- 1Department of Pharmacy, The Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, Qingdao, China
- 2Department of Human Resource, The Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, Qingdao, China
- 3Department of Urology, The Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, Qingdao, China
The tumor suppressor p53 is a transcription factor involved in a variety of crucial cellular functions, including cell cycle arrest, DNA repair and apoptosis. Still, a growing number of studies indicate that p53 plays multiple roles in spermatogenesis, as well as in the occurrence and development of male infertility. The representative functions of p53 in spermatogenesis include the proliferation of spermatogonial stem cells (SSCs), spermatogonial differentiation, spontaneous apoptosis, and DNA damage repair. p53 is involved in various male infertility-related diseases. Innovative therapeutic strategies targeting p53 have emerged in recent years. This review focuses on the role of p53 in spermatogenesis and male infertility and analyses the possible underlying mechanism involved. All these conclusions may provide a new perspective on drug intervention targeting p53 for male infertility treatment.
1 Introduction
Infertility is defined as the failure to conceive after 12 months or more of regular, unprotected sexual intercourse (1). Infertility is a major health problem and social challenge, particularly in an era of low fertility and an aging society (2). The incidence of infertility is estimated to be 12.6%-17.5% among reproductive-aged couples worldwide, and males are responsible for approximately half of all infertility problems (3). In recent years, the increasing prevalence of male infertility has attracted global attention. An analysis of the Global Burden of Disease (GBD) 2019 showed that the global prevalence of male infertility increased significantly, by 76.9%, from 1990 to 2019, along with a steady growth trend in the global burden of male infertility diseases (4). Multiple studies have shown worldwide decreases in sperm counts (5–7). A recent systematic review by Levine et al. (8) revealed that the total sperm count declined by 62.3% between 1973 and 2018, and this decrease has accelerated since 2000. Various causes involved in male infertility have been discussed, mainly including congenital factors (e.g., genetic abnormalities, congenital bilateral absence of the vas deferens, and cryptorchidism), acquired factors (e.g., varicocele, testicular torsion, and genital inflammation), and idiopathic risk factors (e.g., smoking, obesity, and aging) (9). Although significant progress has been made within the past few decades, a considerable proportion of cases of male infertility are diagnosed as idiopathic or unexplained, which means that the underlying mechanisms have not yet been revealed (10). There has also been little progress in drug therapy in the past decade (11). Although the use of assisted reproductive technology (ART) can bring dawn to infertile men, it is not always a panacea, and its safety has been questioned because of comorbidities in the offspring (12). Therefore, research on male infertility has become a global endeavor.
The tumor suppressor protein p53, encoded by TP53 in human and by Tp53 in mice, is a vital regulator of the cellular stress response and a crucial controller of cell fate (13). p53 contains five domains: (1) the transactivation domain (TAD), which is responsible for gene transcription; (2) the proline-rich domain (PRD), which is crucial for p53 stability; (3) the DNA-binding domain (DBD), which is required for DNA binding activity; (4) the tetramerization domain (TD), which is needed for tetramerization of p53; and (5) the C-terminal domain, which is responsible for regulating the binding activity between p53 and the DBD and is influenced by posttranslational modifications (PTMs) of p53 (14). Among these modifications, phosphorylation and acetylation stabilize p53 and increase transcriptional activation, while the effect of methylation on p53 transcriptional activity varies with lysine residues (15). Under physiological conditions, p53 is maintained at a low level mainly due to E3 ligase Mdm2-mediated ubiquitin-mediated degradation. Under stress conditions, p53 can be activated by PTMs or reduced degradation (16). As a transcription factor, p53 is involved in a variety of crucial cellular functions, including cell cycle arrest, DNA repair, apoptosis, autophagy, senescence, and oxidative stress (14).
Multiple studies have shown that p53 is closely related to many developmental disorders or diseases, such as stem cell differentiation, cancer, and cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases (17–19). In recent years, abundant evidence has indicated the crucial role of p53 in spermatogenesis and the pathogenesis of male infertility (20, 21). Excitingly, p53 has proven to be druggable, and efforts toward the development of p53-based therapy are emerging (22). Therefore, we summarized the roles of p53 in spermatogenesis and the mechanisms of p53 in male infertility diseases, which may provide new strategies for male infertility therapies.
2 p53 and spermatogenesis
Spermatogenesis is a unique and complex cell cycle process that is characterized by fine regulation to ensure high-fidelity transmission of genetic material (23). Three stages are involved in spermatogenesis (Figure 1): spermatogonial stem cells (SSCs) differentiate into spermatocytes via mitotic proliferation, spermatocytes transform into spermatids via meiotic division, and spermatids differentiate into spermatozoa (24). p53 appears to be indispensable for normal spermatogenesis, a process that includes a great deal of DNA replication and DNA packaging (25). Here, we clarified the role of p53 in spermatogenesis (Figure 1).
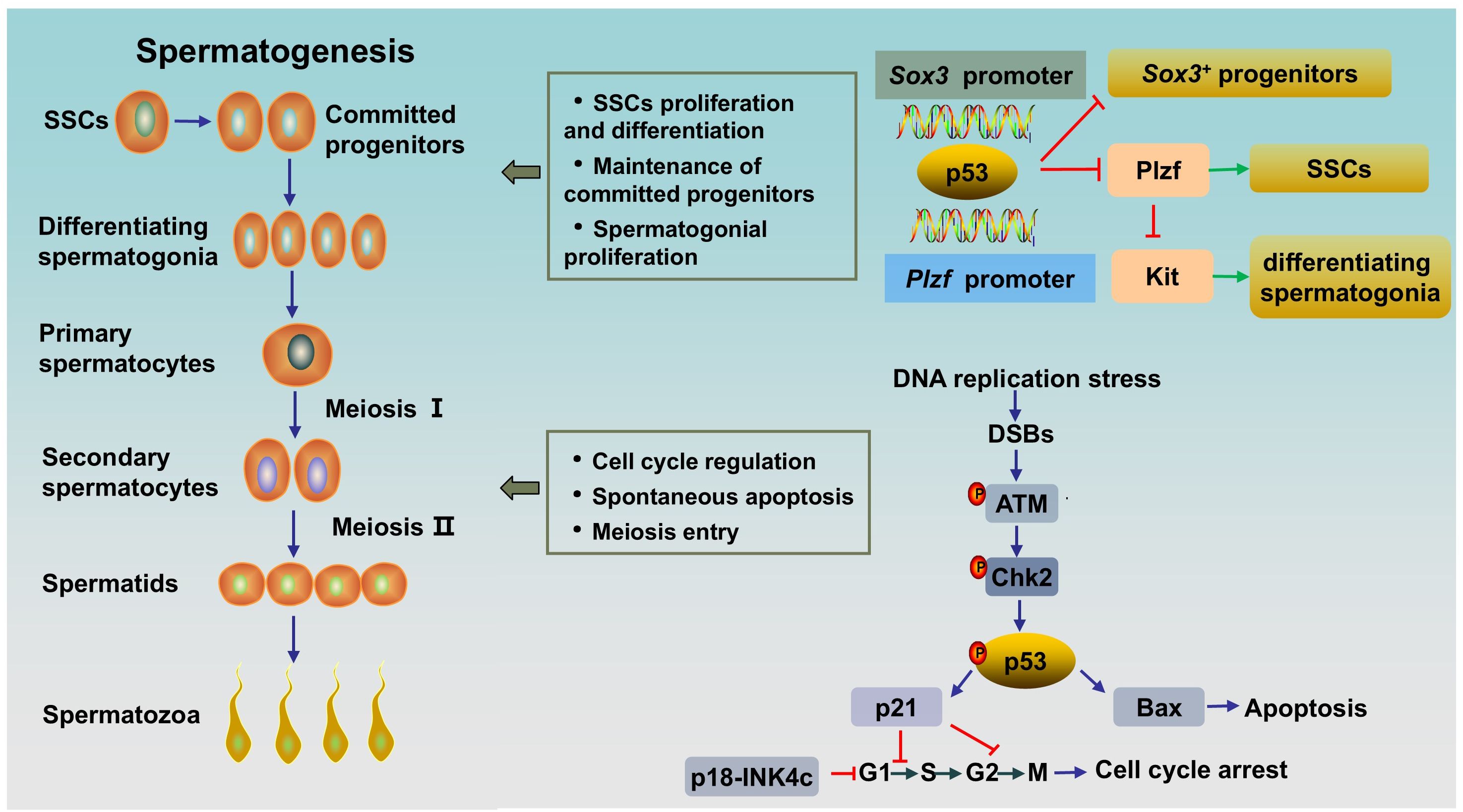
Figure 1. The role of p53 in rodent spermatogenesis. SSCs differentiate into progenitor cells, and the latter subsequently differentiate into differentiating spermatogonia. Differentiating spermatogonia differentiate into spermatocytes, and spermatocytes produce spermatids via meiotic division. Afterwards, round spermatids undergo maturation via spermiogenesis to form spermatozoa. Activated p53 can bind to the Plzf promoter and the Sox3 promoter to negatively regulate Plzf and Sox3, leading to a reduction in the number of Plzf+ SSCs and Sox3+ progenitor spermatogonia. During normal spermatogenesis, ATM/p53/Bax pathway or ATM/p53/p21 pathway are activated in DNA-damaged germ cells to induce spontaneous apoptosis or cell cycle arrest, respectively. SSCs, spermatogonial stem cells; DSBs, DNA double-strand breaks.
2.1 The role of p53 in spermatogonia
The maintenance of spermatogenesis throughout the male’s lifetime relies on SSCs, which possess the ability to self-renew and differentiate into committed spermatogonial progenitor cells (SPCs) (26). SSCs are undifferentiated spermatogonia and a heterogeneous population. In rodent testes, SSCs can be subdivided into Asingle (As), Apaired (Apr) and Aaligned (Aal) spermatogonia and can be distinguished by several genes, including Ngn3, Sox3, Gfrα1 and Plzf (27). Gfrα1+ cells (mainly As, Apr, and some Aal) are stem cells that can transform into Ngn3/Sox3+ (mainly Aal and some Apr) committed SPCs. The latter differentiate into differentiating spermatogonia (type A1-A4, intermediate spermatogonia, type B), thereby entering meiosis after undergoing rapid mitotic division (28). PLZF (As, Apr, and Aal), whose key function is to maintain an undifferentiated state by directly repressing the expression of Kit, a hallmark of spermatogonial differentiation, is crucial for the self-renewal of SSCs (29, 30). By contrast, human testes contain two types of distinct A spermatogonia, identified as Adark and Apale, based on nuclear morphology. Apale are characterized by self-renewal and regular proliferation, while Adark are slow cycling. There are 5 transit amplifying divisions in humans form Adark/Apale undifferentiated spermatogonia to terminally differentiated sperm, while 12 transit amplifying divisions exist in rodents from As spermatogonia to terminally differentiated sperm. However, the larger pool of stem/progenitor cells partly compensates for fewer transit-amplifying cell divisions in human testis. Markers of undifferentiated spermatogonia in human also include GFRa1 and PLZF. And cKIT is a marker of differentiated spermatogonia in human testes, too (31).
It has been proven that p53 has multiple effects on spermatogonia. First, p53 has been shown to participate in the regulation of SSC proliferation and spermatogonial differentiation by regulating PLZF. Increased p53 can bind to the Plzf promoter and negatively regulate Plzf, leading to a reduction in Plzf expression and the number of Plzf+ SSCs in mouse testes, resulting in a decrease in male fertility (32). Interestingly, it has been reported that PLZF could also act as a transcription repressor to decrease p53 levels by inhibiting TP53 transcription and promoting the ubiquitination and degradation of p53 in several cell lines (33). The interaction between the two proteins might indicate the fine regulation of p53 in spermatogenesis. Second, p53 plays an important role in the maintenance of SPCs. A study showed that Csnk1a1, the gene encoded Casein kinase I isoform alpha (CKI-α), knockout accelerated nuclear p53 protein expression by disrupting Mdm2-mediated p53 ubiquitination in mouse spermatogonia. Subsequently, activated p53 negatively regulates Sox3 by binding to the Sox3 promoter, resulting in decreased Sox3+ progenitor spermatogonia, blocked meiosis, and ultimately male infertility. As expected, the p53 inhibitor pifithrin-α partially rescued spermatogenesis in CKI-α-null mice (34). Finally, p53 has been shown to play a role in spermatogonial proliferation and apoptosis. Germ cells expand through mitosis, and p53-mediated apoptosis maintains germline homeostasis. Increased production of differentiating type spermatogonia and decreased clearance of lethally damaged differentiating type spermatogonia can be observed in Tp53 knockout C57BL/6 mouse testes, indicating the key role of p53 in the regulation of cell proliferation and apoptosis in normal spermatogonia (35). Mechanistically, accelerated p53 ubiquitination-mediated degradation and reduced p53 activity result in a decrease in target molecules cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21 and apoptosis regulator Bax levels, and an increase in Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (CDK1) level, thereby accelerating the G2/M phase transition, inhibiting apoptosis and promoting spermatogonial proliferation (36). However, inconsistent results exist. A study by Dai et al. (25) revealed a normal and unaffected undifferentiated spermatogonial population and SSC proliferation rate, accompanied by elevated spermatocyte death and testicular atrophy in Tp53 knockout rats on a Sprague-Dawley background. This inconsistency may be related to the different genetic backgrounds of the animals. In addition, p53 and cyclin-dependent kinase 4 inhibitor C (p18-INK4c, encoded by Cdkn2c in mice) collaborate to control the time from the mitosis phase to meiosis in spermatogonia. p18-INK4c acts as a negative regulator of the cell cycle at the early G1 phase (37). A study has shown that Cdkn2c/Tp53 double knockout mice displayed higher percentage of PCNA (a marker of proliferation expressed in S phase) -positive tubules compared with that in wild type and Cdkn2c-null mice, which indicated Cdkn2c/Tp53 double knockout mice existed active proliferation and continuation of the mitosis phase in spermatogonia, and thus a delay in meiosis entry (20). Besides, in this study, Cdkn2c null mice showed a significantly increased sperm counts as compared to Tp53 null or wild type, while Cdkn2c/Tp53 double knockout mice had much lower sperm counts, which might attributed to the increased apoptosis induced by DNA damage secondary to prolongation of meiosis entry (20). Overall, p53 plays an important role in the differentiation, proliferation, apoptosis and cell cycle regulation of SSCs and spermatogonia.
2.2 The role of p53 in spermatocytes
A1-type spermatogonia are transformed into preleptotene spermatocytes after six divisions and subsequently enter meiosis (38). After meiotic prophase, a prolonged G2 phase that allows a series of chromosome events with active genetic recombination, primary spermatocytes undergo meiosis I to form secondary spermatocytes (39). Subsequently, secondary spermatocytes undergo meiosis II to produce spermatids. The meiosis process can be divided into the following steps: DNA replication, crossover recombination, reductional division and equational division (40). Notably, meiosis is accompanied by DNA replication, DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) and DNA damage repair (41). Consequently, fine control to maintain genomic stability and prevent mutagenesis is needed to avoid meiotic defects.
As the guardian of the genome, p53 appears to be duty-bound to respond to DNA damage during spermatogenesis. In contrast to those in other tissues, p53 levels are significantly greater in the testis. The expression of p53 is observed in the spermatogonium stage, peaks in primary spermatocytes, and slightly decreases in the sperm stage, which is consistent with DNA damage and recombination repair in the meiotic process (42). The high level of p53 in primary spermatocytes emphasizes its role in DNA repair at low DNA damage-dependent premeiotic checkpoints (43). Indeed, failure to resolve DSBs in leptotene and zygotene spermatocytes in Tp53 knockout mice prior to synapsis leads to increased spermatocyte death and testis atrophy (25). Ataxia-telangiectasia mutated protein (ATM) acts as a sensor of DSBs. As an upstream regulator, activated ATM stabilizes p53 through direct or indirect phosphorylation by activating checkpoint kinase 2 (CHK2) (44). The response of activated p53 to damaged DNA is bidirectional. On the one hand, for repairable DNA damage, activated p53 can initiate cell cycle arrest via the downstream target p21, which arrests the cell cycle in G1/S or G2/M, to provide time for correcting DNA damage to promote cell entry into the next normal cell cycle (45). On the other hand, for DNA damage beyond cell repair, p53 induces apoptosis by activating proapoptotic factors (e.g., Bax and Caspase3) and inhibiting the antiapoptotic factor B-cell lymphoma-2 (Bcl-2) (44, 46).
Previous studies have shown that the level of p53 is the key factor that determines whether a cell undergoes growth arrest or apoptosis; that is, low p53 levels lead to growth arrest, while increased p53 levels result in apoptosis (47). Thus, the level of p53 must be precisely regulated. The Cullin-RING E3 ubiquitin ligase (CRL) is an ubiquitin ligase complex that can recognize substrates and then ubiquitinate and degrade them (48). CRL4 is a member of CRL family, which consists of Cullin4, a RING finger and DNA damage binding protein 1 (DDB1)-Cullin4 associated substrate receptors (49). CRL4 is involved in regulating the level of p53 to determine whether p53 induces growth arrest during spermatogenesis (42). It has been reported that Cullin4 promotes p53 ubiquitin degradation, followed by p21 transcriptional inactivation (46). Furthermore, p21 is also a substrate of Cullin. Inactivating the CRL E3 ligase by MLN4924, an inhibitor of Cullin neddylation, results in p21 accumulation. Interestingly, Cullin4, p53 and p21 exhibit similar expression patterns and intensities during spermatogenesis, and they are all highly expressed in primary spermatocytes (42). These findings indicate the critical role of Cullin4 in maintaining p53 homeostasis in primary spermatocytes.
2.3 p53 and germ cell death in spermatogenesis
The apoptosis of germ cells is a normal phenomenon in spermatogenesis and has been widely observed in SSCs, spermatogonia, spermatocytes and spermatids. Approximately 75% of germ cells will undergo spontaneous apoptosis (35). Spontaneous apoptosis occurs in all types of human male germ cells (50). The physiological significance of spontaneous apoptosis is, on the one hand, maintaining the appropriate number of sperm cells to adapt to the limited support capacity of Sertoli cells and, on the other hand, eliminating abnormal germ cells (51). Indeed, p53-mediated germ cell apoptosis is a crucial quality control mechanism. Multiple studies have shown that p53 overexpression or underexpression can impair spermatogenesis (Table 1). p53 eliminates DNA-damaged germ cells during normal spermatogenesis by inducing apoptosis, especially during the progression of meiosis, as we described in Section 2.2. Tp53 knockout (Tp53-/-) mice exhibit decreased spontaneous apoptosis and increased germ numbers, along with an increased percentage of defective sperm and decreased fertility (56). In addition to spontaneous apoptosis, spermatogenesis also involves programmed necroptosis (57). A study by Napoletano et al. (52) have shown that p53 is required to regulate programmed necrosis in spermatogonia during Drosophila spermatogenesis to control germ cell number under physiological conditions. Furthermore, blocking this process can lead to hyperplasia of the Drosophila testes. However, spontaneous germ cell necrosis takes place very sporadically in the testes of wild type or Tp53-/- mutant mice at 6-8 weeks of age (52).
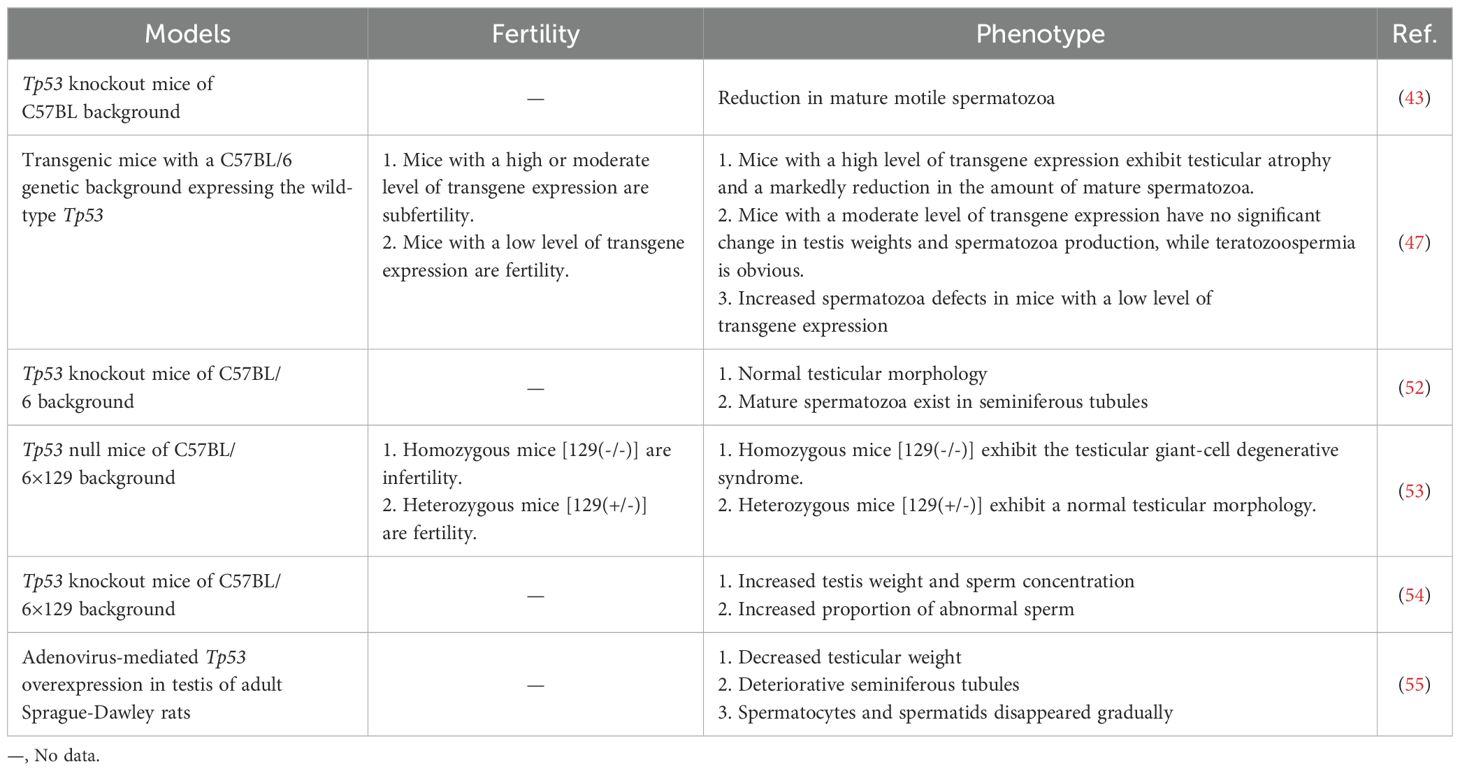
Table 1. Several phenotypes associated with spermatogenesis and function caused by Tp53 genomic knockout or overexpression.
In addition, p53-mediated cell death is important for the response to adverse external stimuli. After irradiation, germ cell death in wild-type rat testes increased. However, there was no significant difference in the germ cell apoptotic response between irradiated or unirradiated Tp53 knockout rats, which suggested that radiation-induced germ cell apoptosis is p53 dependent (25). Similarly, exposure to Ti3C2 nanosheets, a type of 2D nanomaterial, led to increased oxidative DNA damage and subsequent irreversible apoptosis mediated by the ATM/p53 signaling pathway in spermatogonia (58). Additionally, heat induced programmed necrosis in mouse testes is p53-dependent. Germ cell programmed necrosis was induced after heat shock at 42°C for 30 min, while Tp53-/- male mice were resistant to heat-induced necrosis (52).
Taken together, p53-dependent apoptosis and germ cell necroptosis are essential for maintaining appropriate sperm counts and ensuring sperm quality, which ensures successful spermatogenesis progression.
3 Signaling pathways of p53 in infertility
3.1 p53, oxidative stress and infertility
Oxidative stress, which occurs when the antioxidant defense system fails to eliminate reactive oxygen species (ROS), is considered a primary cause of male infertility. A meta-analysis of 65 studies (3819 male infertility patients and 2012 controls) revealed elevated oxidative stress markers and decreased antioxidant defense in seminal plasma from patients with infertility (59). ROS are a kind of normal metabolic byproducts. An appropriate amount of ROS participates in several important physiological processes, including capacitation, hyperactivation and the acrosome reaction. Excessive ROS damage male reproduction via mechanisms related to lipid peroxidation, DNA damage, protein oxidation and mitochondrial dysfunction, leading to decreased reproductive capacity (60). p53 is involved in oxidative stress through several mechanisms (Figure 2).
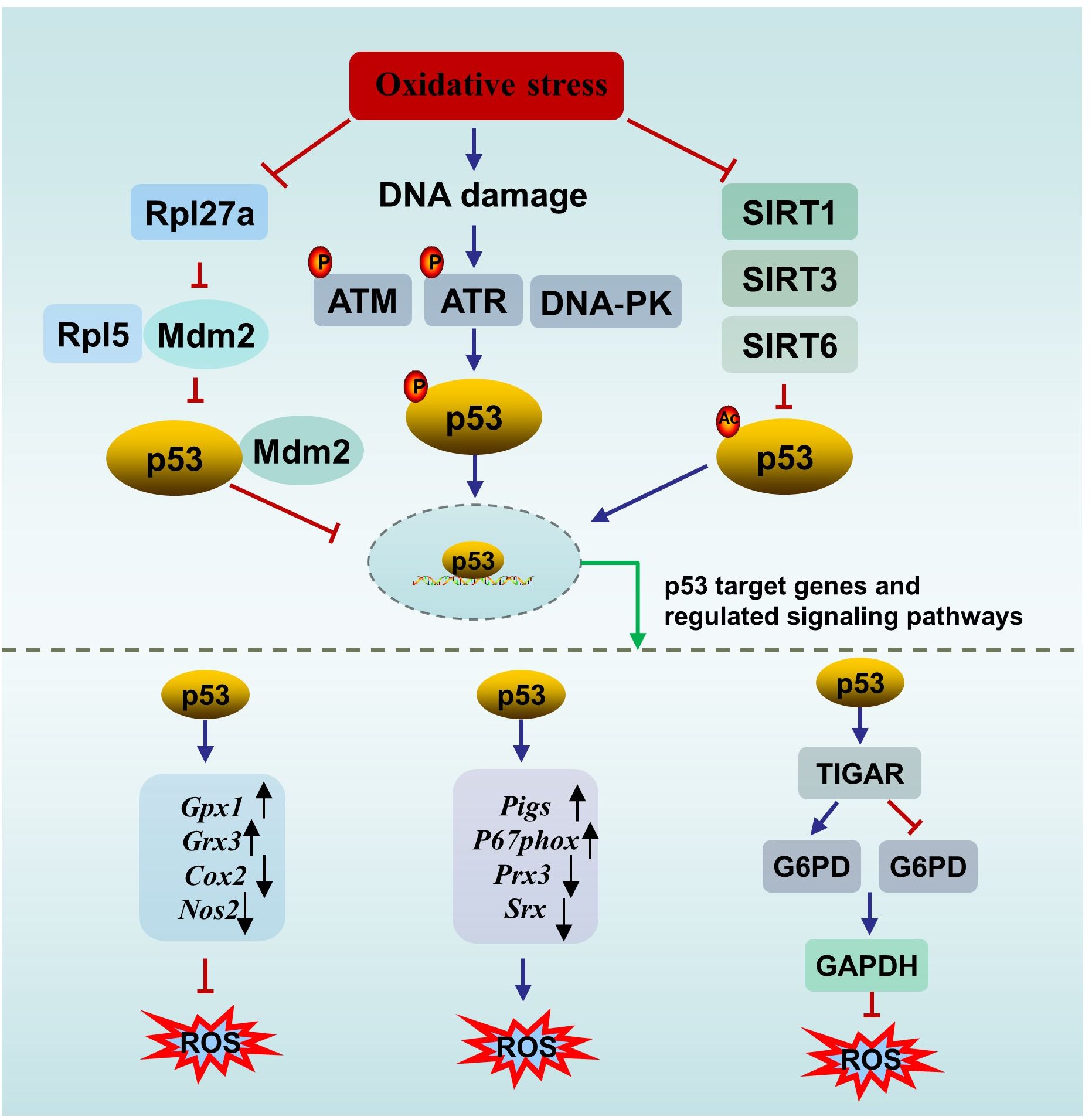
Figure 2. The interplay between p53 and oxidative stress. ATM, ataxia-telangiectasia mutated protein; ATR, ataxia telangiectasia mutated- and Rad3-related kinase; DNA-PK, the DNA-dependent protein kinase; SIRT, sirtuin; ROS, oxygen species; TIGAR, p53 upregulates the downstream gene TP53-induced glycolysis and apoptosis regulator; G6PD, glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase; NADPH, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate.
First, p53 can directly affect oxidative stress or be affected by oxidative stress. On the one hand, p53 directly regulates redox signals by modulating multiple transcriptional targets associated with redox homeostasis and exerts bidirectional effects. p53 exerts prooxidant activity by upregulating its downstream targets, such as p53-inducible genes (Pigs) and the cytosolic subunit of the NADPH oxidase enzyme complex (P67phox), or repressing the expression of peroxiredoxin 3 (Prx3) and sulfiredoxin (Srx). While p53 exerts antioxidant effects by upregulating several antioxidant genes, such as glutathione peroxidase 1 (Gpx1) and glutaredoxin 3 (Grx3), or repressing the expression of dcyclooxygenase-2 (Cox2) and nitric oxide synthase 2 (Nos2) (61). In addition, under oxidative stimuli, p53 upregulates the downstream gene TP53-induced glycolysis and apoptosis regulator (TIGAR) to promote the conversion of the glycolysis pathway to the pentose phosphate pathway, thereby enhancing nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) production to counteract ROS. However, in an environment of excessive stimulation, persistent Tigar expression suppresses phosphofructokinase-1 activity and glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) activity, resulting in the shutdown of the glycolysis pathway without activating the pentose phosphate pathway, ultimately leading to testicular germ cell apoptosis and infertility (62, 63). The complex role of p53 in oxidative stress is not contradictory and is associated with the conditions of the cell. When the cell is in an uncontrollable state, p53 promotes oxidation to initiate programmed cell death. When the cell is in a normal state or a mild stress state, p53 induces antioxidant defense to maintain ROS at a low level to promote cell survival (64).
On the other hand, p53 is sensitive to redox conditions. This can be ascribed to 10 cysteine residues being easily oxidized by ROS (61). A reducing environment is required for the binding of p53 to DNA, in which the thioredoxin (Trx)/thioredoxin reductase (TrxR) system plays a vital role. The Trx/TrxR system is one of the major pathways involved in the regulation of redox homeostasis in male reproduction and can maintain the reduction of its substrates during sperm maturation (65). Ueno et al. (66) reported that Trx functions as a collaborator in p53 binding with DNA. A survey of 80 semen samples revealed that lower TrxR activity is accompanied by a reduction in the total antioxidant capacity (TAC) and in the number of thiol groups, which means that suppressed TrxR activity leads to a deteriorating oxidative status. In parallel, an obvious inverse correlation between p53 levels and TrxR activity was observed (67). In another study, Cordycepin (3’-deoxyadenosine), a nucleotide analogue from Cordyceps militaris L., reversed the increase in p53 and Bax in aged rats by restoring antioxidant defense status through increasing the levels of enzymes (SOD, CAT, GPx, etc.) and nonenzymatic antioxidants (GSH, vitamin C, vitamin E, etc.), resulting in the amelioration of aging-mediated testicular impairment (68). All of these findings suggest an association between the activity of p53 and the redox state.
Second, p53 can be activated by DNA damage induced by ROS. For example, a study by Mu et al. (69) showed that Dendrobium officinale polysaccharides reduced p53-dependent apoptosis in mouse testicular cells induced by oxidative DNA damage, thereby ameliorating testicular injury and decreasing sperm quality. The decrease in the p53 level paralleled the degree of oxidative stress, and the degree of oxidative stress was dose-dependent (69). DNA damage mainly promotes p53 nuclear stability through three pathways to activate downstream targets (e.g., p21, p19, Bax, and Puma) to determine cell fate. Upon DNA DSBs, p53 is activated by the ATM/p53 pathway (70). Similarly, upon DNA single-strand breaks (SSBs), p53 is activated by the ataxia telangiectasia mutated- and Rad3-related kinase (ATR)/p53 pathway. In addition, the DNA‐dependent protein kinase (DNA‐PK) complex can phosphorylate p53 when the DNA strand breaks (71).
Third, p53 can be activated by oxidative stress-induced sirtuin (SIRT) suppression. There are seven types of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+)-dependent histone deacetylase enzymes in SIRTs, including SIRT1- SIRT7 (72). SIRTs can suppress the activity of p53 through posttranscriptional deacetylation of the p53 protein. SIRT1 in murine spermatogonia can be suppressed by oxidative stress of palmitic acid (PA) origin, resulting in elevated acetylated p53, which partly contributes to apoptotic cell death in spermatogonia and subfertility. Melatonin protects against PA-induced damage by restoring acetylated p53 to normal levels through the activation of the SIRT1/p53 pathway (73). Mir-34a is an oxidative stress-responsive RNA that is induced by oxidative stress (74). Mir-34a can directly bind to Sirt1 mRNA, resulting in a decrease in the SIRT1 protein. It has been observed that acetylation of p53 increases via oxidative stress-induced activation of the miR-34a/SIRT1/p53 pathway, resulting in increased testicular cell apoptosis in a type 2 diabetic rat model (75). This observation is in accordance with the findings of Heydari et al. (76) in the testes of mice fed a high-fat diet. Similarly, SIRT3 can deacetylate and inactivate p53 in response to oxidative stress and DNA damage. Melatonin reversed PM2.5-induced GC-2 cell apoptosis through activating the SIRT3/p53 deacetylation pathway. The ameliorating effect of melatonin can be reversed by a specific inhibitor of SIRT3 (3-TYP) (71). Furthermore, it has been reported that SIRT6 is oxidized and suppressed under oxidative stress conditions (77). The BaZiBuShen formula, a Chinese herbal prescription, ameliorated sperm quality in D-galactose (D-gal)/NaNO2-induced aging mice by activating the SIRT6/p53 pathway via its antioxidant properties (78).
In addition, ionizing radiation triggers not only oxidative DNA damage but also ribosomal stress. Rpl5, a ribosomal protein, acts as both sensor and effector of ribosomal stress, which can bind to Mdm2 to inhibit its E3 ligase activity towards p53, thereby stabilizing p53 (79). Rpl27a, another ribosomal protein, may bind to both Mdm2 and Rpl5 to regulate p53 through Mdm2-Rpl5 complex. Under ribosomal stress, the expression of Rpl27a is down-regulated. Decreased Rpl27a weakens its ability to bind to Rpl5 and Mdm2 but promotes the binding of Rpl5 and Mdm2, resulting in the increased stability and activation of p53 and subsequent p53-dependent apoptosis, resulting in testicular structure abnormality and infertility (80, 81). Furthermore, the elimination of oxidative stress significantly inhibits p53-induced apoptosis (80).
In conclusion, p53 can directly regulate oxidative stress through downstream targets, and oxidative stress can subsequently affect p53 activity. Moreover, p53 can be activated by oxidative stress-induced DNA damage, SIRT suppression or ribosomal stress. These mechanisms link oxidative stress, p53 and impaired fertility together.
3.2 p53, apoptosis and infertility
The apoptosis of germ cells is essential for normal spermatogenesis, and p53 plays a key role in this process, as discussed in Section 2.3. Spontaneous apoptosis is characterized by relatively frequency in spermatocytes, a low frequency in spermatogonia, and infrequency in spermatids (67). However, deregulation of apoptosis in male germ cells is significantly related to male infertility (82). Under some pathological conditions and external stimuli, such as irradiation and toxicants, p53-dependent germ cell apoptosis increases dramatically, resulting in germ cell loss and infertility. For example, compared with those in normal controls, significantly greater expression of Tp53 and Casp3 and lower expression of the Bcl-2 gene were detected in the testes of cyclopiazonic acid-exposed mice. Correspondingly, histomorphological abnormalities and decreased sperm numbers were observed in the testes of experimental mice (83).
p53 triggers apoptosis in male germ cells through several pathways (Figure 3). (1) Activated p53 induces apoptosis by promoting the transcription of downstream proapoptotic genes, including Puma, Bax and Noxa. (2) p53 triggers transcription-independent apoptosis by binding directly to antiapoptotic Bcl-2 at the site of the BH3 binding pocket. The binding sites of p53 in Bcl-2 are the same as those of Bax for binding to Bcl-2, leading to the release of Bax and activation of apoptosis (84). (3) p53 can induce apoptosis by promoting the expression of the downstream transcriptional target Perp (p53 apoptosis effector related to PMP-22). It has been reported that Mkrn2 (E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase makorin-2) gene KO in mice leads to impaired spermatogenesis mediated by p53/PERP-mediated apoptosis (85). In parallel, a greater level of PERP expression has been detected in the semen of patients with oligoasthenoteratozoospermia (OAT) than in that of normal individuals (85). PERP stimulates apoptosis by activating Caspase-8 to trigger the mitochondrion-Cytochrome c-caspase protease pathway or facilitating extracellular calcium loading into the endoplasmic reticulum (86). Interestingly, there is a positive feedback loop between PERP and p53. PERP promotes p53 phosphorylation and hinders Mdm2-mediated ubiquitination-mediated degradation of p53, leading to the subsequent stability and activation of p53 (87). (4) p53 drives miR34c expression to promote apoptosis by inhibiting the activity of the antiapoptotic genes Bcl-2 or c-Myc (88). Like other miRNAs, miR34c can inhibit the transcription or initiate the degradation of target gene mRNAs by binding to the 3′UTR (89). A study showed significantly increased levels of miR-34c and p53 in semen from patients with nonobstructive azoospermia and moderate OAT (90). (5) Testicular cell apoptosis can be mediated by the p53-associated extrinsic factor associated with suicide (Fas)/Fas ligand (FasL) death signaling pathway (91). In addition, activated p53 inactivates the serine/threonine kinase Akt by promoting Akt proteolysis mediated by caspase, or by transactivating the PTEN gene, which encodes a phosphatidylinositide phosphatase to prevent Akt activation (92). Subsequently, inactivated Akt depresses downstream nuclear factor Bcl-2 expression to initiate apoptosis (93). Besides, proapoptotic protein Bad, a downstream apoptosis promoter in p53-induced apoptosis in the testis, is inactivated by Akt, resulting in decreased apoptosis (94, 95). Thus, inactivated Akt results in increased apoptosis in testis.
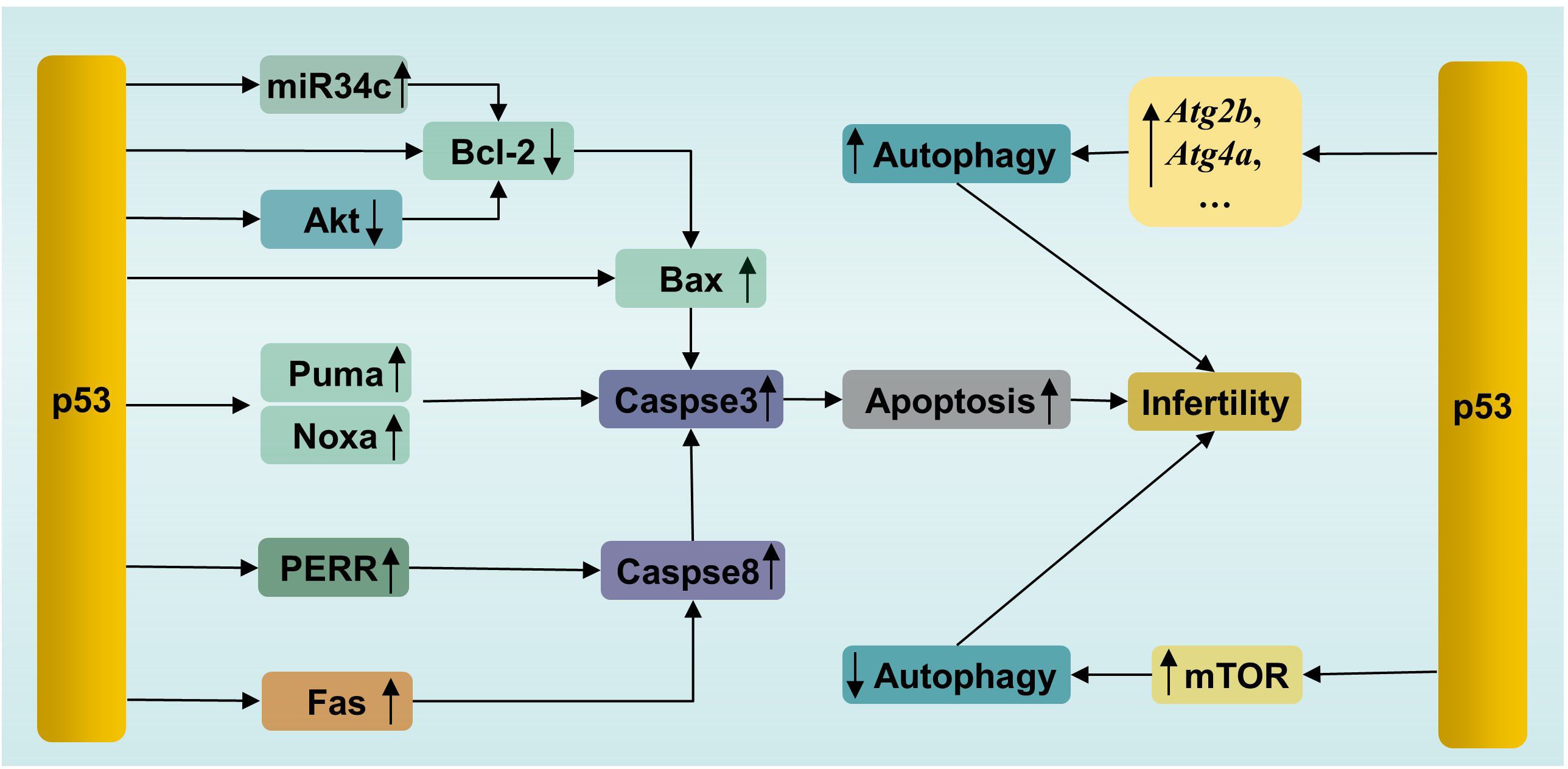
Figure 3. p53-mediated apoptosis and autophagy in male infertility. PERR, p53 apoptosis effector related to PMP-22; Fas, factor associated with suicide.
In short, p53 can induce excessive apoptosis via the intrinsic and extrinsic apoptotic pathways to impair male fertility (96).
3.3 p53, autophagy and infertility
Autophagy is a conserved lysosome-dependent biological process responsible for cellular degradation and recycling, including cytosolic proteins and damaged organelles. Once autophagy is triggered, phagophores are formed first, starting with activation of the UNC-like autophagy-activating kinase 1 (ULK1) initiation complex, followed by autophagy-related protein (ATG)-driven autophagosome formation, in which autophagic cargo is segregated. Subsequently, autophagosomes fuse with lysosomes, where cargo is degraded (97). Under physiological conditions, autophagy participates in multiple physiological processes during spermatogenesis, including spermatid polarization, cellular remodeling and maintenance of the acrosome (98). However, autophagy has two effects on cells. Briefly, moderate induction of autophagy plays a cytoprotective role, which promotes cell survival by removing damaged cell components. However, excessive autophagy causes autophagic death (99). This feature of autophagy is no exception for male germ cells. For example, suppressed autophagy has been observed in flutamide-induced neonatal cryptorchid infertile rats, and retinoic acid improved spermatogenesis by activating autophagy via inhibition of the phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase (PI3K)/Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway (100). In contrast, in another study, excessive autophagy and increased apoptosis have been detected in a murine model of oligoasthenospermia induced by treatment with cyclophosphamide. Schisandrin A, a helpful bioactive lignan, improved sperm quality by mitigating excessive autophagy-induced apoptosis by promoting Akt phosphorylation in this study (101). Akt is one of regulatory proteins connecting apoptosis and autophagy (102). Phosphorylated Akt, on one hand, inhibits autophagy by activating the Akt/mTOR pathway, on the other hand, inhibits apoptosis by phosphorylating Mdm2 at Ser 166 to facilitate the degradation of p53 (103). These studies confirmed that dysregulation of autophagy is related to infertility, as well as the interplay between apoptosis and autophagy.
p53, similar to Akt, is involved not only in apoptosis, as mentioned above, but also in the regulation of autophagy (Figure 3). p53 plays dual roles in autophagy in male germ cells. On the one hand, activated p53 can enhance autophagy by directly inducing the expression of autophagy genes. p53-dependent induction of autophagy genes has been observed in mouse and human cells under DNA damage conditions (104). Many autophagy genes have been identified as p53 target genes (e.g., Atg2b, Atg4a, Atg7, Atg10, and Ulk2) (104). It has been confirmed that p53 promotes autophagy under various stimuli, such as DNA damage and genetic activation (104). Microcystin-leucine-arginine (MC-LR), an intracellular toxin, can trigger oxidative stress-mediated DNA damage, leading to the presence of DSBs, which can be recognized by ATM. Subsequently, ATM phosphorylates the downstream protein p53 and activates p53-induced autophagy by increasing the levels of autophagy proteins, such as Beclin1, ATG5 and LC3-I, resulting in pathological damage in murine testes. In parallel, treatment with the ATM inhibitor KU55933 suppressed autophagy and alleviated this damage by inhibiting the ATM/p53 pathway (105). On the other hand, p53 suppresses autophagy in some cases. In vitro experiments showed that busulfan inhibited autophagy by phosphorylating Akt at Ser473 and subsequently activating the Akt/mTOR pathway, resulting in massive SPCs death. Interestingly, an increase in the level of phosphorylated p53 was accompanied by mTOR-mediated autophagy suppression after busulfan treatment for 2 h to 8 h. Moreover, p53-deficient SPCs exhibited attenuated autophagy inhibition and decreased p-mTOR after busulfan treatment for 6 h. In general, p53 participates in busulfan-induced autophagy inhibition by partly activating mTOR in SPCs (106). The mechanisms by which p53 activates mTOR have been clearly clarified in a recent review by Cui et al. (107). The bilateral effects of p53 on autophagy are considered to be related to its intracellular localization. The nuclear localization of p53 induces autophagy, while the accumulation of p53 in the cytoplasm inhibits autophagy (108). Notably, a previous study demonstrated that p53 induced SPC apoptosis under busulfan stress (70). This suggested that p53 participated in the fine regulation of apoptosis and autophagy in male germ cells. It is still unclear how p53 initiates apoptosis or autophagy under the same stress conditions. The selection tendency of p53 may be related to the intensity and duration of stress, which enable p53 to execute cellular responses suitable for specific cellular states.
4 p53 and male infertility-related diseases
The indispensable role of p53 in spermatogenesis suggests that p53 is closely associated with male infertility and various infertility diseases. The activation of p53 was observed in testicular samples from infertile patients (109). Here, we showed several male infertility-related diseases associated with p53.
4.1 OAT
OAT includes oligospermia and asthenozoospermia, which refers to a sperm cell count lower than 15 million/ml in male ejaculate and/or total motility <40% and progressive motility <32% in a semen sample, and abnormal sperm morphology (110, 111). Several studies have indicated that p53 is elevated in oligoasthenozoospermia. Compared to that in the normozoospermic group, the level of p53 in semen samples from asthenozoospermic donors is greater, as is the level of ROS, leading to increased levels of apoptotic sperm in the ejaculatory semen (67). Another study involving 29 men (11 with asthenozoospermia and 18 controls) showed that the expression of p53 is greater in asthenozoospermic men and that there is a significant negative correlation between p53 levels and sperm motility, as well as between p53 levels and sperm concentration (112). Similarly, a study by Rahbar et al. (113) showed that sperm and testicular tissue samples from individuals with severe OAT and moderate OAT had significantly greater expression of the TP53 and CASP9 genes than those from individuals in the normal sperm group. In parallel, a significant association between p53 and miR‐15b, a microRNA that can stimulate p53 phosphorylation, was also observed in this study (113). Briefly, aberrant activation of p53 might contribute to OAT.
4.2 Varicocele
Varicocele, defined as an abnormal expansion of the pampiniform plexus of gonadal veins above the testicle, is one of the most common causes of male infertility (114). Increased expression of p53 and BAK was observed in ejaculated semen samples from varicocele patients, suggesting the occurrence of remarkably active p53-dependent apoptosis (115). Spermatocytes of the testis are considered the cells mainly affected by varicocele-associated apoptosis (115). The increase in p53, Cytochrome c, and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP)-1 levels has also been observed in varicocele-induced rats, which indicated that oxidative stress-induced p53 activation plays a role in varicocele (116). Moreover, another study showed elevated levels of phosphorylated p53 and a marker of DBSs, phosphorylated histone γ-H2AX accumulation in a time course-dependent manner in varicocele murine models, suggesting that activation of p53-dependent apoptosis is mediated by γ-H2AX (117). Furthermore, an inverse association has been observed between the proportion of the TP53 codon 72 Arg/Arg genotype, and sperm motility in men with varicocele (118). Codon 72 has a polymorphism that encodes the amino acids arginine (Arg 72) or proline (Pro 72), which influences the structure and function of p53. The Arg 72 variant of p53 more potently induces apoptosis by enhancing its interaction with the mitochondria and promoting the release of cytochrome c release (119). The increased testicular temperature has been observed in experimental varicocele models and in man, and is widely considered to be a mechanism by which varicocele affects testicular function. And p53 acts as a master regulator in germ cell apoptosis induced by hyperthermia (120, 121). Those findings suggest that p53 is associated with infertility caused by varicocele.
4.3 Cryptorchidism
Cryptorchidism, a condition in which one or both testes fail to descend into the scrotum, is associated with an increased risk of infertility (122). A rise in testicular temperature was considered a main factor for the impairement of testicular functions in experimental induced cryptorchidism in rodents or men with cryptorchidism (123, 124). A study revealed that the initial phase of germ cell apoptosis induced by heat stress caused by experimental cryptorchidism was mediated by p53-dependent pathway (125). Another study by Zhou et al. (126) showed increased levels of p53 and Fas protein, as well as testicular cell apoptosis, and decreased testicular weight in a surgery-induced cryptorchidism murine model. Moreover, a reduction in the levels of p53 and Fas mediated by the overexpression of Cirp (cold-inducible RNA-binding protein) ameliorated the increase in germ cell apoptosis and testicular injury induced by cryptorchidism. Additionally, testicular orphan receptor-2 (TR2), a member of the steroid-sensitive hormone receptor superfamily is involved in p53-mediated cryptorchidism-related infertility. TR2 is highly expressed in testes, and can regulate retinoic acid receptors/retinoid X receptors (RARs/RXRs) signal pathways (127, 128). A study showed that the expression level of TR2 mRNA decreased with the progression of p53-mediated germ cell apoptosis in the cryptorchid testis of rat and rhesus monkey (128). Future research showed that TR2 was repressed by activating the p53/retinoblastoma gene product (Rb) signaling pathway through the direct combination of Rb and TR2 in surgery-induced cryptorchid testes of rhesus monkeys (129). These results suggest that p53 is involved in cryptorchidism-induced infertility.
4.4 Idiopathic male infertility
Idiopathic male infertility refers to infertility in men with abnormal sperm parameters after excluding possible factors and is responsible for approximately 40% of cases (130). Several studies have shown that p53 polymorphisms are associated with idiopathic male infertility. For instance, a study conducted by Mashayekhi et al. (131) revealed a more frequent Arg allele of the TP53 codon 72 polymorphism in men with idiopathic infertility than in controls. In addition, a case-control study including 580 infertile patients and 580 controls showed a significantly increased risk of genetic variants in TP53 (rs2287498) and MDM2 (rs937283) associated with idiopathic male infertility in a Chinese population (132). However, inconsistent conclusions exist. A case–;control study including 198 idiopathic infertile patients and 233 fertile controls revealed no association between the codon 72 and IVS7 + 72C>T polymorphisms of the TP53 gene and spermatogenetic failure (133). Similarly, another investigation conducted by de Morais et al. (134) revealed no association between the TP53 polymorphism in codon 72 and male idiopathic infertility. It seems that whether the TP53 polymorphism is involved in the pathogenesis of idiopathic male infertility is associated with different demographic factors.
4.5 Testicular torsion
Testicular torsion is a urological emergency accompanied by scrotal pain and ischemia and subsequent testicular ischemia–;reperfusion injury (tIRI), resulting in cell damage and even infertility (135, 136). A study by Shamsi-Gamchi et al. (137) showed that testicular torsion caused severe DNA damage induced by oxidative stress, leading to markedly increased expression of Tp53, p21, cyclin D1, Bax and Casp3 in a time-dependent manner, as well as a significant increase in the apoptosis index, resulting in deteriorated testicular tissue and decreased sperm count in murine testicular tissue within 8 hours after testicular torsion. Mechanically, p53 induced by DNA damage activates p21. Subsequently, p21 binds with Cdk4 to suppress the Cyclin D1/Cdk4-related cell cycling process and finally induce p53/p21-dependent apoptosis (137). Similarly, another study showed that tIRI triggered oxidative stress, thereby upregulating the phosphorylation of p53 and the expression of its downstream proapoptotic factor Puma, resulting in increased apoptosis. In addition, during tIRI, p53 induces sustained expression of the gene Tigar, leading to the failure to convert glycolysis to the pentose phosphate pathway, resulting in testicular germ cell apoptosis (62, 63). In summary, p53-dependent apoptosis and cell cycle arrest are related to testicular injury caused by testicular torsion.
5 Potential therapeutic agents affecting the p53-related pathways in male infertility
Recently, efforts have been made to develop p53-targeted therapies for certain diseases, such as cancer and neuroinflammation (138, 139). As a result, many potential therapeutic agents, including natural and synthetic drugs and small molecule compounds, have been developed. The effects of several agents affecting the p53-related pathways on male infertility are shown in Table 2. Among them, pifithrin-α, a p53 specific inhibitor, directly targets p53 by obstructing the p53 protein in the nucleus (144). Excitingly, innovative therapeutic strategies targeting p53, including Mdm2 inhibitors and mutant p53-restoring compounds, have shown great potential in cancer treatment in clinical trials (145). It can be expected that innovative approaches targeting p53 can be implemented for the treatment of male infertility in the near future.
6 Conclusion remarks
p53 plays a central role in the response to cellular stress and is involved in multiple biological processes. Herein, we present an overview of the essential roles of p53 in normal spermatogenesis and the possible mechanisms by which p53 is involved in male infertility. We conclude that mutated p53 is a risk factor for male infertility and aberrant p53 expression might be related to male infertility. Recently, considerable efforts have been made to develop small molecules targeting p53, which is highly promising for cancer therapies (146). Although testicular microenvironment and pathology differ from the tumoral, considering the high potential of p53 to be targeted for drug therapy, insights into the interplay between p53 and spermatogenesis and male infertility are needed, which opens up avenues for novel p53-based therapeutic interventions. In the context of male infertility, combined therapies that both alleviate testicular stress and target p53 and/or its activated pathways should be more effective than focusing on one alone. However, several questions remain to be answered. How does p53 balance apoptosis and autophagy? Clarification of the specific mechanism that determines this effect is urgently needed. Spermatogenesis is a unique and complex cell cycle process required for fine regulation. The level of p53 must also be precisely regulated. Therefore, when targeting p53, which indicator can be used to detect whether the activation or inhibition of p53 is appropriate? Addressing these concerns will aid in the clinical treatment of infertility with strategies based on the attractive target p53.
Author contributions
JL: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing. XH: Writing – review & editing. LL: Conceptualization, Validation, Writing – review & editing. JS: Validation, Writing – review & editing. QG: Validation, Writing – review & editing. XY: Investigation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. CZ: Investigation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. BN: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Youth Foundation of the Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University (QDFYQN2023105).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Zegers-Hochschild F, Adamson GD, Dyer S, Racowsky C, de Mouzon J, Sokol R, et al. The international glossary on infertility and fertility care 2017. Fertil Steril. (2017) 108:393–406. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2017.06.005
2. Vollset SE, Goren E, Yuan CW, Cao J, Smith AE, Hsiao T, et al. Fertility, mortality, migration, and population scenarios for 195 countries and territories from 2017 to 2100: a forecasting analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet. (2020) 396:1285–306. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30677-2
3. Vander Borght M, Wyns C. Fertility and infertility: Definition and epidemiology. Clin Biochem. (2018) 62:2–10. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2018.03.012
4. Huang B, Wang Z, Kong Y, Jin M, Ma L. Global, regional and national burden of male infertility in 204 countries and territories between 1990 and 2019: an analysis of global burden of disease study. BMC Public Health. (2023) 23:2195. doi: 10.1186/s12889-023-16793-3
5. Carlsen E, Giwercman A, Keiding N, Skakkebaek NE. Evidence for decreasing quality of semen during past 50 years. Bmj. (1992) 305:609–13. doi: 10.1136/bmj.305.6854.609
6. Mishra P, Negi MPS, Srivastava M, Singh K, Rajender S. Decline in seminal quality in Indian men over the last 37 years. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. (2018) 16:103. doi: 10.1186/s12958-018-0425-z
7. Rodprasert W, Virtanen HE, Sadov S, Perheentupa A, Skakkebaek NE, Jørgensen N, et al. An update on semen quality among young Finnish men and comparison with Danish data. Andrology-us. (2019) 7:15–23. doi: 10.1111/andr.12550
8. Levine H, Jørgensen N, Martino-Andrade A, Mendiola J, Weksler-Derri D, Jolles M, et al. Temporal trends in sperm count: a systematic review and meta-regression analysis of samples collected globally in the 20th and 21st centuries. Hum Reprod Update. (2023) 29:157–76. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmac035
9. Agarwal A, Baskaran S, Parekh N, Cho C-L, Henkel R, Vij S, et al. Male infertility. Lancet. (2021) 397:319–33. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(20)32667-2
10. Calogero AE, Cannarella R, Agarwal A, Hamoda TA-AA-M, Rambhatla A, Saleh R, et al. The renaissance of male infertility management in the golden age of andrology. World J Mens Health. (2023) 41:237–54. doi: 10.5534/wjmh.220213
11. Hajiesmailpoor A, Emami P, Kondori BJ, Ghorbani M. Stem cell therapy as a recent advanced approach in male infertility. Tissue Cell. (2021) 73:101634. doi: 10.1016/j.tice.2021.101634
12. Njagi P, Groot W, Arsenijevic J, Dyer S, Mburu G, Kiarie J. Financial costs of assisted reproductive technology for patients in low- and middle-income countries: a systematic review. Hum Reprod Open. (2023) 2023:hoad007. doi: 10.1093/hropen/hoad007
13. Anbarasan T, Bourdon JC. The emerging landscape of p53 isoforms in physiology, cancer and degenerative diseases. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20:6257. doi: 10.3390/ijms20246257
14. Capuozzo M, Santorsola M, Bocchetti M, Perri F, Cascella M, Granata V, et al. p53: from fundamental biology to clinical applications in cancer. Biology. (2022) 11:1325. doi: 10.3390/biology11091325
15. Sabapathy K, Lane DP, Verma CS. Understanding p53 functions through p53 antibodies. J Mol Cell Biol. (2019) 11:317–29. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjz010
16. Yao Y, Zhang Q, Li Z, Zhang H. MDM2: current research status and prospects of tumor treatment. Cancer Cell Int. (2024) 24:170. doi: 10.1186/s12935-024-03356-8
17. Moradi M, Goodarzi N, Faramarzi A, Cheraghi H, Hashemian AH, Jalili C. Melatonin protects rats testes against bleomycin, etoposide, and cisplatin-induced toxicity via mitigating nitro-oxidative stress and apoptosis. Biomed Pharmacother. (2021) 138:111481. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111481
18. Zhao Y, Wu M, Li J, Meng P, Chen J, Huang Z, et al. The spliceosome factor sart3 regulates hematopoietic stem/progenitor cell development in zebrafish through the p53 pathway. Cell Death Dis. (2021) 12:906. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-04215-4
19. Song B, Yang P, Zhang S. Cell fate regulation governed by p53: Friends or reversible foes in cancer therapy. Cancer Commun (Lond). (2024) 44:297–360. doi: 10.1002/cac2.12520
20. Zalzali H, Rabeh W, Najjar O, Abi Ammar R, Harajly M, Saab R. Interplay between p53 and Ink4c in spermatogenesis and fertility. Cell Cycle. (2018) 17:643–51. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2017.1421874
21. Demyashkin G. Morphofunctional characteristics of proliferation and apoptosis of germinal epithelium: pathogenesis of temporary azoospermia after local electron irradiation. Transl Androl Urol. (2023) 12:673–83. doi: 10.21037/tau-22-598
22. Hassin O, Oren M. Drugging p53 in cancer: one protein, many targets. Nat Rev Drug Discovery. (2022) 22:127–44. doi: 10.1038/s41573-022-00571-8
23. Kuwahara Y, Shimada A, Mitani H, Shima A. A critical stage in spermatogenesis for radiation-induced cell death in the medaka fish, Oryzias latipes. Radiat Res. (2002) 157:386–92. doi: 10.1667/0033-7587(2002)157[0386:acsisf]2.0.co;2
24. Nishimura H, L’Hernault SW. Spermatogenesis. Curr Biol. (2017) 27:R988–94. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2017.07.067
25. Dai MS, Hall SJ, Vantangoli Policelli MM, Boekelheide K, Spade DJ. Spontaneous testicular atrophy occurs despite normal spermatogonial proliferation in a Tp53 knockout rat. Andrology. (2017) 5:1141–52. doi: 10.1111/andr.12409
26. Diao L, Turek PJ, John CM, Fang F, Reijo Pera RA. Roles of spermatogonial stem cells in spermatogenesis and fertility restoration. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2022) 13:895528. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.895528
27. Yan R-G, He Z, Wang F-C, Li S, Shang Q-B, Yang Q-E. Transcription factor E4F1 dictates spermatogonial stem cell fate decisions by regulating mitochondrial functions and cell cycle progression. Cell Biosci. (2023) 13:177. doi: 10.1186/s13578-023-01134-z
28. McAninch D, Mäkelä JA, La HM, Hughes JN, Lovell-Badge R, Hobbs RM, et al. SOX3 promotes generation of committed spermatogonia in postnatal mouse testes. Sci Rep. (2020) 10:6751. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-63290-3
29. Filipponi D, Hobbs RM, Ottolenghi S, Rossi P, Jannini EA, Pandolfi PP, et al. Repression of kit expression by Plzf in germ cells. Mol Cell Biol. (2007) 27:6770–81. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00479-07
30. McAninch D, Thomson EP, Thomas PQ. Genome-wide DNA-binding profile of SRY-box transcription factor 3 (SOX3) in mouse testes. Reprod Fertil Dev. (2020) 32:1260–70. doi: 10.1071/rd20108
31. Fayomi AP, Orwig KE. Spermatogonial stem cells and spermatogenesis in mice, monkeys and men. Stem Cell Res. (2018) 29:207–14. doi: 10.1016/j.scr.2018.04.009
32. Gao X, Chen H, Liu J, Shen S, Wang Q, Clement TM, et al. The REGγ-proteasome regulates spermatogenesis partially by P53-PLZF signaling. Stem Cell Rep. (2019) 13:559–71. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2019.07.010
33. Choi WI, Kim MY, Jeon BN, Koh DI, Yun CO, Li Y, et al. Role of promyelocytic leukemia zinc finger (PLZF) in cell proliferation and cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1A (p21WAF/CDKN1A) gene repression. J Biol Chem. (2014) 289:18625–40. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.538751
34. Lu C, Zhang D, Zhang J, Li L, Qiu J, Gou K, et al. Casein kinase 1α regulates murine spermatogenesis via p53-Sox3 signaling. Development. (2022) 149:dev200205. doi: 10.1242/dev.200205
35. Beumer TL, Roepers-Gajadien HL, Gademan IS, van Buul PP, Gil-Gomez G, Rutgers DH, et al. The role of the tumor suppressor p53 in spermatogenesis. Cell Death Differ. (1998) 5:669–77. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4400396
36. Shen Y, Tu W, Liu Y, Yang X, Dong Q, Yang B, et al. TSPY1 suppresses USP7-mediated p53 function and promotes spermatogonial proliferation. Cell Death Dis. (2018) 9:542. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-0589-7
37. Cánepa ET, Scassa ME, Ceruti JM, Marazita MC, Carcagno AL, Sirkin PF, et al. INK4 proteins, a family of mammalian CDK inhibitors with novel biological functions. IUBMB Life. (2007) 59:419–26. doi: 10.1080/15216540701488358
38. Xie Y, Wei B-H, Ni F-D, Yang W-X. Conversion from spermatogonia to spermatocytes: Extracellular cues and downstream transcription network. Gene. (2021) 764:145080. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2020.145080
39. Ishiguro KI. Mechanism of initiation of meiosis in mouse germ cells. Curr Top Dev Biol. (2023) 151:1–26. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctdb.2022.04.005
41. Fujiwara Y, Handel MA, Okada Y. R-loop formation in meiosis: roles in meiotic transcription-associated DNA damage. Epigenomes. (2022) 6:26. doi: 10.3390/epigenomes6030026
42. Wang Y-L, Li D, Yang H-D, He L, Sun W-J, Duan Z-L, et al. The E3 ubiquitin ligase CRL4 regulates proliferation and progression through meiosis in Chinese mitten crab eriocheir sinensis1. Biol Reprod. (2016) 94:65. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.115.137661
43. Schwartz D, Goldfinger N, Kam Z, Rotter V. p53 controls low DNA damage-dependent premeiotic checkpoint and facilitates DNA repair during spermatogenesis. Cell Growth Differ. (1999) 10:665–75.
44. Abuetabh Y, Wu HH, Chai C, Al Yousef H, Persad S, Sergi CM, et al. DNA damage response revisited: the p53 family and its regulators provide endless cancer therapy opportunities. Exp Mol Med. (2022) 54:1658–69. doi: 10.1038/s12276-022-00863-4
45. Karimian A, Ahmadi Y, Yousefi B. Multiple functions of p21 in cell cycle, apoptosis and transcriptional regulation after DNA damage. DNA Repair (Amst). (2016) 42:63–71. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2016.04.008
46. Liu J, Zhao M, Dong X, Zhang Y, Xue J, Duan J, et al. Melatonin ameliorates PM2.5-induced spermatogenesis disorder by preserving H3K9 methylation and SIRT3. Environ Toxicol. (2023) 39:1471–80. doi: 10.1002/tox.24028
47. Allemand I, Anglo A, Jeantet AY, Cerutti I, May E. Testicular wild-type p53 expression in transgenic mice induces spermiogenesis alterations ranging from differentiation defects to apoptosis. Oncogene. (1999) 18:6521–30. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203052
48. Chen Y, Shao X, Cao J, Zhu H, Yang B, He Q, et al. Phosphorylation regulates cullin-based ubiquitination in tumorigenesis. Acta Pharm Sin B. (2021) 11:309–21. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2020.09.007
49. Sang Y, Yan F, Ren X. The role and mechanism of CRL4 E3 ubiquitin ligase in cancer and its potential therapy implications. Oncotarget. (2015) 6:42590–602. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6052
50. Oldereid NB, Angelis PD, Wiger R, Clausen OP. Expression of Bcl-2 family proteins and spontaneous apoptosis in normal human testis. Mol Hum Reprod. (2001) 7:403–8. doi: 10.1093/molehr/7.5.403
51. Kim ED, Barqawi AZ, Seo JT, Meacham RB. Apoptosis: its importance in spermatogenic dysfunction. Urol Clin North Am. (2002) 29:755–765, vii. doi: 10.1016/s0094-0143(02)00093-9
52. Napoletano F, Gibert B, Yacobi-Sharon K, Vincent S, Favrot C, Mehlen P, et al. p53-dependent programmed necrosis controls germ cell homeostasis during spermatogenesis. PloS Genet. (2017) 13:e1007024. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007024
53. Rotter V, Schwartz D, Almon E, Goldfinger N, Kapon A, Meshorer A, et al. Mice with reduced levels of p53 protein exhibit the testicular giant-cell degenerative syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (1993) 90:9075–9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.19.9075
54. Lech T, Golas A, Styrna J. Is p53 controlling spermatogenesis in male mice with the deletion on the Y chromosome? Zygote. (2011) 21:65–70. doi: 10.1017/s0967199411000323
55. Fujisawa M, Shirakawa T, Fujioka H, Gotoh A, Okada H, Arakawa S, et al. Adenovirus-mediated p53 gene transfer to rat testis impairs spermatogenesis. Arch Androl. (2001) 46:223–31. doi: 10.1080/01485010151096568
56. Yin Y, Stahl BC, DeWolf WC, Morgentaler A. p53-mediated germ cell quality control in spermatogenesis. Dev Biol. (1998) 204:165–71. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1998.9074
57. Masola V, Greco N, Tozzo P, Caenazzo L, Onisto M. The role of SPATA2 in TNF signaling, cancer, and spermatogenesis. Cell Death Dis. (2022) 13:977. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05432-1
58. Wei Y, Bao R, Hu L, Geng Y, Chen X, Wen Y, et al. Ti3C2 (MXene) nanosheets disrupt spermatogenesis in male mice mediated by the ATM/p53 signaling pathway. Biol Direct. (2023) 18:30. doi: 10.1186/s13062-023-00382-w
59. Huang C, Cao X, Pang D, Li C, Luo Q, Zou Y, et al. Is male infertility associated with increased oxidative stress in seminal plasma? A-meta analysis. Oncotarget. (2018) 9:24494–513. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.25075
60. Kaltsas A. Oxidative stress and male infertility: the protective role of antioxidants. Medicina. (2023) 59:1769. doi: 10.3390/medicina59101769
61. Rius-Pérez S. p53 at the crossroad between mitochondrial reactive oxygen species and necroptosis. Free Radic Biol Med. (2023) 207:183–93. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2023.07.022
62. Kim J, Devalaraja-Narashimha K, Padanilam BJ. TIGAR regulates glycolysis in ischemic kidney proximal tubules. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. (2015) 308:F298–308. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00459.2014
63. Al-Maghrebi M, Renno WM. Altered expression profile of glycolytic enzymes during testicular ischemia reperfusion injury is associated with the p53/TIGAR pathway: effect of fructose 1,6-diphosphate. PeerJ. (2016) 4:e2195. doi: 10.7717/peerj.2195
64. Liu X, Fan L, Lu C, Yin S, Hu H. Functional role of p53 in the regulation of chemical-induced oxidative stress. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2020) 2020:6039769. doi: 10.1155/2020/6039769
65. Dou Q, Turanov AA, Mariotti M, Hwang JY, Wang H, Lee SG, et al. Selenoprotein TXNRD3 supports male fertility via the redox regulation of spermatogenesis. J Biol Chem. (2022) 298:102183. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102183
66. Ueno M, Matsutani Y, Nakamura H, Masutani H, Yagi M, Yamashiro H, et al. Possible association of thioredoxin and p53 in breast cancer. Immunol Lett. (2000) 75:15–20. doi: 10.1016/s0165-2478(00)00284-4
67. Moradi M-n, Karimi J, Khodadadi I, Amiri I, Karami M, Saidijam M, et al. Evaluation of the p53 and Thioredoxin reductase in sperm from asthenozoospermic males in comparison to normozoospermic males. Free Radic Biol Med. (2018) 116:123–8. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2017.12.038
68. Kopalli SR, Cha K-M, Cho JY, Kim S-K, Koppula S. Cordycepin mitigates spermatogenic and redox related expression in H2O2-exposed Leydig cells and regulates testicular oxidative apoptotic signalling in aged rats. Pharm Biol. (2022) 60:404–16. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2022.2033275
69. Mu Y, Che B, Tang K, Zhang W, Xu S, Li W, et al. Dendrobium officinale polysaccharides improved reproductive oxidative stress injury in male mice treated with cyclophosphamide. Sci pollut Res Int. (2023) 30:106431–41. doi: 10.1007/s11356-023-29874-y
70. Zhang X, Xia Q, Wei R, Song H, Mi J, Lin Z, et al. Melatonin protects spermatogonia from the stress of chemotherapy and oxidation via eliminating reactive oxidative species. Free Radic Biol Med. (2019) 137:74–86. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.04.009
71. Shi T, Dansen TB. Reactive oxygen species induced p53 activation: DNA damage, redox signaling, or both? Antioxid Redox Signal. (2020) 33:839–59. doi: 10.1089/ars.2020.8074
72. Liu M, Yu J, Jin H, Wang S, Ding J, Xing H, et al. Bioinformatics analysis of the SIRT family members and assessment of their potential clinical value. Onco Targets Ther. (2021) 14:2635–49. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S298616
73. Xu D, Liu L, Zhao Y, Yang L, Cheng J, Hua R, et al. Melatonin protects mouse testes from palmitic acid-induced lipotoxicity by attenuating oxidative stress and DNA damage in a SIRT1-dependent manner. J Pineal Res. (2020) 69:e12690. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12690
74. Baker JR, Vuppusetty C, Colley T, Papaioannou AI, Fenwick P, Donnelly L, et al. Oxidative stress dependent microRNA-34a activation via PI3Kα reduces the expression of sirtuin-1 and sirtuin-6 in epithelial cells. Sci Rep. (2016) 6:35871. doi: 10.1038/srep35871
75. Gaderpour S, Ghiasi R, Hamidian G, Heydari H, Keyhanmanesh R. Voluntary exercise improves spermatogenesis and testicular apoptosis in type 2 diabetic rats through alteration in oxidative stress and mir-34a/SIRT1/p53 pathway. Iran J Basic Med Sci. (2021) 24:58–65. doi: 10.22038/ijbms.2020.49498
76. Heydari H, Ghiasi R, Hamidian G, Ghaderpour S, Keyhanmanesh R. Voluntary exercise improves sperm parameters in high fat diet receiving rats through alteration in testicular oxidative stress, mir-34a/SIRT1/p53 and apoptosis. Hormone Mol Biol Clin Invest. (2021) 42:253–63. doi: 10.1515/hmbci-2020-0085
77. Collins JA, Kapustina M, Bolduc JA, Pike JFW, Diekman BO, Mix K, et al. Sirtuin 6 (SIRT6) regulates redox homeostasis and signaling events in human articular chondrocytes. Free Radic Biol Med. (2021) 166:90–103. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2021.01.054
78. Li L, Chen B, An T, Zhang H, Xia B, Li R, et al. BaZiBuShen alleviates altered testicular morphology and spermatogenesis and modulates Sirt6/P53 and Sirt6/NF-κB pathways in aging mice induced by D-galactose and NaNO2. J Ethnopharmacol. (2021) 271:113810. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.113810
79. Liu Y, Deisenroth C, Zhang Y. RP–MDM2–p53 pathway: Linking ribosomal biogenesis and tumor surveillance. Trends Cancer. (2016) 2:191–204. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2016.03.002
80. Said RS, Mohamed HA, Kamal MM. Coenzyme Q10 mitigates ionizing radiation-induced testicular damage in rats through inhibition of oxidative stress and mitochondria-mediated apoptotic cell death. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. (2019) 383:114780. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2019.114780
81. Li H, Zhang H, Huang G, Dou Z, Xie Y, Si J, et al. Heavy ion radiation-induced DNA damage mediates apoptosis via the Rpl27a-Rpl5-MDM2-p53/E2F1 signaling pathway in mouse spermatogonia. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. (2020) 201:110831. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110831
82. Jalili C, Ranjbar Shamsi R, Amiri B, Kakebaraie S, Jalili F, Nasta TZ. Genotoxic and cytotoxic effects of aflatoxin on the reproductive system: Focus on cell cycle dynamics and apoptosis in testicular tissue. Toxicology. (2024) 504:153773. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2024.153773
83. Bonyadi F, Hasanzadeh S, Malekinejad H. Cyclopiazonic acid induced p53-dependent apoptosis in the testis of mice: Another male related risk factor of infertility. Environ Toxicol. (2021) 36:903–13. doi: 10.1002/tox.23092
84. Wei H, Wang H, Wang G, Qu L, Jiang L, Dai S, et al. Structures of p53/BCL-2 complex suggest a mechanism for p53 to antagonize BCL-2 activity. Nat Commun. (2023) 14:4300. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-40087-2
85. Jiang B-H, Qian Y-C, Xie Y-X, Wang C-S, Shi Z-M, Jiang C-F, et al. Mkrn2 deficiency induces teratozoospermia and male infertility through p53/PERP-mediated apoptosis in testis. Asian J Androl. (2020) 22:414–21. doi: 10.4103/aja.aja_76_19
86. Roberts O, Paraoan L. PERP-ing into diverse mechanisms of cancer pathogenesis: Regulation and role of the p53/p63 effector PERP. Acta Rev Cancer. (2020) 1874:188393. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2020.188393
87. Davies L, Spiller D, White MR, Grierson I, Paraoan L. PERP expression stabilizes active p53 via modulation of p53-MDM2 interaction in uveal melanoma cells. Cell Death Dis. (2011) 2:e136. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2011.19
88. Li M, Yu M, Liu C, Zhu H, He X, Peng S, et al. miR-34c works downstream of p53 leading to dairy goat male germline stem-cell (mGSCs) apoptosis. Cell Prolif. (2013) 46:223–31. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12013
89. Pan W, Chai B, Li L, Lu Z, Ma Z. p53/MicroRNA-34 axis in cancer and beyond. Heliyon. (2023) 9:e15155. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e15155
90. Rahbar S, Novin MG, Alizadeh E, Shahnazi V, Pashaei-Asl F, AsrBadr YA, et al. New insights into the expression profile of MicroRNA-34c and P53 in infertile men spermatozoa and testicular tissue. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). (2017) 63:77–83. doi: 10.14715/cmb/2017.63.8.17
91. Duan P, Hu C, Butler HJ, Quan C, Chen W, Huang W, et al. 4-Nonylphenol induces disruption of spermatogenesis associated with oxidative stress-related apoptosis by targeting p53-Bcl-2/Bax-Fas/FasL signaling. Environ Toxicol. (2017) 32:739–53. doi: 10.1002/tox.22274
92. Oren M, Damalas A, Gottlieb T, Michael D, Taplick J, Leal JF, et al. Regulation of p53: intricate loops and delicate balances. Ann N Y Acad Sci. (2002) 973:374–83. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2002.tb04669.x
93. Mitra S, Varghese AC, Mandal S, Bhattacharyya S, Nandi P, Rahman SM, et al. Lead and cadmium exposure induces male reproductive dysfunction by modulating the expression profiles of apoptotic and survival signal proteins in tea-garden workers. Reprod Toxicol. (2020) 98:134–48. doi: 10.1016/j.reprotox.2020.09.006
95. Ortiz RJ, Lizama C, Codelia VA, Moreno RD. A molecular evaluation of germ cell death induced by etoposide in pubertal rat testes. Mol Hum Reprod. (2009) 15:363–71. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gap024
96. Fu G, Dai J, Li Z, Chen F, Liu L, Yi L, et al. The role of STAT3/p53 and PI3K-Akt-mTOR signaling pathway on DEHP-induced reproductive toxicity in pubertal male rat. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. (2020) 404:115151. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2020.115151
97. Lei Y, Zhang E, Bai L, Li Y. Autophagy in cancer immunotherapy. Cells. (2022) 11:2996. doi: 10.3390/cells11192996
98. Rotimi DE, Iyobhebhe M, Oluwayemi ET, Evbuomwan IO, Asaleye RM, Ojo OA, et al. Mitophagy and spermatogenesis: Role and mechanisms. Biochem Biophys Rep. (2024) 38:101698. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2024.101698
99. Gu S, Li X. Regulation of autophagy in cardiovascular diseases by natural products. Adv Exp Med Biol. (2020) 1207:731–6. doi: 10.1007/978-981-15-4272-5_55
100. Long C, Zhou Y, Shen L, Yu Y, Hu D, Liu X, et al. Retinoic acid can improve autophagy through depression of the PI3K-Akt-mTOR signaling pathway via RARα to restore spermatogenesis in cryptorchid infertile rats. Genes Dis. (2022) 9:1368–77. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2021.03.006
101. Ma L, Li B, Ma J, Wu C, Li N, Zhou K, et al. Novel discovery of schisandrin A regulating the interplay of autophagy and apoptosis in oligoasthenospermia by targeting SCF/c-kit and TRPV1 via biosensors. Acta Pharm Sin B. (2023) 13:2765–77. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2023.01.004
102. Sharma P, Kaushal N, Saleth LR, Ghavami S, Dhingra S, Kaur P. Oxidative stress-induced apoptosis and autophagy: Balancing the contrary forces in spermatogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. (2023) 1869:166742. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2023.166742
103. Hara MR, Kovacs JJ, Whalen EJ, Rajagopal S, Strachan RT, Grant W, et al. A stress response pathway regulates DNA damage through β2-adrenoreceptors and β-arrestin-1. Nature. (2011) 477:349–53. doi: 10.1038/nature10368
104. Kenzelmann Broz D, Spano Mello S, Bieging KT, Jiang D, Dusek RL, Brady CA, et al. Global genomic profiling reveals an extensive p53-regulated autophagy program contributing to key p53 responses. Genes Dev. (2013) 27:1016–31. doi: 10.1101/gad.212282.112
105. Tian Z, Liu H, Chen X, Losiewicz MD, Wang R, Du X, et al. The activated ATM/p53 pathway promotes autophagy in response to oxidative stress-mediated DNA damage induced by Microcystin-LR in male germ cells. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. (2021) 227:112919. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112919
106. Wei R, Zhang X, Cai Y, Liu H, Wang B, Zhao X, et al. Busulfan Suppresses Autophagy in Mouse Spermatogonial Progenitor Cells via mTOR of AKT and p53 Signaling Pathways. Stem Cell Rev Rep. (2020) 16:1242–55. doi: 10.1007/s12015-020-10027-4
107. Cui D, Qu R, Liu D, Xiong X, Liang T, Zhao Y. The Cross Talk Between p53 and mTOR Pathways in Response to Physiological and Genotoxic Stresses. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2021) 9:775507. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.775507
108. Wang H, Guo M, Wei H, Chen Y. Targeting p53 pathways: mechanisms, structures, and advances in therapy. Transduction Targeting Ther. (2023) 8:92. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01347-1
109. Jaiswal D, Trivedi S, Agrawal NK, Singh K. Dysregulation of apoptotic pathway candidate genes and proteins in infertile azoospermia patients. Fertil Steril. (2015) 104:736–743.e736. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2015.05.029
110. Daneshmandpour Y, Bahmanpour Z, Hamzeiy H, Mazaheri Moghaddam M, Mazaheri Moghaddam M, Khademi B, et al. MicroRNAs association with azoospermia, oligospermia, asthenozoospermia, and teratozoospermia: a systematic review. J Assist Reprod Genet. (2020) 37:763–75. doi: 10.1007/s10815-019-01674-9
111. Shahrokhi SZ, Salehi P, Alyasin A, Taghiyar S, Deemeh MR. Asthenozoospermia: Cellular and molecular contributing factors and treatment strategies. Andrologia. (2020) 52:e13463. doi: 10.1111/and.13463
112. Ghandehari-Alavijeh R, Zohrabi D, Tavalaee M, Nasr-Esfahani MH. Association between expression of TNF-α, P53 and HIF1α with asthenozoospermia. Hum Fertil (Camb). (2018) 22:145–51. doi: 10.1080/14647273.2018.1493750
113. Rahbar S, Pashaiasl M, Ezzati M, Ahmadi AsrBadr Y, Mohammadi-Dehcheshmeh M, Mohammadi SA, et al. MicroRNA-based regulatory circuit involved in sperm infertility. Andrologia. (2019) 52:e13453. doi: 10.1111/and.13453
114. Munoz-Lopez C, Wong A, Lewis K, Bole R, Vij SC, Lundy SD. The evolving landscape of male varicocele pathophysiology in the era of multi-omics: A narrative review of the current literature. Biol (Basel). (2024) 13:80. doi: 10.3390/biology13020080
115. Chang FW, Sun GH, Cheng YY, Chen IC, Chien HH, Wu GJ. Effects of varicocele upon the expression of apoptosis-related proteins. Andrologia. (2010) 42:225–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0272.2009.00981.x
116. Celik-Ozenci C, Kuscu N, Gungor-Ordueri NE, Tasatargil A, Sahin P, Durmus H. Inhibition of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase may have preventive potential for varicocoele-associated testicular damage in rats. Andrology. (2016) 5:362–9. doi: 10.1111/andr.12305
117. Chang I-Y, Kim J-H, Park K-H, Yoon S-P. Experimental Varicocele Induces p53-Dependent Germ Cell Apoptosis through Activation of γ-H2AX. Urol Int. (2010) 85:216–20. doi: 10.1159/000316356
118. Gentile V, Nicotra M, Minucci S, Ambrosi S, Saccucci P, Gloria-Bottini F, et al. The relationship between p53 codon 72 genetic polymorphism and sperm parameters. A study of men with varicocele. Reprod Med Biol. (2014) 14:11–5. doi: 10.1007/s12522-014-0188-y
119. Whibley C, Pharoah PD, Hollstein M. p53 polymorphisms: cancer implications. Nat Rev Cancer. (2009) 9:95–107. doi: 10.1038/nrc2584
120. Schoor RA, Elhanbly SM, Niederberger C. The pathophysiology of varicocele-associated male infertility. Curr Urol Rep. (2001) 2:432–6. doi: 10.1007/s11934-001-0035-7
121. Guo SJ, Sun ZJ, Li W. New insights about the early diagnosis of fertility impairment in varicoceles: the DNA repair gene example. Med Hypotheses. (2012) 78:536–8. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2012.01.029
122. Rodprasert W, Virtanen HE, Toppari J. Cryptorchidism and puberty. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2024) 15:1347435. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1347435
123. Mieusset R, Fouda PJ, Vaysse P, Guitard J, Moscovici J, Juskiewenski S. Increase in testicular temperature in case of cryptorchidism in boys. Fertil Steril. (1993) 59:1319–21. doi: 10.1016/s0015-0282(16)55999-8
124. Wanta A, Noguchi K, Sugawara T, Sonoda K, Duangchit S, Wakayama T. Expression of protein markers in spermatogenic and supporting sertoli cells affected by high abdominal temperature in cryptorchidism model mice. J Histochem Cytochem. (2023) 71:387–408. doi: 10.1369/00221554231185626
125. Yin Y, DeWolf WC, Morgentaler A. Experimental cryptorchidism induces testicular germ cell apoptosis by p53-dependent and -independent pathways in mice. Biol Reprod. (1998) 58:492–6. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod58.2.492
126. Zhou KW, Zheng XM, Yang ZW, Zhang L, Chen HD. Overexpression of CIRP may reduce testicular damage induced by cryptorchidism. Clin Invest Med. (2009) 32:E103–11. doi: 10.25011/cim.v32i2.6027
127. Mu X, Liu Y. Expression of orphan receptor TR2 mRNA in rhesus monkey (Macaca mulatta) testis. Chin Sci Bull. (1999) 44:927–30. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M910158199
128. Guo C, Hu Z, Zou R, Mu X, Liu Y. Expression and regulation of orphan receptor TR2 mRNA in germ cells of cryptorchid testis in rat and rhesus monkey. Chineses Sci Bull. (2000) 45:720–5. doi: 10.1007/bf02886177
129. Mu X-M, Liu Y-X, Collins LL, Kim E, Chang C. The p53/retinoblastoma-mediated repression of testicular orphan receptor-2 in the rhesus monkey with cryptorchidism. J Biol Chem. (2000) 275:23877–83. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M910158199
130. Boeri L, Pozzi E, Belladelli F, Fallara G, Cilio S, Bertini A, et al. The definition of idiopathic male infertility should include sperm DNA fragmentation values: Findings from a cross-sectional study. Eur Urol. (2023) 83:S947. doi: 10.1016/s0302-2838(23)00714-5
131. Mashayekhi F, Hadiyan SP. A single-nucleotide polymorphism in TP53 may be a genetic risk factor for Iranian patients with idiopathic male infertility. Andrologia. (2012) 44:560–4. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0272.2011.01227.x
132. Huang C, Liu W, Ji G-X, Gu A-H, Qu J-H, Song L, et al. Genetic variants in TP53 and MDM2 associated with male infertility in Chinese population. Asian J Androl. (2012) 14:691–4. doi: 10.1038/aja.2012.39
133. Lu NX, Xia YK, Gu AH, Liang J, Wang SL, Wang XR. Lack of association between polymorphisms in p53 gene and spermatogenetic failure in a Chinese population. Andrologia. (2007) 39:223–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0272.2007.00790.x
134. de Morais MP, Curado RF, e Silva KSF, Moura KKVO, Arruda JT. Male idiopathic infertility and the TP53 polymorphism in codon 72. Genet Mol Res. (2016) 15:gmr15048882. doi: 10.4238/gmr15048882
135. Javdan N, Ayatollahi SA, Choudhary MI, Al-Hasani S, Kobarfard F, Athar A, et al. Capsaicin protects against testicular torsion injury through mTOR-dependent mechanism. Theriogenology. (2018) 113:247–52. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2018.03.012
136. Lacy A, Smith A, Koyfman A, Long B. High risk and low prevalence diseases: Testicular torsion. Am J Emerg Med. (2023) 66:98–104. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2023.01.031
137. Shamsi-Gamchi N, Razi M, Behfar M. Cross-link between mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis and cell cycle checkpoint proteins after experimental torsion and detorsion in rats. Gene. (2021) 795:145793. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2021.145793
138. Duffy MJ, Synnott NC, O’Grady S, Crown J. Targeting p53 for the treatment of cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. (2022) 79:58–67. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2020.07.005
139. Gao J, Liu J, Li Y, Liu J, Wang H, Chai M, et al. Targeting p53 for neuroinflammation: New therapeutic strategies in ischemic stroke. J Neurosci Res. (2023) 101:1393–408. doi: 10.1002/jnr.25200
140. He L, Gong H, You S, Zhang C, Zhong C, Li L. miRNA-138-5p suppresses cigarette smoke-induced apoptosis in testicular cells by targeting Caspase-3 through the Bcl-2 signaling pathway. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. (2021) 35:e22783. doi: 10.1002/jbt.22783
141. Albekairi NA, Al-Hamamah MA, Alshamrani AA, Attia MSM, Nadeem A, Ansari MA, et al. Dapagliflozin mitigated elevated disomic and diploid sperm in a mouse model of diabetes and recover the disrupted Ogg1, Parp1, and P53 gene expression. Biomedicines. (2023) 11:2980. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11112980
142. Eleawa SM, Alkhateeb MA, Alhashem FH, Bin-Jaliah I, Sakr HF, Elrefaey HM, et al. Resveratrol reverses cadmium chloride-induced testicular damage and subfertility by downregulating p53 and Bax and upregulating gonadotropins and Bcl-2 gene expression. J Reprod Dev. (2014) 60:115–27. doi: 10.1262/jrd.2013-097
143. Garcia JM, Guillory B, Donehower LA, Smith RG, Lamb DJ. Ghrelin prevents cisplatin-induced testicular damage by facilitating repair of DNA double strand breaks through activation of p53 in mice1. Biol Reprod. (2015) 93:24. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.115.129759
144. Shen YL, Sun L, Hu YJ, Liu HJ, Kuang XY, Niu XL, et al. P53 inhibitor pifithrin-α prevents the renal tubular epithelial cells against injury. Am J Transl Res. (2016) 8:4040–53.
145. Peuget S, Zhou X, Selivanova G. Translating p53-based therapies for cancer into the clinic. Nat Rev Cancer. (2024) 24:192–215. doi: 10.1038/s41568-023-00658-3
Keywords: p53, male infertility, spermatogenesis, drug target, strategy
Citation: Li J, Huang X, Luo L, Sun J, Guo Q, Yang X, Zhang C and Ni B (2024) The role of p53 in male infertility. Front. Endocrinol. 15:1457985. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1457985
Received: 04 July 2024; Accepted: 27 September 2024;
Published: 14 October 2024.
Edited by:
Meng Liang, Bengbu Medical University, ChinaReviewed by:
Maria Susana Theas, CONICET Institute for Biomedical Research (BIOMED), ArgentinaRabea Ejaz, Rawalpindi Women University, Pakistan
Copyright © 2024 Li, Huang, Luo, Sun, Guo, Yang, Zhang and Ni. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Beibei Ni, bmliZWliZWlAcWR1LmVkdS5jbg==
 Jing Li
Jing Li Xia Huang2
Xia Huang2 Qie Guo
Qie Guo Beibei Ni
Beibei Ni