- Department of Thoracic Surgery, The Second Affiliated Hospital, Jiangxi Medical College, Nanchang University, Nanchang, China
Background: The triglyceride-glucose index (TyG index) is one of the surrogate markers of insulin resistance, and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) reflects systemic inflammation. Existing studies suggest that insulin resistance or systemic inflammation may be indicative of cardiometabolic disease, but few of the existing studies have combined the TyG index and inflammation levels before assessing cardiometabolic multimorbidity. Our study data came from the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study (CHARLS). Participants in this data were followed for 9 years, and we used these data to conduct a long-term analysis to assess the combined effects of the TyG index and hsCRP on cardiometabolic multimorbidity in Chinese adults over 45 years of age.
Purpose: To study the combined effect of TyG index and hsCRP on cardiometabolic multimorbidity in middle-aged as well as elderly Chinese.
Method: The study data came from the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study (CHARLS), which included a total of 4,483 middle-aged and elderly participants who did not have cardiovascular metabolic diseases at baseline, which was from CHARLS 2011, and the last survey was in 2020. A total of five cardiometabolic diseases were considered in this study: diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, heart disease and stroke. A person was defined as having cardiometabolic multimorbidity when he/she had two or more cardiometabolic diseases at the same time. TyG index (median as cut-off) and hsCRP (1mg/L as cut-off) were each divided into two groups and combined into four groups (Group L-L: TyG index<median & hsCRP<1mg/L; Group H-L: TyG index>=median & hsCRP<1mg/L; Group L-H: TyG index<median & hsCRP>=1mg/L; Group H-H: TyG index>=median & hsCRP>=1mg/L). Multiple regression equations were fitted to analyse the combined influence of TyG index and hsCRP on cardiometabolic multimorbidity.
Results: TyG index increases the risk of CMM events independently of hsCRP, as does the reverse. When the TyG index is elevated and hsCRP is also elevated, this condition significantly increases the danger of cardiometabolic multimorbidity in middle-aged and elderly Chinese.
Conclusion: High levels of TyG index and hsCRP can enhance the danger of cardiometabolic multimorbidity in Chinese middle-aged and elderly people, and the joint use of hsCRP and TyG index assessment may be a better way to achieve primary prevention of cardiometabolic multimorbidity in Chinese middle-aged and elderly people.
Introduction
Cardiometabolic diseases (CMD), such as stroke, diabetes and hypertension, are becoming increasingly common and represent a major burden on the health of the population, particularly adults over the age of 45 (1). Cardiometabolic multimorbidity (CMM), which is defined as the simultaneous presence of two or more CMDs (including stroke, diabetes mellitus, heart disease, dyslipidemia, and hypertension). In recent years, CMM has received much attention among the population, especially those aged 45 and above (2–5). With the accelerating ageing of the population, cardiovascular health problems are becoming more prevalent in adults over the age of 45, and CMM not only increases the healthcare burden, but also seriously affects people’s quality of life (6, 7).
HsCRP is an inflammatory marker and its elevation is often closely observed in the development of several chronic diseases (8–12). Studies have shown that hsCRP not only has a significant impact on the development of atherosclerosis, but is also a predictor of cardiovascular events (13, 14). Meanwhile, the TyG index, an emerging metabolic index, has shown good potential for use in the early detection of metabolic syndrome, diabetes and cardiovascular disease (15–20). The TyG index is closely linked to lipid metabolism and insulin resistance, and has therefore attracted much attention in the assessment of cardiovascular and metabolic risk (21–24).
The existing research mainly focused on the independent effects of TyG index and hsCRP on cardiovascular risk, but there is relatively limited research on their combined effects and their combined impact on cardiovascular risk in adults older than 45 yearsold. Therefore, by conducting in-depth analyses of the Chinese population aged 45 years or older, we expect to provide valuable guidance for clinical and public health practice to address the growing cardiovascular-metabolic health challenges.
Based on the China Health and Aging National Tracking Survey (CHARLS), this study aims to systematically evaluate the joint effects of TyG index and hsCRP on CMM among Chinese middle-aged and elderly people, and to provide theoretical support for early detection of cardiovascular diseases and appropriate preventive measures.
Materials and methods
Data sources
The data used in this study came from the China Longitudinal Study of Health and Retirement (CHARLS), which is free and open to the public(http://charls.pku.edu.cn/). The first official CHARLS survey began in 2011, using a probability proportional to size sampling technique, and included a total of 17,708 individuals from approximately 10,000 households in China. Four surveys were conducted after the baseline survey and the results published (2013, 2015, 2018, and 2020) (25).
Study population
Each survey was conducted face-to-face by trained staff and participants using a standardized questionnaire (26). The study used participants from the first visit (2011-2012) as the baseline, with a total of four subsequent follow-up visits. Participants with cardiovascular-metabolic diseases at baseline and missing variables such as sex and age were not included. In the end, our study included 4,483 participants. (see Figure 1 for details).
CMM
Cardiovascular metabolic diseases (CMDs) in this study mainly consisted of diabetes mellitus, hypertension, dyslipidemia, stroke and heart disease, and a CMM event was considered to have occurred when 2 or more CMDs occurred (27, 28). Determination of the occurrence of CMD in patients was confirmed by trained volunteers who were interviewed using a standardized questionnaire. Standardized blood pressure measurements were taken (3 measurements with a sphygmomanometer (Omron HEM-7200 monitor) in a relaxed and comfortable environment after at least 5 minutes of rest), and patients were considered to be hypertensive when their systolic blood pressure was ≥140 mmHg and/or diastolic blood pressure was ≥90 mmHg (26, 29); Participants also underwent blood tests to determine whether they had diabetes mellitus or dyslipidemia.
The time when the participant had a second CMD was considered as the time of onset of CMM. Interviewers underwent rigorous training before participating in the questionnaire, and the questionnaire was highly consistent with its international counterparts. The quality of this questionnaire was thus assured.
Covariates
Gender, age, matrimonial, education, place of living, smoking, drinking, liver disease, kidney disease, sleep time, hsCRP, tyg index, RMS, uric acid, creatinine, uric acid, hemoglobin were the covariates in this study. matrimonial was categorized as ‘Married’ and ‘Other’; Educational level was categorized as ‘Primary school below’, ‘Primary school’, ‘Middle school’, ‘High school and above’; place of living was categorized as ‘Municipalities’, ‘Countryside’; Smoking was categorized as ‘Yes’ and ‘No’; drinking was categorized as ‘Never’, ‘Former’, ‘Current’ and ‘Always’; C-reactive protein (CRP) was quantified by immunoturbidimetric technique. The hsCRP was classified as “<1mg/L” and “>=1mg/L” according to previous literature; TyG index was classified as ‘<median’ and ‘>=median’ based on median (30); RMS was calculated as ASM = 0.193 * weight (kg) + 0.107 * height (cm) - 4.157 * Sex - 0.037 *Age (years) - 2.631, with sex set to 1 for males and 2 for females (31).
Statistical analysis
Continuous data are presented as mean ± standard deviation (Mean+SD) and categorical data as frequencies and percentages (N (%)). TyG index (median as cut-off) and hsCRP (1mg/L as cut-off) were divided into two groups each and combined into four groups (Group L-L: TyG index<median & hsCRP<1mg/L; Group H-L: TyG index>=median & hsCRP<1mg/L; Group L-H: TyG index<median & hsCRP>=1mg/L; Group H-H: TyG index>=median & hsCRP>=1mg/L). Hazard ratios (HR) and 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) between different TyG index, hsCRP and cardiometabolic multimorbidity were calculated using multiple regression analysis. Group L-L was used as the reference group in the multivariate regression analyses, and model I was only controlled for Gender and Age; model II was controlled for all variables: gender; age; marry; education; residence; drink; smoke; liver disease; kidney disease. Sleeping time; RMS; Blood Urea Nitrogen; Creatinine; Total Cholesterol; Uric Acid; Hemoglobin.
Empower Stats (4.2), SPSS (IBM Statistics 26.0) as well as GraphPad Prism (9.0.0) were performed to analyses the data and statistical differences were considered to exist when the p-value was lower than 0.05.
Result
17,708 participants took the first survey. After exclusion, a total of 4,483 participants took part in the current study, and these participants took part in at least one of the CHARLS surveys 2 to 5 (see Figure 1 for details).
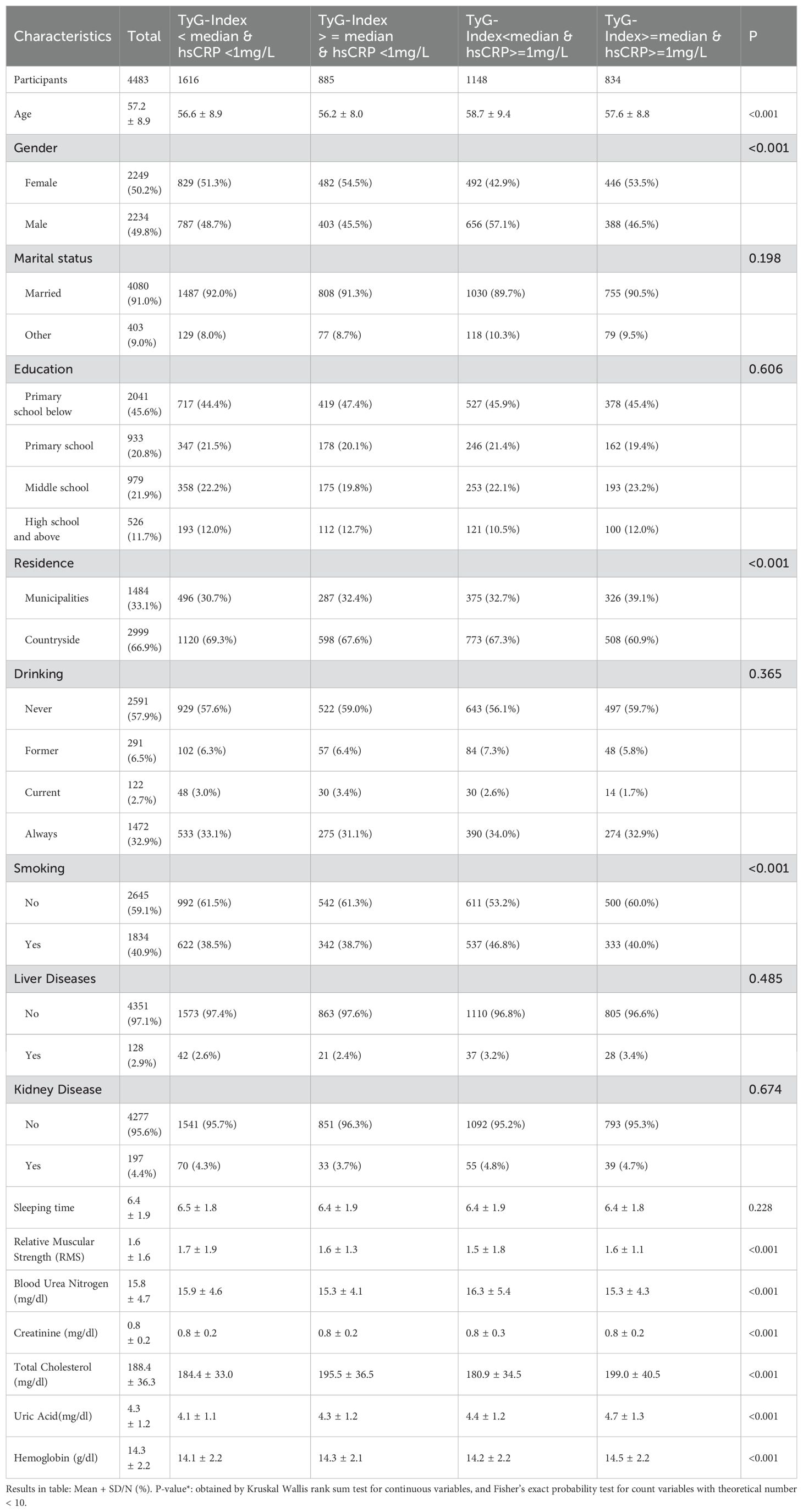
In Table 1, the mean age of the participants who took part in the first (CHARLS 2011) survey was 57.2 ± 8.9 years, with 2234 (49.8%) males and 2249 (50.2%) females, the majority of the participants were married, with educational attainment concentrated below primary school level, and with a majority of their residence being in rural areas.
A total of 965 (22%) of the 4483 participants included in the study had cardiometabolic multimorbidity at the end of the five surveys conducted by CHARLS, 667 (69%) of the participants had heart disease, 241 (5%) of the participants had stroke, 1802 (40%) of the participants had hypertension, 479 (11%) of the participants had diabetes mellitus and 839 (19%) of the participants had dyslipidemia.
The incidence of CMM was 20.0/1000 years for participants in Group L-L; 28.9/1000 years for participants in Group H-L; and 28.9/1000 years for participants in Group L-H had a CMM incidence rate of 24.1/1000 years; and participants in Group H-H had a CMM incidence rate of 37.7/1000 years. Figure 2 illustrates the KM curves of different combinations of TyG index and hsCRP levels with the cumulative incidence of cardiometabolic multimorbidity.
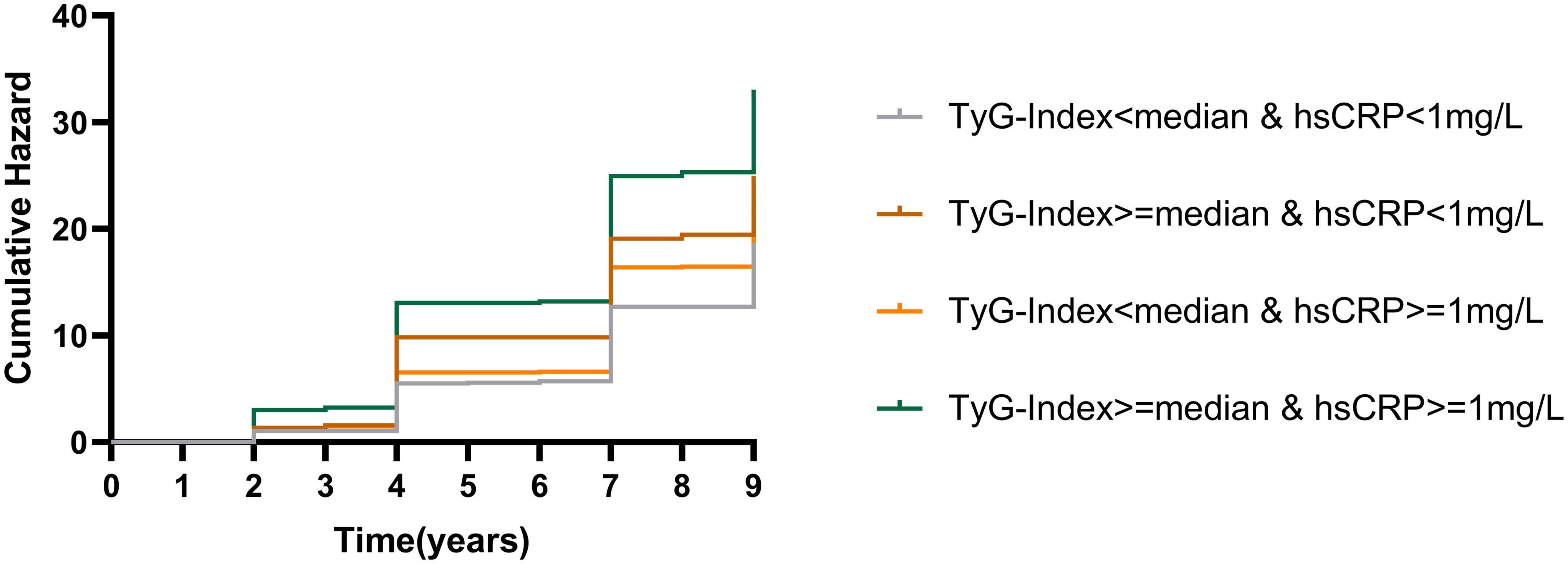
Figure 2. K-M plots of cardiometabolic multimorbidity at different TyG index and hsCRP levels. TyG, triglyceride-glucose index; hsCRP, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein.
Table 2 displays the combined effect of TyG index and hsCRP levels on the hazard of cardiometabolic multimorbidity, using Group L-L as the reference group, and adjusting for confounders (Model II) the group with elevated TyG index alone (HR=1.3, 95%CI=1.1-1.7, p=0.009), the group with elevated hsCRP alone (HR=1.2, 95%CI=1.0-1.5, p=0.036) and the group with both elevated TyG index and hsCRP (HR=2.1, 95%CI=1.7-2.5, p<0.001) participants had a significantly higher risk of CMM. In model II, stroke, hypertension, diabetes and dyslipidemia were all associated with a significantly increased risk of developing CMM with both TyG index and hsCRP elevated compared to the group with neither TyG index nor hsCRP elevated, and although p>0.05 was found for cardiac events, the 95 confidence intervals of the HRs were all greater than 1 (HR=1.3, 95%CI=1.0-1.6, p=0.001, p<0.001). -1.6, p=0.09).
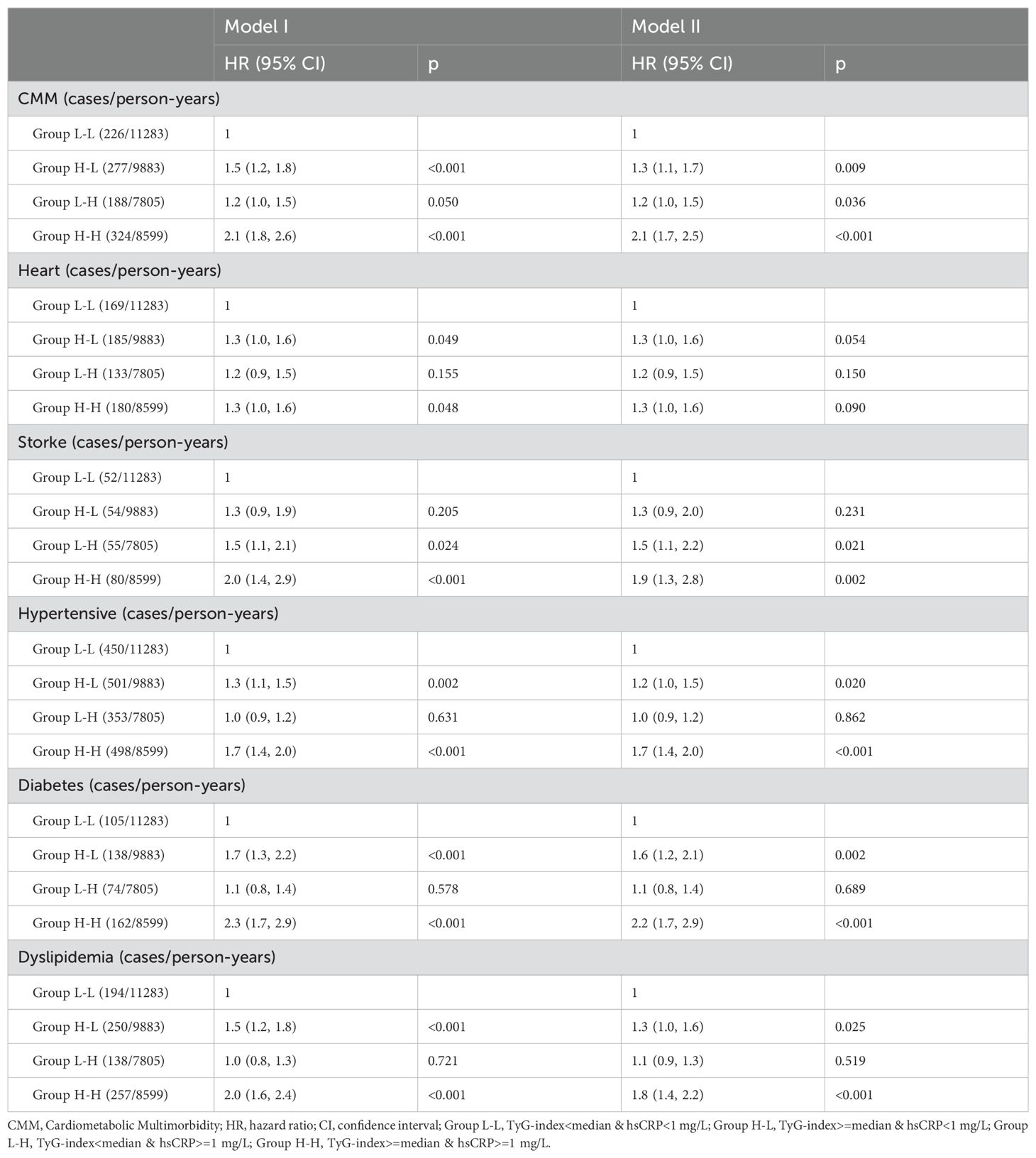
Table 2. Risk of cardiometabolic multimorbidity after co-exposure stratified by TyG-index and hsCRP.
As can be seen from Table 3, participants had a markedly increased hazard of CMM events when hsCRP was elevated, regardless of the level of TyG index; conversely, participants also had a markedly higher hazard of CMM events when TyG index was elevated, regardless of the level of hsCRP. In age strata, the influence of concurrently elevated levels of TyG index and hsCRP on participants was concentrated in those aged 45-69 years, as shown in Figure 3 and Supplementary Figure S1.
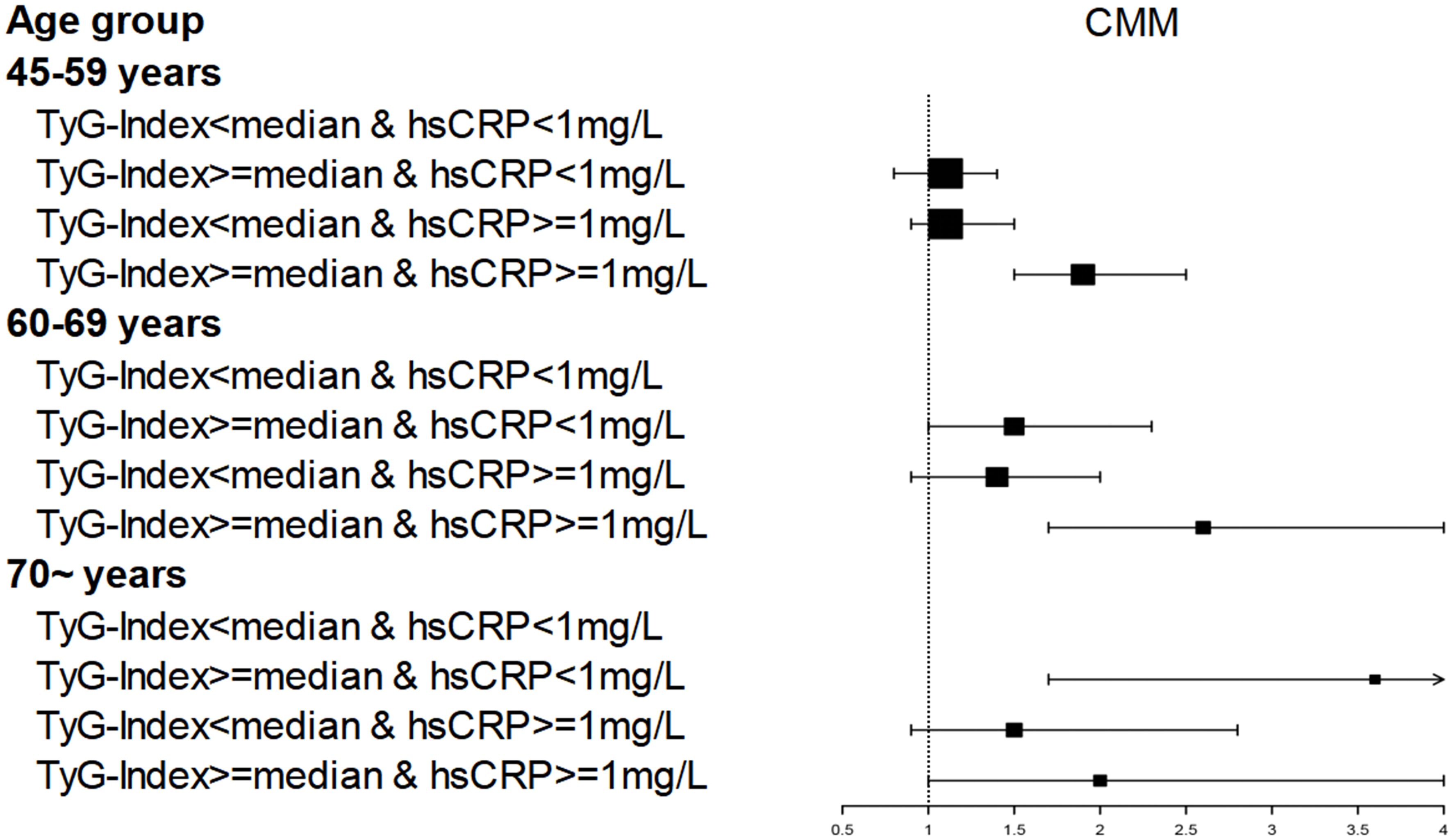
Figure 3. Age affects the association of TyG index and hsCRP levels with CMM occurrence.CMM, Cardiometabolic Multimorbidity; TyG-index, triglyceride-glucose index; hsCRP, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein; HR hazard ratio, CI confidence interval. Number of participants: 45–59 years (n=2903); 60–69 years (n=1090); 70 ~ years (n=490). Dots and lines represent the HR and 95% CI.
Discussion
By analysing the health records of 4,483 middle-aged and older Chinese adults followed for 9 years, we found that increased levels of the TyG index and hsCRP led to an increased risk of cardiometabolic multimorbidity, which was most significant in people aged 45-69 years. Furthermore, we found that both TyG index and hsCRP can influence cardiometabolic multimorbidity independently of each other. This result held true after we adjusted for numerous risk factors.
Previous studies have generally assessed the effect of TyG index or hsCRP on cardiometabolic multimorbidity (CMM).
The TyG index may serve as a useful alternative marker of insulin resistance, which has been shown to contribute to atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease (32–35). Insulin resistance can lead to increased activity of the sympathetic nervous system, making sodium less easily excreted from the body as well as causing vascular excitation (36). Numerous studies have also shown that TyG index is strongly associated with cardiovascular and metabolic diseases (37–39), and Zhao S et al. found that elevated TyG index could lead to arterial stiffness and microvascular damage in northern Shanghai, China (40), and that vascular stiffness and damage play a key role in stroke and cardiac events (41–43). Moreover, several studies have found that the TyG index is strongly associated with the development of cardiovascular metabolic disease, and that elevated TyG index significantly increases the incidence of cardiovascular metabolic diseases (35, 36, 44–48).
hsCRP is one of the more common inflammatory markers, and has been studied by many scholars because of its close relationship with cardiovascular metabolic diseases. The role of inflammation in cardiovascular metabolic diseases is well established, and hsCRP is a well-recognised marker of cardiovascular risk (49, 50). Numerous studies have shown that inflammation levels are significantly associated with atherosclerosis (51, 52). Inflammation has a major role in affecting lipid metabolism and increasing insulin resistance (53–56). Verma et al. found that vascular inflammation is the core factor contributing to atherosclerosis (57), and Ridker et al. demonstrated that not only cholesterol, but also inflammation is not to be underestimated in atherosclerosis risk. Therefore, we should pay attention to the effect of inflammation on atherosclerosis to detect vascular lesions earlier. Many scholars have used the combination of hsCRP and TyG index for the evaluation of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases as well as for the assessment of cancer prognosis (57–60), which shows that the combination of hsCRP and TyG index is of great clinical significance.
Our present study focused on analyzing the joint influence of hsCRP and TyG index on cardiometabolic diseases. We found that participants with both high levels of hsCRP and high levels of TyG index had a significantly higher risk of cardiometabolic diseases than those with low levels of both hsCRP nor TyG index, and this phenomenon is evident in the 45-69 age group. Zuliani et al. have also suggested that indicators of chronic inflammation and insulin resistance should be used more comprehensively when assessing for older adults (61).
We also found that hsCRP significantly assessed the risk of cardiometabolic events when influenced by the TyG index; similarly, the TyG index significantly assessed the risk of cardiometabolic events when influenced by hsCRP, suggesting that hsCRP and TyG indices alone can be used for the early detection of cardiometabolic events in the clinical setting.
The effect of hsCRP and Tyg index on the risk of cardiometabolic multimorbidity may arise from several causes. The mechanisms linking insulin resistance and chronic inflammation to vascular sclerosis, vascular injury, and dyslipidemia are complex. Insulin resistance leads to abnormal lipid metabolism and microvascular injury leading to metabolic diseases and cardiovascular events (33, 40, 62). Under normal circumstances, the endothelial cells of human blood vessels protect the vascular system by synthesizing nitric oxide, while insulin resistance often triggers oxidative stress reactions, leading to increased inflammation and decreased endothelial nitric oxide synthase activity, resulting in reduced production of protective nitric oxide (63–67). In addition, insulin resistance is related to the increase of free fatty acid and reactive oxygen species levels and the onset of dyslipidemia, which will lead to oxidative stress and the release of proinflammatory cytokines, damage insulin signal transduction, and accelerate atherosclerosis (33, 65, 68–70). Furthermore, from a pathological point of view, insulin resistance inhibits PI-3 kinase activity and eNOS expression, ultimately leading to vascular endothelial dysfunction (71, 72). Inflammatory mediators released in response to inflammation can influence insulin regulation of nitric oxide and endothelin-1 affecting vasoregulation, and hsCRP can bind lipoproteins for pro-inflammatory complement activation (73, 74). Inflammation also promotes insulin resistance through the oxidative stress, sympathetic activity and immune responses (16, 41, 75). Insulin resistance can promote the occurrence and development of inflammation, and conversely, the presence of inflammation can also promote insulin resistance.
Sodium dependent glucose transporters 2 inhibitors(SGLT2i)and Glucagon like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1RA) are both new hypoglycemic drugs. Initially, these two drugs were used to treat diabetes. But with further research, researchers have found that SGLT2i and GLP-1RA also have functions of inhibiting fibrosis, inhibiting cell apoptosis, reducing inflammation, and alleviating oxidative stress (76, 77). And multiple studies have shown that SGLT2i and GLP-1RA have protective effects on the cardiovascular system (78–81). In the near future, SGLT2i and GLP-1RA may have significant implications for CMM.
Limitations of the study
The CHAARLS database used in this study has a long follow-up period (2011-2020), is rigorous in data collection, and has data covering 450 village-level units in China. However, there are some limitations. First, cardiac events and strokes were obtained by questionnaire, and although the database has a detailed and rigorous process and face-to-face interviews by professionally trained volunteers, there may still be bias from respondents. Second, although we included many possible influencing factors, some unmeasured confounders (e.g., psychiatric scores and economic situation) may still have an impact on the results. Third, since the participants were all from the Chinese region, it may not be representative for regions such as Europe and the United States.
Conclusion
High levels of TyG index and hsCRP may raise the danger of cardiometabolic multimorbidity in Chinese middle-aged and elderly people, and the joint use of TyG index and hsCRP may be a better way to achieve primary prevention of cardiometabolic multimorbidity in Chinese middle-aged and elderly people.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found below: https://charls.charlsdata.com/users/sign_up/agreement/zh-cn.html.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Institutional Review Board of Peking University (IRB00001052-11015). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
BW: Conceptualization, Methodology, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. SW: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Resources, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. SH: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Resources, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. WH: Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft. SQ: Validation, Writing – review & editing. LZ: Validation, Writing – original draft. LR: Formal Analysis, Writing – review & editing. YW: Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. JX: Data curation, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. National Natural Science Foundation of China, Award Number: 82160410 | Recipient: Yiping Wei; Jiangxi Provincial Department of Science and Technology, Award Number: 20212ACB206018 | Recipient: Yiping Wei; Key Research and Development Program of Jiangxi Province, Award Number: 20223BBG71009 | Recipient: Yiping Wei. Jiangxi Province Graduate Innovation Fund Project [grant number YC2023-B082]; Recipient: Sheng Hu.
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our gratitude to all those who participated in the data collection phase of the CHARLS project, for their time and effort.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fendo.2025.1511319/full#supplementary-material.
Supplementary Figure 1 | TyG index and hsCRP are associated with the risk of cardiometabolic multimorbidity when stratified by age, related to Figure 3.
References
1. Sawaf B, Swed S, Alibrahim H, Bohsas H, Dave T, Nasif MN, et al. Triglyceride-glucose index as predictor for hypertension, CHD and STROKE risk among non-diabetic patients: A NHANES cross-sectional study 2001-2020. J Epidemiol Glob Health. (2024) 14:1152–66. doi: 10.1007/s44197-024-00269-7
2. Wang J, Yang Y, Su Q, Wang J, Zeng H, Chen Y, et al. Association between muscle strength and cardiometabolic multimorbidity risk among middle-aged and older Chinese adults: a nationwide longitudinal cohort study. BMC Public Health. (2024) 24:2012. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-19521-7
3. Ye X, Zhang G, Han C, Wang P, Lu J, Zhang M. The association between Chinese visceral adiposity index and cardiometabolic multimorbidity among Chinese middle-aged and older adults: a national cohort study. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2024) 15:1381949. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1381949
4. Wang M, Su W, Chen H, Li H. Depressive symptoms and risk of incident cardiometabolic multimorbidity in community-dwelling older adults: The China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study. J Affect Disord. (2023) 335:75–82. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2023.04.048
5. Roerecke M. Alcohol’s impact on the cardiovascular system. Nutrients. (2021) 13(10):3419. doi: 10.3390/nu13103419
6. Tahir UA, Gerszten RE. Molecular biomarkers for cardiometabolic disease: risk assessment in young individuals. Circ Res. (2023) 132:1663–73. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.123.322000
7. Aryan L, Younessi D, Zargari M, Banerjee S, Agopian J, Rahman S, et al. The role of estrogen receptors in cardiovascular disease. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21(12):4314. doi: 10.3390/ijms21124314
8. Zhang L, He G, Huo X, Tian A, Ji R, Pu B, et al. Long-term cumulative high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and mortality among patients with acute heart failure. J Am Heart Assoc. (2023) 12:e029386. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.123.029386
9. Cheng ZJ, Wang YF, Jiang XY, Ren WY, Lei SF, Deng FY, et al. High sensitivity C-reactive protein and prediabetes progression and regression in middle-aged and older adults: A prospective cohort study. J Diabetes Investig. (2024) 15:78–86. doi: 10.1111/jdi.14090
10. Stroes ESG, Bays HE, Banach M, Catapano AL, Duell PB, Laufs U, et al. Bempedoic acid lowers high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol: Analysis of pooled data from four phase 3 clinical trials. Atherosclerosis. (2023) 373:1–9. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2023.03.020
11. Tang M, Cao H, Wei XH, Zhen Q, Liu F, Wang YF, et al. Association between high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and diabetic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2022) 13:885516. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.885516
12. Lin CC, Li CI, Liu CS, Liao LN, Yang CW, Lin CH, et al. Association of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes: a Mendelian randomization study. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. (2023) 11(1):e003197. doi: 10.1136/bmjdrc-2022-003197
13. Yang X, Yang X, Yang J, Wen X, Wu S, Cui L. High levels of high-sensitivity C reactive protein to albumin ratio can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease. J Epidemiol Community Health. (2023) 77:721–7. doi: 10.1136/jech-2023-220760
14. Bienstock S, Lee SE, Lin F, Blankstein R, Leipsic J, Patel K, et al. Systemic inflammation with high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and atherosclerotic plaque progression. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. (2024) 17:212–3. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2023.08.019
15. Alizargar J, Bai CH, Hsieh NC, Wu SV. Use of the triglyceride-glucose index (TyG) in cardiovascular disease patients. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2020) 19:8. doi: 10.1186/s12933-019-0982-2
16. Zhang Q, Xiao S, Jiao X, Shen Y. The triglyceride-glucose index is a predictor for cardiovascular and all-cause mortality in CVD patients with diabetes or pre-diabetes: evidence from NHANES 2001-2018. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2023) 22:279. doi: 10.1186/s12933-023-02030-z
17. Xiao S, Zhang Q, Yang HY, Tong JY, Yang RQ. The association between triglyceride glucose-body mass index and all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in diabetes patients: a retrospective study from NHANES database. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:13884. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-63886-z
18. Huang R, Wang Z, Chen J, Bao X, Xu N, Guo S, et al. Prognostic value of triglyceride glucose (TyG) index in patients with acute decompensated heart failure. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2022) 21:88. doi: 10.1186/s12933-022-01507-7
19. Son DH, Lee HS, Lee YJ, Lee JH, Han JH. Comparison of triglyceride-glucose index and HOMA-IR for predicting prevalence and incidence of metabolic syndrome. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. (2022) 32:596–604. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2021.11.017
20. Wan H, Cao H, Ning P. Superiority of the triglyceride glucose index over the homeostasis model in predicting metabolic syndrome based on NHANES data analysis. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:15499. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-66692-9
21. Ramdas Nayak VK, Satheesh P, Shenoy MT, Kalra S. Triglyceride Glucose (TyG) Index: A surrogate biomarker of insulin resistance. J Pak Med Assoc. (2022) 72:986–8. doi: 10.47391/JPMA.22-63
22. Zhao J, Fan H, Wang T, Yu B, Mao S, Wang X, et al. TyG index is positively associated with risk of CHD and coronary atherosclerosis severity among NAFLD patients. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2022) 21:123. doi: 10.1186/s12933-022-01548-y
23. Zhan H, Liu X, Piao S, Rong X, Guo J. Association between triglyceride-glucose index and bone mineral density in US adults: a cross sectional study. J Orthop Surg Res. (2023) 18:810. doi: 10.1186/s13018-023-04275-6
24. Kim S, Lee JW, Lee Y, Song Y, Linton JA. Association between triglyceride-glucose index and low-density lipoprotein particle size in korean obese adults. Lipids Health Dis. (2023) 22:94. doi: 10.1186/s12944-023-01857-5
25. Zhao Y, Hu Y, Smith JP, Strauss J, Yang G. Cohort profile: the China health and retirement longitudinal study (CHARLS). Int J Epidemiol. (2014) 43:61–8. doi: 10.1093/ije/dys203
26. Zuo HJ, Ma JX, Wang JW, Chen XR. Assessing the routine-practice gap for home blood pressure monitoring among Chinese adults with hypertension. BMC Public Health. (2020) 20:1770. doi: 10.1186/s12889-020-09901-0
27. Di Angelantonio E, Kaptoge S, Wormser D, Willeit P, Butterworth AS, Bansal N, et al. Association of cardiometabolic multimorbidity with mortality. Jama. (2015) 314:52–60. doi: 10.1001/jama.2015.7008
28. Itani O, Jike M, Watanabe N, Kaneita Y. Short sleep duration and health outcomes: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression. Sleep Med. (2017) 32:246–56. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2016.08.006
29. Joint Committee for Guideline Revision. 2018 chinese guidelines for prevention and treatment of hypertension-A report of the revision committee of chinese guidelines for prevention and treatment of hypertension. J Geriatr Cardiol. (2019) 16:182–241. doi: 10.11909/j.issn.1671-5411.2019.03.014
30. Feng G, Yang M, Xu L, Liu Y, Yu J, Zang Y, et al. Combined effects of high sensitivity C-reactive protein and triglyceride-glucose index on risk of cardiovascular disease among middle-aged and older Chinese: Evidence from the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. (2023) 33:1245–53. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2023.04.001
31. Wen X, Wang M, Jiang CM, Zhang YM. Anthropometric equation for estimation of appendicular skeletal muscle mass in Chinese adults. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. (2011) 20:551–6.
32. Zhang Z, Zhao L, Lu Y, Meng X, Zhou X. Relationship of triglyceride-glucose index with cardiometabolic multi-morbidity in China: evidence from a national survey. Diabetol Metab Syndr. (2023) 15:226. doi: 10.1186/s13098-023-01205-8
33. Laakso M, Kuusisto J. Insulin resistance and hyperglycaemia in cardiovascular disease development. Nat Rev Endocrinol. (2014) 10:293–302. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2014.29
34. Uetani T, Amano T, Harada K, Kitagawa K, Kunimura A, Shimbo Y, et al. Impact of insulin resistance on post-procedural myocardial injury and clinical outcomes in patients who underwent elective coronary interventions with drug-eluting stents. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. (2012) 5:1159–67. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2012.07.008
35. Yang Y, Huang X, Wang Y, Leng L, Xu J, Feng L, et al. The impact of triglyceride-glucose index on ischemic stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2023) 22:2. doi: 10.1186/s12933-022-01732-0
36. Lee DH, Park JE, Kim SY, Jeon HJ, Park JH. Association between the triglyceride-glucose (TyG) index and increased blood pressure in normotensive subjects: a population-based study. Diabetol Metab Syndr. (2022) 14:161. doi: 10.1186/s13098-022-00927-5
37. Wang L, Cong HL, Zhang JX, Hu YC, Wei A, Zhang YY, et al. Triglyceride-glucose index predicts adverse cardiovascular events in patients with diabetes and acute coronary syndrome. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2020) 19:80. doi: 10.1186/s12933-020-01054-z
38. Zhu Y, Liu K, Chen M, Liu Y, Gao A, Hu C, et al. Triglyceride-glucose index is associated with in-stent restenosis in patients with acute coronary syndrome after percutaneous coronary intervention with drug-eluting stents. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2021) 20:137. doi: 10.1186/s12933-021-01332-4
39. Zhou Q, Yang J, Tang H, Guo Z, Dong W, Wang Y, et al. High triglyceride-glucose (TyG) index is associated with poor prognosis of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2023) 22:263. doi: 10.1186/s12933-023-02001-4
40. Zhao S, Yu S, Chi C, Fan X, Tang J, Ji H, et al. Association between macro- and microvascular damage and the triglyceride glucose index in community-dwelling elderly individuals: the Northern Shanghai Study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2019) 18:95. doi: 10.1186/s12933-019-0898-x
41. Zysset D, Weber B, Rihs S, Brasseit J, Freigang S, Riether C, et al. TREM-1 links dyslipidemia to inflammation and lipid deposition in atherosclerosis. Nat Commun. (2016) 7:13151. doi: 10.1038/ncomms13151
42. Zuniga MC, White SL, Zhou W. Design and utilization of macrophage and vascular smooth muscle cell co-culture systems in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease investigation. Vasc Med. (2014) 19:394–406. doi: 10.1177/1358863X14550542
43. Zhang Y, Wu Z, Li X, Wei J, Zhang Q, Wang J. Association between the triglyceride-glucose index and carotid plaque incidence: a longitudinal study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2022) 21:244. doi: 10.1186/s12933-022-01683-6
44. Liu X, Tan Z, Huang Y, Zhao H, Liu M, Yu P, et al. Relationship between the triglyceride-glucose index and risk of cardiovascular diseases and mortality in the general population: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2022) 21:124. doi: 10.1186/s12933-022-01546-0
45. Han Y, Hai J, Yang X, Lu D, Li J, Yan X, et al. The synergistic effect of triglyceride-glucose index and HbA1c on blood pressure control in patients with hypertension: a retrospective cohort study. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:20038. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-70213-z
46. Liu L, Wu Z, Zhuang Y, Zhang Y, Cui H, Lu F, et al. Association of triglyceride-glucose index and traditional risk factors with cardiovascular disease among non-diabetic population: a 10-year prospective cohort study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2022) 21:256. doi: 10.1186/s12933-022-01694-3
47. Zhou H, Ding X, Lan Y, Fang W, Yuan X, Tian Y, et al. Dual-trajectory of TyG levels and lifestyle scores and their associations with ischemic stroke in a non-diabetic population: a cohort study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2024) 23:225. doi: 10.1186/s12933-024-02313-z
48. Zheng H, Chen G, Wu K, Wu W, Huang Z, Wang X, et al. Relationship between cumulative exposure to triglyceride-glucose index and heart failure: a prospective cohort study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2023) 22:239. doi: 10.1186/s12933-023-01967-5
49. Zimmermann O, Bienek-Ziolkowski M, Wolf B, Vetter M, Baur R, Mailänder V, et al. Myocardial inflammation and non-ischaemic heart failure: is there a role for C-reactive protein? Basic Res Cardiol. (2009) 104:591–9. doi: 10.1007/s00395-009-0026-2
50. Zakai NA, Katz R, Jenny NS, Psaty BM, Reiner AP, Schwartz SM, et al. Inflammation and hemostasis biomarkers and cardiovascular risk in the elderly: the Cardiovascular Health Study. J Thromb Haemost. (2007) 5:1128–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2007.02528.x
51. Zieske AW, Tracy RP, McMahan CA, Herderick EE, Homma S, Malcom GT, et al. Elevated serum C-reactive protein levels and advanced atherosclerosis in youth. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2005) 25:1237–43. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000164625.93129.64
52. Yousuf O, Mohanty BD, Martin SS, Joshi PH, Blaha MJ, Nasir K, et al. High-sensitivity C-reactive protein and cardiovascular disease: a resolute belief or an elusive link? J Am Coll Cardiol. (2013) 62:397–408. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.05.016
53. Xi L, Xiao C, Bandsma RH, Naples M, Adeli K, Lewis GF. C-reactive protein impairs hepatic insulin sensitivity and insulin signaling in rats: role of mitogen-activated protein kinases. Hepatology. (2011) 53:127–35. doi: 10.1002/hep.24011
54. Velásquez-Mieyer PA, Cowan PA, Pérez-Faustinelli S, Nieto-Martínez R, Villegas-Barreto C, Tolley EA, et al. Racial disparity in glucagon-like peptide 1 and inflammation markers among severely obese adolescents. Diabetes Care. (2008) 31:770–5. doi: 10.2337/dc07-1525
55. Tanigaki K, Sundgren N, Khera A, Vongpatanasin W, Mineo C, Shaul PW. Fcγ receptors and ligands and cardiovascular disease. Circ Res. (2015) 116:368–84. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.302795
56. Olefsky JM, Glass CK. Macrophages, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Annu Rev Physiol. (2010) 72:219–46. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-021909-135846
57. Li Q, Song Y, Zhang Z, Xu J, Liu Z, Tang X, et al. The combined effect of triglyceride-glucose index and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein on cardiovascular outcomes in patients with chronic coronary syndrome: A multicenter cohort study. J Diabetes. (2024) 16:e13589. doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.13589
58. Ruan GT, Xie HL, Zhang HY, Liu CA, Ge YZ, Zhang Q, et al. A novel inflammation and insulin resistance related indicator to predict the survival of patients with cancer. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2022) 13:905266. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.905266
59. Cui C, Liu L, Qi Y, Han N, Xu H, Wang Z, et al. Joint association of TyG index and high sensitivity C-reactive protein with cardiovascular disease: a national cohort study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2024) 23:156. doi: 10.1186/s12933-024-02244-9
60. Zhang N, Xiang Y, Zhao Y, Ji X, Sang S, Shao S, et al. Association of triglyceride-glucose index and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein with asymptomatic intracranial arterial stenosis: A cross-sectional study. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. (2021) 31:3103–10. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2021.07.009
61. Zuliani G, Morieri ML, Volpato S, Maggio M, Cherubini A, Francesconi D, et al. Insulin resistance and systemic inflammation, but not metabolic syndrome phenotype, predict 9 years mortality in older adults. Atherosclerosis. (2014) 235:538–45. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2014.05.959
62. Jiang L, Xu HY, Li Y, Shi K, Fang H, Yan WF, et al. The differential effects of dyslipidemia status and triglyceride-glucose index on left ventricular global function and myocardial microcirculation in diabetic individuals: a cardiac magnetic resonance study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2024) 23:345. doi: 10.1186/s12933-024-02435-4
63. Zhang W, Liu L, Chen H, Li S, Wan M, Mohammed AQ, et al. Association between the triglyceride-glucose index and the presence and prognosis of coronary microvascular dysfunction in patients with chronic coronary syndrome. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2023) 22:113. doi: 10.1186/s12933-023-01846-z
64. Dang K, Wang X, Hu J, Zhang Y, Cheng L, Qi X, et al. The association between triglyceride-glucose index and its combination with obesity indicators and cardiovascular disease: NHANES 2003-2018. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2024) 23:8. doi: 10.1186/s12933-023-02115-9
65. Hu Y, Kong Y, Tian X, Zhang X, Zuo Y. Association between Heavy metals and triglyceride-glucose-related index: a mediation analysis of inflammation indicators. Lipids Health Dis. (2025) 24:46. doi: 10.1186/s12944-025-02441-9
66. Bornfeldt KE, Tabas I. Insulin resistance, hyperglycemia, and atherosclerosis. Cell Metab. (2011) 14:575–85. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2011.07.015
67. Davidson JA, Parkin CG. Is hyperglycemia a causal factor in cardiovascular disease? Does proving this relationship really matter? Yes. Diabetes Care. (2009) 32 Suppl 2:S331–3. doi: 10.2337/dc09-S333
68. Konst RE, Guzik TJ, Kaski JC, Maas AHEM, Elias-Smale SE. The pathogenic role of coronary microvascular dysfunction in the setting of other cardiac or systemic conditions. Cardiovasc Res. (2020) 116:817–28. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvaa009
69. Liu H, Wang L, Wang H, Hao X, Du Z, Li C, et al. The association of triglyceride-glucose index with major adverse cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events after acute myocardial infarction: a meta-analysis of cohort studies. Nutr Diabetes. (2024) 14:39. doi: 10.1038/s41387-024-00295-1
70. Ormazabal V, Nair S, Elfeky O, Aguayo C, Salomon C, Zuñiga FA. Association between insulin resistance and the development of cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2018) 17:122. doi: 10.1186/s12933-018-0762-4
71. Koffi C, Soleti R, Nitiema M, Mallegol P, Hilairet G, Chaigneau J, et al. Ethanol Extract of Leaves of Cassia siamea Lam Protects against Diabetes-Induced Insulin Resistance, Hepatic, and Endothelial Dysfunctions in ob/ob Mice. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2019) 2019:6560498. doi: 10.1155/2019/6560498
72. Kuboki K, Jiang ZY, Takahara N, Ha SW, Igarashi M, Yamauchi T, et al. Regulation of endothelial constitutive nitric oxide synthase gene expression in endothelial cells and in vivo: a specific vascular action of insulin. Circulation. (2000) 101:676–81. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.101.6.676
73. Eringa EC, Bakker W, van Hinsbergh VW. Paracrine regulation of vascular tone, inflammation and insulin sensitivity by perivascular adipose tissue. Vascul Pharmacol. (2012) 56:204–9. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2012.02.003
74. Hirschfield GM, Pepys MB. C-reactive protein and cardiovascular disease: new insights from an old molecule. Qjm. (2003) 96:793–807. doi: 10.1093/qjmed/hcg134
75. Aroor AR, Mandavia CH, Sowers JR. Insulin resistance and heart failure: molecular mechanisms. Heart Fail Clin. (2012) 8:609–17. doi: 10.1016/j.hfc.2012.06.005
76. Erdogan BR, Arioglu-Inan E. SGLT2 inhibitors: how do they affect the cardiac cells. Mol Cell Biochem. (2025) 480:1359–79. doi: 10.1007/s11010-024-05084-z
77. Ni L, Yuan C, Chen G, Zhang C, Wu X. SGLT2i: beyond the glucose-lowering effect. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2020) 19:98. doi: 10.1186/s12933-020-01071-y
78. Docherty KF, Jhund PS, Inzucchi SE, Køber L, Kosiborod MN, Martinez FA, et al. Effects of dapagliflozin in DAPA-HF according to background heart failure therapy. Eur Heart J. (2020) 41:2379–92. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa183
79. Bykova A, Serova M, Chashkina M, Kosharnaya R, Salpagarova Z, Andreev D, et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in the context of pathophysiology of diverse heart failure with preserved ejection fraction phenotypes: potential benefits and mechanisms of action. Card Fail Rev. (2024) 10:e14. doi: 10.15420/cfr
80. McMurray JJV, Solomon SD, Inzucchi SE, Køber L, Kosiborod MN, Martinez FA, et al. Dapagliflozin in patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction. N Engl J Med. (2019) 381:1995–2008. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1911303
Keywords: cardiometabolic multimorbidity (CMM), triglyceride glucose index (TyG index), insulin resistance (IR), inflammation, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP)
Citation: Wan B, Wang S, Hu S, Han W, Qiu S, Zhu L, Ruan L, Wei Y and Xu J (2025) The comprehensive effects of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and triglyceride glucose index on cardiometabolic multimorbidity. Front. Endocrinol. 16:1511319. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1511319
Received: 14 October 2024; Accepted: 10 March 2025;
Published: 01 April 2025.
Edited by:
Abraham Wall-Medrano, Universidad Autónoma de Ciudad Juárez, MexicoReviewed by:
Emanuel Vamanu, University of Agricultural Sciences and Veterinary Medicine, RomaniaAshot Avagimyan, Yerevan State Medical University, Armenia
Copyright © 2025 Wan, Wang, Hu, Han, Qiu, Zhu, Ruan, Wei and Xu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jianjun Xu, eHVqaWFuanVuMzUyNkAxNjMuY29t; Yiping Wei, d2VpeWlwMjAwMEBob3RtYWlsLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Bingen Wan
Bingen Wan Silin Wang
Silin Wang Sheng Hu
Sheng Hu Weiqing Han
Weiqing Han Shengyu Qiu
Shengyu Qiu Liancheng Ruan
Liancheng Ruan Yiping Wei
Yiping Wei Jianjun Xu
Jianjun Xu