- 1Huadong Engineering Corporation Limited, Power China, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China
- 2School of Infrastructure Engineering, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, Liaoning, China
The comprehensive cascade reservoir system is extensively used for flood control and power generation. Traditional reservoir scheduling often treats these tasks as competing objectives, prioritizing flood control during the flood season and neglecting power generation benefits. This approach, primarily applied to large floods, leads to hydraulic resource wastage and power generation loss during minor and moderate floods. The lower Jinsha River cascade reservoirs have significant flood control storage capacity, allowing part of the capacity to be used for maintaining higher water levels without compromising safety under minor and moderate floods within a 20-year return period. This paper proposes an optimal scheduling model that considers both flood control and power generation tasks for the lower Jinsha River cascade reservoirs. The Multi-objective Particle Swarm Optimization (MOPSO) algorithm was used to find non-inferior solution sets. An evaluation index system was developed to select optimal solutions under different flood frequencies, using the Minimum Discriminant Information Principle and VIKOR model. The results indicate that the optimal scheduling scheme under 20-year, 10-year, and 5-year return period floods can enhance power generation by 1.64, 1.71, and 1.35 billion kWh, respectively, compared to conventional scheduling. This approach supports coordinated flood control and power generation scheduling, contributing to the high-quality development of the Yangtze River Economic Belt.
1 Introduction
The comprehensive cascade reservoir system is one of the most widely used engineering measures for flood control in river basins (Li and Xu, 2023). It undertakes tasks such as flood control and power generation, often resulting in conflicts between these objectives (Brunner and Sikorska Senoner, 2019). Traditionally, it is believed that flood control tasks and the benefits of power generation are in a competitive relationship and cannot be simultaneously satisfied (Loucks et al., 1981). Consequently, during flood periods, the scheduling of cascade reservoirs typically does not consider power generation benefits. However, this strategy is primarily applied to large floods that exceed downstream flood control standards. Applying the same strategy to minor and moderate floods that meet downstream standards leads to the wastage of hydropower resources.
In recent years, the multi-objective optimal scheduling of reservoirs has been a hot research topic. Traditional reservoir scheduling methods typically optimize for a single objective, overlooking the synergistic effects among multiple objectives. To address this issue, researchers have proposed various multi-objective optimization methods (Ning et al., 2024). applied the improved Advanced Multi-objective Ant Lion Optimization (AMOALO) algorithm to reservoir flood control and scheduling. Using the Pine Reservoir and Dongfeng Reservoir in the Fuzhou River Basin of Dalian as examples, they obtained non-dominated solution sets for different objectives, providing an effective method for solving multi-objective reservoir scheduling problems. Wan et al. (2023) addressed efficiency and flood risk in reservoir scheduling decisions. They proposed a multi-objective synergistic decision-making method based on the synergistic theory of flood resource utilization in reservoirs, offering a basis for flood resource utilization decisions. Hashemi et al. (2024) studied the Masjed-e-Soleyman and Gotvanand Olia dams to construct an optimal dispatch model. The objectives included generating hydroelectric power, meeting downstream demands (drinking water, agriculture, industry, environment), and controlling floods. They constructed four assessment criteria and four indicators (reliability, resilience, vulnerability, and sustainability) to analyze the dispatch results. Wang et al. (2023) developed a pathological two-layer planning model to quantify the relationship between flood control and power generation in optimal reservoir scheduling. This model aims to reduce flood control risks without sacrificing power generation benefits during flood regulation. Huang et al. (2014) developed a nonlinear multi-objective optimization model to coordinate hydropower generation with the joint operation of 15 reservoirs in the Upper Yangtze River Basin. And an extended POA is proposed to accelerate the efficiency and effectiveness of solving nonlinear optimization model. Ouyang et al. (2013) developed an optimization model of multi-objective flood control for cascaded reservoirs to solve scheduling problem of large-scale reservoirs on the middle and upper Yangtze River, considering the requirements such as dam safety, flood control over the upstream area and flood control over the downstream protected area. And they formulated an adaptive algorithm of multi-objective electromagnetism-like mechanism (MOEM) for evolution of the feasible solution sets. Previous research by scholars has largely focused on how to ensure power generation under lower flood risk during major floods, with insufficient analysis on maximizing overall benefits during medium and small floods. We aims to provide a method to specifically address the scheduling strategies that should be employed for the large cascade reservoirs when facing low flood risk.
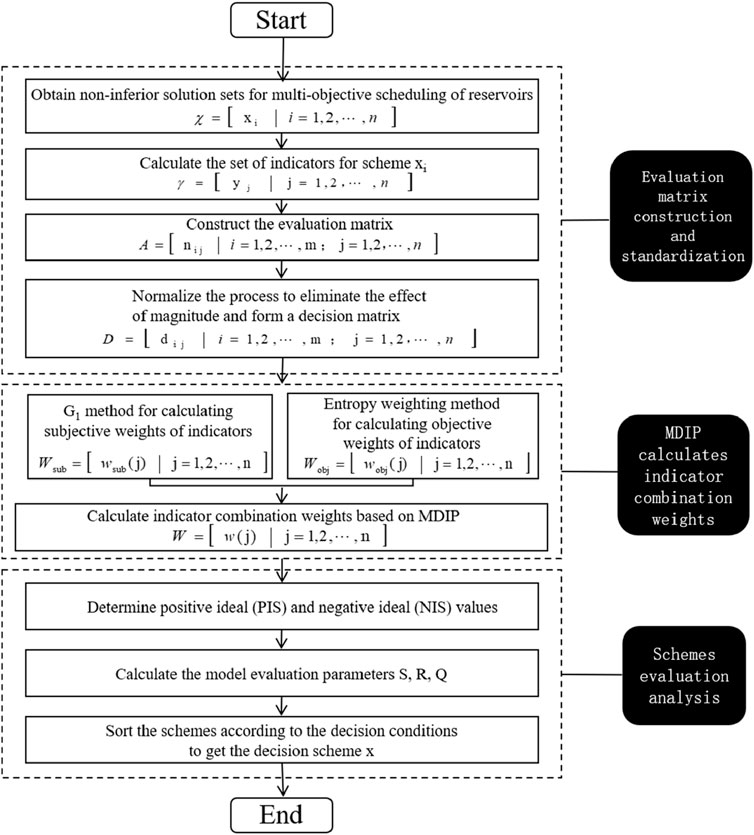
The selection of evaluation indexes and the allocation of weights directly affect the accuracy of multi-objective decision-making (Malekmohammadi et al., 2011; Chen, 1988). A reasonable scheduling scheme needs to adapt to different flood levels in the basin, meeting upstream and downstream flood control needs, and reducing power generation losses and flood risks. This paper starts from the framework of an ‘objective-criteria-indicator’ hierarchical relationship. Five dimensional criteria are selected with the objective of seeking the optimal scheduling scheme under different frequency floods. The multi-objective decision-making index system of the cascade reservoirs is constructed using the non-inferior solution set of multi-objective optimal scheduling as input. The Minimum Discriminant Information Principle (MDIP) combined with the VlseKriterijuska Optimizacija I Komoromisno Resenje (VIKOR) model (Opricovic and Tzeng, 2007) is used to solve the multi-objective decision-making problem of scheduling schemes more rationally, precisely, and efficiently.
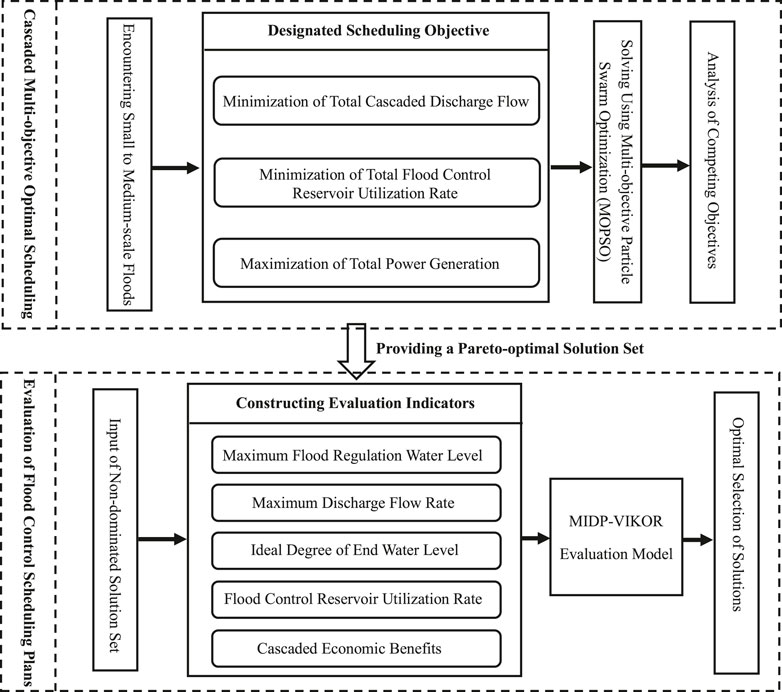
This paper takes the lower Jinsha River cascade reservoirs as the research object. According to the operation demands of flood control and power generation when facing minor and moderate floods, this paper establishes the multi-objective optimal scheduling model for cascade reservoirs to balance power generation, flood flow reduction, and efficient use of flood control capacity. And the Multi-objective Particle Swarm Optimization (MOPSO) algorithm is used to solve and analyze the competitive relationships among these objectives. Then, in order to further evaluate and select the satisfied or optimal one from the flood control scheduling schemes, namely the Pareto non-inferior set solved by MOPSO, this paper establishes an Multi-objective decision-making model including a three layer indicator system and MDIP-VIKOR. The flowchart of different steps of this research is shown in Figure 1.
As opposed to previous studies, this research proposes a new multi-objective optimal scheduling model to address the multiple demands of the cascade reservoirs when facing minor and moderate floods within a 20-year return period or less. The large cascade reservoirs, due to their significant storage and discharge capacity as well as large flood control capacity, can ensure the safety of the reservoirs and downstream protective structures during medium and small floods. They can also utilize part of their capacity to retain floodwaters, thereby reducing peak flow and increasing the overall power generation of the cascade system. The novelty of this paper is that the multi-objective scheduling problem for the cascade reservoirs is systematically analyzed and optimized by MOPSO algorithm, focusing on flood control, power generation, and the utilization of flood control capacity. The goal is to achieve a balance of benefits during medium and small floods. On the other hand, to enhance the accuracy of multi-objective decision-making and identify the best solution for decision-makers, this paper has developed a new multi-objective evaluation indicator system based on the hierarchical relationship of “objectives-criteria-indicators.” It integrates MDIP with VIKOR model to conduct a comprehensive evaluation of various scheduling schemes. Using this method, this paper aims to offer a more reasonable, accurate, and scientifically sound scheduling scheme for the cascade reservoirs when managing floods of varying frequencies.
2 Study area
The Jinsha River originates from the Tanggula Mountain in China and flows through the Tibetan Plateau, the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau, and the western edge of the Sichuan Basin. It covers five provinces: Qinghai, Tibet, Sichuan, Yunnan, and Guizhou, forming the upper part of the Yangtze River, the longest river in China. The Jinsha River basin consists mainly of high mountains and deep valleys, with higher terrain in the north and lower terrain in the south. The natural drop is 5,100 m, accounting for nearly 95% of the total drop of the Yangtze River. This gives the Jinsha River extremely rich hydropower resources and excellent development conditions. The hydropower reserves are estimated to be 112.4 million kWh, making up 16.7% of the country’s hydropower resources and occupying a leading position (Yang et al., 2024).
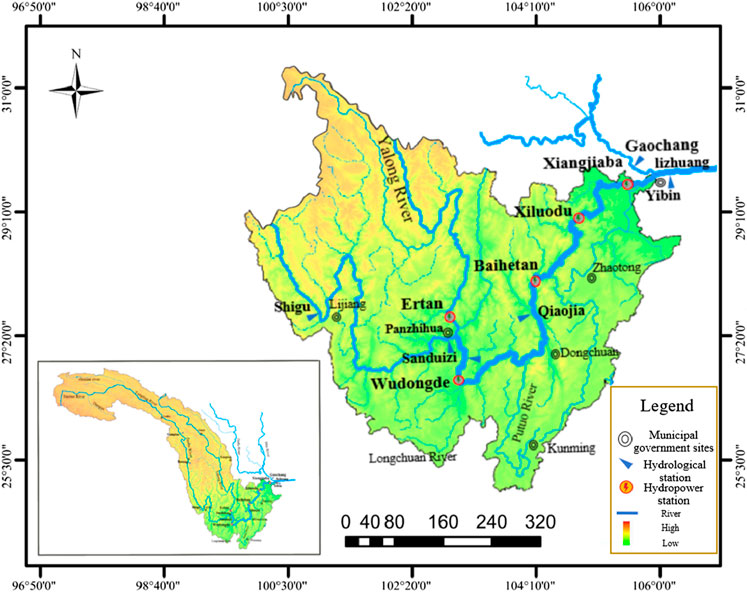
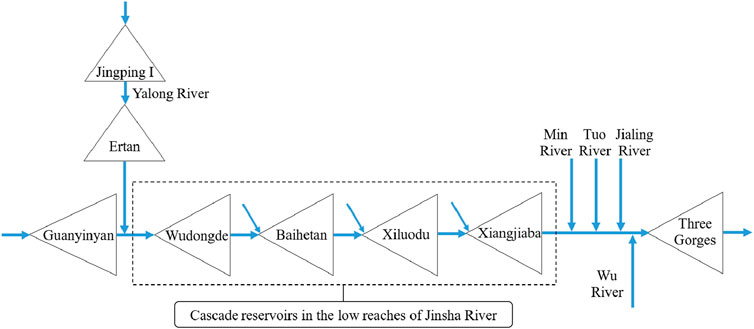
The study area is the lower Jinsha River Basin, shown in Figure 2. It is known for its abundant hydraulic resources and numerous large-scale integrated hydraulic hubs. These hubs play a key role in joint dispatching, flood control, and power generation. The large hydropower hubs of Wudongde, Baihetan, Xiluodu, and Xiangjiaba form cascade reservoirs. These reservoirs are designed for flood control as well as power generation and other benefits, highlighting their crucial controlling role in this region. The topological diagram of cascade reservoirs in the lower reaches of the Jinsha River is shown in Figure 3.
The lower Jinsha River cascade reservoirs have outstanding storage and discharge capacities, and large flood control reservoirs. In the event of a minor or moderate flood within a 20-year return period, the safety of the reservoirs and downstream protection objects will not be affected. Part of the reservoir capacity can be used to store floodwater, reducing the flood peak flow while increasing the overall power generation capacity of the cascades. One of the flood control tasks of the lower Jinsha River cascade reservoirs is to protect Yibin and other cities along the Chuan River from floods. To improve the flood control standard of these towns, about 4.42 billion m³ of flood control storage capacity is reserved. Wudongde, Baihetan, and Xiluodu reservoirs can raise their levels by 24.4 m (not exceeding the normal storage water level), 22.8 m, and 35.0 m respectively, utilizing these capacities. With installed capacities of up to 10.2 million kW, 12.0 million kW, and 14.0 million kW respectively, the cascade reservoirs can store floodwater to reduce flood peak flow during minor and moderate floods. They can also adjust water levels to optimize the head for different power generation benefits depending on storage sequences.
3 Model
3.1 Multi-objective optimal scheduling model for cascade reservoirs
3.1.1 Objective functions
The multi-objective optimal scheduling model for cascade reservoirs is constructed in this paper by taking the maximum peak shaving rate, the minimum utilization rate of total flood control capacity, and the maximum total power generation of the cascades as the scheduling objectives (Li et al., 2024).
Objective function 1: Maximum peak shaving rate.
For optimal scheduling of reservoirs aiming at flood control, the superiority or inferiority of the flood control effect must be taken as one of the discriminating benchmarks. Therefore, the maximum discharge flow of the cascades is minimized as the objective of the flood control dimension (Nihei et al., 2024). The objective function 1 is expressed as Equation 1.
where,
Objective function 2: Minimum utilization rate of total flood control capacity.
One of the main flood control tasks of the cascades is to cooperate with the Three Gorges joint dispatch to reduce the flood control pressure in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River in the event of minor and moderate floods in the Jinsha River. In order to take into account the safety of flood control downstream of Yibin and reserve as much flood control capacity as possible with the Three Gorges flood control, the minimum total flood control capacity utilized by the staircase reservoirs is taken as one of the objectives. The objective function 2 is expressed as Equation 2.
where,
Objective function 3: Maximum total power generation of the cascades.
The four cascade hydropower stations in the lower reaches of the Jinsha River are the main energy bases for sending electricity from west to east in China, and their engineering development tasks are mainly based on power generation. Therefore, the maximum total power generation of the cascades is taken as one of the objectives (Xu et al., 2018). The objective Function 3 is expressed as Equation 3.
where,
3.1.2 Constraints
The constraints of the multi-objective optimal scheduling model are as follows:
Constraint 1: Water balance constraints, as Equation 4.
where,
Constraint 2: Drain Variation Constraints, as Equation 5.
where,
Constraint 3: Safety Drain Constraints, as Equation 6.
where,
Constraint 4: Drainage capacity constraints, as Equation 7.
where,
Constraint 5: Generation flow constraints, as Equation 8.
where,
Constraint 6: Power output constraints, as Equation 9.
where,
Constraint 7: Total Flood control capacity constraints, as Equation 10.
where,
3.1.3 Model solutions
Intelligent algorithms have been widely used to solve multi-objective optimization problems (Zhou et al., 2014; Windsor, 1975; Wei and Hsu, 2008; Wang et al., 2015). The Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) algorithm is one of the most widely used algorithms. It offers advantages such as fast solving speed, low computational complexity, simple operation, and minimal parameter adjustment (Huang, 2015; Kim et al., 2021). PSO can effectively solve high-dimensional and nonlinear problems, providing a set of non-inferior solutions that meet different objectives. The Multi-Objective Particle Swarm Optimization (MOPSO) algorithm is developed rapidly, in which the Pareto dominance is incorporated into PSO to handle problems with several objectives function (Coello, et al., 2004). Now it has been a typical optimization approach for multi-objective problems. MOPSO can provides a set of feasible solutions for the decision-makers or researchers, who will choose the most satisfied one from the solutions according to actual requirements. Compared to PSO, MOPSO perform better in handling the competitive and collaborative relationships among multiple objectives. Especially, it is more suitable for MOPSO to solve the problem of continuous target space.
So we select MOPSO as the optimization algorithm to solve the Multi-objective optimal scheduling for cascade reservoirs in this paper. The discharge flows over 120 flood process periods of the three reservoirs (Wudongde, Baihetan, and Xiluodu) are encoded as decision variables, resulting in 360 decision variables. The time interval period is 6 h. The particle dimension is set to 360, the population size is 300, the maximum number of iterations is 1,000, the maximum allowed speed for particles is 0.1, the number of external file sets is 100, the inertia factor is 0.6, the individual learning factor is 2.0, and the group learning factor is 2.0.
3.1.4 Model inputs and parameters
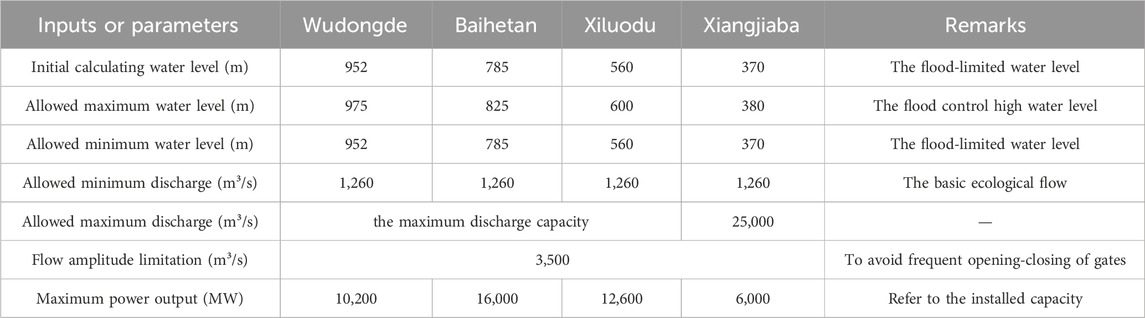
The model inputs include: the reservoirs inflow processes of the frequency P = 5%, P = 10% and P = 20% flood, reservoir level-volume curves, reservoir level-discharge flow curves, discharge capacity curve of hydroelectric power plant and so on. The other inputs and parameters are shown in Table 1.
3.2 Multi-objective decision-making model of flood control scheduling scheme
3.2.1 Evaluation indicator system
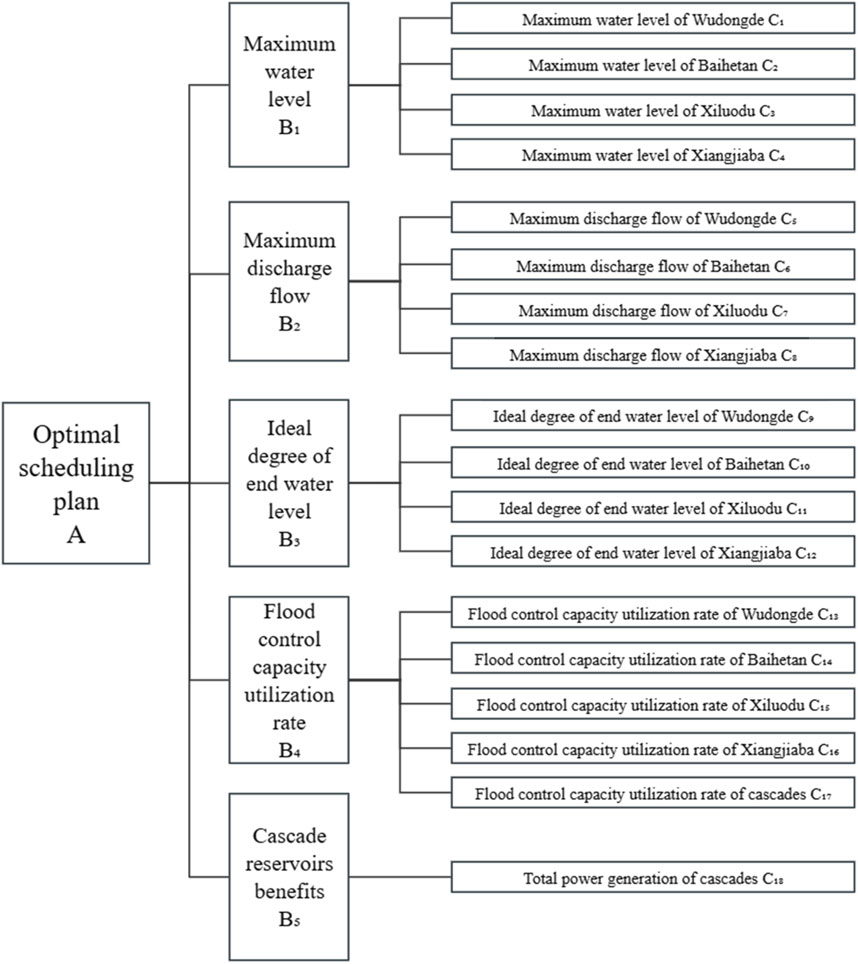
The index system for optimization of reservoir scheduling program is divided into three layers, namely, target layer, criterion layer and index layer in this paper, following the framework of “target-criterion-indicator” hierarchical relationship. The target layer is the relatively preferred option A pursued by multi-objective decision-making, and the criterion layer is the various dimensions of evaluation A (Santonab et al., 2023). Taking into full consideration of the representativeness, operability and comprehensiveness required for the selection of evaluation indexes, the specific contents of the criterion layer are as follows:
(1) Maximum water level during reservoir scheduling B1.
The maximum water level during reservoir dispatching refers to the maximum water level in front of the dam reached by each reservoir of the cascades in the course of a flood, which is related to the flood control safety of the reservoir itself. It is a smaller and better indicator (Santonab et al., 2023).
(2) Maximum discharge flow during reservoir scheduling B2.
The maximum discharge flow of the reservoir is an important indicator for evaluating the safety of the reservoir, which reflects the flood storage capacity of the scheduling program in the process of flood control, and it is directly related to the safety of the downstream protection area. The smaller the maximum discharge flow from the reservoir, the greater the reservoir’s role in storing the field flood, and the safer the downstream protection objects. Therefore, it is a smaller and better indicator (Zhang et al., 2024).
(3) Ideal degree of flood regulation-ended water level B3.
The ideal degree of flood regulation-ended water level refers to the closeness of the final water level of the reservoir to the ideal water level at the end of a flood scheduling by adopting this scheme. The closer the final water level of the reservoir is to the ideal level, the higher the safety coefficient will be when facing the next flood. Therefore, this indicator is the larger the better type of indicator. The ideal water level is set as the flood-limited level of each reservoir in this paper (Ho et al., 2024).
(4) Reservoir flood control capacity utilization rate B4.
The utilization rate of flood control capacity of single reservoir is the capacity corresponding to the maximum water level reached by each cascade reservoir in the process of flood control, minus the capacity corresponding to the flood control limit level of each reservoir, and then divided by the total flood control capacity of each reservoir. The overall flood control capacity utilization rate of the cascades refers to the maximum value of the sum of the flood control capacity used at each moment during the operation of the reservoir group divided by the total flood control capacity of 15.493 billion m3. This indicator is a smaller and better indicator. The smaller the indicator is, the more flood control capacity is reserved in the cascade reservoirs.
(5) Cascade reservoirs benefits B5.
The criterion for the cascade reservoirs benefits reflects the total power generation revenue of the backbone cascade reservoirs in the lower Jinsha River basin, which reflects the benefit of the scheduling process. Therefore, this indicator belongs to the larger is better type of indicator, and the total power generation of the lower Jinsha River cascades in the scheduling process is chosen as the quantitative standard. The main objective of the lower Jinsha River cascade reservoirs is still power generation, and how to ensure the power generation benefit under the premise of utilizing the minimum flood control capacity when facing minor and moderate floods is also one of the focuses of this paper (Zhou et al., 2024).
In addition, the specific index layer is the specific index value of each reservoir under the guideline layer, which is shown in Figure 4 Evaluation indicators system for multi-objective scheduling schemes 4.
3.2.2 Optimal evaluation model
The structure of the MDIP-VIKOR model and the multi-objective decision-making method adopted in this paper are shown in Figure 5 MDIP-VIKOR Model Structure5, and the specific calculation process is as follows:
(1) Indicator weight setting.
Let the subjective weight vector of evaluation indicators be Wsub = {wsub(j)|1 ≤ j ≤ n}, the objective weight vector is Wobs = {wobs(j)|1 ≤ j ≤ n}. The combined weight vector is W = {w(j)|1 ≤ j ≤ n}, where n is the number of total evaluation indicators. The G1 method and entropy weight method are used to set the subjective and objective weights of specific indicators (Osokin, 2017).
(2) Evaluation matrix construction and normalization process.
Let the m to-be-selected programs corresponding to n indicators x1, x2, x3, ..., xm form the set of non-inferior solution programs X. Correspondingly, let the evaluation indicators y1, y2, y3, ..., yn form the set of evaluation indicators Y. The overall evaluation matrix is constructed as A. It is expressed as Equation 11.
The matrix A is standardized according to the economic attributes of each indicator (the larger the better or the smaller the better) using the following formula to obtain the decision matrix D. The indicator dij is expressed as Equations 12 and 13, and the matrix D is expressed as Equation 14.
(i) Benefit-based indicators.
(ii) Cost-based indicators.
(iii) Decision matrix.
(3) Optimization model construction
Next, the principle of Minimum Discriminative Information is used to combine the two assignments. The core idea of MDIP is to find a new weight distribution that minimizes the “distance” (using the Kullback-Leibler dispersion metric) from the subjective and objective assignments. The optimization model is expressed as Equations 15, 16.
The model determines the combination weights of the factors with the constraint of minimizing the information difference, using the Lagrange multiplier method, as shown in the following Equation 17.
(4) Determination of positive and negative ideal values.
According to the specific situation of reservoir operation, the positive ideal value (PIS) and negative ideal value (NIS) of each index in the decision matrix D are determined. The positive ideal value is the maximum value of the larger and better indicator in a certain indicator system, and the negative ideal value is the minimum value of the smaller and better indicator in a certain indicator system. The specific formula is expressed as Equation 18.
(5) Calculate evaluation parameters.
Then, the evaluation parameters in the model are calculated, including individual regret value R (R-value) group utility value S (S-value), and program benefit coefficient Q (Q-value). The R-value is a psychological regret level from the decision-maker, who has not selected the optimal solution in the process of the multi-index decision. Based on Regret Theory, it can be calculated from the comparison between the currently selected solution and other alternative options. The S-value is a utility value that integrates personal preferences and inclinations from the entire decision-maker group. It can be determined by calculating the expected comprehensive utility value of every solution. The Q-value is an important parameter to reflect the comprehensive benefits of the proposed solution in the multi-index evaluation model, which can measure the closeness of each solution to the ideal one. The higher its value, the closer the solution is to the ideal solution. The Q-value integrates the R-value and S-value, and enables MDIP-VIKOR model to maximize the group utility and minimize the individual regret. The specific formulas are expressed as Equations 19–23.
where,
(6) Judgment of Decision Options.
Based on the R-value, S-value and Q-value of each program, the programs are sorted into three different sorting results, and the top program in each sorting result is better than the corresponding bottom program. The decision solutions are determined according to the following two criteria, which is also the relatively optimal.
(i) Criteria for acceptable advantages.
This criterion is used to determine the range of acceptable advantages for decision-making. It is based on the following formula, as Equation 24.
where, the total number of options is denoted by m. The suboptimal and optimal options obtained by ordering according to the Q-value are represented by
(ii) Decision Stability Criteria.
When ranking based on the R-value or S-value, the top-ranked solution is selected to ensure the stability of the decision.
In general, when the decision criterion (i) is not satisfied and each
4 Results and analysis
4.1 Optimal results and analysis
The above model is applied to optimize the scheduling of minor and moderate floods by taking P = 5%, P = 10%, and P = 20% flood frequency amplification as input conditions in a typical year of 1966. We obtained 100 non-inferior solutions using the MOPSO algorithm for different frequency floods.
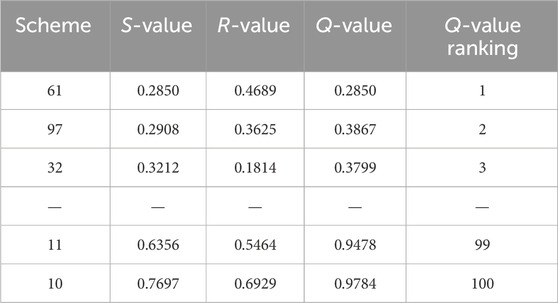
Figure 6 Pareto frontier of multi-objective optimization scheduling results shows the Pareto solution for multi-objective optimization scheduling of cascade reservoirs in the lower reaches of the Jinsha River. It includes typical floods of 20-year, 10-year, and 5-year in 1966. The x, y, and z-axes represent the utilization of total flood control capacity, the maximum peak shaving flow, and the total power generation of the cascades. The Pareto frontier is roughly located on a surface, indicating a significant competitive relationship among the three scheduling objectives. An increase in any one objective affects the performance of the other two, reflecting a degree of mutual constraint.
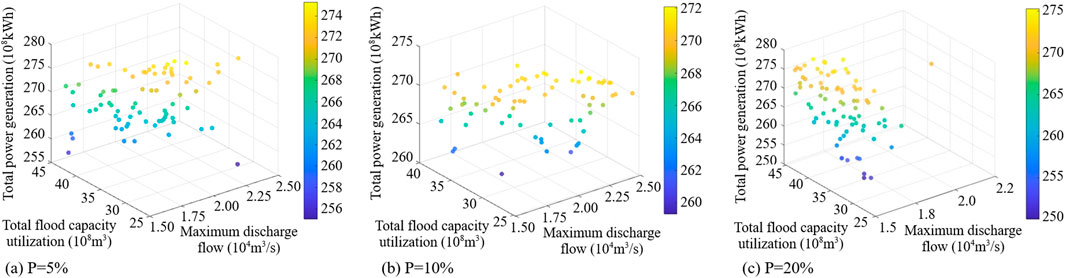
Figure 6. Pareto frontier of multi-objective optimization scheduling results. (A) P = 5% (B) P = 10% (C) P = 20%.
To further analyze the interrelationships between the various objectives, Figure 7 Relationship between various scheduling objectivesshows the two-dimensional projection of the set of non-inferior solutions in Figure 6 onto various planes, using the example of the 20-year flood. Figure 7 shows a negative correlation between the maximum peak shaving rate and the maximum utilization of total flood control capacity. Under the same other conditions, the smaller the maximum discharge flow pursued, the more flood control storage capacity is occupied. This aligns with general reservoir scheduling knowledge, effectively reducing flood peaks and ensuring downstream safety by utilizing flood control capacity to store more floodwater.
Figure 7. Relationship between various scheduling objectives. (A) Power generation and discharge flow (B) flood control capacity and discharge flow (C) power generation and flood control capacity.
Figure 7 Relationship between various scheduling objectives) shows the relationship between discharge flow and total power generation. Although not obvious, they are positively correlated to a certain extent. Analyzing the complex relationship between the cascade reservoirs reveals that increasing the overall discharge flow of the cascade reservoirs will increase the power generation flow of the unit in the actual reservoir scheduling process. However, downstream reservoirs will raise their tailwater level by discharging more flow, which reduces the tailwater level of upstream reservoirs and affects the overall power generation benefit of the cascade to some extent due to the close water conservancy connection of the cascade reservoirs. This analysis proves that cascade reservoirs can achieve better benefits by using more flood control capacity and raising the level and power generation head during reservoir operation in the event of minor and moderate floods. It also improves downstream safety by cutting down more flood volume. Figure 7C shows a significant positive correlation between the use of flood control storage and the total power generation of the cascades. This proves that it is possible to utilize part of the flood control storage in minor and moderate floods to increase the total power generation of the cascades.
4.2 Evaluation results and analysis
Based on the calculation method in the previous section and the scores of each criterion layer in the evaluation index system, the results of evaluating the optimized multi-objective flood control scheduling scheme for cascade reservoirs for minor and moderate floods at each frequency are shown in Table, Table and Table. The 100 non-inferior solutions generated by the optimal scheduling are ranked by the Q-value in this section to make the evaluation parameters more intuitive.
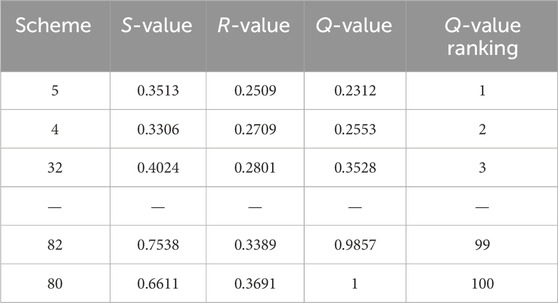
(1) Results of multi-objective evaluation for the frequency P = 5% flood.
According to the decision-making method in the previous section, the results and parameters of the scheme selection from the non-inferior solution set generated by the optimized dispatching of the 20-year flood are shown in Table 2 ranked by Q-value.
Based on the MDIP-VIKOR evaluation model and the Q-value ranking, scheme 5 is ranked first and scheme 4 is ranked second. Scheme 5 is ranked second in S-value and first in R-value, both of which are top-ranked, meeting the criterion of decision-making stability (criterion ii). Additionally, according to decision criterion (i), with 100 decision schemes, Q5-Q4 = 0.0214 > 1/(100-1), which meets the acceptable advantage criterion. Therefore, for a flood with a 20-year return period, scheme 1 is the relatively optimal scheme. In this scheme, the maximum discharge flow of the cascades is 20,900 m³/s, the maximum occupied total flood control capacity is 3.849 billion m³, the capacity utilization rate is 24.84%, and the total power generation of the cascades during the scheduling process is 27.36 billion kWh. Based on the above evaluation and selection results, the relatively optimal dispatching process of the cascade reservoirs in the event of a 20-year return period flood is shown in Figure 8 20-year flood optimal scheduling process.

Figure 8. 20-year flood optimal scheduling process. (A) Wudongde (B) Baihetan (C) Xiluodu (D) Xiangjiaba.
When the inflow of Wudongde Reservoir is small at the beginning of the scheduling, the outgoing flow equals the incoming discharge. After the inflow reaches 17,000 m³/s, the reservoir starts to store floodwater, raising its water level to 970.10 m while reducing the peak flow and maintaining a high level to increase power generation. During this period, the maximum flood control storage capacity of 1.84 billion m³ is used, and the level is slowly lowered to 953.20 m during the withdrawal stage after the flood peak, maintaining the flood-limited water level. Baihetan Reservoir plays an auxiliary role in supporting the downstream reservoirs by appropriately reducing the flood flow. During the operation period, the maximum water level reaches 787.70 m, the maximum used flood control capacity is 430 million m³, and the reserved flood control capacity reaches 7.07 billion m³. Xiluodu Reservoir stores water up to 577.70 m in the upwelling section and maintains a discharge of 19,500 m³/s to bring the level back to the flood-limited water level after maintaining operation for a certain period.
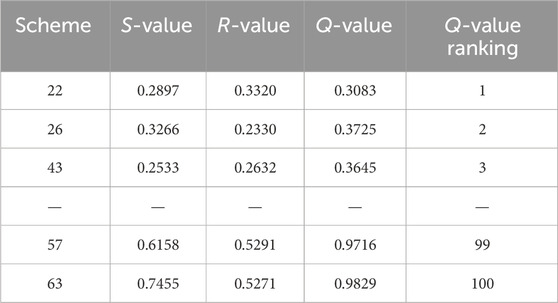
(2) Results of multi-objective evaluation for the frequency P = 10% flood.
The results and parameters of the scheme selection from the non-inferior solution set generated by the optimized dispatching of the 10-year flood are shown in Table 3, ranked by Q-value.
According to the calculation results of the aforementioned evaluation model, scheme 22 and scheme 26 are ranked first and second, respectively, based on Q-value. Scheme 22 is ranked third in S-value evaluation and fifth in R-value evaluation, both of which are top-ranked, indicating it conforms to the principle of stability in decision-making and meets the judgment criterion (ii). The Q-value difference between scheme 22 and scheme 26 is 0.0642 out of 100 decision scenarios, exceeding the criterion of 1/(100-1) for acceptable advantage according to criterion (i). Therefore, scheme 22 is recognized as the relatively optimal choice for the incoming flood of P = 10%. In this scheme, the maximum discharged flow of the cascade reservoirs reaches 17,800 m³/s, and the maximum utilization of the total flood control capacity is 4.070 billion m³, with a utilization rate of 20.94%. The total power generation of the cascade reservoirs during the flood control scheduling process is 27.076 billion kWh. The relatively optimal scheduling process for the cascade reservoirs during the 10-year flood is shown in Figure 9 10-year flood optimal scheduling process9.
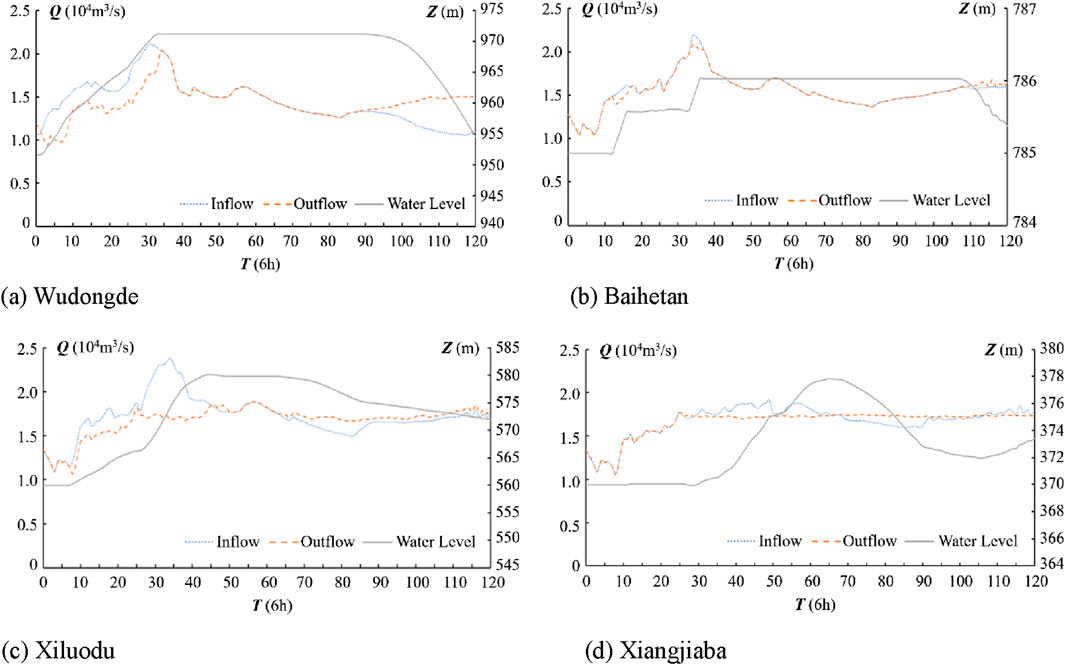
Figure 9. 10-year flood optimal scheduling process. (A) Wudongde (B) Baihetan (C) Xiluodu (D) Xiangjiaba.
To fully utilize flood resources and increase the water head for more power generation, reservoirs begin to store floodwater at the early stage of water rise. Wudongde Reservoir can raise its water level by 16.30 m, generating 5.96 billion kWh during the entire scheduling period, which is 1.00 billion kWh more than without raising the level. Similarly, Xiluodu Reservoir can raise its water level by 20.60 m, generating 8.27 billion kWh, which is 0.72 billion kWh more than without raising the level. However, Baihetan Reservoir plays an auxiliary role in peak shaving, with an overall level variation of 1.10 m. Most of its capacity is reserved to handle possible successive floods and to cooperate with the Three Gorges for flood control in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River. Additionally, Xiangjiaba Reservoir is scheduled according to regular rules and helps smooth the overall outflow process of the cascades.
(3) Results of multi-objective evaluation for the frequency P = 20% flood.
The results and parameters of the scheme selection from the non-inferior solution set generated by the optimized dispatching of the 5-year flood are shown in Table 4, ranked by Q-value.
Based on the Q-value ranking, scheme 61 is ranked first and scheme 97 is ranked second after further analysis of the calculation results. However, the S-value of scheme 61 is ranked 17th and the R-value is ranked 53rd, which does not meet the decision stability criterion (judgment criterion ii). Additionally, there are 100 decision scenarios, and Q61-Q97 = 0.1017 > 1/(100-1), which meets the acceptable advantage criterion (decision criterion i). Therefore, both scheme 61 and scheme 97 are compromises rather than optimal solutions for the P = 20% flood. Generally, a compromise solution is a relatively acceptable or satisfied one for decision maker rather than an optimal solution. The preferences for decision-making vary, and the selected compromise solutions also differ. However, it well balances the power generation, flood flow reduction, and efficient use of flood control capacity in the flood management. Considering that scheme 61 has the highest Q-value, this compromise solution is chosen as the relatively optimal one. As shown in Figure 10 5-year flood optimal scheduling process10, when the cascade reservoirs encounter a 5-year flood, Wudongde Reservoir and Xiluodu Reservoir are mainly used to store the floodwater, while Baihetan Reservoir is used to reduce the flood flow.
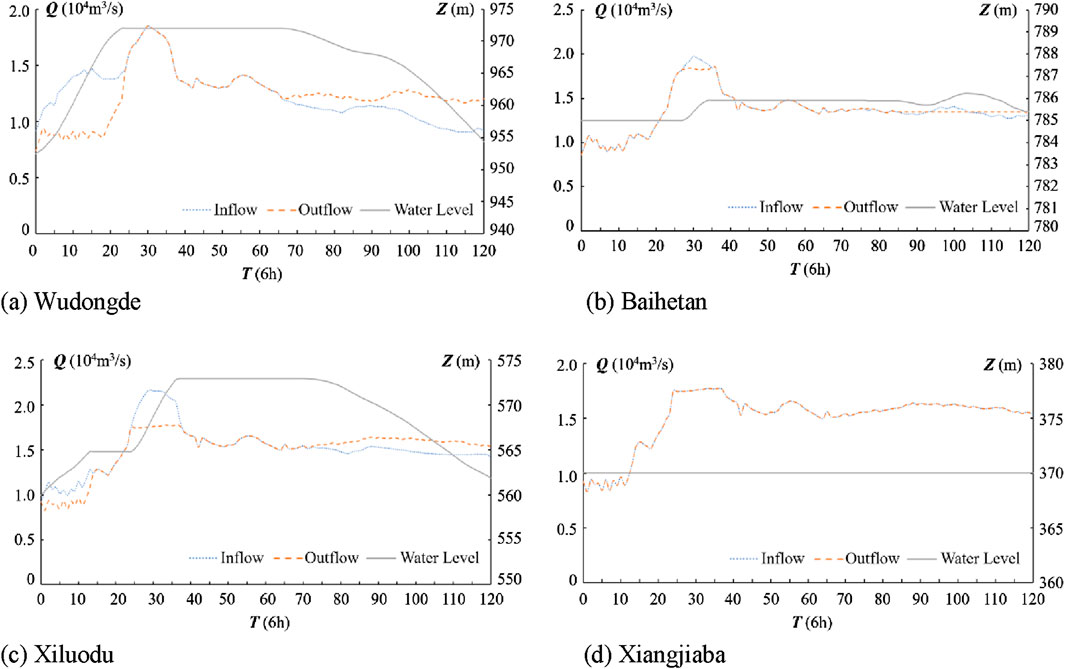
Figure 10. 5-year flood optimal scheduling process. (A) Wudongde (B) Baihetan (C) Xiluodu (D) Xiangjiaba.
When the 5-year flood arrives, Wudongde Reservoir first stores water, raising its level from the flood-limited water level of 952.00 m–972.00 m. After storing part of the floodwater, it maintains a higher water level to increase power generation capacity while providing the maximum power generation flow. Using the water level-capacity curves of each reservoir, it is evident that Baihetan raises its water level less than other reservoirs with the same amount of water storage, despite having a larger capacity. Therefore, in the preferred scheme, Baihetan mainly reduces peak flows. Its maximum flood protection capacity utilization rate is only 2%, making it the primary reservoir for reserved flood protection capacity. By storing a certain amount of water early in the flood, Xiluodu Reservoir raises and maintains a higher water level of 565.00 m to increase power generation. When the flood peak arrives, it stores water to reduce the peak. Xiluodu plays the main storage role in the downstream reservoirs of the cascades, maintaining a water level of 573.00 m until the flood recedes to ensure total benefits. According to conventional rules, Xiangjiaba Reservoir is scheduled with outflow equal to inflow. All of its flood control capacity is used as a backup reserve to handle possible successive floods and coordinate with the Three Gorges scheduling.
5 Conclusion
This paper addresses the scheduling problem of the lower Jinsha River cascade reservoirs when facing the minor and moderate floods of a 20-year return period or less. The aim is to ensure the overall benefits of cascade flood control scheduling while balancing three demands: protecting downstream areas, improving power generation benefits and reserving enough flood control capacity for the Three Gorges and the middle and lower reaches of Yangtze River.
Based on the above three demands, the optimal scheduling model for the Lower Jinsha River cascade reservoirs focuses on three goals: maximizing power generation, minimizing peak outflow, and reducing flood control capacity. Using the Multi-objective Particle Swarm Optimization algorithm, we generated solutions for these objectives under different water supply frequencies and analyzed the relationships between them. The results showed that the level of competition among the objectives varies with different water inflow frequencies. There is strong competition between power generation and reserved capacity, as well as between peak reduction and reserved capacity. In contrast, the correlation between power generation and peak reduction is relatively weak. This indicates that better overall benefits can be achieved by allocating more reservoir capacity for minor and moderate floods.
Additionally, a multi-objective evaluation system with 18 specific indicators was developed. This system considers factors such as flood control, power generation benefits, reservoir safety, and reserve capacity to assist the Three Gorges flood control, based on a hierarchical “objective-criterion-indicator” framework. The evaluation criteria included the maximum water level, maximum discharge flow, ideal end water level, flood control capacity utilization, and cascade benefits. Furthermore, the MDIP-VIKOR evaluation model was used to identify the optimal scheduling schemes for three water inflow conditions (P = 5%, P = 10%, and P = 20%). It was found that the power generation of each scheme increased by 1.64, 1.71, and 1.35 billion kWh, respectively, significantly enhancing the comprehensive benefits of the Lower Jinsha River reservoirs during minor and moderate floods, although the scheduling process of flood only maintains 30 days. In conclusion, this study proposed optimal scheduling strategies for minor and moderate floods, offering valuable guidance for decision-makers in practical applications.
However, in order to translate our research findings into actionable recommendations for decision-makers in flood management, we would like to do more research in the future. Firstly, we should identify or forecast the flood size whether is a minor or moderate flood within a 20-year return period. Secondly, a flood management software would be developed to generate the optimal scheduling scheme in real-time. Lastly, we can take the flood forecasting and the corresponding software to implement the proposed scheduling strategies. Certainly, the reservoir scheduling is a complex multi-objective problem, and there is a curse of dimensionality usually. To further improve multi-objective reservoir scheduling, dimensionality deduction and optimization algorithm for solving efficiency are very essential.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
ZR: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Writing–original draft. BH: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Writing–review and editing. CY: Formal Analysis, Investigation, Software, Validation, Writing–review and editing. XL: Resources, Visualization, Writing–review and editing. XW: Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. The authors acknowledge financial support from Huadong Engineering Corporation Limited of PowerChina funded project (HDY-CG73-20230018).
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our gratitude to all colleagues and institutions involved in this research. Firstly, we appreciate the support and resources provided by Huadong Engineering Corporation Limited, which laid a solid foundation for our study. Additionally, we extend our thanks to BH and his team from Dalian University of Technology for their valuable guidance and advice, which greatly assisted us in addressing various challenges. Furthermore, we acknowledge all colleagues who participated in discussions and provided feedback, as well as our families and friends for their unwavering support throughout this endeavor. Without your support and encouragement, we would not have been able to successfully complete this research. Once again, we extend our sincerest gratitude to everyone involved.
Conflict of interest
Authors ZR, CY, and XL were employed by Huadong Engineering Corporation Limited.
The remaining authors declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The authors declare that this study received funding from Huadong Engineering Corporation Limited of Power China. The funder had the following involvement in the study design, data collection and decision to publish.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Brunner, M. I., and Sikorska Senoner, A. E. (2019). Dependence of flood peaks and volumes in modeled discharge time series: effect of different uncertainty sources. J. Hydrol. 572, 620–629. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.03.024
Chen, S. M. (1988). A new approach to handling fuzzy decision-making problems. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man. Cybern. 18 (6), 1012–1016. doi:10.1109/21.23100
Coello, C. A. C., Pulido, G. T., and Lechuga, M. S. (2004). Handling multiple objectives with particle swarm optimization. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 8 (3), 256–279. doi:10.1109/tevc.2004.826067
Hashemi, S. M. S., Robati, A., and Kazerooni, A. M. (2024). Applying the new multi-objective algorithms for the operation of a multi-reservoir system in hydropower plants. Sci. Rep. 14 (1), 3607. doi:10.1038/s41598-024-54326-z
Ho, H. V., Chau, Q. X. N., Ngo, G. H. N., and Dung Tran, D. (2024). An initial assessment of mobile dam efficiency in raising low-flow water levels in the Vietnamese Mekong Delta. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 1345 (1), 012023. doi:10.1088/1755-1315/1345/1/012023
Huang, C., Wang, Z., Li, S., and Chen, S. (2014). A multi-reservoir operation optimization model and application in the upper Yangtze River Basin I. Principle and solution of the model. J. Hydraulic Eng. 45 (9), 1009–1018. doi:10.13243/j.cnki.slxb.2014.09.001
Huang, X. (2015). The optimal operation of multi-reservoir floodwater resources control based on GA-PSO: 2015 agu fall meeting. San Francisco, United States: Agu.
Kim, Y., Sun, B., Kim, P., Jo, M. B., and Pak, G. H. (2021). A study on optimal operation of gate-controlled reservoir system for flood control based on PSO algorithm combined with rearrangement method of partial solution groups. J. Hydrol. 593, 125783. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125783
Li, R., and Xu, G. (2023). Assessing the impacts of reservoirs on downstream hydrological frequency based on a general rainfall-reservoir index. Front. Earth Sci. 11. doi:10.3389/feart.2023.1204640
Li, Y., Chen, J., Wang, Y., Li, S., Duan, X., Jiang, Z., et al. (2024). Multi-objective modeling and evaluation for energy saving and high efficiency production oriented multidirectional turning considering energy, efficiency, economy and quality. Energy 294, 294130780. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2024.130780
Loucks, D. P., Stedinger, J. R., and Haith, D. A. (1981). Water res plan man. Eaglewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall.
Malekmohammadi, B., Zahraie, B., and Kerachian, R. (2011). Ranking solutions of multi-objective reservoir operation optimization models using multi-criteria decision analysis. Expert Syst. Appl. 38 (6), 7851–7863. doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2010.12.119
Nihei, Y., Ogata, Y., Yoshimura, R., Ito, T., and Kashiwada, J. (2024). Subgrid model of water storage in paddy fields for a grid-based distributed rainfall–runoff model and assessment of paddy field dam effects on flood control. Water 16 (2), 255. doi:10.3390/w16020255
Ning, Y., Ren, M., Guo, S., Liang, G., He, B., Liu, X., et al. (2024). An advanced multi-objective Ant lion algorithm for reservoir flood control optimal operation. Water 16 (6), 852. doi:10.3390/w16060852
Opricovic, S., and Tzeng, G. H. (2007). Extended VIKOR method in comparison with outranking methods. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 178 (2), 514–529. doi:10.1016/j.ejor.2006.01.020
Osokin, N. A. (2017). Approaches to setting weights in composite indicators of sports development: the case of the Football Development Index. Stat. Econ. (4), 54–64. doi:10.21686/2500-3925-2017-4-54-64
Ouyang, S., Zhou, J., Zhang, R., Wang, X., and Wang, H. (2013). Study on optimal scheduling of multi-objective joint flood control for lower Jinsha River cascade reservoirs and Three Gorges reservoir. J. Hydroelectr. Eng. 32 (6), 43–49+56.
Santonab, C., Nirjhar, H. D., Kanak, K., and Chakraborty, S. (2023). A narrative review of multi-objective optimization on the basis of ratio analysis (MOORA) method in decision making. OPSEARCH 60 (4), 1844–1887. doi:10.1007/s12597-023-00676-7
Wan, X., Xue, Y., Hua, L., and Wu, Q. (2023). Multi-objective collaborative decision-making for flood resource utilization in a reservoir. Stoch. Env. Res. Risk 37 (12), 4629–4640. doi:10.1007/s00477-023-02530-0
Wang, J., Huang, W., Ma, G., and Chen, S. (2015). An improved partheno genetic algorithm for multi-objective economic dispatch in cascaded hydropower systems. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 67, 591–597. doi:10.1016/j.ijepes.2014.12.037
Wang, X., Wang, F., Huang, T., Zeng, X., Li, X., and Huang, J. (2023). Modeling competitive-cooperative relationship between flood control and hydropower generation within hierarchical gaming structure of reservoir operation. J. Hydrol. 620 (PA), 129429. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2023.129429
Wei, C. C., and Hsu, N. S. (2008). Multireservoir real-time operations for flood control using balanced water level index method. J. Environ. Manag. 88 (4), 1624–1639. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2007.08.004
Windsor, J. S. (1975). A programing model for the design of multireservoir flood control systems. Water Resour. Res. 11 (1), 30–36. doi:10.1029/wr011i001p00030
Xu, B., Yao, H., Zhong, P. A., Chen, J., Fu, J., Guo, L., et al. (2018). Exploration and attribution of synergistic gains from joint optimal operation of downstream Jinsha River cascade and Three Gorges cascade reservoirs for hydropower generation. Energy Wkly. News 20, 1042–1057. doi:10.2166/hydro.2018.116
Yang, S., Wang, W., Li, H., and Zhang, D. (2024). Investigating the spatiotemporal complexity of rainfall from a chaotic perspective: case study in the Jinsha River Basin, China. J. Hydrol. Eng. 29. doi:10.1061/jhyeff.heeng-6038
Zhang, R., Zhang, S., Wen, X., Yue, Z., and Zhou, Y. (2024). Optimization of short-term hydropower scheduling with dynamic reservoir capacity based on improved genetic algorithm and parallel computing. J. Hydrol. 636131238, 131238. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2024.131238
Zhou, S., Wang, Y., Su, H., Chang, J., Huang, Q., and Li, Z. (2024). Dynamic quantitative assessment of multiple uncertainty sources in future hydropower generation prediction of cascade reservoirs with hydrological variations. Energy 299, 299131447. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2024.131447
Keywords: cascade reservoir scheduling, multi-objective evaluation, MOPSO, VIKOR model, lower reaches of the jinsha river
Citation: Ren Z, He B, Yao C, Lv X and Wang X (2024) Research on optimal scheduling of minor and moderate floods for cascade reservoirs in the lower reaches of the jinsha river considering power generation. Front. Energy Res. 12:1462363. doi: 10.3389/fenrg.2024.1462363
Received: 10 July 2024; Accepted: 20 November 2024;
Published: 06 December 2024.
Edited by:
Abbas Roozbahani, Norwegian University of Life Sciences, NorwayReviewed by:
Atiyeh Bozorgi, Macquarie University, AustraliaHamid Kardan Moghaddam, Water Research Institute, Iran
Copyright © 2024 Ren, He, Yao, Lv and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Bin He, aGViaW5AZGx1dC5lZHUuY24=
 Zaimin Ren1
Zaimin Ren1 Bin He
Bin He