- 1Department of Pharmacy, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
- 2Department of Pharmacy, Jiangxi Mental Health Center, Nanchang, China
- 3West China School of Pharmacy, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
Background: The benefits of sodium-glucose-cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors in the treatment of type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) have been demonstrated, but the occurrence of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) limits their use. The risk of DKA associated with different doses of SGLT2 inhibitous in the treatment of T1DM is unknown. We conducted a network meta-analysis to evaluate the incidence of DKA at different doses in the treatment of T1DM.
Methods: We searched electronic databases and clinical trial registries, including PubMed, Embase (Ovid SP), the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (Ovid SP), and ClinicalTrials.gov, for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) concerning SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with T1DM from inception to December 2023. Literature screening, quality assessment and data extraction were carried out independently by 2 researchers based on the inclusion and exclusion criteria, and statistical analysis was performed using Stata 15.1 software and R 4.1.3.
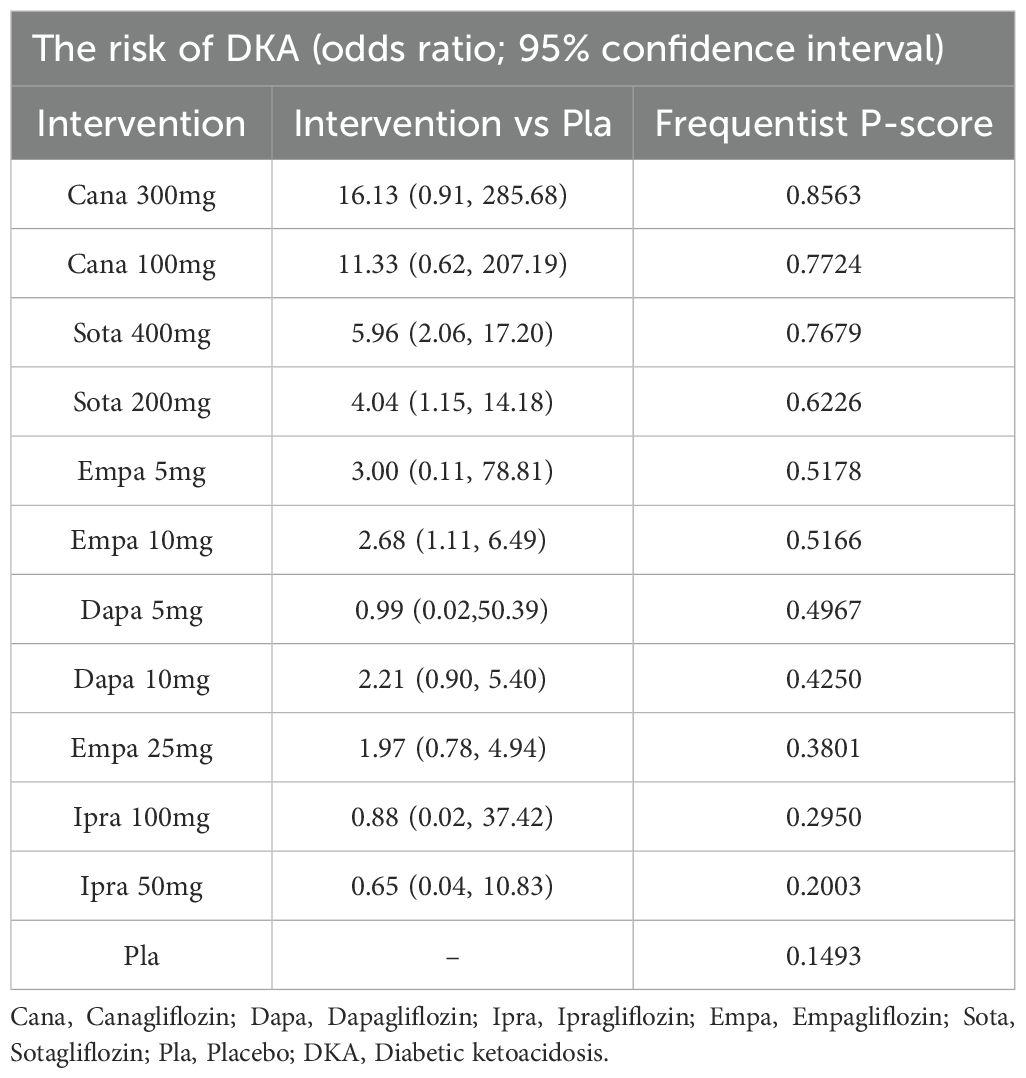
Results: Nineteen clinical studies and one clinical trial were ultimately included. The study involved five different SGLT2 inhibitors. The incidence of DKA in dapagliflozin 5 mg (OR: 2.57, 95% CI: 1.04 to 6.33; P<0.00001), empagliflozin 10 mg (OR: 2.68, 95% CI: 1.11 to 6.49; P<0.00001), sogliflozin 200mg (OR: 4.04, 95% CI: 1.15 to14.18; P<0.00001) and sogliflozin 400mg (OR: 5.96, 95% CI: 2.06 to17.20; P<0.00001) were higher than for the placebo. According to the P scores, SGLT2 inhibitors triggered a lower incidence of DKA than did the placebo. Treatment with 300 mg canagliflozin had the lowest incidence of DKA (P score = 0.8563).
Conclusion: According to our study, 5 mg dapagliflozin,10 mg empagliflozin 200mg sogliflozin and 400mg sogliflozin resulted in DKA when adjunctive insulin was used to treat T1DM. Other SGLT2 inhibitors seem to be safe. However, SGLT2 inhibitors for treating T1DM are off label in China, and adverse reactions should be closely monitored during administration.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/#loginpage, identifier CRD42023416227.
1 Introduction
Type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) is an endocrine disease caused by the combined action of susceptibility genes and environmental factors, leading to destruction of β cells and a lifelong dependence on insulin therapy. Insulin therapy is the mainstay treatment for people with T1DM (1). However, long-term insulin therapy is accompanied by problems such as hypoglycemia, weight gain, insulin resistance, and increased cardiovascular risk (2). Some noninsulin medications may assist in treating hypoglycemia while potentially counteracting these effects and may have cardiovascular and renal benefits to some extent. Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors is one of the adjuvant drugs used to treat T1DM.
SGLT2 inhibitors, such as cagliflozin, dagliflozin, and empagliflozin, are a newer class of antihyperglycemic agents that can improve glycemic control in an insulin-independent manner. Adjuvant therapy in patients with T1DM has been shown to reduce HbA1c, improve glucose time in target range, reduce body weight, and improve blood pressure control in several phase III clinical studies (3).In the 2021 Consensus Report on the Management of Type 1 Diabetes in Adults, issued by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) together with the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD), it was stated that SGLT2 inhibitors should be used with caution, with care taken to adjust insulin doses appropriately when using them, starting with a Start with a low dose of SGLT 2 inhibitor and measure blood ketones regularly (4). The Chinese 2021 guideline for the diagnosis and management of type I diabetes suggests that SGLT2 inhibitors may be considered in T1DM with informed consent and a BMI ≥25 kg/m2 with poor insulin control (5). However, the adjunctive use of SGLT 2 inhibitors in adult patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus increases the absolute risk of DKA by approximately 4% per year (6). Because of the increased incidence of DKA the FDA denied marketing authorization for its treatment of T1DM. In 2021, dapagliflozin 5 mg for T1DM indication was removed across the European Medicines Agency and the MHRA (7).
Considering the benefits that SGLT2 inhibitors bring in the treatment of T1DM, the use of these drugs in the treatment of T1DM is currently being explored, despite the possibility that they may lead to an elevated risk associated with DKA.
We conducted a systematic review and network meta-analysis for the risk of DKA associated with SGLT2 inhibitors in the adjuvant treatment of T1DM, with the aim of providing some reference for the safety convenience of clinical use of SGLT2 inhibitors in the adjuvant treatment of T1DM.
2 Methods
This network meta-analysis was registered in the PROSPERO database (ID: CRD 42023416227) and conducted according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) 2020 guidelines and the statement standard for network meta-analysis (PRISMA-NMA) (Supplementary Tables 1, 2).
2.1 Literature search
A systematic review of the literature using PubMed, Embase (Ovid SP), and Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (Ovid SP) for studies was conducted on December 18th, 2023. We also searched ClinicalTrial.gov for ongoing, unpublished studies. Finally, the reference lists of relevant published research investigating the risk of DKA of SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with T1DM were also screened for potentially relevant studies. The key terms searched in this study are based on the PICOS framework, (Supplementary Table 3). Duplicate records were removed with EndNote X9.
2.2 Study selection
Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) assessing SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with T1DM were evaluated based on the following criteria: (1) Adults (>18 years) with a diagnosis of T1DM. (2) Different medicines must be used in different groups of patients; one group of patients must use SGLT2 inhibitors, and the other group can use other hypoglycemic drugs that are not SGLT2 inhibitors or placebos. (3) Trials reporting on the outcome of the risk of DKA. The exclusion criteria were as follows: 1) pregnant participants; 2) published as abstracts only; and 3) included patients with prediabetes. We had no restriction on language, but all included studies were written in English.
2.3 Data extraction and quality assessment
From eligible studies, the first author’s name, publication year, sample size, follow-up length, intervention and comparison, outcomes, and the characteristics of participants were extracted according to a prespecified protocol. Two investigators (YL and AJ) independently performed the literature search, study selection, and extraction of baseline characteristics and outcome measures and cross-checking. Any discrepancy or ambiguity in this process was resolved by discussion with a 3rd reviewer (NS) when necessary. Two independent investigators adjudicated the quality of evidence using the Risk of Bias (ROB 2) tool for randomized trials through six pre-specified domains (8) The evidence quality of collective outcomes was estimated using the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation (GRADE) framework (9). A comparison-adjusted funnel plot with the Egger test was conducted to assess for publication bias (10).
2.4 Statistical analysis
We used a fixed-effects model-based frequentist framework with a graph-theoretical method by the netmeta package command R (version 4.1.3) to summarize the risk of DKA between different SGLT2 inhibitors (11, 12). Then, the incidence of DKA in the treatment of T1DM with SGLT2 inhibitors was statistically analyzed by P=score to ranking probability of intervention drugs in main analysis by netmeta package in R. Direct and indirect comparisons were accomplished through the self-programmed routines of Stata and the netmeta package of R (10, 13). Because the outcomes included in this study were dichotomous variables, odds ratios (ORs) were used for effect estimation, and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) and P < 0.05 were used as the criteria for significant differences. We estimated the variance in heterogeneity between studies using the DerSimonian–Laird fixed-effects model. We assessed transitivity using descriptive statistics from studies and population baselines (14).
Publication bias was evaluated utilizing funnel plots and Egger’s test, employing the netmeta package in R software. To ensure the robustness of the final results, four sensitivity analyses were conducted, encompassing the following considerations: 1) exclusion of studies with fewer than 100 participants; 2) exclusion of studies with treatment duration <12 weeks; 3) exclusion of studies without an insulin control;4)this analysis was estimated in a Bayesian framework.
3 Results
3.1 Characteristics of eligible studies
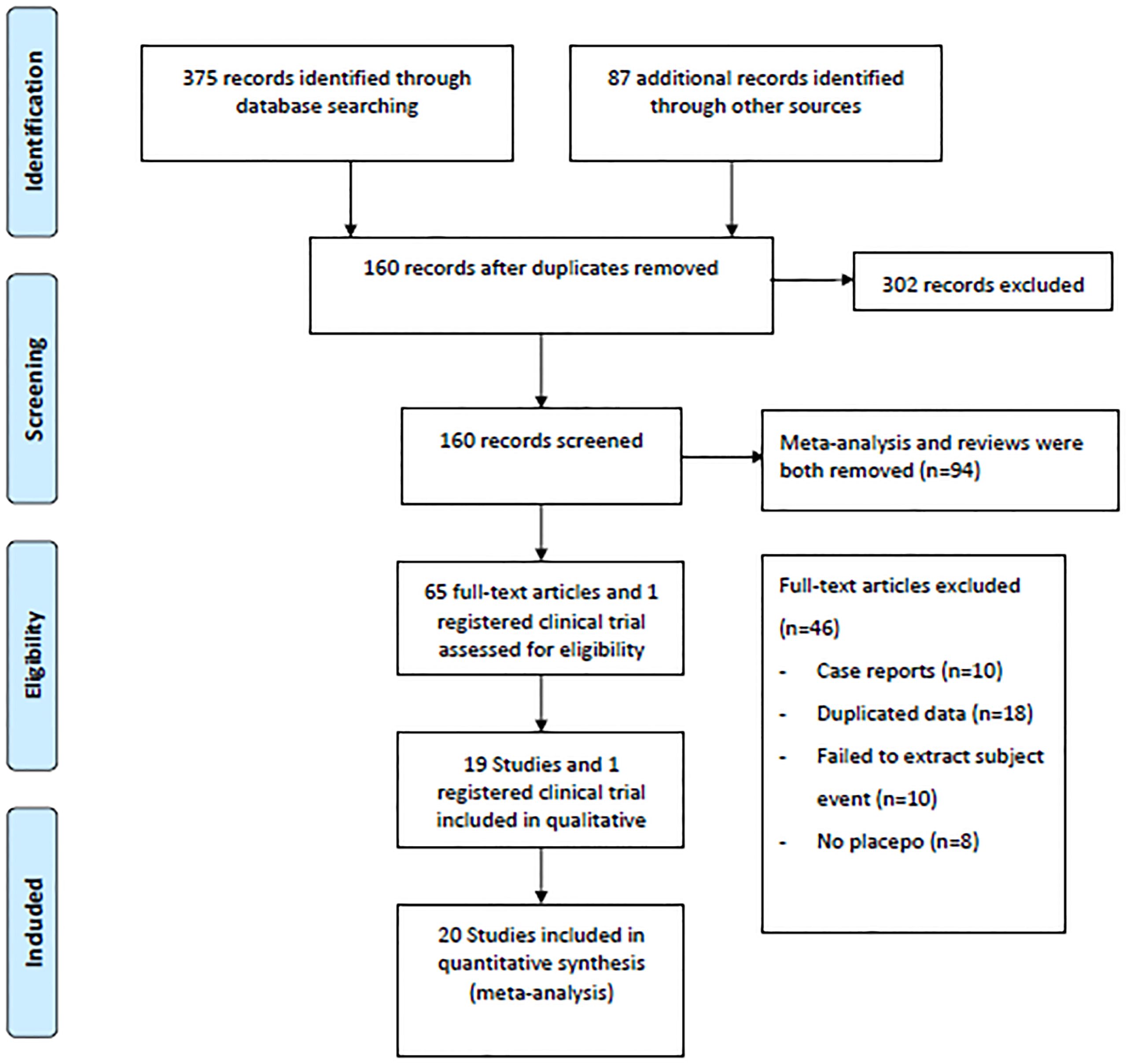
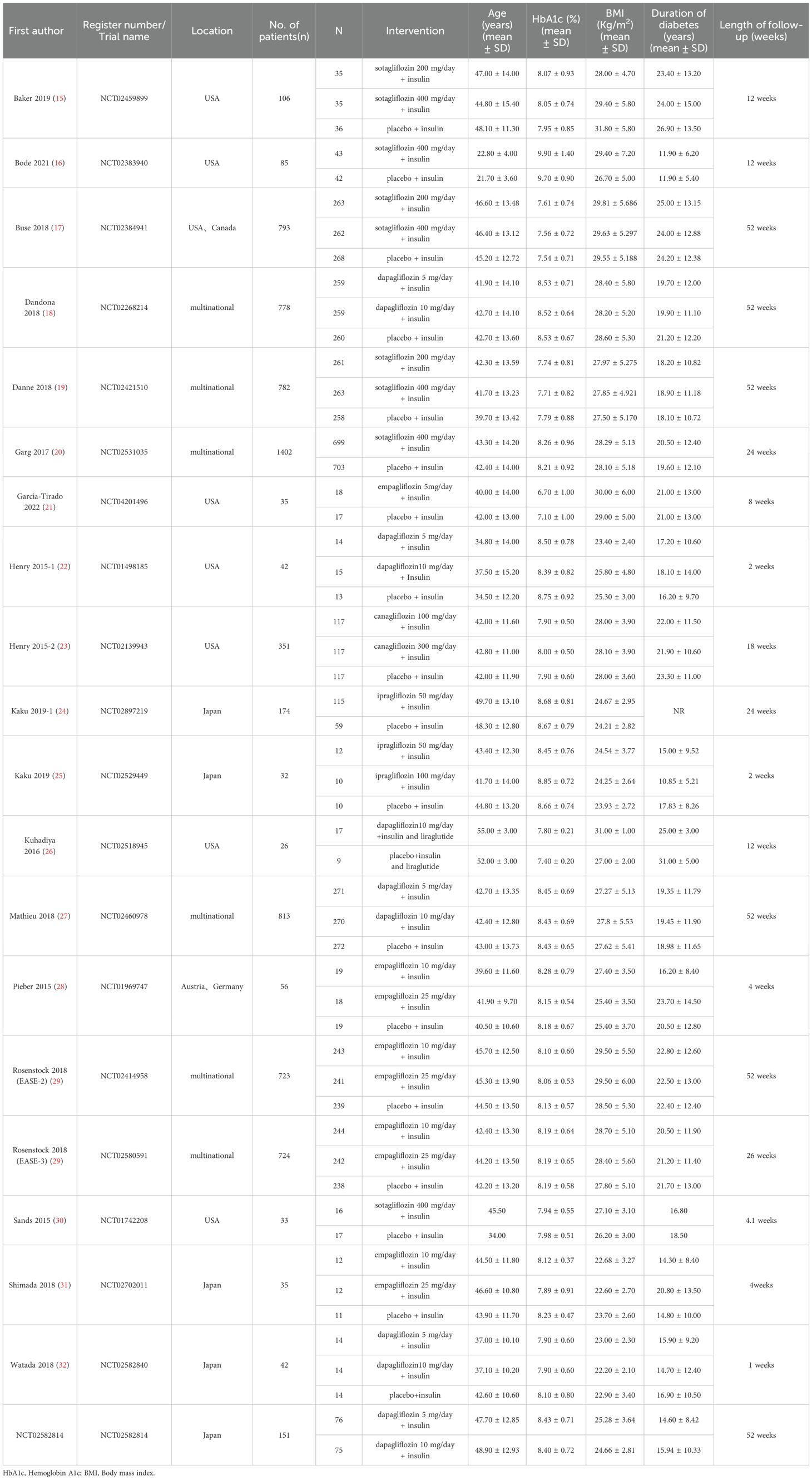
A flow diagram illustrating the literature search process is presented in Figure 1. After screening 375 articles and 87 additional records identified through other sources, a total of 20 studies conducted between 2015 and 2023 were included in the meta-analysis based on predefined criteria (19 articles and 1 registered clinical trial). These studies involved 7183 patients and 135 patients with DKA (15–33). Of the studies included, 6 were multinational country studies, and all of them were registered and published in English. The baseline characteristics of the included studies are presented in Table 1. Among these studies, SGLT2 inhibitors were all adjunctive to insulin for the treatment of T1DM. Nineteen were two-arm studies, and 1 was a single-arm study. Among the twenty studies (the SGLT2 inhibitors retrieved included 1 study about canagliflozin, 6 studies about dapagliflozin, 5 studies about empagliflozin, 2 studies about ipragliflzin and 6 studies about sotagliflozin),14 compared the use of different doses of SGLT2 inhibitors, of which three studies compared sotagliflozin 400 mg/day with 200 mg/day, five studies compared dapagliflozin 5 mg/day with 10 mg/day, and four studies compared empagliflozin 10 mg/day and 25 mg/day. Additionally, two other studies were conducted to compare canagliflozin 100 mg/day with 300 mg/day and ipragliflozin 50 mg/day with 100 mg/day; 19 studies compared SGLT2 inhibitors to placebo. The study included 3497 male participants (48.69%) and 3686 female participants (51.31%), with a mean age of 42.49 years (ranging from 21.70 to 55.00 years); the mean HbA1c was 8.17% (ranging from 6.70 to 9.90%); the baseline mean BMI was 26.98 kg/m2 (ranging from 22.20 to 31.80 kg/m2); the mean T1DM duration was 19.61 years (ranging from 11.90 to 25.00 years); and the mean treatment duration was 23.1 weeks (ranging from 1.0 to 52.0 weeks). In addition, all trials were funded by pharmaceutical companies.
3.2 Risk of bias of included studies
The overall risk of bias was some concerns. The assessment of bias risk for the included studies can be found in Supplementary Table 4. Among the risk of bias arising from the randomization process, one study had some concerns, while the others had a low risk. Regarding the risk of bias due to deviations from the intended interventions, 15 studies had some concerns, and the rest were at low risk. The risk of bias due to missing outcome data, risk of bias in the measurement of the outcome, and risk of bias in the selection of the reported result were all low risk. The overall assessment of the quality of the studies revealed that more than half of the studies exhibited a low risk of bias.
3.3 Results of network meta-analysis
Network plots depicting the results and quality of evidence for different doses of SGLT2 inhibitors are presented in Figure 2. In this diagram, each node symbolizes different doses of SGLT2 inhibitors, whereby the node’s size corresponds to the sample size associated with that intervention. Furthermore, the thickness of the lines connecting the nodes signifies the number of included studies for that specific intervention. The evaluation of inconsistency in the network meta-analysis is shown in Supplementary Figure 1. Additionally, heterogeneity and sensitivity of the network meta-analysis were assessed (Supplementary Table 5, Supplementary Figures 2-4). The results of the heterogeneity test indicated that the differences between the included studies were not statistically significant and were homogeneous (P>0.05).
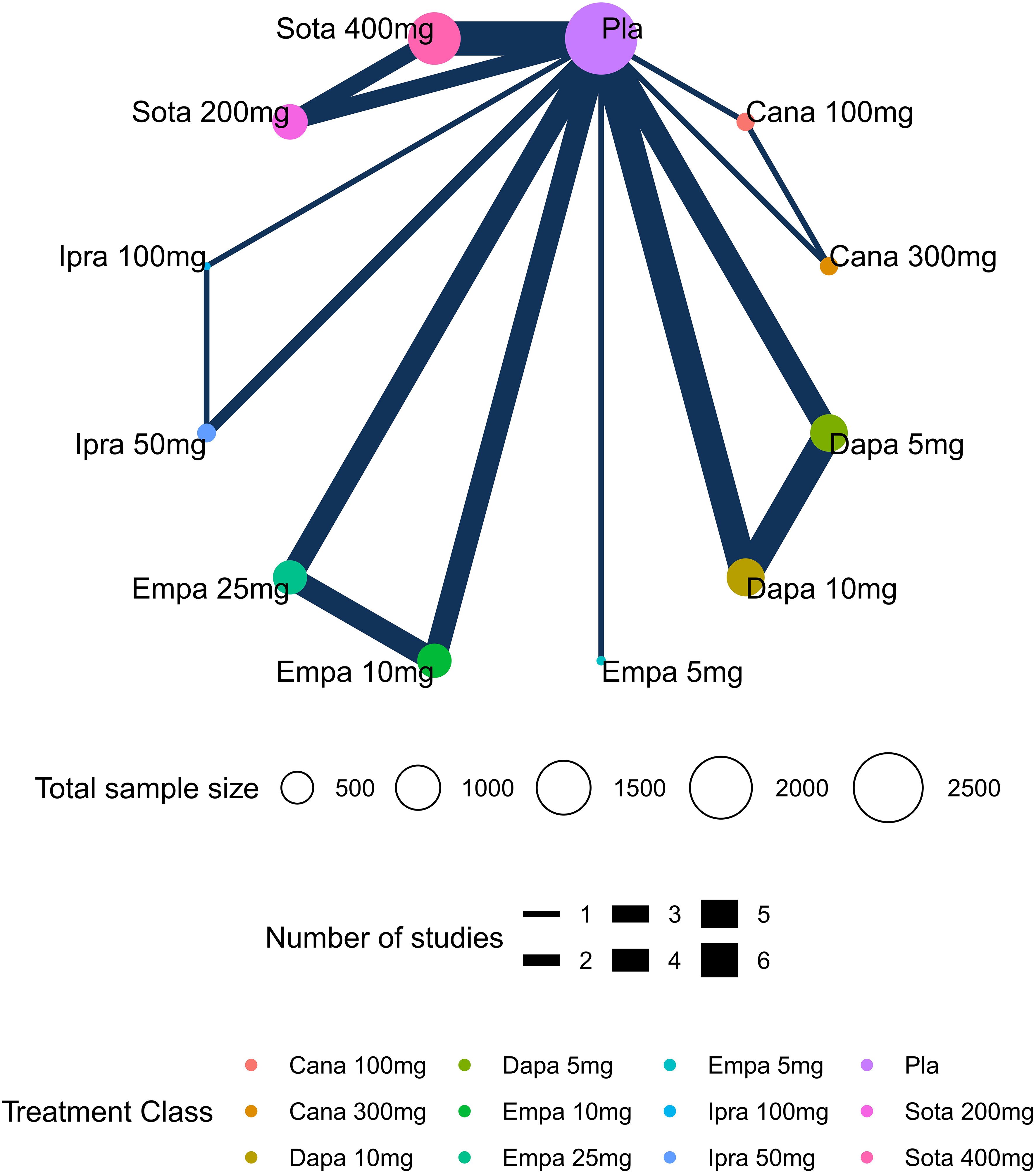
Figure 2. Network plots of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). Nodes in different colors indicate different processing. The node size corresponds to the number of participants treated in the study. The thickness of the edge represents the number of tests. The lack of lines suggests that there have been no head-to-head trials of this outcome between the two treatments.
3.4 DKA
A total of twenty studies, covering 7183 patients, reported the risk of DKA, with a total of 135 DKA events and an incidence rate of 1.88%. In this network meta-analysis, the intervention node included different doses of SGLT2 inhibitors. Compared to the placebo, dapagliflozin 5 mg,empagliflozin 10 mg, sotagliflozin 200mg and sotagliflozin 400mg had significantly greater incidences of DKA (Figure 3). The global I² for the pairwise comparison was 0%, and for the consistency model, the global I² was 0%. The analysis of node split indicated that the results were consistent. The GRADE quality of the network meta-analysis can be seen in Supplementary Table 4.
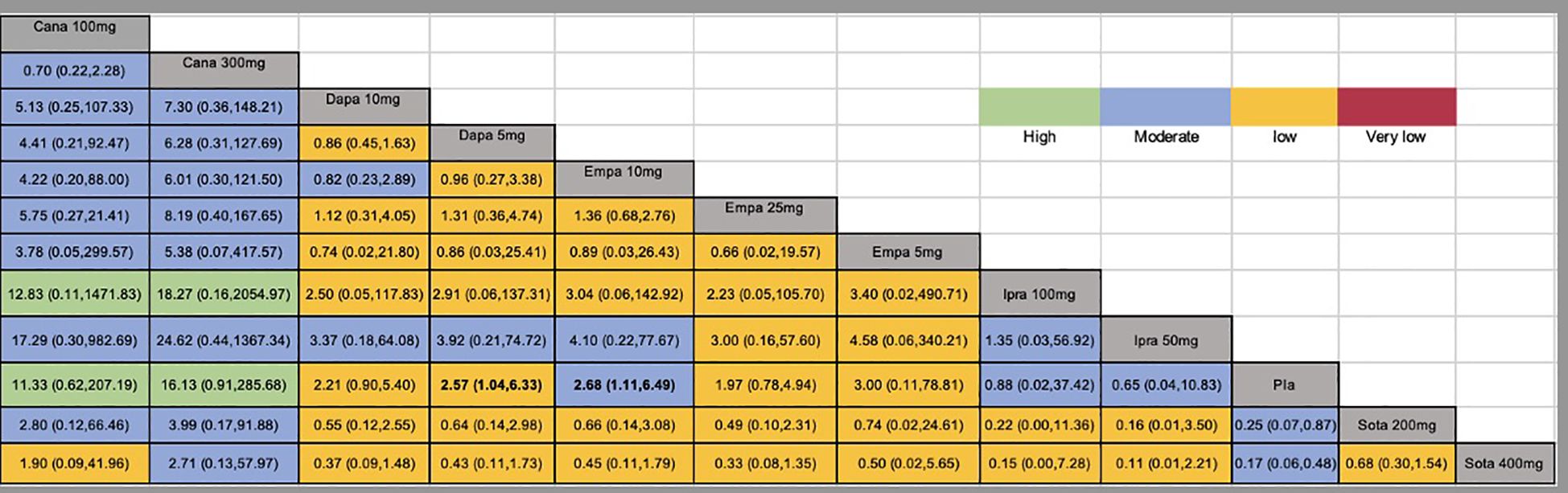
Figure 3. Network estimates (league tables) for different doses of SGLT2 inhibitors. Outcome: The risk of DKA (odds ratio; 95% confidence interval). The league table presented the relative effects of different kinds of SGLT2 inhibitors (the risk of DKA on the column to the risk of DKA of the row). SGLT2, Sodium-glucose co-transporter-2; Cana, Canagliflozin; Dapa, Dapagliflozin; Ipra, Ipragliflozin; Empa, Empagliflozin; Sota, sotagliflozin; Pla, Placebo; DKA, diabetic ketoacidosis.
3.5 Rankings and P scores
The P scores of DKA for various doses of SGLT2 inhibitors are shown in Table 2. A high P score indicated a lower risk of DKA. The P scores of DKA suggested that different doses of SGLT2 inhibitors were associated with different risks of DKA. Table 2 shows that canagliflozin 300 mg had the lowest risk of DKA (P score = 0.8563).
3.6 Funnel plot and sensitivity analysis
Egger’s test indicated that there was no publication bias among the different doses of SGLT2 inhibitors (p = 0.72, Supplementary Figure 5). Supplementary Table 5 shows the results of the sensitivity analyses. The results showed that all sensitivity analyses were consistent with the primary results.
Sensitivity analysis using the Bayesian framework revealed that 100 mg canagliflozin and 300 mg canagliflozin were associated with a greater risk of DKA. Additionally, 10 mg empagliflozin had a greater risk than 25 mg empagliflozin. Other sensitivity analyses were consistent with the primary results.
4 Discussion
At present, SGLT2 inhibitors are exclusively approved for the treatment of T2DM. However, there are potential advantages to utilizing SGLT2 inhibitors in the adjuvant treatment of T1DM, such as better blood sugar control, decreased insulin dosage, weight management and loss, lower blood pressure, and improved blood sugar fluctuation (34). Although there have been reports of SGLT-2i being used for type 1 diabetes, it remains unclear whether such off-label drug use poses any safety risks. According to studies, SGLT-2i might increase the incidence of DKA in T1DM patients, which is a rare occurrence in T2DM. We conducted relevant research during the previous period and discovered that SGLT2 inhibitors were not associated with an elevated risk of DKA compared to the placebo in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Furthermore, no dose-dependent association was observed between SGLT2 inhibitors and the risk of DKA in type 2 diabetes (35). According to the results of the network meta-analysis, SGLT2 inhibitors were not associated with a greater risk of DKA than was a placebo. Except for dapagliflozin 5 mg,empagliflozin 10 mg, sotagliflozin 200mg and sotagliflozin 400mg no risk of DKA was observed with SGLT2 inhibitors as an adjunct to insulin in the treatment of T1DM compared to insulin.
A study has been conducted to compare the safety and efficacy of different hypoglycemic agents when used as adjunctive therapy for T1DM. It was concluded that the risk of DKA and the risk of genital infection were more common with SGLT2 inhibitors than with other hypoglycemic agents (36). However, the study did not compare the incidence of DKA between different doses of SGLT inhibitors. This research is a network meta-analysis of SGLT2 inhibitors at different doses for the treatment of T1DM. The results showed that dapagliflozin 5 mg,empagliflozin 10 mg, sotagliflozin 200mg and sotagliflozin 400mg for the treatment of T1DM had a significantly greater incidence of DKA than the placebo. According to the P scores, SGLT2 inhibitors were associated with a lower risk of DKA than was a placebo, and 300 mg canagliflozin had the lowest risk of DKA, but this difference was not statistically significant compared to that associated with a placebo.
There have also been some reports of DKA caused by dapagliflozin, but the most common primary causes of DKA are insulin pump failure and a missed insulin dose (22). Most of the studies that started adjuvant avoidance of excessive insulin dose reductions at the time of dapagliflozin therapy (18, 26, 28). Subsequent careful reduction of the insulin dose during therapy may be important for reducing the risk of DKA. For empagliflozin, the incidence of DKA was dose-related, and the risk of DKA was associated with concomitant disease or infection with excessive insulin dose reductions or insulin pump failure. The likelihood of DKA was similar for 10 mg and 25 mg, but the clinical manifestations were more severe with 25 mg (29). The study concluded that the incidence of DKA was greater in female patients and those who used insulin pumps. If an SGLT inhibitor is considered for T1DM patients, it should not be used with a low-carbohydrate diet or in patients with a history of excessive alcohol consumption or recent episodes of DKA. Regarding sotagliflozin, six of the studies we included were of sotagliflozin therapy adjunctive to the treatment T1DM (15–17, 19, 20, 30); the overall results suggest that sotagliflozin 400 mg is more susceptible to DKA. after the occurrence of DKA, the majority of patients recovered from discontinuation of sotagliflozin, whereas it is thought that one of the causes of DKA is still the inappropriate operation of or malfunctioning in the use of the insulin pumps. Therefore, it is considered necessary to monitor ketosis while using sotagliflozin and to consider discontinuing the drug before scheduled surgical procedures (17).
In 2020, the National NICE guidance identified dapagliflozin as a treatment with both clinical and economic value for people with T1DM. Furthermore, the guidance provides recommendations for when prescribing dapagliflozin would be appropriate in patients with T1DM. However, in 2021, dapagliflozin combined with insulin was no longer licensed for treating T1DM. Dapagliflozin and sotagliflozin were previously approved for the treatment of T1DM in Europe but were never approved in the United States due to the lack of adequate data on the increased risk of DKA reported in clinical trials, including episodes of euglycemic DKA. Currently, the latest UK Kidney Association guidelines recommend the use of SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with T1DM if they have an eGFR ≥ 20 mL/min/1.73 m2 and a uACR ≥ 25 mg/mmol under the strict direction of a specialized diabetologist (37).
SGLT2 inhibitors can significantly lower glucose levels by reducing glucose reabsorption from the kidneys, resulting in more glucose being excreted through the urine. One of the advantages of SGLT2 inhibitors is that they operate independently of insulin secretion, which means that their efficacy remains unaffected by insulin resistance or β-cell dysfunction. Therefore, the non-insulin-dependent mode of action of SGLT2 inhibitors can also benefit patients with T1DM. Adjuvant therapy with SGLT2 inhibitors reduces the total daily insulin dose in patients with T1DM, and ketone bodies increase when low-dose insulin is insufficient to inhibit lipolysis in peripheral adipose tissue. Therefore, the use of SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with T1DM may increase the incidence of ketone body-related events. However, a significant increase in real-world research evidence is needed to guide clinicians in assessing the true risk of DKA in patients with T1DM under the rigorous scrutiny of clinical trials through careful patient selection and intensive patient and clinical team education.
4.1 Strengths and limitations
This study is the first network meta-analysis of SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with T1DM investigating the risk of DKA. In addition, we included one unpublished trial from a clinical trial database that provided additional DKA data. Previously, we also conducted a systematic review and network meta-analysis of the available evidence for the risk of DKA associated with SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with T2DM (36). Several potential limitations should be acknowledged. First, there are few clinical studies on the use of SGLT2 inhibitors in the treatment of T1DM, and the incidence of DKA is low, which may be biased. Second, none of the included studies distinguished eDKA from DKA. Therefore, our outcome was DKA, not eDKA.
5 Conclusion
Except for 5mg dapagliflozin,10mg empagliflozin,200mg sotagliflozin and 400mg sotagliflozin, no risk of DKA was observed with SGLT2 inhibitors as an adjunct to insulin in the treatment of T1DM compared to insulin. Considering the glucose-lowering mechanism of SGLT2 inhibitors, SGLT2 inhibitors may be useful as an adjunct to insulin for treating T1DM. If available, we recommend canagliflozin because of the P score. However, the treatment of T1DM with SGLT2 inhibitors is off-label, and adverse reactions should be closely monitored during administration.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
YL: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. SY: Writing – review & editing. AJ: Writing – review & editing. DZ: Writing – review & editing. ZC: Writing – review & editing. NS: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. NS was supported by grants from Sichuan Province Science and Technology Support Program (grant number 2023JDR0243) and Health Commission Program (grant number 2020-111).
Acknowledgments
We thank the National Key Clinical Specialties Construction Program for its support of this manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The reviewer SZ declared a past co-authorship with the author NS to the handling editor.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fendo.2024.1453067/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Fourlanos S, Varney MD, Tait BD, Morahan G, Honeyman MC, Colman PG, et al. The rising incidence of type 1 diabetes is accounted for by cases with lower-risk human leukocyte antigen genotypes. Diabetes Care. (2008) 31:1546–1549. doi: 10.2337/dc08-0239
2. Chillaron JJ, Flores, Le-Roux JA, Benaiges D, Pedro-Botet J. Type 1 diabetes, metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular risk. Metabolism. (2014) 63:181–7. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2013.10.002
3. Snaith JR, Holmes-Walker DJ, Greenfield JR. Reducing type 1 diabetes mortality: role for adjunctive therapies? Trends Endocrinol Metab. (2020) 31:150–64. doi: 10.1016/j.tem
4. Holt RIG, DeVries JH, Hess-Fischl A, Hirsch IB, Kirkman MS, Klupa T, et al. The management of type 1 diabetes in adults. A consensus report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetologia. (2021) 44(11):2589–625. doi: 10.1007/s00125-021-05568-3
5. Chinese Diabetes Society, Chinese Endocrinologist Association, Chinese Society of Endocrinology, Chinese Pediatric Society, Zhou Zhiguang. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of type 1 diabetes mellitus in China (2021 edition). Chin J Diabetes Mellitus. (2022) 14:1143–250. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115791-20220916-00474
6. Danne T, Garg S, Peters AL, Buse JB, Mathieu C, Pettus JH, et al. International consensus on risk management of diabetic ketoacidosis in patients with type1 diabetes treated with sodium-glucose cotransporter (SGLT)inhibitors. Diabetes Care. (2019) 42:1147–54. doi: 10.2337/dc18-2316
7. Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency. Dapagliflozin (Forxiga): no longer authorised for treatment of type 1 diabetes mellitus(2021). Available online at: https://www.gov.uk/drug-safety-update/dapagliflozin-forxiga-no-longer-authorised-for-treatment-of-type-1-diabetes-mellitus (Accessed 10 20, 2023).
8. Sterne JAC, Savović J, Page MJ, Elbers RG, Blencowe NS, Boutron I, et al. RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. (2019) 366:l4898. doi: 10.1136/bmj.l4898
9. Puhan MA, Schunemann HJ, Murad MH, Li T, Brignardello-Petersen R, Singh JA, et al. A GRADE Working Group approach for rating the quality of treatment effect estimates from network meta-analysis. BMJ. (2014) 349:g5630. doi: 10.1136/bmj.g5630
10. Chaimani A, Higgins JP, Mavridis D, Spyridonos P, Salanti G. Graphical tools for network meta-analysis in STATA. PloS One. (2013) 8:e76654. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076654
11. Mawdsley D, Bennetts M, Dias S, Boucher M, Welton NJ. Model-based network meta-analysis: a framework for evidence synthesis of clinical trial data. CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. (2016) 5:393–401. doi: 10.1002/psp4.12091
12. Xu C, Niu Y, Wu J, Gu H, Zhang C. Software and package applicating for network meta-analysis: A usage-based comparative study. J Evid Based Med. (2018) 11:176–83. doi: 10.1111/jebm.12264
13. Shim S, Yoon BH, Shin IS, Bae JM. Network meta-analysis: application and practice using Stata. Epidemiol Health. (2017) 39:e2017047. doi: 10.4178/epih.e2017047
14. Cipriani A, Higgins JP, Geddes JR, Salanti G. Conceptual and technical challenges in network meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. (2013) 159:130–7. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-159-2-201307160-00008
15. Baker C, Wason S, Banks P, Sawhney S, Chang A, Danne T, et al. Dose-dependent glycometabolic effects of sotagliflozin on type 1 diabetes over 12 weeks: The inTandem4 trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. (2019) 21:2440–9. doi: 10.1111/dom.13825
16. Bode BW, Cengiz E, Wadwa RP, Banks P, Danne T, Kushner JA, et al. Effects of sotagliflozin combined with intensive insulin therapy in young adults with poorly controlled type 1 diabetes: the JDRF sotagliflozin study. Diabetes Technol Ther. (2021) 23:59–69. doi: 10.1089/dia.2020.0079
17. Buse JB, Garg SK, Rosenstock J, Bailey TS, Banks P, Bode BW, et al. Sotagliflozin in combination with optimized insulin therapy in adults with type 1 diabetes: the North American inTandem1 study. Diabetes Care. (2018) 41:1970–80. doi: 10.2337/dc18-0343
18. Dandona P, Mathieu C, Phillip M, Hansen L, Tschöpe D, Thorén F, et al. Efficacy and safety of dapagliflozin in patients with inadequately controlled type 1 diabetes: the DEPICT-1 52-week study. Diabetes Care. (2018) 41:2552–9. doi: 10.2337/dc18-1087
19. Danne T, Cariou B, Banks P, Brandle M, Brath H, Franek E, et al. HbA1c and Hypoglycemia Reductions at 24 and 52 Weeks With Sotagliflozin in Combination With Insulin in Adults With Type 1 Diabetes: The European inTandem2 Study. Diabetes Care. (2018) 41:1981–90. doi: 10.2337/dc18-0342
20. Garg SK, Henry RR, Banks P, Buse JB, Davies MJ, Fulcher GR, et al. Effects of sotagliflozin added to insulin in patients with type 1 diabetes. N Engl J Med. (2017) 377:2337–48. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1708337
21. Garcia-Tirado J, Farhy L, Nass R, Kollar L, Clancy-Oliveri M, Basu R, et al. Automated insulin delivery with SGLT2i combination therapy in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Technol Ther. (2022) 24:461–70. doi: 10.1089/dia.2021.0542
22. Henry RR, Rosenstock J, Edelman S, Mudaliar S, Chalamandaris AG, Kasichayanula S, et al. Exploring the potential of the SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin in type 1 diabetes: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study. Diabetes Care. (2015) 38:412–9. doi: 10.2337/dc13-2955
23. Henry RR, Thakkar P, Tong C, Polidori D, Alba M. Efficacy and safety of canagliflozin, a sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor, as add-on to insulin in patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care. (2015) 8:2258–65. doi: 10.2337/dc15-1730
24. Kaku K, Isaka H, Sakatani T, Toyoshima J. Efficacy and safety of ipragliflozin add-on therapy to insulin in Japanese patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus: A randomized, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. (2019) 21:2284–93. doi: 10.1111/dom.13807
25. Kaku K, Isaka H, Toyoshima J, Sakatani T. Clinical pharmacology study of ipragliflozin in Japanese patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus: A phase 2, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. (2019) 21:1445–54. doi: 10.1111/dom.13679
26. Kuhadiya ND, Ghanim H, Mehta A, Garg M, Khan S, Hejna J, et al. Dapagliflozin as additional treatment to liraglutide and insulin in patients with type 1 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2016) 101:3506–15. doi: 10.1210/jc.2016-1451
27. Mathieu C, Rudofsky G, Phillip M, Araki E, Lind M, Arya N, et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of dapagliflozin in patients with inadequately controlled type 1 diabetes (the DEPICT-2 study): 52-week results from a randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. (2020) 22:1516–26. doi: 10.1111/dom.14060
28. Pieber TR, Famulla S, Eilbracht J, Cescutti J, Soleymanlou N, Ohansen OE, et al. Empagliflozin as adjunct to insulin in patients with type 1 diabetes: a 4-week, randomized, placebo-controlled trial (EASE-1). Diabetes Obes Metab. (2015) 17:928–35. doi: 10.1111/dom.12494
29. Rosenstock J, Marquard J, Laffel LM, Neubacher D, Kaspers S, Cherney D,Z, et al. Empagliflozin as adjunctive to insulin therapy in type 1 diabetes: the EASE trials. Diabetes Care. (2018) 41:2560–9. doi: 10.2337/dc18-1749
30. Sands AT, Zambrowicz BP, Rosenstock J, Lapuerta P, Bode BW, Garg SK, et al. Sotagliflozin, a dual SGLT1 and SGLT2 inhibitor, as adjunct therapy to insulin in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care. (2015) 38:1181–8. doi: 10.2337/dc14-2806
31. Shimada A, Hanafusa T, Yasui A, Lee G, Taneda Y, Sarashina A, et al. Empagliflozin as adjunct to insulin in Japanese participants with type 1 diabetes: Results of a 4-week, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled phase 2 trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. (2019) 20:2190–9. doi: 10.1111/dom.13351
32. Watada H, Shiramoto M, Ueda S, Tang W, Asano M, Thorén F, et al. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of dapagliflozin in combination with insulin in Japanese patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. (2019) 21:876–82. doi: 10.1111/dom.13593
33. The safety and efficacy of dapagliflozin therapy in combination with insulin in Japanese subjects with T1DM. Available online at: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02582814?term=NCT02582814&rank=1 (Accessed 2, 11, 2023).
34. Jensen ML, Persson F, Andersen GS, Ridderstråle M, Nolan JJ, Carstensen B, et al. Incidence of ketoacidosis in the danish type 2 diabetes population before and after introduction of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors-a nationwide, retrospective cohort study, 1995-2014. Diabetes Care. (2017) 40:e57–8. doi: 10.2337/dc16-2793
35. Yang S, Liu Y, Zhang S, Wu F, Liu D, Wu Q, et al. Risk of diabetic ketoacidosis of SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front Pharmacol. (2023) 14:1145587. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1145587
36. Avgerinos I, Manolopoulos A, Michailidis T, Kitsios K, Liakos A, Karagiannis T, et al. Comparative efficacy and safety of glucose-lowering drugs as adjunctive therapy for adults with type 1 diabetes: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes Metab. (2021) 23:822–31. doi: 10.1111/dom.14291
Keywords: sodium-glucose-cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, the risk of diabetic ketoacidosis, type 1 diabetes mellitus, network meta-analysis, placebo control
Citation: Liu Y, Yang S, Jiang A, Zou D, Chen Z and Su N (2025) Risk of diabetic ketoacidosis caused by sodium glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors in patients with type 1 diabetes: a systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front. Endocrinol. 15:1453067. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1453067
Received: 22 June 2024; Accepted: 03 December 2024;
Published: 31 January 2025.
Edited by:
Soumya Panigrahi, Case Western Reserve University, United StatesReviewed by:
Shengzhao Zhang, Karamay Central Hospital, ChinaCherng Jye Seow, Tan Tock Seng Hospital, Singapore
Copyright © 2025 Liu, Yang, Jiang, Zou, Chen and Su. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Na Su, em95YTE1OUAxNjMuY29t
 Ying Liu
Ying Liu Shiwen Yang
Shiwen Yang Aidou Jiang
Aidou Jiang Dan Zou
Dan Zou Zhaoyang Chen
Zhaoyang Chen Na Su
Na Su