- 1Department of Endocrinology, Suqian First Hospital, Suqian, China
- 2Department of Nephrology, Suqian First Hospital, Suqian, China
Background and purpose: Hashimoto thyroiditis (HT) is an autoimmune disease without infectivity. We compared the differences of blood lymphocytes levels between HT patients and healthy people.
Patients and methods: This study included a total of 84 HT patients whose thyroid function was normal and 60 HT patients with abnormal thyroid function. A corresponding number of medical examination population in our hospital were randomly selected as the control groups. White blood cell count, neutrophil count, neutrophil percentage, lymphocyte count, and lymphocyte percentage were compared between HT patients and healthy population. The correlations between TSH, FT4 and above parameters were further tested.
Results: We found significant differences between HT with normal thyroid function group and control group in lymphocyte count (P<0.001), lymphocyte percentage (P<0.001) and neutrophil percentage (P<0.001), but no differences in sex (P=0.134), age (P=0.200), white blood cell count (P=0.315) and neutrophil count (P=0.790). Significant differences were observed in neutrophil count (P=0.032), neutrophil percentage (P=0.010), lymphocyte count (P=0.010) and lymphocyte percentage (P<0.001) between HT with abnormal thyroid function group and control group, but not in sex (P=0.769), age (P=0.060) and white blood cell count (P=0.156) between the two groups. There were significant differences in white blood cell count (P=0.009) and neutrophil count (P=0.032) between HT patients in the normal thyroid function group and HT patients in the abnormal thyroid function group. Neither FT4 nor TSH was associated with lymphocyte levels or neutrophil levels.
Conclusions: The lymphocyte levels in HT patients were significantly lower than healthy population. The neutrophil count in HT patients with regular thyroid function was lower than those in abnormal thyroid function HT patients.
1 Introduction
Hashimoto thyroiditis (HT), also known as chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis, is characterized by painless, diffuse goiter and the presence of high titer autoantibodies in the serum, and some patients will eventually develop hypothyroidism. In recent years, the prevalence and incidence of HT have been increasing. In China, the rate of thyroid autoimmune antibody elevation is about 14.19% (1) and women aged 30 to 50 are the highest incidence group. HT is a non-infectious autoimmune disease with unknown etiology and interaction between genetic and autoimmune factors. Based on the interactions of environmental factors and genetic background, the autoimmune manifestations of HT occur, causing an imbalance between the self-tolerance mechanisms maintained by regulatory T lymphocytes and B lymphocytes (2–4). The main cause of HT is the activation of cellular and humoral immune responses against autoantigens. The main thyroid antigens that induce antibody-mediated responses are thyroglobulin (Tg), thyroid peroxidase antigen (TPO) and thyroid stimulating hormone receptor (TSHR) (5). Thus, in patients with HT, changes in thyroid hormone levels and metabolism can be observed, leading to corresponding clinical symptoms. About 20-30% of HT patients may develop hypothyroidism (6–8). Thyroid lymphocyte infiltration (especially T cell infiltration) is the main feature of HT. The thyroid is gradually replaced by lymphocytes, which can lead to fibrosis and atrophy of thyroid cells (6). Currently, the diagnosis of HT is determined through clinical manifestations, thyroid ultrasound results and the detection of serum anti-thyroid antigen antibodies (anti-thyroid peroxidase antibodies and thyroglobulin antibodies) (7).
It is lymphocyte migration that is the mechanism causing lymphocyte infiltration in thyroid tissue of HT patients. Lymphocyte migration, being a homing mode of lymphocyte, involves a series of molecules in the specific migration of lymphocytes from blood to various tissues and organs. Studies have verified that lymphocyte migration is also implicated in the pathogenesis of other diseases, such as inflammatory bowel disease, rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus (9–13). Whether the migration of a large number of lymphocytes in the blood to the thyroid tissue due to lymphocyte migration leads to a decrease in the count and percentage of lymphocyte in the blood and whether there are differences in blood lymphocyte count and percentage between HT patients with normal thyroid function and HT patients with hypothyroidism remain to be determined. Consequently, this study aimed to assess the differences in blood lymphocyte levels between HT patients and healthy population.
2 Methods
2.1 Ethical considerations
The research adhered to the Declaration of Helsinki and the local Ethics Committee approved the study.
2.2 Patients and study design
The study encompassed 144 HT patients. HT patients who met the diagnostic criteria and didnot undergone thyroid surgery were included. The following conditions are excluded: (1) HT patients with blood system diseases,tumor or infection, (2) HT patients who declined blood tests, (3) prior treatment with corticosteroids, (4) patients with hyperthyroidism. When the patients were first admitted to the hospital, their gender, age were recorded. On the second day of being hospitalized, venous blood was taken to examine leukocyte count, lymphocyte count, neutrophil count, lymphocyte percentage and neutrophil percentage, thyroid function. Blood routine and thyroid function were detected automatically by machine. Hypothyroidism refers to elevated thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) and decreased free thyroid hormone 4 (FT4), and subclinical hypothyroidism refers to elevated TSH and normal FT4 (14, 15).
To compared the differences of leukocyte count, lymphocyte count, neutrophil count, lymphocyte percentage and neutrophil percentage between HT patients and healthy people, 84 medical examination population in our hospital were randomly chosen as the control group. Their corresponding indicators were also recorded.
Firstly, the differences in white blood cell count, neutrophil count, neutrophil percentage, lymphocyte count, lymphocyte percentage between HT patients with abnormal thyroid function, HT patients with normal thyroid function, and healthy controls were compared. Abnormal thyroid function included hypothyroidism (elevated TSH and decreased FT4) and subclinical hypothyroidism (elevated TSH and normal FT4). Normal thyroid function meant that FT4, FT3 and TSH are normal. If there was a difference, then the correlations between TSH, FT4 and these different parameters were further tested.
2.3 Statistical analysis
Descriptive data were shown as median (interquartile) or percentage. The normality of all numerical variables was examined. For nonparametric tests, the Mann-whitney U test was used, and for categorical variables, the Chi-square test or Fisher's exact test was applied. The correlation among the data was calculated by Pearson correlation analysis or Spearman rank correlation analysis. SPSS 21.0 software was utilized for statistical analysis, and a P-value less than 0.05 indicated statistical significance.
3 Results
3.1 The lymphocyte levels in the HT patient group were markedly decreased compared to those in the control group
According to thyroid function, HT patients were divided into normal thyroid function group and abnormal thyroid function group.60 HT patients with irregular thyroid function as well as 84 HT patients with regular thyroid function were present. We found significant differences between HT with normal thyroid function group and control group in lymphocyte count (P<0.001), lymphocyte percentage (P<0.001) and neutrophil percentage (P<0.001), but no differences in sex (P=0.134), age (P=0.200), white blood cell count (P=0.315) and neutrophil count (P=0.790). Significant differences were observed in neutrophil count (P=0.032), neutrophil percentage (P=0.010), lymphocyte count (P=0.010) and lymphocyte percentage (P<0.001) between HT with abnormal thyroid function group and control group, but not in sex (P=0.769), age (P=0.060) and white blood cell count (P=0.156) between the two groups. Both lymphocyte count and percentage in HT patients group were significantly lower than that in control group, whether thyroid function is normal or not (Table 1).
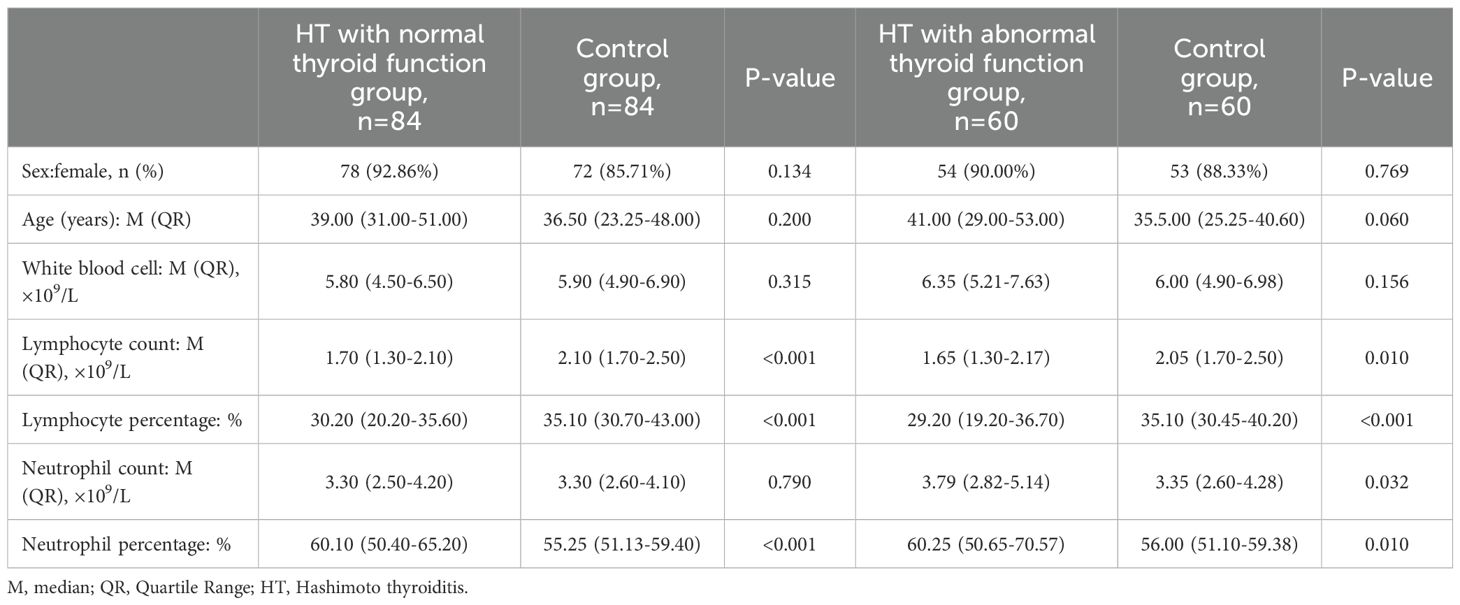
Table 1. Analysis of the differences between HT with normal thyroid function group and Control group, HT with abnormal thyroid function group and Control group.
3.2 Analysis of the differences between HT with regular thyroid function group and HT with irregular thyroid function group
No statistically significant differences were found in sex (P=0.686), age (P=0.843), lymphocyte count (P=0.854), lymphocyte percentage (P=0.107) and neutrophil percentage (P=0.463) when comparing the two groups. However, significant differences existed in white blood cell count (P=0.009) and neutrophil count (P=0.032) between the two groups. Neutrophil count in HT with normal thyroid function group was significantly lower than HT with abnormal thyroid function group (Table 2).
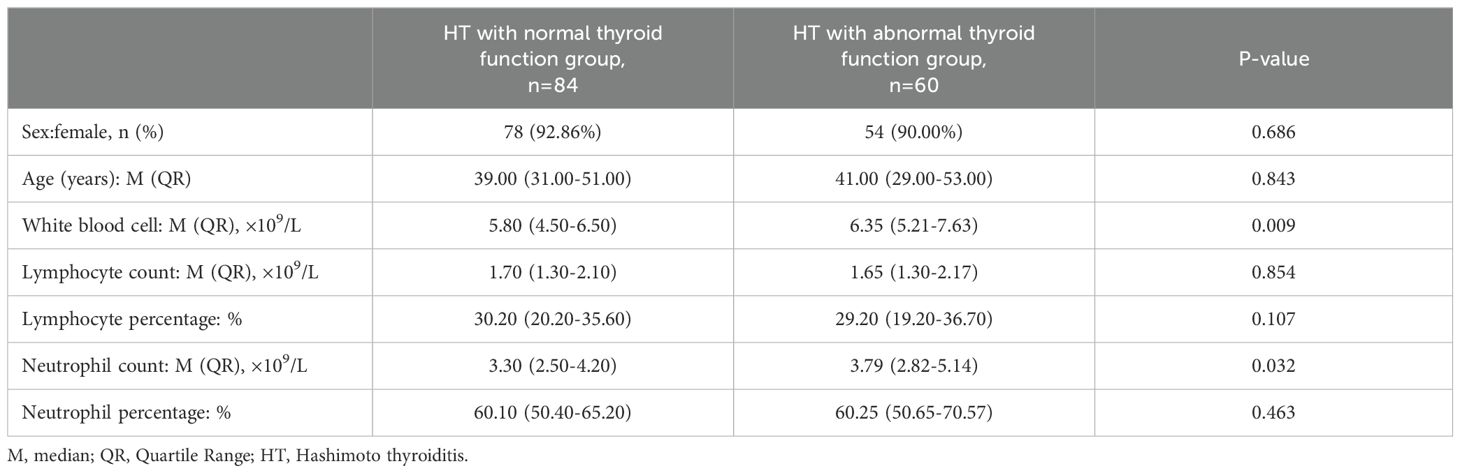
Table 2. Analysis of the differences between HT with normal thyroid function group and HT with abnormal thyroid function group.
3.3 Correlations between FT4, TSH and neutrophil count, neutrophil percentage, lymphocyte count, lymphocyte percentage in the 144 HT patients
According to Table 1, no significant differences was observed in lymphocyte count, neutrophil count, lymphocyte percentage and neutrophil percentage between HT patients and control group. In this study, there were no linear correlations between FT4 and lymphocyte count (r=0.176, P=0.034), lymphocyte percentage (r=0.215, P=0.010), neutrophil count (r=-0.134, P=0.108), neutrophil percentage (r=-0.127, P=0.128). Similarly, there were no linear correlations between TSH and lymphocyte count (r=-0.057, P=0.499), lymphocyte percentage (r=-0.170, P=0.041), neutrophil count (r=0.177, P=0.034, neutrophil percentage (r=0.152, P=0.070) (Figure 1).
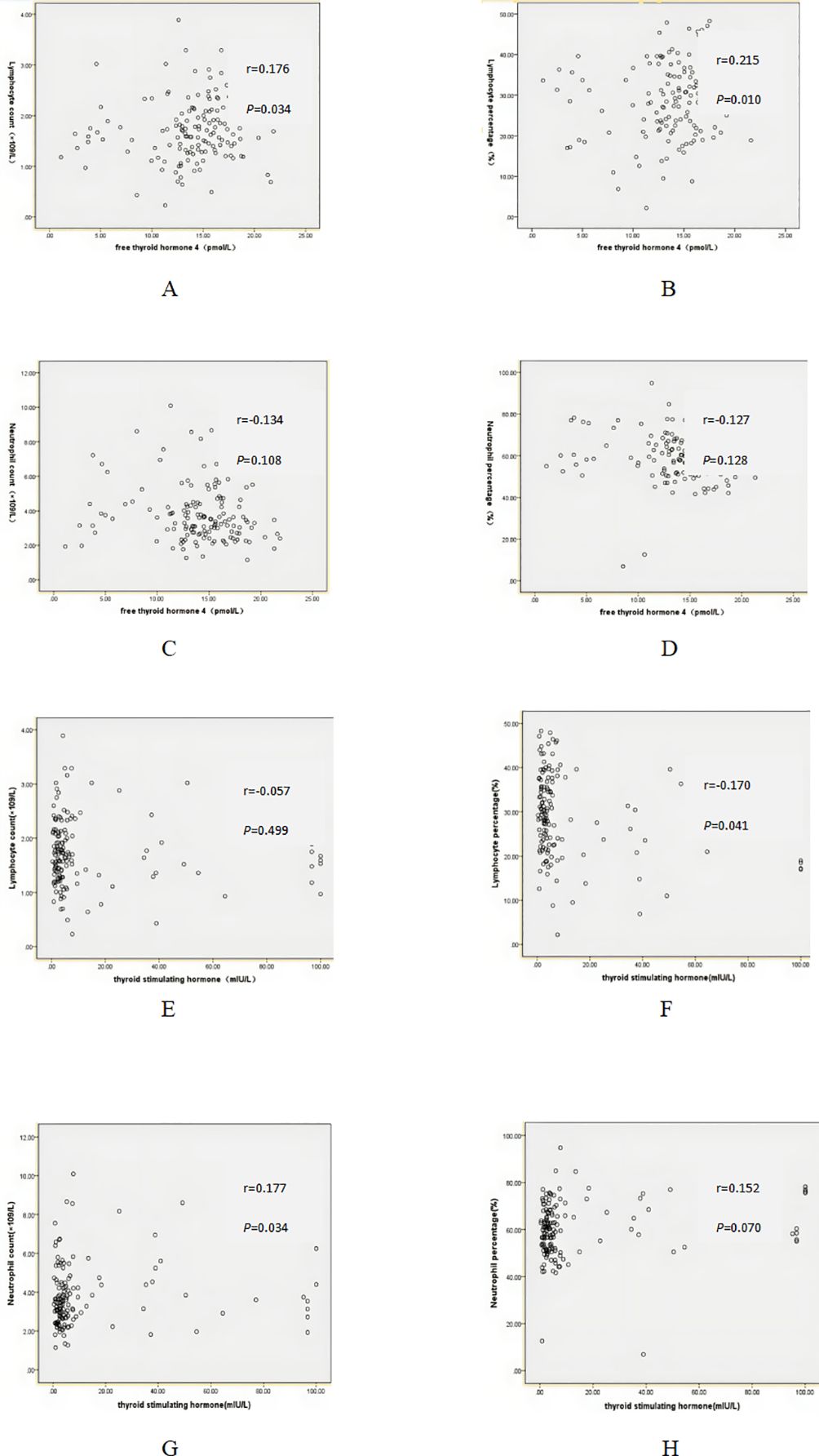
Figure 1. Correlation between free thyroid hormone 4 (FT4), thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) and serum markers. (A) Correlation between FT4 and lymphocyte count. (B) Correlation between FT4 and lymphocyte percentage. (C) Correlation between FT4 and neutrophil count. (D) Correlation between FT4 and neutrophil percentage. (E) Correlation between TSH and lymphocyte count. (F) Correlation between TSH and lymphocyte percentage. (G) Correlation between TSH and neutrophil count. (H) Correlation between TSH and neutrophil percentage.
4 Discussion
HT is an autoimmune disease in which the destruction of the thyroid is the result of lymphocyte infiltration. It affects approximately 160 million people worldwide, and women are 4-10 times more susceptible than men (7, 16). In HT, a cellular immune response with high inflammatory load and apoptosis occurs, resulting in tissue destruction and thyroid dysfunction. Generally, it is thought that HT is the outcome of multiple environmental factors causing immune dysfunction on the basis of genetic predisposition. Nevertheless, the molecular mechanism by which immune dysfunction gives rise to the destruction of thyroid tissue still remains unclear (17–20). Susceptibility genes associated with HT include PTPN22, HLA-DR3, FOXP3, CD40, IL-2Rα and CTLA-4 (20–23).
The massive infiltration of lymphoid cells in the thyroid tissue of HT patients may be due to lymphocyte migration. Through a series of molecular mediations, lymphocyte migration from blood to thyroid tissue leads to lymphocyte infiltration in thyroid tissue. Studies have shown that Th1 cytokines such as interleukin-1, interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor- alfa (TNF-α) can mediate the infiltration and accumulation of antigen-producing B lymphocytes, cytotoxic T cells, and macrophages into thyroid tissue (24, 25). Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) can promote the production of inflammatory Th1 cytokines, including IL-2, TNF-α and IL-6 (26). A study published in 2014 showed that MIF levels were significantly higher in HT patients than in healthy people and were associated with hypothyroidism (27). This result indirectly reflected that lymphocyte migration may be involved in the pathogenesis of HT. In addition, many studies have confirmed that lymphocyte migration plays an important role in the pathogenesis of IBD (28, 29). Studies also confirmed the existence of lymphocyte infiltration in exocrine gland tissue of Sjogren's syndrome (SS), which leads to the injury of SS exocrine gland (30–32). As lymphocyte migrated from the blood to the thyroid tissue, we expected that the levels of lymphocyte in the blood of HT patients may be lower than that of healthy population. Therefore, 84 HT patients with regular thyroid function and 60 HT patients with irregular thyroid function were included to compare the differences of blood lymphocytes levels between the two groups and healthy population. The results indicated that although the total leukocyte count in HT patients had no significant difference compared to that of the healthy population, the lymphocyte count and percentage were notably lower than those of the healthy population, while neutrophil percentage was significantly higher than that of healthy population. A study published in 2020 showed that neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio was statistically higher than healthy population, a result that is consistent with this study (33). In addition, this study also found that the neutrophil count and white blood cell count in HT patients with abnormal thyroid function were significantly higher than those with normal thyroid function. A study showed that over activation and over recruitment of neutrophils at the site of inflammation are thought to contribute to the pathogenesis and progression of IBD (34). The oxidative stress damage caused by the production of reactive oxygen species is involved in the pathogenesis and progression of IBD, and neutrophil cells are an important source of reactive oxygen species. In the inflammatory microenvironment, reactive oxygen species can damage biological macromolecules such as deoxyribonucleic acid, proteins and lipids, thus causing tissue cell damage. Given that the neutrophil count in HT patients with abnormal thyroid function is considerably higher than that in HT patients with normal thyroid function, could it be that the activation of neutrophils aggravates the destruction of thyroid tissue, thereby resulting in hypothyroidism? The mechanism of this remains to be further studied. This study also studied whether FT4 and TSH were correlated with lymphocyte and neutrophil levels, but the results showed that there was no linear correlation. The reason may be that neutrophils only initiate the destruction of thyroid tissue, but not associated with severity. The severity of thyroid tissue destruction may be due to other factors. Just as the level of serum amylase can only be used to diagnose acute pancreatitis, and does not reflect the severity of acute pancreatitis.
This study has certain drawbacks. First, in this study, HT patients with hypothyroidism and subclinical hypothyroidism were collectively referred to as thyroid dysfunction, and were not analyzed separately. Secondly, while this study demonstrated that the neutrophil count in HT patients with irregular thyroid function exceeded that in HT patients with regular thyroid function, it unfortunately did not further dig into the possible mechanism underlying this phenomenon. Specifically, the sample size within this study was relatively limited and it was only a single-center investigation. Consequently, it is anticipated that more comprehensive studies will be carried out in the future, incorporating a larger number of patients to enhance the validity and generalizability of the findings. Whether monitoring lymphocyte levels can be used in the diagnosis and treatment of HT and whether neutrophil activation causes hypothyroidism remain to be investigated.
To sum up, the findings of this study possess significant clinical importance. The lymphocyte levels in HT patients were significantly lower than normal, and the neutrophil counts in abnormal thyroid function HT patients were higher than those in normal thyroid function HT patients.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Ethics Committee of Suqian City. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation in this study was provided by the participants' legal guardians/next of kin.
Author contributions
HX: Writing – original draft. RX: Formal analysis, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Li Y, Teng D, Ba J, Chen B, Du J, He L, et al. Efficacy and safety of long-term universal salt iodization on thyroid disorders: epidemiological evidence from 31 provinces of mainland China. Thyroid. (2020) 30:568–79. doi: 10.1089/thy.2019.0067
2. Bliddal S, Nielsen CH, Feldt-Rasmussen U. Recent advances in understanding autoimmune thyroid disease: the tallest tree in the forest of polyautoimmunity. F1000Res. (2017) 6:1776. doi: 10.12688/f1000research
3. Brix TH, Hegedüs L. Twin studies as a model for exploring the aetiology of autoimmune thyroid disease. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). (2012) 76:457–64. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.2011.04318.x
4. Brand O, Gough S, Heward J. HLA, CTLA-4 and PTPN22: the shared genetic master-key to autoimmunity. Expert Rev Mol Med. (2005) 7:1–15. doi: 10.1017/S1462399405009981
5. Vargas-Uricoechea H. Molecular mechanisms in autoimmune thyroid disease. Cells. (2023) 12(6):918. doi: 10.3390/cells12060918
6. Antonelli A, Ferrari SM, Corrado A, Di Domenicantonio A, Fallahi P. Autoimmune thyroid disorders. Autoimmun Rev. (2015) 14:174–80. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2014.10.016
7. Caturegli P, De Remigis A, Rose NR. Hashimoto thyroiditis: clinical and diagnostic criteria. Autoimmun Rev. (2014) 13:391–7. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2014.01.007
8. Lo MS, Towne M, VanNoy GE, Brownsteine CA, Lanet AA, Chatila TA, et al. Monogenic Hashimoto thyroiditis associated with a variant in the thyroglobulin (TG) gene. J Autoimmun. (2018) 86:116–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2017.09.003
9. Zundler S, Becker E, Weidinger C, Siegmund B. Anti-adhesion therapies in inflammatory bowel disease-molecular and clinical aspects. Front Immunol. (2017) 8:891. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00891
10. Habtezion A, Nguyen LP, Hadeiba H, Butcher EC. Leukocyte trafficking to the small intestine and colon. Gastroenterology. (2016) 150:340–54. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.10.046
11. Bain CC, Montgomery J, Scott CL, Kel GM, Girard-Madoux MJH, Martens L, et al. TGFβR signalling controls CD103+CD11b+ dendritic cell development in the intestine. Nat Commun. (2017) 8:620. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00658-6
12. Kotschenreuther K, Yan S, Kofler DM. Migration and homeostasis of regulatory T cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:947636. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.947636
13. Li Y, Harada T, Juang YT, Kyttaris VC, Wang Y, Zidanic M, et al. Phosphorylated ERM is responsible for increased T cell polarization, adhesion, and migration in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. (2007) 178:1938–47. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.178.3.1938
14. Parretti H, Okosieme O, Vanderpump M. Current recommendations in the management of hypothyroidism: developed from a statement by the British Thyroid Association Executive. Br J Gen Pract. (2016) 66:538–40. doi: 10.3399/bjgp16X687493
15. Bekkering GE, Agoritsas T, Lytvyn L, Heen AF, Feller M, Moutzouri E, et al. Thyroid hormones treatment for subclinical hypothyroidism: a clinical practice guideline. BMJ. (2019) 365:l2006. doi: 10.1136/bmj.l2006
16. Ragusa F, Fallahi P, Elia G, Gonnella D, Paparo SR, Giusti C, et al. Hashimotos thyroiditis: Epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinic and therapy. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2019) 33:101367. doi: 10.1016/j.beem.2019.101367
17. Qiu K, Li K, Zeng T, Liao Y, Min J, Zhang N, et al. Integrative analyses of genes associated with hashimoto's thyroiditis. J Immunol Res. (2021) 2021:8263829. doi: 10.1155/2021/8263829
18. Kuś A, Chaker L, Teumer A, Peeters RP, Medici M. The genetic basis of thyroid function: novel findings and new approaches. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2020) 105(6):dgz225. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgz225
19. Lee HJ, Li CW, Hammerstad SS, Stefan M, Tomer Y. Immunogenetics of autoimmune thyroid diseases: A comprehensive review. J Autoimmun. (2015) 64:82–90. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2015.07.009
20. Koch CA, Antonelli A. Immunoendocrinology: When (neuro)endocrinology and immunology meet. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. (2018) 19:277–82. doi: 10.1007/s11154-018-9479-7
21. Tomer Y, Davies TF. Searching for the autoimmune thyroid disease susceptibility genes: from gene mapping to gene function. Endocr Rev. (2003) 24:694–717. doi: 10.1210/er.2002-0030
22. Jacobson EM, Huber A, Tomer Y. The HLA gene complex in thyroid autoimmunity: from epidemiology to etiology. J Autoimmun. (2008) 30:58–62. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2007.11.010
23. Ban Y, Tomer Y. Genetic susceptibility in thyroid autoimmunity. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev. (2005) 3:20–32. doi: 10.1080/17402520400008897
24. Paschke R, Schuppert F, Taton M, Velu T. Intrathyroidal cytokine gene expression profiles in autoimmune thyroiditis. J Endocrinol. (1994) 141:309–15. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1410309
25. Chistiakov DA. Immunogenetics of hashimoto's thyroiditis. J Autoimmune Dis. (2005) 2:1. doi: 10.1186/1740-2557-2-1
26. Gregory JL, Morand EF, McKeown SJ, Ralph JA, Hall P, Yang YH, et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor induces macrophage recruitment via CC chemokine ligand 2. J Immunol. (2006) 177(11):8072–9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.177.11.8072
27. Ayaz T, Sahin SB, Sahin OZ, Cure MC, Sumer F, Ilkkilic K. Serum macrophage migration inhibitory factor levels in Hashimoto's thyroiditis; a case control study. Thyroid Res. (2014) 7:11. doi: 10.1186/s13044-014-0011-1
28. Trivedi PJ, Adams DH. Chemokines and chemokine receptors as therapeutic targets in inflammatory bowel disease; pitfalls and promise. J Crohns Colitis. (2018) 12:S641–52. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjx145
29. Argollo MC, Kotze PG, Spinelli A, Gomes T, Danese S. The impact of biologics in surgical outcomes in ulcerative colitis. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. (2018) 32-33:79–87. doi: 10.1016/j.bpg.2018.05.014
30. Tian YC, Guo CL, Li Z, You Y, Liu XY, Su JM, et al. Data-independent acquisition-based quantitative proteomic analysis reveals potential salivary biomarkers of primary sjögren's syndrome. Chin Med Sci J. (2024) 39:19–28. doi: 10.24920/004338
31. Kapsogeorgou EK, Christodoulou MI, Panagiotakos DB, Paikos S, Tassidou A, Tzioufas AG, et al. Minor salivary gland inflammatory lesions in Sjögren syndrome: do they evolve. J Rheumatol. (2013) 40:1566–71. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.130256
32. Verstappen GM, Kroese F, Bootsma H. T cells in primary Sjögren's syndrome: targets for early intervention. Rheumatol (Oxford). (2021) 60:3088–98. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kez004
33. Onalan E, Aslan M. Could neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio be a marker in Hashimoto's thyroiditis. J Pak Med Assoc. (2020) 70:1381–3. doi: 10.5455/JPMA.32518
Keywords: Hashimoto thyroiditis, lymphocyte count, lymphocyte percentage, neutrophil count, lymphocyte migration
Citation: Xue H and Xu R (2025) The lymphocyte levels of Hashimoto thyroiditis patients were significantly lower than that of healthy population. Front. Endocrinol. 16:1472856. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1472856
Received: 30 July 2024; Accepted: 08 January 2025;
Published: 27 January 2025.
Edited by:
Joao Dts Anselmo, Hospital do Divino Espírito Santo, PortugalReviewed by:
Yasmin Mohseni, A2 Biotherapeutics, Inc., United StatesViktor Kravchenko, National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine, Ukraine
Copyright © 2025 Xue and Xu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ruyi Xu, MTgyNDg5NzA3NzZAMTYzLmNvbQ==
 Hui Xue
Hui Xue Ruyi Xu2*
Ruyi Xu2*