
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Energy Res., 26 November 2024
Sec. Process and Energy Systems Engineering
Volume 12 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fenrg.2024.1427582
Under the coordinated operation of the transmission and distribution networks, the issue of downstream grid flow returning to the upstream grid is becoming increasingly prominent. This article proposes a process for joint planning of energy storage site selection and line capacity expansion in distribution networks considering the volatility of new energy. This technology uses CHk-means clustering calculations based on actual large-scale operation data of new energy sources to generate typical operating curves. Then, it finely constructs an objective function considering power transmission in the transmission-distribution network, abandonment of new energy, line limits, and energy storage construction. By introducing indicative constraints to the energy storage construction-related constraints, the optimization model achieves a non-iterative direct solution. The results of the constructed new energy high-penetration distribution network example IEEE Case33 show that the output solution of this model can effectively reduce the energy sent back from the distribution network to the main grid. Compared to optimization models that do not consider the integration of new energy sources, the output solution of this model can reduce the abandonment of new energy by at least 50%. It also avoids the numerical problems that may arise from iterative algorithms and logical transformation, demonstrating engineering application value.
In the context of the dual carbon targets of “peak carbon and carbon neutrality” advocated by the Chinese government (Huang et al., 2022), the installed capacity of new energy in various voltage-level grids has increased rapidly. The integration of distributed new energy units on the low-voltage side and centralized new energy stations on the medium- and high-voltage sides has increased the penetration rate of new energy in the grid, leading to overloading of transmission and distribution lines and the phenomenon of reverse power flow (RPF) between grids of different voltage levels (Cai et al., 2023; Unahalekhaka and Sripakarach, 2020). Furthermore, the uncertainty in time and space characteristics of the integrated new energy has caused operational issues in the grid, such as voltage drop at nodes (Iioka et al., 2019), posing greater challenges to the early-stage grid planning business (Cai et al., 2023). Therefore, it is urgently necessary to focus on the objectives and constraints of new grid planning under the coordination of clean energy and secure and stable grid operation in the distribution network planning business stage (Cai et al., 2023; Liu et al., 2021).
Existing literature on grid planning involving the issue of RPF (De Carne et al., 2018) has mostly focused on considering the coordinated planning of transmission and distribution networks. The heterogeneous decomposition (HGD) algorithm (Li et al., 2016; Zhao et al., 2019) has been applied to consider the coordinated operation of transmission and distribution networks in the planning of transmission networks (Liu et al., 2021) and distribution networks (Cai et al., 2023). These works mainly focus on the global optimization of the topology and connectivity of transmission and distribution networks, with a single planning object being transmission/distribution lines, without considering energy storage planning and its important role in the secure and stable operation of the grid. Although RPF issues arise in the grid operation simulation process, further restrictions and research on the above issues have not been explored.
There are related works on different aspects of the issue of RPF. From the perspective of generating units, energy storage can be synchronously configured for photovoltaic/wind power systems (Dratsas et al., 2021; Stecca et al., 2020; Unahalekhaka and Sripakarach, 2020) to improve the adequacy of the distribution system and indirectly alleviate the problem of RPF. From a control perspective (Guerrero et al., 2020), deep control of the grid can be achieved through electric vehicle charging and discharging (Tounsi Fokui et al., 2022), home energy management (Dinh et al., 2020; Zafar et al., 2020), peer-to-peer energy trading (Paudel et al., 2020; Zheng et al., 2022), and directing demand-side response control to indirectly manage RPF. From the perspective of power equipment, RPF issues lead to control and safety operation problems of protective devices (Holguin et al., 2020; Nair and Rajeev, 2022), transformers (Das et al., 2021), and other devices. There is scarce research on the issue of RPF in distribution network planning.
With the rapid development of new energy sources, the volatility and uncertainty issues faced by power systems have become increasingly prominent. Effectively planning the siting of energy storage systems and the expansion of line capacity has become a critical topic in power system planning. Integrating the reasonable layout of energy storage systems with line capacity expansion has emerged as an important solution to address the volatility of new energy sources (Wang et al., 2022). In the joint planning of energy storage siting and line capacity expansion, energy storage systems can not only mitigate the volatility of new energy generation but also provide reactive power support and peak-shaving services for the distribution network, thereby enhancing the reliability of the power grid (Lin et al., 2023). For instance, energy storage systems can store excess electricity when new energy generation is abundant and release it when generation is insufficient, thereby reducing the impact of new energy volatility on the voltage and frequency stability of the grid. Moreover, a well-planned layout of energy storage systems can optimize power flow, reduce line losses, delay the need for line capacity expansion, and lower the operating costs of the distribution network (Ma et al., 2024).
In addressing the issues associated with the output scenarios of new energy, the above works only set the output curves of the new energy unit systems at each node in a simple manner without conducting a detailed analysis of actual data to characterize the output scenarios of new energy units (Baringo and Conejo, 2013; Li et al., 2020).
Although the reported works show a certain level of effectiveness in RPF and dynamic network planning (DNP), they offer the following inadequacies:
(1) With regard to the issue of RPF, existing literature on distribution network planning primarily focuses on the coordinated operation planning between transmission and distribution networks, which may be involved in the grid operation simulation process, but does not prioritize RPF as one of the important planning objectives. More in-depth work related to RPF often involves unit regulation capacity configuration, control modes, and their impacts on operational safety and stability. In summary, there is currently no proposed distribution network planning method specifically targeting the issue of RPF.
(2) The coordinated power grid planning methods related to the issue of RPF mainly focus on single planning objects, often limited to power lines, without considering the beneficial regulatory and limiting effects that pure energy system planning and configuration could have on RPF. Additionally, these studies often rely on preset scenarios in the construction of new energy output scenarios without distilling typical scenarios from actual data, potentially leading to distorted planning results.
To bridge these research gaps, the main contributions of this paper are as follows:
(1) This paper proposes a heuristic k-means algorithm that combines the Careful Seeding method. The CHk-means algorithm overcomes the drawbacks of traditional heuristic algorithms, such as the random selection of initial points, arbitrary setting of parameter k, and susceptibility to outlier influences, by incorporating the Careful Seeding algorithm. The CHk-means algorithm is applied to large-scale wind power and photovoltaic power output data, addressing the high computational complexity of clustering in large datasets and improving the accuracy and stability of clustering results.
(2) This paper introduces a joint planning model for energy storage siting and line capacity expansion in distribution networks, taking into account the volatility of new energy sources. The model considers issues such as power backflow and insufficient accommodation in scenarios with high penetration of new energy sources and mathematically formulates these issues in the objective function. Additionally, the model adjusts the constraint on line transmission capacity to a penalty term in the objective function, allowing for line transmission power limit violations to identify the lines requiring capacity expansion.
(3) In the energy storage siting work of the joint planning model considering the volatility of new energy sources proposed in this paper, binary variables representing energy storage deployment and node power balance equations for candidate energy storage sites are linked using indicator constraints. This form of indicator constraint avoids complex logical representation and transformation work compared to methods like the Big M, providing accurate computational results while avoiding potential numerical computation issues associated with the Big M method and similar approaches.
(4) The effectiveness of the proposed model is validated on the high-penetration new energy IEEE Case33 typical example. The data demonstrate that the model can adapt well to distribution network cases with high proportions of new energy sources. The energy storage deployment and line expansion schemes output by the model effectively reduce potential power backflow between the main grid and distribution network, promoting the local accommodation of new energy sources.
To construct a joint planning model for energy storage siting and line capacity expansion in typical new energy fluctuation scenarios in distribution networks, it is necessary to aggregate a massive amount of wind and photovoltaic power output data to obtain new energy output data under typical scenarios. In this paper, the CHk-means algorithm is employed to build a wind and photovoltaic power output aggregation model, aggregate the actual data of wind and photovoltaic power outputs on a large scale, reduce the complexity of heuristic algorithms in large datasets, and improve the stability of wind and photovoltaic power outputs in typical scenarios.
The Careful Seeding algorithm randomly selects a point from the dataset as the initial cluster center, analyzes the remaining data, calculates the shortest distance
From the formula, when
The Elbow Method determines the optimal number of clusters by calculating the sum of squared errors (SSE) for different numbers of clusters. Once a potential number
Local Outlier Factor (LOF) is a density-based anomaly detection method used to identify data points with lower density as outliers in a dataset (Jia et al., 2023; Si et al., 2024). The calculation of the local outlier factor is defined by the following Equation 2:
The CHk-means algorithm first uses the Elbow Method to calculate the value of
After iterative calculations, the algorithm checks for convergence. If it has not converged, the previous steps are repeated to continue calculating new cluster centers and re-clustering until convergence is achieved. Once the algorithm converges, it outputs the clustering results, completing the clustering process. For specific steps, refer to the diagram in Figure 1.
To establish a joint planning model of energy storage site selection and line capacity expansion in distribution networks considering the volatility of new energy, the construction of the objective function should fully consider the local absorption of new energy sources and strive to avoid the phenomenon of power backflow in distribution networks. The specific form of the objective function is as Equation 3:
1) The term associated with power transmission to the upper-level grid is
2) The terms associated with the curtailment of wind turbines and photovoltaics are
Equations 5, 6 indicate the curtailed energy of the wind turbines and photovoltaic systems, respectively.
3) The term associated with line transmission power is
The term related to line transmission power correlation indicates the direction of line expansion planning.
4) The term associated with energy storage construction is
The constraint construction for the model is as follows.
1) Constraint on the output of new energy sources as Equations 9–12 (Chen et al., 2023).
2) Constraint on energy storage charging and discharging as Equations 13–18 (Liu and Bao, 2023; Yao et al., 2022).
3) Nodal power balance constraint as Equations 19–21.
For the energy storage siting-related issue, the formulation of node power balance constraint is constructed as follows:
Equations 22, 23 indicate that when the binary variable
The distribution network power flow constraint, relaxed in the form of a second-order cone, is described as Equations 24–28:
The model proposed in this paper can be directly solved by advanced commercial solvers, and the solving process is shown in Figure 2. It is worth noting that the model outputs the selection of overloaded lines as the line capacity expansion plan. Whether the overloaded lines are to be supported through capacity expansion or the construction of new lines to ensure the safe and stable operation of the distribution network needs to be further analyzed based on the actual situation of distribution network construction in the planning business. The output results of the model serve as an auxiliary decision-making tool for distribution network planning.
The results of the CHk-means, heuristic k-means, and k-means algorithms on the error sum of squares (SSE), silhouette coefficient (SC), and algorithm runtime were compared against the publicly available datasets with 788 points and the xclara dataset on Kaggle. The results of the comparison are presented in Table 1 below.
The CHk-means error sum of squares (SSE) value decreased by 15.35% compared to k-means and decreased by 16% compared to Hk-means. SSE is used to measure the similarity of elements within each cluster in the clustering result. A smaller SSE indicates a better clustering effect.
The silhouette coefficient (SC) of CHk-means increased by 18.75% compared to k-means and decreased by 17.42% compared to Hk-means. SC is used to measure the compactness and separation of the clustering result, with the coefficient’s values ranging between −1 and 1. A larger value indicates a better clustering result.
The parameter results of using CHk-means for aggregating the model wind turbine output are shown in Table 2.
A new energy high-penetration distribution network example, IEEE Case33, was constructed to validate the effectiveness of the proposed model and its solving process, combined with the wind turbine output and photovoltaic output aggregation models constructed above. The case is shown in Figure 3. The configuration information of the network is presented in Table 3, where both power and capacity are design values.
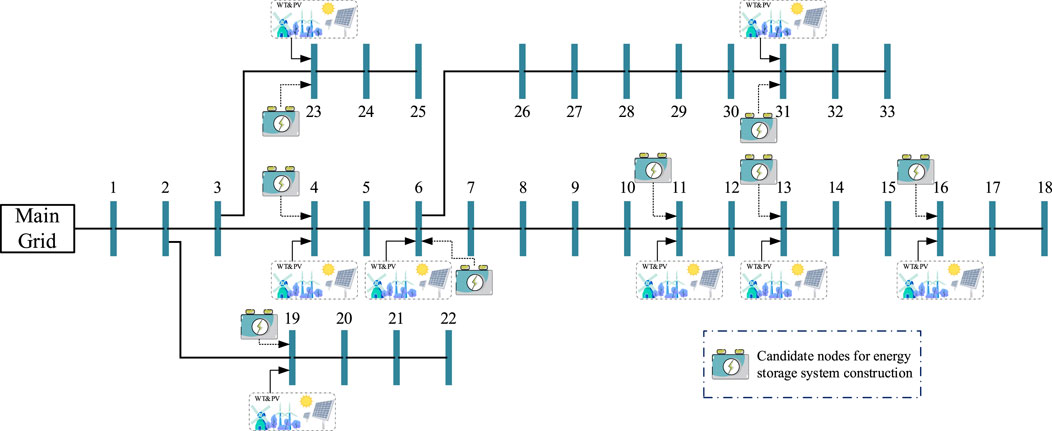
Figure 3. Schematic diagram of IEEE Case33 distribution network with high penetration of new energy.
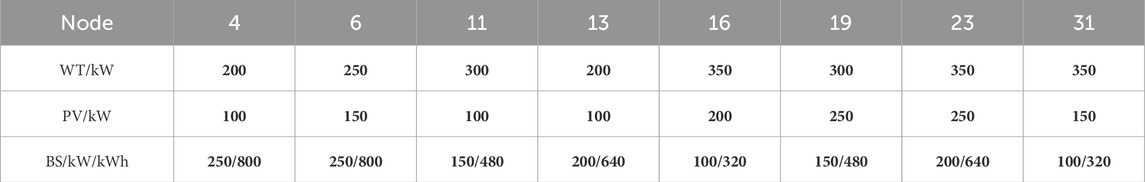
Table 3. Parameter configuration table for IEEE Case33 distribution network with high penetration of new energy.
In this case study, the voltage magnitude limits for each node in the distribution network are 1.1 p.u. and 0.9 p.u. Nodes 4, 6, 11, 13, 16, 19, 23, and 31 are all equipped with wind turbines and photovoltaic connections. These nodes are selected as candidate sites for energy storage to demonstrate on-site integration of new energy sources and reduction of line losses. The design coefficients for some photovoltaic and new energy sources are shown in Figure 4. The data for this case study are based on a granularity of 15 min per day with a total of 96 sampling points. All calculations are conducted using the Gurobi 11.0.0 API for Python on an Intel Core i7-11700F 2.5 GHz processor.
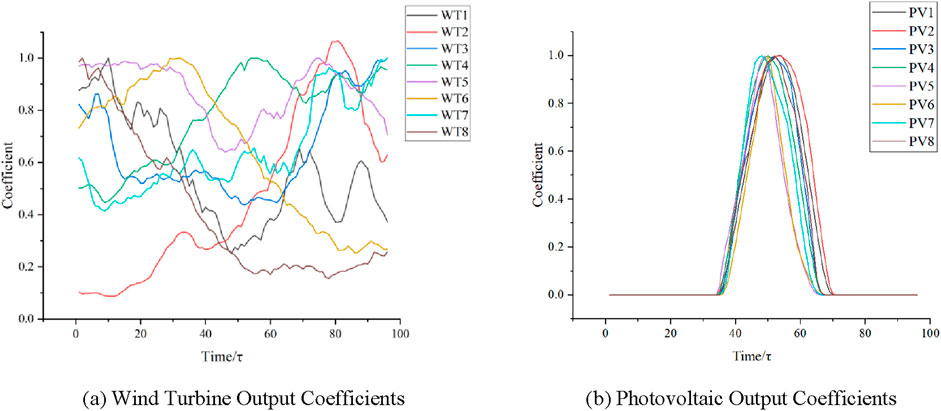
Figure 4. Renewable energy output coefficients. (A) Wind turbine output coefficients. (B) Photovoltaic output coefficients.
The case constructed in the “Case construction” section is modeled using the model proposed in the paper and then solved using a solver. The energy storage system siting is illustrated in Figure 5, showing that energy storage systems should be constructed and deployed at nodes 4, 6, 19, 23, and 31. Additionally, the lines requiring expansion are synchronously selected in the model, namely, lines (3,23), (4,5), (6,26), (10,11), (19,20), (23,24), and (30,31). The operational power of the energy storage systems at each node is depicted in Figure 6, while the curtailed power of the new energy sources is shown in Figure 7.
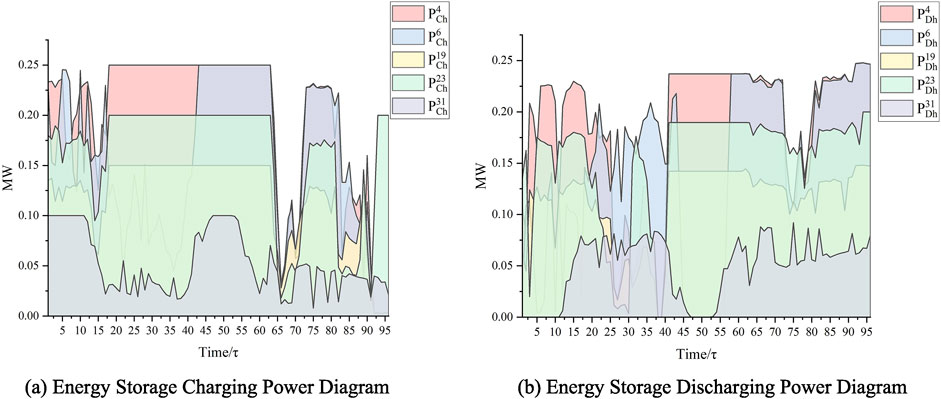
Figure 6. Energy storage charging and discharging power diagram. (A) Energy storage charging power diagram. (B) Energy storage discharging power diagram.
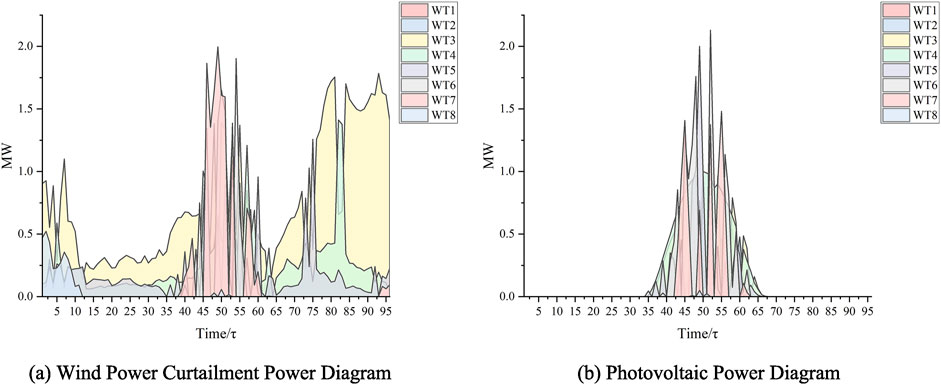
Figure 7. Diagram of curtailed power of new energy sources. (A) Wind power curtailment power diagram. (B) Photovoltaic power diagram.
In the objective function, the decision to relax the term
The decision of whether to relax the terms
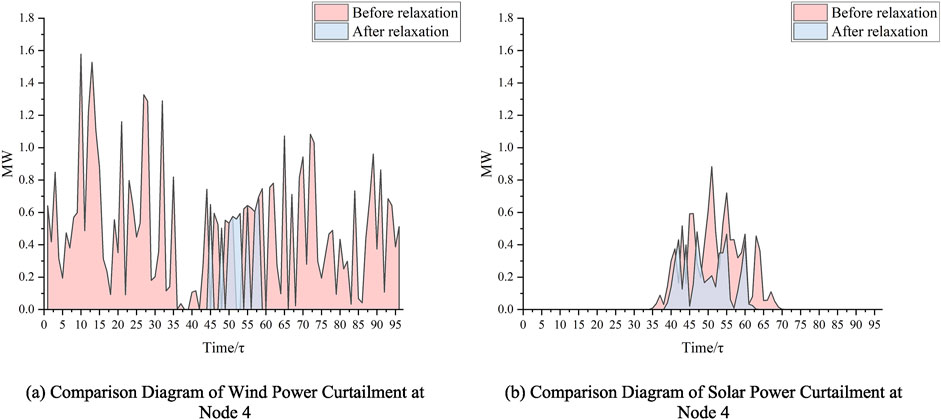
Figure 9. Illustration of wind and solar power curtailment before and after optimization at node 4. (A) Comparison diagram of wind power curtailment at node 4. (B) Comparison diagram of solar power curtailment at node 4.
In a typical distribution network scenario with high penetration of new energy sources, the joint planning model for energy storage siting and line expansion in distribution networks proposed in this paper can effectively enhance the local integration of new energy sources in the distribution network and alleviate the power backflow issue between the main grid and the distribution network. Furthermore, the model constructed in this paper can be directly solved by advanced commercial solvers, avoiding complex mathematical transformations, greatly increasing the confidence in the planning solutions and the numerical stability of the intermediate calculation process.
Based on the original IEEE-33 case, a heavy load scenario is constructed to simulate the adaptability of the proposed mathematical model and algorithm under relatively unbalanced conditions. As shown in Figure 10, the power exchange at Bus 1 connected to the higher-level grid is similar to that in Figure 5. Under this scenario, the proposed planning method still effectively reduces the power exchange between the distribution network and the higher-level grid, thereby maximizing the utilization of local energy resources within the distribution network.
A more refined distribution network planning approach is proposed to adapt to the scenario of high penetration of new energy into the distribution network, addressing the issues of reverse power flow and line overload between the main grid and the distribution network. By leveraging flexible resources with regulatory capabilities, this paper introduces a joint planning technology for energy storage site selection and line capacity expansion in distribution networks, considering the volatility of new energy. This method designs the objective function by incorporating terms for main and distribution network power transmission, renewable energy curtailment, line overload, and energy storage construction. It introduces indicative constraints in the energy storage construction-related constraints, effectively coordinating the planning of energy storage siting and line expansion. This model avoids complex mathematical transformations and can be directly solved by advanced commercial solvers.
The CHk-means algorithm proposed in this paper is shown to effectively address the high computational complexity of clustering in large-scale datasets, thereby improving the accuracy and stability of clustering results, as evidenced by the constructed wind turbine and photovoltaic output aggregation model. The results from the IEEE Case33 example of a distribution network with high penetration of new energy demonstrate that the proposed model can efficiently provide a joint planning solution for energy storage siting and line expansion selection. Compared to optimization models that do not consider the main and distribution network power transmission terms, the output solution of this model can effectively reduce the electricity reverse flow from the distribution network to the main grid. Additionally, compared to optimization models that do not consider renewable energy integration, the output solution of this model can reduce renewable energy curtailment by at least 50%. The direct solvability of the proposed method improves solution efficiency to some extent, avoiding numerical issues that may arise from algorithmic iterations and logical transformations, thus demonstrating practical engineering applicability.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
XF: conceptualization and writing–review and editing. PX: investigation and writing–original draft. CB: software and writing–review and editing. LX: data curation and writing–original draft. NZ: methodology and writing–review and editing. FM: writing–original draft, writing–review and editing, conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, funding acquisition, investigation, methodology, project administration, resources, software, supervision, validation, and visualization.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. The authors declare that this study received funding from the Technology Project “Research on collaborative planning technology for regional power grids and flexible adjustable resources adapted to large-scale new energy integration (Project number: B311LS230008),” State Grid Zhejiang Electric Power Co., Ltd. Lishui Power Supply Company. The funder was not involved in the study design, collection, analysis, interpretation of data, writing of this article, or the decision to submit it for publication.
Authors XF, PX, CB, LX, and NZ were employed by State Grid Zhejiang Electric Power Co., Ltd. Lishui Power Supply Company. Author FM was employed by Guangzhou Shuimu Qinghua Technology Co., Ltd.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors, and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Baringo, L., and Conejo, A. J. (2013). Correlated wind-power production and electric load scenarios for investment decisions. Appl. Energy 101, 475–482. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2012.06.002
Cai, Z., Yang, K., Guo, X., Xiang, Z., Huang, J., and Wang, W. (2023). A distribution network planning method based on the integration of operation and planning and coordinated with the transmission network. Front. Energy Res. 11. doi:10.3389/fenrg.2023.1261028
Chen, Y., Lu, Q., Yang, Y., Liu, Y., Zhang, R., Yang, M., et al. (2023). “A dual-set path recovery model of power system considering the volatility and randomness of new energy unit output,” in 6th International Conference on Energy, Electrical and Power Engineering (CEEPE), Guangzhou, China (IEEE).
Das, D., Hrishikesan, V. M., Kumar, C., and Liserre, M. (2021). Smart transformer-enabled meshed hybrid distribution grid. IEEE Trans. Industrial Electron. 68 (1), 282–292. doi:10.1109/tie.2020.2965489
De Carne, G., Buticchi, G., Zou, Z., and Liserre, M. (2018). Reverse power flow control in a ST-fed distribution grid. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 9 (4), 3811–3819. doi:10.1109/tsg.2017.2651147
Dinh, H. T., Yun, J., Kim, D. M., Lee, K.-H., and Kim, D. (2020). A home energy management system with renewable energy and energy storage utilizing main grid and electricity selling. IEEE Access 8, 49436–49450. doi:10.1109/access.2020.2979189
Dratsas, P. A., Psarros, G. N., and Papathanassiou, S. A. (2021). Battery energy storage contribution to system adequacy. Energies 14 (16), 5146. doi:10.3390/en14165146
Guerrero, J., Gebbran, D., Mhanna, S., Chapman, A. C., and Verbič, G. (2020). Towards a transactive energy system for integration of distributed energy resources: home energy management, distributed optimal power flow, and peer-to-peer energy trading. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 132, 110000. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2020.110000
Holguin, J. P., Rodriguez, D. C., and Ramos, G. (2020). Reverse power flow (RPF) detection and impact on protection coordination of distribution systems. IEEE Trans. Industry Appl. 56 (3), 2393–2401. doi:10.1109/tia.2020.2969640
Huang, R., Zhang, S., and Wang, P. (2022). Key areas and pathways for carbon emissions reduction in Beijing for the “Dual Carbon” targets. Energy Policy 164, 112873. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2022.112873
Iioka, D., Fujii, T., Orihara, D., Tanaka, T., Harimoto, T., Shimada, A., et al. (2019). Voltage reduction due to reverse power flow in distribution feeder with photovoltaic system. Int. J. Electr. Power and Energy Syst. 113, 411–418. doi:10.1016/j.ijepes.2019.05.059
Jia, Y., Lei, Z., Ma, J., and Xiangli, K. (2023). “Thermal runaway fault diagnosis for battery systems based on correlation coefficient and local outlier factor,” in 9th International Conference on Mechanical and Electronics Engineering (ICMEE), Xi'an, China (IEEE).
Klyve, Ø. S., Grab, R., Olkkonen, V., and Marstein, E. S. (2024). Influence of high-resolution data on accurate curtailment loss estimation and optimal design of hybrid PV–wind power plants. Appl. Energy 372, 123784. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2024.123784
Li, J., Zhou, J., and Chen, B. (2020). Review of wind power scenario generation methods for optimal operation of renewable energy systems. Appl. Energy 280, 115992. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2020.115992
Li, Z., Guo, Q., Sun, H., and Wang, J. (2016). Coordinated economic dispatch of coupled transmission and distribution systems using heterogeneous decomposition. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 31 (6), 4817–4830. doi:10.1109/tpwrs.2016.2515578
Lin, L., Ma, X., Ding, W., Cui, H., and Xu, N. (2023). “Reactive power optimization of renewable energy base considering reactive power adjustment capacity of grid-forming energy storage station,” in 6th International Conference on Renewable Energy and Power Engineering (REPE), Beijing, China (IEEE).
Liu, D., Liu, L., Cheng, H., Li, A., Li, G., and Zhang, X. (2021). Transmission expansion planning coordinated with distribution networks based on generalized master-slave splitting theory. Proc. CSEE 41 (17), 5856–5866. doi:10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.201322
Liu, Y., and Bao, Y. (2023). “Optimal scheduling of energy storage considering power and energy capacity nonlinear constraints,” in International Conference on Power System Technology (PowerCon), Jinan, China (IEEE).
Ma, Y., Wang, X., Song, R., and Ding, Y. (2024). “Analysis of the impact of energy storage access on distribution network line loss,” in 3rd International Conference on Energy and Electrical Power Systems (ICEEPS), Guangzhou, China (IEEE).
Nair, D. S., and Rajeev, T. (2022). “Impact of reverse power flow due to high solar PV penetration on distribution protection system,” in Sustainable energy and technological advancements. Editors G. Panda, R. T. Naayagi, and S. Mishra (Springer, Singapore: Advances in Sustainability Science and Technology). doi:10.1007/978-981-16-9033-4_1
Paudel, A., Sampath, L. P. M. I., Yang, J., and Gooi, H. B. (2020). Peer-to-Peer energy trading in smart grid considering power losses and network fees. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 11 (6), 4727–4737. doi:10.1109/tsg.2020.2997956
Puri, D., and Gupta, D. D. (2024). “Enhancing K-means clustering with data-driven initialization and adaptive distance measures,” in International Conference on Emerging Innovations and Advanced Computing (INNOCOMP), Sonipat, India (IEEE).
Si, J., Feng, Q., Yu, C., Zhang, C., Wang, Q., and Buja, G. (2024). “Open circuit fault diagnosis of modular multilevel converter based on local outlier factor detection,” in IEEE 10th International Power Electronics and Motion Control Conference (IPEMC2024-ECCE Asia), 841–845. doi:10.1109/ipemc-ecceasia60879.2024.10567108
Stecca, M., Ramirez Elizondo, L., Batista Soeiro, T., Bauer, P., and Palensky, P. (2020). A comprehensive review of the integration of battery energy storage systems into distribution networks. IEEE Open J. Industrial Electron. Soc., 1. doi:10.1109/ojies.2020.2981832
Tounsi Fokui, W. S., Saulo, M., and Ngoo, L. (2022). Controlled electric vehicle charging for reverse power flow correction in the distribution network with high photovoltaic penetration: case of an expanded IEEE 13 node test network. Heliyon 8 (3), e09058. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e09058
Unahalekhaka, P., and Sripakarach, P. (2020). Reduction of reverse power flow using the appropriate size and installation position of a BESS for a PV power plant. IEEE Access 8, 102897–102906. doi:10.1109/access.2020.2997821
Wang, S., Guo, M., Huang, Z., Lan, L., Lv, R., and Liu, P. (2024). “An energy storage planning and configuration optimization method considering the techno-economic trends,” in 3rd International Conference on Energy, Power and Electrical Technology (ICEPET), Chengdu, China (IEEE).
Wang, S., Li, X., and Hao, Y. (2022). “Analysis on the effect of energy storage on improving the transmission capacity of UHVDC transmission line,” in 7th Asia Conference on Power and Electrical Engineering (ACPEE), Hangzhou, China (IEEE).
Yao, Z., Wu, K., Zhang, Y., Yan, Q., Shi, J., Sun, J., et al. (2022). “Optimal allocation and economic analysis of energy storage capacity of new energy power stations considering the full life cycle of energy storage,” in IEEE 6th Conference on Energy Internet and Energy System Integration (EI2), Chengdu, China (IEEE).
Zafar, U., Bayhan, S., and Sanfilippo, A. (2020). Home energy management system concepts, configurations, and technologies for the smart grid. IEEE Access 8, 119271–119286. doi:10.1109/access.2020.3005244
Žalik, K. R., and Žalik, M. (2023). “Comparison of K-means, K-Means++, X-means and single value decomposition for image compression,” in 27th International Conference on Circuits, Systems, Communications and Computers (CSCC) (IEEE).
Zhao, J., Zhang, Z., Yao, J., Yang, S., and Wang, K. (2019). Heterogeneous decomposition based distributed reactive power optimization method for global transmission and distribution network. Automation Electr. Power Syst. 43 (03), 108–115. doi:10.7500/AEPS20180111009
Zheng, B., Wei, W., Chen, Y., Wu, Q., and Mei, S. (2022). A peer-to-peer energy trading market embedded with residential shared energy storage units. Appl. Energy 308, 118400. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2021.118400
Keywords: reverse power flow, heuristic k-means, energy storage site selection, line capacity expansion, penetration rate of renewable energy
Citation: Feifei X, Xia P, Bowei C, Xiaoshuang L, Zhi N and Miaoyong F (2024) Joint planning of energy storage site selection and line capacity expansion in distribution networks considering the volatility of new energy. Front. Energy Res. 12:1427582. doi: 10.3389/fenrg.2024.1427582
Received: 04 May 2024; Accepted: 30 October 2024;
Published: 26 November 2024.
Edited by:
Umberto Desideri, University of Pisa, ItalyReviewed by:
Stella Morris, Tunku Abdul Rahman University, MalaysiaCopyright © 2024 Feifei, Xia, Bowei, Xiaoshuang, Zhi and Miaoyong. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Feng Miaoyong, MjAyMjIxMDE1NTY4QG1haWwuc2N1dC5lZHUuY24=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.