- 1Department of Medicine, Section of Hematology and Oncology, Tulane University School of Medicine, New Orleans, LA, United States
- 2Tulane University Cancer Center, New Orleans, LA, United States
- 3Department of Cell and Molecular Biology, Tulane University School of Science and Engineering, New Orleans, LA, United States
- 4United States Department of Agriculture Southern Regional Research Center, New Orleans, LA, United States
- 5Department of Microbiology, Immunology, and Genetics, University of North Texas Health Science Center, Fort Worth, TX, United States
- 6Department of Physiology, College of Medicine, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ, United States
- 7Department of Pharmacology, Tulane University School of Medicine, New Orleans, LA, United States
- 8Department of Surgery, Tulane University School of Medicine, New Orleans, LA, United States
- 9Department of Physiology, Tulane University School of Medicine, New Orleans, LA, United States
At the time of breast cancer diagnosis, most patients meet the diagnostic criteria to be classified as obese or overweight. This can significantly impact patient outcome: breast cancer patients with obesity (body mass index > 30) have a poorer prognosis compared to patients with a lean BMI. Obesity is associated with hyperleptinemia, and leptin is a well-established driver of metastasis in breast cancer. However, the effect of hyperleptinemia on angiogenesis in breast cancer is less well-known. Angiogenesis is an important process in breast cancer because it is essential for tumor growth beyond 1mm3 in size as well as cancer cell circulation and metastasis. This review investigates the role of leptin in regulating angiogenesis, specifically within the context of breast cancer and the associated tumor microenvironment in obese patients.
Introduction
All cells, including cancer cells, depend on the vasculature for oxygen, nutrient access and waste removal to support their basic metabolic functions. This is particularly true for fast-growing solid tumors, where the densely packed and metabolically active tumor stroma quickly drives the tumor microenvironment to become acidic and hypoxic. As hypothesized by Dr. Judah Folkman in 1971, cancer must at some point during tumor progression become dependent on the blood vasculature; and, in the absence of tumor neovascularization, the tumor core quickly becomes necrotic, constraining solid tumors to <2mm3 in size due to the limitation imposed by oxygen diffusion distance (7). Many cancers escape this constraint by inducing nearby blood vessels to undergo angiogenesis, such that new blood vessels sprout towards and invade the tumor mass. Resulting blood flow into the tumor brings critical oxygen and nutrients that can support further tumor growth and expansion (8). In addition to being a critical step in tumor growth, cancer neovascularization also provides an essential conduit for metastasis – the process by which some cancer cells escape the primary tumor and invade the blood (or lymphatic) circulation to seed a secondary tumor at a distal tissue site.
Regulation of the angiogenic signaling axis is affected by several disease states, including chronic obesity, which drives a systemic pro-inflammatory state that promotes angiogenesis (9, 10). As obesity becomes more and more prevalent, it is increasingly important to understand how obesity contributes to the pathology of many diseases, including cancer. There is a strong correlation between poor outcomes in cancer and obesity: overweight and obese patients are at increased risk of cancer mortality (11). Additionally, obesity is associated with higher incidence of many cancers, including cancer affecting colorectal, endometrial, and breast tissue (12, 13).
Obesity is associated with higher risk of developing breast cancer – especially in post-menopausal women – and is also associated with larger tumors, positive lymph node status, and shorter disease-free interval with decreased survival (1–3, 14, 15). Furthermore, most breast cancer patients are obese or overweight at diagnosis (1). Thus, there is a pressing need to better understand how obesity interacts synergistically with breast cancer to affect patient outcomes. In particular, identifying the molecular targets which contribute to the obesity-breast cancer axis may allow for the development of novel interventions for breast cancer patients that specifically address obesity’s contribution to their disease progression. In this review, we focus on the role of the adipokine leptin, whose blood concentration is greatly elevated in proportion to patient obesity.
Leptin is a peptide hormone produced and secreted by adipocytes and adipose stem cells (ASCs) and is the primary regulator of long-term balance between energy storage and expenditure (4). Leptin also appears to be an upstream regulator in the obesity-breast cancer axis (5). Obesity-induced hyperleptinemia contributes to poor outcomes across breast cancer subtypes, with increased metastases in triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) and increased tumor growth in estrogen receptor positive breast cancer (5, 16, 17). Separately, leptin is well-established as a potent inducer of angiogenesis, in both physiologic and pathologic contexts (10, 18) pointing to a logical link between elevated leptin and enhanced tumorigenesis. Given the critical role that angiogenesis plays in cancer development and patient survival outcomes, the role of leptin in driving angiogenesis in obese breast cancer patients is of critical relevance.
Angiogenic dysregulation in obesity
The link between obesity and angiogenic dysregulation is well-established in both cancer and non-cancer (e.g., diabetes and cardiovascular disease) contexts, which are more common in obese individuals (19). Figure 1 depicts the effect of obesity-associated dysregulation of angiogenesis in the context of cancer. Adipose tissue is highly vascularized, and several metabolic signaling axes that affect adipose tissue function also regulate angiogenesis. For example, genes that govern adipose tissue expansion in obesity also affect angiogenic signaling, including insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), which is produced by adipocytes near capillaries and which stimulates endothelial cell proliferation and angiogenesis (20). Genes associated with angiogenic patterning, including forkhead box C2 (FOXC2) and apelin (APLN), are also expressed in adipocytes in the context of obesity, which may contribute to adipocyte metabolic function and insulin sensitivity (20). High caloric intake and the resulting obesity-related adipocyte hypertrophy are associated with impaired capillary architecture of associated adipose tissue as demonstrated in Figure 1 (20). Interestingly, many signaling pathways elevated in obesity are also present in cancer and appear to target angiogenic signaling (21). For example, HIF-1α is elevated in adipose tissue macrophages with obesity, and its expression decreases after weight loss (22). HIF-1α is also expressed in many cancers, including breast cancer (23), where it drives the production of the pro-angiogenic signal VEGF. Circulating VEGF itself is also elevated in both obese individuals (9, 24) and in some cancers (25), including breast cancer, where it appears to be prognostic for patient outcome and survival (26, 27). Together, these data suggest that angiogenic dysregulation serves as a nexus between obesity and breast cancer, such that obesity might promote a pro-angiogenic state in the tumor microenvironment that is favorable for breast cancer progression and metastasis.
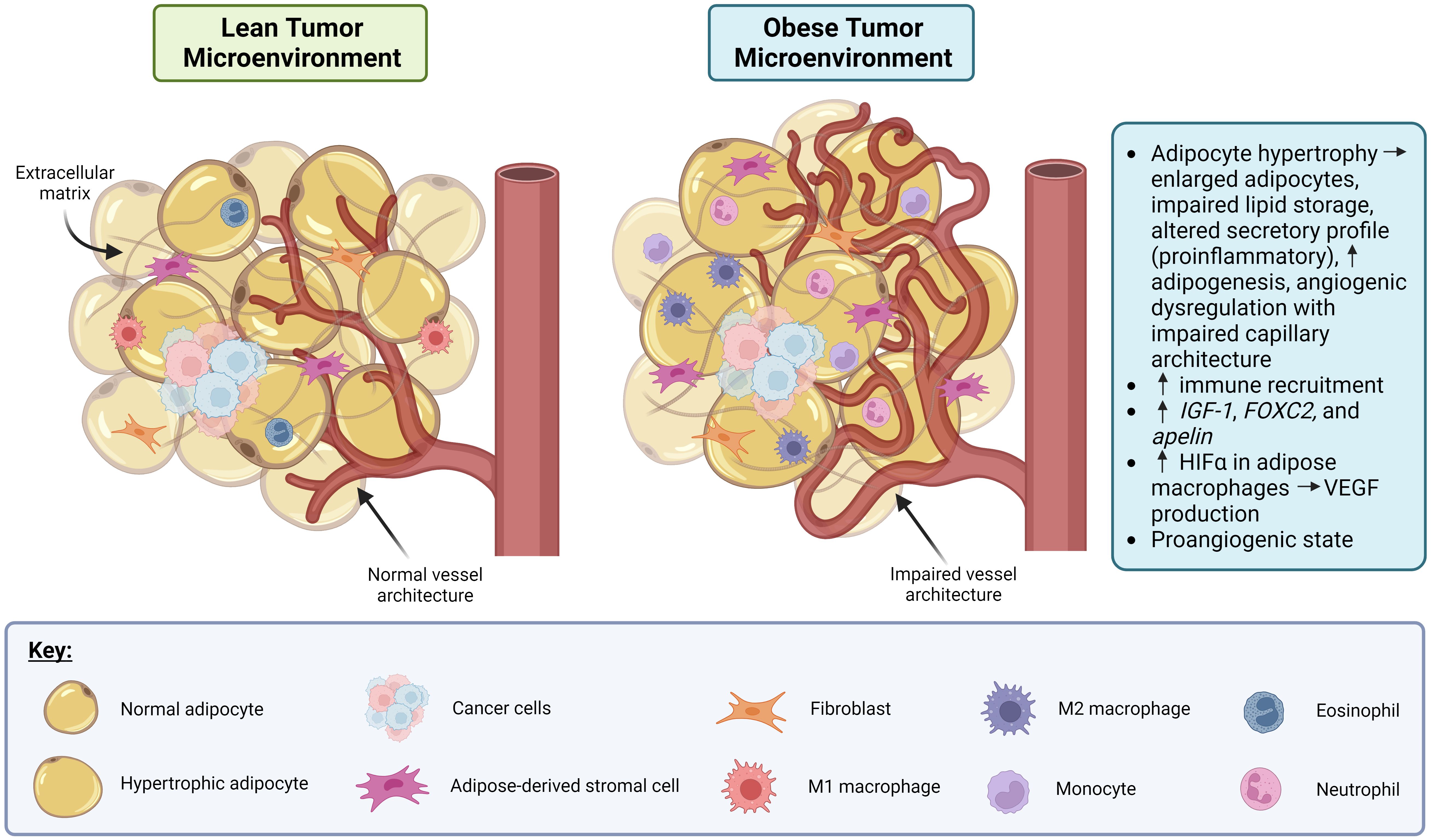
Figure 1. Obesity promotes dysregulation of angiogenesis and induces a pro-inflammatory state in adipose tissue in the context of cancer. In the lean tumor microenvironment (TME), the adipocytes, vasculature and immune involvement are all normal. In the obese TME, adipocyte hypertrophy can occur resulting in the adipocytes becoming enlarged, lipid storage impairment, a pro-inflammatory secretory profile, and angiogenic dysregulation. Also, in the obese TME, immune recruitment is increased via production of IGF-1, FOXC2, and apelin. Macrophages in obese adipose tissue display increased HIFα which drives production of VEGF, leading to a pro-angiogenic state. Created in Biorender. Benz, M. (2024).
Angiogenesis in cancer
Endothelial cells (ECs) form the vascular endothelium, a continuous single-cell layer that faces the lumen of blood vessels and separates circulating blood from surrounding tissues (8, 28). In addition, ECs play critical cell signaling roles in controlling tissue-level blood flow and regulating immune cell adhesion and extravasation (8). Lastly, ECs drive new blood vessel sprouting during angiogenesis, in which avascular tissue secretes pro-angiogenic signals (e.g., VEGF) that stimulate nearby ECs. ECs respond to this pro-angiogenic signal by expressing matrix metalloproteases (MMPs) that digest the extracellular matrix, allowing them to partially detach from the vascular endothelium, proliferate, and migrate towards the source of the pro-angiogenic signal to establish a new vessel sprout (29). Angiogenesis is a critical step during embryonic development to initially establish blood vasculature, and many pro-angiogenic signals are frequently reactivated postnatally both under physiological conditions (e.g., female reproductive tissue cycling, wound healing, etc.) and in pathological settings (e.g., cancer) (30, 31).
Angiogenic activation of ECs is determined by the relative balance of pro- (e.g., VEGF, ANG-1, FGF, etc.) (29) vs. anti- (e.g., thrombospondin-1, angiostatin, interferon α/β) angiogenic factors, a phenomenon referred to as the “angiogenic switch”. Dysregulation of this switch is a classic hallmark of cancer (6, 32). The earliest evidence of this was the observation that implantation of tumor cells induced neovascularization (33). In another classic study, Folkman isolated a soluble factor from human tumor cells -- called Tumor-Angiogenesis Factor (TAF) -- that rapidly stimulated endothelial cells to form capillaries (7). It has since been established that many cancers overexpress several soluble pro-angiogenic signals, as well as their upstream regulators (e.g., Ras, Myc, etc.) (32). Beyond inducing sprouting angiogenesis, tumor cells can also access vascular blood flow by inducing pathological vasculogenesis (the formation of vessels de novo by recruiting circulating endothelial progenitor cells) (34), or by migrating towards and “co-opting” native healthy vessels (35). Indeed, an immunohistochemical study of a human inflammatory breast cancer (IBC) xenograft model revealed that pathological vasculogenesis may be a significant contributor to breast cancer neovascularization (36). Lastly, some tumor cells can transdifferentiate directly into EC and integrate into healthy vasculature, a process termed “vasculogenic mimicry” (37). These non-angiogenic mechanisms may also be affected by obesity in breast cancer but are beyond the scope of the current review.
Angiogenesis in breast cancer
As solid tumors develop, central regions distant from the existing vasculature become hypoxic leading to the stabilization and accumulation of the transactivating factor Hypoxia Inducible Factor-1α (HIF-1α). Like most solid tumors, breast cancer is highly vascularized due to elevated production of soluble pro-angiogenic signals, such as VEGF and FGF that are downstream of HIF-1α in precursor lesions and early-stage cancer (38, 39). HIF-1α induces VEGFA production by both breast cancer stroma and tumor-associated macrophages, which make up ~50% of the total cellular mass in breast cancers (40). White adipose tissue of surrounding breast tissue, which produces a variety of factors that directly regulate the breast cancer tumor microenvironment, also contribute to pro-angiogenic signaling by releasing VEGF, basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF), matrix metalloproteases (MMPs), and interleukin 8 (IL-8) (41, 42). Excess HIF-1α-induced VEGF stimulates local vessel growth and can even enter the systemic blood circulation where it is critical for establishing vasculature within the developing breast cancer. Consistent with these observations, VEGF production and tumor angiogenesis are significantly disrupted in the absence of elevated HIF-1α (43). Indeed, high circulating serum VEGF levels are prognostic for breast cancer progression and patient survival (26, 27, 44), likely because it correlates to tumor vascularity and metastatic potential.
In addition to the previously described data linking circulating VEGF levels to patient outcomes in breast cancer (26, 27, 44), recent transcriptomic studies have directly linked increased expression of many pro-angiogenic genes with poor patient outcomes (44, 45). For example, Guarischi-Sousa et al. conducted a 1000-patient cohort study in which they identified a 153 gene signature for pathological angiogenesis that was predictive for poor prognosis and decreased patient survival in luminal A, luminal B, and basal, but surprisingly, not HER2-positive, breast cancer subtypes (46, 47). This finding is consistent with clinical trials showing that anti-VEGF therapy is not effective in HER2-positive breast cancer patients (AVEREL Trial) (46, 47). Interestingly, some genes identified in the study by Guarischi-Sousa et al. are regulated by obesity-associated leptin signaling, including SERPINE1 and VEGFA (16, 48).
Anti-angiogenic therapy in breast cancer
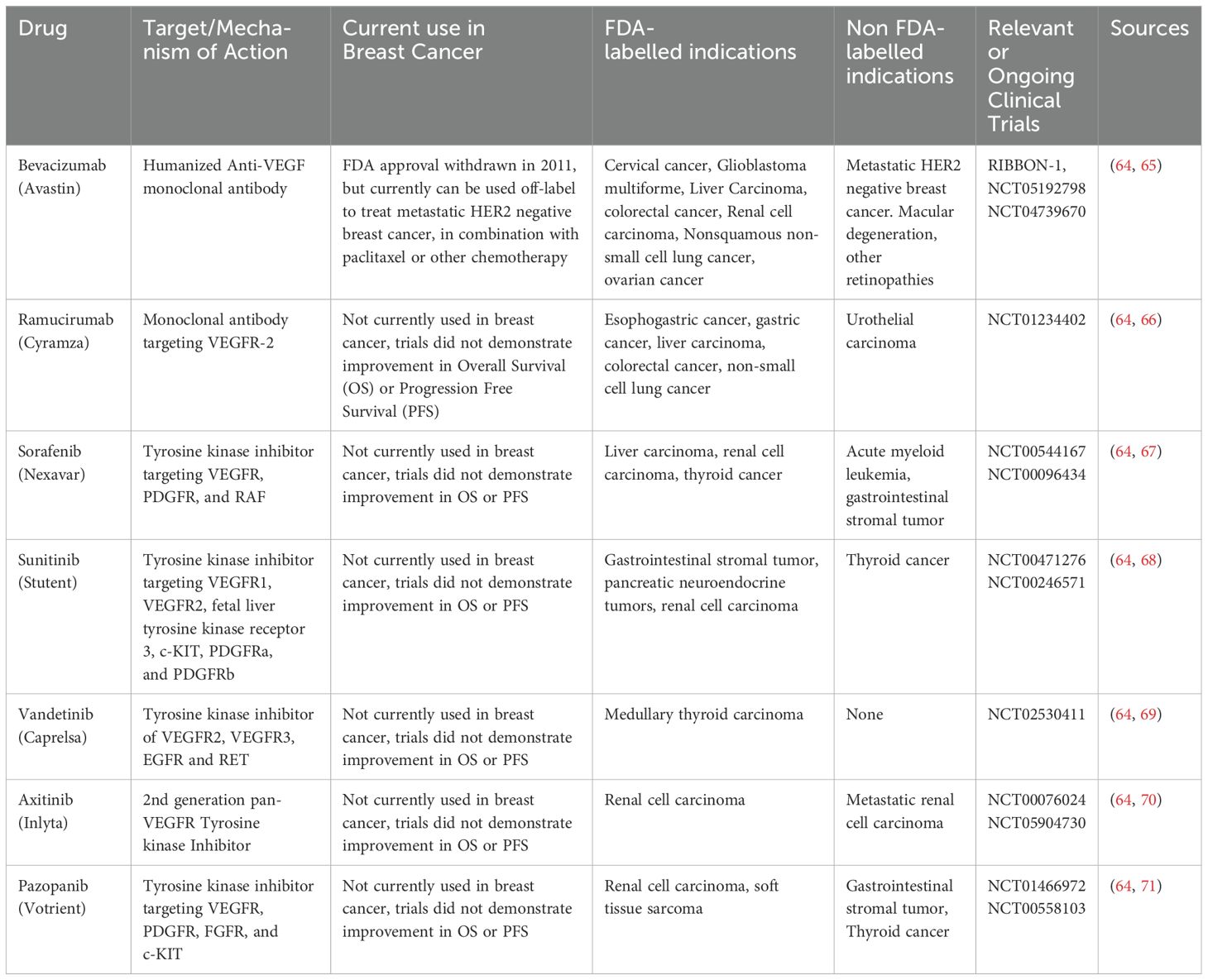
Because of the essential role that tumor neovascularization plays in tumor progression, anti-angiogenic therapy offers, at least in theory, a strategy for halting both tumor growth and metastatic invasion. In reality, however, the angiogenic switch is regulated by a complex (and often functionally redundant) nexus of pro- and anti-angiogenic signals. This may explain why anti-angiogenic monotherapies – such as a humanized monoclonal antibody that binds to and sequesters VEGF-A rendering it signaling-incapable (Avastin/Bevacizumab) has produced only limited improvements for breast cancer patients (49). Anti-angiogenic therapies and their current use in breast cancer is summarized in Table 1. Despite several clinical studies documenting Bevacizumab treatment (either alone or in combination with conventional chemotherapy) to be initially effective in breast cancer (50–52), the RIBBON-1 study found that this did not ultimately translate into significantly increased overall survival (52). This finding, along with the observation that Bevacizumab increases toxicity of standard chemotherapy in this trial, resulted in the FDA withdrawing approval for Bevacizumab for combination treatment of metastatic Her2/neu negative breast cancer in 2011 (53). Although it remains unclear why Her2-negative breast cancer is resistant to Bevacizumab when combined with other chemotherapies, one possibility is that overexpression of other pro-angiogenic/pro-lymphangiogenic growth factors in this cancer type may compensate for inhibition of VEGF-A. Alternatively, ordinarily leaky and disorganized blood vessels may “normalize” following anti-angiogenic therapy which increases access of cytotoxic drugs to the tumor stroma, thereby enhancing their efficacy (54, 55). Indeed, anti-angiogenic drugs have been shown to prune the tumor vasculature by eliminating excess ECs, leading to reduced tumor vessel density in mice (56, 57) while improving tumor vascular perfusion (58). Whether this effect is less likely to occur in some breast cancer types -- thereby contributing to the apparently reduced efficacy of anti-angiogenics in some breast cancers -- is unknown.
In addition to these possibilities, obesity may be a confounding factor in treating breast cancer with an anti-angiogenic approach using Bevacizumab. The expression of inflammatory cytokines and angiogenic factors like interleukin-6 (IL-6) and fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2), which contribute to resistance against anti-angiogenic therapies (59–61), are upregulated in adipocyte-rich hypoxic regions (62). Those regions are more prevalent in tumors from obese mice which likely contributes to anti-VEGF (anti-mouse VEGF antibody-B20-4.1.1) therapy resistance (63). The same study also showed increased systemic concentration of IL-6 and/or FGF-2 in obese patients suggesting possible activation of alternative angiogenic pathways in association with obesity (63).
Nonetheless, combination anti-angiogenic/cytotoxic chemotherapy approaches (including some strategies involving Bevacizumab) have been more promising in a spectrum of solid tumor malignancies, including renal cell, pancreatic, gastric, head and neck, colorectal, glioblastoma, hepatocellular, cervical, ovarian, and importantly several types of breast cancer (64); among these are some (e.g., pancreatic, ovarian, etc.) that – like breast cancer – are more prevalent with patient obesity. Thus, while anti-angiogenics remain a viable strategy for cancer treatment, a better understanding of how angiogenic signaling is dysregulated by both obesity and tumor stroma is needed to better understand how current and new anti-angiogenic approaches can be adapted to improve efficacy in obese breast cancer patients.
ASC-derived leptin is a key regulator of the breast microenvironment
The breast environment is a complex milieu comprised of multiple cell types including adipocytes, ductal epithelial cells, vascular endothelial and mural cells, fibroblasts, immune cells and adipose-derived stromal/stem cells (ASCs). ASCs are a mesenchymal cell type that play key roles in energy and lipid homeostasis, and serve as a major source of endocrine signals, including leptin, which positions ASCs as crucial regulators of signaling crosstalk between the distinct cell populations within healthy (and diseased) breast tissue (28, 75, 76). In particular, ASC contribution to the leptin signaling axis in breast stroma is critical for healthy adipose function in the breast. ASCs are altered by obesity and metabolic diseases, including insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, atherosclerosis, hypertension, and certain cancers (72). In obese patients, for example, increased fat mass dysregulates inflammation- and angiogenesis-associated genes in association with reduced adipose tissue oxygenation, likely contributing to altered adipose tissue homeostasis (73). Adipocyte hypertrophy and hyperplasia also alter the secretory profile of ASCs, resulting in excess production of cytokines and adipokines, including leptin (74), which promote inflammation in obesity (72). For these reasons, ASCs are key regulators of obesity-associated sequelae and disease due in part to their control of leptin signaling.
Adipocyte- and ASC-derived leptin (28, 75, 76) regulates energy balance, metabolism, endocrine signal regulation and immunity (77–80), and increased circulating leptin levels are associated with obesity and its associated sequelae. Indeed, leptin is considered a master regulator of obesity: high levels (i.e., hyperleptinemia) have been shown to significantly increase the risk of glucose and lipid metabolism-associated disorders in obese patients (81), and increased leptin is both necessary and sufficient to induce hypertension in obese mouse models (82).
Hyperleptinemia is also associated with reduced survival rates in obesity-related cancers, including breast cancer (83). This may be due to several effects of altered leptin signaling, including increased cancer cell resistance to anti-estrogenic drugs (e.g., Tamoxifen) (78, 84). Dysregulated leptin signaling in breast cancer may influence tumor growth by acting both directly and indirectly on tumor neovascularization and angiogenesis. For example, in a model of 4T1 mammary carcinoma cells grown adjacent to the mammary fat pad of syngeneic mice (85), leptin receptor antagonists reduced tumor growth by up to 90% and this was associated with reduced VEGF and VEGFR tumor expression. Similarly, leptin knockout in obesity-derived adipocytes reduced tumor growth of triple negative breast cancer (BT20) which was associated with reduced expression of angiogenesis-promoting genes (e.g., SERPINE1, SNAI2, IL-6, TWIST1, and PTGS2) (86). Leptin has also been found to drive metastasis in both an ER+ and ER- context, with leptin knockout in obese ASCs resulting in reduced motility of BC cell lines in vitro and reduced metastasis in an in vivo patient-derived xenograft model of TNBC (5, 87). Thus, in addition to its other regulatory roles, leptin plays a central role in tumor angiogenesis and metastasis in breast cancer (5).
Leptin regulates angiogenesis and metastasis in breast cancer
Leptin is a well-known inducer of angiogenesis, and exogenous leptin classically promotes angiogenic sprouting in corneal explant models (88). In breast cancer, leptin promotes angiogenesis via several mechanisms (Figure 2): i) leptin acts directly on breast cancer stroma to promote the production of soluble pro-angiogenic signals (e.g., VEGF (89), FGF); ii) leptin acts directly on ECs of tumor blood vessels to promote angiogenic activation and enhance angiogenic responses (90); and iii) leptin indirectly promotes angiogenesis by priming the tumor microenvironment for neovascularization through effects on estrogen signaling and immune cell activation. Each of these mechanisms will be explored more in depth in the subsequent sections.
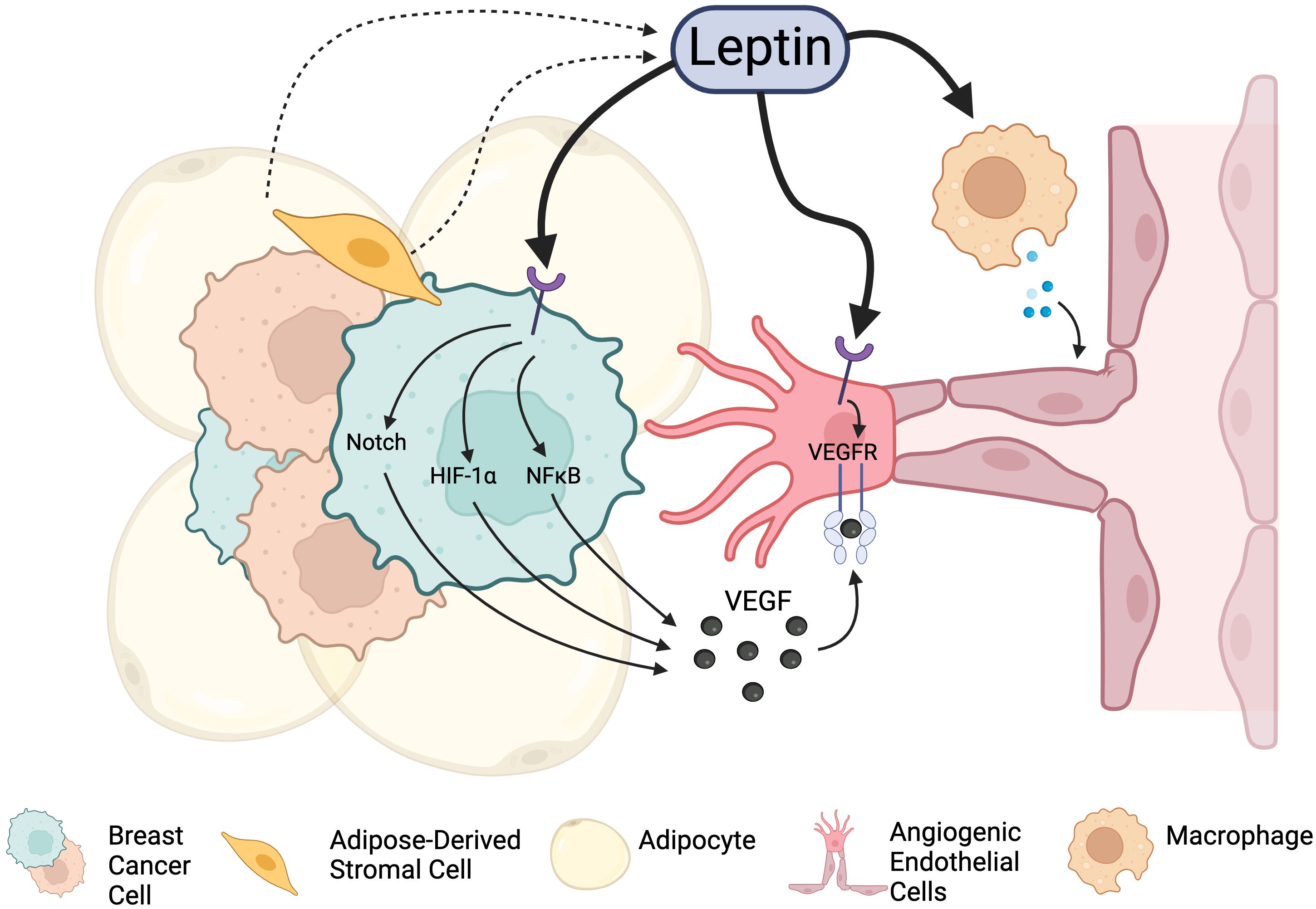
Figure 2. Leptin signaling promotes angiogenesis in the breast cancer TME through integrations with Leptin receptors. Leptin acts directly on cancer cells to stimulate the release of angiogenesis-promoting factors. It also can act on endothelial cells directly to promote proliferation and vascular expansion. Leptin can also indirectly promote angiogenesis through other cell types and factors present in the tumor microenvironment, including immune cells and alteration of estrogen signaling. Created in Biorender. Fang, J.S. (2024).
In addition to these pro-angiogenic effects, leptin also regulates adipocyte capillary fenestration (91), resulting in vessels that may become more permeable to cancer cell extravasation and metastasis. This is a critical effect of leptin on tumor blood vessels in adipose tissue but is beyond the scope of the present review.
Leptin activates breast cancer-expressed leptin receptors to promote angiogenic signaling
Leptin signals directly to breast cancer stromal cells by paracrine and/or autocrine signaling activation of cell surface leptin receptors (LEPRs), ObR-a and ObR-b. Both receptor isoforms are strongly expressed in human breast cancer cell lines and are significantly overexpressed in human breast cancer in comparison to non-transformed mammary gland tissue (92, 93). In addition to promoting tumor cell proliferation, leptin signaling activation upregulates cancer cell production and secretion of soluble VEGFA via NFκB, Sp1, and HIF-1α signaling to induce angiogenic sprouting into the growing tumor mass (85, 94). In particular, HIF-1α binds directly to the hypoxia response element (HRE) of the VEGFA promoter in mammary tumor cells (95), and when the HRE site was deleted from the VEGFA promoter in a luciferase reporter assay, leptin-induced luciferase signal was significantly reduced (86). Gonzalez-Perez and colleagues also reported that leptin-mediated production of HIF-1α and NFκB involves different signaling pathways: the former via canonical (JAK2/STAT3, PI3K/AKT1, and MAPK/ERK1/2) and the latter non-canonical (p38, JNK and to a lesser extent PKC) downstream signaling pathways (86).
Leptin also regulates pro-angiogenic VEGF/VEGFR2 via a distinct Notch/IL-1 signaling axis termed Notch, IL-1, Leptin crosstalk outcome (NILCO) (96). Leptin upregulates Notch signaling effector expression (including Notch1/4 receptors, and Notch ligands Jag1 and Dll4) which upregulates Notch target genes (HEY2, Survivin) and enhances IL-1 expression. Notch signaling is required for leptin-induced pro-angiogenic activation (96), and inhibition of IL-1R type 1 blocks leptin-induced Notch signaling activation, as well as downstream upregulation of HEY2, Survivin, and VEGF/VEGFR2.
Taken together, the above-described studies underscore leptin’s critical role in regulating the expression of soluble pro-angiogenic VEGF in breast cancer cells via multiple intermediate signaling pathways. Thus, overexpressed VEGF in breast cancer stroma critically supports tumor expansion by activating nearby blood vessels to undergo sprouting angiogenesis and tumor neovascularization.
Leptin activates endothelial-expressed LEPRs to directly promote angiogenic activation of tumor ECs
In addition to directly regulating breast cancer cells to increase VEGF expression in the tumor microenvironment, leptin can potently activate angiogenesis by acting directly on tumor endothelial cells. First, Sierra-Honigmann and colleagues found that vein endothelial cells (VECs) express LEPRs in vitro, and that leptin can induce angiogenesis in normal but not leptin receptor-deficient rat corneas (88). Leptin may activate angiogenesis in multiple ways, including by increasing endothelial cell expression of pro-angiogenic factors such as VEGFRs and MMPs, including MMP2 and MMP9, both classic hallmarks of pro-angiogenic activation of ECs (97–99). Leptin also can enhance the activation of proliferation- and migration-associated PI3K/Akt and MAPK signaling pathways (97–99). As a result, ECs display a dose-related angiogenic response to leptin that promotes EC survival, proliferation, migration, and growth (98, 100), as well as their organization into capillary-like structures (100, 101). Direct leptin stimulation of ECs is critical for the angiogenesis that underlies healthy adipose tissue extension (100), as well as for angiogenesis and tumor neovascularization in cancers such as glioblastoma in vitro (101).
Leptin activation of endothelial-expressed leptin receptors promotes VEGF signaling by directly trans-phosphorylating the VEGFR2 receptor and increasing Notch expression which in turn increases VEGF/VEGFR expression in EC (102). VEGFR and Notch are necessary for leptin-induced direct effects on EC: a study by Lanier et al. showed that leptin-induced proliferation and EC tube formation were impaired by either VEGFR or Notch signaling inhibition. The study further demonstrates that leptin-induced VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2 transphosphorylation was necessary for leptin’s actions (102). Separately, Garonna et al. showed that VEGFR2 activation also increases endothelial cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2) expression to induce angiogenesis, and that this response is enhanced in a p38MAPK- and PI3K/Akt -dependent manner (98). COX-2 inhibitors, such as celecoxib, reduce tumor growth in breast cancers (103), indicating the need for further study to determine whether inhibition of these downstream components affects leptin-induced angiogenesis in a breast cancer context.
Additionally, leptin regulates the expression of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS), which produces vasodilatory nitric oxide (NO) to regulate local vasomotor responses and control downstream blood flow and tissue perfusion (100, 104). This is especially relevant in the context of both cancer and obesity-associated fat expansion, as both can lead to metabolic imbalance and excessive production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Resulting oxidative stress can in turn drive endothelial dysfunction due to reduced NO bioavailability (104), and also can be compensated for by leptin-mediated angiogenesis to re-establish tissue (or tumor) blood flow and support metabolic waste removal.
Lastly, leptin may also regulate angiogenesis through the Wnt signaling pathway. Wnt is a potent pro-angiogenic signal, and Wnt2 deficiency is lethal in 50% of embryos due to placental and embryonic vascular defects (105). ECs express several types of Wnt ligand, Wnt receptor, and downstream β-catenin-associated transcription factors (106). Using an in vitro Matrigel assay, Wnt/β-catenin signaling activation is sufficient to promote the formation of capillary networks (106), possibly by transcriptional regulation of pro-angiogenic VEGF (107), Interleukin 8 (IL8) (108), and MMPs (106). Interestingly, some studies have implicated leptin as an upstream regulator of Wnt signaling in ECs. Yu et al. found that leptin activates Wnt pathways in ECs in vitro and in vivo, and that silencing RNA knockdown of Wnt signaling effectively blocks angiogenesis in vitro (109). In these studies, Akt knockdown reduced GSK-3β phosphorylation and β-catenin translocation. Thus, β-catenin translocation can be triggered by either the Wnt/Frizzled or Leptin/Akt signaling axes, and these pathways appear to converge at the level of GSK-3β. Separately, leptin was found to regulate breast cancer cell growth in a Wnt/β-Catenin-mediated manner (110). This same study also showed upregulation of leptin in serum of breast cancer patients in comparison to the healthy individuals. However, it remains unclear to what extent leptin/Wnt signaling crosstalk supports breast cancer growth by specifically promoting tumor neovascularization, or if other outcomes of leptin/Wnt signaling activation predominate in breast cancer tissue.
Indirect leptin-mediated mechanisms of pro-angiogenic activation
Beyond leptin signaling onto breast cancer and endothelial cells to directly control the VEGF/VEFR signaling axis and other pro-angiogenic pathways, leptin can also induce a pro-angiogenic TME through estrogen-signaling in breast adipocytes and by promoting pro-inflammatory signaling by tissue- (or tumor-) resident macrophages, as shown in Figure 3. Both may potentially contribute to angiogenesis in the setting of breast cancer.
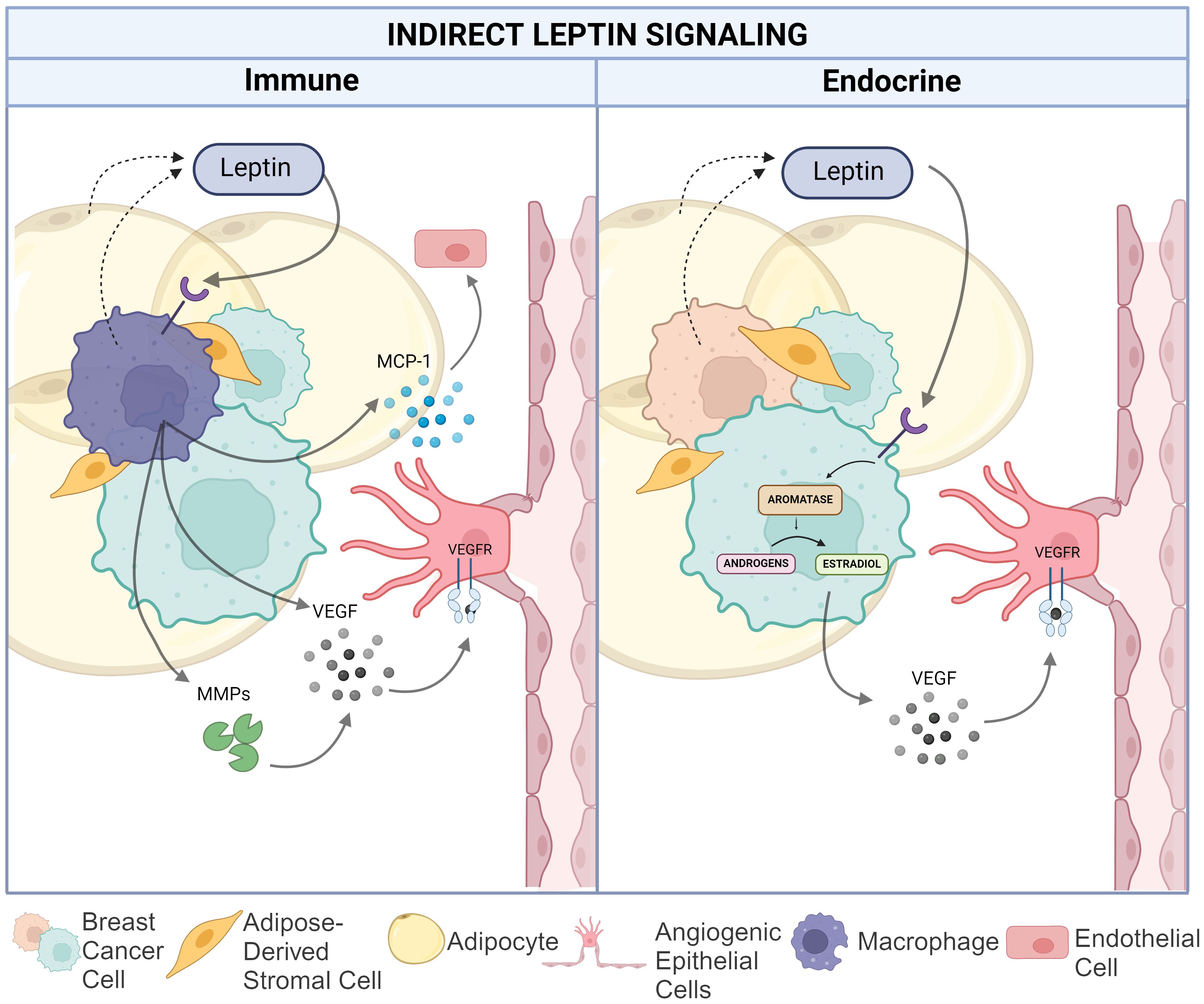
Figure 3. Indirect leptin-mediated pro-angiogenic action in the breast cancer TME. The left panel depicts the impact of leptin on macrophage-mediated angiogenesis via increased matrix metalloproteinase and VEGF production as well as MCP-1 recruitment of endothelial cells. The right panel illustrates leptin induced conversion of androgens to estradiol in TNBC cells resulting in increased VEGF production. Created in Biorender. Hawes, M. (2024).
Leptin-regulated estrogen signaling in adipocytes and breast cancer cells
Estrogen and the estrogen receptor (ER) are essential drivers and therapeutic targets for hormone receptor-positive breast cancer. Leptin interacts with estrogen pathways through several mechanisms to indirectly promote angiogenic signaling in cancer cells and in the tumor microenvironment. In ER+ breast cancer cells, leptin increases aromatase expression and enzymatic activity, leading to an increase in overall estrogen levels (111). In post-menopausal women, circulating estrogen is low, but it can still remain high in breast adipose tissue thereby serving as an estrogen source for breast tumors (112). Multiple mechanisms for maintaining post-menopausal estrogen production in breast have been proposed, including suppression of LKB1/AMPK, suppression of the MAPK/p53 axis, and upregulation of COX2 (83). Leptin-induced aromatase expression also occurs in adipose stromal cells within the tumor microenvironment (113).
Although the link between leptin and estrogen signaling has not been explicitly studied in the context of angiogenesis, estrogen signaling is known to strongly regulate vessel growth. Treatment of cardiac microvascular ECs with estrogen (E2), for example, reduces oxidative stress and inflammatory cytokines, and also promotes endothelial progenitor cell recruitment to sites of vascular damage (114, 115). In breast cancer, increased E2 bioavailability also promotes angiogenesis. In ovariectomized mice, treatment with E2 improved endothelial cell maturation, stabilization, and organization, as well as increased expression of VEGF-A, VEGFR-3, and VEGFR-1 (116). Another study found that Matrigel plugs mixed with ER+ breast cancer cells from estrogen-treated, ovariectomized mice had lower expression levels of soluble VEGFR-1, increased bioavailability of VEGF protein, and increased angiogenesis, compared to untreated controls (117). Increases in VEGF mRNA and VEGF protein expression with estrogen treatment also have been observed in vitro with ER+ cell line, MCF7 (118, 119). Lastly, estrogen signaling can induce HIF1-α nuclear translocation to enhance the release of soluble VEGF (120).
Leptin-regulated cytokine production and immune responses
Leptin also regulates immune responses – both locally in the breast as well as systemically – in a manner that modulates angiogenic responses. Leptin becomes elevated during infection and inflammation, and it regulates cytokine production and immune cell responses in patients (121, 122); both strongly influence angiogenesis. Structurally related to pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., IL-6, IL-11, IL-12, and Oncostatin M), leptin is upregulated by cytokine-induced signaling activation, including by tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) and IL-6 (123). Interestingly, the long form of the LEPR OB-Rb shares structural and functional similarities to IL-6-type cytokine receptors (124).
Leptin acts on multiple cell types of healthy mammary tissue and breast cancer, including on mammary-resident (and tumor-resident) macrophages, which can contribute to tumor neovascularization. Many circulating immune cells including CD34+ hematopoietic cells, CD4+ and CD8+ lymphocytes, and platelets express the long form of the leptin receptor Ob-Rb (124), as well as toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) and inflammatory chemokine C-C chemokine ligand 2 (CCL2) receptor, that enable them to crosstalk with cancer and adipose tissue (125). Macrophages, on the other hand, specifically express the short form of leptin receptor (124). As a result, leptin is a strong chemoattractant for monocytes even at concentrations as low as 1pg/ml (126). Additionally, the treatment of M2 macrophages with leptin activates the IL-8 promotor through the p38/MAPK and MAPK/ERK1/2 pathways leading to increased IL-8 secretion resulting in enhanced tumor growth in vivo and increased migration and invasiveness in breast cancer cell lines (127). Indeed, even slight changes in interstitial leptin concentration can significantly enhance chemoattraction and recruitment of monocytes and macrophages into breast adipose tissue, leading to altered breast cancer migration and metastatic potential in mouse models (126, 128, 129).
Leptin stimulates macrophages to secrete pro-inflammatory and pro-angiogenic cytokines, including IL-1, IL-18, TNFα, NO and pro-angiogenic VEGF (128, 130, 131). Leptin-induced IL-8 is pro-angiogenic in several human cancers, including in colorectal and lung cancer (132), and may also activate angiogenesis in breast cancer. Indeed, IL-8 signaling activation promotes the formation of dense vascular networks in the breast stroma during malignant progression (133). In triple negative xenografts, knockdown of the leptin receptor decreased the level of infiltrating macrophages and CCL2 expression, reducing the secretion of pro-angiogenic cytokines and VEGF (134). Separately, leptin-induced NFκB activation also leads to increased expression of IL-1, which in turn promotes VEGF production in breast cancer in vitro (89). This leptin-cytokine-angiogenesis axis is particularly interesting because it has been proposed as a therapeutic target in certain diseases. In a model of obese breast cancer in humans, it has been suggested that targeting leptin regulation of cytokine production could be potentially therapeutic by decreasing angiogenesis and regulating stem cell function in breast tumors (135).
In addition to directly promoting cytokine production, leptin feeds back onto both the innate and adaptive immune systems, contributing to a systemic pro-inflammatory and pro-angiogenic state. Regarding the adaptive immune system, leptin critically regulates circulating T-cell number and function. Mice lacking leptin production (ob/ob) or leptin receptor (db/db) exhibit thymic atrophy and decreased T-lymphocyte levels, while exogenous leptin rescues thymus proliferation in the thymus of ob/ob mice (136) and can promote thymic proliferation and survival in humans (123). In addition to direct effects on T-cell maturation, Leptin upregulates IL-2 and IFN-γ, and downregulates IL-4 levels, which regulate the phenotypic switching between Th1 and Th2 CD4+ T-cells (124, 137). Leptin also suppresses anti-inflammatory regulatory T-cell (Treg), further contributing to a pro-inflammatory state (137). In patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), for example, increased leptin is associated with decreased Treg cells in the lung due to inhibition of T-cell glycolysis, an essential metabolic pathway for T-cell survival and conversion into Tregs (138). In a separate study of the gastric mucosa, Treg function was affected by Helicobacter pylori vaccination in a leptin-dependent manner (139).
In terms of the innate immune system, leptin regulates the function of macrophages in various ways (137), in addition to being a chemoattractant (129). Leptin triggers calcium influx in macrophages to enable the “leading edge” and “ruffling” structures that allow macrophages to migrate towards leptin, but not towards other chemoattractants such as MCP-1 (126, 140), and also modulates macrophage cytokine secretion profiles (130). In a murine model of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB), post-bypass mice exhibited decreased leptin levels in association with macrophage polarization toward the M2 phenotype (141) and increased Treg levels (142). This suggests a link between weight loss and leptin signaling in macrophage polarization. In a separate study using a human Salmonella typhimurium infection model, gram-negative bacteria activate LEPR signaling in human macrophages. When the LEPR gene was absent, macrophages exhibited increased lysosomal functionality, reducing bacterial burden and inflammation (143). These and other data underscore how leptin functions as a bridge between inflammation and metabolism and can play a central role in the pro-inflammatory signaling that occurs in obesity and other metabolic disorders.
Leptin-induced pro-inflammatory signaling and immune cell activation can indirectly enhance angiogenic responses in breast cancer and other tissues through several mechanisms. These include inducing macrophages to secrete pro-angiogenic VEGF to stimulate angiogenesis, releasing extracellular matrix metalloproteases to degrade local extracellular matrix (144), and producing CCL2 (also known as MCP-1) to recruit endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells for neovascularization (45). M1 vs. M2 macrophages are distinctly involved in different phases of tumor neovascularization, and appropriate temporospatial regulation of M1 and M2 macrophages determines the extent of angiogenic sprouting and vascular growth. Recently, a research group found in a three-dimensional microfluidic angiogenesis model that M2 macrophages are pro-angiogenic in glioblastoma, while M1 macrophages are anti-angiogenic (141). CD4+ T-cells also regulate and promote angiogenesis. Tregs express Neuropilin-1, VEGF, and Leptin (145), and it was recently shown that Tregs stimulate angiogenesis in gliomas through VEGF signaling and in lung ischemia (146, 147), and CD4+ T-cells may regulate angiogenesis via IL-22 signaling (148).
The potential for leptin-based therapeutics to inhibit aberrant angiogenic processes
Given the role of leptin signaling in promoting and regulating angiogenesis, the potential for leptin-based therapeutics in addressing angiogenic disease and aberrant angiogenic processes is being studied in both cancer and non-cancer contexts. Allo-aca, a small peptide inhibitor of LEPRs, has been found to inhibit VEGF signaling effects in an ophthalmic neoangiogenesis model (149). Coroniti et al. found that crosstalk between leptin and VEGF in retinal and corneal endothelial cells resulted in increased proliferation and motility; Allo-aca treatment inhibited chemotaxis and expression of VEGF-induced pathways in vitro as well as choroidal neovascularization in vivo (149). Leptin signaling antagonists also appear to improve outcomes in cardiovascular disease: leptin induces thrombotic events in a mouse model of pulmonary embolism, but event frequency is reduced–and overall survival improved–by treatment with a leptin-neutralizing antibody (150). Leptin signaling also has been found to significantly contribute to post-infarction cardiac remodeling and heart failure (151). In rats, treatment with a LEPR-neutralizing antibody was able to prevent post-injury myocardial hypertrophy and significantly improve cardiac function in rats following coronary artery ligation (151). While not directly relevant to angiogenesis in cancer, these studies indicate that pharmacological agents can interrupt the leptin signaling axis in vascular disease.
Many LEPR antagonists exhibit anti-cancer activity in various cancer subtypes and models, though few studies have specifically examined the effect of LEPR inhibitors on tumor angiogenesis (152). In a colorectal cancer xenograft model, LEPR inhibition (via Allo-aca) blocks NILCO-induced expression of VEGFR1/2, although this did not affect the overall tumor growth rate in mice (153). In breast cancer, Gonzalez et al. reported that a LEPR inhibitor (pegylated LEPRA2) significantly reduces endothelial cell proliferation and tube formation by preventing leptin-induced upregulation of VEGFR and subsequent Notch activation (85). LEPRA2 reduced VEGF secretion and expression in 4T1 murine breast cancer cells, and treatment with LEPRA2 significantly reduced VEGF levels in serum, as well as tumor growth in 4T1 implant tumors (85). However, it remains unclear from these studies whether the observed reduction in tumor growth with LEPR inhibition is due solely to effects on angiogenesis, as LEPRA2 also reduces Cyclin D expression in breast cancer cells in vitro (85). Nonetheless, the same group later confirmed that LEPR2A also reduces tumor growth rate and VEGF/VEGFR2 levels in ER+ (MCF7) and ER- (MDA-MB-231) breast cancer cells and tumor xenografts (154).
Despite these promising results, ongoing challenges limit the use of LEPR antagonists to inhibit angiogenesis in breast cancer patients. As discussed above, leptin is a well-established immune system modulator (155), and the LEPR antagonist Allo-aca affects T cell differentiation and function in mice (156). While this may be desirable in autoimmune conditions, further research is needed to determine how combining this effect with chemotherapy drugs in cancer might impair therapies that require functional T-cells to be effective, such as PD-1 and PDL-1 inhibitors.
Additionally, because leptin is crucial for satiety and metabolic functions, LEPR antagonism often results in weight gain, an unwanted side effect that may limit patient adherence. Furthermore, some data indicate that weight gain is associated with poor outcomes in BC patients making it unclear whether potential benefits of LEPR inhibition of breast cancer angiogenesis would outweigh the negative effects of associated weight gain (10). However, Zabeau et al. have recently created a LEPR antagonist antibody that uncouples the downstream metabolic and immune functions of LEPR (157). Using a single-domain antibody that selectively inhibits LEPR-EGFR crosstalk, they observed no significant changes in food intake, weight gain, or visceral or subcutaneous fat composition in LEPR antibody-treated mice compared to vehicle controls. However, they also observed that treatment blocked leptin’s protection against starvation-induced splenic and thymic atrophy, leading to a decrease in lymphocytes compared to leptin treated controls (157). Thus, it may be possible to avoid unwanted weight gain with LEPR inhibition, and further research is needed to develop such uncoupled LEPR antagonists for clinical use.
Discussion
Given the prevalence of obesity in the general population and specifically among breast cancer patients, it is critical to understand how obesity contributes to breast cancer pathology. In this review, we describe how hyperleptinemia in obesity can drive angiogenesis in breast cancer through its actions on both cancer cells themselves and on other cells in the tumor microenvironment, including endothelial cells and immune cells. Leptin is also able to promote angiogenesis indirectly via upregulation of estrogen signaling. This supports the importance of local stromal remodeling in breast cancer: hyperleptinemia can drive estrogen-dependent alterations to the TME, which can have profound effects on tumors regardless of BC hormone receptor status.
Most studies referenced in this review article were performed using patient-derived xenograft or murine models of breast cancer; however, in the future, more studies exploring the difference in intratumoral microvascular density in obese vs. non-obese patients would provide valuable insight into how obesity (and associated hyperleptinemia) affects angiogenic signaling in breast cancer. Nonetheless, while anti-angiogenic therapies are effective in many cancers, their effectiveness is likely modulated by obesity-associated signaling, such as through the leptin signaling axis. Thus, therapies that jointly target leptin signaling alongside anti-VEGF therapy may help breast cancer patients – many (but not all) of whom are obese – in which conventional anti-VEGF combination therapy is less effective, such as in Her2-negative breast cancer. Future studies should further focus on developing such approaches, which would likely prove beneficial to all breast cancer patients and particularly those who present with obesity at the time of breast cancer diagnosis.
Author contributions
CBL: Conceptualization, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. KT: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. NMC: Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MLH: Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. KS: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MCB: Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. SRD: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. BEB: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. BAB: Writing – review & editing. ECM: Writing – review & editing. BMC: Writing – review & editing. RML: Writing – review & editing. VTH: Writing – review & editing. MEB: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. JSF: Supervision, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was funded in part through a Tulane Center for Aging COBRE Pilot Award (P30GM145498 (JSF)), a Louisiana Cancer Research Center (LCRC) New Investigator Award (M1-CR1305A6 (JSF)), and a Carol Lavin Bernick Faculty award from the Tulane Provost’s Office (JSF). This work was also funded by USDA Project #6054-41000-112-000D (MEB).
Acknowledgments
Figures were created with Biorender.com. We are grateful to Krewe de Pink, an organization of breast cancer survivors, their families, and community members based in New Orleans who are devoted to supporting local breast cancer research. We also want to acknowledge and thank the patients who donate breast cancer tissue.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
BMI, body mass index; EC, endothelial cells; ASC, adipose-derived stem/stromal cells; LEPR, leptin receptor; NO, nitric oxide; OS, overall survival; PFS, progression-free survival; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; FGF, fibroblast growth factor; IL, interleukin; IGF-1, insulin growth factor 1; FOXC2, forkhead box C2; APLN, apelin; HIF-1α, hypoxia inducible factor 1α; TAF, tumor angiogenesis factor; IBC, inflammatory breast cancer; HRE, hypoxia response element; VEC, vein endothelial cells; COX-2, cyclooxygenase 2; ROS, reactive oxygen species; TME, tumor microenvironment.
References
1. Alshamsan BI, Suleman K, Agha N, Abdelgawad MI, Alzahrani MJ, Al-Tweigeri T, et al. Association between obesity and the clinical stage of newly diagnosed breast cancer: Experience with 2212 patients. J Clin Oncol. (2020) 38:e12602–e. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2020.38.15_suppl.e12602
2. Lee K, Kruper L, Dieli-Conwright CM, Mortimer JE. The impact of obesity on breast cancer diagnosis and treatment. Curr Oncol Rep. (2019) 21:41. doi: 10.1007/s11912-019-0787-1
3. Demark-Wahnefried W, Rogers LQ, Gibson JT, Harada S, Fruge AD, Oster RA, et al. Randomized trial of weight loss in primary breast cancer: Impact on body composition, circulating biomarkers and tumor characteristics. Int J Cancer. (2020) 146:2784–96. doi: 10.1002/ijc.v146.10
4. Maffei M, Halaas J, Ravussin E, Pratley RE, Lee GH, Zhang Y, et al. Leptin levels in human and rodent: Measurement of plasma leptin and ob RNA in obese and weight-reduced subjects. Nat Med. (1995) 1:1155–61. doi: 10.1038/nm1195-1155
5. Sabol RA, Bowles AC, Cote A, Wise R, O’Donnell B, Matossian MD, et al. Leptin produced by obesity-altered adipose stem cells promotes metastasis but not tumorigenesis of triple-negative breast cancer in orthotopic xenograft and patient-derived xenograft models. Breast Cancer Res. (2019) 21:67. doi: 10.1186/s13058-019-1153-9
6. Folkman J, Long DM Jr., Becker FF. Growth and metastasis of tumor in organ culture. Cancer. (1963) 16:453–67. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(196304)16:4<453::AID-CNCR2820160407>3.0.CO;2-Y
7. Folkman J. Tumor angiogenesis: therapeutic implications. N Engl J Med. (1971) 285:1182–6. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197111182852108
8. Sobierajska K, Ciszewski WM, Sacewicz-Hofman I, Niewiarowska J. Endothelial cells in the tumor microenvironment. In: Birbrair A, editor. Tumor Microenvironment: Non-Hematopoietic Cells. Springer International Publishing, Cham (2020). p. 71–86.
9. Duggan C, Tapsoba J, Wang C-Y, McTiernan A. Dietary weight loss and exercise effects on serum biomarkers of angiogenesis in overweight postmenopausal women: A randomized controlled trial. Cancer Res. (2016) 76:4226–35. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-0399
10. Barone I, Giordano C, Bonofiglio D, Ando S, Catalano S. The weight of obesity in breast cancer progression and metastasis: Clinical and molecular perspectives. Semin Cancer Biol. (2020) 60:274–84. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2019.09.001
11. Calle EE, Rodriguez C, Walker-Thurmond K, Thun MJ. Overweight, obesity, and mortality from cancer in a prospectively studied cohort of U. S Adults N Engl J Med. (2003) 348:1625–38. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa021423
12. Pati S, Irfan W, Jameel A, Ahmed S, Shahid RK. Obesity and cancer: A current overview of epidemiology, pathogenesis, outcomes, and management. Cancers (Basel). (2023) 15. doi: 10.3390/cancers15020485
13. Harris BHL, Macaulay VM, Harris DA, Klenerman P, Karpe F, Lord SR, et al. Obesity: a perfect storm for carcinogenesis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. (2022) 41:491–515. doi: 10.1007/s10555-022-10046-2
14. Picon-Ruiz M, Morata-Tarifa C, Valle-Goffin JJ, Friedman ER, Slingerland JM. Obesity and adverse breast cancer risk and outcome: Mechanistic insights and strategies for intervention. CA Cancer J Clin. (2017) 67:378–97. doi: 10.3322/caac.21405
15. Reeves GK, Pirie K, Beral V, Green J, Spencer E, Bull D. Cancer incidence and mortality in relation to body mass index in the Million Women Study: cohort study. Bmj. (2007) 335:1134. doi: 10.1136/bmj.39367.495995.AE
16. Strong AL, Ohlstein JF, Biagas BA, Rhodes LV, Pei DT, Tucker HA, et al. Leptin produced by obese adipose stromal/stem cells enhances proliferation and metastasis of estrogen receptor positive breast cancers. Breast Cancer Res. (2015) 17:112. doi: 10.1186/s13058-015-0622-z
17. Strong AL, Strong TA, Rhodes LV, Semon JA, Zhang X, Shi Z, et al. Obesity associated alterations in the biology of adipose stem cells mediate enhanced tumorigenesis by estrogen dependent pathways. Breast Cancer Res. (2013) 15:R102. doi: 10.1186/bcr3569
18. Herrera-Vargas AK, García-Rodríguez E, Olea-Flores M, Mendoza-Catalán MA, Flores-Alfaro E, Navarro-Tito N. Pro-angiogenic activity and vasculogenic mimicry in the tumor microenvironment by leptin in cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. (2021) 62:23–41. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2021.10.006
19. Dai H, Alsalhe TA, Chalghaf N, Riccò M, Bragazzi NL, Wu J. The global burden of disease attributable to high body mass index in 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: An analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study. PloS Med. (2020) 17:e1003198. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1003198
20. Corvera S, Solivan-Rivera J, Yang Loureiro Z. Angiogenesis in adipose tissue and obesity. Angiogenesis. (2022) 25:439–53. doi: 10.1007/s10456-022-09848-3
21. Pellegata NS, Berriel Diaz M, Rohm M, Herzig S. Obesity and cancer-extracellular matrix, angiogenesis, and adrenergic signaling as unusual suspects linking the two diseases. Cancer Metastasis Rev. (2022) 41:517–47. doi: 10.1007/s10555-022-10058-y
22. Cancello R, Henegar C, Viguerie N, Taleb S, Poitou C, Rouault C, et al. Reduction of macrophage infiltration and chemoattractant gene expression changes in white adipose tissue of morbidly obese subjects after surgery-induced weight loss. Diabetes. (2005) 54:2277–86. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.54.8.2277
23. Zhong H, De Marzo AM, Laughner E, Lim M, Hilton DA, Zagzag D, et al. Overexpression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α in common human cancers and their metastases1. Cancer Res. (1999) 59:5830–5.
24. Miyazawa-Hoshimoto S, Takahashi K, Bujo H, Hashimoto N, Saito Y. Elevated serum vascular endothelial growth factor is associated with visceral fat accumulation in human obese subjects. Diabetologia. (2003) 46:1483–8. doi: 10.1007/s00125-003-1221-6
25. Yamamoto Y, Toi M, Kondo S, Matsumoto T, Suzuki H, Kitamura M, et al. Concentrations of vascular endothelial growth factor in the sera of normal controls and cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res. (1996) 2:821–6.
26. Ribatti D, Nico B, Ruggieri S, Tamma R, Simone G, Mangia A. Angiogenesis and antiangiogenesis in triple-negative breast cancer. Transl Oncol. (2016) 9:453–7. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2016.07.002
27. Raghunathachar Sahana K, Akila P, Prashant V, Sharath Chandra B, Nataraj Suma M. Quantitation of vascular endothelial growth factor and interleukin-6 in different stages of breast cancer. Rep Biochem Mol Biol. (2017) 6:33–9.
28. Sabaratnam R, Svenningsen P. Adipocyte-endothelium crosstalk in obesity. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2021) 12:681290. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.681290
29. Carmeliet P, Jain RK. Molecular mechanisms and clinical applications of angiogenesis. Nature. (2011) 473:298–307. doi: 10.1038/nature10144
30. Reynolds LP, Grazul-Bilska AT, Redmer DA. Angiogenesis in the female reproductive organs: pathological implications. Int J Exp Pathol. (2002) 83:151–63. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2613.2002.00277.x
31. Tonnesen MG, Feng X, Clark RA. Angiogenesis in wound healing. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. (2000) 5:40–6. doi: 10.1046/j.1087-0024.2000.00014.x
32. Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. (2011) 144:646–74. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.013
33. Hanahan D, Folkman J. Patterns and emerging mechanisms of the angiogenic switch during tumorigenesis. Cell. (1996) 86:353–64. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80108-7
34. de la Puente P, Muz B, Azab F, Azab AK. Cell trafficking of endothelial progenitor cells in tumor progression. Clin Cancer Res. (2013) 19:3360–8. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-0462
35. Donnem T, Hu J, Ferguson M, Adighibe O, Snell C, Harris AL, et al. Vessel co-option in primary human tumors and metastases: an obstacle to effective anti-angiogenic treatment? Cancer Med. (2013) 2:427–36. doi: 10.1002/cam4.2013.2.issue-4
36. Shirakawa K, Shibuya M, Heike Y, Takashima S, Watanabe I, Konishi F, et al. Tumor-infiltrating endothelial cells and endothelial precursor cells in inflammatory breast cancer. Int J Cancer. (2002) 99:344–51. doi: 10.1002/ijc.10336
37. Seftor RE, Hess AR, Seftor EA, Kirschmann DA, Hardy KM, Margaryan NV, et al. Tumor cell vasculogenic mimicry: from controversy to therapeutic promise. Am J Pathol. (2012) 181:1115–25. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2012.07.013
38. Madu CO, Wang S, Madu CO, Lu Y. Angiogenesis in breast cancer progression, diagnosis, and treatment. J Cancer. (2020) 11:4474–94. doi: 10.7150/jca.44313
39. Maxwell PH, Dachs GU, Gleadle JM, Nicholls LG, Harris AL, Stratford IJ, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 modulates gene expression in solid tumors and influences both angiogenesis and tumor growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (1997) 94:8104–9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.15.8104
40. Lewis CE, Leek R, Harris A, McGee JO. Cytokine regulation of angiogenesis in breast cancer: the role of tumor-associated macrophages. J Leukoc Biol. (1995) 57:747–51. doi: 10.1002/jlb.57.5.747
41. Fain JN. Release of interleukins and other inflammatory cytokines by human adipose tissue is enhanced in obesity and primarily due to the nonfat cells. Vitam Horm. (2006) 74:443–77. doi: 10.1016/S0083-6729(06)74018-3
42. Hausman GJ, Richardson RL. Adipose tissue angiogenesis1,2. J Anim Sci. (2004) 82:925–34. doi: 10.2527/2004.823925x
43. Carmeliet P, Dor Y, Herbert JM, Fukumura D, Brusselmans K, Dewerchin M, et al. Role of HIF-1alpha in hypoxia-mediated apoptosis, cell proliferation and tumour angiogenesis. Nature. (1998) 394:485–90. doi: 10.1038/28867
44. Vartanian RK, Weidner N. Correlation of intratumoral endothelial cell proliferation with microvessel density (tumor angiogenesis) and tumor cell proliferation in breast carcinoma. Am J Pathol. (1994) 144:1188–94.
45. Wang YW, Liu C, Chen YD, Yang B, Chen X, Ma G, et al. An angiogenesis-related lncRNA signature predicts the immune microenvironment and prognosis of breast cancer. Aging (Albany NY). (2023) 15:7616–36. doi: 10.18632/aging.204930
46. Guarischi-Sousa R, Monteiro JS, Alecrim LC, Michaloski JS, Cardeal LB, Ferreira EN, et al. A transcriptome-based signature of pathological angiogenesis predicts breast cancer patient survival. PloS Genet. (2019) 15:e1008482. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008482
47. Gianni L, Romieu GH, Lichinitser M, Serrano SV, Mansutti M, Pivot X, et al. AVEREL: a randomized phase III Trial evaluating bevacizumab in combination with docetaxel and trastuzumab as first-line therapy for HER2-positive locally recurrent/metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. (2013) 31:1719–25. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2012.44.7912
48. Nigro E, Mallardo M, Polito R, Scialò F, Bianco A, Daniele A. Adiponectin and leptin exert antagonizing effects on HUVEC tube formation and migration modulating the expression of CXCL1, VEGF, MMP-2 and MMP-9. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22. doi: 10.3390/ijms22147516
49. Garcia J, Hurwitz HI, Sandler AB, Miles D, Coleman RL, Deurloo R, et al. Bevacizumab (Avastin®) in cancer treatment: A review of 15 years of clinical experience and future outlook. Cancer Treat Rev. (2020) 86:102017. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2020.102017
50. Miller K, Wang M, Gralow J, Dickler M, Cobleigh M, Perez EA, et al. Paclitaxel plus bevacizumab versus paclitaxel alone for metastatic breast cancer. N Engl J Med. (2007) 357:2666–76. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa072113
51. Miles DW, Chan A, Dirix LY, Cortés J, Pivot X, Tomczak P, et al. Phase III study of bevacizumab plus docetaxel compared with placebo plus docetaxel for the first-line treatment of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. (2010) 28:3239–47. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.21.6457
52. Robert NJ, Diéras V, Glaspy J, Brufsky AM, Bondarenko I, Lipatov ON, et al. RIBBON-1: randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase III trial of chemotherapy with or without bevacizumab for first-line treatment of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative, locally recurrent or metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. (2011) 29:1252–60. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2010.28.0982
53. Aalders KC, Tryfonidis K, Senkus E, Cardoso F. Anti-angiogenic treatment in breast cancer: Facts, successes, failures and future perspectives. Cancer Treat Rev. (2017) 53:98–110. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2016.12.009
54. Jain RK. Normalizing tumor vasculature with anti-angiogenic therapy: A new paradigm for combination therapy. Nat Med. (2001) 7:987–9. doi: 10.1038/nm0901-987
55. Lee CG, Heijin M, di Tomaso E, Griffon-Etienne G, Ancukiewicz M, Koike C, et al. Anti-Vascular endothelial growth factor treatment augments tumor radiation response under normoxic or hypoxic conditions. Cancer Res. (2000) 60:5565–70.
56. Yuan F, Chen Y, Dellian M, Safabaksh N, Ferrara N, Jain RK. Time-dependent vascular regression and permeability changes in established human tumor xenografts induced by an anti-vascular endothelial growth factor/vascular permeability factor antibody. Proc Nat Acad Sci. (1996) 93:14765–770. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.25.14765
57. Kadambi A, Mouta Carreira C, Yun CO, Padera TP, Dolmans DE, Carmeliet P, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-C differentially affects tumor vascular function and leukocyte recruitment: role of VEGF-receptor 2 and host VEGF-A. Cancer Res. (2001) 61:2404–8.
58. Hansen-Algenstaedt N, Stoll BR, Padera TP, Dolmans DE, Hicklin DJ, Fukumura D, et al. Tumor oxygenation in hormone-dependent tumors during vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 blockade, hormone ablation, and chemotherapy. Cancer Res. (2000) 60:4556–60.
59. Jain RK, Duda DG, Willett CG, Sahani DV, Zhu AX, Loeffler JS, et al. Biomarkers of response and resistance to antiangiogenic therapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. (2009) 6:327–38. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2009.63
60. Duda DG, Munn LL, Jain RK. Can we identify predictive biomarkers for antiangiogenic therapy of cancer using mathematical modeling? J Natl Cancer Inst. (2013) 105:762–5.
61. Carmeliet P, Jain RK. Principles and mechanisms of vessel normalization for cancer and other angiogenic diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discovery. (2011) 10:417–27. doi: 10.1038/nrd3455
63. Incio J, Ligibel JA, McManus DT, Suboj P, Jung K, Kawaguchi K, et al. Obesity promotes resistance to anti-VEGF therapy in breast cancer by up-regulating IL-6 and potentially FGF-2. Sci Transl Med. (2018) 10, 1–14. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aag0945
64. Elebiyo TC, Rotimi D, Evbuomwan IO, Maimako RF, Iyobhebhe M, Ojo OA, et al. Reassessing vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in anti-angiogenic cancer therapy. Cancer Treat Res Commun. (2022) 32:100620. doi: 10.1016/j.ctarc.2022.100620
65. Bevacizumab. Merative Healthcare Solutions/EBSCO Information Services (2024). Available online at: https://www.dynamed.com/drug-monograph/bevacizumab. Access date: June 4, 2024.
66. Ramucirumab. Merative Healthcare Solutions/EBSCO Information Services. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Greenwood Village, Colorado (2024). https://www.dynamed.com/drug-monograph/ramucirumab.
67. Sorafenib. Merative Healthcare Solutions/EBSCO Information Services (2024). Available online at: https://www.dynamed.com/drug-monograph/sorafenib. Access date, June 5, 2024.
68. Sunitinib. Merative Healthcare Solutions/EBSCO Information Services (2024). Available online at: https://www.dynamed.com/drug-monograph/sunitinib. Access date: June 5, 2024.
69. Vandetanib. Merative Healthcare Solutions/EBSCO Information Services (2024). Available online at: https://www.dynamed.com/drug-monograph/vandetanib. Access date: June 5, 2024.
70. Axitinib. Merative Healthcare Solutions/EBSCO Information Services (2024). Available online at: https://www.dynamed.com/drug-monograph/axitinib. Access date: June 5, 2024.
71. Pazopanib. Merative Healthcare Solutions/EBSCO Information Services (2024). Available online at: https://www.dynamed.com/drug-monograph/pazopanib. Access date: June 5, 2024.
72. Shin S, El-Sabbagh AS, Lukas BE, Tanneberger SJ, Jiang Y. Adipose stem cells in obesity: challenges and opportunities. Biosci Rep. (2020) 40, 1–15. doi: 10.1042/BSR20194076
73. Cifarelli V, Beeman SC, Smith GI, Yoshino J, Morozov D, Beals JW, et al. Decreased adipose tissue oxygenation associates with insulin resistance in individuals with obesity. J Clin Invest. (2020) 130:6688. doi: 10.1172/JCI141828
74. Ritter A, Kreis NN, Hoock SC, Solbach C, Louwen F, Yuan J. Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stromal/stem cells, obesity and the tumor microenvironment of breast cancer. Cancers (Basel). (2022) 14. doi: 10.3390/cancers14163908
75. Fang J, Lu Y, Zheng J, Jiang X, Shen H, Shang X, et al. Exploring the crosstalk between endothelial cells, immune cells, and immune checkpoints in the tumor microenvironment: new insights and therapeutic implications. Cell Death Dis. (2023) 14:586. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-06119-x
76. Andò S, Catalano S. The multifactorial role of leptin in driving the breast cancer microenvironment. Nat Rev Endocrinol. (2012) 8:263–75. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2011.184
77. Gong D-W, Bi S, Pratley RE, Weintraub BD. Genomic structure and promoter analysis of the human obese gene (∗). J Biol Chem. (1996) 271:3971–4. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.8.3971
78. Caruso A, Gelsomino L, Panza S, Accattatis FM, Naimo GD, Barone I, et al. Leptin: A heavyweight player in obesity-related cancers. Biomolecules. (2023) 13. doi: 10.3390/biom13071084
79. Linares RL, Benítez JGS, Reynoso MO, Romero CG, Sandoval-Cabrera A. Modulation of the leptin receptors expression in breast cancer cell lines exposed to leptin and tamoxifen. Sci Rep. (2019) 9:19189. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-55674-x
80. Fernández-Riejos P, Najib S, Santos-Alvarez J, Martín-Romero C, Pérez-Pérez A, González-Yanes C, et al. Role of leptin in the activation of immune cells. Mediators Inflammation. (2010) 2010:568343. doi: 10.1155/2010/568343
81. Aisike G, Kuerbanjiang M, Muheyati D, Zaibibuli K, Lv M-X, Han J. Correlation analysis of obesity phenotypes with leptin and adiponectin. Sci Rep. (2023) 13:17718. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-43550-8
82. Simonds SE, Pryor JT, Ravussin E, Greenway FL, Dileone R, Allen AM, et al. Leptin mediates the increase in blood pressure associated with obesity. Cell. (2014) 159:1404–16. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.10.058
83. Sánchez-Jiménez F, Pérez-Pérez A, de la Cruz-Merino L, Sánchez-Margalet V. Obesity and breast cancer: role of leptin. Front Oncol. (2019) 9:596. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00596
84. Bougaret L, Delort L, Billard H, Le Huede C, Boby C, de la Foye A, et al. Adipocyte/breast cancer cell crosstalk in obesity interferes with the anti-proliferative efficacy of tamoxifen. PloS One. (2018) 13:e0191571. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0191571
85. Gonzalez RR, Cherfils S, Escobar M, Yoo JH, Carino C, Styer AK, et al. Leptin signaling promotes the growth of mammary tumors and increases the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and its receptor type two (VEGF-R2). J Biol Chem. (2006) 281:26320–8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M601991200
86. Gonzalez-Perez RR, Xu Y, Guo S, Watters A, Zhou W, Leibovich SJ. Leptin upregulates VEGF in breast cancer via canonic and non-canonical signalling pathways and NFκB/HIF-1α activation. Cell Signalling. (2010) 22:1350–62. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2010.05.003
87. Sabol RA, Beighley A, Giacomelli P, Wise RM, Harrison MAA, O’Donnnell BA, et al. Obesity-altered adipose stem cells promote ER+ Breast cancer metastasis through estrogen independent pathways. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20. doi: 10.3390/ijms20061419
88. Sierra-Honigmann M, Nath AK, Murakami C, Garcı́a-Cardeña G, Papapetropoulos A, Sessa WC, et al. Biological action of leptin as an angiogenic factor. Science. (1998) 281:1683–6. doi: 10.1126/science.281.5383.1683
89. Zhou W, Guo S, Gonzalez-Perez RR. Leptin pro-angiogenic signature in breast cancer is linked to IL-1 signalling. Br J Cancer. (2011) 104:128–37. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6606013
90. Manjunathan R, Devarajan N, Ragunathan M. Possible Mechanism of Human Recombinant Leptin-Induced VEGF A Synthesis via PI3K/Akt/mTOR/S6 Kinase Signaling Pathway while Inducing Angiogenesis: An Analysis Using Chicken Chorioallantoic Membrane Model. J Vasc Res. (2021) 58:343–60. doi: 10.1159/000516498
91. Cao R, Brakenhielm E, Wahlestedt C, Thyberg J, Cao Y. Leptin induces vascular permeability and synergistically stimulates angiogenesis with FGF-2 and VEGF. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2001) 98:6390–5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.101564798
92. O’Brien SN, Welter BH, Price TM. Presence of leptin in breast cell lines and breast tumors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (1999) 259:695–8. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1999.0843
93. Garofalo C, Koda M, Cascio S, Sulkowska M, Kanczuga-Koda L, Golaszewska J, et al. Increased expression of leptin and the leptin receptor as a marker of breast cancer progression: possible role of obesity-related stimuli. Clin Cancer Res. (2006) 12:1447–53. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-1913
94. Carino C, Olawaiye AB, Cherfils S, Serikawa T, Lynch MP, Rueda BR, et al. Leptin regulation of proangiogenic molecules in benign and cancerous endometrial cells. Int J Cancer. (2008) 123:2782–90. doi: 10.1002/ijc.v123:12
95. Shima DT, Kuroki M, Deutsch U, Ng Y-S, Adamis AP, D’Amore PA. The mouse gene for vascular endothelial growth factor: genomic structure, definition of the transcriptional unit, and characterization of transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulatory sequences (∗). J Biol Chem. (1996) 271:3877–83. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.7.3877
96. Guo S, Gonzalez-Perez RR. Notch, IL-1 and leptin crosstalk outcome (NILCO) is critical for leptin-induced proliferation, migration and VEGF/VEGFR-2 expression in breast cancer. PloS One. (2011) 6:e21467. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0021467
97. Park H-Y, Kwon HM, Lim HJ, Hong BK, Lee JY, Park BE, et al. Potential role of leptin in angiogenesis: leptin induces endothelial cell proliferation and expression of matrix metalloproteinases in vivo and in vitro. Exp Mol Med. (2001) 33:95–102. doi: 10.1038/emm.2001.17
98. Garonna E, Botham KM, Birdsey GM, Randi AM, Gonzalez-Perez RR, Wheeler-Jones CPD. Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 coupled cyclo-oxygenase-2 with pro-angiogenic actions of leptin on human endothelial cells. PloS One. (2011) 6:e18823. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0223400
99. Goetze S, Bungenstock A, Czupalla C, Eilers F, Stawowy P, Kintscher U, et al. Leptin induces endothelial cell migration through Akt, which is inhibited by PPARgamma-ligands. Hypertension. (2002) 40:748–54. doi: 10.1161/01.HYP.0000035522.63647.D3
100. Rahmouni K, Haynes WG. Endothelial effects of leptin: Implications in health and diseases. Curr Diabetes Rep. (2005) 5:260–6. doi: 10.1007/s11892-005-0020-5
101. Ferla R, Bonomi M, Otvos L, Surmacz E. Glioblastoma-derived leptin induces tube formation and growth of endothelial cells: comparison with VEGF effects. BMC Cancer. (2011) 11:303. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-11-303
102. Lanier V, Gillespie C, Leffers M, Daley-Brown D, Milner J, Lipsey C, et al. Leptin-induced transphosphorylation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor increases Notch and stimulates endothelial cell angiogenic transformation. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. (2016) 79:139–50. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2016.08.023
103. Sahu A, Raza K, Pradhan D, Jain AK, Verma S. Cyclooxygenase-2 as a therapeutic target against human breast cancer: A comprehensive review. WIREs Mech Dis. (2023) 15:e1596. doi: 10.1002/wsbm.v15.3
104. Tahergorabi Z, Khazaei M. Leptin and its cardiovascular effects: Focus on angiogenesis. Adv BioMed Res. (2015) 4:79. doi: 10.4103/2277-9175.156526
105. Monkley SJ, Delaney SJ, Pennisi DJ, Christiansen JH, Wainwright BJ. Targeted disruption of the Wnt2 gene results in placentation defects. Development. (1996) 122:3343–53. doi: 10.1242/dev.122.11.3343
106. Néstor T, Masckauchán H, Shawber CJ, Funahashi Y, Li C-M, Kitajewski J. Wnt/β-catenin signaling induces proliferation, survival and interleukin-8 in human endothelial cells. Angiogenesis. (2005) 8:43–51. doi: 10.1007/s10456-005-5612-9
107. Easwaran V, Lee SH, Inge L, Guo L, Goldbeck C, Garrett E, et al. beta-Catenin regulates vascular endothelial growth factor expression in colon cancer. Cancer Res. (2003) 63:3145–53.
108. Lévy L, Neuveut C, Renard C-A, Charneau P, Branchereau S, Gauthier F, et al. Transcriptional activation of interleukin-8 by β-catenin-tcf4. J Biol Chem. (2002) 277:P42386–93. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M207418200
109. Yu F, Fu R, Liu L, Wang X, Wu T, Shen W, et al. Leptin-induced angiogenesis of EA.Hy926 endothelial cells via the akt and wnt signaling pathways in vitro and in vivo. Front Pharmacol. (2019) 10. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01275
110. Liang X, Wang S, Wang X, Zhang L, Zhao H, Zhang L. Leptin promotes the growth of breast cancer by upregulating the Wnt/β−catenin pathway. Exp Therap Med. (2018) 16:767–71. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.6212
111. Catalano S, Marsico S, Giordano C, Mauro L, Rizza P, Panno ML, et al. Leptin enhances, via AP-1, expression of aromatase in the MCF-7 cell line. J Biol Chem. (2003) 278:28668–76. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M301695200
112. Brown KA, Iyengar NM, Zhou XK, Gucalp A, Subbaramaiah K, Wang H, et al. Menopause is a determinant of breast aromatase expression and its associations with BMI, inflammation, and systemic markers. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2017) 102:1692–701. doi: 10.1210/jc.2016-3606
113. Magoffin DA, Weitsman SR, Aagarwal SK, Jakimiuk AJ. Leptin regulation of aromatase activity in adipose stromal cells from regularly cycling women. Ginekol Pol. (1999) 70:1–7.
114. Zhou K, Xiao J, Wang H, Ni B, Huang J, Long X. Estradiol regulates oxidative stress and angiogenesis of myocardial microvascular endothelial cells via the CDK1/CDK2 pathway. Heliyon. (2023) 9:e14305. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e14305
115. Huang H, Xu Z, Qi Y, Zhang W, Zhang C, Jiang M, et al. Exosomes from SIRT1-overexpressing ADSCs restore cardiac function by improving angiogenic function of EPCs. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. (2020) 21:737–50. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2020.07.007
116. Péqueux C, Raymond-Letron I, Blacher S, Boudou F, Adlanmerini M, Fouque MJ, et al. Stromal estrogen receptor-α promotes tumor growth by normalizing an increased angiogenesis. Cancer Res. (2012) 72:3010–9. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-3768
117. Elkin M, Orgel A, Kleinman HK. An angiogenic switch in breast cancer involves estrogen and soluble vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1. JNCI: J Natl Cancer Institute. (2004) 96:875–8. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djh140
118. Buteau-Lozano H, Ancelin M, Lardeux B, Milanini J, Perrot-Applanat M. Transcriptional regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor by estradiol and tamoxifen in breast cancer cells: a complex interplay between estrogen receptors alpha and beta. Cancer Res. (2002) 62:4977–84.
119. Trenti A, Tedesco S, Boscaro C, Trevisi L, Bolego C, Cignarella A. Estrogen, angiogenesis, immunity and cell metabolism: solving the puzzle. Int J Mol Sci. (2018) 19. doi: 10.3390/ijms19030859
120. George AL, Rajoria S, Suriano R, Mittleman A, Tiwari RK. Hypoxia and estrogen are functionally equivalent in breast cancer-endothelial cell interdependence. Mol Cancer. (2012) 11:80. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-11-80
121. Napoleone E, Santo A DI, Amore C, Baccante G, di Febbo C, Porreca E, et al. Leptin induces tissue factor expression in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells: a possible link between obesity and cardiovascular risk? J Thromb Haemost. (2007) 5:1462–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2007.02578.x
122. Park M-C, Chung S-J, Park Y-B, Lee S-K. Pro-inflammatory effect of leptin on peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Joint Bone Spine. (2009) 76(2):170–5. doi: 10.1016/j.jbspin.2008.04.018
123. Iikuni N, Lam QL, Lu L, Matarese G, La Cava A. Leptin and inflammation. Curr Immunol Rev. (2008) 4:70–9. doi: 10.2174/157339508784325046
124. Fantuzzi G, Faggioni R. Leptin in the regulation of immunity, inflammation, and hematopoiesis. J Leukocyte Biol. (2002) 68:437–46. doi: 10.1189/jlb.68.4.437
125. Guo S, Liu M, Wang G, Torroella-Kouri M, Gonzalez-Perez RR. Oncogenic role and therapeutic target of leptin signaling in breast cancer and cancer stem cells. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) Rev Cancer. (2012) 1825:207–22. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2012.01.002
126. Gruen ML, Hao M, Piston DW, Hasty AH. Leptin requires canonical migratory signaling pathways for induction of monocyte and macrophage chemotaxis. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. (2007) 293:C1481–8. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00062.2007
127. Cao H, Huang Y, Wang L, Wang H, Pang X, Li K, et al. Leptin promotes migration and invasion of breast cancer cells by stimulating IL-8 production in M2 macrophages. Oncotarget. (2016) 7:65441–53. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11761
128. Li K, Wei L, Huang Y, Wu Y, Su M, Pang X, et al. Leptin promotes breast cancer cell migration and invasion via IL-18 expression and secretion. Int J Oncol. (2016) 48:2479–87. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2016.3483
129. Walduck AK, Becher D. Leptin, CD4+ Treg and the prospects for vaccination against H. Pylori Infection Front Immunol. (2012) 3, 1–8. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2012.00316
130. Loffreda S, Yang SQ, Lin HZ, Karp CL, Brengman ML, Wang DJ, et al. Leptin regulates proinflammatory immune responses. FASEB J. (1998) 12:57–65. doi: 10.1096/fsb2fasebj.12.1.57
131. Leek RD, Hunt NC, Landers RJ, Lewis CE, Royds JA, Harris AL. Macrophage infiltration is associated with VEGF and EGFR expression in breast cancer. J Pathol. (2000) 190:430–6. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9896(200003)190:4<430::AID-PATH538>3.0.CO;2-6
132. Fousek K, Horn LA, Palena C. Interleukin-8: A chemokine at the intersection of cancer plasticity, angiogenesis, and immune suppression. Pharmacol Ther. (2021) 219:107692. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107692
133. Lin EY, Li JF, Gnatovskiy L, Deng Y, Zhu L, Grzesik DA, et al. Macrophages regulate the angiogenic switch in a mouse model of breast cancer. Cancer Res. (2006) 66:11238–46. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-1278
134. Gelsomino L, Naimo GD, Malivindi R, Augimeri G, Panza S, Giordano C, et al. Knockdown of leptin receptor affects macrophage phenotype in the tumor microenvironment inhibiting breast cancer growth and progression. Cancers (Basel). (2020) 12. doi: 10.3390/cancers12082078
135. Newman G, Gonzalez-Perez RR. Leptin-cytokine crosstalk in breast cancer. Mol Cell Endocrinol. (2014) 382:570–82. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2013.03.025
136. Howard JK, Lord GM, Matarese G, Vendetti S, Ghatei MA, Ritter MA, et al. Leptin protects mice from starvation-induced lymphoid atrophy and increases thymic cellularity in ob/ob mice. J Clin Invest. (1999) 104:1051–9. doi: 10.1172/JCI6762
137. Procaccini C, La Rocca C, Carbone F, De Rosa V, Galgani M, Matarese G. Leptin as immune mediator: Interaction between neuroendocrine and immune system. Dev Comp Immunol. (2017) 66:120–9. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2016.06.006
138. Bruzzaniti S, Bocchino M, Santopaolo M, Calì G, Stanziola AA, D’Amato M, et al. An immunometabolic pathomechanism for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2019) 116:15625–34. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1906303116
139. Yarandi SS, Hebbar G, Sauer CG, Cole CR, Ziegler TR. Diverse roles of leptin in the gastrointestinal tract: Modulation of motility, absorption, growth, and inflammation. Nutrition. (2011) 27:269–75. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2010.07.004
140. Evans JH, Falke JJ. Ca2+ influx is an essential component of the positive-feedback loop that maintains leading-edge structure and activity in macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2007) 104:16176–81. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0707719104
141. Cui X, Morales RT, Qian W, Wang H, Gagner JP, Dolgalev I, et al. Hacking macrophage-associated immunosuppression for regulating glioblastoma angiogenesis. Biomaterials. (2018) 161:164–78. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2018.01.053
142. Xu R, Zhu C, Li Y, Andrade M, Yin DP. Gastric bypass regulates early inflammatory responses in high-fat diet-induced obese mice. J Surg Res. (2022) 273:161–71. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2021.12.027
143. Fischer J, Gutièrrez S, Ganesan R, Calabrese C, Ranjan R, Cildir G, et al. Leptin signaling impairs macrophage defenses against Salmonella Typhimurium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2019) 116:16551–60. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1904885116
145. Pucino V, De Rosa V, Procaccini C, Matarese G. Regulatory T cells, leptin and angiogenesis. 2013 [cited 3/4/2024]. In: Karger AG S, editor. Angiogenesis, Lymphangiogenesis and Clinical Implications. Basel, Switzerland: Karger Internation. (2013). doi: 10.1159/000353557
146. Mu L, Yang C, Gao Q, Long Y, Ge H, DeLeon G, et al. CD4+ and perivascular foxp3+ T cells in glioma correlate with angiogenesis and tumor progression. Front Immunol. (2017) 8. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01451
147. D’Alessio FR. Mouse models of acute lung injury and ARDS. Methods Mol Biol. (2018) 1809:341–50. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-8570-8_22
148. Zhang T, Wahib R, Zazara DE, Lücke J, Shiri AM, Kempski J, et al. CD4+ T cell-derived IL-22 enhances liver metastasis by promoting angiogenesis. Oncoimmunology. (2023) 12:2269634. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2023.2269634
149. Coroniti R, Fario R, Nuno DJ, Otvos L, Scolaro L, Surmacz E. Designer leptin receptor antagonist allo-aca inhibits VEGF effects in ophthalmic neoangiogenesis models. Front Mol Biosci. (2016) 3:67. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2016.00067
150. Konstantinides S, Schäfer K, Neels JG, Dellas C, Loskutoff DJ. Inhibition of endogenous leptin protects mice from arterial and venous thrombosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2004) 24:2196–201. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000146531.79402.9a
151. Purdham DM, Rajapurohitam V, Zeidan A, Huang C, Gross GJ, Karmazyn M. A neutralizing leptin receptor antibody mitigates hypertrophy and hemodynamic dysfunction in the postinfarcted rat heart. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. (2008) 295:H441–6. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.91537.2007
152. Greco M, De Santo M, Comandè A, Belsito EL, Andò S, Liguori A, et al. Leptin-activity modulators and their potential pharmaceutical applications. Biomolecules. (2021) 11. doi: 10.3390/biom11071045
153. Özyurt R, Erkasap N, Özkurt M, Erkasap S, Dimas K, Çakir Gündoğdu A, et al. Targeting of Notch, IL-1, and leptin has therapeutic potential in xenograft colorectal cancer. Turk J Biol. (2023) 47:290–300. doi: 10.55730/1300-0152.2663
154. Rene Gonzalez R, Watters A, Xu Y, Singh UP, Mann DR, Rueda BR, et al. Leptin-signaling inhibition results in efficient anti-tumor activity in estrogen receptor positive or negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. (2009) 11:R36. doi: 10.1186/bcr2321
155. Yu Y, Liu Y, Shi FD, Zou H, Matarese G, La Cava A. Cutting edge: Leptin-induced RORγt expression in CD4+ T cells promotes Th17 responses in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. (2013) 190:3054–8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1203275
156. Wang W, Zhang BT, Jiang QL, Zhao HQ, Xu Q, Zeng Y, et al. Leptin receptor antagonist attenuates experimental autoimmune thyroiditis in mice by regulating Treg/Th17 cell differentiation. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2022) 13:1042511. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1042511
Keywords: leptin, angiogenesis, breast cancer, obesity, hyperleptinemia, tumor microenvironment
Citation: Lagarde CB, Thapa K, Cullen NM, Hawes ML, Salim K, Benz MC, Dietrich SR, Burow BE, Bunnell BA, Martin EC, Collins-Burow BM, Lynch RM, Hoang VT, Burow ME and Fang JS (2024) Obesity and leptin in breast cancer angiogenesis. Front. Endocrinol. 15:1465727. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1465727
Received: 16 July 2024; Accepted: 04 September 2024;
Published: 08 October 2024.
Edited by:
Natalia Simona Pellegata, University of Pavia, ItalyReviewed by:
Vincenza Cifarelli, Saint Louis University, United StatesArunasalam Dharmarajan, Sri Ramachandra Institute of Higher Education and Research, India
Copyright © 2024 Lagarde, Thapa, Cullen, Hawes, Salim, Benz, Dietrich, Burow, Bunnell, Martin, Collins-Burow, Lynch, Hoang, Burow and Fang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Matthew E. Burow, bWJ1cm93QHR1bGFuZS5lZHU=; Jennifer S. Fang, amZhbmc1QHR1bGFuZS5lZHU=
 Courtney B. Lagarde
Courtney B. Lagarde Kapil Thapa
Kapil Thapa Nicole M. Cullen1,2
Nicole M. Cullen1,2 Bruce A. Bunnell
Bruce A. Bunnell Ronald M. Lynch
Ronald M. Lynch Van T. Hoang
Van T. Hoang Matthew E. Burow
Matthew E. Burow Jennifer S. Fang
Jennifer S. Fang