- Department of Business Development and Technology, Aarhus School of Business and Social Sciences (BSS), Aarhus University, Herning, Denmark
With the continued development and progress of industrialisation, modernisation, and smart cities, global energy demand continues to increase. Photovoltaic systems are used to control CO2 emissions and manage global energy demand. Photovoltaic (PV) system public utility, effective planning, control, and operation compels accurate Global Horizontal Irradiance (GHI) prediction. This paper is ardent about designing a novel hybrid GHI prediction method: Bayesian Optimisation algorithm-based Optimized Deep Bidirectional Long Short Term Memory (BOA-D-BiLSTM). This work attempts to fine-tune the Deep Bidirectional Long Short Term Memory hyperparameters employing Bayesian optimisation. Globally ranked fifth in solar photovoltaic deployment, the INDIA Two Region Solar Irradiance Dataset from the NOAA-National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration was used to assess the proposed BOA-D-BiLSTM approach for the long-term prediction horizon. The superior prediction performance of the proposed BOA-D-BiLSTM is highlighted with the help of experimental results and comparative analysis with grid search and random search. Furthermore, the forecasting effectiveness is compared with other models, namely, the Persistence Model, ARIMA, BPN, RNN, SVR, Boosted Tree, LSTM, and BiLSTM. Compared to other forecasting models according to the resulting evaluation error metrics, the suggested BOA-D-BiLSTM model has minor evaluation error metrics, namely, Root Mean Squared Error: 0.0026 and 0.0030, Mean Absolute Error:0.0016 and 0.0018, Mean-Squared Error: 6.6852 × 10−06 and 8.8628 × 10−06 and R-squared: 0.9994 and 0.9988 on both dataset 1 and 2 respectively. The proposed BOA-D-BiLSTM model outperforms other baseline models. Thus, the proposed BOA-D-BiLSTM is a viable and novel potential forecasting model for effective distributed generation planning and control.
1 Introduction
Within the renewable energy canopy, solar energy has emerged as a potentially viable energy source to mitigate the increase in greenhouse gas emissions from fossil fuel combustion and address the ongoing energy issue (Madhiarasan, 2018). According to the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) report on 30 November 2022, India is ranked fifth globally in solar energy deployment, stating that around 70.10 GW (Gigawatt) of installed solar power is now available in India (Ministry of New and Renewable Energy, 2024). Global Horizontal Irradiance (GHI) prediction is necessary for solar energy systems to be deployed effectively because it affects grid stability, system design, and energy planning. Long-term GHI predictions are necessary for strategic planning, guaranteeing appropriate decisions on infrastructure expenditures, resource allocation, and policy creation. As the world moves toward energy from solar energy sources, the need for accurate long-term forecasting has increased since it helps energy suppliers anticipate fluctuation, maximise solar integration and reduce dependency on fossil fuels. Precise solar GHI forecasting is vital for the safe and effective integration of solar power into the grid system. The photovoltaic energy is unstable because of the inherent intermittency of solar irradiance and other climatic conditions. As a result, effective solar irradiance forecasting is regarded as one of the most essential issues in the power grid. Effective planning, balancing, and controlling requires forecasting the GHI in PV systems penetrating energy consumption and production. Long Short Term Memory (LSTM) proved effective in time series and sequence modelling applications. The Bidirectional LSTM is a variant of the LSTM to benefit from better results for real-time applications. Over the past 2 decades, time series, sequence learning, and other real-time applications have widely used BiLSTM (Bidirectional Long Short Term Memory). Fixing optimal hyperparameters requires experience and skill. Manual exploration of optimal hyperparameters is a relatively complex and time-consuming task. Optimisation of hyperparameter setup looks complicated since it varies based on the task to be performed, the dataset to be utilised, and so on, making each circumstance unique. Hyperparameters fine-tuning using trial-and-error, grid search, and random search are well-known methods but have less efficient, computationally costly, and uncertain issues, respectively. In a BiLSTM, significant performance changes occur because of the various hyperparameters. Optimal selection of the hyperparameter leads to outstanding and competing performances.
Estimating the optimal values of the hyperparameters is perplexing and requires much computational effort and cost. Optimisation algorithm-based hyperparameter fine-tuning is vital for better performance. Bayesian optimisation is effective and sensible for identifying the optimal hyperparameters of the BiLSTM. Numerous prediction models have been designed to predict the sporadic and non-linear solar irradiance time series (Global Horizontal Irradiance). However, most of these models bypass the application of Bayesian optimisation to maximise the hyperparameters throughout the training process for neural networks. The present work aims to bridge the gap using a new hybrid prediction approach (BOA-D-BiLSTM). Therefore, this paper strives to use Bayesian optimisation-based BiLSTM hyperparameter optimisation for the global solar irradiance (GHI) prediction task.
The following are the significant contributions of the paper:
• This research contribution provides a robust and reliable prediction model to bridge the gap between existing models and the growing demand for generic and precise prediction.
• The Bayesian optimisation algorithm is used to optimise the hyperparameters of Deep BiLSTM
• Hyperparameter optimisation based on the Bayesian optimisation algorithm is more effective and precise than grid and random search.
• Using two locations of real-time data from India, the analysis highlights the outstanding performance of the proposed BOA-D-BiLSTM model for long-term GHI forecasting.
• The BOA-D-BiLSTM model proposed in this research work was assessed and compared with eight baseline models on two data sets. Ultimately, it was discovered that the BOA-D-BiLSTM model performs better than the eight considered baseline models in terms of the least evaluation error metrics such as RMSE (Root Mean Squared Error), MAE (Mean Absolute Error), R2 (R-squared), and MSE (Mean Squared Error).
Section 1 introduces, discusses motivation, contributes, and highlights the proposed prediction model. Section 2 studied related work concerning the prediction of GHI and the importance of hyperparameter fine-tuning. Section 3 presents the description and concepts of the proposed prediction model. Section 4 discusses the details of the experimental simulation. Section 5 discusses the results and comparative analysis. Section 6 draws the summarised conclusion of the proposed prediction model, limitations, and future research direction.
2 Brief of solar irradiance prediction related work
Researchers and other professionals are increasingly advocating integrating solar energy into smart grids to moderate the dependence on fossil fuels while simultaneously encouraging the ecological and preservation of the environment. Thus, accurate and reliable global horizontal irradiance (GHI) forecasting is essential for predicting the prospective solar power era. The recurrent neural network with optimised hyperparameters performs better GHI prediction. Finding the optimal set of hyperparameters from all possible combinations is challenging if the number of hyperparameters is higher. The Bayesian optimisation algorithm can mitigate the LSTM hyperparameter optimisation problem. The hyperparameters of the GPR (Gaussian process regression) were optimised using Bayesian optimisation for the COVID-19 case forecasting (Alali et al., 2022). Mohammadi et al. (2015) predicted horizontal global solar radiation and used support vector regression (SVR). Two SVRs, the RBF (radial basis function) and the poly (polynomial basis function)—were used to examine the performance of long-term observations for a city in a sunny region of Iran. Moreover, SVR-rf significantly qualified for HGSR prediction utilising n and N, outperforming SVR-poly on accuracy. The gradient-boosted regression tree (GBRT) model, suggested by Persson et al. (2017), constitutes a nonparametric machine learning technique employed in multi-site solar power generation prediction over a forecast timeframe of 1–6 h. In contrast to GBRT model variants and single-site linear autoregressive models overall forecast horizons, the multi-site model showcases superior outcomes based on root mean squared error.
Yu et al. (2019) In this analysis, short-term predictions are made using an LSTM-based technique based on a timeline that includes global horizontal irradiance (GHI) in Atlanta and Hawaii 1 hour and 1 day ahead. According to the daily forecast results, LSTM continues to be more accurate than other models and successfully boosts RNN. Benamrou et al. (2020) introduced a novel hybrid method for predicting GHI hourly in Al-Hoceima, Morocco. The lagged satellite-derived GHI encompassing the point of interest was determined to be the most pertinent feature for this purpose using a deep long- and short-term memory network, Xgboost, Random Forest, and Recursive Feature Elimination with cross-validation. The selected feature was input to the suggested model, and the Grid Search algorithm was used to select the best prediction model. Jumin et al. (2021) Based on data collected in Malaysia, the enhanced decision tree regression (BDTR) model was implemented to forecast variations in solar radiation. The suggested model was then contrasted with neural networks and linear regression. Sensitivity and uncertainty analysis was included to verify the truthfulness of the recommended model. Xiang et al. (2021) proposed a hybrid machine-learning algorithm to predict solar power accurately. The Persistence Extreme Learning Machine (P-ELM) algorithm trains the hybrid model, which performs more proficiently in short-term forecasting than the ELM algorithm.
Bou-Rabee et al. (2022) To obtain precise solar irradiation predictions, a DL model is built that uses the attention mechanism employed in bidirectional long short term memory (BiLSTM) is built. The suggested model works on both sunny and cloudy days to provide better accuracy in various weather situations. Madhiarasan and Louzazni (2022) considered various influencing meteorological parameters as inputs for a novel Combined Long Short-Term Memory Networks (CLSTMN). The suggested prediction model is aggregated and compounded by many inputs associated with six distinct long short-term memory models built to increase the accuracy and generalisation of solar irradiance prediction. Vijay and Saravanan (2022), a Bayesian optimisation-based regression tree (BORT) machine learning technique was used to anticipate the values of global horizontal irradiance (GHI). The analysis of Bayesian optimisation’s performance against grid and random search methods has demonstrated its validity. Medina-Santana et al. (2022) Two deep learning models (feed forward and recurrent neural networks) are utilised to forecast renewable sources over a long period for a site in Michoacan, Mexico, to address the uncertainty surrounding solar resources. Michael et al. (2022) By incorporating stacked LSTM layers, dropout architecture, and LSTM-based model, this work suggests an optimised stacked Bidirectional Long Short Term Memory (BiLSTM)/Long Short Term Memory (LSTM) model for predicting univariate and multivariate hourly time series data. The model’s performance is improved using Bayesian optimisation to adjust six pertinent hyperparameters. The accuracy of the predicted results is equivalent for both GHI and POA (Plane of Array) when using real-world solar data from the Sweihan Photovoltaic Independent Power plant in Abu Dhabi, UAE, and NREL solar data for year-round data.
Li et al. (2023) presented long- and short-term memory networks (BO-LSTM) with a Bayesian algorithm for short-term heat load forecasting. To remove noise from the data, apply the moving average data smoothing technique. The model’s input is ascertained using Pearson’s correlation analysis. Chodakowska et al. (2023) employed data from Poland and Jordan to examine autoregressive integrated moving average (ARIMA) models for the seasonal forecasting of solar radiation under various climatic situations. ARIMA models are used to anticipate solar radiation and may assist in ensuring that solar energy is steadily and firmly integrated into national systems. Krishnan et al. (2024) An ensemble model that uses gradient boosting was built and suggested for India’s different climate zones for forecasting hourly global horizontal irradiance. The autoregressive integrated moving average (ARIMA), 2-layer feed-forward neural network, and long short-term memory (LSTM) are used as benchmarks for the gradient boost-based model; it is noticed an improved set of performance measures was attained by gradient boosting. Herrera-Casanova et al. (2024) deployed the Bayesian optimisation algorithm and BiLSTM in conjunction with bootstrap resampling for interval predictions to provide hour-ahead photovoltaic power prediction. A Bayesian optimisation algorithm (BOA) is used in conjunction with the BiLSTM model to optimise its primary hyperparameters and improve its prediction performance. The suggested model reduces the normalised mean absolute error (nMAE) compared to the MLP and RF comparison models.
The literature shows that identifying optimal hyperparameters in bidirectional long short term memory is crucial, complicated, time-consuming, and expensive. Predicting solar irradiance with accuracy has become much more crucial in light of the growing use of solar energy in power and energy systems globally. Several studies use ML or DL models for PV solar energy forecasting, as shown in the literature study. It is clear from the literature review that using hybrid models, which combine many basic models with optimal hyperparameters, improves prediction accuracy. Still, other research suggests extremely complicated models that require extended training. Although research indicates that hyperparameter tuning can improve prediction model accuracy, some studies carry out this modification by trial and error, taking a long period without ensuring optimal correspondence. With motivation from the existing literature, the BiLSTM optimal hyperparameter set is automatically fine-tuned and identified using the Bayesian optimisation algorithm applied for solar GHI prediction using the two India region datasets in this research work.
3 Proposed bayesian optimisation algorithm-based optimized deep bidirectional long short term memory (BOA-D-BiLSTM)
The proposed BOA-D-BiLSTM mathematical modelling and descriptions are detailed below:
3.1 Deep bidirectional long short term memory network (deep BiLSTM)
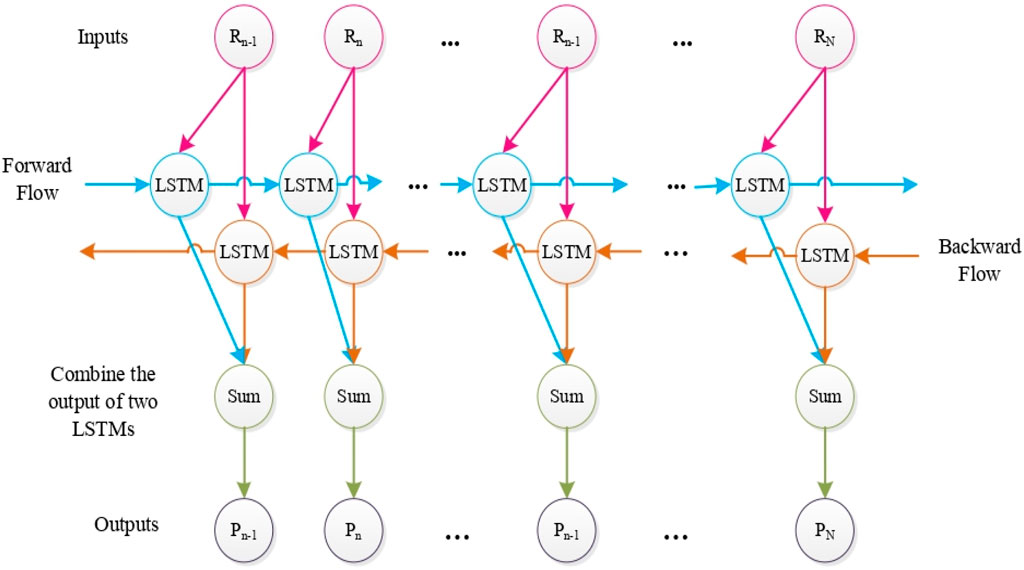
The unique feature is the information process from the past to the future (forward flow) and from the future to the past (backward flow) (Graves and Schmidhuber, 2005). It consists of two LSTM layers, one for the forward information flow and the other for the backward information flow. BiLSTM can extract more complex relationships from the input sequence by considering historical and longitudinal data. By combining the two LSTM layers, the final output is obtained. The prediction may be required to be decided jointly by the previous and subsequent inputs. Improvement in prediction performance uses forward and backward transitions. Thus, making the network learn better and more feasible for real-time applications. Building the deep architecture model involves stacking more than one BiLSTM. Figure 1 shows the simplified BiLSTM model.
BiLSTM simplified mathematical model representation in terms of matrix form.
Mathematical model of BiLSTM and gate updating
The BiLSTM output vector
Where,
Selecting an activation function
3.2 Bayesian optimisation algorithm
The Bayesian optimisation algorithm solves difficulties by finding the optimal parameters that minimise the objective function in a finite area, with lower and upper bounds on each variable, as given by Equation 11 (Pelikan et al., 1999).
Where,
Two fundamental elements that constitute the Bayesian Optimisation Algorithm (BOA):.
• Probabilistic (surrogate) framework: BAYES’ THEOREM serves as the basis for BOA, which approximates the objective function via a surrogate framework in each iteration efficiently sampled. A Gaussian process serves as the best stand-in framework for choosing a desirable group of hyperparameters to assess the actual objective function. The objective function is determined using a surrogate framework and utilised to direct upcoming sampling.
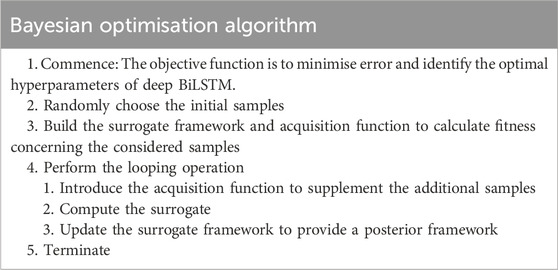
• Acquisition function: The acquisition function intends to discover the most promising group of hyperparameters that should be assessed next by using Bayesian knowledge to determine the optimal observation point in each iteration and propose a new sampling point. The processes of exploration and extraction are balanced through the acquisition function. Exploitation concentrates on areas of the search space that have a greater chance of yielding an improved solution based on the present surrogate framework, whereas exploration pursues less-explored areas of the search space. The Bayesian Optimisation Algorithm Pseudocode is shown in Table 1.
3.3 Proposed BOA-D-BiLSTM
This section is devoted to describing the proposed framework. Deep BiLSTM hyperparameter tweaking is significant in achieving the best model performance. The disadvantages of automatic optimisation strategies like grid and random search are that they take a long time for more giant parameter sets and do not always provide the best finding, respectively. In contrast, the Bayesian optimisation algorithm (BOA) is a well-informed method that evaluates simply the most promising models using a surrogate framework. With fewer sampling points and a quicker computing time, the Bayes theorem is applied to construct the posterior distribution of the objective function.
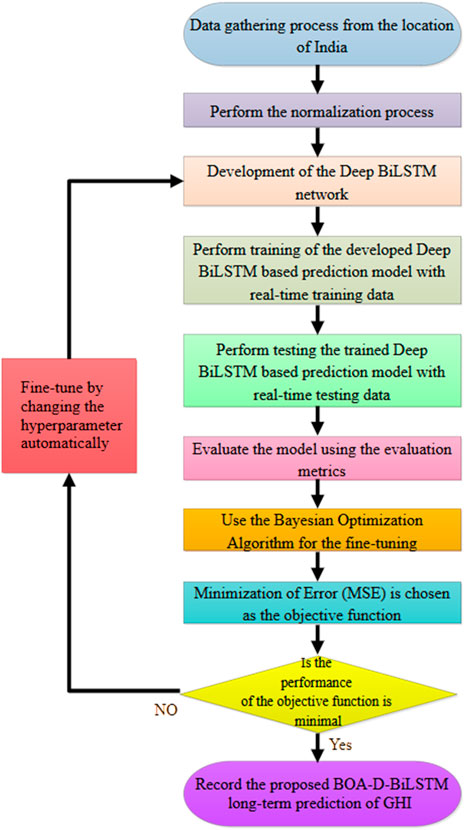
To enhance the long-term prediction of GHI, the best hyperparameters for deep BiLSTM, such as its number of hidden layers, hidden nodes, learning rate, regularisation, and other significant hyperparameters, were found using the Bayesian optimisation method (BOA). The Bayesian optimisation algorithm was used to optimise Deep BiLSTM concerning the optimal and promising hyperparameter and the performance evaluated on the two datasets for the GHI prediction in the long-term horizon. Figure 2 illustrates the proposed BOA-D-BiLSTM prediction model workflow and model built according to the set values and parameters presented in Table 2. The author uses 10 times the number of hyperparameters optimised as the initial samples and then processed with complete samples. The convergence is determined by the minimisation of the MSE.
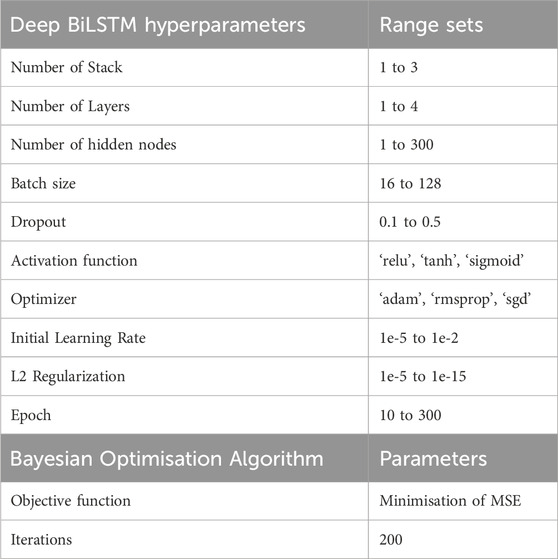
Table 2. Range set of hyperparameters for the Deep BiLSTM and Bayesian optimisation algorithm parameters.
4 Experimental simulation details
The proposed BOA-D-BiLSTM prediction model and other models from the literature are used in the hp laptop system configuration of the AMD Ryzen 5 3550H processor, RAM: 8 GB, 2100 Mhz and GPU: 4 GB. The proposed Deep BiLSTM hyperparameters, namely, the number of stacks, number of hidden layers, number of hidden nodes, learning rate, dropout rate, batch size, optimiser, activation function, and L2 regularisation, are optimally fixed using the Bayesian optimisation algorithm. The Bayesian optimisation algorithm is based on identified optimal hyperparameters associated with prediction model performance assessed based on the India region’s two datasets (Datasets 1 and 2).
4.1 Data source
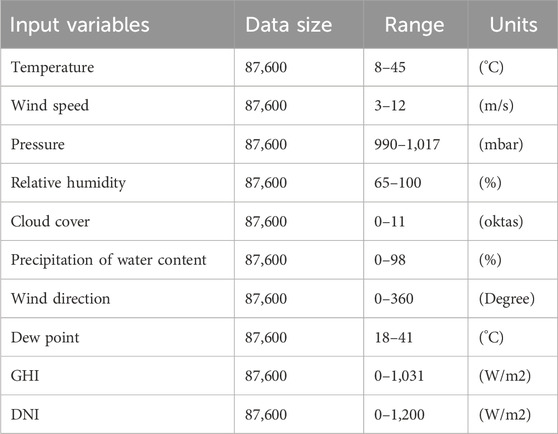
Environmental variables such as temperature, wind speed, pressure, relative humidity, cloud cover, precipitation of water content, wind direction, dew point, and sun irradiance (GHI and DNI (Direct Normal Irradiance (DNI)) are closely related to solar energy fluctuations. Table 3 shows the statistics of the dataset. This research experiment used data from India’s two regions, namely, Chennai and Jammu. We used two data sets of Chennai and Jammu locations in India that contain 10 years of datasets consisting of GHI and other environmental variables for our investigation and simulation evaluation. The daily resolution for each meteorological parameter (Dataset 1 and Dataset 2) is included in the data, encompassing 10 years from 01 January 2013 to 31 December 2022 hourly collected data, which is obtained from the NOAA (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration).
4.2 Normalisation
In this investigation, the collected real-time data was processed in the range (0, 1) using the Min-Max normalisation approach, as represented by the Equation 12.
Where,
4.3 Training and testing data sets
The proposed models possess the ten input nodes: GHI, DNI, temperature, wind speed, pressure, relative humidity, cloud cover, precipitation of water content, wind direction, and dew point. The predicted GHI is the output node. The collected two region datasets (1 and 2) consist of 87,000 data points of all considered inputs, which are separated into training and testing sets based on the ratio 70:30, respectively.
4.4 Evaluation error metrics
This paper used RMSE (Root Mean Squared Error), R2 (R-squared), MSE (Mean Squared Error) and MAE (Mean Absolute Error) as evaluation error metrics to evaluate the proposed Bayesian Optimisation algorithm-based Optimised Deep Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory (BOA-D-BiLSTM) and other baseline prediction model performance. Equations 13–16 state the evaluation metric formulations.
Let, N - the total number of the samples,
5 Results and discussion
Global solar irradiance (GHI) prediction is a vital problem in photovoltaic systems for vendors and power system engineers. The proposed BOA-D-BiLSTM and other baseline models were simulated on MATLAB R2024a. The detailed proposed BOA-D-BiLSTM prediction model result analysis and discussion regarding traditional optimisation methods (grid search and Random search) and comparative result assessment with the other eight baseline models are presented as follows.
5.1 Comparative analysis with other traditional optimisation methods for long-term prediction of global horizontal irradiance
Grid and random search are the traditional methods used to identify the optimal parameter sets and comparative analysis. In the context of the two data sets from the India region, this research constitutes a deep bidirectional long short term memory network that is resilient and optimised for long-term global horizontal radiation (GHI) prediction. The results achieved are tabulated in Table 4. From experimentation observation, it was noticed that grid searches are notoriously time-consuming. The trial-and-error method results in uncertain efficiency, and the grid search is exorbitant in computational complexity. In order to optimally use the network’s capability, hyperparameters must be appropriately configured. Grid Search and Random Search (RS) are common approaches for hyperparameter optimisation. Still, they are computationally costly, may take a long time to analyse, may result in inappropriate hyperparameters, and produce an extensive variance during computation. The advantage of Bayesian optimisation algorithms is that they prevent being trapped in the optimal solution.
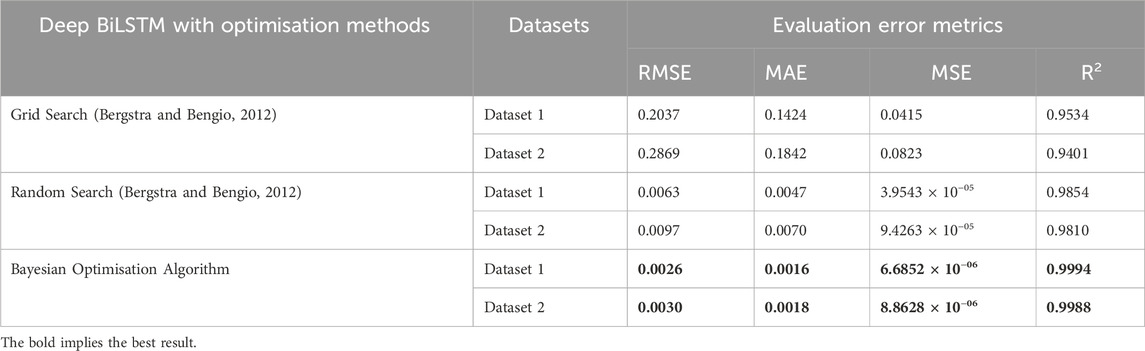
Table 4. Proposed Deep BiLSTM Optimised with Bayesian optimisation algorithm comparative analysis with other traditional optimisation methods.
The Bayesian optimisation algorithm optimises the Deep BiLSTM hyperparameters to overcome the traditional optimisation limitations. The findings suggest that the models’ GHI prediction capabilities are considerably enhanced by adjusting the hyperparameters using random search, grid search, and Bayesian optimisation algorithms. The experimental results show that compared to the grid search, random search-based identified hyperparameters-based Deep BiLSTM results are better but do not surpass the Bayesian optimisation algorithm-based identified hyperparameters-based BiLSTM prediction model for long-term solar GHI prediction application. Random search-based BiLSTM achieves reduced RMSE, MAE, MSE, and R2 compared to grid search-based BiLSTM, but it is not supreme compared to Bayesian optimisation algorithm-based BiLSTM. As the number of hyperparameters rises, grid search algorithms become less effective, and computation time complexity becomes problematic. The approach employs the Bayesian optimisation algorithm to discover the optimal combination in an acceptable time. Moreover, the prediction performance of BiLSTM is greatly enhanced by tweaking hyperparameters during training and testing. With this, it was concluded that the optimised hyperparameter based on the proposed Bayesian optimisation algorithm incurred BiLSTM outperforms in terms of better performance and faster convergence. The Bayesian optimisation algorithm outperforms grid search and random search because it can intelligently navigate complex, high-dimensional parameter spaces with few iterations. Therefore, the authors considered the Bayesian optimisation algorithm accurate and simple compared to the traditional hyperparameter fine-tuning method, which was clearly inferred from Figure 3. The identified significant hyperparameters based on the Bayesian optimisation algorithm based identified significant hyperparameters are tabulated in Table 5. Finding the best set of parameters in an acceptable amount of time may be accomplished through hyperparameter tweaking using Bayesian optimisation. Additionally, it benefits in reducing model overfitting problems.
Figure 3. Comparative analysis of the 3D column of proposed BOA-D-BiLSTM with other traditional optimisation methods.

Table 5. The proposed Bayesian optimisation algorithm identified the optimal significant hyperparameter of the Deep BiLSTM.
5.2 Comparative analysis of proposed BOA-D-BiLSTM with other baseline models
In existing global horizontal prediction applications research, many prediction models were suggested using baseline models such as the persistence model, ARIMA (Autoregressive integrated moving average), RNN (recurrent neural network), BPN (backpropagation neural network), SVR (Support Vector Regression), Boosted Tree, LSTM (Long Short Term Memory) and BiLSTM (Bidirectional Long Short Term Memory). All these models predict values based on the present and past information, and the selection of hyperparameters is not optimal. Still, in real-time applications, consideration of future information along with past and present and optimal hyperparameter-associated neural networks leads to improved prediction performance. To address this issue, the paper uses the deep Bi-LSTM with the Bayesian optimisation algorithm-based optimised hyperparameters to predict the GHI in the long-term horizon time scale. The results of the proposed BOA-D-BiLSTM investigations are examined in the configuration as per Table 5; listed hyperparameters and other parameters of the baseline model are considered as per the literature but evaluated on the India region. The results attained are tabulated in Table 6.
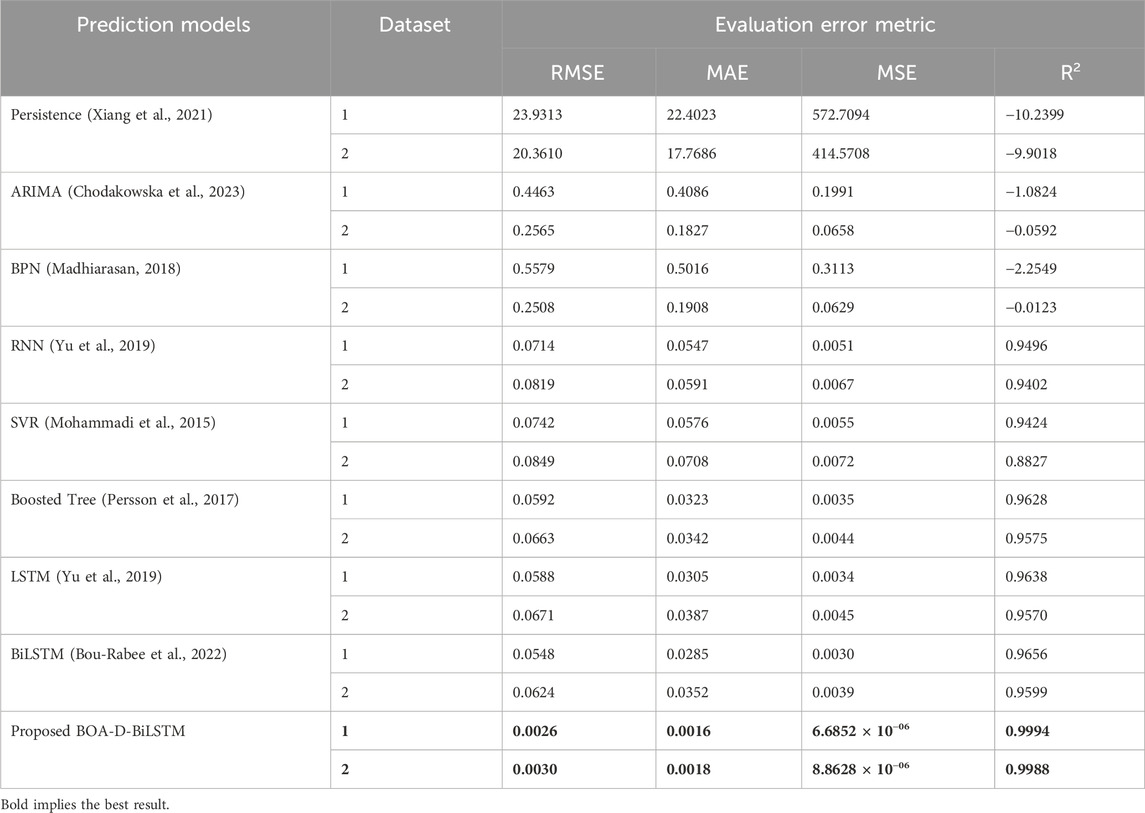
Table 6. Proposed Bayesian Optimisation algorithm-based Optimised Deep Bidirectional Long Short Term Memory (BOA-D-BiLSTM) two datasets based on comparative analysis with the baseline prediction models.
The suggested BOA-D-BiLSTM model performed better than the baseline models when assessed using the MAE, RMSE, MSE and R2. In this research, using the Bayesian optimisation approach, the author determines the best Deep BiLSTM hyperparameter values that lead to greater model precision, as noted in Figures 4–9. The combined use of deep BiLSTM and Bayesian optimisation algorithm in the proposed model yields better-reduced error metrics than the benchmark models, as demonstrated by our comparative analysis and experiment results. The persistence model prediction performance does not produce effective results with high evaluation error metrics compared to other prediction models. ARIMA and BPN models compete for dataset 1, where ARIMA performs better than BPN, and for dataset 2, where BPN performs better than ARIMA. RNN performs better than SVR, BPN, ARIMA and persistence.
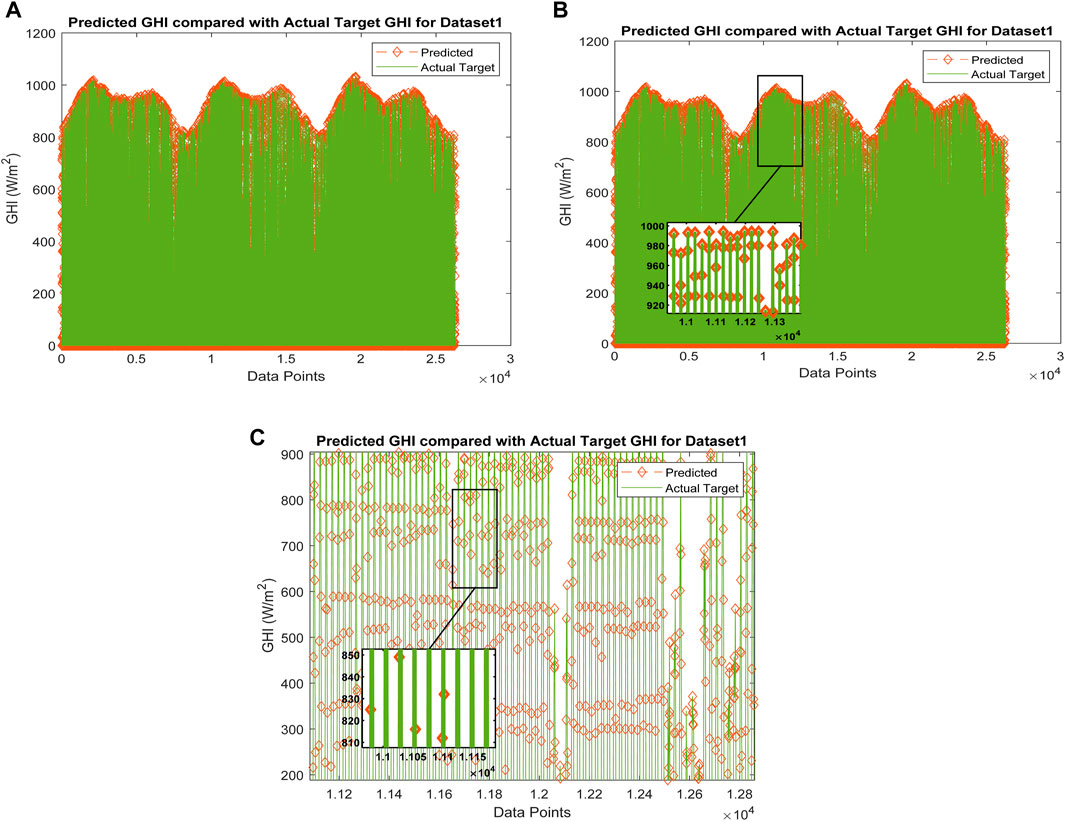
Figure 4. (A) Comparison of the predicted GHI and the actual target GHI for the Chennai region (Dataset 1). (B) Comparison of the predicted GHI and the actual target GHI for the Chennai region (Dataset 1) with the Zoomed-in section view. (C) Comparison of the predicted GHI and the actual target GHI for the Chennai region (Dataset 1) with the Zoomed-in section view.
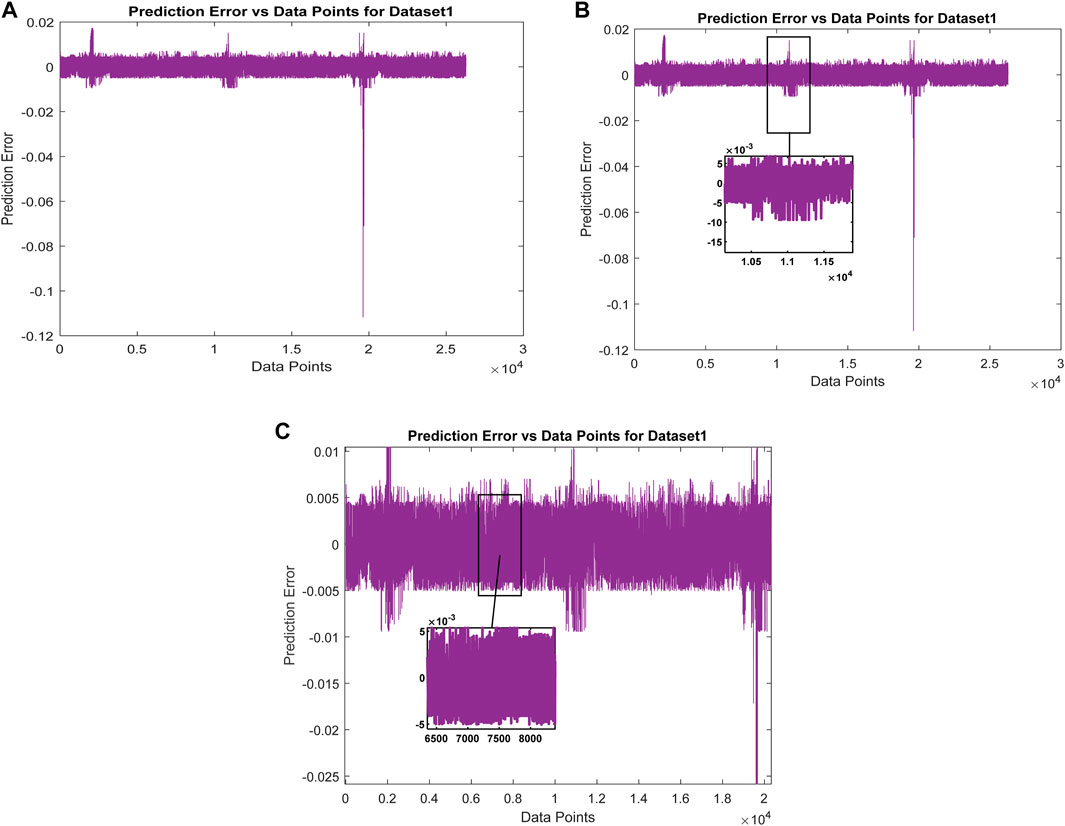
Figure 5. (A) Prediction Error vs. Data Points for Dataset 1. (B) Prediction Error vs. Data Points for Dataset 1 Zoomed-in section view. (C) Prediction Error vs. Data Points for Dataset 1 Zoomed-in section view.
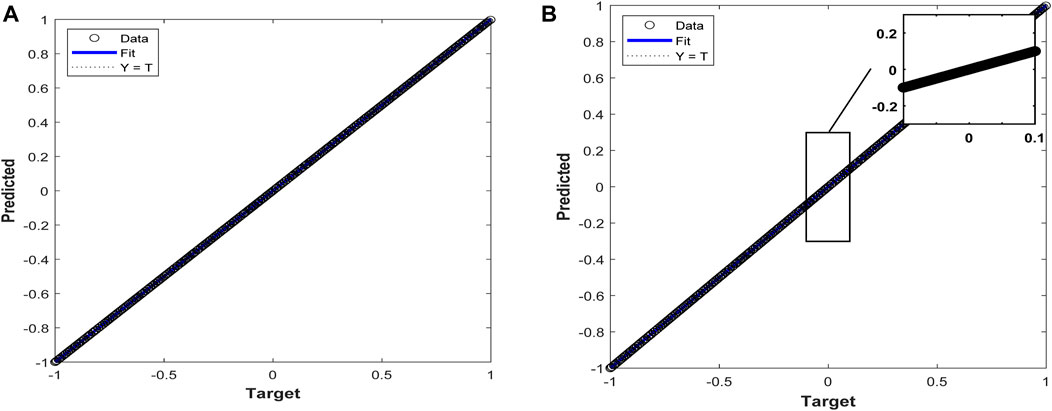
Figure 6. (A) Linear regression plot for the Dataset 1. (B) Linear regression plot for the Dataset 1 Zoomed-in section view.
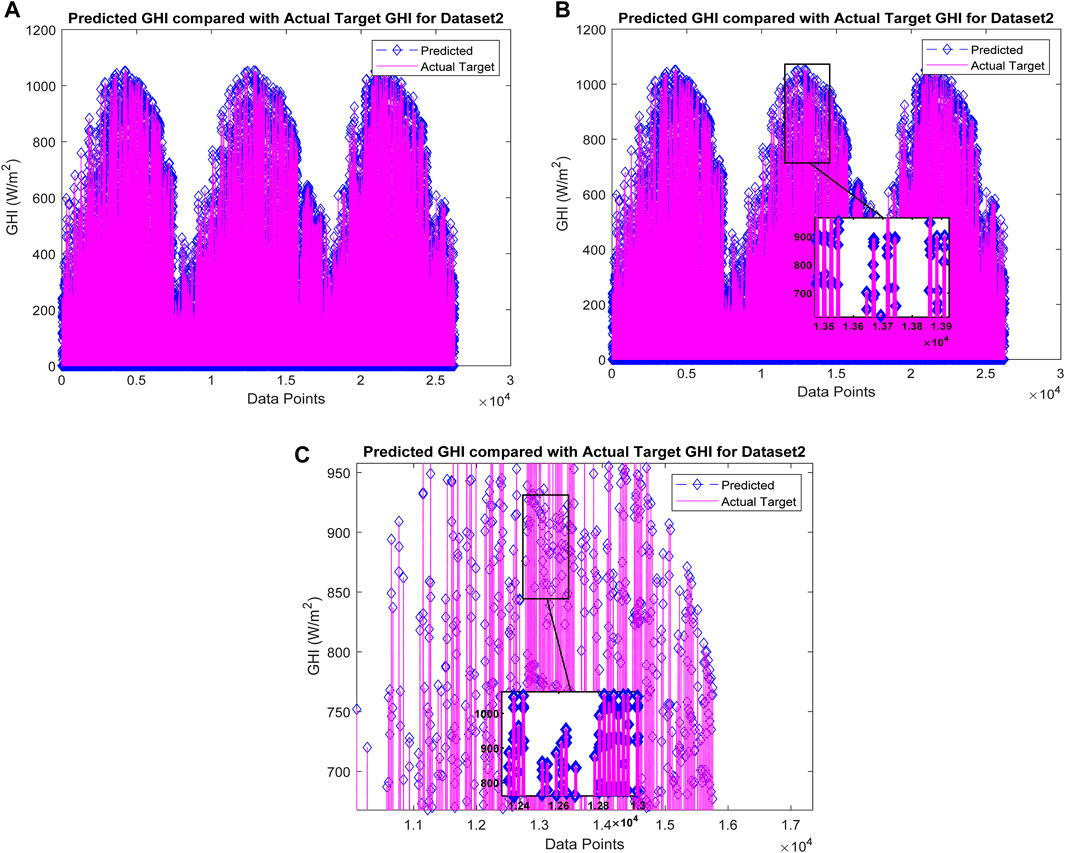
Figure 7. (A) Comparison of predicted GHI and actual target GHI for Jammu region (Dataset 2). (B) Comparison of predicted GHI and actual target GHI for Jammu region (Dataset 2) Zoomed-in section view. (C) Comparison of predicted GHI and actual target GHI for Jammu region (Dataset 2) Zoomed-in section view.
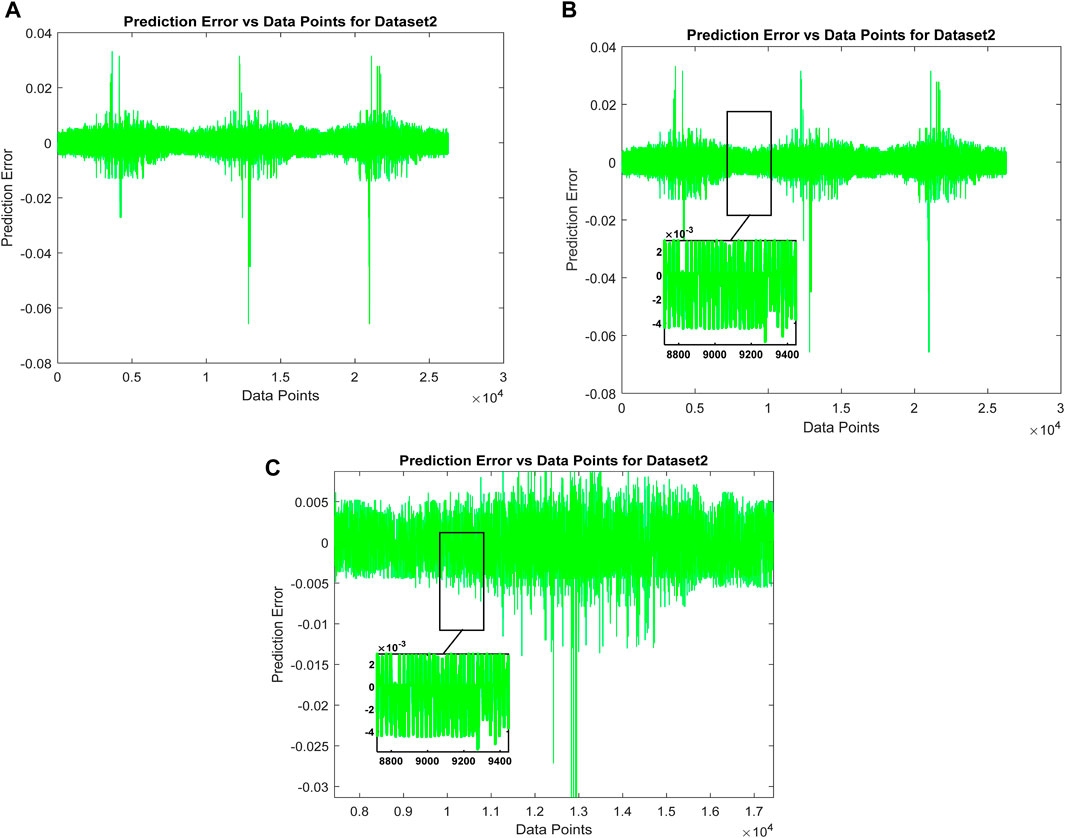
Figure 8. (A) Prediction Error vs. Data Points for Dataset 2. (B) Prediction Error vs. Data Points for Dataset 2 Zoomed-in section view. (C) Prediction Error vs. Data Points for Dataset 2 Zoomed-in section view.
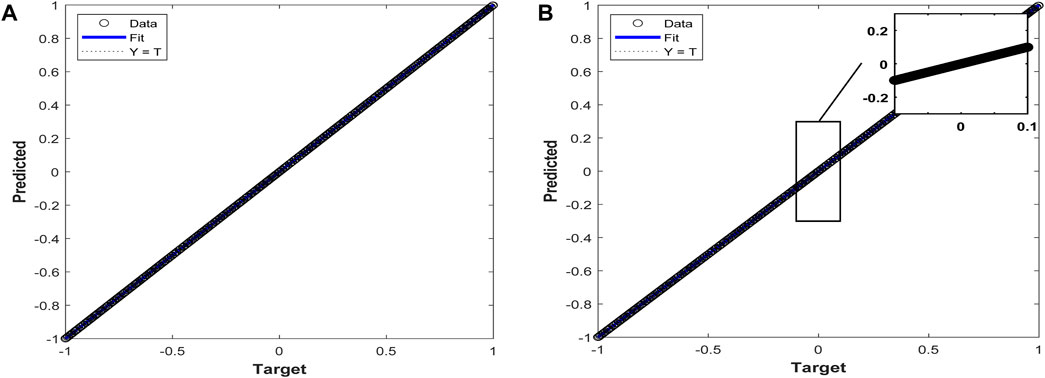
Figure 9. (A) Linear regression plot for the Dataset 2. (B) Linear regression plot for the Dataset 2 Zoomed-in section view.
LSTM has a reduced amount of evaluation metrics than Boosted Tree, but BiLSTM performs better than LSTM, Boosted Tree, SVR, BPN, ARIMA and persistence regarding reduced error. For linear and stationary time series, ARIMA works well; however, it cannot effectively represent the complex, non-linear patterns encountered in GHI data. Although non-linear relationships can be captured by simple LSTMs, such models frequently rely on human expertise or assistance for hyperparameter adjustment, which is challenging and not an optimal option for large-scale applications. To overcome the drawbacks of simpler models like ARIMA and basic LSTMs, the BOA-D-BiLSTM model incorporates the Bayesian Optimisation Algorithm (BOA). The BOA-D-BiLSTM model’s incorporation of BOA ensures optimal configurations with low computing complexity by optimising hyperparameter tweaking. Effectively handling varied and high-dimensional datasets increases scalability in addition to improving forecast accuracy. Regarding predicting, the Deep BiLSTM structure outperforms simpler models by capturing temporal dependencies in both forward and backward directions. The validity and generalisation ability are proved on the two different regions’ data sets. The proposed model performed well and had improved accuracy for both datasets. BOA-D-BiLSTM for the India region dataset 1 achieves MAE: 0.0016, RMSE: 0.0023, MSE: 6.6852 × 10−06 and R2: 0.9994 meanwhile for dataset 2-based evaluations, achieve MAE: 0.0018, RMSE: 0.0030, MSE: 8.8628 × 10−06 and R2: 0.9988. As a result, Table 6 demonstrates the feasibility of using a Bayesian optimisation approach to tune the Deep BiLSTM framework by identifying the perfect combination of hyperparameters that greatly enhances the proposed BOA-D-BiLSTM efficacy that leads the predicted values to exactly match with the actual target of GHI for the two data sets, as noted in Figures 4A–C and Figures 7A–C the zoomed-in view visualises the effectiveness of the proposed model in accurate prediction of GHI in the long-term horizon. Hence, prediction errors are near zero for both datasets 1 and 2, and it is clearly visualised with the help of the prediction error plot and the zoomed-in section view shown in Figures 5A, B and Figures 8A, B. The linear regression plot shows the linear relationship with R = 1 for both datasets, as observed in Figures 6A, B and Figures 9A, B, respectively. Compared to the frequently used time series models, namely, the Persistence Model, ARIMA, BPN, RNN, SVR, Boosted Tree, LSTM, and BiLSTM, the proposed hybrid model BOA-D-BiLSTM can affirm the significant elements of the input information and also integrate forward and backward transitions to improve solar irradiance (GHI) prediction and produce the minor error than the eight baseline models, which is illustrated in Figure 10 for better visualisation of the efficacy of the proposed model.
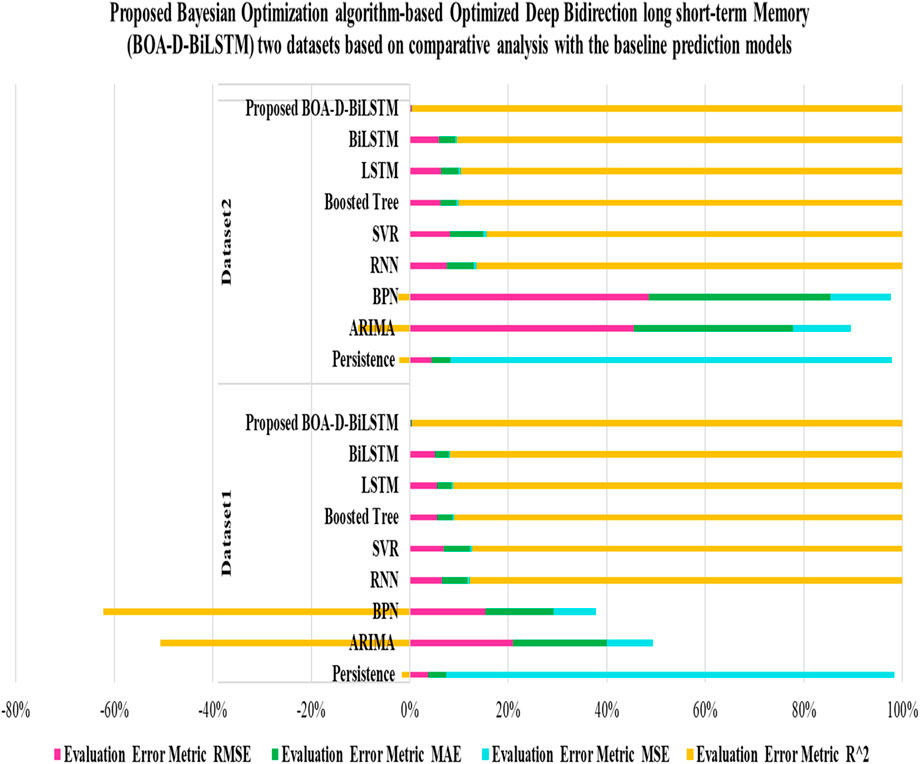
Figure 10. The 2D stacked bar graph of the proposed BOA-D-BiLSTM model performance comparison with other baseline prediction models.
6 Conclusion
However, the intermittent and non-linear character of solar energy and GHI makes integrating PV-produced energy with an electric grid a critical hurdle. The reliable and efficient operation of the photovoltaic system penetrated the grid, which was ensured by an accurate prediction of global solar irradiance (GHI). This paper proposed the long-term horizon global horizontal irradiance prediction using Deep Bidirectional long-term memory with Bayesian optimisation for automatic hyperparameter fine-tuning and fixation. Bayesian optimisation algorithms (BOA) were used to fine-tune the BiLSTM hyperparameters to improve prediction accuracy. The performance of the proposed BOA-D-BiLSTM prediction model is compared with the eight baseline prediction models using the evaluation error metrics (MSE, RMSE, MAE, and R2) to prove the performance validity. The comparative analysis confirms the suitability and outperformability of the proposed BOA-D-BiLSTM prediction model for the long-term GHI prediction application among the other contract prediction models. Further, the potential limitations and future direction are as follows.
Potential Limitation: The limitation of the Bayesian optimisation algorithm is that its run time is quite large when dealing with large amounts of data.
Future direction: The proposed model will be applied to real-time applications in future work. Furthermore, improvements concerning the computational cost and scalability for the real-time application extended using the transformer network, and significant parameters can be explored using the parallel versions of the Bayesian optimisation algorithm for the different horizon-based GHI predictions to speed up the time and overcome the existing potential limitation.
Data availability statement
The data analysed in this study was obtained from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, restrictions apply to get the datasets access. Requests to access these datasets should be directed to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration official website https://www.noaa.gov/.
Author contributions
MM: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
The author expresses his sincere gratitude to NOAA for providing solar irradiance and meteorological data to substantiate and verify the performance and prove its applicability.
Conflict of interest
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Alali, Y., Harrou, F., and Sun, Y. (2022). A proficient approach to forecast COVID-19 spread via optimized dynamic machine learning models. Sci. Rep. 12 (1), 2467. doi:10.1038/s41598-022-06218-3
Benamrou, B., Ouardouz, M., Allaouzi, I., and Ben Ahmed, M. (2020). A proposed model to forecast hourly global solar irradiation based on satellite derived data, deep learning and machine learning approaches. J. Ecol. Eng. 21 (4), 26–38. doi:10.12911/22998993/119795
Bergstra, J., and Bengio, Y. (2012). Random search for hyper-parameter optimisation. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 13 (2).
Bou-Rabee, M. A., Naz, M. Y., Albalaa, I. E., and Sulaiman, S. A. (2022). BiLSTM network-based approach for solar irradiance forecasting in continental climate zones. Energies 15 (6), 2226. doi:10.3390/en15062226
Chodakowska, E., Nazarko, J., Nazarko, Ł., Rabayah, H. S., Abendeh, R. M., and Alawneh, R. (2023). Arima models in solar radiation forecasting in different geographic locations. Energies 16 (13), 5029. doi:10.3390/en16135029
Graves, A., and Schmidhuber, J. (2005). “Framewise phoneme classification with bidirectional LSTM networks,” in Proceedings. 2005 IEEE international joint conference on neural networks, 2005 (IEEE), 4, 2047–2052. doi:10.1109/ijcnn.2005.1556215
Herrera-Casanova, R., Conde, A., and Santos-Pérez, C. (2024). Hour-ahead photovoltaic power prediction combining BiLSTM and bayesian optimization algorithm, with bootstrap resampling for interval predictions. Sensors 24 (3), 882. doi:10.3390/s24030882
Jumin, E., Basaruddin, F. B., Yusoff, Y. B. M., Latif, S. D., and Ahmed, A. N. (2021). Solar radiation prediction using boosted decision tree regression model: a case study in Malaysia. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 28, 26571–26583. doi:10.1007/s11356-021-12435-6
Krishnan, N., Kumar, K. R., and R., S. A. (2024). Solar radiation forecasting using gradient boosting based ensemble learning model for various climatic zones. Sustain. Energy, Grids Netw. 38, 101312. doi:10.1016/j.segan.2024.101312
Li, B., Shao, Y., Lian, Y., Li, P., and Lei, Q. (2023). Bayesian optimization-based LSTM for short-term heating load forecasting. Energies 16 (17), 6234. doi:10.3390/en16176234
Madhiarasan, M. (2018). Certain algebraic criteria for design of hybrid neural network models with applications in renewable energy forecasting. Chennai, India: Anna University. Ph. D. Thesis.
Madhiarasan, M., and Louzazni, M. (2022). Combined long short-term memory network-based short-term prediction of solar irradiance. Int. J. Photoenergy 2022 (1), 1004051–1004119. doi:10.1155/2022/1004051
Medina-Santana, A. A., Hewamalage, H., and Cárdenas-Barrón, L. E. (2022). Deep learning approaches for long-term global horizontal irradiance forecasting for microgrids planning. Designs 6 (5), 83. doi:10.3390/designs6050083
Michael, N. E., Hasan, S., Al-Durra, A., and Mishra, M. (2022). Short-term solar irradiance forecasting based on a novel Bayesian optimized deep Long Short-Term Memory neural network. Appl. Energy 324, 119727. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2022.119727
Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (2024). Solar overview. Available at: https://mnre.gov.in/solar/current-status (Accessed September 14, 2024).
Mohammadi, K., Shamshirband, S., Anisi, M. H., Alam, K. A., and Petković, D. (2015). Support vector regression based prediction of global solar radiation on a horizontal surface. Energy Convers. Manag. 91, 433–441. doi:10.1016/j.enconman.2014.12.015
Pelikan, M., Goldberg, D. E., and Cantu-Paz, E. (1999). “BOA: the Bayesian optimisation algorithm,” in Proceedings of the genetic and evolutionary computation conference (GECCO-99), 525–532.
Persson, C., Bacher, P., Shiga, T., and Madsen, H. (2017). Multi-site solar power forecasting using gradient boosted regression trees. Sol. Energy 150, 423–436. doi:10.1016/j.solener.2017.04.066
Vijay, M., and Saravanan, M. (2022). “Solar irradiance forecasting using bayesian optimization based machine learning algorithm to determine the optimal size of a residential PV system,” in 2022 international conference on sustainable computing and data communication systems (ICSCDS) (IEEE), 744–749.
Xiang, X., Sun, Y., and Deng, X. (2021). Short time solar power forecasting using persistence extreme learning machine approach. In E3S web of conferences, EDP Sciences, (Vol. 294, 01002). doi:10.1051/e3sconf/202129401002
Keywords: deep learning, bidirectional long short term memory, bayesian optimisation algorithm, hyperparameters, prediction, long-term horizon, and global horizontal irradiance
Citation: Madhiarasan M (2025) Bayesian optimisation algorithm based optimised deep bidirectional long short term memory for global horizontal irradiance prediction in long-term horizon. Front. Energy Res. 13:1499751. doi: 10.3389/fenrg.2025.1499751
Received: 21 September 2024; Accepted: 20 January 2025;
Published: 19 February 2025.
Edited by:
Praveen Kumar Balachandran, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, MalaysiaReviewed by:
Mohit Bajaj, Graphic Era University, IndiaVankadara Sampath Kumar, Malla Reddy Engineering College, India
Copyright © 2025 Madhiarasan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Manoharan Madhiarasan, bW1hZGhpYXJhc2FuODlAZ21haWwuY29t, bW1hZGhpYXJhc2FuQGJ0ZWNoLmF1LmRr
†ORCID: Manoharan Madhiarasan, https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2552-0400
 Manoharan Madhiarasan
Manoharan Madhiarasan