- 1The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang Chinese Medical University (Zhejiang Provincial Hospital of Chinese Medicine), Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China
- 2The First Clinical Medical College, Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China
- 3The Second Clinical Medical College, Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China
Background: One of the most common complications of diabetes mellitus is diabetic erectile dysfunction (DMED), a condition that has grown more common in recent years and has a significant impact on patients’ daily lives. The complicated pathophysiological changes of DMED, involving vascular, neurological, muscular, and endocrine variables, have not been well addressed by any one treatment technique, and no widely approved treatment strategy has been developed.
Aim: The objective of this study was to thoroughly examine the complex nature of the pathogenic mechanism of DMED and discover new therapeutic approaches that could improve DMED symptoms.
Methods: Studies and review articles from the past 10 years were considered.
Results: The pathogenesis of DMED encompasses vascular dysfunction, endothelial cell damage, cavernous smooth muscle defects, neurological dysfunction, endocrine/metabolic factors, leukomalacia fibrosis, and psychosocial factors, elucidating complex interplay among the mechanisms underlying DMED. It underscores the need of integrating traditional herbal medicine, energy-based medicine treatments, and advanced techniques like stem cell and gene therapy to enhance therapeutic outcomes. Furthermore, it expresses optimism on the therapeutic potential of new nanobiomaterials in DMED.
Conclusion: Through integrating a complete description of DMED etiology and current therapy methods, this work offers a helpful resource for researchers, doctors, and patients dealing with this difficult condition.
Background
Diabetes Mellitus Erectile Dysfunction (DMED) is a prevalent consequence of diabetes mellitus (DM) that specifically impacts the corpus cavernosum tissue responsible for erectile function. Studies have shown that DMED is prevalent in men with type 1, type 2, and both types of diabetes, with an overall prevalence of 52.5% (1). The incidence of erectile dysfunction (ED) is greater in males with compromised fasting blood glucose and impaired glucose tolerance in comparison to those with normal blood glucose levels (29.2% and 33.2% vs. 14.8%) (2). On the other hand, diabetes is a worldwide health issue, impacting 536.6 million individuals in 2021 and expected to rise to 783.2 million prior to 2045 (3). An analysis of diabetes in China has shown that the occurrence of diabetes in the adult population has increased from 0.67% to 11.2% over the last forty years, affecting almost 140.9 million people (4). An analysis of diabetes in China has shown that the occurrence of diabetes in the adult population has increased from 0.67% to 11.2% over the last forty years, affecting almost 140.9 million people.
Predicting and evaluating illness risk through the use of genetic databases has been the focus of research in recent years. The unique capacity of these databases lies in their ability to efficiently reduce the influence of complicating factors and clarify causal connections. An extensive genome-wide association study included 223,805 Europeans presented evidence that type 2 diabetes is an independent risk factor for erectile dysfunction (ED), therefore reinforcing the robust link between DM and ED (5). Through several processes, including persistent hyperglycemia, variable blood sugar levels, and aberrant glucose metabolism byproducts, diabetes adversely impacts the erectile organ. These elements can hinder the flow of blood, disturb the functioning of blood vessels, degrade the integrity of nerves, weaken the structures of muscles, and disturb the essential endocrine processes involved in the erection mechanism. In our prior study, we investigated the development of DMED and explored the potential of natural drug therapy. Our findings indicate that a combination of leech centipede drugs may enhance the erectile function of diabetic rats by suppressing endothelial cell death and penile fibrosis (6).
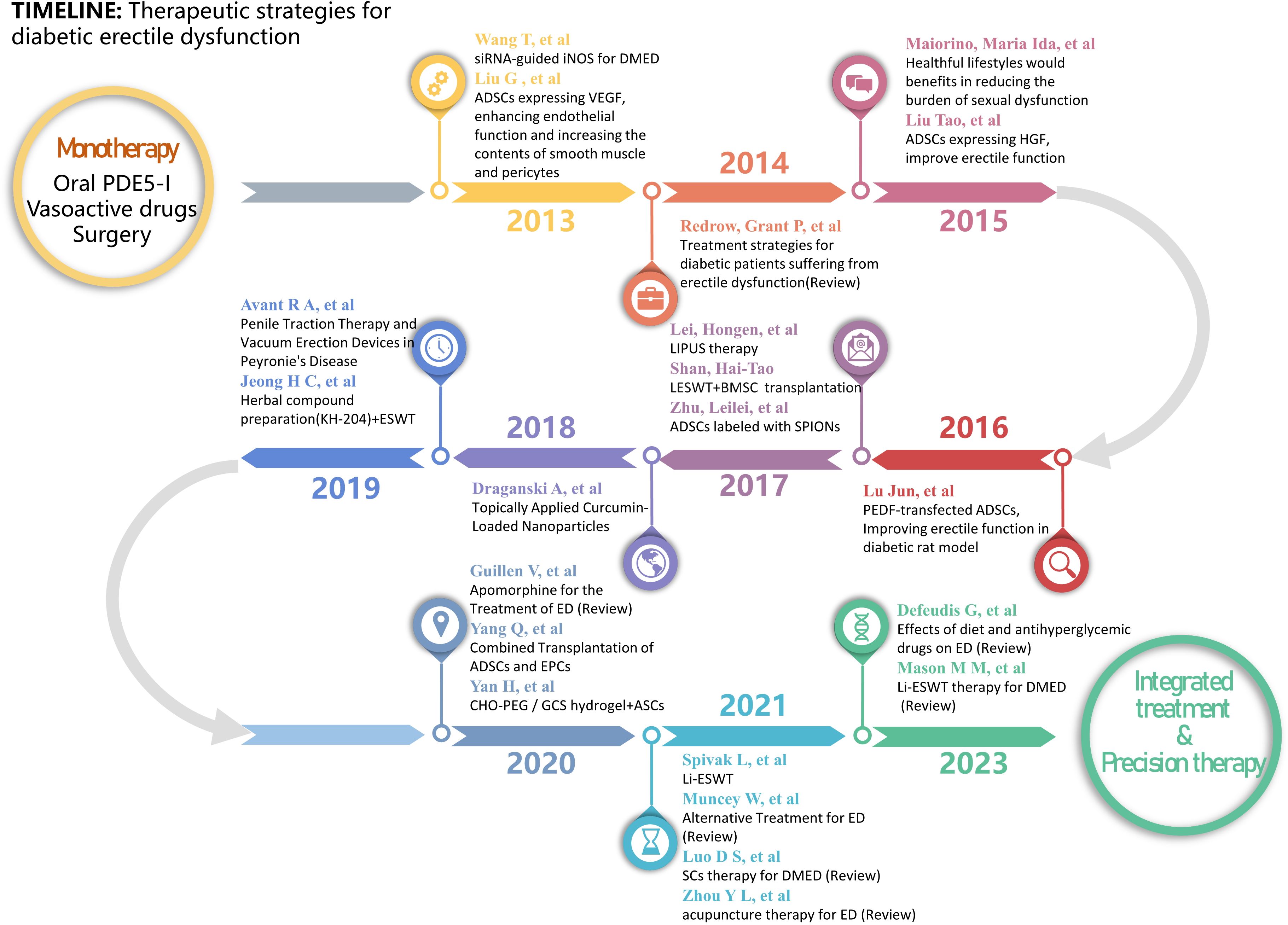
Nevertheless, recent studies on the development of DMED evidence the presence of several mechanisms of injury. The mostly treatment-resistant character of DMED in clinical settings is mostly attributed to the lack of specific therapeutic approaches. Consequently, the study of the development of DMED and the exploration of new treatment methods have continuously been the main areas of research in the field of andrology. This paper presents a succinct summary of the progress achieved in this field throughout the past ten years. A diagram illustrating the study development on the epidemiology and mechanism of DMED is presented in Figure 1. The state of research on DMED therapy approaches is illustrated in Figure 2.
Physiological mechanism of erection
Sexual erection is a complex physiological process that encompasses several systems such as psychology, endocrine function, blood vessels, and nerves. Initiation of sexual desire can occur through audio-visual, tactile, or imaginative stimulus, which then stimulates impulses to the penile cavernous body through the lower hypothalamus center or sacral cord. The activation of guanylate cyclase (GC) through the GTP/cGMP pathway is attributed to the neurotransmitter Nitric Oxide (NO). The outcome of this phenomenon is an elevation in the concentrations of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) in the smooth muscle cells of the cavernous body. Augmented arterial blood flow, hyperemia, and expansion of the penile cavernous body are facilitated by the relaxation of the trabecular smooth muscle induced by the rise in cGMP levels (7). The distended corpus cavernosum exerts pressure on the minor veins located beneath the tunica albuginea, therefore blocking the route of venous outflow. Moreover, the contraction of the pelvic floor muscles might enhance the compression of the corpus cavernosum, therefore increasing its size and structural integrity to aid in achieving an erection (8, 9).
Mechanisms of erectile dysfunction in diabetes: a pathological analysis
Diabetes has the potential to impair male erectile function by disabling blood vessels, nerves, gonadal axis, muscles, and several other organs and tissues. This damage can result from disturbances to many pathways, including the polyol pathway, protein kinase C (PKC) pathway, and others (as shown in Figure 3).
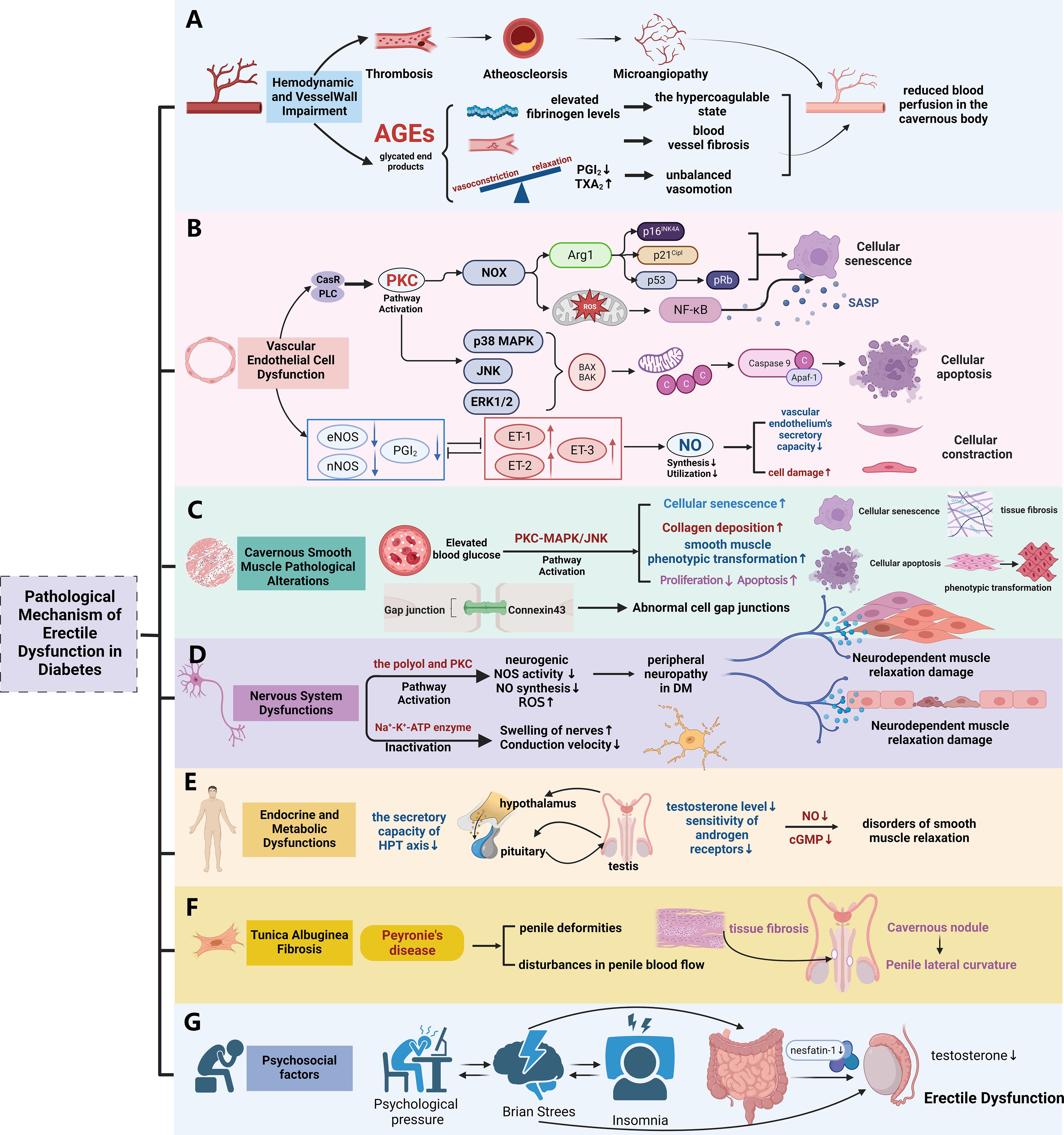
Figure 3. The pathological mechanism of diabetic erectile dysfunction. (A) The pathological mechanism of erectile dysfunction mediated by hemodynamic changes and Vessel Wall Impairment in diabetes; (B) The pathological mechanism of erectile dysfunction mediated by vascular endothelial dysfunction in diabetes; (C) The pathological mechanism of erectile dysfunction mediated by Cavernous Smooth Muscle Pathological Alterations in diabetes; (D) The pathological mechanism of erectile dysfunction mediated by Nervous System Dysfunctions in diabetes; (E) The pathological mechanism of erectile dysfunction mediated by Endocrine and Metabolic Dysfunctions in diabetes; (F) The pathological mechanism of erectile dysfunction mediated by Tunica Albuginea Fibrosis in diabetes; (G) Influence of psychosocial factors on erectile function in patients with diabetes. (Used Abbreviations and symbols in figure: AGEs, advanced glycation end products; PGI2, prostaglandin I2; TXA2, thromboxane; CaSR, calcium-sensing receptor; PLC, phospholipase C; PKC, protein kinase C; NOX, coenzyme oxidase; Arg1, arginase 1; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SASP, Senescent Associated Secretory Phenotypes; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; ET-1, endothelin; DM, diabetes mellitus; HPT axis, hypothalamus-pituitary-testis axis; cGMP, cyclic guanosine monophosphate) Figure created by BioRender.com.
Hemodynamic and vessel wall impairment
Research has demonstrated that individuals with diabetes may have increased viscosity of whole blood and abnormal aggregation of red blood cells. This phenomenon could be attributed to an over activation of platelets and an increased expression of genes involved in cell surface adhesion (10, 11). Furthermore, individuals with type 2 diabetes may exhibit increased concentrations of fibrinogen, the predominant clotting factor in the plasma. Additionally, in diabetic individuals, fibrinogen can stimulate thrombin activation, resulting in the production of insoluble fibrin and ultimately leading to the development of blood clots (12, 13). This mechanism hinders the circulation of blood within the cavernous corpus.
Furthermore, increased glucose metabolism can also impact the artery wall. Advanced glycation end products (AGEs) can induce fibrosis of blood vessels, causing a decrease in the flexibility and compliance of cavernous blood vessels. This ultimately leads to a reduction in blood flow to the cavernous body (14–16). Diabetes also disrupts the equilibrium between vasoconstriction and relaxation receptors, such as prostaglandin I2 (PGI2) and thromboxane (TXA2) (17, 18). Diabetes also disrupts the equilibrium between vasoconstriction and relaxation receptors, such as prostaglandin I2 (PGI2) and thromboxane (TXA2) (19).
Vascular endothelial cell dysfunction
Specialized architecture characterizes the penis, a vascular tissue that includes endothelial cells (ECs) as its innermost layer of blood vessels. Endothelial cells (ECs) play an active role in maintaining the balance of blood vessels and the smooth muscles in their vicinity. Recent research has revealed four main routes that contribute to the damage and dysfunction of endothelial cells in the hyperglycemic setting of diabetic mellitus (DM): the AGEs pathway, polyol pathway, hexosamine pathway, and PKC pathway (20, 21). The investigation of hyperglycemia-triggered vascular endothelial dysfunction in DM includes a primary focus on the PKC pathway. The conventional mechanism of PKC activation is the connection of the calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR) with phospholipase C (PLC) driven by the high-glucose environment. Following this interaction, phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) is broken down, resulting in the formation of diacylglycerol (DAG) and inositol triphosphate (IP3). Later interaction of IP3 with very specific receptors on the endoplasmic reticulum and nucleus triggers the activation of calcium ion channels, so enabling the liberation of calcium ions from the nucleus into the cytoplasm. The activation of PKC proteins situated on the inner side of the plasma membrane is facilitated by this cascade in conjunction with DAG (22, 23).
Following the activation of PKC, two stages of advancement occurred. On one side, it enhances the generation of oxygen free radicals by inhibiting the activity of reduced coenzyme oxidase (NOX), therefore decreasing the accessibility of nitric oxide (NO). The secretory capacity of the vascular endothelium is influenced by the elevation of endothelin (ET-1) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) levels induced by this process. This sequence results in the impairment of endothelium-dependent relaxation of vascular and muscle cells (24). O Conversely, the regular secretion and function of endothelial-derived nitric oxide (NO) contributes to the preservation of the relaxation of cavernosal smooth muscle, vascular smooth muscle cells, and the physiological basis of erection in the penis. In addition, the activation of NOX can enhance the expression of its focal protein, arginase 1 (Arg1), and the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) (25). This, in turn, stimulates an increase in the expression of p16[Ink4a], p21[Cip1], and p53, so facilitating cellular senescence. In contrast, the elimination of the Arg1 gene or its pharmacological suppression effectively inhibits the aging of endothelium cells in diabetic mice (26).
Furthermore, PKC has the ability to initiate the consecutive activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), resulting in the activation of amino-terminal kinases like JNK, ERK, and p38. This sequence of events leads to cellular injury, initiates preprogrammed cell death, increases the expression of pro-apoptotic proteins and Bak, and decreases the expression of the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2. This process promotes the liberation of cytochrome C and mitochondrial DNA from the mitochondrial membrane into the cytoplasm, together with an upregulation of the pro-apoptotic protein Bax (27). Conversely, the expression of the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2 decreases, which in turn promotes the release of cytochrome C from the inner mitochondrial membrane into the cytoplasm. Consequently, the development of apoptotic complexes is triggered, leading to the predetermined death of vascular endothelial cells. Profound mitochondrial failure produces a substantial amount of reactive oxygen species (ROS) that stimulate NF-κB. Upon activation, NF-κB dissociates from inhibitory proteins, therefore enabling its action on the κB configuration of DNA. Moreover, it facilitates the release of many Senescent Associated Secretory Phenotypes (SASP), therefore worsening the process of endothelial cell senescence (28). In conclusion, hyperglycemia in DM patients can induce endothelial cell dysfunction, leading to diminished synthesis and utilization of nitric oxide, consequently fostering the onset and progression of DMED (29).
Cavernous smooth muscle pathological alterations
Cavernous smooth muscle cells (CCSMC) play a vital role in penile erection, constituting 42-50% of the cavernosal cell population. Their relaxation is essential for prompt initiation and sustained maintenance of an erection (30–33). However, increased blood glucose levels can decrease the production of smooth muscle gap junction proteins and change the ratio of myosin subtypes in muscle cells (34). This can result in damage to elastic fibers, atrophy of smooth muscle, excessive buildup of collagen, and a modification in the phenotypic transition of smooth muscle (35–37). When smooth muscle cells undergo a transition from a contractile state to a synthetic state, characterized by enhanced proliferation and migration, the levels of α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) and desmin are reduced, but osteopontin (OPN) is increased (38). Consequently, the contraction of cells is disturbed, which can have a substantial impact on the development of vascular complications and erectile dysfunction in rats with early-onset diabetes (39).
Studies have shown that high glucose levels activate the PKC-MAPK/JNK signaling pathway, which contributes to the phenotypic transformation of smooth muscle cells (40). In diabetic patients, hyperactivation of PKC causes increased contractility and reduced endothelium-dependent relaxation in human CCSMCs (41). It also plays a crucial role in mediating smooth muscle cell senescence, which contributes to vascular aging, vascular calcification, and atherosclerosis (42). By inhibiting PKC upstream signaling, particularly DAG, it is possible to reduce the expression of the MAPK/ERK1/2 and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways, which in turn, mitigates the migration and mitosis of vascular smooth muscle cells in models of atherosclerosis and restenosis (43).
Previous research has shown that CCSMCs in rats with diabetic ED undergo phenotypic transformation. When myocardin gene transfection was performed in these rats, CCSMCs transitioned from a synthetic to a contractile phenotype. This transition was accompanied by up-regulated expressions of marker proteins for contractile smooth muscle cells, namely α-SMA and desmin. On the other hand, the expressions of OPN and Vimentin—marker proteins associated with synthetic smooth muscle cells—were down-regulated. It is noteworthy that this transformation led to a substantial improvement in erectile function (44, 45).
Studies have indicated that downregulation of the CAT/3-MST and DAO/3-MST pathways, coupled with reduced activity of CBS and CSE, leads to a significant decrease in endogenous hydrogen sulfide (H2S) production in the penile tissue of patients with diabetic mellitus erectile dysfunction (DMED). H2S can activate potassium channels on smooth muscle cells, increasing intracellular potassium ion concentration, which results in membrane hyperpolarization. This hyperpolarization inhibits calcium ion influx, reduces actin-myosin sliding, and induces relaxation of corporal smooth muscle cells (CCSMCs), contributing to penile erection. Consequently, the reduction in H2S levels is also a significant factor in the development of erectile dysfunction (ED) (46).
Nervous system dysfunctions
The neurological system regulates the mechanism of regular penile erection. Prolonged hyperglycemia can result in impaired glucose metabolism, insulin pathways, oxygen free radical levels, mitochondrial activity, and microcirculation, therefore causing peripheral neuropathy and degeneration of pudendal sensory neurons (47, 48) and a decrease in sexual stimulus conduction (49). In addition to sensory nerves, degeneration of efferent nerves can also cause a decrease or halt in parasympathetic nerve activity, which regulates the relaxation of cavernous smooth muscles. This can lead to impaired neurogenic NOS activity and reduced NO synthesis (50). In addition to sensory nerves, degeneration of efferent nerves can also cause a decrease or halt in parasympathetic nerve activity, which regulates the relaxation of cavernous smooth muscles. This can lead to impaired neurogenic NOS activity and reduced NO synthesis (51). The over conversion of sorbitol in the polyol pathway is a chronic problem that leads to neurotrophic diseases, producing nerve swelling, distortion, or necrosis and causing long-lasting inflammatory alterations in the peripheral nerves. Moreover, this buildup can have a detrimental impact on the NO-regulated GTP/cGMP pathway, thus resulting in erectile dysfunction (52). The activation of the PKC pathway can stimulate the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), leading to nerve fiber damage and subsequent pathological alterations (53). High sugar levels can impede the uptake of inositol by nerve tissue, therefore reducing the activity of Na+-K+ -ATPase, leading to neuron swelling and reduced conduction velocity (54). Hyperglycemia-induced autonomic nerve injury can result in nerve dysfunction and damage to some autonomic nerves, including adrenergic and cholinergic nerves, which innervate penile blood vessels. The asymmetry in arteriovenous contraction during penile erection might result in penile venous leakage, ultimately leading to ED (55).
Endocrine and metabolic dysfunctions
Optimal release and effective use of male hormones are crucial in promoting sexual desire and preserving male erectile function. Nevertheless, an extended period of elevated glucose levels, as shown in diabetes mellitus (DM), can have a negative impact on the hypothalamus-pituitary-testis axis (HPT axis), resulting in reduced secretion of gonadotropins and the production of total testosterone (TT), combined with impaired functioning of endothelial cells. Ultimately, this sequence of events can lead to hypogonadism, testosterone insufficiency, and reduced sensitivity of androgen receptors, resulting in erectile dysfunction in individuals (56, 57). Furthermore, this sequence of events results in decreased vascular NOS production, reduced expression and function of PDE5, and inhibited release of nNOS by neurons. Consequently, this leads to a reduction in cGMP levels, causing conditions of smooth muscle relaxation and irregularities in the NO/cGMP signaling pathway (58, 59). A meta-analysis of testosterone treatment for T2DMED revealed that individuals with ED had a greater duration of DM, a higher body mass index (BMI), and lower blood testosterone levels in comparison to those without ED. The duration of diabetes mellitus and serum testosterone levels were found to be independent predictors of erectile dysfunction in logistic regression analysis (60). When the total testosterone level (TT) was ≤ 8nmol/L, the application of undecanoate testosterone significantly improved sexual function in DMED patients (61).
Tunica albuginea fibrosis
Persistent high blood sugar levels in the setting of diabetes can trigger the restructuring of the extracellular matrix, finally promoting fibrosis. A significant portion of individuals with diabetes suffer from fibroproliferative illnesses, particularly those that cause the formation of fibrotic plaques in the tunica albuginea, a feature of Peyronie’s degenerative disease (PD). Penile dystrophy (PD) increases the likelihood of significant penile abnormalities and disruptions in penile blood circulation, therefore increasing the vulnerability to erectile dysfunction (62, 63). A study conducted in Iran in 2019 revealed a prevalence of PD amounting to 3.8% among a cohort of 317 men diagnosed with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) (64). In a separate retrospective analysis encompassing 1622 male individuals seeking care at a urological health center, a significant association was established between the presence of T2DM (n = 387; 24%) and PD (P = 0.005) (65).
Psychosocial factors
Diabetes is a metabolic condition requiring lifelong treatment that can result in various complications, placing significant psychological and financial burdens on patients. Emotional instability can significantly impact the erectile function of individuals with diabetes, potentially inhibiting normal penile erection (66). Studies suggest a correlation between sexual function and social, psychological, and organic factors (67). Individuals with diabetic erectile dysfunction often experience heightened states of depression and anxiety, with Nesfatin-1 identified as a potential biomarker for assessing anxiety severity. Those with low serum Nesfatin-1 levels, particularly, must receive psychiatric care (68, 69). In summary, diabetes is a chronic, systemic, and socially impactful disease that affects both physical and mental well-being. Individuals with diabetic erectile dysfunction are particularly prone to mental and psychological challenges.
Modern medical treatment approaches for diabetes mellitus erectile dysfunction
Currently, there is no clear globally validated treatment regimen for DMED. Nevertheless, based on the current body of research and widely accepted recommendations, the optimal treatment strategy entails a combination of basic care and specialized intervention, emphasizing the proactive control of blood sugar levels from the beginning of the illness. This technique requires developing individualized tactics that correspond to the fundamental processes, with the particular therapeutic interventions differing to some extent depending on the clinician’s level of knowledge. (Shown in Figure 4).
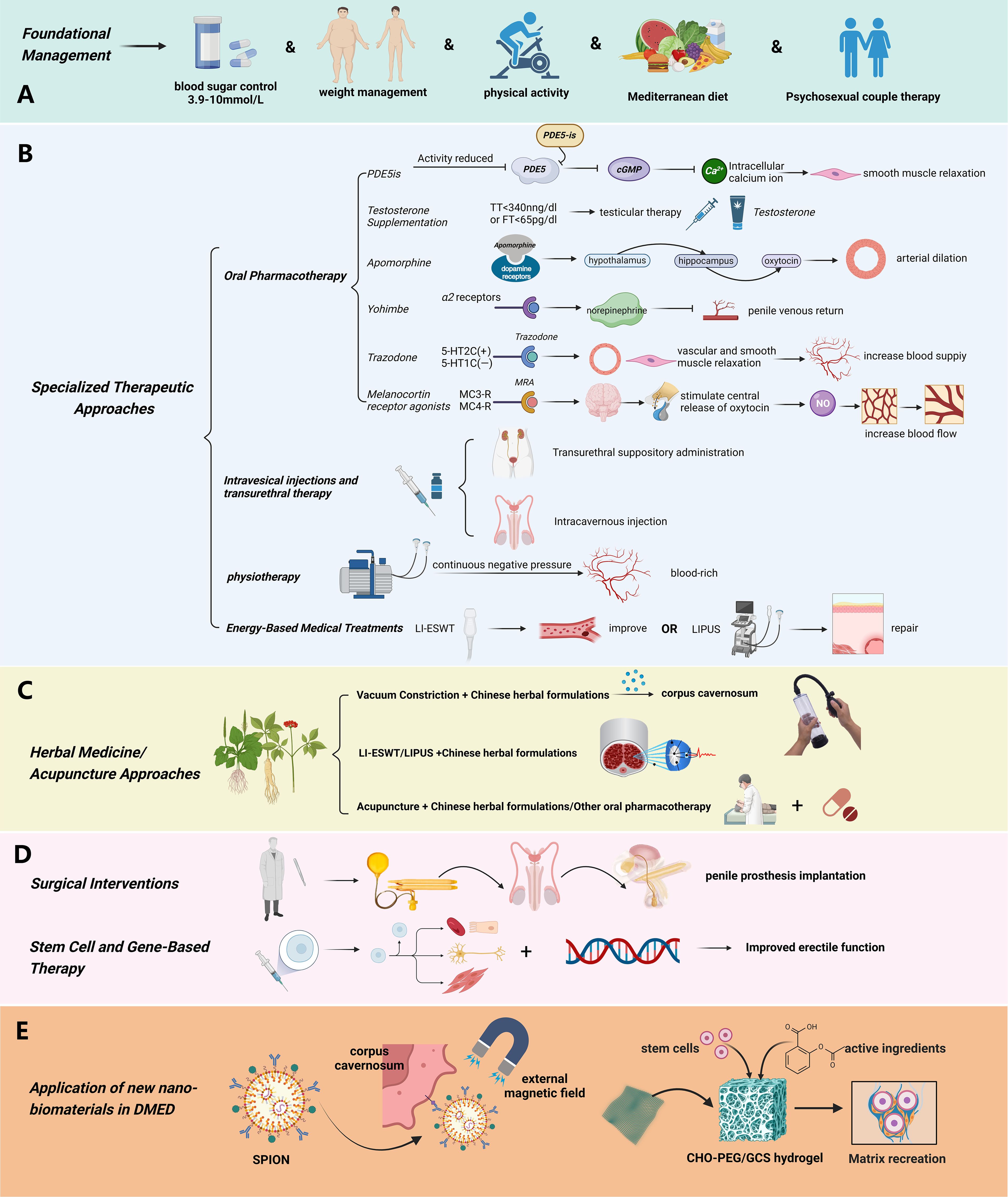
Figure 4. Treatment Strategies of diabetic erectile dysfunction. (A) The basic management plan for diabetic erectile dysfunction mainly includes controlling blood sugar in a reasonable range, weight management, and lifestyle adjustment (proper exercise, Mediterranean diet, etc.); (B) Specialized treatment of diabetic erectile dysfunction mainly includes: oral drug treatment (PDE5is, Testosterone, Apomorphine, Yohimbe, Trazodone), Intracavernosal Injection and Transitional Suppository Therapy, Physiotherapy, Energy Medical Treatments; (C) The comprehensive therapies based on natural drugs mainly include: combination of Chinese herbal medicine with PDE5 inhibitors, Chinese herbal formulas for cavernous body soaking and vacuum construction device, combination of Chinese herbal medicine with extracorporeal shock wave therapy, acupuncture, moxibustion, and acupoint injection with first line drugs and other physical therapied; (D) Surgical Interventions and Stem Cell and Gene-Based Therapy. (Used Abbreviations and symbols in the figure: PDE5is, Phosphodiesterase Type 5 Inhibitors; cGMP, guanosine monophosphate; TT, total testosterone; LI-ESWT, Low-intensity Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy; LIPUS, low-intensity pulsed ultrasound; (E) SPION, Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticle; CHO-PEG/GCS hydrogel, benzaldehyde terminated poly (ethylene glycol)/glycol chitosan hydrogel) Figure created by BioRender.com.
Foundational management
Enhancing blood sugar control stands as the central objective in ameliorating DMED, necessitating consideration of factors such as age of onset and patient body weight. According to guidelines from the American Academy of Clinical Endocrinologists (AACE) on the utilization of novel diabetes management technologies (70), for individuals with general diabetes, a target blood sugar range of 3.9 to 10 mmol/L is recommended. For elderly individuals or those at heightened risk of diabetes-related complications, prioritizing elevated blood sugar control over excessively low levels is crucial to mitigate the risks of hypoglycemia. Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) levels ranging from 6.5% to 7.5% warrant monotherapy, with metformin serving as the preferred initial option. Within the HbA1c range of 7.5% to 9.0%, combination therapy with two agents is typically indicated, with the second agent encompassing either oral or injectable hypoglycemic agents. In cases where HbA1c exceeds 9.0%, a combination of 2 to 3 hypoglycemic agents can be considered, and in instances of notable weight loss, the incorporation of at least one insulin preparation is advised. Since overweight and obesity are independent risk factors for the onset of type 2 diabetes, early weight management is particularly important. According to consensus recommendations on weight management, individualized weight loss is recommended, with weight loss of 5% -15% or more as the weight management goal for T2DM patients (71). In addition, for patients with DM complicated with clear vascular and neuropathy, routine treatment with antioxidants, neurotrophic drugs, and medication to improve microcirculation can be given (72–76). Psychosexual couple therapy is also a fundamental guideline in the treatment of erectile dysfunction (ED). Numerous surveys and experiments have highlighted the indispensable role of the sexual partner’s involvement in medical interventions for ED (77), this often manifests in the psychological and emotional encouragement provided by the partner, as well as their contribution to treatment decision-making. Additionally, the partner plays a crucial role in achieving long-term remission of ED after treatment, with their attitudes, beliefs, and sexual experiences also being significant to the prognosis of ED (78).
Lifestyle modifications exert a favorable impact on blood sugar regulation and enhancement of erectile function. Research substantiates that judicious physical activity imparts a safeguarding effect on male erectile function, thereby diminishing the incidence of DMED (79, 80). Among patients afflicted with DMED, an 8-week exercise regimen involving 45-60 minutes of daily activity exhibited an ameliorative effect on erectile function, in contrast to sedentary controls (81). Multiple antecedent investigations have yielded findings indicative of the Mediterranean diet’s efficacy in safeguarding erectile function. Moreover, antihyperglycemic agents seem to confer a comprehensive safeguarding influence on erectile function (82).
Specialized therapeutic approaches
DMED patients necessitate specialized intervention for erectile concerns in conjunction with routine blood sugar management and lifestyle modifications, with the aim of expeditiously rectifying erectile dysfunction.
Oral pharmacotherapy
Phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors
PDE5is serves as the frontline therapeutic option for erectile dysfunction. These agents foster and sustain erection by obstructing the hydrolysis of cGMP within cavernous smooth muscle via the enzyme PDE5is. This interference extends the duration of cGMP activity, thereby curtailing intracellular calcium levels and preserving smooth muscle relaxation, consequently sustaining penile erection. Presently, several PDE5 inhibitors are available within the Chinese market, encompassing sildenafil, tadalafil, vardenafil, and avanafil. While their therapeutic efficacy is akin, disparities exist in terms of onset and metabolism times. During the medication process, it is important to avoid the concurrent use of nitrate drugs (83) and potent inhibitors of CYP3A4 to prevent an increase in the plasma concentration of phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors (PDE5is) (84).
Testosterone supplementation
Testosterone supplementation yields notable efficacy in cases of DMED coupled with androgen deficiency or insufficiency. Presently, collaborative recommendations from various institutions suggest that mild testosterone deficiency can be identified when serum total testosterone (TT) falls below 340 ng/dl, while severe deficiency is indicated at TT levels below 230 ng/dl, and the administration of testosterone supplementation to patients yields discernible therapeutic benefit (85, 86). Furthermore, the correlation between age, blood sugar level, and free testosterone (FT) is substantial, underscoring the potential value of supporting testosterone supplementation therapy when FT levels dip below 65 pg/ml (87, 88). A meta-analysis encompassing 16 pertinent studies demonstrated that hypogonadal men subjected to testicular therapy exhibited a notably higher rate of erectile dysfunction improvement relative to those receiving placebo (57.0% versus 16.7%) (89).
Apomorphine
Apomorphine functions as an agonist for dopamine D2 receptors. Its mechanism involves stimulating dopamine receptors located in the paraventricular nucleus, consequently engendering activation of the hypothalamus-hippocampus-oxytocin pathway. This signaling cascade is transmitted through the spinal cord to the penis, culminating in arterial dilation within the penile region and engendering heightened blood circulation. This augmented blood flow fosters erection. The drug received approval from the European Medicines Agency in February 2001 for the management of ED, and select studies have demonstrated its safety and efficacy in treating ED patients (90). During the administration, it is crucial to avoid the combination with 5HT3 antagonists to prevent the occurrence of severe adverse reactions such as hypotension, loss of consciousness, or coma (91).
Yohimbe
Yohimbine selectively antagonizes presynaptic α2 receptors, facilitating the liberation of norepinephrine. This phenomenon augments the discharge of norepinephrine from nerve endings within the cavernous body, diminishing the penile venous return and fostering a state of engorged erection (92). Prior to the advent of PDE5 inhibitors in the treatment of ED, yohimbine was extensively employed for this purpose; however, its efficacy and safety profile have not undergone comprehensive evaluation. Presently, its use has waned. During the use of certain medications, it is important to avoid co-administration with monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), such as phenelzine (Parnate) and other antidepressant drugs, to prevent potentially serious adverse reactions (93).
Trazodone
Trazodone functions as an agonist for serotonin 2C receptors (5-HT2C) and an antagonist for 5-HT1A receptors. Besides its central nervous system effects, the drug can also exert alpha2 receptor blockade. Its potential mechanism of action entails α2 receptor blockade, fostering vascular and corpus cavernosum smooth muscle relaxation, thereby augmenting blood supply to the penile corpus cavernosum and facilitating erection. While clinical reports have attested to trazodone’s effectiveness in treating ED, results from meta-analyses suggest no statistically significant difference when compared to placebo (94). When administering medication, special consideration should be given to patients with erectile dysfunction (ED) who have severe heart disease or arrhythmias, as the use of such medications may be contraindicated or require caution in these individuals (95, 96).
Melanocortin receptor agonists
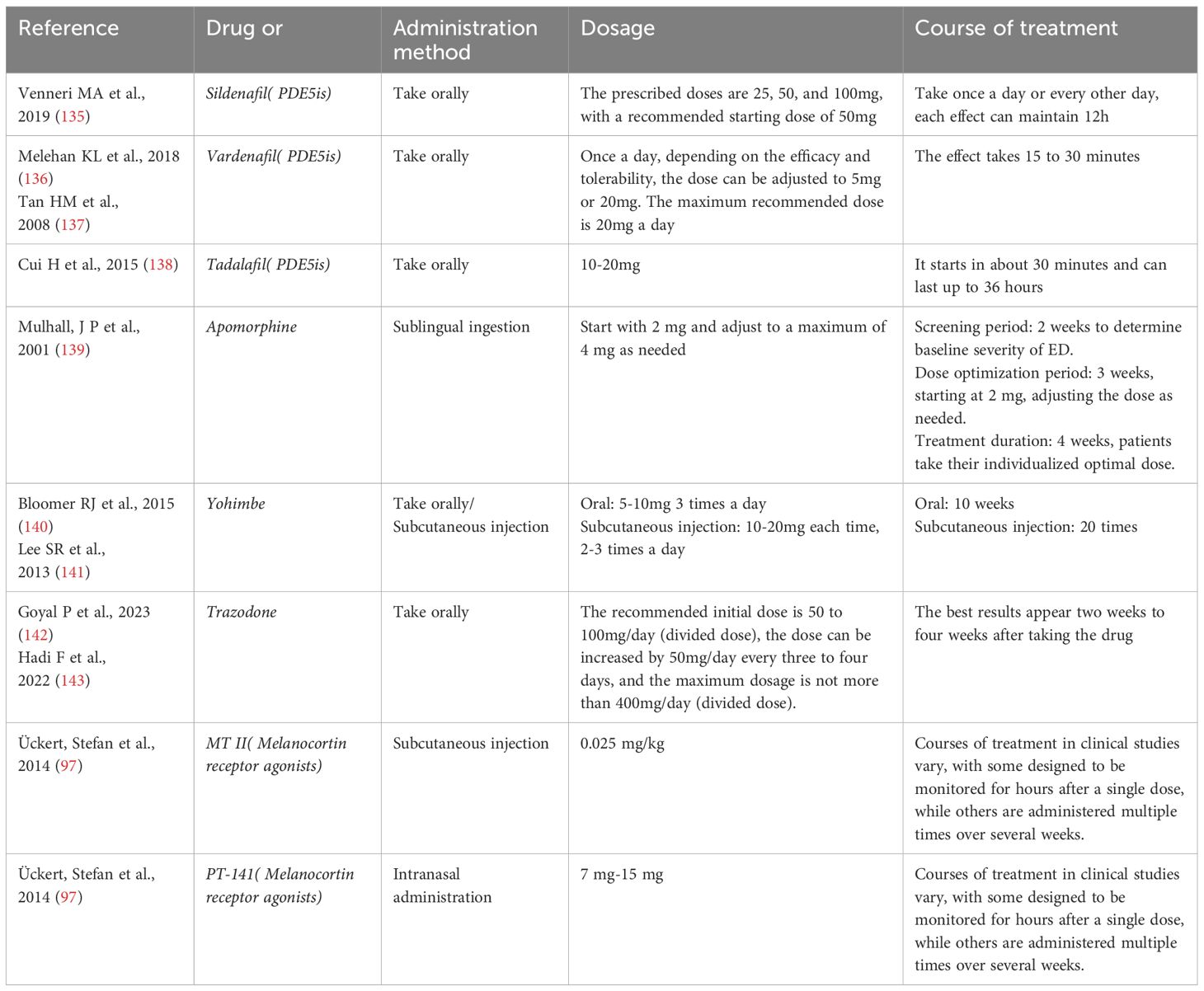
The melanocortin system regulates sexual function by activating melanocortin receptors (MCRs), particularly MC3-R and MC4-R, which are distributed in the hypothalamus and spinal cord. The activation of these receptors stimulates the central and spinal release of oxytocin, which in turn increases the production of nitric oxide (NO), leading to the relaxation and engorgement of the penile erectile tissue, thus facilitating erection. Melanocortin receptor agonists (MRA), such as Melanotan II (MT II) and Bremelanotide (PT-141), mimic this natural process, and they have shown potential in the treatment of male erectile dysfunction (ED) in clinical studies (97). These drugs can directly act on the brain’s sexual behavior control centers, as well as increase penile blood flow by promoting NO production, helping men achieve and maintain erections with or without sexual stimulation. This mechanism differs from that of PDE5 inhibitors, which require sexual stimulation to facilitate erections, whereas MRAs can trigger erections without sexual stimulation, offering a novel pharmacological approach to ED treatment. The usage of the above drugs and the intervention course are detailed in Table 1.
Intracavernosal injection and transurethral suppository therapy
Secondary methods of treating erectile dysfunction include injecting the patient intravenously or administering a suppository through the urinary tract. Their main benefit is that they help speed up the process of getting an erection by allowing the medicine to be absorbed locally and start working quickly. Commonly used drugs include vasoactive intestinal polypeptide, phentolamine, papaverine, and alprostadil. Once they’ve gotten the proper training, males can administer cavernosal injections on their own or with the help of a partner. Localized massage can speed up the erection process, which may have nothing to do with sexual desire, and the erection usually appears within 10 minutes after administration (98). Presently, these approaches find application in the evaluation and diagnosis of ED in China. Nonetheless, intracavernosal self-administration is a practice adopted by only a minuscule proportion, and topical application might precipitate priapism, albuginea fibrosis, and symptoms like penile, urethral pain, or burning sensation (99).
Physiotherapy
Using an elastic band fastened at the base of the penis, the Vacuum Constriction Device (VCD) causes erection by applying constant negative pressure to the penis, which helps to fill the cavernous body with blood and maintain blood perfusion. Notwithstanding the device’s simplicity of use, the erection produced by vacuum suction is described as artificial and mechanical, frequently accompanied by a cold feeling in the treated region. A significant percentage, roughly 50%, of patients indicate discontent with this method (100). VCD is deemed appropriate for individuals who have encountered failure with oral PDE5is therapy and harbor aversion to other, more invasive interventions. Side effects attributed to vacuum suction encompass localized ecchymosis, penile numbness, and delayed ejaculation (101).
Energy-based medical treatments
The main application of Low-intensity Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (LI-ESWT) is to treat moderate vascular erectile dysfunction (ED), which is often linked to impaired cavernous blood arteries and endothelial cell dysfunction in patients with DMED. Therefore, it may be employed either as an independent method or in combination with other pharmacological treatments. Existing research suggests that LI-ESWT can improve the IIEF score and erection hardness score in patients with mild vascular erectile dysfunction. Furthermore, the use of LI-ESWT medication may enhance the effectiveness of PDE5 inhibitors in patients who show insufficient response to first PDE5 inhibitor therapy (102). The clinical investigations indicate that LI-ESWT is a safe and effective therapy for men with well-controlled DM with moderate or improved erectile dysfunction. However, the longevity of the benefit is lower in diabetic men compared to nondiabetic men. Further monitoring is required to assess the therapeutic effect on DMED patients (103, 104).
Low-intensity pulsed ultrasonography (LIPUS) has the capacity to promote tissue healing, accelerate the regeneration of soft tissues, and reduce tissue inflammation (105). Research findings suggest that LIPUS therapy improves erectile function in diabetic rats, corrects abnormalities in penile tissue, increases intracavernous pressure (ICP) levels, increases endothelial and smooth muscle content, increases the expression of eNOS and nNOS, causes changes in collagen and fiber composition, and decreases the TGF-β1/Smad/CTGF signaling pathway (106). One study, a multicenter double-blind Randomized Controlled Trial (RCT), showed that LIPUS significantly improved the IIEF5 score in patients with mild to moderate erectile dysfunction (107). While its underlying molecular mechanism requires further exploration, LIPUS shows potential as a therapy for erectile dysfunction.
Surgical interventions
Surgical procedures are a third-tier method for treating erectile dysfunction. In an increasing number of individuals with DMED who do not respond to medication, penile prosthesis implantation is being considered as a final option. Nevertheless, the surgical modification of cavernous tissue during this operation makes it impossible to achieve future restoration of smooth muscle relaxation. At both national and international levels, the hydraulic three-piece implant is widely regarded as the preferred option for penile prosthesis. Significantly, the satisfaction percentages among the beneficiaries and their partners are very high, accounting for 70% and 90% respectively (108). Infection is a common consequence linked to penile prosthesis, with a prevalence rate of 2%–4% in cases (109). Additional surgical procedures for erectile dysfunction include artery bypass surgery and vein ligation to treat congenital aberrant venous leakage. Nevertheless, vascular surgery is rarely performed by andrologists today because to the questionable effectiveness advantages (110).
Herbal medicine approaches
Traditional Chinese herbal therapy has a well-established history and proven therapeutic effectiveness in the treatment of ED. The integration of Chinese herbal compounds, which have functions such as improving blood circulation, reducing blood stasis, and unblocking meridians, as well as tonifying the kidney, harmonizing the liver, and boosting vital energy and nurturing yin, in combination with oral PDE5 inhibitor administration, has been shown to not only enhance therapeutic outcomes but also exemplify the holistic regulation characteristic of traditional Chinese medicine. Moreover, this method can interfere in fundamental genetic disorders, providing a viable therapeutic approach for reducing erectile dysfunction issues in early-stage diabetic patients. Furthermore, the use of Chinese herbal preparations for treating DMED by cavernous body immersion and vacuum constriction device is a fascinating combination of traditional Chinese and Western medicine. This approach exploits the absorption of medication ingredients to enhance the process of cavernous body repair (111, 112). The combination of traditional Chinese herbal medicine with extracorporeal shock wave therapy has been shown to have a significant synergistic impact in improving erectile function in diabetic erectile dysfunction rats. The aforementioned method not only broadens the scope of clinical treatment options (113), but also emphasizes the potential of integrating acupuncture, moxibustion, and acupoint injection with primary medications and other physical therapies to improve the overall effectiveness in controlling DMED (114, 115).
Stem cell and gene-based therapy
Stem cells, also known as SCs, are distinguished by their ability to differentiate in multiple directions or in a specific one, as well as by their potential to continue self-renewal. They possess substantial utility in the fields of regenerative medicine and tissue engineering. With the development of regenerative medicine ideas and the evidence of successful animal trials, SCs have attracted significant attention as a possible treatment for male erectile dysfunction (116). In their study, Yang et al. (117) introduced stem cells generated from adipose tissue and endothelial progenitor cells into a rat model of DMED. Their findings revealed a significant enhancement in erectile function among the group treated with stem cells as compared to the group treated with DMED four weeks after injection. The effectiveness was much higher when the two types of cells were combined. Moreover, numerous studies have examined the synergistic effects of stem cells used in combination with traditional therapies. One example is the work undertaken by Shan et al. (118) which involved the use of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in conjunction with low-energy shock waves in DMED rats. It was shown that the combination method exhibited superior performance compared to the individual use of stem cells or low-energy shock waves. The study conducted by Bahk et al. (119) included seven patients who were unresponsive to medical treatment and were in need of prosthetic surgery. A dose of 1.5 × 1.7 times the standard of human cord blood cells was administered to these individuals via injection into the corpus cavernosum. Multiple factors were recorded in the trial, including IIEF-5 scores, intercourse profiles, blood glucose diaries, and medication dosages. After careful consideration, only two patients chose to have penile prosthesis implantation, while the other patients successfully restored erectile function and achieved good sexual intercourse.
In brief, although stem cell therapy has shown efficacy in many animal models of erectile dysfunction (ED), there is a scarcity of clinical trial studies on DMED, and several unresolved issues still needs to be tackled. For example, the long-term efficacy and safety of the treatment have not been confirmed, and the standardization of stem cell therapy is insufficient because of significant differences in stem cell synthesis methodology. Furthermore, ethical considerations are also relevant. However, stem cells maintain substantial therapeutic potential, and ongoing investigation of their ability to treat DMED remains encouraging.
Gene therapy is a novel therapeutic method that specifically aims to introduce external genetic material into cells in order to correct or compensate for faulty genes (120). As our understanding of the molecular processes responsible for the pathophysiology of DMED improves, more identified treatment targets are consistently being revealed. A multitude of genetic approaches have been subjected to thorough tests and shown effective in diverse animal models. These approaches mostly involve preclinical and limited clinical studies, which concentrate on cellular targets and various viral vectors/nanoparticles for delivering genes. The majority of gene therapy research conducted on DMED have utilized three primary viral vectors, namely adenovirus, AAV, and HSV, which contain genomes that remain outside the chromosomes within the nucleus. Experimental results suggest that gene therapies including synthetic nitric oxide synthase (NOS) (121, 122), neurotrophic factors (123–125), angiogenic growth factors (126, 127), Ca2+-sensitive maxi-K+ Channels (128), antifibrotic factors (129), and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) (130) may play crucial roles in promoting relaxation of cavernous smooth muscles, preventing fibrosis in cavernous tissue, improving vascular endothelial function, and repairing nerve damage in living organisms. Therefore, these treatments have the capacity to improve erectile function in DMED model organisms.
Hence, it is evident that gene therapy holds the promise to address DMED and diminish patient reliance on PDE5 inhibitors. Moreover, the amalgamation of gene therapy with stem cell therapy could potentially rejuvenate spongy tissue architecture. Leveraging the multilineage potential and limited immunogenicity of stem cells, this combination may facilitate prolonged in vivo target gene expression. Consequently, a notable enhancement in erectile function has been observed in animal models through combination therapy, surpassing the outcomes of stem cell therapy in isolation. Notwithstanding, the present-day application of gene therapy for DMED remains in its formative stages. Although preclinical studies have identified multiple molecular targets with potential for preventing and treating DMED, the lack of sufficient clinical investigation hampers the validation of their applicability. Moreover, existing studies predominantly emphasize therapeutic outcomes, often sidelining varied effects. Additionally, the use of naked DNA and plasmids aims to attenuate immunogenic responses and cytotoxicity. However, their transient gene expression in vivo curtails their ability to engender enduring therapeutic effects in ED treatment.
Application of new nano-biomaterials in DMED
Nanobiomaterials are under increasing development for addressing challenges in DMED treatment, including low oral drug bioavailability, insufficient targeting of organs, systemic adverse reactions, and the stability of stem cell/gene therapy. Carrier materials possessing high biocompatibility, low immunogenicity, active targeting, and low invasiveness are employed to enhance the targeting and efficacy of intervention methods involving stem cells, growth factors, bioactive proteins, and drugs. Some experimental studies have confirmed the effectiveness of these approaches in improving DMED. For instance, Zhu LL et al. (131) transfected superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPION) into rat adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs), creating SPION-ADSCs. These were then injected into the streptozotocin-induced DMED rat penis sponge, and relevant tests were conducted four weeks later. The results demonstrated that the application of an external magnetic field enhanced the homing efficiency of SPION-ADSCs to the corpus cavernosum area, leading to increased smooth muscle and endothelial density in the cavernous body, thereby improving erectile function. Han G et al. (132)developed curcumin-loaded silane-based hydrogel nanoparticles and applied them to the abdominal skin of DMED rats until complete absorption, achieving local non-invasive administration, sustained release, reduced medication frequency, and avoidance of gastrointestinal adverse reactions. This approach significantly improved drug efficiency, benefiting DMED treatment. Lu, et al (133), discovered that the benzaldehyde terminated poly (ethylene glycol)/glycol chitosan (CHO-PEG/GCS) hydrogel is a promising stem cell carrier that enhances adipose stem cells and ameliorates diabetes-induced CD31 fibrosis, apoptosis of positive endothelial cells, α-SMA positive smooth muscle, and NeuN positive nerve fibers. Draganski, Andrew, et al. (134) discovered that topical application of curcumin-loaded nanoparticles (curc-NP) to a T2DM rat model can achieve systemic delivery of curcumin, treating erectile dysfunction (ED) and regulating the body’s expression of inflammatory markers.
Present research on carrier materials primarily concentrates on substances like hydrogels with diverse characteristics, fat-soluble particles, and magnetic particles. These materials can serve as sustained-release stents for local body intervention, enhance drug lipophilicity, or act as scaffolds for various cytokines, stem cells, and drugs. The carrier functions as a supportive structure, offering sustained/controlled release in the target area, thereby enhancing the efficacy of the initial treatment method and minimizing side effects from the intervention. Nevertheless, current research on the utilization of carrier materials in DMED treatment remains confined to animal experiments. Further discussions are necessary regarding the implementation of clinical trials and the promotion of application, all while ensuring safety.
Limitations
In conducting this review on DMED, it’s essential to recognize the inherent limitations. Firstly, our review relies heavily on existing literature and clinical studies, which may have their own biases and methodological limitations. These studies often vary in terms of sample size, design, and duration, which can introduce heterogeneity into the data. Additionally, publication bias may exist, as studies with positive results are more likely to be published than those with negative findings, potentially skewing our analysis. Secondly, while we have attempted to provide a comprehensive overview, the field of DMED research is vast and continually evolving. New studies and treatments may have emerged after our review’s cutoff date, which could affect the completeness and timeliness of our analysis. Lastly, the quality of evidence in some areas, such as the use of traditional Chinese herbal medicine, is not as robust as that in more conventional medical approaches. This limitation highlights the need for more rigorous research in complementary therapies for DMED.
Conclusion and future perspectives
In conclusion, this review provides a synthesized perspective on the complex landscape of DMED based on existing literature and clinical studies. While we have discussed various physiological and pathological mechanisms underlying DMED and outlined a diverse range of treatment options, it is crucial to acknowledge the limitations of our analysis. The reliance on existing research means that our conclusions are contingent on the quality and comprehensiveness of the studies available. Moreover, the rapidly evolving nature of DMED research necessitates ongoing updates and revisions to our understanding and recommendations. Despite these limitations, our review underscores the multifaceted nature of DMED and the need for a holistic approach that combines pharmacological, lifestyle, and alternative therapies to effectively manage this condition.
Beyond the present scope, the DMED research landscape offers a canvas abundant with promise and unexplored avenues. Navigating the complexities of DMED and delving deeper into its enigmatic mechanisms underscore that our journey is far from concluded. Unraveling these complexities and formulating pioneering interventions is now more imperative than before. In the domain of energy medicine, a paradigm-shifting frontier beckons, providing potential solutions that harness the body’s innate healing energies. Investigating the interplay among energy pathways, nerve signaling, and erectile function may reveal novel strategies to mitigate DMED.
Furthermore, the integration of traditional herbal medicine with modern medical practices and other complementary therapies presents an intriguing trajectory for future exploration. This pathway gains significance, especially in light of the historical use of holistic methods in tackling sexual dysfunction. The synergy between ancient wisdom and modern medical advancements holds the potential to provide distinctive insights and innovative treatment directions.
Concurrently, the regenerative potential of stem cells remains a focal point in the realm of therapeutic opportunities. Collaborative efforts spanning stem cell research and DMED may herald breakthroughs that redefine treatment efficacy boundaries. Gene therapy, capable of intervening at the core of molecular dysfunction, introduces a new layer of promise. Tailored genetic interventions could potentially rectify the aberrant pathways underlying DMED. Merging gene therapy with stem cell approaches has the potential to generate a synergy surpassing the constraints of individual approaches, resulting in enduring and impactful therapeutic outcomes.
While progressing, a comprehensive and integrative approach becomes of utmost importance. Integrating traditional herbal medicine, energy medicine, stem cells, and gene therapy with established modalities might yield a diverse array of solutions addressing DMED’s multifaceted nature; using novel biomaterials as vehicles to improve the feasibility and effectiveness of pharmaceutical, stem cell, and gene therapies is worthy of in-depth study.
However, the path ahead is not devoid of challenges. Ethical considerations, safety profiles, and the translation of laboratory findings to clinical efficacy continue to be subjects of close examination. Rigorous experimentation, robust clinical trials, and transparent discussion are imperative for validating and refining these emerging therapeutic paths.
In conclusion, the field of DMED research holds immense potential for further exploration in areas such as biochemistry, traditional medicine, energy medicine, stem cells, and gene therapy. Integrating ancient wisdom and modern science in research methods has shown promising results in the pursuit of revolutionary breakthroughs for DMED treatment. With the continuous efforts of scientists from around the world, we firmly believe that the prevention and control strategy of DMED will be redefined.
Author contributions
JM: Writing – original draft. YC: Writing – original draft. YS: Writing – original draft. JQ: Writing – original draft. CW: Writing – original draft. JJ: Writing – review & editing. QH: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NO. 81804092), the Young Elite Scientists Sponsorship Program by CACM (No. CACM-2022-QNRC2-A01), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (NO. 2023M743146), Zhejiang Chinese Medical University Scientific Research Project for Talent, (NO. 2023RCZXZK47) and the Postdoctoral Fellowship Program of CPSF (No. GZC20232373).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Kouidrat Y, Pizzol D, Cosco T, Thompson T, Carnaghi M, Bertoldo A, et al. High prevalence of erectile dysfunction in diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 145 studies. Diabetes Med. (2017) 34:1185–92. doi: 10.1111/dme.2017.34.issue-9
2. Chen HJ, Yang ZL, Yang NG, Zhang J, Wang J, Zhang XJ, et al. Prevalence of erectile dysfunction in men with pre-diabetes: An investigation in Lanzhou. Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue. (2017) 23:436–40. doi: 10.13263/j.cnki.nja.2017.05.010
3. Sun H, Saeedi P, Karuranga S, Pinkepank M, Ogurtsova K, Duncan BB, et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. (2022) 183:109119. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2021.109119
4. Xu Y, Wang L, He J, Bi Y, Li M, Wang T, et al. Prevalence and control of diabetes in Chinese adults. JAMA. (2013) 310:948–59. doi: 10.1001/jama.2013.168118
5. Yuan C, Jian Z, Gao X, Jin X, Wang M, Xiang L, et al. Type 2 diabetes mellitus increases risk of erectile dysfunction independent of obesity and dyslipidemia: A Mendelian randomization study. Andrology. (2022) 10:518–24. doi: 10.1111/andr.13132
6. Ma JX, Wang B, Ding CF, Li HS, Jiang XJ, Wang CY, et al. Couplet medicines of leech and centipede granules improve erectile dysfunction via inactivation of the CaSR/PLC/PKC signaling in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Biosci Rep. (2020) 40:BSR20193845. doi: 10.1042/BSR20193845
8. Prieto D. Physiological regulation of penile arteries and veins. Int J Impot Res. (2008) 20:17–29. doi: 10.1038/sj.ijir.3901581
9. Konstantinos G, Petros P. Phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors: future perspectives. Curr Pharm Des. (2009) 15:3540–51. doi: 10.2174/138161209789206953
10. Cho YI, Mooney MP, Cho DJ. Hemorheological disorders in diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Sci Technol. (2008) 2:1130–8. doi: 10.1177/193229680800200622
11. Fuller JH, Keen H, Jarrett RJ, Omer T, Meade TW, Chakrabarti R, et al. Haemostatic variables associated with diabetes and its complications. Br Med J. (1979) 2:964–6. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6196.964
12. Barazzoni R, Kiwanuka E, Zanetti M, Cristini M, Vettore M, Tessari P. Insulin acutely increases fibrinogen production in individuals with type 2 diabetes but not in individuals without diabetes. Diabetes. (2003) 52:1851–6. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.52.7.1851
13. Kannel WB, D’Agostino RB, Wilson PW, Belanger AJ, Gagnon DR. Diabetes, fibrinogen, and risk of cardiovascular disease: the Framingham experience. Am Heart J. (1990) 120:672–6. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(90)90026-T
14. Saad MI, Abdelkhalek TM, Saleh MM, Kamel MA, Youssef M, Tawfik SH, et al. Insights into the molecular mechanisms of diabetes-induced endothelial dysfunction: focus on oxidative stress and endothelial progenitor cells. Endocrine. (2015) 50:537–67. doi: 10.1007/s12020-015-0709-4
15. Wongeakin N, Bhattarakosol P, Patumraj S. Molecular mechanisms of curcumin on diabetes-induced endothelial dysfunctions: Txnip, ICAM-1, and NOX2 expressions. BioMed Res Int. (2014) 2014:161346. doi: 10.1155/2014/161346
16. Morel O, Kessler L, Ohlmann P, Bareiss P. Diabetes and the platelet: toward new therapeutic paradigms for diabetic atherothrombosis. Atherosclerosis. (2010) 212:367–76. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2010.03.019
17. Wang M, Li Y, Li S, Lv J. Endothelial dysfunction and diabetic cardiomyopathy. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2022) 13:851941. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.851941
18. Hotston M, Jeremy JY, Persad R, Bloor J, Shukla N. 8-isoprostane F2α up-regulates the expression of type 5 phosphodiesterase in cavernosal vascular smooth muscle cells: inhibition with sildenafil, iloprost, nitric oxide and picotamide. BJU Int. (2010) 106:1794–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2010.09270.x
19. Cheng J, Liu Q, Hu N, Zheng F, Zhang X, Ni Y, et al. Downregulation of hsa_circ_0068087 ameliorates TLR4/NF-kappaB/NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated inflammation and endothelial cell dysfunction in high glucose conditioned by sponging miR-197. Gene. (2019) 709:1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2019.05.012
20. Goldin A, Beckman JA, Schmidt AM, Creager MA. Advanced glycation end products: sparking the development of diabetic vascular injury. Circulation. (2006) 114:597–605. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.621854
21. Gleissner CA, Sanders JM, Nadler J, Ley K. Upregulation of aldose reductase during foam cell formation as possible link among diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2008) 28:1137–43. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.107.158295
22. Das EN, King GL. The role of protein kinase C activation and the vascular complications of diabetes. Pharmacol Res. (2007) 55:498–510. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2007.04.016
23. Williams MD, Nadler JL. Inflammatory mechanisms of diabetic complications. Curr Diabetes Rep. (2007) 7:242–8. doi: 10.1007/s11892-007-0038-y
24. Kizub IV, Pavlova OO, Ivanova IV, Pavlova OO, Ivanova IV, Soloviev AI. Protein kinase C-dependent inhibition of BK(Ca) current in rat aorta smooth muscle cells following gamma-irradiation. Int J Radiat Biol. (2010) 86:291–9. doi: 10.3109/09553000903564042
25. Rojas M, Lemtalsi T, Toque HA, Xu Z, Fulton D, Caldwell RW, et al. NOX2-induced activation of arginase and diabetes-induced retinal endothelial cell senescence. Antioxid (Basel). (2017) 6:43. doi: 10.3390/antiox6020043
26. Shosha E, Xu Z, Narayanan SP, Lemtalsi T, Fouda AY, Rojas M, et al. Mechanisms of diabetes-induced endothelial cell senescence: role of arginase 1. Int J Mol Sci. (2018) 19:1215. doi: 10.3390/ijms19041215
27. Soetikno V, Sari FR, Sukumaran V, Lakshmanan AP, Mito S, Harima M, et al. Curcumin prevents diabetic cardiomyopathy in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats: possible involvement of PKC-MAPK signaling pathway. Eur J Pharm Sci. (2012) 47:604–14. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2012.04.018
28. Kuilman T, Michaloglou C, Vredeveld LC, Douma S, van Doorn R, Desmet CJ, et al. Oncogene-induced senescence relayed by an interleukin-dependent inflammatory network. Cell. (2008) 133:1019–31. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.03.039
29. Chen Y, Zhou B, Yu Z, Yuan P, Sun T, Gong J, et al. Baicalein alleviates erectile dysfunction associated with streptozotocin-induced type I diabetes by ameliorating endothelial nitric oxide synthase dysfunction, inhibiting oxidative stress and fibrosis. J Sex Med. (2020) 17:1434–47. doi: 10.1016/j.jsxm.2020.04.390
30. Redrow GP, Thompson CM, Wang R. Treatment strategies for diabetic patients suffering from erectile dysfunction: an update. Expert Opin Pharmacother. (2014) 15:1827–36. doi: 10.1517/14656566.2014.934809
31. Nehra A, Goldstein I, Pabby A, Nugent M, Huang YH, de las Morenas A, et al. Mechanisms of venous leakage: a prospective clinicopathological correlation of corporeal function and structure. J Urol. (1996) 156:1320–9. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(01)65578-2
32. Yan JF, Huang WJ, Zhao JF, Fu HY, Zhang GY, Huang XJ, et al. The platelet-derived growth factor receptor/STAT3 signaling pathway regulates the phenotypic transition of corpus cavernosum smooth muscle in rats. PloS One. (2017) 12:e0172191. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0172191
33. Chen S, Huang X, Kong X, Sun Z, Zhao F, Huang W, et al. Hypoxia-induced phenotypic transformation of corpus cavernosum smooth muscle cells after cavernous nerve crush injury by down-regulating P38 mitogen-activated protein kinase expression. Sex Med. (2019) 7:433–40. doi: 10.1016/j.esxm.2019.08.005
34. Suadicani SO, Urban-Maldonado M, Tar MT, Melman A, Spray DC. Effects of ageing and streptozotocin-induced diabetes on connexin43 and P2 purinoceptor expression in the rat corpora cavernosa and urinary bladder. BJU Int. (2009) 103:1686–93. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2008.08337.x
35. Zhang X, Kanika ND, Melman A, DiSanto ME. Smooth muscle myosin expression, isoform composition, and functional activities in rat corpus cavernosum altered by the streptozotocin-induced type 1 diabetes. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. (2012) 302:E32–42. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00231.2011
36. Awad H, Salem A, Gadalla A, El Wafa NA, Mohamed OA. Erectile function in men with diabetes type 2: correlation with glycemic control. Int J Impot Res. (2010) 22:36–9. doi: 10.1038/ijir.2009.39
37. Pozzo MJ, Mociulsky J, Martinez ET, Senatore G, Farias JM, Sapetti A, et al. Diabetes and quality of life: initial approach to depression, physical activity, and sexual dysfunction. Am J Ther. (2016) 23:e159–71. doi: 10.1097/01.mjt.0000433949.24277.19
38. Qinyu-Zeng, Shuhua-He, Fengzhi-Chen, Li-Wang, Liren-Zhong, Jialiang-Hui, et al. Administration of H(2)S improves erectile dysfunction by inhibiting phenotypic modulation of corpus cavernosum smooth muscle in bilateral cavernous nerve injury rats. Nitric Oxide. (2021) 107:1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2020.11.003
39. Wei AY, He SH, Zhao JF, liu Y, Liu Y, Hu YW, et al. Characterization of corpus cavernosum smooth muscle cell phenotype in diabetic rats with erectile dysfunction. Int J Impot Res. (2012) 24:196–201. doi: 10.1038/ijir.2012.16
40. Choi T, Lee JW, Kim SK, Yoo KH. Diabetes mellitus promotes smooth muscle cell proliferation in mouse ureteral tissue through the P-ERK/P-JNK/VEGF/PKC signaling pathway. Med (Kaunas). (2021) 57:560. doi: 10.3390/medicina57060560
41. Angulo J, Cuevas P, Fernandez A, Allona A, Moncada I, Martín-Morales A, et al. Enhanced thromboxane receptor-mediated responses and impaired endothelium-dependent relaxation in human corpus cavernosum from diabetic impotent men: role of protein kinase C activity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. (2006) 319:783–9. doi: 10.1124/jpet.106.108597
42. Liu Y, Drozdov I, Shroff R, Beltran LE, Shanahan CM. Prelamin A accelerates vascular calcification via activation of the DNA damage response and senescence-associated secretory phenotype in vascular smooth muscle cells. Circ Res. (2013) 112:e99–e109. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.111.300543
43. Houck KL, Fox TE, Sandirasegarane L, Kester M. Ether-linked diglycerides inhibit vascular smooth muscle cell growth via decreased MAPK and PI3K/Akt signaling. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. (2008) 295:H1657–68. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00141.2008
44. He S, Zhang T, Liu Y, Liu L, Zhang H, Chen F, et al. Myocardin restores erectile function in diabetic rats: phenotypic modulation of corpus cavernosum smooth muscle cells. Andrologia. (2015) 47:303–9. doi: 10.1111/and.2015.47.issue-3
45. Yang F, Zhao JF, Shou QY, Huang XJ, Chen G, Yang KB, et al. Phenotypic modulation of corpus cavernosum smooth muscle cells in a rat model of cavernous neurectomy. PloS One. (2014) 9:e105186. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0105186
46. Zhang Y, Yang J, Wang T, Wang SG, Liu JH, Yin CP, et al. Decreased endogenous hydrogen sulfide generation in penile tissues of diabetic rats with erectile dysfunction. J Sex Med. (2016) 13:350–60. doi: 10.1016/j.jsxm.2016.01.002
47. Zheng H, Sun W, Zhang Q, Zhang Y, Ji L, Liu X, et al. Proinflammatory cytokines predict the incidence of diabetic peripheral neuropathy over 5 years in Chinese type 2 diabetes patients: A prospective cohort study. EClinicalMedicine. (2021) 31:100649. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100649
48. Gur S, Hellstrom W. Harnessing stem cell potential for the treatment of erectile function in men with diabetes mellitus: from preclinical/clinical perspectives to penile tissue engineering. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. (2020) 15:308–20. doi: 10.2174/1574888X14666190828142045
49. Gaunay G, Nagler HM, Stember DS. Reproductive sequelae of diabetes in male patients. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. (2013) 42:899–914. doi: 10.1016/j.ecl.2013.07.003
50. Tamas V, Kempler P. Sexual dysfunction in diabetes. Handb Clin Neurol. (2014) 126:223–32. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-53480-4.00017-5
51. Sandireddy R, Yerra VG, Areti A, Komirishetty P, Kumar A. Neuroinflammation and oxidative stress in diabetic neuropathy: futuristic strategies based on these targets. Int J Endocrinol. (2014) 2014:674987. doi: 10.1155/2014/674987
52. Gur S, Peak TC, Kadowitz PJ, Sikka SC, Hellstrom WJ. Review of erectile dysfunction in diabetic animal models. Curr Diabetes Rev. (2014) 10:61–73. doi: 10.2174/1573399809666131126151024
53. Kizub IV, Klymenko KI, Soloviev AI. Protein kinase C in enhanced vascular tone in diabetes mellitus. Int J Cardiol. (2014) 174:230–42. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2014.04.117
54. Zychowska M, Rojewska E, Przewlocka B, Mika J. Mechanisms and pharmacology of diabetic neuropathy - experimental and clinical studies. Pharmacol Rep. (2013) 65:1601–10. doi: 10.1016/S1734-1140(13)71521-4
55. Mishra RK, Alokam R, Sriram D, Yogeeswari P. Potential role of Rho kinase inhibitors in combating diabetes-related complications including diabetic neuropathy–a review. Curr Diabetes Rev. (2013) 9:249–66. doi: 10.2174/1573399811309030006
56. Wu CH, Lu YY, Chai CY, Su YF, Tsai TH, Tsai FJ, et al. Increased risk of osteoporosis in patients with erectile dysfunction: A nationwide population-based cohort study. Med (Baltimore). (2016) 95:e4024. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000004024
57. Kuchakulla M, Narasimman M, Soni Y, et al. A systematic review and evidence-based analysis of ingredients in popular male testosterone and erectile dysfunction supplements. Int J Impot Res. (2021) 33:311–7. doi: 10.1038/s41443-020-0285-x
58. Agochukwu-Mmonu N, Malaeb BS, Hotaling JM, Braffett BH, Holt SK, Dunn RL, et al. Risk factors for orgasmic and concomitant erectile dysfunction in men with type 1 diabetes: a cross-sectional study. Int J Impot Res. (2021) 33:59–66. doi: 10.1038/s41443-020-0242-8
59. Cao J, Li J, Hao W, Li X, Wang H, Liu L, et al. Correlation of sex hormone and androgen receptor with diabetes mellitus in elderly men. Aging Male. (2011) 14:162–7. doi: 10.3109/13685538.2011.575479
60. Asaduzzaman M, Kamrul-Hasan AB, Islam A, Kabir MA, Chanda PK, Islam MA, et al. Frequency and risk factors of erectile dysfunction among Bangladeshi adult men with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Mymensingh Med J. (2020) 29:66–72. doi: 10.1016/s1530-891x(20)39448-9
61. Hackett G, Cole N, Saghir A, Jones P, Strange RC, Ramachandran S. Testosterone undecanoate improves sexual function in men with type 2 diabetes and severe hypogonadism: results from a 30-week randomized placebo-controlled study. BJU Int. (2016) 118:804–13. doi: 10.1111/bju.2016.118.issue-5
62. Tefekli A, Kandirali E, Erol B, Tunc M, Kadioglu A. Peyronie’s disease: a silent consequence of diabetes mellitus. Asian J Androl. (2006) 8:75–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-7262.2006.00099.x
63. Kendirci M, Trost L, Sikka SC, Hellstrom WJ. Diabetes mellitus is associated with severe Peyronie’s disease. BJU Int. (2007) 99:383–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2007.06611.x
64. Segundo A, Glina S. Prevalence, risk factors, and erectile dysfunction associated with peyronie’s disease among men seeking urological care. Sex Med. (2020) 8:230–6. doi: 10.1016/j.esxm.2019.11.002
65. Askari M, Mohamad MS, Bozorg M, Azizi R, Namiranian N. The prevalence of Peyronie’s disease in diabetic patients-2018-Yazd. Diabetes Metab Syndr. (2019) 13:604–7. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2018.11.039
66. Reheman A, Gao ZY, Tursun X, Pu XP, Wu T, He F, et al. Optimization of extraction technology of majun mupakhi ela and its effect on hydrocortisone-induced kidney yang deficiency in mice. Sci Rep. (2019) 9:4628. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-41006-6
67. Maquera-Afaray J, Cvetkovic-Vega A, Cárdenas MM, Kälviäinen H, Mejia CR. Late diagnosis and advanced disease of HIV in adult patients from a Peruvian social security hospital. Rev Chil Infectol. (2016) 33:20–6. doi: 10.4067/S0716-10182016000700003
68. Ragab A, Ahmed MH, Reda SA, EldinAbdelbary DAK, GamalEl Din SF. Serum nesfatin-1 level in men with diabetes and erectile dysfunction correlates with generalized anxiety disorder-7: A prospective comparative study. Andrology. (2023) 11:307–15. doi: 10.1111/andr.13237
69. Sun W, Bi LK, Xie DD, Yu DX. Serum nesfatin-1 is associated with testosterone and the severity of erectile dysfunction. Andrologia. (2020) 52:e13634. doi: 10.1111/and.13634
70. Grunberger G, Sherr J, Allende M, Blevins T, Bode B, Handelsman Y, et al. American association of clinical endocrinology clinical practice guideline: the use of advanced technology in the management of persons with diabetes mellitus. Endocr Pract. (2021) 27:505–37. doi: 10.1016/j.eprac.2021.04.008
71. Chinese Health Management Association C N S N. Expert consensus on the procedure of body weight management among patients with overweight or obesity (2021). Chin J Health Manage. (2021) 15:317–22. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115624-20210630-00368
72. Jakus V. The role of free radicals, oxidative stress and antioxidant systems in diabetic vascular disease. Bratisl Lek Listy. (2000) 101:541–51.
73. Várkonyi T, Putz Z, Keresztes K, Martos T, Lengyel C, Stirban A, et al. Current options and perspectives in the treatment of diabetic neuropathy. Curr Pharm Des. (2013) 19:4981–5007. doi: 10.2174/13816128113199990310
74. Zatalia SR, Sanusi H. The role of antioxidants in the pathophysiology, complications, and management of diabetes mellitus. Acta Med Indones. (2013) 45:141–7.
75. Mahmood D, Singh BK, Akhtar M. Diabetic neuropathy: therapies on the horizon. J Pharm Pharmacol. (2009) 61:1137–45. doi: 10.1211/jpp.61.09.0002
76. Pfützner A, Forst T. Pioglitazone: an antidiabetic drug with the potency to reduce cardiovascular mortality. Expert Opin Pharmacother. (2006) 7:463–76. doi: 10.1517/14656566.7.4.463
77. Li H, Gao T, Wang R. The role of the sexual partner in managing erectile dysfunction. Nat Rev Urol. (2016) 13:168–77. doi: 10.1038/nrurol.2015.315
78. Dean J, Rubio-Aurioles E, McCabe M, Eardley I, Speakman M, Buvat J, et al. Integrating partners into erectile dysfunction treatment: improving the sexual experience for the couple. Int J Clin Pract. (2008) 62:127–33. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-1241.2007.01636.x
79. Esposito K, Maiorino MI, Bellastella G, Giugliano F, Romano M, Giugliano D. Determinants of female sexual dysfunction in type 2 diabetes. Int J Impot Res. (2010) 22:179–84. doi: 10.1038/ijir.2010.6
80. Maiorino MI, Bellastella G, Esposito K. Lifestyle modifications and erectile dysfunction: what can be expected? Asian J Androl. (2015) 17:5–10. doi: 10.4103/1008-682X.137687
81. Defeudis G, Mazzilli R, Di Tommaso AM, Zamponi V, Carlomagno F, Tuccinardi D, et al. Effects of diet and antihyperglycemic drugs on erectile dysfunction: A systematic review. Andrology. (2023) 11:282–94. doi: 10.1111/andr.13192
82. Sahlender B, Windolf J, Suschek CV. Superoxide dismutase and catalase significantly improve the osteogenic differentiation potential of osteogenetically compromised human adipose tissue-derived stromal cells in vitro. Stem Cell Res. (2022) 60:102708. doi: 10.1016/j.scr.2022.102708
83. Trolle LY, Grotta A, Freyland S, Grannas D, Andersson DP. Risk of death in patients with coronary artery disease taking nitrates and phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2024) 83:417–26. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2023.10.041
84. Shon JH, Ku HY, Bae SY, Oh MK, Yeo CW, Bae SK, et al. The disposition of three phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors, vardenafil, sildenafil, and udenafil, is differently influenced by the CYP3A5 genotype. Pharmacogenet Genomics. (2011) 21:820–8. doi: 10.1097/FPC.0b013e32834b79e6
85. Rosner W, Auchus RJ, Azziz R, Sluss PM, Raff H. Position statement: Utility, limitations, and pitfalls in measuring testosterone: an Endocrine Society position statement. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2007) 92:405–13. doi: 10.1210/jc.2006-1864
86. Wang C, Nieschlag E, Swerdloff RS, Behre H, Hellstrom WJ, Gooren LJ, et al. ISA, ISSAM, EAU, EAA and ASA recommendations: investigation, treatment and monitoring of late-onset hypogonadism in males. Aging Male. (2009) 12:5–12. doi: 10.1080/13685530802389628
87. Morales A, Black A, Emerson L, Barkin J, Kuzmarov I, Day A. Androgens and sexual function: a placebo-controlled, randomized, double-blind study of testosterone vs. dehydroepiandrosterone in men with sexual dysfunction and androgen deficiency. Aging Male. (2009) 12:104–12. doi: 10.3109/13685530903294388
88. Jain P, Rademaker AW, McVary KT. Testosterone supplementation for erectile dysfunction: results of a meta-analysis. J Urol. (2000) 164:371–5. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(05)67363-6
89. Hatzimouratidis K, Hatzichristou DG. A comparative review of the options for treatment of erectile dysfunction: which treatment for which patient? Drugs. (2005) 65:1621–50. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200565120-00003
90. Guillen V, Rueda JR, Lopez-Argumedo M, Solà I, Ballesteros J. Apomorphine for the treatment of erectile dysfunction: systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Sex Behav. (2020) 49:2963–79. doi: 10.1007/s10508-020-01817-5
91. Aboulghasemi N, Hadipour JM, Ghasemi A. Anti-dyskinetic efficacy of 5-HT3 receptor antagonist in the hemi-parkinsonian rat model. IBRO Rep. (2019) 6:40–4. doi: 10.1016/j.ibror.2018.12.001
92. Myers A, Barrueto FJ. Refractory priapism associated with ingestion of yohimbe extract. J Med Toxicol. (2009) 5:223–5. doi: 10.1007/BF03178272
93. Phan JA, Landau AM, Wong DF, Jakobsen S, Nahimi A, Doudet DJ, et al. Quantification of [(11)C]yohimbine binding to α2 adrenoceptors in rat brain in vivo. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. (2015) 35:501–11. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2014.225
94. Fink HA, MacDonald R, Rutks IR, Wilt TJ. Trazodone for erectile dysfunction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BJU Int. (2003) 92:441–6. doi: 10.1046/j.1464-410X.2003.04358.x
95. Teply RM, Packard KA, White ND, Hilleman DE, DiNicolantonio JJ. Treatment of depression in patients with concomitant cardiac disease. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. (2016) 58:514–28. doi: 10.1016/j.pcad.2015.11.003
96. Coupland N, Wilson S, Nutt D. Antidepressant drugs and the cardiovascular system: a comparison of tricylics and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and their relevance for the treatment of psychiatric patients with cardiovascular problems. J Psychopharmacol. (1997) 11:83–92. doi: 10.1177/026988119701100118
97. Ückert S, Bannowsky A, Albrecht K, Kuczyk MA. Melanocortin receptor agonists in the treatment of male and female sexual dysfunctions: results from basic research and clinical studies. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. (2014) 23:1477–83. doi: 10.1517/13543784.2014.934805
98. Perimenis P, Konstantinopoulos A, Perimeni P, Gyftopoulos K, Kartsanis G, Liatsikos E, et al. Long-term treatment with intracavernosal injections in diabetic men with erectile dysfunction. Asian J Androl. (2006) 8:219–24. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-7262.2006.00095.x
99. Williams G, Abbou CC, Amar ET, Desvaux P, Flam TA, Lycklama Nijeholt GA, et al. Efficacy and safety of transurethral alprostadil therapy in men with erectile dysfunction. MUSE Study Group Br J Urol. (1998) 81:889–94. doi: 10.1046/j.1464-410x.1998.00703.x
100. Avant RA, Ziegelmann M, Nehra A, Alom M, Kohler T, Trost L. Penile traction therapy and vacuum erection devices in peyronie’s disease. Sex Med Rev. (2019) 7:338–48. doi: 10.1016/j.sxmr.2018.02.005
101. Pahlajani G, Raina R, Jones S, Ali M, Zippe C. Vacuum erection devices revisited: its emerging role in the treatment of erectile dysfunction and early penile rehabilitation following prostate cancer therapy. J Sex Med. (2012) 9:1182–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1743-6109.2010.01881.x
102. Spivak L, Shultz T, Appel B, Verze P, Yagudaev D, Vinarov A, et al. Low-intensity extracorporeal shockwave therapy for erectile dysfunction in diabetic patients. Sex Med Rev. (2021) 9:619–27. doi: 10.1016/j.sxmr.2019.06.007
103. Lu Z, Lin G, Reed-Maldonado A, Wang C, Lee YC, Lue TF. Low-intensity extracorporeal shock wave treatment improves erectile function: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Urol. (2017) 71:223–33. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2016.05.050
104. Mason MM, Pai RK, Masterson JM, Lokeshwar SD, Chu KY, Ramasamy R. Low-intensity extracorporeal shockwave therapy for diabetic men with erectile dysfunction: A systematic scoping review. Andrology. (2023) 11:270–81. doi: 10.1111/andr.13197
105. Leighton R, Watson JT, Giannoudis P, Papakostidis C, Harrison A, Steen RG. Healing of fracture nonunions treated with low-intensity pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS): A systematic review and meta-analysis. Injury. (2017) 48:1339–47. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2017.05.016
106. Lei H, Xin H, Guan R, Xu Y, Li H, Tian W, et al. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound improves erectile function in streptozotocin-induced type I diabetic rats. Urology. (2015) 86:1211–41. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2015.07.026
107. Muncey W, Sellke N, Kim T, Mishra K, Thirumavalavan N, Loeb A. Alternative treatment for erectile dysfunction: a growing arsenal in men’s health. Curr Urol Rep. (2021) 22:11. doi: 10.1007/s11934-020-01023-9
108. Bettocchi C, Palumbo F, Spilotros M, Lucarelli G, Palazzo S, Battaglia M, et al. Patient and partner satisfaction after AMS inflatable penile prosthesis implant. J Sex Med. (2010) 7:304–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1743-6109.2009.01499.x
109. Selph JP, Carson CR. Penile prosthesis infection: approaches to prevention and treatment. Urol Clin North Am. (2011) 38:227–35. doi: 10.1016/j.ucl.2011.02.007
110. Munarriz R, Thirumavalavan N, Gross MS. Is there a role for vascular surgery in the contemporary management of erectile dysfunction? Urol Clin North Am. (2021) 48:543–55. doi: 10.1016/j.ucl.2021.07.00
111. Sun JM, Liu P, Mao JM, Dong Z, Liang GQ, Han WJ, et al. Clinical observation of Chinese medicine negative pressure suction in treating impotence of kidney-yangdeficiency type. Chin J Hum Sexuality. (2019) 28:117–9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1993.2019.03.034
112. Huang XK. Correlation study of negative pressure aspiration combined with traditional Chinese medicine lavage in the treatment of erectile dysfunction in diabetic patients with kidney deficienc. J North Pharm. (2016) 13:85–6.
113. Jeong HC, Bae WJ, Zhu GQ, Jeon SH, Choi SW, Kim SJ, et al. Synergistic effects of extracorporeal shockwave therapy and modified Ojayeonjonghwan on erectile dysfunction in an animal model of diabetes. Investig Clin Urol. (2019) 60:285–94. doi: 10.4111/icu.2019.60.4.285
114. Zhou Y, Chen S, Zhang D, Lu H, Yao W, Jiang W, et al. The efficacy and safety of acupuncture in the treatment of erectile dysfunction: A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis. Med (Baltimore). (2021) 100:e25892. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000025892
115. Cui Y, Feng Y, Chen L, Zhou Y, Yang XQ, He J, et al. Randomized and controlled research of Chinese drug acupoint injection therapy for erectile dysfunction. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. (2007) 27:881–5.
116. Luo DS, Li YQ, Deng ZQ, Liu GH. Progress and prospect of stem cell therapy for diabetic erectile dysfunction. World J Diabetes. (2021) 12:2000–10. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v12.i12.2000
117. Yang Q, Chen W, Zhang C, Xie Y, Gao Y, Deng C, et al. Combined transplantation of adipose tissue-derived stem cells and endothelial progenitor cells improve diabetic erectile dysfunction in a rat model. Stem Cells Int. (2020) 2020:2154053. doi: 10.1155/2020/2154053
118. Shan HT, Zhang HB, Chen WT, Chen FZ, Wang T, Luo JT, et al. Combination of low-energy shock-wave therapy and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation to improve the erectile function of diabetic rats. Asian J Androl. (2017) 19:26–33. doi: 10.4103/1008-682X.184271
119. Bahk JY, Jung JH, Han H, Min SK, Lee YS. Treatment of diabetic impotence with umbilical cord blood stem cell intracavernosal transplant: preliminary report of 7 cases. Exp Clin Transplant. (2010) 8:150–60.
120. Ibraheem D, Elaissari A, Fessi H. Gene therapy and DNA delivery systems. Int J Pharm. (2014) 459:70–83. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2013.11.041
121. Bivalacqua TJ, Usta MF, Champion HC, Adams D, Namara DB, Abdel-Mageed AB, et al. Gene transfer of endothelial nitric oxide synthase partially restores nitric oxide synthesis and erectile function in streptozotocin diabetic rats. J Urol. (2003) 169:1911–7. doi: 10.1097/01.ju.0000051881.14239.4a
122. Wang T, Li M, Yuan H, Zhan Y, Xu H, Wang S, et al. saRNA guided iNOS up-regulation improves erectile function of diabetic rats. J Urol. (2013) 190:790–8. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2013.03.043
123. Bennett NE, Kim JH, Wolfe DP, Sasaki K, Yoshimura N, Goins WF, et al. Improvement in erectile dysfunction after neurotrophic factor gene therapy in diabetic rats. J Urol. (2005) 173:1820–4. doi: 10.1097/01.ju.0000158056.66236.1f
124. Lu J, Xin Z, Zhang Q, Cui D, Xiao Y, Zhuo J, et al. Beneficial effect of PEDF-transfected ADSCs on erectile dysfunction in a streptozotocin-diabetic rat model. Cell Tissue Res. (2016) 366:623–37. doi: 10.1007/s00441-016-2494-7
125. Pu XY, Wen AM, Zheng XG, Liu JM, Zhou XX, Xu ZP, et al. Insulin-like growth factor-1 gene therapy improves the levels of mRNA and protein of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in aging related erectile dysfunction in rats. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. (2012) 92:128–30. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2012.02.015
126. Liu G, Sun X, Bian J, Wu R, Guan X, Ouyang B, et al. Correction of diabetic erectile dysfunction with adipose derived stem cells modified with the vascular endothelial growth factor gene in a rodent diabetic model. PloS One. (2013) 8:e72790. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0072790
127. Gou X, He WY, Xiao MZ, Qiu M, Wang M, Deng YZ, et al. Transplantation of endothelial progenitor cells transfected with VEGF165 to restore erectile function in diabetic rats. Asian J Androl. (2011) 13:332–8. doi: 10.1038/aja.2010.116
128. Christ GJ, Day N, Santizo C, Sato Y, Zhao W, Sclafani T, et al. Intracorporal injection of hSlo cDNA restores erectile capacity in STZ-diabetic F-344 rats in vivo. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. (2004) 287:H1544–53. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00792.2003
129. Liu T, Peng Y, Jia C, Fang X, Li J, Zhong W. Hepatocyte growth factor-modified adipose tissue-derived stem cells improve erectile function in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Growth Factors. (2015) 33:282–9. doi: 10.3109/08977194.2015.1077825
130. Shen ZJ, Wang H, Lu YL, Zhou XL, Chen SW, Chen ZD. Gene transfer of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide into the penis improves erectile response in the diabetic rat. BJU Int. (2005) 95:890–4. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2005.05422.x
131. Zhu LL, Zhang Z, Jiang HS, Chen H, Chen Y, Dai YT, et al. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle targeting of adipose tissue-derived stem cells in diabetes-associated erectile dysfunction. Asian J Androl. (2017) 19:425–32. doi: 10.4103/1008-682X.179532
132. Han G, Tar M, Kuppam DS, Friedman A, Melman A, Friedman J, et al. Nanoparticles as a novel delivery vehicle for therapeutics targeting erectile dysfunction. J Sex Med. (2010) 7:224–33. doi: 10.1111/j.1743-6109.2009.01507.x
133. Yan H, Rong L, Xiao D, Zhang M, Sheikh SP, Sui X, et al. Injectable and self-healing hydrogel as a stem cells carrier for treatment of diabetic erectile dysfunction. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. (2020) 116:111214. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2020.111214
134. Draganski A, Tar MT, Villegas G, Friedman JM, Davies KP. Topically applied curcumin-loaded nanoparticles treat erectile dysfunction in a rat model of type-2 diabetes. J Sex Med. (2018) 15:645–53. doi: 10.1016/j.jsxm.2018.03.009
135. Venneri MA, Barbagallo F, Fiore D, De Gaetano R, Giannetta E, Sbardella E, et al. PDE5 Inhibition stimulates tie2-expressing monocytes and angiopoietin-1 restoring angiogenic homeostasis in diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2019) 104(7):2623–36. doi: 10.1210/jc.2018-02525
136. Melehan KL, Hoyos CM, Hamilton GS, Wong KK, Yee BJ, McLachlan RI, et al. Randomized trial of CPAP and vardenafil on erectile and arterial function in men with obstructive sleep apnea and erectile dysfunction. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2018) 103(4):1601–11. doi: 10.1210/jc.2017-02389
137. Tan HM, Chin CM, Chua CB, Gatchalian E, Kongkanand A, Moh CL, et al. Efficacy and tolerability of vardenafil in Asian men with erectile dysfunction. Asian J Androl. (2008) 10(3):495–502. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-7262.2008.00388.x
138. Cui H, Liu B, Song Z, Fang J, Deng Y, Zhang S, et al. Efficacy and safety of long-term tadalafil 5 mg once daily combined with sildenafil 50 mg as needed at the early stage of treatment for patients with erectile dysfunction. Andrologia. (2014) 47(1):20–4. doi: 10.1111/and.12216
139. Mulhall JP, Bukofzer S, Edmonds AL, George M; Apomorphine SL Study Group. An open-label, uncontrolled dose-optimization study of sublingual apomorphine in erectile dysfunction. Clin Ther. (2001) 23(8):1260–71. doi: 10.1016/s0149-2918(01)80105-3
140. Bloomer RJ, Schriefer JM, Gunnels TA. Clinical safety assessment of oral higenamine supplementation in healthy, young men. Hum Exp Toxicol. (2015) 34(10):935–45. doi: 10.1177/0960327114565490
141. Lee SR, Schriefer JM, Gunnels TA, Harvey IC, Bloomer RJ. Acute oral intake of a higenamine-based dietary supplement increases circulating free fatty acids and energy expenditure in human subjects. Lipids Health Dis. (2013) 12(148). doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-12-148
142. Goyal P, Kattula D, Rao R, Bhad R, Mishra AK, Dhawan A. Trazodone for sleep disturbance in opioid dependent patients maintained on buprenorphine: a double blind, placebo-controlled trial. Drug Alcohol Depen. (2023) 250(110891). doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2023.110891
Keywords: diabetes mellitus erectile dysfunction, pathological mechanisms, treatment strategies, interdisciplinary approach, clinical implications
Citation: Ma J, Chen Y, Si Y, Qian J, Wang C, Jin J and He Q (2024) The multifaceted nature of diabetic erectile dysfunction: uncovering the intricate mechanisms and treatment strategies. Front. Endocrinol. 15:1460033. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1460033
Received: 05 July 2024; Accepted: 07 October 2024;
Published: 08 November 2024.
Edited by:
Carmine Gazzaruso, University of Milan, ItalyReviewed by:
Giovanni Luca, University of Perugia, ItalyWenchao Xu, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, China
Copyright © 2024 Ma, Chen, Si, Qian, Wang, Jin and He. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Qiang He, cWlhbmdoZTE5NzNAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Juan Jin, bGFuZ18wMThAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Jianxiong Ma1,2
Jianxiong Ma1,2 Yihao Chen
Yihao Chen Juan Jin
Juan Jin