- 1School of Economics and Business Administration, Chongqing University, Chongqing, China
- 2Administrative Committee of Chongqing Economic and Technological Development Zone, Chongqing, China
Introduction: Issuance pricing is an important part of the operation of the securities market. Its pricing is directly related to the interests of issuers, investors and underwriters, as well as the regulatory and resource allocation functions of the securities issuance market. When the industry expectations vary greatly, the company has greater TMT heterogeneity. When the market expectation gap expands, the possibility of risk conversion increases. IPO underpricing occurs in stocks of developed countries, developing countries and emerging countries. Because the issuer and the underwriter investors have different information, for example, the information advantage of the underwriter will bring risks to investors when purchasing IPO shares. IPO underpricing is a compensation for the risks brought by information asymmetry.
Methods: At present, little attention has been paid to how the value of listed companies affects the underpricing of intellectual property. This paper will fill in this gap and empirically study the impact of management ability of senior management team on IPO underpricing. Therefore, starting from the Chinese stock market, this paper studies the evidence of vertical parallel executives, heterogeneity of senior management team and IPO underpricing.
Results: The average values of NCSKEW (C1) and DUVOL (C2) were −0.301 and −0.203, respectively, which were close to the descriptive statistics of the study.
Discussion: The dependent variable data in this paper has certain reliability. The minimum value of NCSKEW is −0.361 and the maximum value is 0.392, indicating that the fragmentation risk of different stocks is relatively high.
1 Introduction
Whether enterprises can take a low-carbon development path depends mainly on financing guarantee and technology research and development level. Because in the process of economic transformation from “high carbon” to “low carbon,” enterprises must eliminate backward equipment and technology and adopt new equipment and technology that meet the requirements of low carbon economy. This requires enterprises to have huge funds as the backing to maintain the continuous capital investment in new equipment and new technology. How to improve the efficiency of financing in a variety of ways to achieve high output at the lowest possible cost of capital is a practical problem faced by all low-carbon enterprises. China’s carbon trading pilot policy is expected to be effective and flexible in reducing carbon emissions by encouraging low-carbon innovation. Based on the sample of selected enterprises, Qi et al. analyzed the impact of this pilot policy on low-carbon innovation using a difference model, and conducted a series of robustness tests to confirm the results. Compared with the traditional and historical intensity distribution methods, the results of this study show that the low-carbon innovation degree is significantly greater when using the benchmark method (Qi et al., 2021). Therefore, the financing efficiency of listed companies in the low-carbon economy sector is a topic worthy of study. Low carbon economy is a new form of economic development, which has been widely recognized. Whether China’s economy can successfully transform depends to a large extent on the development of relevant enterprises, and the start of enterprise development is financing. The transition from private ownership to public ownership through listing (i.e., IPO or IPO) has attracted the attention of academia. Because the company faces governance, strategic and financial challenges and changes in obtaining favorable valuations from the stock market. This is especially true for family businesses, which leads to the growing interest of family business scholars in this topic. Wang et al. systematically reviewed the existing research on family business IPO and evaluated the latest technology in this field (Wang et al., 2022). In the process of economic transformation from “high carbon” to “low carbon,” enterprises must abandon outdated equipment and technology and stay with new equipment and technology that meet the requirements of low carbon economy. This process puts forward very high requirements for the amount of capital of enterprises. Financing activities are the starting point of enterprise financial activities. The uncertainty and information asymmetry surrounding the company’s initial public offering often make it difficult for potential investors to identify the value of the enterprise, thus leading to the company’s initial public offering underpricing. Based on the signal theory, Liu et al. studied the role of organizational reputation in the company’s initial underpricing. We analyzed 463 IPO companies in China from 2010 to 2016, and found that the two dimensions of corporate reputation, known for quality and overall popularity, were significantly negatively correlated with the IPO underpricing of companies. In addition, we find that investors’ attention plays an intermediary role in the negative relationship between corporate reputation and the company’s IPO underpricing (Liu et al., 2020).
The vertical concurrent appointment of executives is a vertical connection between major shareholders and managers, and its influence is mainly manifested in the following two aspects: first, from an agency theory, the vertical part-timers of the company can enhance the major shareholders’ confidence in the company. The intensity of supervision makes it difficult to cover up negative information under larger external supervision, thereby reducing the risk of stock prices falling, which is a “supervision effect”; better control of listed companies by shareholders is also beneficial to the private interests of major shareholders, while major shareholders concealing negative information in order to hollow out small shareholders will increase the risk of stock market collapse, which is the “hollowout effect”; of course, it may also be because the major shareholders assign the company’s management personnel to the company, so that the interests between the major shareholders and the entrusted company can be more coordinated, so that the hollowing out of the small shareholders can be reduced, which is the so-called “exploitation” Empty Effect”. Exactly which effect plays a dominant role is unknown. Differences in TMT background characteristics such as age, tenure, education level, and functional background reflect differences in TMT values, cognitive attitudes, skills, and risk appetite, and ultimately lead to different corporate behaviors and organizational outcomes. From the existing research results, the heterogeneity of TMT background characteristics has an important impact on strategic change, corporate performance, and whether to use corporate venture capital. In the development process of the modern market economy, as an important part of the modern financial system, the capital market is an effective means of resource allocation. China’s economic model involves active government intervention in the financial market. Brunnermeier et al. developed a theoretical framework in which intervention measures can prevent market collapse and volatility explosion, because short-term investors are unwilling to trade with noise traders. In the case of information friction, the government can change the market dynamics, because the noise in its intervention plan becomes an additional factor driving asset prices (Brunnermeier et al., 2022). Sreenu et al. studied whether the use of accounting conservatism in India reduced IPO underpricing, which is a concern of stakeholders and regulators. In addition, this study also examined how information asymmetry affects the meaning of IPO accounting conservatism (Sreenu et al., 2022). Therefore, this paper proposes a research on vertical concurrent executives, TMT heterogeneity and IPO underpricing—evidence from China’s stock market. It is of practical significance to improve the efficiency of the financial market and its impact on the stock market is also of great research value.
The IPO price is jointly determined by the listed company and the underwriter of the shares. As it is the first public offering of the company, there is no experience of the company’s stock issuance and the relevant stock trading price as a reference. Therefore, the determination of IPO price depends on the market forecast of the issuing company and underwriter, as well as the evaluation and judgment of investors. From the practice of issuing in various countries, it is common that the IPO price is moderately lower than the listing price in the secondary market. This is due to the unique information asymmetry in IP0 issuance in the stock market and the uncertainty risk compensation for the issuance waiting period. However, if the difference between the IPO price and the price on the first day of listing in the secondary market is too large, the rationality of IPO pricing is not tenable. A more successful IPO should be priced at the highest price that investors can tolerate. This means that issuing enterprises can raise the maximum required funds through the stock market. If the issue pricing is too low, causing a large issue underpricing, it indicates that the pricing is unsuccessful and unreasonable. In recent years, the government has been working hard to introduce institutional investors. The purpose is to stabilize the market by introducing institutional investors, so that institutional investors can use the large amount of funds in their hands and their professional capabilities to diversify their investments. Compared with individual investors, they have more positive market effects, so the government has formulated a series of policies to create a good investment environment for institutional investors. Hasan et al. evaluated the relationship between accounting conservatism and stock underpricing in a highly asymmetric information environment. The results show that there is no significant relationship between conservatism and no price reduction in the initial and secondary stock issuance. Other research results also show that in the case of asymmetric information, there is a positive relationship between conservatism and underpricing in the initial and secondary issuance (Hasan et al., 2021). The vertical concurrent appointment of the company’s top managers is a relationship arrangement, which reflects the vertical connection between the company and the company, and the main problem in corporate governance is the relationship between the major shareholders and the management.
The research innovation contribution lies in the integration of data mining algorithm and regression equation algorithm to determine the heterogeneity of senior management team and IPO underpricing. It verifies the impact of investors in China’s secondary market on IPO underpricing. In China, the phenomenon of “underpricing” of new shares is directly caused by the enthusiasm, irrational optimism and speculation of investors. The differences of risk tolerance of senior management team members are analyzed. The results show that, in the case of expectation gap, compared with the executive team with less tenure heterogeneity, the executive team with greater tenure heterogeneity from different perspectives and different perspectives has a deeper understanding of expectation gap. And may deal with the impact of the expected gap more quickly. The more heterogeneous the tenure of the senior management team is, the more likely the enterprise is to quickly take risk change actions to cope with the impact of the expected gap. When faced with expectation gap, companies with large difference in TMT education level are more likely to take risk changes to deal with it.
This paper empirically studies the impact of executive team management ability on IPO underpricing. Section 1 is the introduction. This part mainly expounds the research background and significance of China’s stock market, and puts forward the research purpose, method and innovation of this paper. Section 2 mainly summarizes the relevant literature, summarizes the advantages and disadvantages, and puts forward the research ideas of this paper. Section 3 is the method part. Combining scientific algorithms, it focuses on vertical parallel executives, TMT heterogeneity and IPO underpricing. Section 4 is the experimental analysis. In this part, the data set is tested and the research results are analyzed. Section 5, conclusions and prospects. This part mainly reviews the main contents and results of this study, summarizes the research conclusions, and points out the direction of further research.
2 Related work
At present, most of the researches on the financing of listed companies in the low-carbon economy sector are about the financing forms of these enterprises, which are lack of systematicness. Due to the high dependence of low-carbon enterprises on capital, and China’s capital market is not strong and effective. Therefore, it is necessary for low-carbon enterprises to spend energy to improve financing efficiency in order to achieve the goal of maximizing enterprise value. From the perspective of resource dependence and upper-level theory, Li examined how TMT’s IPO restructuring (i.e., management changes before and after IPO) affected the company’s performance in the years after IPO. This point is studied from the perspective of functional complementarity of TMT, that is, the degree of different functional knowledge that the company’s TMT has mastered before and after IPO. The study believes that TMT’s functional complementarities have a positive impact on the company’s performance after IPO. In addition, the administrative discretion positively regulates this relationship through the measurement of CEO duality and TMT’s internal board membership (Li, 2022). Heo and Ryoo investigated whether the issuer’s accounting reporting attributes would affect the initial return of Korean emerging market bond issuance. The empirical results show that, generally speaking, the initial return of newly issued bonds is often negative (overpriced). More importantly, the degree of over pricing is positively related to the level of conditional accounting conservatism, which indicates that accounting conservatism alleviates information asymmetry in public debt financing (Heo and Ryoo, 2021). At this stage, the underwriter contacts investors who are willing to book new shares without price restrictions to understand their demand plans. They believe that in the pre underwriting stage of this IPO, information that is very important for underwriters to determine the issue price and maximize the overall income of the company can be obtained. The problem is how to encourage those investors who have more and more accurate information to truly reflect in the IP0 promotion stage. In order to avoid free riding, underwriters are likely to allocate shares and finally determine the issue price. Take certain measures to ensure that investors who are willing to truthfully reflect their information can obtain greater expected returns than those who are unwilling to truthfully reflect their information. One of the implicit meanings of this model is that the issue price will certainly be lower than the equilibrium price determined by the total market demand, so as to ensure that those investors who are willing to reflect the real demand information can obtain income.
When the information among investors is asymmetric, the effect of information superposition may occur. In order to avoid encountering the “winner’s curse,” the uninformed will understand the purchase intention of other investors before subscribing. When the voice of giving up buying is getting louder and louder, people with information will also doubt whether their information is true, and eventually waver. This is the so-called negative information superposition effect. Assume that emotional investors have optimistic beliefs about the future prospects of IP0. For the downward sloping demand curve of emotional investors, the purpose of the issuer is to rescue their consumer surplus as much as possible. The flooding of the stock market will reduce the stock price, so the best strategy involves controlling the total amount of stocks. The purpose is to prevent the stock price from falling. Finally, the real value of the stock will be displayed naturally and the price will return to the basic value. The IPO prospectus is an important document available to investors. It allows investors to understand the company. When the closing price of the initial public offering (IPO) is higher than its issuing price on the first trading day, IPO underpricing will occur. If investors know whether IPOs may be undervalued, they can obtain considerable returns by subscribing to those undervalued IPOs and selling shares on the first trading day (Tsui and Li, 2021). Eugene Y’s research shows that such a management and social bond formed by vertical concurrent positions is a kind of social capital for subordinate companies, and this bond can promote information exchange, mutual influence and mutual solidarity (Eugene and Horowitz, 2022). Accounting conservatism (AC) is one of the components of financial reporting, which has been widely studied by academia to determine its impact on information quality. Accounting scholars have begun to explore how AC relates to different basic functional areas of organizations. Bhutta et al. examined 408 AC related index publications. The objectives of this work include identifying the main authors, literatures and journals, analyzing the regional distribution, scale and evolution of the knowledge base, exploring the current literature and academic structure, and highlighting contemporary trends (Bhutta et al., 2021). Lee et al. examined the relationship between the heterogeneity of TMT composition and corporate performance. Tissue relaxation is regarded as a regulatory variable affecting the above mediation relationship. Based on the CSR report data of Taiwan listed companies, we find that the heterogeneity of TMT education background and tenure has a negative impact on corporate performance, which is mediated by the greenhouse gas emission strategy (Lee et al., 2021). Ormiston et al. bridged the micro macro gap by addressing the continuous appeals from the strategic leadership, and influenced researchers to check the black box to consider the relationship between CEO characteristics and TMT emotional experience, thus affecting the company’s results. We further consider the role of a key contextual factor in this relationship: TMT heterogeneity. We predict that CEO’s personality, especially emotional stability, is positively related to TMT’s emotional tone (Ormiston et al., 2022). Li and Jones used the concept of population fault line to study the dynamics of TMT subgroups, but the impact of TMT fault line on competitive behavior and performance results has not been well proved. In order to gain a deeper understanding, we developed a model that links TMT fault line, CEO-TMT power gap, competitive behavior and enterprise performance (Li and Jones, 2019). Su et al. examined the impact of TMT participation in decision-making and heterogeneity on management innovation. The research found that TMT participation in decision-making and heterogeneous individuals jointly promoted management innovation. In addition, the influence of TMT participation in decision-making is positively regulated by the company’s age, while the influence of TMT heterogeneity is negatively regulated by the company’s age. This research provides insights for the top management team on the importance of management innovation, and enriches the knowledge of the antecedents of management innovation (Su et al., 2022). Singh and Gupta studied the function and educational heterogeneity of TMT. Research the relationship between TMT quality and IPO listing date performance through the funds raised (Singh and Gupta, 2018). Yang et al. used the institutional theory for reference to explore the relationship between Chinese family participation, government relations and IPO underpricing. Compared with previous literature, we found that IPO underpricing of Chinese family firms tends to be lower than that of non-family firms. In addition, we found that the political relationship of family members enhanced the negative relationship between family participation and IPO underpricing. In contrast, state ownership alleviates these relationships (Yang et al., 2020). There are competing theoretical explanations and conflicting empirical evidence for the phenomenon of IPO underpricing of family firms. Kotlar et al. proposed a behavioral agent model with aversion to the loss realization logic to explain how the decision-making framework and preferences of household owners change during the IPO process, which depends on the initial loss of the current SEW and the new expectations of the future SEW (Kotlar et al., 2018).
The above-mentioned scholars have told a lot about vertical concurrent executives, TMT heterogeneity and IPO underpricing, but basically they only talk about one aspect. Therefore, from the perspective of China’s stock market, this paper uses its related algorithms to describe the vertical concurrent positions of executives, TMT heterogeneity and IPO underpricing, and lay the foundation for the future financial stock market.
3 Methodology
At present, China’s traditional financial institutions generally have the phenomenon of homogeneous competition, and the innovation ability is relatively weak. As a new business, low-carbon economy related business objectively requires financial institutions to innovate business operation mode and develop new green financial instruments under the premise of risk control. Therefore, “Low carbon economy” Development also provides opportunities for relevant financial institutions to innovate and develop. As the goal of developing a low-carbon economy matures, more and more financial institutions, enterprises and even private capital are involved in the field of carbon finance. This is an accelerator for financial institutions to improve their innovation capabilities. While financial institutions can improve their profits and competitiveness through continuous innovation, high profits will also stimulate innovation of the same kind. This will form a virtuous circle, thus To promote the continuous development of low-carbon economy, financial institutions will better meet the needs of society through financial innovation.
3.1 Analysis of the influence mechanism of senior executives’ vertical concurrent jobs
The management ability of top management team is an abstract concept of supervisors. The senior management team is the strategic formulation and implementation layer of the enterprise, responsible for the organization and coordination of the whole enterprise, and has great decision-making power and control power over the enterprise management. Some variable data measuring team management ability are easy to obtain, such as relevant variable data of team composition characteristics. The management ability of the senior management team, that is, the team members rely on their own experience, knowledge, skills and resources. The ability to manage the business operation and achieve the business objectives. With Vertical concurrent appointment of executives is a vertical connection between major shareholders and the company. It can reduce the risk of a company’s stock market collapse from the following two aspects: First, on an agency issue, vertical concurrent appointments of managers can make major shareholders better monitoring of management also makes it harder for management to cover up negative information, thereby reducing the risk of a company’s stock price crashing in the future, a “surveillance effect.” Second, on the second agency issue, the vertical concurrent management of management is a vertical connection between the major shareholder and the company, which can reduce the contradiction between the major shareholder and the minor shareholder, and also reduce the major shareholder’s influence on the company. Hollowing can also reduce the cover-up of negative information about the company, thereby reducing the company’s future stock crash risk, reflecting the “less hollowing effect” on top managers.
3.1.1 Test the “supervision effect” hypothesis
Based on the hypothesis of “supervision effect”, a hypothesis based on the first agency theory is put forward, that is, the vertical concurrent appointment of the company’s top managers can enhance the company’s monitoring ability, reduce the company’s internal interests, reduce the bad information within the company, and then Reduce the risk of a company’s stock price falling. On the basis of the hypothesis of “supervision effect,” it can be concluded that when an agency problem of the company becomes more and more serious, that is, when the top management conceals self-interest such as bad information, the vertical concurrent management of the management as a means of supervision by major shareholders, its “supervision effect” will be more obvious.
3.1.2 Test the hypothesis of “less hollowing effect”
The theory of “less hollowing effect” mainly starts with the type of agency conflict. The hypothesis of “less hollowing effect” refers to a vertical relationship between the company’s top managers and the company, which allows top managers to have a certain influence on the decision-making of major shareholders, and also can affect the interests of major shareholders and the company. Bundled together, so as to avoid the loss of large shareholders hollowing out the company. If executives are concurrently held vertically, the risk of stock declines can be reduced because it can reduce the cost of hollowing out large shareholders.
If the second type of agency conflict is more serious, that is, the ability to supervise large shareholders is weak, large shareholders are likely to hollow out small shareholders, causing the stock market to plummet. If the second type of proxy conflict is milder, that is, the major shareholders can get more supervision and restraint, then the major shareholders are more likely to want to empty their shares, thereby reducing the risk of the stock price falling. That is to say, if vertical concurrent executives can reduce the risk of a company’s stock collapse, then the risk of stock price declines with vertical executive concurrent appointments is mainly concentrated in those second-tier companies with larger agency conflicts. In addition, executive support can improve the implementation of enterprise management practices by promoting employee authorization, establishing incentive mechanisms and enhancing communication between functional departments. A scientific and fair performance quantitative assessment system is needed to truly evaluate the work performance of each employee objectively and impartially, so that each assessment, reward and punishment can be based on, and provide a basis for further staff reduction and efficiency increase. The incentive mechanism of quantitative performance assessment can further enhance the incentive function of internal distribution, and adapt to the needs of modern enterprise downsizing and efficiency enhancement. At the same time, the results of quantitative performance appraisal are not only reflected in material distribution, but also in non-material distribution. Such as training opportunities, honors, promotion opportunities, laid-off diversion, etc. In order to give more effective play to the incentive role of quantitative performance assessment and stimulate the ability of every employee, the enterprise is full of vitality and vitality.
Low carbon procurement corresponds to the enterprise’s low carbon strategy, aiming to meet the low carbon demand of products. The implementation of low-carbon procurement must fully consider the requirements of manufacturing and R&D departments. The low carbon attitude of senior executives is conducive to the communication and collaboration between multi-functional departments, and can ensure the effective implementation of low-carbon procurement. The low carbon attitude of senior executives makes the requirements for low carbon management clearer, and will strengthen the sharing of knowledge and technology related to low carbon management with suppliers.
The vertical concurrent role of senior executives will enhance the tax avoidance motivation of enterprises. According to the tunneling theory of large shareholders, the vertical concurrent role of senior executives improves the control power of large shareholders, provides convenience for large shareholders to seize or transfer enterprise resources, and causes the loss of enterprise cash resources. Tax avoidance by enterprises can directly save tax payment and increase the disposable cash flow of enterprises. The vertical concurrent role of senior executives will expand the tax avoidance space of enterprises. On the one hand, the vertical concurrent role of senior executives has aggravated the agency problem and the degree of information asymmetry, providing opportunities for tax avoidance activities of enterprises; On the other hand, the vertical concurrent tenure of senior executives has also improved the ability of management to avoid taxes, making it more difficult to supervise them.
3.2 Theoretical analysis of TMT
3.2.1 The regulatory role of TMT age heterogeneity
The experiences of peers are often the same, and this shapes their perceptions and beliefs. But young managers are more likely to make risky decisions because “trying out new, unprecedented strategies” can help them build their authority and reputation, which in turn can advance their careers. Older managers tend to avoid risky decisions for the following reasons: first, they have a strong ability to protect their financial and job security; while older managers often lack the analysis and processing of information to adapt to changing circumstances. Therefore, the age difference of TMT also increases when making risky decisions.
In the case of differences in expectations, although TMT has a large age heterogeneity and can help avoid extreme risk aversion and extreme risk appetite, the multiple perspectives and perspectives it provides can also help TMT better understand expectations difference. However, since TMT members vary widely in their risk tolerance, TMT can be highly divided in responding to expectations differences, making it difficult for TMT to reach consensus, leading companies to adopt risky behavioral changes in response to expectations difference. Generally speaking, the greater the environmental heterogeneity, the higher the complexity of the system. Therefore, it is a commonly adopted control method to reduce the impact of environmental heterogeneity on the system by improving the system’s environmental adaptability and response speed to changes in environmental conditions. In the project, the project manager uses available resources to balance the factors that restrict each other.
3.2.2 Moderating role of TMT tenure heterogeneity
Tenure is the length of time that a specific individual works in a specific enterprise, and it represents the accumulation of individual professional and organizational-related knowledge. TMT members with shorter tenures bring different perspectives and different logics to explain events. Therefore, when tenure heterogeneity is large, TMT is more likely to see the world in different ways, which helps TMT to deeply dissect a specific problem or objective phenomenon, and ultimately have a positive impact on the enterprise.
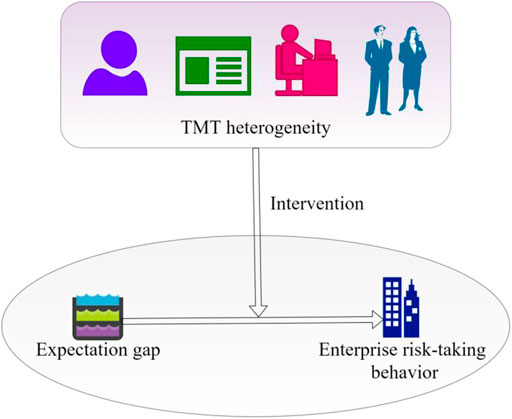
The enterprise will change its innovation behavior under the condition of expectation gap. Specifically, enterprises will increase their R&D intensity. Considering that the change actions taken by enterprises to solve performance problems are more or less risky. The expectation gap is positively increasing the possibility of enterprise’s risk taking change behavior. In the expectation gap situation, compared with TMT with less tenure heterogeneity, TMT with different perspectives and diverse viewpoints with large tenure heterogeneity have a deeper understanding of the expectation gap and may respond more quickly to the shock of the expectation gap. The greater the heterogeneity of TMT tenure, the more likely firms are to take risky change behaviors quickly in response to the shock of the expectation gap.
3.2.3 The moderating effect of TMT educational level heterogeneity
The heterogeneity of TMT education is manifested by the heterogeneity of TMT educational background and educational level. Although everyone in TMT is highly educated, this does not necessarily bring competitive advantages to the company. The reason is that the same cognitive structure and mind map make it impossible for TMT to conduct business search in an innovative way, thus causing TMT to fall into a state of “groupthink”. In sharp contrast, the diversity of TMT in terms of cognitive perspectives, information sources, and capabilities enables TMT to scan the business environment in an all-round way and formulate innovative solutions.
In the situation of expectation gap, TMT with large educational level heterogeneity can effectively avoid “groupthink,” and can understand and deeply interpret the expectation gap from multiple cognitive perspectives, which helps TMT realize the reflection behind the expectation gap, which in turn increases the possibility of companies implementing change-response behaviors under the condition of expectations gap. This means that TMT with greater educational level heterogeneity will have a relatively higher propensity to engage in risk-taking activities. To sum up, it can be speculated that when faced with a gap in expectations, companies with greater heterogeneity in TMT education levels are more likely to respond by taking risky changes.
3.2.4 Moderating role of TMT functional background heterogeneity
The functional background has a great influence on the cognitive basis of managers, and its inherent meaning is: sensitivity to specific stimuli, priority awareness of opportunities, interpretation of tasks, discussion of tasks, and promotion of the company’s competitiveness. preference. Heterogeneity in functional context can capture managers’ skills and available network resources, while greater heterogeneity in functional context can lead to skills, abilities, open-mindedness, broader networks, and greater capacity for complex problems. Provide creative solutions.
In the expectation gap situation, although the large functional background heterogeneity promotes TMT understanding of the expectation gap, there are serious differences in the risky change behaviors that TMT members with different functional backgrounds may take in response to the expectation gap. This kind of disagreement hinders the cohesion and effective decision-making of the TMT, which makes it difficult for the TMT to reach a consensus on which risky change behaviors to take, and ultimately reduces the possibility of enterprises adopting risky changes to deal with the gap in expectations.
The theoretical test model of this paper is shown in Figure 1.
The difference in tenure and age hinders the communication between team members and the effective allocation of resources, which limits the growth of the enterprise. Therefore, it is better to choose members with small differences in age and tenure, so that everyone can have discussions at the same level. At the same time, communication between members is more smooth, reducing communication costs. Teams with highly heterogeneous professional backgrounds can obtain more external resources, diversified skills and practical theoretical knowledge. Problems can be examined and analyzed from various perspectives to effectively improve the quality of decision-making. Gender heterogeneity has a significant positive correlation with corporate performance, and coordinating gender differences in teams can not only improve team efficiency. It is also conducive to the male and female management to give full play to their talents. Team building cannot be separated from an equal and free corporate culture.
3.3 Theories related to IPO underpricing
3.3.1 Theoretical model of IPO pricing
The discounted earnings model is used to estimate the market value of a business, which is discounted based on the future cash flow of the business and the future value of the business. Due to the different assumptions about the company’s future cash flow, the earnings discount model can be subdivided into a cash flow constant model, a stable growth model and a multi-stage growth model.
① Cash flow constant model: in this model, it is assumed that the cash flow of some enterprises is very stable and will not change over time. It is
If it is assumed that the company can operate for an unlimited number of periods and generate constant income cash flow stably every year, it is shown in Eq. 2:
② Stable growth model: in the stable growth model, it is considered that the future cash flow of the enterprise is
③ Multi-stage growth model: in many cases, the company’s cash flow is not as simple as the above two models assume, neither static nor changing at a steady growth rate. A model that meets the assumption of this simple case can be expressed by Eq. 4:
Selecting low carbon suppliers is the simplest way to achieve low carbon emissions in the supplier sector. However, large-scale supplier replacement may affect the flexibility of the enterprise, and the cost, quality, innovation and other objectives of the enterprise may be adversely affected. Work with suppliers to reduce carbon emissions as a better option. Low carbon collaboration with suppliers mainly refers to the design of low carbon management behavior. Enterprises directly participate in the carbon management of suppliers. Reflect the high degree of vertical integration between enterprises and suppliers, help to improve the utilization rate of new low-carbon technologies of both sides, and enhance the confidence of enterprises in low-carbon investment. Therefore, low carbon collaboration with suppliers will help enterprises implement low carbon procurement. Discounted profit models are theoretically the most accurate for valuing a business if an accurate forecast of the company’s future cash flows can be made. However, most of the companies financing in the capital market are in the early stage of development or growth stage, there are huge risks and potential growth space, so it is difficult to accurately predict the company’s future cash flow.
3.3.2 Price-earnings ratio pricing model
The price-earnings ratio pricing model is actually a way of estimating the value of a company by comparing financial data. Commonly used financial indicators include price-to-book ratio, EBIT multiple, sales revenue multiple, and customer number multiple. Among the many financial sources, the most common method to use the price-earnings ratio as a way to assess the value of a new stock is a public company. When using the price-earnings ratio to evaluate the market value of a new stock, the price-earnings ratio of the listed company must be valued first, and then the market value of the listed company must be estimated by multiplying the estimated price-earnings ratio by the expected earnings of the listed company. When using the financial data comparison method to estimate the intrinsic value of new shares, the financial data often used are shown in Table 1.
3.3.3 IPO offering mechanism
To study and analyze IPO issues, it is also necessary to introduce concepts such as IPO offering mechanism and its evolution at home and abroad, especially in China. IPO offering mechanism has always been considered an important factor affecting IPO underpricing.
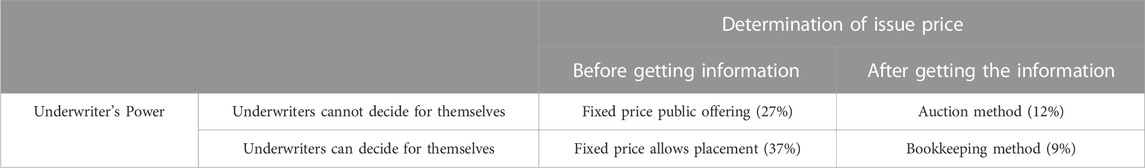
The IPO offering mechanism is usually a transaction mechanism for selling shares to investors, which includes the whole process of IPO pricing, issuance and sale to investors. Chemmanur et al. analyzed the relationship between venture capital (VC) support and the quality of senior management team (TMT) during the initial public offering (IPO) of the company, and the impact of VC support and TMT quality on its post IPO business performance growth and IPO company valuation, using the manually collected data from a large number of start-up company listing samples (Chemmanur et al., 2021). Ichikohji et al. investigated how the performance of start-up companies in the period before the initial public offering (IPO) was affected by the macro environment. The study found that the average time from entrepreneurship to IPO is relatively long for companies operating in a favorable economic environment. This may be because the favorable economic environment and improved business conditions have stimulated startups that have been taking a wait-and-see attitude (Ichikohji et al., 2022). Its purpose is to avoid information asymmetry in the IPO market, ensure the information disclosure of IPO issuers, and effectively reduce the underpricing rate. There are three widely used IPO offering mechanisms, as shown in Table 2.
Generally speaking, the fixed price method does not price through the market mechanism, lacks an effective price discovery process, and the subjective judgment ability is in the dominant position, but the procedure is simple and can save the cost of issuance. The general initial income levels of the above three pricing mechanisms are shown in Table 3.
3.4 Data mining
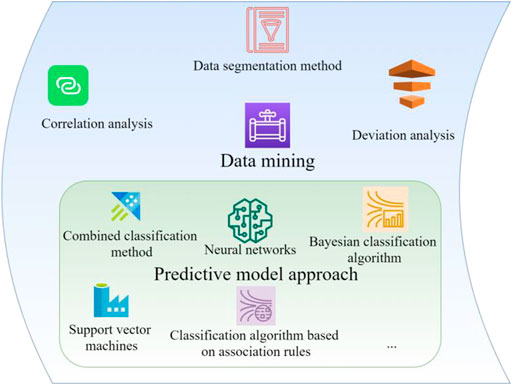
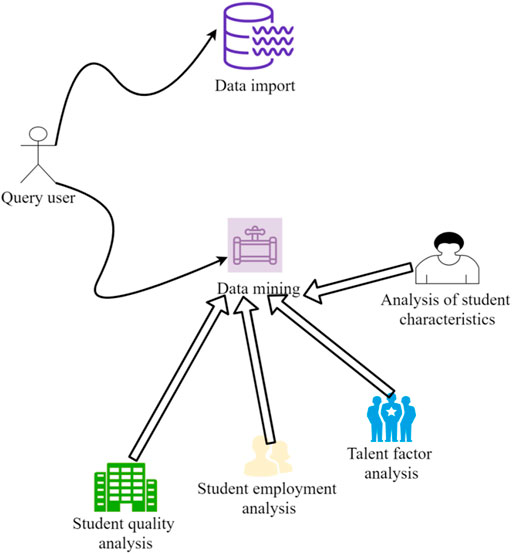
For the collection of Chinese stock market data, data mining technology needs to be used. The data mining method is shown in Figure 2.
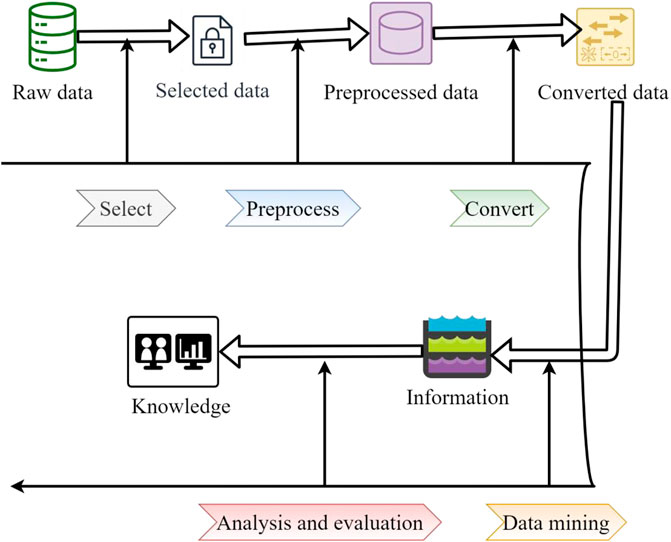
The basic process of data mining is shown in Figure 3. The system use case diagram is shown in Figure 4. The steps in the process are described as follows.
(1) Preparatory stage: This stage includes defining problems, understanding objects, collecting data, etc., collecting internal and external data related to enterprise objects, and filtering out data suitable for data mining. It is necessary to have a clear understanding and clear purpose of the problem to be solved, which is of great help to the subsequent knowledge evaluation and analysis. And this step is also the most time-consuming, accounting for about half of the entire data mining.
(2) Preprocessing: including data cleaning, compression, transformation, etc. Investigate the quality of the data in order to prepare it for further analysis and determine the type of mining operations.
(3) Data mining: Data mining includes the design and modeling of algorithms. In data mining, how to construct an analytical model suitable for mining algorithms is crucial to the success or failure of data mining.
(4) Follow-up work: This stage includes interpreting, outputting, evaluating, analyzing and using the results, and interpreting and evaluating the results. The analysis methods it adopts are generally based on data mining operations, and often use visualization techniques. Data visualization is a scientific and technological research on the visual representation of data. The visual representation of this data is defined as information extracted in a summary form, including various attributes and variables of corresponding information units. The process of representing the data in a large dataset in the form of graphics and images, and using data analysis and development tools to discover the unknown information therein. Compared with special technical methods such as stereo modeling, data visualization covers a much wider range of technical methods. The data visualization in this paper is displayed by understanding the line graph of the trend program.
When designing normalized database logic, appropriate rules for breaking normalization should also be considered. The so-called data model optimization is to determine the dependencies between data and eliminate redundant links in the relational model. In research, it can be further studied by algorithms, as shown in Eqs 5–8.
Therefore, the corresponding algorithm formulas are proposed according to the properties as shown in Eqs. 9, 10.
3.5 Model design
Using the regression equation, as shown in Eq. 11.
1) Negative return skewness coefficient NCSKEW, as shown in Eq. 12.
2) The upper and lower volatility ratio DUVOL of yield, as shown in Eq. 13.
In the part of heterogeneity analysis of institutional investors, according to their shareholding characteristics, that is, whether they can show the stability of time and industry dimension in the shareholding of relevant listed companies, dummy variables are set according to the heterogeneity, and by comparing the current year’s shareholding ratio with The ratio of the standard deviation of the shareholding ratio in the previous 3 years is compared with the median of the industry in the current year. If it exceeds the median, the value is 1, representing a stable type; if it is less than the median, it is 0, representing a transaction-oriented institutional investor, as shown in the Eq. 14 shown.
The structure of the securities market is undergoing significant changes, that is, from the past individual investors as the main body to institutional investors as the main body. The fund has fallen into the risk of decentralized investment, and the structure has changed. Therefore, the mainstream operation behavior of institutional investors has undergone significant changes. As one of the largest institutional investors in the market, the shares held by funds have changed from relatively centralized to relatively decentralized. The reduction of shareholding concentration indicates that the funds are not more concentrated in one or several stocks than in the securities market. Instead, it adopts a decentralized strategy to invest funds evenly or relatively evenly in each fund portfolio. This can also be seen from the following analysis of shareholding quantity.
The reconstructed illiquidity index, Amihud, is used as an index to measure the stock liquidity risk in this paper, and Eq. 15 is obtained.
4 Result analysis and discussion
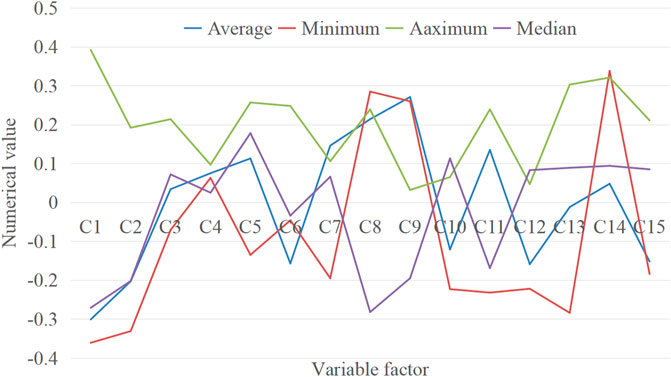
This paper collects IPO underpricing, TMT, senior executives’ vertical part-time jobs and other relevant data from IPO prospectuses of listed companies in China’s A-share market and other databases. The sample is composed of 550 companies listed in China’s A-share market from 2011 to 2019, using a stepwise linear regression method with appropriate control variables. The business model of low-carbon industry development is relatively new and needs a large amount of funds to support it. It is necessary to vigorously explore various financing channels and ways. The government should encourage and support the listed companies on the main board, small and medium-sized board, GEM and science and technology innovation board to actively carry out low-carbon business, develop low-carbon economy and provide strong capital support. The government can also encourage companies to go public and issue bonds to carry out low-carbon business by lowering the listing standards and bond issuance standards. At the same time, energy conservation and emission reduction enterprises can issue corporate bonds, medium and long-term bills and short-term financing bonds to obtain financial support from the bond market. Strong financial support can expand the scale of the carbon financial market. Stata15.1 software was used to descriptive statistics of the samples, followed by the mean, minimum, maximum and median of the research variables and control variables in this paper, and the overall distribution of the variables was observed, as shown in Figure 5.
It can be seen from Figure 5 that the mean values of NCSKEW (C1) and DUVOL (C2) are −0.301 and −0.203, respectively, which are close to the values of the descriptive statistics studied. The dependent variable data in this paper have certain reliability. The minimum value of NCSKEW is −0.361 and the maximum value is 0.392, indicating that the degree of dispersion of the crash risk of different stocks is relatively large. Another indicator DUVOL (C3) also has the same situation, which also shows that this paper studies its influencing factors. necessity. Regarding the liquidity risk indicator Amihud (C4), the minimum value is 0.063 and the maximum value is 0.097, indicating that the scale of Chinese listed companies has a large difference.
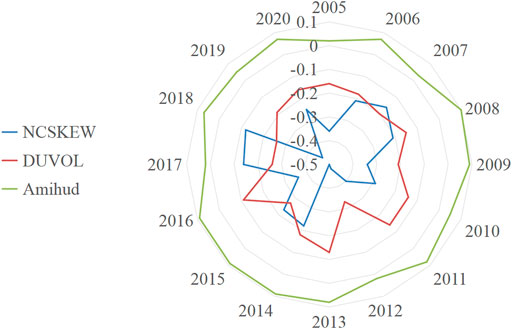
It can be seen from Figure 6 that the average value of NCSKKEW and DUVOL has a relatively large fluctuation range, reaching the lowest point in 2015 and 2012, indicating that the probability of a relatively stable crash risk in the stock market is small. Subsequently, the risk of stock crashes in 2017 and 2018 increased sharply, and the Shenzhen and Shanghai indexes fell by more than 24% in 2018. China’s stock market has been hit hard by the 18-year-old Sino-US trade war, and at the same time, a rise in the illiquidity factor value means a drop in stock liquidity. In 2019, as the impact of the trade dispute dissipated and the domestic economy recovered, the risk of a stock market price crash and the resulting volatility in liquidity.
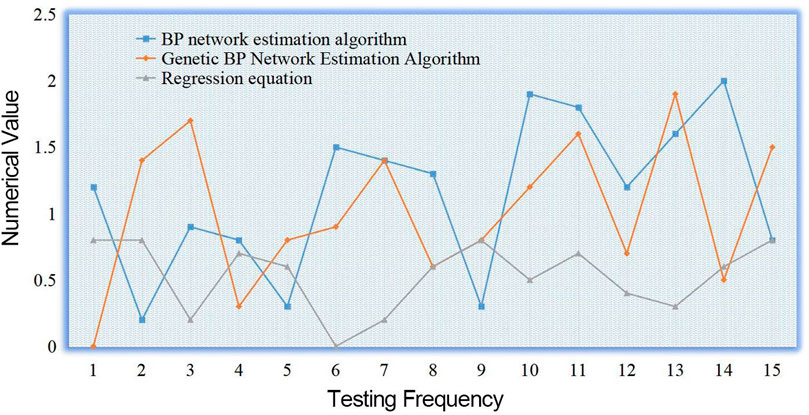
By constructing the function of the key variable system and using the regression equation, the dynamic search of the optimal evaluation scheme is carried out under the premise of dimension direction and multi-objective constraints. It can be seen from Figure 7 that the overall fluctuation of the regression equation is relatively minimum, and the error value is basically within 1, indicating that the numerical error effect of this method is the best. BP network estimation algorithm and genetic BP network estimation algorithm have the highest error fluctuation and data sparsity. Therefore, the two evaluation schemes are different from the regression equation.
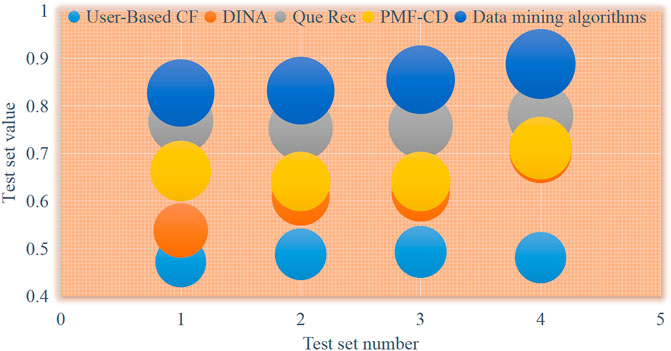
In the experiment process, in order to observe different data sparse degrees of applying different algorithms and observe their effects, this paper selects 70%, 50%, 30%, and 10% from all data sets as test data sets, and the rest are used as training data sets. That is, when 70% of the data is randomly selected as the test data, it means that the remaining 30% is used as the training set for the test set data, and the same is true for 50%, 30%, and 10%. In addition, within the range of the difficulty value of 0.6, the stock market resources are divided into simple stock market resources and complex stock market resources, and a comparative study of the recommendation effects of different types of stock market resources is carried out, as shown in Figures 8, 9 shown.
It can be seen from Figures 8, 9 that with the continuous reduction of the test set ratio, that is, the continuous increase of the training set ratio, the recommendation accuracy of the data mining algorithm in the simple stock market resources and the complex stock market resources is generally better than other methods. Four algorithms. Specifically, when recommending simple stock market resources, the P1 value is 8.6% higher than the other four algorithms as a whole, and can reach 0.888 when the test set is 10%; when recommending complex stock market resources, the P1 value is higher than the other four algorithms. These algorithms have an average improvement of 5.6%, reaching 0.958 at 10% in the test set. The above results show that the data mining algorithm is effective in increasing the recommendation accuracy and improving the recommendation results, ensuring a higher recommendation accuracy.
5 Conclusion
This paper confirms that there is a positive relationship between the age heterogeneity of senior management team and innovation output performance. The career background heterogeneity of senior management team tenure heterogeneity has a positive relationship with innovation process performance. There is a weak positive correlation between the heterogeneity of senior management team’s professional background and innovation output performance. The age heterogeneity, occupational background heterogeneity, gender heterogeneity, professional background heterogeneity and tenure heterogeneity of senior executives in high-tech enterprises have a stronger impact on enterprise innovation performance. The results verify the impact of investors in China’s secondary market on IPO underpricing. In China, the enthusiasm, irrational optimism and speculation of investors directly led to the phenomenon of “underpricing” of new shares. The greater the power of senior executives, that is, their vertical part-time positions will have a greater impact on the risk of future stock collapse of the company. The management ability of the senior management team is positively related to the market valuation of the enterprise. Excellent managers enhance the value of the enterprise. The management ability of the top management team has a demonstrative effect on the enterprise value, and a good management team can act as the value signal of the enterprise. Transfer the real value of the enterprise to outsiders, and reduce the degree of information asymmetry of the enterprise in the stock market, thus affecting the valuation of investors and reducing IPO underpricing. However, in reality, there are also many different performance feedback. When faced with different performance feedback, how the heterogeneous TMT will explain, and what kind of risk changes or what kind of behavioral risk changes need to be further explored in future research.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
XZ performed methodology and validation, GF made the formal analysis and data curation, YR wrote the original draft.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Bhutta, U., Martins, J. N., Mata, M. N., Raza, A., Dantas, R. M., Correia, A. B., et al. (2021). Intellectual structure and evolution of accounting conservatism research: Past trends and future research suggestions. Int. J. Financial Stud. 9 (3), 35. doi:10.3390/ijfs9030035
Brunnermeier, M. K., Sockin, M., and Xiong, W. (2022). China’s model of managing the financial system. Rev. Econ. Stud. 89 (6), 3115–3153. doi:10.1093/restud/rdab098
Chemmanur, T. J., Gupta, M., Simonyan, K., and Tehranian, H. (2021). The relationship between venture capital backing and the top management team quality of firms going public and implications for initial public offerings. J. Bus. Ventur. 36 (6), 106148. doi:10.1016/j.jbusvent.2021.106148
Eugene, Y., and Horowitz, J. M. (2022). The role of the PERT in the management and therapeutic decision-making in pulmonary embolism. Eur. Heart J. Acute Cardiovasc. Care 15 (3), 131–137.
Hasan, H. F., Khalbas, H. N., and Kadhim, S. C. (2021). Accounting conservatism and stock underpricing in high information asymmetry setting. Industrial Eng. Manag. Syst. 20 (4), 756–768. doi:10.7232/iems.2021.20.4.756
Heo, K., and Ryoo, S. (2021). The effect of accounting conservatism on the pricing of newly issued bonds: Evidence from korea. Acad. Account. Financial Stud. J. 25 (1), 1–13.
Ichikohji, T., Nakano, K., and Ogami, M. (2022). Hot market (Abenomics) impact on the time to IPO. Ann. Bus. Adm. Sci. 21 (2), 47–60. doi:10.7880/abas.0220125a
Kotlar, J., Signori, A., De Massis, A., and Vismara, S. (2018). Financial wealth, socioemotional wealth, and IPO underpricing in family firms: A two-stage gamble model. Acad. Manag. J. 61 (3), 1073–1099. doi:10.5465/amj.2016.0256
Lee, T., Liu, W. T., and Yu, J. X. (2021). Does TMT composition matter to environmental policy and firm performance? The role of organizational slack. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 28 (1), 196–213. doi:10.1002/csr.2042
Li, J. (2022). TMT functional complementarity and post-IPO performance: Evidence from the US biotechnology industry. Long. Range Plan. 55 (6), 102178. doi:10.1016/j.lrp.2021.102178
Li, M., and Jones, C. D. (2019). The effects of TMT faultlines and CEO-TMT power disparity on competitive behavior and firm performance. Group and Organ. Manag. 44 (5), 874–914. doi:10.1177/1059601118813790
Liu, Y., Cheng, P., OuYang, Z., and Wang, A. (2020). Information asymmetry and investor valuations of initial public offerings: Two dimensions of organizational reputation as stock market signals. Manag. Organ. Rev. 16 (4), 945–964. doi:10.1017/mor.2019.28
Ormiston, M. E., Wong, E. M., and Ha, J. (2022). The role of CEO emotional stability and team heterogeneity in shaping the top management team affective tone and firm performance relationship. Leadersh. Q. 33 (3), 101543. doi:10.1016/j.leaqua.2021.101543
Qi, S. Z., Zhou, C. B., Li, K., and Tang, S. Y. (2021). Influence of a pilot carbon trading policy on enterprises’ low-carbon innovation in China. Clim. Policy 21 (3), 318–336. doi:10.1080/14693062.2020.1864268
Singh, B., and Gupta, K. (2018). Relationship between management quality certification and IPO underpricing: Evidence from India. J. Entrepreneursh. Manag. 7 (3), 1.
Sreenu, N., Pradhan, A. K., Xuan, V. V., and Naik, B. K. R. (2022). Impact of accounting conservatism on IPO under-pricing: Evidence from India. Cogent Econ. Finance 10 (1), 2132641. doi:10.1080/23322039.2022.2132641
Su, Z., Chen, J., Guo, H., and Wang, D. (2022). Top management team’s participative decision-making, heterogeneity, and management innovation: An information processing perspective. Asia Pac. J. Manag. 39 (1), 149–171. doi:10.1007/s10490-021-09752-2
Tsui, C. S. K., and Li, K. C. K. (2021). IPO underpricing and prospectus readability: A machine learning approach. J. Appl. Bus. Econ. 23 (7), 151–159.
Wang, H., He, W., and Yang, Y. (2022). Is heterogeneity better? The impact of top management team characteristics on enterprise innovation performance. Behav. Sci. 12 (6), 164. doi:10.3390/bs12060164
Keywords: vertical concurrent executives, TMT heterogeneity, IPO underpricing, low carbon economy, China’s stock market
Citation: Zhou X, Feng G and Ren Y (2023) Analysis of TMT heterogeneity and IPO underpricing of listed companies in the low carbon economy sector: Evidence from China’s stock market. Front. Energy Res. 11:1119738. doi: 10.3389/fenrg.2023.1119738
Received: 09 December 2022; Accepted: 23 January 2023;
Published: 03 February 2023.
Edited by:
Wen-Tsao Pan, Hwa Hsia University of Technology, TaiwanReviewed by:
XiaoRan Sun, Hebei Finance University, ChinaZhengmin Li, Wuhan University, China
Zhongfang Tu, Hainan Normal University, China
Copyright © 2023 Zhou, Feng and Ren. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Guan Feng, MjAxNTAyMDEwMTdAY3F1LmVkdS5jbg==
 Xiaohua Zhou1
Xiaohua Zhou1 Guan Feng
Guan Feng