- 1Power Dispatch and Control Center of China Southern Power Grid, Guangzhou, China
- 2Electric Power Research Institute, CSG, Guangzhou, China
The intermittency and uncertainty of renewable energy generations, such as wind power, present great challenges to the secure and stable operation of power grids. To accommodate a high penetration of renewable energy, it is vital to coordinate multiple flexible resources to deal with the intermittency and uncertainty of renewable energy and ensure the network security. In this paper, we propose a two-stage stochastic flexible dispatching method for power systems with large-scale wind power, which considers the coordination of unit commitment, optimal transmission switching, and optimal control of phase-shifting transformers within a unified framework. On the grid side, flexibility is improved through phase-shifting transformer regulation and optimal transmission switching. On the source side, flexibility is fully exploited through two-stage stochastic unit commitment. In the day-ahead scheduling stage, transmission topology optimization and unit commitment schemes are determined based on the predicted load demand and renewable energy output. In the real-time dispatching stage, phase-shifting transformers and unit outputs are adjusted and dispatched based on the possible scenarios of load demand and renewable energy output. The effectiveness of the proposed method is verified through case studies on the IEEE RTS-24 system and IEEE 118-bus system.
1 Introduction
Vigorously developing renewable energy sources, such as wind power, has become an important strategy for countries around the world to cope with energy resource constraints, environmental deterioration, and climate warming (Mai et al., 2014; Bai et al., 2015). Compared with traditional power sources, such as thermal plants and hydropower, wind power is characterized by strong intermittency, randomness, and uncertainty. These factors lead to more complex power flow distribution and variable operation modes, presenting severe challenges to the security of power grids and restricting the large-scale development of renewable energy sources. Therefore, improving the flexibility of power grids through comprehensive utilization of various resources is of great significance to ensure the secure operation of power grids and improve the absorption capacity of renewable energy (Mohandes et al., 2019).
Unit commitment (UC) is one of the basic methods for the optimal dispatch of power grids (Aharwar et al., 2023). It aims to enhance energy efficiency and significantly improve the flexibility of the power grid while adhering to constraints such as system load and standby requirements, line power flow limits, unit ramp rates, and minimum on–off times (Ummels et al., 2007).
Many scholars have studied the problem of unit commitment for power systems with wind power (Naghdalian et al., 2020). Xiong et al. (2013) introduced fuzzy theory to address the uncertainty associated with large-scale intermittent power supply. The output of intermittent power supply was represented by fuzzy parameters, which enhance the traditional deterministic unit commitment model by transforming deterministic system constraints into constraints based on fuzzy parameters. Additionally, fuzzy chance constraints were formulated using the credibility theory. Consequently, a mathematical model of fuzzy chance-constrained UC with multiple fuzzy parameters was established. Zhou et al. (2016) proposed a hierarchical unit commitment model for power systems with a high penetration of wind power. The proposed model divides wind power output into different intervals based on confidence levels and employs distinct scheduling strategies for each wind power output interval. Wu et al. (2022) established a scenario-based security-constrained unit commitment method for power systems with wind power and BESSs, and a deep learning-based approach to tackle the SCUC problem was designed. For the power grid with high penetration of intermittent renewable energy, quick-start gas units are utilized to address the power imbalance problem described by Wang et al. (2022). The authors proposed a two-stage, distributionally robust unit commitment framework, which considers both regular and flexible generation resources. In short, scholars at home and abroad have carried out a lot of studies on UC to better capture the potentials of various flexible resources to deal with renewable energy. Wu et al. (2024) designed a closed-loop forecast-and-decision framework-based UC, where the predicted wind power scenarios are expressed as functions of adjustable parameters.
However, the secure operation of a power grid needs to meet various network security constraints, such as power flow constraints. In order to fully accommodate the uncertainty and intermittency of renewable energy, it is not only enough to consider the dispatching of flexible power resources but we also need to further explore the flexibility of the power grid (Mohandes et al., 2019).
Optimal transmission switching (OTS) is a crucial method for improving the operational flexibility of power systems. Power system operators can change the network topology by switching on/off some lines, which helps allow for the dynamic selection of the optimal network topology, thereby enhancing the flexibility, economy, and security of power system operations (Numan et al., 2023). In the past few decades, numerous studies have focused on OTS and its applications in power systems. Fisher et al. (2008) introduced the concept of optimal transmission switching for the first time, aiming to reduce power system operation costs. Qiu and Wang (2015) employed chance constraints to address the uncertainty associated with wind power and determined the optimal network topology over multiple periods to maximize economic benefits. Villumsen et al. (2013) considered optimal transmission switching in the line capacity expansion planning problem, and a two-stage stochastic mixed-integer programming model was proposed. This study demonstrated that optimizing the transmission network structure in large-scale wind power congestion networks can reduce power generation costs and enhance the economic viability of optimal line expansion schemes. Based on forecast data for next-day load and renewable energy output, Zhao et al. (2019) proposed a method for transmission network structure optimization that minimizes system operation costs while ensuring compliance with safety operation constraints and the full integration of renewable energy sources. To reduce transmission congestion, an optimal transmission switching model was proposed by Zhang H. et al. (2018), which considers N-1 security constraints. The proposed model employs a scenario-based stochastic optimization method to account for the impacts of load fluctuations and uncertainties in wind power output. Saavedra et al. (2020) studied the applications of OTS and UC models in the context of the electricity market, which can help improve the operation cost and power imbalance.
In addition to OTS, flexible AC transmission equipment, such as phase-shifting transformers (PSTs), plays a crucial role in enhancing the operational flexibility of the grid (Amrr et al., 2020). By phase-shifting transformers, the voltage phase angles of a branch can be adjusted to control and improve the distribution of power flow. This capability allows for the regulation of active power flow within the power grid, the elimination of electromagnetic circulation in ring networks, and the enhancement of transmission across various sections (Zhang X. et al., 2018; Verboomen et al., 2008). Based on the DC power flow model, Lima et al. (2003) proposed an optimization configuration method for transmission-controlled phase-shifting transformers in large-scale power systems, formulating the model as a mixed-integer linear programming problem. In the optimal power flow problem, the regulation of PSTs can minimize the overall cost of power generation. Ding et al. (2017) acknowledged that multiple optimal solutions exist for PST phase angle adjustments and suggested that controlling a small subset of PSTs may yield better economic outcomes. Consequently, an optimization method for determining the subset of PST phase angle adjustments is proposed. Yang et al. (2021) introduced a method for the online melting of ice on transmission lines using phase-shifting transformers, theoretically outlining the principles of online ice melting and providing a basis for calculating power consumption and voltage decrease during the ice-melting process. In light of the voltage fluctuations and deviations in active distribution networks caused by the high penetration of distributed power sources and their impact on the magnitude, direction, and equalization of power flow, Yan et al. (2024) examined the topology and operational principles of dual-core phase-shifting transformers and summarized the gear control strategies employed when applying phase-shifting transformers for voltage regulation and power flow control, respectively.
In summary, to accommodate a high penetration of renewable energy, the power grids must be flexible enough to ensure the power balance and network security constraints. Numerous studies have been conducted on unit commitment, optimal transmission switching, and the optimal control of phase-shifting transformers. However, there are two notable gaps in the existing studies. First, there is a scarcity of studies focusing on the utilization of phase-shifting transformers to help renewable energy. Second, existing studies have not simultaneously addressed how to coordinate unit commitment, optimal transmission switching, and optimal operation of phase-shifting transformers across different time scales of grid scheduling to accommodate renewable energy effectively.
Therefore, this paper proposes a two-stage stochastic dispatch method for power systems with large-scale wind power, which considers the coordination of unit commitment, optimal transmission switching, and optimal control of PSTs in a unified framework.
2 Model formulation
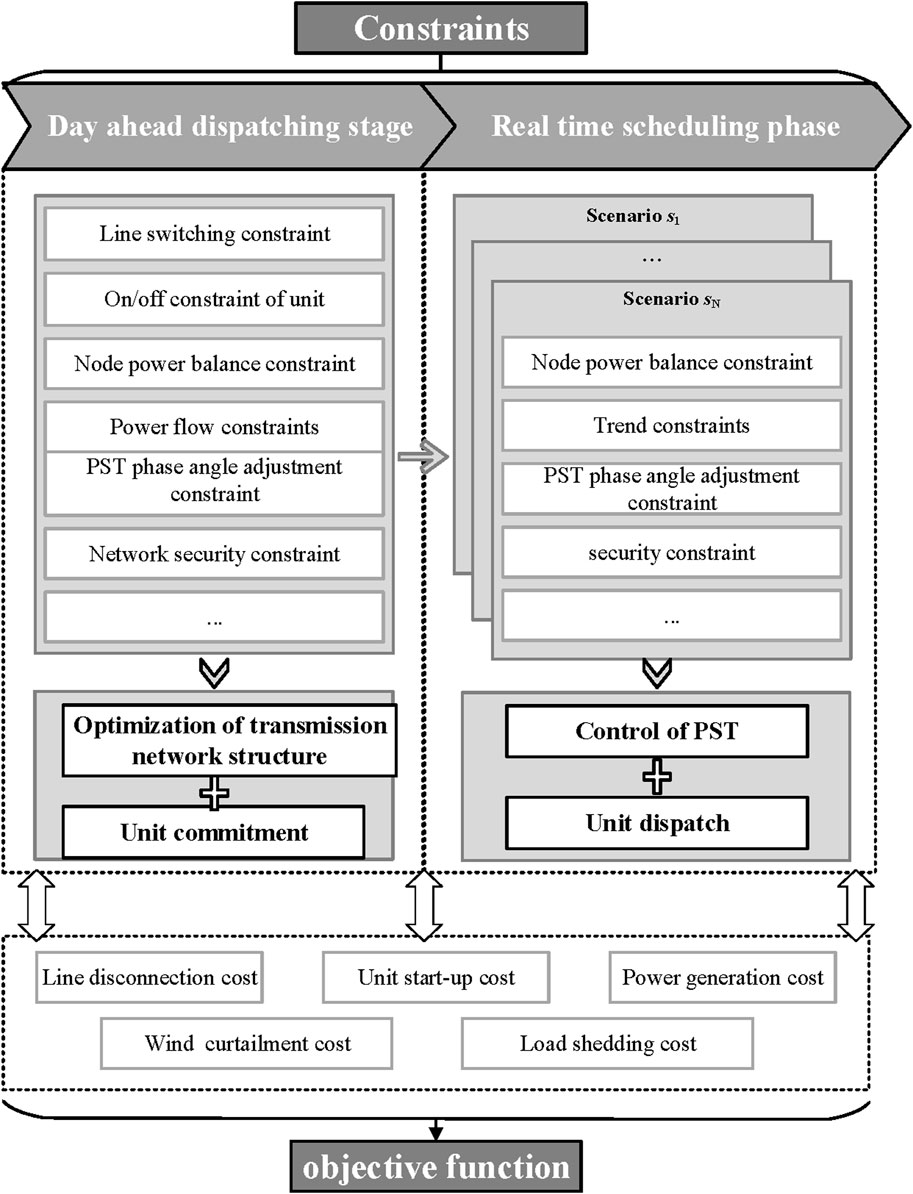
In the daily operation of a power grid, it is not advisable to frequently open and close transmission lines. Therefore, assuming that the network topology remains unchanged throughout a single operating day, the network topology and the unit scheduling plan for each hour are determined based on forecast curves of renewable energy generation and system load for the following day. Real-time scheduling involves regulating the phase angle of phase-shifting transformers and adjusting the unit’s power outputs. In this paper, an ideal PST is considered, meaning that the voltage amplitude changes caused by the PST are not taken into account, and its inherent impedance is disregarded. The framework of the proposed method is illustrated in Figure 1.
2.1 Objective function
The objective function of the proposed model is to minimize the total operating cost of the system, as illustrated in Equation 1. Specifically, the total operating cost comprises a weighted sum of the line switching cost, the start-up cost of units, the power generation cost, the wind curtailment cost, and the load shedding cost.
where Ctotal denotes the total operating cost of the system; Cbran is the line switching cost, which can be calculated using Equation 2; Cstart represents unit’s start-up cost;
Equation 3 represents the unit start-up cost, where
Equations 4, 5 represent the total generation cost for the forecast scenario and the operational scenario s, respectively.
where
Equations 6–9 represent the costs associated with abandoning renewable energy and the costs of load shedding in the forecast scenario and scenario s, respectively.
where
2.2 Constraints
2.2.1 Day-ahead scheduling constraints
Equations 10, 11 represent the constraints indicating the switchable lines and the maximum number of off lines, respectively. In practice, to ensure the security and stability of the power system, only certain specific lines are allowed to be disconnected, and there is an upper limit on the number of lines that can be opened.
where
Equation 12 enforces the startup states of the units.
According to Equation 12, the values of each variable are shown in the following table. Only when
Equations 13, 14 represent the minimum up time constraint and the minimum down time constraint of unit k, respectively.
where
Equation 15 refers to the bus power balance constraint.
where
Equation 16 denotes the branch power flow constraint considering both the branch breaking state and PST regulation mode.
where buses i and j are the start and end nodes of branch l, respectively. M is a maximum positive number. rl and xl represent the resistance and reactance of branch l, respectively.
Equation 17 indicates that the active power output of each unit must remain within its permissible limit range.
where
Equation 18 represents the ramping constraint of unit k.
Equations 19, 20 enforce the up reserve and down reserve of the system, respectively.
where
Equation 21 denotes the phase angle limit of each node, where
Equation 22 is the constraint of branch phase angle adjustment for branch l with a PST.
where
Equation 23 is the phase angle constraint of the reference node, i.e., the voltage phase angle of the reference node is 0.
Equation 24 denotes the load shedding constraint.
Equation 25 is the active power output reduction constraint of wind farm k.
2.2.2 Real-time dispatching constraints
Equation 26 represents the bus power balance constraint for each operational scenario.
where
Equation 27 is the branch power flow constraint considering both the branch breaking state and PST regulation mode under each operation scenario.
where
Equation 28 specifies the active power output limits of unit k under each operation scenario.
The ramp limits of units are enforced in Equation 29.
The up-reserve and down-reserve constraints of the system are expressed as Equations 30, 31, respectively.
where
Equation 32 is the phase angle constraint of each node in each running scenario.
Equation 33 specifies the limits for the phase angle of PSTs.
The phase angle of the reference node is enforced to be 0, as shown in Equation 34.
Equation 35 shows the load shedding constraints in each scenario.
The power curtailment of each wind farm is limited by Equation 36.
In summary, the proposed model is as follows:
The proposed model is formulated as a mixed-integer linear programming (MILP) problem, which can be efficiently solved by commercial solvers.
3 Case study
In this section, the modified IEEE RTS-24 bus system and the modified IEEE-118 bus system are used to verify the validity of the proposed method. The proposed model is solved by MATLAB and Gurobi on a computer with Intel Core I5-10400 (2.90 GHz) and 16 GB RAM.
3.1 IEEE RTS-24 system
3.1.1 Introduction
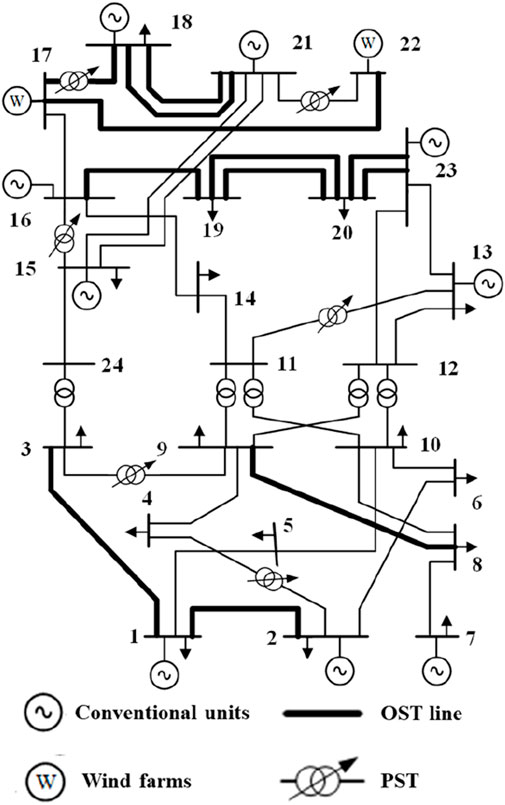
The diagram of the IEEE RTS-24 bus system is shown in Figure 2. It consists of 24 buses and 33 lines. Five transformers are located on lines L3–24, L9–11, L9–12, L10–11, and L10–12, dividing the system into a low voltage zone and a high voltage zone. Two wind farms are located at buses 17 and 22, with capacities of 800 MW and 1,000 MW, respectively. The coefficients of line switching cost, penalty cost of wind curtailment, and load shedding cost are set as 1,000, 1,000, and 1,000,000, respectively.
The switchable lines and PSTs are also shown in Figure 2. The maximum number of lines that can remain open is 3. Set the value to 10° for
3.1.2 Result analysis
In the day-ahead scheduling stage, two branches of line, i.e., L20–23, are disconnected. In addition, lines L13–23 and L12–23 are either fully loaded or nearly fully loaded in most scenarios and time periods. Consequently, the disconnection of the two branches of line L20–23 is implemented to prevent the wind farm and other associated units from transmitting excess power to bus 23. This excess power could flow through lines L13–23 and L12–23, potentially leading to line overload.
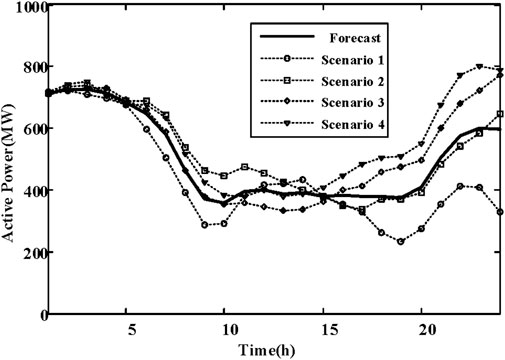
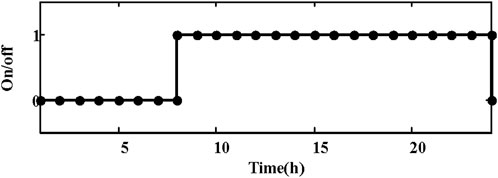
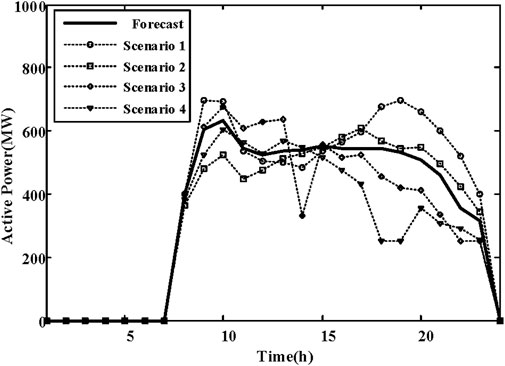
In the day-ahead scheduling stage, each unit is configured based on the forecast scenario. Take the unit at bus 18 as an example. Its operational state is illustrated in Figure 5. By analyzing the system load demand and the wind power output curve, it is evident that during the first period (1–7), the system load demand is low, while the wind power output is high. Consequently, the unit at bus 18 is shut down to accommodate the wind power. As the system load increases and the wind power output decreases, the unit begins to increase output to meet the system load.
Taking the unit located at bus 18 as an example, the output results of this unit during the day-ahead scheduling and real-time scheduling stages are illustrated in Figure 6. During periods 1–7 and 24, the output level is 0 because the unit is shut down. The unit’s output is adjusted differently for various scenarios in both the day-ahead scheduling and real-time scheduling stages, thereby enhancing the flexibility of the power supply. For instance, in scenario 1, during the period from 18 to 20, the wind power is low. At this time, the output of the unit at bus 18 is increased to a higher level, effectively ensuring the power balance.
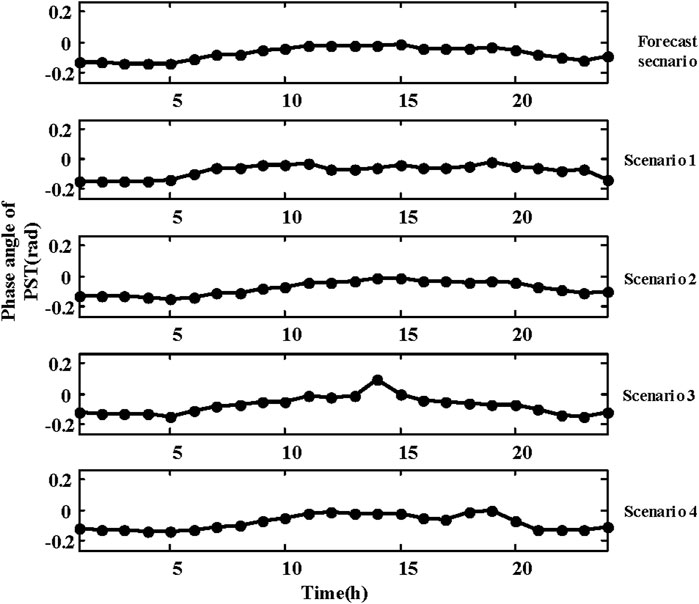
Taking the PST on lines L15–16 as an example, the results for the day-ahead scheduling and the real-time scheduling stages are illustrated in Figure 7. Generally, in each scenario, the phase angle difference between buses 16 and 15 increases when the PST phase angle is adjusted negatively during periods of high wind power output (such as periods 1–7). It facilitates a greater flow of power from bus 16 to bus 15, thereby aiding in accommodating wind power by other regional loads. Conversely, during periods of low wind power output (such as periods 10–15), the phase angle of the PST is decreased. Therefore, through the proposed method, the PST phase angle is adjusted differently across various scenarios in both the day-ahead scheduling and real-time scheduling stages, thereby improving the flexibility of the grid.
3.1.3 Influences of different PST configurations
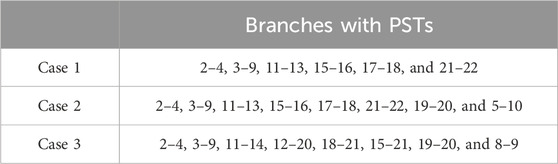
To illustrate the influences of different PST configurations, the following three cases are analyzed. The PST configurations of different cases are given in Table 1. There are six PSTs in Case 1 and eight PSTs in cases 2 and 3. The total cost of different cases is shown in Figure 8. The results show that, compared with Case 1, two more PSTs are installed in Case 2, which helps further improve the system’s flexibility and reduce the total cost and wind curtailment costs. Although the number of PSTs in cases 2 and 3 is the same, Case 2 has a lower total cost. Therefore, the location of PSTs has a significant impact on the system’s flexibility, and the proposed method can be further used to help determine the optimal planning of PSTs.
3.1.4 Comparison with existing methods
In order to verify the effectiveness of the proposed method presented in this paper, it is compared with the optimal scheduling method (Wang et al., 2021), which as shown in Table 2 only considers unit combination and OTS. The dispatch scheme of OTS and unit commitment for the day-ahead scheduling stage was derived using the optimal scheduling method solely focused on unit combination and OTS. These results were then applied to the model proposed in this paper to validate the effectiveness of the coordination among OTS, unit commitment, and control of PST.

Table 2. Values of variables in Equation 12.
The total cost of the proposed method is
After calculations, the result is −5.89%, indicating that compared to the traditional method, the proposed method can significantly enhance the overall efficiency of power grid operations through the coordination of unit combinations, optimal transmission switching, and control of phase-shifting transformers.
3.2 IEEE 118-bus system
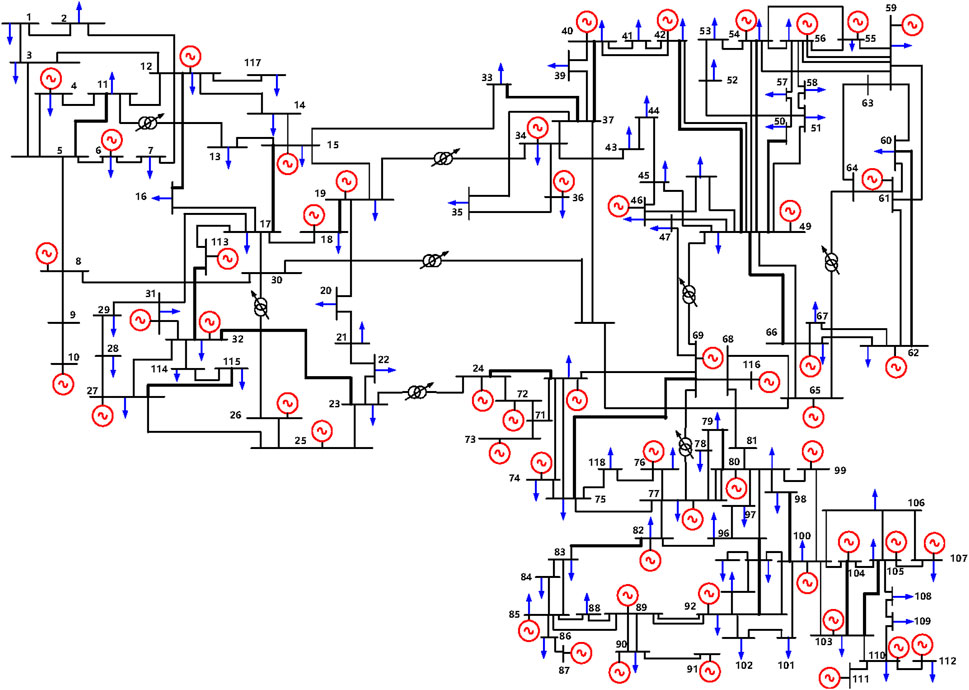
In order to check the adaptability of the proposed method to large-scale systems, a modified IEEE-118 bus system is further analyzed. The diagram of the IEEE 118-bus system is given in Figure 9. As shown in the figure, eight phase-shifting transformers are installed in the system, and all the switchable lines are marked in black. The detailed parameters of the system are provided by Wang et al. (2008).
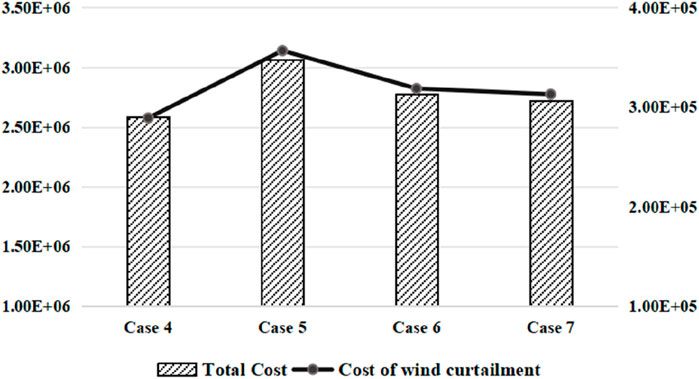
Four cases are studied to corroborate the effectiveness of the proposed method as follows.
Case 4: the proposed method.
Case 5: only considering unit commitment.
Case 6: considering both unit commitment and OTS.
Case 7: considering both unit commitment and optimal control of PSTs.
Under the same load and wind power output scenarios, the results obtained by the abovementioned four methods are shown in Figure 10. The results show that the total cost and the cost of wind curtailment for Case 4 are the lowest, and these costs for Case 5 are the highest. Compared with Case 5, the wind curtailment costs of cases 6 and 7 are also improved. It shows that to effectively integrate wind power, it is necessary to fully utilize the flexibility of power infrastructure, and OTS and PST are effective means. Furthermore, compared with the existing methods, i.e., Case 5–Case 7, the proposed method can coordinate unit commitment, OTS, and control of PST at the same time and effectively improve the flexibility of power systems.
4 Conclusion
To improve the flexibility of power grids, accommodate a high penetration of renewable energy, and improve the operation efficiency, a two-stage stochastic scheduling method is proposed, which takes into account the coordination of various resources through unit commitment, optimal transmission switching, and optimal control of phase-shifting transformers. In the day-ahead dispatching stage, according to the load demand and the forecast output of renewable energy, optimal transmission switching and unit commitment are determined. In the real-time scheduling phase, the phase angle of PSTs and the unit’s output are adjusted according to load demand and potential scenarios for renewable energy output. The modified IEEE RTS-24 system and the modified IEEE-118 bus are used to verify the effectiveness of the proposed method. The results show that the integrated coordination of optimal transmission switching, unit commitment, and optimal control of phase-shifting transformers can improve the operational flexibility and economic benefit of the power grid.
There are still some issues that can be improved in the future. First, in the proposed method, only DC power flow constraints are considered in this paper, so AC power flow constraints can be further considered in the future. Second, flexible resources on the user side, such as demand response, are not currently considered. Third, the optimal planning method of PST can be further studied based on the proposed model.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
AL: software and writing–review and editing. LZ: writing–review and editing and conceptualization. YM: methodology and writing–review and editing. HZ: conceptualization and writing–original draft. YG: investigation and writing–review and editing. TZ: validation and writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study received funding from the Science and Technology Project of China Southern Power Grid Co. Ltd. (000000KK52210140).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The authors declare that this study received funding from China Southern Power Grid Co. Ltd. The funder had the following involvement in the study: they collected and analyzed data for the study, and provided some practical system operation indicators that needed to assist in the research.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Aharwar, A., Naresh, R., Sharma, V., and Kumar, V. (2023). Unit commitment problem for transmission system, models and approaches: a review. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 223, 109671. doi:10.1016/j.epsr.2023.109671
Amrr, S. M., Jamil Asghar, M. S., Ashraf, I., and Meraj, M. (2020). A comprehensive review of power flow controllers in interconnected power system networks. IEEE Access 8, 18036–18063. doi:10.1109/access.2020.2968461
Bai, J., Xin, S., Liu, J., and Zheng, K. (2015). Roadmap of realizing the high penetration renewable energy in China. Proc. Chin. Soc. Electr. Eng. 35 (14), 699–705. doi:10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.2015.14.026
Ding, T., Bo, R., Bie, Z., and Wang, X. (2017). Optimal selection of phase shifting transformer adjustment in optimal power flow. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 32 (3), 2464–2465. doi:10.1109/tpwrs.2016.2600098
Fisher, E. B., O'Neill, R. P., and Ferris, M. C. (2008). Optimal transmission switching. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 23 (3), 1346–1355. doi:10.1109/tpwrs.2008.922256
Grigg, C., Wong, P., Albrecht, P., Allan, R., Bhavaraju, M., Billinton, R., et al. (1999). The IEEE reliability test system-1996. A report prepared by the reliability test system task force of the application of probability methods subcommittee. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 14 (3), 1010–1020. doi:10.1109/59.780914
Lima, F. G. A., Galiana, F. D., Kockar, I., and Munoz, J. (2003). Phase shifter placement in large-scale systems via mixed integer linear programming. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 18 (3), 1029–1034. doi:10.1109/tpwrs.2003.814858
Liu, C., Zhu, H., Zhou, M., Deng, R., Tang, Y., and Du, W. (2024). Phase shifting transformer-based mitigation strategy for load redistribution attacks in power system optimal power flow. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 15 (5), 5127–5138. doi:10.1109/tsg.2024.3390158
Mai, T., Maureen Hand, M., Baldwin, S. F., Wiser, R. H., Brinkman, G. L., Denholm, P., et al. (2014). Renewable electricity futures for the United States. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 5 (2), 372–378. doi:10.1109/tste.2013.2290472
Mohandes, B., Moursi, M. S. E., Hatziargyriou, N., and Khatib, S. E. (2019). A review of power system flexibility with high penetration of renewables. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 34 (4), 3140–3155. doi:10.1109/tpwrs.2019.2897727
Naghdalian, S., Amraee, T., Kamali, S., and Capitanescu, F. (2020). Stochastic network-constrained unit commitment to determine flexible ramp reserve for handling wind power and demand uncertainties. IEEE Trans. Industrial Inf. 16 (7), 4580–4591. doi:10.1109/tii.2019.2944234
Numan, M., Abbas, M. F., Yousif, M., Ghoneim, S. S. M., Mohammad, A., and Noorwali, A. (2023). The role of optimal transmission switching in enhancing grid flexibility: a review. IEEE Access 11, 32437–32463. doi:10.1109/access.2023.3261459
Qiu, F., and Wang, J. (2015). Chance-constrained transmission switching with guaranteed wind power utilization. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 30 (3), 1270–1278. doi:10.1109/tpwrs.2014.2346987
Saavedra, R., Street, A., and Arroyo, J. M. (2020). Day-ahead contingency-constrained unit commitment with co-optimized post-contingency transmission switching. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 35 (6), 4408–4420. doi:10.1109/tpwrs.2020.2996499
Ummels, B. C., Gibescu, M., Pelgrum, E., Kling, W. L., and Brand, A. J. (2007). Impacts of wind power on thermal generation unit commitment and dispatch. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 22 (1), 44–51. doi:10.1109/tec.2006.889616
Verboomen, J., Van Hertem, D., Schavemaker, P. H., Kling, W. L., and Belmans, R. (2008). Analytical approach to grid operation with phase shifting transformers. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 23 (1), 41–46. doi:10.1109/tpwrs.2007.913197
Villumsen, J. C., Bronmo, G., and Philpott, A. B. (2013). Line capacity expansion and transmission switching in power systems with large-scale wind power. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 28 (2), 731–739. doi:10.1109/tpwrs.2012.2224143
Wang, J., Shahidehpour, M., and Li, Z. (2008). Security-constrained unit commitment with volatile wind power generation. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 23 (3), 1319–1327. doi:10.1109/tpwrs.2008.926719
Wang, S., Zhao, C., Fan, L., and Bo, R. (2022). Distributionally robust unit commitment with flexible generation resources considering renewable energy uncertainty. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 37 (6), 4179–4190. doi:10.1109/tpwrs.2022.3149506
Wang, W., Zhang, T., Xuan, W., Li, H., Liu, Z., and Wang, K. (2021). Power system planning method considering unit commitment and optimal transmission switching. Proc. CSU-EPSA 33 (2), 108–115. doi:10.19635/j.cnki.csu-epsa.000621
Wu, H., Ke, D., Song, L., Liao, S., Xu, J., Sun, Y., et al. (2024). A novel stochastic unit commitment characterized by closed-loop forecast-and-decision for wind integrated power systems. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 39 (2), 2570–2586. doi:10.1109/tpwrs.2023.3313776
Wu, T., Zhang, Y., and Wang, S. (2022). Deep learning to optimize: security-constrained unit commitment with uncertain wind power generation and BESSs. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 13 (1), 231–240. doi:10.1109/tste.2021.3107848
Xiong, H., Xiang, T., Chen, H., Lin, F., and Su, J. (2013). Research of fuzzy chance constrained unit commitment containing large-scale intermittent power. Proc. Chin. Soc. Electr. Eng. 33 (13), 36–44. doi:10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.2013.13.003
Yan, Xi, Wang, Y., and Jia, J. (2024). Application analysis of dual-core phase-shifting transformers in active distribution network voltage and power flow regulation. J. North China Electr. Power Univ. 51 (3), 20–29. doi:10.3969/j.ISSN.1007-2691.2024.03.03
Yang, Q., Ban, G., Xie, B., Zeng, H., Wen, Y., and Ma, X. (2021). Deicing method and simulation of phase-shifting transformer for on-load transmission lines. Power Syst. Technol. 45 (8), 3349–3355. doi:10.13335/j.1000-3673.pst.2020.1048
Zhang, H., Cheng, H., Zeng, P., Zhang, J., and Lu, J. (2018a). Optimal transmission switching considering N-1 security network constraints. Electr. Power Autom. Equip. 38 (2), 123–129. doi:10.16081/j.issn.1006-6047.2018.02.016
Zhang, X., Shi, D., Wang, Z., Zeng, B., Wang, X., Tomsovic, K., et al. (2018b). Optimal allocation of series FACTS devices under high penetration of wind power within a market environment. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 33 (6), 6206–6217. doi:10.1109/tpwrs.2018.2834502
Zhao, B., Hu, Z., and Song, Y. (2019). Robust optimization of transmission topology with renewable energy sources considering N-1 security constraint. Automation Electr. Power Syst. 43 (4), 16–24. doi:10.7500/AEPS20180927003
Keywords: renewable energy generation, unit commitment, optimal transmission switching, phase-shifting transformer, power systems
Citation: Lei A, Zhao L, Mei Y, Zhen H, Gao Y and Zhou T (2025) A two-stage flexible scheduling method for power systems with wind power considering the coordination of multiple resources. Front. Energy Res. 12:1503086. doi: 10.3389/fenrg.2024.1503086
Received: 28 September 2024; Accepted: 05 December 2024;
Published: 06 January 2025.
Edited by:
Yiji Lu, University of Glasgow, United KingdomCopyright © 2025 Lei, Zhao, Mei, Zhen, Gao and Zhou. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hongyue Zhen, NjczNjI3MjA2QHFxLmNvbQ==
 Aoyu Lei1
Aoyu Lei1 Hongyue Zhen
Hongyue Zhen