- 1Department of Biomedical Engineering and Chemical Engineering, University of Texas at San Antonio, San Antonio, TX, United States
- 2Department of Chemical Engineering, University of Petroleum and Energy Studies, Dehradun, India
- 3NASA MIRO Center for Advanced Measurements in Extreme Environments (CAMEE), University of Texas at San Antonio, San Antonio, TX, United States
- 4Texas Sustainability Research Institute (TSERI), University of Texas at San Antonio, San Antonio, TX, United States
Market-driven deployment of inexpensive (but intermittent) renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar, in the electric power grid necessitates grid-stabilization through energy storage systems Redox flow batteries (RFBs), with their rated power and energy decoupled (resulting in a sub-linear scaling of cost), are an inexpensive solution for the efficient electrochemical storage of large amounts of electrical energy. Titanium-based RFBs, first developed by NASA in the 1970s, are an interesting albeit less examined chemistry and are the focus of the present review. Ti, constituting 0.6% of the Earth’s crust and an ingredient in inexpensive white paints, is amongst the few elements (V and Mn being some others) which exhibit multiple soluble oxidation states in aqueous electrolytes. Further, the very high (approaching 10 M) solubility of Ti in low pH solutions suggests the possibility of developing exceptionally high energy density aqueous Redox Flow Batteries systems. With these advantages in mind, we present the state-of the-art in Ti-RFBs with a focus on Ti/Mn, Ti/Fe and Ti/Ce couples and systems that use Ti as an additive (such as Ti/V/Mn). The inherent advantages of inexpensive Ti actives and relatively high energy density is contrasted with potential side-reactions resulting in reduced energy efficiency. Technological pathways are presented with a view to overcoming critical bottlenecks and a vision is presented for the future development of Ti-RFBs.
1 Introduction
The rapid, market-driven deployment of economical but intermittent renewable energy sources such as solar and wind necessitates the integration of reliable energy storage solutions with the electric grid to ensure grid stability and reliability. Amongst various energy storage technologies redox flow batteries (RFBs) are an economical solution at scale due to their characteristic decoupling of energy and power that ensures sublinear scaling of cost (Chen et al., 2009; Zhao et al., 2015). A plethora of possible RFBs have been investigated and proposed in the literature, such as, Fe-X (X = Cr, Mn, Fe, Zn) (Fedkiw and Watts, 1984; Skyllas-Kazacos et al., 2011; Gong et al., 2016; Selverston et al., 2017; Archana et al., 2020; Zhen et al., 2020), V-X (X = Mn, Ce, Br, V) (Chen et al., 2009; Prifti et al., 2012; Cunha et al., 2015; Zhao et al., 2015; Sankarasubramanian et al., 2019; Reynard et al., 2020; Raja et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2021) and Zn-X (X = Ce, Br, Mn, V) (Chen et al., 2009; Leung et al., 2011; Dewage et al., 2015; Zhao et al., 2015; Jiang et al., 2018; Ulaganathan et al., 2019; Naresh et al., 2021) RFBs. Critically, the translation of these RFBs to the market hinges on numerous factors, namely - 1) cell potential, 2) energy density (a function of salt solubility in the electrolyte), 3) chemical and electrochemical stability of the cell components, and finally (and possibly most importantly) 4) availability of the redox active species at low marginal cost and at scale. The energy storage cost of RFBs hinges on the cost of the electrolyte actives and their degradation and loss during operation. The loss of electrolyte due to crossover results in poor coulombic efficiency at the system level and hinders economical operation. The crossover of electrolyte species is largely determined by the nature of the separator employed. Three classes of separators are typically encountered in RFBs i.e., cation exchange membrane (CEM), anion exchange membrane (AEM), and porous membrane (PM) (Varcoe et al., 2014; Barry et al., 2021). The two classes of ion exchange membranes operate on the principle of charge-based repulsion and hence exclusion of redox active species. Selectivity is conferred by the nature of the charged species attached to the separator backbone and density of these species. Porous separators, on the other hand, rely on size-based exclusion of redox active species. Here, ionic species and chemical species in solution (irrespective of charge) are prevented from crossing over on the basis of their size relative to the pores across the separator. CEMs (typically Nafion®) are relatively expensive and exhibit high ionic conductivity. Given that most RFBs utilize cationic redox species, the use of CEMs in these systems results in cation cross-over and hence a drastic reduction in capacity over time (Gubler, 2019). This makes CEMs suitable only for systems employing catholytes and anolytes consisting of different oxidation states of the same chemical species (e.g., V2+/V3+ and V4+/V5+ in all-V RFBs). AEMs, on the other hand, mitigate cation crossover but typically exhibit lower ionic conductivity and chemical stability compared to CEMs (Barry et al., 2021). PMs allow the cross-over of the ions that have smaller diameter than the pore size of the separator irrespective of the nature of the charge they carry and hence show poor ion selectivity (Lu et al., 2017). All separators may require mechanical rebalancing to adjust the osmotic pressure (Bhattarai et al., 2019) and chemical rebalancing to maintain electrolyte purity (Wu et al., 1983; Fedkiw and Watts, 1984).
All-V RFBs are the farthest along the commercialization route and have been reported to operate at typical power densities of 100 mW cm−2 with cycle life of 10–15 years with 1000 cycle per year (Holland-Cunz et al., 2018). A recent study has reported small, lab-scale (4cm2 electrode area, 20 ml catholyte and anolyte) all-V RFB operating for ∼20,000 cycles at 600 mA cm−2 (>8 months) (Jiang et al., 2020). Despite concerns stemming from component degradation while operating at such current densities, the demonstration of similar cycle life (even at lower current density) at a practical, pilot scale would be a major advancement in commercializing all-V RFBs. Although the V-X family of RFBs are quite successful in terms of providing high power densities with stability, the availability of V in the earth’s crust and its susceptibility to degradation during cycling is a limiting factor for successful industrialization. On the other hand, the Ti-X (X = Fe, Mn, Ce) family of RFBs offer several advantages over the V-X systems as -
1) Ti is ca 50x as abundant as V in the Earth’s crust and is produced at ca 100x the rate of V (Figures 1A,B).
2) The market price of Ti is 1/10th that of V in the US (Figures 1A,B).
3) The half-cell potential of Ti4+/Ti3+ redox couple is 0.1 V (vs SHE) as compared to -0.26 V (vs SHE) for V3+/V2+ which makes Ti4+/Ti3+ redox couple less prone to hydrogen evolution side reactions (Figure 1C).
4) The maximum possible storage capacity of Ti-Ce RFBs would be 9.9 TWh as compared to 6.95 TWh for all-V RFBs considering all exploitable worldwide reserves of V, Ti, and Ce.
5) The Ti-X (X = Fe, Mn, Ce) RFBs also meets the DOE cost target of <100 $/kWh (Dong et al., 2015; Kaku et al., 2016; Funding opportunity announcement advanced research projects agency, 2016; Kaku et al., 2019; Sankarasubramanian et al., 2021).
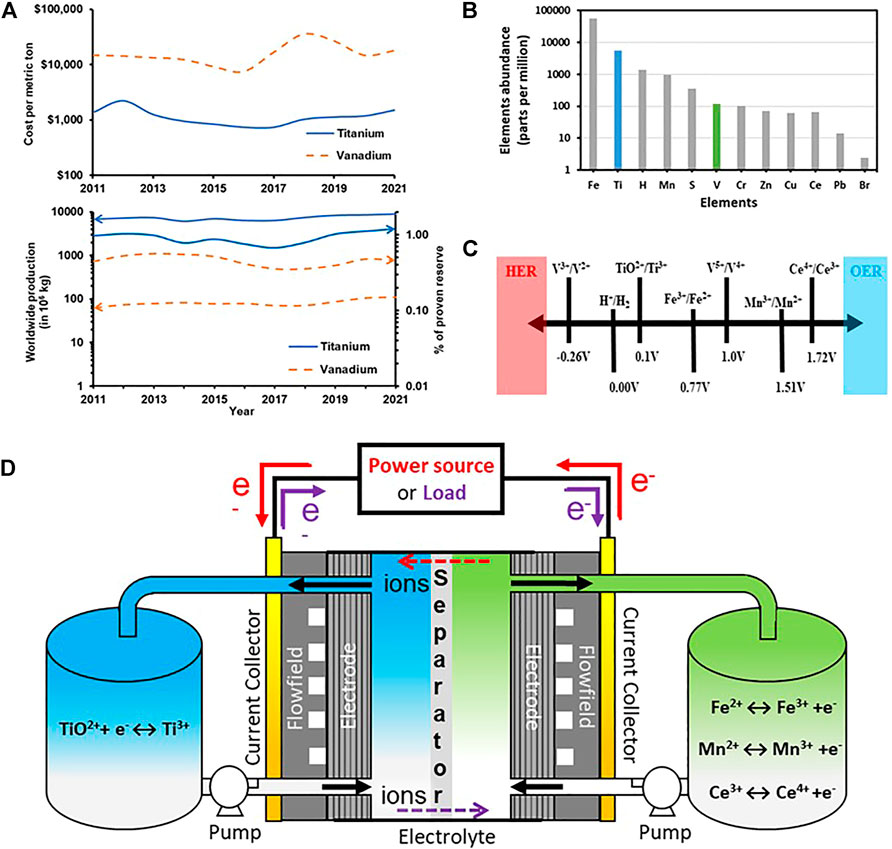
FIGURE 1. (A) Cost per metric ton, worldwide production, and proven reserves of Ti, and V; (B) Abundance of Ti in the Earth crust (C) Half-cell potentials (vs SHE); for some redox couple for possible use in RFBs; (D) Schematic diagram of Ti- X (X = Fe, Mn, Ce) RFBs.
Given these advantages, in this work we critically review the developmental state of Ti-X RFBs and chart a course for their future development.
2 The Ti-X (X = Fe, Mn, Ce) family of RFBs
A schematic representation of Ti-X RFBs is shown in Figure 1D. The anolyte is the Ti salt dissolved in an acid and the catholytes are either Fe or Mn or Ce dissolved in their appropriate acidic counterparts. As discussed in literature, the oxidation states of Ti vary from +2 to +4 and the Ti ions exist stable in the salts as Ti3+ (+3 oxidation state), and TiO2+ (+4 oxidation state) but not as Ti2+. Their stability is confined to a very narrow region i.e., ∼1 pH and lesser, as seen in the Pourbaix diagram (Pourbaix, 1966). TiOSO4 (titanium oxysulfate) and TiCl3 (titanium chloride) with Ti in +4 and +3 oxidation state are the most widely used salts for Ti-X RFBs with supporting electrolytes including H2SO4, HCl, HNO3 and H3PO4. Thus, the solvation and coordination of Ti species in the strong acidic electrolytes influences the reversibility and stability of the Ti4+/Ti3+redox couple and impacts the energy density of the Ti-X RFBs. The following section summarizes Ti solution chemistry in the context of RFBs.
2.1 Ti4+complexes in acids
Extensive literature report (Lingane and Kennedy, 1956; Miyanaga et al., 1990; Kavan et al., 1993; Cservenyák et al., 1996; Sole, 1999; Bahdad, 2020; Tsurumura et al., 2020; Choe et al., 2021) the solvation behavior of Ti4+/Ti3+ redox couple with different ligands in various acids solutions like H2SO4, HCl, HNO3 and H3PO4. The redox stability of Ti4+/Ti3+ is influenced by the formation of different reaction/intermediate complexes that appear in various acids as discussed below. Critically, we are considering only strong mineral acids in our discussion given that the Ti4+/Ti3+ redox couple is stable only in low pH (< ca pH 1.5) conditions.
2.1.1 The H2SO4 system
In case of H2SO4 solution comprising dissolved TiOSO4 salt, hereafter called the Ti-O-SO4 system, the half-cell reaction is represented by the following equation,
The Ti3+ and Ti4+ (i.e., as TiO2+) species of the redox couple co-exist in the concentrated Ti-SO4 system. Ti4+ is the most stable oxidation state of Ti. The high charge density (ratio of charge to ionic radius) of Ti4+ prevents it from forming simply hydrated [Ti(H2O)6]4+ (Miyanaga et al., 1990). Ti4+ appears as [Ti(OH)2(H2O)4]2+ in 1 M H2SO4 aqueous solutions (Bahdad, 2020) and in solutions where 0.04 < pH < 1 (Beukenkamp and Herrington, 1960; Kotsyubynsky et al., 2017), represented in short as TiO2+. These TiO2+ complexes tend to form oligomers (Figure 2A) when the oxo-oxygen of the titanyl ion is readily protonatable through hydrolysis reactions (Shepherd, 2013). The formation of oligomers is predominant when the concentration of TiO2+ is between 0.1–0.5 M, the H+ concentration between 1.0–2.5 M, and the temperature between 236–323 K (Comba and Merbach, 1987). In the presence of H+, SO42- and HSO4–ions (H2SO4 dissociation products in an aqueous solution (Choe et al., 2021)), Ti4+ forms complexes containing SO42- or HSO4– ligands exhibiting the possible structures shown in Figure 2B. The competing coordination of Ti4+ to SO42- or HSO4- depends on the strength of SO42- concentration in the electrolyte [for e.g., 3 M H2SO4 concentration results in the dominance of Ti4+ to SO42- coordination (Bahdad, 2020)]. The coordination of HSO4- with Ti4+ proceeds through a deprotonation pathway wherein H+ is accepted by a proton acceptor such as H2O to form H3O+ or Ti=O+ to form Ti-OH SO42- and a Ti4+-SO42- complex results. At higher SO42- concentrations (and higher pH values), Ti4+ is predicted to exist as either mononuclear complexes (chelating complexes) or multinuclear complexes (bridging bidentate complexes) (Kotsyubynsky et al., 2017). Mononuclear complexes are formed by the coordination of Ti4+ ion with SO42- leading to formation of [Ti(OH)2SO4(H2O)3]0 , [Ti(OH)2(SO4)2(H2O)2]2− and [Ti=O(OH)2(H2O)3]0. The multinuclear complexes are formed either due to polymerized Ti4+ complexes formed via oxygen atoms leading to -Ti-O-Ti-O- zigzag structures (Tsurumura et al., 2018) or via formation of [Ti2O2(H2O)5(OH)2SO4] (Choe et al., 2021). These Ti4+ complexes are either electrically neutral or anionic in the Ti-O-SO4 system under high pH conditions. Ti4+ tends to form multinuclear complexes (nanoscale aggregates) in solutions of high SO42- and Ti4+ concentrations which eventually results in the nucleation and precipitation to TiO2. Thus, high pH conditions (typically with high SO42- concentrations and low H+ concentration) are to be avoided when designing electrolytes for Ti RFBs.
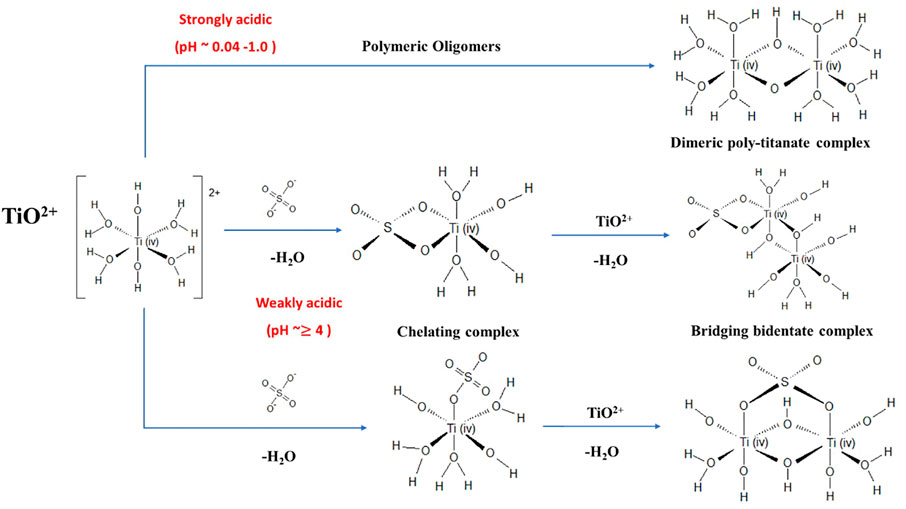
FIGURE 2. Schematic representation of various Ti4+ complexes under weakly and strongly acidic conditions.
Upon electrochemical reduction of Ti4+ to Ti3+, there occurs substantial change in the structures of Ti-ion complexes and nanoscale Ti4+ aggregates are gradually disrupted to yield mononuclear Ti3+ complexes (Tsurumura et al., 2020). The Ti3+ ion is stable at very low pH (< ca 1.5) as seen through Pourbaix diagram. In dilute (higher pH) aqueous solutions, Ti3+ usually exists in the form of [Ti(H2O)6]3+. Literature also report using EXAFS (Extended X-ray Absorption Fine Structure) analysis, that Ti-Ti bond does not exist in Ti3+ solution, and the possibility for Ti-O bond exists in Ti3+ solution (Miyanaga et al., 1990) with Ti3+ ions existing in various other forms in aqueous solutions as Ti(OH)2+, TiO+, Ti(OH)2+, and other complexes (Sole, 1999). However, with H2SO4 solution, Ti3+ react with SO42- ion to form Ti3+-SO42- complexes (Cservenyák et al., 1996).
2.1.2 The HCl system
In case of HCl solutions containing TiCl3 salt, both the H+, and Cl− ions play a significant role in the reversibility of Ti4+/Ti3+ redox couple. Ti3+ exist as a TiOH3+ complex in acidified solutions (pH 2–2.5) and, due to hydrolysis of Ti3+, Ti(OH)22+ is formed with proton liberation as shown below (Kavan et al., 1993; Lokhande et al., 2004),
Unfortunately, Ti(OH)22+ leads to the formation of TiO2 by precipitation as shown above, through an intermediate Ti(iv)oxo species which limits the reversibility of the redox couple. The Ti(iv)oxo species consist of partly dehydrated polymeric Ti(IV) hydroxide (Kavan et al., 1993), which get converted to TiO2 (Lokhande et al., 2005). The Ti4+ ions in HCl exist in the form of TiOCl+, an oxy-chloro ion which reduces to a Ti3+ chloro complex, TiCl4- as shown below,
The Ti3+/Ti4+ redox couple was found to be reversible only in >1 M HCl solution. The irreversibility observed in <1 M HCl solutions indicates the necessity of Cl− ion for the reversibility of Ti4+ and Ti3+ as shown in Eq. 4 (Lingane and Kennedy, 1956). In the presence of HCl and H2O, Ti4+ ions form unstable [Ti(OH)2(H2O)4]Cl2 which eventually results in the formation of TiO2. In the context of RFBs requiring high reversibility of the Ti4+/Ti3+ redox couple, addition of (unfortunately unstable) organic compounds with oxygen-containing functional groups, such as acetylacetone, can partially suppress the hydrolysis reaction owing to the affinity between TiO2+ and oxygen-containing functional groups (Wang et al., 1984). HCl concentrations up to 6 M have been found to mitigate the precipitation of TiO2 (Qiao et al., 2022). However, it enhances H+ concentration in the electrolyte and accelerates another undesired side reaction, namely the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER), thereby decreasing the RFB efficiency. The choice of the catholyte to be paired with the Ti anolyte can also preclude the use of HCl supporting electrolytes due to the occurrence of the chlorine evolution reaction (+1.36V vs. SHE).
2.1.3 The HNO3 system
In case of HNO3 solutions containing TiOSO4, the salt dissolves as small clusters as observed through Small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) experiments (Molina et al., 2017). The analysis of TiOSO4 dissolved in 1 M HNO3 solution, suggests that the clusters contain a dense 1.2 nm diameter core (dominated by Ti–oxo) with a dynamic shell of water, sulfate, and nitrate which also results in precipitation for any dilution below 0.25 M TiOSO4 (Molina et al., 2017). No complexation of Ti4+ was observed in dilute HNO3 solutions (0.73–2.2 mM.L−1) with 0.05 mM.L−1 ortho-titanic acid (TiH4O4) due to their weak tendency to form nitrato complexes with most metal ions (Morris et al., 1978). This is markedly different from the formation of divalent mononuclear species like [Ti(OH)2]2+ in H2SO4 solutions (Mangold et al., 2021). But, however HNO3 is not actively used as supporting electrolyte due to the reduction of NO3− leading to degraded performance during cycling in RFBs (Xie et al., 2011a).
2.1.4 The H3PO4 system
Studies with H3PO4 solutions containing Ti salts are very scarce in the literature (Lingane and Kennedy, 1956; Oldenburg et al., 2018; Mangold et al., 2021) as the solubility and stability of Ti4+ ions in these systems is a practical limitation (Lingane and Kennedy, 1956). The reversibility of Ti4+/Ti3+ redox couple and their stability was studied under different concentrations (1–10 M) of H3PO4 with 10 mM and lower concentrations of Ti4+ [as the Ti(OH)4 salt]. It was found that a 10 mM solution of Ti4+ ions in 1M H3PO4 was unstable and precipitated after 24 h but stabilized in 4M H3PO4 without any phase separation. But upon increasing the Ti4+ ion concentrations to >10 mM, the electrolyte was again unstable in 4M H3PO4 leading to precipitation. Interestingly, the reversibility of Ti4+/Ti3+ redox couple is more pronounced at 1M H3PO4 as compared to 4M H3PO4 (Shepherd, 2013). In this electrolyte system, Ti4+ is present as mononuclear (µ = 1) or polynuclear (µ > 1) free cation(s), [(TiO)µ] 2µ+ in diluted H3PO4 solutions (<0.1 mol.L−1). Ti4+ ions progressively form [(TiO)µ(H3-mPO4)δ]2µ−δm complexes as the concentration of H3PO4 is increased to >1 mol.L−1 and [(TiO)µ(H3-mPO4)δ(H3-nPO4)β]2µ−δm-βn complexes at >6 mol.L−1 H3PO4 (Mangold et al., 2021). The poor solubility and reversibility of Ti solutions in H3PO4 precludes their use in RFBs.
2.2 Performance of Ti RFBs
Given the discussion above, reports on the Ti-X family of RFBs consist predominantly of systems using H2SO4 as the supporting electrolyte due to the stability and reversibility of the Ti4+/Ti3+ redox couple at relatively high Ti concentrations (∼0.5–1.5 M). This configuration also avoids any side reactions (H2-, Cl2-, and NO2- evolution) thereby increasing the overall energy efficiency of the RFBs.
Ti - Fe RFB: Fe based RFBs (coupled with Ti or Cr) have been widely investigated by NASA in the early 1970s due to the low cost and abundant supply of Fe. These RFBs can achieve a theoretical energy density of nine Wh. L−1 (at 0.67V open circuit potential (OCP)). Cr-Fe RFBs was initially assessed for space applications and scale-up studies were conducted, but the system was not commercially developed due to several drawbacks like, low energy density of the mixed electrolyte (containing both Fe and Cr in the anolyte and catholyte), membrane fouling, the slow Cr redox kinetics requiring expensive noble metal catalysts and parasitic HER on the Cr side (Skyllas-Kazacos et al., 2011). The Ti-Fe RFBs was studied by Thaller in aqueous HCl solution (Thaller and inventor, 1976). In this system, during the charge cycle, Ti4+ (i.e., TiO2+) reduced to Ti3+ on the negative side and Fe2+ is oxidized to Fe3+ in positive side. The half-cell charge reactions of the Ti-Fe RFB are,
Initially, TiCl3 and FeCl3 were the salts used at the anolyte and catholyte respectively in the HCl supported electrolytes. This system suffered from the formation of TiO2 particles as an undesired side reaction, decreasing the overall coulombic efficiency. The maximum current density of these initial Ti-Fe RFBs with HCl supporting electrolyte was 8.16–14 mAcm−2 with a nominal cell voltage around 0.67V (Savinell et al., 1979). Recent improvements in Ti-Fe RFBs have consisted of using H2SO4 as supporting electrolyte instead of HCl and using TiOSO4 and FeSO4 salts in the anolyte and catholyte respectively. In the presence of H2SO4, the interaction between H2O and Ti4+ ions are diminished, thereby inhibiting the formation of Ti(OH)22+ and improving the stability of the electrolyte. Such as second generation Ti-Fe RFB with bismuth (Bi) catalyst at the positive electrode and a carbon felt at the negative electrode exhibited a diffusion coefficient of 19.18×10–8cm2 s−1 for Fe3+/Fe2+ and 0.36×10–8cm2 s−1 for Ti4+/Ti3+ (Qiao et al., 2022) with a rate constant of 3.828×10–4cm s−1 for Fe3+/Fe2+ and 0.203×10–4cms−1 for Ti4+/Ti3+ respectively (Qiao et al., 2022). It suggests that both the diffusion coefficient and rate constant for Fe3+/Fe2+ is higher than Ti4+/Ti3+ with the reactions of Ti redox couple being rate limited. The Ti-Fe RFBs in 3M H2SO4 were cycled at current densities as high as 120 mAcm−2 with the highest energy efficiency of 85.6% (at 40 mAcm−2). This system showed 80% discharge capacity after 1000 cycles (30 min per cycle) with a low-capacity decay of 0.193 Ah. cycle−1 (Qiao et al., 2022). CEMs like Nafion® 212, sulfonated poly (ether ketone) (SPEEK) have been used in Ti-Fe RFB. Non-fluorinated SPEEK is predominantly used as it reduces the cost for energy production from $165.79/kWh (Nafion® 212) to $88.22/kWh (SPEEK) (Qiao et al., 2022).
Ti-Mn RFB: Ti-Mn RFBs was first developed by Dong et al, (2012) where a relatively high OCP of 1.41 V was obtained (as compared to 0.67 V for Ti-Fe RFBs) resulting in superior power density (Dong et al., 2015; Kaku et al., 2016). These RFBs can achieve a theoretical energy density of 18.9 Wh. L−1. The half-cell charge redox reactions of Ti-Mn RFB are represented by the following equations.
Unfortunately, Mn3+ is highly unstable and inclined to form manganese dioxide (MnO2) via the following reaction-
The precipitated MnO2 particles start to aggregate and hinder the flow of electrolyte by blocking the pores of the membrane thereby reducing the columbic efficiency. So, it is required to reduce the formation of MnO2 particles as well as to ensure that the MnO2 particle are small enough to avoid aggregation and prevent membrane fouling (Kaku et al., 2016). Several approaches have been proposed for stabilization of Mn3+ such as by increasing the acidity, by increasing the Mn2+ concentration, or via complex formation (Davies, 1969). However, increasing Mn2+ concentration necessitates limiting the cycling of the cell to only 50% state of charge (SOC) to prevent Mn3+ disproportionation, thereby negating any advantages due to increased reactant concentration. On the other hand, the formation of Mn complexes (i.e., MnOOH) results in loss of electro-activity (Dong et al., 2015; Bahdad et al., 2021).
The disproportionation reaction and the morphology of MnO2 were significantly influenced by addition of H2SO4 solution containing TiO2+ ions (Kaku et al., 2016). TiOSO4 solutions of varying molarities was added to 1M MnSO4 and the characteristic of the composite electrolyte was studied in the context of suppressing the disproportionation of Mn3+ ions. The MnO2 aggregates were found to be > 1000 nm without adding TiOSO4 or with the addition of 0.25M TiOSO4 in MnSO4. The particles size reduced to less than 100 nm with addition of 0.5M–1M of TiOSO4 in MnSO4 (Kaku et al., 2016). The optimal composition of 1.5 M TiOSO4 in the 1 M MnSO4 electrolyte improved the performance of the Ti-Mn RFB in terms of energy density to achieve ∼11.75 Wh. L−1 (accounting for the electrolyte in both tanks) with coulombic efficiency of 99.8% and energy efficiency of 88.7%, both of which were stable over 40 cycles (Dong et al., 2015; Dong et al., 2017; Kaku et al., 2019). Unfortunately, the addition of TiOSO4 with MnSO4 also reduces the cell voltage by more than 100 mV and increases the cost of energy components (Kaku et al., 2016). An alternate approach using V5+ ions to stabilize the Mn electrolyte has also been proposed (Reynard et al., 2020). These V/Ti/Mn RFB systems will exhibit higher voltages compared to the Ti/Mn system given the lower standard electrode potential of the V3+/V2+ couple (-0.26V vs SHE). But this system is economically unattractive given the increased cost associated with the use of vanadium and thus we do not believe this is a viable future direction. Various thicknesses of Nafion® i.e., Nafion® 115, Nafion® 212, Nafion® 211 have been evaluated to investigate their impact on the performance of Ti-Mn RFBs. The energy efficiency was found to be function of separator thickness with the energy efficiency being 84%, 83%, and 81% for Nafion® 211 (25 μm), Nafion® 212 (51 μm), and Nafion® 115 (127 μm) respectively (Kaku et al., 2017).
Ti-Ce RFB: An alternative Ti based RFB which provides a higher OCP compared to, Ti-Fe and Ti-Mn RFBs, are Ti-Ce RFB. The OCP of Ti-Ce RFB is 1.61V, which results in higher operating power density at the same operating current density and higher energy density for the same electrolyte concentration compared to Ti-Fe and Ti-Mn systems (Sankarasubramanian et al., 2021). These RFBs can achieve a theoretical energy density of 19.4 Wh/L. The half-cell redox reactions of Ti-Ce RFB are represented by the following equations.
The Ce Pourbaix diagram shows that cerium ions are soluble in strong acids but forms stable, insoluble hydroxyl complexes above pH ∼7. Given the exceptionally high standard reduction potential for Ce (the highest amongst all the catholyte candidates considered here), the stability of the supporting electrolyte is a particular concern - HCl and HNO3 cannot be used due to their side reactions that produce Cl2 and NO2 respectively (Sankarasubramanian et al., 2021). The Ce4+/Ce3+ redox couple exhibits unusual solubility behavior as a function of the supporting electrolyte (acid) concentration. The solubility of both species in this redox couple decreases in inverse proportion to H2SO4 concentration and the highest concentration achieved was 0.5M Ce in 1M H2SO4 (Xie et al., 2011b). But interestingly, in CH3SO3H, the solubility of Ce3+ decreases and the solubility of the Ce4+ increases with increasing acid concentration and this results in a solubility maximum of 0.9M Ce in 4M CH3SO3H (Kreh et al., 1989; Shi et al., 1989; Sankarasubramanian et al., 2021). Thus, the energy density of this system is circumscribed by the solubility of the Ce catholyte as TiOSO4 is highly soluble in both H2SO4 and CH3SO3H (Sankarasubramanian et al., 2021). On the other hand, the Ti electrode is the rate-limit electrode (relevant for achieving higher operating current densities) as the rate constants of the Ce4+/Ce3+ couple is 3x that of the Ti4+/Ti3+ redox couple (Klingler and Kochi, 1981; Sankarasubramanian et al., 2021). Cyclic voltammetry shows the anodic to cathodic peak separation for Ti3+/Ti4+ to be 1V and 0.67V for the Ce4+/Ce3+ couple (Sankarasubramanian et al., 2021), indicating these reactions are not electrochemically reversible and suggesting high charge and discharge overpotentials (Bard and Faulkner, 2000). Nevertheless, in both H2SO4 and CH3SO3H supporting electrolytes, the Ti-Ce RFB exhibited nearly 100% coulombic efficiency with over 70% energy efficiency (charging and discharging at 100 mA/cm2) during 1300 and 700 h of diurnal cycling, respectively (Sankarasubramanian et al., 2021). These cells employed highly permselective quaternary cardo-poly ether ketone (QPEK-C) AEM separators (Yun et al., 2014; Yun et al., 2015; Yun et al., 2016) which demonstrated negligible crossover (<0.4%) over 1000 h of operation with 24 h cycle as compared to commercial CEM which suffers from drastic cation crossover and loss in capacity early in the cycling of the RFB (Sankarasubramanian et al., 2021).
3 Future Directions and Prospects
The Ti-X family of RFBs represent an interesting new direction in the development of aqueous RFB systems given their high theoretical energy density and economic competitiveness enabled by the high solubility and low cost of Ti. We anticipate the following future directions –
1) Unlocking the high energy density of the Ti electrolyte by pairing it with a stable and high solubility counter electrolyte. The long-term stability of the low pH Ti electrolytes needs to be demonstrated.
2) Catalyzing Ti4+/Ti3+ redox kinetics to overcome its nature as the rate-limiting electrode. The catalysts should be low cost to preserve the cost advantage enjoyed by the Ti electrolyte.
3) Increasing the thermal stability of the Ti electrolyte to prevent TiO2 formation by hydrolysis.
4) Using AEM and pore tailored PM instead of CEM to reduce crossover of the predominantly cationic redox active species, thereby enabling electrode decoupled RFBs. (Wang et al., 2018).
The continued development of these systems is anticipated to result in a commercially viable, high-energy density aqueous RFB that can economically be integrated into the electric grid.
Author contributions
SIUA and MS contributed equally to this manuscript. SIUA and MS prepared the first draft of the manuscript. All authors reviewed and revised the manuscript. SS conceived and supervised the project.
Funding
The authors acknowledge funding from the US Department of Energy through grant # DE-FE0032011. SS gratefully acknowledges funding through a start-up grant from the University of Texas at San Antonio.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Archana, K. S., Suresh, S., Ragupathy, P., and Ulaganathan, M. (2020). Investigations on new Fe–Mn redox couple based aqueous redox flow battery. Electrochimica Acta 345, 136245. doi:10.1016/j.electacta.2020.136245
Bahdad, A. O. O. (2020). Characterization of the electron transfer reaction mechanism of TiOSO4 and MnSO4 in sulfuric acid solution. Kansas, US: University of Kansas.
Bahdad, A. O. O., Li, Y., and Van Nguyen, T. (2021). Characterization of the electrochemical behavior of MnSO4 with and without TiOSO4 in H2SO4 solution. J. Electrochem. Soc. 168 (7), 070524. doi:10.1149/1945-7111/ac0e4e
Bard, A. J. B., and Faulkner, L. R. (2000). Electrochemical methods: Fundamentals and applications. 2 ed. New York: Wiley.
Barry, E., Burns, R., Chen, W., De Hoe, G. X., De Oca, J. M. M., de Pablo, J. J., et al. (2021). Advanced materials for energy-water systems: The central role of water/solid interfaces in adsorption, reactivity, and transport. Chem. Rev. 121 (15), 9450–9501. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.1c00069
Beukenkamp, J., and Herrington, K. D. (1960). Ion-exchange investigation of the nature of titanium(IV) in sulfuric acid and perchloric acid. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 82 (12), 3025–3031. doi:10.1021/ja01497a014
Bhattarai, A., Whitehead, A. H., Schweiss, R., Scherer, G. G., Skyllas-Kazacos, M., Wai, N., et al. (2019). Anomalous behavior of anion exchange membrane during operation of a vanadium redox flow battery. ACS Appl. Energy Mat. 2 (3), 1712–1719. doi:10.1021/acsaem.8b01816
Chen, H., Cong, T. N., Yang, W., Tan, C., Li, Y., and Ding, Y. (2009). Progress in electrical energy storage system: A critical review. Prog. Nat. Sci. 19 (3), 291–312. doi:10.1016/j.pnsc.2008.07.014
Choe, Y-K., Tsuchida, E., Tokuda, K., Otsuka, J., Saito, Y., Masuno, A., et al. (2021). First-principles molecular dynamics simulation study on Ti4+ ion in aqueous sulfuric acid. AIP Adv. 11 (3), 035224. doi:10.1063/5.0038061
Comba, P., and Merbach, A. (1987). The titanyl question revisited. Inorg. Chem. 26 (8), 1315–1323. doi:10.1021/ic00255a024
Cservenyák, I., Kelsall, G. H., and Wang, W. (1996). Reduction of TiIV species in aqueous hydrochloric and sulfuric acids II. ECE model of the behaviour in sulfate media. Electrochimica Acta 41 (4), 573–582. doi:10.1016/0013-4686(95)00344-4
Cunha, Á., Martins, J., Rodrigues, N., and Brito, F. P. (2015). Vanadium redox flow batteries: A technology review. Int. J. Energy Res. 39 (7), 889–918. doi:10.1002/er.3260
Davies, G. (1969). Some aspects of the chemistry of manganese (III) in aqueous solution. Coord. Chem. Rev. 4 (2), 199–224. doi:10.1016/s0010-8545(00)80086-7
Dewage, H. H., Wu, B., Tsoi, A., Yufit, V., Offer, G., and Brandon, N. (2015). A novel regenerative hydrogen cerium fuel cell for energy storage applications. J. Mat. Chem. A Mat. 3 (18), 9446–9450. doi:10.1039/c5ta00571j
Dong, Y., Kaku, H., Miyawaki, H., Tatsumi, R., Moriuchi, K., and Shigematsu, T. (2017). Titanium-manganese electrolyte for redox flow battery. SEI Tech. Rev. 84, 35
Dong, Y-R., Shigematsu, T., Kumamoto, T., Kubata, M., and inventors, (2012). Sumitomo electric industries, ltd., assignee. Redox flow battery. Alexandria, VA: United States Patent and Trademark Office.
Dong, Y. R., Kaku, H., Hanafusa, K., Moriuchi, K., and Shigematsu, T. (2015). A novel titanium/manganese redox flow battery. ECS Trans. 69 (18), 59–67. doi:10.1149/06918.0059ecst
Kaku, H., Yamaguchi, H., Dong, Y- R., Tatsumi, R., Miyatake, K., Moriuchi, K.et al. (2019). “A 10kW class Ti/Mn redox flow battery,” in ECS meeting abstracts (IOP Publishing).
Fedkiw, P. S., and Watts, R. W. (1984). A mathematical model for the iron/chromium redox battery. J. Electrochem. Soc. 131 (4), 701–709. doi:10.1149/1.2115676
Funding opportunity announcement advanced research projects agency (2016). Energy (arpa-E) duration addition to electricity storage (DAYS). Dep. Energy. Governmental Announcement.
Gong, K., Xu, F., Grunewald, J. B., Ma, X., Zhao, Y., Gu, S., et al. (2016). All-soluble all-iron aqueous redox-flow battery. ACS Energy Lett. 1 (1), 89–93. doi:10.1021/acsenergylett.6b00049
Gubler, L. (2019). Membranes and separators for redox flow batteries. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 18, 31–36. doi:10.1016/j.coelec.2019.08.007
Holland-Cunz, M. V., Cording, F., Friedl, J., and Stimming, U. (2018). Redox flow batteries—concepts and chemistries for cost-effective energy storage. Front. Energy 12 (2), 198–224. doi:10.1007/s11708-018-0552-4
Jiang, H. R., Sun, J., Wei, L., Wu, M. C., Shyy, W., and Zhao, T. S. (2020). A high power density and long cycle life vanadium redox flow battery. Energy Storage Mater. 24, 529–540. doi:10.1016/j.ensm.2019.07.005
Jiang, T., Lin, H., Sun, Q., Zhao, G., and Shi, J. (2018). Recent progress of electrode materials for zinc bromide flow battery. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 13, 5603–5611. doi:10.20964/2018.06.34
Kaku, H., Dong, Y. R., Hanafusa, K., Moriuchi, K., and Shigematsu, T. (2016). Effect of Ti(IV) ion on Mn(III) stability in Ti/Mn electrolyte for redox flow battery. ECS Trans. 72 (10), 1–9. doi:10.1149/07210.0001ecst
Kaku, H., Kawagoe, Y., Dong, Y-R., Tatsumi, R., Moriuchi, K., and Shigematsu, T. (2017). Enhanced performance of Ti/Mn redox flow battery. ECS Trans. 77 (11), 173–183. doi:10.1149/07711.0173ecst
Kavan, L., O'Regan, B., Kay, A., and Grätzel, M. (1993). Preparation of TiO2 (anatase) films on electrodes by anodic oxidative hydrolysis of TiCl3. J. Electroanal. Chem. 346 (1), 291–307. doi:10.1016/0022-0728(93)85020-h
Klingler, R. J., and Kochi, J. K. (1981). Electron-transfer kinetics from cyclic voltammetry. Quantitative description of electrochemical reversibility. J. Phys. Chem. 85 (12), 1731–1741. doi:10.1021/j150612a028
Kotsyubynsky, V. O., Myronyuk, I. F., Chelyadyn, V. L., Hrubiak, A. B., Moklyak, V. V., and Fedorchenko, S. V. (2017). The effect of sulphate anions on the ultrafine titania nucleation. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 12 (1), 369. doi:10.1186/s11671-017-2144-3
Kreh, R. P., Spotnitz, R. M., and Lundquist, J. T. (1989). Mediated electrochemical synthesis of aromatic aldehydes, ketones, and quinones using ceric methanesulfonate. J. Org. Chem. 54 (7), 1526–1531. doi:10.1021/jo00268a010
Leung, P. K., Ponce-de-León, C., Low, C. T. J., Shah, A. A., and Walsh, F. C. (2011). Characterization of a zinc–cerium flow battery. J. Power Sources 196 (11), 5174–5185. doi:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2011.01.095
Lingane, J. J., and Kennedy, J. H. (1956). Polarography of titanium in strong mineral acid media. Anal. Chim. Acta 15, 294–300. doi:10.1016/0003-2670(56)80053-6
Lokhande, C., Sun-Ki, M., Jung, K-D., and Joo, O-S. (2004). Cathodic electrodeposition of amorphous titanium oxide films from an alkaline solution bath. J. Mater. Sci. 39 (21), 6607–6610. doi:10.1023/b:jmsc.0000044903.93296.a4
Lokhande, C. D., Min, S-K., Jung, K-D., and Joo, O-S. (2005). Cathodic electrodeposition of amorphous titanium oxide films from an alkaline solution bath. J. Mat. Sci. 40 (2), 491–494. doi:10.1007/s10853-005-6111-5
Lu, W., Yuan, Z., Zhao, Y., Zhang, H., Zhang, H., and Li, X. (2017). Porous membranes in secondary battery technologies. Chem. Soc. Rev. 46 (8), 2199–2236. doi:10.1039/c6cs00823b
Mangold, L., Halleux, H., Leclerc, S., Moncomble, A., Cote, G., and Chagnes, A. (2021). New insights for titanium(iv) speciation in acidic media based on UV-visible and 31P NMR spectroscopies and molecular modeling. RSC Adv. 11 (43), 27059–27073. doi:10.1039/d1ra04284j
Miyanaga, T., Watanabe, I., and Ikeda, S. (1990). Structures of hydrated titanium and vanadium ions in aqueous solutions studied by X-ray absorption spectroscopy. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 63 (11), 3282–3287. doi:10.1246/bcsj.63.3282
Molina, P. I., Kozma, K., Santala, M., Falaise, C., and Nyman, M. (2017). Aqueous bismuth titanium–oxo sulfate cluster speciation and crystallization. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 56 (51), 16277–16281. doi:10.1002/anie.201709539
Morris, D. F., MacCarthy, J. D., and Newton, R. J. (1978). Outer-sphere and inner-sphere interactions in the formation of metal-ion nitrate complexes. Electrochimica Acta 23 (12), 1383–1386. doi:10.1016/0013-4686(78)80021-8
Naresh, Rp, Mariyappan, K., Dixon, D., Ulaganathan, M., and Ragupathy, P. (2021). Investigations on new electrolyte composition and modified membrane for high voltage Zinc−Manganese hybrid redox flow batteries. Batter. Supercaps 4 (9), 1464–1472. doi:10.1002/batt.202100071
Oldenburg, F. J., Bon, M., Perego, D., Polino, D., Laino, T., Gubler, L., et al. (2018). Revealing the role of phosphoric acid in all-vanadium redox flow batteries with DFT calculations and in situ analysis. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 20 (36), 23664–23673. doi:10.1039/c8cp04517h
Pourbaix, M. (1966). Atlas of electrochemical equilibria in aqueous solutions. Oxford; New York: Pergamon Press.
Prifti, H., Parasuraman, A., Winardi, S., Lim, T. M., and Skyllas-Kazacos, M. J. M. (2012). Membranes for redox flow battery applications. Membranes 2 (2), 275–306. doi:10.3390/membranes2020275
Qiao, L., Fang, M., Liu, S., Zhang, H., and Ma, X. (2022). New-generation iron–titanium flow batteries with low cost and ultrahigh stability for stationary energy storage. Chem. Eng. J. 434, 134588. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2022.134588
Raja, M., Khan, H., Sankarasubramanian, S., Sonawat, D., Ramani, V., and Ramanujam, K. (2021). Binder-free thin graphite fiber mat sandwich electrode architectures for energy-efficient vanadium redox flow batteries. Catal. Today 370, 181–188. doi:10.1016/j.cattod.2021.02.012
Reynard, D., Maye, S., Peljo, P., Chanda, V., Girault, H. H., and Gentil, S. (2020). Vanadium–manganese redox flow battery: Study of MnIII disproportionation in the presence of other metallic ions. Chem. Eur. J. 26 (32), 7250–7257. doi:10.1002/chem.202000340
Sankarasubramanian, S., Zhang, Y., He, C., Gregory, T., and Ramani, V. (2021). An aqueous, electrode-decoupled redox-flow battery for long duration energy storage. Research. Square. Pre-print.
Sankarasubramanian, S., Zhang, Y., and Ramani, V. (2019). Methanesulfonic acid-based electrode-decoupled vanadium–cerium redox flow battery exhibits significantly improved capacity and cycle life. Sustain. Energy Fuels 3 (9), 2417–2425. doi:10.1039/c9se00286c
Savinell, R. F., Liu, C. C., Galasco, R. T., Chiang, S. H., and Coetzee, J. F. (1979). Discharge characteristics of a soluble iron-titanium battery system. J. Electrochem. Soc. 126 (3), 357–360. doi:10.1149/1.2129043
Selverston, S., Savinell, R. F., and Wainright, J. S. (2017). Zinc-iron flow batteries with common electrolyte. J. Electrochem. Soc. 164 (6), A1069–A1075. doi:10.1149/2.0591706jes
Shepherd, S. (2013). An investigation into aqueous titanium speciation utilising electrochemical methods for the purpose of implementation into the sulfate process for titanium dioxide manufacture. Callaghan, NSW: University of Newcastle. Degree Thesis.
Shi, L., Wang, W., Wang, Y., and Huang, Y. (1989). The first example of a catalytic Wittig-type reaction. Tri-n-butylarsine-catalyzed olefination in the presence of triphenyl phosphite. J. Org. Chem. 54 (9), 2027–2028. doi:10.1021/jo00270a001
Skyllas-Kazacos, M., Chakrabarti, M. H., Hajimolana, S. A., Mjalli, F. S., and Saleem, M. (2011). Progress in flow battery research and development. J. Electrochem. Soc. 158 (8), R55. doi:10.1149/1.3599565
Sole, K. C. (1999). Recovery of titanium from the leach liquors of titaniferous magnetites by solvent extraction: Part 1. Review of the literature and aqueous thermodynamics. Hydrometallurgy 51 (2), 239–253. doi:10.1016/s0304-386x(98)00081-4
Thaller, L. H., and inventor, (1976). The United States of America as represented by the Administrator of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration, assignee.” in Electrically rechargeable redox flow cell. The United States of America patent US3996064A.
Tsurumura, T., Ohkubo, K., Tanaka, T., and Fujii, K. (2020). Structural study on Ti-ion complexes in concentrated aqueous electrolytes: Raman spectroscopy and high-energy X-ray total scattering. J. Mol. Liq. 305, 112867. doi:10.1016/j.molliq.2020.112867
Tsurumura, T., Tanaka, T., Yagi, K., Morita, M., Kameda, Y., and Fujii, K. (2018). Local structures of titanium-ion complexes in redox flow battery electrolytes as revealed by X-ray scattering with difference analysis. J. Mol. Liq. 261, 468–472. doi:10.1016/j.molliq.2018.04.074
Ulaganathan, M., Suresh, S., Mariyappan, K., Periasamy, P., and Pitchai, R. (2019). New zinc–vanadium (Zn–V) hybrid redox flow battery: High-voltage and energy-efficient advanced energy storage system. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 7 (6), 6053–6060. doi:10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b06194
Varcoe, J. R., Atanassov, P., Dekel, D. R., Herring, A. M., Hickner, M. A., Kohl, P. A., et al. (2014). Anion-exchange membranes in electrochemical energy systems. Energy Environ. Sci. 7 (10), 3135–3191. doi:10.1039/c4ee01303d
Wang, Y., Lin, M., and Wan, C. (1984). A study of the discharge performance of the Ti/Fe redox flow system. J. power sources 13 (1), 65–74. doi:10.1016/0378-7753(84)80054-3
Wang, Z., Sankarasubramanian, S., and Ramani, V. (2018). Advances in anion exchange membranes for electrochemical energy conversion. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 12, 240–245. doi:10.1016/j.coelec.2018.11.011
Wang, Z., Sankarasubramanian, S., Willey, J., Feng, H., Xu, H., and Ramani, V. (2021). Engineering block co-polymer anion exchange membrane domains for highly efficient electrode-decoupled redox flow batteries. Sustain. Energy Fuels 5 (14), 3606–3616. doi:10.1039/d1se00543j
Wu, C. D., Calvo, E. J., and Yeager, E. (1983). Electrochemical studies of redox systems for energy storage. Cleveland, OH: Center for Electrochemical Sciences. NASA.
Xie, Z., Xiong, F., and Zhou, D. (2011). Study of the Ce3+/Ce4+ redox couple in mixed-acid media (CH3SO3H and H2SO4) for redox flow battery application. Energy fuels. 25 (5), 2399–2404. doi:10.1021/ef200354b
Xie, Z., Zhou, D., Xiong, F., Zhang, S., and Huang, K. (2011). Cerium-zinc redox flow battery: Positive half-cell electrolyte studies. J. Rare Earths 29 (6), 567–573. doi:10.1016/s1002-0721(10)60499-1
Yun, S., Parrondo, J., and Ramani, V. (2015). A vanadium-cerium redox flow battery with an anion-exchange membrane separator. ChemPlusChem 80 (2), 412–421. doi:10.1002/cplu.201402096
Yun, S., Parrondo, J., and Ramani, V. (2016). Composite anion exchange membranes based on quaternized cardo-poly(etherketone) and quaternized inorganic fillers for vanadium redox flow battery applications. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 41 (25), 10766–10775. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.04.060
Yun, S., Parrondo, J., and Ramani, V. (2014). Derivatized cardo-polyetherketone anion exchange membranes for all-vanadium redox flow batteries. J. Mat. Chem. A 2 (18), 6605–6615. doi:10.1039/c4ta00166d
Zhao, H., Wu, Q., Hu, S., Xu, H., and Rasmussen, C. N. (2015). Review of energy storage system for wind power integration support. Appl. Energy 137, 545–553. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.04.103
Keywords: energy storage, redox flow batteries, titanium, kinetics, solvation, energy storage (batteries)
Citation: Ahmed SIU, Shahid M and Sankarasubramanian S (2022) Aqueous titanium redox flow batteries—State-of-the-art and future potential. Front. Energy Res. 10:1021201. doi: 10.3389/fenrg.2022.1021201
Received: 17 August 2022; Accepted: 21 September 2022;
Published: 10 October 2022.
Edited by:
Sheng S. Zhang, United States Army Research Laboratory, United StatesReviewed by:
Yuxun Ren, University of Maryland, United StatesCopyright © 2022 Ahmed, Shahid and Sankarasubramanian. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Shrihari Sankarasubramanian, U2hyaWhhcmkuc2Fua2FyYXN1YnJhbWFuaWFuQHV0c2EuZWR1
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Sheikh Imran Uddin Ahmed
Sheikh Imran Uddin Ahmed Mohamed Shahid
Mohamed Shahid Shrihari Sankarasubramanian
Shrihari Sankarasubramanian