- 1Department of Gastroenterology, Taixing People’s Hospital, Taixing, China
- 2School of Public Health, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
- 3Hubei Biomass-Resource Chemistry and Environmental Biotechnology Key Laboratory, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
Background: Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), systemic immune-inflammation index(SII), and prognostic nutritional index (PNI) are diagnostic markers for cancer, but their combined significance in gastric cancer (GC) with lymph node metastasis remains unclear. The aim of this study was to evaluate the association between these serum biomarkers and lymph node metastasis in patients with GC.
Methods: Records of patients with GC were reviewed retrospectively. Univariate and multivariate logistic regression were performed to examine the association between tumor markers, serum biomarkers and lymph node metastasis in GC. Based on the results of multivariate regression, a nomogram was developed and verified.
Results: Of the 395 patients aged 68.5 ± 9.1 years, 192 (48.6%) were diagnosed with lymphatic node metastasis. After adjusting for confounding factors, CEA (Odd ratio (OR):2.21; 95%CI: 1.17-3.81) and SII (OR:1.02; 95%CI: 1.01-1.04) was identified as significant risk factors, while PNI (OR:0.90; 95%CI: 0.85~0.96) was a protective factor for lymph node metastasis. The established nomogram by incorporating CEA, SII, PNI, differentiation, and tumor diameter can effectively predict lymph node metastasis in GC.
Conclusion: CEA, SII, PNI, differentiation, and tumor diameter were significantly associated with lymph node metastasis in patients with GC, and the combination of CEA, SII, PNI, differentiation, and tumor diameter has a better diagnostic value than either index alone.
1 Introduction
Gastric cancer (GC) is a significant global public health issue, especially in East Asian countries (1). In 2020, GC was ranked the fifth most frequently diagnosed cancer, and the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths in the word, with more than 1 million cases and over 768,000 deaths (2). GC has the highest incidence and mortality rate in China. Upon diagnosis, approximately 75% of cases were already in the advanced stage of GC, with the majority accompanied by lymph node metastasis (3). Lymph node metastasis is an important influencing factor in the prognosis and the selection of optimal treatment approach among patients with GC. Therefore, it is necessary to evaluate whether lymph node metastasis occurs in patients with GC before surgery (4). At present, the clinical diagnosis of preoperative GC with lymph node metastasis mostly relies on auxiliary examinations, such as upper endoscopy, 18-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) positron emission tomography integrated with computed tomography (PET-CT), and abdominal ultrasonography(AUS), which cannot be reliably utilized to confirm or exclude lymph node metastasis (5, 6). Furthermore, tissue biopsy cannot be routinely used in patients with GC due to its invasiveness and high cost. Thus, it is crucial to explore inexpensive and powerful predictors for lymph node metastasis in patients with GC (7).
Previous studies have focused on tumor markers, which are quantifiable circulating substances associated with malignant diseases to predict GC (8). Among several tumor markers, carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) and carbohydrate antigen 19-9 (CA19-9) are common tumor associated antigens (9, 10). However, previous studies regarding the association of CEA and CA19-9 with GC yield inconsistent findings (11, 12). Furthermore, only a few investigations have examined the diagnosis significance of these markers for lymph node metastasis in patients with GC.
Accumulating evidence have shown a critical role of the inflammatory microenvironment and nutritional status in the tumorigenesis and progression of GC (13). It has been found that the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR), which are indicators of systemic inflammation, can affect tumor progression by inhibiting apoptosis, promoting angiogenesis, and damaging DNA (14). Moreover, the systemic immune-inflammation index (SII), a novel inflammatory marker derived from the counts of peripheral blood neutrophils, platelets, and lymphocytes, can serve as a promising indicator of various inflammatory and immune pathways within the body and exhibit greater stability in diagnosis compared to PLR and NLR (15). Several studies showed that SII can predict the prognosis of malignant tumors, including squamous cell carcinoma (16), lung cancer, and breast cancer (17). Furthermore, it has been found that malnourished patients affect immune cell metabolism, resulting in immune dysregulation and the development of cancer. Evidence have also shown that the prognostic nutrition index (PNI), a novel index of an individual’s nutritional status, plays an important role in predicting the metastasis of various malignant tumors (18, 19). PNI can be used as a prognostic factor for survival in GC patients receiving adjuvant chemotherapy (20). Besides, PNI variability was associated with survival outcomes in gastrointestinal cancers (21). Although PLR, NLR, and CEA have been reported to be associated with GC prognosis (9, 22), their clinical correlations with GC remain controversial. Furthermore, the diagnostic values for the combined effects of these indicators in GC are unclear.
Therefore, we conducted a retrospective study to evaluate the associations of CEA, CA125, CA19-9, CA724, NLR, PLR, SII, and PNI in patients with GC, and further examined their combination on the diagnostic value of lymph node metastasis in patients with GC.
2 Methods
2.1 Ethical statement
This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and its subsequent amendments (23), and has been approved by the ethics committee of Taixing People’s Hospital (LS2023007). Due to the retrospective nature of this study without interacting with patients or using personal identifying information, the need of obtaining informed consent has been waived.
2.2 Study population
This study was conducted in Taixing People’s Hospital, Jiangsu Province, China. Records of 395 preoperative patients with GC who admitted to the hospital from March 2020 to March 2023 were reviewed. All patients were pathologically confirmed as GC and did not receive any therapy before admission. The inclusion criteria were as follows: (1)patients were staged according to the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC)/Union for International Cancer Control (UICC) 8th edition staging system (24). (2) Only patients with complete clinical and pathological features were included in this study. Patients with preoperative radiotherapy and/or chemotherapy, antiplatelet agent therapy within the last 6 months, blood malignancies, and history of other malignant tumors were excluded.
Clinical and pathological data including gender, age tumor-node-metastasis (TNM) stage, differentiation, tumor diameter, and histological morphology were obtained from the patient’s medical records. The neutrophil, lymphocyte, platelet, and monocyte counts were collected using a routine blood test within three days before surgery. The serum albumin level was measured by hepatic function test before surgery. NLR, SII, PLR, and PNI were calculated using the following formula as follows: NLR= neutrophil counts/lymphocyte counts, SII= platelet counts × neutrophil counts/lymphocyte counts, PLR=absolute platelet count/lymphocyte count, PNI = serum albumin level (g/L) + 5 × absolute lymphocyte count (mm3) (25).
2.3 Statistical analysis
According to the laboratory reference values, the cut-off value of CEA, CA19-9, carbohydrate antigen 724 (CA724), and carbohydrate antigen 125 (CA125) was determined with the upper limit of normal defined as 5ng/ml, 27 U/ml, 6.9 U/ml, and 35 U/ml, respectively. The differences between patients with lymphatic metastasis and non-lymph node metastasis were compared by independent sample t-test for continuous variables and by chi-square test for categorical variables, respectively. Logistic regression was employed to explore the association between serum marker and lymph node metastasis in patients with GC. Significant diagnostic factors identified by univariate analysis were further assessed with multivariate logistic regression model after adjusting potential confounders using the “enter” method. Spearman correlation analysis was used to evaluate the correlations between SII, PNI, CEA and clinical variables (e.g., age, tumor diameter, differentiation, etc.) in the logistic regression model to determine whether these variables were independent. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve (AUC) was used to determine the sensitivity and specificity for predicting lymph node metastasis by the parameters. The F-score was used to evaluate the performance of a classification model, measuring the accuracy of the model by balancing precision and recall (26). A nomogram was developed based on the multivariate logistic regression model. Calibration curve and decision curve analysis (DCA) were used to evaluate the performance of the nomogram model. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. All analyses were performed using R 4.3.
3 Results
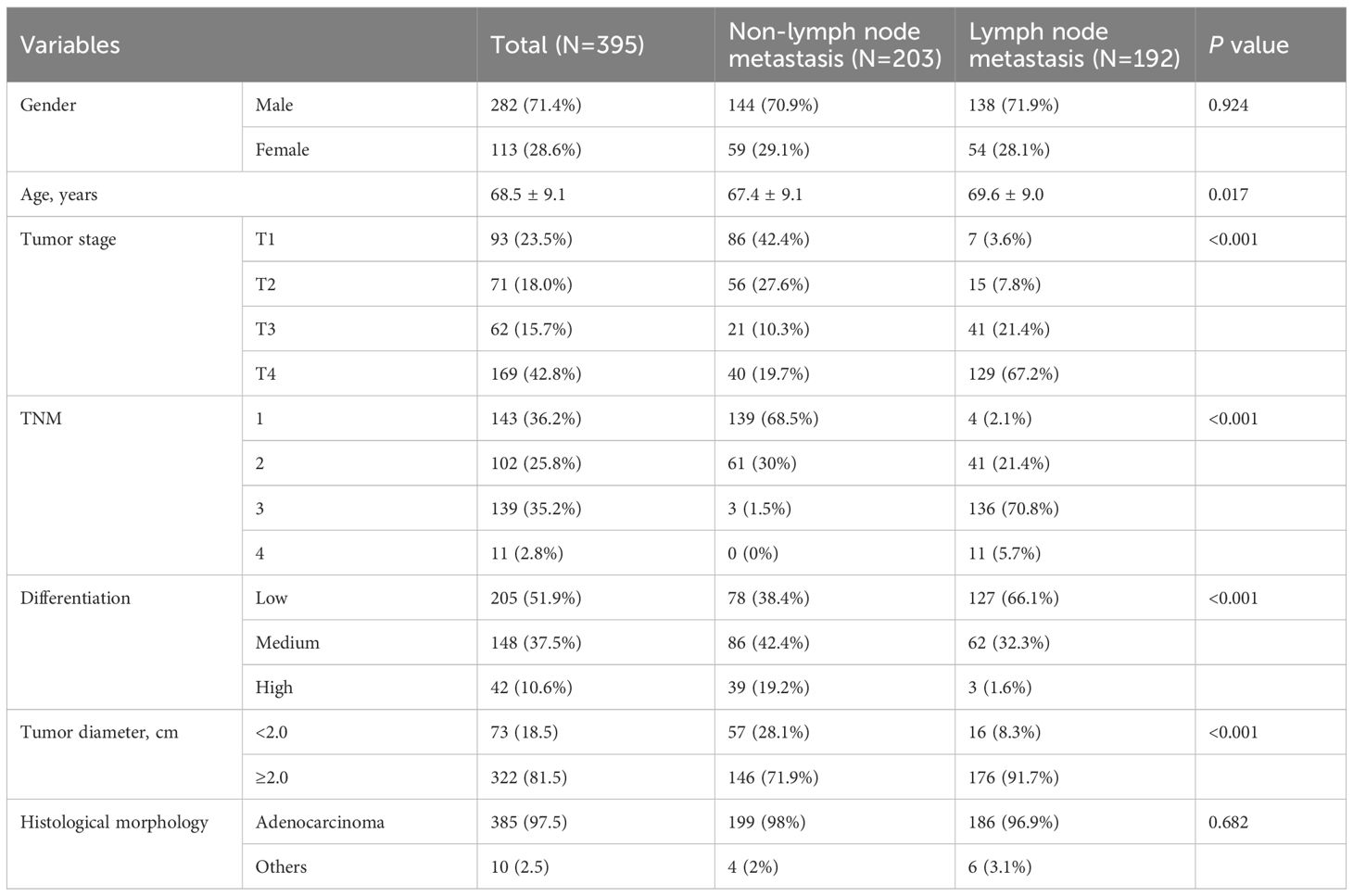
Table 1 displays the characteristics of patients. Of the 395 patients aged 68.5 ± 9.1 years, 192(48.6%) were diagnosed with lymphatic metastasis, and 282 (71.4%) were males. The average tumor diameter was 4.2 ± 2.2 cm. The results show that lymph node metastasis was significantly correlated with age (P=0.017), tumor stage, TNM, degree of differentiation and tumor diameter (P<0.001).
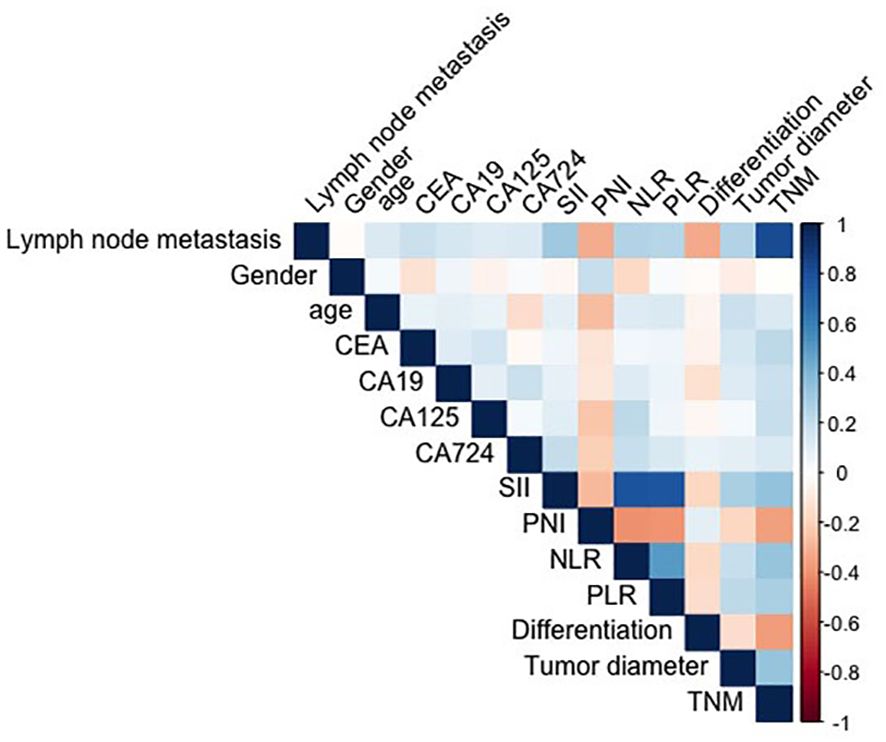
The spearman correlation analysis showed that the correlation coefficient between SII, PNI, CEA and other clinical variables (e.g., age, tumor diameter, differentiation, etc.) was less than 0.3, and the variables were independent. There was significant collinearity between TNM stage and lymphatic metastasis (0.817)(Figure 1). Table 2 shows the univariate and multivariate logistic regression analysis of diagnostic factors in patients with lymph node metastasis. After adjusting for confounding factors, CEA (Odd ratio (OR):2.11; 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.17-3.81), SII (OR:1.02; 95%CI: 1.01-1.04), tumor diameter (OR:2.43; 95%CI: 1.23-4.79)were identified as significant risk factors that affect lymph node metastasis, while PNI (OR:0.90; 95%CI: 0.85-0.96) was associated with a lower risk for lymph node metastasis in GC.
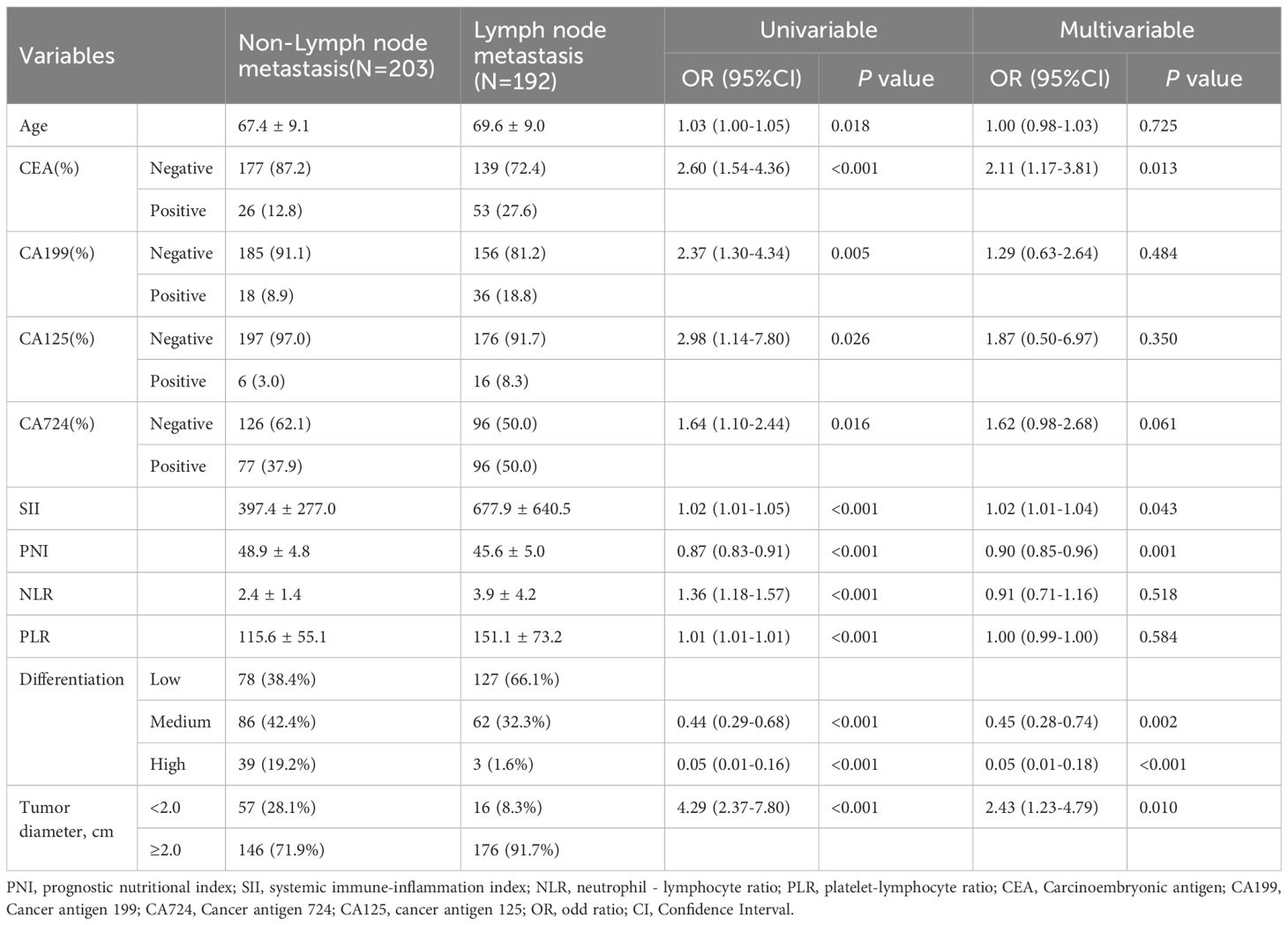
Table 2. Logistic regression analysis for diagnostic factors in GC patients with lymph node metastasis.
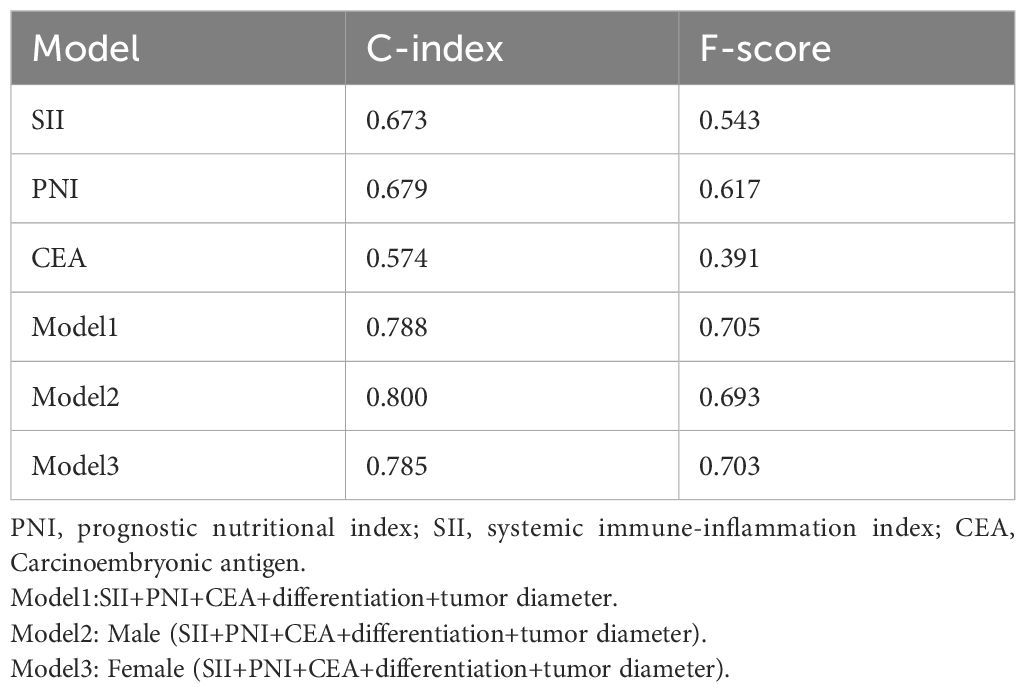
The ROC analysis of CEA, PNI, and SII is shown in Figure 2. The AUC of the PNI, SII, and CEA for lymph node metastasis was 0.679, 0.673, and 0.574, respectively. After applying the Bonferroni correction, the PNI, and SII demonstrated higher diagnostic accuracy compared to CEA in detecting lymph node metastasis (p<0.001). The combined diagnosis of lymph node metastasis in patients with GC using CEA, SII, PNI, differentiation, and tumor diameter yielded an AUC of 0.788, which was significantly higher than single diagnostic indicator. In male patients, the AUC for the joint diagnosis of CEA, SII, PNI, differentiation, and tumor diameter was 80.0%, while in female patients, the AUC was 78.5% (Figure 3). The accuracy and comprehensive performance of comprehensive model in predicting lymphatic metastasis were better than that of single index (Table 3). The ROC analysis of PLR, NLR, CA19-9, CA125, and CA724 is shown in Supplementary Figure S1. The AUC of the PLR, NLR, CA19-9, CA125, and CA724 for lymph node metastasis was 0.644, 0.649, 0.549, 0.527, and 0.560, respectively.
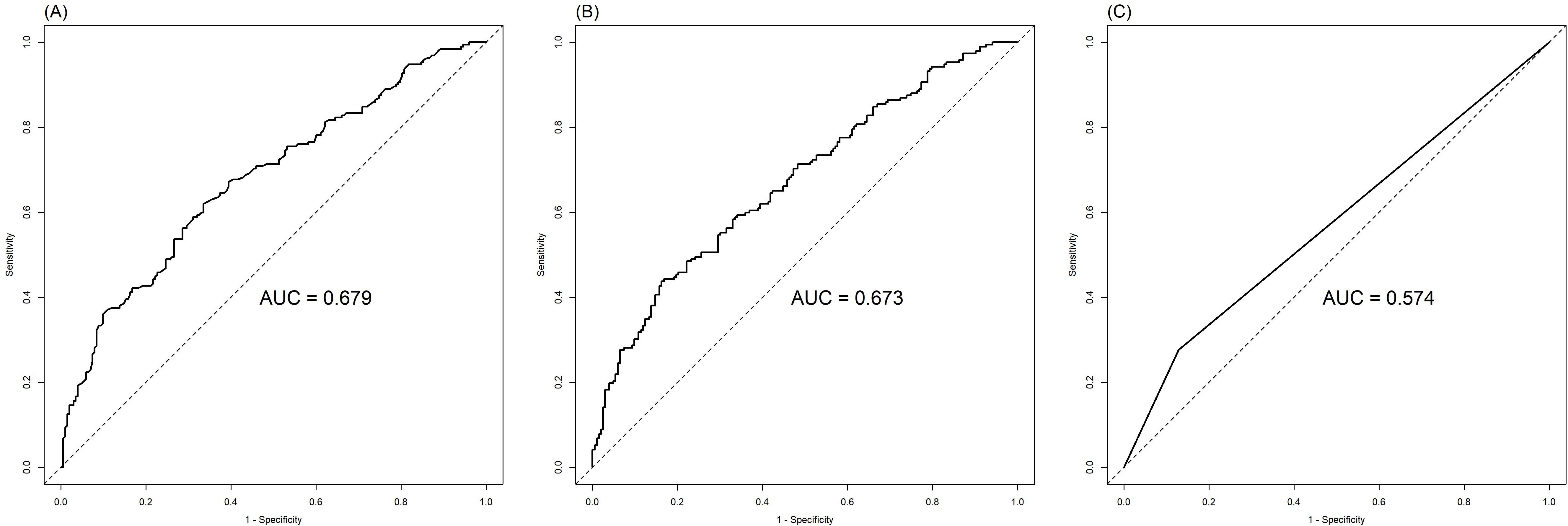
Figure 2. Comparison of PNI (A), SII (B) and CEA (C) in the diagnosis of lymph node metastasis of GC.
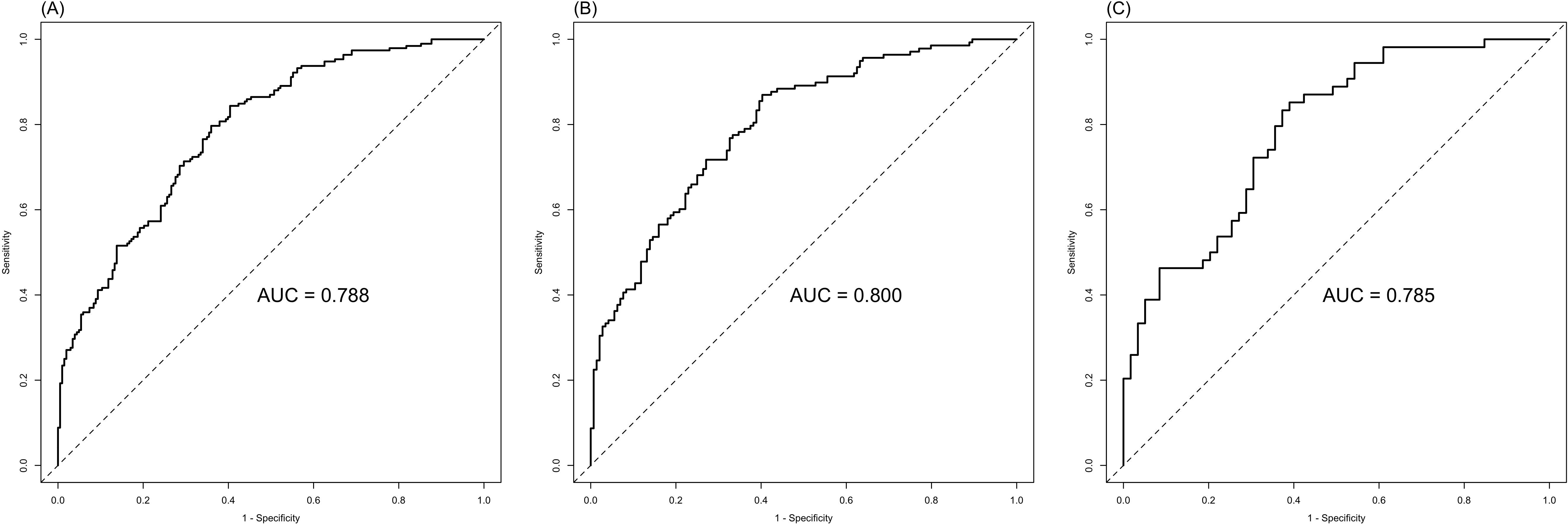
Figure 3. Combined SII, PNI, CEA, differentiation, and tumor diameter in the diagnosis of lymph node metastasis of GC. (A) ALL; (B) Male; (C) Female.
Based on the results of multivariate logistic regression, CEA, SII, PNI, differentiation, and tumor diameter were included in the nomogram model (Figure 4A). DCA showed greater net benefits (Figure 4B). In addition, calibration curves also show good agreement between predictions and observations (Figure 4C).
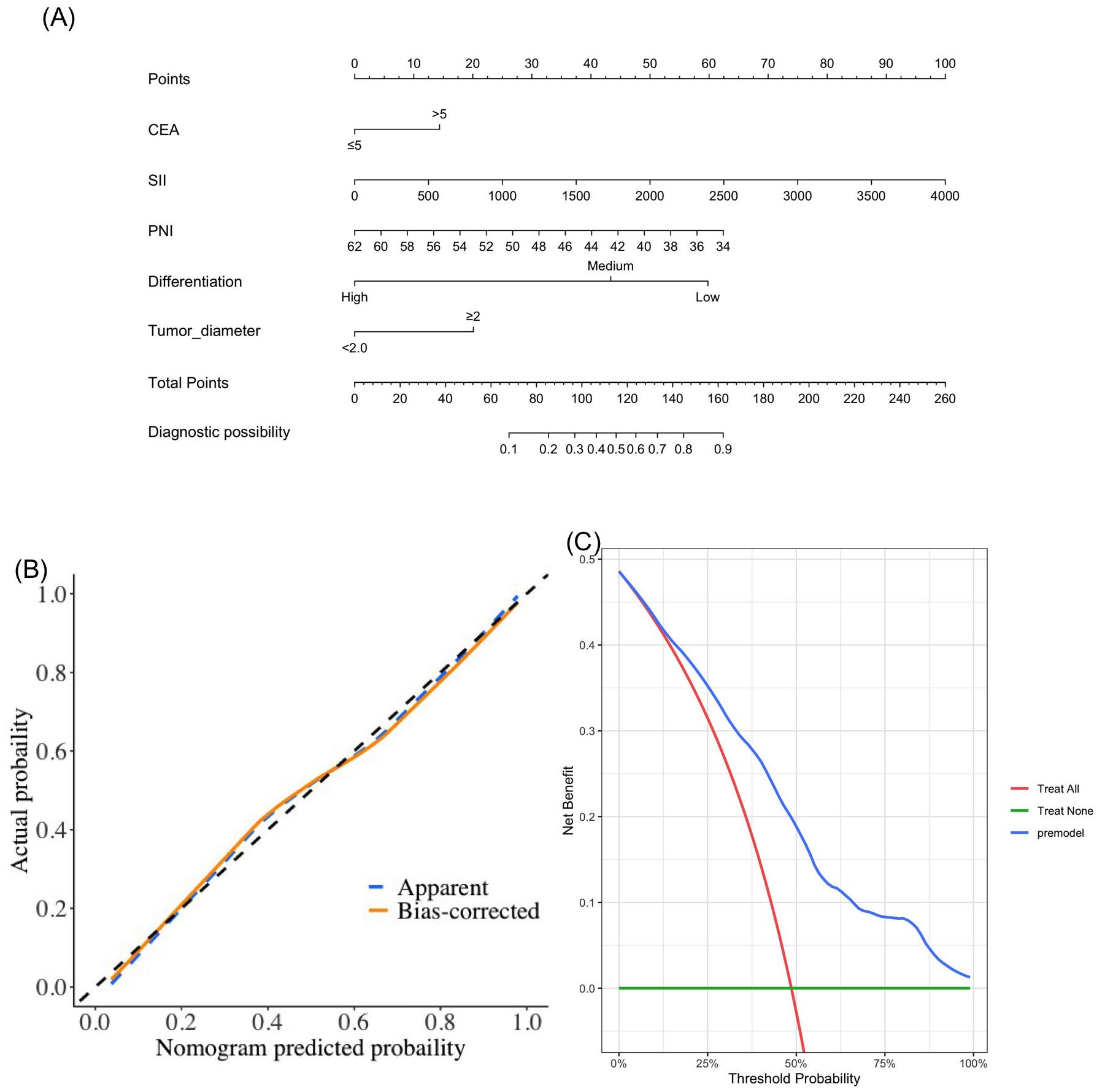
Figure 4. The novel nomogram (A), calibration curve (B) and decision curve (C) in the diagnosis of lymph node metastasis.
4 Discussion
Given the asymptomatic presentation in most patients with GC prior to advanced disease stages, early GC detection assumes paramount importance (27). The main manifestation of GC metastasis is the involvement of lymph node metastasis, which is closely related to the prognosis of patients with GC. In addition, accurate assessment of preoperative lymph node status is important for the choice of GC treatment options. Therefore, it is of great significance to explore accurate preoperative diagnosis of lymph node metastasis for the formulation of treatment plans and prognosis evaluation of patients with GC (28). After a series of analyses, we used CEA, SII and PNI to develop a clinical diagnostic model for lymph node metastasis in patients with GC.
The relationship between inflammatory makers and various tumors has become the current research hotspot. Systemic inflammatory responses have been significantly associated with poor prognosis in patients with cancers (16, 29, 30). Persistent inflammatory responses can stimulate tumor growth, invasion, and metastasis (31). Of the three inflammatory factors (SII, PLR, and NLR) in the present study, SII was the only independent prognostic factor for lymph node metastasis in patients with GC in the full-adjusted statistical models. Our results were consistent with the findings by Cao et al (32). Matsubara et al. also showed that SII was an independent prognostic factor in patients with endometrial cancer and could more precisely predict survival than PLR and NLR (33). In contrast to PLR and NLR, SII consists of three peripheral blood parameters (neutrophils, platelets, and lymphocytes) (34). It can comprehensively reflect the balance of host immunity and inflammation, and dynamically obtain information about host inflammation, immune response and clinical treatment (35). Platelets deliver adenosine triphosphate into the circulation and promote tumorigenesis (36). Lymphocytes control tumor growth by secreting cytokines such as interferon-γ (IFN-γ) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) which interact with each other (37). Neutrophil and platelets can stimulate cancer progression by producing vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and interleukin-6 to enhance tumor angiogenesis and tumor cell epithelial-mesenchymal transition (38, 39).
Patients with cancers are at a high risk of malnutrition due to the proliferation of tumor cells and adverse effects of treatment (34, 40). Previous studies have found that PNI was a prognostic marker for various malignancies. In this study, PNI had a significant negative association with lymph node metastasis in patients with GC. The reason that PNI could be used as a prognostic factor for lymph node metastasis in GC lies in the fact that PNI was calculated from serum albumin concentration and peripheral blood lymphocyte count. Serum albumin may reflect the overall nutritional status of the body, and low serum albumin levels indicate poor nutrition in the host, which can negatively affect overall health, such as damage to the body’s cellular immunity, humoral immunity and phagocytic function and other defense mechanisms, increase inflammatory response, and promote tumor cell invasion function, thereby promoting the occurrence and progression of tumors (41, 42).
Previous research suggest that CEA, CA19-9, CA724, and CA125 are classical tumor markers for GC (43). In the present study, the multivariate analysis showed that CEA with a cut-off of 5ng/ml was an independent risk factor for lymph node metastasis in patients with GC, which could be used for early screening. Nevertheless, CA19-9, CA724, and CA125 were not significantly associated with lymph node metastasis in GC. CEA, a carcino-embryonic antigen, has been shown to play a role in programmed cell death and cell adhesion. Our results are similar with a previous study by Feng et al., who found that among several tumor markers including CEA, CA19-9, and CA125, elevation of CEA level was an independent prognostic factor for the poor prognosis of early GC (9). In addition, the combination of these tumor markers had a relatively low diagnostic value. Therefore, a more sensitive prediction model is warranted to be constructed in further studies.
In the present study, we found that the combination of CEA, SII, PNI, differentiation, and tumor diameter increased the AUC under the ROC to 0.788, which means that the combined index could improve the diagnosis of lymph node metastasis in patients with GC than single marker. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study integrating tumor markers, inflammatory and nutritional indicators to diagnose lymphatic metastasis in GC. In subgroup analyses, the diagnostic sensitivity in male (AUC=0.800) was significantly higher than females (AUC=0.785). This result is consistent with the findings of a previous study showing higher diagnostic significance of systematic markers of inflammation in male than female GC patients (14). This might be explained by a more intense response immune system to lymphatic metastasis of GC cells in males than females, resulting in an increase in the proportion of neutrophils and platelets, and CEA in patients with GC is closely related to lymphatic metastasis (5). Therefore, it is warranted to include the gender factors in the early diagnosis of GC with lymph node metastasis to improve the application value of combined diagnostic indicators.
There are some limitations in this study. Firstly, blood indicators might have been affected by infection and blood circulation capacity. Secondly, we used a single-center retrospective data to build the predictive model, which may be subject to selection bias, Thus, it is necessary to conduct a large-scale prospective study with long-term follow-up from multi-centers to validate our findings. Lastly, the blood neutrophil, lymphocyte, platelet and monocyte was collected at a single time point when admission. Thus, future research should assess the dynamic changes of blood samples in multiple time points.
5 Conclusions
Our study demonstrated that CEA, SII, PNI, differentiation, and tumor diameter were significantly associated with lymph node metastasis in patients with GC, indicating these indices can be used for monitoring of GC patients. In addition, the established nomogram by incorporating CEA, SII, PNI, differentiation, and tumor diameter can effectively predict lymph node metastasis in GC. Therefore, the combined screening of tumor markers and blood routine indicators are recommended in clinical practice to assist in the early diagnosis of lymph node metastasis in patients with GC. Our results may provide a new biological target for the clinical diagnosis and facilitate the process of treatment of GC.
Data availability statement
Data from this study are available upon request from the corresponding author when necessary.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by The ethics committee of Taixing People’s Hospital (LS2023007). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation was not required from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin because Due to the retrospective nature of this study without interacting with patients or using personal identifying information, the need of obtaining informed consent has been waived.
Author contributions
X-RD: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. M-ZZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. LC: Resources, Software, Writing – review & editing. X-WG: Methodology, Software, Writing – review & editing. Z-XL: Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. K-FY: Software, Writing – review & editing. Q-QH: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. H-WC: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Software, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the participants in this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fendo.2025.1522349/full#supplementary-material
Supplementary Figure 1 | Comparison of PLR, NLR, CA19-9, CA125, and CA724 in the diagnosis of lymph node metastasis. (A) PLR, (B) NLR, (C) CA19-9, (D) CA125, (E) CA724.
References
1. López MJ, Carbajal J, Alfaro AL, Saravia LG, Zanabria D, Araujo JM, et al. Characteristics of gastric cancer around the world. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. (2023) 181:103841. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2022.103841
2. Ajani JA, D'Amico TA, Bentrem DJ, Chao J, Cooke D, Corvera C, et al. Gastric cancer, version 2.2022, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Cancer Netw. (2022) 20:167–92. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2022.0008
3. Liang H. Progress in conversion therapy for stage IV gastric cancer. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. (2021) 24:107–11. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn.441530-20201215-00661
4. Dong D, Fang MJ, Tang L, Shan XH, Gao JB, Giganti F, et al. Deep learning radiomic nomogram can predict the number of lymph node metastasis in locally advanced gastric cancer: an international multicenter study. Ann Oncol. (2020) 31:912–20. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2020.04.003
5. Wang K, Jiang X, Ren Y, Ma Z, Cheng X, Li F, et al. The significance of preoperative serum carcinoembryonic antigen levels in the prediction of lymph node metastasis and prognosis in locally advanced gastric cancer: a retrospective analysis. BMC Gastroenterol. (2020) 20:100. doi: 10.1186/s12876-020-01255-6
6. Kwee RM, Kwee TC. Imaging in assessing lymph node status in gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. (2009) 12:6–22. doi: 10.1007/s10120-008-0492-5
7. Ding P, Guo H, Sun C, Yang P, Kim NH, Tian Y, et al. Combined systemic immune-inflammatory index (SII) and prognostic nutritional index (PNI) predicts chemotherapy response and prognosis in locally advanced gastric cancer patients receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy with PD-1 antibody sintilimab and XELOX: a prospective study. BMC Gastroenterol. (2022) 22:121. doi: 10.1186/s12876-022-02199-9
8. Zhou YC, Zhao HJ, Shen LZ. Preoperative serum CEA and CA19-9 in gastric cancer–a single tertiary hospital study of 1,075 cases. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. (2015) 16:2685–91. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2015.16.7.2685
9. Feng F, Tian Y, Xu G, Liu Z, Liu S, Zheng G, et al. Diagnostic and prognostic value of CEA, CA19-9, AFP and CA125 for early gastric cancer. BMC Cancer. (2017) 17:737. doi: 10.1186/s12885-017-3738-y
10. Batra P, Narasannaiah AH, Reddy V, Subramaniyan V, K V M, R Y, et al. Prognostic value of tumor markers in gastric cancer: A tertiary cancer centre experience. Cureus. (2023) 15:e42328. doi: 10.7759/cureus.42328
11. Kotzev AI, Draganov PV. Carbohydrate antigen 19-9, carcinoembryonic antigen, and carbohydrate antigen 72-4 in gastric cancer: is the old band still playing? Gastrointest. Tumors. (2018) 5:1–13. doi: 10.1159/000488240
12. Lin JP, Lin JX, Ma YB, Xie JW, Yan S, Wang JB, et al. Prognostic significance of pre- and post-operative tumour markers for patients with gastric cancer. Br J Cancer. (2020) 123:418–25. doi: 10.1038/s41416-020-0901-z
13. Xiang S, Yang YX, Pan WJ, Li Y, Zhang JH, Gao Y, et al. Prognostic value of systemic immune inflammation index and geriatric nutrition risk index in early-onset colorectal cancer. Front Nutr. (2023) 10:1134300. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1134300
14. Fang T, Wang Y, Yin X, Zhai Z, Zhang Y, Yang Y, et al. Diagnostic sensitivity of NLR and PLR in early diagnosis of gastric cancer. J Immunol Res. (2020) 2020:9146042. doi: 10.1155/2020/9146042
15. Wang Q, Zhu D. The prognostic value of systemic immune-inflammation index (SII) in patients after radical operation for carcinoma of stomach in gastric cancer. J Gastrointest. Oncol. (2019) 10:965–78. doi: 10.21037/jgo.2019.05.03
16. Gao Y, Guo W, Cai S, Zhang F, Shao F, Zhang G, et al. Systemic immune-inflammation-index (SII) is useful to predict survival outcomes in patients with surgically resected esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Cancer. (2019) 10:3188–96. doi: 10.7150/jca.30281
17. Nøst TH, Alcala K, Urbarova I, Byrne KS, Guida F, Sandanger TM, et al. Systemic inflammation markers and cancer incidence in the UK Biobank. Eur J Epidemiol. (2021) 36:841–8. doi: 10.1007/s10654-021-00752-6
18. Chen M, Yang Y, He C, Chen L, Cheng J. Nomogram based on prognostic nutrition index and Chest CT imaging signs predicts lymph node metastasis in NSCLC patients. J X-Ray Sci Technol. (2022) 30:599–612. doi: 10.3233/XST-211080
19. Duan W, Wang W, He C. A novel potential inflammation-nutrition biomarker for predicting lymph node metastasis in clinically node-negative colon cancer. Front Oncol. (2023) 13:995637. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.995637
20. Korkmaz M, Eryılmaz MK, Er MM, Koçak MZ, Demirkıran A, Karaağaç M, et al. Is the prognostic nutritional index a prognostic marker for the survival of patients with lymph-node positive stage II-III gastric cancer who receive adjuvant chemotherapy? J Gastrointest. Cancer. (2023) 54:962–9. doi: 10.1007/s12029-023-00972-x
21. Kocak MZ, Coban S, Araz M, Eryilmaz MK, Artac M. Prognostic biomarkers in metastatic colorectal cancer: delta prognostic nutritional index, delta neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio, and delta platelet to lymphocyte ratio. Support. Care Cancer. (2023) 31:357. doi: 10.1007/s00520-023-07829-w
22. Wang H, Gong H, Tang A, Cui Y. Neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio predicts lymph node metastasis in patients with gastric cancer. Am J Transl Res. (2023) 15:1412–20.
23. Zhang M, Ding C, Xu L, Ou B, Feng S, Wang G, et al. Comparison of a tumor-ratio-metastasis staging system and the 8th AJCC TNM staging system for gastric cancer. Front Oncol. (2021) 11:595421. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.595421
24. In H, Ravetch E, Langdon-Embry M, Palis B, Ajani JA, Hofstetter WL, et al. The newly proposed clinical and post-neoadjuvant treatment staging classifications for gastric adenocarcinoma for the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) staging. Gastric Cancer. (2018) 21:1–9. doi: 10.1007/s10120-017-0765-y
25. Huai Q, Luo C, Song P, Bie F, Bai G, Li Y, et al. Peripheral blood inflammatory biomarkers dynamics reflect treatment response and predict prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer patients with neoadjuvant immunotherapy. Cancer Sci. (2023) 114:4484–98. doi: 10.1111/cas.15964
26. Wang Z, Gao H, Wang X, Grzegorzek M, Li J, Sun H, et al. A multi-Task Learning based applicable AI model simultaneously predicts stage, histology, grade and LNM for cervical cancer before surgery. BMC Womens Health. (2024) 24:425. doi: 10.1186/s12905-024-03270-1
27. Mao Y, Liu J, Li J, Qiu Y, Wang Z, Li B, et al. Elevation of preoperative serum hs-CRP is an independent risk factor for malnutrition in patients with gastric cancer. Front Oncol. (2023) 13:1173532. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1173532
28. Zhang J, Zhang L, Duan S, Li Z, Li G, Yu H. Single and combined use of the platelet-lymphocyte ratio, neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio, and systemic immune-inflammation index in gastric cancer diagnosis. Front Oncol. (2023) 13:1143154. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1143154
29. Deng Y, Zhao Y, Qin J, Huang X, Wu R, Zhou C, et al. Prognostic value of the C-reactive protein/albumin ratio and systemic immune-inflammation index for patients with colorectal liver metastasis undergoing curative resection. Pathol Oncol Res. (2021) 27:633480. doi: 10.3389/pore.2021.633480
30. Li M, Li Z, Wang Z, Yue C, Hu W, Lu H. Prognostic value of systemic immune-inflammation index in patients with pancreatic cancer: a meta-analysis. Clin Exper. Med. (2022) 22:637–46. doi: 10.1007/s10238-021-00785-x
31. Crusz SM, Balkwill FR. Inflammation and cancer: advances and new agents. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. (2015) 12:584–96. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2015.105
32. Cao X, Xue J, Yang H, Han X, Zu G. Association of clinical parameters and prognosis with the pretreatment systemic immune-inflammation index (SII) in patients with gastric cancer. JCPSP-J. Coll Physicians Surg. (2021) 31:83–8. doi: 10.29271/jcpsp.2021.01.83
33. Matsubara S, Mabuchi S, Takeda Y, Kawahara N, Kobayashi H. Prognostic value of pre-treatment systemic immune-inflammation index in patients with endometrial cancer. PloS One. (2021) 16:e248871. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0248871
34. Zheng L, Zou K, Yang C, Chen F, Guo T, Xiong B. Inflammation-based indexes and clinicopathologic features are strong predictive values of preoperative circulating tumor cell detection in gastric cancer patients. Clin Transl Oncol. (2017) 19:1125–32. doi: 10.1007/s12094-017-1649-7
35. Wang BL, Tian L, Gao XH, Ma XL, Wu J, Zhang CY, et al. Dynamic change of the systemic immune inflammation index predicts the prognosis of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after curative resection. Clin Chem Lab Med. (2016) 54:1963–9. doi: 10.1515/cclm-2015-1191
36. He H, Guo W, Song P, Liu L, Zhang G, Wang Y, et al. Preoperative systemic immune-inflammation index and prognostic nutritional index predict prognosis of patients with pulmonary neuroendocrine tumors after surgical resection. Ann Transl Med. (2020) 8:630. doi: 10.21037/atm-19-4476
37. Ferrone C, Dranoff G. Dual roles for immunity in gastrointestinal cancers. J Clin Oncol. (2010) 28:4045–51. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2010.27.9992
38. Baranyai Z, Jósa V, Tóth A, Szilasi Z, Tihanyi B, Zaránd A, et al. Paraneoplastic thrombocytosis in gastrointestinal cancer. Platelets. (2016) 27:269–75. doi: 10.3109/09537104.2016.1170112
39. Hu Z, Zhao X, Wu Z, Qu B, Yuan M, Xing Y, et al. Lymphatic vessel: origin, heterogeneity, biological functions, and therapeutic targets. Signal Transduction Targeting Ther. (2024) 9:9. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01723-x
40. Kaymak ZA, Ozkan EE. The prognostic value of decrease in prognostic nutritional index in stage III non-small cell lung cancer patients during curative thoracic radiotherapy. Indian J Cancer. (2021) 60:18–23. doi: 10.4103/ijc.IJC_14_20
41. Zhou J, Yang D. Prognostic significance of hemoglobin, albumin, lymphocyte and platelet (HALP) score in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatocell. Carcinoma. (2023) 10:821–31. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S411521
42. Liu J, Hu G, Zhai C, Wang J, Xu W, Xie J, et al. Predictive value of nutritional indicators with regard to the survival outcomes in patients with metastatic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma treated with camrelizumab. Oncol Lett. (2023) 25:198. doi: 10.3892/ol.2023.13784
Keywords: gastric cancer, lymph node metastasis, carcinoembryonic antigen, systemic immune-inflammation index, prognostic nutritional index
Citation: Dai X-r, Zhang M-z, Chen L, Guo X-w, Li Z-x, Yan K-f, He Q-q and Cheng H-w (2025) Diagnostic value of systemic immune-inflammation index and prognostic nutritional index combined with CEA in gastric cancer with lymph node metastasis. Front. Endocrinol. 16:1522349. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1522349
Received: 04 November 2024; Accepted: 10 March 2025;
Published: 14 April 2025.
Edited by:
Seema Parte, Stanford University, United StatesReviewed by:
Mehmet Zahid Kocak, Meram Faculty of Medicine, TürkiyeKangping Yang, Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, China
Copyright © 2025 Dai, Zhang, Chen, Guo, Li, Yan, He and Cheng. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hong-wei Cheng, Njc2NTMwODk5QHFxLmNvbQ==; Qi-qiang He, aGVxaXFpYW5nQGdtYWlsLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Xiao-rong Dai1†
Xiao-rong Dai1† Min-zhe Zhang
Min-zhe Zhang Xin-wei Guo
Xin-wei Guo Qi-qiang He
Qi-qiang He