 112473. doi:10.1016/j.molliq.2020.112473
Kurniawan, T. A., Mengting, Z., Fu, D., Yeap, S. K., Othman, M. H. D., Avtar, R., et al. (2020). Functionalizing TiO2 with graphene oxide for enhancing photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue (MB) in contaminated wastewater. J. Environ. Manag. 270, 110871. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110871
Lau, Y. Y., Wong, Y. S., Teng, T. T., Morad, N., Rafatullah, M., and Ong, S. A. (2014). Coagulation-flocculation of azo dye acid orange 7 with green refined laterite soil. Chem. Eng. J. 246, 383–390. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2014.02.100
Linsebigler, A. L., Lu, G., and Yates, J. T. (1995). Photocatalysis on TiO2 surfaces: principles, mechanisms, and selected results. Chem. Rev. 95 (3), 735–758. doi:10.1021/cr00035a013
Luque, P. A., Nava, O., Soto-Robles, C. A., Chinchillas-Chinchillas, M. J., Garrafa-Galvez, H. E., Baez-Lopez, Y. A., et al. (2020). Improved photocatalytic efficiency of SnO2 nanoparticles through green synthesis. Optik 206, 164299. doi:10.1016/j.ijleo.2020.164299
Ma, C., Lee, J., Kim, Y., Cheol, W., Jung, H., and Yang, W. (2021). Rational design of α-Fe2O3 nanocubes supported BiVO4 Z-scheme photocatalyst for photocatalytic degradation of antibiotic under visible light. J. Colloid And Interface Sci. 581, 514–522. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2020.07.127
Mallick, P., and Dash, B. N. (2013). X-Ray diffraction and UV-visible characterizations of α -Fe 2 O 3 nanoparticles annealed at different temperature. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol 3(5), 130–134. doi:10.5923/j.nn.20130305.04
Munawar, T., Mukhtar, F., Yasmeen, S., Naveed-ur-Rehman, M., Nadeem, M. S., Riaz, M., et al. (2021). Sunlight-induced photocatalytic degradation of various dyes and bacterial inactivation using CuO–MgO–ZnO nanocomposite. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 28, 42243–42260. doi:10.1007/s11356-021-13572-8
Naga, P., Kumar, V., Ummey, S., Kalyani, L., Cherukuri, C. S., Barla, S., et al. (2019). Antibacterial efficacy of green synthesized α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles using Sida cordifolia plant extract. Heliyon 5, e02765. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02765
Nair, G. M., Sajini, T., and Mathew, B. (2022). Advanced green approaches for metal and metal oxide nanoparticles synthesis and their environmental applications. Talanta Open 5, 100080. doi:10.1016/j.talo.2021.100080
Navada, K. M., Nagaraja, G. K., Neetha, J., Souza, D., Kouser, S., Ravikumar, R., et al. (2021). Nanostructures for paracetamol sensing and biomedical applications. Ceram. Int. 47 (23), 33651–33666. doi:10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.08.275
Nayak, A. K., and Pal, A. (2021). Enhanced adsorption of gentian violet dye from water using lignocellulosic agricultural waste modified with di- and tri-carboxylic acids: artificial intelligence modeling, practical comprehension, mechanistic and regeneration analyses. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 9 (4), 105578. doi:10.1016/j.jece.2021.105578
Nguyen, C. H., Fu, C. C., and Juang, R. S. (2018). Degradation of methylene blue and methyl orange by palladium-doped TiO2 photocatalysis for water reuse: efficiency and degradation pathways. J. Clean. Prod. 202, 413–427. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.08.110
Nikooe, N., and Saljoughi, E. (2017). Preparation and characterization of novel PVDF nanofiltration membranes with hydrophilic property for filtration of dye aqueous solution. Appl. Surf. Sci. 413, 41–49. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.04.029
Noruozi, A., and Nezamzadeh-ejhieh, A. (2020). Preparation, characterization, and investigation of the catalytic property of α -Fe 2 O 3 -ZnO nanoparticles in the photodegradation and mineralization of methylene blue. Chem. Phys. Lett. 752, 137587. doi:10.1016/j.cplett.2020.137587
Panchal, P., Paul, D. R., Sharma, A., Hooda, D., Yadav, R., Meena, P., et al. (2019). Phytoextract mediated ZnO/MgO nanocomposites for photocatalytic and antibacterial activities. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 385, 112049. doi:10.1016/j.jphotochem.2019.112049
Peng, J., Lu, Z., Lu, J., Ma, Z., Song, M., Liu, X., et al. (2019). Enhanced selectivity for photodegrading ciprofloxacin by a magnetic photocatalyst modified with a POPD – CdS heterojunction embedded imprinted layer. New J. Chem. 43, 2610–2623. doi:10.1039/c8nj05710a
Priya, R., Faruq, M., and Suresh, S. (2020). Highly effective photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue using PrO2–MgO nanocomposites under UV light. Optik 206, 2–8. doi:10.1016/j.ijleo.2020.164318
Rashid, M., Price, N. T., Gracia Pinilla, M. Á., and O’Shea, K. E. (2017). Effective removal of phosphate from aqueous solution using humic acid coated magnetite nanoparticles. Water Res. 123, 353–360. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2017.06.085
Ritter, L., Solomon, K. R., Forget, J., Stemeroff, M., and O’leary, C. (2001). “PERSISTENT ORGANIC POLLUTANTS an assessment report on: DDT-Aldrin-Dieldrin-Endrin-Chlordane heptachlor-hexachlorobenzene mirex-toxaphene polychlorinated biphenyls dioxins and furans the international programme on chemical safety,” in IPCS within the framework of the inter-organization programme for the sound management of chemicals (IOMC).
Rouquerol, F., Rouquerol, J., and Maurin, P. L. (2013). Adsorption by powders and porous solids principles, methodology and applications. Academic Press Is an Imprint of Elsevier. doi:10.1016/B978-0-08-097035-6.09991-5
Sajid, M. M., Khan, S. B., Shad, N. A., Amin, N., and Zhang, Z. (2018). Visible light assisted photocatalytic degradation of crystal violet dye and electrochemical detection of ascorbic acid using a BiVO4/FeVO4 heterojunction composite. RSC Adv. 8, 23489–23498. doi:10.1039/c8ra03890b
Sanakousar, M. F., Vidyasagar, C. C., Jiménez-pérez, V. M., Jayanna, B. K., Shridhar, A. H., and Prakash, K. (2021). Efficient photocatalytic degradation of crystal violet dye and electrochemical performance of modified MWCNTs/Cd-ZnO nanoparticles with quantum chemical calculations. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2, 100004. doi:10.1016/j.hazadv.2021.100004
Sarma, G. K., Khan, A., El-Toni, A. M., and Rashid, M. H. (2019). Shape-tunable CuO-Nd(OH)3 nanocomposites with excellent adsorption capacity in organic dye removal and regeneration of spent adsorbent to reduce secondary waste. J. Hazard. Mater. 380, 120838. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.120838
Schöttner, L., Nefedov, A., Yang, C., Heissler, S., Wang, Y., and Wöll, C. (2019). Structural evolution of α-Fe2O3(0001) surfaces under reduction conditions monitored by infrared spectroscopy. Front. Chem. 7, 451–512. doi:10.3389/fchem.2019.00451
Song, Y., Yang, L., Xu, M., Lu, Q., Li, W., Ren, C., et al. (2020). Boosted photocatalytic activity induced NAMPT-Regulating therapy based on elemental bismuth-humic acids heterojunction for inhibiting tumor proliferation/migration/inflammation. Biomaterials 254, 120140. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2020.120140
Sughra, G., Shamaila, J., Sajjad, S., Khan, A., Maria, L., and Cristina, M. (2022). Enhanced electron transport by Fe 2 O 3 on NCQDs – MgO nanostructure for solar photocatalysis and electrocatalytic water splitting. Appl. Nanosci. 12 (6), 1815–1827. doi:10.1007/s13204-022-02424-7
Sun, L., Shao, Q., Zhang, Y., Jiang, H., Ge, S., Lou, S., et al. (2020). N self-doped ZnO derived from microwave hydrothermal synthesized zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 toward enhanced photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue. J. Colloid And Interface Sci. 565, 142–155. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2019.12.107
Suresh, R., Sandoval, C., Ramírez, E., Álvarez, Á., Mansilla, H. D., Mangalaraja, R. V., et al. (2018). Solid-state synthesis and characterization of α-Fe 2 O 3 @ ZnO nanocomposites with enhanced visible light driven photocatalytic activity. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 29 (23), 20347–20355. doi:10.1007/s10854-018-0170-2
Ullah, A., Kareem, A., Nami, S. A. A., Shoeb, M., and Rehman, S. (2018). Biology Biogenic synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles using Agrewia optiva and Prunus persica phyto species: characterization, antibacterial and antioxidant activity. J. Photochem. and Photobiol. B Biol. 185, 262–274. doi:10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2018.06.009
Wang, J., White, W. B., and Adair, J. H. (2005). Optical properties of hydrothermally synthesized hematite particulate pigments. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 3454, 3449–3454. doi:10.1111/j.1551-2916.2005.00643.x
Wang, Y., Michel, F. M., Choi, Y., Eng, P. J., Levard, C., Siebner, H., et al. (2016). Pb, Cu, and Zn distributions at humic acid-coated metal-oxide surfaces. Geochimica Cosmochimica Acta 188, 407–423. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2016.05.009
Wang, Y., Zhou, C., Wu, J., and Niu, J. (2020). Insights into the electrochemical degradation of sulfamethoxazole and its metabolite by Ti/SnO 2 -Sb/Er-PbO 2 anode. Chinese Chem. Let, 31, 2673, 2677. doi:10.1016/j.cclet.2020.03.073
Warren, C., and Grzybowski, B. A. (2012) Enhanced photocatalytic activity of hybrid Fe2O3-Pd nanoparticulate catalysts. Chem. Sci, 3–8.
Weldegebrieal, G. K. (2020). Photocatalytic and antibacterial activityof CuO nanoparticles biosynthesized using Verbascum thapsus leaves extract. Optik 204, 164230. doi:10.1016/j.ijleo.2020.164230
Wu, W., Shan, G., Xiang, Q., Zhang, Y., Yi, S., and Zhu, L. (2017). Effects of humic acids with different polarities on the photocatalytic activity of nano-TiO2 at environment relevant concentration. Water Res. 122, 78–85. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2017.05.010
Xu, G., Sun, J., Wang, G., Zhang, X., Deng, Z., Huo, L., et al. (2021). Graphitic carbon-doped mesoporous Fe 2 O 3 nanoparticles for long- life Li-ion anodes. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 4, 6689–6699. doi:10.1021/acsanm.1c00649
Xue, S., Xiao, Y., Wang, G., Fan, J., Wan, K., He, Q., et al. (2021). Adsorption of heavy metals in water by modifying Fe3O4 nanoparticles with oxidized humic acid. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 616 (1), 126333. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.126333
Yang, H., He, D., Liu, C., Zhang, T., Qu, J., Jin, D., et al. (2022). Visible-light-driven photocatalytic disinfection by S-scheme α-Fe2O3/g-C3N4 heterojunction: bactericidal performance and mechanism insight. Chemosphere 287 (P1), 132072. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132072
Yang, Z., Wang, F., Zhang, C., Zeng, G., Tan, X., Yu, Z., et al. (2016). Utilization of LDH-based materials as potential adsorbents and photocatalysts for the decontamination of dyes wastewater: a review. RSC Adv. 6 (83), 79415–79436. doi:10.1039/c6ra12727d
Zhang, J., Zhao, W., Li, Z., Lu, G., and Zhu, M. (2021). Visible-light-assisted peroxymonosulfate activation over Fe (II)/V (IV) self-doped FeVO 4 nanobelts with enhanced sulfamethoxazole degradation: performance and mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 403, 126384. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2020.126384
Zhang, L., Sellaoui, L., Franco, D., Dotto, G. L., Bajahzar, A., Belmabrouk, H., et al. (2020). Adsorption of dyes brilliant blue, sunset yellow and tartrazine from aqueous solution on chitosan: analytical interpretation via multilayer statistical physics model. Chem. Eng. J. 382, 122952. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2019.122952
Zhang, S., Yi, J., Chen, J., Yin, Z., Tang, T., Wei, W., et al. (2019). Spatially confined Fe2O3 in hierarchical SiO2@TiO2 hollow sphere exhibiting superior photocatalytic efficiency for degrading antibiotics. Chem. Eng. J. 380, 122583. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2019.122583
Zhou, M., and He, J. (2007). Degradation of azo dye by three clean advanced oxidation processes: wet oxidation, electrochemical oxidation and wet electrochemical oxidation-A comparative study. Electrochimica Acta 53 (4), 1902–1910. doi:10.1016/j.electacta.2007.08.056
Zhou, S., Fu, Z., Xia, L., Mao, Y., Zhao, W., Wang, A., et al. (2021). In situ synthesis of ternary hybrid nanocomposites on natural Juncus effusus fiber for adsorption and photodegradation of organic dyes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 255, 117671. doi:10.1016/j.seppur.2020.117671
Zhou, Y., Yu, M., Liang, H., Chen, J., Xu, L., and Niu, J. (2021). Applied Catalysis B: environmental Novel dual-effective Z-scheme heterojunction with g-C 3 N 4, Ti 3 C 2 MXene and black phosphorus for improving visible light-induced degradation of ciprofloxacin. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 291, 120105. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2021.120105
Keywords: photocatalyst, nanocomposite, gentian violet, degradation, green synthesis
Citation: Tedla H, Goddati M, Wondemagegnehu EB, Tufa LT, Mekonnen A and Lee J (2024) Phytoextract-assisted synthesis of Fe2O3/MgO nanocomposites for efficient photocatalytic degradation of gentian violet. Front. Environ. Chem. 5:1323752. doi: 10.3389/fenvc.2024.1323752
Received: 18 October 2023; Accepted: 11 November 2024;
Published: 06 December 2024.
Edited by:
Mohammad Mansoob Khan, Universiti Brunei Darussalam, BruneiReviewed by:
Xiang Ma, Taiyuan Institute of Technology, ChinaNur Ashmalina Haji Abd Rahman, Universiti Brunei Darussalam, Brunei
Copyright © 2024 Tedla, Goddati, Wondemagegnehu, Tufa, Mekonnen and Lee. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Eshetu Bekele Wondemagegnehu, ZXNoZXR1YmVrZWxlQGdtYWlsLmNvbQ==; Lemma Teshome Tufa, dHVmYTIwMDNAY251LmFjLmty; Jaebeom Lee, bmFub2xlZWxhYkBjbnUuYWMua3I=
 Haileyesus Tedla
Haileyesus Tedla Mahendra Goddati
Mahendra Goddati Eshetu Bekele Wondemagegnehu1*
Eshetu Bekele Wondemagegnehu1* Lemma Teshome Tufa
Lemma Teshome Tufa