- 1Siping Power Supply Co. Ltd., Jilin Electric Power Co. Ltd., Siping, China
- 2School of Electrical Engineering, Northeast Electric Power University, Jilin, China
Introduction:: Mitigating three-phase unbalance in rural distribution networks is a significant challenge, especially with the integration of photovoltaic and energy storage systems (PESS). While Distributed Static Transfer Switches (STS) offer a promising solution by regulating load phase sequences, conventional approaches are costly and inefficient, limiting large-scale implementation.
Methods:: To address these limitations, we propose a bi-level optimization model for the siting and capacity optimization of STS in rural networks. The upper-layer model focuses on minimizing investment and maintenance costs for STS, while considering branch loss reduction and three-phase unbalance mitigation. The lower-layer model aims to minimize three-phase unbalance in daily operations, with the integration of PESS. We use the hyperparameter alternating iteration (HAI) method to iteratively refine the bi-level model and obtain optimal planning and operational solutions.
Results:: We applied the proposed model to an IEEE-13 benchmark case study. The results demonstrated that the bi-level optimization approach effectively reduced three-phase unbalance in the rural distribution system while minimizing STS planning costs.
Discussion:: This innovative approach provides a cost-effective and efficient solution for mitigating three-phase unbalance in rural distribution networks, enhancing the feasibility of large-scale STS deployment. The integration of PESS further contributes to system stability, making this model a robust tool for future network planning.
1 Introduction
Agricultural electrification has been remarkable in recent years worldwide, triggered by the widespread deployments of high-power and large-capacity applications into rural distribution networks. However, the substantial novel application into the distribution networks poses obviously various risks, including voltage fluctuations and the three-phase balance (Camilo et al., 2021). In this various adverse effect, the three-phase unbalance in rural distribution networks often causes a chain of challenges, such as increased branch losses, reduced transmission capacity, overheating of distribution transformers, and other derivatives concerns (Islam et al., 2019; Hashmi et al., 2022). Addressing the three-phase unbalance untimely within the agricultural distribution network may lead to a notable decrease in the lifetime of transformers, transmission branches, and communication applications. This scenario creates a substantial risk to the security and reliability of the distribution network (Sun et al., 2020; Zheng et al., 2020).
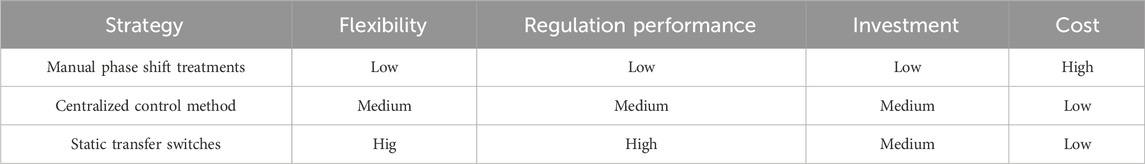
Manual phase shift treatments are the conventional solution for three-phase unbalance governance and mitigation in rural distribution networks (Kataray et al., 2023). However, this operation is not only cost-labor-intensive but also lacks dynamic regulation to match the three-phase load after phase shifting. Utilities have been exploring innovative strategies and novel technologies aimed at enhancing the stability of voltage and reducing the unbalance degree to ensure the stable operation of distribution networks. These strategies primarily consist of two majors: the deployment of power electronic devices and reactive power compensation (Gu et al., 2021; Mohammed et al., 2022). Another study employed a microgrid central controller to monitor the voltage at the common coupling point and order unbalanced voltage compensation commands to distributed power sources via a communication, initially mitigating the three-phase unbalance (Brandao et al., 2019). The authors designed a central secondary controller and sent signals to the local control units of distributed power sources for balancing the voltage in an islanded microgrid (Lou et al., 2020). However, the contribution was limited due to the bandwidth constraints of the communication. Other relative studies leveraged the hidden nexus between negative sequence reactive power and negative sequence voltage to automatically balance voltage among distributed power sources and allocate compensation tasks efficiently to minimize dependence on communication. Nevertheless, the response speed of the compensation was affected by the process of data measurement and filtering (Sargolzaei et al., 2019; Zhao et al., 2020; Hou et al., 2021). In a different approach, authors improved the voltage unbalance coefficient of inverter voltage by regulating the negative-sequence output impedance of the power supply (Ghahderijani et al., 2019). However, this method is invalid for optimally sharing the negative-sequence current when interconnecting branch impedances differ. To break this limitation, the research introduced a distributed collaborative negative-sequence equalization method via a dynamic consensus algorithm (Lu et al., 2022). This approach aims to propose an independent central controller and efficiently compensates for unbalanced voltages without additional requirements. A separate study implemented an accurate distribution of three-phase currents without data exchange (Zargar et al., 2020), while yet in another design, authors proposed an intelligent phase-switching strategy, the multi-objective function underlined the number of phase-switching actions and calculated current unbalance value (Tarhan et al., 2023). The main work (Fu et al., 2020) employed a mixed-integer nonlinear programming model to optimize power flow under three-phase unbalanced operation during microgrid islanding. While extensive research has been focusing on the capabilities of power electronic devices in addressing three-phase unbalances, the development of rational planning and reasonable sizing for the devices remains a research gap.
As aforementioned above in Table 1, the potential of STS has been demonstrated in governance and mitigation of three-phase unbalance. The deployment and planning of STS still need to be studied. The focus of this article will also be underlined in the siting and capacity configurations of STS. The critical properties of the proposed computational procedure and the overall contributions of the paper are summarized as follows:
1) The studies focus on the hybrid investment than (Liu et al., 2020; Islam et al., 2022a; Liu et al., 2022; Tang and Jheng, 2023), especially incorporating the cost of abandoned sunlight and the cost of three-phase unbalance. The upper layer is a novel design for minimizing the annual comprehensive operating cost of the distribution network with various factors such as STS costs of installation and maintenance, branch losses, three-phase unbalance costs, and any associated disposal costs. The model is more practical to match real-world planning concepts.
2) This article also details a three-phase operation model for distribution networks with daily governance and mitigation of three-phase unbalance. It is a more novel consideration than the conventional methods (Islam et al., 2022b; Huang et al., 2023; Sun et al., 2023). The minimized value of three-phase unbalance is the mission of the optimization with operation constraints. The solution is utilized to seek the optimal locations of STS.
3) The hyperparametric alternating iteration (HAI) (Dong et al., 2021) method is detailed and leveraged to compute the bi-level model to optimize and output a compromise solution for the operators or managers of the distribution grid.
The rest paper is organized as follows: Section 2 details the main governance program of three-phase unbalance mitigation. Section 3 introduces the bi-level optimization model. In Section 4, the HAI computational procedure and counterpart of variables are listed. In Section 5, case studies are performed to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method. Section 6 concludes this paper.
2 Three-phase unbalance governance via PESS and STS in rural distribution networks
In rural low-voltage distribution networks, a substantial number of single-phase loads randomly accessing the buses cause a high risk of three-phase unbalance of current and voltage within the distribution network. This section delves into the measures for the production and propagation of three-phase unbalance via exploration of the inducement in distribution networks.
2.1 Three-phase unbalance in the rural distribution network
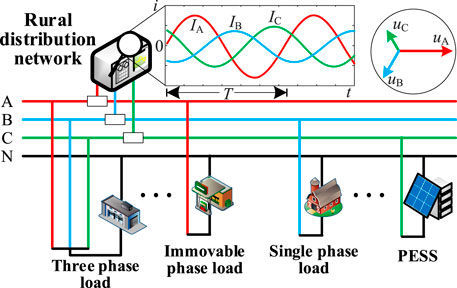
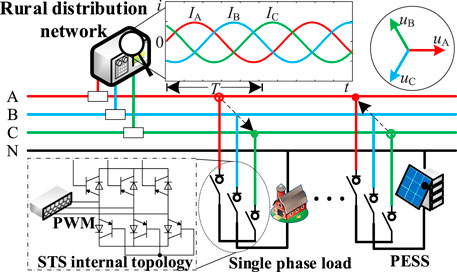
In rural three-phase distribution networks, the system always operates in an unreasonable mode, the amplitudes of the three-phase currents (or voltages) are excursions outside the security range in the rural networks. As per the utility regulations, the allowable limit for unbalance at the point of standard connection is set at 20% during normal mode. Figure 1 illustrates the state of three-phase unbalance operation in rural distribution networks.
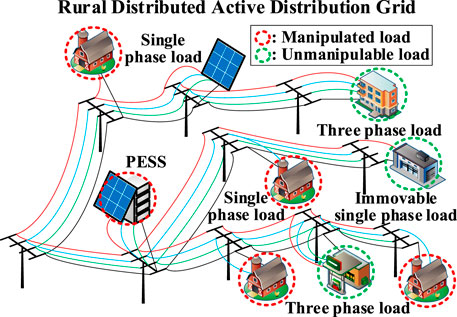
From Figure 1, the main reason for operation with three-phase unbalance in rural distribution networks is the uneven connections of three-phase loads into distribution transformers. Three-phase unbalance stemming from an imprudent distribution of load is essentially a challenge related to the allocation of electric power flow. The direct reason for these problems is users’ randomized connection of single-phase loads in rural distribution networks. Additionally, at the initial stage of distribution network construction, the deployment of load connection lacks foresight, further exacerbating the three-phase unbalance within the distribution network. Therefore, it is imperative to reorganize the various loads in rural distribution networks and develop strategies for governance and mitigation of three-phase unbalance. Figure 2 illustrates the multiple loads in rural distribution networks.
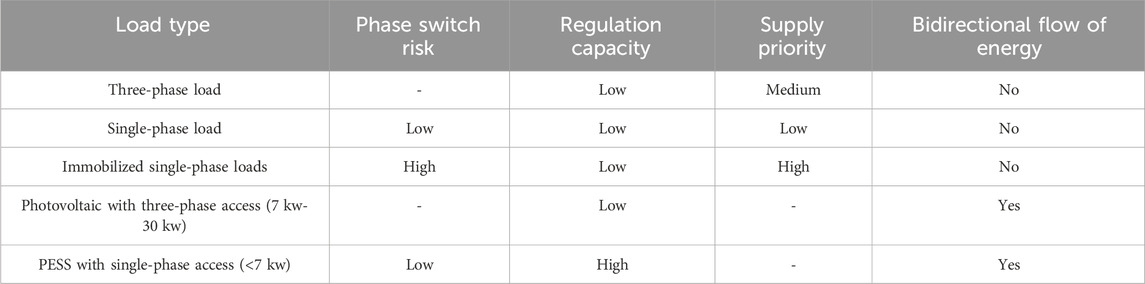
Figure 2 depicts the rural network loads, mainly comprising three-phase loads, single-phase loads, immobilized single-phase loads, and PESS. The mainstreamed program to address the three-phase unbalance in rural distribution networks is the prudent distribution of electric loads to ensure voltage and current balance across all three phases. The balance is met possibly through phase regulation and load reallocation. Thus, these loads are categorized based on respective characterization to participate in three-phase unbalance regulation, as detailed in Table 2.
As shown in Table 2, the electricity quality of the networks may improve through the participation of STS within the distribution network. On the other hand, immobilized single-phase loads have stringent requirements for high electricity quality and may not tolerate the risk of the continuous actions of STS. Therefore, this study focuses on the three-phase unbalance governance through single-phase loads and PESS with single-phase access. In the practical operation of rural low-voltage distribution networks, the irregular fluctuations of phase inconsistencies at different time intervals must be dynamically regulated.
2.2 Three-phase unbalance governance via STS and PESS
Sensible utilization of STS highlights the rescheduling of single-phase loads involved in regulating the particular phase with high voltage and low current. The operation is required to the operation with a maintained power supply. The employment of an intelligent control module and communication device is to be utilized to receive and send real-time instructions to STS, minimizing three-phase unbalances. STS may strategically be installed in accessed branches of single-phase loads and PESS in a distribution network. Online real-time switching facilitates three-phase balance and optimal scheduling. The anticipated operational state of rural distribution networks with phase regulation is visualized in Figure 3.
As illustrated in Figure 3, the single-phase loads connected to STS can be dynamically switched to match the requirement at any time. Furthermore, the trade-off of charge or discharge for batteries of PESS alters bidirectional power flow, thereby matching to regulate the three-phase unbalance. The flexibility is obviously a valuable feature of PESS in regulation. With the capabilities of STS and PESS to be observed in regulating three-phase unbalance, the study focuses on determining how to meet the unbalanced requirements within the exact planning of STS.
3 Siting and capacity planning of STS with PESS in rural distribution networks
STS installation leads to increased investment and maintenance costs in the distribution grid. Fortunately, the operating costs within the distribution network are continuously reduced to counterbalance the additional expenses of STS. In addition to one-off expenses and fixed costs of STS, we take account of the daily cost, owing to the switching actions and the losses. Therefore, this paper develops a bi-level planning-operation model for STS deployments, contributing a framework to tackle this multifaceted trade-off.
3.1 Upper-level model
The upper level mainly focuses on the optimal planning of STS with various factors, encompassing the costs associated with STS installation and maintenance, branch losses, additional three-phase unbalances, and abandoned sunlight. Within this framework, an optimization mathematical model is developed with the objective of minimizing the consolidated annual cost of STS.
3.1.1 Objective function
The objective function of the minimization consolidated cost for STS planning can be shown in Equation 1 as follows:
where
3.1.1.1 Cost of installation and maintenance of STS
In a typical rural low-voltage distribution network, a single branch is typically deployed with one terminal communication and multiple STS. The terminal communication sends the Pulse-Width Modulation (PWM) signals to STS based on the control strategy. STS then executes a command, mitigating the three-phase balance within the substation area. The cost associated with the installation and maintenance of STS can be formulated in Equation 2 as:
where
3.1.1.2 Aging costs in rural distribution networks
Three-phase unbalances in rural distribution networks lead to the accelerated aging of transformers and other applications. The degree of the aging process is directly influenced by the value of the three-phase unbalance within the distribution network. This can be modeled in Equation 3 as:
where
3.1.1.3 Branch loss costs in the rural distribution network
The three-phase unbalance, in addition to causing equipment deterioration, increases branch losses, the costs can be abstracted in Equation 4 as:
where
3.1.1.4 Costs of sunlight abandonment of PESS
PESS may be requested to charge from the grid to mitigate three-phase unbalance during specific periods. However, if the PV is substantial at the time, it may lead to power abandonment due to the power limitations on charging. The cost can be formulated in Equation 5 as:
where
4 Constraints of STS
The three-phase unbalance regulation function of STS contributes to a reduction in operating costs but results in increased investment costs. Therefore, we set limitations on the total number of STS during the early planning stages. This ensures that the installations of STS remain economically viable and efficient.
4.1 Quantity constraints of STS installations
where
4.2 Current constraints of STS:
where
Equations 6, 7 are shown to enhance the constraints for optimization model. The upper-layer model mainly concentrates on the challenge related to the investment of STS. However, we also recognize that STS needs to meet the operational requirements after installation in the distribution network. Thus, the paper proceeds to develop a lower-layer optimization model, addressing the operational three-phase unbalance within rural low-voltage distribution networks. This ensures a comprehensive optimization of the effective governance of three-phase unbalances in such networks.
4.2.1 Lower-level model
The lower model underlines the operation of rural three-phase distribution networks after deployments of STS. It primarily focuses on evaluating the mitigation of three-phase unbalance within the system, taking into account the contribution of PESS. This lower model aims to ensure that the distribution network operates efficiently while mitigating three-phase unbalance.
4.2.1.1 Objective function
The minimized three-phase unbalance can be proposed here in Equation 8 as follows:
The calculation of three-phase unbalance mainly incorporates the three-phase current unbalance of the rural network, which can be presented in Equation 9 as follows:
5 Operation constraints of a three-phase distribution network
In rural low-voltage distribution networks, the topology typically resembles a radial network, and it frequently operates in a three-phase open-loop configuration (Mateo et al., 2020). This paper develops a more comprehensive model that encompasses the requirements for three-phase voltage and current values via the Dist-flow model. The Dist-flow model is valuable for its ability to linearize the AC model of the distribution network while preserving the essential characteristics of variables within the equations. By this foundation, the paper develops a three-phase distribution network operation model that offers a more accurate representation of network operation and performance.
a) The energy balance constraint for a rural three-phase distribution network can be modeled in Equation 10 as:
where Ae is the node-branch correlation matrix;
The switch of STS, as well as the charging and discharging power regulation of PESS, led to the regulation of three-phase power within the grid. This process involves transferring power from the high-load phase to the low-load phase through STS can be formulated in the Equation 11 as follows:
where
b) The three-phase distribution branch voltage balance can be presented in Equation 12 as:
where
c) The energy balance of three-phase distribution networks can be expressed in Equation 13 as:
d) The node voltage security constraint can be expressed in Equation 14 as:
where
e) The three-phase distribution transformer output power constraint can be modeled in Equations 15-18 as:
where
where
f) Branch security constraints are shown in the Equation 19 as follow:
where
5.1 The operational constraints of STS
a) The transfer power of STS can be represented as are represented in the Equations 20, 21 as follow:
where
b) STS switch constraints are shown in the Equation 22 as:
5.2 Operation constraints of PESS
a) The output of the PESS can be formulated in the Equations 23, 24 as:
where
where
b) The operation constraints of the three-phase inverter at the point of connection of the PESS to the distribution network can be modeled in the Equations 25-29 as:
where
where
c) The output of the photovoltaic can be formulated in the Equations 30-33 as:
where
The conversion efficiency of the PV can be modeled as:
where
The PV temperature can be shown as:
where
where WPV is the total power generated by PV;
d) The energy storage model can be expressed in the Equation 34 as:
where
The charging and discharging constraints can be expressed in the Equation 35 as:
where
The battery energy constraint can be expressed in the Equation 36 as:
where,
The planning and operation bi-level model for three-phase unbalance mitigation in this article, takes into account various types of costs and operational benefits. Below, we present the customized calculation algorithm.
6 Calculation algorithms for bi-level model
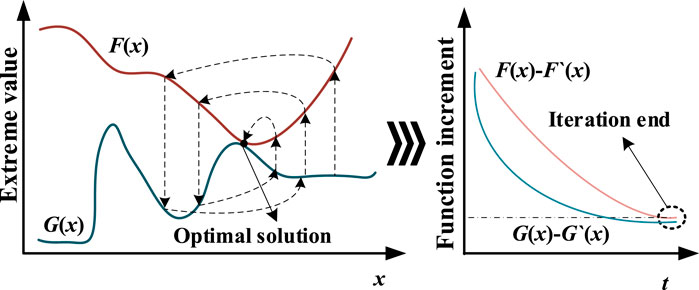
Traditional optimization algorithms are complex to solve the developed bi-level model, owing to the challenges in ensuring that the results are optimal solutions. This difficulty primarily arises in internal optimization problems involving integer variables because it is challenging to find closed solutions within the defined range. To overcome these challenges, this paper leveraged a hyperparameter alternating iteration. Method for solving the model. The flow of this method is illustrated in Figure 4 (Tarhan et al., 2023).
The HAI method consists of two steps:
1) Fix the lower layer hyperparameters (in this paper is the installation position of STS) (Tarhan et al., 2023), and optimize the upper layer parameters (the minimum number of STS installations) on the basis of calculating the three-phase unbalance, network loss and the cost of sunlight abandonment: the solution of the bi-level optimization problem is regarded as an iterative optimization procedure, and then the gradient descent algorithm is utilized to find the optimal solution of the objective function of the upper layer.
The descending gradient of the upper model mainly incorporates the number of STS installations, and its iterative process is expressed in the Equation 37 as:
where
2) Fix the upper layer parameters (number of STS installations) and optimize the lower layer hyper-parameters (installation positions of STSs): After computing the planning quantities of the upper layer, the branch bounding method is used to calculate the lower layer model to localize the position, and then the gradient of the upper layer model is updated. The iterations can be in the Equations 38, 39 as:
The above two processes apply for several iterations, specifically in different applications that need to set separate loop-stopping conditions based on the training and validation errors to stop the iteration.
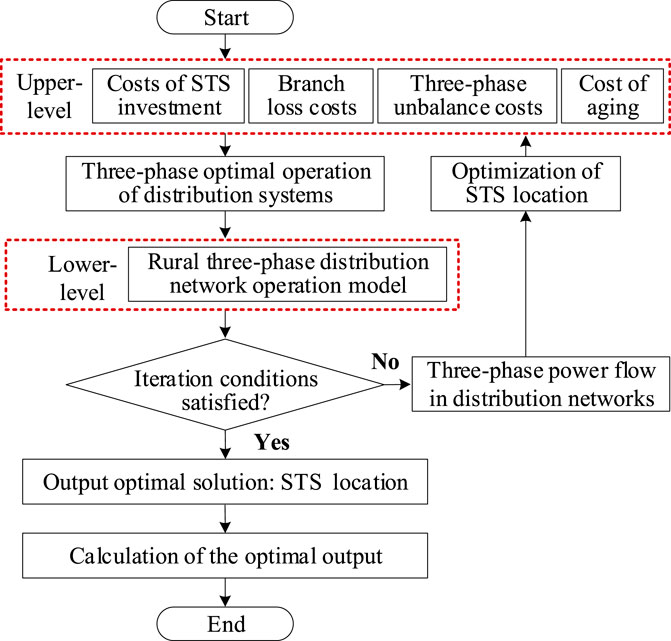
Through iteration, the final state is optimal, merger planning and operation, and the solution flow of this computational method is shown in Figure 5.
The specific solution flow of the STS siting and capacity configuration of the bi-level optimal allocation model in the rural distribution network is shown in Figure 5, and the detailed steps of the procedures are as follows:
1) Initial parameters such as system network loss and three-phase unbalance and sunlight abandonment through distribution network current calculation.
2) According to the initial parameters, the gradient descent algorithm and other optimization algorithms are leveraged to calculate the upper optimization model of STS siting and capacity configuration and record the minimum installation quantity ns of STS.
3) Substitute the quantity of STS installation into the bi-level model as a limit and optimize the lower level, As shown in Equations 1, 6, 7 utilizing the branch delimitation algorithm to estimate the switch state and installation location of the STS.
4) Input the STS access location as parameters and further calculate the distribution network loss, degree of three-phase unbalance, As shown in Equations 8, 10, 22 and sunlight abandonment rate through the constraints, as shown in Figures 9A–D;.
5) Substitute the obtained distribution network loss, three-phase unbalance degree, As shown in Equations 23-36 and sunlight abandonment as inputs again to the upper model and recalculate the installed number of STSs ns.
6) Judge whether the iteration termination meets the conditions of the optimal solution of the lower layer model, As shown in Equation 37 if the optimal solution is held, then the calculation is finished, and the optimal scheme is output; otherwise, repeat the second step.
7 Case study
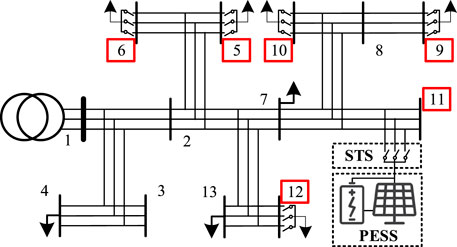
In this paper, As shown in Equations 38, 39 an IEEE-13 three-phase test benchmark is utilized to verify the rationality and accuracy of the developed optimization model, and the topology of the system is shown in Figure 6.
In Figure 6, the IEEE-13 three-phase system consists of five single-phase loads and eight three-phase loads. Distribution transformer is located at bus 1, and the PESS is connected to bus 11. The PV involves a single 7 kW installation with a total rated power of 1.2 MW. The energy storage has a maximum capacity of 1 MWh. Buses enclosed within the red lines represent buses participating in three-phase unbalance regulation. The access phase sequence may be regulated with loads that can reduce the degree of three-phase unbalance based on the control signals from STS. For the study, it is assumed that the STS has a lifetime of 5 years, and an annual discount rate of 8% is applied to evaluate costs and investments.
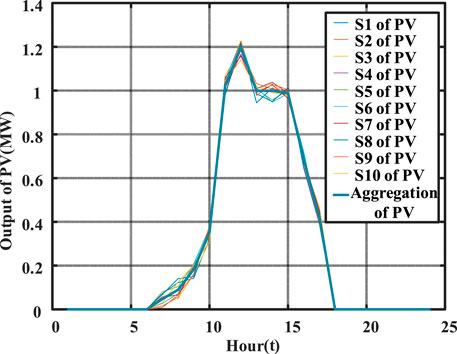
In this paper, the Monte Carlo method has been employed for simulating PV power generation. This method involves generating random values to affect the output of PV. The simulated values are then aggregated using the weighted entropy to calculate the output of PV, illustrated in Figure 7.
7.1 Analysis of STS planning results in different scenarios
Several operational scenarios are designed for comparative analysis to demonstrate the effectiveness of the planning strategy proposed in this paper:
Scenario 1: No three-phase unbalance governance.
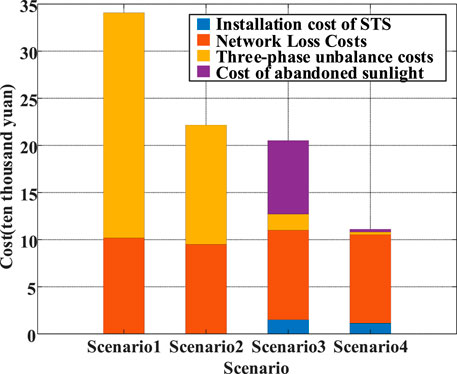
Scenario 2: Governance through manual phase change method; Scenario 3: Three-phase unbalance governance using only STS; Scenario 4: Three-phase unbalance governance by STS + PESS; The comprehensive cost variation of the method proposed in this paper is shown in Figure 8. The total number of STS planning in S3 is 4, (bus 5, 9, 10, and 12), while the planned number of STS in S4 is 3, (bus 9, 11, and 12).
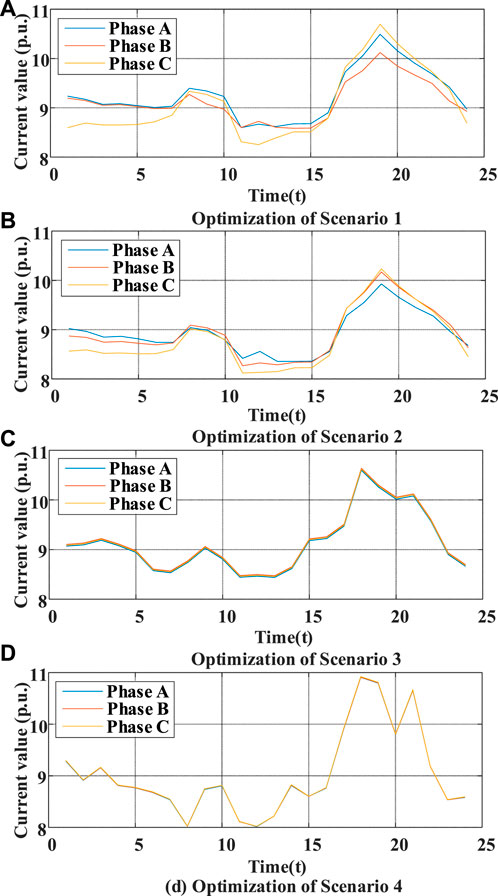
In Figure 8, compared with S1 and S2, the solution of S3 can significantly cut the three-phase unbalance cost. Still, the regulation process constrains the PV output and increases the cost of sunlight abandonment, leading to an insignificant decrease in operating cost compared with S2. And the method proposed in this paper, S4, take into account both PV and three-phase unbalance regulation, significantly reducing the total operation cost of the system. The three-phase current values for the four scenarios are shown in Figure 9.
As shown in Figure 9, the current trend of the distribution transformer in the four scenarios is similar. However, the three-phase unbalance of the distribution transformer current occurs in S1 and S2, which seriously affects the lifetime. The current values in the distribution transformers in S4 converge, and this phenomenon occurs due to the PESS participation in three-phase unbalance regulation. It may regulate the output base on the three-phase balance of the system, balancing the three-phase loads under the premise of ensuring the safe operation of the system, which reacts to the advantages of the utilization of the PESS and the STS to participate in three-phase jointly unbalance governance and mitigation as proposed in this paper. The three-phase unbalance degree under four scenarios is further analyzed.
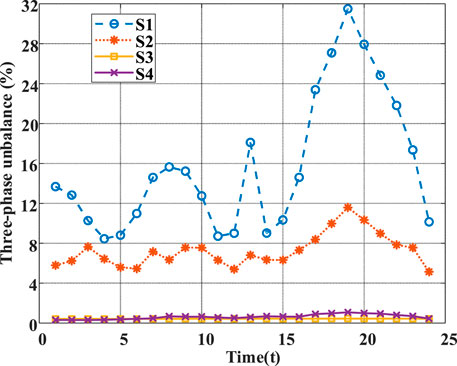
Figure 10 demonstrates the three-phase unbalance of the four scenarios, the three-phase unbalance in S2 still fails to satisfy the security operation requirements, although there is a particular improvement compared to S1. Whereas the three-phase unbalance of S3 and S4 is significantly reduced in the distribution networks, the action of STS is further analyzed as shown in Figure 11.
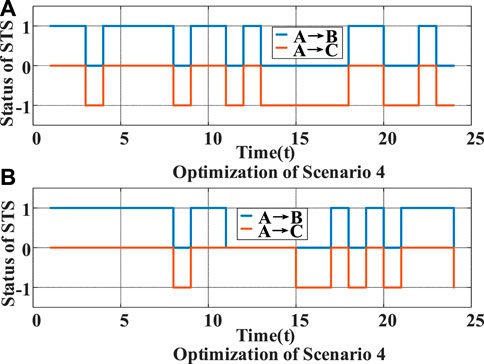
As shown in Figures 11A, B, due to the participation of PESS in the three-phase unbalance regulation, the number of STS switches on bus 9 in S4 is significantly less than that in S3, and the three-phase unbalance regulation can be satisfied at the same time.
7.2 Analysis of optimization results of PESS in different scenarios
Utilizing the combination of PESS and STS to regulate the three-phase unbalance of the distribution network can reduce sunlight abandonment and improve the utilization efficiency of energy storage. The comparison of different scenarios is shown in Figures 12, 13.
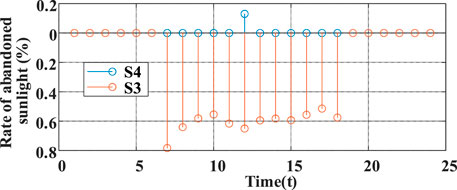
The results of the S3 and S4 for sunlight abandonment are compared in Figure 12, and it can be seen that S3 is significantly higher than that of S4. The main reason for this result is that S3 only utilizes STS to regulate the three-phase unbalance and, therefore, PV abandonment during specific periods to minimize three-phase unbalance. To ensure the three-phase balance of the transformer, the optimization reflects the limitation of the grid-connected power of PV in multiple periods. A large number of sunlight abandonment time periods show up, and the highest abandonment rate is 78%. The utilization of PESS to participate in the regulation of the three-phase unbalance consumes more PV power generation, and the energy change of the energy storage is shown in Figure 13.
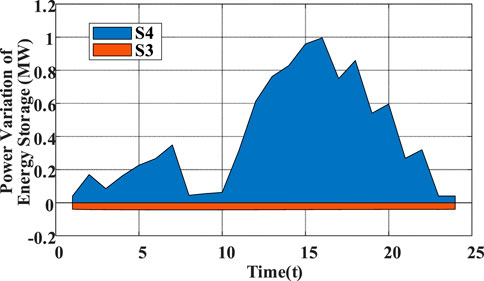
Figure 13 compares the energy variation of the energy storage in S3 and S4. The utilization of energy storage in S4 is significantly improved, while S3 has a high rate of sunlight abandonment along with the idle state of energy storage. Therefore, S4, corresponding to the algorithm proposed in this paper, is also able to consume renewable energy under the condition of governance and mitigation of the three-phase unbalance.
7.3 Optimization with different parameter configurations
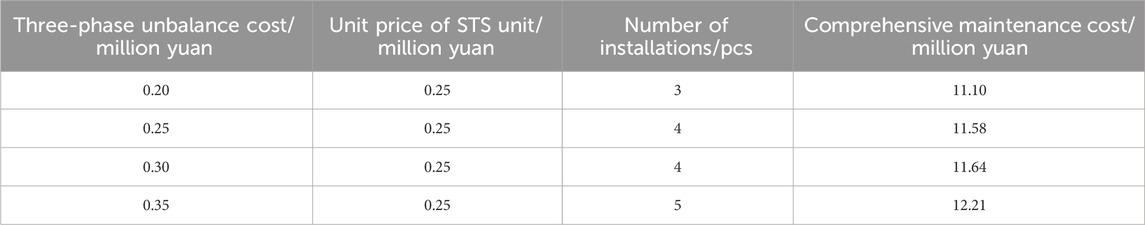
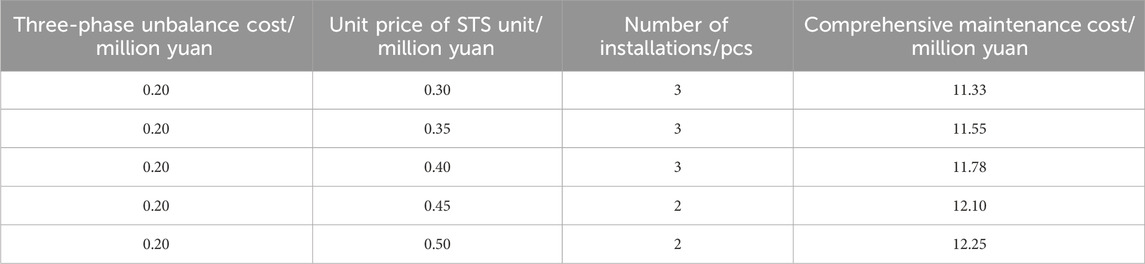
To further analyze the sensitivity of the STS siting and capacity configuration model for rural distribution networks developed in this paper. We further explored the mechanisms of parameter effects on optimization, such as STS cost and three-phase unbalance cost. The effectiveness of the model proposed in this paper is further validated and shown in Table 3.
Tables 3, 4 show the comprehensive maintenance cost and the number of installations when the repair and unit prices increase, respectively. As the repair cost of the three-phase unbalance increases, the total maintenance cost increases continuously when it reaches 0.35 million yuan, the installation of STS to governance the three-phase unbalance of the installation and maintenance costs are too high need to deploy more STS. Assuming that the price of the STS continues to increase, its benefits are lower, and this paper proposes a model that can reduce the total number of STS. Therefore, the model proposed in this paper still applies in the case of various parameters.
8 Conclusion
This paper introduces an STS siting and capacity configuration model designed for three-phase unbalances governance and mitigation in rural distribution networks. The optimization model is a bi-level for the planning operation of STS. The case study demonstrates that the model presented in this paper effectively regulates three-phase unbalances while minimizing the required quantity of STS installations. Furthermore, the results under various planning parameters reveal the robustness of this model, showcasing its ability to operate effectively under diverse operating conditions and offer optimal planning solutions. Notably, the quality of three-phase unbalance regulation is inversely proportional to the price of STS and directly proportional to the cost of three-phase unbalance. Future research will delve deeper into three-phase unbalance planning strategies, considering load variations, seasonal factors, and other intricate aspects to further enhance the governance and mitigation of three-phase unbalances in rural distribution networks.
Data availability statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found here: https://images.shoutwiki.com/mindworks/7/7e/IEEE_13_Bus_Power_System.pdf.
Author contributions
JZ: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing–original draft. KJ: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing–original draft. JF: Conceptualization, Data curation, Writing–original draft. CH: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing–original draft. SZ: Investigation, Methodology, Writing–original draft. JS: Conceptualization, Data curation, Writing–original draft. HC: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Writing–original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research is supported by the State Grid Jilin Electric Power Co., Ltd., 2021JBGS-02. The funder was not involved in the study design, collection, analysis, interpretation of data, the writing of this article, or the decision to submit it for publication.
Conflict of interest
Authors JZ, KJ, JF, CH, and SZ were employed by Siping Power Supply Co., Ltd. and Jilin Electric Power Co., Ltd.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The authors declare that this study received funding from State Grid Jilin Electric Power Co., Ltd.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Brandao, D. I., Araujo, L. S., Alonso, A. M. S., dos Reis, G. L., Liberado, E. V., and Marafao, F. P. (2019). Coordinated control of distributed three-and single-phase inverters connected to three-phase three-wire microgrids. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 8 (4), 3861–3877. doi:10.1109/jestpe.2019.2931122
Camilo, F. M., Castro, R., Almeida, M. E., and Fernão Pires, V. (2021). Energy management in unbalanced low voltage distribution networks with microgeneration and storage by using a multi-objective optimization algorithm. J. Energy Storage 33, 102100. doi:10.1016/j.est.2020.102100
Dong, X., Shen, J., Wang, W., Shao, L., Ling, H., and Porikli, F. (2021). Dynamical hyperparameter optimization via deep reinforcement learning in tracking. IEEE Trans. Pattern Analysis Mach. Intell. 43 (5), 1515–1529. doi:10.1109/tpami.2019.2956703
Fu, L., Liu, B., Meng, K., and Dong, Z. Y. (2020). Optimal restoration of an unbalanced distribution system into multiple microgrids considering three-phase demand-side management. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 36 (2), 1350–1361. doi:10.1109/tpwrs.2020.3015384
Ghahderijani, M. M., Camacho, A., Moreira, C., Castilla, M., and Garcia de Vicuna, L. (2019). Imbalance-voltage mitigation in an inverter-based distributed generation system using a minimum current-based control strategy. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 35 (3), 1399–1409. doi:10.1109/tpwrd.2019.2945472
Gu, N., Cui, J., and Wu, C. (2021). Power-electronics-enabled transactive energy market design for distribution networks. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 13 (5), 3968–3983. doi:10.1109/tsg.2021.3127544
Hashmi, M. U., Koirala, A., Ergun, H., and Van Hertem, D. (2022). Flexible and curtailable resource activation in three-phase unbalanced distribution networks. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 212, 108608. doi:10.1016/j.epsr.2022.108608
Hou, Y., Li, Q., Zhang, C., Lu, G., Ye, Z., Chen, Y., et al. (2021). The state-of-the-art review on applications of intrusive sensing, image processing techniques, and machine learning methods in pavement monitoring and analysis. Engineering 7 (6), 845–856. doi:10.1016/j.eng.2020.07.030
Huang, R., Xu, J., Chen, Q., Guo, X., and Cao, H. (2023). Reconstructed phase voltages based power following control for three-phase buck rectifier under unbalanced phase voltages and wide AC input frequency. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 38 (2), 2022–2031. doi:10.1109/tpel.2022.3217306
Islam, M. R., Lu, H., Hossain, M. J., and Li, L. (2019). Mitigating unbalance using distributed network reconfiguration techniques in distributed power generation grids with services for electric vehicles: a review. J. Clean. Prod. 239, 117932. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.117932
Islam, M. Z., Reza, M. S., Hossain, M. M., and Ciobotaru, M. (2022a). Three-phase PLL based on adaptive clarke transform under unbalanced condition. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Industrial Electron. 3 (2), 382–387. doi:10.1109/jestie.2021.3065205
Islam, M. Z., Reza, M. S., Hossain, M. M., and Ciobotaru, M. (2022b). Accurate estimation of phase angle for three-phase systems in presence of unbalances and distortions. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 71, 1–12. doi:10.1109/tim.2021.3132831
Kataray, T., Nitesh, B., Yarram, B., Sinha, S., Cuce, E., Shaik, S., et al. (2023). Integration of smart grid with renewable energy sources: opportunities and challenges–A comprehensive review. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assessments 58, 103363. doi:10.1016/j.seta.2023.103363
Liu, S., Cui, X., Lin, Z., Lin, Z., Lian, Z., et al. (2020). Practical method for mitigating three-phase unbalance based on data-driven user phase identification. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 35 (2), 1653–1656. doi:10.1109/tpwrs.2020.2965770
Liu, S., Lin, Z., Li, J., Wen, F., Ding, Y., Wang, Q., et al. (2022). Bi-Level optimal placement model of phase switch devices for mitigating three-phase unbalance in low-voltage areas. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 37 (4), 3149–3152. doi:10.1109/tpwrs.2022.3156438
Lou, G., Gu, W., Lu, X., Xu, Y., and Hong, H. (2020). Distributed secondary voltage control in islanded microgrids with consideration of communication network and time delays. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 11 (5), 3702–3715. doi:10.1109/tsg.2020.2979503
Lu, J., Zhang, B., Hou, X., and Guerrero, J. M. (2022). A distributed control strategy for unbalanced voltage compensation in islanded ac microgrids without continuous communication. IEEE Trans. Industrial Electron. 70 (3), 2628–2638. doi:10.1109/tie.2022.3169841
Mateo, C., Postigo, F., de Cuadra, F., Roman, T. G. S., Elgindy, T., Dueñas, P., et al. (2020). Building large-scale US synthetic electric distribution system models. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 11 (6), 5301–5313. doi:10.1109/tsg.2020.3001495
Mohammed, N., Lashab, A., Ciobotaru, M., and Guerrero, J. M. (2022). Accurate reactive power sharing strategy for droop-based islanded AC microgrids. IEEE Trans. Industrial Electron. 70 (3), 2696–2707. doi:10.1109/tie.2022.3167141
Sargolzaei, A., Yazdani, K., Abbaspour, A., Crane, C. D., and Dixon, W. E. (2019). Detection and mitigation of false data injection attacks in networked control systems. IEEE Trans. Industrial Inf. 16 (6), 4281–4292. doi:10.1109/tii.2019.2952067
Sun, J., Aboutanios, E., and Smith, D. B. (2023). Low cost and precise frequency estimation in unbalanced three phase power systems. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 38 (2), 767–776. doi:10.1109/tpwrd.2022.3197814
Sun, W., Neumann, F., and Harrison, G. P. (2020). Robust scheduling of electric vehicle charging in LV distribution networks under uncertainty. IEEE Trans. Industry Appl. 56 (5), 5785–5795. doi:10.1109/tia.2020.2983906
Tang, C.-Y., and Jheng, J.-H. (2023). An active power ripple mitigation strategy for three-phase grid-tied inverters under unbalanced grid voltages. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 38 (2), 27–33. doi:10.1109/tpel.2022.3198410
Tarhan, İ., Zografos, K. G., Sutanto, J., et al. (2023). A quadrant shrinking heuristic for solving the dynamic multi-objective disaster response personnel routing and scheduling problem. Eur. J. Operational Res. doi:10.1016/j.ejor.2023.09.002
Zargar, B., Angioni, A., Ponci, F., and Monti, A. (2020). Multiarea parallel data-driven three-phase distribution system state estimation using synchrophasor measurements. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 69 (9), 6186–6202. doi:10.1109/tim.2020.2967512
Zhao, J., Netto, M., Huang, Z., Yu, S. S., Gomez-Exposito, A., Wang, S., et al. (2020). Roles of dynamic state estimation in power system modeling, monitoring and operation. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 36 (3), 2462–2472. doi:10.1109/tpwrs.2020.3028047
Keywords: three-phase unbalance, static phase-change switches, siting and capacity optimization, rural distribution networks, hyperparameter alternating iteration
Citation: Zhang J, Jia K, Feng J, Hao C, Zheng S, Shao J and Chen H (2025) Siting and capacity configurations of static transfer switches for three-phase unbalance governance in rural distribution networks: a bi-level optimization programme. Front. Energy Res. 12:1325477. doi: 10.3389/fenrg.2024.1325477
Received: 21 October 2023; Accepted: 04 March 2024;
Published: 22 April 2025.
Edited by:
Yue Zhou, Cardiff University, United KingdomReviewed by:
Yajuan Guan, Aalborg University, DenmarkZixuan Wang, North China Electric Power University, China
Ning Yan, Shenyang University of Technology, China
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Jia, Feng, Hao, Zheng, Shao and Chen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Junyan Shao, amFpbnNoYW85MkBnbWFpbC5jb20=
 Jiguo Zhang1
Jiguo Zhang1 Junyan Shao
Junyan Shao