
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Endocrinol., 12 February 2025
Sec. Reproduction
Volume 16 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2025.1496803
This article is part of the Research TopicAdvances in the Study of the Developmental Process and Gene State of Gametes and EmbryosView all 8 articles
Objective: To assess whether trigger-day progesterone (P) levels in conventional in vitro fertilization (c-IVF)/intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) cycles are associated with blastocyst culture outcomes.
Methods: In this retrospective analysis, 747 eligible patients (747 cycles) who adopted the gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) antagonist protocol and underwent c-IVF/ICSI between January 2021 to June 2024 were recruited. The P cutoff values were 1.0 and 1.5 ng/ml when trigger-day serum P was measured, and 4177 day3 (D3) embryos for blastocyst culture were grouped according to trigger-day P levels. Furthermore, the effects of trigger-day P on blastocyst culture outcomes were evaluated.
Results: In total, 747 cycles, 4177 D3 embryos for blastocyst culture were analyzed. After adjustments, multivariate logistic regression analysis revealed that compared with those in the normal level group, available blastocyst rate (adjusted OR, 0.780; 95% CI, 0.645-0.942; P=0.010) and D5 available blastocyst rate (adjusted OR, 0.736; 95% CI, 0.604-0.898; P=0.003) in the high level group were significantly reduced. Subgroup analysis showed that when female age was less than 35 years old, compared with that (36.30%) in the normal level group, the D5 available blastocyst rate (36.92%, adjusted OR, 0.744; 95% CI, 0.602-0.920; P=0.006) in the high level group was significantly reduced. In ICSI cycles, compared with that (28.69%) in the normal level group, the D5 available blastocyst rate (19.13%, adjusted OR, 0.369; 95% CI, 0.194-0.703; P=0.002) in the high level group was significantly decreased.
Conclusion(s): This study demonstrated that in the c-IVF/ICSI population, the trigger-day slightly elevated P (1.0-1.5ng/ml) was not related to blastocyst culture outcomes, while the trigger-day elevated P (>1.5ng/ml) was an important factor affecting D5 available blastocyst rate, especially when the woman was younger than 35 years old or insemination type was ICSI.
With the maturity of embryo culture technology, many reproductive centers will carry out blastocyst culture for day 3 (D3) available cleavage-stage embryos cultured in vitro. By prolonging the embryo culture time, embryos with low developmental potential or genetic defects will be eliminated to a certain extent, and embryos with more developmental potential will be further screened out (1). Blastocyst transfer also improves the endometrial receptivity, increases the chance of implantation, improves the clinical pregnancy rate, and reduces the occurrence of multiple pregnancies, premature births and low birth weight infants (2–5). However, not all patients are suitable for blastocyst culture. Blastocyst culture has a certain risk that some embryos will be eliminated during the culture process, resulting in fewer or no available blastocysts for patients. At present, there is a lack of effective indicators to accurately predict the outcomes of blastocyst culture.
A large number of studies have confirmed that during conventional in vitro fertilization (c-IVF)/intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) controlled ovarian stimulation (COS), trigger-day elevated progesterone (P) not only reduces endometrial receptivity (6–8), advances the implantation window (9), and leads to lower clinical pregnancy rates, ongoing pregnancy rates, and live birth rates (10–21), but also affects embryo quality (6, 19, 22). However, there is still insufficient evidence on whether trigger-day elevated P level will also affect the outcomes of blastocyst formation on day 5 (D5) or day6 (D6) and increase the risk of no available blastocyst. The existing few studies are also partial, including only ICSI/preimplantation genetic testing (PGT) cycles or only top-quality blastocyst formation rate (6). Therefore, the purpose of this study was to evaluate the effects of trigger-day elevated P on available blastocyst rate, top-quality blastocyst rate and blastocyst formation time in c-IVF/ICSI cycles to provide reference for assisted reproductive technology (ART) clinical work.
This retrospective cohort study included 1095 c-IVF/ICSI cycles of COS with gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) antagonist protocol from January 2021 to June 2024. The cycle exclusion criteria were as follows: The women over 40 years old; Chromosomal abnormalities in the male or female partners; More than 2 c-IVF/ICSI cycles; Missed relevant data; Low ovarian response. Oocytes or day3 cleavage-stage embryos (D3 embryos) those met any of the following criteria were excluded: Abnormal fertilized or unfertilized oocytes; Unavailable D3 embryos; Frozen or transplanted D3 embryos. Ultimately, 747 cycles (747 eligible patients), with a total of 4177 D3 embryos for blastocyst culture were included in this study. Owing to the retrospective nature of the study, informed consent was waived. All operations were carried out in conformity with the applicable rules and regulations.
As described in a prior study (23), patients adopted the same protocol, namely, GnRH antagonist protocol. The dosage of gonadotropin (Gn) was individually coordinated according to the basic characteristics and responses of each patient. Continuous transvaginal ultrasound scans and serum estradiol (E2), luteinizing hormone (LH) and P were used to track the cycles. Triggering was employed with 250 µg recombinant human chorionic gonadotropin (r-hCG, Merck Serono, Geneva, Switzerland) and 3,000 IU u-HCG (Livzon, Guangzhou, China). Thirty-six hours later, oocytes were retrieved under the guidance of transvaginal ultrasound and cultured in incubator for 2 ~ 4 hours prior to fertilization.
Based on the total progressively motile sperm cell count (TPMC) after semen treatment on the day of oocyte retrieval, c-IVF (TPMC≥5 million) or ICSI (TPMC < 5 million) insemination method was selected. Fertilization was observed 20h after c-IVF or 17h after ICSI. The D3 embryos were scored on the third day after oocyte retrieval (24). Grade I, grade II and grade III embryos were defined as available embryos, Grade IV embryos were defined as unavailable embryos (discarded embryos). According to the condition of the patients, the D3 available embryos could be frozen, transferred or continued to culture until D5 or D6. If blastocyst culture was performed, the blastocysts were scored on D5 or D6 after oocyte retrieval based on previous literature (25, 26). The available blastocysts were considered as an expanded, hatching, or hatched blastocyst with ICM/TE grading (AA, AB, BA, BB, AC, CA, BC, CB, and CC) in this study. The top-quality blastocysts were considered as an expanded, hatching, or hatched blastocyst with high ICM/TE grading (AA, AB, BA, and BB).
The sex hormones (E2, LH, P) concentrations were measured from 8:00 am to 9:00 am on the trigger-day by siemens automatic chemiluminescence immunoanalyzer (ADVIA Centaur CP). The detection limit of chemiluminescence immunoassay was 0.03 ng/mL, the sensitivity was 0.15 ng/ml, the coefficient of variation within the group was 3.0%, and the coefficient of variation between the groups was 5.5%. The same detection method was used throughout the study and calibrated regularly to reduce unnecessary errors.
The key result of the study was D5 available blastocyst rate, with other indicators being D6 available blastocyst rate and top-quality blastocyst rate. Available blastocyst rate was defined as number of available blastocysts per cultured, top-quality blastocyst rate was defined as number of top-quality blastocysts per cultured (11).
Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS Statistics for Windows version 26. Trigger-day P was regarded as a categorical variable, cycles were divided into the following three groups according to trigger-day P levels: The normal level group included cycles in which trigger-day P were less than 1.0ng/ml; The slightly elevated level group included cycles in which trigger-day P were between 1.0 ~ 1.5 ng/ml; The High level group included cycles in which trigger-day P were more than 1.50 ng/ml. Currently, there was no clear cut-off value for trigger-day P, so these cut-off values were chosen based on clinical practice. Trigger-day elevated P (>1.5 ng/ml) may affect embryo quality (11, 19). Additionally, the physiological P range is generally believed to be less than 1.0ng/ml. And in a retrospective analysis in 2022 (27), Wei et al. also set the threshold of slightly elevated P at 1.0ng/ml. Therefore, 1.0 ng/mL and 1.50 ng/ml were selected as the cut-off values of slightly elevated P level and high P level, respectively. After analysis by Kolmogorov-Smirnov method, all the continuous variables did not conform to normal distribution, which were presented as interquartile interval and were compared between groups using the Kruskal-Wallis test. We used frequencies (percentages) to represent categorical variables and used pearson chi-square test or likelihood ratio test to analyze the differences between groups. Multivariate logistic regression model was established to calculate the adjusted relative risks (RRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs). Potential confounders were selected according to routine clinical practice, existing literature reports (28, 29) and variables with significant differences (P<0.05) in the univariate analysis, and adjustments were made for these confounding variables in the analysis of changes in each outcome between groups to explore the relationship between trigger-day P and blastocyst culture outcomes. Adjusted confounding variables included female age, male age, infertility duration, infertility factors, female body mass index (BMI), total antral follicle count (AFC), cycle number, Gn total dosage, trigger-day E2 level, trigger-day LH level, dominant follicle number, insemination type, D3 embryo numbers for blastocyst culture. All tests were bilateral, and statistical significance was defined as P<0.05.
A total of 1095 cycles (12209 oocytes) underwent GnRH antagonist protocol for controlled ovarian stimulation and adopted c-IVF/ICSI. Among them, 22 cycles (124 oocytes) with women over 40 years old, 79 cycles (831 oocytes) with male or female chromosomal abnormalities, 14 cycles (100 oocytes) with more than 2 cycles, 8 cycles (81 oocytes) with missed relevant data and 58 cycles (143 oocytes) with low response were excluded. In 10930 oocytes (914 cycles), 3 519 abnormal fertilized or unfertilized oocytes (3 cycles), 861 D3 unavailable embryos (6 cycles), 2373 frozen or transferred D3 embryos (158 cycles) were excluded. Finally, 4177 D3 embryos for blastocyst culture (747 cycles) were included in the analysis (Figure 1).
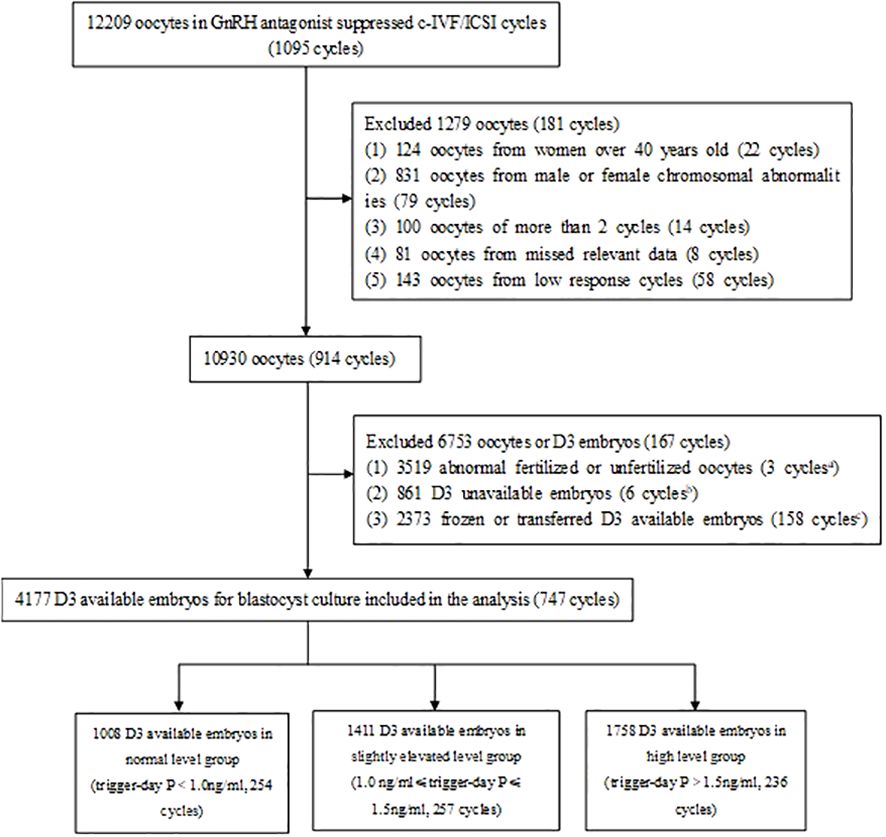
Figure 1. Study flowchart. GnRH, gonadotropin-releasing hormone; c-IVF, conventional in vitro fertilization; ICSI, intracytoplasmic sperm injection, D3, day 3; P, progesterone. 3 cycles in which all oocytes were abnormal fertilized or unfertilized were excluded. 6 cycles in which all D3 embryos were unavailable were excluded. 158 cycles in which all D3 available embryos were frozen or transferred were excluded.
Among them, There were 1008 D3 embryos (254 cycles) in normal trigger-day P group (P<1.0 ng/ml), 1411 D3 embryos (257 cycles) in slightly elevated trigger-day P group (1.0≤P ≤ 1.5 ng/ml), and 1758 D3 embryos (236 cycles) in high trigger-day P group (P>1.5 ng/ml) (Figure 1, Table 1). There were no significant differences in the following indicators grouped by trigger-day P: female age, male age, infertility duration, type of infertility, infertility factors, gravidity, parity and miscarriage (P>0.05). Female BMI (24.0 vs. 23.4 vs. 23.2, P=0.019) significantly decreased with increasing trigger-day P, total antral follicle count (AFC, 12 vs. 14 vs. 18) and the proportion of the first cycles (84.65% vs. 93.00 vs. 94.07, P<0.001) significantly increased with increasing trigger-day P (Table 1).
The results indicated that the dominant follicle number and trigger-day E2 level were significantly increased respectively with increasing trigger-day P (P<0.05). Gn total dosage, trigger-day LH level, insemination type were no significant differences between groups (P>0.05, Table 1).
As shown in Table 1, There were no significant differences in the available blastocyst rate (47.42% vs. 48.05% vs. 49.37%, P=0.572), D5 available blastocyst rate (35.62% vs. 36.29% vs. 36.23%, P=0.933), D6 available blastocyst rate (11.80% vs. 11.76% vs. 13.14%, P=0.420), top-quality blastocyst rate (10.62% vs. 12.33% vs. 11.66%, P=0.430) and D5 top-quality blastocyst rate (10.62% vs. 11.83% vs. 10.98%, P=0.605) among the three groups. D6 top-quality blastocyst rate (0.00 vs. 0.50 vs. 0.68, P=0.036) were significantly increased respectively with increasing trigger-day P.
In the multivariate logistic regression model, compared with those in the normal level group, available blastocyst rate (adjusted OR, 0.864; 95% CI, 0.726-1.029; P=0.100), D5 available blastocyst rate (adjusted OR, 0.845; 95% CI, 0.704-1.015; P=0.072), D6 available blastocyst rate (adjusted OR, 1.003; 95% CI, 0.768-1.311; P=0.980), top-quality blastocyst rate (adjusted OR, 1.004; 95% CI, 0.763-1.323; P=0.975), D5 top-quality blastocyst rate (adjusted OR, 0.937; 95% CI, 0.710-1.238; P=0.649) in the slightly elevated level group were no significant change; D6 available blastocyst rate (adjusted OR, 1.064; 95% CI, 0.799-1.417; P=0.670), top-quality blastocyst rate (adjusted OR, 0.859; 95% CI, 0.635-1.161; P=0.323) and D5 top-quality blastocyst rate (adjusted OR, 0.787; 95% CI, 0.579-1.069; P=0.126) in the high level group were also no significant change; available blastocyst rate (adjusted OR, 0.780; 95% CI, 0.645-0.942; P=0.010) and D5 available blastocyst rate (adjusted OR, 0.736; 95% CI, 0.604-0.898; P=0.003) in the high level group were significantly reduced (Table 2).
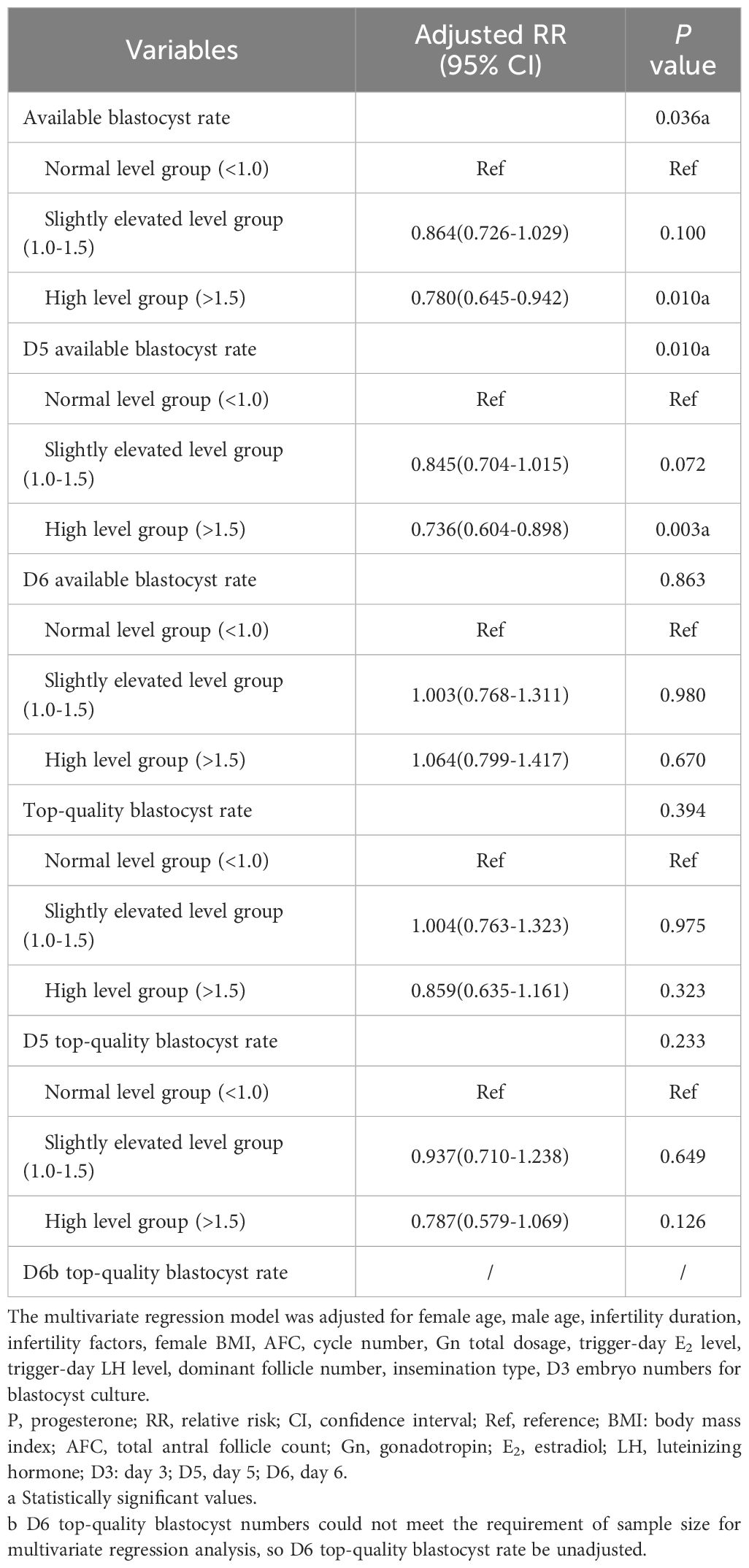
Table 2. Adjusted blastocyst culture outcomes in c-IVF/ICSI cycles stratified by trigger-day P level (ng/ml).
Then, we carried out subgroup analysis of adjusted D5 available blastocyst rate in c-IVF/ICSI cycles based on female age (<35 vs ≥35 years) and insemination type (c-IVF vs ICSI). When female age was less than 35 years old, the D5 available blastocyst rate was 36.69%. Compared with that (36.30%) in the normal level group, the D5 available blastocyst rate (36.67%, adjusted OR, 0.841; 95% CI, 0.693-1.021; P=0.081) in the slightly elevated level group had no significant change, which (36.92%, adjusted OR, 0.744; 95% CI, 0.602-0.920; P=0.006) in the high level group was significantly reduced. When female age was 35 years old or more, the D5 available blastocyst rate was 31.26%, which (33.70%, adjusted OR, 1.019; 95% CI, 0.556-1.867; P=0.951; 28.86%, adjusted OR, 0.772; 95% CI, 0.394-1.514; P=0.452) in the slightly elevated level group and the high level group had no significant change compared with that (30.58%) in the normal level group. In c-IVF cycles, the D5 available blastocyst rate was 38.77%, which (39.32%, adjusted OR, 0.916; 95% CI, 0.749-1.120; P=0.393; 38.81%, adjusted OR, 0.820; 95% CI, 0.662-1.015; P=0.069) in the slightly elevated level group and the high level group had no significant change compared with that (37.83%) in the normal level group. In ICSI cycles, the D5 available blastocyst rate was 22.98%. And compared with that (28.69%) in the normal level group, the D5 available blastocyst rate (20.78%, adjusted OR, 0.675; 95% CI, 0.413-1.105; P=0.118) in the slightly elevated level group had no significant change, which (19.13%, adjusted OR, 0.369; 95% CI, 0.194-0.703; P=0.002) in the high level group was significantly decreased (Table 3).
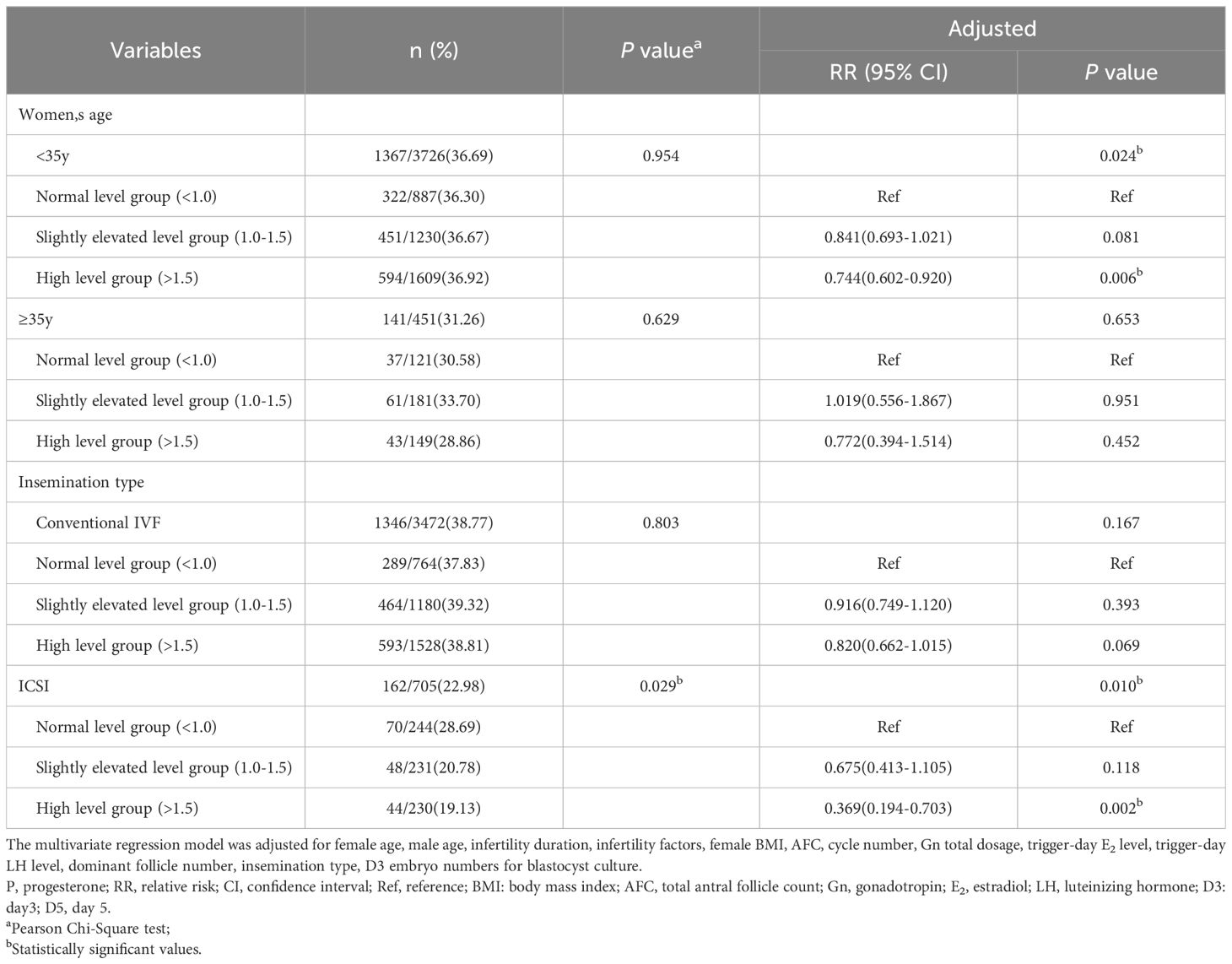
Table 3. Subgroup analysis of D5 available blastocyst rate in c-IVF/ICSI cycles stratified by trigger-day P level (ng/ml).
The results of our study showed that the trigger-day slightly elevated P (1.0-1.5ng/ml) was not related to blastocyst culture outcomes, while the trigger-day elevated P (>1.5ng/ml) was an important factor affecting D5 available blastocyst rate, especially when the woman was younger than 35 years old or insemination type was ICSI.
This study showed that there was no statistical difference in the D6 available blastocyst rate between different trigger-day P level groups. And after adjusting for confounders, the increase of trigger-day P did not affect the D6 available blastocyst rate. Although there was no significant difference in the D5 available blastocyst rate among different trigger-day P level groups, after adjusting for confounders, it was shown that the trigger-day elevated P (>1.5ng/ml), not the trigger-day slightly elevated P (1.0-1.5ng/ml) would lead to a decrease in the D5 available blastocyst rate. In the subgroup analysis of female age (< 35 vs ≥35 years) and insemination type (c-IVF vs ICSI), it was concluded that when the trigger-day P was more than 1.5ng/ml, the adjusted D5 available blastocyst rate would decrease significantly in two subgroups of women younger than 35 years and ICSI cycles. To our knowledge, few studies to date had evaluated whether trigger-day P affect available blastocyst rate. Only a retrospective analysis by Racca et al. (19) reported 3400 ICSI cycles with GnRH antagonist protocol for COS. Grouping by trigger-day P values (≤0.50, 0.51-1.49, ≥1.50 ng/ml), and their results showed that the available blastocyst rate on day 5 decreased with the increase of trigger-day P (48.8%, 47.8%, and 38.8%, respectively). However, the P cut-off values and detection method of Racca et al. (19) were different from those in our study, and the study of Racca et al. only included ICSI cycles, only involved D5 available blastocyst rate, did not analyze D6 available blastocyst rate and adjust confounders.
Our data showed that in c-IVF/ICSI cycles, the trigger-day P level was irrelevant to top-quality blastocyst rate. A single-center retrospective cohort study by Turgut et al. (30) in 2020 included 1485 ICSI cycles with GnRH antagonist protocol for COS. They stratified according to serum P levels (< 0.8 ng/ml; 0.8-1.49 ng/ml; ≥1.5 ng/ml). Generalized estimating equations (GEE) analysis also did not show that the effect of P levels on top-quality blastocyst rate had any statistical significance [OR, 1.07; 95%CI, 0.98-1.16; P=0.113; OR, 0.93; 95%CI, 0.80-1.07; P=0.32]. In 2023, Li et al. (11) recruited 504 eligible patients who underwent PGT for retrospective analysis, and grouped according to trigger-day P levels (cut-off values were 0.5 and 1.5 ng/ml, respectively) to assess the effect of trigger-day P on embryo quality. Their results showed that there was no significant difference in top-quality blastocyst rate (8.71% vs. 8.24% vs. 7.94%) among different P levels (P>0.05). These findings are consistent with our conclusion. However, all patients included in Li et al. (11) adopted a gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist long-acting protocol and underwent PGT cycles (aneuploid blastocysts were excluded). Moreover, all D3 available embryos were cultured to D5 or D6. The P cut-off values of (0.5 and 1.5 ng/ml) were also different from those in our study. Confounding variables (such as female age) were also not adjusted. Although Turgut et al. (30) analyzed various confounding factors and made adjustments through GEE, the inclusion of only ICSI cycles may limit the overall application of their conclusions, and their definition of top-quality blastocyst rate was inconsistent with the present study. However, the above results that there was no correlation between trigger-day P level and top-quality blastocyst rate contradicted the studies of Kim et al. (6). In 2017, Kim et al. (6) found for the first time that the increase of trigger-day P in GnRH antagonist IVF/ICSI cycles was associated with a lower top-quality blastocyst rate. The reasons for the inconsistency between the findings of Kim et al. (6) and the conclusions of our study may be as follows: First, no embryos were transferred or frozen on D3 in the study of Kim et al. (6), all D3 available embryos were cultured to D5 or D6; Second, their definition of top quality blastocyst was also different from ours; Moreover, they statistically analyzed the top-quality blastocyst rate as a continuous variable, but, statistically, frequencies (such as top-quality blastocyst rate) should be described by categorical variables.
Animal studies had shown that lower P levels during the follicular phase can promote oocyte development in vitro (31). We conjecture that the high trigger-day P level delays embryo development or reduces embryo development potential by affecting oocyte quality, and large activation of the zygotic genome after the D3 embryonic phase cannot counteract the adverse effect of high trigger-day P level on embryo quality, leading to a decrease in D5 available blastocyst rate. However, the molecular mechanism by which high trigger-day P level affect blastocyst quality remains unclear. In addition, the underlying mechanism that causes trigger-day higher P level during ART is also unknown. Studies had shown that the number of follicles, the FSH drive and the LH activity were the three main factors that lead to increased P concentration during COS (32). According to the present study and earlier studies (13, 15, 20), trigger-day high P is usually accompanied by high E2. We also noticed that with the increase of trigger-day P, the female BMI gradually decreased, and the number of AFC and dominant follicles gradually increased.
All patients in this single-center study received a uniform ovarian stimulation protocol. Morphological assessment of blastocyst was performed by an experienced embryologist under equivalent laboratory conditions. Multiple regression logic analysis model was also used to explain the influence of various confounding factors on blastocyst culture outcomes, and subgroup analysis was performed according to female age and insemination type to ensure the reliability of the results.
However, due to the limitations of retrospective study, there were inevitable biases even if the impact of potential confounders was minimized. First, we used c-IVF/ICSI as a model, and the results cannot be extrapolated to all infertile populations. Second, trigger-day P does not have a definite cut-off value, which varies between studies at different centers and may vary depending on the detection method.
In summary, we used the c-IVF/ICSI cycles as a model to determine the relationship between trigger-day P and blastocyst culture outcomes. The results showed that the trigger-day slightly elevated P (1.0-1.5ng/ml) was not related to blastocyst culture outcomes, while the trigger-day elevated P (>1.5ng/ml) was an important factor affecting D5 available blastocyst rate, especially when the woman was younger than 35 years old or insemination type was ICSI. Because this study included c-IVF/ICSI patients treated with GnRH antagonist, it was unclear whether our findings can be extrapolated to populations using other protocols or to all infertility population. On the other hand, due to the small sample size and retrospective analysis in this study, the existence of bias cannot be ruled out, so it is recommended to carry out a randomized controlled trial with a larger sample size. In conclusion, in clinical practice, we should treat this result with caution. In order to predict the blastocyst culture outcomes, each center needs to evaluate the P threshold according to its own detection method when selecting D3 embryos for blastocyst culture.
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
The studies involving humans were approved by Ethics Committee of Yuncheng Central Hospital, Shanxi Province. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation was not required from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and institutional requirements.
YS: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JW: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft. LZ: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft. YC: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft. AZ: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing, Resources.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
1. Raju GAR, Prakash GJ, Krishna KM, Madan K. Vitrification of human early cavitating and deflated expanded blastocysts: clinical outcome of 474 cycles. J Assisted Reprod Genet. (2009) 26:523–9. doi: 10.1007/s10815-009-9356-0
2. Glujovsky D, Farquhar C, Quinteiro Retamar AM, Alvarez Sedo CR, Blake D. Cleavage stage versus blastocyst stage embryo transfer in assisted reproductive technology. Cochrane Database Systematic Rev. (2016) 30:CD002118. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002118.pub5
3. Guerif F, Lemseffer M, Bidault R, Gasnier O, Saussereau MH, Cadoret V, et al. Single Day 2 embryo versus blastocyst-stage transfer: a prospective study integrating fresh and frozen embryo transfers. Hum Reprod. (2009) 24:1051–8. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dep018
4. The practice committees of the american society for reproductive medicine and the society for assisted reproductive technology. Blastocyst culture transfer clinical-assisted reproduction: committee opinion. Fertility Sterility. (2013) 99:667–72. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2013.01.087
5. Wei D, Sun Y, Liu J, Liang X, Zhu Y, Shi Y, et al. Live birth after fresh versus frozen single blastocyst transfer (Frefro-blastocyst): study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials. (2017) 18:253–9. doi: 10.1186/s13063-017-1993-5
6. Kim S, Vanni VS, Somigliana E, Reschini M, Pagliardini L, Marotta E, et al. Top quality blastocyst formation rates in relation to progesterone levels on the day of oocyte maturation in GnRH antagonist IVF/ICSI cycles. PloS One. (2017) 12:e0176482. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0176482
7. Van Vaerenbergh I, Fatemi HM, Blockeel C, Van Lommel L, In’t Veld P, Schuit F, et al. Progesterone rise on HCG day in GnRH antagonist/rFSH stimulated cycles affects endometrial gene expression. Reprod BioMedicine Online. (2011) 22:263–71. doi: 10.1016/j.rbmo.2010.11.002
8. Xiong Y, Hu L, Zhang T, Wang M, Xu H, Li TC, et al. Effects of high progesterone in in-vitro fertilization cycle on DNA methylation and gene expression of adhesion molecules on endometrium during implantation window. J Assisted Reprod Genet. (2019) 37:33–43. doi: 10.1007/s10815-019-01623-6
9. Healy M, Patounakis G, Zanelotti A, Devine K, DeCherney A, Levy M, et al. Does premature elevated progesterone on the day of trigger increase spontaneous abortion rates in fresh and subsequent frozen embryo transfers? Gynecological endocrinology: Off J Int Soc Gynecological Endocrinol. (2017) 33:472–5. doi: 10.1080/09513590.2017.129161
10. Kong N, Liu J, Jiang Y, Zhu Y, Zhang C, Yan G, et al. Adverse impact of elevated progesterone levels on human chorionic gonadotropin trigger day on blastocyst transfer outcomes in gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist cycles. Eur J obstetrics gynecology Reprod Biol. (2022) 276:107–12. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2022.07.007
11. Li J, Cui Y, Shi H, Bu Z, Wang F, Sun B, et al. Effects of trigger-day progesterone in the preimplantation genetic testing cycle on the embryo quality and pregnancy outcomes of the subsequent first frozen-thawed blastocyst transfer. Front Endocrinol. (2023) 14:990971. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.990971
12. Tsai Y-R, Huang F-J, Lin P-Y, Kung F-T, Lin Y-J, Lin Y-C, et al. Progesterone elevation on the day of human chorionic gonadotropin administration is not the only factor determining outcomes of in vitro fertilization. Fertility Sterility. (2015) 103:106–11. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2014.10.019
13. Bosch E, Labarta E, Crespo J, Simón C, Remohí J, Jenkins J, et al. Circulating progesterone levels and ongoing pregnancy rates in controlled ovarian stimulation cycles for in vitro fertilization: analysis of over 4000 cycles. Hum Reprod. (2010) 25:2092–100. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deq125
14. Arvis P, Lehert P, Guivarc'h-Levêque A. Both high and low HCG day progesterone concentrations negatively affect live birth rates in IVF/ICSI cycles. Reprod BioMedicine Online. (2019) 39:852–9. doi: 10.1016/j.rbmo.2019.07.001
15. Healy MW, Yamasaki M, Patounakis G, Richter KS, Devine K, DeCherney AH, et al. The slow growing embryo and premature progesterone elevation: compounding factors for embryo-endometrial asynchrony. Hum Reprod. (2017) 32:362–7. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dew296
16. Ochsenkühn R, Arzberger A, von Schönfeldt V, Gallwas J, Rogenhofer N, Crispin A, et al. Subtle progesterone rise on the day of human chorionic gonadotropin administration is associated with lower live birth rates in women undergoing assisted reproductive technology: a retrospective study with 2,555 fresh embryo transfers. Fertility Sterility. (2012) 98:347–54. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2012.04.041
17. Santos-Ribeiro S, Polyzos NP, Haentjens P, Smitz J, Camus M, Tournaye H, et al. Live birth rates after IVF are reduced by both low and high progesterone levels on the day of human chorionic gonadotrophin administration. Hum Reprod. (2014) 29:1698–705. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deu151
18. Sun Q-Y, Bu Z, Zhao F, Wang K, Guo Y, Su Y, et al. Serum progesterone elevation adversely affects cumulative live birth rate in different ovarian responders during in vitro fertilization and embryo transfer: A large retrospective study. PloS One. (2014) 9:e100011. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0100011
19. Racca A, Santos-Ribeiro S, De Munck N, Mackens S, Drakopoulos P, Camus M, et al. Impact of late-follicular phase elevated serum progesterone on cumulative live birth rates: is there a deleterious effect on embryo quality? Hum Reprod. (2018) 33:860–8. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dey031
20. Venetis CA, Kolibianakis EM, Bosdou JK, Tarlatzis BC. Progesterone elevation and probability of pregnancy after IVF: a systematic review and meta-analysis of over 60 000 cycles. Hum Reprod Update. (2013) 19:433–57. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmt014
21. Xu J, Zhang C, Wang S, Zhang S. Impact of progesterone concentration on human chorionic gonadotropin trigger day on clinical outcomes with one top-quality cleavage-stage embryo or blastocyst transfer in fresh in vitro fertilization cycles. Front Endocrinol. (2023) 14:1085287. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1085287
22. Tokgoz VY, Tekin AB. Serum progesterone level above 0.85 ng/mL and progesterone/estradiol ratio may be useful predictors for replacing cleavage-stage with blastocyst-stage embryo transfer in fresh IVF/ICSI cycles without premature progesterone elevation. Arch gynecology obstetrics. (2022) 305:1011–9. doi: 10.1007/s00404-021-06304-3
23. Sun Y, Zhu A. Effect of body mass index on progesterone level on trigger day in gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonist cycles. Gynecological Endocrinol. (2024) 40:2364892. doi: 10.1080/09513590.2024.2364892
24. Li M, Wang H, Ma C, Shi J. Transferring two grades I cleavage-stage embryo might not be a good protocol. Gynecological endocrinology: Off J Int Soc Gynecological Endocrinol. (2017) 33:557–9. doi: 10.1080/09513590.2017.1302420
25. Shi W, Jin L, Liu J, Zhang C, Mi Y, Shi J, et al. Blastocyst morphology is associated with the incidence of monozygotic twinning in assisted reproductive technology. Am J Obstetrics Gynecology. (2021) 225:654.e1–.e16. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2021.06.101
26. Shi W, Zhou H, Chen L, Xue X, Shi J. Live birth rate following frozen-thawed blastocyst transfer ishigher in high-grade day 6 blastocysts than in low-grade day 5 blastocysts. Front Endocrinol. (2022) 13:1066757. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1066757
27. Wei L, Zhao Y, Xu C, Zhang C. Slightly elevated progesterone on HCG trigger day has an impacton pregnancy outcomes of fresh single blastocyst transfer cycles under an early follicular phase prolonged protocol cycle. Int J women's Health. (2022) 14:1761–8. doi: 10.2147/ijwh.S385362
28. Borgstrøm MB, Grøndahl ML, T WK, Kd A, Thomsen T, Bentin-Ley U, et al. Is paternal age associated with transfer day, developmental stage, morphology, and initial hCG-rise of the competent blastocyst leading to live birth? A multicenter cohort study. PloS One. (2022) 17:e0270664. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0270664
29. Hong YH, Kim HK, Nho EJ, Youm HW, Kim SK, Lee JR, et al. Predictors of blastocyst formation rate in elective day 5 transfer cycle. J obstetrics gynaecology: J Institute Obstetrics Gynaecology. (2020) 40:863–8. doi: 10.1080/01443615.2019.1676212
30. Turgut EN, Ecemis S, Boynukalin KF, Gultomruk M, Yarkiner Z, Findikli N, et al. Being on the side of old findings: progesterone elevation on the day of oocyte maturation induction does not affect embryological parameters throughout the blastocyst culture period. Arch Gynecology Obstetrics. (2020) 303:581–7. doi: 10.1007/s00404-020-05792-z
31. Urrego R, Herrera-Puerta E, Chavarria NA, Camargo O, Wrenzycki C, Rodriguez-Osorio N. Follicular progesterone concentrations and messenger RNA expression of MATER and OCT-4 in immature bovine oocytes as predictors of developmental competence. Theriogenology. (2015) 83:1179–87. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2014.12.024
Keywords: conventional in vitro fertilization (c-IVF), intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), trigger-day progesterone (P), gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) antagonist, available blastocyst rate, top-quality blastocyst rate
Citation: Sun Y, Wang J, Zhang L, Chang Y and Zhu A (2025) Effects of trigger-day progesterone in c-IVF/ICSI cycles on blastocyst culture outcomes. Front. Endocrinol. 16:1496803. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1496803
Received: 15 September 2024; Accepted: 27 January 2025;
Published: 12 February 2025.
Edited by:
Bo Huang, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, ChinaReviewed by:
Fu-Jen Huang, Specialist Hospital, PolandCopyright © 2025 Sun, Wang, Zhang, Chang and Zhu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Aizhen Zhu, emh1YWl6aGVuODc2OEAxNjMuY29t
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.