- 1Power Dispatching and Control Center of Guizhou Power Grid Co., Ltd., Guiyang, China
- 2State Key Laboratory of HVDC, Electric Power Research Institute, China Southern Power Grid Co., Ltd. (CSG), Guangzhou, Guangdong, China
To enhance the transmission capabilities in power system scheduling, this paper develops a unit commitment model that incorporates dynamic transmission line capacities and proposes an efficient solving algorithm. A multi-scenario unit commitment model that integrates dynamic transmission line capacities is introduced, using quantile regression to construct a data-driven capacity increase model based on historical environmental data. The model is solved using Lagrangian relaxation and the Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers (ADMM) to decouple dynamic constraints, allowing the dual problem to be decomposed into sub-problems and solved iteratively. The proposed model and algorithm are validated using the IEEE-118 and IEEE-300 test cases, demonstrating their effectiveness in handling dynamic transmission line capacities and improving scheduling performance.The approach provides a robust and flexible solution for power system scheduling, enhancing reliability and economic efficiency.
1 Introduction
With the rapid advancement of the global energy transformation, the extensive penetration of renewable energy, notably wind and solar power, presents formidable hurdles to the adaptability and steadiness of electrical grids. Amidst this evolving landscape, the attainment of carbon neutrality has emerged as a collective aspiration for the global community (Li et al., 2019; Xu et al., 2024; Zhu and Li, 2024). This ambition, however, intensifies the congestion plaguing power system transmission lines, standing as a cardinal impediment to the efficacious assimilation of renewable energies (Elavarasan et al., 2020; Kroposki, 2017). Framed within this context, the principal endeavor of unit commitment (UC) dilemmas that contemplate renewable energy paradigms centers on ascertaining the operational status of power plants across distinct intervals within the scheduling horizon. The overarching aim is to curtail operational expenditures whilst concurrently honoring safety protocols under multifarious scenarios of renewable energy production and upholding network flow restrictions. Deliberations on UC frameworks and their resolutions bear considerable weight in maximizing the potential for renewable energy integration and materializing aspirations of carbon emission reductions, an area that has garnered profound scholarly attention from researchers across the globe over extended periods (Han et al., 2023; Yuan et al., 2024).
In essence, the UC problem is pivotal for day-ahead dispatch and ensuring the operational security of power systems. Ongoing studies pertaining to Security-Constrained Unit Commitment (SCUC) predominantly concentrate on the reformulation of model (Ding et al., 2017; Du et al., 2019; Meus et al., 2018; Morales-España and Tejada-Arango, 2019), the management of transmission line constraints (Xavier et al., 2019; Lee et al., 2014), and methodologies aimed at expediting the resolution of SCUC problems (Yang et al., 2022; Xu et al., 2020; Lu et al., 2020). By employing strategies such as unit clustering and splitting the decision-making process into two distinct stages, the formulation of the SCUC problem becomes increasingly detailed and all-encompassing. The application of techniques like temporal decomposition, which separates the problem temporally, and dynamic programming algorithms, which efficiently solve problems by breaking them down into simpler subproblems, leads to a substantial improvement in the speed and effectiveness of finding solutions to SCUC challenges. While these investigations have tackled a myriad of challenges, they fall short in a significant aspect: the prevalent use of rudimentary static transmission line constraints in modeling. Such an approach falls short in managing the transient overloading hazards stemming from the intermittent nature of renewable energy sources. Additionally, the static transmission line capacity settings tend to err on the side of caution, curtailing the transmission reach of electric power produced by units with lower operating costs, thereby eroding the economic feasibility of the resultant SCUC solutions. As a result, in light of the escalating dimensions of power systems and the heightened imperative for cost-effectiveness in SCUC decisions, there exists a pressing requirement for research endeavors focused on augmenting the capacities of transmission lines and amplifying the transmission aptitude of power system network.
Regarding the mitigation of transmission line congestion, prevailing solutions predominantly encompass power flow regulation (Zhang et al., 2021; Peng et al., 2024; Yao and Zhang, 2024) and adjustments within the electricity market dynamics (Tosatto et al., 2020; Ye et al., 2016; Sun et al., 2020). These studies primarily introduce supplementary mechanisms aimed at modulating power flows within the electrical grid and alleviating congestion on transmission lines, without fundamentally escalating the intrinsic capacity of the lines themselves. To rectify this deficiency, the notion of dynamic line rating (DLR) has been conceptualized and advocated. In reality, the capacity of transmission lines is inherently fluid, fluctuating in response to atmospheric and environmental shifts. Dynamic line ratings afford the capability of real-time estimation, factoring in a plethora of relevant parameters, thereby circumventing the financial burden associated with physical line expansions. Their implementation is pivotal in ameliorating instances of line congestion and fortifying the transmission efficacy of power systems.
Present methodologies for attaining dynamic augmentation of transmission line capacities are predominantly grounded in physical models, a domain explored in depth across various academic works (Kim and Morcos, 2013; Dawson and Knight, 2018; Douglass et al., 2016; Cheng et al., 2021). These researches excel in providing real-time simulations of transmission line dynamic capacities. Nonetheless, the reliance on physical models necessitates access to a plethora of line-specific physical parameters, a requirement that often entails substantial investments in terms of human and financial resources, thus limiting practical applicability. Contrary to the resource-intensive real-time simulations underpinned by physical models, data-driven modeling strategies demand merely the acquisition of meteorological parameters pertinent to the geographical locale housing the transmission line. Once gathered, these data can be harnessed within regression methodologies to compute the coefficients integral to the model. An additional advantage is that the resultant dynamic transmission line capacity models are typically articulated as mathematical expressions, facilitating their seamless integration into analyses spanning a multitude of power system concerns. Over the recent past, this approach has progressively captured the interest and focus of the scholarly realm (Liu et al., 2023; Bhattarai et al., 2018; Morozovska et al., 2021; Kirilenko et al., 2021).
Consequently, integrating data-driven dynamic capacity models into SCUC problems enables the introduction of dynamic transmission line capacities by leveraging historical data on weather and environmental parameters. This integration can substantially decrease operational costs of the system, underscoring its significant research merit. Yet, the inherent complexity of SCUC models as mixed-integer programming problems makes them arduous to resolve. The integration of dynamic transmission line constraints only exacerbates this complexity. At present, predominant approaches to accelerate the problem-solving process entail the utilization of decomposition algorithms (Muralikrishnan et al., 2020; Trivedi et al., 2015; Feng et al., 2023), converting the issue into a linear programming problem (Qu et al., 2023; Qu et al., 2024; Ding et al., 2022), and leveraging smart algorithms (Zhu and Gao, 2020; Baziar et al., 2021; Ponciroli et al., 2020). Note that reference 34 proposes a convex hull representation for the SCUC problem, converting it into a linear programming problem. This approach ensures the accuracy of the solution while enabling rapid acquisition of the SCUC solution. However, in scenarios accounting for dynamic transmission line constraints, variables exhibit pronounced interconnectivity, posing challenges to decoupling efforts. Moreover, intricate constraints obstruct the transformation of the model into one involving solely continuous variables.
To address the inadequacies and challenges prevalent in contemporary research, this article introduces an innovative SCUC model for power systems that explicitly incorporates the dynamic capacity of transmission lines. Grounded in the thermal equilibrium equation governing the line, a predictive model for transmission line temperature is formulated employing superquantile regression techniques, subsequently morphing into a dynamic transmission line capacity model. Building upon this novel foundation, a bespoke algorithm is devised to tackle the model at hand. Anchored in the core iterative architecture of the Lagrangian relaxation algorithm, the problem is decomposed into a series of single-unit subproblems. Leveraging the fundamental tenet of the Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers (ADMM), the dynamic transmission line constraints are meticulously decoupled, facilitating an iterative resolution of each subproblem’s variables via alternating multipliers, culminating in the comprehensive resolution of the model. The main contributions of this paper can be summarized as follows:
1. A stochastic optimization model for power system multi-scenario SCUC that takes into account dynamic transmission line capacities is proposed. In parallel with addressing the uncertainty associated with renewable energy, we have employed a data-driven methodology to formulate a dynamic transmission line capacity model, seamlessly embedding it within the UC model.
2. An algorithm tailored to solve this model, anchored in the principles of Lagrangian relaxation and the Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers (ADMM), has been conceived. Through the strategic decomposition of the problem and the decoupling of the dynamic transmission line model, our algorithm facilitates an efficient and swift resolution of the overarching problem.
The overall structure of this paper is as follows: firstly, in Section 2, the formulations of UC and dynamic line rating model are given. Secondly, the proposed algorithm for solving the D-SCUC model are given in Section 3. And in Section 4, two UC cases are employed to demonstrate the advantages of D-SCUC model and proposed solving algorithm. Finally, we summarize the full text in Section 5.
2 Concept and model of SCUC considering dynamic capacity increase of transmission lines
2.1 Multi-scenario SCUC model
The main task of SCUC is to determine the start-stop state of the unit in each period of the scheduling cycle, and its goal is to minimize the operating cost under the premise of satisfying the coupling constraints of the system and the physical constraints of the single unit (Ding et al., 2021). The system coupling constraints include power balance constraints, system rotation reserve constraints, transmission line capacity constraints, etc. The single unit operation physical constraints include unit start-stop logic constraints, ramp constraints, and minimum start-stop time constraints (Ju et al., 2023). The model is presented as follows:
Equation 1 constitutes the objective function, targeting the minimization of aggregate start-up and shut-down costs for generating units alongside the expectation of operational expenses across diverse scenarios, aiming for their absolute minimum. The objective function f is typically a quadratic function of the generator output and does not include cross-terms with the start-up and shut-down variables of the units. During the computation, this function is generally piecewise linearized. Equations 2–4 delineate the system constraints, encompassing the requirement for power balance, the stipulation for system reserves, and the static transmission line limitations, respectively. Equation 5 articulates the logical constraints that dictate the interrelation between the start-up and shut-down states of the units. Equations 6, 7 serve to uphold the condition that the uninterrupted operation period of each unit surpasses the stipulated minimum durations. Equation 8 imposes that the output levels of the units remain confined within predefined upper and lower bounds, concurrently adhering to the constraints imposed by their operational statuses. Lastly, Equations 9, 10 are dedicated to ensuring that the ramp-up and ramp-down rates of the units do not transgress the established maximum limits, and that the generation output during these transitional periods remains within the prescribed safety margins.
2.2 Dynamic capacity increase model of transmission lines
As the foundational elements for the DLR model and the superquantile regression model, rather than the focal points of this paper, the heat balance equation and polynomial regression are described in the Supplementary Appendix.
Although QR is already versatile and widely used for quantifying risk, its capabilities can be expanded by using super quantile regression (SQR) to estimate the cumulative tail behavior of a random variable. Unlike QR, which focuses on quantifying the risk based on the probability of undesirable events, SQR provides insight into the magnitude of these events. This feature is particularly valuable in applications where understanding the consequences of undesirable events is necessary.
The α-super quantile function of a continuous random variable y is defined as its tail expectation. In relation to the quantile function (46), the upper-tail α-super quantile function can be expressed in Equation 11:
Similar to other regressions, the linear SQR model is an estimator of the conditional α-super quantile of y in Equation 12:
where yα is the estimated upper-tail α-super quantile; α is the super quantile level of the random variable; βα is the model parameter vector. The lower tail α-super quantile function and its corresponding regression model can be defined similarly. As SQR is evolved from QR, it benefits from the ability to determine its model parameter vector βα by solving a linear programming problem.
Based on the concept of HBE and several regression models, the dynamic capacity increase model is constructed. In the modeling process, a quantile regression model is used to quantify the temporal characteristics of conductor temperature. This model mainly forecasts the α-quantile Ttα of conductor temperature at time period t based on the input vector of environmental parameters for the previous k time periods. The input vector consists of weather-related parameters, including wind speed Ws, wind direction angle Wa, ambient temperature Ta, solar radiation Qs and conductor temperature It. Specifically, the input vector has the following form:
In Equation 13, I (Xu et al., 2024), I, Ws, Wa, Ta and Qs are all row vectors representing the current and previous k time periods’ conductor current and quadratic terms, wind speed, wind direction angle, ambient temperature, and solar radiation, respectively, as shown below:
It can be seen that Equation 13 includes several cross-product terms of row vectors. These cross-product terms can better explore the dependencies between input parameters. By more effectively modeling the correlations between these parameters, these cross-terms enhance the influence of hyper-parameters on estimation.
Based on this, the construction of the big data-based model follows similar steps. The quantile regression model for a given risk level is obtained by solving an optimization model. The input vector
Ttα is the estimated
When using the equation to represent a specific transmission line which requires dynamic capacity increase, the model takes the following form:
where Tl,t,s is the α-hyperquantile of the estimated temperature of the transmission line at the time period t, and the remaining variables correspond to the variable contents of the Equations 13, 14. The model describes the functional relationship between current and temperature of conductor and provides model support for the SCUC model.
2.3 The dynamic security constrained unit commitment model (D-SCUC)
On the basis of the transmission line temperature prediction model shown in Equation 16, it is modified to embed dynamic transmission line constraints into SCUC model. The resulting dynamic transmission line constraint is as follows.
where Tlmax is the maximum temperature of the selected transmission line l, and the meaning of other variables is the same as that of Equation 16 From the DC power flow theory and the resulting power transfer distribution factor (PTDF), the relationship between the wire current and the transmission line power can be calculated as follows:
Above all, the dynamic security-constrained unit commitment model (D-SCUC) is described in the following form, which combines the dynamic line capacities with the SCUC model:
As evidenced by Equations 19–21, the optimization model encompasses both integer and discrete variables, with quadratic components featured in both the objective function and the dynamic transmission line constraints. This configuration presents significant computational difficulties when applied to large-scale systems. In response to these challenges, we propose a solution algorithm predicated on an enhanced Lagrangian relaxation methodology.
3 Modified Lagrangian relaxation method for D-SCUC
Given that the proposed D-SCUC model is inherently a Mixed Integer Programming (MIP) problem, the conventional branch-and-bound method incurs significant computational time and memory overhead, with the complexity exacerbated by the inclusion of dynamic capacity expansion models. In this paper, we propose an innovative solution algorithm for the UC model that incorporates dynamic transmission line capacity, which combines Lagrangian Relaxation with the Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers (ADMM). The essence of the algorithm lies in decomposing the dual form of the original problem into a series of smaller, more manageable subproblems, while leveraging the ADMM to efficiently handle coupling variables associated with dynamic transmission line constraints. This strategy dramatically reduces the scale of discrete variables, effectively addressing issues of lengthy computation times and high memory consumption, thereby enabling the solvability of large-scale, complex D-SCUC models.
More precisely, with regard to the system constraints that link the variables of different generating units within the model, Lagrangian multipliers are introduced to formulate a min-max dual problem from the primary optimization task. This facilitates the disentanglement of variables across individual units. Upon this groundwork, the dual problem’s solution entails calculating both the values of the unit variables and the associated Lagrange multipliers pertinent to system constraints. This dual pursuit is executed through an alternating iterative procedure, wherein, particularly for constraints concerning the dynamic augmentation capabilities of transmission lines, the ADMM is harnessed. This ensures the decoupling and computation of unit variables throughout the iterative process. The detailed formulation of dual problem and the iteration algorithm are discussed as follows.
The crux of the Lagrangian Relaxation Algorithm lies in the strategic introduction of Lagrange multipliers to relax challenging, highly-coupled constraints within the model. This transformation retains tractable constraints while constructing the Lagrangian function and its dual problem. The overarching goal is to derive high-quality approximate solutions to the original problem. Owing to the presence of complex, tightly-coupled constraints associated with dynamic transmission line capacities that defy straightforward relaxation, the Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers (ADMM) is employed. This methodology ensures convergence during the iterative process by adeptly handling the inter-unit coupling variables. By partitioning the problem into more manageable subproblems and iteratively solving them in an alternating fashion, ADMM facilitates the computation of unit variables while maintaining consensus across the entire system. This approach not only addresses the issue of high variable coupling but also enhances the scalability and efficiency of solving large-scale optimization problems, particularly those prevalent in power systems characterized by dynamic transmission line constraints.
3.1 Formulation of dual problem
Based on the aforementioned D-SCUC model, it is evident that the system constraints—power balance, reserve requirements and line flow limits—couple all unit variables together. Conversely, unit-specific constraints are separable by unit. Thus, the application of the Lagrangian Relaxation method becomes feasible for relaxing these system constraints. This relaxation transforms the original problem into a collection of decoupled single-unit subproblems, each pertaining to an individual generator without inter-unit dependencies.
3.1.1 Dual problem (DP)
The Dual problem is formulated in Equations 22–24.
Firstly, non-negative multipliers λ, μ, and ρ₁, ρ₂ are respectively introduced for the power balance constraint (2), the reserve requirement constraint (3), and the static transmission line capacity constraint (4), (17). This leads to the formulation of the corresponding Lagrangian functions, from which the dual problem, denoted as Dual Problem (DP) and illustrated in Equation 31, is derived. It is noteworthy that this dual problem comprises separable unit-specific constraints. However, it includes quadratic terms related to line flows that prevent the decoupling of unit variables, thus precluding a direct dual decomposition to solve the subproblems.
A detailed exposition follows, delineating the methodology employed for addressing the dynamic transmission line constraints, along with an outline of the algorithmic procedures that facilitate their management within the overarching optimization framework.
3.2 Dynamic transmission line constraint handling and iterating process
Dynamic transmission line constraints involve quadratic terms of line flows, making it difficult to decouple them using conventional methods. Therefore, this paper proposes an ADMM-based approach to address the issue of coupling caused by transmission line constraints, enabling the iterative solution of the D-SCUC model proposed in this article.
3.2.1 Introduction to ADMM algorithm
The Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers (ADMM) is employed to address situations in dual problems where the objective function is separable, yet variables are coupled through constraints. At its core, ADMM embodies the strategy of iteratively fixing one variable while solving for another, thereby facilitating the decoupling of variables and subproblems during the optimization process.
As an example, consider the convex problem in Equation 25:
The problem’s structure allows the objective function to be decomposed into distinct components f1 and f2, although the variables remain interconnected due to the presence of linear constraints. Subsequently, we outline the iterative format characteristic of the ADMM method. Initially, the augmented Lagrangian function pertinent to the optimization problem is defined in (Equation 26):
In this context, ρ > 0 denotes the coefficient of the quadratic penalty term, and λ represents the vector of Lagrange multipliers associated with the constraints. Typically, the Lagrangian function method proceeds with iterative updates in the manner shown in Equation 27:
The above expression represents the two primary steps involving optimization over variables and multipliers respectively, during the kth iteration. However, considering that jointly optimizing over x1 and x2 in the first step can sometimes be challenging, minimizing with respect to one variable while keeping the other fixed might be simpler. As a result, we can contemplate alternating minimization over x1 and x2, which constitutes the fundamental concept of the ADMM. The iterative scheme can be summarized in Equation 28:
From the aforementioned iterative steps, it is clear that the first step involves fixing x2 and λ, and then minimizing with respect to x1; the second step fixes x1 and λ, and minimizes with respect to x2; the third step updates the Lagrange multiplier λ. Unlike unconstrained optimization problems, the ADMM method is applied to constrained optimization problems. Therefore, the convergence criteria of the algorithm should rely on the optimality conditions for constrained problems, namely, the Karush-Kuhn-Tucker (KKT) conditions. Generally speaking, assessing the convergence of the algorithm requires monitoring whether two residuals are sufficiently small:
The expressions in Equation 29 represent, respectively, the primal feasibility and the dual feasibility of the problem.
Together, primal and dual feasibility, along with complementary slackness and stationarity conditions, constitute the KKT conditions, which are necessary for a point to be a local optimum in a constrained optimization problem. Monitoring these residuals during the iterative process of an algorithm such as ADMM is critical for assessing convergence to an optimal solution.
3.2.2 Reformulation of dual problem
Following the central philosophy of the ADMM algorithm, it is evident that within the objective function’s separable structure, the alternating solution mechanism involves fixing the variables pertaining to other subproblems while solely addressing the variables relevant to the current subproblem. This process facilitates the decoupling of subproblems. Nonetheless, specific to the D-SCUC model and its dual counterpart introduced herein, the landscape is characterized by a separable objective function juxtaposed against coupled constraints. Consequently, an approach mirroring the foundational concept of ADMM can be implemented, enabling problem dissection amidst the intricacies posed by constraint coupling. This strategy ensures that despite the interdependencies enforced by constraints, the problem can still be effectively decomposed and managed through an iterative process akin to ADMM, ultimately aiming for an optimized solution.
The above statement highlights the practical considerations involved in dealing with dynamic transmission line constraints within an optimization framework. Rather than directly integrating these constraints into the Lagrangian through dual multipliers, which would escalate computational complexity, a decoupling strategy is employed. This involves separating the dynamic transmission line constraints and integrating them into the respective subproblems associated with individual generating units. By doing so, the problem becomes more tractable for iterative solution methods, such as those employed in distributed optimization schemes. Each subproblem Subproblem-i is then designed to handle the specific constraints and objectives pertinent to the ith generating unit during τ-th iteration, streamlining the overall optimization process.
Subproblem-i
In Equation 30, terms that are not dependent on the variables of the subproblem have been abstracted away; these can be reintroduced post-subproblem resolution to retrieve the solution to the overarching problem. It becomes apparent that, relative to the dual problem (DP), this particular subproblem enacts a substantial modification to the dynamic transmission line constraints (specifically Equations 17, 18). The corresponding modifications to the aforementioned two constraints are illustrated in Equations 32, 33. At the τ-th iteration phase, within the power flow computation pertaining to the ith subproblem, there’s utilization of the solution set for generator variables emanating from the subproblems indexed from 1 through i-1, all within the current iteration. Conversely, for the generator output variables indexed from i + 1 to the terminal ones—those whose subproblem solutions have yet to be derived in the current round—the solutions are drawn from the preceding iteration. While this operational methodology may yield less precise line flow calculations, it nonetheless safeguards compliance with the dynamic transmission line constraints and facilitates the convergence of the overarching iterative procedure.
However, It must be emphasized that, considering uncertainties stemming from the choice of initial solutions and step lengths among other factors, during the iterative process, there is a significant risk that the transmission line constraints will not be satisfied. This violation could lead to the failure in finding feasible solutions for the subproblems. To mitigate this challenge, a penalty factor denoted as ql,t,s is integrated into the algorithmic framework. This factor’s index is directly linked to the power flow computations executed at every iteration. With the addition of this penalty factor, the adjusted formulation of the subproblem takes on the following appearance shown in Equations 34–36:
Subproblem-i
In Equation 34, m is the penalty coefficient used to control the weight of the penalty factor. The introduction of the penalty factor serves to penalize the violation of transmission line constraints, encouraging the iterative procedure to gravitate towards solutions that adhere closely to these constraints. This adjustment is pivotal in ensuring that the iterative method remains effective and robust, capable of delivering feasible solutions despite the inherent complexities and uncertainties within the optimization problem.
Upon establishing the aforementioned subproblem optimization model Subproblem-i, the subsequent section will delineate the iterating process for solving the overall dual problem.
3.2.3 Iterating process
From the previous exposition on the ADMM algorithm, it is clear that the overall solution process involves an iterative procedure for variables and dual multipliers. Building upon this foundation, the following sections will detail the comprehensive solution process for the D-SCUC model proposed in this paper, along with the criteria for assessing convergence.
In the insight gleaned from the prior section, it becomes clear that each iteration within the subproblems employs the dual multipliers’ values garnered from the preceding iteration. Consequently, establishing the initial values of these dual multipliers assumes paramount importance. Two methodologies are viable for initializing the dual multipliers: they can commence identically at zero across the board, or one can opt for relaxing all integer variables present in the primal problem into continuous counterparts. This relaxation facilitates the computation of initial values for the multipliers that correspond to the constraints of the system. Rigorous experimentation has substantiated that both strategies are endowed with commendable attributes of convergence.
On the other hand, the updating of multipliers is also of great importance. The formula for calculating the residuals is as follows shown in Equations 37–40:
Herein, gbalt,s, gret,s, gline+l,t,s and gline-l,t,s present the subgradients associated with the active power balance constraint, the reserve constraint, and the maximum transmission capacity constraints for line l under scenario s, respectively. The power flow pl,t,s on line l at time period t under scenario s may be consulted following Equation 18. The method for updating the dual multipliers is as follows:
where α1-α4 refer to the step sizes used in the iterative procedure. Typically, to reduce the oscillatory behavior that can occur during iterations, an adaptive subgradient iteration algorithm is utilized. This type of algorithm decreases the step size incrementally with each iteration, helping to stabilize the convergence of the optimization process.
In terms of the problem’s convergence criteria, consideration is given to both the relative duality gap between the primal and dual formulations and the magnitude of the residuals. Post-each iteration, scrutiny is applied to ascertain if the residual indicative of the power balance constraint, delineated in Supplementary Equation A46, is adequately minute, alongside verifying the fulfillment of inequalities articulated in Supplementary Equations A47–A49. Moreover, leveraging the solution procured from the recent iteration, discrete computations are conducted to derive solutions for both the primal and dual problems, followed by a comparative analysis to evaluate if the gap between them is sufficiently diminutive. Upon the satisfaction of all aforementioned stipulations, one can deduce that a satisfactory solution to the underlying problem has been attained.
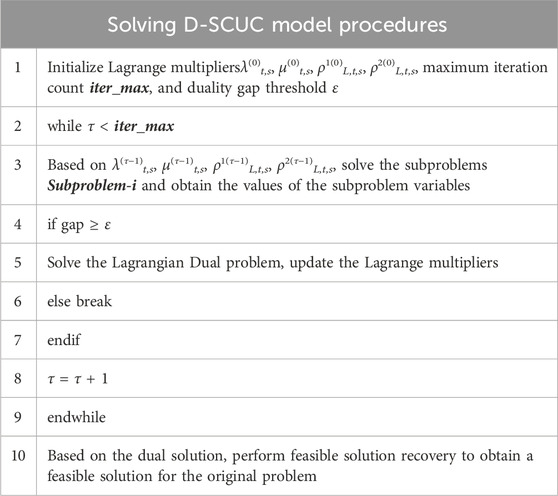
In summary, the overall problem-solving process proceeds as follows:
1. Determine the initial values of the multipliers λ(0)t,s, μ(0)t,s, ρ1(0)l,t,s, ρ2(0)l,t,s and set the conditions for iteration termination;
2. In the τ-th iteration, utilizing the multiplier valuesλ(τ−1)t,s, μ(τ−1)t,s, ρ1(τ−1)l,t,s, ρ2(τ−1)l,t,s, calculate the single-unit subproblems Subproblem-i individually;
3. Based on the solutions to the subproblems, compute the residual gbalt,s, verify whether the constraints of the primal problem are satisfied, and calculate the duality gap;
4. If the convergence criteria are met, terminate the computation and return the results;
5. Otherwise, update the multipliers according to Equation 41, and return to step 2 to continue the iteration.
The pseudo-code is shown in Table 1 for solving the proposed D-SCUC model.
4 Case studies
To validate the effectiveness of the proposed model and method, this section conducts computational verification on the IEEE-118 system and the IEEE-300 system. The computer configuration used for these calculations includes an AMD Ryzen™ 9 7900X CPU running at 4.7 GHz, with 32 GB of RAM. The algorithm is implemented in Python, wherein the Lagrangian relaxation framework and iterative algorithm are realized using Python. Subproblems are constructed and solved utilizing the Gurobi API.
4.1 Dynamic line rating model validation
In the research conducted herein, the IEEE 118-bus system was selected as the test case, encompassing a network topology featuring 118 nodes, inclusive of 54 generation units, interconnected via 177 transmission lines, and serving 91 loads, thereby furnishing the dataset for the SCUC model. Aiming to investigate the impact of the dynamic capacity augmentation model on system operation expenses and the alleviation of transmission line congestion, a prototypical single-scenario representation of renewable energy from a provincial context was employed. This scenario entailed the modification of select conventional thermal power units from the baseline case to renewable energy installations, with their respective power generation levels being predetermined.
Additionally, an analytical computation is performed on the SCUCmodel that incorporates dynamic transmission line capacities. Parameters pertinent to transmission lines within this dynamic capacity augmentation framework are derived through the resolution of a planning model, leveraging historical data specific to the region. In the course of practical computations, dynamic capacity constraints are enforced on transmission lines encompassed within the set denoted as Lined, whereas static transmission line constraints persist for alternative conductors. A selection of various upper bound values for transmission line temperatures is made, with the ensuing outcomes delineated in Table 2.
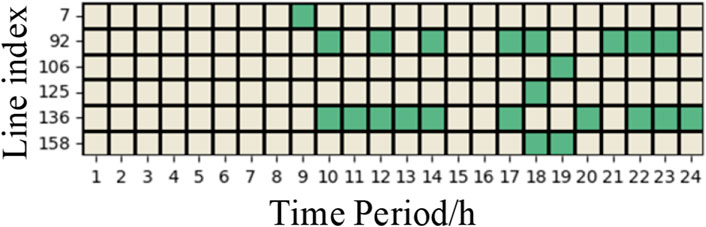
The quartet of columns—Tmax, fval, ∑Pline and n—respectively denote the maximum designated transmission line temperature, the computed operational expenditure, the cumulative power across transmission lines, and the aggregate count of intervals wherein transmission line loading surpasses the static constraint threshold. As per the tabulated insights, within the temperature setting spectrum from 75°C to 100°C, the operational cost exhibits a sequential diminution from 2,142,780 to 2,132,563, paralleled by a progressive escalation in the total transmission line load summation from 173,515 to 176,603, and a rise in the tally of congestion instances from 3 to 44. Moreover, under the temperature settings delineated above, a heatmap encompassing both congested conduits and those benefiting from dynamic capacity enhancements is illustrated in Figure 1. The interpretation of grid squares mirrors that of Figure 2, wherein a deepening hue signifies an elevation in power magnitude. A comparative analysis with Figure 2 reveals that an upsurge in the prescribed temperature correlates with a marked proliferation of time segments characterized by elevated transmission line loads, concomitant with an augmentation in transmission line loads themselves.
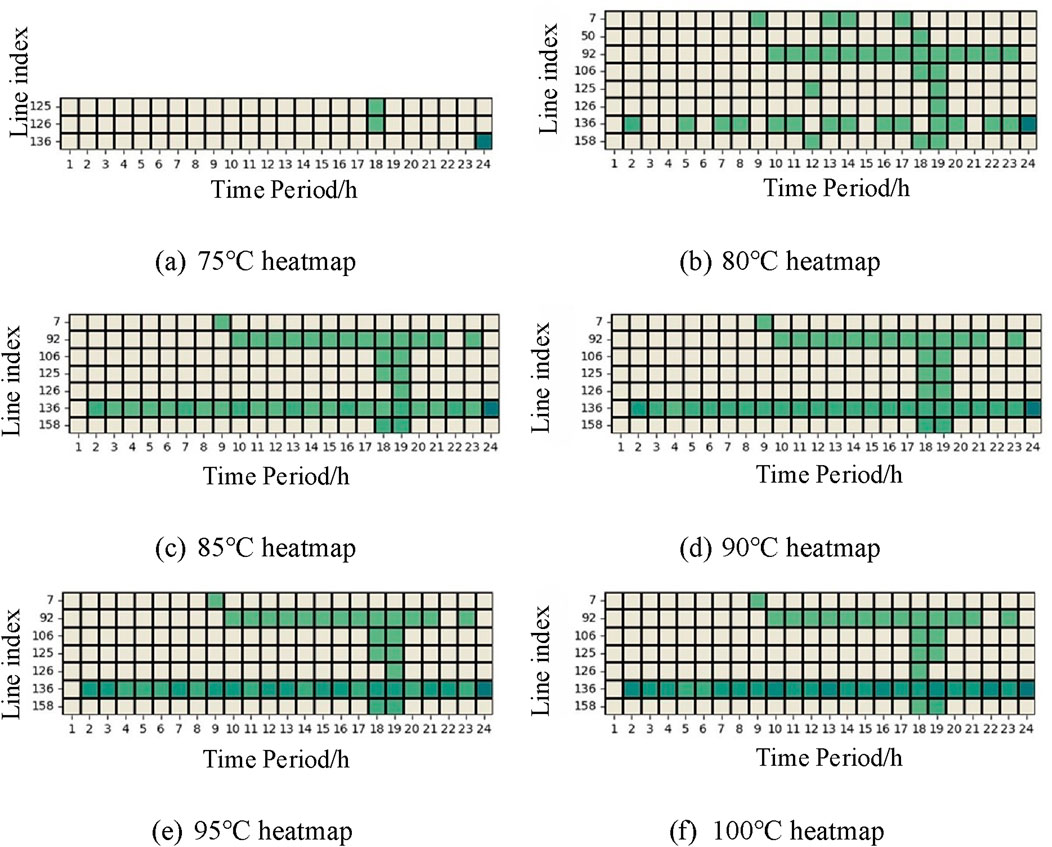
Figure 1. Heatmaps of Congested Lines and Capacity-Increased Lines under Different Temperatures. (A) 75°C heatmap. (B) 80°C heatmap. (C) 85°C heatmap. (D) 90°C heatmap. (E) 95°C heatmap. (F) 100°C heatmap.
4.2 Validation of the proposed solving algorithm
In this section, we address the proposed Lagrangian Relaxation algorithm to validate its efficacy in resolving the D-SCUC model that incorporates dynamic transmission line capacity enhancements. The IEEE-300 bus system serves as the platform for simulation calculations, featuring a network topology comprising 69 generating units, 60 transformers, 304 transmission lines, and 185 load nodes. Following the approach outlined previously, a portion of the conventional thermal power units are substituted with renewable energy counterparts. A selection of various representative renewable energy scenarios from a specific locale is employed for the computation of the D-SCUC model under multiple scenarios. The parameters for the transmission line models are obtained through training with historical data.
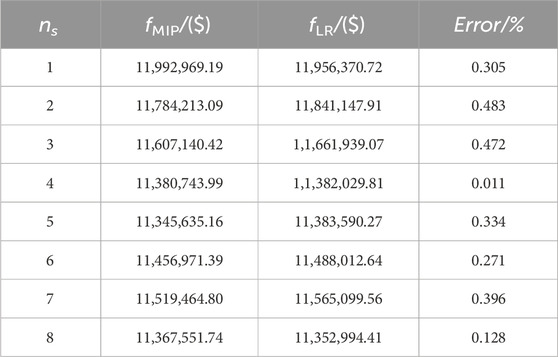
Initially, for test cases encompassing a scenario count spanning from 1 to 8, computations are executed employing both the Gurobi Mixed Integer Programming (MIP) solver and the Lagrangian Relaxation framework. Concerning the Lagrangian Relaxation algorithm, a dual gap threshold of 0.01 is utilized, signifying that once the dual gap dips beneath this threshold, a solution of sufficient quality is deemed to have been attained. The magnitudes of the calculated operating costs and corresponding relative errors are delineated in Table 3. The quartet of columns within the table signifies the scenario quantity, the outcomes derived from the MIP solver, the results emanating from the Lagrangian Relaxation framework, and the relative error, respectively. As evidenced, under differing counts of renewable energy scenarios, the discrepancies between solutions procured via the Lagrangian Relaxation algorithm and those yielded by the solver remain confined within a margin of 0.5%, indicative of the high-caliber approximations delivered by the proposed Lagrangian Relaxation algorithm.
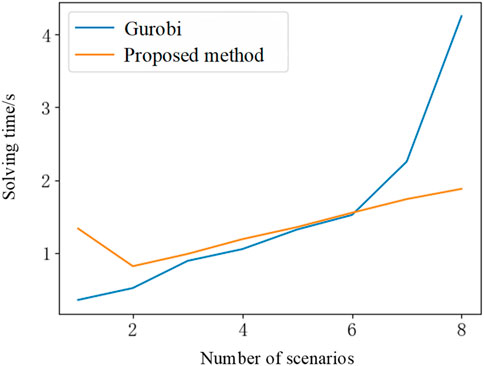
Building upon the validation of algorithmic accuracy, this study contrasts the temporal performance of two algorithms and explores their respective solution velocities in relation to the quantity of scenarios. Pertaining to the aforementioned eight resolution contexts, graphical representation delineates the correlation between scenario count and computational duration for both algorithms, illustrated in Figure 3.
From the graph, it can be observed that when the number of scenarios is small, the Lagrangian Relaxation algorithm takes more time than the Mixed Integer Programming (MIP) method. However, as the number of scenarios increases, the time complexity of the MIP method rises significantly with the increase in scenarios, whereas, in contrast, the solution time for Lagrangian Relaxation grows at a relatively slower pace. This phenomenon aligns with the characteristics of both solving algorithms.
In Gurobi’s implementation of the MIP method, branch-and-cut techniques are typically employed, which involve partitioning and contracting the feasible region to find a more precise range for the problem’s feasible domain, thus facilitating the solving process. Since this algorithm involves the generation of branches, its solution space grows exponentially with the increase in variables, resulting in slower solution times when dealing with a large number of scenarios.
On the other hand, the Lagrangian Relaxation algorithm decouples the D-SCUC subproblems across multiple scenarios. While an increase in the number of scenarios does add complexity to the subproblems, they remain greatly simplified compared to their original form, and thus the solution time does not drastically increase. Theoretically, it has been proven that the iteration time for the Lagrangian Relaxation algorithm is approximately linearly related to the number of variables. Consequently, the Lagrangian Relaxation algorithm is better suited for solving large-scale, multi-scenario SCUC problems.
Lastly, with regard to the iterative procedure of the Lagrangian algorithm, its iteration curve is illustrated in Figure 4.
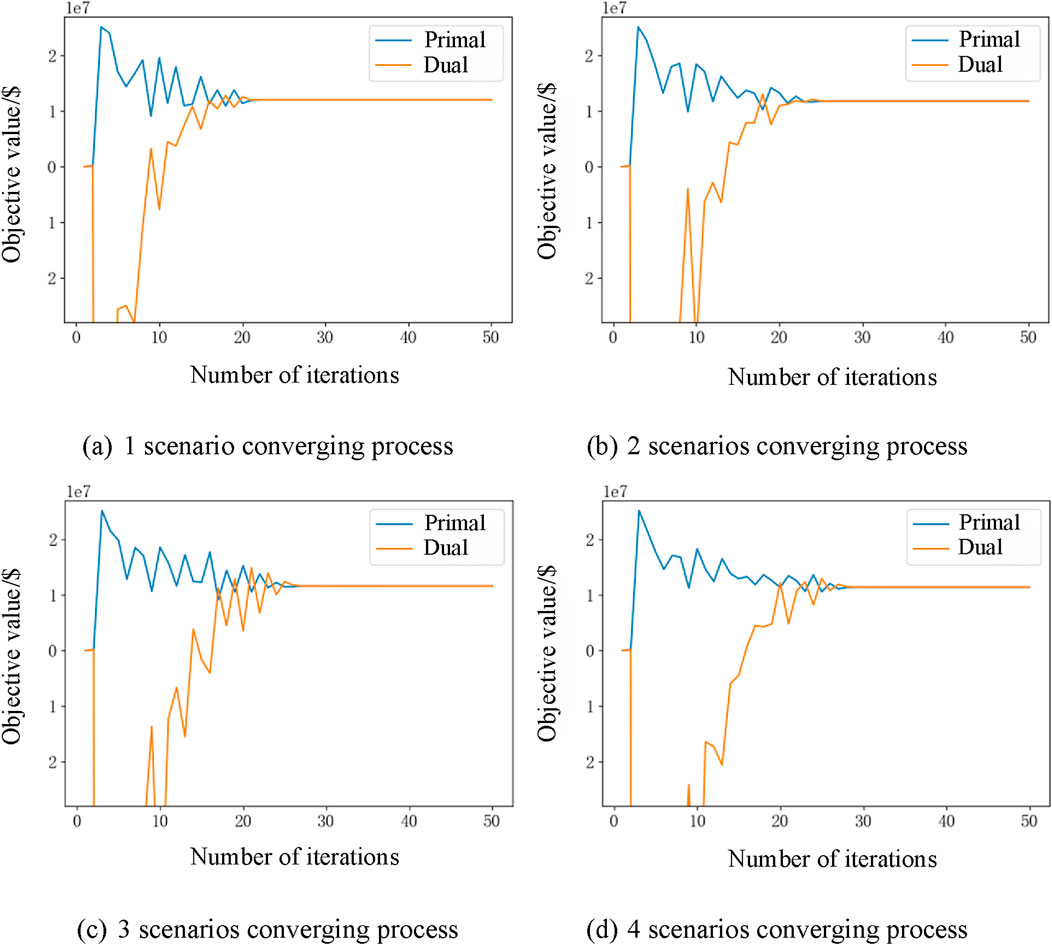
Figure 4. The convergence of the Lagrangian relaxation algorithm under different scenarios. (A) 1 scenario converging process. (B) 2 scenarios converging process. (C) 3 scenarios converging process. (D) 4 scenarios converging process.
As depicted in the chart, following a specific number of iterations, both the values of the original (primal) problem and its dual counterpart converge to a particular interval. Nonetheless, there is n’t a strict inequality with the primal being greater than the dual. This is attributable to the nature of the subgradient algorithm, which during its iterative process, cannot ensure a strict adherence to a descent direction. This characteristic is directly influenced by the choice of the step size at each iteration.
5 Conclusion
To address the issues of poor economic performance and high computational time expenditure in power system UC models due to low transmission line capacities, this paper presents a SCUC model for power systems that takes into account dynamic line rating enhancements, along with an ADMM-based solution algorithm specifically designed for this model. The model employs data-driven modeling for transmission lines to depict the temporal coupling between line temperature and load, thus effectively increasing the transmission line capacity. By utilizing the Lagrangian relaxation framework, the dual problem of the model is formulated and decomposed into subproblems for iterative resolution, tackling the computational overhead challenge in solving SCUC problems.
The proposed model and algorithm have been applied to the IEEE-118 and IEEE-300 test systems. Test results demonstrate that the D-SCUC model considering dynamic line rating improvements can significantly boost transmission line efficiency and reduce system operational costs. Furthermore, the proposed algorithm exhibits notable improvements in computational efficiency compared to conventional solvers.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
JD: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. NT: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. QZ: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. CT: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. PX: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. LC: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This paper is supported by the Science and Technology Project of Guizhou Power Grid Company of China: Key Technologies for Optimal Scheduling Considering Security Constraints in Power Market Environment (GZKJXM20222442).
Conflict of interest
Authors JD, NT, and QZ were employed by Power Dispatching and Control Center of Guizhou Power Grid Co., Ltd. Authors CT, PX, and LC were employed by China Southern Power Grid Co., Ltd.
The authors declare that this study received funding from Guizhou Power Grid Company. The funder had the following involvement in the study: study design, data collection and analysis.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fenrg.2024.1479347/full#supplementary-material
References
Baziar, A., Bo, R., Ghotbabadi, M. D., Veisi, M., and Rehman, W. U. (2021). Evolutionary algorithm-based adaptive robust optimization for AC security constrained unit commitment considering renewable energy sources and shunt FACTS devices. IEEE Access 9, 123575–123587. doi:10.1109/access.2021.3108763
Bhattarai, B. P., Gentle, J. P., McJunkin, T., Hill, P. J., Myers, K. S., Abboud, A. W., et al. (2018). Improvement of transmission line ampacity utilization by weather-based dynamic line rating. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 33 (4), 1853–1863. doi:10.1109/tpwrd.2018.2798411
Cheng, Y., Liu, P., Zhang, Z., and Dai, Y. (2021). Real-time dynamic line rating of transmission lines using live simulation model and tabu search. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 36 (3), 1785–1794. doi:10.1109/tpwrd.2020.3014911
Dawson, L., and Knight, A. M. (2018). Applicability of dynamic thermal line rating for long lines. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 33 (2), 719–727. doi:10.1109/tpwrd.2017.2691671
Ding, T., Jia, W., Shahidehpour, M., Han, O., Sun, Y., and Zhang, Z. (2022). Review of optimization methods for energy hub planning, operation, trading, and control. IEEE Trans. Sustain Energy 13 (3), 1802–1818. doi:10.1109/tste.2022.3172004
Ding, T., Li, C., Yang, Y., Jiang, J., Bie, Z., and Blaabjerg, F. (2017). A two-stage robust optimization for centralized-optimal dispatch of photovoltaic inverters in active distribution networks. IEEE Trans. Sustain Energy 8 (2), 744–754. doi:10.1109/tste.2016.2605926
Ding, T., Zeng, Z., Qu, M., Catalão, J. P., and Shahidehpour, M. (2021). Two-stage chance-constrained stochastic thermal unit commitment for optimal provision of virtual inertia in wind-storage systems. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 36 (4), 3520–3530. doi:10.1109/tpwrs.2021.3051523
Douglass, D., Chisholm, W., Davidson, G., Grant, I., Lindsey, K., Lancaster, M., et al. (2016). Real-time overhead transmission-line monitoring for dynamic rating. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 31 (3), 921–927. doi:10.1109/tpwrd.2014.2383915
Du, E., Zhang, N., Kang, C., and Xia, Q. (2019). A high-efficiency network-constrained clustered unit commitment model for power system planning studies. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 34 (4), 2498–2508. doi:10.1109/tpwrs.2018.2881512
Elavarasan, R. M., Shafiullah, G., Padmanaban, S., Kumar, N. M., Annam, A., Vetrichelvan, A. M., et al. (2020). A comprehensive review on renewable energy development, challenges, and policies of leading Indian states with an international perspective. IEEE Access 8, 74432–74457. doi:10.1109/access.2020.2988011
Feng, F., Zhang, P., Bragin, M. A., and Zhou, Y. (2023). Novel resolution of unit commitment problems through quantum surrogate Lagrangian relaxation. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 38 (3), 2460–2471. doi:10.1109/tpwrs.2022.3181221
Han, O., Ding, T., Zhang, X., Mu, C., He, X., Zhang, H., et al. (2023). A shared energy storage business model for data center clusters considering renewable energy uncertainties. Renew. Energy 202, 1273–1290. doi:10.1016/j.renene.2022.12.013
Ju, C., Ding, T., Jia, W., Mu, C., Zhang, H., and Sun, Y. (2023). Two-stage robust unit commitment with the cascade hydropower stations retrofitted with pump stations. Appl. Energy 334, 120675. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2023.120675
Kim, S. D., and Morcos, M. M. (2013). An application of dynamic thermal line rating control system to up-rate the ampacity of overhead transmission lines. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 28 (2), 1231–1232. doi:10.1109/tpwrd.2012.2234940
Kirilenko, A., Esmaili, M., and Chung, C. Y. (2021). Risk-averse stochastic dynamic line rating models. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 36 (4), 3070–3079. doi:10.1109/tpwrs.2020.3045589
Kroposki, B. (2017). Integrating high levels of variable renewable energy into electric power systems. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean. Energy. 5 (6), 831–837. doi:10.1007/s40565-017-0339-3
Lee, C., Liu, C., Mehrotra, S., and Shahidehpour, M. (2014). Modeling transmission line constraints in two-stage robust unit commitment problem. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 29 (3), 1221–1231. doi:10.1109/tpwrs.2013.2291498
Li, X., Shi, D., Li, Y., and Zhen, X. (2019). Impact of carbon regulations on the supply chain with carbon reduction effort. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man. Cybern. Syst. 49 (6), 1218–1227. doi:10.1109/tsmc.2017.2741670
Liu, J., Zang, H., Cheng, L., Ding, T., Wei, Z., and Sun, G. (2023). A transformer-based multimodal-learning framework using sky images for ultra-short-term solar irradiance forecasting. Appl. Energy 342, 121160. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2023.121160
Lu, R., Ding, T., Qin, B., Ma, J., Fang, X., and Dong, Z. (2020). Multi-stage stochastic programming to joint economic dispatch for energy and reserve with uncertain renewable energy. IEEE Trans. Sustain Energy 11 (3), 1140–1151. doi:10.1109/tste.2019.2918269
Meus, J., Poncelet, K., and Delarue, E. (2018). Applicability of a clustered unit commitment model in power system modeling. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 33 (2), 2195–2204. doi:10.1109/tpwrs.2017.2736441
Morales-España, G., and Tejada-Arango, D. A. (2019). Modeling the hidden flexibility of clustered unit commitment. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 34 (4), 3294–3296. doi:10.1109/tpwrs.2019.2908051
Morozovska, K., Heleno, M., Meza, A. V., and Hilber, P. (2021). Including dynamic line rating into the optimal planning of distributed energy resources. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 12 (6), 5052–5059. doi:10.1109/tsg.2021.3109130
Muralikrishnan, N., Jebaraj, L., and Rajan, C. C. A. (2020). A comprehensive review on evolutionary optimization techniques applied for unit commitment problem. IEEE Access 8, 132980–133014. doi:10.1109/access.2020.3010275
Peng, H., Zhang, J., Zhou, J., Shi, G., Wang, J., and Cai, X. (2024). Delta-type serial shunt soft normally-open points with wide power flow regulation range in distributed network. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron 71 (7), 6501–6511. doi:10.1109/tie.2023.3310008
Ponciroli, R., Stauff, N. E., Ramsey, J., Ganda, F., and Vilim, R. B. (2020). An improved genetic algorithm approach to the unit commitment/economic dispatch problem. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 35 (5), 4005–4013. doi:10.1109/tpwrs.2020.2986710
Qu, M., Ding, T., Mu, C., Zhang, X., Pan, K., and Shahidehpour, M. (2024). Linearization method for large-scale hydro-thermal security-constrained unit commitment. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 21 (2), 1754–1766. doi:10.1109/tase.2023.3241491
Qu, M., Ding, T., Sun, Y., Mu, C., Pan, K., and Shahidehpour, M. (2023). Convex hull model for a single-unit commitment problem with pumped hydro storage unit. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 38 (5), 4867–4880. doi:10.1109/tpwrs.2022.3215463
Sun, J., Chen, M., Liu, H., Yang, Q., and Yang, Z. (2020). Workload transfer strategy of urban neighboring data centers with market power in local electricity market. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 11 (4), 3083–3094. doi:10.1109/tsg.2020.2967803
Tosatto, A., Weckesser, T., and Chatzivasileiadis, S. (2020). Market integration of HVDC lines: internalizing HVDC losses in market clearing. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 35 (1), 451–461. doi:10.1109/tpwrs.2019.2932184
Trivedi, A., Srinivasan, D., Pal, K., Saha, C., and Reindl, T. (2015). Enhanced multiobjective evolutionary algorithm based on decomposition for solving the unit commitment problem. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 11 (6), 1346–1357. doi:10.1109/tii.2015.2485520
Xavier, Á. S., Qiu, F., Wang, F., and Thimmapuram, P. R. (2019). Transmission constraint filtering in large-scale security-constrained unit commitment. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 34 (3), 2457–2460. doi:10.1109/tpwrs.2019.2892620
Xu, Y., Ding, T., Qu, M., and Du, P. (2020). Adaptive dynamic programming for gas-power network constrained unit commitment to accommodate renewable energy with combined-cycle units. IEEE Trans. Sustain Energy 11 (3), 2028–2039. doi:10.1109/tste.2019.2951616
Xu, Z., Guan, X., Jiang, H., Liu, Y., Zhang, Z., Chen, H., et al. (2024). Carbon neutrality computational cost optimization for economic dispatch with carbon capture power plants in smart grid. IEEE Trans. Sustain Comput. 9 (3), 354–370. doi:10.1109/tsusc.2023.3284827
Yang, Q., Wang, J., Yin, H., and Li, Q. (2022). A fast calculation method for long-term security-constrained unit commitment of large-scale power systems with renewable energy. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean. Energy. 10 (5), 1127–1137. doi:10.35833/mpce.2021.000155
Yao, C., and Zhang, Y. (2024). Direct power flow controller with continuous full regulation range. IEEE Trans. Power Electron 39 (5), 5449–5461. doi:10.1109/tpel.2024.3367366
Ye, H., Ge, Y., Liu, X., and Li, Z. (2016). Transmission line rating attack in two-settlement electricity markets. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 7 (3), 1346–1355. doi:10.1109/tsg.2015.2426418
Yuan, Y., Ding, T., Chang, X., Jia, W., and Xue, Y. (2024). A distributed multi-objective optimization method for scheduling of integrated electricity and hydrogen systems. Appl. Energy 355, 122287. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2023.122287
Zhang, Y., Wang, L., and Li, W. (2021). Autonomous DC line power flow regulation using adaptive droop control in HVDC grid. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 36 (6), 3550–3560. doi:10.1109/tpwrd.2020.3044978
Zhu, H., and Li, D. (2024). A carbon emission adjustment model considering green finance factors in the context of carbon neutrality. IEEE Access 12, 88174–88188. doi:10.1109/access.2024.3417355
Zhu, Y., and Gao, H. (2020). Improved binary artificial fish swarm algorithm and fast constraint processing for large scale unit commitment. IEEE Access 8, 152081–152092. doi:10.1109/access.2020.3015585
Nomenclature
Indices and sets
I Indices for units
T Indices for time periods
s Indices for scenarios
b Indices for buses
l Indices for transmission lines
Gen Set of thermal units
Re Set of renewable units
Bus Set of Nodes
S Set of scenarios
L Set of transmission line
Lines Set of transmission line with static capacity
Lined Set of transmission line with dynamic capacity
Parameter and constants
T Number of time periods
Cui Startup cost for unit i
Cdi Shutdown cost for unit i
Prei,t,s Power output of renewable energy unit i at time period t, under scenario s
Db,t Load demand on bus b during time period t
Pmaxi, Pmini Upper and lower limits of the power output for thermal unit i
Fmaxl Maximum power flow on transmission line l
HPTDFl,t Power transfer distribution factor
Toni, Toffi Minimum Start-up time and down time periods for thermal unit i
Rupi, Rdowni Maximum ramp up and down limit for thermal unit i
Rstarti, Rshuti Maximum power output during startup and shutdown for thermal unit i
Functions and variables
ui,t, di,t Startup and shutdown variable of thermal unit i in time period t
xi,t Status variable of thermal unit i in time period t
Pi,t,s Power output variable of thermal unit i in time period t under scenario s
f Running cost function of thermal unit i
π Scenario probability function
Keywords: unit commitment, dynamic line rating, Lagrangian relaxation, alternating direction method of multipliers, sub-gradient algorithms
Citation: Dai J, Tian N, Zhao Q, Tang C, Xuan P and Cheng L (2024) An ADMM approach for unit commitment with considering dynamic line rating. Front. Energy Res. 12:1479347. doi: 10.3389/fenrg.2024.1479347
Received: 12 August 2024; Accepted: 28 August 2024;
Published: 30 October 2024.
Edited by:
Tao Ding, Xi’an Jiaotong University, ChinaReviewed by:
Chunyu Zhang, Taizhou University, ChinaLizi Luo, Nanjing University of Science and Technology, China
Copyright © 2024 Dai, Tian, Zhao, Tang, Xuan and Cheng. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Chong Tang, dGFuZ2Nob25nQGNzZy5jbg==
 Jiang Dai1
Jiang Dai1 Chong Tang
Chong Tang