
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
SYSTEMATIC REVIEW article
Front. Endocrinol., 03 April 2025
Sec. Reproduction
Volume 16 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2025.1567787
This article is part of the Research TopicA Lifecourse Perspective on Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): Bridging Gaps in Research and PracticeView all 17 articles
Background: Insulin resistance (IR) is regarded as a significant role in the pathophysiology of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), hence early identification of IR in PCOS patients is crucial for their treatment. Recent researches indicate that Waist-to-Height Ratio (WHtR) differs in patients with PCOS accompanied by IR compared to those with PCOS alone; however, a consensus has yet to be reached. This research presents a meta-analysis of current data to propose a straightforward new index for diagnosing PCOS with insulin resistance.
Objective: This study aims to assess the correlation between WHtR and insulin resistance in individuals with polycystic ovarian syndrome by meta-analysis and the synthesis of research information. This study will offer prognostic insights into the onset of insulin resistance in individuals with polycystic ovaries.
Methods: This systematic review has finalized registration (CRD42025638798) on the PROSPERO platform. We conducted a search of prominent databases, including PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, The Cochrane Library, and performed manual searches. Observational studies of relevance (cohort, case-control, or cross-sectional) published before January 13, 2025, were considered. The methodological quality of case-control studies and cohort studies was evaluated using the NOS tool. Simultaneously, AHRQ criteria were employed to evaluate cross-sectional research. The study outcomes were reported as mean ± sd. The aggregated data was analyzed using StataMP17.0.
Results: A meta-analysis encompassing nine studies with 3012 participants identified a significant correlation between an increased WHtR and the onset of insulin resistance in individuals with polycystic ovarian syndrome (SMD: 1.07, 95% CI: 0.81, 1.32, p = 0.000).
Conclusion: Patients with PCOS and insulin resistance will exhibit a greater WHtR compared to those with PCOS without insulin resistance. Thus, the incidence of insulin resistance in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome can be anticipated by monitoring the WHtR.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/view/CRD42025638798, identifier CRD42025638798.
Polycystic ovarian syndrome is a prevalent gynecological endocrine and reproductive illness, affecting 10 - 13% of women of reproductive age (1), and its pathophysiology is intricate, including several variables, with no clear treatment now available. Insulin resistance is regarded as a significant contributor to the onset of PCOS (2), with research indicating that 30% - 60% of PCOS patients exhibit obesity and IR (3, 4). Furthermore, the majority of contemporary therapeutic treatment protocols for PCOS emphasize the enhancement of patients’ IR (3). Consequently, the prompt identification of insulin resistance in a patient is critically important for the diagnosis and management of polycystic ovary syndrome.
The prevailing gold standard for insulin resistance detection, the high insulin-glucose clamp test, is intricate and expensive (5). Other methodologies and indices for assessing abnormalities in glucose tolerance metabolism, such as the glucose tolerance test (GTT) and homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR), entail significant operational and measurement demands, rendering them unsuitable for screening and early diagnosis. Consequently, there is a need to identify a straightforward and easily measurable index for diagnosing PCOS with insulin resistance. Consequently, it is essential to identify a straightforward and easily quantifiable index for the diagnosis of PCOS with insulin resistance. Considering that a majority of patients with PCOS and IR exhibit a pronounced inclination towards obesity, and recognizing the robust correlation between WHtR and both obesity and IR, a study on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) revealed a reduction in patients’ body mass index (BMI) concomitant with a decrease in WHtR (6). This shows the importance of WHtR in assessing obesity and insulin resistance in individuals. In comparison to the existing high insulin-glucose clamp experiment, together with GTT and HOMA-IR, the assessment of WHtR is more straightforward and broadly applicable.
Consequently, we conducted a meta-analysis and review to explore the correlation between WHtR and IR in PCOS and its clinical implications for diagnosing IR.
This study adhered to the most updated Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA-2020) criteria for reporting (Supplementary Table S1). This systematic review was registered with PROSPERO (CRD42025638798) before initiation.
Relevant observational studies were identified through PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, The Cochrane Library databases, and literature tracking methods such as hand searches.
The search keywords included: “polycystic ovary syndrome,” “PCOS,” “insulin resistance,” “waist-to-height ratio,” “WHtR,” etc. Keywords were amalgamated utilizing Boolean logic, with disparate categories linked by “AND” and identical categories connected by “OR,” while searches incorporated combinations of subject and free terms. All articles published before January 13, 2025, were incorporated in the search. Detailed search methodologies and formulae for each database are available in Supplementary Table S2.
(1) The study population comprised patients with PCOS (2); The study analyzed the disparities in WHtR levels between IR and non-insulin-resistant (non-IR) individuals (3); The study documented WHtR levels for the IR and Non-IR groups separately, expressed as mean ± sd (4); The study design was observational, including cohort, case-control, and cross-sectional studies.
(1) Non-thesis research, including reviews and conference abstracts (2); Animal research (3); In cases of duplication, only the entry with the most comprehensive information was retained.
Both investigators independently conducted the literature screening process in accordance with the aforementioned inclusion and exclusion criteria. Firstly, two reviewers independently read the titles and abstracts of the searched studies to exclude irrelevant studies. Then, the full text of the remaining studies was to be read and make the final selection. The inter-rater agreement for selecting studies with the Kappa score was calculated by IBM SPSS Statistics 25. Following the identification of papers for inclusion in the analysis, data extraction was conducted independently. The gathered information comprised the name and publication year of the first author, the study’s geographical region, details regarding the study population (age and sample size), the study design, diagnostic criteria for PCOS, the definition of insulin resistance, and the conclusion of the study (data for WHtR).
The methodological quality of case-control and cohort studies was assessed using the NOS (Newcastle-Ottawa Scale) rating scale. The assessment encompassed three dimensions: subject selection, comparability, and exposure, comprising a total of 8 score criteria out of a possible 9 points. The assessment criteria were as follows: (1) A score of 7-9 was classified as a high-quality study; (2) a score of 4-6 was classified as a moderate-quality study; and (3) a score of less than 4 was classified as a low-quality study. The Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) was employed to assess the quality of the cross-sectional studies, comprising 11 items with responses of “yes,” “no,” and “unclear,” while “yes” was assigned a score of 1, and “no” and “unclear” received a score of 0. The grading criteria were delineated as follows: (1) a score of 8-11 was classified as a high-quality study; (2) a score of 4-7 was classified as medium-quality; and (3) a score of 0-3 was classified as a low-quality study.
This study employed StataMP17.0 for the comprehensive analysis of data. The outcome indicator was a continuous variable, and the disparity in WHtR levels between the IR and non-IR groups was assessed for significance by gathering mean ± sd in both groups, with SMD (95% CI) serving as the effect size. The significance criterion was established at 0.05. Chi-square tests and Cochrane Q-tests were employed to assess heterogeneity among groups, whereas I² was utilized to quantify the extent of heterogeneity across the included studies. If I² ≤ 50%, this indicated good homogeneity among trials, which were examined using a fixed-effects model. If I² > 50%, it indicated inadequate homogeneity and elevated heterogeneity, necessitating analysis through a random effects model. When heterogeneity was excessive, the origin of heterogeneity was investigated by sensitivity analysis and subgroup analysis. We performed a sensitivity analysis by excluding literature one by one and analyzing the remaining included literature in general. The results of the sensitivity analysis are presented in the form of a sensitivity map. Egger’s test was employed to identify publication bias in the chosen studies. The Funnel plot test was not performed due to the small number of literatures included in the change study and the results presented by the Funnel plot test did not fully reflect the bias between publications.
A total of 134 articles were acquired via four databases and manual searches. Following the evaluation of titles and abstracts pertinent to this study, 99 publications were removed, resulting in a total of 35 papers remaining with a Kappa score of 0.847. Two studies were inaccessible, and following a meticulous full-text examination of the remaining 33 papers, the application of inclusion and exclusion criteria, along with a thorough assessment, resulted in the exclusion of two reviews, one meta-analysis, and 21 articles without pertinent data. Ultimately, nine observational studies remained with an inter-rater agreement Kappa score of 0.807. The detailed information about the Kappa score between the reviewers was shown in Supplementary Table S4. A total of nine publications were included, as illustrated in Figure 1.
Eight of the nine documents are in English, while one is in Portuguese. Seven cross-sectional studies and two case-control studies were incorporated. The experimental group consisted of 1721 individuals, while the control group contained 1291, resulting in a total of 3012 participants (Table 1).
This systematic review comprised nine publications. This review identified two cohort studies as high-quality, each with an NOS score of 9. Of the remaining seven cross-sectional studies, AHRQ scores ranged from 6 to 8; one study was classified as high quality, while six were deemed moderate quality. The overall quality was sufficient, as demonstrated in Tables 2A and 2B.
This research comprised nine studies with 3012 patients diagnosed with PCOS to evaluate the correlation between WHtR and IR in this population. Patients with PCOS exhibiting IR demonstrated markedly elevated WHtR compared to those without IR (SMD: 1.07, 95% CI: 0.81, 1.32, p = 0.000, I2 = 84.8%) (Figure 2). Moreover, sensitivity analysis demonstrated that the aggregated results from this study were dependable (Figure 3). This reveals a notable correlation between an increased WHtR and the onset of IR in individuals with PCOS.
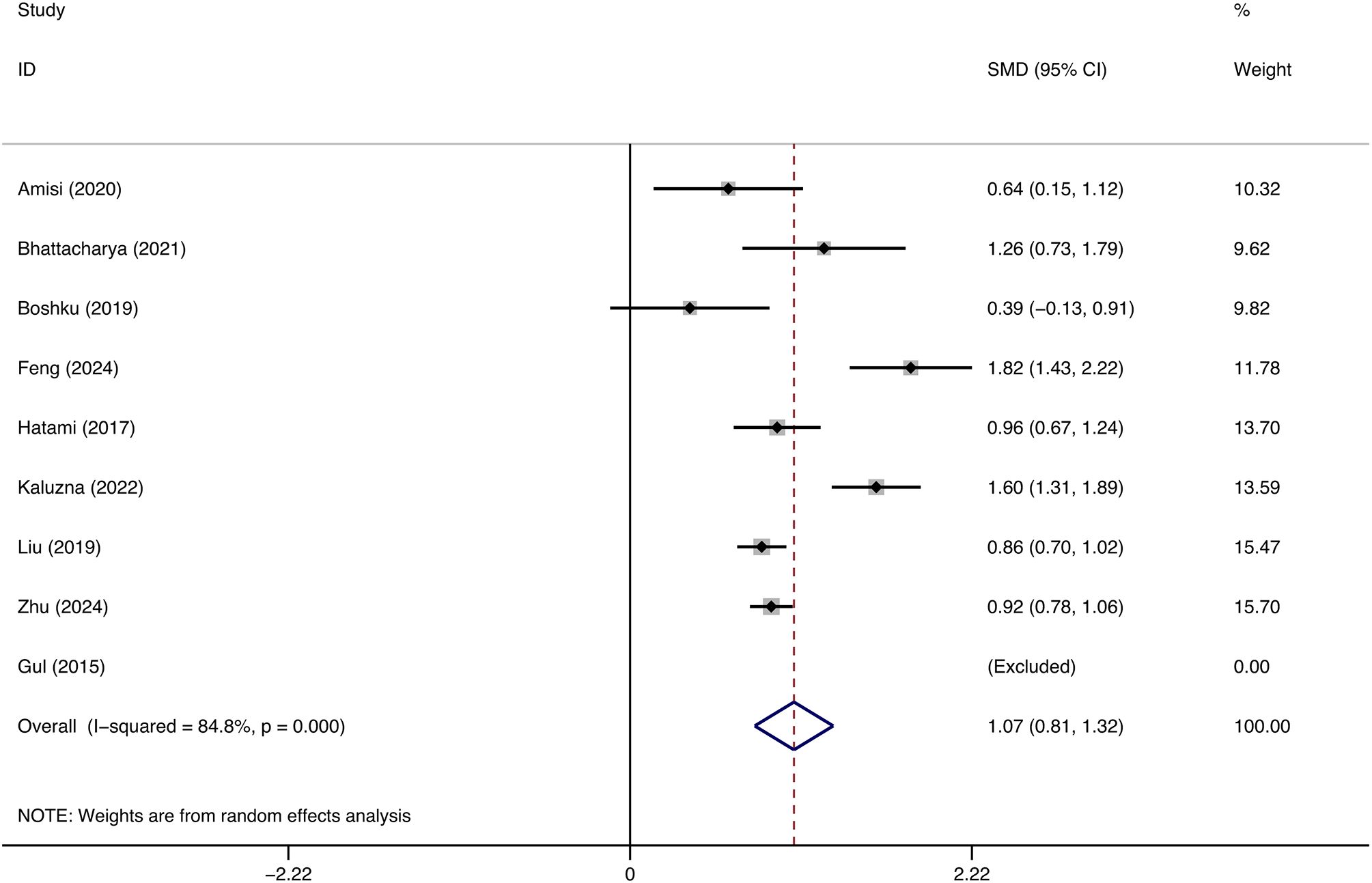
Figure 2. The association between waist-to-height ratio and insulin resistance in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome.
The study was segmented into two subgroups according to geographic regions, with each analyzed individually. China and India were classified as Eastern nations, whereas Iran, Congo, and European nations were designated as Western and Central countries. The subgroup of Eastern countries included four studies demonstrating a significant correlation between increased WHtR and the onset of insulin resistance in individuals with polycystic ovarian syndrome (SMD: 1.16, 95% CI: 0.83, 1.48, p = 0.000, I2 = 86.0%). In a subgroup analysis of five studies from Western and Central nations, the WHtR of patients with polycystic ovarian syndrome exhibiting insulin resistance was markedly elevated compared to those without insulin resistance (SMD: 0.93, 95% CI: 0.41, 1.44, p = 0.000, I2 = 87.1%) (Figure 4).
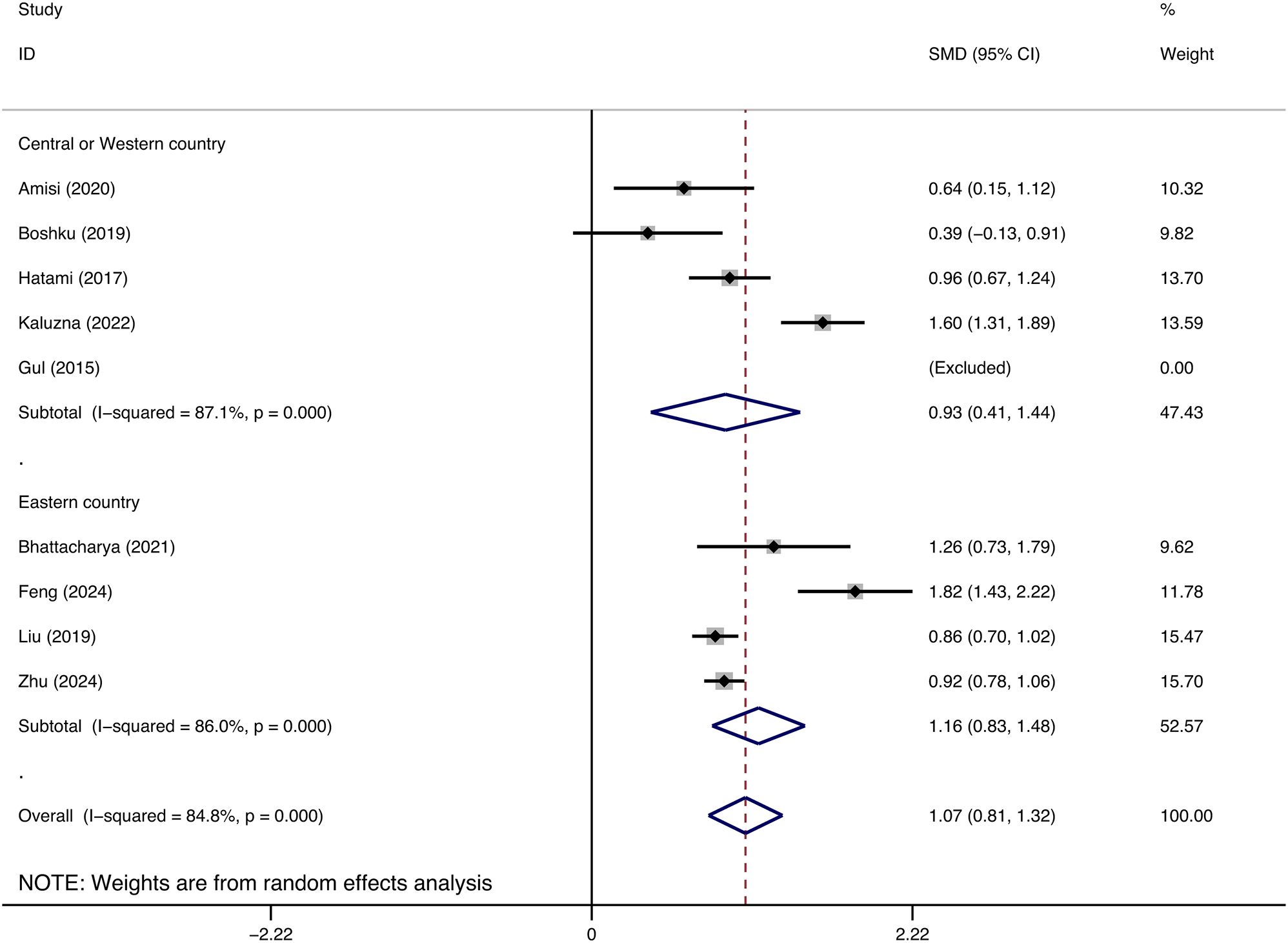
Figure 4. Subgroup analyses on difference of waist-to-height ratio and insulin resistance in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome in different areas.
Egger’s regression test indicated no substantial publication bias in the data (p > 0.05), as demonstrated in Supplementary Table S3.
PCOS is an endocrine disorder associated with insulin resistance, hyperinsulinemia, dyslipidemia, obesity, and various metabolic alterations (11). The pathogenesis is intricate, with current understanding indicating a strong correlation between PCOS and insulin resistance (4). Most patients with insulin resistance exhibit disturbances in energy metabolism, resulting in alterations in physical test indicators, such as the prevalence of MASLD (Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease), which is linked to WHtR (14). In individuals with PCOS and insulin resistance, there are associated alterations in WHtR; nevertheless, the discrepancies in WHtR between those with PCOS and insulin resistance versus those with PCOS alone remain contentious and have yet to be standardized (2, 7, 8, 10, 15). After our meta-analysis, the results showed that there are some variations in WHtR between patients with PCOS alone and PCOS with IR, and the WHtR of patients with PCOS with IR is higher than that of patients with PCOS alone. The most common method for detecting insulin resistance in PCOS patients is the HOMA-IR index; however, this index is complex to measure and not easy to clinically screen for PCOS patients with IR. While BMI, a commonly used measure of patient body composition, is easy to measure, a global pooled study analysis showed that individuals may have uneven fat and muscle distribution due to a variety of factors, which may be overlooked by BMI when detecting obesity levels in patients (16). Meanwhile, the 2023 edition of the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and the American Endocrine Society’s Comprehensive Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Medical Care of Obese Patients in the U.S. also suggested that waist circumference can be used as an indicator of a patient’s risk of obesity, and that, in addition to BMI, waist circumference in different regions and populations should also be included as an indicator for the consideration of obesity (17). Therefore, the use of WHtR in the assessment of central obesity is more accurate than other anthropometric measures such as BMI (18), suggesting that WHtR seems to be able to be used in the pre-screening and prediction of patients with PCOS with IR. Although WHtR is more straightforward to measure and exhibits a distinction between patients with simple PCOS and those with PCOS accompanied by insulin resistance, several studies indicate that WHtR is significantly associated with central obesity. Its accuracy in evaluating central obesity surpasses that of other anthropometric measures, such as BMI (18), implying that WHtR may be effectively utilized for the pre-screening of patients with PCOS and IR. The existing studies also support this view, in a study from Kolkata, India, it was clearly demonstrated that WHtR can be used to predict IR in patients with PCOS in this region, and the critical value of WHtR in patients with PCOS with IR in this region was 0.62 (8), and in a study from Zhengzhou, China, it was demonstrated that WHtR is a good predictor for patients with POCS with IR in this region, and the critical value of WHtR in this region was 0.519 (5), and there are also studies from Iran and Poland also proved this view (13, 19). Although existing studies have proved that WHtR is able to play a role in the prediction of POCS with IR, the prediction cutoff values in the above studies only represent the situation in this region, and they still have limitations in the application of a large range of relevant indexes. Predictive cutoff values still need to be measured in further large-scale studies.
To further investigate the correlation between WHtR and PCOS in insulin-resistant patients, we performed a subgroup analysis based on the patients’ geographical regions. The findings indicated that the association between increased WHtR and PCOS with IR was more pronounced in Eastern countries, potentially linked to obesity resulting from Eastern dietary practices (20). Research indicates that patients with PCOS and IR are more prone to obesity (21), and individuals with obesity typically exhibit elevated WHtR (22). Consequently, it can be inferred that energy metabolism disorders in PCOS patients with IR, resulting in obesity, significantly contribute to increased WHtR values.
Nonetheless, our study possesses certain limitations, including significant heterogeneity. The discrepancy may be attributable to the limited sample size of the study participants. Furthermore, there is a paucity of research regarding the correlation between insulin resistance and WHtR in polycystic ovarian syndrome, and the limited number of studies may have resulted in analytical bias. The analysis also failed to account for the impact of varying patient disease duration on WHtR, hence introducing potential bias in the results. We also found that the HOMA-IR, an indicator of insulin resistance, was not consistent in some of the studies, which ranged from 2.6-3.8, and most of the studies had a cut-off value of 3 or less for the HOMA-IR, with just one study having a cut-off value of 3 or more, so our calculated correlation of WHtR may be biased. Moreover, our study included mainly articles from cross-sectional studies, so although statistically there is a strong correlation between WHtR and PCOS with IR, the causal relationship between the two remains to be explored in further studies.
Given that enhancing insulin resistance in individuals with polycystic ovary syndrome by exercise remains the primary therapeutic approach (3, 4), identifying a straightforward and easily measurable indication for screening polycystic ovary syndrome with insulin resistance is crucial. Patients diagnosed with PCOS in the early stages can have their WHtR measured, and if it exceeds the normal threshold, diet and exercise interventions can be initiated in advance, and further testing of glucose metabolism indicators can be performed for diagnosis, which can help in the treatment and prognosis of the disease. However, even though WHtR is easy to measure and strongly correlated with PCOS with IR, patients with suspected PCOS with IR need to be tested for glucose to confirm the diagnosis according to the Rotterdam Guidelines 2023 (1), and therefore we believe that WHtR can be used as a pre-screening aid, which is important in underdeveloped areas where glucose is not detected. In the meantime, more relevant studies should be conducted in the future, for example, by implementing prospective studies to examine whether changes in WHtR are associated with changes in insulin resistance over time in patients with PCOS.
In conclusion, a significant link exists between WHtR and PCOS with IR. It holds significant clinical relevance for the future prediction of PCOS onset with insulin resistance and for screening PCOS patients for preexisting insulin resistance.
In conclusion, this meta-analysis established a robust correlation between WHtR and polycystic ovary syndrome with insulin resistance, offering significant insights into the utilization of WHtR for the pre-diagnosis and screening of PCOS with IR. Nevertheless, additional epidemiological and experimental investigations are required to ascertain the clinical applicability of WHtR for diagnosing insulin resistance in individuals with PCOS.
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/Supplementary Material.
YL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. CZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. DL: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. HC: Resources, Writing – review & editing. XD: Project administration, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
We thank all the researchers for their contribution in changing the study. At the same time, we also thank Foshan Fosun Chan Cheng Hospital for providing support and help to our team.
The research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fendo.2025.1567787/full#supplementary-material
Supplementary Table 1 | PRISMA 2020 checklist.
Supplementary Table 2 | Search strategies of each database.
Supplementary Table 3 | The Egger’s regression test of air pollution.
Supplementary Table 4 | The detailed information about the Kappa score between the reviewers.
1. Teede HJ, Tay CT, Laven JJE, Dokras A, Moran LJ, Piltonen TT, et al. Recommendations from the 2023 international evidence-based guideline for the assessment and management of polycystic ovary syndrome. Eur J Endocrinol. (2023) 189:G43–64. doi: 10.1093/ejendo/lvad096
2. Liu T, Wang Q, Huang W, Tan J, Liu D, Pei T, et al. Anthropometric indices to predict insulin resistance in women with polycystic ovary syndrome in China. Reprod BioMed Online. (2019) 38:101–7. doi: 10.1016/j.rbmo.2018.10.001
3. Azziz R. Polycystic ovary syndrome. Obstet Gynecol. (2018) 132:321–36. doi: 10.1097/aog.0000000000002698
4. Cassar S, Misso ML, Hopkins WG, Shaw CS, Teede HJ, Stepto NK. Insulin resistance in polycystic ovary syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis of euglycaemic-hyperinsulinaemic clamp studies. Hum Reprod. (2016) 31:2619–31. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dew243
5. Zhu M, Wang K, Feng J, Liu Y, Guan M, Wang Y, et al. The waist-to-height ratio is a good predictor for insulin resistance in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2024) 15:1502321. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1502321
6. Maleki Sedgi F, Mohammad Hosseiniazar M, Alizadeh M. The effects of replacing ghee with rapeseed oil on liver steatosis and enzymes, lipid profile, insulin resistance and anthropometric measurements in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a randomised controlled clinical trial. Br J Nutr. (2024) 131:1985–96. doi: 10.1017/s0007114524000564
7. Amisi CA, Ciccozzi M, Pozzilli P. Wrist circumference: A new marker for insulin resistance in African women with polycystic ovary syndrome. World J Diabetes. (2020) 11:42–51. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v11.i2.42
8. Bhattacharya K, Sengupta P, Dutta S, Chaudhuri P, Das Mukhopadhyay L, Syamal AK. Waist-to-height ratio and BMI as predictive markers for insulin resistance in women with PCOS in Kolkata, India. Endocrine. (2021) 72:86–95. doi: 10.1007/s12020-020-02555-3
9. Boshku AA, Panova DI. Lipid profile in relation to antropometric indices and insulin resistance in overweingt women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Atherosclerosis. (2019) 287:e135. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2019.06.398
10. Feng Y, Li M, Li X, Tang Q, Li X, Ji X, et al. Characteristics of different obesity metabolic indexes and their correlation with insulin resistance in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome. Reprod Sci. (2024) 31:2829–35. doi: 10.1007/s43032-024-01532-9
11. Gul OO, Cander S, Gul B, Açıkgoz E, Sarandol E, Ersoy C. Evaluation of insulin resistance and plasma levels for visfatin and resistin in obese and non-obese patients with polycystic ovary syndrome. Eur Cytokine Network. (2015) 26:73–8. doi: 10.1684/ecn.2015.0370
12. Hatami H, Montazeri SA, Hashemi N, Ramezani Tehrani F. Optimal cutoff points for anthropometric variables to predict insulin resistance in polycystic ovary syndrome. Int J Endocrinol Metab. (2017) 15:e12353–e. doi: 10.5812/ijem.12353
13. Kałużna M, Czlapka-Matyasik M, Kompf P, Moczko J, Wachowiak-Ochmańska K, Janicki A, et al. Lipid ratios and obesity indices are effective predictors of metabolic syndrome in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Ther Adv Endocrinol Metab. (2022) 13:20420188211066699. doi: 10.1177/20420188211066699
14. Hu M, Yang J, Gao B, Wu Z, Wu Y, Hu D, et al. Prediction of MASLD using different screening indexes in Chinese type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetol Metab Syndr. (2025) 17:10. doi: 10.1186/s13098-024-01571-x
15. Saghafi-Asl M, Pirouzpanah S, Ebrahimi-Mameghani M, Asghari-Jafarabadi M, Aliashrafi S, Sadein B. Lipid profile in relation to anthropometric indices and insulin resistance in overweight women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Health Promot Perspect. (2013) 3:206–16. doi: 10.5681/hpp.2013.024
16. Zhou B, Bennett JE, Wickham AP, Singleton RK, Mishra A, Carrillo-Larco RM. General and abdominal adiposity and hypertension in eight world regions: a pooled analysis of 837 population-based studies with 7·5 million participants. Lancet. (2024) 404:851–63. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(24)01405-3
17. Garvey WT, Mechanick JI, Brett EM, Garber AJ, Hurley DL, Jastreboff AM, et al. American association of clinical endocrinologists and american college of endocrinology comprehensive clinical practice guidelines for medical care of patients with obesity. Endocr Pract. (2016) 22 Suppl 3:1–203. doi: 10.4158/ep161365.Gl
18. Zhang X, Lu X, Pan X, Shen S, Tong N. Role of waist circumference-to-height ratio in assessing adiposity, predicting type 2 diabetes mellitus and other cardiometabolic diseases. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. (2024) 49:1062–72. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2024.240259
19. Jabczyk M, Nowak J, Jagielski P, Hudzik B, Borszcz J, Zubelewicz-Szkodzińska B. Interplay between lipid profile and anthropometric measures as indicators of cardiometabolic risk in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Front Endocrinol. (2024) 15:1398017. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1398017
20. Maddie N, Chacko N, Matatov D, Carrillo-Sepulveda MA. Western diet promotes the progression of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease in association with ferroptosis in male mice. Physiol Rep. (2024) 12:e70139. doi: 10.14814/phy2.70139
21. Diamanti-Kandarakis E, Dunaif A. Insulin resistance and the polycystic ovary syndrome revisited: an update on mechanisms and implications. Endocr Rev. (2012) 33:981–1030. doi: 10.1210/er.2011-1034
Keywords: waist-to-height ratio, polycystic ovary syndrome, WHtR, PCOS, insulin resistance, meta-analysis
Citation: Lan Y, Zhong C, Li D, Chen H and Dai X (2025) Association between waist-to-height ratio and insulin resistance in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome: a meta-analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 16:1567787. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1567787
Received: 28 January 2025; Accepted: 17 March 2025;
Published: 03 April 2025.
Edited by:
Bassel H. Al Wattar, Anglia Ruskin University, United KingdomReviewed by:
Liwen Xiao, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), ChinaCopyright © 2025 Lan, Zhong, Li, Chen and Dai. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yuxiang Lan, MTg5MjIwNTA3NDBAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†These authors share first authorship
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.