- 1Isfahan Gastroenterology and Hepatology Research Center, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan, Iran
- 2Metabolic Liver Disease Research Center, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan, Iran
- 3Department of Biostatistics and Epidemiology, School of Public Health, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan, Iran
- 4Isfahan Endocrine and Metabolism Research Center, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan, Iran
Objectives: Insulin resistance plays a critical role in the pathophysiology of diabetes mellitus and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Moreover, insulin resistance has a central role in atherogensis as the major leading cause of cardiovascular disease (CVD). The aim of the present study was to assess the frequency of pre-diabetes and evaluate the cardiometabolic risk factors among NAFLD patients, comparing those with pre-diabetes to those with normal glucose tolerance.
Methods: In the current retrospective case-control study, the data of 1031 NAFLD patients was retrieved. Based on blood glucose levels, 337 diabetics, 340 pre-diabetes, and, 354 normal glucose patients were diagnosed. After excluding diabetic NAFLD patients, 694 individuals were divided into two groups: normal glucose and pre-diabetes. Various variables, such as age, anthropometric measurements, hypertension, systolic and diastolic blood pressure, and lipid profiles, were extracted from patient files. Statistical analysis was conducted to assess cardiovascular risk factors in NAFLD patients.
Results: Higher age, female gender, higher BMI, triglyceride, waist and hip circumference and waist-to-hip ratio were found in pre-diabetic NAFLD individuals compared with normoglycemic ones (P-value<0.05). Multivariable age-, sex-, BMI- and smoking- adjusted logistic regression showed a predicting role of pre-diabetes and NAFLD concurrence with metabolic syndrome (P-value<0.001, OR:4.31, 95% CI: 2.95- 6.29), but not CVD (P-value=0.353, OR:1.37, 95% CI: 0.71- 2.61).
Conclusion: In this study, nearly one-third of NAFLD patients had pre-diabetes. The mean value of age, BMI, TG, waist and Hip circumference was significantly higher in pre-diabetic patients. The concurrence of pre-diabetes and NAFLD was a predicting factor for metabolic syndrome, but not CVD events.
Background
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is known as the most common chronic liver disease worldwide (1). Diagnosis of NAFLD is approved when fat saturation consists of more than 5% liver weight in the absence of alcohol overuse and other causes of liver steatosis (2). NAFLD can progress to NASH (non-alcoholic steatohepatitis), advanced fibrosis, cirrhosis, and eventually hepatocellular carcinoma (3). The frequency of NAFLD worldwide is estimated at 25%, and there is an upward trend in the number of NAFLD cases from 83 million in 2015 to 101 million by 2030 in the United States (4). NAFLD mostly occurs in the Middle East and South America (5). The estimated frequency of NAFLD in Iran is nearly 33.9% and it is announced by 39.3% of Isfahan’s population (6–8).
In addition, the population involvement in NAFLD is increasing worldwide due to the obesity epidemic (9). NAFLD can cause primary insulin resistance or may be the result of insulin resistance thus it is strongly associated with components of the metabolic syndrome including obesity, insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, and hypertension (10).
Furthermore, pre-diabetic individuals are up to two folds at increased risk of developing diabetes mellitus. Insulin resistance is the mainstay in the pathophysiology of diabetes mellitus (11–13) which is common between NAFLD and diabetes mellitus (14).
Atherosclerosis is an ongoing inflammatory process leading to the formation of plaques in arterial wall. The pathophysiology of atherogenesis is multifactorial; nevertheless, all the process occurs due to an interaction of pro-inflammation, endothelial bed dysfunction and oxidative stress (15, 16). Surfing the literature has shown a direct and critical association between insulin resistance and atherogenesis. Given that, insulin resistance is associated with increased serum level of pro-inflammatory factors such as interleukin 1 (IL-1), IL-6 and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), as well as free oxygen radicals responsible for oxidative stress. Moreover, inappropriate platelet aggregation and calcium plaque deposition in intima-media layer of arteries leading to endothelial dysfunction is well-elucidated in individuals with insulin resistance (17).
Theoretically, as the trace of insulin resistance can be detected in NAFLD and prediabetes, the coincidence of both might make individuals more and more prone to CVDs. A recent meta-analysis of 34,000 patients with NAFLD and insulin resistance over seven years found that NAFLD and insulin resistance increased the risk of mortality and morbidity in CVD by 65%. In fact, the most common cause of death in patients with NAFLD is cardiovascular causes (18). Nevertheless, limited number of researchers have investigated the impact of NAFLD and prediabetes on the incidence of CVD, an issue that is aimed to be evaluated in the current retrospective case-control study.
Methods study design and participants
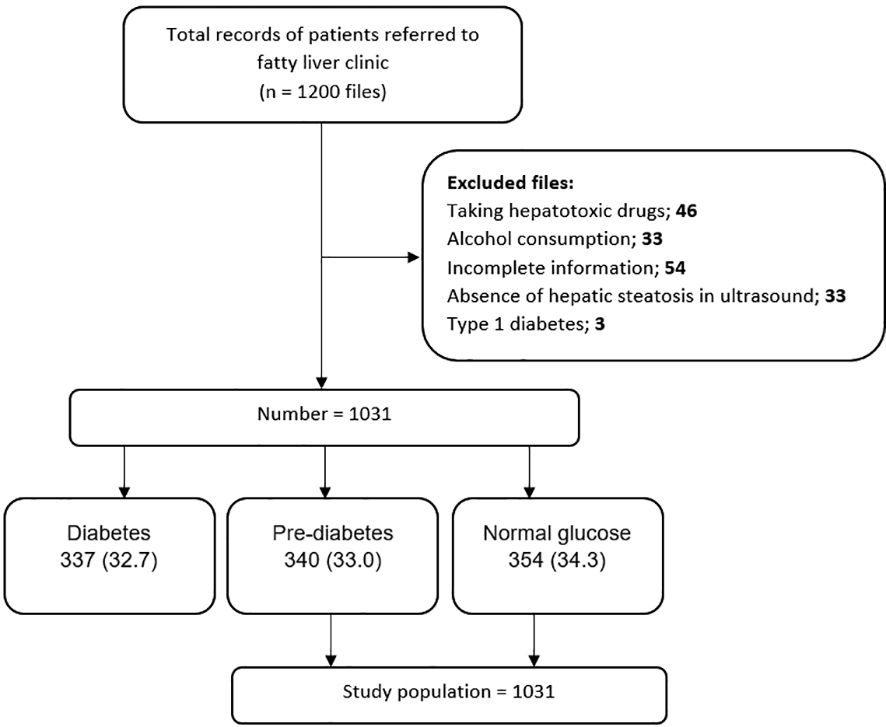
This research is a retrospective case-control study. The data of 1200 patients referred to the Fatty Liver Clinic of the Endocrine and Metabolism Research Center, affiliated with Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, from 2012 to 2017 were retrieved. Diagnosis of fatty liver was made based on the presence of hepatic steatosis in the ultrasound available in the files for patients who did not have a history of consuming too much alcohol and was ruled out for other hepatic steatosis reasons. These excluded cases contain chronic liver diseases (e.g., viral and autoimmune diseases) and chronic use of drugs such as glucocorticoids, sodium valproate, methotrexate, amiodarone, tamoxifen, and anti-retroviral agents for HIV. See Figure 1 for an overview of the statistics. Our data was obtained by considering the history of the diseases and performing some tests, such as checking for viral hepatic markers. The information deficiency in patients’ profiles, especially concerning the main variable of the study, namely the uncertainty of the pre-diabetes status, was not reviewed. Inclusion criteria consisted of NAFLD patients while the exclusion ones were diabetic patients.
Procedures and assessment of variables
In this study, among the 1,200 considered cases, 1031 NAFLD patients were included, which were subdivided into three groups: group1 = normal glucose, group2 = pre-diabetes, and group3 = type2 diabetes. According to the American Diabetes Association guidelines, the normal glucose criterion is fasting blood glucose (FBS) < 100 mg/dl, the HbA1c < 5.7%, or the blood glucose two hours after using 75 g of glucose (BS 2hr OGTT) < 140 mg/dl. The pre-diabetic criterion is FBS (100 -125 mg/dl), HbA1c (5.7% -6.4%), or BS 2 hr OGTT between 140 and 199 mg/dl. The type2 diabetes criterion is FBS ≥ 126 mg/dl, HbA1c ≥ 6.5%, BS 2hr OGTT ≥ 200 mg/dl, or random plasma glucose ≥ 200 mg/dL in patients with hyperglycemic symptoms (19). The last group, containing 337 type 2 diabetic cases, was excluded after matching the whole 1,031 NAFLD patients to their related groups. Finally, 694 NAFLD patients, groups 1 and 2, were included in the study (Figure 1). We evaluated the frequency of pre-diabetes and normal glucose patients and the comparison of cardiovascular risk factors between the prior mentioned groups in NAFLD patients.
Information such as age, gender, height, weight, waist, hip and wrist circumference, medical and drug history, the status of pre-diabetes and diabetes, hypertension, systolic and diastolic blood pressure, lipid profiles (Total Cholesterol, LDL Cholesterol, HDL Cholesterol, and Triglyceride (TG)), Serum Glutamic Oxaloacetic Transaminase (SGOT), Serum Glutamic Pyruvic Transaminase (SGPT), and degree of the fatty liver based on ultrasound were extracted from the files. All the measures were done at the time of NAFLD diagnosis when the patients were primarily diagnosed as NAFLD and referred to our clinic for the first time.
We considered the usage of antihypertensive drugs, a patient’s statement of blood pressure, registered systolic blood pressure of ≥140 (mm Hg), or diastole blood pressure of ≥ 90 (mm Hg) as hypertension or a sign of high blood pressure (20). BMI was calculated by dividing weight (kg) by height squared (m2). We categorized this index into 6 groups: BMI<18.5 as less than normal, 18.5-24.9 as normal, 25-29.9 as overweight, 30-34.99 as obesity grade one, 35-39.9 as grade two obesity, and ≥40 as grade three obesity. Waist-hip circumference ratio (WHR) was considered abnormal for values more than 0.9 in women and more than 1 in men. According to the Adult Treatment Panel III, defining the metabolic syndrome, the presence of three or more of the following characteristics was considered as the presence of metabolic syndrome: Waist circumference > 102 cm in men and > 88 cm in women, triglyceride levels ≥ 150 mg/dl, HDL levels < 40 mg/dl in men and < 50 mg/dl in women, systolic blood pressure ≥ 130 mmHg or diastolic blood pressure ≥ 85 mmHg, fasting plasma glucose levels ≥ 100 mg/dl, or drug treatment for elevated blood glucose. For SGPT and SGOT enzymes, we considered values ≤ 40 U/L as normal, 41-120 U/L as more than normal, and values> 120 U/L as much more than normal (20). The stages of NAFLD were determined using ultrasound data in the patient records. Those with at least two ultrasounds, with an equal degree of hepatic contrast, were classified into one of these three categories: mild steatosis, moderate steatosis, and severe steatosis. We recorded any patient who had a history of myocardial infarction, unstable angina, angina pectoris, coronary artery stenosis or any type of revascularization intervention, heart failure, or hospitalization due to heart disease as cardiovascular disease (CVD). The patients with CVD history was requested to bring their medical records in order to confirm the diagnosis. These assessments were done at the time of NAFLD diagnosis when the patients referred to our clinic for the first time.
The Ethics Committee of Isfahan University of Medical Sciences approved the current study (code: IR.MUI.MED.REC.1399.326).
Statistical analysis
Continuous and categorical variables are reported as mean ± standard deviation (SD) and frequency (percentage). The normality of continuous variables was evaluated using the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test and Q-Q plot, and non-normally positive skewed distributed data such as lipid indices were subjected to logarithmic transformation. Continuous and categorical data were compared between pre-diabetics and normal glucose NAFLD patients using independent samples t-test (or non-parametric Mann-Whitney U test) and chi-square tests. Multiple binary logistic regressions in crude and adjusted models were used to evaluate the risk of (odds ratio) hypertension, cardiovascular disease, and metabolic syndrome in pre-diabetic NAFLD patients compared to normal blood glucose ones. The data were controlled for age, sex, BMI and smoking in the adjusted model. All statistical analyses were done using the Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS, version 16.0 for Windows, 2006, SPSS, Inc, Chicago, IL). P-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
In this study, 1031 patients with NAFLD were included, of which 354 (34.3%) had normal glucose, 340 (33%) were pre-diabetic, and 337 (32.7%) had type 2 diabetes (Figure 1).
After excluding patients with type 2 diabetes, a total of 694 individuals with NAFLD (51% with normal glucose and 49% with pre-diabetes) with a mean age of 45.94 ± 11.26 were included in the analysis.
Out of the 354 people with normal glucose and 340 people with pre-diabetes, 43.9% and 56.1% were female, respectively.
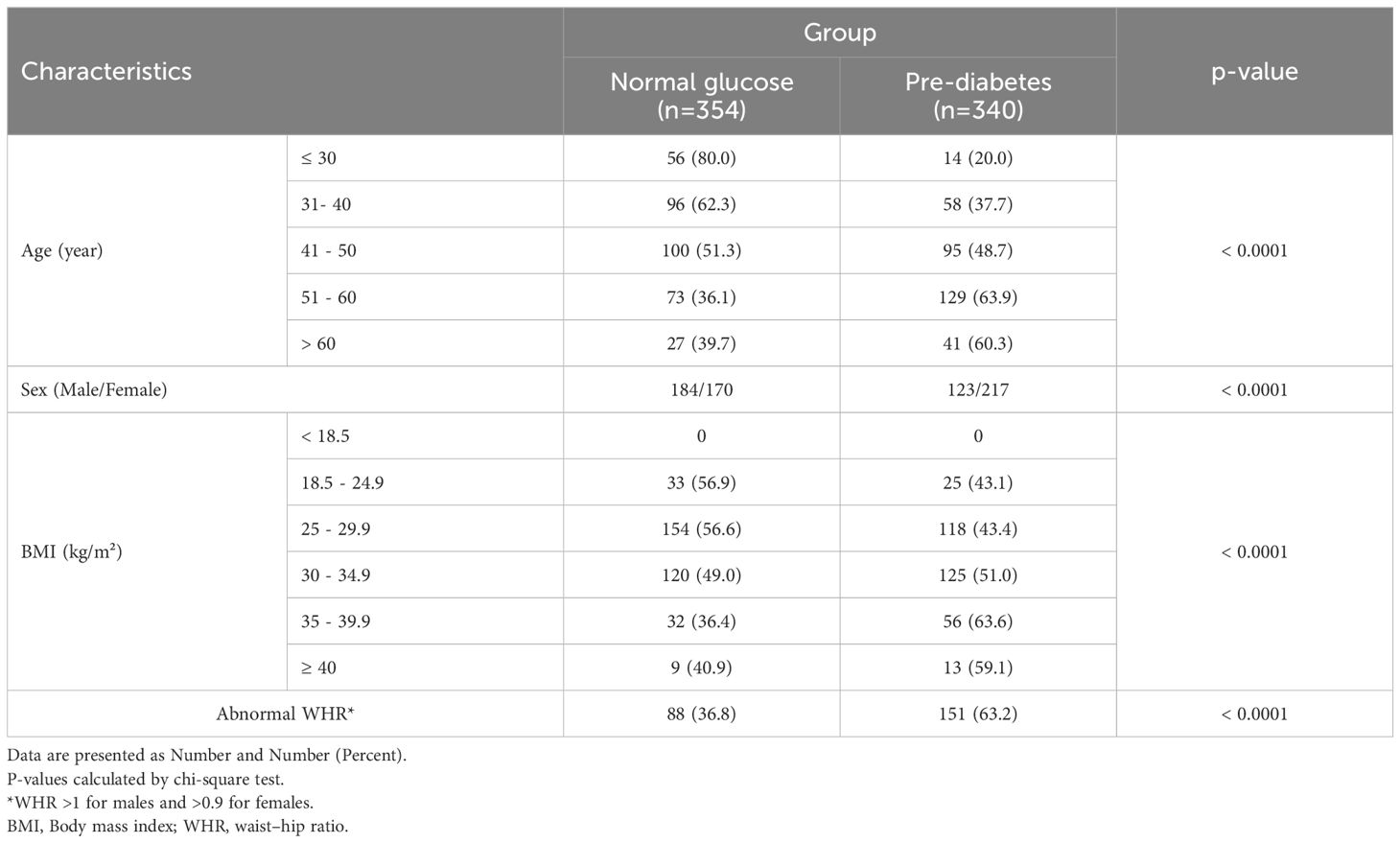
Table 1 presents the frequency of pre-diabetes across categories of age, gender, and anthropometric indices groups. The frequency of pre-diabetes in older people and females was significantly higher (P< 0.0001). In addition, we observed an increasing trend in terms of pre-diabetics along with increasing BMI, from 0 for BMI< 18.5 kg/m2 to 63% for 35 ≤BMI < 39.9 kg/m2 (P<0.0001). The frequency of pre-diabetes in NAFLD patients with abnormal WHR was significantly higher than in people with normal WHR (P<0.0001).
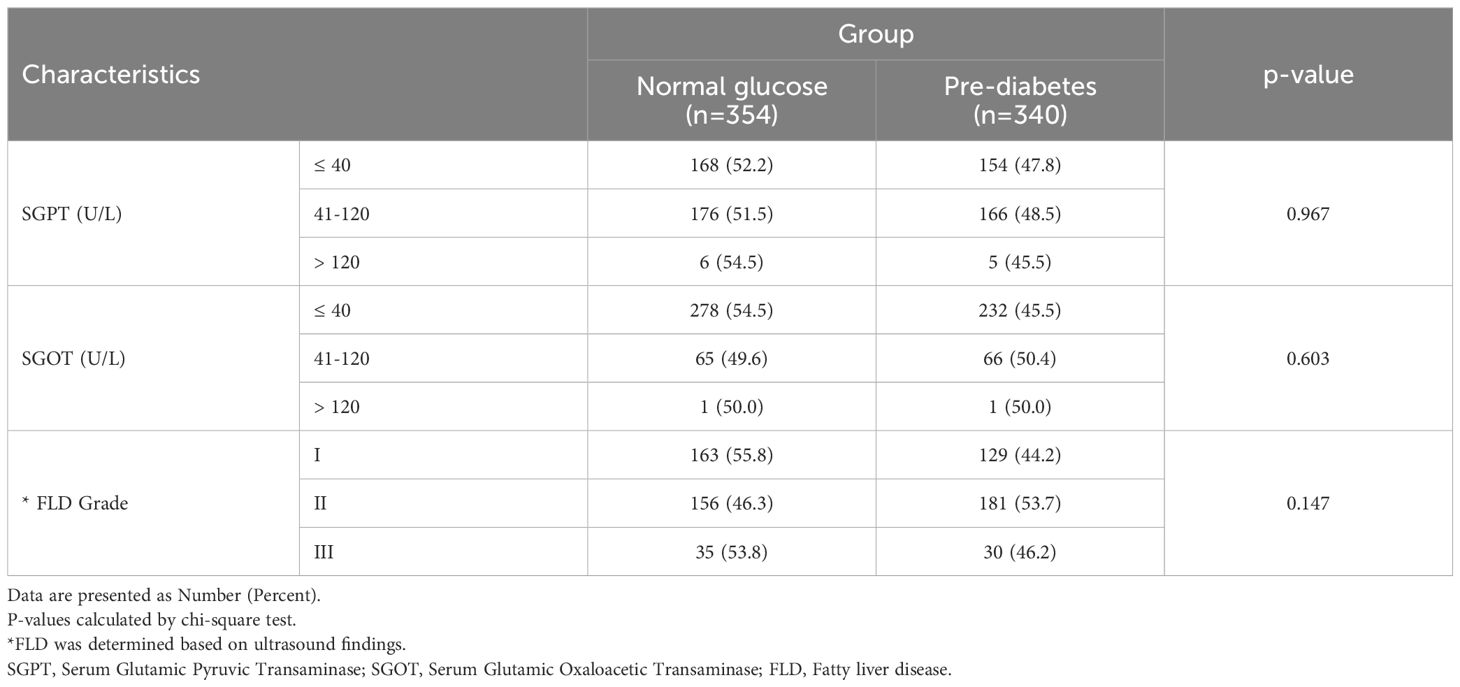
The frequency of pre-diabetes was not significantly different across SGPT and SGOT and NAFLD grades (P>0.1) (Table 2).
Table 3 presents the mean value of different cardiometabolic variables in pre-diabetic and normal glucose NAFLD patients. Among them, the mean value of BMI (P<0.0001), TG (p<0.0001), waist (P<0.0001), hip circumference (P=0.014), and WHR (p=0.008) were significantly higher in pre-diabetic than normal glucose cases.
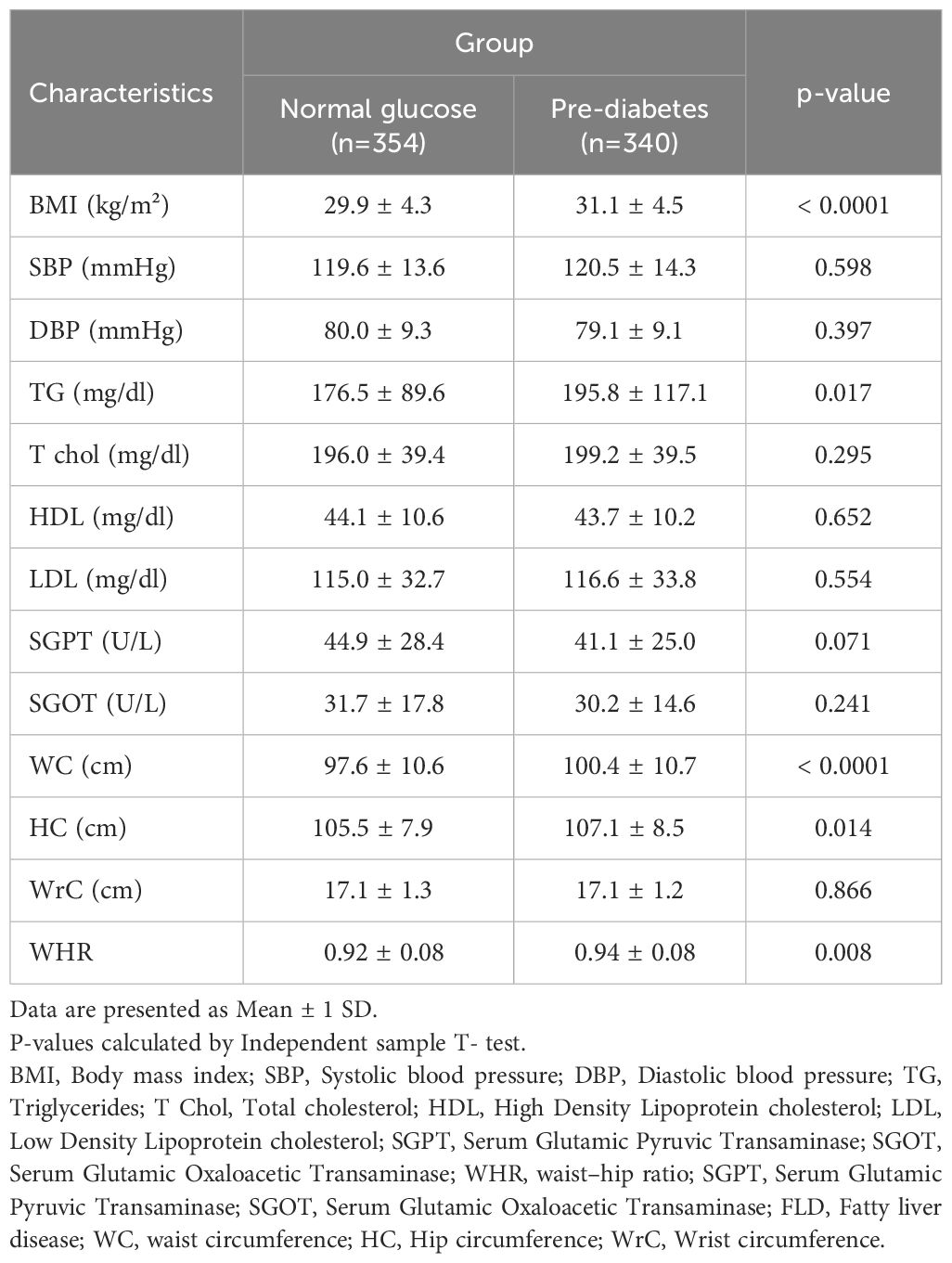
Table 3. Comparison of anthropometric and cardiometabolic characteristics in study population by group.
The comparison of various parameters in terms of fatty liver disease grading but regardless of the patients’ glycemic status revealed statistically that BMI (P-value<0.001), serum triglyceride (P-value=0.001), SGPT (P-value=0.026), waist circumference (P-value<0.001), hip circumference (P-value<0.001) and wrist circumference (P-value<0.001) statistically differed in individuals with different severity of fatty liver disease. Detailed data are demonstrated in Table 4.
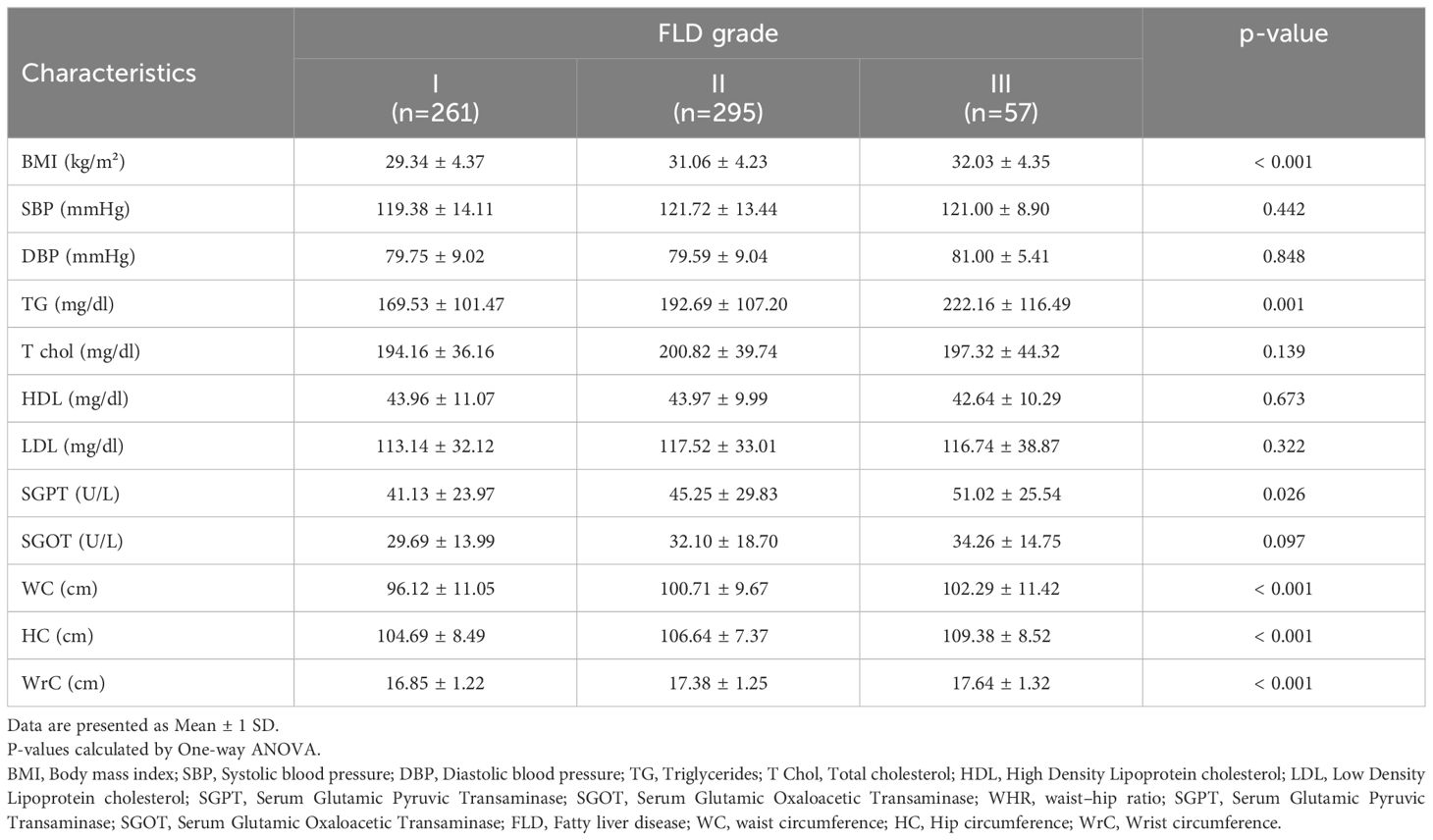
Table 4. Comparison of anthropometric and cardiometabolic characteristics in study population based on FLD grading.
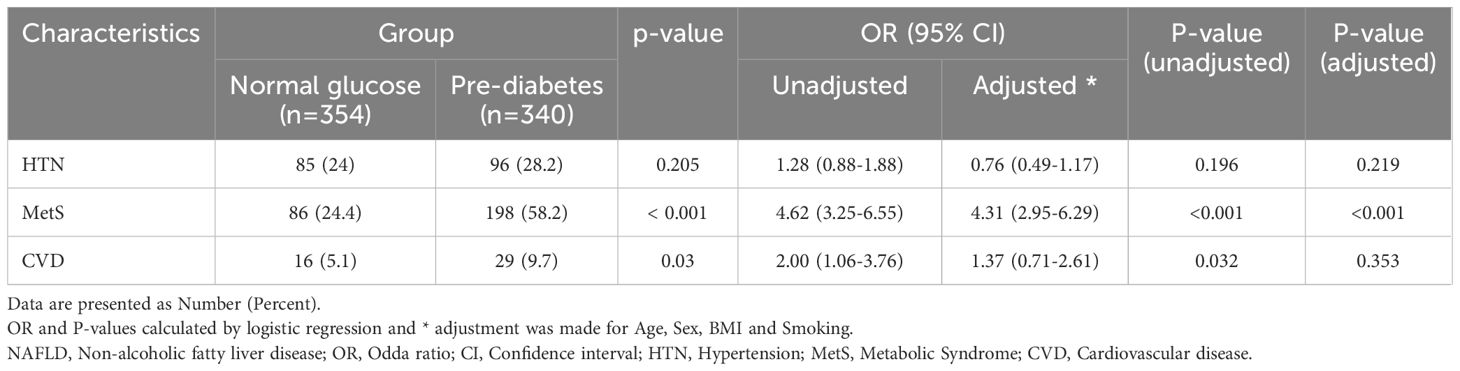
We conducted a comparative analysis to examine the frequency of CVD, hypertension, and metabolic syndrome in patients diagnosed with NAFLD, specifically comparing those with pre-diabetes to individuals with normal glucose levels (Table 5). Our findings revealed a significantly higher frequency of metabolic syndrome (P<0.0001) and history of CAV (P=0.03) in patients with pre-diabetes. However, no significant association was observed between blood glucose levels and hypertension in two groups (P > 0.05). Further logistic regression investigations showed that pre-diabetic status was a standalone predictor of metabolic syndrome in both unadjusted and adjusted models. Given that, the NAFLD individuals with pre-diabetes was at 4.62 (P-value<0.001, OR:4.62, 95% CI: 3.25- 6.55) and 4.31 (P-value<0.001, OR:4.31, 95% CI: 2.95- 6.29) times increased risk of developing metabolic syndrome in unadjusted and adjusted logistic regression analyses, respectively. Furthermore, CVD was 2 folds (P-value=0.032, OR:2 95% CI: 1.06- 3.76) more among pre-diabetic NAFLD patients compared with normoglycemic ones in unadjusted model, while the adjustments for age, sex, BMI and smoking led to an insignificant role for CVD (P-value=0.353, OR:1.37, 95% CI: 0.71- 2.61).
Discussion
The main scope of the current study was to investigate the cardiometabolic parameters among the NAFLD individuals with pre-diabetes. Accordingly, we found that those NAFLD meeting pre-diabetes criteria were generally older and predominantly consisted of female gender. Except for triglyceride, other cardiometabolic parameters did not differ with normoglycemic individuals; however, anthropometric indices including BMI, WC, HC and WHR were remarkably higher among pre-diabetic cases. Further evaluations revealed that concurrent NAFLD and pre-diabetes was accompanied by more than 4 times increased risk of metabolic syndrome development, but we found no role for concurrence of NAFLD and prediabetes to predict hypertension or CVD.
In our study, the considered NAFLD population with including criteria, the frequency of pre-diabetes patients is 49%. This percentage is similar to a study conducted by Said Taharboucht et al. in Algeria in 2020 on 213 NAFLD patients among whom prediabetes was detected in 85 individuals accounting for 40% (21). Nevertheless this rate variably differs in other studies. For instance, Cuthbertson and colleagues perform an ongoing investigation of NAFLD in Finland finding that 25.44% of their cases developed prediabetes (22). Another study by Kitazawa et al. reported that 2.96% (770/26,014 cases) of individuals with NAFLD met the criteria for prediabetes, while 26.1% (777/2977 cases) were high-risk individuals for prediabetes development (23). This rate is while the only other study conducted in this field in Iran by Pakzad et al. on 80 NAFLD patients reported a 55% frequency of pre-diabetes (24). Logically, this considerable variability can be attributed to several factors such as the differences in the definition of NAFLD and prediabetes, the sample population, the study design and the determined criteria for including the individuals
We observed that pre-diabetic NAFLD individuals were generally older than normoglycemic ones. Similarly Song et al. presented that NAFLD cases with abnormal glycemic state compatible with prediabetes are older (25). Cuthbertson and colleagues also stated a similar pattern of age distribution among NAFLD individuals developing pre-diabetes (22).
The number of pre-diabetic women was significantly higher than that of pre-diabetic men. This finding is consistent with what was presented by Kitazawa et al. who presented that females are more prone to develop pre-diabetes than men (23). This outcome has been confirmed in other studies, as well (26–28). It seems that the lipid distribution and metabolism as well as hormone differences might be responsible for higher risk of diabetic changes in women suffering NAFLD (26).
We found a significant association between increased BMI, waist circumference, hip circumference, waist-to-hip ration and abnormal WHR and pre-diabetes in NAFLD. These measures have been widely experimented in the literature with firm verifying documentations (26, 29–31). It is clear that obesity has a direct association with NAFLD. On the other hand, it is well-elucidated that obese people are at increased risk of developing diabetic changes as adipose tissue releases increased amounts of non-esterified fatty acids, glycerol, hormones, proinflammatory cytokines and other factors that are involved in the development of insulin resistance (32).
Since long time ago BMI was an indicator of obesity; however, nowadays we know that BMI has significant limitation to distinguish excess adipose tissue. Accordingly, other parameters such as waist and hip circumference and their ration as the indices of peripheral adipose tissue have been emerged revealing a better association with body metabolism, insulin resistance and diabetes development (33–35). Nevertheless, our findings regarding higher measures of these indices in prediabetic NAFLD individuals compared with normoglycemic ones are in agreement with the evidence.
In the current study, we found no significant relationship between SGOT and SGPT enzyme values as well as the grading of fatty liver disease in pre-diabetes compared to normal glucose. The same result was posed in a study by Komshilova et al.; they believed that normal liver enzymes did not rule out necrosis, inflammation, and fibrotic changes in the liver, and up to 70% of patients with NAFLD may have normal enzymes (36). Taharboucht et al., represented a similar observation (21).
The current study showed a clear relationship between increased triglyceride in pre-diabetic NAFLD patients compared to another group. This result is in line with the Indian study (30) and the one in Algeria (21). However, in the present study, there was no significant relationship between cholesterol, LDL, and HDL in pre-diabetes compared to normal glucose patients. Although, it should be mentioned that some of our patients used statins, which lead to lower cholesterol and LDL (37). Therefore, the findings regarding cholesterol-related lipid profile can be considered as source of bias that needs further evaluations.
The logistic regression evaluations revealed that pre-diabetes in NAFLD was a predictor of metabolic syndrome, but not CVD. The predicting role for metabolic syndrome seems logical considering the associations presented above, however we assume that the small number of study population with CVD is responsible for this lacking of association. Moreover, the observational design of our study limits its ability to generalize the prognostic role of pre-diabetes in NAFLD for CVD events.
It is well-evidenced that a large number of NAFLD individuals are prone to develop impaired glucose tolerance or impaired fasting glucose, pre-diabetes and progressively, come down with diabetes mellitus (31, 38–42). This fact majorly contributes to the similar pathogenesis of NAFLD and pre-diabetes, insulin resistance. Given that, insulin resistance is associated with the release of a myriad of lipid metabolites, proinflammatory cytokines and hepatokines (e.g., fetuin A, fetuin B and angiopoietin‐like protein) which in turn leads to developing diabetes mellitus (43, 44). This pathogenesis is similar in pre-diabetic patients, as well; whereas, it is confirmed that up to 70% of them would turn into diabetes mellitus (45).
Moreover, the nature of NAFLD is associated with increased risk of CVD independent of the presence of hypertension, diabetes, and obesity by endothelial dysfunction (46). This relation can be attributed to the pathogenesis of insulin resistance in NAFLD contributing in the process of atherogensis through oxidative stress, endothelial dysfunction and excessive proinflammation (15, 16, 47, 48).
Although in line with our findings, Hubbard et al. presented no heightened risk for CVD in patients with pre-diabetes (49); theoretically, the individuals with pre-diabetes with a similar pathogenesis are at increased risk of developing CVD (50).
Despite the strong points of our study among which the large study population can be named, this investigation meets several limitations. One of the limitations of this study is its retrospective observational method and absence of a control group without fatty liver disease. Biopsy is known as the gold standard but invasive procedure for NAFLD diagnosis, thus we limited our analysis to the ultrasound results in the patients’ file (1, 51). The third limitation of this study may be attributed to the adjustments. Despite all of the adjustments done in the analyses, it is still possible that unmeasured confounders such as the current use of chronic medications (glucose lowering, antiplatelet agents, lipid lowering and cardioprotective agents), occupation, daily activity, physical activity and dietary habits can potentially interfere with part of the associations. Another remarkable limitation of our study is failure to follow the patients assessing the risk of developing CVD events or diabetes mellitus within time. Although this issue significantly questions the design of our study, further investigations are strongly recommended.
Therefore, we can claim that this population can be a sample of almost the entire fatty liver community in this region. Also, very few studies on the frequency of pre-diabetes have been conducted in the NAFLD population. All in all, the main scope of conducting such studies is to detect the cases prone to disease related to insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome in early stages and provide a thorough guideline to prevent from the progression of the condition toward life-threatening CVDs and reduce the burden of treatment. We have previously investigated this association in the population of diabetic individuals (8); nevertheless, preventive strategies in prediabetes might have significantly positive effects on the health of general population, mostly those who are not aware of their threatened health such as the individuals with NAFLD and prediabetes. Given that, further larger screening schedules in the community of Iran are recommended to explore the individuals with NAFLD and prediabetes or diabetes mellitus and initiate medications by which hepato- and cardioprotection can be achieved. Although we have not evaluated the impact of medications in preventive setting on NAFLD, prediabetes and CVDs, evidence in the literature have presented favorable outcomes. However, rarely studies have focused on prediabetes and the major body of evidence have concentrated on NAFLD and diabetes (52, 53). Drugs such as the insulin-sensitizing thiazolidinediones, glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) agonists and sodium-glucose Cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors have prompted promising outcomes in this regard (53–57).
Conclusion
In our study, nearly one-third of the population of NAFLD patients are pre-diabetic. We found a significant relationship between age, BMI, abnormal WHR, TG, and metabolic syndrome with pre-diabetes compared to normal glucose NAFLD cases. Moreover, pre-diabetes in NAFLD was a predicting factor for metabolic syndrome, but not associated with increased risk of CVD. In order to improve the generalizability of the association between cardiovascular disease and NAFLD, it is recommended to conduct further studies with prospective design in different regions and various subpopulations.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Isfahan University of Medical Sciences Ethics Committee. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
AT: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. ZE: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. AF: Formal analysis, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. BI: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. ES: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MA: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MK: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Younossi ZM, Koenig AB, Abdelatif D, Fazel Y, Henry L, Wymer M. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Journa64l. (2016) 64:73–84. doi: 10.1002/hep.28431
2. Valenti L, Bugianesi E, Pajvani U, Targher G. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: cause or consequence of type 2 diabetes? Journa36l. (2016) 36:1563–79. doi: 10.1111/liv.13185
3. Perumpail BJ, Khan MA, Yoo ER, Cholankeril G, Kim D, Ahmed A. Clinical epidemiology and disease burden of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Journa23l. (2017) 23:8263–76. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i47.8263
4. Younossi ZM, Blissett D, Blissett R, Henry L, Stepanova M, Younossi Y, et al. The economic and clinical burden of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in the United States and Europe. Journa64l. (2016) 64:1577–86. doi: 10.1002/hep.28785
5. Friedman SL, Neuschwander-Tetri BA, Rinella M, Sanyal AJ. Mechanisms of NAFLD development and therapeutic strategies. Journa24l. (2018) 24:908–22. doi: 10.1038/s41591-018-0104-9
6. Adibi A, Maleki S, Adibi P, Etminani R, Hovsepian S. Prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and its related metabolic risk factors in isfahan, Iran. Journa6l. (2017) 6:47. doi: 10.4103/2277-9175.204590
7. Moghaddasifar I, Lankarani KB, Moosazadeh M, Afshari M, Ghaemi A, Aliramezany M, et al. Prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and its related factors in Iran. Journa7l. (2016) 7:149–60.
8. Barati M, Teimouri A, Feizi A, Iraj B, Karimifar M. Investigation of cardiovascular risk factors in diabetic and nondiabetic patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Journa29l. (2024) 29:51. doi: 10.4103/jrms.jrms_830_23
9. Karamfilova V, Gateva A, Assyov Y, Alexiev A, Savov A, Yaneva N, et al. PNPLA3 I148M polymorphism in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, obesity and prediabetes. Journa28l. (2019) 28:433–8. doi: 10.15403/jgld-506
10. Younossi ZM, Golabi P, de Avila L, Paik JM, Srishord M, Fukui N, et al. The global epidemiology of NAFLD and NASH in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Journa71l. (2019) 71:793–801. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.06.021
11. Mantovani A, Byrne CD, Bonora E, Targher G. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and risk of incident type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis. Journa41l. (2018) 41:372–82. doi: 10.2337/dc17-1902
12. Remus Popa A, Fratila O, Rus M, Anca Corb Aron R, Mihai Vesa C, Pantis C, et al. Risk factors for adiposity in the urban population and influence on the prevalence of overweight and obesity. Journa20l. (2020) 20:129–33. doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.8662
13. Vesa CM, Popa L, Popa AR, Rus M, Zaha AA, Bungau S, et al. Current data regarding the relationship between type 2 diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular risk factors. Journa10l. (2020) 10:1–17. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics10050314
14. Bungau S, Behl T, Tit DM, Banica F, Bratu OG, Diaconu CC, et al. Interactions between leptin and insulin resistance in patients with prediabetes, with and without NAFLD. Journa20l. (2020) 20:197. doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.9327
15. Tajmirriahi M, Saadatnia M, Shemirani H, Sadeghi M, Chamasemani A, Safaei A. The incidence of cardiovascular events in small versus large ischemic stroke; a three-year cohort study. Journa19l. (2023) 19:35. doi: 10.48305/arya.2023.26660.2820
16. Sadeghi M, Heshmat-Ghahdarijani K, Talaei M, Safaei A, Sarrafzadegan N, Roohafza H. The predictive value of atherogenic index of plasma in the prediction of cardiovascular events; a fifteen-year cohort study. Journa66l. (2021) 66:418–23. doi: 10.1016/j.advms.2021.09.003
17. Khosravi A, Sadeghi M, Farsani ES, Danesh M, Heshmat-Ghahdarijani K, Roohafza H, et al. Atherogenic index of plasma: A valuable novel index to distinguish patients with unstable atherogenic plaques. Journa27l. (2022) 27:45. doi: 10.4103/jrms.jrms_590_21
18. Maurice J, Manousou P. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Journa18l. (2018) 18:245–50. doi: 10.7861/clinmedicine.18-3-245
19. Standards of medical care in diabetes-2018 abridged for primary care providers. Journa36l. (2018) 36:14–37. doi: 10.2337/cd17-0119
20. Jameson JL, Fauci AS, Kasper DL, Hauser SL, Longo DL, Loscalzo J. Harrison’s principles of internal medicine. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill Education (2018). p. 20e.
21. Taharboucht S, Guermaz R, Brouri M, Chibane A. Pre-diabetes and NAFLD; A study of an Algerian population sample. Journa1l. (2020) 1:100060. doi: 10.1016/j.endmts.2020.100060
22. Cuthbertson DJ, Koskinen J, Brown E, Magnussen CG, Hutri-Kähönen N, Sabin M, et al. Fatty liver index predicts incident risk of prediabetes, type 2 diabetes and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Journa53l. (2021) 53:1257–65. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2021.1956685
23. Kitazawa A, Maeda S, Fukuda Y. Fatty liver index as a predictive marker for the development of diabetes: A retrospective cohort study using Japanese health check-up data. Journa16l. (2021) 16:e0257352. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0257352
24. Pakzad B, Veldani N, Akbari M. Determination of frequency of diabetes and pre-diabetes in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and comparison with a control group. Journa33l. (2016) 33:2440–7.
25. Song Q-R, Liu S-L, Bi Y-G, Chen S-H, Wu S-L, Cai J. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with cardiovascular outcomes in subjects with prediabetes and diabetes: a prospective community-based cohort study. Journa9l. (2022) 9:889597. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.889597
26. Zou J, Xiong H, Zhang H, Hu C, Lu S, Zou Y. Association between the cardiometabolic index and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: insights from a general population. Journa22l. (2022) 22:20. doi: 10.1186/s12876-022-02099-y
27. Younossi ZM, Koenig AB, Abdelatif D, Fazel Y, Henry L, Wymer M. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease—meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Journa64l. (2016) 64:73–84. doi: 10.1002/hep.28431
28. Cuthbertson DJ, Brown E, Koskinen J, Magnussen CG, Hutri-Kähönen N, Sabin M, et al. Longitudinal analysis of risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in adulthood. Journa39l. (2019) 39:1147–54. doi: 10.1111/liv.2019.39.issue-6
29. Liu M, Wang J, Zeng J, Cao X, He Y. Association of NAFLD with diabetes and the impact of BMI changes: A 5-year cohort study based on 18,507 elderly. Journa102l. (2017) 102:1309–16. doi: 10.1210/jc.2016-3440
30. Rajput R, Ahlawat P. Prevalence and predictors of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in prediabetes. Journa13l. (2019) 13:2957–60. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2019.07.060
31. Mantovani A, Petracca G, Beatrice G, Tilg H, Byrne CD, Targher G. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and risk of incident diabetes mellitus: an updated meta-analysis of 501 022 adult individuals. Journa70l. (2021) 70:962–9. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-322572
32. Kahn SE, Hull RL, Utzschneider KM. Mechanisms linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Journa444l. (2006) 444:840–6. doi: 10.1038/nature05482
33. Zou Y, Sheng G, Yu M, Xie G. The association between triglycerides and ectopic fat obesity: an inverted U-shaped curve. Journa15l. (2020) 15:e0243068. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0243068
34. Sheng G, Xie Q, Wang R, Hu C, Zhong M, Zou Y. Waist-to-height ratio and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in adults. Journa21l. (2021) 21:239. doi: 10.1186/s12876-021-01824-3
35. Tomas Ž, Škarić-Jurić T, Zajc Petranović M, Jalšovec M, Rajić Šikanjić P, Smolej Narančić N. Waist to height ratio is the anthropometric index that most appropriately mirrors the lifestyle and psychological risk factors of obesity. Journa76l. (2019) 76:539–45. doi: 10.1111/1747-0080.12520
36. Komshilova K, Mazurina N, Troshina E, Shvangiradze T, Bogomolov P, Melnichenko G, et al. Metabolic markers of cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus in various clinical and morphological forms of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with abdominal obesity. Journa4l. (2018) 4:175–. doi: 10.5455/ijsm.ct-scan-children-mild-head-injury
37. Stone NJ, Robinson JG, Lichtenstein AH, Bairey Merz CN, Blum CB, Eckel RH, et al. ACC/AHA guideline on the treatment of blood cholesterol to reduce atherosclerotic cardiovascular risk in adults: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. Journa63l. (2013) 63:2889–934. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.11.002
38. Yamada T, Fukatsu M, Suzuki S, Wada T, Yoshida T, Joh T. Fatty liver predicts impaired fasting glucose and type 2 diabetes mellitus in Japanese undergoing a health checkup. Journa25l. (2010) 25:352–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2009.05998.x
39. Bae JC, Rhee EJ, Lee WY, Park SE, Park CY, Oh KW, et al. Combined effect of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and impaired fasting glucose on the development of type 2 diabetes: a 4-year retrospective longitudinal study. Journa34l. (2011) 34:727–9. doi: 10.2337/dc10-1991
40. Ekstedt M, Franzén LE, Mathiesen UL, Thorelius L, Holmqvist M, Bodemar G, et al. Long-term follow-up of patients with NAFLD and elevated liver enzymes. Journa44l. (2006) 44:865–73. doi: 10.1002/hep.21327
41. Fujii H, Kawada N, JSGo N. The role of insulin resistance and diabetes in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Journa21l. (2020) 21:3863. doi: 10.3390/ijms21113863
42. Stefan N, Cusi K. A global view of the interplay between non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and diabetes. Journa10l. (2022) 10:284–96. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(22)00003-1
43. Tilg H, Moschen AR, Roden M. NAFLD and diabetes mellitus. Journa14l. (2017) 14:32–42. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2016.147
44. Targher G, Lonardo A, Byrne CD. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and chronic vascular complications of diabetes mellitus. Journa14l. (2018) 14:99–114. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2017.173
45. Lee J, Cho YK, Kang YM, Kim HS, Jung CH, Kim HK, et al. The impact of NAFLD and waist circumference changes on diabetes development in prediabetes subjects. Journa9l. (2019) 9:17258. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-53947-z
46. Nasiri-Ansari N, Androutsakos T, Flessa CM, Kyrou I, Siasos G, Randeva HS, et al. Endothelial cell dysfunction and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): A concise review. Journa11l. (2022) 11:1–32. doi: 10.3390/cells11162511
47. Targher G, Corey KE, Byrne CD. NAFLD, and cardiovascular and cardiac diseases: Factors influencing risk, prediction and treatment. Journa47l. (2021) 47:101215. doi: 10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101215
48. Li M, Wang H, X-j Z, Cai J, Li H. NAFLD: An emerging causal factor for cardiovascular disease. Journa38l. (2023) 38:255–65. doi: 10.1152/physiol.00013.2023
49. Hubbard D, Colantonio LD, Tanner RM, Carson AP, Sakhuja S, Jaeger BC, et al. Prediabetes and risk for cardiovascular disease by hypertension status in black adults: the jackson heart study. Journa42l. (2019) 42:2322–9. doi: 10.2337/dc19-1074
50. Cai X, Zhang Y, Li M, Wu JH, Mai L, Li J, et al. Association between prediabetes and risk of all cause mortality and cardiovascular disease: updated meta-analysis. Journa370l. (2020) 370:1–12. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m2297
51. Chalasani N, Younossi Z, Lavine JE, Charlton M, Cusi K, Rinella M, et al. The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Journa67l. (2018) 67:328–57. doi: 10.1002/hep.29367
52. Ferguson D, Finck BN. Emerging therapeutic approaches for the treatment of NAFLD and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Journa17l. (2021) 17:484–95. doi: 10.1038/s41574-021-00507-z
53. Lian J, Fu J. Pioglitazone for NAFLD patients with prediabetes or type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis. Journa12l. (2021) 12:615409. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.615409
54. Khodeer DM. Beyond glycemic control: cardiovascular, renal, and hepatic benefits of GLP-1 receptor agonists. Journa1l. (2024) 1:15–26. doi: 10.21608/sasj.2024.396448
55. Sumida Y, Yoneda M, Tokushige K, Kawanaka M, Fujii H, Imajo K, et al. Hepatoprotective effect of SGLT2 inhibitor on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Journa2020l. (2020) 2020:17. doi: 10.36502/2020/droa.6159
56. Androutsakos T, Nasiri-Ansari N, Bakasis A-D, Kyrou I, Efstathopoulos E, Randeva HS, et al. SGLT-2 inhibitors in NAFLD: expanding their role beyond diabetes and cardioprotection. Journa23l. (2022) 23:3107. doi: 10.3390/ijms23063107
Keywords: non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), pre-diabetes, diabetes, cardiometabolic risk factors, BMI, metabolic syndrome
Citation: Teimouri A, Ebrahimpour Z, Feizi A, Iraj B, Saffari E, Akbari M and Karimifar M (2025) Pre-diabetes and cardiovascular risk factors in NAFLD patients: a retrospective comparative analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 16:1416407. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1416407
Received: 12 April 2024; Accepted: 13 January 2025;
Published: 07 February 2025.
Edited by:
Mónica Muñoz Úbeda, Complutense University of Madrid, SpainReviewed by:
Nancy Lucero Martínez Rodríguez, Federico Gómez Children’s Hospital, MexicoBasmah Eldakhakhny, King Abdulaziz University, Saudi Arabia
Copyright © 2025 Teimouri, Ebrahimpour, Feizi, Iraj, Saffari, Akbari and Karimifar. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Mozhgan Karimifar, bW96aGdhbl9rYXJ5bXlmYXJAeWFob28uY29t
 Azam Teimouri
Azam Teimouri Zahra Ebrahimpour
Zahra Ebrahimpour Awat Feizi
Awat Feizi Bijan Iraj
Bijan Iraj Elahe Saffari
Elahe Saffari Mojtaba Akbari
Mojtaba Akbari Mozhgan Karimifar
Mozhgan Karimifar